Page 1

Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Text Part Number: OL-2365-02
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCIP, the Cisco Arrow logo, the Cisco Powered Network mark, the Cisco Systems Verified logo, Cisco Unity, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, iQ
Breakthrough, iQ Expertise, iQ FastTrack, the iQ Logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, Networking Academy, ScriptShare, SMARTnet, TransPath, and
Voice LAN are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, Discover All That’s Possible, The Fastest Way to
Increase Your Internet Quotient, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE,
CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital,
the Cisco Systems logo, Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, GigaStack, Internet Quotient,
IOS, IP/TV, LightStream, MGX, MICA, the Networkers logo, Network Registrar, Pac ke t, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, RateMUX, Registrar,
SlideCast, StrataView Plus, Stratm, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S.
and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Web site are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a
partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0208R)
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
Copyright © 2002, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Page 3

Preface xiii
Audience xiii
Purpose xiii
Organization xiii
Conventions xiv
Related Documentation xv
Obtaining Documentation xvi
World Wide Web xvi
Documentation CD-ROM xvi
Ordering Documentation xvi
Documentation Feedback xvi
Obtaining Technical Assistance xvii
Cisco.com xvii
Technical Assistance Center xvii
Contacting TAC by Using the Cisco TAC Website xvii
Contacting TAC by Telephone xviii
CONTENTS
CHAPTER
1 Product Overview 1-1
1.1 Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System 1-1
1.1.1 Features 1-3
1.1.2 Configurations 1-3
1.1.2.1 Cisco 6260 System with a POTS Splitter Configuration 1-4
1.1.2.2 Cisco 6260 System Without a POTS Splitter Configuration 1-4
1.1.2.3 IMA Configuration 1-4
1.1.2.4 Subtended Network Configuration 1-6
1.2 Cisco 6260 System Overview 1-10
1.2.1 Cisco 6260 Card Compartment 1-10
1.2.2 Cisco 6260 Connectors 1-12
1.2.3 Cisco 6260 Cards 1-13
1.2.3.1 Quad-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card Overview 1-13
1.2.3.2 Quad-Port DMT ATU-C over ISDN Line Card Overview 1-15
1.2.3.3 Quad-Port Flexi ATU-C Line Card Overview 1-17
1.2.3.4 Quad-Port STU-C Line Card Overview 1-19
1.2.3.5 Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card Overview 1-21
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
iii
Page 4

Contents
1.2.3.6 Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Over ISDN Line Card Overview 1-23
1.2.3.7 Octal-Port G.SHDSL SHTU-C Line Card Overview 1-25
1.2.3.8 Line Card Intermixing 1-27
1.2.3.9 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card Overview 1-30
1.2.3.10 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card Overview 1-32
1.2.3.11 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card Overview 1-35
1.2.3.12 Network Clocking Overview 1-39
1.2.3.13 Redundancy Overview 1-39
1.2.3.14 Redundancy in Subtended Configurations 1-41
1.2.4 Cisco 6260 I/O Modules 1-41
1.2.4.1 E3 I/O Module Overview 1-41
1.2.4.2 E1 I/O Module Overview 1-42
1.2.4.3 OC-3c I/O Module Overview 1-43
1.2.4.4 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pins 1-44
1.2.5 PEM 1-45
1.2.6 Fan Tray 1-47
1.2.7 Air Filters 1-48
1.2.8 ESD Jack 1-48
1.2.9 Third-Party POTS Splitter 1-49
CHAPTER
1.3 Management Software 1-49
1.3.1 Management Software-Generated Alarms 1-49
2 Preparing for Installation 2-1
2.1 Safety Requirements 2-1
2.1.1 Safety Guidelines 2-1
2.1.2 Warning Definition 2-2
2.1.3 Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage 2-9
2.1.4 General Maintenance Guidelines 2-10
2.1.4.1 Hot Swapping Cards 2-10
2.1.4.2 Hot Swapping I/O Modules 2-10
2.1.4.3 Installation and Replacement Suggestions 2-11
2.2 Site Requirements 2-11
2.2.1 Environmental Requirements 2-11
2.2.1.1 Temperature, Altitude, and Humidity 2-12
2.2.1.2 Ventilation 2-12
2.2.1.3 Space 2-13
2.2.2 Power Requirements 2-14
2.2.3 Rack-Mounting Requirements 2-15
iv
2.3 Required Tools and Equipment 2-16
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 5

2.4 Unpacking the Cisco 6260 System 2-18
2.5 Verifying Contents 2-18
2.6 Inspecting for Damage 2-18
Contents
CHAPTER
3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration 3-1
3.1 Installation Checklist 3-2
3.2 Installation Procedures 3-3
3.2.1 Measure Rack Space 3-3
3.2.2 Install the Third-Party POTS Splitter 3-3
3.2.3 Attach Ear Brackets to the Cisco 6260 3-4
3.2.4 Install the Cisco 6260 Chassis 3-5
3.2.5 Install Blank Faceplates 3-6
3.2.6 Ground the Cisco 6260 3-7
3.2.7 Ground the Third-Party POTS Splitter 3-8
3.2.8 Connect the Cisco 6260 to the Third-Party POTS Splitter 3-9
3.2.9 Connect the Third-Party POTS Splitter to the MDF or to the Cross Connect 3-9
3.2.10 Attach Cisco 6260 Power Connections 3-9
3.2.11 Connect the Alarm and BITS Clock Contacts 3-13
3.2.12 Apply Power 3-14
3.2.13 Verify Fan Tray Operation 3-15
3.2.14 Connect the Cisco 6260 System to the Network 3-15
3.2.14.1 E3 Network Connection 3-15
3.2.14.2 E1 Network Connection 3-16
3.2.14.3 OC-3c Network Connection 3-17
3.2.15 Install a Subtended Network Configuration 3-18
3.2.15.1 Connect the E3 Subtending Network Configuration 3-18
3.2.15.2 Connect the E1 Subtending Network Configuration 3-19
3.2.15.3 Connect the OC-3c Subtending Network Configuration 3-20
3.2.16 Connect the Ethernet to the Management Network 3-20
3.2.17 Connect a Console Terminal 3-21
3.2.18 Connect the Auxiliary Port 3-21
3.2.19 Complete Initial Configuration 3-22
3.2.19.1 Before You Begin 3-22
3.2.19.2 Using the System Configuration Dialog 3-22
CHAPTER
OL-2365-02
4 Installing a Cisco 6260 Without a POTS Splitter Configuration 4-1
4.1 Installation Checklist 4-2
4.2 Installation Procedures 4-2
4.2.1 Measure Rack Space 4-2
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
v
Page 6

Contents
4.2.2 Attach Ear Brackets to the Cisco 6260 4-4
4.2.3 Install the Cisco 6260 Chassis 4-5
4.2.4 Install Blank Faceplates 4-6
4.2.5 Ground the Cisco 6260 4-7
4.2.6 Connect the Cisco 6260 to the MDF 4-8
4.2.7 Attach Cisco 6260 Power Connections 4-9
4.2.8 Connect the Alarm and BITS Clock Contacts 4-12
4.2.9 Apply Power 4-13
4.2.10 Verify Fan Tray Operation 4-14
4.2.11 Connect the Cisco 6260 System to the Network 4-14
4.2.11.1 E3 Network Connection 4-14
4.2.11.2 E1 Network Connection 4-15
4.2.11.3 OC-3c Network Connection 4-16
4.2.12 Install a Subtended Network Configuration 4-17
4.2.12.1 Connect the E3 Subtending Network Configuration 4-17
4.2.12.2 Connect the E1 Subtending Network Configuration 4-18
4.2.12.3 Connect the OC-3c Subtending Network Configuration 4-19
4.2.13 Connect the Ethernet to the Management Network 4-19
4.2.14 Connect a Console Terminal 4-20
4.2.15 Connect the Auxiliary Port 4-20
4.2.16 Complete Initial Configuration 4-21
4.2.16.1 Before You Begin 4-21
4.2.16.2 Using the System Configuration Dialog 4-21
CHAPTER
vi
5 Troubleshooting 5-1
5.1 Hot-Swappable FRUs 5-1
5.2 Basic Checks 5-2
5.3 Contacting the Cisco TAC for Help 5-2
5.4 System-Wide Problems 5-3
5.5 FRU-Specific Problems 5-8
5.5.1 NI-2 Card Problems 5-8
5.5.2 NI-2 Card Redundancy Problems 5-9
5.5.3 Line Card Problems 5-10
5.5.4 I/O Module Problems 5-14
5.5.5 Fan Tray Problems 5-15
5.5.6 PEM Problems 5-16
5.6 Alarms 5-17
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 7

Contents
CHAPTER
6 Upgrading and Maintaining the Cisco 6260 System 6-1
6.1 Backing Up Software 6-1
6.2 Fan Tray Maintenance 6-2
6.2.1 Replacing or Cleaning the Air Filter 6-2
6.2.1.1 Required Tools and Equipment 6-2
6.2.1.2 Removing an Air Filter 6-3
6.2.1.3 Cleaning the Air Filter 6-4
6.2.1.4 Replacing the Air Filter 6-4
6.2.2 Removing and Replacing the Fan Tray 6-4
6.3 Installing and Replacing Hardware 6-6
6.3.1 xTU-C Line Card 6-7
6.3.1.1 Installing an xTU-C Line Card 6-7
6.3.1.2 Removing an xTU-C Line Card 6-9
6.3.2 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card 6-9
6.3.2.1 Installing a DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card 6-10
6.3.2.2 Removing a DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card 6-12
6.3.3 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card 6-12
6.3.3.1 Installing a DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card 6-13
6.3.3.2 Removing a DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card 6-14
6.3.4 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card 6-15
6.3.4.1 Installing an OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card 6-16
6.3.4.2 Removing an OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card 6-17
6.3.5 I/O Module 6-17
6.3.5.1 Installing an I/O Module 6-18
6.3.5.2 Removing an I/O Module 6-19
6.3.6 PEM 6-20
6.3.6.1 Installing the PEM 6-20
6.3.6.2 Removing the PEM 6-22
APPENDIX
OL-2365-02
A Technical Specifications A-1
A.1 Hardware Specifications A-1
A.1.1 Cisco 6260 Chassis A-2
A.1.2 Quad-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card A-3
A.1.3 Quad-Port DMT over ISDN Line Card A-4
A.1.4 Quad-Port Flexi ATU-C Line Card A-4
A.1.5 Quad-Port STU-C Line Card A-5
A.1.6 Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card A-6
A.1.7 Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Over ISDN Line Card A-7
A.1.8 Octal-Port G.SHDSL SHTU-C Line Card A-7
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
vii
Page 8

Contents
A.1.9 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card A-8
A.1.10 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card A-9
A.1.11 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card A-10
A.1.12 I/O Module A-11
A.1.13 PEM A-11
A.1.14 Fan Tray A-12
A.2 Software Specifications A-12
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
I
NDEX
B Port Mapping Specifications B-1
B.1 Port Mapping Table B-1
B.2 Standard Telco Color Chart B-6
C Connector and Pinout Specifications C-1
C.1 xDSL Connectors C-1
C.2 I/O Module Connectors C-1
C.2.1 E3 I/O Module BNC Connectors C-2
C.2.2 E1 I/O Module RJ-48c Connectors C-2
C.3 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pins C-3
C.4 Console and Auxiliary Ports C-4
C.5 Ethernet Port C-5
viii
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 9

Figure 1-1 Cisco 6260 Chassis Components 1-2
Figure 1-2 Inverse Multiplexing and Recombining of ATM Cells Through IMA Groups 1-5
Figure 1-3 Subtended Network Configuration with DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Cards 1-8
Figure 1-4 Subtended Network Configuration Using DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Cards 1-9
Figure 1-5 Daisy Chain Topology for OC-3c Interfaces 1-10
Figure 1-6 Cisco 6260 Card Slots 1-12
Figure 1-7 Cisco 6260 Champ Connectors 1-13
Figure 1-8 4xDMT Faceplate 1-14
Figure 1-9 4xDMT over ISDN Faceplate 1-16
Figure 1-10 4xflexi Faceplate 1-18
Figure 1-11 4xSDSL Faceplate 1-20
Figure 1-12 8xDMT Faceplate 1-22
Figure 1-13 8xDMT Over ISDN Faceplate 1-24
Figure 1-14 8xG.SHDSL Faceplate 1-26
Figure 1-15 8xG.SHDSL Deployment in the Cisco 6260 System. 1-29
FIGURES
Figure 1-16 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card Faceplate 1-31
Figure 1-17 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card Faceplate 1-34
Figure 1-18 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card Faceplate 1-37
Figure 1-19 E3 I/O Module 1-42
Figure 1-20 E3 I/O Module 1-43
Figure 1-21 OC-3c I/O Module 1-43
Figure 1-22 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pins Close-Up 1-44
Figure 1-23 PEM Faceplate 1-46
Figure 1-24 Cisco 6260 Fan Tray 1-47
Figure 1-25 Air Filters 1-48
Figure 2-1 Air Flow Through Intake and Exhaust Vents on the Cisco 6260 Chassis. 2-13
Figure 3-1 Mounting Options for Ear Brackets 3-4
Figure 3-2 Screw the Mounting Aids to the Rack 3-5
Figure 3-3 Mounting Aids Support the Chassis During Installation 3-6
Figure 3-4 System Ground Connection 3-8
Figure 3-5 Strip and Square Off Power and Ground Wires 3-10
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
ix
Page 10

Figures
Figure 3-6 Positioning the Power and Ground Terminals to Accept Wires 3-11
Figure 3-7 Insert Grounding Wire into Grounding Receptacle 3-12
Figure 3-8 Connecting Power to the Terminal Block 3-13
Figure 3-9 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pins Close-up 3-14
Figure 3-10 E3 I/O Module BNC Connectors 3-16
Figure 3-11 E1 I/O Module BNC Connectors 3-17
Figure 3-12 E3 I/O Module BNC Connectors 3-18
Figure 3-13 E1 I/O Module RJ-48 Connectors 3-19
Figure 4-1 Mounting Options for Ear Brackets 4-4
Figure 4-2 Screw the Mounting Aids to the Rack 4-5
Figure 4-3 Mounting Aids Support the Chassis During Installation 4-6
Figure 4-4 System Ground Connection 4-8
Figure 4-5 Strip and Square Off Power and Ground Wires 4-10
Figure 4-6 Positioning the Power and Ground Terminals to Accept Wires 4-10
Figure 4-7 Insert Grounding Wire into Grounding Receptacle 4-11
Figure 4-8 Connecting Power to the Terminal Block 4-12
Figure 4-9 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pins Close-up 4-13
Figure 4-10 E3 I/O Module BNC Connectors 4-15
Figure 4-11 E1 I/O Module BNC Connectors 4-16
Figure 4-12 E3 I/O Module BNC Connectors 4-17
Figure 4-13 E1 I/O Module RJ-48 Connectors 4-18
Figure 6-1 Removing the Bezel and Air Filters 6-3
Figure 6-2 Close-up View of Cisco 6260 Chassis with Fan Trays and Bezel 6-5
Figure 6-3 xTU-C Line Card Installation 6-8
Figure 6-4 Positioning the Locking Tab for the xTU-C Line Card Installation and Removal 6-8
Figure 6-5 NI-2 Card Installation 6-11
Figure 6-6 Positioning the Locking Tab for NI-2 Card Removal and Installation 6-11
Figure 6-7 I/O Interface Module Retaining Screws 6-20
Figure 6-8 PEM Installation 6-21
Figure C-1 xDSL Connector Pin Locations C-1
Figure C-2 BNC Connectors on the E3 I/O Module C-2
Figure C-3 RJ-48c Connectors on the E1 I/O Module C-2
Figure C-4 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pins Close-Up C-3
Figure C-5 NI-2 Card Console and Auxiliary Connector C-4
Figure C-6 NI-2 Card Management Ethernet Connector C-5
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
x
OL-2365-02
Page 11

Table 1 Font Conventions xiv
Table 2 Command Syntax Conventions xiv
Table 1-1 IMA Group Interface Names 1-6
Table 1-2 Cisco 6260 Card Slot Assignments 1-11
Table 1-3 4xDMT LED Indicators 1-14
Table 1-4 4xDMT over ISDN LED Indicators 1-16
Table 1-5 4xflexi LED Indicators 1-18
Table 1-6 4xSDSL LED Indicators 1-20
Table 1-7 8xDMT LED Indicators 1-22
Table 1-8 8xDMT over ISDN LED Indicators 1-24
Table 1-9 8xG.SHDSL LED Indicators 1-26
Table 1-10 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card LED Group Indicators 1-32
Table 1-11 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card LED Group Indicators 1-35
Table 1-12 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card LED Group Indicators 1-38
Table 1-13 Pin Assignments for the Cisco 6260 I/O Module 1-45
TABLES
Table 1-14 PEM LEDs 1-46
Table 2-1 CO Operating Environment Requirements 2-12
Table 2-2 Rack Space Calculation for the Cisco 6260 System Configurations 2-14
Table 2-3 Power Calculation for the Cisco 6260 System 2-14
Table 2-4 Tool and Equipment Requirements Checklist 2-16
Table 3-1 Installation Checklist—Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration 3-2
Table 3-2 Terminal Settings 3-21
Table 4-1 Installation Checklist—Cisco 6260 without a POTS Splitter Configuration 4-2
Table 4-2 Terminal Settings 4-20
Table 5-1 Service Interruptions Caused by Replacing FRUs 5-1
Table 5-2 System-Wide Problems 5-3
Table 5-3 NI-2 Card Problems 5-8
Table 5-4 NI-2 Card Cold Redundancy Problems 5-9
Table 5-5 Line Card Problems 5-10
Table 5-6 I/O Module Problems 5-14
Table 5-7 Fan Tray Problems 5-15
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
xi
Page 12

Tables
Table 5-8 PEM Problems 5-16
Table 5-9 Chassis Alarm 5-17
Table 5-10 Card Slot Alarms 5-17
Table 5-11 Line Card Alarms 5-17
Table 5-12 IOS Controller Alarms 5-17
Table 5-13 OC-3c/Synchronous Transfer Mode (STM-1) Network Interface Alarms 5-18
Table 5-14 DS3/E3 Network Interface Alarms 5-18
Table 5-15 E1 Network Interface Alarms 5-19
Table 5-16 IMA Link Network Interface Alarms 5-19
Table 5-17 IMA Group Alarms 5-20
Table 5-18 NI-2 Card Redundancy Alarms 5-20
Table 5-19 Fan Tray Alarms 5-21
Table 5-20 Power Alarms 5-21
Table A-1 Cisco 6260 Hardware Specifications A-2
Table A-2 Quad-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card Specifications A-3
Table A-3 Quad-Port DMT Over ISDN Line Card Specifications A-4
Table A-4 Quad-Port Flexi ATU-C Line Card Specifications A-4
Table A-5 Quad-Port STU-C Line Card Specifications A-5
Table A-6 Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card Specifications A-6
Table A-7 Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Over ISDN Line Card Specifications A-7
Table A-8 Octal-port G.SHDSL SHTU-C Line Card Specifications A-7
Table A-9 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card Specifications A-8
Table A-10 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card Specifications A-9
Table A-11 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card Specifications A-10
Table A-12 I/O Module Specifications A-11
Table A-13 PEM Specifications A-11
Table A-14 Fan Tray Specifications A-12
Table A-15 Software Specifications A-12
Table B-1 Port Mapping for Cisco 6260 Subscriber Connectors B-2
Table B-2 Standard Telco Color Chart B-6
Table C-1 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pin Mapping C-3
Table C-2 Pin Assignments for the NI-2 Card Console and Auxiliary Connectors C-4
Table C-3 Pin Assignments for the NI-2 Card Management Ethernet Connector C-5
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
xii
OL-2365-02
Page 13

Audience
Purpose
Preface
This preface explains the audience, purpose, and organization of the Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation
Guide. It also defines the conventions that are used to present instructions and information.
The Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide is intended for use by central office (CO) technicians and
maintenance personnel who are responsible for installing, configuring, and maintaining the Cisco 6260
system. A familiarity with telco products and networking systems is recommended.
The Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide describes how to set up, install, and troubleshoot the
Cisco 6260 system. After completing the installation procedures covered in this guide, refer to the
appropriate related documents to provision your Cisco 6260 system. For additional information on
related documentation, see the “Related Documentation” section on page xv.
Organization
The Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide is organized as follows:
OL-2365-02
• Chapter 1, “Product Overview,” provides an overview of the Cisco 6260 and describes the system
hardware components.
• Chapter 2, “Preparing for Installation,” provides the requirements necessary to prepare for the
installation of the Cisco 6260 system.
• Chapter 3, “Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration,” provides installation
procedures for a Cisco 6260 system with a POTS splitter configuration.
• Chapter 4, “Installing a Cisco 6260 Without a POTS Splitter Configuration,” provides installation
procedures for a Cisco 6260 system without a POTS splitter configuration.
• Chapter 5, “Troubleshooting,” provides troubleshooting procedures for hardware and software
conditions in the Cisco 6260.
• Chapter 6, “Upgrading and Maintaining the Cisco 6260 System,” provides procedures for removing
and installing system components, as well as information on maintaining the Cisco 6260 system.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
xiii
Page 14
Conventions
Conventions
This publication uses the document conventions listed in this section.
Table 1 Font Conventions
Preface
• Appendix A, “Technical Specifications,” provides the technical specifications for the
Cisco 6260 system.
• Appendix B, “Port Mapping Specifications,” provides cabling guidelines and port mapping tables
for the Cisco 6260 system.
• Appendix C, “Connector and Pinout Specifications,” provides information about connectors and
pinouts for the Cisco 6260 system.
• Glossary.
• Index.
Convention Definition Sample
Times bold Text body font used for any argument,
command, keyword, or punctuation that is
This is similar to the UNIX
route command.
part of a command that the user enters in
text and command environments.
Also used for names of some GUI elements.
Times italic Text body font used for publication names
and for emphasis.
Courier
Font used for screen displays, prompts,
See the Cisco 6200 Series User
Guide for further details.
Are you ready to continue? [Y]
and scripts.
Courier bold
Table 2 Command Syntax Conventions
Font used to indicate what the user enters in
examples of command environments.
Login: root
Password: <password>
Convention Definition Sample
Vertical bar ( | ) Separates alternative, mutually
offset-list {in | out} offset
exclusive elements.
Square brackets ([ ]) Indicate optional elements. [no] offset-list {in | out} offset
Braces ({ }) Indicate a required choice. offset-list {in | out} offset
Braces within square brackets
([{ }])
Indicate a required choice within
an optional element.
[{letter\number}Enter]
xiv
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 15

