Page 1

Formato: 135mm x 190mm
P. 37
P. 03
Manual de uso
Megóhmetro Digital
Digital Insulation Tester
User guide
MD5060e
CIRCUTOR SA.
Vial Sant Jordi s/n · 08232 Viladecavalls
Barcelona - Spain
Phone: (+34) 93 7452900 - Fax: (+34) 93 7452914
Page 2

MD-5060e
Megóhmetro digital hasta 5 kV
Manual de uso
GF-2020RA
© 2016 CIRCUTOR. Todos los derechos reservados.
3
Page 3

Precauciones de seguridad
· Deberán leerse y comprenderse las Precauciones de seguridad y el Manual
de Uso antes de usar el instrumento.
· Respete rigurosamente las normas de seguridad para el trabajo con alta
tensión cuando utilice este equipo. Las tensiones generadas son peligrosas.
· Nunca conecte o desconecte las puntas de prueba con el megóhmetro en
funcionamiento o mientras el indicador luminoso de Alta Tensión está
encendido. Si tiene que hacer alguna modificación al conexionado hágala con
el equipo apagado.
· No haga cortocircuitos entre los bornes de salida de alta tensión y los bornes
+R o Guard mientras el megóhmetro está funcionando. Además de ser
peligroso para el operador, puede provocar la actuación de los fusibles que
protegen las salidas del equipo.
· Antes de conectar el megóhmetro verifique, usando pértigas adecuadas, que
no existan potenciales peligrosos en los puntos a los que se conectará.
· El panel del equipo, bornes y conectores deben mantenerse secos y limpios.
Este equipo debe ser operado únicamente por personas
calificadas, aplicando rigurosamente las normas de seguridad
pertinentes.
Símbolos utilizados en el equipo
Atención, riesgo de descarga eléctrica.
Atención, referirse al manual de uso.
Batería
Impresora
Capacitancia
Backlight
El equipo está conforme con las directrices actuales de la U.E.
El contenedor de basura tachado significa que, en la Unión Europea, el
producto deberá ser objeto de una recogida selectiva de los residuos
para el reciclado de los aparatos eléctricos y electrónicos de conformidad
con la directiva WEEE 2002/96/CE.
4
Page 4

Índice
1. Descripción............................................................................................................6
2. Función de los controles del panel........................................................................7
2.1. Teclado...........................................................................................................8
2.2. Display..........................................................................................................10
3. Batería e recarga.................................................................................................11
4. Conectando el MD-5060e....................................................................................12
5. Uso del borne “Guard” (G)...................................................................................14
6. Configurando los ensayos...................................................................................15
6.1. Definiendo la tensión de prueba...................................................................15
6.2. Seleccionando el modo de operación..........................................................16
6.3. Modo normal.................................................................................................16
6.4. Modo SVT (ensayos por escalones de tensión)..........................................16
6.5. Modo “TIMER”..............................................................................................18
6.6. Modo de ensayos “Pasa / No pasa”.............................................................19
7. Realizando ensayos.............................................................................................20
7.1. Midiendo el índice de absorción dieléctrica.................................................22
7.2. Midiendo el índice de polarización (PI)........................................................23
8. Otras funciones....................................................................................................24
8.1. Backlight.......................................................................................................24
8.2. Filtro..............................................................................................................24
8.3. Voltímetro C.C./C.A. True RMS...................................................................24
8.4. Medición da corriente de fuga......................................................................24
8.5. Medición de capacitancia.............................................................................25
8.6. Hold..............................................................................................................25
8.7. Verificación del estado de la batería............................................................26
8.8. Memoria........................................................................................................26
8.9. Auto-apagado...............................................................................................26
9. Software...............................................................................................................27
9.1. USB Drivers..................................................................................................27
9.2. Software CIR Logger....................................................................................27
10. Impresora...........................................................................................................28
11. Limpieza.............................................................................................................28
12. Especificaciones técnicas..................................................................................29
13. Boletín técnico 32..............................................................................................32
5
Page 5

1. Descripción
El megóhmetro digital modelo MD-5060e es uno de los equipos más
avanzados de la línea CIRCUTOR de analizadores de aislación y uno de
los más completos y sofisticados del mercado internacional. Emplea una
tecnología de probada eficacia, que proporciona mediciones seguras,
confiables y precisas de resistencias de aislamiento hasta 5 TΩ con 4
tensiones de prueba preseleccionadas: 500 V - 1 kV - 2,5 kV - 5 kV.
Otras tensiones de prueba pueden ser seleccionadas en pasos de 25 V,
100 V o 500 V.
El equipo está controlado por un microprocesador, lo que facilita su
operación y permite la introducción de funciones avanzadas tales como:
Selección automática del rango, Memoria para hasta 4000 mediciones,
Voltímetro C.A./C.C., Medición automática de los Índices de Polarización
y de Absorción Dieléctrica, Medición de la Corriente de Fuga y de la
Capacitancia, “TIMER” para programar el tiempo del ensayo de
resistencia, “Límite” que permite realizar ensayos del tipo “Pasa / No
pasa” con límite programable. Ensayo de escalones de tensión,
impresora incorporada, reloj en tiempo real y calendario para
identificación de las mediciones. Cronómetro incorporado indicando el
tiempo transcurrido desde el inicio del ensayo en minutos y segundos.
La interface USB permite la comunicación del equipo con una
computadora para transmitir los datos registrados. El software CIR
Logger, analiza los resultados y los presenta por medio de gráficos y
tablas, generando automáticamente el protocolo de ensayo. La impresora
incorporada registra en papel los valores a cada 15 segundos, como
documento de las mediciones realizadas.
Por sus características constructivas este instrumento es robusto, con
excelente desempeño tanto en laboratorio como en los trabajos de
campo, en condiciones ambientales rigurosas, típicas de las regiones
tropicales.
6
Page 6

2. Función de los controles del panel
CIRCUTOR SA - Vial Sant Jordi, s/n
08232 Viladecavalls (Barcelona) Spain
MD5060e
Borne de salida de tensión (-V)
Borne Guard (G)
Borne de referencia cero (+R)
Display
Teclado
Led de alta tensión
Llave de encendido
Puerta de comunicación USB
Entrada de la fuente de alimentación
Impresora
7
Page 7

2.1. Teclado
Tecla Función LED
Enciende/Apaga la impresora Indica impresora
encendida
Hold - Congela en el display la última lectura La función Hold está
activada
Batería - exhibe en el display el estado de
carga de la batería
–
Filtro - Activa el filtro que minimiza
interferencias de ruido externo
Indica que el filtro está
activado
Muestra en el display el valor calculado
como resultado de un Ensayo de Escalones
de Tensión (SVT), de Índice de Polarización
(PI) y de Índice de Absorción Dieléctrica
(DAI)
–
Backlight - activa la iluminación del display –
Capacitancia - exhibe el valor de
capacitancia
–
Activada permite la programación del Modo
de Operación (Normal, SVT o con TIMER de
tiempo seleccionable).
Indica que está
habilitada la selección
del Modo de Operación
8
Page 8

Activada, permite la programación de las
tensiones de ensayo en pasos de 25 V
Pasos de 25 V activado
Activada, permite la programación de las
tensiones de ensayo en pasos de 100 V
Pasos de 100 V activado
Activada, permite la programación de las
tensiones de ensayo en pasos de 500 V
Pasos de 500 V activado
Selección de la tensión de ensayo de 500 V Indica 500 V
seleccionado
Selección de la tensión de ensayo de 1 kV Indica 1 kV seleccionado
Selección de la tensión de ensayo de 2,5 kV Indica 2,5 kV
seleccionado
Selección de la tensión de ensayo de 5 kV Indica 5 kV seleccionado
Estas teclas (disminuir o aumentar) permiten
seleccionar el valor que está siendo
programado
–
Activada permite la programación del límite
para el ensayo “Pasa / No pasa”
Indica cuando la
resistencia medida sea
inferior al límite
programado
Start - Inicia el ensayo Indica que está siendo
ejecutado el ensayo
Stop - Fin del ensayo –
9
Page 9

2.2. Display
En el display alfanumérico LCD son exhibidos el resultado de las
mediciones en la unidad correspondiente, el tiempo transcurrido desde el
inicio de la medición, la tensión de ensayos seleccionada, la indicación
analógica por bargraph y diversos mensajes al operador.
10
Page 10

