Page 1

AN241
Analog Input Buffer Architectures
by Kevin L Tretter
1. Introduction
There are many considerations that must be taken into account when designing and implementing an analog input buffer. These include negligible noise contribution, input biasing, isolation from switched capacitor currents, maintaining a low output impedance so as not to cause distortion, and providing antialias filtering appropriate for the modulator sampling rate.
This application note provides several filter topologies that address the above concerns. The following analog input buffers have been divided into four categories: fully differential, single-ended to differential, single-ended with dedicated reference pins for each channel, and single-ended with a common, or shared,
reference.
2. Fully Differential Analog Input Buffer
2.1 Applicable Converters
A fully differential analog input buffer is ideal for use with the following Cirrus Logic audio converters:
- CS5361
- CS5381
- CS4272
- CS42528/26/18/16
- CS42428/26/18/16
2.2 Introduction to Differential Signals
A differential signal can be defined as two nodes that have equal but opposite signals around a fixed point
(called the common mode level). The two signal nodes are typically referred to as positive and negative
(or non-inverting and inverting), as shown in the following example of a differential sine wave:
CSxxxx
3.91 V
2.50 V
1.09 V
3.91 V
2.50 V
1.09 V
Full Scale Input Level = (AIN+) - (AIN-) = 5.64 Vpp
Figure 1. Example of a Differential Signal
AIN+
AIN-
http://www.cirrus.com
Copyright Cirrus Logic, Inc. 2003
(All Rights Reserved)
OCT ‘03
AN241REV1
1
Page 2
AN241
In the above example, the full scale input voltage is 5.64 Vpp (differentially), with each leg swinging
2.82 Vpp. Please note that the full scale input voltage level may vary from part to part. Also, the common
mode level (which in the above example is 2.5 0V) can also vary depending on the converter.
2.3 Recommended Filter Topology
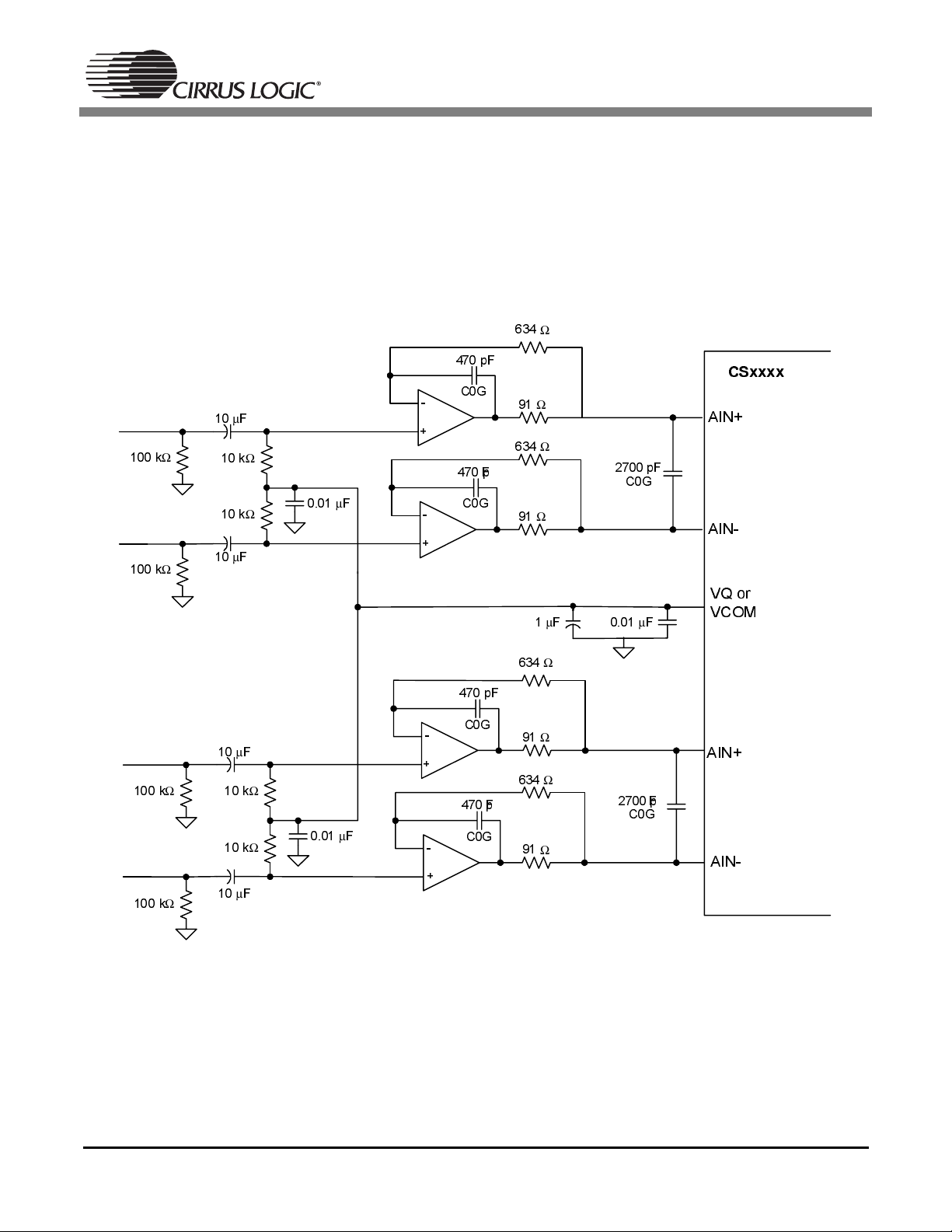
Figure 2 shows a fully differential analog input buffer. This buffer provides proper biasing, isolation from
the switched capacitor currents, low output impedance, and anti-alias filtering. The noise contribution of
this buffer is determined primarily by the noise floor of the op-amp.
