Page 1

Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
April 10, 2015
Cisco Systems, Inc.
www.cisco.com
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide.
Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers
are listed on the Cisco website at
www.cisco.com/go/offices.
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this
URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display
output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in
illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco 3900 Series,Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Software Configuration Guide
© 2009-2014 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

Objectives
Preface
This preface describes the objectives, audience, organization, conventions of this guide, and the
references that accompany this document set. The following sections are provided:
• Objectives, page iii
• Audience, page iii
• Organization, page iii
• Conventions, page v
• Related Documentation, page vi
• Searching Cisco Documents, page vii
This guide provides an overview and explains how to configure the various features for the Cisco 1900
series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 3900 series integrated services routers generation 2 (ISR G2). Some
information may not apply to your particular router model.
Audience
This document is written for experienced technical workers who install, monitor, and troubleshoot
routers under a service contract, or who work for an information technology (IT) department.
Organization
This guide is divided into three parts:
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
• Part 1—Configuring the Router
• Part 2—Configuring the Access Point
• Part 3—Appendix
2iii
Page 4
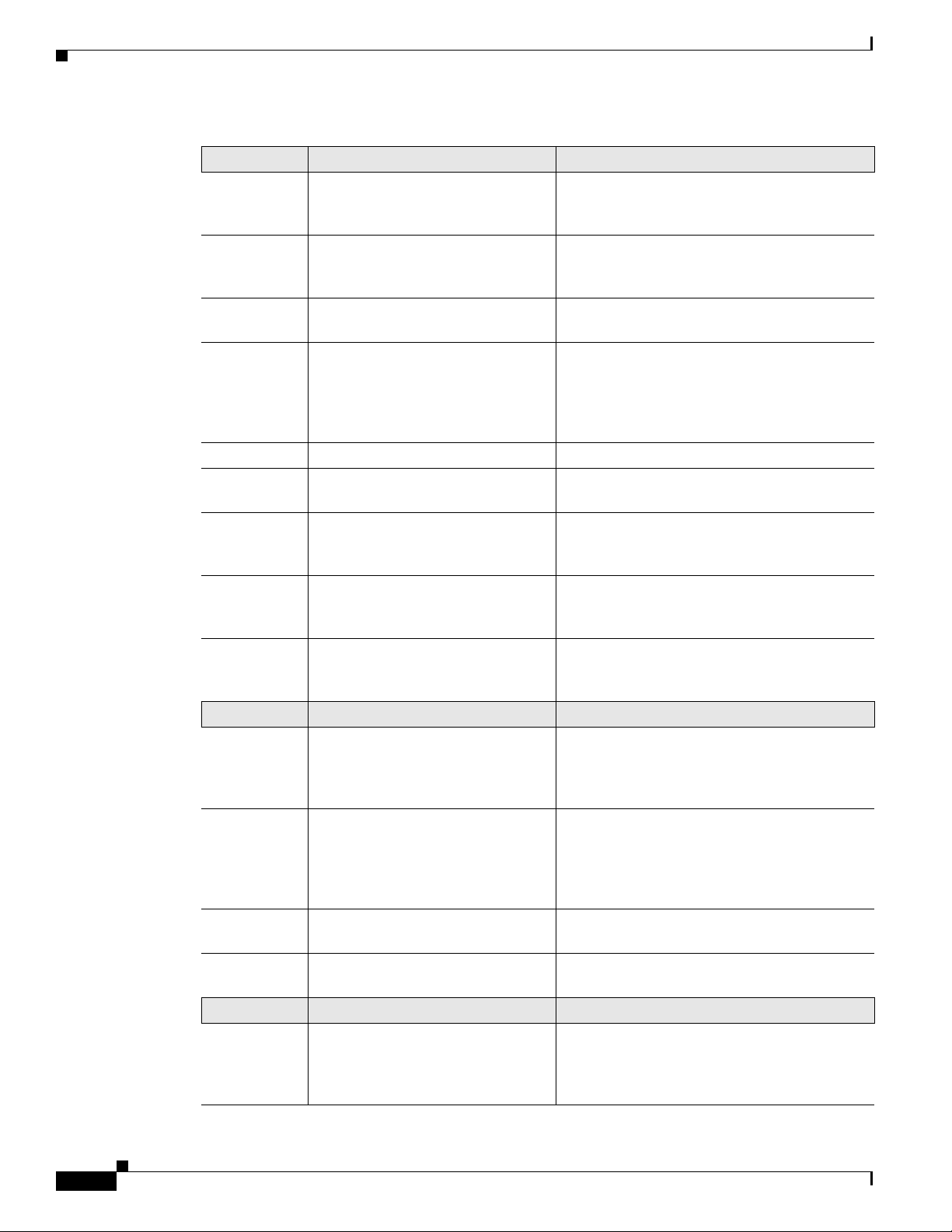
Organization
Part 1 Configuring the Router Description
Module 1
Overview of Hardware and Software Describes new hardware and software features
in this release, features by platform, new slots,
common ports, and getting started tasks.
Module 2
Basic Router Configuration Describes how to perform the basic router
configuration, interface configuration, and
routing configuration.
Module 3
Module 4
Configuring Backup Data Lines and
Remote Management
Configuring Power Efficiency
Management
Describes how to configure backup interfaces,
dial backup, and remote management.
Describes the hardware and software power
efficiency management features on the router.
See Cisco EnergyWise Configuration Guide for
information about configuring power efficiency
management on modules and interface.
Module 5
Module 6
Module 7
Configuring Security Features Describes how to configure security features.
Unified Communications on Cisco
Integrated Services Routers
Configuring Next-Generation
High-Density PVDM3 Modules
Describes voice application services that are
supported on these routers.
Describes how to configure the new
next-generation PVDM3
router.
Module 8
Multi-Gigabit Fabric
Communication
Describes how modules and interface cards
inter-communicate using the MGF
router.
Module 9
Upgrading the Cisco IOS Software Describes how to upgrade the Cisco IOS
software image on the router or the access
point.
Part 2 Configuring the Access Point Description
Module 1
Wireless Overview Describes the autonomous image and recovery
image shipped on the Cisco 1941W access point
flash. Explains the default autonomous mode
and Cisco Unified mode.
Module 2
Configuring the Wireless Device Describes how to configure the autonomous
wireless device, how to upgrade the
autonomous software to Cisco Unified
software, and how to configure a Unified
wireless device.
Module 3
Configuring the Radio Settings Describes how to configure the radio settings
for the wireless device.
Module 4
Administering the Wireless Device Describes many administration tasks for the
wireless device.
Part 3 Appendix Description
Appendix A
Cisco IOS CLI for Initial
Configuration
Describes how to perform the initial
configuration of the router using the Cisco IOS
CLI, and additional configuration procedures
for the router.
1
installed on your
2
on the
Preface
2iv
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 5

Chapter Preface
Conventions
Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
Appendix B
Using CompactFlash Memory Cards Describes how to use Advanced Capability CF3
memory cards on the router.
Appendix C
Using ROM Monitor Describes how to use the ROM monitor to
manually load a system image, upgrade the
system image when there are no TFTP servers
or network connections, or prepare for disaster
recovery.
Appendix D
Changing the Configuration
Register Settings
Describes the 16-bit configuration register in
NVRAM and how to make changes to the
register settings using the Cisco IOS CLI.
1. PVDM3 = packet voice/data module
2. MGF = Multi-Gigabit Fabric.
3. CF = CompactFlash.
Convention Indication
bold font Commands and keywords and user-entered text appear in bold font.
italic font Document titles, new or emphasized terms, and arguments for which you supply
values are in italic font.
[ ] Elements in square brackets are optional.
{x | y | z } Required alternative keywords are grouped in braces and separated by
vertical bars.
[ x | y | z ] Optional alternative keywords are grouped in brackets and separated by
vertical bars.
string A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the string or
the string will include the quotation marks.
courier font Terminal sessions and information the system displays appear in courier font.
< > Non-printing characters such as passwords are in angle brackets.
[ ] Default responses to system prompts are in square brackets.
!, # An exclamation point (!) or a pound sign (#) at the beginning of a line of code
indicates a comment line.
Note Means reader take note.
Tip Means the following information will help you solve a problem.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might perform an action that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
2v
Page 6

Related Documentation
Timesaver Means the described action saves time. You can save time by performing the action described in
the paragraph.
Preface
Warning
Means reader be warned. In this situation, you might perform an action that could result in
bodily injury.
Related Documentation
In addition to the Cisco 1900 series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 3900 series ISR Software
Configuration Guide (this document), the following reference guides are included:
Type of Document Links
Hardware
• Read Me First for the Cisco 1900 Series, 2900 Series, and 3900 Series
Integrated Services Routers.
• Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco 1900 Series
Integrated Services Routers.
• Cisco 2900 Series and 3900 Series Integrated Services Routers
Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Hardware Installation
Guide.
• Cisco Modular Access Router Cable Specifications
• Installing, Replacing, and Upgrading Components in Cisco Modular
Access Routers and Integrated Services Routers
2vi
• Overview of Cisco Network Modules for Cisco Access Routers
• Cisco Interface Cards for Cisco Access Routers
• Installing Cisco Network Modules in Cisco Access Routers
• Installing Cisco Interface Cards in Cisco Access Routers
Regulatory Compliance
• Declarations of Conformity and Regulatory Information for Cisco
Access Products with 802.11a/b/g and 802.11b/g Radios
• Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco 2900 Series
Integrated Services Routers
• Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for Cisco 3900 Series
Integrated Services Routers
Software Activation
Configuration
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
• Software Activation for Cisco Integrated Services Routers
• Cisco IOS Software Activation Configuration Guide
• Cisco CP Express User’s Guide
Page 7

Chapter Preface
Type of Document Links
Cisco Internet Operating
System Software (IOS)
Cisco IOS software release 15.0 is the next IOS release following the Cisco
IOS 12.4(24)T release. For information about new features in Cisco IOS
software release 15.0, see the Cisco IOS software pages at Cisco.com.
Go here to read a product bulletin that specifies the software feature sets
available for Cisco 1900, 2900 and 3900 Series Integrated Services
Routers in release 15.0. It also issues recommendations for Flash and
DRAM memory configuration.
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/iosswrel/ps8802/ps5460/
product_bulletin_c25-566278_ps10537_Products_Bulletin.html
Wireless
Vo i c e
Modules
• Cisco IOS Command Reference for Cisco Aironet Access Points and
• Wireless LAN Controllers
• Unified Wireless LAN Access Points
• Cisco IOS Voice Port Configuration Guide
• SCCP Controlled Analog (FXS) Ports with Supplementary Features in
• Cisco SRE Internal Service Modules Configuration Guide.
• Cisco Services Ready Engine Configuration Guide.
Searching Cisco Documents
Bridges, versions 12.4(10b) JA and 12.3(8) JEC
Cisco IOS Gateways
• Cisco SRE Service Modules Configuration Guide.
• Connecting Cisco EtherSwitch Service Modules to the Network.
• Cisco EtherSwitch Service Modules Feature Guide.
Searching Cisco Documents
To search a Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) document using a web browser, press Ctrl-F
(Windows) or Cmd-F (Apple). In most browsers, the option to search whole words only, invoke case
sensitivity, or search forward and backward is also available.
To search a PDF document in Adobe Reader, use the basic Find toolbar (Ctrl-F) or the Full Reader
Search window (Shift-Ctrl-F). Use the Find toolbar to find words or phrases within a specific document.
Use the Full Reader Search window to search multiple PDF files simultaneously and to change case
sensitivity and other options. Adobe Reader’s online help has more information about how to search PDF
documents.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
2vii
Page 8

Searching Cisco Documents
Preface
2viii
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 9

Overview of the Hardware and Software
The Cisco 3900 series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 1900 series integrated services routers (ISRs) offer
secure, wire-speed delivery of concurrent data, voice, and video services. The modular design of these
routers provides maximum flexibility, allowing you to configure your router to meet evolving needs.
The routers offer features such as hardware-based virtual private network (VPN) encryption
acceleration, intrusion-protection and firewall functions, and optional integrated call processing and
voice mail. A wide variety of legacy network modules and interfaces, service modules (SMs), internal
services modules (ISMs), next-generation packet voice/data modules (PVDM3), Services Performance
Engines (SPEs), high-density interfaces for a wide range of connectivity requirements, and sufficient
performance and slot density for future network expansion requirements and advanced applications are
available.
Power-saving hardware and software features are incorporated throughout the series. These routers
provide access to the multi-gigabit fabric, which provides a connection between switch ports without
using up external ports. The logical Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interface on the router connects external and
internal modules through the backplane for LAN and WAN switching. Software feature upgrades are
provided through software licensing.
The following sections describe the Cisco 3900 series, 2900 series, and 1900 series ISRs:
• Feature Information, page 2
• New Features by Platform, page 4
• New Slots, page 4
• New Slots and Ports by Platform, page 5
• Common Ports, page 6
• Licensing, page 6
• Getting Started, page 7
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
1
Page 10

Feature Information
Feature Information
Table 1 Feature Information
Feature Description
Services Performance
Engine
Cryptographic Engine
Accelerator
USB Console Cisco 3900 series, 2900 series, and 1900 series ISRs provide an additional
Power Management Some modules and interface cards that are inserted in new slots provide
Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
1
SPEs
are modular motherboards on Cisco 3900 series ISRs. The SPE
houses PVDM3 slots, system memory slots, and the ISM slot. The SPE
provides a modular approach to system upgrades. You simply slide out the
SPE from the router to replace internal modules, or upgrade the SPE to
improve router performance. See Cisco 2900 series and 3900 series
Integrated Services Routers Hardware Installation Guide for instructions.
Cisco 3900 series routers with either Services Performance Engine 200 or
Services Performance Engine 250 have an onboard cryptographic
accelerator that is shared between SSLVPN and IPSec. By default,
acceleration of SSL is disabled so IPSec performance is maximized.
See the “Configuring Security Features” section on page 127 in this guide
for information about enabling the SSLVPN feature.
mechanism for configuring the system through a USB
2
serial console port.
The traditional RJ-45 serial console port is also available.
hardware and software power management features described below:
• High efficiency AC power supplies
• Electrical components with built-in power saving features, such as
RAM select and clock gating
• Ability to disable unused clocks to modules and peripherals
• Ability to power down unused modules and put peripherals into a
reset state, put front panel ports and unused internal components in a
shutdown or reset state
Advanced Capability
CompactFlash
Cisco 3900 series, 2900 series, and 1900 series ISRs use Advanced
Capability CF
3
memory to store the system image, configuration files, and
some software data files.
SFP/Gigabit Ethernet Port Cisco 2921, Cisco 2951 and Cisco 3900 Series routers have an
SFP/Gigabit Ethernet port that supports copper and fiber concurrent
connections. Media can be configured for failover redundancy when the
network goes down. For more information, see the “Configuring Backup
Data Lines and Remote Management” section on page 97.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
2
Page 11

Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
Table 1 Feature Information (continued)
Feature Description
New Modules and
Interface Cards
Multi-Gigabit Fabric
Communication
Integrated Application
Services Features
Feature Information
Cisco 3900 series, 2900 series, and 1900 series ISRs introduce the
following new modules and interface cards, which are inserted in the
following new router slots:
• EHWIC
• PVDM3
• ISM
• SM
Note See the router’s product page at Cisco.com for a complete list of
supported modules and interfaces.
Cisco 3900 series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 1900 series ISRs use a
4
MGF
for the new modules and interface cards to inter-communicate on
the router. Legacy modules that support Cisco HIMI
5
also support MGF
to inter-communicate on the router. Next generation module drivers
integrate with the MGF to perform port configurations, configure packet
flow, and control traffic buffering. All configurations are performed from
the module-side, which may or may not lead to changes on the MGF. For
more information, see the “Configuring Multi-Gigabit Fabric
Communication” section on page 211.
Cisco 3900 series, 2900 series, and 1900 series ISRs offer integrated
security features and voice features.
• See the “Configuring Security Features” section on page 127
• See the “Unified Communications on Cisco Integrated Services
Routers” section on page 169
1. SPE = Services Performance Engine
2. USB = universal serial bus
3. CF = CompactFlash
4. MGF = multi-gigabit fabric
5. HIMI = High-Speed Intrachassis Module Interconnect
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
3
Page 12

Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
New Features by Platform
New Features by Platform
Table 2 shows new feature support by platform.
Table 2 New Features in this Release by Platform
Features 1941 1941W 2901 2911 2921 2951 3925 3925E 3945 3945E
Services Performance Engine N N N N N N Y Y Y Y
Cryptographic Engine
N N N N N N Y
1
Y Y
Acceleration
USB Serial Console Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
Power Management Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y
New Module and Interface Card
YY Y Y YYYYYY
Features
Advanced Capability
YY Y Y YYYYYY
CompactFlash
SFP/Gigabit Ethernet Port N N N N Y Y Y Y Y Y
Multi-Gigabit Fabric
YY Y Y YYYYYY
Communication
Integrated Application Services Y
1. Must have Services Performance Engine 200 installed in the router.
2. Must have Services Performance Engine 250 installed in the router.
3. Does not support Voice application services.
4. Does not support Voice application services. Includes embedded wireless access point that supports Cisco Unified Wireless Architecture.
3
4
Y
Y Y YYYYYY
2
Y
New Slots
Cisco 3900 series, 2900 series, and 1900 series ISRs have introduced new slots on the chassis. The first
column in Tabl e 3 lists the new slot names. The second column lists the corresponding old slot names.
Modules previously inserted in the old slots now insert in the new slots with the help of an adapter card.
For instance, network modules (NMs), enhanced network modules (NMEs), and extension voice
modules (EVMs) use an adapter, or carrier card, to insert into the SM slot. See your router’s hardware
installation guide for adapter information.
Table 3 New Slot Names and Old Slot Names
New Slot Names Old Slot Names
EHWIC HWIC,HWIC-DW, WIC, VWIC, VIC
ISM AIM
1
PVDM3 PVDM
SM NM, NME, EVM
2
SPE
1. AIM is not supported in this release. See your hardware installation guide for more information.
2. The SPE is available only on the Cisco 3900 series ISRs.
—
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
4
Page 13

Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
New Slots and Ports by Platform
This section provides the type and number of the slots and ports available in the Cisco 3900 series,
2900 series, and 1900 series ISRs.
• Cisco 3900 Series ISRs, page 5
• Cisco 2900 Series ISRs, page 5
• Cisco 1900 Series ISRs, page 6
Cisco 3900 Series ISRs
Table 4 lists the slots and ports available on Cisco 3900 series routers.
To view the installation guide, see the following URL
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/2900/hardware/installation/guide/Hardware_Installati
on_Guide.html
Table 4 Cisco 3900 Series Routers
New Slots and Ports by Platform
Router EHWIC SM
Cisco 39454 41 14 23
Cisco 3945E 3 4 1 0 3 2 4
Cisco 39254 21 14 23
Cisco 3925E 3 2 1 0 3 2 4
1. One RJ-45 GE + two combo GE/SFPs.
2. Four RJ-45 GE, or three RJ-45 GE + one combo GE/SFP, or two RJ-45 GE + two combo GE/SFP.
3. One RJ-45 GE + two combo GE/SFPs, or three RJ-45 GEs.
4. Four RJ-45 GE, or three RJ-45 GE + one combo GE/SFP, or two RJ-45 GE + two combo GE/SFP.
Cisco 2900 Series ISRs
Table 5 lists the slots and ports available on Cisco 2900 series routers.
To view the installation guide, see the following URL
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/2900/hardware/installation/guide/Hardware_Installati
on_Guide.html
Table 5 Cisco 2900 Series Routers
Router EHWIC SM
Cisco 29514 22 13 22 1
Cisco 29214 11 13 22 1
Cisco 29114 11 12 23 0
Cisco 29014 00 12 23 0
Dbl-Wide
SM ISM PVDM3 CF
Dbl-Wide
SM ISM PVDM3 CF
GE (RJ-45)/
SFP ports SPE
1
2
3
4
GE (RJ-45)
ports
GE (RJ-45)/
SFP ports
1
1
1
1
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
5
Page 14
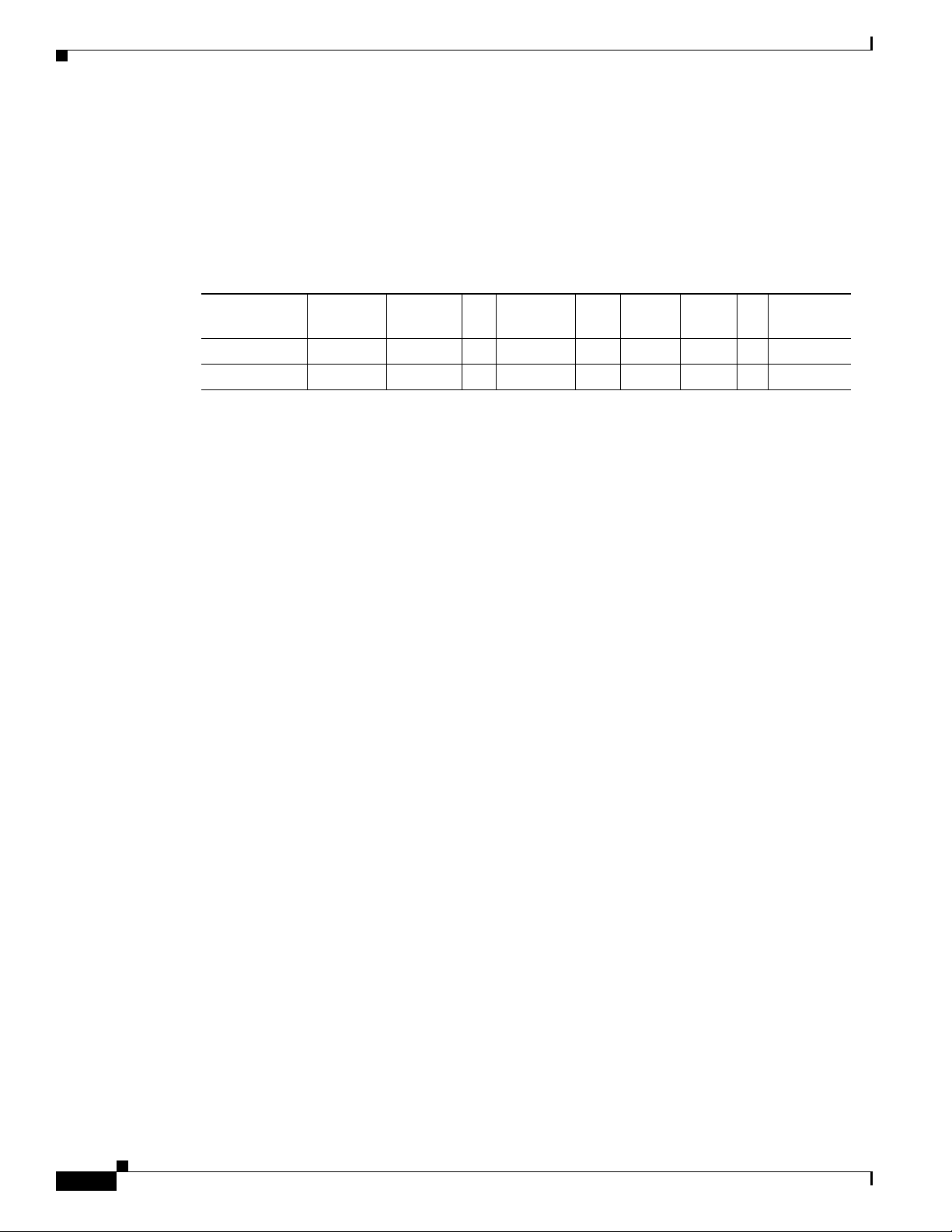
Common Ports
Cisco 1900 Series ISRs
Table 6 lists the slots and ports available on Cisco 1900 series routers.
To view the installation guide, see the following URL
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/1900/hardware/installation/guide/1900_HIG.html
Table 6 Cisco 1900 Series ISR Routers
Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
Router EHWIC
Cisco 1941 2 1 0 0 1 0 0 2 2
Cisco 1941W 2 1 0 0 0 0 1 2 2
1. One of the two EWHIC slots is adouble-wide EWHIC slot,giving the appearance of three EWHIC slots.
Common Ports
The following ports are common among Cisco 3900 series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 1900 series
routers:
• Gigabit Ethernet RJ45—Ports available through an RJ45 connector.
• Gigabit Ethernet RJ45/SFP—Ports available through RJ45- SFP connectors. Connection supports
fail-over if the secondary connection goes down.
• RS232 Aux—Supports modem control lines and remote administration for box-to-box redundancy
applications.
• RS232 Serial Console—Supports modem control lines and remote administration of the router with
the proprietary cable shipped in the box.
• Type A USB 2.0—Supports USB-based flash memory sticks, security tokens, and USB-compliant
devices.
• Type B mini-port USB Serial Console—Supports modem control lines and remote administration of
the router using a type B USB-compliant cable.
Dbl-Wide
1
EHWIC SM
Dbl-Wide
SM ISM PVDM3 WLAN CF
GE (RJ-45)
ports
Licensing
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
6
Cisco 3900 series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 1900 series ISRs support Cisco IOS software
entitlement. Your router is shipped with the software image and the corresponding permanent licenses
for the technology packages and features that you specified preinstalled. You do not need to activate or
register the software prior to use. If you need to upgrade or install a new technology package or feature
see Software Activation on Integrated Services Router,
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html.
Page 15

Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
Getting Started
See the router-specific hardware installation guide to install the router in an appropriate location.
Connect the router with the appropriate cables. Supply power to the router and perform the initial
software configuration using Cisco Configuration Professional Express. After the initial configuration
is completed, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Follow instructions in the “Basic Router Configuration” section on page 13 to perform additional router
configurations.
Step 2 (Optional) If you are setting up the Cisco 1941W ISR, follow instructions in the “Configuring the
Wireless Device” section on page 247 to configure the embedded wireless device on the router.
Step 3 Follow instructions in the “Configuring Security Features” section on page 127 to configure security
features on the router.
Step 4 Follow instructions in the “Unified Communications on Cisco Integrated Services Routers” section on
page 169 to configure Voice features on the router.
Getting Started
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
7
Page 16
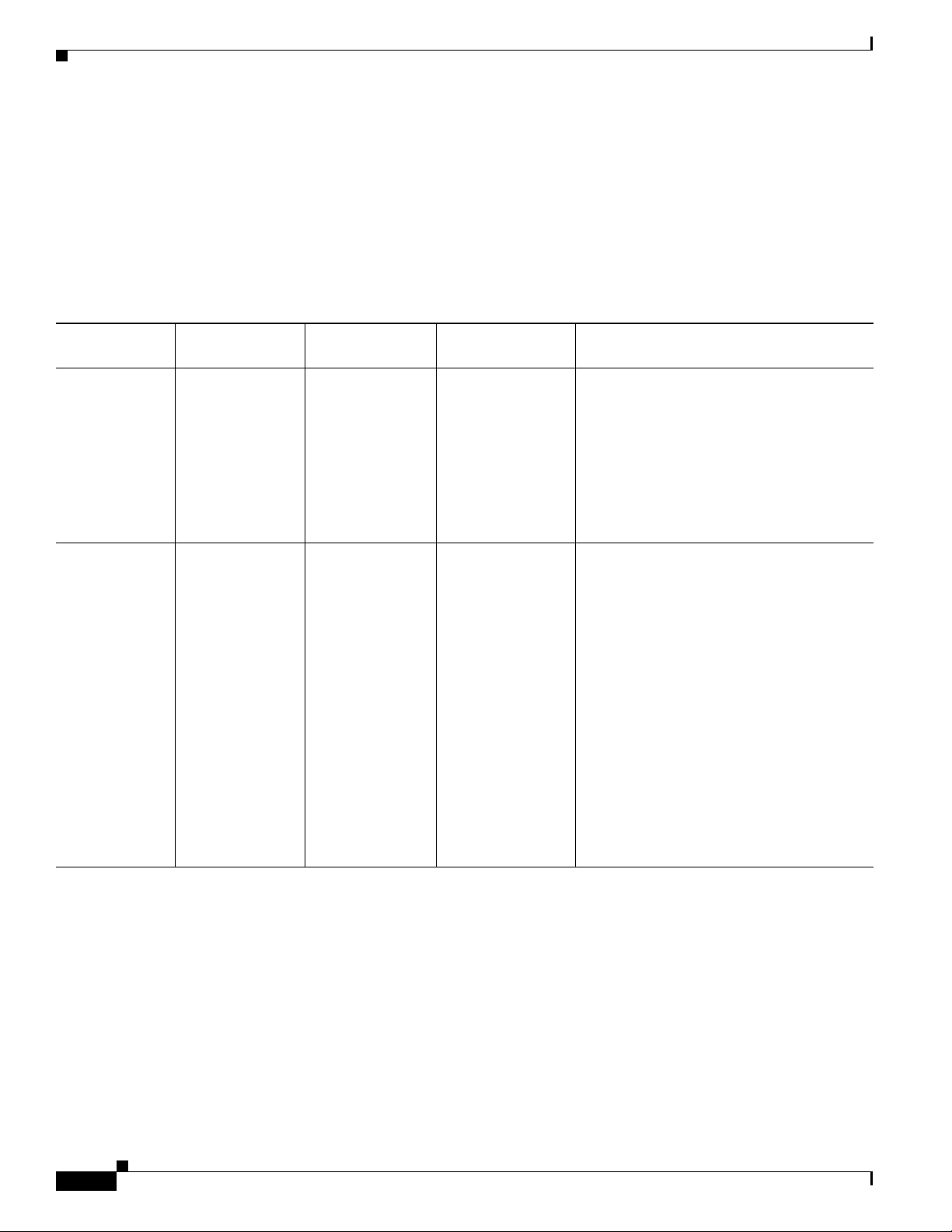
IOS Commands
IOS Commands
Table 7 lists the Cisco IOS commands and features that can trigger an erase, write, or erase and write
operation on a device's boot flash. The erase or write of an attribute on the boot flash can hold the CPU
for a few milliseconds to complete the operation. The CPU hold can result in a functional impact on
protocols or applications that are extremely time sensitive, for instance, Bidirectional Forwarding
Detection (BFD) or routing protocols which use finely tuned short timers. For example, OSPF with fast
hellos and short dead timers.
Table 7 Cisco IOS Commands
Functionality Command Name Description
Write to NV
memory.
Changing the
configuration
register value.
write memory This command
writes the device's
configuration in to
the Non-Volatile
RAM (NVRAM)
on the boot flash.
Use this command
in privileged
EXEC mode.
config-register
value
The router has a
16-bit
configuration
register in
NVRAM. Each bit
has value 1 (on or
set) or value 0 (off
or clear), and each
bit setting affects
the router
behavior upon the
next reload power
cycle. Use this
command in
Global
configuration
mode.
Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
Configuration
Example Impact
Router#write
memory
A BFD flap is triggered when one of the
following configuration elements are
activated or deactivated and configuration is
saved to memory:
(config)#warm-reboot
(config)#boot config
(config)#boot system
Router(config)#
Potential enough to flap bfd.
config-register
0xvalue
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
8
Page 17

Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
Table 7 Cisco IOS Commands
Functionality Command Name Description
Copy running
configuration to
startup
configuration.
copy
running-config
startup-config
This command
copies running
configuration to
startup
configuration.
Changing boot
variables.
boot {bootstrap |
config |host|
netowrk |
system}
This command
configures
bootstrap image
file, configuration
file, router
specific config
file, Networkwide
config file or
system image file.
Setting the
system software
clock manually.
clock set
hh:mm:ss day
month year
To manually set
the system
software clock,
use one of the
formats of the
clock set
command in
privileged EXEC
mode.
Configuration
Example Impact
Router#copy
running-config
startup-config
A BFD flap is not triggered for all 'write
mem' commands. For instance, when the
configuration attributes changes without
either a write or an erase+write on the
NVRAM, the BFD is not triggered.
In the following example, when one of the
configuration elements are
activated/deactivated and the configuration
is saved using the 'write mem' command, the
flap is triggered:
(config)#warm-reboot
(config)#boot config
(config)#boot system
Router(config)#bo
Potential enough to flap bfd.
ot bootstrap
Router#clock set
Potential enough to flap bfd.
13:32:00 23 July
1997
Note Every time the command is issued.
IOS Commands
clock set
hh:mm:ss day
month year
clock set
hh:mm:ss month
day year
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
9
Page 18

IOS Commands
Table 7 Cisco IOS Commands
Functionality Command Name Description
Random
Entropy
No special
Command exists
for this.
After the system
boot up, entropy is
collected by
accessing the
security chip. This
is potential
enough to flap the
BFD session
immediately after
the router boots
up.
Crashing the
router on user’s
wish.
test crash This is a hidden
Cisco IOS
command to crash
the Cisco router
on a user’s wish.
License EULA license accept
end user
agreement
To accept the
End-user License
Agreement
(EULA) for all
Cisco IOS
software packages
and features at one
time.
RTC Battery
Failure
No CLI Write the event of
losing battery for
Real Time Clock.
Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
Configuration
Example Impact
No command Potential enough to flap bfd.
Router#test crash Potential enough to flap bfd.
Router(config)#lice
Potential enough to flap bfd.
nse accept end
user agreement
No CLI Potential enough to flap bfd.
Note This is a one-time event during a
hardware failure.
Erasing NV
memory.
Erasing
startup-config
Erasing NV
memory.
Writing
configuration to
memory.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
10
erase nvram This command
erases the nvram:
file system.
erase
startup-config
This command
erases startup
configurations.
write erase This command
erases the NV
memory.
write This command
quickly saves
config to memory.
Router#erase
Potential enough to flap bfd.
nvram:
Router#erase
Potential enough to flap bfd.
startup-config
Router#write erase Potential enough to flap bfd.
Router#write Potential enough to flap bfd.
Page 19

Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
Table 7 Cisco IOS Commands
Functionality Command Name Description
Reloading the
router.
reload This command
reloads the router.
The reload time is
written to NV
memory.
Enabling warm
rebooting.
warm-reboot
count value
Enables a router to
warm-reboot.
uptime value
New software
license boot.
license boot
module
module-name
level license-level
To boot a new
software license
on routing
platforms, use the
license boot
module command
in global
configuration
mode.
Configuration
Example Impact
Router#reload Potential enough to flap bfd.
Router(config)#
Potential enough to flap bfd.
warm-reboot
count 10 uptime
10
Router(config)#
Potential enough to flap bfd.
license boot
module c2900
technology-packa
ge datak9
IOS Commands
Enabling or
disabling USB
ports.
Disabling access
to ROMMON.
config mode :
hw-module usb
[no] service
password-recove
ry
Enable or disable
USB ports from
IOS config mode.
This command
disables all access
to ROMMON.
Router(config)#hw
-module usb
disable
Router(config)#no
hw-module usb
disable
Router# no service
password-recover
y
Will trigger a BFD flap.
Potential enough to flap bfd.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
11
Page 20

IOS Commands
Chapter Overview of the Hardware and Software
12
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 21

Basic Router Configuration
This module provides configuration procedures for Cisco 3900 series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 1900
series integrated services routers (ISRs). It also includes configuration examples and verification steps
whenever possible.
Note See Appendix A, “Cisco IOS CLI for Initial Configuration” for information on how to perform the initial
configuration using the Cisco Internet Operating System (IOS) command line interface on Cisco 3900
series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 1900 series integrated services routers.
Basic Configuration
• Default Configuration, page 14
• Configuring Global Parameters, page 15
Interface Configuration
• Interface Ports, page 17
• Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces, page 18
• Configuring Wireless LAN Interfaces, page 19
• Configuring Interface Card and Module Interfaces, page 19
• Configuring a Loopback Interface, page 19
Routing Configuration
• Configuring Command-Line Access, page 21
• Configuring Static Routes, page 23
• Configuring Dynamic Routes, page 25
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
13
Page 22

Default Configuration
Default Configuration
When you boot up your Cisco router for the first time, you notice some basic configuration has already
been performed. Use the show running-config command to view the initial configuration, as shown in
the following example.
Router# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 723 bytes
!
version 12.4
no service pad
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
logging message-counter syslog
!
no aaa new-model
!
no ipv6 cef
ip source-route
ip cef
!
!
!
!
multilink bundle-name authenticated
!
!
archive
log config
hidekeys
!
!
!
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no ip address
shutdown
duplex auto
speed auto
!
ip forward-protocol nd
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
14
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 23

Chapter Basic Router Configuration
!
no ip http server
!
!
!
!
!
control-plane
!
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 3
login
!
exception data-corruption buffer truncate
scheduler allocate 20000 1000
end
Configuring Global Parameters
Configuring Global Parameters
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
To configure the global parameters for your router, follow these steps.
1. configure terminal
2. hostname name
3. enable secret password
4. no ip domain-lookup
Command Purpose
configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode, when using the
console port.
Example:
Router> enable
Router# configure terminal
Router(config)#
hostname name
Use the following to connect to the router with a
remote terminal:
telnet router name or address
Login: login id
Password: *********
Router> enable
Specifies the name for the router.
Example:
Router(config)# hostname Router
Router(config)#
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
15
Page 24

Configuring I/O Memory Allocation
Command Purpose
Step 3
enable secret password
Example:
Router(config)# enable secret cr1ny5ho
Router(config)#
Step 4
no ip domain-lookup
Example:
Router(config)# no ip domain-lookup
Router(config)#
For complete information on global parameter commands, see the Cisco IOS Release configuration
guide documentation set.
Configuring I/O Memory Allocation
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Specifies an encrypted password to prevent
unauthorized access to the router.
Disables the router from translating unfamiliar
words (typos) into IP addresses.
Example
To reallocate the percentage of DRAM in use for I/O memory and processor memory on Cisco 3925E
and Cisco 3945E routers, use the memory-size iomem i/o-memory-percentage command in global
configuration mode. To revert to the default memory allocation, use the no form of this command. This
procedure enables smartinit.
Syntax Description
i/o-memory-percentage The percentage of DRAM allocated to I/O memory. The values permitted
are 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, and 50. A minimum of 201 MB of memory is
required for I/O memory.
Tip We recommend that you configure the memory-size iomem below 25%. Any value above 25% should be
used only for enhancing IPSec performance.
When you specify the percentage of I/O memory in the command line, the processor memory
automatically acquires the remaining percentage of DRAM memory.
The following example allocates 25% of the DRAM memory to I/O memory and the remaining 75% to
processor memory:
Router#config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)# memory-size iomem 5
IO memory size too small: minimum IO memory size is 201M
Router(config)#
Router(config)# memory-size iomem ?
<5-50> percentage of DRAM to use for I/O memory: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 40, 50
16
Router(config)# memory-size iomem 25
Smart-init will be disabled and new I/O memory size will take effect upon reload.
Router(config)# end
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 25
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Verifying IOMEM Setting
Router# show run
Current configuration : 6590 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 16:48:41 UTC Tue Feb 23 2010 !
version 15.1
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
service internal
!
hostname Router1
!
!
no aaa new-model
!
memory-size iomem 25
!
Interface Ports
Interface Ports
Table 1 lists the interfaces that are supported on Cisco 3900 series, Cisco 2900 series, and Cisco 1900
series integrated services routers.
Table 1 Interfaces by Cisco Router
Slots, Ports, Logical
Interface, Interfaces 1941 2901
1
2911 & 2921 2951 & 3925 & 3945 3925E & 3945E
Onboard GE ports Gi0/0,Gi0/1 Gi0/0,Gi0/1 Gi0/0,Gi0/1,GI0/2 Gi0/0,Gi0/1,GI0/2 Gi0/0,Gi0/1,GI0/2,
GI0/3
Onboard WLAN Wlan-ap0 not supported not supported not supported not supported
Onboard WLAN GE
connection to MGF
Onboard ISM GE
interface on the PCIe
Onboard ISM GE
connection to MGF
USB usbflash0,
Interfaces on HWIC
and VWIC
Interfaces on Double
Wide-HWIC
Interfaces on SM not supported not supported interface1/port interface1-2/port
Wlan-Gi0/0 not supported not supported not supported not supported
2
service-module
-name-ISM 0/0
service-module
-name-ISM 0/1
usbflash1
usbtoken0,
usbtoken1
interface0/0/
port
interface0/1/
port
interface0/1
port
service-modulename-ISM 0/0
service-modulename-ISM 0/1
usbflash0,
usbflash1
usbtoken0,
usbtoken1
interface0/0/port
interface0/1/port
interface0/2/port
interface 0/3/port
interface0/1/port
interface0/3/port
service-modulename-ISM 0/0
service-modulename-ISM 0/1
usbflash0,
usbflash1
usbtoken0,
usbtoken1
interface0/0/port
interface0/1/port
interface0/2/port
interface 0/3/port
interface0/1/port
interface0/3/port
service-modulename-ISM 0/0
service-modulename-ISM 0/1
usbflash0,
usbflash1
usbtoken0,
usbtoken1
interface0/0/port
interface0/1/port
interface0/2/port
interface 0/3/port
interface0/1/port
interface0/3/port
interface1-4/port
not supported
not supported
usbflash0, usbflash1
usbtoken0,
usbtoken1
<int>0/0/<port>
<int>0/1/<port>
<int>0/2/<port>
<int>0/1/<port>
3
interface1-2/port
4
interface1-4/port
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
17
Page 26

Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
Table 1 Interfaces by Cisco Router (continued)
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Slots, Ports, Logical
Interface, Interfaces 1941 2901
Interfaces on Double
not supported not supported not supported interface 2/port5
Wide-SM
Interfaces HWIC on
not supported not supported interface1wic-slot/
SM
Interfaces VWIC on
SM
1. On the Cisco 2901 router, the numbering format for configuring an asynchronous interface is 0/slot/port. To configure the line associated with an
asynchronous interface, simply use the interface number to specify the asynchronous line. For example, line 0/1/0 specifies the line associated with
interface serial 0/1/0 on a WIC-2A/S in slot 1. Similarly, line 0/2/1 specifies the line associated with interface async 0/2/1 on a WIC-2AM in slot 2.
2. MGF = multi-gigabit fabric
3. Applies only to Cisco 2951, Cisco 3925, and Cisco 3925E routers.
4. Applies only to Cisco 3945 and Cisco 3945E routers.
5. Applies only to Cisco 2951, Cisco 3925, and Cisco 3925E routers.
6. Applies only to Cisco 3945 and Cisco 3945E routers.
7. Applies only to Cisco 2951, Cisco 3925, and Cisco 3925E routers.
8. Applies only to Cisco 3945 and Cisco 3945E routers.
1
2911 & 2921 2951 & 3925 & 3945 3925E & 3945E
interface 2/port
6
interface 4/port
interface1-2/wic-
7
slot/port
interface1-4/wic-
8
slot/port
port
interface4/port
interface1-2/wicslot/port
interface1-4/wicslot/port
Configuring Gigabit Ethernet Interfaces
To manually define onboard Gigabit Ethernet (GE) interfaces, follow these steps, beginning in global
configuration mode.
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
1. interface gigabitethernet slot/port
2. ip address ip-address mask
3. no shutdown
4. exit
Command Purpose
interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Enters the configuration mode for a Gigabit
Ethernet interface on the router.
Example:
Router(config)# interface gigabitethernet 0/1
Router(config-if)#
ip address ip-address mask
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the
specified GE interface.
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 192.168.12.2
255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#
18
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 27

Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Command Purpose
Step 3
Step 4
no shutdown
Example:
Router(config-if)# no shutdown
Router(config-if)#
exit
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Router(config)#
Configuring Wireless LAN Interfaces
The wireless LAN interface on the Cisco 1941W router enables connection to the router through
interface wlan-ap0. For more information about configuring a wireless connection, see the
“Configuring the Wireless Device” section on page 247.
Configuring Wireless LAN Interfaces
Enables the GE interface, changing its state
from administratively down to administratively
up.
Exits configuration mode for the GE interface
and returns to global configuration mode.
Configuring Interface Card and Module Interfaces
To configure interface cards and modules inserted in internal services module (ISM), enhanced
high-speed WAN interface card (EHWIC), Ethernet WAN interface card (EWIC), and service module
(SM) slots, see the appropriate interface card or module configuration documents on Cisco.com.
Configuring a Loopback Interface
The loopback interface acts as a placeholder for the static IP address and provides default routing
information.
For complete information on the loopback commands, see the Cisco IOS Release configuration guide
documentation set.
To configure a loopback interface, follow these steps, beginning in global configuration mode.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. interface type number
2. ip address ip-address mask
3. exit
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
19
Page 28

Configuring a Loopback Interface
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Command Purpose
interface type number
Enters configuration mode for the loopback
interface.
Example:
Router(config)# interface Loopback 0
Router(config-if)#
ip address ip-address mask
Sets the IP address and subnet mask for the
loopback interface.
Example:
Router(config-if)# ip address 10.108.1.1
255.255.255.0
Router(config-if)#
exit
Exits configuration mode for the loopback
interface and returns to global configuration
Example:
Router(config-if)# exit
Router(config)#
mode.
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Example
The loopback interface in this sample configuration is used to support Network Address Translation
(NAT) on the virtual-template interface. This configuration example shows the loopback interface
configured on the gigabit ethernet interface with an IP address of 200.200.100.1/24, which acts as a static
IP address. The loopback interface points back to virtual-template1, which has a negotiated IP address.
!
interface loopback 0
ip address 200.200.100.1 255.255.255.0 (static IP address)
ip nat outside
!
interface Virtual-Template1
ip unnumbered loopback0
no ip directed-broadcast
ip nat outside
!
Verifying Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured the loopback interface, enter the show interface loopback
command. You should see verification output similar to the following example.
Router# show interface loopback 0
Loopback0 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is Loopback
Internet address is 200.200.100.1/24
MTU 1514 bytes, BW 8000000 Kbit, DLY 5000 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation LOOPBACK, loopback not set
Last input never, output never, output hang never
Last clearing of "show interface" counters never
Queueing strategy: fifo
Output queue 0/0, 0 drops; input queue 0/75, 0 drops
20
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 29

Chapter Basic Router Configuration
5 minute input rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
5 minute output rate 0 bits/sec, 0 packets/sec
0 packets input, 0 bytes, 0 no buffer
Received 0 broadcasts, 0 runts, 0 giants, 0 throttles
0 input errors, 0 CRC, 0 frame, 0 overrun, 0 ignored, 0 abort
0 packets output, 0 bytes, 0 underruns
0 output errors, 0 collisions, 0 interface resets
0 output buffer failures, 0 output buffers swapped out
Another way to verify the loopback interface is to ping it:
Router# ping 200.200.100.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 200.200.100.1, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/2/4 ms
Configuring Command-Line Access
To configure parameters to control access to the router, follow these steps, beginning in global
configuration mode.
Configuring Command-Line Access
Note The TTY lines are asynchronous lines used for inbound or outbound modem and terminal connections
SUMMARY STEPS
and can be seen in a router or access server configuration as line x. The specific line numbers are a
function of the hardware built into or installed on the router or access server. In Cisco ISR G2 series
routers, the TTY lines are incremented by 1 and start with line number3 instead of line number 2 in Cisco
ISR G1 series routers. In ISR G2 series routers, line number 2 cannot be accessed since it has been used
for the second core feature.TTY lines are not static and line numbers can be changed in future when more
features are added similar to the second core.
1. line [aux | console | tty | vty] line-number
2. password password
3. login
4. exec-timeout minutes [seconds]
5. line [aux | console | tty | vty] line-number
6. password password
7. login
8. end
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
21
Page 30

Configuring Command-Line Access
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Command Purpose
line [aux | console | tty | vty] line-number
Enters line configuration mode, and specifies the
type of line.
Example:
Router(config)# line console 0
Router(config-line)#
password password
This example specifies a console terminal for
access.
Specifies a unique password for the console
terminal line.
Example:
Router(config-line)# password 5dr4Hepw3
Router(config-line)#
login
Enables password checking at terminal session
login.
Example:
Router(config-line)# login
Router(config-line)#
exec-timeout minutes [seconds]
Sets the interval that the EXEC command
interpreter waits until user input is detected. The
Example:
Router(config-line)# exec-timeout 5 30
Router(config-line)#
default is 10 minutes. Optionally, add seconds to
the interval value.
This example shows a timeout of 5 minutes and
30 seconds. Entering a timeout of 0 0 specifies
never to time out.
line [aux | console | tty | vty] line-number
Specifies a virtual terminal for remote console
access.
Example:
Router(config-line)# line vty 0 4
Router(config-line)#
password password
Specifies a unique password for the virtual
terminal line.
Example:
Router(config-line)# password aldf2ad1
Router(config-line)#
login
Enables password checking at the virtual terminal
session login.
Example:
Router(config-line)# login
Router(config-line)#
end
Exits line configuration mode, and returns to
privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config-line)# end
Router#
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
22
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 31

Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Example
The following configuration shows the command-line access commands.
You do not need to input the commands marked “default.” These commands appear automatically in the
configuration file generated when you use the show running-config command.
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 10 0
password 4youreyesonly
login
transport input none (default)
stopbits 1 (default)
line vty 0 4
password secret
login
!
Configuring Static Routes
Configuring Static Routes
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Static routes provide fixed routing paths through the network. They are manually configured on the
router. If the network topology changes, the static route must be updated with a new route. Static routes
are private routes unless they are redistributed by a routing protocol.
To configure static routes, follow these steps, beginning in global configuration mode.
1. ip route prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type interface-number [ip-address]}
2. end
Command Purpose
ip route prefix mask {ip-address | interface-type
interface-number [ip-address]}
Example:
Router(config)# ip route 192.168.1.0
255.255.0.0 10.10.10.2
Router(config)#
end
Specifies the static route for the IP packets.
For details about this command and about
additional parameters that can be set, see Cisco
IOS IP Command Reference, Volume 2 of 4:
Routing Protocols, Release 12.3
Exits router configuration mode, and enters
privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config)# end
Router#
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
23
Page 32

Configuring Static Routes
Example
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
In the following configuration example, the static route sends out all IP packets with a destination IP
address of 192.168.1.0 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 on the Gigabit Ethernet interface to another
device with an IP address of 10.10.10.2. Specifically, the packets are sent to the configured PVC.
You do not need to enter the command marked “(default).” This command appears automatically in the
configuration file generated when you use the show running-config command.
!
ip classless (default)
ip route 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.10.10.2!
24
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 33

Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Verifying Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured static routing, enter the show ip route command and look
for static routes signified by the “S.”
You should see verification output similar to the following:
Router# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, FastEthernet0
Configuring Dynamic Routes
Configuring Dynamic Routes
In dynamic routing, the network protocol adjusts the path automatically, based on network traffic or
topology. Changes in dynamic routes are shared with other routers in the network.
The Cisco routers can use IP routing protocols, such as Routing Information Protocol (RIP) or Enhanced
Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), to learn routes dynamically. You can configure either of
these routing protocols on your router.
• “Configuring Routing Information Protocol” section on page 25
• “Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol” section on page 27
Configuring Routing Information Protocol
To configure the RIP routing protocol on the router, follow these steps, beginning in global configuration
mode.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. router rip
2. version {1 | 2}
3. network ip-address
4. no auto-summary
5. end
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
25
Page 34