Preface
Related Documentation
Table 2 Command Syntax Conventions (continued)
Convention Definition Sample
Boldface Indicates commands and keywords
[no] offset-list {in | out} offset
that are entered literally as shown
Italics Indicate arguments for which you
offset-list {in | out} offset
supply values.
Note In contexts that do not
allow italics, arguments are
enclosed in angle brackets
(< >).
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
manual.
Timesaver Means the described action saves time. You can save time by performing the action described in
the paragraph.
Tip Means the following information will help you solve a problem. The tip information might not be
troubleshooting or even an action, but could be useful information, similar to a Timesaver.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Warning
Means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any
equipment, you must be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with
standard practices for preventing accidents. To see translated versions of the warning, refer to the
Regulatory Compliance and Safety document that accompanied the device.
Related Documentation
A complete list of all DSL product-related documentation is available on the World Wide Web at
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/dsl_prod/index.htm.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
xv
Page 16

Obtaining Documentation
Obtaining Documentation
The following sections provide sources for obtaining documentation from Cisco Systems.
World Wide Web
You can access the most current Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at the following sites:
• http://www.cisco.com
• http://www-china.cisco.com
• http://www-europe.cisco.com
Documentation CD-ROM
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships
with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM is updated monthly and may be more current than
printed documentation. The CD-ROM package is available as a single unit or through an
annual subscription.
Preface
Ordering Documentation
Some Cisco documentation is available in the following ways:
• Registered Cisco Direct Customers can order Cisco Product documentation from the Networking
Products MarketPlace:
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/order/order_root.pl
• Registered Cisco.com users can order the Documentation CD-ROM through the online
Subscription Store:
http://www.cisco.com/go/subscription
• Nonregistered CCO users can order documentation through a local account representative by calling
Cisco corporate headquarters (California, USA) at 408 526-7208 or, in North America, by calling
800 553-NETS(6387).
Documentation Feedback
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit technical
comments electronically. Click the Feedback link at the top of the Cisco documentation page. After you
complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco.
You can e-mail your comments to bug-doc@cisco.com.
xvi
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 17

Preface
To submit your comments by mail, write to the following address:
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Document Resource Connection
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco provides Cisco.com as a starting point for all technical assistance. Customers and partners can
obtain documentation, troubleshooting tips, and sample configurations from online tools. For Cisco.com
registered users, additional troubleshooting tools are available from the TAC website.
Cisco.com
Cisco.com is the foundation of a suite of interactive, networked services that provides immediate, open
access to Cisco information and resources at anytime, from anywhere in the world. This highly
integrated Internet application is a powerful, easy-to-use tool for doing business with Cisco.
Cisco.com provides a broad range of features and services to help customers and partners streamline
business processes and improve productivity. Through Cisco.com, you can find information about Cisco
and our networking solutions, services, and programs. In addition, you can resolve technical issues with
online technical support, download and test software packages, and order Cisco learning materials and
merchandise. Valuable online skill assessment, training, and certification programs are also available.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Customers and partners can self-register on Cisco.com to obtain additional personalized information and
services. Registered users can order products, check on the status of an order, access technical support,
and view benefits specific to their relationships with Cisco.
To access Cisco.com, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com
Technical Assistance Center
The Cisco TAC website is available to all customers who need technical assistance with a Cisco product
or technology that is under warranty or covered by a maintenance contract.
Contacting TAC by Using the Cisco TAC Website
If you have a priority level 3 (P3) or priority level 4 (P4) problem, contact TAC by going to the
TAC we bs it e:
http://www.cisco.com/tac
P3 and P4 level problems are defined as follows:
• P3—Your network performance is degraded. Network functionality is noticeably impaired, but most
business operations continue.
• P4—You need information or assistance on Cisco product capabilities, product installation, or basic
product configuration.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
xvii
Page 18

Obtaining Technical Assistance
In each of the above cases, use the Cisco TAC website to quickly find answers to your questions.
To register for Cisco.com, go to the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/register/
If you cannot resolve your technical issue by using the TAC online resources, Cisco.com registered users
can open a case online by using the TAC Case Open tool at the following website:
http://www.cisco.com/tac/caseopen
Contacting TAC by Telephone
If you have a priority level 1(P1) or priority level 2 (P2) problem, contact TAC by telephone and
immediately open a case. To obtain a directory of toll-free numbers for your country, go to the
following website:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
P1 and P2 level problems are defined as follows:
• P1—Your production network is down, causing a critical impact to business operations if service is
not restored quickly. No workaround is available.
Preface
• P2—Your production network is severely degraded, affecting significant aspects of your business
operations. No workaround is available.
xviii
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 19

Product Overview
This chapter provides an overview of the Cisco 6260 Digital Subscriber Line (DSL) Access Multiplexer
(DSLAM) and its related components, collectively known as the Cisco 6260 system. This chapter contains
the following sections:
• Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System, page 1-1
• Cisco 6260 System Overview, page 1-10
• Management Software, page 1-49
1.1 Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
The Cisco 6260 system is part of the Cisco DSL product family that provides end-to-end service by
carrying voice or data traffic, or both, between a subscriber’s home or office, a telephone central office
(CO), and various networks beyond. The Cisco 6260 system sends and receives subscriber data (often
Internet service) over existing copper telephone lines, concentrating all traffic onto a single high-speed
trunk for transport to the Internet or a corporate intranet. Before traveling over telephone lines to the
DSLAM at the CO, data is modulated by xDSL customer premises equipment (CPE) devices, which are
connected to PCs or routers at the subscriber site.
The Cisco 6260 system may include the following components:
CHAPTER
1
OL-2365-02
• Cisco 6260 chassis—A carrier class DSLAM.
–
xDSL Transmission Unit—central office (xTU-C) line cards and second generation network
interface (NI-2) card(s)
–
Input/output module
–
Power entry modules (PEMs)
–
Fan trays
Figure 1-1 shows the location of the Cisco 6260 chassis components.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-1
Page 20
Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
Figure 1-1 Cisco 6260 Chassis Components
Chapter 1 Product Overview
5
6
4
NI-2
NI-2
-DS3/E3-DS3/E3
-DS3/E3-DS3/E3
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
3
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
2
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
INPUT OK
OUT FAIL
FAN TRAY 1
FANTRAY 2
ACO
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
RESET
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
T
R
N
K
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
-4DMT
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
-4DMT
1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
TRNK 1
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
S
B
T
D
2
SBTD 2
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
ALARMS
CRITICAL
MAJOR
MINOR
SBTD 3
S
B
T
D
3
POWER
STATUS
ACTIVE
FAN 1
FAN 2
C
N
STATUS
STATUS
S
L
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
A
U
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
X
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
E
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
N
E
T
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
1
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACO
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
RESET
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ALARMS
CRITICAL
MAJOR
MINOR
POWER
STATUS
ACTIVE
FAN 1
FAN 2
C
N
S
L
A
U
X
E
N
E
T
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
TRNK 1
SBTD 2
SBTD 3
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
Cisco 6260
INPUT OK
OUT FAIL
FAN TRAY 1
FANTRAY 2
2
1
49174
1 PEMs 4 I/O module
2 Fan trays 5 Subscriber champ connectors
xTU-C line cards (slots 1 to 9, 12 to 17, 18 to
26, and 27 to 32)
3
POTS splitters (optional). The POTS splitter is a passive device that supports simultaneous voice
•
6 NI-2 card(s)
(basic telephone service) and data services.
Note POTS splitters are available from Cisco Ecosystem partners. Please verify the compatibility with
your Cisco representative.
For POTS splitter information, refer to the vendor documentation.
• Management software—Provisions and manages the Cisco 6260 system.
–
Cisco IOS—A command-line interface (CLI) that is available for network
element provisioning.
–
Cisco DSL Manager (CDM)—An element management system designed to configure and
manage the 6xxx series of Cisco IOS software-based DSLAMs through a graphical-user
interface (GUI). CDM provides the following areas of network management: fault,
configuration, performance, and security. CDM runs within the Cisco Element Manager
Framework (EMF); both are installed on Sun workstations.
1-2
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 21

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Note See the “Hardware Specifications” section on page A-1 for minimum software and network management
1.1.1 Features
Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
Cisco EMF is based on an object model in which network elements or modules represent the
managed entity. Each object is defined by a class and specific attributes. An object can represent
a network element or a more abstract entity such as a link relationship, a network, or a container
such as a site, shelf, or region.
release requirements per Cisco 6260 chassis component.
The Cisco 6260 system includes the following features:
• Supports ADSL, SDSL, and SHDSL.
• ANSI T1.413 Discrete Multitone (DMT), G.DMT, G.lite, and single-pair, high-speed DSL
(G.SHDSL) modem support.
• E3, E1, and OC-3c network transmission connections.
• Small footprint that terminates up to 240 ADSL, 120 SDSL, or 240 G.SHDSL subscriber
connections and multiplexes them onto a network trunk.
• European Telecommunication Standards Institute (ETSI) compliant, 19-inch (48.26 cm) chassis.
• Completely front-accessible chassis for cabling and maintenance, eliminating the need for access to the
back of the unit.
• Chassis has 30 line card slots, redundant power entry modules (PEMs), and two-speed,
software-controlled cooling fans.
• Manageable through IOS or CDM.
• Supports subtending of as many as twelve Cisco 6260 chassis for a maximum of 3120 subscribers.
• Building integrated timing supply (BITS) clock input.
• Facility alarm input.
• Supports the entire range of virtual channel identifier (VCI)/virtual path identifier (VPI)
connections, and connections are not limited by memory.
• ATM Forum User-Network Interface (UNI) Version 3.1 compliant.
• Nonblocking ATM switching architecture.
• Allows up to four ATM classes of service simultaneously.
1.1.2 Configurations
This guide provides information about the following configurations:
• Cisco 6260 system with a POTS splitter
OL-2365-02
• Cisco 6260 system without a POTS splitter
• Inverse multiplexing over ATM (IMA)
• Subtended network
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-3
Page 22

Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
1.1.2.1 Cisco 6260 System with a POTS Splitter Configuration
The Cisco 6260 system with a POTS splitter configuration supports up to 240 data subscribers. To
increase subscribership, you can add chassis to your system.
This configuration can include the following hardware components:
• Cisco 6260 chassis
–
Quad-port DMT ATU-C line cards (4xDMTs)
–
Quad-port DMT ATU-C over ISDN line cards (4xDMTs over ISDN)
–
Quad-port flexi ATU-C line cards (4xflexis)
–
Octal-port DMT ATU-C line cards (8xDMTs)
–
Octal-port DMT ATU-C over ISDN line cards (8xDMTs over ISDN)
–
DS3/2DS3, DS3+T1/E1 IMA, or OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card
–
E3, E1, or OC-3c I/O module
–
PEM(s)
–
Fan Trays
Chapter 1 Product Overview
• Third-party POTS splitter
1.1.2.2 Cisco 6260 System Without a POTS Splitter Configuration
The Cisco 6260 system without a POTS splitter configuration supports up to 240 data subscribers. To
increase subscribership, you can add chassis to your system.
This configuration can include the following hardware components:
• Cisco 6260 chassis
–
Quad-port DMT ATU-C line cards (4xDMTs)
–
Quad-port DMT ATU-C over ISDN line cards (4xDMTs over ISDN)
–
Quad-port flexi ATU-C line cards (4xflexis)
–
Quad-port STU-C line cards (4xSDSLs)
–
Octal-port DMT ATU-C line cards (8xDMTs)
–
Octal-Port G.SHDSL SHTU-C line cards (8xG.SHDSL)
–
DS3/2DS3, DS3+T1/E1 IMA, or OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card
–
E3, E1, or OC-3c I/O module
–
PEM(s)
–
Fan Trays
1.1.2.3 IMA Configuration
The DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card uses inverse multiplexing over ATM (IMA) technology to aggregate
multiple low-speed links into one larger virtual network trunk or IMA group. An inverse multiplexer
appears to your ATM switch router as one logical pipe. IMA provides you with modular bandwidth to
access the ATM network between T1/E1 and DS3/E3 rates. The Cisco 6260 system allows you to
combine up to eight E1 lines to form an IMA group.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-4
OL-2365-02
Page 23
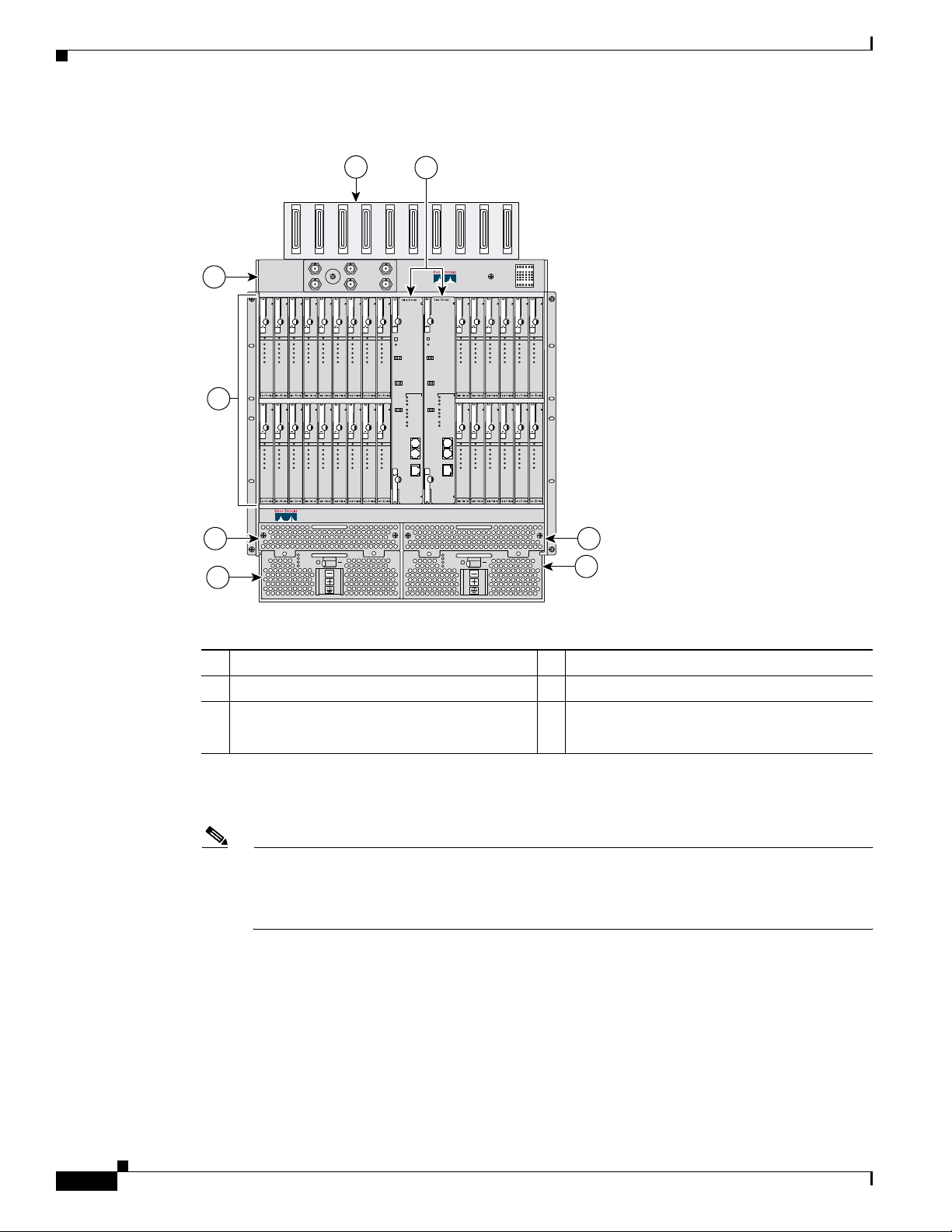
Chapter 1 Product Overview
IMA breaks up the ATM cell stream, distributes the cells over the multiple physical links of an IMA
group, and recombines the cells into a single stream at the other end of the connection. The ATM cells
are distributed in a round-robin fashion over the physical links of the IMA group, recombined at the
receiving IMA group, and passed in their original form to the ATM layer (see Figure 1-2). Using the
multiple links of an IMA group increases the logical link bandwidth to approximately the sum of the
individual link rates. The physical links should be nominally the same length to avoid excessive
intragroup delay. We recommend that all of the links in an IMA group be bundled together between the
source and the destination.
Figure 1-2 Inverse Multiplexing and Recombining of ATM Cells Through IMA Groups
Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
Single ATM cell
stream from
ATM layer
IMA group
PHY
PHY
PHY
Physical link 0
Physical link 1
Physical link 2
IMA virtual link
PHY
PHY
PHY
IMA group
Original cell
stream passed
to ATM layer
18092
E1 I/O modules have eight ports. You can use the eight ports on the E1 I/O modules as independent ATM
links or in the IMA mode. The following bullets are examples of possible IMA groups, independent ATM
links, and mixed modes. In examples of IMA groups, two links are assumed per group.
• Four IMA groups with any combination of eight links
• Three IMA groups and up to two independent ATM links
• Two IMA groups and up to four independent ATM links
OL-2365-02
• One IMA group and up to six independent ATM links
• No IMA group and up to eight independent ATM links
The E1 (1.544 Mbps) IMA port adapters provide network trunk or subtend connectivity and are used for
intercampus or wide-area links. The E1 IMA port adapters support unshielded twisted-pair (UTP)
connectors. The order of assignment of links to an IMA group is not restricted.
The IMA group interfaces use a naming convention different from those used by the other interfaces in
the system. IMA group interfaces are named with the convention atm<slot>/ima<group>, where <slot>
is the slot number for the DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card and <group> is the IMA group number from 0 to
3. Table 1- 1 lists the interface naming conventions.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-5
Page 24

Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
Table 1-1 IMA Group Interface Names
Interface Name
DS3 link atm0/1
T1/E1 link 0 atm0/2
T1/E1 link 1 atm0/3
T1/E1 link 2 atm0/4
T1/E1 link 3 atm0/5
T1/E1 link 4 atm0/6
T1/E1 link 5 atm0/7
T1/E1 link 6 atm0/8
T1/E1 link 7 atm0/9
IMA group 0 atm0/ima0
IMA group 1 atm0/ima1
IMA group 2 atm0/ima2
IMA group 3 atm0/ima3
Chapter 1 Product Overview
1.1.2.4 Subtended Network Configuration
The term subtending refers to the host chassis, and subtended refers to the downstream chassis in a
subtended network.
Note For information on enabling redundancy in subtended network configurations, see the “Redundancy in
Subtended Configurations” section on page 1-41.
A subtended network configuration
• Services and aggregates the data from one or more Cisco 6260 chassis into a subtending host chassis
to take advantage of the data network interface on the subtending host chassis.
• Reduces the number of ATM edge-switch ports required to terminate the chassis.
• Supports a Cisco 6260 system with a POTS splitter and a Cisco 6260 system without a POTS
splitter configuration.
A subtended network configuration supports the following features:
• Four arbitration priorities, one for each quality of service (QoS) level. The supported QoS service
levels are
–
Constant bit rate (CBR) for rate-limited services that require guaranteed bandwidth and
bounded delay
–
Variable bit rate real time (VBR-rt) for delay-sensitive voice and video services
1-6
–
Variable bit rate nonreal time (VBR-nrt) for high-priority data services
–
Unspecified bit rate (UBR) for low-priority data services
• Explicit forward congestion indication (EFCI) marking for available bit rate (ABR) service support.
• Guaranteed frame rate (GFR).
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 25

