Page 1

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 1
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series
Deployment Guide
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series are adaptable for all mobile professionals, from users on the move within an
office environment to nurses and doctors in a healthcare environment to associates working in the warehouse, on the sales floor,
or in a call center. Staff, nurses, doctors, educators, and IT personnel can be easily reached when mobile utilizing a Bluetooth
headset. The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series are Bluetooth 2.1 + EDR compliant and supports both the headset
and handsfree profiles. The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series are MIL-STD-810F, Method 516.5, Procedure I
compliant. The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G is IP54 rated protecting it from dust, liquid splashes and moisture,
where the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G-EX is IP64 rated for complete dust protection and also certified for use in
explosive and hazardous environments.
This guide provides information and guidance to help the network administrator deploy the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone
7925G Series successfully in a wireless LAN environment.
Page 2
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 2
Revision History
Date
Comments
10/13/2008
Initial Version
11/17/2009
1.3(3) Release
5/3/2010
1.3(4) Release
8/30/2010
1.3(4)SR2 Release and 7925G-EX
12/15/2010
1.4(1) Release
Page 3

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 3
Contents
Requirements for the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.................................................................................................6!
Site Survey...............................................................................................................................................................................................6!
RF Validation..........................................................................................................................................................................................6!
Call Control ............................................................................................................................................................................................7!
Supported Protocols................................................................................................................................................................................ 7!
Supported Access Points .........................................................................................................................................................................7!
Supported Antennas ................................................................................................................................................................................9!
Phone Models and Localization .............................................................................................................................................................10!
Phone Models........................................................................................................................................................................................ 10!
7925G-EX Certifications.......................................................................................................................................................................11!
Atmospheres Explosibles (ATEX) Zone 2/Class 22 Certification ...................................................................................................11!
Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Class I/Division II Certification........................................................................................11!
World Mode (802.11d)..........................................................................................................................................................................12!
Supported Countries..........................................................................................................................................................................12!
Language Support ................................................................................................................................................................................. 13!
Radio Characteristics..............................................................................................................................................................................13!
Bluetooth ..................................................................................................................................................................................................14!
Bluetooth Profiles..................................................................................................................................................................................14!
Coexistence (802.11b/g + Bluetooth) ...................................................................................................................................................15!
Wireless Security ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 15!
Extensible Authentication Protocol - Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling (EAP-FAST) .....................................................16!
Extensible Authentication Protocol – Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) .......................................................................................17!
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP).........................................................................................................................19!
Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM)...................................................................................................................................... 20!
EAP and User Database Compatibility ................................................................................................................................................21!
Voice Security ..........................................................................................................................................................................................21!
Power Management.................................................................................................................................................................................22!
Protocols ...............................................................................................................................................................................................23!
Unscheduled Auto Power Save Delivery (U-APSD)........................................................................................................................23!
Power Save Poll (PS-POLL).............................................................................................................................................................23!
Active Mode......................................................................................................................................................................................23!
Delivery Traffic Indicator Message (DTIM).........................................................................................................................................23!
Scan Modes ...........................................................................................................................................................................................24!
Quality of Service (QoS) .........................................................................................................................................................................24!
Configuring QoS in Cisco Unified Communications Manager ............................................................................................................24!
Configuring QoS Policies for the Network ...........................................................................................................................................25!
Configuring Cisco IOS Access Points..............................................................................................................................................25!
Configuring Cisco Switch Ports........................................................................................................................................................25!
Page 4

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 4
Configuring Switch Ports for Wired IP Phones ................................................................................................................................26!
Sample Voice Packet Capture...........................................................................................................................................................27!
Call Admission Control......................................................................................................................................................................... 27!
Pre-Call Admission Control..............................................................................................................................................................28!
Roaming Admission Control ............................................................................................................................................................29!
Traffic Classification (TCLAS) .............................................................................................................................................................29!
Roaming ...................................................................................................................................................................................................30!
Interband Roaming................................................................................................................................................................................ 30!
Channel Parking................................................................................................................................................................................30!
Multicast...................................................................................................................................................................................................31!
Designing the Wireless LAN for Voice..................................................................................................................................................31!
Planning Channel Usage ......................................................................................................................................................................31!
5 GHz (802.11a)................................................................................................................................................................................32!
Using Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) on Access Points....................................................................................................32!
2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) .........................................................................................................................................................................33!
Signal Strength and Coverage...........................................................................................................................................................34!
Configuring Data Rates ........................................................................................................................................................................37!
Call Capacity ........................................................................................................................................................................................37!
Dynamic Transmit Power Control (DTPC) .......................................................................................................................................... 38!
Multipath...............................................................................................................................................................................................39!
Verification with Site Survey Tools.......................................................................................................................................................40!
Cisco 792xG Neighbor List ..............................................................................................................................................................40!
Cisco 792xG Site Survey .................................................................................................................................................................. 40!
Configuring Cisco Unified Communications Manager .......................................................................................................................43!
Phone Button Templates .......................................................................................................................................................................43!
Softkey Templates.................................................................................................................................................................................. 43!
Security Profiles....................................................................................................................................................................................44!
G.722 Advertisement .............................................................................................................................................................................45!
Product Specific Configuration Options............................................................................................................................................... 45!
Configuring the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller and Access Points .................................................................................... 50!
SSID / WLAN Settings ...........................................................................................................................................................................51!
Controller Settings ................................................................................................................................................................................ 53!
802.11 Network Settings........................................................................................................................................................................55!
Auto RF.............................................................................................................................................................................................56!
EDCA Parameters.............................................................................................................................................................................59!
DFS (802.11h)...................................................................................................................................................................................59!
Call Admission Control Settings...........................................................................................................................................................60!
Configuring QoS Basic Service Set (QBSS)..........................................................................................................................................63!
Configuring Auto-Immune ....................................................................................................................................................................64!
Configuring the WLAN Controller EAP-Request and EAPOL-Key Timeouts......................................................................................65!
Configuring Proxy ARP ........................................................................................................................................................................66!
Configuring TKIP Countermeasure Holdoff Time................................................................................................................................66!
Page 5

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 5
VLANs and Autonomous Access Points ................................................................................................................................................67!
Configuring the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series ........................................................................................................67!
Configuring the Network Profile Parameters.......................................................................................................................................68!
Installing Certificates............................................................................................................................................................................72!
Using Templates to Configure Phones..................................................................................................................................................78!
Bluetooth Configuration........................................................................................................................................................................78!
Upgrading Phone Firmware.................................................................................................................................................................79!
Wavelink Avalanche..............................................................................................................................................................................80!
Using the Bulk Deployment Utility .......................................................................................................................................................87!
Default Export...................................................................................................................................................................................90!
Bulk Export.......................................................................................................................................................................................90!
Pushing Configuration Files to the Cisco 792xG..............................................................................................................................91!
Configuring the Local Phone Book and Speed Dials............................................................................................................................91!
Increased Font ......................................................................................................................................................................................93!
Using Phone Designer ..........................................................................................................................................................................94!
IP Phone Services ....................................................................................................................................................................................96!
Extensible Markup Language (XML)....................................................................................................................................................96!
Java Mobile Information Device Profile (MIDP).................................................................................................................................97!
Troubleshooting.......................................................................................................................................................................................97!
Stream Statistics....................................................................................................................................................................................97!
Network Statistics..................................................................................................................................................................................99!
Wireless LAN Statistics .......................................................................................................................................................................101!
Traffic Stream Metrics (TSM).............................................................................................................................................................101!
Phone Logs.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 102!
Trace Modules.................................................................................................................................................................................103!
Trace Levels.................................................................................................................................................................................... 104!
Radio Status Indicator.........................................................................................................................................................................104!
Hardware Diagnostics ........................................................................................................................................................................105!
Firmware Recovery.............................................................................................................................................................................105!
Restoring Factory Defaults ................................................................................................................................................................. 106!
Capturing a Screenshot of the Phone Display .................................................................................................................................... 106!
Healthcare Environments.....................................................................................................................................................................106!
Cleaning the Phone................................................................................................................................................................................107!
Phone Accessories..................................................................................................................................................................................107!
Additional Documentation....................................................................................................................................................................109!
Page 6

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 6
Requirements for the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series are IEEE 802.11a/b/g wireless IP phones that provide voice
communications.
The wireless LAN must be validated to ensure it meets the requirements to deploy the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G
Series.
Site Survey
Before deploying the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series into a production environment, a site survey must be
completed by a Cisco certified partner with the advanced wireless LAN specialization. During the site survey the RF spectrum
can be analyzed to determine which channels are usable in the desired band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz). Typically there is less
interference in the 5 GHz band as well as more non-overlapping channels, so 5 GHz is the preferred band for operation and
even more highly recommended when the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G or 7925G Series is to be used in a mission
critical environment. The site survey will include heatmaps showing the intended coverage plan for the location. The site
survey will also determine which access point platform type, antenna type, access point configuration (channel and transmit
power) to use at the location. See the “Designing the Wireless LAN for Voice” section for more information.
Refer to the Steps to Success website for additional information.
http://www.cisco.com/go/stepstosuccess
RF Validation
In order to determine if VoWLAN can be deployed, the environment must be evaluated to ensure the following items meet
Cisco guidelines.
Signal
The cell edge should be designed to -67 dBm where there is a 20-30% overlap of adjacent access points at that signal level.
This ensures the 7925G Series phone always has adequate signal and can hold a signal for at least 5 seconds in order to roam seamlessly.
Channel Utilization
Channel Utilization levels should be kept under 50%.
If using the 7925G Series phone, this is provided via the QoS Basic Service Set (QBSS), which equates to around 105.
Noise
Noise levels should not exceed -92 dBm, which allows for a Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) of 25 dB where a -67 dBm signal should be
maintained.
Packet Loss / Delay
Per voice guidelines, packet loss should not exceed 1% packet loss, otherwise voice quality can be degraded significantly.
Jitter should be kept at a minimal (< 100 ms)
Retries
802.11 retransmissions should be less than 20%.
Multipath
Multipath should be kept to a minimal as this can create nulls and reduce signal levels.
Many different tools and applications can be used to evaluate these items in order to certify the deployment.
Cisco Spectrum Expert
Page 7

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 7
AirMagnet (Survey, WiFi Analyzer, VoFi Analyzer, Spectrum Analyzer)
Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS) for Unified Wireless LAN management
Call Control
For call control, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports only Skinny Client Control Protocol (SCCP) on
the following applications:
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager 4.3, 5.1, 6.0, 6.1, 7.0, 7.1, 8.0 and later
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express 4.3 and later (Minimum of 12.4(15)T7)
• SRST 4.3 and later (Minimum of 12.4(15)T7)
Device Support in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Cisco Unified Communications Manager requires a device package to be installed or service release update in order to enable
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series device support.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager 5.1 or higher requires signed COP files.
Device packages for Cisco Unified Communications Manager are available at the following location.
http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/sw-voice.shtml
Supported Protocols
Supported voice and wireless LAN protocols include these:
• Real Time Protocol (RTP)
• G.711u-law, G.711a-law, G.729a, G.729ab, G.722, iLBC
• Real Time Control Protocol (RTCP)
• Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
• Syslog
• CCX v4
• Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM)
• Traffic Specification (TSPEC)
• Traffic Classification (TCLAS)
• Unscheduled Auto Power Save Delivery (U-APSD)
• Power Save Poll (PS-POLL)
Supported Access Points
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series are supported on both the Cisco Unified and Autonomous solutions.
• Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller
Minimum = 5.2.193.0
Recommended = 7.0.98.0 or later
• Cisco IOS Access Points (Autonomous)
Page 8

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 8
Minimum = 12.3(8)JEA2 or later
Recommended = 12.4(10b)JA3 or later (does not apply to 1100, 1200, 1230)
Note: VoWLAN is not currently supported in conjunction with outdoor MESH technology (1500 series).
3rd party access points are not supported, as there is no interoperability testing performed against 3rd party access points.
Page 9

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 9
The table below lists the modes that are supported by each Cisco access point.
Cisco AP
Series
802.11a
802.11b
802.11g
802.11n
Autonomous
Unified
500
No
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1100
No
Yes
Optional
No
Yes
Yes
1130AG
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1140
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
1200
Optional
Yes
Optional
No
Yes
Yes
1230AG
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1240AG
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
1250
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
1260
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
3500
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Supported Antennas
Some of the Cisco Access Points require external antennas.
Please refer to the following URL for the list of supported antennas and how these external antennas should be mounted.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/wireless/ps7183/ps469/product_data_sheet09186a008008883b.html
Page 10

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 10
3rd party antennas are not supported, as there is no interoperability testing performed against 3rd party antennas including
Distributed Antenna Systems (DAS) and Leaky Coaxial Systems.
Please refer to the following URL for more info on Cisco Wireless LAN over Distributed Antenna Systems.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/wireless/ps5678/ps6973/positioning_statement_c07-565470.html
Note: The Cisco 1130, 1140 and 3502i series access points are to be mounted on the ceiling as they have omni-directional
antennas.
Phone Models and Localization
Phone Models
Cisco manufactures four Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G models and one Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G-EX
model.
The regulatory domain can be identified by navigating to Settings > Model Information > WLAN Regulatory Domain and
then referencing the Regulatory Domain number in the table below.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G-EX is configured like the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G –W model,
which requires an 802.11d enabled access point.
Use the following tables to identify specific phone versions that support these regulatory domains for use around the world:
7925G
Part Number
Regulatory
Domain
Regulatory
Domain
Number
Band Range
Available
Channels
Channel Set
CP-7925G-A-K9
FCC
(Americas)
1050
2.412 – 2.462 GHz
5.180 – 5.240 GHz
5.260 – 5.320 GHz
5. 500 – 5.700 GHz
5.745 – 5.805 GHz
11
4
4
8
4
1-11
36,40,44,48
52,56,60,64
100-140
149,153,157,161
CP-7925G-E-K9
ETSI
(Europe)
3051
2.412 – 2.472 GHz
5.180 – 5.700 GHz
13
19
1-13
36-48,52-64,100-140
CP-7925G-P-K9
Japan
4157
2.412 – 2.472 GHz
2.412 – 2.484 GHz
5.180 – 5.700 GHz
13 (OFDM)
14 (CCK)
19
1-13
1-14
36-48,52-64,100-140
CP-7925G-W-K9
Rest of
World
5252
Uses 802.11d to identify available channels and transmit
powers
7925G-EX
Part Number
Regulatory
Band Range
Available
Channel Set
Page 11