634
Ω
100 k
100 k
100 k
100 k
470 pF
CSxxxx
C0G
-
10µF
Ω
10 k
10 k
Ω
Ω
0.01µF
+
470 pF
C0G
-
91
634
91
Ω
AIN+
Ω
2700 pF
C0G
Ω
AIN-
Ω
10µF
+
VQ or
1µF
634
Ω
470 pF
C0G
-
10µF
Ω
10 k
10 k
Ω
Ω
0.01µF
+
470 pF
C0G
-
-
91
634
91
Ω
Ω
Ω
0.01µF
2700 pF
C0G
VCOM
AIN+
AIN-
+
Ω
10µF
Figure 2. Fully Differential Input Buffer
2.4 Overview of the Filter Topology
2.4.1 High Pass Filter and DC Biasing
The first stage of the buffer forms a high pass filter and provides the proper biasing to the positive terminals of the op-amps. The high pass filter is formed from the combination of the AC-coupling capacitor
along with the resistor to the bias voltage reference (VQ or VCOM, depending on the naming convention).
The 3 dB corner of the high pass filter can be calculated as follows:
2
Page 3

AN241
F
C
where: R is the value of the resistor (in Ohms)
C
is the value of the capacitor (in Farads)
R
In the input buffer shown in Figure 2,
mately 1.59 Hz. Typically, this corner should be at least one decade below the bandwidth of interest in
order to prevent a significant droop in the frequency response.
The proper DC biasing (common mode level) is set via the on-chip reference (VQ or VCOM). In the input
buffer shown above, the bias is set through a 10k
eral implications. Since the input impedance into the op-amp is extremely high, the effective input impedance into the analog input buffer will be determined by the value of the resistor to the bias voltage in
parallel with the 100 k
mately 9 k
ure 2, the AC-coupling capacitor will initially be charged up via the on-chip reference (VQ or VCOM). This
charge up time is dependent on the size of the AC-coupling capacitor and the amount of series resistance
to the reference voltage supply. The reference pin (VQ or VCOM) has an associated output impedance
that must also be considered when calculating the charge up time. The time constant can be calculated
as follows:
Ω.
Ideally, the larger this input impedance the better. However, in the input buffer shown in Fig-
Ω
shunt resistor. In the input buffer shown above, the input impedance is approxi-
= 10 kΩ and C = 10µF. This places the 3 dB corner at approxi-
1
=
RC
π
2
Ω
resistor. Please note that this resistor value has sev-
RC=
τ
R
where
In the input buffer shown in Figure 2,
pin), and C = 10µF. This produces a time constant of 0.35 s. This would indicate that the capacitor will
charge up to within 99% of the final DC value in approximately 1.75 s (which is 5 time constants). The
100 k
gardless of whether or not there is an input signal source present.
2.4.2 Op Amp Circuitry and Anti-Aliasing Capacitor
The op-amp topology used in the input buffer shown in Figure 2 addresses two issues. First, it provides
an extremely low output impedance and therefore minimizes the amount of distortion presented to the
converters internal sampling circuits. By placing the 91
divided by the open-loop gain of the op-amp, providing a sub-ohm output impedance. Secondly, this opamp topology provides a low pass filter. Using the recommended values, this filter remains flat throughout
the audio passband and provides approximately 2 0dB of rejection at the modulator sampling rate (where
the converter is susceptible to aliasing). The characteristics of this low pass filter can be changed by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop. However, it is important to maintain
a flat frequency response throughout the passband of interest and to provide reasonable attenuation at
the input sampling rate of the converter. Also, low value resistors should be used to minimize the addition
of resistor thermal noise.
= the amount of resistance between the AC-coupling capacitor and reference voltage (in
Ohms)
C
= the value of capacitance of the AC-coupling capacitor (in Farads)
R
= 35 kΩ (assuming a 25kΩ output impedance on the reference
Ω
resistors to ground on the input node allow a DC path to charge the AC-coupling capacitors, re-
Ω
resistor in the feedback loop, it’s resistance is
3
Page 4

AN241
Figure 2 implements a common mode capacitor between the positive and negative nodes of the differential inputs. This capacitor is commonly referred to as the anti-aliasing capacitor, and performs several
functions. The value of the capacitor affects the overall low pass filter response and the amount of attenuation at the modulator sampling rate. This capacitor also acts as a charge reservoir for the internal sampling capacitors. Since this capacitor is located in the signal path, it is very important not to use capacitors
with a large voltage coefficient (such as general purpose ceramics) since they can degrade signal linearity.
3. Single-Ended to Differential Input Buffer
3.1 Applicable Converters
A single-ended to differential analog input buffer is ideal for use with the following Cirrus Logic audio converters:
- CS5361
- CS4272
- CS42528/26/18/16
- CS42428/26/18/16
3.2 Introduction
A single-ended signal consists of only one signal line and hence requires only one input pin. Single-ended
inputs typically require less input buffer components, but also have several disadvantages. First, at a given voltage level, a single-ended input cannot produce as much signal swing as a differential signal, hence
reducing the dynamic range. Also, single-ended inputs are more prone to errors caused by DC offsets and
coupled-noise.
