Page 1

CHA PTER
6
Logical Object Dialog Boxes
This chapter describes the C65/76M dialog boxes for the logical objects. The following logical object
dialog boxes are available in the C65/76M:
• C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box, page 6-3
• C6576M Software Dialog Box, page 6-13
• C6576M Syslog Dialog Box, page 6-29
• C6576M VTP Dialog Box, page 6-34
• C6576M VLAN Dialog Box, page 6-37
• C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box, page 6-52
• C6576M BGP Dialog Box, page 6-68
• C6576M OSPF Dialog Box, page 6-78
• C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box, page 6-92
• C6576M IS-IS Dialog Box, page 6-100
• C6576M NDE Configuration Dialog Box, page 6-106
• C6576M STP Dialog Box, page 6-111
• C6576M ACL Configuration Dialog Box, page 6-113
• C6576M Loopback Dialog Box, page 6-117
• C6576M QoS Dialog Box, page 6-119
• C6576M QoS Policy Map Dialog Box, page 6-127
Table 6-1 lists the pop-up menu launch points for all C65/76M dialog boxes.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-1
Page 2
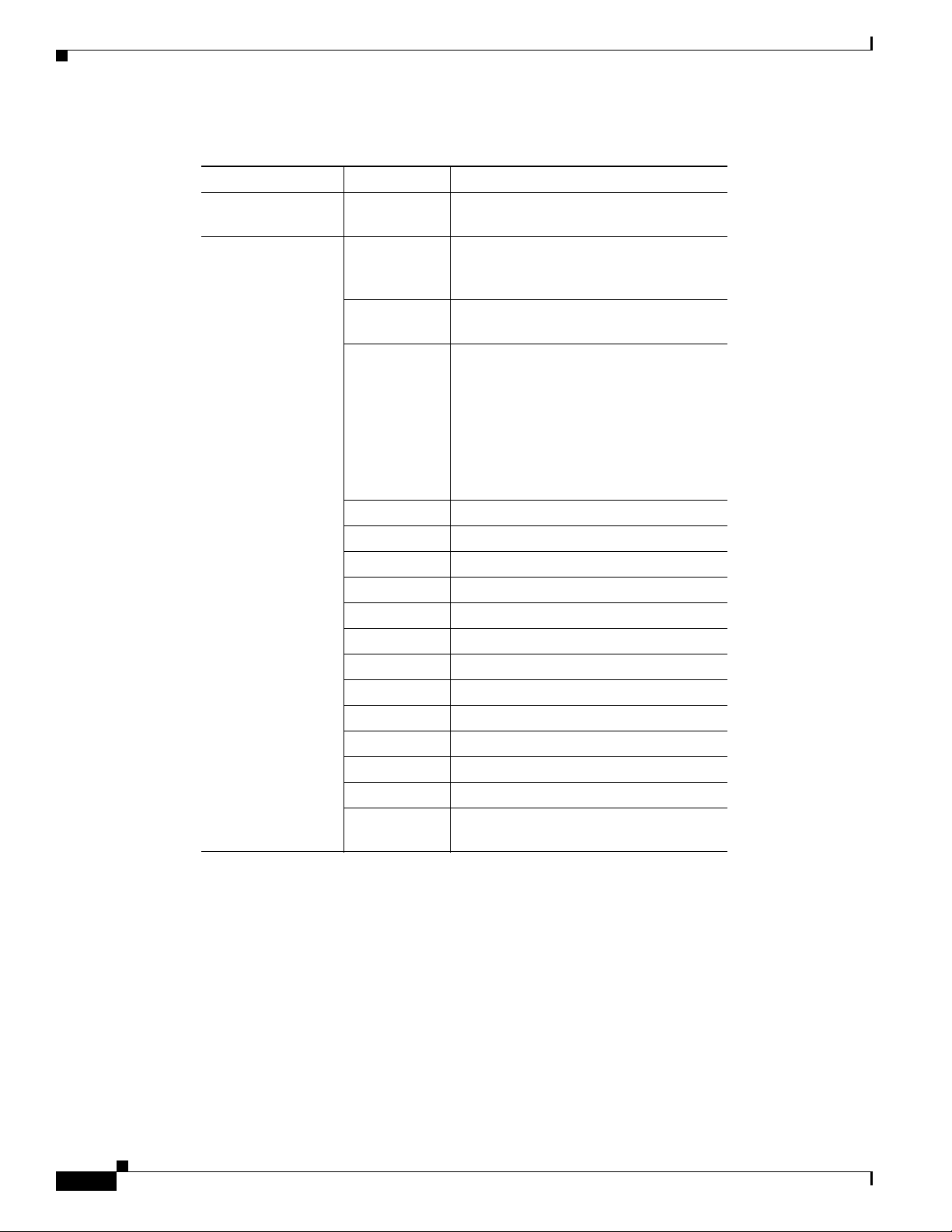
Table 6-1 Launch Points for the C65/76M Dialog Boxes
Container Object Dialog Box
Network
Physical
Network
Element
Container
(site, bay,
All dialogs (under the Cisco 6500/7600
Series Manager menu entry)
All dialogs (under the Cisco 6500/7600
Series Manager menu entry)
shelf, etc.)
Network
Element
NE Config/Mgmt Dialog
All logical object dialogs
Software Software Dialog
Syslog Dialog
VTP Dialog
VLAN Dialog
EtherChannel Dialog
BGP Dialog
OSPF Dialog
EIGRP Dialog
EtherChannel EtherChannel Dialog
Syslog Syslog Dialog
EIGRP EIGRP Dialog
BGP BGP Dialog
OSPF OSPF Dialog
VTP VTP Dialog
VLAN VLAN Dialog
STP STP Dialog
ISIS IS-IS Dialog
ACL ACL Dialog
NDE NDE Dialog
Loopback Loopback Dialog
QoS QoS Dialog
QoS Policy Map Dialog
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
6-2
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 3
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
The C6576M NE Config/Mgmt dialog box provides monitoring and management information for
properties related to the Catalyst 6000 family switch or Cisco 7600 series Internet Router. These
properties include the Telnet and Enable passwords, global performance logging, and SNMP properties
for the entire switch. This dialog box can be launched from a Network Element object within the
Network or Physical views.
The Network Element object list (left-hand side of the dialog box) allows multiple objects to be selected,
so that configuration changes can be applied to multiple Network Element objects at the same time.
Configuration Tab
Figure 6-1 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M Network Element dialog box.
Figure 6-1 Configuration Tab of the C6576M Network Element Dialog Box
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
System Area
IP Address Area
The System area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following information:
• System Name—Fully qualified name of the switch or router.
The IP Address area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following information:
• IP Address—IP address used to access the switch or router.
• MSFC—IP address of the management agent on the MSFC daughter card (only in Hybrid OS).
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-3
Page 4
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
Operating System Area
The Operating System area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following
information:
• Expected OS Type—This attribute is used by a client that initiates a deployment context to indicate
the type of operating system expected on a managed device. This can only be changed when the
device is decommissioned.
• Active OS Type—The operating system type detected on the managed device.
IOS Session
The IOS Session area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following information:
• Username—User name to establish an IOS management session with the device over telnet.
• Password—Password to establish an IOS management session with the device over telnet.
• EXEC Password—Password to enter privileged EXEC mode.
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Cat OS Session Area
The Cat OS Session area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following
information:
• Same As IOS?—If enabled, the IOS telnet username and password will be used to connect to the
• Username—User name to establish a CatOS management session with the device over telnet.
• Password—Password to establish a CatOS management session with the device over telnet.
• EXEC Password—Password to enter privileged EXEC mode in a CatOS session.
Note If the above passwords are incorrect, some dialog box values may report as ERROR.
Reset System Area
The Reset System area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following information:
• Last Restart Reason—Text message displaying why the switch or router was restarted.
• Reset button—Button used to reset the switch or router. This action power cycles the switch or
Supervisor module over CatOS in Hybrid OS configurations.
router. If clicked, a pop-up is displayed asking if you really want to reset the switch or router (see
Figure 6-2).
6-4
Note Only users with administrative privileges can use the Reset button.
Note Any changes to the running configuration will be saved automatically when the switch or router is reset
using the Reset button.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 5
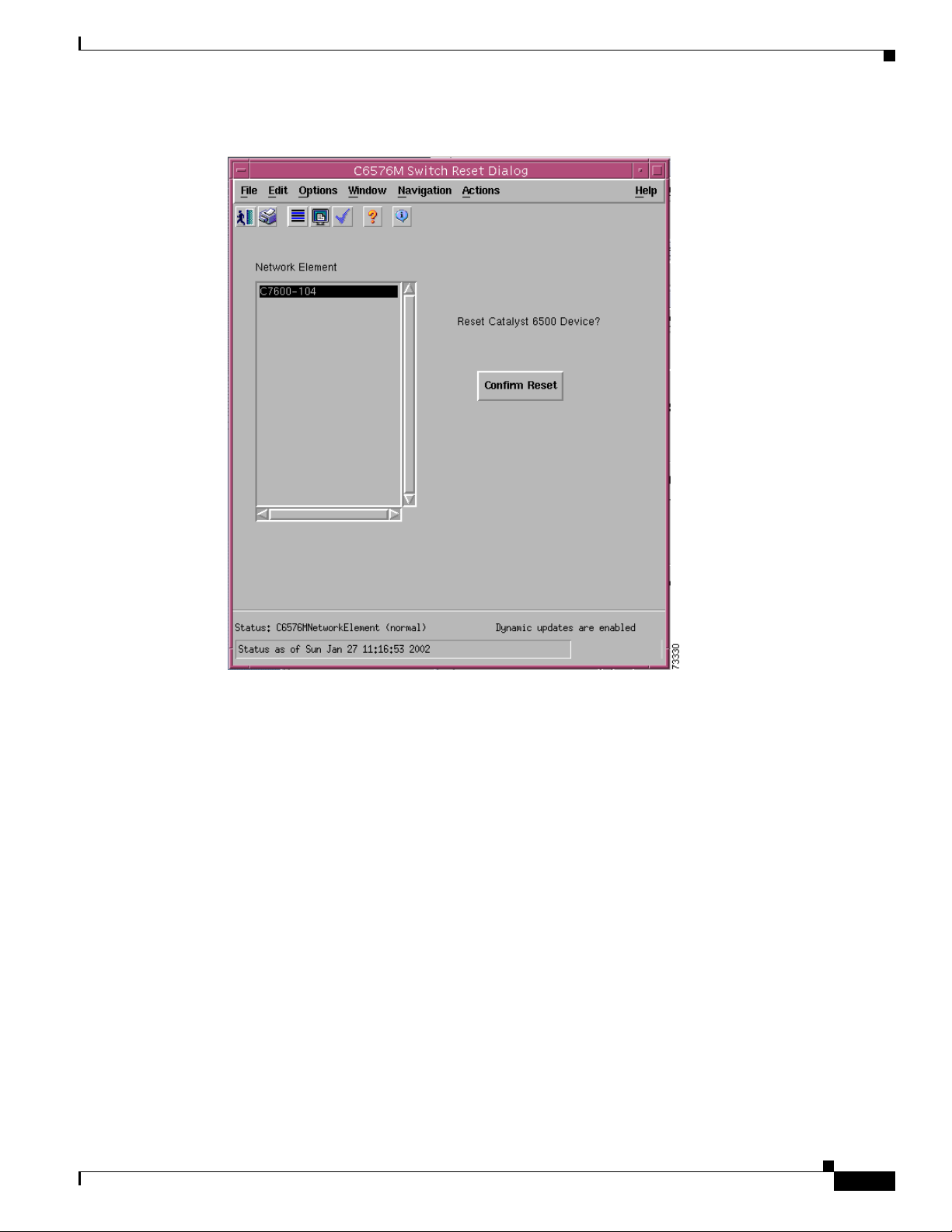
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-2 Confirmation Reset Window for a Network Element
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
Actions Area
Status Field
The Actions area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following information:
• Commission button— Commissions the object manually. You can commission the object only if
the object is in a decommissioned state. Clicking this button forces a subchassis discovery to be
executed, and propagates the commissioned status to all subobjects.
• Decommission button—Decommissions the object manually and propagates the decommissioned
status to all subobjects. In the decommissioned state, the properties of the object are not monitored.
As a result, data displayed in the configuration window is not guaranteed to be current.
The display-only Status field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
• discovery—CEMF is trying to determine the contents and configuration of the switch/router.
• normal—Presence polling is performed periodically.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-5
Page 6
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
• discoverylostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device during discovery, which occurs if
the SNMP read community is incorrect.
• mismatched—The network element for the given IP address does not corrspond to a Catalyst 6000
family switch or Cisco 7600 series Internet Router.
System Information Tab
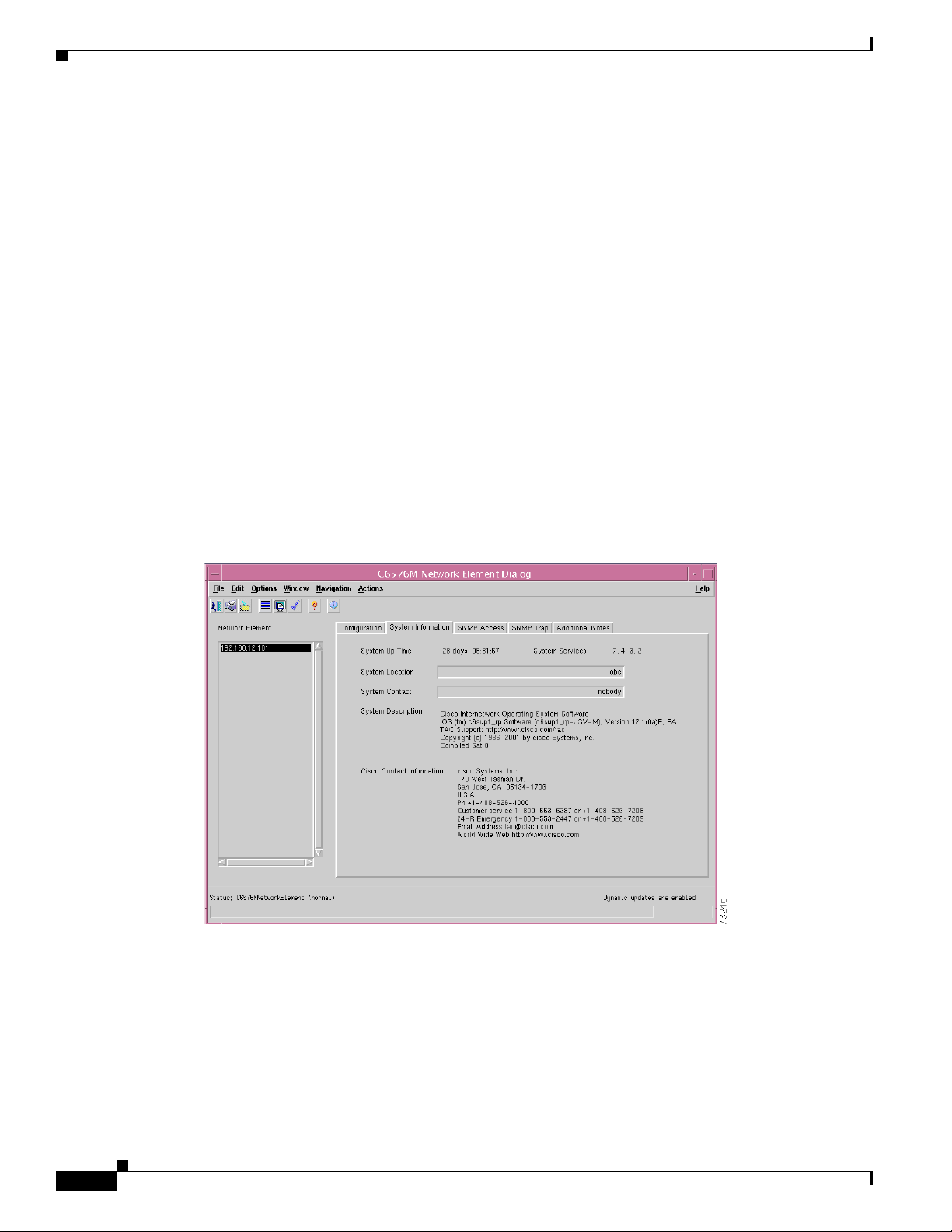
Figure 6-3 shows the System Information tab of the C6576M Network Element dialog box.
The System Information tab provides the following information:
• System Up Time—The duration of time indicating how long the system has been running. This
attribute is read-only.
• System Services—List of OSI layers supported by the switch or router. This attribute is read-only.
• System Location—Displays the location of the switch or router.
• System Contact—Displays the name of the person who is the contact for this switch/router.
• System Description—A multiline text description of the switch/router. This attribute is read-only.
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Cisco Contact Information—Details on how to contact Cisco Systems. This attribute is read-only.
Figure 6-3 System Information Tab of the C6576M Network Element Dialog Box
6-6
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 7
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
SNMP Tab
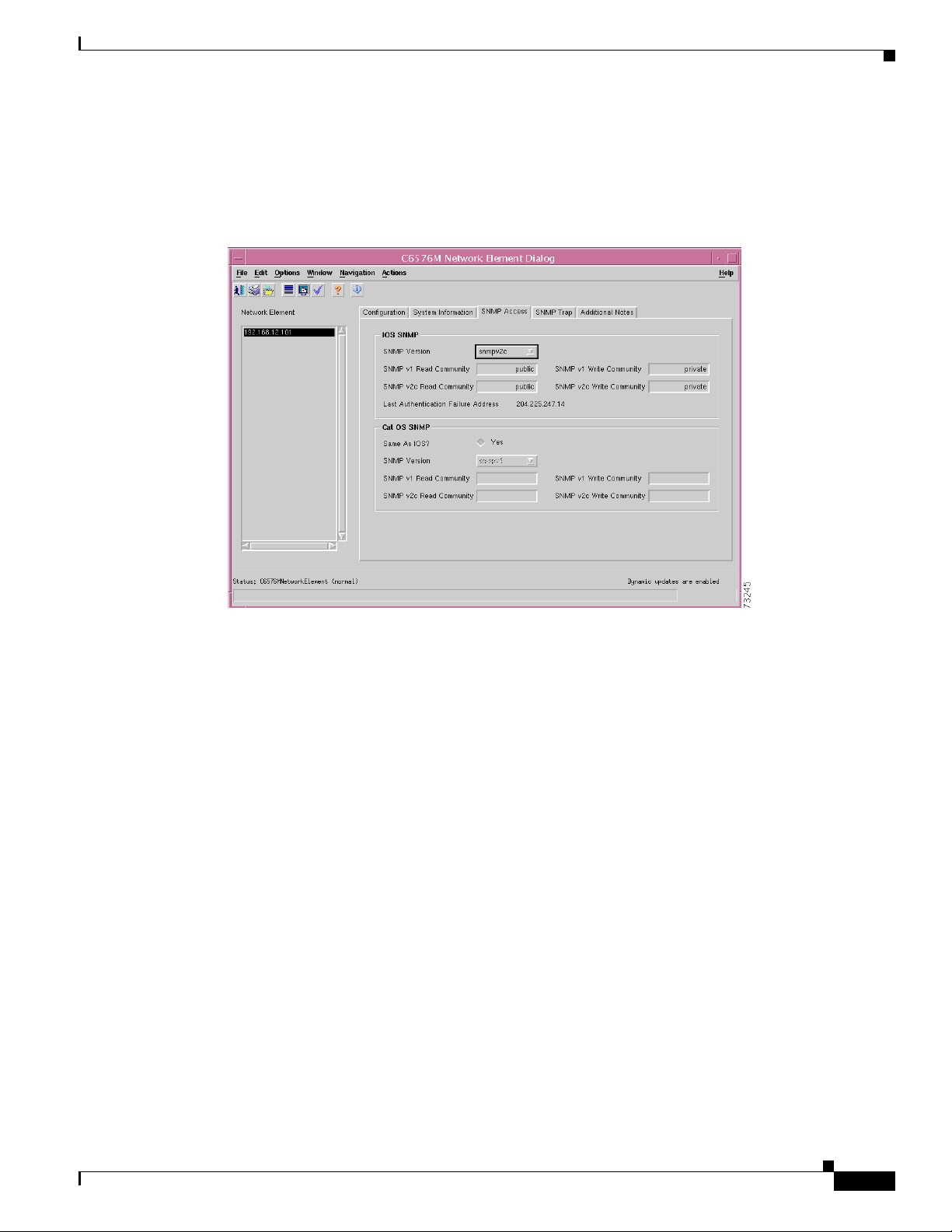
Figure 6-4 shows the SNMP tab of the C6576M Network Element dialog box.
Figure 6-4 SNMP Access Tab of the C6576M Network Element Dialog Box
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
IOS SNMP Area
The IOS SNMP area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following information:
• SNMP Version—The version of the SNMP agent running on the switch or router. The version is one
of these values:
–
SNMPv1
–
SNMPv2c
–
SNMPv3—Not supported by the Catalyst 6000 family switches or the Cisco 7600 series
Internet Routers
• SNMP v1 Read Community—The v1 community string used to read data from the agent.
• SNMP v2c Read Community—The v2c community string used to read data from the agent.
• Last Authentication Failure Address—The IP address of the last host that caused an SNMP
authentication failure to occur.
• SNMP v1 Write Community—The v1 community string used to write data to the agent.
• SNMP v2c Write Community—The v2c community string used to write data to the agent.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-7
Page 8