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 11
Domain
Number
Channels
CP-7925G-EX-K9
5252
2.412 – 2.484 GHz
5.180 – 5.240 GHz
5.260 – 5.320 GHz
5. 500 – 5.700 GHz
5.745 – 5.805 GHz
14
4
4
11
4
1-14
36,40,44,48
52,56,60,64
100-140
149,153,157,161
Note: 802.11j (channels 34, 38, 42, 46) and channel 165 are not supported.
7925G-EX Certifications
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G-EX has both Atmoshpheres Explosibles (ATEX) Zone 2/Class 22 and Canadian
Standards Association (CSA) Class1/Division II certifications in order to allow it to be used in hazardous and explosive
environments.
Atmospheres Explosibles (ATEX) Zone 2/Class 22 Certification
Organizations in the European Union must follow the ATEX directives to protect employees from explosion risk in areas with
an explosive atmosphere.
• ATEX 95 equipment directive 94/9/EC
Equipment and protective systems intended for use in potentially explosive atmospheres.
• ATEX 137 workplace directive 99/92/EC
Minimum requirements for improving the safety and health protection of workers potentially at risk from explosive
atmospheres.
Areas classified into zones (0, 1, 2 for gas-vapor-mist and 20, 21, 22 for dust) must be protected from effective sources of
ignition. Equipment and protective systems intended to be used in zoned areas must meet the requirements of the directive.
Zone 0 and 20 require Category 1 marked equipment, zone 1 and 21 required Category 2 marked equipment and zone 2 and 22
required Category 3 marked equipment. Zone 0 and 20 are the zones with the highest risk of an explosive atmosphere being
present.
Certification ensures that the equipment is fit for its intended purpose and that adequate information is supplied with it to ensure
that it can be used safely.
Canadian Standards Association (CSA) Class I/Division II Certification
Laws and regulations in most municipalities, states, and provinces in North America require certain products to be tested to a
specific standard or group of standards when they are to be deemed intrinsically safe when used in an explosive environment.
In North America, hazardous locations have traditionally been defined by the following combination of Class and Division:
• Class I - A location where a quantity of flammable gas or vapor, sufficient to produce an explosive or ignitable
mixture, may be present in the air.
• Class II - A location made hazardous by the presence of combustible or electrically conductive dust, including Groups
E (metal dust), F (coal dust) and G (grain dust).
• Class III - A location made hazardous by the presence of easily ignitable fibers in the air, but not likely in sufficient
quantities to produce ignitable mixtures.
Page 12

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 12
• Division 1 - A location where a classified hazard is likely to exist.
• Division 2 - A location where a classified hazard does not normally exist but is possible under abnormal conditions.
Internationally (and more recently in North America, for Class I hazardous locations), areas where explosive gas atmospheres
are likely to be present are divided into three IEC-defined Zones:
• Zone 0 - An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is continuously present or present for long periods.
• Zone 1 - An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere is likely to occur in normal operation.
• Zone 2 - An area in which an explosive gas atmosphere does not normally exist.
World Mode (802.11d)
If using the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G World (-W) model, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G-EX
model, then it is required to enable 802.11d. The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series gives precedence to 802.11d to
determine the channels and transmit powers to use and inherits its client configuration from the associated access point.
Enable World Mode (802.11d) for the corresponding country where the access point is located.
If 802.11d information is not available from the access point, then the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G (-A, -E, -P)
model uses the locally configured regulatory domain. If the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series -A, -E or -P model
is taken to another country, where the access point uses a different regulatory domain, then 802.11d will be required for the
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series to operate successfully.
When using 802.11a, enable 802.11d to discover which channels can potentially be used in the network. Specifically, for
802.11h support, the phone passively scans some of the 5 GHz channels (DFS) first before actively scanning any network
channels.
If using 2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) and 802.11d is not enabled, then the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7925G Series can attempt to use
channels 1-11 and reduced transmit power.
Note: World Mode is enabled automatically for the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller.
World Mode must be enabled manually for Cisco Autonomous Access Points using the following commands:
Interface dot11radio X
world-mode dot11d country US both
Supported Countries
Below are the countries and their 802.11d codes that are supported by the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
Argentina (AR)
India (IN)
Poland (PL)
Australia (AU)
Indonesia (ID)
Portugal (PT)
Austria (AT)
Ireland (IE)
Puerto Rico (PR)
Belgium (BE)
Israel (IL)
Romania (RO)
Brazil (BR)
Italy (IT)
Russian Federation (RU)
Bulgaria (BG)
Japan (JP)
Saudi Arabia (SA)
Canada (CA)
Korea (KR / KP)
Singapore (SG)
Chile (CL)
Latvia (LV)
Slovakia (SK)
Colombia (CO)
Liechtenstein (LI)
Slovenia (SI)
Page 13

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 13
Costa Rica (CR)
Lithuania (LT)
South Africa (ZA)
Cyprus (CY)
Luxembourg (LU)
Spain (ES)
Czech Republic (CZ)
Malaysia (MY)
Sweden (SE)
Denmark (DK)
Malta (MT)
Switzerland (CH)
Estonia (EE)
Mexico (MX)
Taiwan (TW)
Finland (FI)
Monaco (MC)
Thailand (TH)
France (FR)
Netherlands (NL)
Turkey (TR)
Germany (DE)
New Zealand (NZ)
Ukraine (UA)
Gibraltar (GI)
Norway (NO)
United Arab Emirates (AE)
Greece (GR)
Oman (OM)
United Kingdom (GB)
Hong Kong (HK)
Panama (PA)
United States (US
Hungary (HU)
Iceland (IS)
Peru (PE)
Phillipines (PH)
Venezuela (VE)
Vietnam (VN)
Note: Compliance information is available on the Cisco Product Approval Status web site at the following URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/cse/prdapp/jsp/externalsearch.do?action=externalsearch&page=EXTERNAL_SEARCH
Language Support
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series currently supports the following languages.
Bulgarian
English
Japanese
Serbian
Catalan
Finnish
Korean
Slovak
Chinese
French
Norwegian
Slovenian
Croatian
German
Polish
Spanish
Czech
Greek
Portuguese
Swedish
Danish
Hungarian
Romanian
Dutch
Italian
Russian
The corresponding locale package must be installed to enable support for that language. English is the default language on the
phone.
Download the locale packages from the Localization page at the following URL:
http://www.cisco.com/kobayashi/sw-center/telephony/callmgr/locale-installer.shtml
Radio Characteristics
The following table lists the data rates, ranges, and receiver sensitivity info for Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
802.11a
Data Rate
Range
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power is 16 dBm
6 Mbps
604 ft (184 m)
-91 dBm
9 Mbps
604 ft (184 m)
-90 dBm
Page 14

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 14
12 Mbps
551 ft (168 m)
-88 dBm
18 Mbps
545 ft (166 m)
-86 dBm
24 Mbps
512 ft (156 m)
-82 dBm
36 Mbps
420 ft (128 m)
-80 dBm
48 Mbps
322 ft (98 m)
-77 dBm
54 Mbps
289 ft (88 m)
-75 dBm
802.11g
Data Rate
Range
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power is 16 dBm
6 Mbps
709 ft (216 m)
-91 dBm
9 Mbps
650 ft (198 m)
-90 dBm
12 Mbps
623 ft (190 m)
-87 dBm
18 Mbps
623 ft (190 m)
-86 dBm
24 Mbps
623 ft (190 m)
-82 dBm
36 Mbps
495 ft (151 m)
-80 dBm
48 Mbps
413 ft (126 m)
-77 dBm
54 Mbps
394 ft (120 m)
-76 dBm
802.11b
Data Rate
Range
Receiver Sensitivity
Max Tx Power is 17 dBm
1 Mbps
1,010 ft (308 m)
-96 dBm
2 Mbps
951 ft (290 m)
-85 dBm
5.5 Mbps
919 ft (280 m)
-90 dBm
11 Mbps
902 ft (275 m)
-87 dBm
Note: Receiver sensitivity is the minimum signal needed to decode a packet at a certain data rate.
See the “Designing the Wireless LAN for Voice” section for more information on signal requirements.
Bluetooth
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports Bluetooth Class 2 technology allowing for wireless headset
communications.
Bluetooth enables low bandwidth wireless connections within a range of 30 feet, however it is recommended to keep the
Bluetooth device within 10 feet of the phone.
Up to five headsets can be connected, but only the last one connected is used as the default.
The Bluetooth device does not need to be within direct line-of-sight of the phone, but barriers, such as walls, doors, etc. can
potentially impact the quality.
Bluetooth utilizes the 2.4 GHz frequency just like 802.11b/g and many other devices (i.e. microwave ovens, cordless phones,
etc.), so the Bluetooth quality can potentially be interfered with due to using this unlicensed frequency.
Bluetooth Profiles
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports both the Bluetooth Headset and Handsfree Profiles.
With a Bluetooth Headset Profile capable headset, the following call functions can be performed.
-Ring
Page 15

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 15
-Answer a call
-End a call
-Volume Control
With Bluetooth Handsfree Profile (HFP) support, the following features can also be available if supported by the Bluetooth headset.
-Last Number Redial
-Call Waiting
-Divert / Reject
-3 way calling (Hold & Accept and Release & Accept)
For more information, refer to the documentation from the Bluetooth headset manufacturer.
Coexistence (802.11b/g + Bluetooth)
If using Coexistence where 802.11b/g and Bluetooth are used simultaneously, then there are some limitations and deployment
requirements to be considered as they both utilize the 2.4 GHz frequency.
Capacity
When using Coexistence (802.11b/g + Bluetooth), call capacity is reduced due to the utilization of CTS to protect the 802.11g
and Bluetooth transmissions.
Multicast Audio
Multicast audio from Push To Talk (PTT), Music on Hold (MMOH) and other applications are not supported when using
Coexistence.
Data Rate Configuration
It is recommended to only enable 802.11g (OFDM) data rates (i.e. > 12 Mbps) to prevent from engaging in CTS for 802.11g
protection when using Coexistence, which can impact voice quality.
Note: It is highly recommended to use 802.11a if using Bluetooth due to 802.11b/g and Bluetooth both utilizing 2.4 GHz, but
also due to the above limitations.
Wireless Security
When deploying a wireless LAN, security is essential.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports the following wireless security features.
Authentication
• WPA (802.1x authentication + TKIP encryption)
• WPA2 (802.1x authentication + AES encryption)
• WPA-PSK (Pre-Shared key + TKIP encryption)
• WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared key + AES encryption)
• EAP-FAST (Extensible Authentication Protocol – Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling)
Page 16

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 16
• EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol – Transport Layer Security)
• PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol)
• LEAP (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol)
• CCKM (Cisco Centralized Key Management)
• Open and Shared Key
Encryption
• AES (Advanced Encryption Scheme)
• TKIP / MIC (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol / Message Integrity Check)
• WEP (40-bit and 128-bit Wired Equivalent Protocol)
Extensible Authentication Protocol - Flexible Authentication via Secure
Tunneling (EAP-FAST)
This client server security architecture encrypts EAP transactions within a Transport Level Security (TLS) tunnel between the
access point and the Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) server such as the Cisco Access Control Server
(ACS).
The TLS tunnel uses Protected Access Credentials (PACs) for authentication between the client (phone) and the RADIUS
server. The server sends an Authority ID (AID) to the client (phone), which in turn selects the appropriate PAC. The client
(phone) returns a PAC-Opaque to the RADIUS server. The server decrypts the PAC with its master-key. Both endpoints now
have the PAC key and a TLS tunnel is created. EAP-FAST supports automatic PAC provisioning, but it must enable don the
RADIUS server.
To enable EAP-FAST, a certificate must be installed.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series currently supports only automatic provisioning of the PAC, so enable
“Allow anonymous in-band PAC provisioning” on the RADIUS server as shown below.
Both EAP-GTC and EAP-MSCHAPv2 must be enabled when “Allow anonymous in-band PAC provisioning” is enabled.
EAP-FAST requires that a user account be created on the authentication server.
Page 17