Chapter 1 Product Overview
• Tree or daisy chain topology configurations for E3 subtended Cisco 6260 chassis.
• Star topology configurations for E1 or IMA group subtended Cisco 6260 chassis.
• Daisy chain configurations for OC-3c subtended Cisco 6260 chassis.
• Fair access to the trunk port for each subtended chassis.
• A network trunk port that operates as fast as any subtended link.
The NI-2 card provides one of following types of subtended network connections:
• An E3 ATM interface
• A high-speed OC-3c optical ATM interface that supports single-mode fiber (SMF)
• A high-speed OC-3c optical ATM interface that supports multimode fiber (MMF) short range
• Up to eight E1 interfaces when you are using the DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card in conjunction with
• Up to four IMA interfaces when you are using the DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card in conjunction with
The following sections detail the different types of subtending network connections.
Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
intermediate range
the E1 I/O module.
the E1 I/O module.
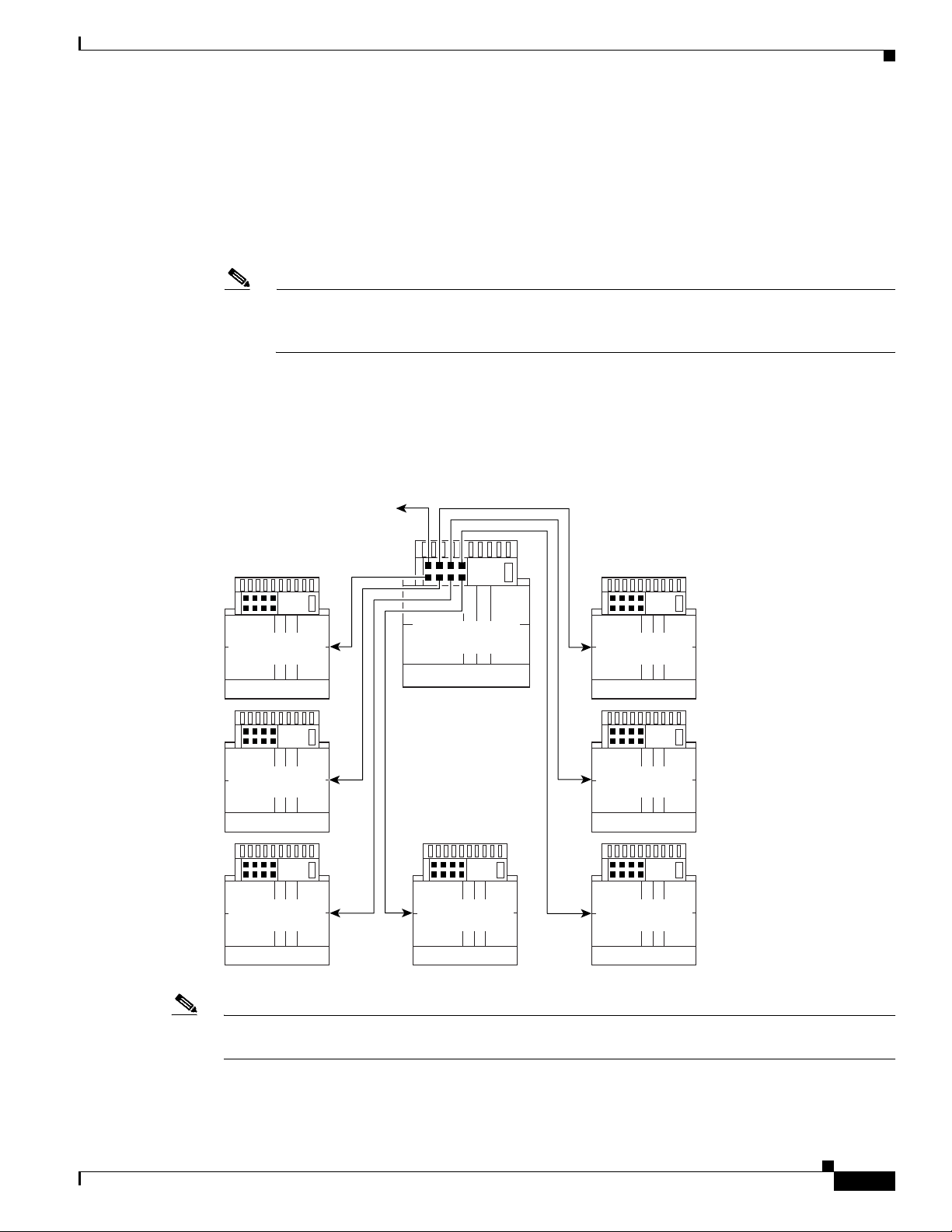
1.1.2.4.1 Subtended Network Configuration with DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Cards
In a subtended network configuration using DS3/2DS3 NI-2 cards, you can subtend a Cisco 6260
chassis to four tiers, with up to 12 chassis, all connecting through one subtending host chassis to the
ATM backbone.
When the DS3/2DS3 NI-2 card is installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis, it adopts E3 functionality.
Figure 1-3 shows E3-configured Cisco 6260 systems subtended in a combined subtending tree topology
with daisy chain. The subtending host chassis at the top of the subtending tree connects directly to the
ATM switch. The middle two Cisco 6260 chassis in the lowest level are daisy chained. You make
network interface connections at the I/O module that is installed on the front of the Cisco 6260 chassis.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-7
Page 26
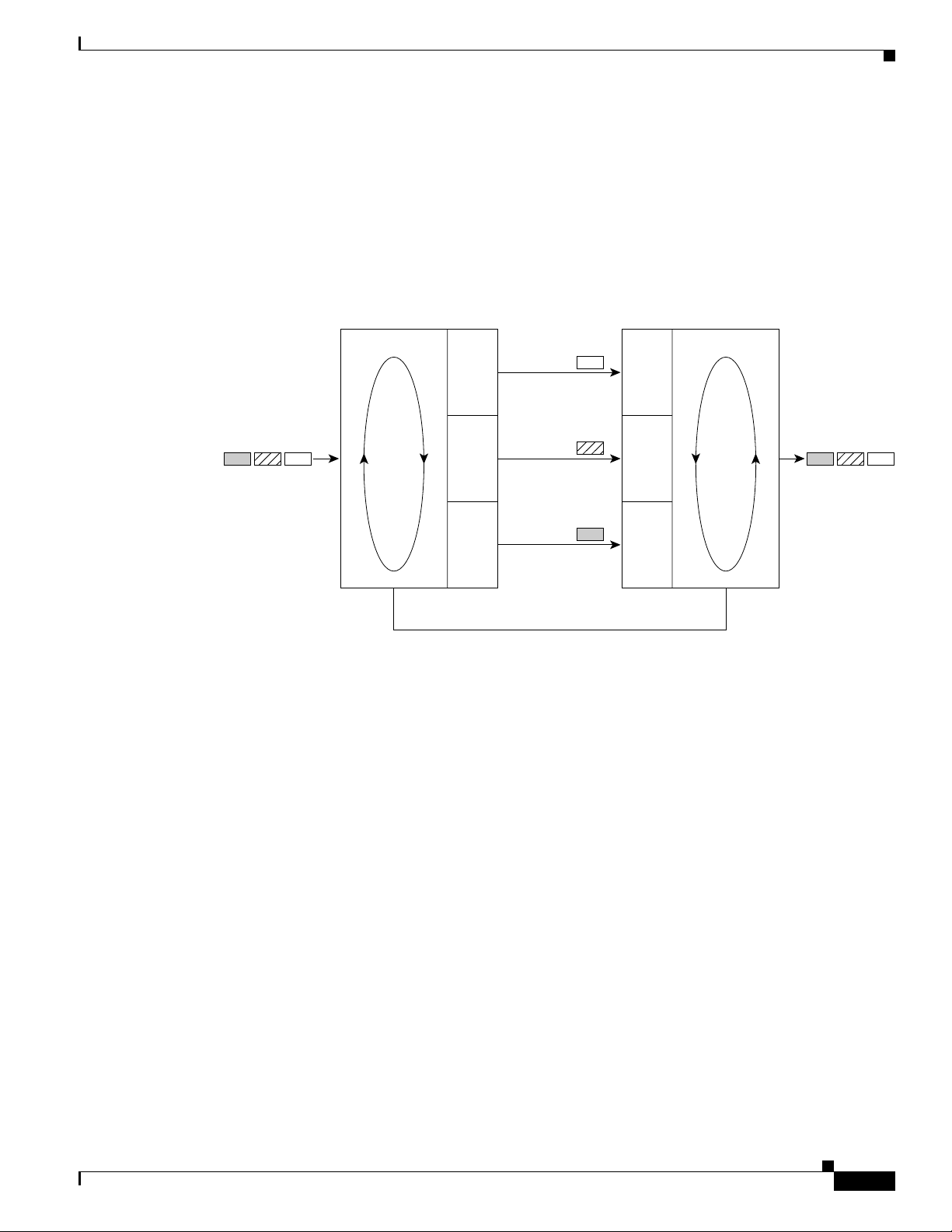
Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
Figure 1-3 Subtended Network Configuration with DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Cards
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Network
1
trunk
Cisco 6260
To p
chassis
Cisco 6260
2
Cisco 6260
7
Cisco 6260
4
3
Cisco 62608
Cisco 6260Cisco 6260
Cisco 62609
56
Cisco 6260
Cisco 626010
Cisco 6260
Cisco 626011
12
Cisco 6260
26391
For each chassis in a subtended network configuration to have fair access to the shared network trunk,
the chassis must have a unique ID number. The subtending host chassis places this ID number in the GFC
field of the ATM header of each cell; this ID number is then used to forward cells up the tree to the
network trunk.
Note You can subtend Cisco 6260 chassis with DS3/2DS3 NI-2 cards in a continuous daisy chain. However,
a daisy-chained subtending scheme is not optimal for data throughput for Cisco 6260 chassis that use
DS3/2DS3 NI-2 cards.
Cisco IOS software does not manage the primary Cisco 6260 chassis and all subtended Cisco 6260
chassis as a single large Cisco 6260 system. Each Cisco 6260 chassis supports an independent Cisco IOS
processor and MIBs.
1-8
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 27
Chapter 1 Product Overview
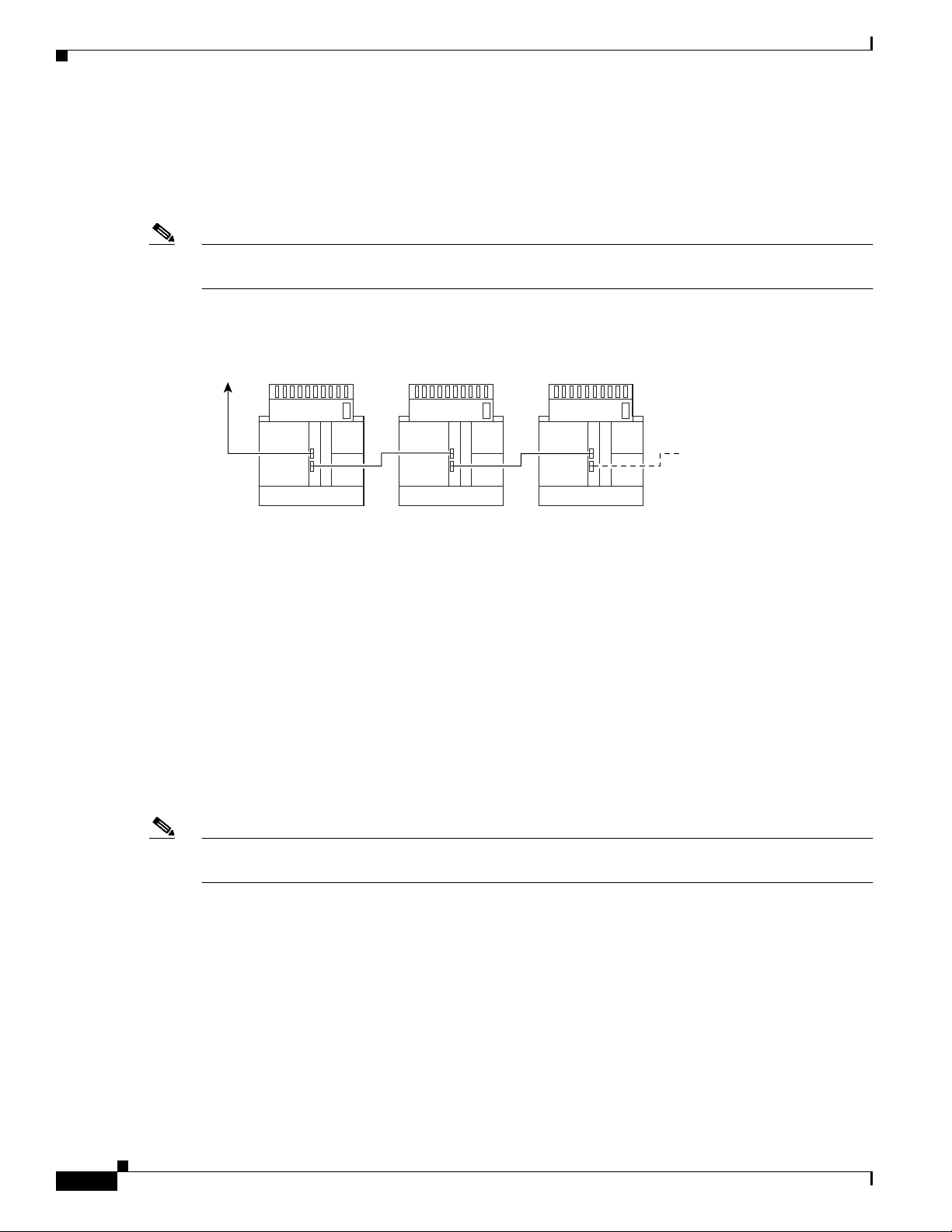
1.1.2.4.2 Subtended Network Configuration with DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Cards
In a subtended network configuration using DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 cards, you can subtend Cisco 6260
systems in a star topology. The eight E1 links can be used as network trunk or subtend interfaces or can
be combined into trunk or subtend IMA groups in the following two ways:
• E1 IMA group or E1 User-Network Interface (UNI) as the network trunk with seven subtended node
chassis
Note If you are using an E1 trunk to the network, the trunk connection originates at one of the RJ-48
receptacle connectors on the E1 I/O module. Therefore, you can have only seven subtended
node chassis.
• Up to seven individual E1 interfaces or up to four IMA groups, or a combination of the two
Figure 1-4 shows an example of a subtended network with a star topology. The subtending host chassis
in the middle of the star topology connects directly to the ATM switch.
Figure 1-4 Subtended Network Configuration Using DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Cards
Introduction to the Cisco 6260 System
Subtended node
chassis 1
Subtended node
chassis 2
Subtended node
chassis 3
Network
trunk
Subtending host
chassis
Subtended node
chassis 4
Subtended node
chassis 5
Subtended node
chassis 6
Subtended node
chassis 7
OL-2365-02
54390
Note Consult with your network architect or Cisco customer service representative for examples of other
subtending topology configurations.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-9
Page 28
Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.1.2.4.3 Subtended Network Configuration with OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Cards
In a subtended network configuration using OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 cards (SMF or MMF), you can subtend
up to 12 OC-3c configured chassis in a daisy chain, all connecting through one subtending host chassis
to the ATM backbone (see Figure 1-5).
Note The Cisco 6260 chassis can also serve as the subtending host chassis to, or as a subtended node chassis
from, the Cisco 6100, Cisco 6130, Cisco 6015, or Cisco 6160 chassis.
Figure 1-5 Daisy Chain Topology for OC-3c Interfaces
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Network
trunk
To p
chassis
Cisco 6260 Cisco 6260 Cisco 6260
1st subtended
chassis
1.2 Cisco 6260 System Overview
The Cisco 6260 system consists of circuitry and connections that reside within a chassis, an enclosure
that allows modular insertion and removal of various field-replaceable units (FRUs). The Cisco 6260
system includes
• A card compartment with 32 slots: 30 slots for xTU-C line cards and two slots for NI-2 cards
• A set of connectors that serve subscriber lines with or without POTS splitters
• An I/O module
• Compartments for two PEMs, two fan trays, and air filters.
See Figure 1-1 for the location of the system components in the Cisco 6260 chassis.
2nd subtended
chassis
Up to 10 more
subtended
chassis
26392
Note For hardware specifications for the Cisco 6260 chassis, see the “Cisco 6260 Chassis” section on
page A-2.
1.2.1 Cisco 6260 Card Compartment
The Cisco 6260 chassis contains a 32-slot card compartment holds NI-2 cards and xTU-C line cards.
Table 1-2 describes each card slot assignment for the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-10
OL-2365-02
Page 29

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-2 Cisco 6260 Card Slot Assignments
Card Slot Card Assignment
1 to 9 4xDMT, 4xDMT over ISDN, 4xflexi, 4xSDSL
10 NI-2 card
11 Secondary (redundant) NI-2 card
12 to 32 4xDMT, 4xDMT over ISDN, 4xflexi, 4xSDSL, 8xDMT, 8xDMT
1. 4xSDSLs and G.SHDSLs can be used only in a Cisco 6260 system without a POTS
2. 8xDMT over ISDN can be used only in a Cisco 6260 system with a POTS splitter configuration.
Note You can purchase blank faceplates for empty Cisco 6260 card slots.
splitter configuration.
8xDMT over ISDN
2
, or 8xG.SHDSL
over ISDN, or 8xG.SHDSL
Cisco 6260 System Overview
1
1
, 8xDMT,
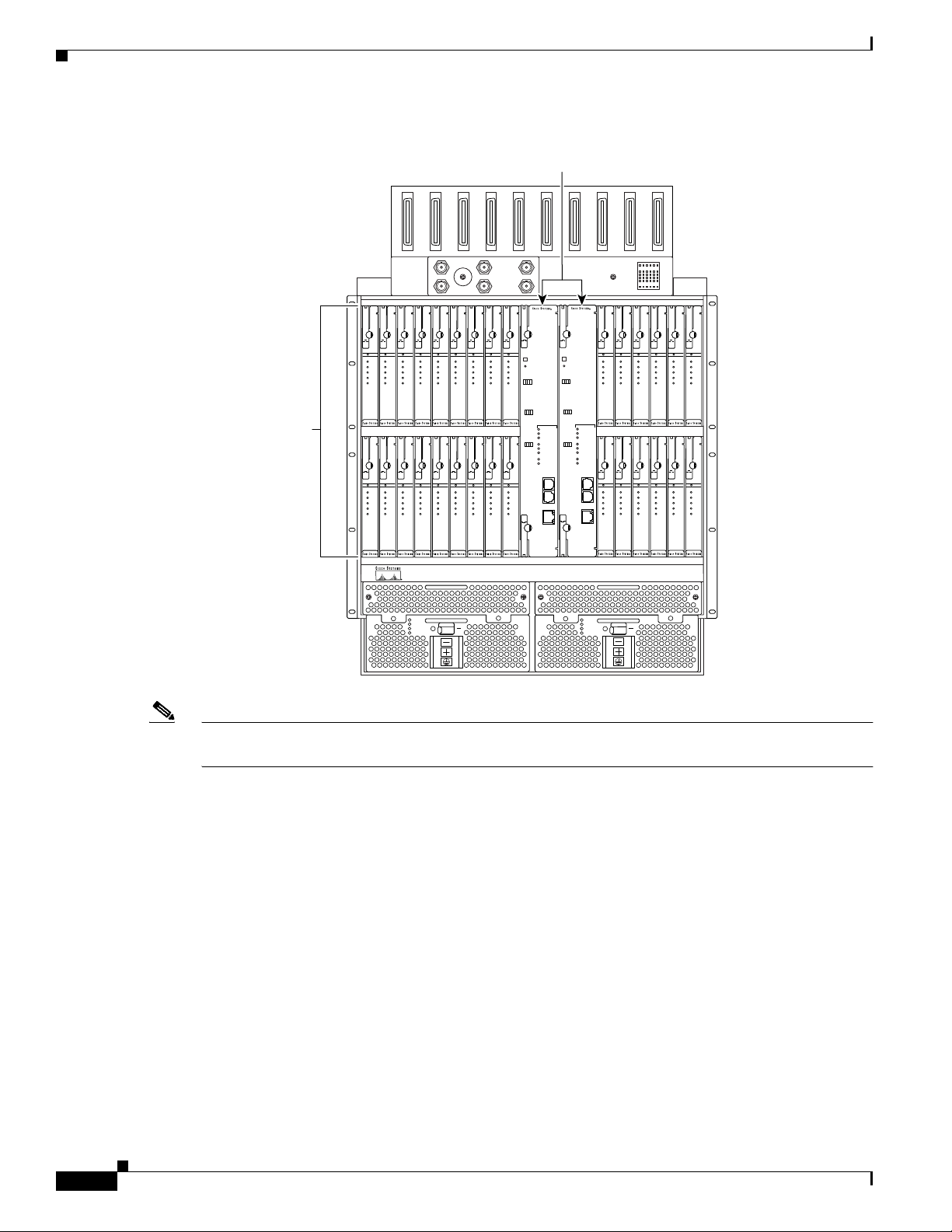
Figure 1-6 identifies the Cisco 6260 card slots. Each slot on a chassis is numbered along the top of the
chassis. In this guide, the slot numbers are shown on the cards for easy reference and readability. These
slots are referred to in subsequent sections of this chapter and elsewhere in this guide.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-11
Page 30
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Figure 1-6 Cisco 6260 Card Slots
xTU-C line cards
30 universal
NI-2 card slots
NI-2
NI-2
-DS3/E3-DS3/E3
-DS3/E3-DS3/E3
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
123456789 121314151617
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32
ATUC-1
-4DMT
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
ACO
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
RESET
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
TRNK 1
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
TRNK 1
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
R
T
R
T
X
X
C
E
L
S
S
S
K
T
T
T
A
A
T
T
10 11
SBTD 2
SBTD 2
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
R
T
R
T
X
X
-4DMT
-4DMT
C
E
L
S
S
S
K
T
ALARMS
T
T
A
A
T
T
CRITICAL
MAJOR
MINOR
SBTD 3
SBTD 3
POWER
R
T
R
T
STATU S
X
X
C
E
ACTIVE
L
S
S
S
K
T
T
T
A
A
FAN 1
T
T
FAN 2
C
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
-4DMT
N
STATUS
S
L
ACTIVE
A
U
ATU-C 1
X
ATU-C 2
ACT
ATU-C 3
E
ATU-C 4
N
E
T
LNK
ATUC-1
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACO
ACTIVE
ALARMS
CRITICAL
MAJOR
MINOR
POWER
STATUS
ACTIVE
FAN 1
FAN 2
C
N
S
L
A
U
X
E
N
E
T
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ACT
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
LNK
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
RESET
TRNK 1
R
T
R
T
X
X
C
E
L
S
S
S
K
T
T
T
A
A
T
T
SBTD 2
R
T
R
T
X
X
C
E
L
S
S
S
K
T
T
T
A
A
T
T
SBTD 3
R
T
R
T
X
X
C
E
L
S
S
S
K
T
T
T
A
A
T
T
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
STATUS
STATUS
STATUS
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
ATUC-1
-4DMT
-4DMT
-4DMT
Cisco 6260
Chapter 1 Product Overview
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
-4DMT
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
-4DMT
Note Slot 10 is the primary NI-2 card slot, and Slot 11 is the secondary NI-2 card slot. A secondary NI-2 card,
when installed in Slot 11, provides cold redundancy.
1.2.2 Cisco 6260 Connectors
Ten female RJ-21 (Champ) subscriber connectors are located at the top of the chassis, facing forward.
These 50-pin sockets provide the DSL subscriber connections. Each subscriber connector serves three
line card slots. Figure 1-7 depicts the Cisco 6260 subscriber connectors.
IN
P
U
T
O
K
O
U
T
F
A
IL
F
A
N
T
R
A
Y
1
F
A
N
T
R
A
Y
2
IN
P
U
T
O
K
O
U
T
F
A
IL
F
A
N
T
R
A
Y
1
F
A
N
T
R
A
Y
2
50177
1-12
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 31