Configuring Dynamic Routes
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Command Task
router rip
Enters router configuration mode, and enables RIP
on the router.
Example:
Router> configure terminal
Router(config)# router rip
Router(config-router)#
version {1 | 2}
Specifies use of RIP version 1 or 2.
Example:
Router(config-router)# version 2
Router(config-router)#
network ip-address
Specifies a list of networks on which RIP is to be
applied, using the address of the network of each
Example:
Router(config-router)# network 192.168.1.1
Router(config-router)# network 10.10.7.1
Router(config-router)#
no auto-summary
directly connected network.
Disables automatic summarization of subnet routes
into network-level routes. This allows subprefix
Example:
Router(config-router)# no auto-summary
Router(config-router)#
end
routing information to pass across classful network
boundaries.
Exits router configuration mode, and enters
privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config-router)# end
Router#
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Example
26
The following configuration example shows RIP version 2 enabled in IP network 10.0.0.0 and
192.168.1.0.
To see this configuration, use the show running-config command from privileged EXEC mode.
!
Router# show running-config
router rip
version 2
network 10.0.0.0
network 192.168.1.0
no auto-summary
!
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 35

Chapter Basic Router Configuration
Verifying Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured RIP, enter the show ip route command and look for RIP
routes signified by “R.” You should see a verification output like the example shown below.
Router# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
R 3.0.0.0/8 [120/1] via 2.2.2.1, 00:00:02, Ethernet0/0
Configuring Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
Configuring Dynamic Routes
SUMMARY STEPS
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
To configure Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol GRP (EGRP), follow these steps, beginning
in global configuration mode.
1. router eigrp as-number
2. network ip-address
3. end
Command Purpose
router eigrp as-number
Enters router configuration mode, and enables
EIGRP on the router. The autonomous-system
Example:
Router(config)# router eigrp 109
Router(config)#
network ip-address
number identifies the route to other EIGRP routers
and is used to tag the EIGRP information.
Specifies a list of networks on which EIGRP is to
be applied, using the IP address of the network of
Example:
Router(config)# network 192.145.1.0
Router(config)# network 10.10.12.115
Router(config)#
end
directly connected networks.
Exits router configuration mode, and enters
privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config-router)# end
Router#
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
27
Page 36

Configuring Dynamic Routes
Example
The following configuration example shows the EIGRP routing protocol enabled in IP networks
192.145.1.0 and 10.10.12.115. The EIGRP autonomous system number is 109.
To see this configuration use the show running-config command, beginning in privileged EXEC mode.
Router# show running-config
...
!
router eigrp 109
network 192.145.1.0
!
...
Verifying Configuration
To verify that you have properly configured IP EIGRP, enter the show ip route command, and look for
EIGRP routes indicated by “D.” You should see verification output similar to the following:
Router# show ip route
Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP
D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area
N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2
i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2
ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route
o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route
Chapter Basic Router Configuration
network 10.10.12.115
Gateway of last resort is not set
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
C 10.108.1.0 is directly connected, Loopback0
D 3.0.0.0/8 [90/409600] via 2.2.2.1, 00:00:02, Ethernet0/0
28
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 37

Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
This chapter provides procedures for configuring the network interface device functionality, Ethernet
data plane loopback, IEEE connectivity fault management, and Y.1731 performance monitoring, and
contains the following sections:
• Configuring a Network Interface Device on the L3 Interface, page 29
• Ethernet Data Plane Loopback, page 32
• CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP, page 38
• Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3 Subinterface), page 54
Configuring a Network Interface Device on the L3 Interface
Configuring a Network Interface Device (NID) enables support for the NID functionality on the router
without including a NID hardware in the network. This feature combines the Customer-Premises
Equipment (CPE) and the NID functionality into a physical device. The following are the advantages of
configuring the NID functionality:
• Eliminates a physical device.
• Supports both the managed CPE feature set and the NID requirements.
Note This feature is supported only if you have purchased the DATA technology package functionality
(datak9) licensing package. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the
Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html.
Configuring the NID
The following steps describe how to configure the NID:
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
29
Page 38

Configuring a Network Interface Device on the L3 Interface
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Step 4 port-tagging
Step 5 encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
Step 6 set cos cos-value
Step 7 end
DETAILED STEPS
Command Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router>enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Example:
Router#configure terminal
interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Example:
Router(config)#interface
gigabitethernet 0/2
port-tagging
Example:
Router(config-if)#port-tagging
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
Example:
Router(config-if-port-tagging)#encaps
ulation dot1q 10
set cos cos-value
Example:
Router(config-if-port-tagging)#set
cos 6
end
Specifies an interface and enters the interface
configuration mode.
Inserts the VLAN ID into a packet header to identify
which Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) the packet
belongs to.
Defines the encapsulation format as IEEE 802.1Q
(dot1q), and specifies the VLAN identifier.
Sets the Layer 2 class of service (CoS) value to an
outgoing packet end.
Exits the interface configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-if-port-tagging)#end
Configuration Example
This configuration example shows how to configure the NID:
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
30
Page 39

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2
Router(config-if)#port-tagging
Router(config-if-port-tagging)#encapsulation dot1q 10
Router(config-if-port-tagging)#set cos 6
Router(config-if-port-tagging)#end
Verifying the NID Configuration
Use the following commands to verify the port tagging sessions:
• show run int
• ping
Use the show run int command to display the port tagging sessions:
Router#show run int gi0/2
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 10585 bytes
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
no ip address
duplex auto
speed auto
port-tagging
encapsulation dot1q 10
set cos 6
exit
end
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2.1101
encapsulation dot1Q 100
ip address 132.1.101.4 255.255.255.0
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2.1102
encapsulation dot1Q 100
ip address 132.1.102.4 255.255.255.0
!
Configuring a Network Interface Device on the L3 Interface
Use the ping command to verify the connectivity with port tagging configured:
Router#ping 132.1.101.3
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 132.1.101.3, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/4 ms
router#
Troubleshooting the NID Configuration
Table 1 lists the debug commands to troubleshoot the issues pertaining to the NID functionality.
The Cisco IOS Master Command List at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html provides more information
about these commands.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
31
Page 40

Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Caution Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can diminish the performance
of the router or even render it unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot
specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco technical support staff.
Note Before you run any of the debug commands listed in the following table, ensure that you run the logging
buffered debugging command, and then turn off console debug logging using the no logging console
command.
Table 1 debug Commands for NID Configuration
debug Command Purpose
debug ethernet nid configuration Enables debugging of configuration-related issues.
debug ethernet nid packet egress Enables debugging of packet processing (VLAN tag
debug ethernet nid packet ingress Enables debugging of packet processing (VLAN tag
Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
push) on the egress side.
pop) on the ingress side.
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
The Ethernet Data Plane Loopback feature provides a means for remotely testing the throughput of an
Ethernet port. You can verify the maximum rate of frame transmission with no frame loss.
Note This feature is supported only if you have purchased the DATA technology package functionality
(datak9) licensing package. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the
Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html.
Note Internal Ethernet data plane loopback is not supported.
Restrictions for Configuring External Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Follow the guidelines and take note of the restrictions listed here when configuring Ethernet data plane
loopback on a Layer 3 interface:
• Only external loopback (packets coming from the wire side) on the L3 dot1q subinterface and
(untagged) main interface are supported.
• To perform a MAC swap, the destination address and source address must be swapped for the
packets that are looped back. If the destination address is broadcast or multicast, the MAC address
is used as the source address for the packets that are looped back.
• Loopback operations are supported at line rate.
32
• Untagged frames are not supported on a subinterface. However, the frames for dot1q and qinq are
supported on a subinterface.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 41

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
361482
Router 1
Gi 0/0
Gi 0/0.1101
customer 1101
vlan 1101
Gi 0/0.1102
customer 1102
vlan 1102
Gi 0/0.1101
customer 1101
vlan 1101
Gi 0/0.1102
customer 1102
vlan 1102
Gi 0/0Gi 0/2
Gi 0/2.1101
Gi 0/2.1102
Provider
vlan 100
Carrier
vlan 10
Gi 0/2
Gi 0/2.1101
Gi 0/2.1102
vlan 100
Router 2
Metro Ethernet
• dot1ad is not supported on the main interface. However, untagged frames are supported on the main
interface.
• Single VLAN is supported as a filtering option for a subinterface, but VLAN list and VLAN range
are not supported.
• Only MAC address is supported as a filtering option for the main interface.
• For the filtering option, the destination MAC cannot be combined with inner VLAN or outer VLAN.
• There is no support for L3 and L4 loopback. Source and destination IP address or source and
destination ports will not be swapped.
• Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) packets are transparent to the data plane loopback
configuration and cannot be looped back.
• Packets coming from the other side of the wire where loopback is configured and having the same
destination MAC address are dropped.
• The broadcast and multicast IP addresses of the broadcast and multicast IP frames that are received
cannot be used as the source IP address of the frame when it is sent back to the initiator. In such a
case, the IP address of the subinterface is used as the source IP address of the frame when it is sent
back to the initiator.
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Configuring External Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Configuring external Ethernet data plane loopback is permitted on a Layer 3 main interface and
subinterfaces.
Figure 1 represents a sample topology to configure Ethernet data plane loopback.
Figure 1 Sample Topology
Gi 0/0
Gi 0/0.1101
customer 1101
vlan 1101
Gi 0/0.1102
customer 1102
vlan 1102
The following steps show how to configure external Ethernet data plane loopback on a subinterface using
single and double tagging. (The procedure to configure external Ethernet data plane loopback on the
main interface is similar to this procedure.)
Router 1
Gi 0/2.1101
Provider
vlan 100
Gi 0/2.1102
Metro Ethernet
Carrier
vlan 10
Gi 0/2
Gi 0/2.1101
vlan 100
Gi 0/2.1102
Router 2
Gi 0/0Gi 0/2
Gi 0/0.1101
customer 1101
vlan 1101
Gi 0/0.1102
customer 1102
vlan 1102
361482
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 interface gigabitethernet slot/port.sub-port
Step 4 encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
33
Page 42

Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Step 5 ethernet loopback permit external
Step 6 end
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
or
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id second-dot1q inner vlan-id
Command Purpose
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router>enable
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router#configure terminal
interface gigabitethernet
slot/port.sub-port
Specifies the subinterface and enters the subinterface
configuration mode.
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Example:
Router(config)#interface
gigabitethernet 0/2.1101
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
or
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
second-dot1q inner vlan-id
Example:
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation
dot1q 100
or
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation
dot1q 100 second-dot1q 1101
ethernet loopback permit external
Example:
Router(config-subif)#ethernet
loopback permit external
end
Example:
Router(config-subif)#end
Defines the encapsulation format as IEEE 802.1Q
(dot1q), and specifies the VLAN identifier.
For double tagging, use the second-dot1q keyword and
the inner vlan-id argument to specify the VLAN tag.
Configures Ethernet external loopback on the
subinterface.
Exits the subinterface configuration mode.
34
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 43

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
To start Ethernet data plane loopback, run the following command:
Command Purpose
Step 1
ethernet loopback start local
interface gigabitethernet
slot/port.sub-port external timeout
none
Starts Ethernet external loopback on a subinterface.
Enter timeout as none to have no time out period for the
loopback.
Example:
Router#ethernet loopback start local
interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101
external timeout none
To stop Ethernet data plane loopback, perform the following steps:
Command Purpose
Step 1
ethernet loopback stop local
interface gigabitethernet
slot/port.sub-port id session-id
Stops Ethernet external loopback on a subinterface.
Enter the value of the loopback session ID to specify the
loopback session that you want to stop.
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Example:
Router#ethernet loopback stop local
interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 id
1
Step 2
show ethernet loopback active
Displays information to verify if the loopback session has
ended.
Example:
Router#show ethernet loopback active
Configuration Examples for Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
This example shows how to configure Ethernet data plane loopback using single tagging:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100
Router(config-subif)#ethernet loopback permit external
Router(config-subif)#end
This example shows how to configure Ethernet data plane loopback using double tagging:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100 second-dot1q 1101
Router(config-subif)#ethernet loopback permit external
Router(config-subif)#end
This example shows how to start an Ethernet data plane loopback:
Router#ethernet loopback start local interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 external timeout
none
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
35
Page 44

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
This is an intrusive loopback and the packets matched with the service will not be able to
pass through. Continue? (yes/[no]):
Enter yes to continue.
This example shows how to stop an Ethernet data plane loopback:
Router#ethernet loopback stop local interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101 id 1
Router#*Oct 21 10:16:17.887: %E_DLB-6-DATAPLANE_LOOPBACK_STOP: Ethernet Dataplane Loopback
Stop on interface GigabitEthernet0/2 with session id 1
Router#show ethernet loopback active
Total Active Session(s): 0
Total Internal Session(s): 0
Total External Session(s): 0
Verifying the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback Configuration
Use the following commands to verify the Ethernet data plane loopback configuration:
• show ethernet loopback permitted
• show ethernet loopback active
Use the show ethernet loopback permitted command to view the loopback capabilities per interface:
Router#show ethernet loopback permitted
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Interface SrvcInst Direction
Dot1q/Dot1ad(s) Second-Dot1q(s)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Gi0/2.1101 N/A External
100 1101
Use the show ethernet loopback active command to display the summary of the active loopback
sessions on a subinterface:
Router#show ethernet loopback active
Loopback Session ID : 1
Interface : GigabitEthernet0/2.1101
Service Instance : N/A
Direction : External
Time out(sec) : none
Status : on
Start time : *10:17:46.930 UTC Mon Oct 21 2013
Time left : N/A
Dot1q/Dot1ad(s) : 100
Second-dot1q(s) : 1101
Source Mac Address : Any
Destination Mac Address : Any
Ether Type : Any
Class of service : Any
Llc-oui : Any
Total Active Session(s): 1
Total Internal Session(s): 0
Total External Session(s): 1
Use the show ethernet loopback active command to display the summary of the active loopback
sessions on the main interface:
Router#show ethernet loopback permitted
Loopback Session ID : 1
Interface : GigabitEthernet0/2
36
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 45

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Service Instance : N/A
Direction : External
Time out(sec) : none
Status : on
Start time : *10:14:23.507 UTC Mon Oct 21 2013
Time left : N/A
Dot1q/Dot1ad(s) : 1-100
Second-dot1q(s) : 1-1101
Source Mac Address : Any
Destination Mac Address : Any
Ether Type : Any
Class of service : Any
Llc-oui : Any
Total Active Session(s): 1
Total Internal Session(s): 0
Total External Session(s): 1
Troubleshooting the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback Configuration
Table 2 lists the debug commands to troubleshoot issues pertaining to the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
feature.
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
The Cisco IOS Master Command List at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html provides more information
about these commands.
Caution Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can diminish the performance
of the router or even render it unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot
specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco technical support staff.
Note Before you run any of the debug commands listed in the following table, ensure that you run the logging
buffered debugging command, and then turn off console debug logging using the no logging console
command.
Table 2 debug Commands for Ethernet Data Plane Loopback Configuration
debug Command Purpose
debug elb-pal-pd all Displays all the debugging information about the
Ethernet data plane loopback configuration.
debug elb-pal-pd error Displays debugging information about Ethernet data
plane loopback configuration errors.
debug elb-pal-pd event Displays debugging information about Ethernet data
plane loopback configuration changes.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
37
Page 46

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
IEEE Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) is an end-to-end per-service Ethernet-layer Operations,
Administration, and Maintenance (OAM) protocol. CFM includes proactive connectivity monitoring,
fault verification, and fault isolation for large Ethernet metropolitan-area networks (MANs) and WANs.
Note This feature is supported only if you have purchased the DATA technology package functionality
(datak9) licensing package. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the
Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html.
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet CFM
• A specific domain must be configured. If it is not, an error message is displayed.
• Multiple domains (different domain names) having the same maintenance level can be configured.
However, associating a single domain name with multiple maintenance levels is not permitted.
Configuring Ethernet CFM (Port MEP)
Complete these steps to configure and enable Ethernet CFM on a port Maintenance End Point (MEP):
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm ieee
Step 4 ethernet cfm global
Step 5 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level value
Step 6 service service-name port
Step 7 continuity-check interval value
Step 8 end
Step 9 configure terminal
Step 10 interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Step 11 ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name mpid mpid-value service service-name
Step 12 end
38
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 47

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
DETAILED STEPS
Command Purpose
Step 1
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router>enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router#configure terminal
Step 3
ethernet cfm ieee
Enables the IEEE version of CFM.
Example:
Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee
Step 4
ethernet cfm global
Enables CFM processing globally on the router.
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Example:
Router(config)#ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
value
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)#ethernet cfm
domain carrier level 2
service service-name port
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)#service carrier
port
continuity-check interval value
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-ch
eck interval 100m
end
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#end
configure terminal
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level,
and enters the Ethernet CFM configuration mode.
level can be any value from 0 to 7.
Creates a service on the interface and sets the
config-ecfm-srv submode.
Enables sending continuity check messages at the set
interval.
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode.
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router#configure terminal
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
39
Page 48

CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Command Purpose
Step 10
interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Example:
Router(config)#interface
gigabitethernet 0/2
Step 11
ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name
mpid mpid-value service service-name
Example:
Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep
domain carrier mpid 44 service
carrier
Step 12
end
Example:
Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#end
Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Specifies an interface and enters the interface
configuration mode.
Sets a port to a maintenance domain and defines it as an
MEP.
Note The values for domain and service must be the
same as the values configured for CFM.
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode.
Configuration Example for Ethernet CFM (Port MEP)
This example shows how to configure Ethernet CFM on a port MEP:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee
Router(config)#ethernet cfm global
Router(config-ecfm)#ethernet cfm domain carrier level 2
Router(config-ecfm)#service carrier port
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check interval 100m
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#end
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2
Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain carrier mpid 44 service carrier
Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#end
Verifying the Ethernet CFM Configuration on a Port MEP
Use the following commands to verify Ethernet CFM configured on a port MEP:
• show ethernet cfm domain
• show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
• show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
• ping ethernet mpid mpid-value domain domain-name service service-name cos value
• traceroute ethernet mpid mpid-value domain domain-name service service-name
• show ethernet cfm error configuration
40
Use the show ethernet cfm domain command to view details about CFM maintenance domains:
Router#show ethernet cfm domain carrier
Domain Name: carrier
Level: 2
Total Services: 1
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 49

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Services:
Type Id Dir CC CC-int Static-rmep Crosscheck MaxMEP Source MA-Name
Port none Dwn Y 100ms Disabled Disabled 100 Static carrier
Router#
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command to view the MEPs that are configured
locally on a router. The following is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points
local command:
Router#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
Local MEPs:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name Lvl MacAddress Type CC
Ofld Domain Id Dir Port Id
MA Name SrvcInst Source
EVC name
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------44 carrier 2 5657.a844.04fa Port Y
No carrier Down Gi0/2 none
carrier N/A Static
N/A
Total Local MEPs: 1
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Local MIPs: None
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote command to display information about remote
maintenance point domains or levels. In the following example, carrier, Provider, and customer are the
maintenance point domains that are configured.
On router 1:
Router1#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------43 carrier 5657.a86c.fa92 Up N/A
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier Port none N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 44 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
33 Provider 5657.a86c.fa92 Up Up
5 Provider Gi0/2.100
- Provider Vlan 100 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 34 Domain: Provider MA: Provider
3101 customer 5657.a86c.fa92 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1101
- customer1101 S,C 100,1101 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 4101 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
3102 customer 5657.a86c.fa92 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1102
- customer1102 S,C 100,1102 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 4102 Domain: customer MA: customer1102
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
41
Page 50

CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Total Remote MEPs: 4
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote command to view the details of a remote
maintenance point domain:
On router 1:
Router1#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote domain carrier service carrier
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------43 carrier 5657.a86c.fa92 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier S,C 100,1101 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 44 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
Total Remote MEPs: 1
Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
On router 2:
Router2#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote domain carrier service carrier
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------44 carrier 5657.g945.04fa Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier S,C 100,1101 N/A
N/A 0s
MPID: 43 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
Use the ping command to verify if Loopback Messages (LBM) and Loopback Replies (LBR) are
successfully sent and received between the routers:
Router1#ping ethernet mpid 44 domain carrier service carrier cos 5
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5 Ethernet CFM loopback messages to 5657.a86c.fa92, timeout is 5 seconds:!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
Router1#
Use the traceroute command to send the Ethernet CFM traceroute messages:
Router#traceroute ethernet mpid 44 domain carrier service carrier
Type escape sequence to abort. TTL 64. Linktrace Timeout is 5 seconds
Tracing the route to 5657.a86c.fa92 on Domain carrier, Level 2, service carrier
Traceroute sent via Gi0/2
42
B = Intermediary Bridge
! = Target Destination
* = Per hop Timeout
------------------------------------------------------------------------------- MAC Ingress Ingr Action Relay Action
Hops Host Forwarded Egress Egr Action Previous Hop
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 51

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
! 1 5657.a86c.fa92 Gi0/2 IngOk RlyHit:MEP
Not Forwarded 5657.g945.04fa
Router#
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
43
Page 52

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Configuring Ethernet CFM (Single-Tagged Packets)
Complete these steps to configure and enable Ethernet CFM for single-tagged packets:
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm ieee
Step 4 ethernet cfm global
Step 5 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
Step 6 service service-name vlan vlan-id direction down
Step 7 continuity-check
Step 8 interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Step 9 ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name mpid value service service-name
Step 10 interface gigabitethernet slot/port.subinterface
Step 11 encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
Step 12 end
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Command Purpose
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router>enable
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router#configure terminal
ethernet cfm ieee
Enables the IEEE version of CFM.
Example:
Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm global
Enables CFM processing globally on the router.
Example:
Router(config)#ethernet cfm global
44
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 53

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Command Purpose
Step 5
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
value
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level,
and enters the Ethernet CFM configuration mode.
level can be any value from 0 to 7.
Example:
Router(config)#ethernet cfm domain
customer level 7
Step 6
service service-name vlan vlan-id
direction down
Enters the CFM service configuration mode.
vlan—Specifies the VLAN.
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)#service
customer1101 vlan 100 direction down
Step 7
continuity-check
Enables sending continuity check messages.
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-ch
eck
Step 8
interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Specifies an interface and enters the interface
configuration mode.
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#interface
gigabitethernet 0/2
ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name
mpid mpid-value service service-name
Example:
Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep
domain customer mpid 100 service
customer1101
interface gigabitethernet
slot/port.subinterface
Example:
Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#interface
gigabitethernet 0/2.1
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
Example:
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation
dot1q 100
end
Sets a port to a maintenance domain and defines it as an
MEP.
Note The values for domain and service must be the
same as the values that were configured for CFM.
Specifies a subinterface and enters the subinterface
configuration mode.
Defines the encapsulation format as IEEE 802.1Q
(dot1q), and specifies the VLAN identifier.
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config-subif)#end
Configuration Example for Ethernet CFM (Single-Tagged Packets)
This example shows how to configure Ethernet CFM for single-tagged packets:
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
45
Page 54

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee
Router(config)#ethernet cfm global
Router(config)#ethernet cfm domain customer level 7
Router(config-ecfm)#service customer1101 vlan 100 direction down
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check
Router(config)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2
Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain customer mpid 100 service customer1101
Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100
Router(config-subif)#end
Verifying the Ethernet CFM Configuration for Single-Tagged Packets
Use the following commands to verify Ethernet CFM configured for single-tagged packets:
• show ethernet cfm domain
• show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
• show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
• show ethernet cfm error configuration
Use the show ethernet cfm domain command to display the maintenance point domains configured in
the network. In the following example, customer, enterprise, and carrier maintenance point domains are
configured:
Router#show ethernet cfm domain
Domain Name: customer
Level: 7
Total Services: 1
Services:
Type Id Dir CC CC-int Static-rmep Crosscheck MaxMEP Source MA-Name
Vlan 100 Dwn Y 10s Disabled Disabled 100 Static customer1101
Domain Name: enterprise
Level: 6
Total Services: 1
Services:
Type Id Dir CC CC-int Static-rmep Crosscheck MaxMEP Source MA-Name
Vlan 110 Dwn Y 10s Disabled Disabled 100 Static custservice
Domain Name: carrier
Level: 2
Total Services: 1
Services:
Type Id Dir CC CC-int Static-rmep Crosscheck MaxMEP Source MA-Name
Vlan 200 Dwn Y 10s Disabled Disabled 100 Static carrier
Router#
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command to view the local MEPs. The following
is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command:
Router#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name Lvl MacAddress Type CC
Ofld Domain Id Dir Port Id
MA Name SrvcInst Source
EVC name
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------100 customer 7 70ca.9b4d.a400 Vlan Y
46
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 55

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
No customer Down Gi0/2 100
customer1101 N/A Static
N/A
400 enterprise 6 70ca.9b4d.a400 Vlan I
No enterprise Down Gi0/1 110
custservice N/A Static
N/A
44 carrier 2 70ca.9b4d.a400 Vlan N
No carrier Down Gi0/2 200
carrier N/A Static
N/A
Total Local MEPs: 3
Local MIPs: None
Router#
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote command to display information about remote
maintenance point domains or levels.
The following example displays the continuity check messages exchanged between remote MEPs:
On router 1:
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Router1#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain Ingress
RDI MA Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------110 customer 70ca.9b4d.a400 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2
- customer1101 Vlan 100 N/A
N/A 12s
MPID: 100 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
410 enterprise 70ca.9b4d.a400 Up Up
6 enterprise Gi0/1
- custservice Vlan 110 N/A
N/A 12s
MPID: 400 Domain: enterprise MA: custservice
43 carrier 70ca.9b4d.a400 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier Vlan 200 N/A
N/A 12s
MPID: 44 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
Total Remote MEPs: 3
Router1#
On router 2:
Router2#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain Ingress
RDI MA Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
47
Page 56

CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
100 customer 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2
- customer1101 Vlan 100 N/A
N/A 2s
MPID: 110 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
400 enterprise 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
6 enterprise Gi0/1
- custservice Vlan 110 N/A
N/A 2s
MPID: 410 Domain: enterprise MA: custservice
44 carrier 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2
- carrier Vlan 200 N/A
N/A 2s
MPID: 43 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
Total Remote MEPs: 3
Router2#
Use the show ethernet cfm error configuration command to view Ethernet CFM configuration errors
(if any). The following is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm error configuration command:
Router#show ethernet cfm error configuration
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------CFM Interface Type Id Level Error type
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Gi0/2 S,C 100 5 CFMLeak
Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Configuring Ethernet CFM (Double-Tagged Packets)
Complete these steps to configure and enable Ethernet CFM for double-tagged packets:
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm ieee
Step 4 ethernet cfm global
Step 5 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level value
Step 6 service service-name vlan vlan-id inner-vlan inner-vlan-id direction down
Step 7 continuity-check
Step 8 interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Step 9 ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name mpid mpid-value service service-name
Step 10 interface gigabitethernet slot/port.subinterface
Step 11 encapsulation dot1q vlan-id second-dot1q inner vlan-id
Step 12 end
48
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 57

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
DETAILED STEPS
Command Purpose
Step 1
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router>enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router#configure terminal
Step 3
ethernet cfm ieee
Enables the IEEE version of CFM.
Example:
Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee
Step 4
ethernet cfm global
Enables CFM processing globally on the router.
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Example:
Router(config)#ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
0 to 7
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)#ethernet cfm
domain customer level 7
service service-name vlan vlan-id
inner-vlan inner vlan-id direction
down
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)#service
customer1101 vlan 100 inner-vlan 30
direction down
continuity-check
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-ch
eck
interface gigabitethernet slot/port
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level,
and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode.
level can be any value from 0 to 7.
Enters the CFM service configuration mode.
The following are the parameters:
• vlan—Specifies the VLAN.
• inner-vlan—The inner-vlan keyword and the inner
vlan-id argument specify the VLAN tag for
double-tagged packets.
Enables sending continuity check messages.
Specifies an interface and enters the interface
configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#interface
gigabitethernet 0/2
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
49
Page 58

CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Command Purpose
Step 9
ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name
mpid mpid-value service service-name
Example:
Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep
domain customer mpid 100 service
customer1101
Step 10
interface gigabitethernet
slot/port.subinterface
Example:
Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#interface
gigabitethernet 0/2.1101
Step 11
encapsulation dot1q vlan-id
second-dot1q inner vlan-id
Example:
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation
dot1q 100 second-dot1q 30
Step 12
end
Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Sets a port to a maintenance domain and defines it as an
MEP.
Note The values for domain and service must be the
same as the values configured for CFM.
MPID—Specifies the maintenance endpoint identifier.
Specifies a subinterface and enters the subinterface
configuration mode.
Defines the encapsulation format as IEEE 802.1Q
(dot1q), and specifies the VLAN identifier.
Use the second-dot1q keyword and the inner vlan-id
argument to specify the VLAN tag.
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config-subif)#end
Configuration Example for Ethernet CFM (Double-Tagged Packets)
This example shows how to configure Ethernet CFM for double-tagged packets:
Router>enable
Router#configure terminal
Router(config)#ethernet cfm ieee
Router(config)#ethernet cfm global
Router(config-ecfm)#ethernet cfm domain customer level 7
Router(config-ecfm)#service customer1101 vlan 100 inner-vlan 30 direction down
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#continuity-check
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2
Router(config-if)#ethernet cfm mep domain customer mpid 100 service customer1101
Router(config-if-ecfm-mep)#interface gigabitethernet 0/2.1101
Router(config-subif)#encapsulation dot1q 100 second-dot1q 30
Router(config-subif)#end
Verififying the Ethernet CFM Configuration for Double-Tagged Packets
Use the following commands to verify Ethernet CFM configured for double-tagged packets:
• show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
• show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
• ping ethernet mpid mpid-value domain domain-name service service-name cos value
50
• traceroute ethernet mpid mpid-value domain domain-name service service-name
• show ethernet cfm error configuration
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 59

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command to view the local MEPs. The following
is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local command:
Router#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points local
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------100 customer 8843.e154.6f01 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1101
- customer1101 S, C 100, 30 N/A
N/A 58s
MPID: 100 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
Router#
Use the show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote command to display the remote maintenance
point domains. In the following example, customer, carrier, and enterprise are the maintenance point
domains that are configured:
On router 1:
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Router1#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------110 customer 8843.e154.6f01 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1101
- customer1101 S, C 100, 30 N/A
N/A 58s
MPID: 100 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
43 carrier 8843.e154.6f01 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2.2
- carrier S, C 50, 20 N/A
N/A 58s
MPID: 44 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
410 enterprise 8843.e154.6f01 Up Up
6 enterprise Gi0/1.1
- custservice S, C 200, 70 N/A
N/A 58s
MPID: 400 Domain: enterprise MA: custservice
Router1#
On router 2:
Router2#show ethernet cfm maintenance-points remote
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------MPID Domain Name MacAddress IfSt PtSt
Lvl Domain ID Ingress
RDI MA Name Type Id SrvcInst
EVC Name Age
Local MEP Info
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
51
Page 60

CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
100 customer 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
7 customer Gi0/2.1101
- customer1101 S, C 100, 30 N/A
N/A 40s
MPID: 110 Domain: customer MA: customer1101
44 carrier 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
2 carrier Gi0/2.2
- carrier S, C 50, 20 N/A
N/A 40s
MPID: 43 Domain: carrier MA: carrier
400 enterprise 0026.99f7.0b41 Up Up
6 enterprise Gi0/1.1
- custservice S, C 200, 70 N/A
N/A 40s
MPID: 410 Domain: enterprise MA: custservice
Router2#
Use the ping command to verify if Ethernet CFM loopback messages are successfully sent and received
between the routers:
Router#ping ethernet mpid 100 domain customer service customer1101 cos 5
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5 Ethernet CFM loopback messages to 8843.e154.6f01, timeout is 5 seconds:!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 1/1/1 ms
Router#
Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Use the traceroute command to send the Ethernet CFM traceroute messages:
Router#traceroute ethernet mpid 100 domain customer service customer1101
Type escape sequence to abort. TTL 64. Linktrace Timeout is 5 seconds
Tracing the route to 8843.e154.6f01 on Domain customer, Level 7, service customer1101,
vlan 100 inner-vlan 30
Traceroute sent via Gi0/2.1101
B = Intermediary Bridge
! = Target Destination
* = Per hop Timeout
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
MAC Ingress Ingr Action Relay Action
Hops Host Forwarded Egress Egr Action Previous Hop
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------! 1 8843.e154.6f01 Gi0/2.1101 IngOk RlyHit:MEP
Not Forwarded 5657.a86c.fa92
Use the show ethernet cfm error configuration command to view Ethernet CFM configuration errors
(if any). The following is a sample output of the show ethernet cfm error configuration command:
Router#show ethernet cfm error configuration
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------CFM Interface Type Id Level Error type
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Gi0/2 S,C 100,30 5 CFMLeak
Gi0/2 S,C 100,30 1 CFMLeak
Troubleshooting Ethernet CFM Configuration
Table 3 lists the debug commands to troubleshoot issues pertaining to the Ethernet CFM configuration.
The Cisco IOS Master Command List at
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
52
Page 61

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html provides more information
about these commands.
Caution Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can diminish the performance
of the router or even render it unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot
specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco technical support staff.
Note Before you run any of the debug commands listed in the following table, ensure that you run the logging
buffered debugging command, and then turn off console debug logging using the no logging console
command.
Table 3 debug Commands for Ethernet CFM Configuration
debug Command Purpose
debug ethernet cfm all Enables all Ethernet CFM debug messages.
debug ethernet cfm diagnostic Enables low-level diagnostic debugging of Ethernet
CFM general events or packet-related events.
debug ethernet cfm error Enables debugging of Ethernet CFM errors.
debug ethernet cfm packets Enables debugging of Ethernet CFM message
packets.
debug ecfmpal all Enables debug messages for all Ethernet CFM
platform events.
debug ecfmpal api Displays debug messages for all Ethernet CFM
platform API events.
debug ecfmpal common Displays debug messages for all Ethernet CFM
platform common events.
debug ecfmpal ecfmpal Enables debugging of all Ethernet CFM platform
events.
debug ecfmpal epl Enables debugging of all Ethernet CFM platform
endpoint list (EPL) events.
debug ecfmpal isr Enables debugging of all Ethernet CFM platform
interrupt service request (ISR) events.
CFM Support on Routed Port and Port MEP
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
53
Page 62