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 17
If anonymous PAC provisioning is not allowed in the product wireless LAN environment then a staging Cisco ACS can be
setup for initial PAC provisioning of the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
This requires that the staging ACS server be setup as a slave EAP-FAST server and components are replicated from the product
master EAP-FAST server, which include user and group database and EAP-FAST master key and policy info.
Ensure the production master EAP-FAST ACS server is setup to send the EAP-FAST master keys and policies to the staging
slave EAP-FAST ACS server, which will then allow the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series to use the provisioned
PAC in the production environment where “Allow anonymous in-band PAC provisioning” is disabled.
When it is time to renew the PAC, then authenticated in-band PAC provisioning will be used, so ensure that “Allow
authenticated in-band PAC provisioning” is enabled.
Ensure that the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series has connected to the network during the grace period to ensure it
can use its existing PAC created either using the active or retired master key in order to get issued a new PAC.
Is recommended to only have the staging wireless LAN pointed to the staging ACS server and to disable the staging access
point radios when not being used.
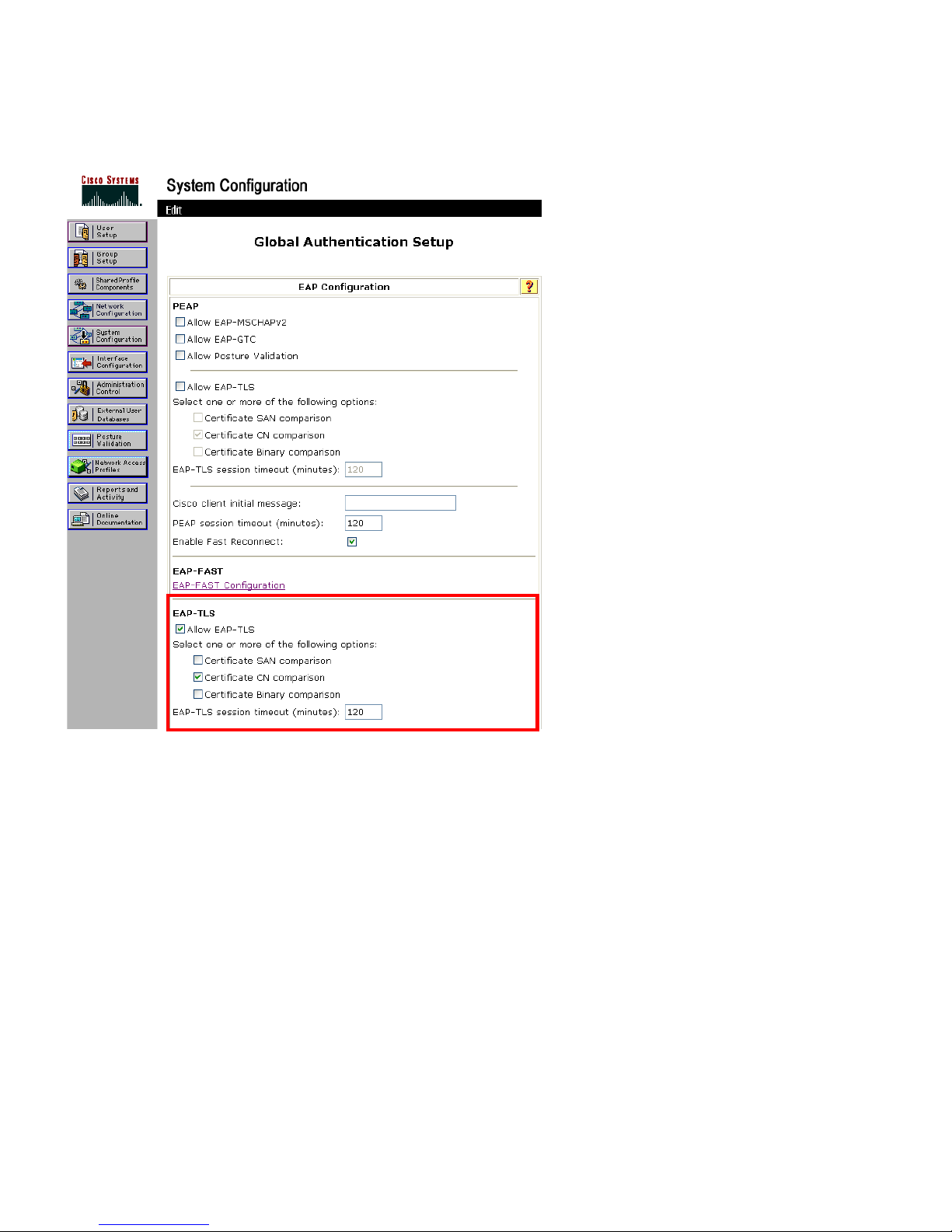
Extensible Authentication Protocol – Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS)
Extensible Authentication Protocol Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) is using the TLS protocol with PKI to secure
communications to the authentication server.
TLS provides a way to use certificates for both user and server authentication and for dynamic session key generation.
Either the internal Manufacturing Installed Certificate (MIC) or a user installed certificate can be used for authentication.
Page 18
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 18
EAP-TLS provides excellent security, but requires client certificate management.
Ensure that “Certificate CN Comparison” is selected when enabling EAP-TLS.
EAP-TLS also requires that a user account be created on the authentication server matching the common name of the certificate
imported into the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
It is recommended to use a complex password for this user account.
Page 19

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 19
See the “Installing Certificates” section for more information.
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP)
Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol (PEAP) uses server-side public key certificates to authenticate clients by creating
an encrypted SSL/TLS tunnel between the client and the authentication server.
The ensuing exchange of authentication information is then encrypted and user credentials are safe from eavesdropping.
MS-CHAP v2 is the current supported inner authentication protocol (GTC is not supported).
Page 20

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 20
PEAP (MS-CHAPv2) requires that a user account be created on the authentication server.
The authentication server can be validated via importing a certificate into the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
See the “Installing Certificates” section for more information.
Cisco Centralized Key Management (CCKM)
When using 802.1x type authentication, it is recommended to implement CCKM to enable fast roaming. 802.1x can introduce
delay during roaming due to its requirement for full re-authentication. CCKM centralizes the key management and reduces the
number of key exchanges. WPA and WPA2 introduce additional transient keys and can lengthen roaming time.
When CCKM is utilized, roaming times can be reduced from 400-500 ms to less than 100 ms, where that transition time from
one access point to another will not be audible to the user.
As of the 1.3(4) release, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports CCKM with WPA2 (AES or TKIP), WPA
(TKIP or AES) and 802.1x (WEP) authentication.
Authentication
Key Management
Encryption
EAP-FAST
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
AES, TKIP, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
EAP-TLS
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
AES, TKIP, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
Page 21

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 21
PEAP
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
AES, TKIP, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
LEAP
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
AES, TKIP, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
AKM
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
AES, TKIP, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
CCKM was not supported with WPA2 in release 1.3(3) or earlier.
WPA Version
Cipher
Prior to 1.3(4)
1.3(4) and later
TKIP
Supported
Supported
WPA
AES
Not Supported
Supported
TKIP
Not Supported
Supported
WPA2
AES
Not supported
Supported
EAP and User Database Compatibility
The following chart indicates which EAP and database configurations are supported by the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone
7925G Series.
Database
LEAP
EAP-TLS
PEAP
(MS-CHAPv2)
EAP-FAST
(Phase Zero)
ACS
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Windows SAM
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
Windows AD
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
LDAP
No
Yes
No
No
ODBC (ACS for
Windows only)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
LEAP Proxy
RADIUS Server
Yes
No
Yes
Yes
All Token Servers
No
No
No
No
Voice Security
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports the following voice security features.
• Certificates
• Image authentication
• Device authentication
• File authentication
Page 22
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 22
• Signaling authentication
• Secure Cisco Unified SRST
• Media encryption (SRTP)
• Signaling encryption (TLS)
• Certificate authority proxy function (CAPF)
• Secure profiles
• Encrypted configuration files
• Settings Access (can limit user access to configuration menus)
• Locked network profiles
• Administrator password
Power Management
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series has an option for a standard or extended battery.
The standard battery can provide up to 180 hours standby time or up to 9.5 hours talk time.
The extended battery can provide up to 240 hours standby time or up to 13 hours talk time.
When the access point supports the Cisco Client Extensions (CCX) proxy ARP information element, the idle battery life will be
optimized.
When on call U-APSD, PS-POLL, or active mode can be utilized depending on the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G
Series and Access Point configuration.
To extend on call battery life, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series can use U-APSD or PS-POLL power save
methods.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will use either U-APSD or PS-POLL when in idle (no active phone call).
There can be up to 40-50% reduction of battery life when on call and using Coexistence (802.11b/g + Bluetooth).
The table below lists the maximum on call and idle times for each 802.11 mode and battery type.
802.11 Mode
Call State
Standard
Battery
Extended
Battery
2.4 GHz
On Call
9.5
13
On Call + Bluetooth
5.5
7
Idle
180
240
Idle + Bluetooth Enabled
165
200
5 GHz
On Call
9
11
On Call + Bluetooth
7
10
Idle
180
240
Idle + Bluetooth Enabled
165
200
Page 23

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 23
If the access point does not support CCX or proxy ARP is not enabled, then the idle battery life will be up to fifty percent less.
See the “Configuring Proxy ARP” section for more information.
Protocols
Unscheduled Auto Power Save Delivery (U-APSD)
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will use U-APSD (Unscheduled Auto Power Save Delivery) for power save
when in idle mode or when a phone call is active if WMM is enabled, where U-APSD is supported.
U-APSD helps optimize battery life.
Below is a sample packet sequence when using U-APSD.
Power Save Poll (PS-POLL)
If Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM) is disabled, which will disable U-APSD support, or U-APSD support is not available on the
access point, then the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will use PS-POLL for power save when in idle mode and
when a phone call is active.
Below is a sample packet sequence when using PS-POLL.
Active Mode
If the “Call Power Save Mode” is set to “None”, then the phone will use active mode and no power save will be used, which
will reduce the battery life.
Delivery Traffic Indicator Message (DTIM)
Increasing the DTIM period can also increase the battery life. The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series can use the
DTIM period to schedule wakeup periods to check for broadcast and multicast packets as well as any unicast packets.
For optimal battery life and performance, we recommend setting the DTIM period to “2” with a beacon period of “100 ms”.
Page 24

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 24
The DTIM period is a tradeoff between battery life and multicast performance.
Broadcast and multicast traffic will be queued until the DTIM period when there are power save enabled clients associated to
the access point, so DTIM will determine how quickly these packets can be delivered to the client. If using multicast
applications, a shorter DTIM period can be used.
Scan Modes
When using only one access point, select Single Access Point Mode on the phone to reduce scanning and optimize battery life
for phones that do not roam.
When using multiple access points where roaming is required, “Single AP Mode” should not be enabled. Instead use the auto
(default) or continuous scan mode, which will allow for seamless roaming.
Continuous scan mode can be optionally enabled to allow for better location tracking.
Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service enables queuing to ensure high priority for voice traffic. To implement appropriate queuing for voice traffic,
use the following suggestions:
• Ensure that WMM is enabled on the access point.
• Create a QoS policy on the access point giving priority to voice (RTP) and call control (SCCP) traffic and apply that
profile to the desired interfaces.
Traffic Type
DSCP
802.1p
WMM UP
Voice (RTP)
EF (46)
5
6
Call Control (SCCP)
CS3 (24)
3
4
• Be sure that RTP packets have the proper QoS markings and other protocols are not using the same QoS markings.
• Select the “Platinum” QoS profile for the voice wireless LAN when using Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller
technology and set the 802.1p tag to “6”.
• Enable Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) preservation on the Cisco IOS switch and/or use a QoS policy to set
DSCP to EF for RTP traffic (UDP port range 16384-32767) on the Cisco IOS router.
For more information about TCP and UDP ports used by the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series and the Cisco
Unified Communications Manager, refer to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager TCP and UDP Port Usage document
at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cucm/port/7_1_2/CCM_7.1.2PortList.pdf
Configuring QoS in Cisco Unified Communications Manager
The SCCP DSCP values are configured in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager enterprise parameters. Cisco Unified
Communications Manager uses the default value of CS3 to have devices set the DSCP marking for SCCP packets as shown in
the Enterprise Parameters Configuration page.
Page 25

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 25
Configuring QoS Policies for the Network
Set up QoS policies and settings for the following network devices.
Configuring Cisco IOS Access Points
Use the following QoS policy on the Cisco IOS access point (AP) to enable DSCP to CoS (UP) mapping. This allows RTP
packets to be placed into the voice queue, if those packets are marked correctly, when received at the access point level.
class-map match-all RTP
match ip dscp ef
class-map match-all SCCP
match ip dscp cs3
!
policy-map Voice
class RTP
set cos 6
class SCCP
set cos 4
!
interface dot11radioX
service-policy input Voice
service-policy output Voice
Configuring Cisco Switch Ports
Configure the Cisco access point switch ports and uplink switch ports for DSCP trust.
mls qos
!
interface X
mls qos trust dscp
Page 26

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 26
Note: When using the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller, DSCP trust must be implemented or trust the UDP data ports
used by the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller (LWAPP = 12222 and 12223; CAPWAP = 5246 and 5247) on all
interfaces where wireless packets will traverse to ensure QoS markings are correctly set. Versions prior to 5.2 use LWAPP,
where versions 5.2 and later use CAPWAP.
Configuring Switch Ports for Wired IP Phones
Enable the Cisco wired IP phone switch ports for Cisco phone trust
mls qos
!
Interface X
mls qos trust device cisco-phone
mls qos trust dscp
If DSCP markings are not preserved, then the below configuration can be used to set the DSCP based on the TCP or UDP port
to map RTP and SCCP correctly.
Ensure the following QoS policy is not applied to an interface where wireless traffic traverses.
If using non-secure SCCP, then TCP port 2000 is used. TCP port 2443 is used for secure SCCP.
ip access-list extended SCCP
permit tcp any eq 2000 any
permit tcp any any eq 2000
permit tcp any eq 2443 any
permit tcp any any eq 2443
!
ip access-list extended RTP
permit udp any range 16384 32767 any
permit udp any any range 16384 32767
!
class-map match-all SCCP
match access-group name SCCP
class-map match-all RTP
match access-group name RTP
!
policy-map Voice
class RTP
set dscp ef
!
class SCCP
set dscp cs3
!
interface X
service-policy input Voice
service-policy output Voice
Page 27

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 27
Sample Voice Packet Capture
This packet capture below shows that RTP packets bound for the Cisco Unified IP Phone 7925G over the air should be marked
with DSCP = EF and UP = 6.
Call Admission Control
Inbound and outbound call admission control can be enabled on the access point.
• Enable Call Admission Control / Wi-Fi MultiMedia Traffic Specifications (TSPEC)
• Set the desired maximum RF bandwidth that is allocated for voice traffic (default = 75%)
• Set the bandwidth that is reserved for roaming clients (default = 6%)
The minimum PHY rate can be configured for which the phone is to use when Call Admission Control (CAC) is enabled.
• Enable a data rate that is enabled on the access point. (Default setting is 12 Mbps)
• Cisco Access Points will only accept a minimum PHY rate of 5.5, 6, 11, 12 or 24 Mbps, so ensure that one of these
rates are enabled.
As of the 1.3(3) release, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will auto-negotiate the minimum PHY rate to be
used for TSPEC. By default it will try the locally configured minimum PHY rate (i.e. 12 Mbps) first, but if that data rate is not
enabled on the access point, then it will try the next highest enabled data rate on the access point. If there is not a higher data
rate enabled, then it will then try the next lowest data rate as the minimum PHY rate.
Page 28