3.3 Recommended Filter Topology
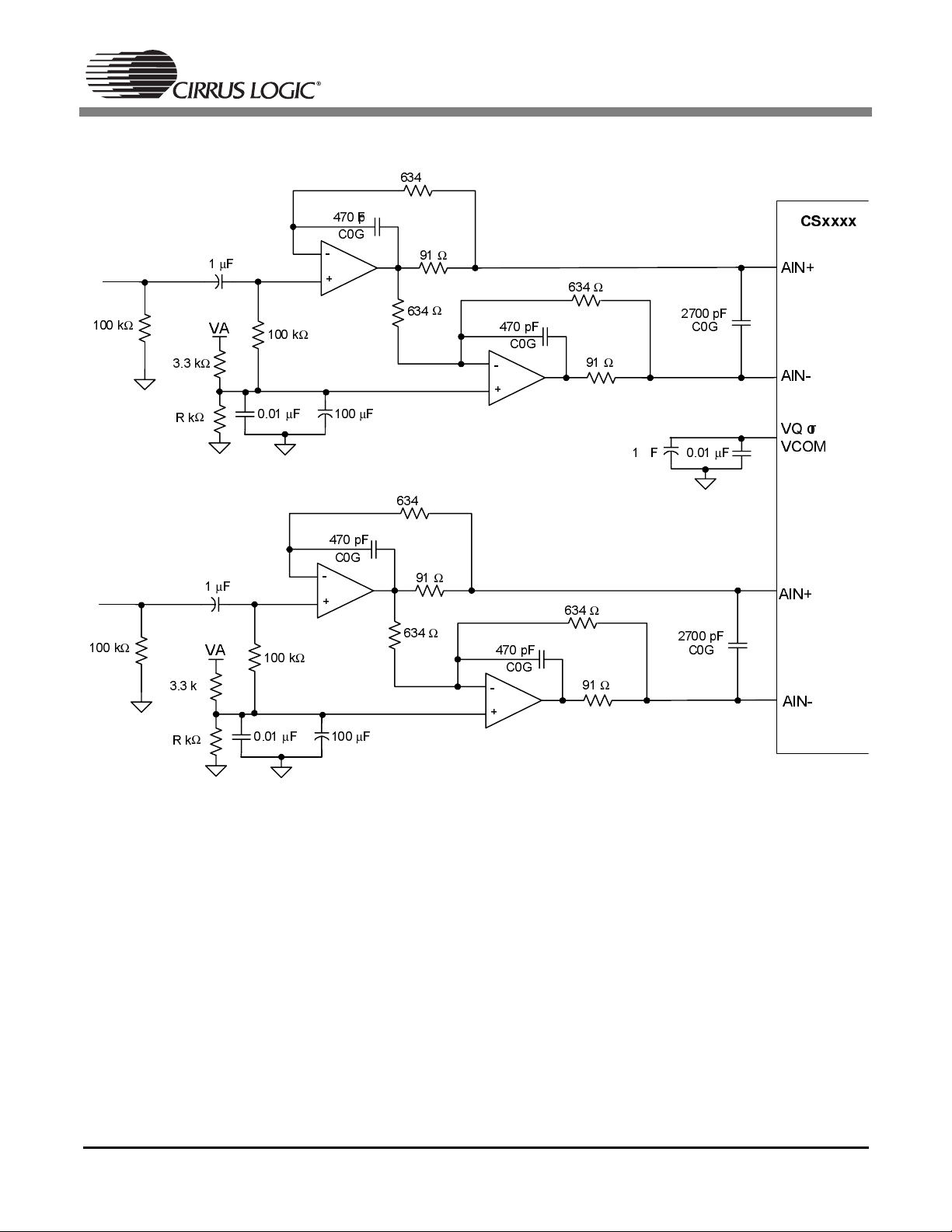
Figure 3 shows a single-ended to differential analog input buffer. This buffer provides proper biasing, isolation from the switched capacitor currents, low output impedance, and anti-alias filtering. The second opamp stage is set up in an inverting configuration to produce the negative node of the differential input. In
the input buffer shown below, the second stage has unity gain, and the single-ended input level will effectively be doubled when presented differentially to the converter. For example, a 2Vpp single-ended input
will provide a 4Vpp differential input to the converter.
4
Page 5
634
AN241
Ω
100 k
100 k
470 pF
C0G
1µF
Ω
Ω
3.3 k
Rk
3.3 k
Rk
VA
Ω
Ω
1µF
VA
Ω
Ω
100 k
0.01µF100µF
100 k
0.01µF100µF
-
+
Ω
470 pF
C0G
-
+
Ω
634
634
634
91
91
Ω
634
Ω
Ω
470 pF
C0G
Ω
634
91
91
Ω
Ω
-
+
Ω
Ω
Ω
470 pF
C0G
-
+
2700 pF
C0G
0.01µF1µF
2700 pF
C0G
CSxxxx
AIN+
AIN-
VQ or
VCOM
AIN+
AIN-
Figure 3. Single-Ended to Differential Input Buffer
3.4 Overview of the Filter Topology
3.4.1 High Pass Filter and DC Biasing
The first stage of the buffer forms a high pass filter and provides the proper biasing to the positive terminals of the op-amps. The value of the resistors denoted as “R” will vary depending on the optimal DC bias
for the given converter. Typically this is around half of the VA voltage supply. The high pass filter is formed
from the combination of the AC-coupling capacitor along with the resistor that connects the positive terminal of the op-amp to the DC bias voltage. The 3dB corner of the high pass filter can be calculated as
follows:
5
Page 6

AN241
1
=
F
C
π
CR
2
EQ
where:
In the input buffer shown in Figure 3,
R
is the value of the equivalent resistance (in Ohms)
EQ
C
is the value of the capacitor (in Farads)
REQ
= 100 kΩ and C = 1.0µF. This places the 3 dB corner at approximately 1.59 Hz. Typically, this corner should be at least one decade below the bandwidth of interest
in order to prevent a significant droop in the frequency response.
Since the input impedance into the op-amp is extremely high, the effective input impedance into the analog input buffer will be determined by the value of the resistor to the bias voltage in parallel with the 100 k
shunt resistor. In the input buffer shown above, the input impedance is approximately 50 k
Ω.
Ideally, the
Ω
larger this input impedance the better. However, in the input buffer shown in Figure 3, the AC-coupling
capacitor will initially be charged up via the resistor divider on VA. This charge up time is dependent on
the size of the AC-coupling capacitor and the amount of series resistance to the reference voltage supply.