3. Batería e recarga
El MD-5060e usa una batería recargable de LiFePO4 12 V - 6000 mAh.
Al final de su vida útil, esta batería debe ser reciclada o colocada en
lugar apropiado, para proteger el medio ambiente.
Procedimiento de recarga:
· Compruebe si el MD-5060e está apagado y conéctelo a la red de
energía a través de la fuente de alimentación.
· El indicador de recarga ( ) se encenderá en color
rojo, y permanecerá así hasta que la batería esté totalmente recargada.
Entonces, la luz quedará verde, y permanecerá así hasta que el MD-
5060e sea desconectado de la red.
Luz verde y roja alternadas Evaluación del estado inicial de la batería al
conectar la fuente, durante un segundo.
Luz roja permanente Batería en carga.
Luz roja intermitente Indica problema de carga de la batería.
Luz verde permanente Carga finalizada con éxito. Batería OK.
Realice un ciclo de carga completa antes de utilizar el equipo por primera vez, o
después de un tiempo sin uso (La batería pierde parte de su carga estando
almacenada). La batería recargable no presenta “efecto memoria” por lo que
puede ser cargada tantas veces como se desee. Cargue la batería antes de
almacenar el equipo y no deje pasar más de 30 días sin repetir el proceso de
carga.
IMPORTANTE: mientras el equipo está conectado a la red la tecla START está
inhibida, por lo que no pueden realizarse mediciones.
11
Page 11

4. Conectando el MD-5060e
ATENCIÓN: todos los procedimientos abajo indicados deben ser
realizados con el aparato apagado, para mayor seguridad del operador.
Asegúrese de que no existen diferencias de potencial entre los puntos a
los cuales se conectará el MD-5060e, ni entre éstos y tierra.
Al ser conectado, el equipo entra automáticamente en el modo voltímetro
y pasa a exhibir en el display la tensión y la corriente presentes en el
circuito.
El circuito a ser probado debe estar desenergizado para evitar
interferencias en la medición. Si el equipo detectar tensión mayor que
60 V presente en el circuito el MD-5060e no permitirá el inicio de la
medición.
12
Page 12

Conecte el terminal de seguridad del cable rojo al borne de salida de
tensión -V del megóhmetro. Conecte el terminal del cable negro al borne
de REFERENCIA CERO (+R) y los terminales cocodrilo al elemento a
medir como indica la figura abajo.
CIRCUTOR SA - Vial Sant Jordi, s/n
08232 Viladecavalls (Barcelona) Spain
MD5060e
PUNTA DE
PRUEBA NEGRA
PUNTA DE
PRUEBA ROJA
Los terminales “cocodrilo” en el diseño son meramente ilustrativos.
13
Page 13

5. Uso del borne “Guard” (G)
Dependiendo de la medición a realizar, se puede emplear o no el borne
Guard (G). Durante las mediciones, el equipo debe estar eléctricamente
referido a tierra para evitar lecturas inestables. Cuando se mide aislación
respeto de tierra, el borne R está conectado a tierra y se cumple la
condición de fijar el potencial del equipo. Cuando a medición se realiza
entre dos puntos que no están conectados a tierra (por ejemplo, entre
dos conductores de fase en un cable trifásico), el borne GUARD del
megóhmetro se debe conectar a tierra. Esto implica que siempre que se
mide, uno de los bornes, GUARD o R, debe estar conectado a tierra,
pero no ambos simultáneamente.
CIRCUTO R S A - Vi al S a nt Jo rd i, s /n
08232 Vi lade ca vall s (Bar ce lon a) Spa in
MD5060e
PUNTA DE
PRUEBA VERDE
(GUARD)
PUNTA DE
PRUEBA ROJA
PUNTA DE
PRUEBA NEGRA
Los terminales “cocodrilo” en el diseño son meramente ilustrativos.
El Boletín Técnico 32, reproducido al final de este manual, explica el uso
del borne GUARD para eliminar el efecto de resistencias parásitas sobre
el resultado de las mediciones.
14
Page 14

6. Configurando los ensayos
El megóhmetro MD-5060e es un instrumento versátil, que permite
efectuar diversos tipos de ensayos de aislación de forma automática,
registrando en su memoria interna y/o imprimiendo todos los resultados.
Es necesario definir adecuadamente los ensayos a ser realizados,
configurando los siguientes parámetros antes de iniciar las mediciones:
Tensión de prueba, Duración de los ensayos para ensayos en el modo
“TIMER”, Tensión máxima para ensayos de escalones de tensión (SVT) y
Límite de resistencia mínima para ensayos “Pasa / No pasa”.
6.1. Definiendo la tensión de prueba
Para definir el valor de la tensión de prueba, es necesario seleccionar
primero una de las teclas de ajuste de tensión:
. Estas
teclas habilitan tanto la selección de las tensiones pre-programadas (
) así como las teclas
y
, que aumentan o disminuyen
el valor de la tensión de prueba en pasos de 25 V, 100 V o 500 V,
dependiendo de la tecla de ajuste de tensión seleccionada.
Siempre que el equipo sea encendido la tecla estará seleccionada.
Para salir del modo de selección de la tensión, presione nuevamente la
tecla de ajuste que esté seleccionada en el momento.
Nota: la tensión de prueba es el único parámetro que puede ser
modificado durante los ensayos.
15
Page 15

6.2. Seleccionando el modo de operación
El megóhmetro MD-5060e tiene cuatro modos de operación: Normal, con
“TIMER”, SVT y “Pasa / No pasa”. Los tres primeros son seleccionados
usando la tecla ; el modo de ensayos “Pasa / No pasa” se activa
presionando la tecla .
6.3. Modo normal
El modo normal es usado en la medición de resistencia con tensión
única, sin límite de tiempo. Cuando está seleccionado, no hay ninguna
indicación especial en el display.
6.4. Modo SVT (ensayos por escalones de tensión)
Usando la tecla , es posible configurar el MD-5060e para la
realización de ensayos de escalones de tensión; cuando este modo está
seleccionado, el display exhibe la sigla SVT.
16
Page 16

En este modo de operación, el usuario no define una tensión de prueba
específica, sino un valor máximo de tensión; el aparato iniciará los
ensayos aplicando una tensión de 500 V, y aumentará este valor en
escalones de 500 V a cada minuto hasta alcanzar la tensión máxima
programada. En cada etapa, el MD-5060e mide la resistencia antes de
pasar al escalone siguiente.
Usando las teclas de ajuste de tensión, determine el valor de la tensión
máxima - que será, en todos los casos, un múltiplo de 500 V, hasta un
límite de 5000 V.
Es recomendable usar la tecla para seleccionar este valor; las teclas
y pueden ser usadas, pero si el valor seleccionado no fuera un
múltiplo de 500, este será redondeado hacia abajo.
El resultado de los ensayos se calcula con la siguiente fórmula:
=
SVT
R
R
V MAX
500
Después de finalizados los ensayos se puede recuperar el valor
presionando la tecla .
17
Page 17

6.5. Modo “TIMER”
Usando la tecla , es posible configurar el MD-5060e para la
realización de un ensayo con duración preestablecida; Cuando este
modo está seleccionado, el display muestra el tiempo programado. Use
las teclas y
para definir la duración de los ensayos en 1 minuto,
3 minutos, 10 minutos, 30 minutos o 90 minutos.
18
Page 18

6.6. Modo de ensayos “Pasa / No pasa”
Presione la tecla para determinar el límite inferior de aislación para
ensayos del tipo “Pasa / No pasa”. Seleccione este valor usando las
teclas y ; los valores posibles son 10 MΩ, 100 MΩ, 1 GΩ o
10 GΩ.
Durante un ensayo “Pasa / No pasa”, el MD-5060e indicará con un BIP
intermitente y con el led de la tecla parpadeando cuando la
resistencia de aislación sea inferior al límite programado. El led de la
tecla permanecerá parpadeando hasta el fin de los ensayos, o hasta
que el valor de la resistencia medida sea superior al límite programado.
19
Page 19

7. Realizando ensayos
Después de haber configurado el tipo de
medición deseada, presione la tecla . El
indicador de ALTA TENSIÓN se encenderá
indicando que el megóhmetro está aplicando
alta tensión al elemento bajo prueba.
Durante algunos segundos el sistema inteligente de autorango buscará el
rango más conveniente para el valor que está midiendo. En ese tiempo el
display mostrará el mensaje:
Apenas el MD-5060e seleccione la escala adecuada, el display mostrará
el número de ensayos, el valor de la tensión seleccionada, exhibirá el
valor de la tensión aplicada y de la corriente de fuga, fecha y hora,
iniciará la cuenta del tiempo transcurrido y será exhibida la indicación del
valor de la resistencia con su unidad correspondiente, y se iniciará la
indicación analógica por bargraph. Para finalizar los ensayos, presione la
tecla . En ese instante el MD-5060e los últimos valores medidos
quedarán congelados en el display. Presionándose nuevamente la tecla
el equipo retornará a la función voltímetro.
Ejemplo:
20
Page 20

El valor medido es de 602 GΩ con tensión seleccionada de 2.500 V. El
display exhibirá el número del ensayo (12), el valor de la resistencia
medida (602 GΩ, el tiempo transcurrido (06:25 minutos), la tensión
aplicada (2,51 kV), la corriente de fuga (4,17 nA), la fecha y la hora.
OBS.: Si la resistencia a ser medida sobrepasara el límite de 5TΩ@ 5kV,
será exhibido el mensaje: R > 5TΩ
ATENCIÓN: Nunca conecte o desconecte los cables de prueba con el
megóhmetro en funcionamiento o mientras el led de Alta Tensión se
encuentre encendido. Si hubiera necesidad de modificar las conexiones,
éstas deberán hacerse con los potenciales descargados (led de Alta
tensión apagado).
21
Page 21