C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
Cat OS SNMP Area
The Cat OS SNMP area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following
information:
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Same As IOS?—If enabled, the IOS SNMP version and communities will be used to access the
SNMP Agent on the Supervisor module in Hybrid OS configurations.
• SNMP Version—The version of the SNMP agent running on the switch or router. The version is one
of these values:
–
SNMPv1
–
SNMPv2c
–
SNMPv3—Not supported by the Catalyst 6000 family switches or the Cisco 7600 series
Internet Routers
• SNMP v1 Read Community—The v1 community string used to read data from the agent.
• SNMP v2c Read Community—The v2c community string used to read data from the agent.
• SNMP v1 Write Community—The v1 community string used to write data to the agent.
• SNMP v2c Write Community—The v2c community string used to write data to the agent.
SNMP Trap Tab
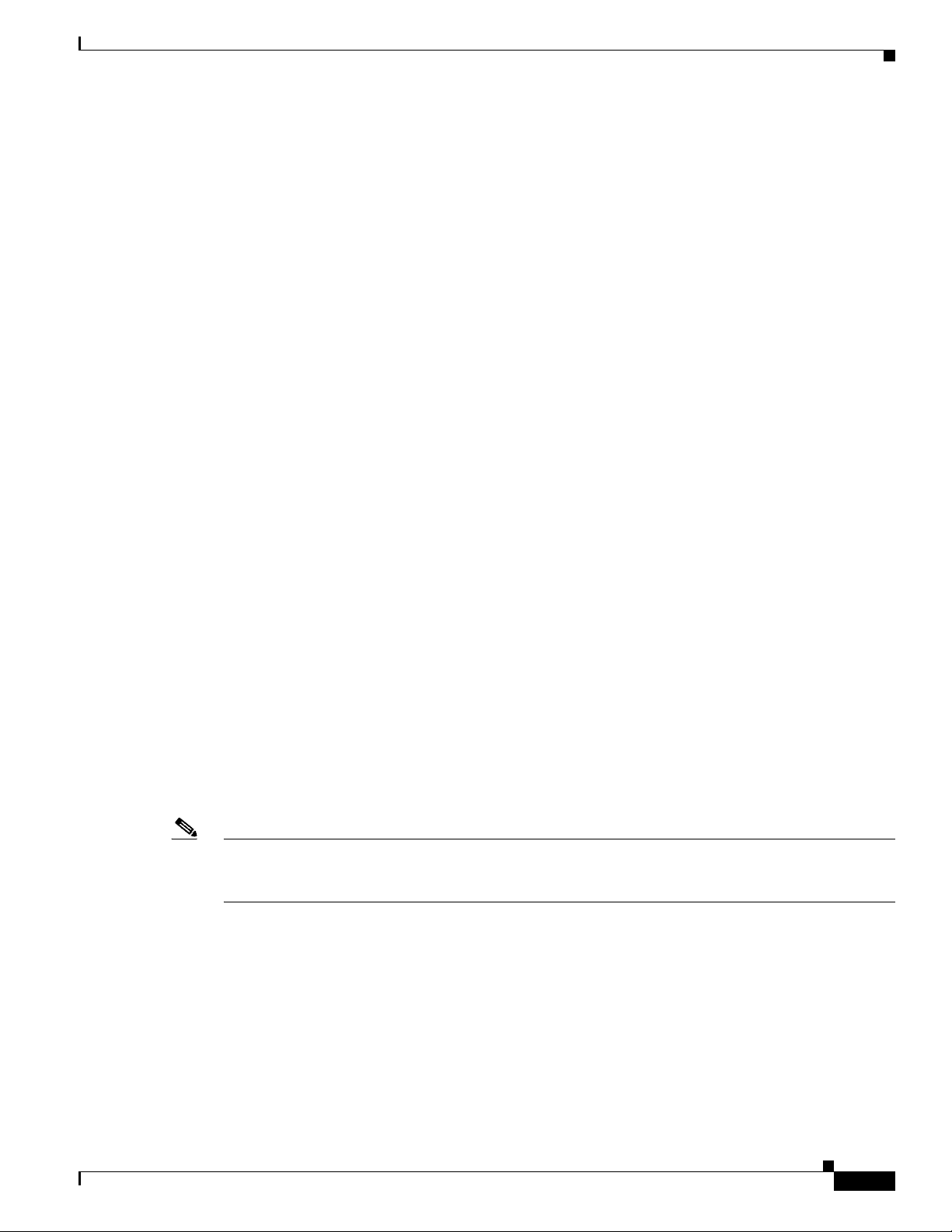
Figure 6-5 shows the SNMP Trap tab of the C6576M Network Element dialog box.
Figure 6-5 SNMP Trap Tab of the C6576M Network Element Dialog Box
6-8
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 9
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Trap Generation Area
The Trap Generation area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following
information:
• SNMP Trap Status—Indicates the level at which SNMP traps are enabled. The level is one of these
values:
–
–
–
–
• Enable button—Enables all SNMP trap generation from the switch or router.
• Disable button—Disables all SNMP trap generation from the switch or router.
SNMP Trap Area
The SNMP Trap area of the C6576M Network Element dialog box provides the following information:
• Trap Client IP Table—IP address table to which SNMP traps generated by the switch or router are
sent.
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
disabled
layer2Only
layer3Only
layer2And3
–
Trap Client IP—The IP address to which SNMP traps are sent.
–
Client Community—The community string used within the SNMP trap.
–
SNMP Version—Version of the SNMP protocol used by CEMF to communicate with the
managed device. This field has the following values:
• snmpv1
• snmpv2c
–
Notification Layer - Indicates the level at which the SNMP trap client is defined. The level is
one of these values:
• layer2Only
• layer3Only
• layer2And3
Note The IP address of the CEMF server host should be in this list at all times. If it is not, then CEMF will
not receive any traps from the switch or router, which might result in an event being reported in an
untimely fashion or an event being missed.
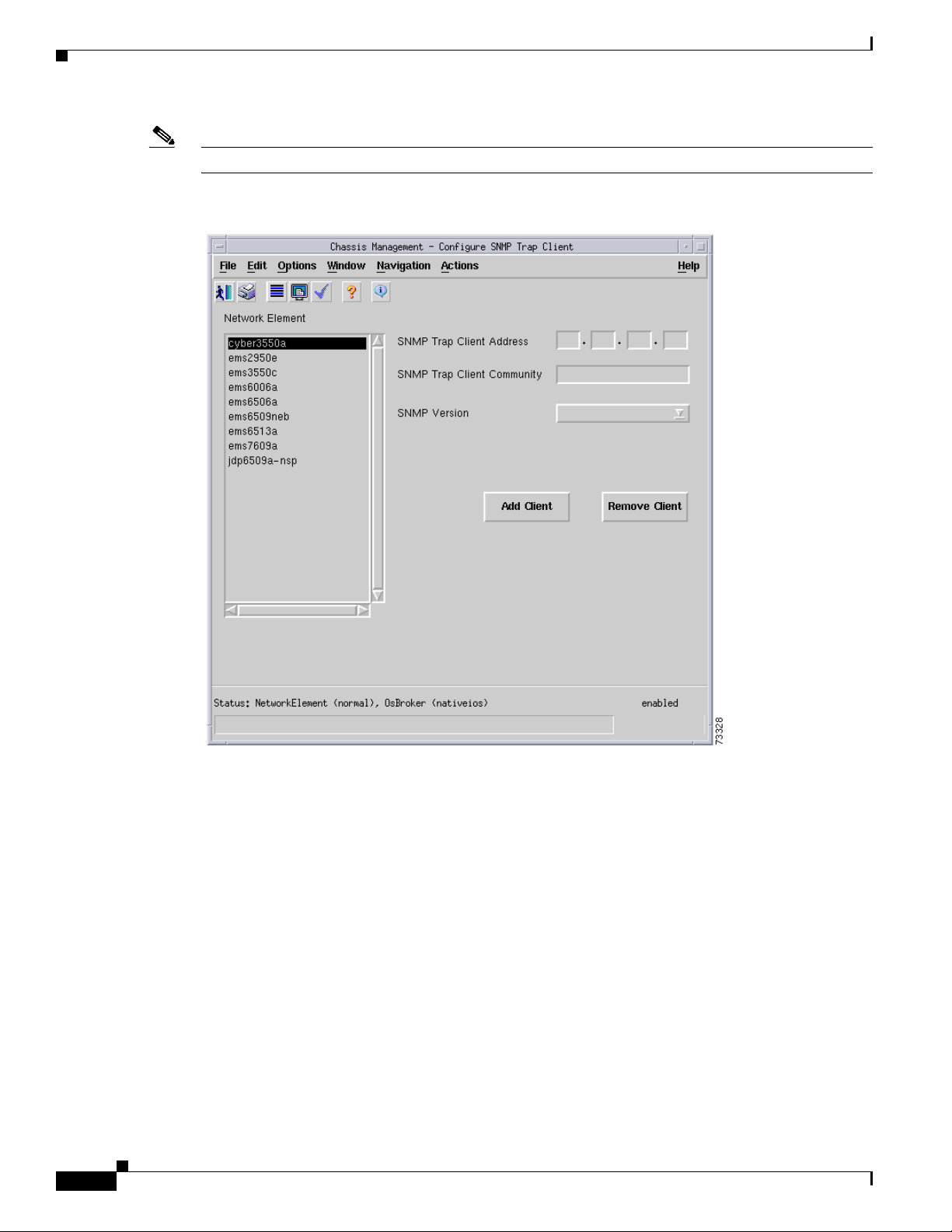
• Configure button—Displays the subdialog box, shown in Figure 6-6, for modifying the Trap Client
list.
–
SNMP Trap Client Address—The IP address to which SNMP traps are sent.
–
SNMP Trap Client Community String—The community string used within the SNMP trap.
–
Add Client button—Adds a client to the client list.
–
Remove Client button—Removes the client from the client list.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-9
Page 10
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
Note An error is reported if a nonexistent client is removed or if an existing client is added.
Figure 6-6 Configure Trap Client List Popup Window
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
6-10
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 11

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-11
Page 12
C6576M NE Config/Mgmt Dialog Box
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-7 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Network Element dialog box.
Figure 6-7 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Network Element Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes. For example, this information
can include text indicating why global performance logging is turned on.
6-12
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 13
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
C6576M Software Dialog Box
This dialog box provides information on the IOS image and configuration of the switch or router. This
dialog box is launched from a Network Element object within the Network or Physical view and the
Software object in the Physical view.
You can choose only one software object at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog box.
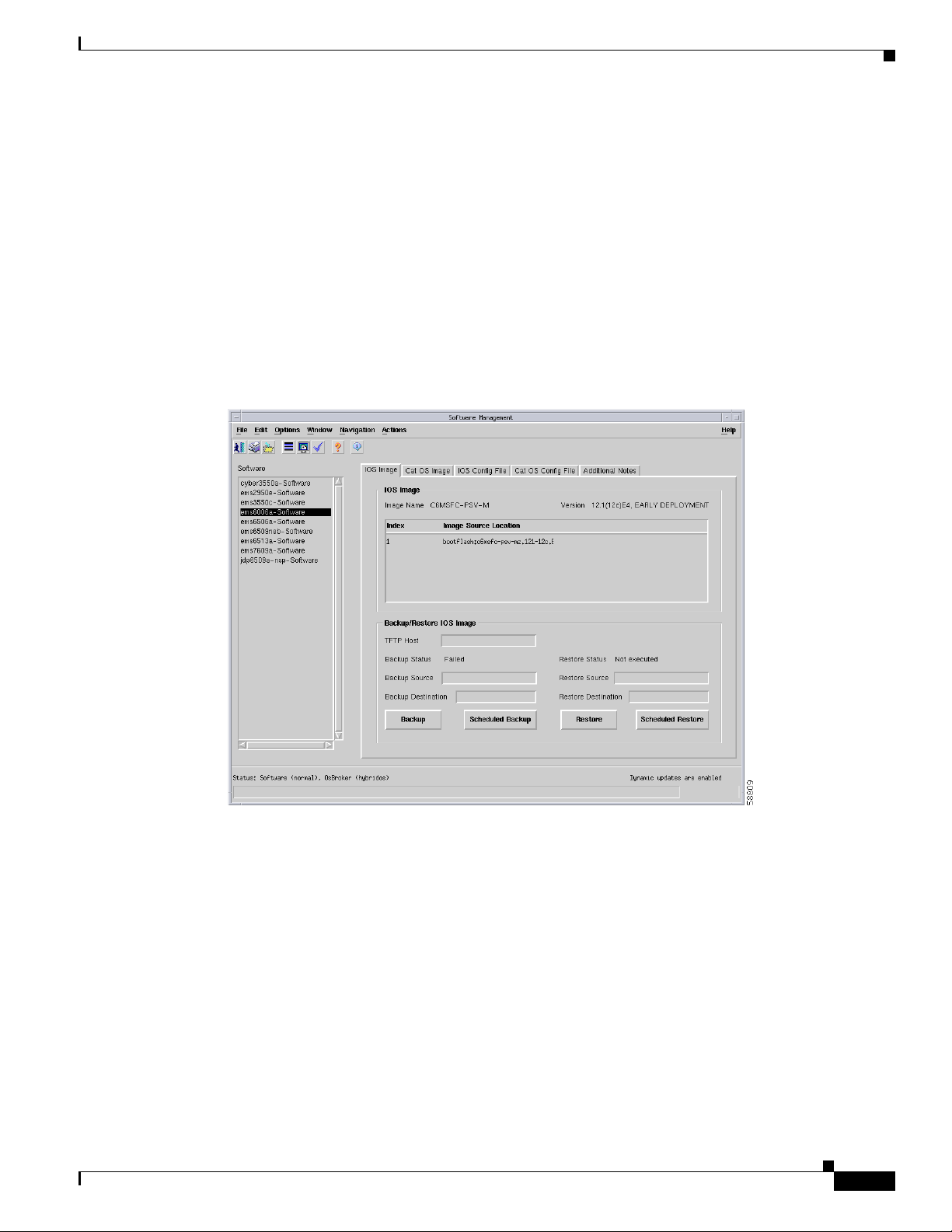
IOS Image Tab
Figure 6-8 shows the IOS Image tab of the C6576M Software dialog box.
Figure 6-8 IOS Image Tab of the C6576M Software Dialog Box
C6576M Software Dialog Box
IOS Image Area
The IOS Image area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following information:
• Image Name—Name of the IOS image currently executing on the switch or router.
• Version—Version of the currently executing IOS image.
• Index—Index of the Image Source Location item in the table.
• Image Source Location—The list of files (in order) that are used to boot the switch or router.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-13
Page 14