The time constant can be calculated as follows:
=
τ
CR
S
R
where
= the amount of resistance between the AC-coupling capacitor and reference voltage (in
S
Ohms)
C
= the value of capacitance of the AC-coupling capacitor (in Farads)
R
In the input buffer shown in Figure 3,
≈ 100 kΩ, and C = 1.0µF. This produces a time constant of 0.1 s.
S
This would indicate that the capacitor will charge up to within 99% of the final DC value in approximately
0.5 s (which is 5 time constants). The 10 0kΩ resistors to ground on the input nodes allow a DC path to
charge the AC-coupling capacitors, regardless of whether or not there is an input signal source present.
3.4.2 Op Amp Circuitry and Anti-Aliasing Capacitor
The op-amp topology used in the input buffer shown in Figure 3 addresses two issues. First, it provides
an extremely low output impedance and therefore minimizes the amount of distortion presented to the
converters internal sampling circuits. By placing the 91Ω resistor in the feedback loop, it’s resistance is
divided by the open-loop gain of the op-amp, providing a sub-ohm output impedance. Secondly, this opamp topology provides a low pass filter. Using the recommended values, this filter remains flat throughout
the audio passband and provides approximately 2 0dB of rejection at the modulator sampling rate (where
the converter is susceptible to aliasing). The characteristics of this low pass filter can be changed by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop. However, it is important to maintain
a flat frequency response throughout the passband of interest and to provide reasonable attenuation at
the input sampling rate of the converter. Also, low value resistors should be used to minimize the addition
of resistor thermal noise.
Figure 3 implements a common mode capacitor between the positive and negative nodes of the converters differential inputs. This capacitor is commonly referred to as the anti-aliasing capacitor, and performs
several functions. The value of the capacitor affects the overall low pass filter response and the amount
of attenuation at the modulator sampling rate. This capacitor also acts as a charge reservoir for the internal sampling capacitors. Since this capacitor is located in the signal path, it is very important not to use
6
Page 7

AN241
capacitors with a large voltage coefficient (such as general purpose ceramics) since they can degrade
signal linearity.
4. Single-Ended Input Buffer with Dedicated Reference Pins
4.1 Applicable Converters
A single-ended analog input buffer with dedicated reference pins is ideal for use with the following Cirrus
Logic audio converters:
- CS5351
- CS4271
- CS42528/26/18/16 (Note: Full performance will not be realized with a single-ended implementation.)
- CS42428/26/18/16 (Note: Full performance will not be realized with a single-ended implementation.)
4.2 Introduction
A single-ended signal consists of only one signal line and hence requires only one input pin. Some converters have a dedicated reference pin for each channel, as well as an on-chip reference. These pins are
typically labeled VQx. Please check the datsheet for the particular converter to determine the naming convention of the VQx pins.
4.3 Recommended Filter Topology #1
Figure 4 shows a single-ended analog input buffer with dedicated reference pins. This filter implements
one op-amp per channel, and uses a third op-amp to properly bias the analog inputs and independent
channel reference pins. This buffer provides proper biasing, isolation from the switched capacitor currents, low output impedance, and anti-alias filtering.
100 k
100 k
634
Ω
470 pF
C0G
F
1
µ
100 k
100 k
F
µ
Ω
Ω
Ω
1
Ω
Figure 4. Single-Ended Input Buffer with Dedicated Reference Pins (Example #1)
-
+
+
-
470 pF
C0G
91
91
634
Ω
2700 pF
C0G
-
+
1µF 0.01µF
2700 pF
C0G
Ω
Ω
CSxxxx
AINL
VQ
in_left
VQ
out
VQ
in_right
AINR
7
Page 8

AN241
4.4 Overview of Filter Topology #1
4.4.1 High Pass Filter and DC Biasing
The first stage of the buffer forms a high pass filter from the combination of the AC-coupling capacitor
along with the resistor that connects the positive terminal of the op-amp in the input signal path to the DC
bias voltage. The 3 dB corner of the high pass filter can be calculated as follows:
F
C
where:
In the input buffer shown in Figure 4,
imately 1.59 Hz. Typically, this corner should be at least one decade below the bandwidth of interest in
order to prevent a significant droop in the frequency response.
Since the input impedance into the op-amp is extremely high, the effective input impedance into the analog input buffer will be determined by the value of the resistors to the bias voltage in parallel with the
Ω
100 k
ally, the larger this input impedance the better. However, in the input buffer shown in Figure 4, the ACcoupling capacitor will initially be charged up via the op-amp connected to the on-chip voltage reference.
This charge up time is dependent on the size of the AC-coupling capacitor and the amount of series resistance to the DC-biasing op-amp. The time constant can be calculated as follows:
shunt resistors. In the input buffer shown above, the input impedance is approximately 50 kΩ. Ide-
R
where
= the amount of resistance between the AC-coupling capacitor and the DC-biasing op-amp (in
Ohms)
R
is the value of the resistor (in Ohms)
C
is the value of the capacitor (in Farads)
R
= 100 kΩ and C = 1.0µF. This places the 3 dB corner at approx-
1
=
RC
π
2
RC=
τ
C
= the value of capacitance of the AC-coupling capacitor (in Farads)
R
In the input buffer shown in Figure 4,
This would indicate that the capacitor will charge up to within 99% of the final DC value in approximately
0.5 s (which is 5 time constants). The 100 kΩ resistors to ground on the input node allow a DC path to
charge the AC-coupling capacitors, regardless of whether or not there is an input signal source present.
4.4.2 Op Amp Circuitry and Anti-Aliasing Capacitor
The op-amp topology used in the input buffer shown in Figure 4 addresses two issues. First, it provides
an extremely low output impedance and therefore minimizes the amount of distortion presented to the
converters internal sampling circuits. By placing the 91Ω resistor in the feedback loop, it’s resistance is
divided by the open-loop gain of the op-amp, providing a sub-ohm output impedance. Secondly, this opamp topology provides a low pass filter. Using the recommended values, this filter remains flat throughout
the audio passband and provides approximately 2 0dB of rejection at the modulator sampling rate (where
the converter is susceptible to aliasing). The characteristics of this low pass filter can be changed by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop. However, it is important to maintain
a flat frequency response throughout the passband of interest and to provide reasonable attenuation at
8
=100 kΩ, and C = 1.0µF. This produces a time constant of 0.1 s.