7.1. Midiendo el índice de absorción dieléctrica
Al presionar la tecla durante los ensayos, el valor del índice de
absorción dieléctrica (DAI – Dielectric Absortion Index) será exhibido en
el display. Solamente es posible aplicar esta función después de un
mínimo de 1 minuto de medición; en caso de que la tecla sea presionada
antes de este límite mínimo, el display mostrará el mensaje de exhibición
do valor do DAI, pero no mostrará ningún valor.
El índice de polarización es el cociente entre los valores de la resistencia
de aislamiento medidos a los 60 y 30 segundos, y es útil en el
mantenimiento preventivo y predictivo de bobinados (presentes en
transformadores, motores, generadores, etc.).
=
DAI
R
R
60 segundos
30 segundos
22
Page 22

7.2. Midiendo el índice de polarización (PI)
Al presionar la tecla durante los ensayos, el valor del índice de
polarización (PI – Polarization Index) será exhibido en el display.
Solamente es posible aplicar esta función después de un mínimo de 10
minutos de medición; En caso de que la tecla sea presionada antes de
este límite mínimo, el display mostrará el mensaje de exhibición del valor
del PI, pero no mostrará ningún valor.
El índice de polarización es el cociente entre los valores de la resistencia
de aislamiento medidos a los 10 minutos y a 1 minuto. Este índice es útil
para detectar el deterioro de la resistencia de aislación por la presencia
excesiva de polvo, suciedad y grasas o por la acción de agentes
químicos y físicos.
=
PI
R
R
10 minutos
1 minuto
23
Page 23

8. Otras funciones
8.1. Backlight
El display del equipo posee backlight. Para accionarlo, presione la tecla
. Después de 10 segundos el backlight se auto apagará con el
objetivo de economizar la carga de la batería. Para reactivarlo, presione
nuevamente la tecla .
8.2. Filtro
Cuando esté realizando mediciones en transformadores o máquinas de
grandes dimensiones en presencia de campos electromagnéticos muy
fuertes, es posible que la lectura del equipo se torne inestable, sobretodo
para valores de resistencias mayores que 100 MΩ. En estos casos, es
conveniente presionar la tecla antes de iniciar la medición, activando
el filtro que permite alcanzar el valor de resistencia de aislación en una
curva ascendente sin oscilaciones.
8.3. Voltímetro C.C./C.A. True RMS
Para utilizar esta función, conecte las puntas de prueba y encienda el
MD-5060e. Automáticamente será exhibido el valor medido en el display.
C.A. C.C.
10 V hasta 1000 Vr.m.s. 10 V hasta 1000 V
Precisión: ±(5% de la lectura + 3 dígitos)
8.4. Medición da corriente de fuga
Durante los ensayos, el megóhmetro mide y exhibe en el display el valor
de la corriente de fuga en un intervalo de 1 nA hasta 3 mA, con una
Precisión de ±(10% de la lectura + 3 dígitos).
24
Page 24

8.5. Medición de capacitancia
El valor de capacitancia es obtenido realizándose una medición de
resistencia de aislación. Después del término de la medición (Cuando la
tecla
haya sido presionada), aguarde el LED de alta tensión quedar
apagado y presione la tecla y el valor de la capacitancia será
exhibido en el display.
Tensión Capacitancia
500 V 50 nF hasta 10 µF
1.000 V 50 nF hasta 5 µF
2.500 V 30 nF hasta 2 µF
5.000 V 30 nF hasta 1 µF
Precisión: ± 10% del valor medido ± 3 dígitos
Observación: en la medición de valores inferiores a 50 nF, será exhibido
“0” en el display.
8.6. Hold
Permite retener en el display la última lectura efectuada en el instante en
que se presionó la tecla sin interrumpir los ensayos. Al presionar
nuevamente la tecla, el megóhmetro actualiza el valor medido de
resistencia y el cronómetro. El led sobre la tecla encendido y la letra
H en el display indican que esta función fue activada.
25
Page 25

8.7. Verificación del estado de la batería
Mantenga la tecla presionada para verificar la carga de la batería
durante una medición. En la escala analógica de barras, se mostrará una
representación visual aproximada de la carga remanente; además, el
display mostrará el mensaje “Battery OK” si la carga fuese suficiente, o
“Battery Low” si la carga estuviese baja. En este último caso, es
altamente recomendable recargar la batería antes de usar el aparato. En
caso de que la carga de la batería esté por debajo del 20% del total, el
mensaje de batería débil (Battery Low) aparecerá automáticamente en
el display.
8.8. Memoria
Este equipo tiene una memoria interna para hasta 4000 valores de
medición (aprox. 280 ensayos de DAI o 30 ensayos de PI). Esta memoria
es administrada por el equipo de modo cíclico. Cuando la memoria este
completa, a medida que se van realizando nuevos ensayos se van
borrando definitivamente los más antiguos. Por razones de precaución,
siempre descargue la memoria del equipo para una computadora cuando
terminar los ensayos.
8.9. Auto-apagado
El MD-5060e apaga automáticamente después de 10 minutos de
inactividad, o después de 95 minutos continuos de medición sin que sea
verificado el estado de la batería.
26
Page 26
9. Software
9.1. USB Drivers
Para instalar los drivers necesarios para la comunicación entre la
computadora y el equipo, siga el procedimiento abajo:
1. Conecte el equipo a la computadora a través del cable USB.
2. Si se detecta una conexión a internet, el Windows irá buscar los
drivers en el sitio Windows Update y los instalará automáticamente. Si
no se encuentra ningún driver automáticamente, insiera el CD-ROM,
fornecido con el equipo, en su computadora y ejecute el archivo “usb-
install.exe” y haga clic en “Install”.
9.2. Software CIR Logger
Este software facilita la comunicación entre el equipo y una computadora
con sistema operacional Windows. Permite sincronizar la fecha y hora del
reloj interno del equipo con la fecha y hora de la computadora, transferir
los dados almacenados, limpiar la memoria, transferir en tiempo real los
valores medidos, generar gráficos y protocolos de ensayos, etc. Las
instrucciones de instalación y uso están incluidas en el propio software.
27
Page 27

10. Impresora
Para activar la impresión automática de los resultados, presione la tecla
. Los valores medidos serán impresos cada 15 segundos, mientras
que el índice de absorción dieléctrica y el índice de polarización serán
impresos después de transcurridos 1 y 10 minutos, respectivamente. La
impresión puede ser iniciada o terminada en cualquier momento, sin
embargo es recomendable conectar la impresora antes de iniciar los
ensayos, para la impresión completa del título.
Atención: No tire del papel. La impresora puede ser fácilmente
dañada.
La impresora utiliza papel térmico de 56 mm de ancho, en una bobina de
30 mm de diámetro. La siguiente figura muestra como insertar
correctamente el papel.
Tire de la palanca situada en la tapa.
Inserte la bobina de papel como se muestra en la figura.
Mantenga la punta del papel fuera de la impresora y cierre la tapa.
11. Limpieza
El panel del equipo, bornes y conectores deben mantenerse secos y
limpios. La limpieza debe efectuarse utilizando un paño humedecido en
agua y detergente suave o alcohol isopropílico (asegúrese de que los
productos a ser utilizados en la limpieza no afecten plásticos).
28
Page 28

12. Especificaciones técnicas
Tensiones de prueba :
500, 1000, 2500, 5000 V con selección
rápida.
De 500 V hasta 5 kV seleccionables en
pasos de 25 V, 100 V o 500 V. Tensión
continua, negativa en relación a la tierra.
Alcance :
5 TΩ @ 5 kV
Voltímetro C.C. :
10 V hasta 1000 Vcc
Precisión: ±(5% de la lectura + 3 dígitos)
Voltímetro C.A. :
10 V hasta 1000 V r.m.s.
Precisión: ±(5% de la lectura + 3 dígitos)
Protección de sobretensión :
CAT. III – 600 V
Medición de corriente :
1 nA hasta 3 mA
±(10% de la lectura + 3 dígitos)
Medición de capacitancia :
50 nF hasta 10 µF @ 500 V
50 nF hasta 5 µF @ 1.000 V
30 nF hasta 2 µF @ 2.500 V
30 nF hasta 1 µF @ 5.000 V
Precisión: ±10% de la lectura ± 3 dígitos
Corriente de cortocircuito :
Máx. 3 mA
Display :
Alfanumérico, presenta las mediciones en
forma digital y analógica por bargraph.
Precisión de las tensiones de
prueba
:
± 3% del valor nominal sobre una resistencia
de 10 GΩ
Precisión del megóhmetro :
± 5% de la lectura entre 1MΩ y 1TΩ @ 5kV
± 20% de la lectura entre 1TΩ y 5TΩ @ 5kV
(Para tensiones de prueba menores, el límite
superior es reducido proporcionalmente)
± 20% de la lectura entre 10kΩ y 100kΩ
± 10% de la lectura entre 100kΩ y 1MΩ
29
Page 29