C6576M Software Dialog Box
Backup/Restore IOS Image Area
The Backup/Restore IOS Image area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following
information:
• TFTP Host—The IP address or hostname of the TFTP server that the IOS image was restored from
or backed up to.
• Backup Status—Status of the last image backup operation. The Backup Status has the following
values:
–
Ok—The backup operation completed without errors.
–
Failed—The backup operation failed.
–
Not executed—A backup has not been executed.
• Backup Source—The IOS image file to be backed up. Specify the full path to the image (for
example, “slot0:c6sup12-jsv-mz.121-6.E.bin”).
• Backup Destination—The destination filename on the TFTP Host to which the image will be backed
up.
• Restore Status—Status of the last image restore operation. The Restore Status has the following
values:
–
Ok—The restore operation completed without errors.
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
Failed—The restore operation failed.
–
Not executed—A restore has not been executed.
• Restore Source—The filename of the IOS image that will be restored from the TFTP Host to the
switch or router.
• Restore Destination—The destination filename on the switch or router to which the image will be
restored. The file attribute can include the file system as well as the filename; for example:
Slot0:/c6sup22jsv.bin.
• Backup button—Backs up the IOS image specified in the Backup Source attribute to the file
specified in the Backup Destination attribute on the TFTP Host.
• Scheduled Backup button—Schedules the backup of an IOS image file (from the device to the
TFTP server). Launches the dialog box shown in Figure 6-9:
–
Date—The date when the backup will start. The format is MM/DD/YYYY.
–
Hour—The hour when the backup will start. It is a 24-hour clock.
–
Minute—The minute when the backup will start.
• Restore button—Restores an IOS image. Copies the Restore Source file from the TFTP Host to the
Restore Destination location/file.
Note The Switch or router needs to be reset in order to run with the new IOS image.
• Scheduled Restore button—Schedules the restore operation of an IOS image file (from the TFTP
server to the device). Launches the dialog box shown in Figure 6-9:
–
Date—The date when the restore will start. The format is MM/DD/YYYY.
–
Hour—The hour when the restore will start. It is a 24-hour clock.
6-14
–
Minute—The minute when the restore will start.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 15

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-9 Scheduled Backup/Restore IOS Image Dialog Box
Note An alarm is generated if the Backup Status and Restore Status attributes are set to Failed. (See Chapter 8,
“Alarms and Alarm Management.”)
Status Field
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
• discovery—CEMF is trying to determine the contents and configuration of the Chassis object.
C6576M Software Dialog Box
• normal—Presence polling of the object.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
• discoverylostcomms—CEMF lost communication with the device during discovery.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-15
Page 16
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Cat OS Image Tab
Figure 6-10 shows the Cat OS Image tab of the C6576M Software dialog box.
Figure 6-10 Cat OS Image Tab of the C6576M Software Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Catalyst OS Image Area
The Catalyst OS Image area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following information:
• Image Name—Name of the Cat OS image currently executing on the switch or router.
• Version—Version of the currently executing Cat OS image.
• Image Source Location—The list of files (in order) that are used to boot the switch or router.
Backup/Restore Catalyst OS Image Area
The Backup/Restore Catalyst OS Image area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following
information:
• TFTP Host—The IP address or hostname of the TFTP server that the Cat OS image was restored
from or backed up to.
• Backup Status—Status of the last image backup operation. The Backup Status has the following
values:
–
Ok—The backup operation completed without errors.
–
Failed—The backup operation failed.
–
Not executed—A backup has not been executed.
6-16
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 17

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Backup Source—The Cat OS image file to be backed up. Specify the full path to the image (for
example, “slot0:c6sup12-jsv-mz.121-6.E.bin”).
• Backup Destination—The destination filename on the TFTP Host to which the image will be backed
up.
• Restore Status—Status of the last image restore operation. The Restore Status has the following
values:
–
Ok—The restore operation completed without errors.
–
Failed—The restore operation failed.
–
Not executed—A restore has not been executed.
• Restore Source—The filename of the Cat OS image that will be restored from the TFTP Host to the
switch or router.
• Restore Destination—The destination filename on the switch or router to which the image will be
restored. The file attribute can include the file system as well as the filename; for example:
Slot0:/c6sup22jsv.bin.
• Backup button—Backs up the Cat OS image specified in the Backup Source attribute to the file
specified in the Backup Destination attribute on the TFTP Host.
• Scheduled Backup button—Schedules the backup of a Cat OS image file (from the device to the
TFTP server). Launches the dialog box shown in Figure 6-11:
–
Date—The date when the backup will start. The format is MM/DD/YYYY.
C6576M Software Dialog Box
–
Hour—The hour when the backup will start. It is a 24-hour clock.
–
Minute—The minute when the backup will start.
• Restore button—Restores an Cat OS image. Copies the Restore Source file from the TFTP Host to
the Restore Destination location/file.
Note The Switch or router needs to be reset in order to run with the new Cat OS image.
• Scheduled Restore button—Schedules the restore operation of an Cat OS image file (from the
TFTP server to the device). Launches the dialog box shown in Figure 6-11:
–
Date—The date when the restore will start. The format is MM/DD/YYYY.
–
Hour—The hour when the restore will start. It is a 24-hour clock.
–
Minute—The minute when the restore will start.
Figure 6-11 Scheduled Backup/Restore Cat OS Image Dialog Box
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-17
Page 18
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Note An alarm is generated if the Backup Status and Restore Status attributes are set to Failed. (See Chapter 8,
“Alarms and Alarm Management.”)
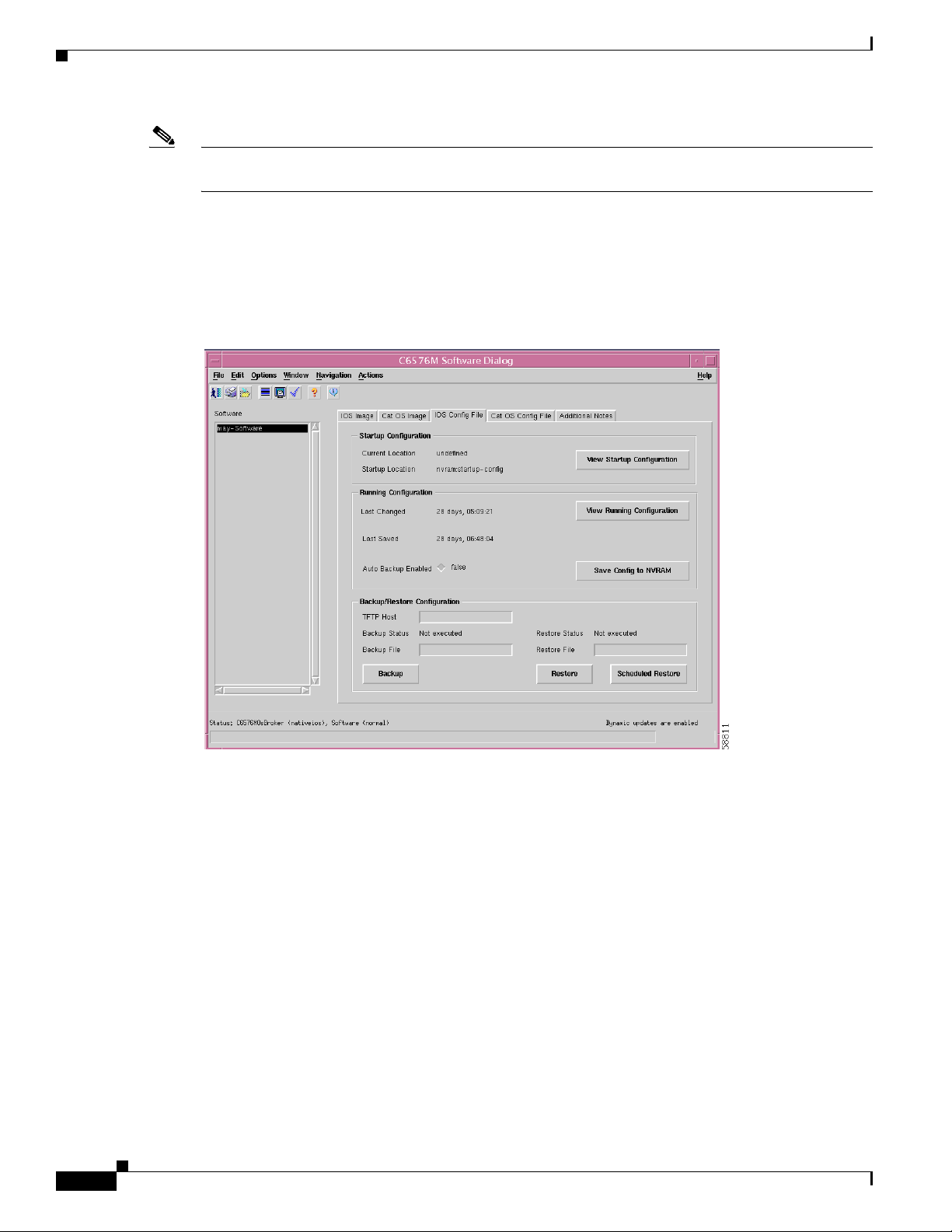
IOS Config File Tab
Figure 6-12 shows the IOS Config File tab of the C6576M Software dialog box.
Figure 6-12 IOS Config File Tab of the C6576M Software Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
6-18
The running configuration file can be edited by selecting the pop-up menu option of the network element
object, shown in Figure 6-13.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 19
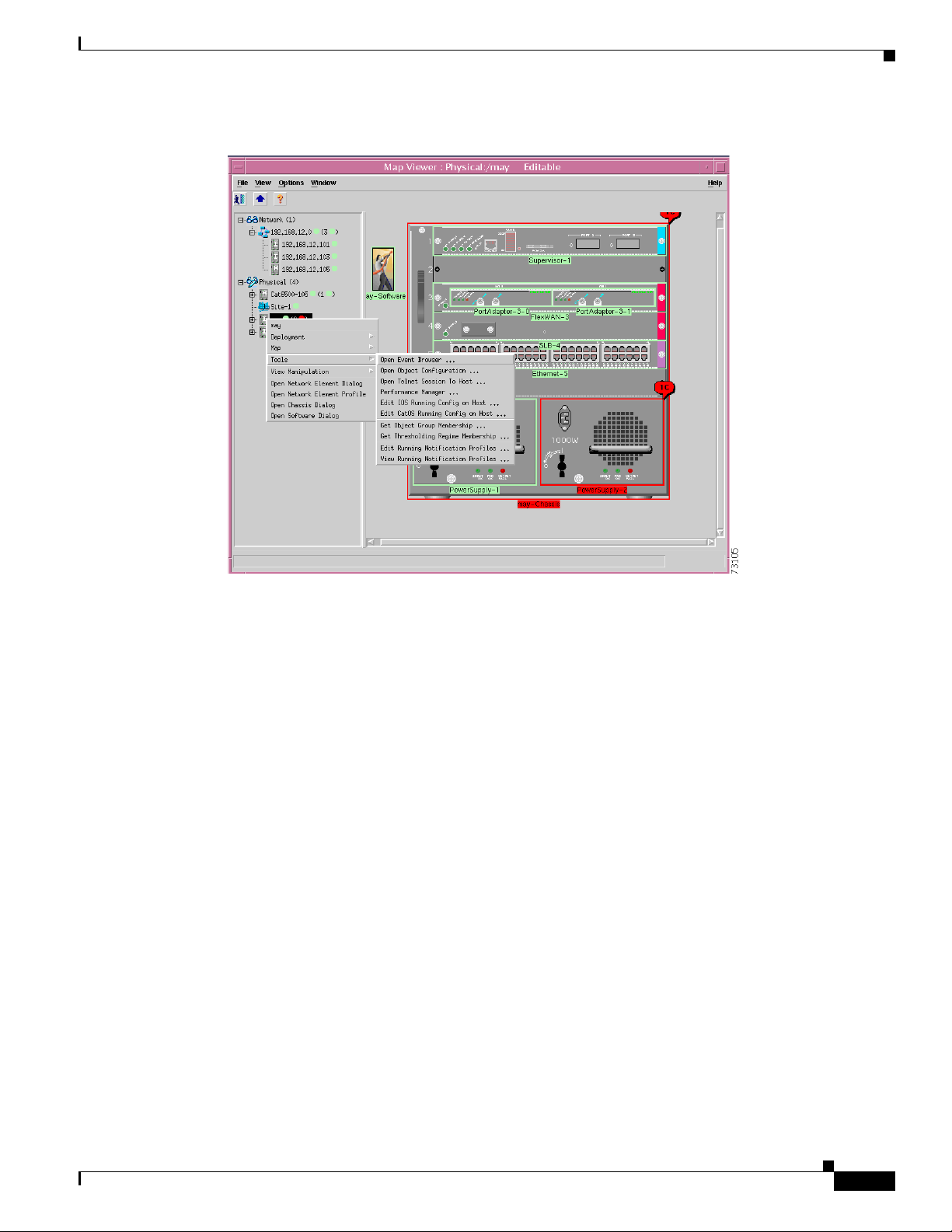
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-13 Pop-up Menu Option to Edit the Running Configuration File
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Startup Configuration Area
The Startup Configuration area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following information:
• Current Location—The location of the startup configuration file that will be used on the next restart.
If this location is not set, then undefined is displayed. This attribute is read-only.
• Startup Location—The location of the startup configuration file that was used the last time the
system was booted up. This attribute is read-only.
• View Startup Configuration button—Displays the startup configuration in a text box (see
Figure 6-14). This attribute is read-only.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-19
Page 20
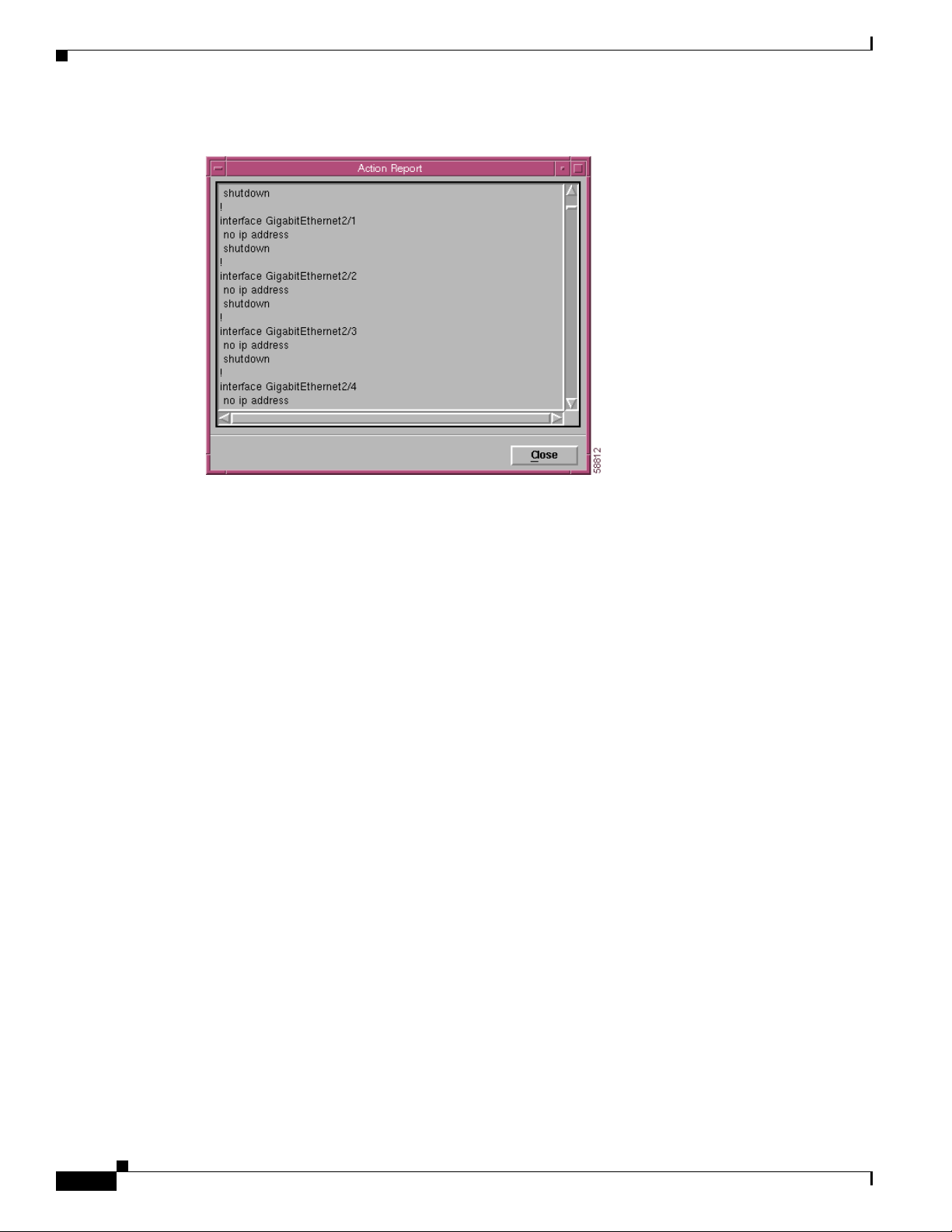
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Figure 6-14 Startup Configuration Window Action Report
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Running Configuration Area
The Running Configuration area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following
information:
• Last Changed—The time since the running configuration was last changed. This attribute is
read-only.
• Last Saved—The time since the running configuration was last saved. This attribute is read-only.
• Auto Backup Enabled—The backup action is executed automatically whenever the Save Running
Configuration action is executed.
• View Running Configuration button—Displays the current running configuration in a text box (see
Figure 6-15).
• Save Config to NVRAM—Saves the current running configuration to the location specified by the
Startup Location attribute (see Figure 6-15).
6-20
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 21