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 28
In releases prior to 1.3(3), the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series would use the static minimum PHY rate
configured locally.
If 12 Mbps is not enabled on the access point, then the next highest enabled data rate must be 24 Mbps. For example, if 12
Mbps is disabled but 18 Mbps is enabled, the phone will try the next highest rate of 18 Mbps and fail because that minimum
PHY rate for CAC is not supported by the Cisco access point.
The dynamic minimum PHY rate is useful for deployments that require higher capacity where 24 Mbps and higher data rates
are only enabled. For this high capacity deployment configuration and with release 1.3(3), the minimum PHY rate would be
adjusted to 24 Mbps automatically even if the phone is configured statically for a minimum PHY rate of 12 Mbps. In releases
prior to 1.3(3), the minimum PHY rate would have to be changed to 24 Mbps manually from the default of 12 Mbps in order for
CAC to work correctly for this deployment configuration.
If an 802.11b AP is used, the highest available date rate would be 11 Mbps, so 12 Mbps can not be used as the minimum PHY
rate. For this 802.11b (11 Mbps) deployment configuration and with release 1.3(3), the minimum PHY rate would be adjusted
to 11 Mbps automatically even if the phone is configured statically for a minimum PHY rate of 12 Mbps. In releases prior to
1.3(3), the minimum PHY rate would have to be changed to 11 Mbps manually from the default of 12 Mbps in order for CAC
to work correctly for this deployment configuration.
There is no support for load-based CAC or multiple streams on the autonomous access points therefore it is not recommended
to enable CAC on autonomous access points.
If CAC is enabled on the autonomous access point, then SRTP and barge calls will fail.
Pre-Call Admission Control
If Call Admission Control (TSPEC) is enabled on the access point, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series sends an
Add Traffic Stream (ADDTS) to the access point to request bandwidth in order to place or receive a call. If the AP sends an
ADDTS successful message then the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series establishes the call. If the call is rejected
by the access point and the wireless IP phone has no other access point to roam to, then phone displays “Network Busy”. If the
admission is refused, there is no messaging from the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series to inform the remote
endpoint that there is insufficient bandwidth to establish the call, so the call can continue to ring out within the system until the
remote user terminates the call.
Page 29

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 29
Roaming Admission Control
During a call, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series measures Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) and
Packet Error Rate (PER) values for the current and all available access points to make roaming decisions.
If the original access point where the call was established had Call Admission Control (TSPEC) enabled, then the wireless IP
phone will send an ADDTS request during the roam to the new access point.
For more information about Call Admission Control and QoS, refer to the “Cisco Unified Wireless Quality of Service” chapter
in the Enterprise Mobility Design Guide at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Mobility/emob41dg/eMob4.1.pdf
Traffic Classification (TCLAS)
Traffic Classification (TCLAS) helps to ensure that the access point properly classifies voice packets.
Without proper classification, voice packets will be treated as best effort which will defeat the purpose of TSPEC and QoS in
general.
TCP and UDP port information will be used to set the UP (User Priority) value.
The previous method of classification depends upon preservation of DSCP value throughout the network, where the DSCP
value maps to a particular queue (BE, BK, VI, VO).
However, the DSCP values are not always preserved as this can be viewed as a security risk.
TCLAS is supported in the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller release 5.1.151.0 and later.
Using port based QoS policies is inadequate as all data packets use the same UDP port (LWAPP = 12222; CAPWAP = 5246)
and the access point uses the outside QoS marking to determine which queue the packets should be placed in.
With TCLAS, DSCP preservation is not a requirement.
Call Admission Control (TSPEC) must be enabled on the access point in order to enable TCLAS.
TCLAS will be negotiated within the ADDTS packets, which are used to request bandwidth in order to place or receive a call.
Page 30

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 30
Roaming
When using 802.1x type authentication, it is recommended to implement CCKM to enable fast roaming. 802.1x can introduce
delay during roaming due to its requirement for full re-authentication. CCKM centralizes the key management and reduces the
number of key exchanges. WPA introduces additional transient keys and can lengthen roaming time.
As of the 1.3(4) release, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports CCKM with WPA2 (AES or TKIP), WPA
(TKIP or AES) and 802.1x (WEP) authentication.
Authentication
Roaming Time
WPA/WPA2 Personal
150 ms
WPA/WPA2 Enterprise
300 ms
CCKM
< 100 ms
Interband Roaming
Some deployments may use one band for indoor (i.e. 5 GHz) and the other for outdoor coverage (i.e. 2.4 GHz). In this case, set
the phone to either Auto-a or Auto-b/g mode, depending on the preferred band.
For Auto-a and Auto-b/g modes, this is giving preference to one band over another. At power on, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP
Phone 7925G Series will scan all 2.4 and 5 GHz channels then attempt to associate to an access point for the configured
network using the preferred band if available. If the preferred band is not available, then the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone
7925G Series will try to use the less preferred band if available. If the phone roams out of coverage of the preferred band,
where the less preferred band signal is available, then the phone will attempt to associate to that less preferred band.
As of the 1.3(4) release, seamless interband roaming between 5 Ghz and 2.4 Ghz bands is supported as both bands are now
scanned simultaneously when on call.
In order for the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series to roam from the preferred band to the less preferred band (i.e.
roam to 2.4 GHz when configured for Auto-a mode), all access points in the preferred band must have a signal low enough to
match the less preferred band roam threshold and the RSSI differential threshold for roaming must be met. In order to roam
back to the preferred band, there must be at least one access point with sufficient signal matching the preferred band roam
threshold.
Prior to the 1.3(4) release, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series would have to roam out of range of the current
band before it would attempt to roam to the other band when configured for an Auto 802.11 mode (i.e. Auto-a, Auto-bg, AutoRSSI), where the user may experience choppy audio with the weak signal, followed up with a small second audio gap before
looking for the least preferred band. Then once it has failed over to a less preferred band (i.e. associated to 802.11b/g when
phone configured for Auto-a), there was no mechanism in place to check to see if the preferred band is available again or not in
order to roam back to the preferred band.
It is recommended to perform a spectrum analysis to ensure that the desired bands can be enabled in order to perform seamless
interband roaming.
Channel Parking
Channel Parking is a sub-feature of interband roaming, which is designed to conserve idle battery life when the Cisco Unified
Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series are configured for an Auto 802.11 mode and continuous scan mode is enabled in the Cisco
Unified Communications Manager.
Continuous scan mode enables constant scanning of all channels regardless of call state, which can also help with location.
When configured for auto scan mode, typically the phone is only scanning when on call and not in idle unless the current signal
drops below a certain RSSI threshold.
Page 31

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 31
When channel parking is active, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will discontinue the scanning of the 5 GHz
band and potentially roam to a 2.4 GHz neighbor, but also may stay on the currently connected 5 GHz AP if that is the strongest
signal received.
Channel parking will occur when the phone is in idle mode and there are at least four 2.4 GHz access points available where at
least one of those four access points has met the RSSI threshold to enable channel parking.
If configured for Auto-a and continuous scanning is enabled, the phone can potentially roam to 2.4 GHz when in idle even when
the phone is in good 5 GHz coverage as the Auto-RSSI logic is used when in idle, regardless of whether 5 GHz channels are
parked or not. When on call the local configured mode will be used (i.e. Auto-a), so it will attempt to associate to the preferred
band if available.
Channel parking will become inactive either when there are less than four 2.4 GHz access points, the RSSI for all 2.4 GHz
access points is low enough to meet the RSSI threshold to disable channel parking or there is a current inbound or outbound
call. When channel parking becomes inactive, the phone will rapidly scan the 5 GHz band, where it can potentially roam back
to 5 GHz if configured for Auto-a, as roaming is based on band preference and then RSSI when on call.
When the call is terminated, channel parking may become active again.
Multicast
When enabling multicast in the wireless LAN, impacts on battery life, performance, and capacity must be considered.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series uses the DTIM period to receive the queued broadcast and multicast
packets.
If there are many packets queued up, then they client may have to stay awake longer thus potentially reducing battery life.
With multicast, there is no reliability that the packet will be received the by the client.
The multicast traffic will be sent at the highest basic data rate enabled on the access point, so will want to ensure that only the
lowest enabled rate is configured as the only basic rate.
The client will send the IGMP join request to receive that multicast stream. The client will send the IGMP leave when the
session is to be ended.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports the IGMP query feature, which can be used to reduce the amount
of multicast traffic on the wireless LAN when not necessary.
Ensure that IGMP snooping is also enabled on all switches.
Note: If using Coexistence where 802.11b/g and Bluetooth are being used simultaneously, then multicast voice is not
supported.
Designing the Wireless LAN for Voice
The following network design guidelines must be followed in order to accommodate for adequate coverage, call capacity and
seamless roaming for the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
For more information about these topics, refer to the “VoWLAN Design Recommendations” chapter in the Enterprise Mobility
Design Guide at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Mobility/emob41dg/eMob4.1.pdf
Planning Channel Usage
Use the following guidelines to plan channel usage for these wireless environments.
Page 32

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 32
5 GHz (802.11a)
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) and Transmit Power Control
(TPC) from 802.11h, which are required when using channels operating at 5.25 - 5.725 GHz, which are 15 of the 23 possible
channels.
DFS dynamically instructs a transmitter to switch to another channel whenever radar signal is detected. If the access point
detects radar, the radio on the access point goes on hold for at least 60 seconds while the access point passively scans for
another usable channel.
TPC allows the client and access point to exchange information, so that the client can dynamically adjust the transmit power.
The client uses only enough energy to maintain association to the access point at a given data rate. As a result, the client
contributes less to adjacent cell interference, which allows for more densely deployed, high-performance wireless LANs.
Lower power on the client provides longer battery life because less power is used by the radio.
5 GHz channels overlap their adjacent channel, so there should be at least 1 channel of separation for adjacent access points.
Using Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) on Access Points
For autonomous solution access points, select Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) to use auto channel selection.
When DFS is enabled, enable at least one band (bands 1-4).
For unified access points, enable Auto RF unless there is an intermittent interferer in an area which select access points can have
the channel statically assigned.
In case of radar activity, have at least one access point per area that uses a non-DFS channel (UNII-1). This ensures that a
channel is available when an access point’s radio is in its hold-off period while scanning for a new usable channel.
For autonomous access points, enable band 1 only which allows the access point to use only a UNII-1 channel.
For unified access points, can manually select a UNII-1 channel (channels 36, 40, 44, 48) for the desired access points.
A UNII-3 channel (5.745 - 5.805 GHz) can optionally be used if available.
Page 33

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 33
In this diagram, 5 GHz cells use a non-DFS channel while other nearby cells use DFS channels to permit maximum call
capacity under all conditions.
For 5 GHz, 20 channels are available in the Americas and 19 channels in Europe and Japan.
Where UNII-3 is available, it is recommend to use UNII-1, UNII-2 and UNII-3, to utilize a 12 channel set.
If planning to use UNII-2 extended channels (channels 100 - 140), it is recommended to disable UNII-2 (channels 52-64) on the
access point to avoid having so many channels enabled.
Having many 5 GHz channels enabled in the wireless LAN can delay discovery of new access points.
2.4 GHz (802.11b/g)
In the 2.4 GHz (802.11b/g environment, only non-overlapping channels must be utilized when deploying VoWLAN. Nonoverlapping channels have 22 MHz of separation and are at least 5 channels apart.
There are only 3 non-overlapping channels in the 2.4 GHz frequency range (channels 1, 6, 11). In Japan, channel 14 can be
utilized as a fourth non-overlapping channel when using 802.11b access points.
Ch 161
Ch 52
Ch 36
Ch 60
Ch 56
Ch 48
Ch 149
Ch 44
Minimum 20% Overlap
Page 34

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 34
Non-overlapping channels must be used and allow at least 20 percent overlap with adjacent channels when deploying phones in
the 802.11b/g environment.
Signal Strength and Coverage
To ensure acceptable voice quality, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series should always have a signal of -67 dBm
or higher when using 2.4 or 5 GHz and ensure the Packet Error Rate (PER) is no higher than 1%.
A minimum Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) of 25dB = -92dBm noise level with -67 dBm signal should be maintained.
It is recommended to have at least two access points on non-overlapping channels with at least -67 dBm signal with the 25 dB
SNR to provide redundancy.
To achieve maximum capacity and throughput, the wireless LAN should be designed to 24 Mbps. Higher data rates (36-54
Mbps) can optionally be enabled.
Recommended to set the minimum data rate to 11 Mbps or 12 Mbps for 2.4 GHz (dependent upon 802.11b client support
policy) and 12 Mbps for 5 GHz, which should also be the only rate configured as a basic rate.
Due to the above requirements, a single channel plan should not be deployed.
For more information about signal strength and cell edge design, refer to the “VoWLAN Design Recommendations” chapter in
the Enterprise Mobility Design Guide at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Mobility/emob41dg/eMob4.1.pdf
Ch 1
Ch 6
Ch 11
Ch 6
Ch 6
Ch 11
Ch 1
Ch 11
Minimum 20% Overlap
Page 35

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 35
When designing the placement of access points, be sure that all key areas have sufficient coverage (signal).
Typical wireless LAN deployments for data only applications do not provide coverage for some areas where VoWLAN service
is necessary such as elevators, stairways, and outside corridors.
Wireless LAN interference is generated by microwave ovens, 2.4 GHz cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, or other electronic
equipment operating in the 2.4 GHz band.
Microwave ovens operate on 2450 MHz, which is between channels 8 and 9 of 802.11b/g. Some microwaves are shielded more
than others and that shielding reduces the spread of the energy. Microwave energy can impact channel 11, and some
microwaves can affect the entire frequency range (channels 1 through 11). To avoid microwave interference, select channel 1
for use with access points that are located near microwaves.
Most microwave ovens, Bluetooth, and frequency hopping devices do not have the same effect on the 5 GHz frequency. The
802.11a technology provides more non-overlapping channels and typically lower initial RF utilization. For voice deployments,
it is suggested to use 802.11a for voice and use 802.11b/g for data.
However there are products that also utilize the non-licensed 5 GHz frequency (i.e. 5.8 GHz cordless phones, which can impact
UNII-3 channels).
Noise
Level
RSSI /
Signal
Strength
Power (dBm)
Signal to
Noise
Ratio
Time (Seconds)
Page 36

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 36
The Cisco Unified WCS can be utilized to verify signal strength and coverage.
Break Room
(Microwave Ovens
2450 MHz)
File / Supply
Room
Stairwells (Reinforced
Building Area)
Lab
Cubes
CEO
Office
Elevator
Shafts
Conference
Room
Page 37