Características avanzadas :
• Cálculo automático del Índice de
polarización
• Cálculo automático del Índice de absorción
dieléctrica
• Ensayos “Pasa / No pasa” y de tiempo fijo
• Prueba de escalones de tensión
• Memoria para hasta 4000 mediciones
• Filtro para minimizar interferencias
Impresora :
Imprime el tiempo transcurrido, la tensión
realmente aplicada al elemento bajo prueba
y la resistencia medida.
Interface con la computadora :
USB
Cronómetro incorporado :
Indica el tiempo transcurrido desde el inicio
de la medición en el formato mm:ss, hasta
90:00
Índice de protección
ambiental
:
IP54 (con la tapa cerrada)
Seguridad :
Conforme con IEC 61010-1
Compatibilidad
electromagnética (E.M.C.)
:
Conforme con IEC 61326-1
Inmunidad a las radiaciones
electromagnéticas
:
Conforme con IEC 61000-4-3
Inmunidad electrostática :
Conforme con IEC 61000-4-2
Alimentación :
Batería recargable interna de LiFePO4 12 V
- 6000 mAh
Cargador de batería : 12 V - 2 A
Temperatura de operación :
-5°C a +50°C
Temperatura de
almacenamiento
:
-25°C a +65°C
Humedad :
95% RH (sin condensación)
30
Page 30

Peso del equipo :
Aprox. 4,3 kg.
Dimensiones :
340 x 295 x 152 mm
Accesorios provistos :
• 3 Cables de medición
• Fuente de alimentación
• Cable USB
• Bolsa para transporte
• Manual de operación
• Licencia de uso del software CIR Logger
Especificaciones técnicas sujetas a alteraciones sin aviso previo.
31
Page 31
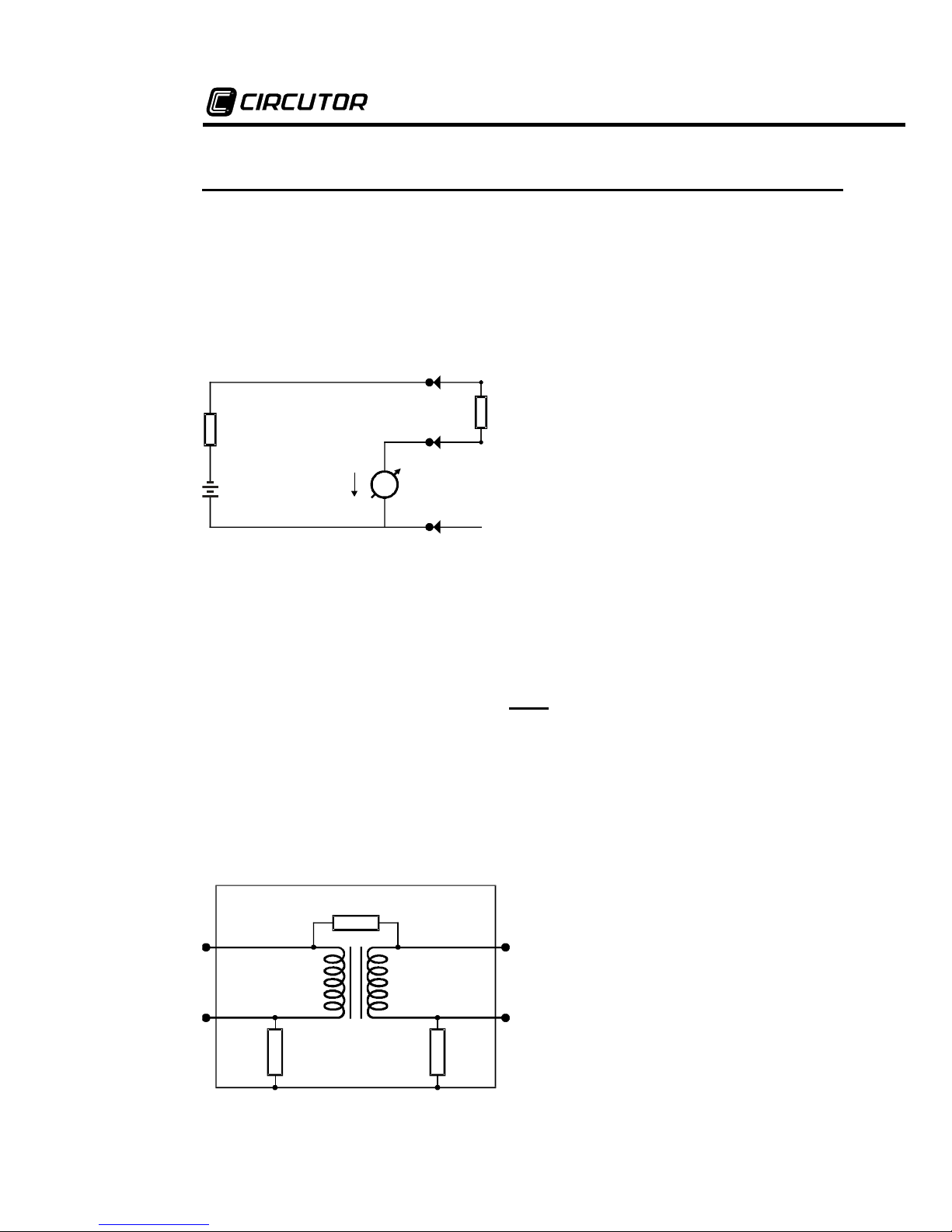
13. Boletín técnico 32
Utilidad del borne “Guard” de los megóhmetros
Cuando se realizan mediciones de resistencias de aislamiento con megóhmetros,
especialmente con instrumentos de alta sensibilidad, que miden resistencias de
valor muy alto, resulta conveniente el empleo del borne “Guard”, que permite
independizar la medida realizada de las resistencias parásitas. Para comprender
mejor la función de este borne conviene comenzar analizando el esquema básico
del megóhmetro.
A
Guard
+R Rx -V
i
Ri
Vt
Vt : Generador de tensión de c.c.
Ri : Resistencia interna del generador
A : Nano-amperímetro del
microprocesador
La resistencia incógnita (Rx) se conecta entre los bornes -V y +R. Su valor
determina la corriente que circula en el circuito, que es leída por el circuito de
corriente del microprocesador representado en la figura como un nanoamperímetro A. El valor de Rx puede ser determinado mediante la siguiente
ecuación:
Rx
= V
Ri
-
En muchos casos, la resistencia que se pretende medir aparece en paralelo con
otras resistencias parásitas cuya influencia en el valor medido debe minimizarse.
Un ejemplo típico de esta condición es el caso en que se debe medir la resistencia
de aislamiento entre primario y secundario de un transformador montado dentro de
una carcaza metálica:
R
1
R
x
R
2
A
B
Rx : Resistencia de aislamiento entre
primario y secundario.
R1 : Resistencia de aislamiento entre
primario y carcaza.
R2 : Resistencia de aislamiento entre
secundario y carcaza.
32
Page 32
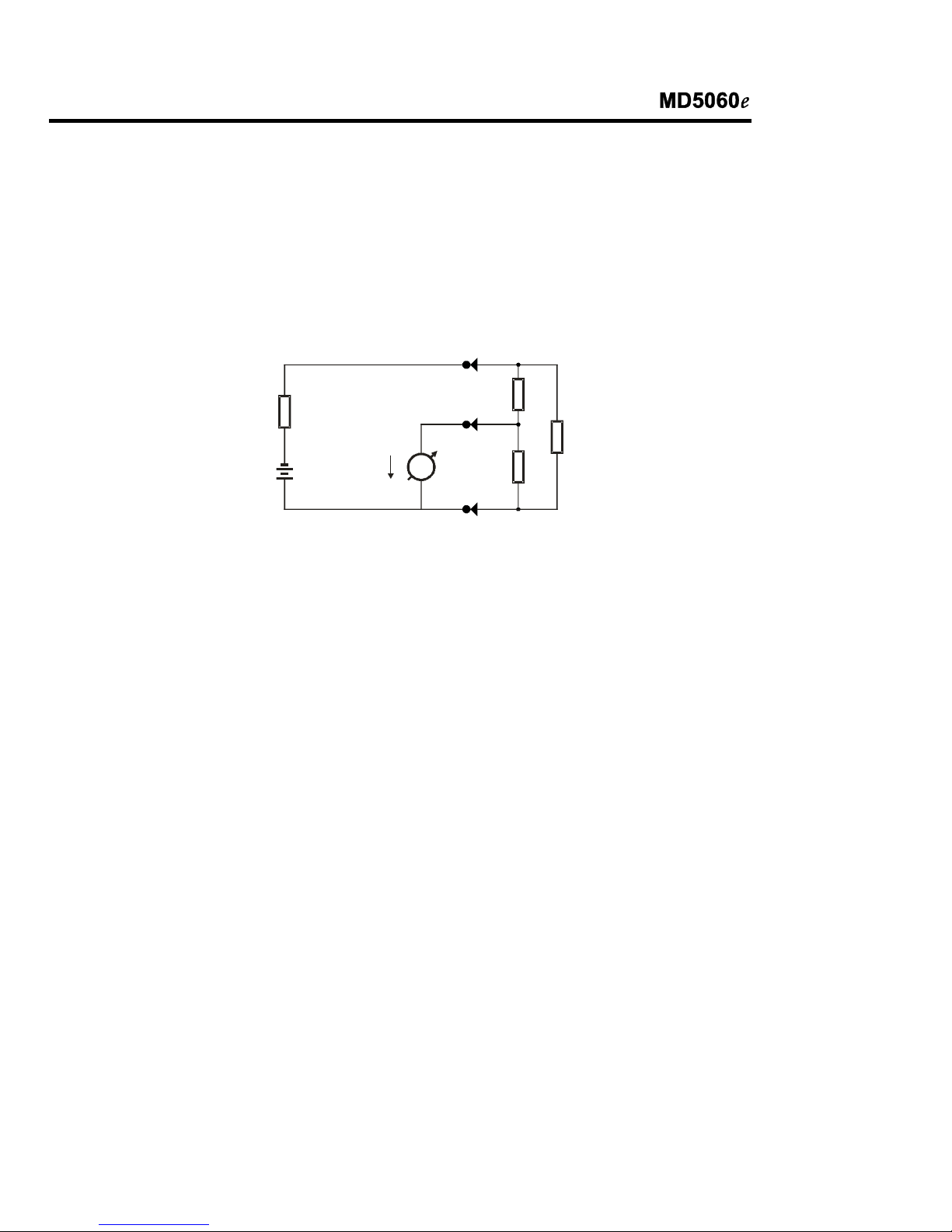
Si conectamos el megóhmetro (a través de los bornes -V y +R) a los terminales A
y B del transformador y ya que las resistencias de las espiras de cada lado del
transformador son despreciables frente a la de aislamiento entre primario y
secundario, aparecerá para el megóhmetro una resistencia Rx en paralelo con R1
+ R2, por lo que el megóhmetro indicará una resistencia menor que la esperada.
La situación se modifica si conectamos la carcaza del transformador al borne
Guard. Resulta el siguiente circuito:
A
Guard
+R
Rx
-V
i Ri R2 R1
Vt
En el circuito de la figura se observa que R2 está en paralelo con una resistencia
de bajo valor (la del nano-amperímetro) y por lo tanto, tiene una influencia
despreciable en la lectura.
Por la resistencia R1 circula una corriente que no pasa por el circuito de corriente
del microprocesador (nano-amperímetro) y por lo tanto no afecta la lectura.
Haciendo un análisis más detallado se observa que la corriente a través de R1
genera un pequeño error, ya que produce una caída de tensión adicional en R2,
pero que se puede considerar totalmente despreciable.
Para todos los efectos prácticos de utilización del megóhmetro se debe considerar
que, si R1 y R2 son mayores que 100 MΩ, cualquier valor de Rx será medido con
un error despreciable utilizando el borne Guard del que resultaría de realizar la
lectura sin la utilización del mismo.
Un ejemplo numérico permite cuantificar lo anteriormente expuesto. Supongamos
los siguientes valores:
Rx = 3.000 MΩ
R1 = 100 MΩ
R2 = 100 MΩ
El valor medido sin utilizar el borne Guard sería de 187,5 MΩ y por lo tanto
totalmente inútil. En cambio, utilizando el borne Guard conectado a la carcaza, se
mide el valor de 3.000 MΩ.
33
Page 33