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Figure 1-7 Cisco 6260 Champ Connectors
1
1-3
The Cisco 6260 subscriber connectors are numbered 1 to 10. See the “Port Mapping Table” section on
page B-1 for information about how subscriber connectors correspond to line card slots and ports.
See Figure 1-1 for the location of the subscriber connectors on the Cisco 6260 chassis.
18-20
Cisco 6260 System Overview
2
3
4-6
4
21-23
5
7-9
6
24-26
7
27-29
8
12-14
9
30-32
10
15-17
49963
1.2.3 Cisco 6260 Cards
This section contains the following information:
• Quad-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card Overview, page 1-13
• Quad-Port DMT ATU-C over ISDN Line Card Overview, page 1-15
• Quad-Port Flexi ATU-C Line Card Overview, page 1-17
• Quad-Port STU-C Line Card Overview, page 1-19
• Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card Overview, page 1-21
• Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Over ISDN Line Card Overview, page 1-23
• DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card Overview, page 1-30
• DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card Overview, page 1-32
• OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card Overview, page 1-35
Some line cards can be intermixed within the Cisco 6260 chassis. See the “Line Card Intermixing”
section on page 1-27 for intermixing guidelines.
1.2.3.1 Quad-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card Overview
The quad-port DMT ATU-C line card (4xDMT)
• Supports four ADSL modem connections
OL-2365-02
• Converts ADSL modulation from the line into digital data streams to and from the NI-2 card
• Negotiates the line rate with the CPE when it trains and bases the rate on line quality and distance
If provisioned, the 4xDMT rate adapts to the maximum bit rate negotiable on the line. The maximum bit
rate settings are provisioned in the management software.
The chassis can include up to 30 4xDMTs for a total of 120 ADSL modem connections.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-13
Page 32

Cisco 6260 System Overview
Note For hardware specifications for the 4xDMT line card, see the “Quad-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card”
section on page A-3.
1.2.3.1.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-8 shows a close-up of the 4xDMT faceplate.
Figure 1-8 4xDMT Faceplate
1
2
Chapter 1 Product Overview
3
4
5
6
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATUC-1
-4DMT
26373
1 Ejector lever 4 ACTIVE LED
2 Locking tab 5 Modem port status LEDs
3 STATUS LED 6 Extraction tab
Table 1-3 describes the 4xDMT LED indicator functions.
Table 1-3 4xDMT LED Indicators
1-14
LED State Function
STATUS Green slow blinking The self-test is in progress.
Green fast blinking The image download is in progress.
Green solid The status is OK.
Red The self-test or line card has failed.
Off The ATU-C line card has had a power failure.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 33

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-3 4xDMT LED Indicators (continued)
LED State Function
ACTIVE Green solid The line card is activated.
ATUC-1 Green solid Modem 1 is trained.
ATUC-2 Green solid Modem 2 is trained.
ATUC-3 Green solid Modem 3 is trained.
ATUC-4 Green solid Modem 4 is trained.
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Off The line card is not in service.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 1.
Off Modem 1 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 2.
Off Modem 2 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 3.
Off Modem 3 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 4.
Off Modem 4 is idle.
1.2.3.2 Quad-Port DMT ATU-C over ISDN Line Card Overview
The quad-port DMT ATU-C over ISDN line card (4xDMT over ISDN)
• Supports four ADSL modem connections
• Converts ADSL modulation from the line into digital data streams to and from the NI-2 card
• Negotiates the line rate with the CPE when it trains and bases the rate on line quality and distance
• Contains filters that reject the ISDN spectrum (or signal) during operation
• Separates DMT signals from, or combines them with, ISDN signals, if the CPE includes ISDN
telephone service (in a configuration with a connected POTS splitter)
If provisioned, the 4xDMT over ISDN rate adapts to the maximum bit rate negotiable on the line. The
maximum bit rate settings are provisioned in the management software.
The chassis can include up to 30 4xDMT over ISDN line cards, for a total of 120 ADSL
modem connections.
Note For hardware specifications for the 4xDMT over ISDN line card, see the “Quad-Port DMT over ISDN
Line Card” section on page A-4.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-15
Page 34

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.3.2.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-9 shows a close-up of the 4xDMT over ISDN faceplate.
Figure 1-9 4xDMT over ISDN Faceplate
1
2
Chapter 1 Product Overview
3
4
5
6
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C 1
ATU-C 2
ATU-C 3
ATU-C 4
ATUC
-4DMT-ISDN
38352
1 Ejector lever 4 ACTIVE LED
2 Locking tab 5 Modem port status LEDs
3 STATUS LED 6 Extraction tab
Table 1-3 describes the 4xDMT over ISDN LED indicator functions.
Table 1-4 4xDMT over ISDN LED Indicators
1-16
LED State Function
STATUS Green slow blinking The self-test is in progress.
Green fast blinking The image download is in progress.
Green solid The status is OK.
Red The self-test or line card has failed.
Off The ATU-C line card has had a power failure.
ACTIVE Green solid The line card is activated.
Off The line card is not in service.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 35

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-4 4xDMT over ISDN LED Indicators (continued)
LED State Function
ATUC-1 Green solid Modem 1 is trained.
ATUC-2 Green solid Modem 2 is trained.
ATUC-3 Green solid Modem 3 is trained.
ATUC-4 Green solid Modem 4 is trained.
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 1.
Off Modem 1 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 2.
Off Modem 2 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 3.
Off Modem 3 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 4.
Off Modem 4 is idle.
1.2.3.3 Quad-Port Flexi ATU-C Line Card Overview
The quad-port flexi ATU-C line card (4xflexi)
• Supports DMT line encoding
• Supports four ADSL modem connections
• Converts ADSL modulation from the line into digital data streams to and from the NI-2 card
• Negotiates the line rate with the CPE when it trains and bases the rate on line quality and distance
If provisioned, the 4xflexi rate adapts to the maximum bit rate negotiable on the line. The maximum bit
rate settings are provisioned in the management software.
The Cisco 6260 chassis can include up to 30 4xflexi line cards for a total of 120 ADSL
modem connections.
The edge connector key, located on the rear of the 4xflexi, connects the 4xflexi to the backplane of the
chassis. Two edge connector keys are available for the 4xflexi: one has six notches, and one has seven
notches. Only the seven-notched edge connector key can be installed in the Cisco 6260.
Note For hardware specifications for the 4xflexi, see the “Quad-Port Flexi ATU-C Line Card” section on
page A-4.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-17
Page 36

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.3.3.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-10 shows a close-up of the 4xflexi faceplate.
Figure 1-10 4xflexi Faceplate
1
2
Chapter 1 Product Overview
3
4
5
6
7
STATUS
ACTIVE
CAP
DMT
G.LITE
A1
A2
A3
A4
4X FLEXI
28509
1 Ejector lever 5 Line card mode LEDs
2 Locking tab 6 Modem port status LEDs
3 STATUS LED 7 Extraction tab
4 ACTIVE LED
Table 1-5 describes the 4xflexi LED indicator functions.
1-18
Table 1-5 4xflexi LED Indicators
LED State Function
STATUS Green slow blinking The self-test is in progress.
Green fast blinking The image download is in progress.
Green solid The status is OK.
Red The self-test or line card has failed.
Off The ATU-C line card has had a power failure.
ACTIVE Green solid The line card is activated.
Off The line card is not in service.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 37

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-5 4xflexi LED Indicators (continued)
LED State Function
CAP Green solid The line card is in CAP mode.
DMT Green solid The line card is in DMT mode.
G.LITE Green solid The line card is in G.lite mode.
A1 Green solid Modem 1 is trained.
A2 Green solid Modem 2 is trained.
A3 Green solid Modem 3 is trained.
A4 Green solid Modem 4 is trained.
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Note CAP mode is not available on the
4xflexi in a Cisco 6260.
Off The line card is not in CAP mode.
Off The line card is not in DMT mode.
Note G.lite mode is not available on the
4xflexi in a Cisco 6260.
Off The line card is not in G.lite mode.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 1.
Off Modem 1 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 2.
Off Modem 2 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 3.
Off Modem 3 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 4.
Off Modem 4 is idle.
1.2.3.4 Quad-Port STU-C Line Card Overview
The quad-port STU-C line card (4xSDSL)
• Supports 2B1Q line encoding
• Is designed for use in a Cisco 6260 system without a POTS splitter configuration
• Supports four SDSL modem connections
• Converts SDSL modulation from the line into digital data streams to and from the NI-2 card
The negotiated bit rate is the lower of the following rates:
• The provisioned bit rate set for the 4xSDSL in the management software
• The assigned bit rate at the CPE
The chassis can include up to 30 4xSDSLs for a total of 120 SDSL modem connections.
Note For hardware specifications for the 4xSDSL line card, see the “Quad-Port STU-C Line Card” section on
page A-5.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-19
Page 38

Cisco 6260 System Overview
The edge connector key, located on the rear of the 4xSDSL, connects the 4xSDSL to the backplane of
the chassis. Two edge connector keys are available for the 4xSDSL: one has six notches, and one has
seven notches. Only the seven-notched edge connector key can be installed in the Cisco 6260.
1.2.3.4.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-11 shows a close-up of the 4xSDSL faceplate.
Figure 1-11 4xSDSL Faceplate
1
2
Chapter 1 Product Overview
3
4
5
6
STATUS
ACTIVE
STU-C 1
STU-C 2
STU-C 3
STU-C 4
4X SDSL
2B1Q
18461
1 Ejector lever 4 ACTIVE LED
2 Locking tab 5 Modem port status LEDs
3 STATUS LED 6 Extraction tab
Table 1-6 describes the 4xSDSL LED indicator functions.
Table 1-6 4xSDSL LED Indicators
1-20
LED State Function
STATUS Green slow blinking The self-test is in progress.
Green fast blinking The image download is in progress.
Green solid The status is OK.
Red The self-test or line card has failed.
Off The ATU-C line card has had a power failure.
ACTIVE Green solid The line card is activated.
Off The line card is not in service.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 39

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-6 4xSDSL LED Indicators (continued)
LED State Function
STU-C 1 Green solid Modem 1 is trained.
STU-C 2 Green solid Modem 2 is trained.
STU-C 3 Green solid Modem 3 is trained.
STU-C 4 Green solid Modem 4 is trained.
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 1.
Off Modem 1 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 2.
Off Modem 2 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 3.
Off Modem 3 is idle.
Green blinking Training is in progress for modem 4.
Off Modem 4 is idle.
1.2.3.5 Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card Overview
The octal-port DMT ATU-C line card (8xDMT)
• Supports eight ADSL modem connections
• Converts ADSL modulation from the line into digital data streams to and from the NI-2 card
• Negotiates the line rate with the CPE when it trains and bases the rate on line quality and distance
If provisioned, the 8xDMT rate adapts to the maximum bit rate negotiable on the line. The maximum bit
rate settings are provisioned in the management software.
The chassis can include up to 30 8xDMTs for a total of 240 ADSL modem connections.
Note For hardware specifications for the 8xDMT line card, see the “Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Line Card”
section on page A-6.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-21
Page 40

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.3.5.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-12 shows a close-up of the 8xDMT faceplate.
Figure 1-12 8xDMT Faceplate
1
2
Chapter 1 Product Overview
3
4
5
6
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C1
ATU-C2
ATU-C3
ATU-C4
ATU-C5
ATU-C6
ATU-C7
ATU-C8
8X DMT8 GSI
45678
1 Ejector lever 4 ACTIVE LED
2 Locking tab 5 Modem port status LEDs
3 STATUS LED 6 Extraction tab
Table 1-7 describes LEDs on the 8xDMT.
Table 1-7 8xDMT LED Indicators
1-22
LED State Function
STATUS Green slow blinking
Green solid
Red
Off
ACTIVE Green solid
Off
ATU-C 1 Green solid
Green blinking
Off
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
No errors, but no connection established.
The image download is in progress.
NI-2 communication established.
The self-test or line card has failed.
The ATU-C line card has had a power failure.
The line card is activated.
The line card is not in service.
Modem 1 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 1.
Modem 1 is idle.
OL-2365-02
Page 41

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-7 8xDMT LED Indicators (continued)
LED State Function
ATU-C 2 Green solid
ATU-C 3 Green solid
ATU-C 4 Green solid
ATU-C 5 Green solid
ATU-C 6 Green solid
ATU-C 7 Green solid
ATU-C 8 Green solid
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Modem 2 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 2.
Modem 2 is idle.
Modem 3 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 3.
Modem 3 is idle.
Modem 4 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 4.
Modem 4 is idle.
Modem 5 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 5.
Modem 5 is idle.
Modem 6 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 6.
Modem 6 is idle.
Modem 7 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 7.
Modem 7 is idle.
Modem 8 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 8.
Modem 8 is idle.
1.2.3.6 Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Over ISDN Line Card Overview
The octal-port DMT ATU-C over ISDN line card (8xDMT over ISDN)
• Supports eight ADSL modem connections
• Converts ADSL modulation from the line into digital data streams to and from the NI-2 card
• Negotiates the line rate with the CPE when it trains and bases the rate on line quality and distance
Note For hardware specifications for the 8xDMT over ISDN line card, see the “Octal-Port DMT ATU-C Over
ISDN Line Card” section on page A-7.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-23
Page 42

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.3.6.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-13 shows a close-up of the 8xDMT over ISDN faceplate.
Figure 1-13 8xDMT Over ISDN Faceplate
1
2
Chapter 1 Product Overview
3
4
5
6
STATUS
ACTIVE
ATU-C1
ATU-C2
ATU-C3
ATU-C4
ATU-C5
ATU-C6
ATU-C7
ATU-C8
ATUC-8-
DMT-I
54481
1 Ejector lever 4 ACTIVE LED
2 Locking tab 5 Modem port status LEDs
3 STATUS LED 6 Extraction tab
Table 1-7 describes LEDs on the 8xDMT over ISDN.
Table 1-8 8xDMT over ISDN LED Indicators
1-24
LED State Function
STATUS Green slow blinking
Green solid
Red
Off
ACTIVE Green solid
Off
ATU-C 1 Green solid
Green blinking
Off
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
No errors, but no connection established.
The image download is in progress.
NI-2 communication established.
The self-test or line card has failed.
The ATU-C line card has had a power failure.
The line card is activated.
The line card is not in service.
Modem 1 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 1.
Modem 1 is idle.
OL-2365-02
Page 43

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-8 8xDMT over ISDN LED Indicators (continued)
LED State Function
ATU-C 2 Green solid
ATU-C 3 Green solid
ATU-C 4 Green solid
ATU-C 5 Green solid
ATU-C 6 Green solid
ATU-C 7 Green solid
ATU-C 8 Green solid
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Modem 2 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 2.
Modem 2 is idle.
Modem 3 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 3.
Modem 3 is idle.
Modem 4 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 4.
Modem 4 is idle.
Modem 5 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 5.
Modem 5 is idle.
Modem 6 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 6.
Modem 6 is idle.
Modem 7 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 7.
Modem 7 is idle.
Modem 8 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 8.
Modem 8 is idle.
1.2.3.7 Octal-Port G.SHDSL SHTU-C Line Card Overview
The octal-port G.SHDSL SHTU-C line card (8xG.SHDSL)
• Supports eight SHDSL modem connections
• Supports trellis coded pulse amplitude modulation (TC-PAM) line encoding
• Converts G.SHDSL modulation from the line into digital data streams to and from the NI-2 card
• Supports fixed and adaptive rate modes
• Has deployment guidelines when used in the Cisco 6260 system; see the “Guidelines for Intermixing
8xG.SHDSLs—Cisco IOS Release 12.2(7)DA and Later” section on page 1-28.
Note For hardware specifications for the 8xG.SHDSL line card, see the “Octal-Port G.SHDSL SHTU-C Line
Card” section on page A-7.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-25
Page 44

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.3.7.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-14 shows a close-up of the 8xG.SHDSL faceplate.
Figure 1-14 8xG.SHDSL Faceplate
1
2
Chapter 1 Product Overview
3
4
5
6
STAT US
ACTIVE
SHTU-C1
SHTU-C2
SHTU-C3
SHTU-C4
SHTU-C5
SHTU-C6
SHTU-C7
SHTU-C8
STUC-8SHDSL-1
45677
1 Ejector lever 4 ACTIVE LED
2 Locking tab 5 Modem port status LEDs
3 STATUS LED 6 Extraction tab
Table 1-9 describes the 8xG.SHDSL LED indicator functions.
Table 1-9 8xG.SHDSL LED Indicators
1-26
LED Label State Function
STATUS Green slow blinking
Green fast blinking
Green solid
Red
Off
ACTIVE Green solid
Off
SHTU-C1 Green solid
Green blinking
Off
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
No errors, but no connection established.
The image download is in progress.
NI-2 communication established.
The self-test or line card has failed.
The line card has a power failure.
The line card is activated.
The line card is not in service.
Modem 1 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 1.
Modem 1 is idle.
OL-2365-02
Page 45

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-9 8xG.SHDSL LED Indicators (continued)
LED Label State Function
SHTU-C2 Green solid
SHTU-C3 Green solid
SHTU-C4 Green solid
SHTU-C5 Green solid
SHTU-C6 Green solid
SHTU-C7 Green solid
SHTU-C8 Green solid
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Green blinking
Off
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Modem 2 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 2.
Modem 2 is idle.
Modem 3 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 3.
Modem 3 is idle.
Modem 4 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 4.
Modem 4 is idle.
Modem 5 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 5.
Modem 5 is idle.
Modem 6 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 6.
Modem 6 is idle.
Modem 7 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 7.
Modem 7 is idle.
Modem 8 is trained.
Training is in progress for modem 8.
Modem 8 is idle.
1.2.3.8 Line Card Intermixing
Note Figure 1-6 shows the Cisco 6260 chassis slot numbers.
The Cisco 6260 chassis supports line card intermixing. This section uses the terms halves and quadrants.
The Cisco 6260 chassis consists of two halves:
• Slots 1 to 9 and slots 18 to 26 (left half of the chassis)
• Slots 12 to 17 and slots 27 to 32 (right half of the chassis)
The Cisco 6260 chassis consists of four quadrants:
• Slots 1 to 9 (top left quadrant)
• Slots 12 to 17 (top right quadrant)
• Slots 18 to 26 (bottom left quadrant)
• Slots 27 to 32 (bottom right quadrant)
The following sections describe the line card intermixing guidelines for the Cisco 6260.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-27
Page 46

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.3.8.1 Guidelines for Intermixing xDSL Line Cards
Mixing line cards of different modulation types in the same quadrant of any Cisco DSLAM is prohibited.
Different modulation types are allowed in the same half of a chassis with the exceptions of slots 18 and
34 in the Cisco 6160 beginning with Cisco IOS release 12.2(7)DA. Mixing line cards of the same
modulation type (for example, 4xFlexiDMT and 8xDMT line cards) in a quadrant is allowed.
1.2.3.8.2 Guidelines for Intermixing 8xG.SHDSLs—Cisco IOS Release 12.1(7)DA2, 12.2(1b)DA, and 12.2(5)DA
The Cisco 6260 chassis can be fully populated with 8xG.SHDSLs while retaining QoS, as long as the
upstream bandwidth is provisioned at a maximum of 5 Mbps for even ports and a maximum of 5 Mbps
for odd ports per line card. Once an 8xG.SHDSL is installed in a chassis quadrant, no ADSL line cards
can be installed in that same quadrant.
1.2.3.8.3 Guidelines for Intermixing 8xG.SHDSLs—Cisco IOS Release 12.2(7)DA and Later
The Cisco 6260 system supports up to 16 8xG.SHDSLs installed per chassis while retaining QoS. Once
an 8xG.SHDSL is installed in a quadrant, no ADSL line cards can be installed in that same quadrant.
Figure 1-15 illustrates the optimal deployment of 8xG.SHDSLs in the Cisco 6260 chassis with quadrant
intermixing of ADSL line cards in the Cisco 6260 chassis. For example:
• If 4 8xG.SHDSLs are installed in the left side of the chassis, only 21 ADSL line cards can be
installed in the remaining chassis quadrants.
Note No ADSL line cards can be installed in the same quadrant as the 8xG.SHDSLs.
• If 4 8xG.SHDSLs are installed in the right side of the chassis, only 24 ADSL line cards can be
installed in the remaining chassis quadrants.
Note No ADSL line cards can be installed in the same quadrant as the 8xG.SHDSLs.
Caution Random cell loss may occur if the guidelines for 8xG.SHDSL deployment in a system are exceeded.
1-28
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 47