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 37
Configuring Data Rates
It is recommended to disable rates below 12 Mbps for 802.11a and below 12 Mbps for 802.11b/g deployments where capacity
and range are factored in for best results.
If 802.11b clients are not allowed in the wireless LAN, then it is recommended to disable the 1, 2, 5.5, 11 Mbps data rates.
When 802.11b clients exist in the wireless network, then an 802.11b rate must be enabled and only an 802.11b rate can be
configured as a basic rate. In this case, is suggested to enable the data rates 11 Mbps and higher.
If using Coexistence where 802.11b/g and Bluetooth are being used simultaneously, then the data rates below 11 Mbps should
be disabled. If 802.11b clients are not allowed in the wireless network, then it is strongly recommended to disable the data rates
below 12 Mbps. This will eliminate the need to send CTS frames for 802.11g protection as 802.11b clients can not detect these
OFDM frames.
The recommended data rate configuration is the following:
802.11 Mode
Basic (Mandatory)
Data Rates
Supported (Optional)
Data Rates
Disabled
Data Rates
802.11a
12 Mbps
18 - 24, <36-54> Mbps
6, 9, <36-54> Mbps
802.11b
11 Mbps
None
1, 2, 5.5 Mbps
802.11g
12 Mbps
18 – 24, <36-54> Mbps
6, 9, <36-54> Mbps
802.11b/g
11 Mbps
12 – 24, <36-54> Mbps
1, 2, 5.5, 6, 9, <36-54> Mbps
Data rates higher than 24 Mbps (36, 48 and 54 Mbps) can optionally be enabled or disabled, but there is no advantage from a
capacity or throughput perspective to enable these rates for a voice application.
Enabling these rates could potentially increase the number of retries for a data frame.
Other applications may be able to benefit from having these higher data rates enabled.
Note: Some environments may require that a lower data rate be enabled due to use of legacy clients, environmental factors or
maximum range is required.
Set only the lowest data rate enabled as the single basic rate. Multicast packets will be sent at the highest basic data rate
enabled.
Note that capacity and throughput are reduced when lower rates are enabled.
If Call Admission Control (TSPEC) is enabled then the Traffic Stream Rate Set (TSRS) feature will also be enabled, which will
allow lower rates to be enabled for legacy devices, but prevent the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series to transmit at
rates below 12 Mbps for 802.11a and 11 Mbps for 802.11b/g, while also allow set the ceiling data rate to a more reliable data
rate (24 Mbps). Disallowing packets to be transmitted at lower rates preserves capacity. Sending voice frames at a more
reliable rate initially can potentially reduce the number of retries of a data frame to ensure the packet transmission is successful
on the first try.
See the “Product Specific Configuration Options” section for information on how to configure the Restricted Data Rates
options on the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series in order to utilize the TSRS feature.
Call Capacity
Design the network to accommodate the desired call capacity.
The Cisco Access Point can support up to 27 bi-directional RTP streams for both 802.11a and 802.11g at a data rate of 24 Mbps
or higher. To achieve this capacity, there must be minimal wireless LAN background traffic and radio frequency (RF)
utilization.
Page 38

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 38
The number of calls may vary depending on the data rate, initial channel utilization, and the environment.
Max # of Streams
802.11 Mode
Data Rate
13
802.11a or 802.11g + Bluetooth Disabled
6 Mbps
20
802.11a or 802.11g + Bluetooth Disabled
12 Mbps
27
802.11a or 802.11g + Bluetooth Disabled
24 – 54 Mbps
When using Coexistence (802.11b/g + Bluetooth), call capacity is reduced to the following:
Max # of Streams
802.11 Mode
Data Rate
4
802.11b/g + Bluetooth Enabled
11, <12-54> Mbps
7
802.11g + Bluetooth Enabled
12, <18-54> Mbps
Note: It is highly recommended to use 802.11a if using Bluetooth.
Prior to release 1.3(3), only 2 bi-directional RTP streams were supported when using Coexistence.
Dynamic Transmit Power Control (DTPC)
To successfully exchange packets between the wireless IP phone and the access point, Dynamic Transmit Power Control
(DTPC) should be enabled.
When using an access point that supports DTPC, set the client power to match the local access point power.
Do not use default setting of Max power for client power on Cisco autonomous access points as that will not advertise DTPC to
the client.
If the access point does not support DTPC, then the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will use the highest
available transmit power depending on the current 802.11 mode and data rate.
The transmit power on the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series can also optionally be configured to match the
highest transmit power of an access point in the wireless LAN. This setting prevents one-way audio when RF traffic is heard in
one direction only.
By default the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will use the highest available transmit power by default (i.e. 17
dBm / 50 mW for 2.4 GHz and 16 dBm / 40 mW for 5 GHz).
The access point’s radio transmit power should not have a transmit power greater than what the Cisco Unified Wireless IP
Phone 7925G Series can support.
Page 39

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 39
Multipath
Multipath occurs when RF signals take multiple paths from a source to a destination.
A part of the signal goes to the destination while another part bounces off an obstruction, then goes on to the destination. As a
result, part of the signal encounters delay and travels a longer path to the destination which creates signal energy loss.
When the different waveforms combine, they cause distortion and effect the decoding capability of the receiver as the signal
quality is poor.
Multipath can exist in environments where there are reflective surfaces (i.e. metal, glass, etc.). Avoid mounting access points
on these surfaces.
Below is a list of multipath effects:
Data Corruption
Occurs when multipath is so severe that the receiver is unable to detect the transmitted information.
Signal Nulling
Occurs when the reflected waves arrive exactly out of phase with the main signal and cancel the main signal completely.
Increased Signal Amplitude
Occurs when the reflected waves arrive in phase with the main signal and add on to the main signal thereby increasing the
signal strength.
Decreased Signal Amplitude
Occurs when the reflected waves arrive out of phase to some extent with the main signal thereby reducing the signal
amplitude.
Use of Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM), which is used by 802.11a and 802.11g, can help to reduce issues
seen in high multipath environments.
100
50 mW
Page 40

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 40
If using 802.11b in a high multipath environment, lower data rates should be used in those areas (i.e. 1 and 2 Mbps).
Use of antenna diversity can also help in such environments.
Verification with Site Survey Tools
These are many tools and applications that can be utilized to verify coverage, quality and configuration.
• Cisco Wireless Control System (WCS) for Unified Wireless LAN management
• Cisco Wireless LAN Solution Engine (WLSE) for Autonomous Wireless LAN management
• Cisco Spectrum Expert
• AirMagnet (Survey, WiFi Analyzer, VoFi Analyzer, Spectrum Analyzer)
• Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series
Cisco 792xG Neighbor List
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series can be utilized to verify coverage by using the Neighbor List menu.
By Default, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series only scans when the current signal lowers to a certain threshold,
so only one access point may be visible in the list if configured for auto scan mode.
To see all access points in the neighbor list menu, place a call from the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series to a
wired IP phone, where scanning occurs constantly while the phone call is active in auto scan mode.
Otherwise configure continuous scan mode.
The connected access point will be highlighted in red.
Access the neighbor list menu on the phone by pressing Settings > Status > Neighbor List
Cisco 792xG Site Survey
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series has a Site Survey application, which is an offline mode that gathers
information about the access points for the configured network profile and generates and HTML report after exiting the
application.
Page 41

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 41
To access the Site Survey application, navigate to Settings > Status > Site Survey.
To view the HTML report, select System > Site Survey from the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series webpage.
This information can be utilized to confirm access point configuration as well as coverage.
The neighbor table shows which access points (along the column) are neighbors of the access points with the strongest signal
listed in the row. The percentage of time that the access point had the highest RSSI is displayed as well as the RSSI range for
that access point when it was observed. The access point name is hyperlinked to the access point detail listed below.
Page 42

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 42
Page 43

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 43
Configuring Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Cisco Unified Communications Manager provides many different phone, calling and security features.
Phone Button Templates
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports 6 lines. The default phone button template includes support for 2
lines and 4 speed dials.
Custom phone button templates can be created with the option for many different features, which can then be applied on a
phone by phone basis.
Softkey Templates
Custom softkey templates can be created with the option of giving additional feature access or limiting feature access.
Softkeys are assigned based on the state of the phone (on hook, connected, on hold, ring in, off hook, connected transfer, digits
after first, connected conference, ring out, off hook with feature, remote in use, connected no feature).
The order of the softkeys can also be arranged when creating a custom softkey template.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series has 2 softkeys available. The feature listed first in the softkey template will
be displayed on the left softkey if on a call, where the other features will be listed under the options menu on the right softkey.
Page 44

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 44
Security Profiles
Security profiles can be utilized to enable authenticated mode or encrypted mode, where signaling, media and phone
configuration file encryption.
The Certificate Authority Proxy Function (CAPF) to be operational.
Each Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series has a Manufactured Installed Certificate (MIC).
Page 45

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 45
G.722 Advertisement
Cisco Unified Communications Manager versions 5.0 and later support the ability to configure whether G.722 is to be a
supported codec system wide or not.
Earlier versions of Cisco Unified Communications Manager do not have this capability, where a Cisco Unified Wireless IP
Phone 7925G Series will attempt to use G.722 assuming the other endpoint also advertises G.722 capabilities.
If using a version of Cisco Unified Communications Manager prior to 5.0 and want to disable G.722 capabilities, then the latest
device package will need to be applied to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager to enable this product specific
configuration option for each Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
For more information, refer to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager documentation.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Product Specific Configuration Options
On the IP Phone Configuration page in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration, the following Cisco Unified
Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series configuration options are available.
For an explanation of these options, click the "?" on the configuration page.
Product specific configuration options can be configured in bulk via the Bulk Admin Tool if using Cisco Unified
Communications Manager 5.0 and later. If using a prior version, then must be configured separately.
As of the 1.4(1) release Multiple Level Vendor Configuration is allowed to override common settings.
Some of the product specific configuration options can be configured on an enterprise phone, common phone profile or
individual phone configuration level.
Page 46

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 46
Field Name
Description
Disable Speakerphone
Speakerphone capabilities can optionally be disabled.
Gratuitous ARP
Determines whether the phone will learn MAC addresses from Gratuitous ARP
responses or not.
Settings Access
Settings Access can be used to limit user access to certain menus (i.e. Network
Profiles).
Web Access
This parameter indicates whether the phone will accept connections from a web
browser or another HTTP client. Web Access can be set to Full, where
configuration changes can be made remotely or Read Only to provide information
but not allowing changes to be made.
Locked Profiles
Individual profiles can also be locked, which does not allow the user to modify
those settings.
Page 47

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 47
Load Server
A load server can be specified in IP format (x.x.x.x) if wanting to use an alternate
TFTP server for phone firmware downloads.
Admin Password
The admin password is used for web access. With Cisco Unified Communications
Manager 5.0 or later the admin password must be managed in Communications
Manager Administrator page, where previous versions allow local management.
Special Numbers
Special numbers can be programmed to dial out regardless of keypad lock state (i.e.
911).
Application URL
The application URL can be configured, which will convert the application button
to a service URL button or as a speed dial.
The application URL can be configured to link to a Push To Talk server for quick
access.
(I.e. PTT server =
http://x.x.x.x:8085/PushToTalk/displayPhoneGroupsMenu.do?sep=#DEVICENAM
E#)
To configure the application button as a speed dial, enter in the format as “Dial:X”
(i.e. Dial:23675).
“Send” Key Action
“Send” key action determines whether the green dial button is to use onhook
dialing and serve as last number redial, where a list of previously dialed numbers
will be listed, or to use offhook dialing, which will play dial tone.
Phone Book Web Access
Phone book web access must be set to “Allow Admin” in order to access the phone
book via the web page.
Unlock-Settings Sequence
By default, **# must be entered to unlock a menu that contains configurable items,
which can optionally be disabled.
Application Button Activation
Timer
The activation timer and priority of the application button can also be specified.
This determines how long the button must be pressed and held to activate.
Application Button Priority
If the priority is low, then will only function when the keypad is unlocked and on
the home screen. Medium priority will allow the application button to function
when in any menu or XML screen and high priority will allow the application
button to function when in any state including keypad lock.
Out of Range Alert
An out of range alert can be configured to beep once or periodically to audibly
notify the user that they have traveled out of the coverage area.
Scan Mode
Scan mode allows for auto, continuous, and single AP options, where auto
primarily scans only when on call and single AP only at power on.
Restricted Data Rates
The restricted data rates feature utilizes the Traffic Stream Rate Set (TSRS)
information element from CCX v4, which can define a data range (upper and
lower) for the client to use (i.e. 12 - 24 Mbps). This can be beneficial for
environments that have legacy clients requiring lower data rates to be enabled on
the access point, but also preventing other clients from downshifting to lower rates,
which lowers overall throughput and capacity. When enabled the Cisco Unified
Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will not transmit below 12 Mbps for 802.11a and
11 Mbps for 802.11b/g.
Power Off When Charging
Power off when charging feature will power off the phone when placed on AC
power.
Page 48

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 48
Cisco Discover Protocol (CDP)
Enables or disables CDP.
Advertise G.722 Codec
G.722 capabilities can be configured on a phone by phone basis and optionally
override the system default.
Home Screen
By default the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will show the
traditional screen with the four icons for directory, services, settings and line
access.
FIPS Mode
The Federal Information Process Standards (FIPS) mode can optionally be enabled.
Auto Line Select
When enabled, indicates that the phone will shift the call focus to incoming calls on
all lines. When disabled, the phone will only shift the focus to incoming calls on
the currently used line.
Bluetooth
Indicates whether the Bluetooth device on the phone is enabled or disabled.
File System Verification
This parameter indicates whether the phone will perform a file system integrity
check as part of the firmware upgrade process. Enable this option to troubleshoot
file system issues. This feature may impact phone performance if it is enabled.
Minimum Ring Volume
This parameter controls the minimum ring volume on the phone. This value is set
by the administrator, and can not be changed by an end user. The end user can
increase the ring volume, but may not decrease the ring volume below the level
defined. The minimum ring volume range is from 0 to 7, with 0 (silent) being the
default value.
Below shows the main phone screen (left) and line view (right) display options for the home screen.
Note: If configuring the “Admin Password” in Cisco Unified Communications Manager versions 5.1, 6.0, 6.1, 7.0, 7.1, 8.0 or
later and web access is set to “Full”, then it is recommended to enable TFTP encryption via the device security profile.
As of the 1.3(3) release, if settings access is set to “Disabled”, then the current ring volume will be locked in and will no longer
be configurable.
To configure product specific configuration options for the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series with Cisco Unified
Communications Manager Express, create an ephone template with the necessary options.
Page 49