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-15 Running Configuration Window Action Report
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Backup/Restore Configuration Area
The Backup/Restore Configuration area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following
information:
• TFTP Host—The IP address or hostname of the TFTP server that the startup or running
configurations were backed up to or restored from.
Note The TFTP Host field must be configured in order to back up and restore the configuration. The TFTP
Host must be accessible from the managed device, and there must be sufficient disk space on the host to
store the device’s startup configuration.
• Backup Status—Status of the last backup action. This attribute (read-only) hashas the following
values:
–
Ok—The backup completed successfully.
–
Failed—The backup failed.
–
Not executed—The backup operation was not executed.
• Backup File—The name of the file to which the startup configuration will be copied.
Note If the TFTP server is not the CEMF server, then the file specified by the Backup File field must already
exist. If it does not, the backup action will fail. If the TFTP server is the CEMF server, the file will be
automatically created.
• Backup button—Backs up the current startup configuration to the TFTP server. The backup
filename is specified by the Backup File attribute.
• Restore Status—Status of the last restore action. This attribute (read-only) has the following values:
–
Ok—The restore operation completed successfully.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-21
Page 22
C6576M Software Dialog Box
• Restore File—The name of the configuration file that will be restored.
• Restore button—Restores the file specified in the Restore File attribute from the TFTP Host to the
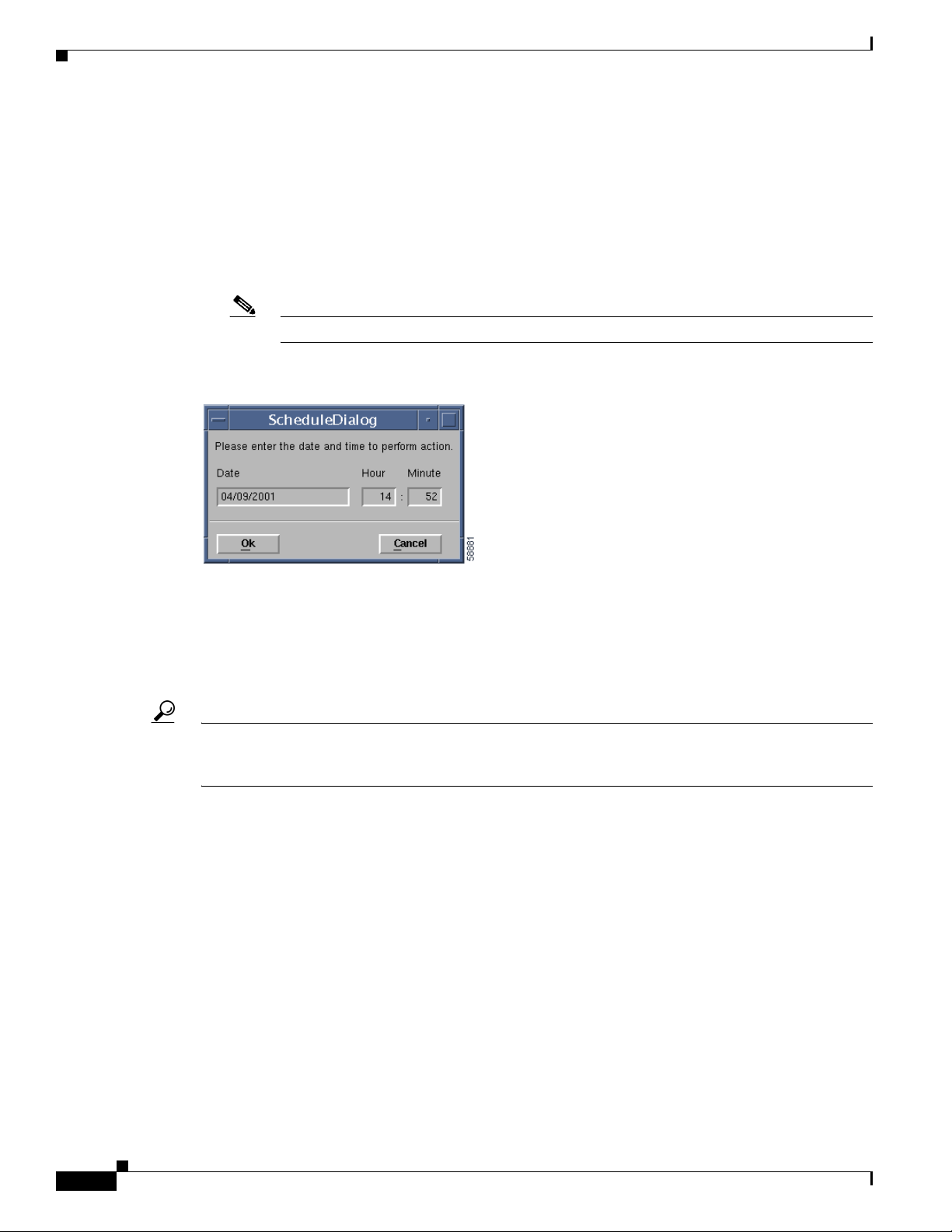
• Scheduled Restore—Schedules the restore operation. It will launch the dialog box shown in
Figure 6-16 Scheduled Restore Configuration Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
Failed—The restore operation failed.
–
Not executed—The restore operation was not executed.
startup configuration.
Figure 6-16.
Note The switch or router needs to be reset for the new configuration to take effect.
The Scheduled Restore Configuration dialog box provides the following information:
• Date—The date when the restore will start. The format is MM/DD/YYYY.
• Hour—The hour when the restore will start. It is a 24-hour clock.
• Minute—The minute when the restore will start.
Tip The configuration Backup/Restore actions are used to upload the switch or router startup configuration
to a server. The configuration can then be edited on the server and downloaded back to the switch or
router.
6-22
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 23
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
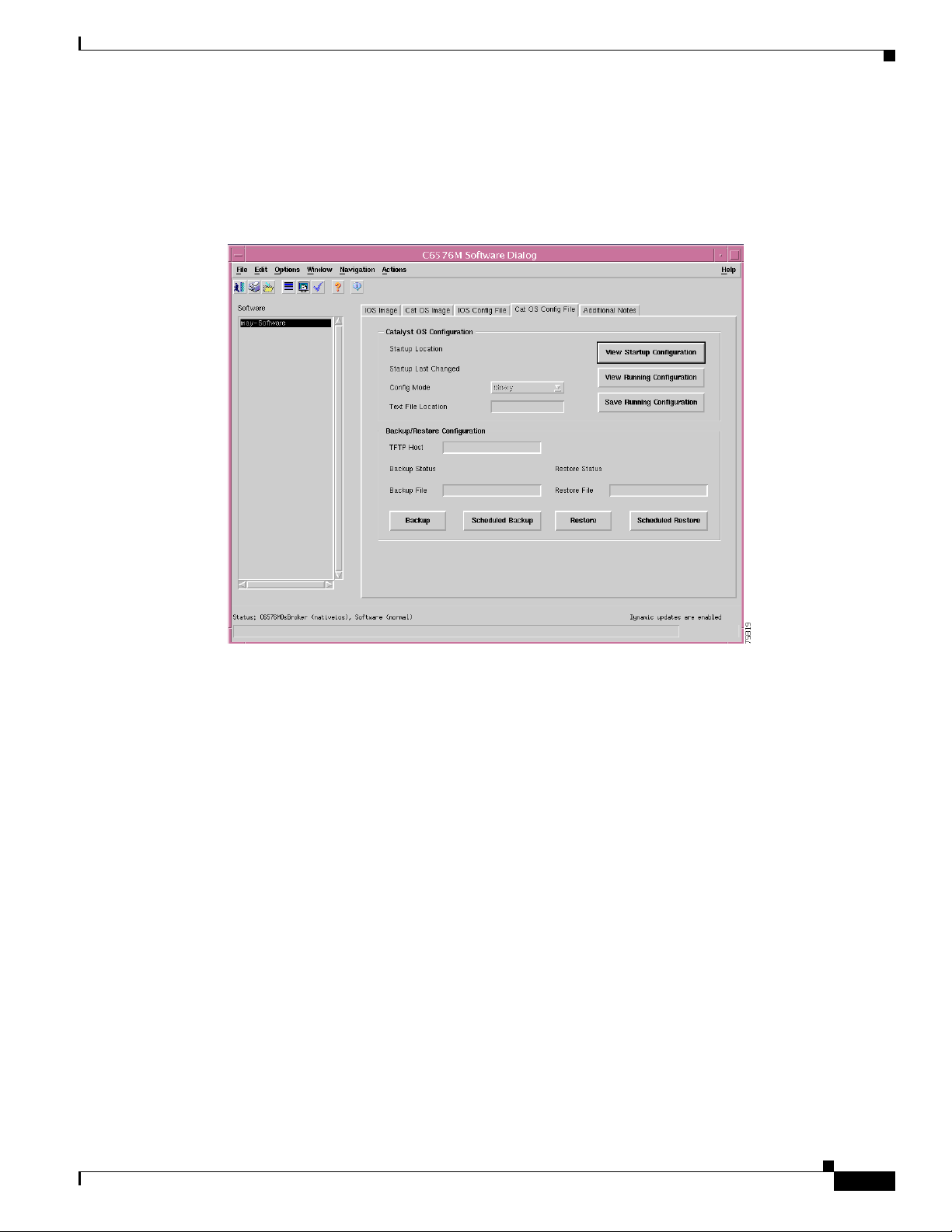
Cat OS Config File Tab
Figure 6-17 shows the Cat OS Config File tab of the C6576M Software dialog box.
Figure 6-17 Cat OS Config File Tab of the C6576M Software Dialog Box
C6576M Software Dialog Box
The running configuration file can be edited by selecting the pop-up menu option of the network element
object, shown in Figure 6-18.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-23
Page 24
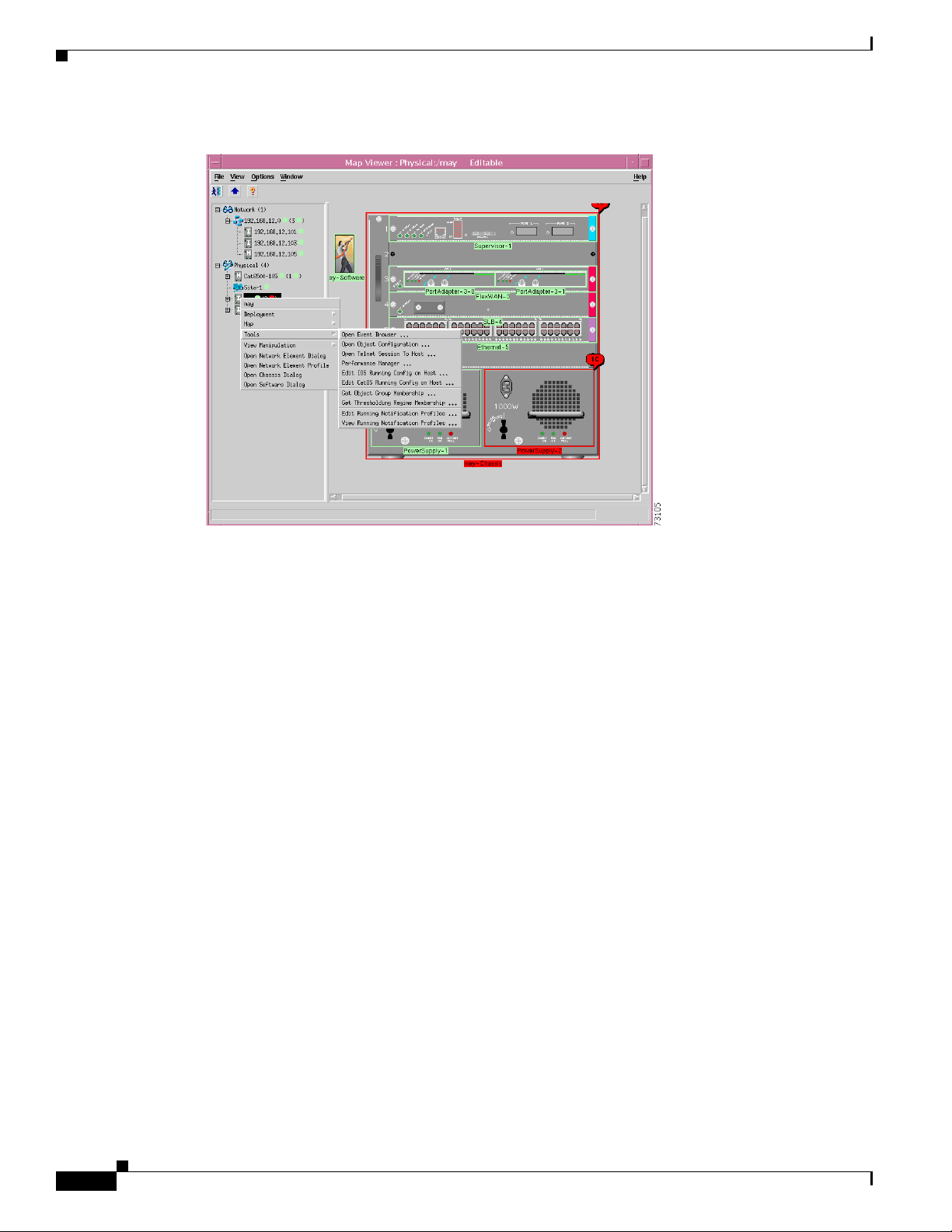
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Figure 6-18 Pop-up Menu Option to Edit the Running Configuration File
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Startup Configuration Area
The Startup Configuration area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following information:
• Current Location—The location of the startup configuration file that will be used on the next restart.
If this location is not set, then undefined is displayed. This attribute is read-only.
• Startup Location—The location of the startup configuration file that was used the last time the
system was booted up. This attribute is read-only.
• Config Mode—Cat OS configuration mode. The mode can be one of these values:
–
binary—In binary config mode, any changes to the running configuration are automatically
written to NVRAM.
–
text—In text file configuration mode, the changes are only written to DRAM.
• Text File Location—The location of the Cat OS text configuration file which can be either NVRAM
or a file in the FLASH file system.
• View Startup Configuration button—Displays the startup configuration in a text box (see
Figure 6-19). This attribute is read-only.
6-24
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 25
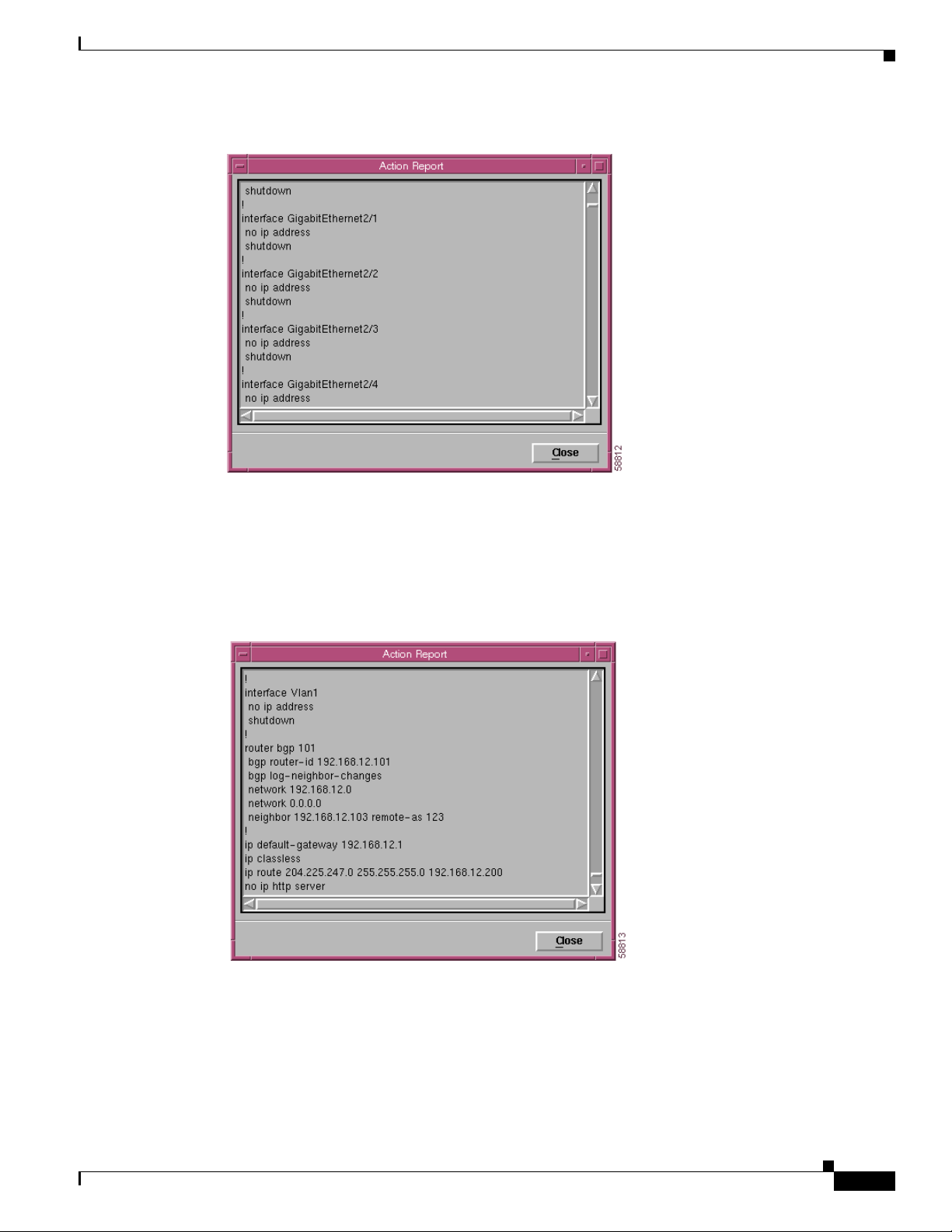
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-19 Startup Configuration Window Action Report
C6576M Software Dialog Box
• View Running Configuration button—Displays the current running configuration in a text box (see
Figure 6-20).
• Save Running Configuration button—Saves the current running configuration to the location
specified by the Startup Location attribute (see Figure 6-20).
Figure 6-20 Running Configuration Window Action Report
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-25
Page 26
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Backup/Restore Configuration Area
The Backup/Restore Configuration area of the C6576M Software dialog box provides the following
information:
• TFTP Host—The IP address or hostname of the TFTP server that the startup or running
configurations were backed up to or restored from.
Note The TFTP Host field must be configured in order to back up and restore the configuration. The TFTP
Host must be accessible from the managed device, and there must be sufficient disk space on the host to
store the device’s startup configuration.
• Backup Status—Status of the last backup action. This attribute (read-only) hashas the following
values:
–
Ok—The backup completed successfully.
–
Failed—The backup failed.
–
Not executed—The backup operation was not executed.
• Backup File—The name of the file to which the startup configuration will be copied.
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Note If the TFTP server is not the CEMF server, then the file specified by the Backup File field must already
exist. If it does not, the backup action will fail. If the TFTP server is the CEMF server, the file will be
automatically created.
• Backup button—Backs up the current startup configuration to the TFTP server. The backup
filename is specified by the Backup File attribute.
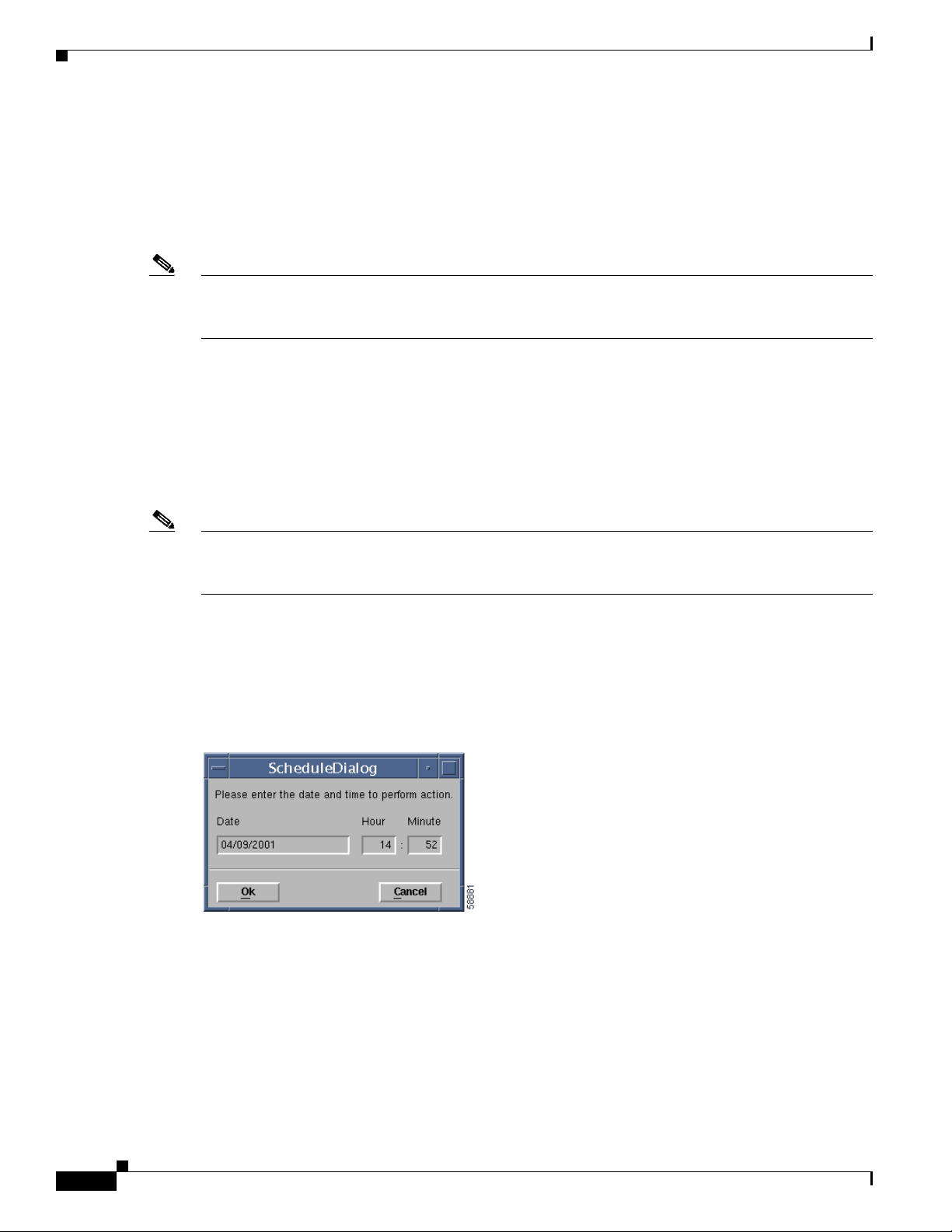
• Scheduled Backup—Schedules the backup operation. It will launch the dialog box shown in
Figure 6-21.
Figure 6-21 Scheduled Backup Configuration Dialog Box
The Scheduled Backup Configuration dialog box provides the following information:
• Date—The date when the restore will start. The format is MM/DD/YYYY.
• Hour—The hour when the restore will start. It is a 24-hour clock.
6-26
• Minute—The minute when the restore will start.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 27