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Figure 1-15 8xG.SHDSL Deployment in the Cisco 6260 System.
Cisco 6260 System Overview
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
Number of ADSL line cards in the chassis
4
3
2
1
0
12345678910111213141516
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
Number of ADSL line cards in the chassis
4
3
2
1
0
12345678910111213141516
Number of 8xG.SHDSLs in the left side Number of 8xG.SHDSLs in the right side
69298
1.2.3.8.4 Guidelines for Intermixing 8xG.SHDSLs—Cisco IOS Release 12.2(12)DA and Later for NI2-155SM-155SM2 or
NI2-155MM-155MM2 Only
This section describes intermixing in Cisco IOS Release 12.2(12)DA and later for NI2-155SM-155SM2
or NI2-155MM-155MM2 only. All other NI2s, including NI2-155SM-155SM and
NI2-155MM-155MM, follow guidelines as described in the “Guidelines for Intermixing
8xG.SHDSLs—Cisco IOS Release 12.2(7)DA and Later” section on page 1-28.
The Cisco 6015, Cisco 6160, and Cisco 6260 can be fully populated with 8xG.SHDSLs while
retaining QoS.
• In the Cisco 6160 and Cisco 6260, once an 8xG.SHDSL is installed in a chassis quadrant, no other
type of line card can be installed in that same quadrant.
• In the Cisco 6015, intermixing is limited to chassis halves.
Note In order to provision 18.5 Mbps per line card in a chassis fully populated with 8xG.SHDSLs, an
OC-3c/OC-3c single-mode fiber (SMF) or multi-mode fiber (MMF) NI-2 card (NI2-155SM-155SM2
and NI2-155MM-155MM2) must be installed in the chassis.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-29
Page 48

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.3.9 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card Overview
The DS3/2DS3 NI-2 card
• Provides the network E3 network trunk interface through BNC connectors located on the E3 I/O
module.
Note The Cisco 6260 system does not support the DS3 interface. When the DS3/2DS3 NI-2 card and
the E3 I/O module are installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis, the system adopts E3 functionality.
• Connects to the xTU-C line cards through point-to-point serial data buses on the backplane
• Contains the ATM switch fabric
• Provides CO facility alarm relay contact interfaces and an alarm cut-off (ACO) button
• Provides visual and audible operating status alerts
• Is manageable through Cisco IOS software or through CDM
• Provides Cisco IOS-based ATM QoS
• Controls timing and redundancy
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Note The BITS interface is connected through the E3 I/O module located on the front of the Cisco
6260.
• Supports the aggregation of up to 12 subtended node chassis that are configured for E3 operation in
a tree topology.
• Provides two E3 subtend interfaces through BNC connectors located on the I/O module.
Note For hardware specifications for the DS3/2DS3 NI-2 card, see the “DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card” section on
page A-8.
1-30
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 49

Chapter 1 Product Overview
1.2.3.9.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-16 shows a close-up of the DS3/2DS3 NI-2 card faceplate.
Figure 1-16 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card Faceplate
Cisco 6260 System Overview
1
NI-2
-DS3/E3-DS3/E3
2
3
4
5
2
TRNK 1
R
T
X
E
S
S
T
T
A
T
SBTD 2
T
E
S
T
SBTD 3
T
E
S
T
ACO
RESET
T
X
S
T
A
T
R
T
X
X
S
S
T
T
A
A
T
T
R
T
X
X
S
S
T
T
A
A
T
T
R
C
L
K
R
C
K
L
R
C
L
K
ALARMS
CRITICAL
MAJOR
MINOR
POWER
STATUS
ACTIVE
FAN 1
FAN 2
C
N
S
L
A
U
X
E
N
E
T
6
7
8
9
10
ACT
11
LNK
OL-2365-02
1
44216
1 Ejector lever 7 Card status LED group
2 Locking tab 8 Fan alarm LED group
CNSL—An RJ-45 receptacle that provides a
3 ACO button 9
serial connection to a system console.
AUX—An RJ-45 receptacle that provides
connection to an auxiliary device (such as a
modem) used to remotely configure the
4 Maintenance RESET port 10
Interface status LED groups: TRNK
2
SBTD
2, and SBTD 3, which show the status
1
1,
of the network trunk and subtend connections
5
on the I/O module. 11
system.
ENET—An RJ-45 10BaseT receptacle that
complies with Ethernet standards and that
provides connection to a system Ethernet.
6 System alarm LED group
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-31
Page 50

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1. TRNK = trunk
2. SBTD = s ubtend
Table 1-1 0 describes the LED group indicators and their functions.
Table 1-10 DS3/2DS3 NI-2 Card LED Group Indicators
LED Group LED State Function
Interface
status LED
(5 in
Figure 1-16)
System alarm
(6 in
Figure 1-16)
Card status
(7 in
Figure 1-16)
Chapter 1 Product Overview
TEST Amber solid Cisco IOS detects that an obtrusive test (loopback) is
active on this interface.
Off Cisco IOS does not detect obtrusive test activity.
1
RX
STAT
Amber solid The receiver detects a physical layer problem.
Off The receiver does not detect a physical layer problem.
2
TX
STAT
Amber solid The transmitter detects a physical layer problem.
Off The transmitter does not detect a physical layer
problem.
3
RCLK
Green solid Hardware detects an incoming clock signal.
Off Hardware does not detect an incoming clock signal.
CRITICAL Red A critical alarm is active.
MAJOR Red A major alarm is active.
MINOR Amber A minor alarm is active.
POWER Green The NI-2 card has power.
STATUS Green The operational status of the NI-2 card.
• On—There are no internal faults or problems.
ACTIVE Green The NI-2 card is operating as the active NI-2 card in
Fan alarm
FAN 1 Red The fan module or fan tray is not operational and is in
(8 in
Figure 1-16)
ENET
interface LED
(11 in
Figure 1-16)
FAN 2 Off The fan tray is off.
ACT Green solid or
blinking
Off The Ethernet interface is inactive.
LNK Green solid The Ethernet link is connected and enabled.
1. RX = receive
2. TX = transmit
3. RCLK = receive clock
1.2.3.10 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card Overview
The DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card
• Provides the following network trunk and subtend interfaces:
• Off—The NI-2 card has not booted properly, or a
problem is preventing normal operation.
the chassis.
alarm mode.
The Ethernet interface is active.
1-32
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 51

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Note Network trunk and subtend connectors for the DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 cards are located on the
• Connects to the xTU-C line cards through point-to-point serial data buses on the backplane
• Contains the ATM switch fabric
• Provides CO facility alarm relay contact interfaces and an ACO button
• Provides visual and audible operating status alerts
• Is manageable through Cisco IOS software or CDM
• Provides Cisco IOS-based ATM QoS
• Controls timing through an internal clock or BITS interface, or from an ATM interface (E1)
Note The BITS interface is connected through the I/O module located on the front of the Cisco 6260.
–
E1
–
E1 IMA group
E1 I/O module on the front of the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Cisco 6260 System Overview
• Supports the aggregation of up to seven subtended node chassis that are configured for E1 or E1
IMA group operation in a daisy-chain, tree, or star topology
• Provides E1 subtend interfaces through RJ-48c connectors located on the E1 I/O module.
1.2.3.10.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-17 shows a close-up of the DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card faceplate.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-33
Page 52

Cisco 6260 System Overview
Figure 1-17 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card Faceplate
Chapter 1 Product Overview
1
NI-2
DS3+T1/E1 IMA
2
3
4
5
2
T
E
S
T
ACO
RESET
T
R
X
X
S
S
T
T
A
A
T
T
DS3 1
T1/E1 2
T1/E1 3
T1/E1 4
T1/E1 5
T1/E1 6
T1/E1 7
T1/E1 8
T1/E1 9
R
C
L
K
ALARMS
CRITICAL
MAJOR
MINOR
POWER
STAT U S
ACTIVE
FAN 1
FAN 2
C
N
S
L
A
U
X
E
N
E
T
6
7
8
9
10
ACT
11
LNK
1
42366
1 Ejector lever 7 Card status LED group
2 Locking tab 8 Fan alarm LED group
CNSL—An RJ-45 receptacle that provides a
3 ACO button 9
serial connection to a system console.
AUX—An RJ-45 receptacle that provides
connection to an auxiliary device (such as a
modem) used to remotely configure the
Maintenance RESET port
4
10
system.
Interface status LED groups: DS3 1, T1/E1 2,
T1/E1 3, T1/E1 4, T1/E1 5, T1/E1 6, T1/E1 7,
T1/E1 8, and T1/E1 9, which show the status
of the network trunk and subtend connections
on the I/O module 11
5
ENET—An RJ-45 10BaseT receptacle that
complies with Ethernet standards and that
provides connection to a system Ethernet.
6 System alarm LED group
1-34
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 53

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-1 1 describes the LED group indicators and their functions.
Table 1-11 DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 Card LED Group Indicators
LED Group LED State Function
Interface
status LED
(5 in
Figure 1-17)
System alarm
(6 in
Figure 1-17)
Card status
(7 in
Figure 1-17)
Cisco 6260 System Overview
TEST Amber solid Cisco IOS detects that an obtrusive test (loopback) is
active on this interface.
Off Cisco IOS does not detect obtrusive test activity.
RX STAT Amber solid The receiver detects a physical layer problem.
Off The receiver does not detect a physical layer problem.
TX STAT Amber solid The transmitter detects a physical layer problem.
Off The transmitter does not detect a physical layer
problem.
RCLK Green solid Hardware detects an incoming clock signal.
Off Hardware does not detect an incoming clock signal.
CRITICAL Red A critical alarm is active.
MAJOR Red A major alarm is active.
MINOR Amber A minor alarm is active.
POWER Green The NI-2 card has power.
STATUS Green The operational status of the NI-2 card.
• On—There are no internal faults or problems.
ACTIVE Green The NI-2 card is operating as the active NI-2 card in
Fan alarm
FAN 1 Red The fan module or fan tray is not operational and is in
(8 in
Figure 1-17)
ENET
FAN 2 Red The fan module or fan tray is not operational and is in
ACT Green solid or
interface LED
(11 in
Figure 1-17)
LNK Green solid The Ethernet link is connected and enabled.
1.2.3.11 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card Overview
The OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card
• Provides the network OC-3c network trunk interface through optical connectors located on the NI-2
card faceplate. The following two versions of the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card are available to support
the network trunk interface:
–
SMF intermediate range
–
MMF short range
• Off—The NI-2 card has not booted properly, or a
problem is preventing normal operation.
the chassis.
alarm mode.
alarm mode.
The Ethernet interface is active.
blinking
Off The Ethernet interface is inactive.
OL-2365-02
• Connects to the xTU-C line cards through point-to-point serial data buses on the backplane
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-35
Page 54

Cisco 6260 System Overview
• Contains the ATM switch fabric
• Provides CO facility alarm relay contact interfaces and an ACO button
• Provides visual and audible operating status alerts
• Is manageable through Cisco IOS software or CDM
• Provides Cisco IOS-based ATM QoS
• Controls timing and redundancy
Note The BITS interface is connected through the OC-3c I/O module located on the front of the Cisco
• Supports the aggregation of up to 12 subtended node chassis configured for OC-3c operation in a
• Provides an OC-3c subtend interface through optical connectors located on the NI-2 card faceplate.
Note For hardware specifications for the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card, see the “OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card” section
on page A-10.
Chapter 1 Product Overview
6260 chassis.
daisy chain configuration.
1-36
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 55

Chapter 1 Product Overview
1.2.3.11.1 Faceplate Features
Figure 1-18 shows a close-up of the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card faceplate.
Figure 1-18 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card Faceplate
Cisco 6260 System Overview
1
NI-2
-155SM-155SM
7
2
3
4
5
6
5
2
ACO
RESET
TRNK 1
R
T
R
T
X
X
C
E
L
S
S
S
K
T
T
T
A
A
T
T
T
X
ALARMS
R
CRITICAL
X
MAJOR
MINOR
POWER
STATUS
ACTIVE
T
FAN 1
X
FAN 2
R
X
C
N
S
L
SBTD 2
A
U
X
R
T
R
T
X
X
C
E
L
S
S
S
K
T
T
A
T
ACT
T
A
E
T
N
E
T
LNK
8
9
10
11
12
13
OL-2365-02
1
26372
1 Ejector lever 8 System alarm LED group
2 Locking tab 9 Card status LED group
3 ACO button 10 Fan alarm LED group
CNSL—An RJ-45 receptacle that provides a
4 Maintenance RESET port 11
serial connection to a system console.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-37
Page 56

Cisco 6260 System Overview
5
6
7 Model number
Table 1-1 2 describes the LED group indicators and their functions.
Interface status LED groups: TRNK 1 and
SBTD 2, which show the status of the network
trunk and subtend connections. 12
Two optical interface connector pairs: TRNK
1 and SBTD 2
• TRNK 1—for network trunk interface TX
and RX data optical cables. On a
subtended node chassis, these TX and RX
cables connect to SBTD 2 on the
subtending host chassis.
• SBTD 2—for subtended node chassis TX
and RX data optical cables. 13
Chapter 1 Product Overview
AUX—An RJ-45 receptacle that provides
connection to an auxiliary device (such as a
modem) used to remotely configure the
system.
ENET—An RJ-45 10BaseT receptacle that
complies with Ethernet standards and that
provides connection to a system Ethernet.
Table 1-12 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card LED Group Indicators
LED Group LED State Function
Interface
status LED
(5 in
Figure 1-18)
TEST Amber solid Cisco IOS detects that an obtrusive test (loopback) is
active on this interface.
Off Cisco IOS does not detect obtrusive test activity.
RX STAT Amber solid The receiver detects a physical layer problem.
Off The receiver does not detect a physical layer problem.
TX STAT Amber solid The transmitter detects a physical layer problem.
Off The transmitter does not detect a physical layer
problem.
RCLK Green solid Hardware detects an incoming clock signal.
Off Hardware does not detect an incoming clock signal.
System alarm
(7 in
Figure 1-18)
CRITICAL Red A critical alarm is active.
MAJOR Red A major alarm is active.
MINOR Amber A minor alarm is active.
Card status
(8 in
Figure 1-18)
POWER Green The NI-2 card has power.
STATUS Green The operational status of the NI-2 card.
• On—There are no internal faults or problems.
1-38
• Off—The NI-2 card has not booted properly, or a
problem is preventing normal operation.
ACTIVE Green The NI-2 card is operating as the active NI-2 card in
the chassis.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 57

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Table 1-12 OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 Card LED Group Indicators (continued)
LED Group LED State Function
Fan alarm
FAN 1 Red The fan module or fan tray is not operational and is in
(9 in
Figure 1-18)
ENET
FAN 2 Red The fan module or fan tray is not operational and is in
ACT Green solid or
interface LED
(12 in
Figure 1-18)
LNK Green solid The Ethernet link is connected and enabled.
1.2.3.12 Network Clocking Overview
The NI-2 card receives its network timing signal from any one of the following sources:
• A BITS clock. When a BITS clock is the network timing signal source, the Cisco 6260 chassis
receives a clock signal through designated pins on the I/O module and distributes the signal through
the Cisco 6260 backplane.
• An internal clock.
Cisco 6260 System Overview
alarm mode.
alarm mode.
The Ethernet interface is active.
blinking
Off The Ethernet interface is inactive.
• E3 or OC-3c network trunk interface. An NI-2 card synchronizes with the network timing source
and provides a clock reference signal to line cards in the Cisco 6260 chassis and to subtended
node chassis.
The active NI-2 card supplies a redundant pair of clock signals to all cards in the chassis. This same
clock reference can be propagated to subtended systems via the trunk and subtended interface ports.
This is done by configuring the subtending port of the root system to source the network-derived
clock. The trunk port of the subtended system is configured as the network clock source for that
chassis. This chain continues down the subtended tree.
1.2.3.13 Redundancy Overview
Redundancy is available for the Cisco 6260 system. The following forms of redundancy are available:
• NI-2 card cold redundancy, which allows a standby NI-2 card to take over system operations in the
event of a complete failure of the active NI-2 card.
• Automatic protection switching (APS) link redundancy, which is available on OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2
card network trunk and subtend interfaces.
Note Line card redundancy is not currently supported in the Cisco 6260 system.
1.2.3.13.1 NI-2 Card Redundancy
NI-2 card redundancy requires that two NI-2 cards be installed in the chassis. The primary card is
installed in slot 10 of the chassis, and the secondary card is installed in slot 11. Either the primary or the
secondary NI-2 card can serve as the active NI-2 card. The interface types must be the same for both the
primary and secondary NI-2 cards. The following NI-2 cards support cold redundancy in the Cisco 6260
chassis:
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-39
Page 58

Cisco 6260 System Overview
• DS3/2DS3
• DS3+T1/E1 IMA
• OC-3c/OC-3c (SMF and MMF)
During steady-state operations, one NI-2 card functions as the active unit, and the other functions as the
standby unit. The active NI-2 card displays a green ACTIVE LED. In an active state, the NI-2 card
• Has full Ethernet, auxiliary port, and console access
• Communicates with line cards
• Has full access to the environmental monitoring subsystem
• Has access to the optical interfaces on the standby NI-2 card
• Allows remote access to the file system of the standby NI-2 card
The standby NI-2 card plays a minimal role during steady-state operations. In a standby state, the
NI-2 card
• Receives configuration changes from the active NI-2 card (when the cards are configured
• Has no Ethernet, auxiliary port, or console access
Chapter 1 Product Overview
for synchronization)
• Does not communicate with line cards
• Has no access to the environmental monitoring subsystem
• Generates only APS alarms, which are reported via the active card
For management purposes, the primary and secondary NI-2 cards appear as one element. The cards share
one IP address.
Note For information on NI-2 card cold redundancy switchover conditions, refer to the Upgrading DSLAMs
for NI-2 Card and APS Link Redundancy document.
1.2.3.13.2 APS Link Redundancy
APS link redundancy provides recovery from a cut fiber or the failure of an OC-3c optical TX or optical
RX interface on an NI-2 card. APS link redundancy is available on OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card network
trunk and subtend interfaces.
APS link redundancy is nonrevertive. After a switchover from the primary to the secondary fiber occurs,
the active NI-2 card switches back to the primary fiber only if it is manually forced through a
command-line interface (CLI) or if a failure condition occurs on the secondary fiber. However, if a
failure condition occurs on the secondary fiber while the primary fiber is still in a failed state, a switch
back to the primary fiber does not occur.
Note The OC-3c ports on the standby NI-2 card are available for APS link redundancy only if the standby NI-2
card is working and in a STANDBY-READY state.
1-40
For more information on APS link redundancy, refer to the Upgrading DSLAMs for NI-2 Card and APS
Link Redundancy document.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 59

Chapter 1 Product Overview
1.2.3.14 Redundancy in Subtended Configurations
NI-2 card redundancy is supported in an E3 subtend tree or daisy-chain or in an OC-3c subtend
daisy-chain if both the subtending host chassis and the subtended node chassis have primary and
secondary NI-2 cards installed. An NI-2 card failure on a node in a subtend tree or daisy-chain
temporarily interrupts traffic to all subtended node chassis.
NI-2 card redundancy is not supported in DS3+T1/E1 IMA subtended configurations.
APS link redundancy is supported in subtending configurations only if all of the following conditions
exist:
1. The subtending host chassis is configured for OC-3c/OC-3c operation;
2. The subtending host chassis has a secondary NI-2 card installed; and
3. The subtended node chassis have primary and secondary OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 cards installed.
1.2.4 Cisco 6260 I/O Modules
This section contains the following information:
Cisco 6260 System Overview
• E3 I/O Module Overview, page 1-41
• E1 I/O Module Overview, page 1-42
• OC-3c I/O Module Overview, page 1-43
A Cisco 6260 chassis must have an I/O module installed. The I/O module is delivered installed near the
top of the Cisco 6260 chassis, just below the subscriber connectors. Figure 1-1 shows the location of the
I/O module on the Cisco 6260 chassis.
1.2.4.1 E3 I/O Module Overview
The E3 I/O module provides the Cisco 6260 chassis with a network trunk interface connector and
connectors to subtend other DSLAMs to the chassis. The E3 I/O module also provides the alarm pinouts
and BITs clock input circuits for the Cisco 6260 system.
The E3 I/O module works with the DS3/2DS3 NI-2 card in the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Note The Cisco 6260 does not support the DS3 interface. When the DS3/2DS3 NI-2 card is installed in
the Cisco 6260 chassis with an E3 I/O module, the NI-2 card adopts E3 functionality.
Figure 1-19 shows a close-up of the E3 I/O module.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-41
Page 60