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 49
"service phone <module> <value>"
Field Name
Module
Value
Disable Speakerphone
disableSpeaker
false = Enabled; true = Disabled
Gratuitous ARP
garp
0 = Enabled; 1 = Disabled
Settings Access
settingsAccess
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled; 2 = Restricted
Web Access
webAccess
0 = Full; 1 = Disabled; 2 = ReadOnly
Locked Profiles
WLANProfile<1-4>
0 = Unlocked; 1 = Locked, 2 = Restricted
Load Server
loadServer
x.x.x.x
Admin Password
adminPassword
(i.e. Cisco)
Special Numbers
specialNumbers
(i.e. 411,911)
Application URL
PushToTalkURL
http://x.x.x.x
“Send” Key Action
sendKeyAction
0 = Onhook Dialing; 1 = Offhook Dialing
Phone Book Web Access
phoneBookWebAccess
0 = Deny All; 1 = Allow Admin
Unlock-Settings Sequence
unlockSettingsSequence
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled
Application Button Activation
Timer
appButtonTimer
0 = Disabled; <1-5> = <1-5> seconds
Application Button Priority
appButtonPriority
0 = Low; 1 = Medium; 2 = High
Out of Range Alert
outOfRangeAlert
0 = Disabled; 1 = Beep Once; <2-4> = Beep every
<10,30,60> seconds
Scan Mode
scanningMode
0 = Auto; 1 = Single AP; 2 = Continuous
Restricted Data Rates
restrictDataRates
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled
Power Off When Charging
powerOffWhenCharging
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled
Cisco Discover Protocol (CDP)
cdpEnable
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled
Advertise G.722 Codec
g722CodecSupport
0 = Use System Default; 1 = Disabled; 2 = Enabled
Home Screen
homeScreen
0 = Main Phone Screen; 1 = Line View
FIPS Mode
fipsMode
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled
Auto Line Select
autoSelectLineEnable
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled
Bluetooth
bluetooth
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled
File System Verification
fileSystemVerificationEnable
0 = Disabled; 1 = Enabled
Minimum Ring Volume
minimumRingVolume
0 = Silent; <1-7> = Different Volume Levels
Page 50

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 50
Application Button
thumbButton1
PTTH<1-6>
With Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express, the “thumbButton1” command can tie the application button to a
specific line.
For example, if line 2 is an intercom line tied to a multicast paging group, then this can be configured to achieve Push To Talk.
Enable individual phone configuration files with the following commands.
telephony-service
cnf-file perphone
create cnf-files
For more information on these features, see the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Administration Guide or the Cisco
Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Release Notes.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/phones/ps379/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/phones/ps379/prod_release_notes_list.html
Configuring the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller and Access
Points
When configuring the access points, use the following guidelines:
• Set “Quality of Service (QoS)” to “Platinum”.
• Ensure the “WMM Policy” is set to “Allowed” or “Required”
• Ensure “Aironet IE” is enabled
• Disable “P2P (Peer to Peer) Blocking Action” / “Public Secure Packet Forwarding (PSPF)”
• Disable “DHCP Address Assignment”
• Ensure “MFP Client Protection” is set to disabled or optional
• Ensure “Client Band Select” is not enabled
• Ensure “Admission Control Mandatory” is “Enabled” for Voice
• Ensure “Load-based CAC” is “Enabled” for Voice
• Ensure “Admission Control Mandatory” is “Disabled” for Video
• Ensure the “EDCA Profile” is set to “Voice Optimized”
• Ensure “Enable Low Latency MAC” is disabled
• Ensure “Aggressive Load Balancing” in the Controller configuration or “Client Load Balancing” in the WLAN
configuration are disabled
• Enable “Symmetric Mobile Tunneling Mode” if Layer 3 mobility is being used
• Ensure “ARPUnicast” is disabled, where proxy ARP will then be enabled
• Ensure that “DTPC” is “Enabled”
• Enable “Short Preamble” if using 2.4 GHz
Page 51

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 51
Note: If clients from other regions are present and will attempt to associate with the wireless LAN, then ensure that World
Mode (802.11d) is enabled.
When using 802.1x authentication, it is recommended to implement CCKM to offer fast secure roaming.
SSID / WLAN Settings
The SSID to be used by voice clients can be configured to only apply to a certain 802.11 radio type.
It is recommended to have the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series operate on the 5 GHz band due to have many
channels available and not as many interferers as the 2.4 GHz band has.
In order to utilize CCKM, enable WPA2 policy with AES encryption and 802.1x + CCKM for authenticated key management
type when the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series is running firmware version 1.3(4) or later in order to enable fast
secure roaming.
If the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series is running firmware version 1.3(3) or earlier, then enable WPA policy
with TKIP encryption and 802.1x + CCKM for authenticated key management type in order to enable fast secure roaming.
Page 52

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 52
The WMM policy can be set to “Required” only if the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series or other WMM enabled
phones will be using this SSID.
If 7920 or other non-WMM clients will associate using this SSID, then ensure the WMM policy is set to “Allowed”.
Enable “7920 AP CAC” to advertise Qos Basic Service Set (QBSS) to the client.
Configure session timeout as necessary. It is recommended to extend the timeout to avoid possible interruptions during reauthentication (i.e. 86400).
Enable Aironet Extensions (Aironet IE).
Ensure P2P Blocking Action should be disabled.
Disable client exclusion for the voice SSID.
DHCP Address Assignment should be disabled.
MFP client protection should be disabled or only set to optional.
For optimal battery performance and quality, use DTIM of 2 with a beacon period of 100ms.
Ensure Client Load Balancing and Client Band Select are disabled for the voce SSID.
Page 53

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 53
For the autonomous access point, ensure that the SSID is configured for open + eap as and network-eap when using 802.1x
authentication.
As of the 1.3(2) release, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series utilizes open + eap when doing 802.1x
authentication, but utilized network-eap in previous releases.
dot11 ssid voice
vlan 21
authentication open eap eap_methods
authentication network-eap eap_methods
authentication key-management wpa cckm
admit-traffic
If the autonomous access point is registered to a WDS (Wireless Domain Services) server, ensure both leap and eap types of
authentication are enabled in the WDS configuration.
wlccp authentication-server infrastructure method_Infrastructure
wlccp authentication-server client mac method_Clients
wlccp authentication-server client eap method_Clients
wlccp authentication-server client leap method_Clients
wlccp wds priority 255 interface BVI1
Controller Settings
In releases prior to 6.0, Aggressive Load Balancing was configured in the General Controller settings.
In 6.0 and later, this is referred to as Client Load Balancing and is configurable under the WLAN configuration (SSID
settings).
Page 54

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 54
If using layer 3 mobility, then symmetric tunneling should be enabled .
In the recent versions, Symmetric Mobility Tunneling is enabled by default and non-configurable.
When multiple Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controllers are to be in the same mobility group, then the IP address and MAC
address of each Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller should be added to the Static Mobility Group Members configuration.
Page 55

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 55
802.11 Network Settings
If using 5 GHz, ensure the 802.11a network status is set to enabled.
Set the beacon period to 100ms.
Ensure DTPC Support is enabled.
If using 802.11n capable access points, ensure ClientLink is enabled.
Configure 12 Mbps as the mandatory (basic) rate and 18 – 24 or 54 Mbps as supported (optional) rates.
36-54 Mbps can optionally be disabled, if there are not any applications that can benefit from those rates.
Enable CCX Location Measurement.
Page 56

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 56
If using 2.4 GHz, ensure the 802.11b/g network status and 802.11g is set to enabled.
Set the beacon period to 100ms.
Use the short preamble setting in the 2.4 GHz radio configuration setting on the access point when no legacy clients that require
a long preamble are present in the wireless LAN. By using the short preamble instead of long preamble, the wireless network
performance is improved.
Ensure DTPC Support is enabled.
If using 802.11n capable access points, ensure ClientLink is enabled.
Configure 12 Mbps as the mandatory (basic) rate and 18 – 24 or 54 Mbps as supported (optional) rates assuming that there will
not be any 802.11b only clients that will connect to the wireless LAN.
If there are existing 802.11b clients, then 11 Mbps should be set as the mandatory (basic) rate and 12-24 or 54 Mbps as
supported (optional).
36-54 Mbps can optionally be disabled, if there are not any applications that can benefit from those rates.
Enable CCX Location Measurement.
Auto RF
When using the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller it is recommended to enable Auto RF to manage the channel and
transmit power settings. If electing to utilize the Auto-RF feature on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller, it is
recommended to use version 4.1.185.0 or later.
Configure the access point transmit power level assignment method for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which band is to be
utilized.
Page 57

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 57
If using 5 GHz, ensure that channel 165 is not enabled in the DCA list as the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series
does not support channel 165.
If using 2.4 GHz, only channels 1, 6, and 11 should be enabled in the DCA list.
Page 58

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 58
Individual access points can be configured to override the global setting to use dynamic channel and transmit power assignment
for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which band is to be utilized.
Other access points enabled can be enabled for Auto RF and workaround the access points that are statically configured.
This may be necessary if there is an intermittent interferer present in an area.
Enable ClientLink if using 802.11n capable access points.
CleanAir should be enabled if using capable access points (i.e. Cisco Aironet 3500 Series).
Page 59

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 59
EDCA Parameters
Set the EDCA profile for “Voice Optimized” and disable “Low Latency MAC” for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which
band is to be utilized.
Low Latency MAC (LLM) reduces the number of retransmissions to 2-3 per packet depending on the access point platform, so
it can cause issues if multiple data rates are enabled.
LLM is not supported on the Cisco 802.11n access points.
DFS (802.11h)
In the DFS (802.11h) configuration, channel announcement and quite mode should be enabled.
Power constraint should be left un-configured or set to 0 dBm as DTPC will be used by the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone
7925G Series to control the transmission power.
In later versions of the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller it does not allow both TPC (Power Constraint) and DTPC
(Dynamic Transmit Power Control) to be enabled simultaneously.
Page 60

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 60
Call Admission Control Settings
Enable Call Admission Control (TSPEC) for Voice and configure maximum bandwidth and reserved roaming bandwidth
percentages for either 5 or 2.4 GHz depending on which band is to be utilized.
Maximum bandwidth default setting for voice is 75% where 6% of that bandwidth is reserved for roaming clients.
Roaming clients are not limited to using the reserved roaming bandwidth, but is to reserve some bandwidth in case all other
bandwidth is utilized.
Will want to ensure load-based CAC is enabled, which is available in the 4.1 release for the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN
Controller, but not currently available on the autonomous access point platform.
Load-based CAC will account for non-TSPEC clients as well as other energy on the channel.
Enable Traffic Stream Metrics (TSM).
Page 61

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 61
Call Admission Control for Video should be disabled.
After enabling Call Admission Control, the following configuration should be enabled, which can be displayed in the “show
run-config”.
Page 62

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 62
Call Admision Control (CAC) configuration
Voice AC - Admission control (ACM)............ Enabled
Voice max RF bandwidth........................ 75
Voice reserved roaming bandwidth.............. 6
Voice load-based CAC mode..................... Enabled
Voice tspec inactivity timeout................ Disabled
Video AC - Admission control (ACM)............ Disabled
Voice Stream-Size............................. 84000
Voice Max-Streams............................. 2
Video max RF bandwidth........................ 25
Video reserved roaming bandwidth.............. 6
The voice stream-size and voice max-streams values can be adjusted as necessary by using the following command.
config 802.11a cac voice stream-size 84000 max-streams 2
Ensure QoS is setup correctly under the WLAN / SSID configuration, which can be displayed via “show wlan <WLAN id>”.
Quality of Service............................... Platinum (voice)
WMM.............................................. Allowed
Dot11-Phone Mode (7920).......................... ap-cac-limit
Wired Protocol................................... 802.1P (Tag=6)
When enabling Call Admission Control on the autonomous access point, the admission must be unblocked on the SSID as well.
It is required to enable Call Admission Control on the SSID configuration, regardless of Admission Control being enabled for
Voice or Video.
Load-based CAC and support for multiple streams are not present on the autonomous access points therefore it is not
recommended to enable CAC on autonomous access points.
The autonomous access point only allows for 1 stream and the stream size is not customizable, therefore SRTP and barge will
not work if CAC is enabled.
dot11 ssid voice
vlan 21
authentication open eap eap_methods
authentication network-eap eap_methods
authentication key-management wpa cckm
admit-traffic
Also ensure that the PHY rate configured on the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series is enabled as a nominal rate in
the STREAM configuration of the autonomous access point.
Recommend to use the defaults, where 5.5, 6.0, 11.0, 12.0 and 24.0 Mbps are enabled as nominal rates for 802.11b/g and 6.0,
12.0 and 24.0 Mbps enabled for 802.11a.
If enabling the STREAM feature either directly or via selecting “Optimized Voice” for the radio access category in the QoS
configuration section, ensure that only voice packets (RTP) are being put into the voice queue. Signaling packets (SCCP)
should be put into a separate queue. This can be ensured by setting up a QoS policy mapping the DSCP to the correct queue.
For more information about Call Admission Control and QoS, refer to the “Configuring QoS” chapter in the Cisco IOS
Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Aironet Access Points at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/wireless/access_point/12.3_8_JA/configuration/guide/s38qos.html
Page 63

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 63
Configuring QoS Basic Service Set (QBSS)
There are three different versions of QoS Basic Service Set (QBSS) that the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series
supports.
The first version from Cisco was on a 0-100 scale and was not based on clear channel assessment (CCA), so it does not account
for channel utilization, but only the 802.11 traffic traversing that individual access point’s radio. So it does not account for
other 802.11 energy or interferers using the same frequencies. The max threshold is defined on the client side, which is set to
45. This would allow for up to 7 calls at 11 Mbps plus some background traffic.
QBSS is also a part of 802.11e, which is on a 0-255 scale and is CCA based. So this gives a true representation on how busy
the channel is. The max threshold is also defined on the client side, which is set to 105.
The second version from Cisco is based on the 802.11e version, but allows the default max threshold of 105 to be optionally
configured.
Each version of QBSS can be optionally be configured on the access point.
For the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller, enabling WMM will enable the 802.11e version of QBSS. There are also the
“7920 Client CAC” and “7920 AP CAC” options, where “7920 Client CAC” will enable Cisco version 1 and “7920 AP
CAC” enables Cisco version 2. See the “SSID / WLAN QoS Settings” section for more info.
For the Cisco Autonomous Access Point, “dot11 phone” or “dot11 phone dot11e” will enable QBSS.
“Dot11 phone” will enable the 2 Cisco versions, where “dot11 phone dot11e” will enable both CCA versions (802.11e and
Cisco version 2). It is recommended to enable “dot11 phone dot11e”.
Page 64