Apuntes
34
Page 34

Apuntes
35
Page 35

Apuntes
36
Page 36

MD-5060e
5 kV Insulation tester
User guide
© 2016 CIRCUTOR. All rights reserved.
37
Page 37

Safety warnings
· Before to use this instrument the User guide and Safety warnings must be
read and understood.
· Safety procedures and rules for working near high voltage energized systems
must be observed during the use of this equipment. The generated voltages
may be dangerous.
· Do not connect or disconnect the test leads during the measurement.
· Be careful not to make short-circuit between the terminals while a
measurement is running, because it could be dangerous for the operator.
· Be sure that there are not any voltage difference between the points to which
the equipment will be connected to, neither between them and ground.
· The panel, terminals and connectors of the equipment must stay dry and
clean.
This equipment should be used only by a trained and competent
person, strictly applying suitable safety rules.
Used symbols
Caution, risk of electric shock.
Caution, refer to User Guide.
Battery
Printer
Capacitance
Voltmeter
Equipment complies with current EU Directives.
The rubbish bin with a line through it means that in the European Union,
the product must undergo selective disposal for the recycling of electric
and electronic material, in compliance with Directive WEEE 2002/96/EC.
38
Page 38

Index
1. Description...........................................................................................................40
2. Panel control functions.........................................................................................41
2.1. Keyboard......................................................................................................42
2.2. Display..........................................................................................................44
3. Charging battery...................................................................................................45
4. Connecting the MD-5060e...................................................................................46
5. Use of “Guard” (G) terminal.................................................................................48
6. Setting tests.........................................................................................................49
6.1. Test voltage definition...................................................................................49
6.2. Selection of the operation mode...................................................................50
6.2.1. Normal mode.........................................................................................50
6.2.2. SVT Mode (step voltage tests)..............................................................50
6.2.3. “TIMER” Mode.......................................................................................52
6.2.4. “Pass / Fail” Test mode..........................................................................53
7. How to perform tests............................................................................................54
7.1. Measurement of the Dielectric Absorption Index (DAI)................................56
7.2. Measurement of the Polarization Index (PI).................................................57
8. Other functions.....................................................................................................58
8.1. Backlight.......................................................................................................58
8.2. Filter..............................................................................................................58
8.3. True RMS AC/DC Voltmeter........................................................................58
8.4. Leakage current measurement....................................................................58
8.5. Capacitance measurement..........................................................................59
8.6. Hold..............................................................................................................59
8.7. Internal memory............................................................................................60
8.8. Battery status check.....................................................................................60
8.9. Auto power-off..............................................................................................60
9. Software...............................................................................................................61
9.1. USB Drivers..................................................................................................61
9.2. CIR Logger software.....................................................................................61
10. Printer.................................................................................................................62
11. Cleaning.............................................................................................................62
12. Technical specifications.....................................................................................63
13. Application note 32............................................................................................66
39
Page 39

1. Description
The digital insulation tester model MD-5060e is at the cutting edge of
CIRCUTOR’ insulation analyzer equipment and it is one of the more
complete and sophisticated of the international market. It uses an efficient
well experienced technology, which provides safe, reliable and accurate
measurements of insulation resistances up to 5 TΩ, with 4 pre-selected
test voltages: 500 V - 1 kV - 2.5 kV - 5 kV. Other test voltages may be
selected in steps of 25 V, 100 V, or 500 V.
A microprocessor controls the equipment, making the operation easier
and enabling the incorporation of advanced features such as: Auto-range
selection, Memory enabling storing up to 4000 readings, AC/DC
voltmeter, Polarization and Dielectric absorption index automatic
measurement, Measurement of Leakage Current and Capacitance,
“TIMER” to program resistance test time, “Limit” allowing making test type
“Pass / Fail” with programmable limit. Step Voltage Test, Built-in Printer,
Real Time Clock and Calendar for measurement identification. Built-in
chronometer, indicating elapsed time, in minutes and seconds, since the
test started.
The USB interface enables communication of the equipment with a
computer to transmit registered data. The CIR Logger software analyzes
the results and shows through charts and tables, automatically generating
the test protocol. The built-in printer records values on paper every each
15 seconds, as a measurement taken document.
Due to its constructive features, this instrument is strong delivering an
excellent performance both with laboratory and field works, under hard
environment conditions.
40
Page 40

2. Panel control functions
CIRCUTOR SA - Vial Sant Jordi, s/n
08232 Viladecavalls (Barcelona) Spain
MD5060e
Voltage output terminal (-V)
Guard (G) Terminal
Zero reference terminal (+R)
Display
Keyboard
High Voltage led
On / Off key
USB communication port
Power supply input
Printer
41
Page 41

2.1. Keyboard
Key Function LED
Turns the printer on/off Indicates that the printer
is turned on.
Hold - Freeze the last reading on the display The Hold function is on
Battery - exhibits the battery charge status
on the display
–
Filter - Activates the filter that minimizes the
interferences of the external noise
Indicates that the filter is
on
Shows the calculated value on the display as
a result of a Step Voltage Test (SVT),
Polarization Index (PI) and Dielectric
Absorption Index (DAI)
–
Backlight - activates the display light –
Capacitance - exhibit the capacitance value –
Activated enables the programming of the
Operation Mode (Normal, SVT or with
TIMER of selectable time)
Indicates that the
selection of the
Operation Mode is
enabled
42
Page 42