Cisco 6260 System Overview
Figure 1-19 E3 I/O Module
Chapter 1 Product Overview
1
2
RX
P1
TX
E3 75-ohm coaxial BNC connectors. The P1
RX and TX connectors serve as the network
1
trunk interface. 3
E3 75-ohm coaxial BNC connectors. The P2
and P3 RX and TX connectors serve as
2
subtend connectors to additional chassis.
Note For hardware specifications for the E3 I/O module, see the “I/O Module” section on page A-11.
1.2.4.2 E1 I/O Module Overview
PEM 1/PEM 2
AUD_CRIT/AUD_MAJ
AUD_MIN/VIS_CRIT
VIS_MAJ/VIS_MIN
STAT_ALARMS
BITS_A/BITS_B
3
60V
0.5 A MAX
L
O
G
IC
IN
P
U
T
S
B
IT
S
C
L
O
C
K
44751
RX
P2
TX
RX
P3
TX
Six rows of six wire-wrap pins that support
CO alarm relay interfaces and BITS clock
input circuits.
The E1 I/O module provides eight E1 interfaces that can be allocated as either individual E1 network
trunk or subtend interfaces, or as IMA group trunk or subtend interfaces. The E1 I/O module also
provides the alarm pinouts and BITS clock input circuits for the Cisco 6260 system.
The E1 I/O module works with the DS3+T1/E1 IMA NI-2 card in the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Figure 1-20 shows a close-up of the E1 I/O module.
1-42
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 61

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Figure 1-20 E3 I/O Module
Cisco 6260 System Overview
1
J1
J5
J2
J6
Four sets of two verically-paired E1 120-ohm
RJ-48c connectors that can be used as a
network trunk connection, an individual E1
subtend link, a connection to an IMA
subtending group, or a connection to an IMA
group trunk interface. 2
1
Note For hardware specifications for the E1 I/O module, see the “I/O Module” section on page A-11.
1.2.4.3 OC-3c I/O Module Overview
PEM 1/PEM 2
AUD_CRIT/AUD_MAJ
AUD_MIN/VIS_CRIT
VIS_MAJ/VIS_MIN
STAT_ALARMS
BITS_A/BITS_B
2
60V
0.5 A MAX
L
O
G
IC
IN
P
U
T
S
B
IT
S
C
L
O
C
K
54326
J3
J7
J4
J8
Six rows of six wire-wrap pins that support
CO alarm relay interfaces and BITS clock
input circuits.
No network trunk or subtending port connectors are needed on the OC-3c I/O module. These connectors
are present on the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card faceplate.
The OC-3c I/O module works with the OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 card in the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Figure 1-21 shows a close-up of the OC-3c I/O module, including the wire-wrap pins located on the right
side of the I/O module faceplate that support CO alarm relay interfaces and BITS clock input circuits.
Figure 1-21 OC-3c I/O Module
OC-3c I/O MODULE
OC-3c I/O MODULE
Note For hardware specifications for the OC-3c I/O module, see the “I/O Module” section on page A-11.
PEM 1/PEM 2
AUD_CRIT/AUD_MAJ
AUD_MIN/VIS_CRIT
VIS_MAJ/VIS_MIN
STAT_ALARMS
BITS_A/BITS_B
60V
0.5 A MAX
L
O
G
IC
IN
P
U
T
B
IT
S
C
L
O
C
S
K
26675
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-43
Page 62

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.4.4 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pins
Located on the right side of each I/O module faceplate are 36 wire-wrap pins that support
• Central office alarm relay interfaces (visual and audible critical, major, and minor)
• BITS clock input circuits
• Wire-wrap and socket-type connections
Both the alarm relay and the BITS clock connections are optional. If you connect the alarm relays, they
transmit critical, major, and minor alarms to a separate, external alarm device. The alarm device uses a
bell, light, or some other signal to alert service personnel to the change in system status. If you connect
the BITS interface, the Cisco 6260 can receive a clock signal from an E1 line.
Figure 1-22 shows a close-up of the wire-wrap pins.
Figure 1-22 I/O Module Wire-Wrap Pins Close-Up
Chapter 1 Product Overview
PEM 1/PEM 2
AUD_CRIT/AUD_MAJ
AUD_MIN/VIS_CRIT
VIS_MAJ/VIS_MIN
STAT_ALARMS
BITS_A/BITS_B
60V
0.5 A MAX
LOGIC
INPUTS
BITS
CLO
CK
44750
These pins support the following items:
• Visual critical alarm
• Visual major alarm
• Visual minor alarm
• Audible critical alarm
• Audible major alarm
• Audible minor alarm
• Power module alarms
• Remote alarm cut off
• Reserved (several pins are reserved for future specification)
Each of the wire-wrap pins is connected to the NI-2 cards in the Cisco 6260 chassis; however, only one
NI-2 card manages the alarms. The ACO switch on the NI-2 card faceplate shuts off the audible alarms
generated by the Cisco 6260 system software.
1-44
One of the alarm relay functions provided by the wire-wrap connector is an ACO circuit that you can wire to
your external alarm device. To use this feature, connect the alarm device so that it can close the contact
between pin 5 and pin 6 in row 5.
The connector also provides contacts for the following features, all of which can be used separately:
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 63

Chapter 1 Product Overview
• Audible alarms—Wire pins whose signals begin with AUD
• Visible alarms—Wire pins whose signals begin with VIS
• Power alarms—Wire pins whose signals begin with PEM
• BITS clock—Wire pins whose signals begin with RX_BITS
Note There is one set of contacts for audible alarms and one set for visual alarms. You can use either or both
sets of contacts.
You can wire the alarm relay contacts as normally open (NO) or normally closed (NC). (One exception
is the ACO circuit, which can be wired as NO only.) Use common (CO) pins for both the NO and NC
wiring methods.
Table 1-13 Pin Assignments for the Cisco 6260 I/O Module
Wiring Method Pins to Use
Normally open Pin 2 in rows 1, 2, 3, 4 (NO)
Normally closed Pin 3 in rows 1, 2, 3, 4 (NC)
1. GND = ground
Pin 5 in rows 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 (NO)
Pin 1 in rows 1, 2, 3, 4 (CO)
Pin 4 in rows 1, 2, 3, 4 (CO)
Pin 6 in row 5 (GND
1
)
Pin 6 in rows 1, 2, 3, 4 (NC)
Pin 1 in rows 1, 2, 3, 4 (CO)
Pin 4 in rows 1, 2, 3, 4 (CO
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Note For more information on how the wire-wrap pins map to the alarms, see the “Port Mapping Table”
1.2.5 PEM
OL-2365-02
section on page B-1.
The Cisco 6260 system is equipped with one or two –48/–60V direct current (DC) PEMs, which
distribute DC power within the chassis. The Cisco 6260 requires only one active PEM to operate; if two
PEMs are installed, the second PEM serves as a hot backup to the first.
Each PEM should be connected to a single DC power source. DC power (–48V) enters the chassis
through the terminal blocks on the front of each PEM. For full power redundancy, two PEMs must be
installed in the chassis, and the two PEMs must be connected to two separate DC power sources.
In a system with two PEMs installed, you can remove and replace each individual PEM while the system
continues to operate. (A system with a single PEM must be powered down before the PEM is removed.)
In addition, you can replace a PEM in a chassis with a single PEM installed without shutting down
system power by first removing the blank faceplate from the second slot, installing a replacement PEM
in the second slot, and then removing the first PEM. The blank faceplate can then be installed in the
empty first PEM slot.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-45
Page 64

Cisco 6260 System Overview
Note The PEMs reside at the bottom of the chassis, and they are installed and accessed from the
front (see Figure 1-1 for the location of the PEM in the Cisco 6260 chassis). Each PEM is
held in place by the overhanging lip of the fan tray above it. You must remove the fan tray
before you can remove the PEM.
To turn off a Cisco 6260 that has two PEMs, you must flip the circuit breakers on both PEMs
to the OFF (0) position.
The Cisco 6260 can be ordered with only one PEM installed, and with a blank faceplate
installed in place of a second PEM.
Figure 1-23 shows a close-up of the PEM faceplate.
Figure 1-23 PEM Faceplate
1
INPUT OK
OUT FAIL
FAN TRAY 1
FANTRAY 2
Chapter 1 Product Overview
2
3
48430
4
PEM and fan tray status LEDs
1
Extraction handle
2
Two-position circuit breaker—the positions
3
are Off (0) and On (1)
Negative (-), positive (+), and ground DC
4
power terminal blocks
Note For hardware specifications for the PEM, see the “PEM” section on page A-11.
Table 1-1 4 describes the PEM LED indicators and their functions.
Ta b l e 1- 1 4 P E M LE D s
LED State Function
Input OK Green –48V power is available to the chassis.
Out Fail Red The PEM is not distributing power to the chassis.
Fan Tray 1 Green The fans in this tray are operating normally.
Red One or more fans in this tray have failed.
Fan Tray 2 Green The fans in this tray are operating normally.
Red One or more fans in this tray have failed.
1-46
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 65

Chapter 1 Product Overview
1.2.6 Fan Tray
Note The Cisco 6260 system requires that a fan tray be installed when the system is in operation.
Cisco 6260 System Overview
Two fan trays are installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis below the line cards. Each tray houses four fans.
The compartments for the two fan trays are located side by side near the bottom of the chassis, just above the
PEMs (see Figure 1-1 for the location of the fan trays in the Cisco 6260 chassis). As you face the chassis,
fan tray 1 is on the left; and fan tray 2 is on the right.
A narrow bezel fits across the chassis to hold the air filters and fan trays in place.
Figure 1-24 shows a close-up view of the fan tray.
Figure 1-24 Cisco 6260 Fan Tray
26374
The fans have two speeds. By default, they run at low speed. The system turns up the fan speed when
• It senses high temperatures within the chassis.
• One or more fans fail.
• The other fan tray is removed.
The fan speed returns to normal (low speed) when
• Temperatures within the chassis fall to acceptable levels.
• A missing fan tray is reinstalled in the chassis.
Caution The fans in both fan trays must run continuously. The system might suffer thermal damage if the fans in either
tray stop for more than 5 minutes.
An air filter is located above each fan tray. The air filters must be removed and cleaned periodically. See
the “Replacing or Cleaning the Air Filter” section on page 6-2 for instructions on cleaning the air filters.
Note For hardware specifications for the fan tray, see the “Fan Tray” section on page A-12.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-47
Page 66

Cisco 6260 System Overview
1.2.7 Air Filters
Two air filters are located at the bottom of the Cisco 6260 chassis. The air filters must be removed and
cleaned periodically. See Chapter 6, “Upgrading and Maintaining the Cisco 6260 System,” for complete
instructions on cleaning and replacing the air filter. Figure 1-25 shows the location of the air filters and
the protective bezel that covers them.
Figure 1-25 Air Filters
Chapter 1 Product Overview
P
EM
1/PEM
2
AUD
_CR
IT/AUD_MAJ
AU
D_M
IN
/VIS_C
RIT
V
IS
_M
AJ/VIS_M
IN
STAT_ALARM
S
BU
S_A
/B
ITS_B
N
I-2
N
I
-1
5
5
S
M
-1
5
5
S
M
B
L
A
N
K
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
C
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
C
2
A
T
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
A
T
U
C
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
A
T
U
C
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
S
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
T
-4
D
M
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
T
IV
E
A
C
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
U
-C
2
A
T
U
U
-C
3
A
T
U
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
T
-4
D
M
T
O
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
R
E
S
E
2
3
4
U
S
IV
E
-C
1
-C
2
-C
3
-C
4
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
TRUNK 1
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
T
R
T
R
A
T
X
U
C
X
4
E
A
T
U
-C
C
4
S
L
S
S
T
K
T
T
A
A
T
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
A
L
A
R
M
S
C
R
IT
IC
A
M
A
J
O
R
M
IN
O
R
P
O
W
E
R
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
T
IV
E
F
A
N
1
F
A
N
2
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
C
N
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
S
L
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
A
T
U
SBTD 2
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
U
A
T
U
-C
3
X
A
T
U
-C
3
T
R
T
R
X
X
E
A
C
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
4
S
L
S
S
T
K
T
T
E
A
A
T
T
N
E
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
A
T
U
C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
A
T
D
U
M
C
T
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
L
T
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
A
T
U
C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
A
T
D
U
M
C
T
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
TU
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
26894
Cisco 6260
1.2.8 ESD Jack
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-48
An electrostatic discharge (ESD) jack is located on the top of the chassis at the right front corner. Before
removing any components from the chassis or installing any components, ground yourself by using the
ESD jack.
OL-2365-02
Page 67

Chapter 1 Product Overview
1.2.9 Third-Party POTS Splitter
For information about the third-party POTS splitter, refer to the vendor documentation.
1.3 Management Software
You can provision and manage the Cisco 6260 system through the following management software:
–
Cisco IOS—A command-line interface (CLI) that is available for network
element provisioning.
–
Cisco DSL Manager (CDM)—An element management system designed to configure and
manage the 6xxx series of Cisco IOS software-based DSLAMs through a graphical-user
interface (GUI). CDM provides the following areas of network management: fault,
configuration, performance, and security. CDM runs within the Cisco Element Manager
Framework (EMF); both are installed on Sun workstations.
Cisco EMF is based on an object model in which network elements or modules represent the
managed entity. Each object is defined by a class and specific attributes. An object can represent
a network element or a more abstract entity such as a link relationship, a network, or a container
such as a site, shelf, or region.
Management Software
Note If your network contains multiple SUN workstations, you must dedicate one workstation as the
server and use all additional workstations as clients. The server should be the repository and
distributor of database information from which the clients request information. The client
workstations allow multiple users to monitor the managed network.
1.3.1 Management Software-Generated Alarms
The Cisco 6260 includes CO alarm LED indicators and relays that indicate system status. You can wire
CO facility alarm relay contacts for either normally open or normally closed operations. The supported
alarms that are generated by the management software are:
• CRITICAL—A critical condition is indicated when the CRITICAL LED in the NI-2 card faceplate
lights.
–
When a critical alarm occurs, the critical visual and audible alarm relays are activated.
–
A critical alarm affects many or all subscribers that are connected to the node. (For example,
failure of the NI-2 card or the network trunk connection can cause a critical alarm.)
–
Critical alarms clear after you fix the condition that triggered the alarm.
–
Audible alarms are turned off when you press the ACO button on the NI-2 card faceplate or clear
the alarm in the Cisco IOS software.
• MAJOR—A major alarm condition is indicated when the MAJOR LED in the NI-2 card faceplate
lights.
OL-2365-02
–
When a major alarm occurs, the major visual and audible alarm relays are also activated.
–
Many of the subscribers that are connected to the node are affected.
–
Major alarms clear after you fix the condition that triggered the alarm.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
1-49
Page 68

Management Software
Chapter 1 Product Overview
–
Audible alarms are turned off when you press the ACO button on the NI-2 card faceplate or clear
the alarm in the Cisco IOS software.
• MINOR—A minor alarm condition is indicated when the MINOR LED in the NI-2 card faceplate
lights.
–
When a minor alarm occurs, the minor visual and audible alarm relays are also activated.
–
A small number of subscribers that are connected to the node are affected.
–
Minor alarms clear after you fix the condition that triggered the alarm.
–
Audible alarms are turned off when you press the ACO button on the NI-2 card faceplate or clear
the alarm in the Cisco IOS software.
Visual and audible alarm relay contacts can be wired from the Cisco 6260 to CO alarm devices (remote
lights or bells, for example) located anywhere within the facility.
The visual and audible alarm relays are located on the I/O module, but the NI-2 card hardware operates
them.
For more information about alarms that are generated in the management software, see Chapter 5,
“Troubleshooting.”
1-50
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 69

CHAPTER
2
Preparing for Installation
This chapter tells you how to prepare for the installation of the Cisco 6260 system.
The chapter contains the following sections:
• Safety Requirements, page 2-1
• Site Requirements, page 2-11
• Required Tools and Equipment, page 2-16
• Unpacking the Cisco 6260 System, page 2-18
• Verifying Contents, page 2-18
• Inspecting for Damage, page 2-18
Caution Before you start the installation procedures, read the entire chapter for important information and safety
warnings.
2.1 Safety Requirements
This section describes safety requirements for the Cisco 6260 system. Before you install the Cisco 6260
system, ensure that all the criteria in this section are met. The section describes the following
safety requirements:
• Safety Guidelines, page 2-1
• Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage, page 2-9
• General Maintenance Guidelines, page 2-10
2.1.1 Safety Guidelines
Before working on the equipment, be aware of standard safety guidelines and the hazards that are
involved in working with electrical circuitry to prevent accidents. Adhere to the following cautions and
warnings and those throughout the guide for safe and hazard-free installation.
Note To see translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer to the Regulatory Compliance
and Safety Information for the Cisco 6260 System document.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-1
Page 70

Safety Requirements
Caution Installing the cards in the chassis with the power leads reversed can damage the line cards.
Caution If fuses are already installed in the fuse and alarm panel, remove them. You can replace the fuses after
Caution If the power connections are improperly made and power is applied while the cards are installed, the
Caution It is important that the chassis cooling fans run continuously.
Caution Any card that is only partially connected to the backplane can disrupt system operation.
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
the system is installed. Do not power up the system while you install and connect the system.
cards and chassis could be damaged.
2.1.2 Warning Definition
Warning
Waarschuwing
Varoitus
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you
work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar
with standard practices for preventing accidents. To see translations of the warnings that appear
in this publication, refer to the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information document that
accompanied this device.
Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die lichamelijk letsel kan
veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij
elektrische schakelingen betrokken risico's en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van standaard
maatregelen om ongelukken te voorkomen. Voor vertalingen van de waarschuwingen die in deze
publicatie verschijnen, kunt u het document Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
(Informatie over naleving van veiligheids- en andere voorschriften) raadplegen dat bij dit toestel is
ingesloten.
Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi johtaa ruumiinvammaan. Ennen
kuin työskentelet minkään laitteiston parissa, ota selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä vaaroista ja
tavanomaisista onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista. Tässä julkaisussa esiintyvien varoitusten
käännökset löydät laitteen mukana olevasta Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
-kirjasesta (määräysten noudattaminen ja tietoa turvallisuudesta).
2-2
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 71

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Safety Requirements
Attention
Warnung
Avvertenza
Advarsel
Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une situation pouvant
causer des blessures ou des dommages corporels. Avant de travailler sur un équipement, soyez
conscient des dangers posés par les circuits électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures
couramment utilisées pour éviter les accidents. Pour prendre connaissance des traductions
d’avertissements figurant dans cette publication, consultez le document Regulatory Compliance
and Safety Information (Conformité aux règlements et consignes de sécurité) qui accompagne cet
appareil.
Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die zu einer
Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie mit der Arbeit an irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie
sich der mit elektrischen Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der Standardpraktiken zur
Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt. Übersetzungen der in dieser Veröffentlichung enthaltenen
Warnhinweise finden Sie im Dokument Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
(Informationen zu behördlichen Vorschriften und Sicherheit), das zusammen mit diesem Gerät
geliefert wurde.
Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. La situazione potrebbe causare infortuni alle
persone. Prima di lavorare su qualsiasi apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi ai
circuiti elettrici ed essere al corrente delle pratiche standard per la prevenzione di incidenti. La
traduzione delle avvertenze riportate in questa pubblicazione si trova nel documento Regulatory
Compliance and Safety Information (Conformità alle norme e informazioni sulla sicurezza) che
accompagna questo dispositivo.
Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon som kan føre til personskade. Før du
utfører arbeid på utstyr, må du vare oppmerksom på de faremomentene som elektriske kretser
innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med vanlig praksis når det gjelder å unngå ulykker. Hvis du vil se
oversettelser av de advarslene som finnes i denne publikasjonen, kan du se i dokumentet
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Overholdelse av forskrifter og
sikkerhetsinformasjon) som ble levert med denne enheten.
Aviso
¡Advertencia!
Varning!
Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação que lhe poderá causar danos
físicos. Antes de começar a trabalhar com qualquer equipamento, familiarize-se com os perigos
relacionados com circuitos eléctricos, e com quaisquer práticas comuns que possam prevenir
possíveis acidentes. Para ver as traduções dos avisos que constam desta publicação, consulte o
documento Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Informação de Segurança e
Disposições Reguladoras) que acompanha este dispositivo.
Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física. Antes de manipular
cualquier equipo, considerar los riesgos que entraña la corriente eléctrica y familiarizarse con los
procedimientos estándar de prevención de accidentes. Para ver una traducción de las advertencias
que aparecen en esta publicación, consultar el documento titulado Regulatory Compliance and
Safety Information (Información sobre seguridad y conformidad con las disposiciones
reglamentarias) que se acompaña con este dispositivo.
Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan leda till personskada.
Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara medveten om farorna med elkretsar och
känna till vanligt förfarande för att förebygga skador. Se förklaringar av de varningar som
förkommer i denna publikation i dokumentet Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
(Efterrättelse av föreskrifter och säkerhetsinformation), vilket medföljer denna anordning.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-3
Page 72

Safety Requirements
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Before opening the chassis, disconnect the telephone-network cables to avoid contact with
telephone-network voltages.
Do not work on the system or connect or disconnect cables during periods of lightning activity.
Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source.
For personal safety, the ground wire must connect to safety (earth) ground at both the equipment and
supply side of the DC wiring (unless the local electrical code requirements are different).
Incorrect connection of this or connected equipment to a general purpose outlet could result in a
hazardous situation.
Do not touch the power supply when the power cord is connected. For systems with a power switch,
line voltages are present within the power supply even when the power switch is off and the power
cord is connected. For systems without a power switch, line voltages are present within the power
supply when the power cord is connected.
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Secure all power cabling when installing this unit to avoid disturbing field-wiring connections.
The power supply circuitry for the equipment can constitute an energy hazard. Before you install or
replace the equipment, remove all jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches). Metal objects
can come into contact with exposed power supply wiring or circuitry inside the DSLAM equipment.
This could cause the metal objects to heat up and cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the
equipment.
The customer 48 volt power system must provide reinforced insulation between the primary AC power
and the 48 VDC output.
Hold the PEM by the sheet-metal carrier (top and front) only. Internal components may be hot.
Before working on a chassis or working near power supplies, unplug the power cord on AC units;
disconnect the power at the circuit breaker on DC units.
Care must be given to connecting units to the supply circuit so that wiring is not overloaded.
2-4
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 73