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 64
Below are the commands to change the QBSS max threshold for each platform type.
Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller = “config advanced 802.11b 7920VSIEConfig call-admission-limit <value>”
Cisco Autonomous Access Point = “dot11 phone cac-thresh <value>”
Configuring Auto-Immune
It is recommended to disable the Auto-Immune feature on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller.
The Auto-Immune feature was introduced in the 4.2.176.0 release, which was enabled by default and non-configurable.
As of the 4.2.207.0, 5.2.193.0 and 6.0.182.0 releases this feature is disabled by default but can be enabled optionally.
To view the Auto-Immune configuration on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and
enter the following command.
(Cisco Controller) >show wps summary
Auto-Immune
Auto-Immune.................................... Disabled
Page 65

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 65
Client Exclusion Policy
Excessive 802.11-association failures.......... Enabled
Excessive 802.11-authentication failures....... Enabled
Excessive 802.1x-authentication................ Enabled
IP-theft....................................... Enabled
Excessive Web authentication failure........... Enabled
Signature Policy
Signature Processing........................... Enabled
To disable the Auto-Immune feature on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and enter
the following command.
(Cisco Controller) >config wps auto-immune disable
Configuring the WLAN Controller EAP-Request and EAPOL-Key Timeouts
If using EAP, the EAP-Request Timeout on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller should be set to at least 20 seconds.
In later versions of Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller software, the default EAP-Request Timeout was changed from 2 to
30 seconds.
The default timeout on the Cisco ACS server is 20 seconds.
To view the EAP configuration on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and enter the
following command.
(Cisco Controller) >show advanced eap
EAP-Identity-Request Timeout (seconds)........... 30
EAP-Identity-Request Max Retries................. 2
EAP Key-Index for Dynamic WEP.................... 0
EAP Max-Login Ignore Identity Response........... enable
EAP-Request Timeout (seconds).................... 30
EAP-Request Max Retries.......................... 2
EAPOL-Key Timeout (milliseconds)...................... 1000
EAPOL-Key Max Retries............................ 2
To change the EAP-Request Timeout on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the controller and enter
the following command.
(Cisco Controller) >config advanced eap request-timeout 30
As of 6.0.182.0 release, the EAPOL-Key Timeout is configurable in milliseconds, where in previous releases it was only
allowed to be configured in seconds.
It is recommended to set the EAPOL_Key timeout to 200 milliseconds.
Page 66

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 66
The EAPOL-Key Timeout should not exceed 1 second (1000 milliseconds).
Configuring Proxy ARP
To advertise the proxy ARP information element, ensure that Aironet extensions are enabled.
Ensure proxy ARP is enabled, where ARP Unicast Mode will be displayed as disabled on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN
Controller.
Telnet or SSH to the controller and enter “show network” or “show network summary” depending on the Cisco Unified
Wireless LAN Controller version.
If ARP Unicast Mode is enabled, enter “config network arpunicast disable”.
As of the 5.1.151.0 release, proxy ARP is always enabled and non-configurable.
For autonomous access points, enter “dot11 arp-cache optional”.
Configuring TKIP Countermeasure Holdoff Time
TKIP countermeasure mode can occur if the Access Point receives two message integrity check (MIC) errors within a 60
second period. When this occurs, the Access Point will de-authenticate all TKIP clients associated to that 802.11 radio and
holdoff any clients for the countermeasure holdoff time (default = 60 seconds).
To change the TKIP countermeasure holdoff time on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controller, telnet or SSH to the
controller and enter the following command:
(Cisco Controller) >config wlan security tkip hold-down <nseconds> <wlan-id>
Page 67

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 67
For the autonomous Access Point, enter the time in seconds to holdoff clients if a TKIP countermeasure event occurs.
Interface dot11radio X
countermeasure tkip hold-time <nseconds>
For more information about these topics, refer to the Enterprise Mobility Design Guide at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/solutions/Enterprise/Mobility/emob41dg/eMob4.1.pdf
VLANs and Autonomous Access Points
Segment wireless voice and data into separate VLANs.
When using autonomous access points, use a dedicated native VLAN. Autonomous access points use Inter-Access Point
Protocol (IAPP), which is a multicast protocol.
For the native VLAN, it is recommend not to use VLAN 1 to ensure that IAPP packets are exchanged successfully.
Ensure that Public Secure Packet Forwarding (PSPF) is not enabled for the voice VLAN as this will prevent clients from
communicating directly when associated to the same access point. If PSPF is enabled, then the result will be no way audio.
The network ID in the SSID configuration, should only be disabled if Layer 3 mobility is enabled where the Wireless LAN
Services Module (WLSM) is deployed.
Configuring the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series
There are three methods for configuring network settings on the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series:
Configuring Phones with the Keypad
The network profiles can be configured by navigating to Settings > Network Profiles.
It may be required to unlock the screen by pressing **#.
For more information, refer to the “Configuring Settings on the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series” in the
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Administration Guide at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/phones/ps379/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html
Configuring Phones with the Web Interface
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series has an HTTPS enabled web interface that can be accessed via the
802.11a/b/g radio or USB.
If using USB, then set a static IP on the PC’s USB network interface (i.e. 192.168.1.X /24). By default, the Cisco Unified
Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series USB is statically set to 192.168.1.100 /24.
In order to make configuration changes via the web interface, then web access must be set to “Full”, which will also enable a
few additional menus.
Log into the administration web pages by using these defaults:
username = “admin” / password = “Cisco”
Page 68

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 68
Note: It is not recommended to use the 192.168.1.0 /24 network for the wireless LAN interface as that network is used by the
USB interface by default. If wanting to use the 192.168.1.0 /24 network for the wireless LAN, then either change the USB IP
address on the phone or do not charge the phone via USB.
Configuring Phones with Wavelink Avalanche
Wavelink Avalanche is a comprehensive management solution for the Wireless LAN enterprise providing complete visibility
and control of Wireless LAN infrastructure and mobile client devices from a central console.
Wavelink Avalanche eases the configuration, deployment and management of Wireless LAN networks while offering extensive
flexibility through the support of a wide range of mobile devices and infrastructure.
Refer to the Wavelink section below for more info.
For more information, refer to the “Using the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Web Pages” in the
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Administration Guide at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/phones/ps379/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html
Configuring the Network Profile Parameters
Use the following guidelines to configure network profiles.
• The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports multiple network profiles that allow one SSID per
network profile. 0 length SSIDs are not allowed.
• 5 different 802.11 modes are available.
Auto-RSSI
802.11a
802.11b/g
Auto-a
Auto-b/g
• As of the 1.3(3) release, Auto-a is the default 802.11 mode, so it will scan both 2.4 and 5 GHz channels and attempt to
on the 5 GHz band if the configured network is available.
• In previous releases, the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series would default to Auto-RSSI mode, which
would attempt to associate to the access point with the strongest signal.
• 802.11a mode will only scan 5 GHz channels and 802.11b/g mode will only scan 2.4 GHz channels, where it will then
attempt to associate to an access point if the configured network is available.
• For Auto-a and Auto-b/g modes, this is giving preference to one band over another. At power on, will scan all 2.4 and
5 GHz channels then attempt to associate to an access point for the configured network using the preferred band if
available. If the preferred band is not available, then the Cisco Unified Wireless Phone 7925G will try to use the less
preferred band if available. If the phone roams out of coverage of the preferred band, where the less preferred band
signal is available, then the phone will attempt to associate to that less preferred band.
• To extend battery life, ensure the call power save mode is configured for U-APSD/PS-POLL mode to utilize power
save mode during active calls.
• Active mode “None” may need to be used instead of U-APSD/PS-POLL if the access point does not support power
save enabled clients.
• As of the 1.3(3) release, the Prompt Mode feature can be optionally enabled. When enabled, the password will not be
stored in flash, but only in memory after entering manually after each power on sequence for seamless roaming.
However, the username can be stored after entering at the prompt, but can be overridden at the next login. If the
prompt is dismissed, then there is a “Login” softkey presented in order to invoke the login process. The Prompt Mode
feature is only supported with Network Profile 1. If multiple network profiles are enabled and Prompt Mode is
enabled, then the user would have to dismiss the login in order to switch to other enabled network profiles.
Page 69

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 69
• Below are the available security modes supported and which key management and encryption types can be used for
each mode.
Security Mode
Key Management
Encryption
Open
N/A
N/A
Open+WEP
Static
WEP (40 or 128 bit)
Shared Key
Static
WEP (40 or 128 bit)
LEAP
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
TKIP, AES, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
EAP-FAST
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
TKIP, AES, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
EAP-TLS
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
TKIP, AES, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
PEAP
802.1x, WPA, WPA2
TKIP, AES, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
AKM
802.1x, WPA, WPA2, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK
TKIP, AES, WEP (40 or 128 bit)
Open with WEP and Shared Key security modes require that the static WEP settings be entered.
Key Style
Key Size
Characters
ASCII
40
5
ASCII
128
13
HEX
40
10 (0-9, A-F)
HEX
128
26 (0-9, A-F)
• The AKM security mode is an auto authentication mode that can use either LEAP for 802.1x authentication or
WPA Pre-Shared Key.
• If using 802.11i (Pre-Shared key), enter the ASCII or hexadecimal formatted key.
Pre-Shared Key requires that a passphrase be entered in ASCII or hexadecimal format.
ASCII = 8-63 characters
HEX = 64 characters (0-9,A-F)
• AKM mode requires a key management type to be enabled on the Access Point.
For 802.1x authentication methods, WPA, WPA2 or CCKM is required.
For non-802.1x authentication, WPA-PSK or WPA2-PSK is required.
• If using open authentication plus WEP encryption or shared key authentication, enter the static WEP key
information that matches the access point configuration.
Note: CCKM will be negotiated if enabled on the Access Point when using 802.1x authentication with LEAP, EAP-FAST,
EAP-TLS, PEAP or AKM modes.
WEP with AKM is only applicable with 802.1x authentication (not WPA-PSK).
Page 70

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 70
If using 802.1x authentication via LEAP, EAP-FAST, PEAP or AKM (authenticated key-management) authentication modes,
then a username and password must be configured. AKM mode will use LEAP as the 802.1x method.
• Select whether to use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) or configure static IP information.
• If option 150 or 66 is not configured to provide the TFTP server IP address via the network’s DHCP scope, then enter
the TFTP server IP address info.
• To enable PEAP with server validation, select “Validate Server Certificate” after importing the authentication server
certificate.
• When using EAP-TLS, select either “Manufacturing Issued” or “User Installed” for the “Client EAP-TLS
Certificate” option after selecting EAP-TLS.
Note: WEP128 is listed as WEP104 on the Cisco Unified Wireless LAN Controllers.
Page 71

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 71
Note: If the TFTP IP is changed which is not included in the current Certificate Trust List (CTL) file, then TFTP will fail and
may prevent the phone from registering successfully to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager. The CTL file will need to
be erased manually in the Security Configuration menu from the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
Configuring Advanced Network Profile Settings
In the Advanced Network Profile settings, the minimum PHY rate can be adjusted. If 12 Mbps is not enabled in the wireless
LAN, then this parameter may need to be configured or enable 12 Mbps on the access point.
By limiting number of channels to be scanned, this can help reduce the time for access point discovery while passively scanning
DFS channels in 802.11a mode. This can also help preserve battery life.
If using this feature, then only disable those channels that are not used in the wireless LAN. If a channel is disabled that is
currently used by an access point, then the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series might not associate to the wireless
LAN successfully.
If all channels that are used in the wireless LAN are disabled on the phone, then use one of these methods to browse to the
Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series webpage:
• USB cable connected to the PC where full web access was previously enabled
• Re-enable all channels by using the factory default
Page 72

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 72
Installing Certificates
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports DER encoded binary X.509 certificates, which can be utilized with
EAP-TLS or for authentication server validation when using PEAP (MS-CHAPv2).
Extensible Authentication Protocol Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) is using the TLS protocol with PKI to secure
communications to the authentication server.
TLS provides a way to use certificates for both user and server authentication and for dynamic session key generation.
EAP-TLS provides excellent security, but requires client certificate management.
Page 73

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 73
Microsoft Certificate Authority (CA) servers are recommended as we have certified interoperability only with those CA types.
Other CA server types may not be completely interoperable with the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
Can utilize either the internal MIC (Manufacturing Installed Certificate) or install a User Installed certificate to be used for
authentication.
To use the MIC in the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series, the Manufacturing Root and Manufacturing CA
certificates must be exported and installed onto the RADIUS server.
After selecting “Export”, import the certificates into the RADIUS server and enable them in the certificate trust list.
For the user installed certificate method, select “Install” on the main certificates page, which will launch the installation wizard.
To generate the certificate signing request, enter the certificate information and import the certificate from the Certificate
Authority (CA) server that is signing the certificate. The signing CA root certificate is used for validation purposes to ensure
that the user certificate was indeed signed by the correct CA.
The Common Name defaults to “CP-7925G-SEP<MAC_Address>”, but can be customized, but must not be greater than 32
characters.
Browse to the Certificate Authority certificate and select “Submit”.
Only certificates with a key size of 1024 or 2048 are supported.
Certificates dated January 1 2038 and later are not supported.
Page 74

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 74
After “Submit” is selected, the certificate will then be generated.
The certificate will then be displayed and is now ready to be signed.
Select all of the certificate data in order to copy it to the Certificate Authority server to be signed.
Page 75

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 75
Select the method to submit a certificate request by using a base-64 encoded PKCS file.
Paste the certificate data from the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series to the Certificate Authority signing server and
submit for signing.
When the certificate has been signed, download the CA certificate in DER encoded format (base 64 encoded certificates are not
supported).
Ensure Client Authentication is listed in the Enhanced Key Usage section of the certificate details.
Page 76

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 76
After selecting “Import Step”, browse to the signed user certificate and select “Import” to complete the process.
Once the certificate is installed successfully, a confirmation page will be displayed.
The CA chain should already be enabled in the authentication server’s certificate trust list.
The authentication server certificate must also be imported into the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series for both the
MIC and User Installed methods. If the authentication server certificate was signed by a Certificate Authority (CA) server, then
that DER encoded root certificate will need to be imported into the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
If the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series has not registered to a Cisco Unified Communications Manager yet, then
the date and time must be configured manually for the first time.
Page 77

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 77
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series must be restarted after installing the certificate.
Click on the hyperlink to navigate to the “Phone Restart” page.
Click the “Restart” button to power cycle the phone.
Page 78