Page 9

AN241
the input sampling rate of the converter. Also, low value resistors should be used to minimize the addition
of resistor thermal noise.
Figure 4 implements a common mode capacitor between the analog input and the associated reference
voltage pin on each channel of the converter. This capacitor is commonly referred to as the anti-aliasing
capacitor, and performs several functions. The value of the capacitor affects the overall low pass filter response and the amount of attenuation at the input sample rate of the converter. This capacitor also acts
as a charge reservoir for the internal sampling capacitors. Since this capacitor is located in the signal path,
it is very important not to use capacitors with a large voltage coefficient (such as general purpose ceramics) since they can degrade signal linearity.
4.5 Recommended Filter Topology #2
Figure 5 shows a single-ended analog input buffer with dedicated reference pins. This filter implements
one op-amp per channel, and uses passive components to properly bias the analog inputs and independent channel reference pins. This buffer provides proper biasing, isolation from the switched capacitor
currents, low output impedance, and anti-alias filtering.
Ω
634
100 k
VA
Ω
100 k
µ
4.7
F
Ω
Ω
Rk
470 pF
C0G
-
+
Ω
91
2700 pF
VA
C0G
Ω
100 k
CSxxxx
AINL
VQ
in_left
100 k
4.7µF
4.7µF
VA
Ω
100 k
4.7µF
Ω
Ω
Rk
+
-
470 pF
C0G
91
634
Rk
100 k
Rk
Ω
Ω
Ω
1µF 0.01µF
VA
Ω
Ω
2700 pF
C0G
VQ
VQ
AINR
out
in_right
Figure 5. Single-Ended Input Buffer with Dedicated Reference Pins (Example #2)
9
Page 10

AN241
4.6 Overview of Filter Topology #2
4.6.1 High Pass Filter and DC Biasing
The first stage of the buffer forms a high pass filter from the combination of the AC-coupling capacitor
along with the resistor divider that biases the positive terminal of the op-amp to the proper DC bias voltage. The value of the resistors denoted as “R” will vary depending on the optimal DC bias for the given
converter. Typically this is around half of the VA voltage supply. A high pass filter is also formed from the
resistor divider and capacitor to ground on the reference voltage pin of each channel. The 3dB corner of
the high pass filter can be calculated as follows:
1
=
F
C
π
CR
2
EQ
where:
In the input buffer shown in Figure 5,
R
is the value of the resistor divider in parallel (in Ohms)
EQ
C
is the value of the capacitor (in Farads)
REQ
≈
50 kΩ (100 k
Ω RkΩ
) and C = 4.7µF. This places the 3 dB
corner at approximately 0.68 Hz. Typically, this corner should be at least one decade below the bandwidth
of interest in order to prevent a significant droop in the frequency response.
Since the input impedance into the op-amp is extremely high, the effective input impedance into the analog input buffer will be determined by the parallel combination of the resistors in the biasing divider in par-
Ω
allel with the 100 k
Ω.
33 k
Ideally, the larger this input impedance the better. However, in the input buffer shown in Figure 5,
shunt resistor. In the input buffer shown above, the input impedance is approximately
the AC-coupling capacitor will initially be charged up via the resistor divider. This charge up time is dependent on the size of the AC-coupling capacitor and the amount of resistance to the VA voltage supply.
The time constant can be calculated as follows:
=
τ
CR
EQ
R
where
= the amount of resistance between the AC-coupling capacitor and the voltage supply (in
EQ
Ohms)
C
= the value of capacitance of the AC-coupling capacitor (in Farads)
In the input buffer shown in Figure 5,
R
≈ 50 kΩ (100 k
EQ
Ω RkΩ
), and C = 4.7µF. This produces a
time constant of approximately 0.24 s. This would indicate that the capacitor will charge up to within 99%
of the final DC value in approximately 1. 2s (which is 5 time constants). The 10 0k
Ω
resistors to ground
on the input node allow a DC path to charge the AC-coupling capacitor, regardless of whether or not there
is an input signal source present.
4.6.2 Op Amp Circuitry and Anti-Aliasing Capacitor
The op-amp topology used in the input buffer shown in Figure 5 addresses two issues. First, it provides
an extremely low output impedance and therefore minimizes the amount of distortion presented to the
converters internal sampling circuits. By placing the 91Ω resistor in the feedback loop, it’s resistance is
divided by the open-loop gain of the op-amp, providing a sub-ohm output impedance. Secondly, this opamp topology provides a low pass filter. Using the recommended values, this filter remains flat throughout
the audio passband and provides approximately 2 0dB of rejection at the modulator sampling rate (where
10
Page 11

AN241
the converter is susceptible to aliasing). The characteristics of this low pass filter can be changed by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop. However, it is important to maintain
a flat frequency response throughout the passband of interest and to provide reasonable attenuation at
the modulator sampling rate of the converter. Also, low value resistors should be used to minimize the
addition of resistor thermal noise.
Figure 5 implements a common mode capacitor between the analog input and the associated reference
voltage pin on each channel of the converter. This capacitor is commonly referred to as the anti-aliasing
capacitor, and performs several functions. The value of the capacitor affects the overall low pass filter response and the amount of attenuation at the input sample rate of the converter. This capacitor also acts
as a charge reservoir for the internal sampling capacitors. Since this capacitor is located in the signal path,
it is very important not to use capacitors with a large voltage coefficient (such as general purpose ceramics) since they can degrade signal linearity.