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Safety Requirements
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Network hazardous voltages are present in the T1 PRI cable. If you detach the cable, detach the end
away from the router first to avoid possible electric shock. Network hazardous voltages are also
present in the area of the T1 PRI (RJ-48C) ports, regardless of whether power is off or on.
The telecommunications lines must be disconnected 1) before unplugging the main power connector
or 2) while the housing is open.
Hazardous network voltages are present in WAN ports regardless of whether power to the router is
OFF or ON. To avoid electric shock, use caution when working near WAN ports. When detaching
cables, detach the end away from the router first.
To reduce the risk of electric shock when servicing any individual unit, disconnect the power cord or
cords that connect the unit to the AC powerstrip or DC busbar. When working with a DC system,
remove the busbar connector before working on a device. Exposed live voltages are present at the
device end; exposure to these may cause injury.
A voltage mismatch can cause equipment damage and may pose a fire hazard. If the voltage indicated
on the label is different from the power outlet voltage, do not connect the chassis to that receptacle.
Warning
Warning
Warning
To prevent bodily injury when mounting or servicing this unit in a rack, you must take special
precautions to ensure that the system remains stable. The following guidelines are provided to ensure
your safety:
—This unit should be mounted at the bottom of the rack if it is the only unit in the rack.
—When mounting this unit in a partially filled rack, load the rack from the bottom to the top with the
heaviest component at the bottom of the rack.
—If the rack is provided with stabilizing devices, install the stabilizers before mounting or servicing
the unit in the rack.
The ports labeled “Ethernet,” “10BaseT,” “Token Ring,” “Console,” and “AUX” are safety extra-low
voltage (SELV) circuits. SELV circuits should only be connected to other SELV circuits. Because the
BRI circuits are treated like telephone-network voltage, avoid connecting the SELV circuit to the
telephone network voltage (TNV) circuits.
Ethernet cables must be shielded when used in a central office environment.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-5
Page 74

Safety Requirements
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
An exposed wire lead from a DC-input power source can conduct harmful levels of electricity. Be sure
that no exposed portion of the DC-input power source wire extends from the terminal block plug.
This equipment is intended to be grounded. Ensure that the host is connected to earth ground during
normal use.
Metal objects heat up when connected to power and ground, and can cause serious burns.
To prevent personal injury or damage to the chassis, lift the unit only by grasping the chassis
underneath its lower edge.
Never attempt to lift the chassis with the handles on the power supplies, fan trays, or the switching
modules. These handles are not designed to support the weight of the chassis. Using them to lift or
support the chassis can result in severe damage to the equipment and serious bodily injury.
Two people are required to lift the chassis. Use the handles on the chassis sides. To prevent injury,
keep your back straight and lift with your legs, not your back. To prevent damage to the chassis and
components, never attempt to lift the chassis with the handles on the power supplies, the filter
module, or on the blower assembly. These handles are not designed to support the weight of
the chassis.
2-6
Warning
If you use wiring terminations, use only the recommended ferrules. These terminations should be the
appropriate size for the wires and should clamp the conductor firmly.
Warning
Before connecting or disconnecting ground or power wires to the chassis, ensure that power is
removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel
board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF position, and tape the switch
handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF position. Use a voltmeter to test for 0 (zero) voltage at the
power terminals on the chassis.
Warning
This unit has more than one power supply connection; all connections must be removed completely
to completely remove power from the unit.
Warning
Only a DC power source that is isolated from AC mains with reinforced insulation, and that complies
with the other safety extra-low voltage (SELV) requirements in one or more of the following: UL 60950,
UL1950, CSA 950, EN 60950, and IEC950, can be connected to a Cisco 6260 system. This requirement
ensures that in a catastrophic power source fault condition, hazardous voltages are not present on
power terminals and connectors.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 75

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Safety Requirements
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Class 1 laser product.
Do not stare into the beam or view it directly with optical instruments.
This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area is where
access can only be gained by service personnel through the use of a special tool, lock and key, or
other means of security, and is controlled by the authority responsible for the location.
When installing the unit, always make the ground connection first and disconnect it last.
This equipment is to be installed and maintained by service personnel only as defined by AS/NZS 3260
Clause 1.2.14.3 Service Personnel.
A readily accessible two-poled disconnect device must be incorporated in the fixed wiring.
To reduce the risk of fire, use only No. 26 AWG or larger telecommunication line cord.
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence of a suitably installed
ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are
uncertain that suitable grounding is available.
During this procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the card. Do not directly
touch the backplane with your hand or any metal tool, or you could shock yourself.
Use copper conductors only.
Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: they prevent exposure to
hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic interference (EMI)
that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct the flow of cooling air through the chassis. Do not
operate the system unless all cards, faceplates, front covers, and rear covers are in place.
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-7
Page 76

Safety Requirements
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Connect the unit only to DC power source that complies with the Safety Extra-Low Voltage (SELV)
requirements in IEC 60950 based safety standards.
Do not use this product near water; for example, near a bathtub, washbowl, kitchen sink or laundry
tub, in a wet basement, or near a swimming pool.
Never install telephone wiring during an electrical storm.
Never install telephone jacks in wet locations unless the jack is specifically designed for
wet locations.
Never touch uninsulated telephone wires or terminals unless the telephone line has been
disconnected at the network interface.
Use caution when installing or modifying telephone lines.
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Avoid using a telephone (other than a cordless type) during an electrical storm. There may be a remote
risk of electric shock from lightning.
Do not use a telephone to report a gas leak in the vicinity of the leak.
To prevent personal injury or damage to the chassis, never attempt to lift or tilt the chassis using the
handles on the port adapters; these types of handles are not designed to support the weight of the unit.
Lift the unit only by grasping the chassis underneath its lower edge.
This equipment needs to be grounded. Use a green and yellow 14 AWG ground wire to connect the
host to earth ground during normal use.
This is a Class A product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control Council for Interference by
Information Technology Equipment (VCCI). If this equipment is used in a domestic environment, radio
disturbance may arise. When such trouble occurs, the user may be required to take corrective
actions.
2-8
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 77

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Safety Requirements
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
The DS3 ports are not intended to be connected to cables that run outside the building where it is
installed. For any connections outside the building, the DS3 ports must be connected to a network
termination unit (NTU). NTU devices should comply with appropriate national safety standards such
as UL 1950, CSA 950, EN 60950, IEC 950, and AS 3260.
This product requires short-circuit (overcurrent) protection, to be provided as part of the building
installation. Install only in accordance with national and local wiring regulations.
High-performance devices on this card can get hot during operation. To remove the card, hold it by
the faceplate and bottom edge. Allow the card to cool before touching any other part of it or before
placing it in an antistatic bag.
Do not reach into a vacant slot or chassis while you install or remove a module or a fan. Exposed
circuitry could constitute an energy hazard.
2.1.3 Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Proper electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection is required whenever you handle Cisco equipment. ESD
damage, which can occur when electronic cards or components are improperly handled, results in
complete or intermittent failures. Use an antistatic strap during handling.
Follow these guidelines to prevent ESD damage:
• Always use an ESD ankle or wrist strap and ensure that it makes good skin contact.
• Connect the equipment end of the strap to the ESD jack on the top of the chassis at the right
front corner.
• When you install a component, use available ejector levers or captive installation screws to properly
seat the bus connectors in the backplane or midplane. These devices prevent accidental removal,
provide proper grounding for the system, and help to ensure that bus connectors are properly seated.
• When you remove a component, use available ejector levers or captive installation screws to release
the bus connectors from the backplane or midplane.
• Handle the I/O module by the edges only; avoid touching the printed circuit boards or connectors.
• Avoid touching the printed circuit boards or connectors on the NI-2 cards or line cards.
• Place a removed component board-side-up on an antistatic surface or in a static-shielding
container. If you plan to return the component to the factory, immediately place it in a
static-shielding container.
• Avoid contact between the printed circuit boards and clothing. The wrist strap protects components
from ESD voltages on the body only; ESD voltages on clothing can still cause damage.
Caution Periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap. Ensure that the measurement is between 1
and 10 megohms.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-9
Page 78

Safety Requirements
2.1.4 General Maintenance Guidelines
This section covers the following topics:
• Hot Swapping Cards, page 2-10
• Hot Swapping I/O Modules, page 2-10
• Installation and Replacement Suggestions, page 2-11
2.1.4.1 Hot Swapping Cards
Hot swapping allows you to remove and replace cards without disconnecting the system power. The
Cisco 6260 chassis supports hot swapping for the following cards:
• Quad-port DMT ATU-C (4xDMT)
• Quad-port DMT ATU-C over ISDN (4xDMT over ISDN)
• Quad-port flexi ATU-C (4xflexi)
• Quad-port STU-C (4xSDSL)
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
• Octal-port DMT ATU-C (8xDMT)
• Octal-port DMT ATU-C (8xDMT over ISDN)
• Octal-port G.SHDSL SHTU-C (8xG.SHDSL)
When the system detects that you have added or removed a line card, it automatically runs diagnostic
and discovery routines and acknowledges the presence or absence of the line card. If you remove and
replace a line card with one of the same type, the newly installed line card receives the same provisioning
as the original card. The system resumes operation without any operator intervention.
Note Hot swapping line cards interrupts service for the subscribers assigned to that line card.
The Cisco 6260 also supports hot swapping for the DS3/2DS3 and OC-3c/OC-3c NI-2 cards. Hot
swapping active NI-2 cards interrupts service for the entire system until the NI-2 card is replaced or until
a redundant NI-2 takes over system operations. However, you can hot swap standby NI-2 cards without
interrupting service.
2.1.4.2 Hot Swapping I/O Modules
Hot swapping allows you to remove and replace an I/O module without disconnecting the system power.
The Cisco 6260 chassis supports hot swapping for the I/O module, but removing the I/O module
interrupts the service for the entire system until it is replaced.
2-10
Caution The I/O module must be installed and replaced by a trained technician only.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 79

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
2.1.4.3 Installation and Replacement Suggestions
The following are recommended installation and replacement practices for the Cisco 6260 system cards
and modules.
Caution Any card that is only partially connected to the backplane can disrupt system operation.
• Do not force the line card into its slot. This action can damage the pins on the backplane if they are
not aligned properly with the card.
• Ensure that the card is straight and not at an angle when you install the card in the slot. Installing
the card at an angle can damage the card. Use the guide rails to install the card correctly.
• Fully depress the ejector tabs to ensure that the card connector mates with the backplane correctly.
Firmly seat the card in the slot by locking the card.
• Ensure that the I/O module is straight and parallel to the top of the chassis when you attach the
module to the chassis. The pins on the connectors can be damaged if the module is not
installed correctly.
Site Requirements
2.2 Site Requirements
This section describes requirements for the site at which the Cisco 6260 system is to be installed. Before
you install the Cisco 6260 system, ensure that all the criteria in this section are met. The section
describes the following:
• Environmental Requirements, page 2-11
• Power Requirements, page 2-14
• Rack-Mounting Requirements, page 2-15
2.2.1 Environmental Requirements
Proper operation of the Cisco 6260 system depends on a proper environment. Before you install the
Cisco 6260 system, ensure that all the criteria in this section are met. This section describes the following
environmental requirements:
• Temperature, Altitude, and Humidity, page 2-12
• Ventilation, page 2-12
• Space, page 2-13
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-11
Page 80

Site Requirements
2.2.1.1 Temperature, Altitude, and Humidity
The Cisco 6260 system can tolerate a wide range of temperatures. Tabl e 2 -1 provides the Cisco
recommendations for temperature, altitude, and humidity conditions in a central office (CO)
environment.
Table 2-1 CO Operating Environment Requirements
Environmental Specifications Description
Temperature
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
41º to 104ºF (5º to 40ºC)—Operating
23º to 131ºF (–5º to 55ºC)—Short-term operating
Warning
2.2.1.2 Ventilation
Altitude
Humidity
To prevent the system from overheating, do not operate it in an area that exceeds the maximum
recommended ambient temperature of 104°F (40°C).
0 to 10,000 ft (0 to 3048 m)
5 to 95% (noncondensing)
The Cisco 6260 fans maintain a suitable operating temperature for the internal circuitry. Ensure that the
air intake vents at the lower front of the chassis and the air exhaust vents on the top of the chassis are
not obstructed in any way.
The third-party POTS splitters do not dissipate heat and should be positioned at the bottom of the rack.
2-12
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 81

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
The air intake vents are located at the bottom front of the chassis, and the air exhaust vents are located
on top of the chassis, as depicted in Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1 Air Flow Through Intake and Exhaust Vents on the Cisco 6260 Chassis.
S
TA
T
U
S
S
T
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
A
C
T
IV
E
A
A
TU
-C
1
A
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
Site Requirements
P
E
M
1
/P
E
M
2
A
U
D
_
C
R
I
T
/
A
U
D
_
M
A
J
A
U
D
_
M
I
N
6
/
0
V
V
IS
_
C
R
IT
1
A
M
A
V
X
IS
_
M
A
J
/V
I
S
_
M
IN
S
T
A
T
_
A
L
A
R
M
S
B
U
S
_
A
/
B
IT
S
_
B
N
I-2
N
I
-1
5
5S
M
-1
55
S
M
B
LA
N
K
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
TA
T
U
S
S
T
A
TU
S
S
T
A
T
US
S
T
A
TU
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
TIV
E
A
U
-C
1
U
-C
2
U
-C
3
U
-C
4
-1
T
T
A
T
U
S
C
T
IV
E
U
-C
1
U
-C
2
U
-C
3
U
-C
4
-1
T
C
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
A
T
U
C
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
A
T
U
-C
1
A
TU
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
TU
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
U
-C
1
A
T
U-C
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
T
-4
D
M
T
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
T
IV
E
A
C
TIV
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
O
1
A
TU
-C
1
A
TU
-C
1
R
E
S
E
2
3
4
U
S
E
-C
1
-C
2
-C
3
-C
4
T
A
TU
-C
2
A
TU
-C
2
TRUNK 1
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
T
R
T
R
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
X
U
-C
X
4
E
C
S
L
S
S
T
K
T
T
A
A
T
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
A
L
A
R
M
S
C
R
IT
IC
A
L
M
A
J
O
R
M
IN
O
R
P
O
W
E
R
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
T
IV
E
F
A
N
1
F
A
N
S
A
A
A
A
A
A
T
U
-4
D
M
2
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
C
N
C
T
IV
E
A
C
TIV
E
S
L
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
TU
-C
2
A
SBTD 2
T
U
-C
2
U
T
U
-C
3
X
A
T
U
-C
3
T
R
T
R
X
X
E
C
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
S
L
S
S
T
K
T
T
E
A
A
T
T
N
E
T
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
T
-4
D
M
T
S
TA
T
U
S
S
TA
TU
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
CT
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U-C
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
U
-C
4
A
TU
-C
A
4
T
U
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
Cisco 6260
S
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
1
A
T
U
-C
1
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
T
U
S
S
TA
T
U
S
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
26681
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U-C
2
A
T
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
TU
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
A
T
D
U
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
A
TU
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
A
T
D
U
M
C
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
2.2.1.3 Space
Note Refer to the appropriate vendor documentation for the dimensions of the third-party POTS splitter.
OL-2365-02
The Cisco 6260 system fits in either a 19-inch (48.26 cm) wide rack or a 23-inch (58.42 cm) wide rack,
if extenders are installed. See Table 2- 2 for individual rack space requirements.
The Cisco 6260 chassis is 23.5 inches (59.69 cm) in height and 10.86 inches (27.58 cm) in depth, taking
13.43 rack units (RUs) of space per chassis. (An RU is equal to 1.75 inches or 4.45 cm.)
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-13
Page 82

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Site Requirements
Depending on your configuration type, plan accordingly so that the CO rack accommodates your needs.
Use Tab le 2 -2 to calculate the rack space necessary for your Cisco 6260 system configuration.
Table 2-2 Rack Space Calculation for the Cisco 6260 System Configurations
Line Instructions Calculation
Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
1
Total number of Cisco 6260 chassis in the rack (include subtending host and subtended
node chassis).
2
Total number of POTS splitters1 in the rack.
3
Number of RUs required for the POTS splitter2.
4
Multiply 13.43 RUs by the total number of chassis on line 1.
5
Multiply line 3 by the total number of POTS splitters on line 2.
6
Add lines 4 and 5 for the total number of RUs needed with your Cisco 6260 with a POTS
splitter configuration.
Cisco 6260 without a POTS Splitter Configuration
6
Total number of Cisco 6260 chassis in the rack.
7
Multiply 13.43 RUs by the total number of chassis on line 6 for the total number of RUs needed with
your Cisco 6260 without a POTS splitter configuration.
1. Third-party POTS splitter
2. See the documentation that accompanied the third-party POTS splitter to determine the number of RUs required. One RU is equal to 1.75
inches (4.45 cm).
2.2.2 Power Requirements
The CO power source or rectifier supplies external power to the system as –48V direct current (DC) from
the fuse and alarm panel. Power connections from the fuse and alarm panel are wired separately to the
Cisco 6260 chassis. Connections for single- and dual-power feeds are provided. The power input
connections are redundant, and only one is required for system operation. The nominal voltage is –48
VDC; the minimum operating value is –36 VDC; and the maximum operating value is –60 VDC.
Caution Before you connect the system to a power source, verify that the power source is properly grounded and
that it falls within the internal power supply rating.
The typical power required for your Cisco 6260 system will depend on your configuration type. Use
Table 2-3 to calculate the power required for each of the Cisco 6260 system components and the total
power required for the system.
Table 2-3 Power Calculation for the Cisco 6260 System
Line Instructions Calculation
1
2
If you are using 4xDMTs, multiply 16.5W by the total number of 4xDMTs installed in the
chassis.
If you are using 4xDMT over ISDNs, multiply 16.5W by the total number of 4xDMT over
ISDNs installed in the chassis.
2-14
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 83

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Site Requirements
Table 2-3 Power Calculation for the Cisco 6260 System
Line Instructions Calculation
3
If you are using 4xflexis, multiply 17.5W by the total number of 4xflexis installed in the
chassis.
4
If you are using 4xSDSLs, multiply 9W by the total number of 4xSDSLs installed in the
chassis.
5
If you are using 8xDMTs, multiply 24W by the total number of 8xDMTs installed in the
chassis.
6
If you are using 8xDMT over ISDNs, multiply 24 W by the total number of 8xDMT over
ISDNs installed in the chassis.
7
If you are using 8xG.SHDSLs, multiply 16.5W by the total number of 8xG.SHDSLs installed
in the chassis.
8
9
10
11
Multiply 33.5W by the number of NI-2 cards installed in the chassis.
Enter 50W for each PEM.
Enter 34.5W for each fan tray.
Add lines 1 through 10. This is the typical power required for the Cisco 6260.
2.2.3 Rack-Mounting Requirements
We recommend that you mount the Cisco 6260 system in a rack. Ensure that vertical hole spacing on the
rack rails meets standard EIA-310-C or ETS300 requirements—1 inch (2.54 cm) spacing.
The Cisco 6260 fits into a 19-inch wide rack, or an ETSI 600-mm-wide (23-inch-wide) rack or cabinet.
Warning
Warning
Two people are required to lift the chassis. Grasp the chassis underneath the lower edge and lift with
both hands. To prevent injury, keep your back straight and lift with your legs, not your back.
To prevent bodily injury when mounting or servicing this unit in a rack, you must take special
precautions to ensure that the system remains stable. The following guidelines are provided to ensure
your safety:
—This unit should be mounted at the bottom of the rack if it is the only unit in the rack.
—When mounting this unit in a partially filled rack, load the rack from the bottom to the top with the
heaviest component at the bottom of the rack.
—If the rack is provided with stabilizing devices, install the stabilizers before mounting or servicing
the unit in the rack.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-15
Page 84

Required Tools and Equipment
2.3 Required Tools and Equipment
Table 2-4 lists the tools and equipment you need to install and connect the Cisco 6260
system components as detailed in Chapter 3, “Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS
Splitter Configuration,” and Chapter 4, “Installing a Cisco 6260 Without a POTS
Splitter Configuration.”
Table 2-4 also lists the tools and equipment you need to remove and install the Cisco 6260 system
components as detailed in Chapter 6, “Upgrading and Maintaining the Cisco 6260 System.”
Table 2-4 Tool and Equipment Requirements Checklist
Check Tools and Equipment
Hardware Components
Cisco 6260 chassis
Line cards (if not already installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis)
• 4xDMT
• 4xDMT over ISDN
• 4xflexi
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
• 4xSDSL
• 8xDMT
• 8xDMT over ISDN
• 8xG.SHDSL
NI-2 card(s) (if not already installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis)
• DS3/2DS3
• DS3+T1/E1 IMA
• OC-3c/OC-3c SMF
I/O module (if not already installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis)
• E3
• E1
• OC-3c
Blank faceplates
Fan trays (if not already installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis)
PEMs (if not already installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis)
Champ cables
Third-party vendor POTS splitter
Software Components
Cisco IOS
•
• CDM
Too ls
A 3/16-inch flat-head screwdriver
A Phillips-head screwdriver
1
or MMF
4
2
3
2-16
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 85