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 78
Using Templates to Configure Phones
Phone configuration templates can be exported and imported to other phones for quick configuration. The phone configuration
template will be encrypted using the specified encryption key (8-20 characters).
In order to access the Backup Settings menu, the web access must be set to “Full”.
For security reasons, the Wireless LAN security information (Username/Password, WPA Pre-shared key information, and WEP
key information) is not exported by default. In order to export this Wireless LAN security information, the network profile
must be configured to allow this capability. For each network profile where the Wireless LAN security information is to be
exported, configure the “Export Security Credentials” option to “True”. After selecting “True”, the Wireless LAN security
information will need to be re-entered. This will then allow that information to be exported and then imported to other Cisco
Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series phones.
Bluetooth Configuration
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series supports Bluetooth to allow wireless headset communications.
To pair a Bluetooth headset to the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series, follow the instructions below.
1. Choose Settings > Phone Settings > Bluetooth
2. Select “Enable” then select the left softkey “Save”
3. Select “Device List”
4. Select “Scan” (ensure the Bluetooth headset is in pairing mode)
5. Select “Pair” after the Bluetooth headset is discovered
6. Enter the Bluetooth passkey (will attempt to use 0000)
7. Select “Connect” after the Bluetooth headset is paired successfully
Page 79

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 79
Upgrading Phone Firmware
There are two methods for upgrading the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series firmware, which is either via wireless
TFTP or the phone web interface.
Wireless TFTP
To upgrade the phone firmware, run the executable for Cisco Unified Communications Manager version 4.1, 4,2 and 4.3 or
install the COP file for versions 5.1, 6.0, 6.1, 7.0, 7.1, 8.0 and later.
For information on how to install the COP file on CM versions 5.1 and later, refer to the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Operating System Administrator Guide at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cucm/cucos/7_1_2/cucos/iptpch7.html
During TFTP server download, the phone configuration file is parsed and the device load is identified. The phone
downloads the firmware files to flash if it is not running the specified image already.
Cisco Unified Communications Manager device load takes precedence over the TFTP firmware version.
The Load Server can be specified as an alternate TFTP server to retrieve firmware files in the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone
7925G Series product specific configuration in Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration.
To install the firmware on Cisco Unified Communications Manager Express, extract the contents of the TAR file and upload
into the router’s flash. Each file will need to be enabled for TFTP download. Configure the phone load and reset the phones to
upgrade the firmware.
Page 80

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 80
Example below:
tftp-server flash: CP7925G-1.4.1.LOADS
tftp-server flash:APPSH-1.4.1.SBN
tftp-server flash:GUIH-1.4.1.SBN
tftp-server flash:JSYSH-1.4.1.SBN
tftp-server flash:JUIH-1.4.1.SBN
tftp-server flash:SYSH-1.4.1.SBN
tftp-server flash:TNUXH-1.4.1.SBN
tftp-server flash:TNUXRH-1.4.1.SBN
tftp-server flash:WLANH-1.4.1.SBN
!
telephony-service
load 7925 CP7925G-1.4.1.LOADS
Web Interface
The phone firmware can be upgraded via the web interface by navigating to Phone Upgrade and browsing to the firmware TAR
file.
In order to access the Phone Upgrade menu, the web access must be set to “Full”.
Note: If the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series registers to Cisco Unified Communications Manager, web access to
the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series gets set to read-only mode. In this mode, firmware upgrades via the web
interface are not allowed.
Ultimately the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will use what is set as the phone load in the Cisco Unified
Communications Manager.
Wavelink Avalanche
The Wavelink Avalanche server IP address can be set either via DHCP option 149 or statically.
To provide the server IP address automatically, configure option 149 on the DHCP server.
ip dhcp pool 10.10.11.0
network 10.10.11.0 255.255.255.0
default-router 10.10.11.1
dns-server 10.10.10.20
domain-name cisco.com
option 150 ip 10.10.10.22
option 149 ip 10.10.11.128
Custom parameters can also be set via the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series web page in order to help group
clients for better management.
Page 81

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 81
When clients register with the Wavelink server, they will appear in the console.
To set client properties right click on the client and select “Client Settings”.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series will have parameters enabled by default.
Page 82

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 82
EnablerVer = 3.11-01
ModelName = CP7925G
Additional properties can be added as necessary for better client management.
Mobile Device Groups can be created to group clients based on client properties.
Enter the selection criteria either manually or using the wizard after right clicking on the mobile device group and selecting
“Settings”.
Page 83

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 83
To install the 7925G Configuration Utility for Wavelink Avalanche, select “Install Software Package” under the Software
Management menu.
Browse to the 7925G Configuration Utility package file (i.e. 7925CU-1.3.1.AVA).
Create a software collection to add the package to.
The license agreement will be displayed, after selecting “Next”,
Click on “Finish” when the installation is complete.
Note: The 7925CU must be installed locally on the Wavelink Avalanche server.
Page 84

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 84
The software package must then be enabled by right clicking on the package and selecting “Enable Package”.
Selection collections can also be created with their own selection criteria to determine which clients should receive the software
package.
Page 85

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 85
To configure the software package, right click on the package and select “7921CU”.
The 7925G Configuration Utility will then be launched.
Enter the profile name and enable the profile.
Configure the network profiles by specifying the Wireless LAN credentials.
PEAP and EAP-TLS are not supported in the Configuration Utility for Wavelink.
Page 86

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 86
Configure the network settings for the network profile.
Ensure that Wavelink server enable is set to “Yes”.
Configure whether the client will get the Wavelink IP info from DHCP or configured statically.
Page 87

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 87
Optionally set additional client parameters as necessary.
When the template has been completely configured, then select “Export to Wavelink” under the File menu.
A confirmation will then be displayed after the template has been exported successfully.
After the template has become available, will then need to push the package to the necessary clients.
This can be done on a device group or client level.
To update a single client, right click on it and select “Update Now”.
Can also optionally set “Force package sync during Update Now” in the client properties.
Using the Bulk Deployment Utility
The Bulk Deployment Utility for the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series is intended to help quicken the
provisioning and deployment process of many phones when unique 802.1x accounts are used with EAP-FAST, PEAP (MSCHAPv2) or LEAP or if a common set of credentials are used by all phones (i.e. WPA2-PSK or a common 802.1x account).
The utility allows the creation configuration files, which can be exported then enabled for TFTP download by the Cisco Unified
Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
This utility does not support certificate provisioning, which would be required in order to support server validation for PEAP or
EAP-TLS.
The utility does allow PEAP to be configured, but without the server validation option.
The Bulk Deployment Utility supports up to 1000 entries per CSV for export. If more than 1000 phones are being deployed,
then multiple CSV files will need to be created and imported.
If doing a bulk export, the username and password is applied to network profile 1 only.
Page 88

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 88
Before exporting the TFTP downloadable configuration files, a template must be created containing the Network Profile, USB,
Trace and Wavelink settings.
Configure the Profile Name as necessary.
Configure the network profile WLAN settings (SSID, 802.11 mode, Security Mode, WLAN credentials) to match the voice
WLAN.
If planning to use unique 802.1x accounts with the Bulk Export method, the username and password do not need to be
configured, as that will be specified in the CSV file.
By default, DHCP is enabled and is the recommended method, otherwise, would need a template per phone if planning to use
static IP addressing.
An alternate TFTP server can be set if the Cisco Communications Manager’s TFTP server IP is not set in option 150 for the
DHCP scope.
Page 89

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 89
Templates can be created for later use, by selecting File > Save As.
Do not overwrite the “7921Cfg.xml” file as that is the default template used when the utility opens.
Phone configuration files can be exported by either the Default Export method or the Bulk Export method.
If a common set of credentials is to be used by all phones (i.e. WPA2-PSK or a common 802.1x account), then use the Default
Export method.
If unique 802.1x accounts are to be deployed, then use the Bulk Export method.
Page 90

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 90
Default Export
If needing to deploy the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series with identical WLAN settings, then select the “Default
Export” method.
After selecting “Default Export” the utility will create a TFTP downloadable configuration file based on the common data
entered, which is exported to the application install path (C:\Program Files\Cisco Systems\7921BD).
A confirmation window will be displayed when the default TFTP downloadable config file has been exported successfully.
The default file will be in the format of “WLANDefault.xml”, which the phone does a TFTP get for when it powers on or
during re-provisioning.
Bulk Export
If needing to deploy the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series with unique 802.1x accounts utilizing EAP-FAST,
PEAP or LEAP, then select the “Bulk Export” method.
The common data entered plus a CSV containing the phone MAC address, username and password will be used to create the
template.
After selecting “Bulk Export”, a prompt to display the CSV file will be presented.
Up to 1000 entries are supported per CSV file.
The “userinfo.csv” file in the install path can be used as a template.
MAC,Username,Password
Page 91

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 91
001e7abb19c8,admin,Cisco
Once the CSV file is imported, the utility will create TFTP downloadable configuration files for each phone, which are exported
to the application install path (C:\Program Files\Cisco Systems\7921BD).
A confirmation window will be displayed when the TFTP downloadable config files have been exported successfully.
The files will be in the format of “WLAN<MAC>.xml”, which the phone does a TFTP get for when it powers on or reprovisions.
Pushing Configuration Files to the Cisco 792xG
The Bulk Deployment Utility does not have TFTP server capabilities, so a 3rd party TFTP server will need to be installed and
have the phone configuration files enabled for TFTP download.
It is recommended to install the TFTP server on the same system where the Bulk Deployment Utility is installed and have a
staging environment setup with the default phone credentials in order for the phone to auto-download the configuration files by
simply powering on the phones.
The staging environment setup, would need to have a single access point with the SSID “cisco” where the security mode is set
to open authentication and option 150 of the DHCP scope for the staging network to be configured to point to the TFTP server
hosting the phone configuration files.
It is not recommended to copy the configuration files to the Cisco Communication Manager’s TFTP server.
Once the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series gets its configuration file, then it will re-provision with the new
settings and attempt to join the intended WLAN based on the new credentials received.
The Bulk Deployment Utility is available for download on CCO.
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/ip-7900ser-crypto
Configuring the Local Phone Book and Speed Dials
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series contains local phone book and speed dials support.
As of the 1.4(1) release up to 200 contacts (100 contacts in previous releases).
99 speed dials referenced from the local phone book can be added for quick dial access. Speed dial #1 is reserved for
voicemail.
The left softkey on the home screen can be programmed for “Message” to access voice mail or to “PhBook” to access the local
phone book.
The local phone book and speed dials can be configured via the local keypad or via the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G
Series web interface. Since the web password is not managed by the user, the web interface is primarily intended for use by the
system administrator, where they can upload information into the phone book for the user. This requires that the “Phone Book
Web Access” product specific configuration item be set to “Allow Admin” as well as web access set to “Full”.
Page 92

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 92
The phone book data can be exported which can be imported onto other phones.
XML and CSV formats are supported as well as the CSV format used by the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7920.
Page 93

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 93
Increased Font
As of the 1.4(1) release, there are options for default (original) font or increased font.
The font size can optionally be configured locally on the phone.
(Settings>Phone Settings>Display Settings>Font Size)
Page 94

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 94
Default Font
Increased Font
Using Phone Designer
The Phone Designer application allows the ability to have a customer wallpaper and ringtone for each phone.
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series is supported in Phone Designer version 7.1(3) and later.
Page 95

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 95
Personalization must also be enabled in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager either in Enterprise Parameters, Common
Phone Profile or on a per phone level.
After installing the phone designer, a username and password as well as the IP address of the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager must be configured.
The user account must be created in the Cisco Unified Communications Manager and associated to the corresponding phone.
In order to configure the wallpaper, either select a pre-defined wallpaper or import a wallpaper from the local computer by
selecting “Import”.
To display the wallpaper on the phone, select “Preview on Phone”.
To activate and save the wallpaper to the phone flash, select “Save to Phone”.
In order to configure the ringtone, either select a pre-defined ringtone or import a ringtone from the local computer by selecting
“Import”.
To hear the ringtone on the phone, select “Preview on Phone”.
To activate and save the ringtone to the phone flash, select “Save to Phone”.
Page 96

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 96
The Phone Designer application can be downloaded from the following location.
http://tools.cisco.com/support/downloads/go/Redirect.x?mdfid=278875240
IP Phone Services
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series is capable of supporting Extensible Markup Language (XML) applications
as well as Java Mobile Information Device Profile (MIDP) applications.
Java MIDP support is included in the 1.4(1) release for the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
For information on IP phone services configuration, refer to the following URL.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cucm/admin/8_0_2/ccmcfg/b06phsrv.html
Extensible Markup Language (XML)
The following document provides the information needed for eXtensible Markup Language (XML) and X/Open System
Interface (XSI) programmers and system administrators to develop and deploy IP phone services.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cuipph/all_models/xsi/8_0_1/xsi_dev_guide.html
Below are features that are unique to the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series.
Page 97

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 97
Vibrate URI
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cuipph/all_models/xsi/8_0_1/supporteduris.html#wp1052264
Device URI
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/voice_ip_comm/cuipph/all_models/xsi/8_0_1/supporteduris.html#wp1078268
Java Mobile Information Device Profile (MIDP)
The following document provides the information needed for Java Mobile Information Device Profile (MIDP) programmers
and system administrators to develop and deploy IP phone services.
http://developer.cisco.com/web/jmapi/home
Troubleshooting
Stream Statistics
The Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series provides call statistic information, where MOS, jitter and packet counters
are displayed. DSCP for transmit and receive paths are also displayed, which can help to ensure that packets are being placed
into the correct queues upstream and downstream.
Browse to the phone’s web interface (https://x.x.x.x) and select “Stream Statistics” to view this information.
Page 98

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 98
This information is also available locally on the phone under Settings > Status > Call Statistics or if on a phone call press the
center button twice.
For more information, see the “Troubleshooting the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series” chapter in the Cisco
Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Administration Guide at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/phones/ps379/prod_maintenance_guides_list.html
Page 99

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 99
Network Statistics
Queue statistics can also be displayed by navigating to Settings > Status > Network Statistics.
If on a phone call, should see the “DataRcvVO” counter increasing assuming QoS has been deployed correctly.
This reflects that voice packets are being properly marked as UP6 (VO) downstream to the Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone
7925G Series.
Page 100

Cisco Unified Wireless IP Phone 7925G Series Deployment Guide 100
 Loading...
Loading...