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Tip The configuration Backup/Restore actions are used to upload the switch or router startup configuration
to a server. The configuration can then be edited on the server and downloaded back to the switch or
router.
• Restore Status—Status of the last restore action. This attribute (read-only) has the following values:
–
Ok—The restore operation completed successfully.
–
Failed—The restore operation failed.
–
Not executed—The restore operation was not executed.
• Restore File—The name of the configuration file that will be restored.
• Restore button—Restores the file specified in the Restore File attribute from the TFTP Host to the
startup configuration.
• Scheduled Restore—Schedules the restore operation. It will launch the dialog box shown in
Figure 6-22.
Note The switch or router needs to be reset for the new configuration to take effect.
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Figure 6-22 Scheduled Restore Configuration Dialog Box
The Scheduled Restore Configuration dialog box provides the following information:
• Date—The date when the restore will start. The format is MM/DD/YYYY.
• Hour—The hour when the restore will start. It is a 24-hour clock.
• Minute—The minute when the restore will start.
Tip The configuration Backup/Restore actions are used to upload the switch or router startup configuration
to a server. The configuration can then be edited on the server and downloaded back to the switch or
router.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-27
Page 28
C6576M Software Dialog Box
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-23 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Software dialog box.
Figure 6-23 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Software Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the object.
6-28
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 29
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
This dialog box displays attributes for the system log messages on the switch or router. This dialog box
can be launched from a Software object or Syslog object within the Physical view.
You can choose more than one Software object at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog
box.
IOS Tab
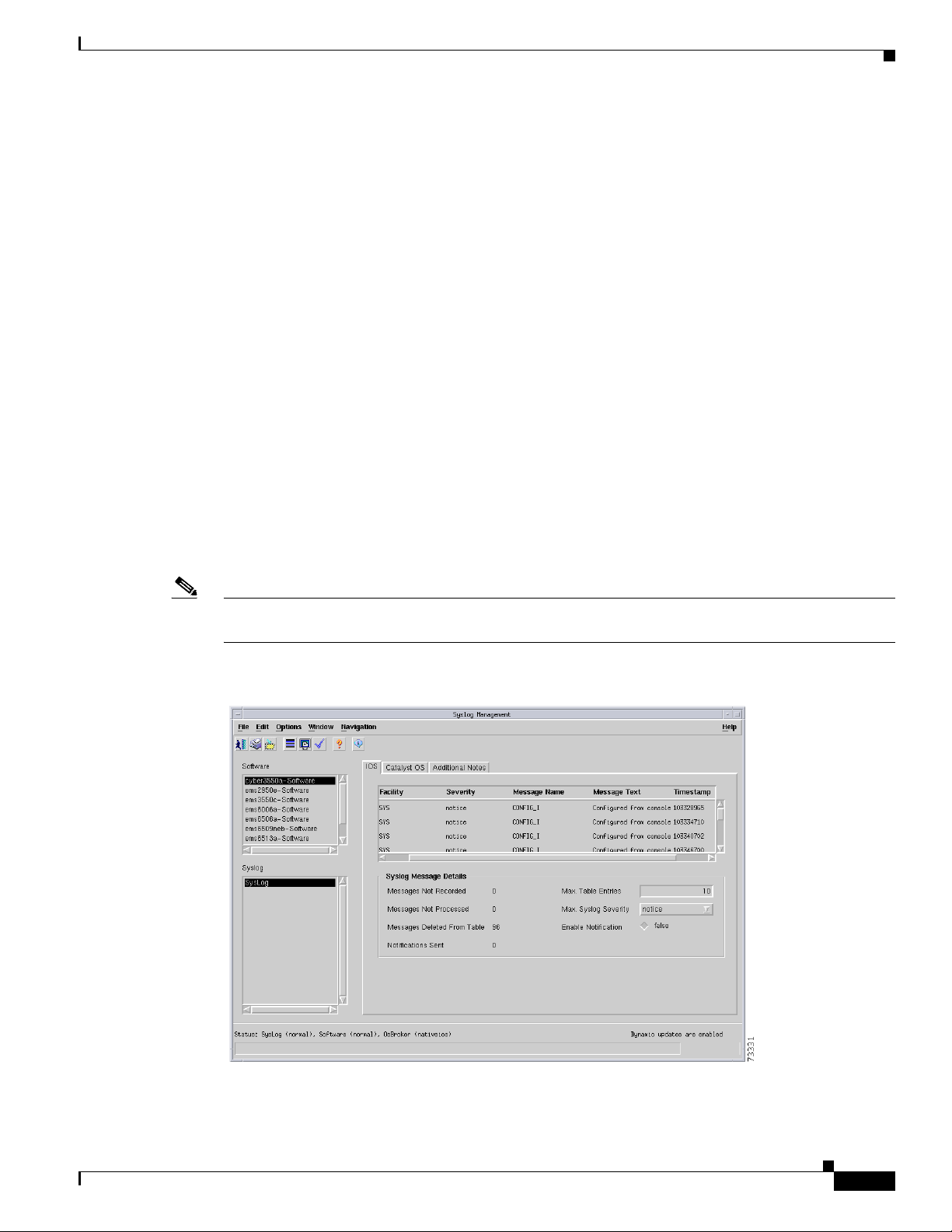
Figure 6-24 shows the IOS tab of the C6576M Syslog dialog box.
The IOS tab provides the following information:
• Facility—The facility that generated the syslog message.
• Severity—The severity of the message.
• Message Name—Identifies the message type. The Message Name and Facility together uniquely
identify a message type.
C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
• Message Text—The text of the message. If the message text exceeds 255 characters, the message is
truncated to 254 characters and an asterisk (*) is appended to the text to indicate that the message
has been truncated.
• Timestamp—The timestamp when the message was generated.
Note An alarm will be generated for each entry in this table. (See Chapter 8, “Alarms and Alarm
Management.”)
Figure 6-24 IOS Tab of the C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-29
Page 30
C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
Syslog Message Details Area
The Syslog Message Details area of the C6576M Syslog dialog box provides the following information:
• Messages Not Recorded—The number of syslog messages not recorded. A message is not recorded
if it has a severity value greater than the Max. Syslog Severity attribute. This attribute is read-only.
• Messages Not Processed—The number of messages that were not processed due to a lack of system
resources. This attribute is read-only.
• Messages Deleted From Table—The number of messages that were deleted from the table in order
to make room for new messages. The maximum number of messages kept in the table is dependent
on the Max. Table Entries attribute. This attribute is read-only.
• Notifications Sent—The number of syslog notifications sent. This attribute is read-only.
• Max. Table Entries—The maximum number of messages in the syslog table. When this limit has
been reached, the oldest messages are deleted to make room for newer messages.
• Max. Syslog Severity—The maximum severity that will be recorded. Messages with a higher
numeric value of severity will not be recorded. This attribute has one of the following values (listed
in ascending order of severity):
–
emergency (1)
–
alert (2)
–
critical (3)
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Status Field
–
error (4)
–
warning (5)
–
notice (6)
–
info (7)
–
debug (8)
Note The greatest severity state has the smallest numeric value of severity. For example, the emergency state
has a value of (1) and is more severe than the info state, which has a value of (7). If you set Max. Syslog
Severity to 7, then all states except debug will be recorded. This is because the debug state has a value
of (8), which is greater than the value of the Max. Syslog Severity attribute.
• Enable Notifications—SNMP syslog notifications are sent whenever a new syslog message is
generated and recorded.
–
true—Notifications enabled.
–
false—Notifications disabled.
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
6-30
• normal—Presence polling of the object.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 31

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Catalyst OS Tab
Figure 6-25 shows the Catalyst OS tab of the C6576M Syslog dialog box.
The Catalyst OS tab provides the following information:
• Facility—The facility that generated the syslog message.
• Severity—The severity of the message.
• Message Name—Identifies the message type. The Message Name and Facility together uniquely
identify a message type.
• Message Text—The text of the message. If the message text exceeds 255 characters, the message is
truncated to 254 characters and an asterisk (*) is appended to the text to indicate that the message
has been truncated.
• Timestamp—The timestamp when the message was generated.
Note An alarm will be generated for each entry in this table. (See Chapter 8, “Alarms and Alarm
Management.”)
C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
Figure 6-25 Catalyst OS Tab of the C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-31
Page 32

C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
Syslog Message Details Area
The Syslog Message Details area of the C6576M Syslog dialog box provides the following information:
• Messages Not Recorded—The number of syslog messages not recorded. A message is not recorded
if it has a severity value greater than the Max. Syslog Severity attribute. This attribute is read-only.
• Messages Not Processed—The number of messages that were not processed due to a lack of system
resources. This attribute is read-only.
• Messages Deleted From Table—The number of messages that were deleted from the table in order
to make room for new messages. The maximum number of messages kept in the table is dependent
on the Max. Table Entries attribute. This attribute is read-only.
• Notifications Sent—The number of syslog notifications sent. This attribute is read-only.
• Max. Table Entries—The maximum number of messages in the syslog table. When this limit has
been reached, the oldest messages are deleted to make room for newer messages.
• Max. Syslog Severity—The maximum severity that will be recorded. Messages with a higher
numeric value of severity will not be recorded. This attribute has one of the following values (listed
in ascending order of severity):
–
emergency (1)
–
alert (2)
–
critical (3)
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
error (4)
–
warning (5)
–
notice (6)
–
info (7)
–
debug (8)
Note The greatest severity state has the smallest numeric value of severity. For example, the emergency state
has a value of (1) and is more severe than the info state, which has a value of (7). If you set Max. Syslog
Severity to 7, then all states except debug will be recorded. This is because the debug state has a value
of (8), which is greater than the value of the Max. Syslog Severity attribute.
• Enable Notifications—SNMP syslog notifications are sent whenever a new syslog message is
generated and recorded.
–
true—Notifications enabled.
• false—Notifications disabled.
6-32
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 33

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-26 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M Syslog dialog box.
Figure 6-26 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
C6576M Syslog Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the object.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-33
Page 34

C6576M VTP Dialog Box
C6576M VTP Dialog Box
The VTP dialog box allows you to configure VTP domains on the switch or router. This dialog box can
be launched from a Software object or VTP object within the Physical view.
You can choose more than one Software object at a time from the object list on the left side of the dialog
box.
Details Tab
Figure 6-27 shows the Details tab of the C6576M VTP dialog box.
Figure 6-27 Details Tab for the C6576M VTP Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
VTP Area
6-34
The VTP area of the C6576M VTP dialog box provides the following information:
• Mode—An indication of whether the local system is acting as a VTP Client or as a VTP server in
this management domain. The value “transparent”.
–
client—Users cannot create, edit, or delete VLANs.
–
server—Users can create, delete, and edit VLANs for this management domain.
–
transparent—Indicates that a device is not supporting VTP for this VTP management domain.
Note It is not possible to configure VLANs on a device where Mode is equal to client.
• Domain Name—The name of the management domain in which this switch or router is
participating.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 35

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Max. VLAN Storage—Estimate of the maximum number of VLANs about which the local system
can recover complete VTP information after a reboot. If the number of defined VLANs is greater
than this value, then the system cannot act as a VTP Server. For a device that has no means to
calculate the estimated number, this value is -1. This attribute is read-only.
• Pruning—An indication of whether VTP pruning is enabled or disabled in this management
domain. This value can only be modified by local/network management when the Mode is server.
• Version—The current version of the VTP that is in use by this management domain.
• Update button—Updates any configuration changes made in this dialog box (see Figure 6-28).
Note The Update button must be used to save configuration changes to the VTP dialog box. The save icon has
been removed from the icon bar from the top of the dialog box.
Note The Mode must be set to server or transparent in order to save all configuration changes (Mode, Domain
Name, Pruning, Version) to the VTP dialog box.
C6576M VTP Dialog Box
Note If the Mode is not set to server and the Update button is used, a message is displayed indicating that
changes to the “Pruning” and “Version in Use” attributes are ignored (Figure 6-28). These values can
only set when the Mode is set to server.
Figure 6-28 Update Button Selected in Client Mode Message
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-35
Page 36

C6576M VTP Dialog Box
Status Field
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
• normal—Presence polling of the object.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-29 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M VTP dialog box.
Figure 6-29 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M VTP Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Notes Area
6-36
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the object.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 37

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
This dialog box provides attributes for VLAN configurations. This dialog box can be launched from the
Software object or VLAN object in the Physical view.
You can choose only one Software object and one VLAN object at a time from the object list on the left
side of the dialog box.
Status Tab
Figure 6-30 shows the Status tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box.
Figure 6-30 Status Tab for the C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Interface Status Area
The Details area of the C6576M VLAN dialog box provides the following information:
• VLAN Number—The number of the VLAN.
• Name—The VLAN identification name.
• Type—The type of VLAN. This value is always Ethernet.
• Operational Status—The state of this VLAN. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
operational
–
suspended
–
mtuTooBigForDevice—Indicates that this device cannot participate in this VLAN because the
VLAN’s MTU is larger than the device can support.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-37
Page 38

C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• mtuTooBigForTrunk—Indicates that while this VLAN’s MTU is supported by this device, it is too
large for one or more of the device’s trunk ports.
• VLAN OS Type —The type of VLAN. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
catOsOnly - the VLAN exists on a hybrid chassis in the CatOS configuration only
–
msfcIosOnly - the VLAN exists on a hybrid chassis in the MSFC IOS configuration only
–
catOsAndMsfcIos - the VLAN exists on a hybrid chassis in both the CatOS and IOS
configurations
–
nativeIos - the VLAN exists on a chassis running native IOS (no CatOS)
• Create VLAN in CatOS Running Config —If the VLAN OS Type is msfcIosOnly, this button will
create the corresponding entries for this VLAN in the CatOS configuration
• Create VLAN in IOS Running Config —If the VLAN OS Type is catOsOnly, this button will
create the corresponding entries for this VLAN in the IOS configuration
• Add VLAN button—Adds a VLAN. Launches the subdialog box shown in Figure 6-31.
Specify the VLAN number to be added and click the Add VLAN button. The string VLAN- will
prepended to the VLAN number specified.
Note The newly added VLAN will not appear automatically in the VLAN object list (bottom left of
Figure 6-30). To refresh the VLAN list, reselect the appropriate Software object.
6-38
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 39

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-31 Add VLAN Subdialog Box
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Status Field
• Delete VLAN button—Deletes the currently selected VLAN. If you click this button, you are asked
to confirm deletion of the current VLAN (see Figure 6-32).
Figure 6-32 Delete VLAN Subdialog Box
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
• normal—Presence polling of the object.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-39
Page 40

C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Configuration Tab
Figure 6-33 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box.
Figure 6-33 Configuration Tab for the C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Configuration Area
• MAC Address—MAC address of the VLAN interface.
Note Native IOS a VLAN that is in a suspended state is only partially manageable. The MAC Address
field will display a value of ERROR (or blank) as a result.
• Interface MTU—Layer 2 (link layer) maximum transmission unit on Ethernet VLAN. This
determines the maximum size of Ethernet frames transmitted on the VLAN interface. The value is
read-only on Ethernet and FastEthernet VLANs. The value is read-write on GigabitEthernet
VLANs.
Note IOS 12.1(8a)E5 caveat: Jumbo frame support is incompatible with the IS-IS routing protocol.
Leave the MTU size at the default value on any interface where IS-IS provides routing.
• IP Address—Primary IP address of interface. Value is nil on a layer-2 interface.
• Netmask—Subnet mask for the primary IP address.
• Clear IP Address ——After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for this interface.
6-40
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 41