4.7 Recommended Filter Topology #3
Figure 6 shows a single-ended analog input buffer with dedicated reference pins. This filter implements
one op-amp per channel, and uses a third op-amp to properly bias the independent channel reference
pins. This input buffer topology offers some unique advantages. First, the analog inputs to the op-amps
do not need to be AC-coupled (although they can be), which allows the input impedance of the buffer to
be set without regard to any charge up times. This can also be advantageous if the op-amps are restricted
±
to limited supply rails of
prevent the op-amp from clipping. Secondly, this input buffer topology allows for some signal gain, as determined by the resistor R
itor currents, and anti-alias filtering. On disadvantage of this topology is the large AC-coupling capacitor
directly on the input sampling node. The ESR of the capacitor will increase distortion, especially at low
frequencies where the ESR of the capacitor is generally much greater.
5 V. In this case, it is optimal to have an input referenced to ground in order to
. Finally, this buffer provides proper biasing, isolation from the switched capac-
g
Rg
470 pF
634
Ω
CSxxxx
C0G
-
91
Ω
470µF
AINL
Ω
Ω
2700 pF
C0G
2700 pF
C0G
VQ
VQ
VQ
in_left
out
in_right
100 k
100 k
Ω
Gain
Ω
+
634
Rg
+=
1
+
10 k
-
+
1µF 0.01µF
10 k
AINR
-
470 pF
Rg
Figure 6. Single-Ended Input Buffer with Dedicated Reference Pins (Example #3)
C0G
91
634
Ω
Ω
470µF
11
Page 12

AN241
4.8 Overview of Filter Topology #3
4.8.1 Op Amp Circuitry
The op-amp topology used in the input buffer shown in Figure 6 addresses two issues. First, it provides
an extremely low output impedance and therefore minimizes the amount of distortion presented to the
converters internal sampling circuits. By placing the 91Ω resistor in the feedback loop, it’s resistance is
divided by the open-loop gain of the op-amp, providing a sub-ohm output impedance (not including the
ESR of the AC-coupling capacitor). Secondly, this op-amp topology provides a low pass filter. Using the
recommended values, this filter remains flat throughout the audio passband and provides approximately
20 dB of rejection at the modulator sampling rate (where the converter is susceptible to aliasing). The
characteristics of this low pass filter can be changed by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop. However, it is important to maintain a flat frequency response throughout the
passband of interest and to provide reasonable attenuation at the input sampling rate of the converter.
Also, low value resistors should be used to minimize the addition of resistor thermal noise.
4.8.2 High Pass Filter and DC Biasing
The outputs of the op-amps are AC-coupled to the converter, with the converter inputs being biased to
the proper voltage level through a 10 kΩ resistor from the DC-biasing op-amp. The AC-coupling capacitor
and resistor from the biasing op-amp form a high pass filter. The 3 dB corner of the high pass filter can be
calculated as follows:
F
C
where:
In the input buffer shown in Figure 6,
mately 0.03 Hz. Typically, this corner should be at least one decade below the bandwidth of interest in
order to prevent a significant droop in the frequency response. The value of the AC-coupling capacitor
must be large in order to prevent the DC resistance of the capacitor from degrading signal linearity. Please
note that with 470µF aluminum electrolytic capacitors, distortion will begin to increase at input frequencies below 100 Hz.
In Figure 6, the AC-coupling capacitor will initially be charged up via the op-amp connected to the on-chip
voltage reference. This charge up time is dependent on the size of the AC-coupling capacitor and the
amount of series resistance to the op-amp. The time constant can be calculated as follows:
where
R
= the amount of resistance between the AC-coupling capacitor and the op-amp (in Ohms)
C
= the value of capacitance of the AC-coupling capacitor (in Farads)
R
is the value of the resistor to the biasing op-amp (in Ohms)
C
is the value of the AC-coupling capacitor (in Farads)
R
= 10 kΩ and C = 470µF. This places the 3 dB corner at approxi-
1
=
RC
π
2
=
τ
RC
R
In the input buffer shown in Figure 6,
proximately 4.7 s. This would indicate that the capacitor will charge up to within 99% of the final DC value
in approximately 23.5 s (which is 5 time constants).
12
= 10 kΩ, and C = 470µF. This produces a time constant of ap-
Page 13

AN241
4.8.3 Anti-Aliasing Capacitor
Figure 6 implements a common mode capacitor between the analog input and the associated reference
voltage pin on each channel of the converter. This capacitor is commonly referred to as the anti-aliasing
capacitor, and performs several functions. The value of the capacitor affects the overall low pass filter response and the amount of attenuation at the modulator sampling rate. This capacitor also acts as a charge
reservoir for the internal sampling capacitors. Since this capacitor is located in the signal path, it is very
important not to use capacitors with a large voltage coefficient (such as general purpose ceramics) since
they can degrade signal linearity.
5. Single-Ended Input Buffer with a Common Reference Pin
5.1 Applicable Converters
A single-ended analog input buffer with a common reference pin is ideal for use with the following Cirrus
Logic audio converters:
- CS5340
- CS5341
- CS5342
- CS42406
5.2 Introduction
A single-ended signal consists of only one signal line and hence requires only one input pin. Single-ended
inputs typically require less input buffer components, but also have several disadvantages. First, at a given voltage level, a single-ended input cannot produce as much signal swing as a differential signal, hence
reducing the dynamic range. Also, single-ended inputs are more prone to errors caused by DC offsets and
coupled-noise.