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3
Subinterface)
Y.1731 Performance Monitoring (PM) provides a standard Ethernet PM function that includes
measurement of Ethernet frame delay, frame delay variation, frame loss, and frame throughput
measurements specified by the ITU-T Y-1731 standard and interpreted by the Metro Ethernet Forum
(MEF) standards group.
Note This feature is supported only if you have purchased the DATA technology package functionality
(datak9) licensing package. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the
Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html.
Frame Delay
Ethernet frame delay measurement is used to measure frame delay and frame delay variations. Ethernet
frame delay is measured using the Delay Measurement Message (DMM) method.
Restrictions for Configuring Two-Way Delay Measurement
Follow the guidelines and restrictions listed here when you configure two-way delay measurement:
• Y.1731 PM measurement works only for a point-to-point network topology.
• The granularity of the clock for delay measurement is in seconds and nanoseconds.
• CFM Y.1731 packets work with a maximum of two VLAN tags. The expected behavior is not
observed with more VLAN tags. Also, CFM Y.1731 packets do not work with untagged cases.
Configuring Two-Way Delay Measurement
The following steps show how to configure two-way delay measurement. Both single and double tagging
methods are included in the steps listed below.
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ip sla operation number
Step 4 ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain value vlan vlan-id mpid value cos value source mpid value
or
54
ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain value vlan vlan-id inner-vlan inner vlan-id mpid value cos value
source mpid value
Step 5 aggregate interval seconds
Step 6 exit
Step 7 ip sla schedule operation number start-time {start time | now}
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 63

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
Step 8 end
DETAILED STEPS
Command Purpose
Step 1
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Step 3
ip sla operation number
Enables the IP SLA configuration.
operation-number—The IP SLA operation you want to
configure.
Configures a two-way delay measurement.
Note Both single tagging and double tagging are
Step 4
Example:
Router(config)# ip sla 1101
ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain value
vlan vlan-id mpid value cos value
source mpid value
or
The following are the parameters:
ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain value
vlan vlan-id inner-vlan inner vlan-id
mpid value cos value source mpid
value
• delay—Specifies the delay distribution parameter.
Example:
Router(config-ip-sla)# ethernet y1731
delay DMM domain customer vlan 100
mpid 3101 cos 1 source mpid 4101
• vlan—Specifies the VLAN.
• inner-vlan—The inner-vlan keyword and the inner
or
Router(config-ip-sla)# ethernet y1731
delay DMM domain customer vlan 100
inner-vlan 1101 mpid 3101 cos 1
source mpid 4101
• cos—Specifies the CoS. The value can be any
supported.
Note DMM is the only supported delay distribution
parameter.
vlan-id argument specify the VLAN tag for
double-tagged packets.
number between 0 and 7.
Note For double-tagged packets, the cos value
corresponds to the value specified for the
outer tag.
• mpid—Specifies the destination MPID.
• source—Specifies the source MPID.
Step 5
aggregate interval seconds
Configures the Y.1731 aggregation parameter, where
aggregate interval refers to the interval at which the
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#
aggregate interval 30
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
packets are sent.
seconds—Specifies the length of time, in seconds.
55
Page 64

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
Command Purpose
Step 6
exit
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# exit
Step 7
ip sla schedule operation number life
{value | forever} start-time value
Example:
Router(config)#ip sla schedule 1101
life forever start-time now
Step 8
end
Example:
Router(config)#end
Exits the router configuration mode.
Schedules the two-way delay measurement.
• life—Specifies a period of time (in seconds) to
execute. The value can also be set as forever.
• start-time—Specifies the time at which to start the
entry. The options available are after, hh:mm,
hh:mm:ss, now, and pending.
Exits the router configuration mode and returns to the
privileged EXEC mode.
Configuration Examples for Two-Way Delay Measurement
This example shows how to configure two-way delay measurement using single tagging:
router>enable
router#configure terminal
router(config)#ip sla 1101
router(config-ip-sla)#ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain customer vlan 100 mpid 3101 cos 1
router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#aggregate interval 30
router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#exit
router(config)#ip sla schedule 1102 life forever start-time now
router(config)#end
This example shows how to configure two-way delay measurement using double tagging:
router>enable
router#configure terminal
router(config)#ip sla 1101
router(config-ip-sla)#ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain customer vlan 100 inner-vlan 1101
mpid 3101 cos 1 source mpid 4101
router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#aggregate interval 30
router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#exit
router(config)#ip sla schedule 1101 life forever start-time now
router(config)#end
Verifying Two-Way Delay Measurement Configuration
Use the following commands to verify the performance-monitoring sessions:
• show run | sec ip sla
56
• show ip sla summary
• show ip sla statistics entry-number
• show ip sla configuration entry-number
• show ethernet cfm pm session summary
• show ethernet cfm pm session detail session-id
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 65

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
• show ethernet cfm pm session db session-id
The following are the sample outputs of the commands listed above:
Router#show run | sec ip sla
ip sla auto discovery
ip sla 1101
ethernet y1731 delay DMM domain customer vlan 100 inner-vlan 1101 mpid 3101 cos
1 source mpid 4101
ip sla schedule 1101 life forever start-time now
Router#show ip sla summary
IPSLAs Latest Operation Summary
Codes: * active, ^ inactive, ~ pending
ID Type Destination Stats Return Last
(ms) Code Run
----------------------------------------------------------------------*1101 y1731-delay Domain:customer V - OK 27 seconds ag
lan:100 CVlan:110 o
1 Mpid:3101
Router#show ip sla statistics
IPSLAs Latest Operation Statistics
IPSLA operation id: 1101
Delay Statistics for Y1731 Operation 1101
Type of operation: Y1731 Delay Measurement
Latest operation start time: *10:43:12.930 UTC Mon Oct 21 2013
Latest operation return code: OK
Distribution Statistics:
Interval
Start time: *10:43:12.930 UTC Mon Oct 21 2013
Elapsed time: 15 seconds
Number of measurements initiated: 7
Number of measurements completed: 7
Flag: OK
Router#show ip sla configuration 1101
IP SLAs Infrastructure Engine-III
Entry number: 1101
Owner:
Tag:
Operation timeout (milliseconds): 5000
Ethernet Y1731 Delay Operation
Frame Type: DMM
Domain: customer
Vlan: 100
CVlan: 1101
Target Mpid: 3101
Source Mpid: 4101
CoS: 1
Max Delay: 5000
Request size (Padding portion): 64
Frame Interval: 1000
Clock: Not In Sync
Threshold (milliseconds): 5000
Schedule:
Operation frequency (seconds): 30 (not considered if randomly scheduled)
Next Scheduled Start Time: Start Time already passed
Group Scheduled : FALSE
Randomly Scheduled : FALSE
Life (seconds): Forever
Entry Ageout (seconds): never
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
57
Page 66

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
Recurring (Starting Everyday): FALSE
Status of entry (SNMP RowStatus): Active
Statistics Parameters
Frame offset: 1
Distribution Delay Two-Way:
Number of Bins 10
Bin Boundaries: 5000,10000,15000,20000,25000,30000,35000,40000,45000,-1
Distribution Delay-Variation Two-Way:
Number of Bins 10
Bin Boundaries: 5000,10000,15000,20000,25000,30000,35000,40000,45000,-1
Aggregation Period: 30
History
Number of intervals: 2
Router#show ethernet cfm pm session summary
Number of Configured Session : 150
Number of Active Session: 2
Number of Inactive Session: 148
Router#
Router(config)#show ethernet cfm pm session detail 0
Session ID: 0
Sla Session ID: 1101
Level: 7
Service Type: S,C
Service Id: 100,1101
Direction: Down
Source Mac: 5352.a824.04fr
Destination Mac: 5067.a87c.fa92
Session Version: 0
Session Operation: Proactive
Session Status: Active
MPID: 4101
Tx active: yes
Rx active: yes
RP monitor Tx active: yes
RP monitor Rx active: yes
Timeout timer: stopped
Last clearing of counters: *00:00:00.000 UTC Mon Jan 1 1900
DMMs:
Transmitted: 117
DMRs:
Rcvd: 117
1DMs:
Transmitted: 0
Rcvd: 0
LMMs:
Transmitted: 0
LMRs:
Rcvd: 0
VSMs:
Transmitted: 0
VSRs:
Rcvd: 0
SLMs:
Transmitted: 0
SLRs:
Rcvd: 0
Test ID 0
Router1#
58
Router#show ethernet cfm pm session db 0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------- TX Time FWD RX Time FWD
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 67

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
TX Time BWD RX Time BWD Frame Delay
Sec:nSec Sec:nSec Sec:nSec
---------------------------------------------------------------------------Session ID: 0
****************************************************************************
3591340722:930326034 3591340663:866791722
3591340663:866898528 3591340722:930707484 0:274644
****************************************************************************
3591340723:927640626 3591340664:864091056
3591340664:864182604 3591340723:927976302 0:244128
****************************************************************************
3591340724:927640626 3591340665:864091056
3591340665:864167346 3591340724:927961044 0:244128
****************************************************************************
3591340725:927671142 3591340666:864121572
3591340666:864213120 3591340725:928006818 0:244128
****************************************************************************
3591340726:927655884 3591340667:864106314
3591340667:864197862 3591340726:927991560 0:244128
****************************************************************************
3591340727:927732174 3591340668:864167346
3591340668:864533538 3591340727:928327236 0:228870
****************************************************************************
3591340728:927655884 3591340669:864121572
3591340669:864197862 3591340728:928006818 0:274644
****************************************************************************
3591340729:927671142 3591340670:864121572
3591340670:864197862 3591340729:927991560 0:244128
****************************************************************************
Troubleshooting Two-Way Delay Measurement Configuration
Table 4 lists the debug commands to troubleshoot issues pertaining to the two-way delay measurement
configuration. The Cisco IOS Master Command List at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios/mcl/allreleasemcl/all_book.html provides more information
about these commands.
Caution Because debugging output is assigned high priority in the CPU process, it can diminish the performance
of the router or even render it unusable. For this reason, use debug commands only to troubleshoot
specific problems or during troubleshooting sessions with Cisco technical support staff.
Note Before you run any of the debug commands listed in the following table, ensure that you run the logging
buffered debugging command, and then turn off console debug logging using the no logging console
command.
Table 4 debug Commands for Two-Way Delay Measurement Configuration
debug Command Purpose
debug epmpal all Enables debugging of all Ethernet performance
monitoring (PM) events.
debug epmpal api Enables debugging of Ethernet PM API events.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
59
Page 68

Chapter Configuring Ethernet CFM and Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on Layer 3 Interfaces
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring on a Routed Port (L3 Subinterface)
Table 4 debug Commands for Two-Way Delay Measurement Configuration (continued)
debug Command Purpose
debug epmpal rx Enables debugging of Ethernet PM packet-receive
debug epmpal tx Enables debugging of Ethernet PM packet-transmit
events.
events.
60
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 69

Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Ethernet virtual connection (EVC) infrastructure is a Layer 2 platform-independent bridging
architecture that supports Ethernet services. This chapter provides procedures for configuring EVC
Bridge Domain (BD) and the features it supports on the Cisco Integrated Services Routers (ISR) G2.
• Configuring EVCs on Cisco ISR G2 Router, page 61
• Ethernet Data Plane Loopback, page 64
• Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD, page 68
• Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring for EVC BD, page 87
• Support for Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVI) on ISR G2 Metro Ethernet BD, page 90
• EVC Quality of Service (QoS), page 92
Configuring EVCs on Cisco ISR G2 Router
Configuring an EFP and a BD on the Cisco ISR G2 Router
Configuring a service instance on a Layer 2 port creates an EFP on which you can configure EVC
features.
Note • You cannot use the same VLAN ID for encapsulating on a Layer 3 sub-interface and an EFP (service
instance) on a WAN interface.
• If there is a sub-interface and service-instance both configured on a WAN interface for untagged
traffic, then the traffic will always go to the main interface and the service-instance with untagged
traffic will not work.
Perform this task to configure an EFP.
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
61
Page 70

Configuring EVCs on Cisco ISR G2 Router
Step 3 interface type number
Step 4 service instance id ethernet
Step 5 encapsulation encapsulation-type vlan-id
Step 6 rewrite ingress tag translate 1-to-1 dot1q vlan-id symmetric
Step 7 bridge-domain bridge-id
Step 8 end
DETAILED STEPS
Command Purpose
Step 1
enable
Example:
Router> enable
Step 2
configure terminal
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Enables privileged EXEC mode.
• Enter your password if prompted.
Enters global configuration mode.
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Example:
Router# configure terminal
interface type number
Example:
Router(config)# interface
gigabitethernet 0/1
service instance id ethernet
Example:
Router(config-if)# service instance 1
ethernet
encapsulation encapsulation-type
vlan-id
Example:
Router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation
dot1q 1
rewrite ingress tag translate 1-to-1
dot1q vlan-id symmetric
Example:
Router(config-if-srv)# rewrite
ingress tag translate 1-to-1 dot1q 1
symmetric
Enters interface configuration mode.
• The example shows how to configure Gigabit
Ethernet interface 0/1 and enter interface
configuration mode.
Configures an Ethernet service instance on an interface
and enters Ethernet service configuration mode.
• The example shows how to configure Ethernet
service instance 1.
Defines the encapsulation type.
• The example shows how to define dot1q as the
encapsulation type.
(Optional) Specifies the encapsulation adjustment to be
performed on a frame ingressing a service instance.
• The example shows how to specify translating a
single tag defined by the encapsulation command to
a single tag defined in the rewrite ingress tag
command with reciprocal adjustment to be done in
the egress direction.
62
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 71

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Command Purpose
Step 7
Step 8
bridge-domain bridge-id
Example:
Router(config-if-srv)# bridge-domain
1
end
Configures the bridge domain.
• The example shows how to configure bridge domain
1.
Returns to privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
router(config-if-srv)# end
Configuration Examples for EVCs on the Cisco ISR G2 Router
When a WAN interface is configured with both an EFP and a subinterface, and the dot1q encapsulation
with the same VLAN ID is used, the traffic on the subinterface gets a higher priority than the traffic on
an EFP.
Note the following configuration order before you configure EVC:
Order 1: If you configure the subinterface with the same VLAN ID first, then the configuration of EFP
using the same VLAN ID is blocked as shown below:
router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
router(config)#int gi0/0
irouter(config-if)# service instance 2 ethernet evc1
router(config-if-srv)# encapsulation dot1q 102
Invalid configuration on ServInst 2(Gi0/0). The VLAN ID (102) has already been configured
on interface GigabitEthernet0/0.102
Configuring EVCs on Cisco ISR G2 Router
Order 2: If you configure EFP first using the same VLAN ID, then you can still configure the
subinterface using the same VLAN ID. However, traffic will flow on the subinterface with higher
priority and not on the EFP.
Configuring an EFP and a subinterface using the same VLAN ID for dot1q encapsulation is allowed and
configurable as show in order 2. However, the use of an EFP and subinterface is mutually exclusive.
There will not be any traffic through the EFP. Traffic only goes through the subinterface because
untagged packets have high priority than tagged packets.
Example Configuring EFPs on a Gigabit Ethernet Interface
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
no ip address
negotiation auto
service instance 1 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q 201
rewrite ingress tag translate 1-to-1 dot1q 300 symmetric
bridge-domain 1
!
service instance 2 ethernet
encapsulation default
bridge-domain 1
!
service instance 3 ethernet
encapsulation priority-tagged
bridge-domain 2
!
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
63
Page 72

Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
The Ethernet Data Plane Loopback feature allows you to test services and throughput of an Ethernet port
or a device using a test generator. You can verify the maximum rate of frame transmission with no frame
loss. This feature allows bidirectional throughput measurement, and on-demand or out-of-service
(intrusive) operation during service turn-ups. This feature is used for testing during service turn-ups and
troubleshooting of services after a turn-up.
If you need to test a service while it is live, you do this without disrupting any of the live data traffic. To
achieve this, you use test traffic that differs from live data traffic. For example, the traffic from a test
generator contain the source MAC address of the test generator, or test traffic is assigned a particular
Class of Service (Cos). Irrespective of the method used, the device looping back the traffic must be able
to filter out the test traffic and leave the data traffic untouched.
Note Configuring Ethernet Data Plane Loopback on a device does not indicate the start of an actual session.
Features Supported for Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
• Locally-enabled Ethernet Data Plane Loopback on all Ethernet interface types, such as physical and
bundle interfaces and sub-interfaces and Pseudowire Head End (PWHE) interfaces.
• In the case of Layer 2 and Layer 3 interfaces, only external loopback is supported. External loopback
is the type of loopback where all traffic received on the ingress interface is blindly sent out of the
egress interface.
• When a Bundle interface is placed into loopback, traffic on all bundle link members are looped back.
• MAC address must always be swapped on looped-back traffic.
• Supports dropping of packets received in the non-loopback direction.
• Allows the application of multiple filters to loopback only a subset of traffic received by an interface
and only drop the corresponding reverse-direction traffic.
• Provides an option to specify a time period after which the loopback is automatically terminated.
Restrictions of Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
• EVC xconnect is not supported.
• Only single VLAN is supported as the filtering options, but the vlan-list/vlan range is not supported.
• Maximum of 10 active sessions is only supported.
Configuring Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
64
Perform this task to configure Ethernet Data Plane Loopback.
Note Configuring or permitting Ethernet Data Plane Loopback is not the same as starting an actual loopback
session.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 73