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
VLAN Membership Tab
Figure 6-34 shows the VLAN Membership tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box.
Figure 6-34 VLAN Membership Tab for the C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
VLAN Membership Area
The VLAN Membership area displays the members of this VLAN.
• VLAN Membership Table—Members are identified by the slot and port numbers in the table.
• Add/Remove Members button—Adds or removes a VLAN member. Launches the subdialog box,
shown in Figure 6-35.
Specify the slot and port number of the interface that you want to add to the VLAN or delete from
the VLAN.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-41
Page 42

C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-35 Add/Remove VLAN Members Subdialog Box
6-42
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 43

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Global Tab
Figure 6-36 shows the Global tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box.
Figure 6-36 Global Tab of the C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
802.1Q Trunk Remapped VLANs Area
This area lists the mappings between 802.1Q and ISL VLANs. The information in this area is common
to all VLAN objects for a particular switch or router:
• 802.1Q Trunk Remapped VLANs Table—This table lists the following:
–
802.1Q VLAN Number—The 802.1Q VLAN number to be mapped.
–
ISL VLAN Number—The ISL VLAN to which the 802.1Q VLAN number is to be mapped.
• Add/Remove Mapping button—Adds or removes a mapping. Launches the subdialog box shown
in Figure 6-37.
Note A maximum of eight mappings are supported by the Catalyst 6000 family switch and the Cisco 7600
series Internet Router.
Enter the 802.1Q VLAN and ISL VLAN numbers for which a mapping is to be added or removed.
Note The valid range for 802.1Q VLAN numbers is 1001 to 4095. The valid range of ISL VLAN numbers is
1 to 1000.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-43
Page 44

C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-37 Add/Remove VLAN Mapping Subdialog Box
•
802.1Q VLAN Number—The 802.1Q VLAN number to be mapped.
• ISL VLAN Number—The ISL VLAN to which the 802.1Q VLAN number is to be mapped.
• Add Mapping button—Adds mapping of 802.1Q and ISL VLANs specified by the 802.1Q VLAN
Number and ISL VLAN Number fields.
• Add/Remove Mapping button—Removes mapping of 802.1Q and ISL VLANs specified by the
802.1Q VLAN Number and ISL VLAN Number fields.
6-44
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 45

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
STP Tab
Figure 6-38 shows the VLAN STP tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box.
Figure 6-38 VLAN STP Tab for the C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
STP Area
Root Area
The STP area of the C6576M VLAN dialog provides the following information:
• Spanning Tree Protocol—Configures whether or not Spanning Tree Protocol is enabled for this
virtual LAN. This attribute has one of the following values:
–
enabled
–
disabled
–
notApplicable
• Primary Root—Configures whether or not the switch is the root node in the STP instance. If there
is no spanning tree instance for the VLAN, the value is nil.
The Root area of the C6576M VLAN dialog provides the following information:
• Current Root Priority—Bridge priority of the current root switch in the spanning tree instance. If
there is no spanning tree instance for the VLAN, the value is nil. This attribute is read-only.
• Root Interface—If this switch is not the root of the spanning tree, indicates the local port used to
reach the root node. This is a local port that is a member of the VLAN. This value should match the
Name field in the Interface dialog box corresponding to the root port (for example, “FastEthernet
2/5”). If the switch is currently the root or there is no spanning tree instance for the VLAN, the value
is nil. This attribute is read-only.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-45
Page 46

C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Root Election Area
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Current Root MAC—Bridge identifier address. This is the MAC address of the VLAN on the root
bridge in the STP instance. If there is no spanning tree instance for the VLAN, the value is nil. This
attribute is read-only.
• Root Path Cost—If this is not the root of the spanning tree, indicates the path cost to the root (this
is the path cost of the root port). If the switch is currently the root or there is no spanning tree
instance for the VLAN, the value is nil. This attribute is read-only.
The Root Election area of the C6576M VLAN dialog provides the following information:
• Root Preference—STP root priority. This attribute may has following values:
–
no (0)
–
primary (1)
–
secondary (2)
• Hello Time—Hello-time in seconds.
• Diameter—Specifies the network diameter (maximum number of bridges between two end nodes).
If specified, the switch will calculate the optimal hello-time, forward-time, and max-age. User may
optionally specify an explicit hello-time.
• Set Root button—Configures the root priority of the device in the VLAN STP instance. This action
will set the VLAN STP bridge-priority and reset the hello-time, forward-delay, and max-age timers.
This action does not guarantee that the switch will be elected the STP root, it only sets these values.
Advanced Area
The Advanced area of the C6576M VLAN dialog box allows you to configure the attributes described
in this section. While these attributes are configurable, this is not the recommended method for
configuring them. Alternately, if you specify a network diameter but no hello time, forward-delay timer,
or max-age timer, using the Set Root button (in the Root Election Area) causes the switch to
automatically calculate the optimal hello time, forward-delay timer, and max-age timer for that diameter.
• Hello Time—Indicates how often the switch broadcasts hello messages to other switches in the STP
domain. If there is no spanning tree instance for the VLAN, value is nil. You can optionally provide
a diameter and hello-time to override the calculated value. If no diameter or hello-time are provided,
the switch will use the default hello time of 2 seconds.
• Priority—Spanning tree bridge priority. If there is no spanning tree instance for the VLAN, the
value is nil.
• Forward Delay—Forward delay timer for STP state transitions. Determines how long each of the
listening and learning states will last before the interface begins forwarding. If there is no spanning
tree instance for the VLAN, the value is nil. If no diameter is specified, the switch will use the
default delay of 15 seconds.
• Max Age—Describes the amount of time that STP protocol information received by a switch is
stored before it expires. If there is no spanning tree instance for the VLAN, the value is nil. If no
diameter is specified, the switch will use the default duration of 20 seconds.
6-46
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 47

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
QoS Tab
Figure 6-39 shows the QoS tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box.
Figure 6-39 QoS Tab of the VLAN Dialog Box
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
QoS Area
The QoS area allows you to enable or disable Microflow policing of bridged traffic on the VLAN, and
attach or detach service policies to VLAN interfaces.
Note To enable QoS, the managed device must be a VTP server or operating in VTP transparent mode.
• Microflow Policing Enabled—Indicates whether Microflow policing of bridged traffic is enabled
on the VLAN.
• Input Service Policy—Indicates the QoS policy map applied to the VLAN.
• Modify Policy button—Attaches an input QoS policy map to the VLAN interface. This action may
fail if the policy map is not suitable for use with an Ethernet VLAN.
Note The policy map name must identify an existing policy map on the device.
• Remove Policy button—Detaches an input QoS policy map from the VLAN interface.
Membership QoS Area
The Membership QoS area allows you to enable or disable VLAN-based QoS on the VLAN’s member
interfaces.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-47
Page 48

C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
EoMPLS Tab
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Enable VLAN-Based QoS button—Enables VLAN-based QoS on each of the VLAN’s member
interfaces.
• Disable VLAN-Based QoS button—Disables VLAN-based QoS on each of the VLAN’s member
interfaces.
Figure 6-40 shows the EoMPLS tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box.
Figure 6-40 EoMPLS Tab of the C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
EoMPLS Area
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-48
This area contains the followng information:
• Destination IP—Describes where packets are to be sent. A value of “0 0 0 0” will clear any
previously configured value.
• VC ID—Label applied to packets entering the tunnel. A value of “0” will clear any previously
configured value.
Page 49

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
VLAN Database Tab
Figure 6-41 shows the VLAN Database tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box. There is no VLAN
Database in Hybrid OS.
Figure 6-41 VLAN Database Tab of the C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
VLAN Database Backup/Restore Area
The VLAN Database Backup/Restore area of the C6576M VLAN dialog box allows you to back up and
restore the VLAN configuration to a remote TFTP server.
• TFTP Host—The IP address of the TFTP server to which the VLAN configuration is backed up or
restored from.
• Backup Status—Status of the last VLAN configuration backup operation. The Backup Status has
the following values:
–
Ok—The backup operation completed without errors.
–
Failed—The backup operation failed.
–
Not executed—A backup has not been executed.
• Backup File—Name of the file on the TFTP server to which the VLAN configuration will be
copied to.
• Save config file before reset— “true” indicates that the VLAN configuration file will be saved
before switch reset.
• Restore Status—Status of the last VLAN configuration restore operation. The Restore Status has the
following values:
–
Ok—The restore operation completed without errors.
–
Failed—The restore operation failed.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-49
Page 50

C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Caution The Restore and Schedule Restore buttons will cause the switch to be reset after the VLAN database
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
Not executed—A restore has not been executed.
• Restore File—Name of the file on the TFTP server to which the VLAN configuration will be
restored from.
• Backup button—Backs up the VLAN configuration to the file specified in the Backup File field on
the TFTP Host.
• Restore button—Restores a VLAN configuration backup or loads a new VLAN configuration.
Copies the file specified by the Restore File field from the TFTP Host to the switch or router.
restoration process is complete.
• Schedule Restore button—Schedules the restore operation. Launches the dialog box shown in
Figure 6-42.
Figure 6-42 Scheduled Restore VLAN Configuration Dialog Box
Note An alarm is generated if the Backup Status and Restore Status attributes are set to Failed. (See Chapter 8,
“Alarms and Alarm Management.”)
Note VLAN Database Backup/Restore is not supported in VTP Client/Transparent mode as of IOS
12.1(8a)EX and later.
6-50
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 51

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-43 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M VLAN dialog box.
Figure 6-43 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
C6576M VLAN Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the object.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-51
Page 52

C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
This dialog box provides attributes for EtherChannel configurations. This dialog box can be launched
from the Software object or EtherChannel objects in the Physical view.
Status Tab
Figure 6-44 shows the Status tab of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box.
Figure 6-44 Status Tab of the C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Interface Status Area
The Details area of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box provides the following information:
• EtherChannel ID—The EtherChannel number.
• Description—Description of the EtherChannel.
• Administrative Status—The desired state of the EtherChannel interface. The status has the
Note This is read-only in Hybrid OS. If the EtherChannel exists, the value is always up (1).
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-52
following values:
–
testing (read-only)—Indicates that no operational packets can be passed.
–
up
–
down
Page 53

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Note When a managed system initializes, all interfaces start with Administrative Status in the down state. As
a result of either explicit management action or per configuration information retained by the managed
system, Administrative Status is then changed to either the up(1) or “testing (read-only)”(3) states (or
remains in the down(2) state).
• Delete EtherChannel button—Deletes the EtherChannel instance selected in the EtherChannels
object selection list. All interface members of this EtherChannel must be removed before the
EtherChannel instance can be deleted. This only applies to Native IOS devices only, on hybrid
devices the EtherChannel will automatically delete on removal of the last member.
Status Field
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
• normal—Presence polling of the object.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-53
Page 54

C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Configuration Tab
Figure 6-45 shows the Configuration tab of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box.
Figure 6-45 Configuration Tab of the C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
General Area
Note The Bandwidth attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth
Note The Delay attribute is an informational parameter used only to communicate the current bandwidth to
The General area provides the following information:
• Interface Mode—The current operational mode of the interface. This field has the following values:
–
switchport—Layer 2.
–
routed—Layer 3.
• Speed—The transmission speed in bits per second of the EtherChannel interface.
• Bandwidth—Overwrites default bandwidth in kilobits per second.
to the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP and OSPF); you cannot adjust the actual bandwidth
of an interface with this command.
• Delay—Specifies the delay in tens of microseconds for an interface or network segment.
the higher-level protocols (such as IGRP, EIGRP); you cannot adjust the actual delay of an interface with
this command.
6-54
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 55

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Distribution Protocol—Protocol used for load balancing on the EtherChannel. This field has the
following values:
–
–
• Distribution Address—Address used for load balancing on the EtherChannel. This field has the
following values:
–
–
–
Layer 2 Area
The Layer 2 area contains the following information:
• MTU—The size of the largest datagram (frame) which can be sent or received on the
EtherChannel, specified in octets. This is also the maximum size of Layer 3 datagrams sent
on the EtherChannel.
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
ip—IP address.
mac—MAC address.
source
destination
both
Layer 3 Area
The Layer 3 area contains the following information:
• IP Address—IP address of the EtherChannel interface.
• Netmask—The subnet mask associated with the EtherChannel IP Address. The value of the mask
is in the format of an IP address with all the network bits set to 1 and all the host bits set to 0.
• Clear IP Address —After receiving confirmation, will unset the IP address for the EtherChannel.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-55
Page 56

C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Membership Tab
Figure 6-46 shows the Membership tab of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box.
Figure 6-46 Membership Tab of the C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Global EtherChannel Ports Assignment Area
This area lists the EtherChannel assignments for all interfaces on the selected software (switch) instance
and is not specific to any EtherChannel instance. In native IOS, this can be used to add ports to an
EtherChannel instanceby setting the operational mode to “manual” or “auto” and specifying the channel
number. If the specified channel number does not exist, it will be immediately created on the switch. In
hybrid mode, this area assigns ports to channel admin groups, from which the switch will automatically
form active EtherChannel instances. The table contains the following information:
• Slot—Slot number of the interface.
• Port—Port number of the interface.
• Operation Mode—The operation mode of the interface in the admin group. This field has one of
the following values:
–
off—The interface does not belong to an admin group. Setting the value to this selection will
remove the interface from the current admin group. Note that removing the last interface from
an active EtherChannel instance on a hybrid switch will automatically delete the EtherChannel,
while in native IOS the EtherChannel will still need to be deleted using the Delete EtherChannel
button on the Status Tab.
–
manual or auto—Indicates that the port is to belong to the admin group with the indicated PAgP
operational mode. Setting the value to this selection with an admin group specified will
immediately add the interface to the indicated EtherChannel in native IOS or to the admin group
(from which an EtherChannel may form) in hybrid OS.
6-56
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 57

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Admin Group—In native IOS, this is the EtherChannel identifier that the interface belongs to (or
the new EtherChannel to be created). In hybrid OS, this is the channel group to which the interface
belongs.
Note When a new EtherChannel is created, either through Admin Group assignment in native IOS or dynamic
formation in hybrid OS, the EtherChannel list on this dialog will not automatically update with the new
EtherChannel object. Reselect the appropriate software object to refresh the list.
EtherChannel Ports Area
The EtherChannel Ports area lists the interfaces that belong to the selected EtherChannel:
• Slot—Slot number of the interface.
• Port—Port number of the interface.
• Operation Mode—The PAgP operational mode of the component interface. This field has one of
the following values:
–
–
–
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
desirable—PAgP packets sent on interface. If no data packets are received, the interface is never
attached to a portchannel and cannot be used for data.
desirableSilent—PAgP packets sent on interface. If no data packets received after some
timeout, the interface is attached by itself, to a portchannel and can be used for data.
automatic—PAgP packets are not sent on interface until at least one PAgP packet is received
which indicates the sender is operating in desirable or desirableSilent mode. If no data packets
received, the interface is never attached to a portchannel and cannot be used for data.
–
automaticSilent—PAgP packets are not sent on interface until at least one PAgP packet is
received which indicates the sender is operating in desirable or desirableSilent mode. If no data
packets received after some timeout, the interface is attached by itself, to a portchannel and can
be used for data.
• Port State—State of the PAgP state machine on this interface. The state has the following values:
–
portDown—The current operational state of the interface is not up.
–
portUp—The current operational state of the interface is up, no packets yet received.
–
dataReceived—Data packets, but no PAgP packets, have been received.
–
upData—Interface is aggregated, but no PAgP packets have been received.
–
pagpReceived—One or more PAgP packets have been received.
–
biDirectional—Interface has passed PAgP packets in both directions.
–
upPagp—Interface is aggregated by means of PAgP.
–
upMult—Interface is aggregated to an agport, but connects to more than one external device.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-57
Page 58

C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Routing Protocol Tab
Figure 6-47 shows the Routing Protocol tab of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box.
Figure 6-47 Routing Protocol Tab of the C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
EIGRP Area
ISIS Area
The EIGRP area of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box provides the following information:
• EIGRP Interface Table—A list of the EIGRP processes. The following attributes can be configured
for a EIGRP process:
• Bandwidth Utilization (%)—Percentage of the EtherChannel interface bandwidth that the EIGRP
protocol can use.
• Hold Time (sec)—Length of time in seconds that neighbors should consider the sender valid.
• Hello Interval (sec)—Interval in seconds between hello packets.
The ISIS area of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box provides the following information:
• ISIS Enabled—Indicates whether or not IS-IS routing is enabled on the interface. This attribute is
read-only.
–
true—IS-IS routing is enabled.
–
false—IS-IS routing is disabled.
• Area Tag—The IS-IS routing area in which the interface participates. If mutli-area IS-IS is
configured on the device, the IS-IS area must be named. Otherwise, this value may be an implicit
null tag. This attribute is read-only.
6-58
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 59

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Level 1 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 1
routing.
• Level 2 Hello Interval—Length of time between hello packets generated on the interface for level 2
routing.
• Level 1 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 1 (intra-area) route calculation.
• Level 2 Metric—Cost of the interface for IS-IS level 2 (inter-area) route calculation.
• Level 1 Priority—Determines which router on a LAN will be the designated router or Designated
Intermediate System (DIS).
• Level 2 Priority—Determines which router on a LAN will be the designated router or Designated
Intermediate System (DIS).
• Enable IS-IS button—Enables IS-IS routing on the interface.
Note To enable IS-IS on an interface, the user must specify an IS-IS routing process that is already
deployed on the device. If the process does not exist, the action will fail.
• Disable IS-IS button—Disables IS-IS routing on the interface.
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
STP Tab
Figure 6-48 shows the STP tab of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box.
Figure 6-48 STP Tab for the C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
The area at the top of the STP tab provides the following information:
• Guard Mode—Indicates whether or not STP guard mode is enabled on an interface. The possible
values are:
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-59
Page 60