5.3 Recommended Filter Topology
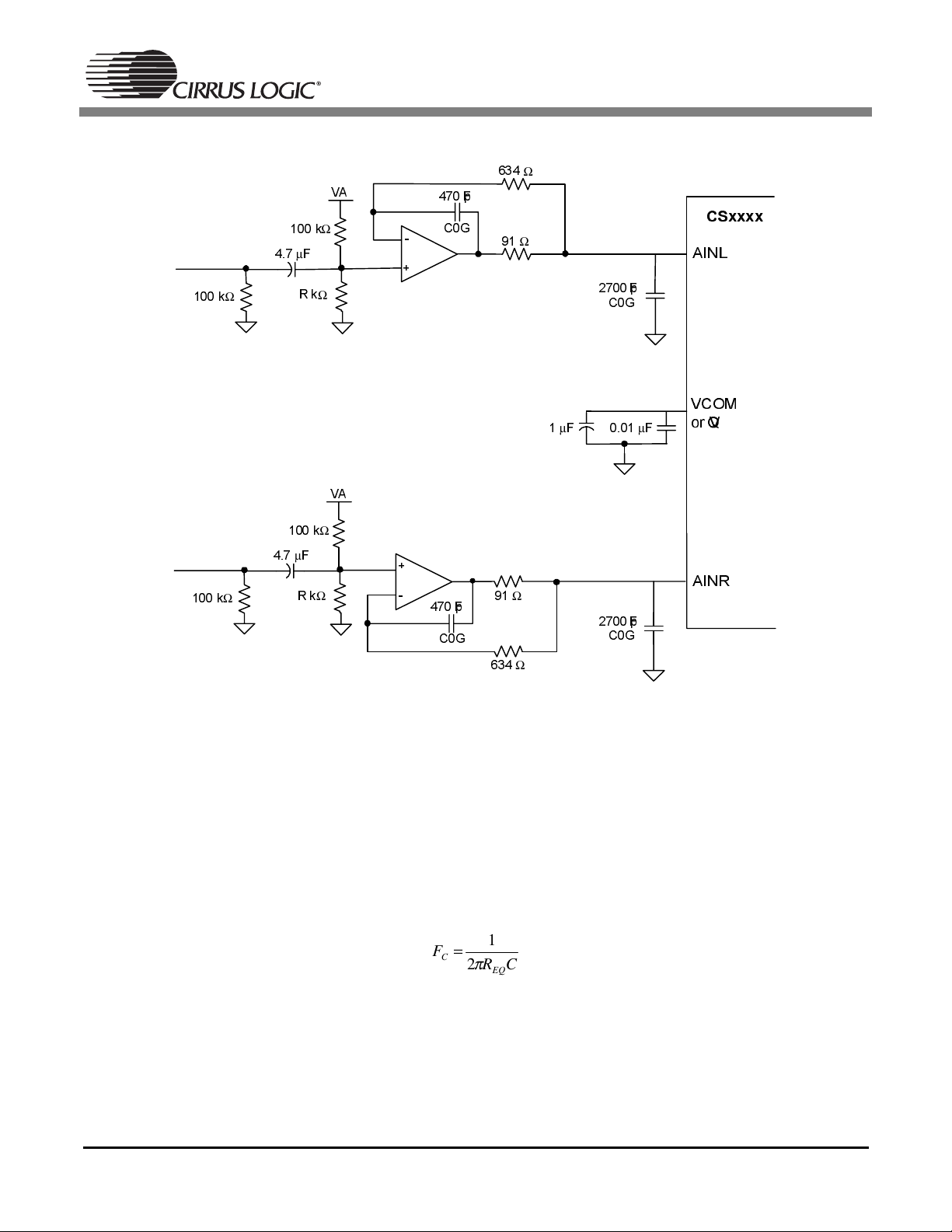
Figure 7 shows a single-ended analog input buffer. This buffer provides proper biasing, isolation from the
switched capacitor currents, low output impedance, and anti-alias filtering.
13
Page 14
100 k
AN241
634
Ω
VA
100 k
Ω
4.7µF
Rk
Ω
Ω
VA
470 pF
C0G
-
91
Ω
CSxxxx
AINL
+
2700 pF
C0G
VCOM
1µF
0.01µF
or VQ
100 k
Ω
4.7µF
+
AINR
100 k
Rk
Ω
Figure 7. Single Ended Input Buffer with a Common Reference Pin
Ω
-
470 pF
C0G
91
634
Ω
2700 pF
C0G
Ω
5.4 Overview of Filter Topology
5.4.1 High Pass Filter and DC Biasing
The first stage of the buffer forms a high pass filter from the combination of the AC-coupling capacitor
along with the resistor divider that biases the positive terminal of the op-amps to the proper DC bias voltage. The value of the resistors denoted as “R” will vary depending on the optimal DC bias for the given
converter. Typically this is around half of the VA voltage supply. Please refer to the converter datasheet
for the recommended input bias voltage. The 3dB corner of the high pass filter can be calculated as follows:
F
C
1
=
π
CR
2
EQ
14
where:
R
is the value of the resistor divider in parallel (in Ohms)
EQ
C
is the value of the AC-coupling capacitor (in Farads)
Page 15

AN241
REQ
In the input buffer shown in Figure 7,
≈
50 kΩ (100 k
corner at approximately 0.68 Hz. Typically, this corner should be at least one decade below the bandwidth
of interest in order to prevent a significant droop in the frequency response.
Since the input impedance into the op-amp is extremely high, the effective input impedance into the analog input buffer will be determined by the parallel combination of the resistors in the divider in parallel with
Ω
the 10 0k
shunt resistor. In the input buffer shown above, the input impedance is approximately 33k
Ideally, the larger this input impedance the better. However, in the input buffer shown in Figure 7, the ACcoupling capacitor will initially be charged up via the resistor divider. This charge up time is dependent on
the size of the AC-coupling capacitor and the amount of resistance to the VA voltage supply. The time
constant can be calculated as follows:
=
τ
Ω RkΩ
CR
EQ
) and C = 4.7µF. This places the 3 dB
Ω.
where
R
= the amount of resistance between the AC-coupling capacitor and the voltage supply (in
EQ
Ohms)
C
= the value of capacitance of the AC-coupling capacitor (in Farads)
In the input buffer shown in Figure 7,
R
≈ 50 kΩ (100 k
EQ
Ω RkΩ
), and C = 4.7µF. This produces a
time constant of approximately 0.24 s. This would indicate that the capacitor will charge up to within 99%
of the final DC value in approximately 1. 2s (which is 5 time constants). The 10 0kΩ resistors to ground
on the input nodes allow a DC path to charge the AC-coupling capacitor, regardless of whether or not
there is an input signal source present.