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Table 2-4 Tool and Equipment Requirements Checklist (continued)
Check Tools and Equipment
Required Tools and Equipment
Necessary equipment for ESD protection—Required whenever you handle Cisco DSLAM
equipment, which includes the chassis and cards
Mounting screws—To mount the Cisco 6260 to the rack
Wire-wrapping tool
Wire stripper
Wire for connections:
• 12 american wire gauge (AWG) black and red copper solid or stranded—Used for
Cisco 6260 chassis power connections
• 10 AWG or thicker green or green with yellow stripes copper stranded—Used for the
Cisco 6260 chassis grounding
Tie wraps (optional)
Ferrites that yield an impedance of 53 ohms at 25 MHz and 177 ohms at 100 MHz—For
connecting the Ethernet to the management network
Coaxial cable:
• Type 734A or equivalent
• Type 735A or equivalent
Fiber cable (SMF or MMF)—Used to connect the OC-3c NI-2 card
RJ-45 serial cable to connect the console and auxiliary connectors
RJ-45 connector, straight-through 10BaseT/100BaseTX Ethernet, half/full-duplex
compliant with IEEE 802.3
1. SMF = single-mode fiber.
2. MMF = multimode fiber.
3. The third-party vendor POTS splitter is used in a Cisco 6260 with a POTS splitter configuration only.
4. CDM = Cisco DSL Manager.
Note The Cisco 6260 system has no internal user-serviceable parts.
Warning
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-17
Page 86

Unpacking the Cisco 6260 System
2.4 Unpacking the Cisco 6260 System
Each Cisco 6260 system chassis is securely packaged in a shipping box. The Cisco 6260 system
components ship with the line cards and NI-2 card(s) installed in the chassis.
Caution Proper ESD protection is required whenever you handle Cisco DSLAM equipment. Installation
and maintenance personnel should be properly grounded using ground straps to eliminate the risk of
ESD damage to the equipment. Cards are subject to ESD damage whenever they are removed from the
chassis.
To unpack the Cisco 6260 system, complete the following steps:
Step 1 Inspect the packing containers.
If any damage or other signs of mishandling are evident, inform both the local freight carrier and Cisco
before unpacking. Your freight carrier can provide you with the procedures necessary to file a claim
for damages.
Step 2 Carefully open the box.
Step 3 Remove all packing material.
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
Step 4 Remove the chassis from the box.
Warning
Step 5 Carefully open the additional boxes, remove the packing material, and remove the contents.
Step 6 Open the accessory kits and boxes that contain the cables, ferrites, and management software. Do not
Two people are required to lift the chassis. Grasp the chassis underneath the lower edge and lift with
both hands. To prevent injury, keep your back straight and lift with your legs, not your back.
use a knife to open these boxes.
2.5 Verifying Contents
To verify that your shipment is complete, make sure that you received everything on your packing list,
and then compare your packing list to your order. If any items are missing or you need additional
information, contact the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) at one of the following:
• 800 553-2447
• 408 526-7209
• tac@cisco.com
2.6 Inspecting for Damage
After you verify that all of the equipment is included, carefully examine the assemblies, cards, and cables
for any damage resulting from shipping. If you suspect any damage from shipping, contact your local
freight carrier for procedures on damage claims.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-18
OL-2365-02
Page 87

Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
If you observe any physical defects in the items you ordered, obtain standard warranty service by
delivering the defective part, accompanied by a copy of the dated proof-of-purchase, to the
Cisco Systems Corporate Service Center or an Authorized Cisco Systems Service Center during the
applicable warranty period. Contact the Cisco TAC for the location of your nearest service center.
See the back of the title page for Cisco Systems supplementary warranty information for hardware and
software products.
Inspecting for Damage
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
2-19
Page 88

Inspecting for Damage
Chapter 2 Preparing for Installation
2-20
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 89

CHAPTER
3
Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS
Splitter Configuration
This chapter provides installation procedures for a Cisco 6260 with a POTS splitter configuration.
Note The installation procedures in this chapter apply to a Cisco 6260 system shipped with the individual
hardware components already installed. For information about installing or replacing hardware
components in the Cisco 6260 chassis, see Chapter 6, “Upgrading and Maintaining the
Cisco 6260 System.”
Warning
Caution Before you begin the installation procedures, read the entire chapter for important information and safety
Note Before installing and cabling the equipment, be aware of standard safety practices and the
Tip See the “Cisco 6260 System with a POTS Splitter Configuration” section on page 1-4 for more
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
warnings.
hazards involved in working with electrical circuitry to prevent accidents. See the “Safety
Requirements” section on page 2-1 for cautions and warnings that are necessary to ensure a safe and
hazard-free installation.
To see translations of the warnings that appear in this publication, refer to the Regulatory Compliance
and Safety Information for the Cisco 6260 System document.
information about Cisco 6260 with a POTS splitter configuration components.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
3-1
Page 90

Installation Checklist
3.1 Installation Checklist
When you install a Cisco 6260 with a POTS splitter configuration, be sure that you follow the installation
procedures in the proper sequence. Table 3 - 1 is a checklist of the installation steps in the order in which
they should occur. Detailed installation instructions are located in the sections following Table 3 - 1 .
Caution Proper ESD protection is required whenever you handle Cisco equipment. Installation and maintenance
personnel should be properly grounded using ground straps to eliminate the risk of ESD damage to the
equipment. Cards are subject to ESD damage whenever they are removed from the chassis.
Table 3-1 Installation Checklist—Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
Check Installation Procedure
1. Measure the rack space.
2. Install the third-party POTS splitter(s) in the rack.
3. Attach Cisco 6260 ear brackets.
4. Install the Cisco 6260 chassis in the rack.
5. Install blank faceplates.
6. Ground the Cisco 6260.
7. Ground the third-party POTS splitter.
8. Connect the Cisco 6260 chassis to the third-party POTS splitter.
9. Connect the third-party POTS splitter to the MDF
necessary.
10. Attach the Cisco 6260 power connections.
11. Connect the alarm and BITS clock contacts (optional).
12. Apply power to the system.
13. Verify that the fan trays are operational.
14. Connect the Cisco 6260 to the network.
15. Install a subtended network configuration (optional).
16. Connect the Ethernet to the management network.
17. Connect a console terminal.
18. Connect the auxiliary port (optional).
19. Complete the initial configuration.
1. MDF = main distrubution frame
Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
1
or to the cross connect, as
3-2
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 91

Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
3.2 Installation Procedures
The following sections detail the installation procedures for a Cisco 6260 with a POTS
splitter configuration.
3.2.1 Measure Rack Space
For the rack to remain stable, you must install your Cisco 6260 system from the bottom to the top of the
rack.
Before you install any of the chassis, measure the total rack space required to install your system. The
required rack space depends on the number of Cisco 6260 chassis and third-party POTS splitters that you
plan to use. The number of chassis increases if you plan to install a subtended network.
Note See Chapter 2, “Preparing for Installation,” to determine the total rack space you need for your
configuration.
Installation Procedures
Warning
Warning
Warning
To prevent bodily injury when mounting or servicing this unit in a rack, you must take special
precautions to ensure that the system remains stable. The following guidelines are provided to ensure
your safety:
—This unit should be mounted at the bottom of the rack if it is the only unit in the rack.
—When mounting this unit in a partially filled rack, load the rack from the bottom to the top with the
heaviest component at the bottom of the rack.
—If the rack is provided with stabilizing devices, install the stabilizers before mounting or servicing
the unit in the rack.
Two people are required to lift the chassis. Grasp the chassis underneath the lower edge and lift with
both hands. To prevent injury, keep your back straight and lift with your legs, not your back.
Never attempt to lift the chassis with the handles on the power supplies, fan trays, or the switching
modules. These handles are not designed to support the weight of the chassis. Using them to lift or
support the chassis can result in severe damage to the equipment and serious bodily injury.
If you plan to expand your system to include more chassis in the future, allow space in the rack for
additions, keeping in mind the weight distribution and stability of the rack.
3.2.2 Install the Third-Party POTS Splitter
The third-party POTS splitter is installed directly below the Cisco 6260 chassis in the rack.
Refer to the appropriate vendor documentation for installation procedures for the third-party
POTS splitter.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
3-3
Page 92

Installation Procedures
3.2.3 Attach Ear Brackets to the Cisco 6260
Verify that the ear brackets on the sides of the chassis are in the proper configuration to fit the rack, and if
necessary, reinstall them. Ear brackets can be installed in two ways, as shown in Figure 3-1:
Figure 3-1 Mounting Options for Ear Brackets
Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
PEM 1/PEM 2
AUD_CRIT/AUD_MAJ
AUD_MIN/VIS_CRIT
60V
1 A MAX
VIS_MAJ/VIS_MIN
STAT_ALARMS
BUS_A/BITS_B
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
TA
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
TIV
E
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
Cisco 6260
Bracket orientation for
ETS 600-mm rack
PEM 1/PEM 2
AUD_CRIT/AUD_MAJ
AUD_MIN/VIS_CRIT
VIS_MAJ/VIS_MIN
STAT_ALARMS
BUS_A/BITS_B
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
Cisco 6260
Bracket orientation
for 19-inch rack
60V
1 A MAX
26876
3-4
For Cisco 6260 installation in an ETSI 600-mm (23- inch) rack, attach the L-shaped ear brackets so that
the short sides are against the chassis wall and the long sides protrude from the chassis.
For Cisco 6260 installation in a 19-inch rack, attach the ear brackets so that the long side of each L is
against the chassis wall and the short side protrudes from the chassis.
Note The ear brackets are installed in the factory for a 19-inch rack configuration.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 93

Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
3.2.4 Install the Cisco 6260 Chassis
Complete the following steps to install the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Installation Procedures
Warning
Two people are required to lift the chassis. Grasp the chassis underneath the lower edge and lift with
both hands. To prevent injury, keep your back straight and lift with your legs, not your back.
Step 1 Connect a grounding strap to the ESD grounding jack that is located on the top right of the front of the
Cisco 6260 chassis.
Step 2 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, attach the two mounting aids to the rack above the third-party POTS
splitter. Use two screws for each mounting aid, as shown in Figure 3-2. The lower edge of the mounting aid
lines up with the bottom of the chassis.
Figure 3-2 Screw the Mounting Aids to the Rack
26877
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
3-5
Page 94

Installation Procedures
Step 3 Carefully lift the chassis from underneath and rest it on the mounting aids, as shown in Figure 3-3.
Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
Figure 3-3 Mounting Aids Support the Chassis During Installation
PEM 1/PEM 2
AUD_CRIT/AUD_MAJ
AUD_MIN/VIS_CRIT
60V
1 A MAX
VIS_MAJ/VIS_MIN
STAT_ALARMS
BUS_A/BITS_B
N
I-
2
N
I
-1
5
5S
M
1
55
S
M
B
L
A
N
K
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
TU
-C
4
A
TU
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
A
T
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
A
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
T
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
TU
-C
2
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
D
M
T
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
TA
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
TIV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
A
TU
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
3
A
TU
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
D
M
T
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
TIV
E
A
C
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
3
A
TU
-C
4
A
T
U
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
T
U
S
S
T
A
IV
E
A
C
T
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
O
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
TU
-C
1
R
E
S
E
-C
2
-C
3
-C
4
T
U
S
IV
E
-C
1
-C
2
-C
3
-C
4
T
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
TRUNK 1
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
T
R
T
R
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
X
4
X
E
C
S
L
S
S
T
K
T
T
A
A
T
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
A
L
A
R
M
S
C
R
IT
IC
A
L
M
A
J
O
R
M
IN
O
R
P
O
W
E
R
R
E
A
D
Y
A
C
T
IV
E
F
A
N
1
F
A
N
2
S
TA
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
C
N
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
S
L
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
A
T
U
-C
2
A
SBTD 2
T
U
-C
2
U
A
T
U
-C
3
X
A
T
U
-C
3
T
R
T
R
X
X
E
A
C
TU
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
S
L
S
S
T
K
T
T
E
A
A
T
T
N
E
T
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
TIV
E
A
C
T
A
T
U
-C
1
A
TU
-C
1
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
TU
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
A
T
D
U
M
C
T
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
TA
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
TU
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
A
T
D
U
M
C
T
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
TIV
E
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
-C
2
A
TU
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
Cisco 6260
26878
Step 4
Push the chassis back into the rack.
Step 5 Using a Phillips-head screwdriver, screw the ear brackets on the chassis to the rack. Use two screws at the
top of each ear bracket and two at the bottom (four screws per bracket). For stability, make sure you use at
least one round hole at each end of each bracket (the ear brackets have both round and oval holes).
Step 6 Repeat Step 1 through Step 5 for each Cisco 6260 chassis that you are installing.
3.2.5 Install Blank Faceplates
Blank faceplates should occupy any empty slots in the Cisco 6260 chassis. Blank faceplate installation
is similar to line card installation.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
3-6
OL-2365-02
Page 95

Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
Complete the following steps to install blank faceplates in the Cisco 6260:
Step 1 Connect a grounding strap to the ESD grounding jack that is located on the top right of the front of the
Cisco 6260 chassis.
Step 2 Vertically align the blank faceplate edge with the guides at the top and bottom of the slot.
Step 3 Lift up on the ejector tab and gently apply pressure to the bottom of the faceplate while pushing the blank
faceplate into the slot.
Step 4 Push on the faceplate to fully seat the blank faceplate.
Step 5 Press down on the ejector tab to secure the faceplate.
3.2.6 Ground the Cisco 6260
Complete the following steps to connect the grounding lug on the Cisco 6260.
Installation Procedures
Warning
When you are installing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and disconnected
last.
Warning
Before connecting or disconnecting ground or power wires to the chassis, ensure that power is
removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel
board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF position, and tape the switch
handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF position. Use a voltmeter to test for 0 (zero) voltage at the
power terminals on the chassis.
Step 1 Ensure that power in the direct current (DC) circuit is off.
Step 2 Remove all paint or oxidation from the rack at the point of the grounding connection.
Step 3 Measure enough wire to connect the Cisco 6260 to the rack. Use 10 American Wire Gauge (AWG) green
or green with yellow stripes wire to ground the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Note Use only as much wire as is necessary to make the connection.
Step 4 Use a wire stripping tool to remove the covering from the end of the grounding wire. The manufacturer
of the grounding lug might have a specific recommendation about the length of wire to be stripped.
Step 5 Insert the stripped end of the grounding wire into the open end of the grounding lug. Be careful not to
leave any wire strands outside the lug.
OL-2365-02
Step 6 Use the crimping tool to compress the lug onto the wire.
Step 7 To verify the quality of the crimp, inspect it and tug gently on the wire.
Step 8 Locate the three grounding holes on the Cisco 6260 side panel. (See Figure 3-4.)
Step 9 Match the holes in the grounding lug to the appropriately spaced pair of grounding holes on the side of
the chassis. Use the top two holes for a 5/8-inch lug, as shown in Figure 3-4. Use the bottom two holes
for a 3/4-inch lug.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
3-7
Page 96

Installation Procedures
Figure 3-4 System Ground Connection
PEM 1/PEM 2
AUD_CRIT/AUD_MAJ
AUD_MIN/VIS_CRIT
60V
1 A MAX
VIS_MAJ/VIS_MIN
STAT_ALARMS
BUS_A/BITS_B
Grounding
holes in
side of
chassis
S
T
A
TU
S
S
T
A
T
US
S
TA
T
U
S
A
C
TIV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
T
U-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
T
A
T
U
S
A
C
TIV
A
E
C
T
IV
E
A
C
T
IV
E
A
T
U
-C
A
1
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
1
A
T
U
-C
A
2
T
U
-C
2
A
T
U
-C
2
A
TU
-C
A
3
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
3
A
T
U
-C
A
4
T
U
-C
4
A
T
U
-C
4
Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
Grounding
lug
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
A
T
U
C
-1
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
-4
D
M
T
Step 10
Cisco 6260
Insert the screws through the holes in the lug and the chassis. Use the Phillips-head screwdriver to tighten
26677
the screws and secure the grounding lug firmly to the chassis.
Step 11 Prepare the other end of the grounding wire and connect it to an appropriate grounding point in your site.
Step 12 Repeat Step 1 through Step 11 for each Cisco 6260 chassis, as necessary.
3.2.7 Ground the Third-Party POTS Splitter
Refer to the appropriate vendor documentation for grounding procedures for the third-party
POTS splitter.
Note Do not ground the components in a rack by chaining them together.
3-8
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 97

Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
Installation Procedures
3.2.8 Connect the Cisco 6260 to the Third-Party POTS Splitter
Refer to the appropriate vendor documentation for cabling procedures for the third-party POTS splitter.
3.2.9 Connect the Third-Party POTS Splitter to the MDF or to the Cross Connect
Refer to the appropriate vendor documentation for procedures for connecting the POTS splitter to the
MDF or to the cross connect.
3.2.10 Attach Cisco 6260 Power Connections
External power is supplied to the system as –48 VDC from the central office (CO) power source or
rectifier to the fuse and alarm panel. Power is fed from the fuse and alarm panel to receptacles in terminal
blocks located on the power entry modules (PEMs) installed in the Cisco 6260 chassis.
Connect the power connections on each PEM to separate power sources to achieve full power redundancy. If
you do not require power redundancy, use the terminals on a single PEM, or connect both PEMs to a single
power source.
Complete these instructions to connect the Cisco 6260 system to a –48 VDC power source. Ground the
chassis before you attempt this procedure, as described in the “Ground the Cisco 6260” section on
page 3-7.
Note See Chapter 2, “Preparing for Installation,” for the calculation tables that you need to determine the
minimum power requirements for your system.
Caution To prevent the system from powering up, do not install the fuses at this time. If the fuses are already
installed in the fuse and alarm panel, remove them. You can replace the fuses after the system is installed
and connected.
Follow these instructions to attach the power connections to the Cisco 6260 PEM:
Step 1 Verify that power in the DC circuit is off.
Warning
Before connecting or disconnecting ground or power wires to the chassis, ensure that power is
removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is OFF, locate the circuit breaker on the panel
board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit breaker to the OFF (0) position, and tape the
switch handle of the circuit breaker in the OFF (0) position. Use a voltmeter to test for 0 (zero) voltage
at the power terminals on the chassis.
OL-2365-02
Step 2 Connect a grounding strap to the ESD grounding jack that is located on the top right of the front of the
Cisco 6260 chassis.
Step 3 Prepare the wire for the Cisco 6260 power and grounding connections, as follows:
a. Measure enough wire (6 to 10 AWG multistranded copper wire) to connect each of the PEM power
connections to the fuse and alarm panel, as well as enough to connect the grounding receptacle on
the PEM terminal block to the grounding connection at the DC power source.
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
3-9
Page 98

Installation Procedures
Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
b. Cut the ends of the power and ground wires so that the ends are straight, not slanted.
c. Measure 0.43 inch (11 mm) up from the end of each power and ground wire and place a mark at that
point. These are the wire ends that will be connected to the Cisco 6260.
d. Use the wire stripping tool to remove 0.43 inch (11 mm) of the covering from both ends of each
wire. Trim the ends of the covering so that they are straight, as shown in Figure 3-5, not slanted.
Figure 3-5 Strip and Square Off Power and Ground Wires
0.43 in.
(11 mm)
26689
Warning
Remove the covering from exactly the specified length of each power wire. If you strip too much of
the covering, exposed wire protruding from the terminal block will create an electrical hazard. If you
strip too little of the covering, the wire may not make a good contact with the terminal, or it may not
be held securely in place in the terminal block.
Step 4 Use a flat-head screwdriver to turn all three screws on the terminal block counterclockwise to open the
terminal connectors: + (positive), – (negative), and ground. This step ensures that the correct opening is
presented for the wires, as shown in Figure 3-6.
3-10
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
Page 99

Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
Figure 3-6 Positioning the Power and Ground Terminals to Accept Wires
INPUT OK
OUT FAIL
FAN TRAY 1
FANTRAY 2
Correct
terminal
position
(open)
Installation Procedures
INPUT OK
OUT FAIL
FAN TRAY 1
FANTRAY 2
26693
Incorrect
terminal
position
(closed)
Step 5 Insert the end of the grounding wire into the grounding receptacle, which is the bottom receptacle in the
terminal block on the PEM (see Figure 3-7). The stripped part of the wire must be fully inserted into the
terminal block so that no bare wire is exposed.
Step 6 Ensure that no wire strands are left outside the connector.
OL-2365-02
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
3-11
Page 100

Installation Procedures
Step 7 Using the screwdriver and a clockwise motion, tighten the ground screw in the terminal block. Gently tug on
Chapter 3 Installing a Cisco 6260 with a POTS Splitter Configuration
the wire to ensure that it is firmly in place.
Figure 3-7 Insert Grounding Wire into Grounding Receptacle
INPUT OK
OUT FAIL
FAN TRAY 1
FANTRAY 2
INPUT OK
OUT FAIL
FAN TRAY 1
FANTRAY 2
26690
Step 8 Make sure that the other end of the grounding wire is connected to ground at the DC power source.
Step 9 If you are connecting two power sources to the Cisco 6260 system, repeat Step 2 through Step 8 for the
second PEM.
Warning
Only a DC power source that is isolated from the AC main power source with reinforced insulation,
and that complies with the other safety extra-low voltage (SELV) requirements in UL1950, CSA 950 3rd
Edition, EN 60950, and IEC950, can be connected to a Cisco 6260 system. This requirement ensures that
in a catastrophic power source fault condition, hazardous voltages are not present on power
terminals and connectors.
3-12
Cisco 6260 Hardware Installation Guide
OL-2365-02
 Loading...
Loading...