C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Access Mode Area
The Access Mode area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
root
–
none
• PortFast Enabled—Indicates whether or not an interface is enabled to move directly to the
forwarding state on link up. This is a read-only attribute. Portfast can be configured on a trunking
interface, but it only has an effect when the interface is in access mode. The following are possible
values:
–
true
–
false
• Port Priority—Describes the STP port priority of this interface. This is a metric used to represent
the location of an interface in a network topology. It is used to determine which port will be placed
in a blocking state when two or more ports are part of a loop. The default value is 128 in all versions
of IOS, 32 in all versions of CatOS. The valid values are:
–
Native IOS 12.1(6)E and earlier:Integer (0..248) [increments of 8]
–
Native IOS 12.1(8a)E and later:Integer (0..252) [increments of 4]
–
CatOS 6.3:Integer(0..63)
–
CatOS 7.1:Integer(1..63)
• Port Cost—Describes the STP port cost for this interface. The port cost is a metric used to represent
the speed of the interface. STP will use this value in determining the preferred path when a loop is
detected in the network.
Note On a Hybrid OS device, the port cost cannot be configured directly. The actual port cost used is
a calculated value and is the one being displayed.
Per VLAN STP Setting Area
The Per VLAN STP Setting area in the STP tab of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides
the following information:
• STP VLAN Table—Describes the STP per-VLAN configurations of a trunking interface. There is
one entry for each explicit per-VLAN spanning tree configuration on the interface.
Note The VLAN STP instance does not have to be currently carried on the trunk in order to configure the
per-VLAN STP settings. The settings will take effect when the interface actually begins trunking the
VLAN traffic.
6-60
• Priority—Describes the STP VLAN port priority of this interface. The VLAN port priority is used
on trunking interfaces. On any switch port that is not in trunking mode, the STP port priority is used
instead. The default value is 128 in all versions of IOS, 32 in all versions of CatOS. The valid values
are:
–
Native IOS 12.1(6)E and earlier:Integer (0..248) [increments of 8]
–
Native IOS 12.1(8a)E and later:Integer (0..252) [increments of 4]
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 61

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
CatOS 6.3:Integer(0..63)
–
CatOS 7.1:Integer(1..63)
• Cost—Describes the STP VLAN path cost of this interface. The VLAN path cost is only used on
trunking interfaces. On any switch port that is not in trunking mode, the STP port path cost is used
instead.
Note Default values for priority and cost will be used if you do not provide one of these arguments. You must
provide a nondefault value for at least one of these arguments, otherwise the action will fail.
• Add/Remove Per VLAN STP Setting button—Launches a subdialog box to add and remove an
explicit STP VLAN configuration to the interface. The configuration will only have an effect if the
interface is in trunking mode and the VLAN has an associated STP instance. The interface does not
currently need to be configured as a trunking port, nor does the VLAN or the VLAN STP instance
need to exist. Figure 6-49 shows the subdialog box that is displayed when the Add/Remove Per
VLAN STP Setting button is selected. The subdialog box contains the following items:
–
VLAN—Idenifies the VLAN STP instance. This is the numeric identifier of the access mode
VLAN or a VLAN that is carried on the trunk.
–
Priority—Describes the STP VLAN port priority of this interface.
–
Cost—Describes the STP VLAN path cost of this interface.
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
–
Add button—Adds an explicit STP VLAN configuration to the interface.
–
Remove button—Removes an explicit STP VLAN configuration to the interface.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-61
Page 62

C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Figure 6-49 Add / Remove Per VLAN STP Setting Subdialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
6-62
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 63

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
STP Status Area
The STP Status area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
• STP VLAN Status Table—Describes the status of the active STP VLAN port configurations of the
interface. Data is displayed in the following columns:
–
–
–
–
HSRP Tab
Figure 6-50 shows the HSRP tab of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box.
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
VLAN—Idenifies the VLAN STP instance that this status applies to. This is the numeric
identifier of the access mode VLAN or a VLAN that is carried on the trunk.
Port—Unique port identifier for the interface in the STP instance. This identifier is unique for
that port across all devices in the STP management domain.
State—Describes the interface state in the STP instance.
Port Cost—Indicates the current calculated port path cost of the interface in the STP instance.
Figure 6-50 HSRP Tab for the C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-63
Page 64

C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
HSRP Area
Note There may be multiple groups deployed on an interface. Using a group number on one logical or
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
The HSRP area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
• HSRP Group Table—Describes HSRP groups deployed on an interface.
physical interface does not preclude using it on another.
• Virtual IP—Primary virtual IP address of the HSRP group. If this address is not configured, the
agent will attempt to discover the virtual address through a discovery process which scans the hello
messages.
• Preempt—If enabled, the current router will attempt to overthrow a lower priority active router and
attempt to become the active router. If disabled, this router will become the active router only if
there is no such router or the active router fails.
–
true—Preempt enabled.
–
false—Preempt disabled.
• Delay Minimum—Time difference (in seconds) between a router power up and the time it can start
preempting the currently active router. This value is only applicable when preemption is enabled.
• Priority—Priority value that prioritizes a potential hot standby router. The range is 1 to 255, where
1 indicates the lowest priority and 255 indicates the highest priority. The default priority value is
100. The router in the HSRP group with the highest priority value becomes the active router.
• Hello Interval—Hello interval in milliseconds. If this value is not configured, it can be learned from
the active router.
• Hold Interval—Hold interval in milliseconds. If this value is not configured, it can be learned from
the active router.
• Add/Remove HSRP Group button—This action deploys or remove an HSRP group on the interface.
The HSRP group may optionally be assigned a primary IP address. If no address is explicitly
assigned, the device will attempt to discover the virtual IP address from the active server using hello
messages. Figure 6-51 shows the subdialog box that is displayed when you click the button.
6-64
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 65

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-51 HSRP Group Configure Subdialog Box
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Secondary IP Area
The Secondary IP area of the C6576M Ethernet Interface dialog box provides the following information:
• HSRP Secondary Address Table—Describes secondary IP addresses of HSRP groups deployed on
the interface. Data is displayed in the following columns:
–
Group Number—Unique identifier of an HSRP group.
–
Secondary IP—Secondary IP address of HSRP group.
• Modify HSRP Group button—Figure 6-52 shows the subdialog box that is displayed when the
Modify button is clicked. This subdialog box is used to modify the following C6576M Ethernet
Interface attributes of a given HSRP group:
–
Secondary IP
–
Virtual IP
–
Preempt
–
Delay Minimum
–
Priority
–
Hello Interval
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-65
Page 66

C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
–
Figure 6-52 HSRP Secondary IP Modify Subdialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Hold Interval
6-66
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 67

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-53 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M EtherChannel dialog box.
Figure 6-53 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
C6576M EtherChannel Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the object.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-67
Page 68

C6576M BGP Dialog Box
C6576M BGP Dialog Box
The C6576M BGP dialog box provides information for the IOS Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). This
dialog box can be launched from the Software object or BGP object in the Physical view.
BGP Tab
Figure 6-54 shows the BGP tab of the C6576M BGP dialog box.
Figure 6-54 BGP Tab of the C6576M BGP Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
BGP Information Area
The BGP Information area of the C6576M BGP dialog box provides the following information:
• Local AS ID—Autonomous system number for the local BGP process. This attribute has a value of
• Enable button—Enables BGP on the switch or router. Launches the dialog box shown in
• Disable button—Disables BGP on the switch or router.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-68
0 if BGP is disabled on the switch or router.
Figure 6-55.
To enable BGP on the switch or router, specify the BGP autonomous system number and then click
Enable BGP. An error will be reported if BGP is already enabled on the switch or router.
Page 69

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-55 BGP Enable Dialog Box
C6576M BGP Dialog Box
BGP Network Path Attribute Table Area
The BGP Network Path Attribute Table area contains information about paths to destination networks
received from all BGP peers. This area contains the following columns:
• Peer IP Address—IP address of the peer from which the path information was learned. This address
is 0.0.0.0 if this information was learned internally.
• IP Address—IP address of the destination network.
• Network Mask—Length of the destination network IP adddress prefix in the Network Layer
Reachability Information field.
• Path Origin—Ultimate origin of the path information. This has the following values:
–
igp—Interior Gateway Protocol advertised with a network router configuration command.
–
egp—Exterior Gateway Protocol.
–
incomplete—Unknown origin. Usually, a router that is distributed into BGP from an IGP.
• Border Router IP Address—Address of the border router that should be used for the destination
network.
• Multiple Exit Point Discriminate Metric—Metric used to discriminate between multiple exit
points to an adjacent autonomous system. A value of -1 indicates the absence of this attribute.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-69
Page 70

C6576M BGP Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Degree of Preference—Degree of preference for an advertised route. A value of -1 indicates an
absence of this attribute.
• Add/Remove Network Path Attribute Entry button—Adds or removes specific network(s) to be
advertised (or not to be advertised) by the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). Launches the dialog box
shown in Figure 6-56.
Specify the IP and network mask of the network to be added or removed from the BGP process.
Figure 6-56 Add or Remove BGP Path Attributes Dialog Box
Status Field
6-70
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
• normal—Presence polling of the object.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 71

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Neighbor Tab
Figure 6-57 shows the Neighbor tab of the C6576M BGP dialog box.
Figure 6-57 Neighbor Tab of the C6576M BGP Dialog Box
C6576M BGP Dialog Box
BGP Neighbor Table Area
This area lists the BGP neighbors of the local BGP process:
• Neighbor IP Address—Remote IP address of this entry’s BGP neighbor.
• Neighbor ID—IP address of the neighbor.
• Remote AS—Autonomous system number of the neighbor.
• State—Operational state of the connection between the neighbor and local BGP process. This field
has the following values:
–
idle
–
connect
–
active
–
opensent
–
openconfirm
–
established
• Negotiated Version—Negotiated version of BGP running between the two neighbors.
• Add/Remove Neighbor Entry button—Adds or removes BGP neighbors from this table. Launches
the dialog box shown in Figure 6-58.
Specify the neighbor IP address and remote AS number to add or remove the neighbor from the local
BGP neighbor table.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-71
Page 72

C6576M BGP Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-58 Add or Remove BGP Peers Dialog Box
6-72
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 73

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Redistribution Tab
Figure 6-59 shows the Redistribution tab of the C6576M BGP dialog box.
Figure 6-59 Redistribution Tab of the C6576M BGP Dialog Box
C6576M BGP Dialog Box
Redistribution Table Area
This area describes the route redistribution configuration of the BGP routing process. Routes learned
from other interior and exterior routing protocols may be redistributed into the BGP routing domain.
• Protocol—Source protocol from which routes are being distributed into BGP.
–
–
–
• AS/Tag—The autonomous system tag identifying the BGP routing domain.
• IS-IS Routing Level—Indicates IS-IS route level redistribution. This field has the following values:
–
–
–
–
• Metric—BGP metric used to weigh the redistributed route. If no value is specified for Default
Metric (in the BGP tab), this value defaults to 0.
IS-IS
EIGRP
OSPF
none—For protocols other than IS-IS.
level-1—Local area/intra-area dedistribution.
level-1-2—Redistribution for both inter and intra-area routing.
level-2—Backbone/interarea redistribution (default).
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-73
Page 74

C6576M BGP Dialog Box
Default Metric Area
This area has one attribute:
• Default Metric—Default metric used for route redistribution. This metric is used when and explicit
metric is not given during route redistribution process.
Edit Redistribution Table Area
This area allows changes to be made to the Redistribution Table:
• Protocol—Source protocol from which routes are being distributed. This attribute along with Source
ID uniquely identifies a source of network paths to be redistributed through BGP. There may be, at
most, one redistribution entry for a given source of network path information.
• AS/Tag—The autonomous system tag identifying the BGP routing domain.
• IS-IS Routing Level—Indicates IS-IS route level redistribution. This field has the following values:
–
level-1—Local area/intra-area dedistribution.
–
level-1-2—Redistribution for both inter and intra-area routing.
–
level-2—Backbone/interarea redistribution (default).
• Metric—BGP metric used to weigh the redistributed route. If no value is specified for Default
Metric (in the BGP tab), this value defaults to 0.
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Add button—Enables route redistribution from another IP routing process into the BGP routing
domain. Routes may be learned from an IS-IS, EIGRP, or OSPF routing process.
• Delete button—Disables route redistribution from another IP routing process into the BGP routing
domain.
6-74
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 75

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Distribution List Tab
Figure 6-60 shows the Distribution List tab of the C6576M BGP dialog box.
Figure 6-60 Distribution List Tab of the C6576M BGP Dialog Box
C6576M BGP Dialog Box
Distribution List Table Area
This area describes filtering of routing updates sent or received by the routing process.
• ACL ID—Unique identifer of an ACL for filtering routing updates sent or received by a routing
process. The ACL specifies which network routes will be permitted or denied in routing updates.
This field has the following values:
–
<1-199>—Standard access list number.
–
<1300-2699>—Expanded access list number.
–
alphanumeric—Named access list.
• Direction—Indicates whether the filter will be applied against routing updates received by the
routing process or advertised by the routing process.
–
in—Applies to updates received.
–
out—Applies to updates advertised.
• Interface—Identifies a particular interface that the filter is applied to. For an incoming filter,
suppresses routing updates received on a specific interface; if not specified, routing updates are
suppressed on all interfaces. For an outgoing filter, suppresses routes from being advertised on a
particular interface; if not specified, route advertisements are suppressed on all interfaces.
–
Null 0
–
FastEthernet <slot>/<port> (Native IOS only)
–
GigabitEthernet <slot>/<port> (Native IOS only)
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-75
Page 76

C6576M BGP Dialog Box
–
GE-WAN <slot>/<port>
–
POS <slot>/<port>
–
ATM <slot>/<subslot>/<port>
–
Port-channel <n> (Native IOS only)
–
VLAN <n>
• Protocol—Identifies the routing protocol source of network routes.
• Source ID—Identifies the routing process from which routes are being distributed. This field may
have the following values:
–
IS-IS—This is either an implicit null tag or the tag of a named IS-IS routing process.
–
BGP—This is a 16-bit autonomous system ID in the range of 1 to 65535.
–
EIGRP—This is a 16-bit autonomous system ID in the range of 1 to 65535.
–
OSPF—This is a 16-bit OSPF process ID in the range of 1 to 65535.
Edit Distribution Table Area
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
This area allows changes to be made to the Distribution Table attributes described in the “Distribution
List Table Area” section on page 6-75:
• ACL ID—Unique identifer of an ACL for filtering routing updates sent/received by a routing
process.
• Direction—Indicates whether the filter will be applied against routing updates received by the
routing process or advertised by the routing process.
• Interface—Identifies a particular interface that the filter is applied to.
• Protocol—Identifies a protocol source of network routes.
• Source ID—Identifies a specific routing process instance that redistributed routes are derived from.
• Add button—Specifies a filter for suppressing or allowing distribution of network routes through
BGP.
• Delete button—Removes a filter for suppressing or allowing distribution of network routes through
BGP.
6-76
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 77

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-61 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M BGP dialog box.
Figure 6-61 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M BGP Dialog Box
C6576M BGP Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the object.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-77
Page 78

C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
The C6576M OSPF dialog box provides information for all IOS Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing
protocol processes. This dialog box can be launched from the Software object or OSPF objects in the
Physical view.
Details Tab
Figure 6-62 shows the Details tab of the C6576M OSPF dialog box.
Figure 6-62 Details Tab of the C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
OSPF Area
6-78
The OSPF area of the C6576M OSPF dialog box describes the OSPF area configurations:
• Process ID—Process number of this OSPF process.
• Router ID—Unique identifier of the router in the autonomous system. By convention, to ensure
uniqueness this defaults to the value of one of the router’s IP interface addresses.
• Administrative Status—Administrative status of this OSPF router process. The enabled value
denotes that the OSPF process is active on at least one interface; the disabled value indicates that all
interfaces are disabled.
• Area Border Router—Flag to note whether or not this router is an area border router.
• AS Border Router—Flag to note whether or not this router is configured as an autonomous system
border router.
• Add button—Adds an OSPF process to the switch or router. Launches the dialog box shown in
Figure 6-63.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 79

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Note The Catalyst 6000 family switches and the Cisco 7600 series Internet Routers support only three
OSPF processes.
Specify the OSPF Process ID (number only) and click Add to create the OSPF process on the switch
or router. The string “OSPF-” will be prepended automatically to the process ID.
Note A newly created OSPF process will not automatically be listed in the OSPF object list (bottom
left of Figure 6-62). To list the new process, reselect the current Software object from the
Software object list (top left of Figure 6-62).
• Remove button—Deletes the currently selected OSPF process.
Figure 6-63 Add OSPF Processes Dialog Box
C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-79
Page 80

C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Status Field
Area Tab
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
• normal—Presence polling of the object.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
Figure 6-64 shows the Area tab of the C6576M OSPF dialog box.
Figure 6-64 Area Tab of the C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Area Configuration Area
This describes OSPF NSSA and stub area configurations. The information for a particular area can be
displayed by selecting the desired area from the Areas list. When you select an area, the following
information is provided:
• Area ID—Identifies a stub or NSSA area adjacent to the router. The identifier can be specified as
either a decimal value or as an IP address.
• Area Type—Type of area. The type has the following values:
–
–
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-80
default—Not a stub or NSSA area.
stub—Information on external routes are not sent to stub areas.
Page 81

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
nssa—Similar to a stub area but autonomous system external routes can be imported into the
area.
• Auth. Type—Authentication type for the area. The authentication type must be the same for all routers
and access servers in an area. The authentication password for all OSPF routers on a network must be the
same if they are to communicate with each other using OSPF. The Authentication type has the
following values:
–
none—The area does not enforce any authentication.
–
simple—Simple password authentication is used.
–
md5—MD5 authentication is enabled for the area.
• Def. Cost—Default cost for the area. Use this value only on an area border router attached to a stub
area. It provides a metric for the summary default route generated by the area border router into the stub
area.
• NSSA Def. Info. Orig.—Generates a Type 7 default into the NSSA area. This argument takes effect only
on an NSSA area border router or an NSSA AS border router
• NSSA No Redistrib.—Used when the router is a NSSA area border router and routes are to be imported
only into the normal areas, but not into the NSSA area.
C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
.
Network Tab
• Stub No Summary—Indicates that an area border router is sending summary link advertisements into
the stub area.
• Remove Area—Removes an explicit NSSA or stub area configuration to the OSPF routing process.
The action can only be used on an area border router attached to a stub or NSSA area.
Figure 6-65 shows the Network tab of the C6576M OSPF dialog box.
Figure 6-65 Network Tab of the C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-81
Page 82