5.4.2 Op Amp Circuitry and Anti-Aliasing Capacitor
The op-amp topology used in the input buffer shown in Figure 7 addresses two issues. First, it provides
an extremely low output impedance and therefore minimizes the amount of distortion presented to the
converters internal sampling circuits. By placing the 91
Ω
resistor in the feedback loop, it’s resistance is
divided by the open-loop gain of the op-amp, providing a sub-ohm output impedance. Secondly, this opamp topology provides a low pass filter. Using the recommended values, this filter remains flat throughout
the audio passband and provides approximately 2 0dB of rejection at the modulator sampling rate (where
the converter is susceptible to aliasing). The characteristics of this low pass filter can be changed by adjusting the values of the resistors and capacitors in the feedback loop. However, it is important to maintain
a flat frequency response throughout the passband of interest and to provide reasonable attenuation at
the input sampling rate of the converter. Also, low value resistors should be used to minimize the addition
of resistor thermal noise.
Figure 7 implements a capacitor from the analog input to ground on each channel of the converter. This
capacitor is commonly referred to as the anti-aliasing capacitor, and performs several functions. The value
of the capacitor affects the overall low pass filter response and the amount of attenuation at the modulator
sampling rate. This capacitor also acts as a charge reservoir for the internal sampling capacitors. Since
this capacitor is located in the signal path, it is very important not to use capacitors with a large voltage
coefficient (such as general purpose ceramics) since they can degrade signal linearity.
15
Page 16

AN241
C
C
v
t
o
a
g
o
o
d
A
t
t
C
V
W
S
T
C
C
t
.
ontacting Cirrus Logic Support
For a complete listing of Direct Sales, Distributor, and Sales Representative contacts, visit the Cirrus Logic web site at:
http://www.cirrus.com/
IMPORTANT NOTICE
irrus Logic, Inc. and its subsidiaries ("Cirrus") believe that the information contained in this document is accurate and relia ble. However, the information
is subject to change without notice and is provided "AS IS" without warranty of any kind (express or implied). Customers are adv ised to obtain the latest
ersion of relevant information to verify, before placing orders, that information being relied on is current and complete. All products are sold subject to
he terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment, including those pertaining to warranty, patent infringement, and limitation
f liability. No responsibility is assumed by Cirrus for the use of this information, including use of this information as the b asis for manufacture or sale of
ny items, or for infringement of patents or other rights of third parties. This document is the property of Cirrus and by furni shing this information, Cirrus
rants no license, express or implied under any patents, mask work rights, copyrights, trademarks, trade secrets or other intellectual property rights. Cirrus
wns the copyrights associated with the information contained herein and gives consent for copies to be made of the information only for use within your
rganization with respect to Cirrus integrated circuits or other products of Cirrus. This consent does not extend to other copying such as copying for general
istribution, advertising or promotional purposes, o r for creating any work for resale.
n export permit needs to be obtained from the competent authorities of the Japanese Government if any of the products or technologies described in
his material and controlled under the "Foreign Exchange and Foreign Trade Law" is to be exported or taken out of Japan. An export license and/or quota
needs to be obtained from the competent authorities of the Chinese Government if any of the products or technologies described in this material is subject
o the PRC Foreign Trade Law and is to be exported or taken out of the PRC.
ERTAIN APPLICATIONS USING SEMICONDUCTOR PRODUCTS MAY INVOLVE POTENTIAL RISKS OF DEATH, PERSONAL INJURY, OR SEERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE ("CRITICAL APPLICATIONS"). CIRRUS PRODUCTS ARE NOT DESIGNED, AUTHORIZED OR
ARRANTED FOR USE IN AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS, MILITARY APPLICATIONS, PRODUCTS SURGICALLY IMPLANTED INTO THE BODY, LIFE SUP-
PORT PRODUCTS OR OTHER CRITICAL APPLICATIONS (INCLUDING MEDICAL DEVICES, AIRCRAFT SYSTEMS OR COMPONENTS AND PER-
ONAL OR AUTOMOTIVE SAFETY OR SECURITY DEVICES). INCLUSION OF CIRRUS PRODUCTS IN SUCH APPLICATIONS IS UNDERSTOOD
O BE FULLY AT THE CUSTOMER'S RISK AND CIRRUS DISCLAIMS AND MAKES NO WARRANTY, EXPRESS, STATUTORY OR IMPLIED, IN-
LUDING THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR PARTICULAR PURPOSE, WITH REGARD TO ANY CIRRUS
PRODUCT THAT IS USED IN SUCH A MANNER. IF THE CUSTOMER OR CUSTOMER'S CUSTOMER USES OR PERMITS THE USE OF CIRRUS
PRODUCTS IN CRITICAL APPLICATIONS, CUSTOMER AGREES, BY SUCH USE, TO FULLY INDEMNIFY CIRRUS, ITS OFFICERS, DIRECTORS,
EMPLOYEES, DISTRIBUTORS AND OTHER AGENTS FROM ANY AND ALL LIABILITY, INCLUDING ATTORNEYS' FEES AND COSTS, THAT MAY
RESULT FROM OR ARISE IN CONNECTION WITH THESE USES.
irrus Logic, Cirrus, and the Cirr us Logic logo designs are trademarks of Cirrus L ogic, Inc. All other brand and product names in this document may be
rademarks or service marks of their respective owners.
16
 Loading...
Loading...