Activated, enables programming of 25 V
step tests voltages
25 V steps activated
Activated, enables programming of 100 V
step tests voltages
100 V steps activated
Activated, enables programming of 500 V
step tests voltages
500 V steps activated
Selection of 500 V test voltage Indicates 500 V selected
Selection of 1 kV test voltage Indicates 1 kV selected
Selection of 2.5 kV test voltage Indicates 2.5 kV selected
Selection of 5 kV test voltage Indicates 5 kV selected
These keys (decrease or increase) enable
the selection of the value that is being
programmed.
–
Activates / enables programming of the limit
for the “Pass / Fail” test
Indicates when the
measured resistance is
lower than programmed
limit
Start - Start test Indicates that the test is
being executed
Stop - End of test –
43
Page 43

2.2. Display
Measurement results in the corresponding measuring unit, elapsed time
since the measurement started, selected test voltage, analogue indication
by means of a bargraph and several messages to the operator are
displayed on alphanumeric LCD.
44
Page 44
3. Charging battery
The MD-5060e uses a rechargeable LiFePO4 12 V - 6000 mAh.
At the end of battery useful life, the battery must be recycled or
disposed of properly, in order to protect the environment.
Charging procedure:
· Check if the MD-5060e is turned-off and connect it to the mains (AC
adapter).
· The charging indicator ( ) will turn on red and will
remain that way until the battery is totally charged. Then the light will
remain green and keep in that way until the MD-5060e is disconnected
of the mains.
Alternate green and red
lights
Evaluation of the battery initial status when the
source is connected, during one second.
Steady red light Battery under charge.
Flashing red light The battery was not successfully charged. It
denotes some trouble in the battery charging
process.
Steady green light The charge has successfully finished. The battery
is OK.
The rechargeable battery does not have “memory effect” and there are no
restrictions to start charging it as many times as is needed. However the battery
could be damaged if remains in deep discharge for a while.
To avoid this effect, charge the battery before left the equipment in storage and
don’t let pass more than 30 days without recharge, even if the instrument wasn’t
used (under storage, the battery loses part of its charge).
IMPORTANT: while the equipment is connected to the mains supply the START
key is inhibited, so you will not be able to make measurements.
45
Page 45

4. Connecting the MD-5060e
ATTENTION: For a safe operation, the procedures detailed below should
be carried out with the device Powered-Off.
Please, do check if there is no difference of potential voltages between
the points where the MD-5060e shall be connected to. Please, check the
same between those points and the ground.
At the time of the connection and power-on, the equipment automatically
enters in the voltmeter mode and begins to exhibit the circuit voltage in
the display.
The circuit to be tested must be de-energized to avoid interferences in the
measurement. The equipment will block the start of measurement if it
detects a voltage greater than 60 V in the circuit.
46
Page 46

Connect the red cable security terminal to the equipment (-V) output
terminal, the terminal of the black cable to the zero reference (+R)
terminal and the “alligator” terminals to the element to be measured as
indicated in the next figure.
CIRCUTOR SA - Vial Sant Jordi, s/n
08232 Viladecavalls (Barcelona) Spain
MD5060e
RED
TEST LEAD
BLACK
TEST LEAD
The test leads in the picture are merely illustrative.
47
Page 47

5. Use of “Guard” (G) terminal
Depending on the measurement to be made, the Guard (G) may be used
or not. During the measurements, the equipment should be electrically
grounded to avoid unsteady readings. When insulation is measured
regarding grounding, the R terminal is connected to earth and the
condition by means of which the equipment potential setting is fulfilled. If
the measurement is performed between two parts, which are not
grounded (for example, between two phase conductors in a three-phase
cable), the equipment GUARD terminal must be grounded. This implies
that whenever a measurement is performed, one of the GUARD or R
terminals must be grounded, but not both of them simultaneously.
CIRCUTOR SA - Vial Sant Jo rdi, s/n
08232 Viladecavalls (Barcelo na) S pain
MD5060e
GUARD
(GREEN)
RED
TEST LEAD
BLACK
TEST LEAD
Technical Note 32, reproduced at the end of the manual, explains the
usage of GUARD terminal in order to eliminate the parasite resistance
effect over the result of measurements.
48
Page 48

6. Setting tests
The insulation tester MD-5060e is an extremely versatile instrument that
enables automatic performance of several types of insulation tests, and
records them in its internal memory and/or prints the results. Thus, it is
necessary to appropriately define the tests to be performed, setting the
following parameters before starting the measurement: Test voltage, Test
duration for “TIMER” mode test, Maximum Voltage for step voltage test
(SVT) and Minimum resistance limit for “Pass/ Fail” tests.
6.1. Test voltage definition
In order to define the test voltage value, first it is necessary to select one
of voltage adjustment keys:
. These keys enable both the
pre-programmed voltage selection ( ) and the and
keys which increase or decrease the value of the step voltage test for
25 V, 100 V or 500 V, depending on the selected voltage adjustment key.
As long as the equipment is on, the voltage adjustment key
will be
selected. Please, press again the adjustment key selected at the moment
with the aim of leaving the test voltage selection mode.
Note: Test voltage is the only one parameter that may be modified during
tests.
49
Page 49

6.2. Selection of the operation mode
The MD-5060e insulation tester has four operation modes: Normal, with
“TIMER”, SVT and “Pass / Fail”. The first three modes are selected using
the key; the “Pass/ Fail” test mode is activated pressing key.
6.2.1. Normal mode
The normal mode is used in the resistance measurement with unique
voltage, without time limit. When selected, there are no special indications
in the display.
6.2.2. SVT Mode (step voltage tests)
The use of key allows the MD-5060e setting for the performance of a
step voltage test; when this mode is selected, the display shows the SVT
abbreviation.
50
Page 50

Under this operation mode, the user does not define a specific voltage
test, but a maximum voltage value. The device will start the test applying
a 500 V voltage and increase this value in 500 V steps each minute until
reaching the programmed voltage. At each stage, the MD-5060e
measures the resistance before advancing towards the following step.
The use of voltage adjusting keys, determines the value of the highest
voltage – which will be, in all cases, a multiple of 500 V, up to a 5000 V
limit. It is advisable to use the key in order to select this value;
and keys may be used, but if the selected value is not a multiple of
500, it will be rounded down.
The test result is calculated according to the following formula:
=
SVT
R
R
V MAX
500
After test ending, the value may be recovered by pressing key.
51
Page 51

6.2.3. “TIMER” Mode
The use of key allows the MD-5060e setting for the performance of a
pre-set - duration test; when this mode is selected, the display shows the
programmed time. Use and keys to define the duration of the
tests in 1 minute, 3 minutes, 10 minutes, 30 minutes or 90 minutes.
52
Page 52

6.2.4. “Pass / Fail” Test mode
Press key in order to determine the lower insulation limit for type
“Pass / Fail” test. Select this value using and keys. Possible
values are 10 MΩ, 100 MΩ, 1 GΩor 10 GΩ.
During a “Pass/ Fail” test, the MD-5060e will indicate when the insulation
resistance is lower than the programmed limit, both with an intermittent
beep and the key led flashing. The key led will remain flashing
until the end of tests, or until the measurement of the resistance value is
greater than the programmed limit.
53
Page 53

7. How to perform tests
After having set the desired measurement, press
key. The HIGH VOLTAGE indicator will turn
on indicating that the insulation tester is applying
high voltage to the element under test.
During some seconds the intelligent auto-range system will search for the
most convenient range for the value under measure. At this moment the
display will show the message “WAIT...”.
As soon as the MD-5060e selects the appropriate range, the display will
show the number of test, the selected voltage value, exhibiting the value
of the applied voltage and the leakage current, date and time, will start
counting the elapsed time and the resistance value indication will be
exhibited with its corresponding unit, and the analogue indication will start
by bargraph. In order to end the test, press the key. At that moment,
last measured values will remain frozen in the MD-5060e display. By
pressing the key again, the equipment will return to the voltmeter
function.
Example:
54
Page 54