C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Network Masks Area
The table in this area displays the networks associated with the selected OSPF process. This table
contains the following information:
• Area ID—Area ID assigned to the networks and subnets.
• Network Number—IP address of the network.
• Network Mask—Netmask associated with the IP address.
• Add/Remove Networks—Adds or removes networks from the OSPF process. Launches the dialog
Figure 6-66 Add or Remove OSPF Networks Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
box shown in Figure 6-66.
Specify the Network IP Address, Wildcard Mask, and the Area ID to be added or removed from the
OSPF process.
6-82
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 83

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Global Tab
Figure 6-67 shows the Global tab of the C6576M OSPF dialog box.
Figure 6-67 Global Tab of the C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Global Network Configuration Table
This describes the OSPF view of all interfaces on the router. This table contains the following columns:
• Link Index—Unique identifier of an interface on the router. This value is equal to the unique
identifier of the interface if this is a Layer 2 (address-less) interface. If the interface is a Layer 3
(addressed) interface, this value is 0. This identifier is dynamic, it may change over the lifetime of
an interface.
• IP Address—IP address of the interface.
• Area ID—Unique identifier of the area to which the interface connects. An Area ID of 0.0.0.0 is
used for the OSFP backbone.
• Network Type—OSPF interface type. OSPF network type can be NBMA even on a broadcast media
such as Ethernet. This column has the following values:
–
broadcast
–
nbma
–
pointToPoint
–
pointToMultipoint
• Admin Status—OSPF interface’s administrative status.
–
enabled—Indicates that neighbor relationships can be formed on the interface, and the interface
will be advertised as an internal route to some area.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-83
Page 84

C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
disabled—Indicates that the interface is external to OSPF.
• Trans. Priority—The priority of this interface. Used in multiaccess networks, this field is used in the
designated router election algorithm. The value 0 signifies that the router is not eligible to become
the designated router on this particular network. If more than one router has the same value, the
routers use their router ID as a tie breaker.
• Trans. Delay (sec)—The estimated number of seconds it takes to transmit a link state update packet
over this interface.
• Retrans. Interval (sec)—The number of seconds between link-state advertisement retransmissions
for adjacencies belonging to this interface. This value is also used when retransmitting database
description and link-state request packets.
• Hello Interval (sec)—The length of time, in seconds, between the hello packets that the router sends
on the interface. This value must be the same for all routers attached to a common network.
• Trans. Dead (sec)—The number of seconds that a router’s hello packets have not been seen before
its neighbors declare the router down. This should be some multiple of the hello interval. This value
must be the same for all routers attached to a common network.
• Polling Interval (sec)—The larger time interval, in seconds, between the hello packets sent to an
inactive nonbroadcast multiaccess neighbor.
• State—The OSPF interface state.
• Designated Router—IP address of the designated router.
• Backup Designated Router—IP address of the backup designated router.
• Authentication Key—Password to be used by neighboring OSPF routers on a network segment that
is using OSPF simple password authentication. Ignored if ospfAuthType is not “simple”.
6-84
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 85

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Neighbor Tab
Figure 6-68 shows the Neighbor tab for the C6576M OSPF dialog box.
Figure 6-68 Neighbor Tab of the C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Global Neighbor Routers Area
This area lists all OSPF neighbors for all OSPF processes. This area consists of the following columns:
• Neighbor Link Index—Unique identifier of the interface on which the neighbor can be reached. This
value is set to 0 if the interface has an IP address.
• Neighbor IP Address—IP address of the neighbor. On links without addresses, this address will not
be 0.0.0.0, but the address of another of the neighbor’s interfaces.
• Neighbor Router ID—IP address uniquely identifying the neighbor router in the autonomous
system.
• Neighbor Priority—Priority of this neighbor in the designated router election algorithm. The value
0 signifies that the neighbor is not eligible to become the designated router on this particular
network.
• Neighbor State—The state of the relationship with this Neighbor. This column may have the
following values:
–
down
–
attempt
–
init
–
twoWay
–
exchangeStart
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-85
Page 86

C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
exchange
–
loading
–
full
• Neighbor Entry Status—This variable displays the status of the entry. Setting the variable to
“invalid” can make it inoperative.
• Add/Remove Neighbors—Adds or removes neighbors. Launches the dialog box shown in
Figure 6-69.
When adding a new neighbor, specify the neighbor router’s IP address and the cost associated for
this neighbor, and click the Add button.
To remove a neighbor, choose the neighbor in the Neighbor Table and click the Remove button. The
Neighbor IP Address and Cost are displayed for the neighbor selected.
Figure 6-69 Add or Remove OSPF Neighbors Dialog Box
6-86
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 87

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Redistribution Tab
Figure 6-70 shows the Redistribution tab of the C6576M OSPF dialog box.
Figure 6-70 Redistribution Tab of the C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-87
Page 88

C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Redistribution Table Area
This area describes the route redistribution configuration of the OSPF routing process. Routes learned
from other interior and exterior routing protocols may be redistributed into the OSPF routing domain.
• Protocol—Source routing protocol from which routes are being distributed into OSPF.
–
–
–
–
• AS/Tag—The autonomous system tag identifying the BGP routing domain.
• IS-IS Routing Level—Indicates IS-IS route level redistribution. This field has the following values:
–
–
–
–
• Metric—OSPF metric used to weigh the redistributed route. If no value is specified for Default
Metric (in the General tab), this value defaults to 0.
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
IS-IS
EIGRP
OSPF
BGP
none—For protocols other than IS-IS.
level-1—Local area/intra-area dedistribution.
level-1-2—Redistribution for both inter and intra-area routing.
level-2—Backbone/interarea redistribution (default).
• Subnets—Indicates whether or not subnets will be considered for redistribution into OSPF. This
column has the value of either ‘true’ or ‘false’.
Default Metric Area
• Default Metric—Default OSPF metric used for redistributed routes. This metric is used when an
explicit metric is not given in the Metric entry of the Redistribution tab. A value of 0 indicates that
no default metric has been specified.
Edit Redistribution Table Area
This area allows changes to be made to the attributes in the Redistribution Table. These attributes are
discussed in detail in the “Redistribution Table Area” section on page 6-88.
• Protocol—Source routing protocol from which routes are being distributed into OSPF.
• AS/Tag—The autonomous system tag identifying the BGP routing domain.
• IS-IS Routing Level—Indicates IS-IS route level redistribution.
• Metric—OSPF metric used to weigh the redistributed route.
• Subnets—Indicates whether or not subnets will be considered for redistribution into OSPF.
• Add button—Enables route redistribution from another IP routing process into the OSPF routing
domain. Routes may be learned from an IS-IS, EIGRP, or BGP routing process.
• Delete button—Disables route redistribution from another IP routing process into the BGP routing
domain.
6-88
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 89

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Distribution List Tab
Figure 6-71 shows the Distribution List tab of the C6576M OSPF dialog box.
Figure 6-71 Distribution List Tab of the C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Distribution List Table Area
This area describes filtering of routing updates sent or received by the routing process.
• ACL ID—Unique identifer of an ACL for filtering routing updates sent or received by a routing
process. The ACL specifies which network routes will be permitted or denied in routing updates.
This field has the following values:
–
<1-199>—IP standard access list number.
–
<1300-2699>—IP expanded access list number.
–
alphanumeric—Named access list.
• Direction—Indicates whether the filter will be applied against routing updates received by the
routing process or advertised by the routing process.
–
in—Applies to updates received.
–
out—Applies to updates advertised.
• Interface—Identifies a particular interface that the filter is applied to. For an incoming filter,
suppresses routing updates received on a specific interface; if not specified, routing updates are
suppressed on all interfaces. For an outgoing filter, suppresses routes from being advertised on a
particular interface; if not specified, route advertisements are suppressed on all interfaces.
–
Null 0
–
FastEthernet <slot>/<port> (Native IOS only)
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-89
Page 90

C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
–
GigabitEthernet <slot>/<port> (Native IOS only)
–
GE-WAN <slot>/<port>
–
POS <slot>/<port>
–
ATM <slot>/<subslot>/<port>
–
Port-channel <n> (Native IOS only)
–
VLAN <n>
• Protocol—Source routing protocol from which routes are being distributed into OSPF.
• Source ID—Identifies a specific routing process instance that redistributed routes are derived from.
Edit Distribution Table Area
This area allows changes to be made to the Distribution Table:
• ACL ID—Unique identifer of an ACL for filtering routing updates sent or received by a routing
process.
• Direction—Indicates whether the filter will be applied against routing updates received by the
routing process or advertised by the routing process.
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Interface—Identifies a particular interface that the filter is applied to.
• Protocol—Source routing protocol from which routes are being distributed into OSPF.
• Source ID—Identifies a specific routing process instance that redistributed routes are derived from.
• Add button—Specifies a filter for suppressing or allowing distribution of network routes through
OSPF routing process.
• Delete button—Removes a filter for suppressing or allowing distribution of network routes through
OSPF routing process.
6-90
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 91

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-72 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M OSPF dialog box.
Figure 6-72 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
C6576M OSPF Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the object.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-91
Page 92

C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
The C6576M EIGRP dialog box provides information on the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing
Protocol (EIGRP) enabled in IOS. This dialog box is launched from the Software object or EIGRP
objects in the Physical view.
Note All information in this dialog box is retrieved or set using IOS commands. If the IOS Telnet or the Enable
password specified in the Network Element dialog box is incorrect, attributes in this dialog box might
be displayed as ERROR.
Details Tab
Figure 6-73 shows the Details tab of the C6576M EIGRP dialog box.
Figure 6-73 Details Tab of C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Configuration Area
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-92
The Configuration area of the C6576M EIGRP dialog box provides the following information:
• Autonomous System—Autonomous system number for this EIGRP process.
• Router Summarization—If true, subnet routes are summarized automatically into network-level
routes. Automatic summarization is performed when there are two or more networks associated with
the EIGRP process.
Page 93

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Stuck In Active—Length of time (in minutes) that a route stays active. This value determines the
maximum period of time that an EIGRP router will wait for replies to its queries. If this value is set too
low, there might not be enough time for all the neighboring routers to send their replies to the active
router.
• Log Neighbor Changes—If true, changes to neighbor adjacencies are logged. This can be useful to
monitor the stability of the routing system and help detect problems.
• Log Neighbor Warnings—If true, neighbor warning messages are logged.
• Delete EIGRP button—Deletes the currently selected EIGRP process from the switch or router.
• Add EIGRP button—Adds EIGRP processes to the switch or router. Launches the dialog box shown
in Figure 6-74. Specify the following attributes and click Add to add an EIGRP process to IOS:
–
Autonomous System Number—Autonomous system number for this EIGRP process.
–
IP Address—IP address of a local network. A local network must be specified to add an EIGRP
process.
–
Wildcard Mask—Mask to be used with the IP address. This field is optional.
Figure 6-74 Add EIGRP Processes Dialog Box
C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
Note If no netmask is provided, the EIGRP routing process is only deployed on a single network.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-93
Page 94

C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
Local Networks Area
This area describes the networks supported by EIGRP. EIGRP will send routing updates on the
interfaces in the networks. If the network of an interface is not specified, it will not be advertised by
EIGRP. This area consists of the following columns:
• IP Address—IP address of an interface or a range of interfaces in a network supported by the EIGRP
• IP Wildcard Mask—Network wildcard bitmask. Enabled bits indicate wildcard bits in the IP
• Add/Remove Local Network button—Defines or disables the interfaces that an EIGRP process will
Figure 6-75 Add or Remove Networks to the EIGRP Process Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
routing process.
address. This allows multiple interfaces to be specified in a single network entry.
run on. EIGRP sends updates to the interfaces in the specified networks. Also, if the network of an
interface is not specified, it will not be advertised in any IGRP or Enhanced IGRP update. The
wildcardmask can be used to specify a range of interfaces supported by the EIGRP routing process.
Launches the dialog box shown in Figure 6-75.
Specify the IP address and IP mask of the entry to be added or removed from the local network table.
6-94
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 95

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Status Field
The Status display-only field located at the bottom of the window indicates the current state of the object.
This field has the following values:
• decommissioned—CEMF is not actively monitoring the object attributes.
• normal—Presence polling of the object.
• normallostcomms—CEMF has lost communication with the device from the normal state.
Redistribution Tab
Figure 6-76 shows the Redistribution tab of the C6576M EIGRP dialog box.
Figure 6-76 Redistribution Tab of the C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
Redistribution Table Area
This area describes the route redistribution configuration of the EIGRP routing process. Routes learned
from other interior and exterior routing protocols may be redistributed into the EIGRP routing domain.
• Protocol—Source routing protocol from which routes are being distributed into EIGRP.
–
–
–
–
–
IS-IS
EIGRP
BGP
OSPF
static
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-95
Page 96

C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
• Source ID—Identifies the routing process from which routes are being distributed. This field may
have the following values:
–
IS-IS—This is either an implicit null tag or the tag of a named IS-IS routing process.
–
EIGRP—This is a 16-bit autonomous system ID in the range of 1..65535
–
BGP—This is a 16-bit autonomous system ID in the range of 1..65535
–
OSPF—This is a 16-bit OSPF process ID in the range of 1..65535
• IS-IS Routing Level—Indicates IS-IS route level redistribution. This field has the following values:
–
none—For protocols other than IS-IS.
–
level-1—Local area/intra-area dedistribution.
–
level-1-2—Redistribution for both inter- and intra-area routing.
–
level-2—Backbone/interarea redistribution (default).
• Bandwidth—Bandwidth metric. This redistribution metric must be specified for protocols other
than EIGRP if the Default Metric in the Details tab is nil.
• Delay—Delay metric. This redistribution metric must be specified if the Default Metric is nil.
• Reliability—Reliability metric. 0 is least reliable, 255 is 100 percent reiliable. This redistribution
metric must be specified if the default metric is nil.
• Loading—Loading metric. This indicates the effective bandwidth of the network paths where 0 is
least loaded and 255 is 100 percent loaded. This redistribution metric must be specified if the
Default Metric is nil.
Metric Default Area
• MTU—Maximum transmission unit of the path metric. This redistribution metric must be specified
if the Default Metric is nil.
• Default Metric—Default metric used for route redistribution. This metric is used when and explicit
metric is not given during route redistribution process.
6-96
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 97

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Edit Redistribution Table Area
This area allows changes to be made to the attributes shown in the Redistribution Table. These attributes
are discussed in detail in the “Redistribution Table Area” section on page 6-95.
• Protocol—Source routing protocol from which routes are being distributed into EIGRP. This field
may have the following values:
–
IS-IS
–
EIGRP
–
OSPF
–
BGP
–
static
• IS-IS Routing Level—Indicates IS-IS route level redistribution.
• Delay—Delay metric.
• Loading—Loading metric.
• Source ID—Identifies the routing process from which routes are being distributed.
• Bandwidth—Bandwidth metric.
• Reliability—Reliability metric.
C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
• MTU—Maximum transmission unit of the path metric.
• Add button—Enables route redistribution from another IP routing process into the EIGRP routing
domain. Routes may be learned from an IS-IS, OSPF, or BGP routing process.
• Delete button—Disables route redistribution from another IP routing process into the EIGRP
routing domain.
Distribution List Tab
Figure 6-77 shows the Distribution List tab of the C6576M EIGRP dialog box.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-97
Page 98

C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-77 Distribution List Tab of the C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
Distribution List Table Area
This area describes filtering of routing updates sent or received by the routing process.
• ACL ID—Unique identifer of an ACL for filtering routing updates sent or received by a routing
process. The ACL specifies which network routes will be permitted or denied in routing updates.
This field has the following values:
–
<1-199>—IP standard access list number.
–
<1300-2699>—IP expanded access list number.
–
alphanumeric—Named access list.
• Direction—Indicates whether the filter will be applied against routing updates received by the
routing process or advertised by the routing process.
–
in—Applies to updates received.
–
out—Applies to updates advertised.
• Interface—Identifies a particular interface that the filter is applied to. For an incoming filter,
suppresses routing updates received on a specific interface; if not specified, routing updates are
suppressed on all interfaces. For an outgoing filter, suppresses routes from being advertised on a
particular interface; if not specified, route advertisements are suppressed on all interfaces.
–
Null 0
–
FastEthernet <slot>/<port> (Native IOS only)
–
GigabitEthernet <slot>/<port> (Native IOS only)
–
GE-WAN <slot>/<port>
6-98
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
Page 99

Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
–
POS <slot>/<port>
–
ATM <slot>/<subslot>/<port>
–
Port-channel <n> (Native IOS only)
–
VLAN <n>
• Protocol—Source routing protocol from which routes are being distributed into EIGRP. This field
may have the following values:
–
none
–
OSPF
–
EIGRP
–
BGP
–
static
• Source ID—Identifies a specific routing process instance that redistributed routes are derived from.
Edit Distribution List Table Area
C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
This area allows changes to be made to the Distribution Table:
• ACL ID—Unique identifer of an ACL for filtering routing updates sent/received by a routing
process.
• Interface—Identifies a particular interface that the filter is applied to.
• Protocol—Source routing protocol from which routes are being distributed into EIGRP. This field
may have the following values:
–
OSPF
–
EIGRP
–
BGP
–
static
• Direction—Indicates whether the filter will be applied against routing updates received by the
routing process or advertised by the routing process.
• Source ID—Identifies a specific routing process instance that redistributed routes are derived from.
• Add button—Specifies a filter for suppressing or allowing distribution of network routes through
EIGRP routing process.
• Delete button—Removes a filter for suppressing or allowing distribution of network routes through
EIGRP routing process.
Additional Notes Tab
Figure 6-78 shows the Additional Notes tab of the C6576M EIGRP dialog box.
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
6-99
Page 100

C6576M IS-IS Dialog Box
Chapter 6 Logical Object Dialog Boxes
Figure 6-78 Additional Notes Tab of the C6576M EIGRP Dialog Box
Notes Area
The Notes area is a text box that allows you to type in additional notes for the object.
C6576M IS-IS Dialog Box
The C6576M IS-IS dialog box provides information on the OSI Intermediate System to Intermediate
System (IS-IS) routing process on a Catalyst 6000/6500 series switch or Cisco 7600 series Internet
Router. This dialog box is launched from the Software object or IS-IS objects in the Physical view.
Details Tab
Figure 6-79 shows the Details tab of the C6576M IS-IS dialog box.
6-100
Cisco 6500/7600 Series Manager User Guide
 Loading...
Loading...