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 configure
Step 2 interface [GigabitEthernet |] interface-path-id
Step 3 ethernet loopback permit {external | internal}
Step 4 end
or
commit
DETAILED STEPS
Command Purpose
Step 1
configure
Example:
Router# configure
Step 2
interface [GigabitEthernet |]
interface-path-id
Example:
router(config)# interface 0/1
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters interface configuration mode and specifies the
Ethernet interface name and notation
rack/slot/module/port.
Note The example indicates an 8-port
10-Gigabit Ethernet interface in
modular services card slot 1.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
65
Page 74

Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
Command Purpose
Step 3
ethernet loopback permit {external |
internal}
Example:
Router(config-if-srv)# ethernet
loopback permit external
Step 4
end
or
commit
Example:
router(config-if-srv)# commit
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Configures ethernet loopback externally or internally on
an interface. External loopback allows loopback of traffic
from wire. Internal loopback allows loopback of traffic
from the bridge domain.
Saves configuration changes.
• When you issue the end command, the system
prompts you to commit changes:
Uncommitted changes found, commit them before
exiting(yes/no/cancel)?
[cancel]:
– Entering yes saves configuration changes to the running
configuration file, exits the configuration session, and
returns the router to EXEC mode.
– Entering no exits the configuration session and returns
the router to EXEC mode without committing the
configuration changes.
– Entering cancel leaves the router in the current
configuration session without exiting or committing the
configuration changes.
• Use the commit command to save the configuration
Configuration Examples for Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
This example shows how to configure Ethernet Data Plane Loopback:
Router# configure
Router(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 0/1
Router((config-if-srv)# ethernet loopback permit external
This example shows how to start an Ethernet Data Plane Loopback:
Router# ethernet loopback start local interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
external
[source mac-address <addr>]
[destination mac-address <addr>]
[ether-type <etype>]
[{dot1q <vlan-ids> [second-dot1q <vlan-ids>] |
dot1ad <vlan-ids> [dot1q <vlan-ids>]}]
[cos <cos>]
[llc-oui <oui>]
[timeout {<length> | none}]
This example shows how to stop an Data Plane Loopback:
Router# ethernet loopback stop local interface <name> id <id>
changes to the running configuration file and remain
within the configuration session.
66
This example shows how to extend an Ethernet Data Plane Loopback:
router# ethernet loopback extend local interface <name> id <id> length
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 75

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
<length>
Verifying the Ethernet Data Plane Loopback Configuration
Use the show ethernet loopback permitted command to display all the permitted interfaces which run
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback sessions:
router# show ethernet loopback permitted
Interface Direction
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------GigabitEthernet0/0/0/0 External
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1.100 Internal
GigabitEthernet 0/1.200 External, Internal
Use the show ethernet loopback active command to view active sessions:
Router# show ethernet loopback active interface GigabitEthernet 0/1.200
Local: GigabitEthernet0/1.200, ID 1
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Direction: Internal
Time out: 2 hours
Time left: 00:01:17
Status: Active
Filters:
Dot1ad: 100-200
Dot1q: Any
Source MAC Address: aaaa.bbbb.cccc
Destination MAC Address: Any
Ethertype: 0x8902
Class of Service: Any
LLC-OUI: Any
Local: GigabitEthernet0/1.200, ID 2
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------Direction: External
Time out: 10 minutes
Time left: 00:00:00
Status: Stopping
Filters:
Dot1q: 500
Second-dot1q: 200
Source MAC Address: Any
Destination MAC Address: Any
Ethertype: Any
Class of Service: 4
LLC-OUI: Any
Ethernet Data Plane Loopback
For each loopback session listed, this information is displayed:
• Header containing the Interface name and session ID, which uniquely identify the local loopback
session,
• Direction which specifies the direction of the loopback,
• Time out – the time out period specified when the loopback was started,
• Time left – the amount of time left until the loopback session is automatically stopped,
• Status – the status of the loopback session,
• Filters – details of the filters specified when the loopback session was started. Similar to the start
CLI, only the filters supported by the platform are displayed.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
67
Page 76

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
IEEE CFM is an end-to-end per-service Ethernet-layer Operations, Administration, and Maintenance
(OAM) protocol. CFM includes proactive connectivity monitoring, fault verification, and fault isolation
for large Ethernet metropolitan-area networks (MANs) and WANs.
CFM over EVC BD (Up mep) and CFM over EVC BD (Down mep) features are supported on CFM over
EVC BD.
CFM over Xconnect (Up mep) and CFM over Xconnect (Down mep) features are not supported on CFM
over EVC BD.
The benefits of Ethernet CFM are:
• End-to-end service-level OAM technology
• Reduced operating expense for service provider Ethernet networks
• Competitive advantage for service providers
Note This feature is supported only if you have purchased the appxk9 licensing package. CFM over EVC BD
is available only on the Cisco 890 series ISR and ISRG2 platforms. For more information about
managing software activation licenses on the Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html.
Restrictions for Configuring Ethernet CFM
• A specific domain must be configured. If it is not, an error message is displayed.
• Multiple domains (different domain names) having the same maintenance level can be configured.
However, associating a single domain name with multiple maintenance levels is not permitted.
Configuring Ethernet CFM
• Provisioning the Network (CE-A), page 68
• Provisioning the Network (CE-B), page 70
• Provisioning Service (CE-A), page 73
• Provisioning Service (CE-B), page 76
• Configuring and Enabling the Cross-Check Function (CE-A), page 78
• Configuring and Enabling the Cross-Check Function (CE-B), page 80
• Configuration Examples for Configuring Ethernet CFM for the Cisco ISR G2 Routers, page 81
Provisioning the Network (CE-A)
Complete these steps to configure provisioning the network (CE-A):
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
68
Page 77

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
Step 4 mep archive-hold-time minutes
Step 5 exit
Step 6 ethernet cfm global
Step 7 ethernet cfm ieee
Step 8 ethernet cfm traceroute cache
Step 9 ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
Step 10 ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
Step 11 snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config] [loop] [cross-connect]
Step 12 snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mep-unknown] [mep-missing] [service-up]
Step 13 end
DETAILED STEPS
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Command Purpose
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
level-id
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a particular
maintenance level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration
mode.
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain
Customer level 7
mep archive-hold-time minutes
Sets the amount of time that data from a missing MEP is
kept in the continuity check database or that entries are
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# mep
archive-hold-time 60
exit
held in the error database before they are purged.
Returns the device to global configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# exit
Step 6
ethernet cfm global
Enables CFM processing globally on the device.
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm global
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
69
Page 78

Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Command Purpose
Step 7
Step 8
ethernet cfm ieee
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache
Step 9
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size
entries
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache size 200
Step 10
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
hold-time minutes
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Enables the CFM IEEE version of CFM.
• This command is automatically issued when the
ethernet cfm global command is issued.
Enables caching of CFM data learned through traceroute
messages.
Sets the maximum size for the CFM traceroute cache
table.
Sets the amount of time that CFM traceroute cache entries
are retained.
Step 11
Step 12
Step 13
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache hold-time 60
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm
cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config]
[loop] [cross-connect]
Example:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable
traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down
config loop cross-connect
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm
crosscheck [mep-unknown]
[mep-missing] [service-up]
Example:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable
traps ethernet cfm crosscheck
mep-unknown
end
Example:
Router(config)# end
Enables SNMP trap generation for Ethernet CFM
continuity check events.
Enables SNMP trap generation for Ethernet CFM
continuity check events in relation to the cross-check
operation between statically configured MEPs and those
learned via CCMs.
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode.
Provisioning the Network (CE-B)
Complete these steps to configure provisioning the network (CE-B):
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
70
Page 79

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id [direction outward]
Step 4 mep archive-hold-time minutes
Step 5 exit
Step 6 ethernet cfm global
Step 7 ethernet cfm ieee
Step 8 ethernet cfm traceroute cache
Step 9 ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
Step 10 ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
Step 11 snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config] [loop] [cross-connect]
Step 12 snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck [mep-unknown] [mep-missing] [service-up]
Step 13 end
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Command Purpose
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
level-id [direction outward]
Defines an outward CFM maintenance domain at a
particular maintenance level and enters Ethernet CFM
configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain
Customer level 7 direction outward
mep archive-hold-time minutes
Sets the amount of time that data from a missing MEP is
kept in the continuity check database or that entries are
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# mep
archive-hold-time 60
exit
held in the error database before they are purged.
Returns the device to global configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# exit
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
71
Page 80

Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Command Purpose
Step 6
ethernet cfm global
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm global
Step 7
Step 8
ethernet cfm ieee
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache
Step 9
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size
entries
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Enables CFM processing globally on the device.
Enables the CFM IEEE version of CFM.
• This command is automatically issued when the
ethernet cfm global command is issued.
Enables caching of CFM data learned through traceroute
messages.
Sets the maximum size for the CFM traceroute cache
table.
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
Step 13
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
hold-time minutes
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache hold-time 60
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm
cc [mep-up] [mep-down] [config]
[loop] [cross-connect]
Example:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable
traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down
config loop cross-connect
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm
crosscheck [mep-unknown]
[mep-missing] [service-up]
Example:
Router(config)# snmp-server enable
traps ethernet cfm crosscheck
mep-unknown
end
Sets the amount of time that CFM traceroute cache entries
are retained.
Enables SNMP trap generation for Ethernet CFM
continuity check events.
Enables SNMP trap generation for Ethernet CFM
continuity check events in relation to the cross-check
operation between statically configured MEPs and those
learned via CCMs.
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode.
72
Example:
Router(config)# end
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 81

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Provisioning Service (CE-A)
Perform this task to set up service for Ethernet CFM. Optionally, when this task is completed, you may
configure and enable the cross-check function. To perform this optional task, see "Configuring and
Enabling the Cross-Check Function (CE-A)".
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
Step 4 service {ma-name | ma-num | vlan-id vlan-id | vpn-id vpn-id} [port | vlan vlan-id [direction down]]
Step 5 continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep]
Step 6 continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep]
Step 7 continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep]
Step 8 exit
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Step 9 mep archive-hold-time minutes
Step 10 exit
Step 11 ethernet cfm global
Step 12 ethernet cfm ieee
Step 13 ethernet cfm traceroute cache
Step 14 ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
Step 15 ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
Step 16 interface type number
Step 17 ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name mpid mpid {port | vlan vlan-id}
Step 18 ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name mpid mpid {port | vlan vlan-id}
Step 19 end
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Command Purpose
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
73
Page 82

Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Command Purpose
Step 3
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
level-id
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain
Customer level 7
Step 4
service {ma-name | ma-num | vlan-id
vlan-id | vpn-id vpn-id} [port | vlan
vlan-id [direction down]]
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# service
Customer1 vlan 101 direction down
Step 5
continuity-check [interval time |
loss-threshold threshold | static
rmep]
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a particular
maintenance level and enters Ethernet CFM configuration
mode.
Configures an MA within a maintenance domain and
enters CFM service configuration mode.
• If a service is already configured and you configure a
new MA name and also specify the direction down
keyword, a second service is added that maps to the
same VLAN. If you configure a new MA name and
do not specify the direction down keyword, the
service is renamed to the new MA name.
Enables the transmission of CCMs.
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#
continuity-check
continuity-check [interval time |
loss-threshold threshold | static
rmep]
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#
continuity-check interval 10
continuity-check [interval time |
loss-threshold threshold | static
rmep]
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#
continuity-check loss-threshold 10
exit
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit
mep archive-hold-time minutes
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# mep
archive-hold-time 60
exit
Configures the time period between CCM transmissions.
• The values supported are platform dependent.
Sets the number of CCMs that should be missed before
declaring that a remote MEP is down.
Returns the device to Ethernet CFM configuration mode.
Sets the amount of time that data from a missing MEP is
kept in the continuity check database or that entries are
held in the error database before they are purged.
Returns the device to global configuration mode.
74
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# exit
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 83

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Command Purpose
Step 11
ethernet cfm global
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm global
Step 12
Step 13
ethernet cfm ieee
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache
Step 14
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size
entries
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Enables CFM processing globally on the device.
Enables the CFM IEEE version of CFM.
• This command is automatically issued when the
ethernet cfm global command is issued.
Enables caching of CFM data learned through traceroute
messages.
Sets the maximum size for the CFM traceroute cache
table.
Step 15
Step 16
Step 17
Step 18
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
hold-time minutes
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache hold-time 60
interface type number
Example:
Router(config)# interface ethernet
0/3
ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name
mpid mpid {port| vlan vlan-id}
Example:
Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep
domain Customer mpid 701 vlan 100
ethernet cfm mep domain domain-name
mpid mpid {port| vlan vlan-id}
Sets the amount of time that CFM traceroute cache entries
are retained.
Specifies an interface and enters interface configuration
mode.
Sets a port as internal to a maintenance domain and
defines it as a MEP.
Sets a port as internal to a maintenance domain and
defines it as a MEP.
Example:
Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep
domain Customer mpid 701 vlan 100
Step 19
end
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
75
Page 84

Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Provisioning Service (CE-B)
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id [direction outward]
Step 4 mep archive-hold-time minutes
Step 5 service {ma-name | ma-num | vlan-id vlan-id | vpn-id vpn-id} [port | vlan vlan-id [direction down]]
Step 6 continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep]
Step 7 continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep]
Step 8 continuity-check [interval time | loss-threshold threshold | static rmep]
Step 9 exit
Step 10 exit
Step 11 ethernet cfm global
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Step 12 ethernet cfm ieee
Step 13 ethernet cfm traceroute cache
Step 14 ethernet cfm traceroute cache size entries
Step 15 ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time minutes
Step 16 interface type number
Step 17 ethernet cfm mep level level-id [inward | outward domain domain-name] mpid id vlan{any | vlan-id
Step 18 end
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
| , vlan-id | vlan-id - vlan-id | vlan-id - vlan-id}
Command Purpose
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
level-id [direction outward]
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level
and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode.
76
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain
Customer level 7 direction outward
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 85

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Command Purpose
Step 4
mep archive-hold-time minutes
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# mep
archive-hold-time 60
Step 5
service {ma-name | ma-num | vlan-id
vlan-id | vpn-id vpn-id} [port | vlan
vlan-id [direction down]]
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# service
Customer1 vlan 101 direction down
Step 6
continuity-check [interval time |
loss-threshold threshold | static
rmep]
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Sets the amount of time that data from a missing MEP is
kept in the continuity check database or that entries are
held in the error database before they are purged.
Configures an MA within a maintenance domain and
enters CFM service configuration mode.
• If a service is already configured and you configure a
new MA name and also specify the direction down
keyword, a second service is added that maps to the
same VLAN. If you configure a new MA name and
do not specify the direction down keyword, the
service is renamed to the new MA name.
Enables the transmission of CCMs.
Step 7
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#
continuity-check
continuity-check [interval time |
loss-threshold threshold | static
rmep]
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#
continuity-check interval 10
continuity-check [interval time |
loss-threshold threshold | static
rmep]
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)#
continuity-check loss-threshold 10
exit
Example:
Router(config-ecfm-srv)# exit
exit
Configures the time period between CCM transmissions.
• The values supported are platform dependent.
Sets the number of CCMs that should be missed before
declaring that a remote MEP is down.
Returns the device to Ethernet CFM configuration mode.
Returns the device to global configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# exit
Step 11
ethernet cfm global
Enables CFM processing globally on the device.
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm global
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
77
Page 86

Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Command Purpose
Step 12
Step 13
ethernet cfm ieee
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache
Step 14
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size
entries
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache size 200
Step 15
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
hold-time minutes
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Enables the CFM IEEE version of CFM.
• This command is automatically issued when the
ethernet cfm global command is issued.
Enables caching of CFM data learned through traceroute
messages.
Sets the maximum size for the CFM traceroute cache
table.
Sets the amount of time that CFM traceroute cache entries
are retained.
Step 16
Step 17
Step 18
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm
traceroute cache hold-time 60
interface type number
Example:
Router(config)# interface ethernet
0/3
ethernet cfm mep level level-id
[inward | outward domain domain-name]
mpid id vlan{any | vlan-id | ,
vlan-id | vlan-id - vlan-id | vlan-id
- vlan-id}
Example:
Router(config-if)# ethernet cfm mep
level 7 outward domain Customer mpid
701 vlan 100
end
Example:
Router(config-if)# end
Router#
Specifies an interface and enters interface configuration
mode.
Provisions an interface as a domain boundary.
Returns the router to the privileged EXEC mode.
Configuring and Enabling the Cross-Check Function (CE-A)
Perform this task to configure and enable cross-checking for a down MEP. This task requires you to
configure and enable cross-checking on two devices. This task is optional.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
78
Page 87