The display exhibits the test number (12), the measured resistance value
(602 GΩ, the voltage selected of 2500 V, the elapsed time (6:25
minutes), the applied voltage (2.51 kV), the leakage current (4.17 nA),
date and time.
NOTE: If the resistance measured is greater than 5 TΩ@ 5 kV, the
following message will be exhibited: R > 5TΩ
ATTENTION: Please, never connect or disconnect the test leads with the
equipment under operation or while the High Voltage led is on. If there is
a need to modify the connections, this should be done with discharged
potentials (High Voltage led off)
55
Page 55
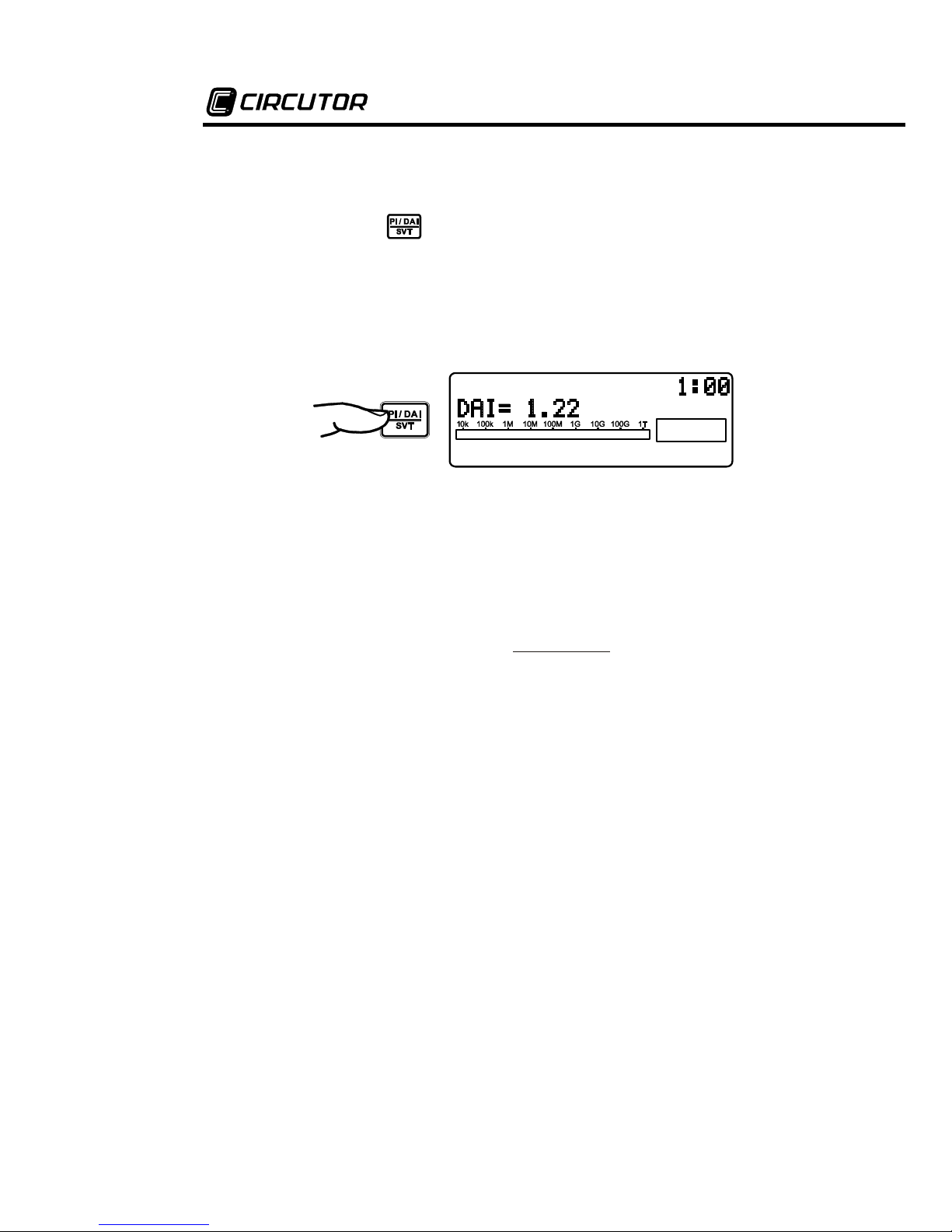
7.1. Measurement of the Dielectric Absorption
Index (DAI)
When pressing the key during the test, the Dielectric Absorption
Index (DAI) value will be exhibited on the display. It is only possible to
apply this function after a minimum of 1 minute of measurement; in case
the key is pressed before this minimum limit, the display will show the
message of value exhibition of DAI value, but will not show any value.
The polarization index is the quotient between the values of the insulation
resistance measured at the 60 and 30 second, and it is useful for
preventive and predictive maintenance of windings (present in
transformers, motors, generators, etc.).
=
DAI
R
R
60 seconds
30 seconds
56
Page 56

7.2. Measurement of the Polarization Index (PI)
When pressing the key during the test, the Polarization Index (PI)
value will be exhibited on the display. It is only possible to apply this
function after a minimum of 10 minutes of measurement; in case the key
is pressed before this minimum limit, the display will show the message of
value exhibition of PI value, but will not show any value.
The polarization index is the quotient between the values of the insulation
resistance measured both in 10 minutes and 1 minute. This index is
useful to detect the damage of the insulation resistance by the excessive
presence of dust, dirt and greases or through the action of chemical and
physical agents.
=
PI
R
R
10 minutes
1 minute
57
Page 57

8. Other functions
8.1. Backlight
The equipment display has a backlight. In order to activate it, press
key. After 10 seconds the backlight will auto-turn off. If you want to
reactivate it, press key again.
8.2. Filter
When insulation measurements are carried out in transformers or in large
dimension machines, in presence of strong electromagnetic fields, it is
possible for the equipment reading to be unstable, especially for
resistance values higher than 100 MΩ. In these cases it is convenient to
press the key before starting the measurement activating the filter
which allows for the reaching of the insulation resistance value in an
upward curve without significant oscillation.
8.3. True RMS AC/DC Voltmeter
In order to use this function, connect the test points and turn on MD5060e. The measured value will be exhibited automatically in the display.
AC DC
10 V up to 1000 Vr.m.s. 10 V up to 1000 V
Precision: ± (5% of the reading + 3 digits)
8.4. Leakage current measurement
During the tests, the equipment measures and exhibits in the display the
leakage current value within a range of 1 nA up to 3 mA, with a Precision
of ± (10% of the reading + 3 digits).
58
Page 58

8.5. Capacitance measurement
The capacitance value is obtained by measuring the insulation resistance.
After finishing measuring (When the
key has been pressed), wait the
high voltage LED turn off, and press the key and the capacitance
value will be exhibited on the display.
Voltage Capacitance
500 V 50 nF up to 10 µF
1,000 V 50 nF up to 5 µF
2,500 V 30 nF up to 2 µF
5,000 V 30 nF up to 1 µF
Precision: ± 10% of the measured value ± 3 digits
Note: “0” will be exhibited on the display when measuring values lower
than 50 nF
8.6. Hold
This function allows holding the last performed reading on the display at
the moment when pressing the key, without interrupting the test.
When this key is pressed again, the equipment updates the resistance
and chronometer values. The led of key and the letter H on the
display indicate that the function has been activated
59
Page 59
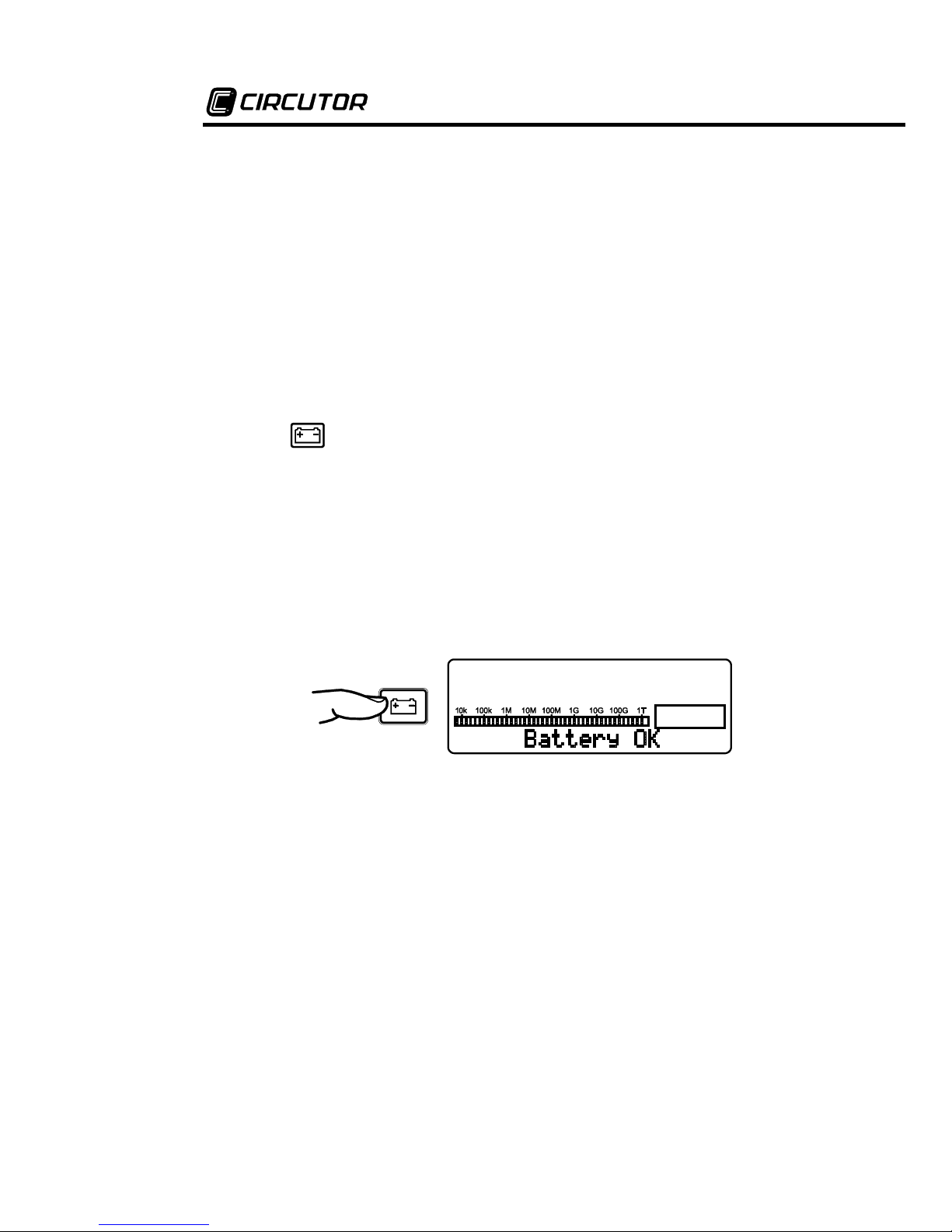
8.7. Internal memory
This equipment has an internal memory for up to 4000 measured values
(approx. 280 DAI tests or 30 PI tests). This memory is administrated by
the instrument and works in a cyclic way, this means, when the memory is
full, the oldest values in the memory will be replaced by the newest ones.
To avoid lost of data, always download the internal memory after finish
the measurements.
8.8. Battery status check
Hold the key pressed in order to check the battery status during
measurements. The analogue bargraph will give an approximate visual
representation of the remaining charge percentage; additionally, the
display will show the message “Battery OK” if the charge is enough, or
“Battery Low” if the charge is low. In this last case, it is highly advisable
to charge the battery before using the apparatus. If battery charge is
under 20% of the total, the message Battery Low will automatically
appears on the display.
8.9. Auto power-off
The MD-5060e auto-turns off after 10 minutes of inactivity, or after 95
minutes of measuring without checking the battery status.
60
Page 60