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
Step 4 mep mpid mpid
Step 5 exit
Step 6 ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay delay
Step 7 exit
Step 8 ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable | disable} domain domain-name] {port | vlan {vlan-id | vlan-id
- vlan-id | , vlan-id - vlan-id}}
DETAILED STEPS
Command Purpose
Step 1
enable
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Step 2
Step 3
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Example:
Router>enable
configure terminal
Example:
Router# configure terminal
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
level-id
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain
Customer level 7
mep mpid mpid
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# mep mpid 702
exit
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# exit
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck
start-delay delay
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm mep
crosscheck start-delay 60
Enter your password when prompted.
Enters the global configuration mode.
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level
and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode.
Statically defines the MEPs within a maintenance
association.
Returns the device to global configuration mode.
Configures the maximum amount of time that the device
waits for remote MEPs to come up before the cross-check
operation is started.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
79
Page 88

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Command Purpose
Step 7
exit
Returns the device to privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config)# exit
Step 8
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable |
disable} domain domain-name] {port |
vlan {vlan-id | vlan-id - vlan-id | ,
vlan-id - vlan-id}}
Enables cross-checking between the list of configured
remote MEPs of a domain and MEPs learned through
CCMs.
Example:
Router# ethernet cfm mep crosscheck
enable domain cust4 vlan 100
Configuring and Enabling the Cross-Check Function (CE-B)
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ethernet cfm domain domain-name level level-id
Step 4 mep mpid mpid
Step 5 exit
Step 6 ethernet cfm mep crosscheck start-delay delay
Step 7 exit
Step 8 ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable | disable} domain domain-name] {port | vlan {vlan-id | vlan-id
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
- vlan-id | , vlan-id - vlan-id}}
Command Purpose
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router>enable
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
80
Example:
Router# configure terminal
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 89

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Command Purpose
Step 3
ethernet cfm domain domain-name level
level-id
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm domain
Customer level 7
Step 4
mep mpid mpid
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# mep mpid 702
Step 5
exit
Example:
Router(config-ecfm)# exit
Step 6
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck
start-delay delay
Example:
Router(config)# ethernet cfm mep
crosscheck start-delay 60
Step 7
exit
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
Defines a CFM maintenance domain at a specified level
and enters Ethernet CFM configuration mode.
Statically defines the MEPs within a maintenance
association.
Returns the device to global configuration mode.
Configures the maximum amount of time that the device
waits for remote MEPs to come up before the cross-check
operation is started.
Returns the device to privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config)# exit
Step 8
ethernet cfm mep crosscheck {enable |
disable} domain domain-name] {port |
vlan {vlan-id | vlan-id - vlan-id | ,
vlan-id - vlan-id}}
Enables cross-checking between the list of configured
remote MEPs of a domain and MEPs learned through
CCMs.
Example:
Router# ethernet cfm mep crosscheck
enable domain cust4 vlan 100
Configuration Examples for Configuring Ethernet CFM for the Cisco ISR G2 Routers
The following two examples show configurations for a network. Configurations are shown not only for
the Carrier Ethernet Cisco ISR G2 Routers, but also for the devices used at the access and core of the
service provider’s network.
• Example: Provisioning a Network, page 81
• Example: Provisioning Service, page 84
Example: Provisioning a Network
This configuration example shows only CFM-related commands. All commands that are required to set
up the data path and configure the VLANs on the device are not shown. However, it should be noted that
CFM traffic will not flow into or out of the device if the VLANs are not properly configured.
CE-A Configuration
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
81
Page 90

Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
!
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm mip auto-create level 7 vlan 1-4094
!
interface gigabitethernet3/2
ethernet cfm mip level 7 vlan 101 <<<< Manual MIP
ethernet cfm mep domain ServiceProvider-L4 mpid 401 vlan 101
ethernet cfm mep domain OperatorA-L1 mpid 101 vlan 101
!
interface gigabitethernet4/2
ethernet cfm mip level 1 vlan 101 <<<< Manual MIP
!
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop config
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-up
U-PE A Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
!
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm mip auto-create level 7 vlan 1-4094
!
interface gigabitethernet3/2
ethernet cfm mip level 7 vlan 101 <<<< Manual MIP
ethernet cfm mep domain ServiceProvider-L4 mpid 401 vlan 101
ethernet cfm mep domain OperatorA-L1 mpid 101 vlan 101
!
interface gigabitethernet4/2
ethernet cfm mip level 1 vlan 101 <<<< Manual MIP
!
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop config
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-up
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
82
PE-AGG A Configuration
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm domain OperatorA-L1 level 1
mep archive-hold-time 65
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1OpA vlan 101
!
interface gigabitethernet3/1
ethernet cfm mip level 1 vlan 101 <<<< Manual MIP
!
interface gigabitethernet4/1
ethernet cfm mip level 1 <<<< Manual MIP
N-PE A Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
!
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 91

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider-L4 level 4
mep archive-hold-time 60
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1 vlan 101
continuity-check
!
ethernet cfm domain OperatorA level 1
mep archive-hold-time 65
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1OpA vlan 101
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet3/0
ethernet cfm mip level 1 <<<< manual MIP
!
interface gigabitethernet4/0
ethernet cfm mip level 4 <<<< manual MIP
!
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop config
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-up
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
U-PE B Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm domain Customer-L7 level 7
mip auto-create
service Customer1 vlan 101 direction down
!
ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider-L4 level 4
mep archive-hold-time 60
service MetroCustomer1 vlan 101
continuity-check
!
ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2
mip auto-create
mep archive-hold-time 65
service MetroCustomer1OpB vlan 101
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet1/0
ethernet cfm mip level 7 <<<< manual MIP
!
interface gigabitethernet2/0
ethernet cfm mip level 2 <<<< manual MIP
!
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop config
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-up
PE-AGG B Configuration
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
!
ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
83
Page 92

Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
mep archive-hold-time 65
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1OpB vlan 101
!
interface gigabitethernet1/1
ethernet cfm mip level 2 <<<< manual MIP
!
interface gigabitethernet2/1
ethernet cfm mip level 2 <<<< manual MIP
N-PE B Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
!
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4
mep archive-hold-time 60
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1 vlan 101
continuity-check
!
ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2
mep archive-hold-time 65
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1OpB vlan 101
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet1/2
ethernet cfm mip level 2 <<<< manual MIP
!
interface gigabitethernet2/2
ethernet cfm mip level 4 <<<< manual MIP
!
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop config
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-up
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
CE-B Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm domain Customer-L7 level 7
service Customer1 vlan 101 direction down
continuity-check
!
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm cc mep-up mep-down cross-connect loop config
snmp-server enable traps ethernet cfm crosscheck mep-missing mep-unknown service-up
Example: Provisioning Service
CE-A Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
84
Page 93

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm domain Customer-L7 level 7
service Customer1 vlan 101 direction down
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet3/2
ethernet cfm mep domain Customer-L7 mpid 701 vlan 101
U-PE A Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm mip auto-create level 7 vlan 1-4094
!
ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider-L4 level 4
mep archive-hold-time 60
service MetroCustomer1 vlan 101
continuity-check
!
ethernet cfm domain OperatorA-L1 level 1
mep archive-hold-time 65
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1OpA vlan 101
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet3/2
ethernet cfm mip level 7 vlan 101 <<<< Manual MIP
ethernet cfm mep domain ServiceProvider-L4 mpid 401 vlan 101
ethernet cfm mep domain OperatorA-L1 mpid 101 vlan 101
!
interface gigabitethernet4/2
ethernet cfm mip level 1 vlan 101 <<<< Manual MIP
Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
PE-AGG A Configuration
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm domain OperatorA-L1 level 1
mep archive-hold-time 65
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1OpA vlan 101
!
interface gigabitethernet3/1
ethernet cfm mip level 1 vlan 101 <<<< Manual MIP
!
interface gigabitethernet4/1
ethernet cfm mip level 1 <<<< Manual MIP
N-PE A Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
!
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
85
Page 94

Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) over EVC BD
!
ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider-L4 level 4
mep archive-hold-time 60
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1 vlan 101
continuity-check
!
ethernet cfm domain OperatorA level 1
mep archive-hold-time 65
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1OpA vlan 101
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet3/0
ethernet cfm mip level 1 <<<< manual MIP
!
interface gigabitethernet4/0
ethernet cfm mip level 4 <<<< manual MIP
ethernet cfm mep domain OperatorA mpid 102 vlan 101
U-PE B Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm domain Customer-L7 level 7
mip auto-create
service Customer1 vlan 101 direction down
!
ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider-L4 level 4
mep archive-hold-time 60
service MetroCustomer1 vlan 101
continuity-check
!
ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2
mep archive-hold-time 65
service MetroCustomer1OpB vlan 101
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet1/0
ethernet cfm mip level 7 <<<< manual MIP
ethernet cfm mep domain ServiceProvider-L4 mpid 402 vlan 101
ethernet cfm mep domain OperatorB mpid 201 vlan 101
!
interface gigabitethernet2/0
ethernet cfm mip level 2 <<<< manual MIP
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
86
N-PE B Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm domain ServiceProvider level 4
mep archive-hold-time 60
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1 vlan 101
continuity-check
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 95

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
!
ethernet cfm domain OperatorB level 2
mep archive-hold-time 65
mip auto-create
service MetroCustomer1OpB vlan 101
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet1/2
ethernet cfm mip level 2 <<<< manual MIP
!
interface gigabitethernet2/2
ethernet cfm mip level 4 <<<< manual MIP
ethernet cfm mep domain OperatorB mpid 202 vlan 101
CE-B Configuration
!
ethernet cfm global
ethernet cfm ieee
ethernet cfm traceroute cache
ethernet cfm traceroute cache size 200
ethernet cfm traceroute cache hold-time 60
!
ethernet cfm domain Customer-L7 level 7
service Customer1 vlan 101 direction down
continuity-check
!
interface gigabitethernet3/2
ethernet cfm mep domain Customer-L7 mpid 702 vlan 101
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring for EVC BD
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring for EVC BD
Y.1731 Performance Monitoring (PM) provides a standard Ethernet PM function that includes
measurement of Ethernet frame delay, frame delay variation, frame loss, and frame throughput
measurements specified by the ITU-T Y-1731 standard and interpreted by the Metro Ethernet Forum
(MEF) standards group.ITU-T Y.1731 feature supports key operation and maintenance standards that
provide for automated end-to-end management and monitoring of Ethernet service by service providers.
Note This feature is supported only if you have purchased the DATA technology package functionality
(datak9) licensing package. For more information about managing software activation licenses on the
Cisco ISR and Cisco ISR G2 platforms, see
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/routers/access/sw_activation/SA_on_ISR.html.
Configuring a Sender MEP for a Single-Ended Ethernet Delay or Delay Variation Operation
Perform this task to configure a sender MEP on the source device.
Before You Begin
Time synchronization is required between the source and destination devices in order to provide accurate
one-way delay (latency) or delay-variation measurements. Configure either Precision Time Protocol
(PTP) or Network Time Pprotocol (NTP) on both the source and destination devices.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
87
Page 96

Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring for EVC BD
Note To display information about remote (target) MEPs on destination devices, use the show ethernet cfm
maintenance-points remote command.
SUMMARY STEPS
Step 1 enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Step 3 ip sla operation-number
Step 4 ethernet y1731 delay dmm domain domain-name {evc evc-id | vlan vlan-id} {mpid target-mp-id |
mac-address target-address} cos cos {source {mpid source-mp-id | mac-address source-address}}
Step 5 clock sync
Step 6 aggregate interval seconds
Step 7 distribution {delay | delay-variation} one-way number-of-bins boundary[,...,boundary]
Step 8 frame interval milliseconds
Step 9 frame offset offset-value
Step 10 frame size bytes
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Step 11 history interval intervals-stored
Step 12 max-delay milliseconds
Step 13 owner owner-id
Step 14 end
DETAILED STEPS
Step 1
Step 2
Step 3
Command Purpose
enable
Enables the privileged EXEC mode.
Enter your password when prompted.
Example:
Router> enable
configure terminal
Enters the global configuration mode.
Example:
Router# configure terminal
ip sla operation-number
Begins configuring an IP SLAs operation and enters IP
SLA configuration mode.
Example:
Router(config-term)# ip sla 10
88
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 97

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Command Purpose
Step 4
ethernet y1731 delay dmm domain
domain-name {evc evc-id | vlan
vlan-id} {mpid target-mp-id |
mac-address target-address} cos cos
{source {mpid source-mp-id |
mac-address source-address}}
Example:
Router(config-ip-sla)# ethernet y1731
delay dmm domain xxx evc yyy mpid 101
cos 4 source mpid 100
Step 5
clock sync
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# clock
sync
Step 6
aggregate interval seconds
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#
aggregate interval 900
Step 7
distribution {delay |
delay-variation} one-way
number-of-bins
boundary[,...,boundary]
Support for Y.1731 Performance Monitoring for EVC BD
Begins configuring a single-ended Ethernet delay
operation and enters IP SLA Y.1731 delay configuration
mode.
(Optional) Indicates that the end points are synchronized
and thus allows the operation to calculate one-way delay
measurements.
(Optional) Configures the length of time during which the
performance measurements are conducted and the results
stored.
(Optional) Specifies measurement type and configures
bins for statistics distributions kept.
Step 8
Step 9
Step 10
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#
distribution delay-variation one-way
5 5000,10000,15000,20000,-1
frame interval milliseconds
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# frame
interval 100
frame offset offset-value
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# frame
offset 1
frame size bytes
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# frame
size 32
(Optional) Sets the gap between successive frames.
(Optional) Sets the value for calculating delay variation
values.
(Optional) Configures padding size for frames.
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
89
Page 98

Support for Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVI) on ISR G2 Metro Ethernet BD
Command Purpose
Step 11
Step 12
Step 13
Step 14
history interval intervals-stored
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#
history interval 2
max-delay milliseconds
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)#
max-delay 5000
owner owner-id
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# owner
admin
end
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
(Optional) Sets the number of statistics distributions kept
during the lifetime of an IP SLAs Ethernet operation.
(Optional) Sets the amount of time an MEP waits for a
frame.
(Optional) Configures the owner of an IP SLAs operation.
Exits to privileged EXEC mode.
Example:
Router(config-sla-y1731-delay)# end
What to Do Next
To add proactive threshold conditions and reactive triggering for generating traps, see the “Configuring
Proactive Threshold Monitoring" module of the IP SLAs Configuration Guide.
When you are finished configuring proactive threshold monitoring for this operation, see the
"Scheduling IP SLAs Operations" section to schedule the operation.
Support for Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVI) on ISR G2 Metro
Ethernet BD
You can connect a SVI with a Metro Ethernet BD to re-direct the traffic from a switch port onto the BD
and vice versa, as shown in Figure 1.
90
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
Page 99

Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
Figure 1 Re-directing the traffic from a SV1 onto the BD and vice versa
Bridge-Domain
SVI
Switch
Support for Switch Virtual Interfaces (SVI) on ISR G2 Metro Ethernet BD
EVC
EVCEVC
Once the SV1 is connected, packets coming into a switch port is re-directed to the SVI and onto the BD.
On entering the BD, the source MAC address is learned and the packet is bridged. In the opposite
direction, packets coming onto the BD from an EVC via the switch port are directed out the SVI.
Restrictions for SVI support on BDs
• Only one SVI may be associated with a BD.
• There is no EVC (i.e. service instance) configuration on an SVI.
• All packets on the BD, including those from EVCs, should be tagged, with the VLAN tag specifying
the VLAN id of the SVI.
• Only access port configurations are supported.
Configuring SVI as Access Port
First you configure the switch port to add an access port SVI to a BD. After this you need to define the
associated VLAN interface.
Note The BD id does not have to match the VLAN id in the dot1q tag, but all packets on the BD must be tagged
with that VLAN number. So an EVC could be configured in which the BD id matches the VLAN id.
364528
Configuration Examples to add an Access Port SVI to a BD
This example shows how to add an Access Port SVI to a BD:
interface GigabitEthernet4
switchport access vlan 40
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
91
Page 100

EVC Quality of Service (QoS)
no ip address
end
This example shows how to define the associated VLAN interface:
interface Vlan40
no ip address
bridge-domain 40
end
This example shows the BD id matching with the VLAN id:
interface GigabitEthernet8
no ip address
duplex auto
speed auto
service instance 40 ethernet
encapsulation dot1q 40
bridge-domain 40
!
End
Chapter Configuring Ethernet Virtual Connection Bridge Domain
EVC Quality of Service (QoS)
For information about EVC QoS, see
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/ios-xml/ios/qos_mqc/configuration/xe-3s/qos-mqc-xe-3s-book/q
os-evc.html.
92
Cisco 3900 Series, Cisco 2900 Series, and Cisco 1900 Series Integrated Services Routers Generation 2 Software Configuration Guide
 Loading...
Loading...