9. Software
9.1. USB Drivers
To install the USB drivers required for the communication between PC
and equipment follow the instructions:
1. Connect the equipment in the PC using the USB cable.
2. If there is an available Internet connection, Windows will silently
connect to the Windows Update website and install any suitable driver
it finds for the device. If no suitable driver is automatically found then
you need to insert the CD-ROM, supplied with the equipment, in the
PC, run the executable “usb-install.exe” and click in “Install”.
9.2. CIR Logger software
This software makes communication between the equipment and a
computer with Windows operative system easier. It makes possible to
synchronize the date and time of the equipment internal clock with the
computer date and clock, to transfer the stored date, to clear the memory,
to generate test graphics and protocols, etc. The installation and
operation instructions are included in the software.
61
Page 61

10. Printer
In order to enable the printing function press key. Measured values
will be printed each 15 seconds, and the Dielectric Absorption Index and
Polarization Index will be printed after 1 minute and 10 minutes
respectively. Printing may be started or stopped at any time during the
test. However, it is convenient to turn the printer on before starting the
test in order to print it complete, including the heading.
ATTENTION: Don’t pull the paper. The printer can be easily damaged.
This printer uses 56 mm-wide thermal paper, which comes in a 30 mmdiameter reel.
Pull the lever located on the lid.
Insert the paper reel as shown in the figure.
Keep the tip of the paper out of the printer and close the lid.
11. Cleaning
The panel, terminals and connectors of the equipment must stay dry and
clean. Cleaning should be made using a wet cloth in water and a soft
detergent or isopropyl alcohol (be sure that the products to be used for
cleaning does not affect plastic goods).
62
Page 62

12. Technical specifications
Test voltages
:
500 - 1,000 - 2,500 - 5,000 V with fast
selection.
From 500 V to 5 kV selectable in 25 V, 100 V or
500 V steps. DC, negative in relation to
grounding.
Maximum resistance reading
:
5 TΩ @ 5 kV
DC Voltmeter
:
10 V up to 1000 Vdc
Precision: ± (5% of the reading + 3 digits)
AC voltmeter
:
10 V up to 1000 V r.m.s.
Precision: ± (5% of the reading + 3 digits)
Over voltage protection
:
CAT. III – 600 V
Current measurement
:
1 nA up to 3 mA
± (10% of the reading + 3 digits)
Capacitance measurement
:
50 nF up to 10 µF @ 500 V
50 nF up to 5 µF @ 1,000 V
30 nF up to 2 µF @ 2,500 V
30 nF up to 1 µF @ 5,000 V
Precision: ± 10% of the reading ± 3 digits
Short circuit current
:
Max. 3 mA
Display
:
Alphanumeric. It exhibits measurements both
digitally and analogically by bargraph.
Test voltages accuracy
:
± 3% of nominal value over a 10 GΩ resistance
Equipment accuracy
:
± 5% of reading between 1MΩ and 1TΩ @ 5kV
± 20% of reading between 1TΩ and 5TΩ @
5kV
(For lower test voltages, the superior limit is
proportionally reduced)
± 20% of the reading between 10kΩ and 100kΩ
± 10% of the reading between 10kΩ and 1MΩ
63
Page 63

Advanced features
:
• Automated Polarization Index computing
• Automated Dielectric Absorption Index
computing
• “Pass-fail” and fixed time tests
• Step Voltage Test
• Memory for up to 4000 measurements
• Filter to minimize interferences
Printer
:
Prints elapsed time, actual voltage applied to
the element under test and measured
resistance
PC Interface
:
USB
Built-in chronometer
:
Indicates elapsed time from the beginning of
the measurement mm:ss format, up to 90:00
Environmental protection
index
:
IP54 (with closed lid)
Safety
:
In accordance with IEC 61010-1
Electromagnetic
compatibility (E.M.C.)
:
In accordance with IEC 61326-1
Electromagnetic irradiation
immunity
:
In accordance with IEC 61000-4-3
Electrostatic immunity
:
In accordance with IEC 61000-4-2
Power supply
:
Internal rechargeable battery 12 V - 6000 mAh
Battery charger
:
AC Adapter: 12 V - 2 A
Operating temperature
:
-5°C to 50°C
Storage temperature
:
-25°C to 65°C
Humidity
:
95% RH (non condensing)
Equipment weight
:
Approx. 4.3 kg
Dimensions
:
340 x 295 x 152 mm
64
Page 64

Supplied accessories
:
• 3 measurement cables
• AC Adapter
• USB cable
• Carrying bag
• Operation manual
• License for CIR Logger software
Subject to technical change without notice.
65
Page 65

13. Application note 32
Use of “Guard” terminal in insulation testers
When insulation resistance measurements are performed with insulation
testers, especially with high sensitivity instruments measuring high
resistance values, the use of the GUARD terminal avoids the harmful
influence of stray resistances.
In order to better explain the function of this terminal, let us start reviewing
the insulation tester basic circuit diagram of fig. 1.
Where:
Vt : DC high-voltage generator
Ri : Generator internal resistance
A : Indicator meter (micro-ammeter)
The unknown resistance (Rx) is connected between V and R terminals.
Its value determines the current passing through the circuit, which in turn
is indicated by the micro-ammeter. The value of Rx can be determined as
follows:
In many cases the resistance to be measured is in parallel with other
stray resistances which influence on Rx should be minimized.
66
Page 66

A typical example of this situation is when the insulation resistance
between primary and secondary windings of a transformer mounted
inside a metal housing is to be measured.
Rx: Insulation resistance between primary and secondary winding.
R1: Insulation resistance between primary winding and housing.
R2: Insulation resistance between secondary winding and housing.
If the insulation tester (terminals V and R) is connected to transformer
terminals A and B, and considering that the resistance of the coils on
each side of the transformer may be disregarded, Rx appears to be in
parallel with (R1 + R2). The situation is changed if we connect the
transformer housing to GUARD terminal. Then the circuit will be:
67
Page 67

In the circuit of Fig. 3 it may be noted that R1 is in parallel with a lowvalue resistance (the one from the micro-ammeter) therefore its influence
is reduced during reading.
Through resistance R2 circulates a current which is not passing through
the meter and consequently does not affect the reading. In fact, current
through R2 originates a certain error, since it creates an additional voltage
drop in R1 which was not regarded during equipment calibration. As
regards the practical use of instrument, it shall be considered that if R1
and R2 are higher than 100 MΩ, any value of Rx will be measured with an
insignificant error. For example: Let us consider Rx = 3000 MΩ and R1 =
R2 = 100 MΩ, the reading without using the GUARD terminal would be
187.5 MΩ, which is quite wrong. On the other hand, if the GUARD
terminal is properly used, we would have 3000 MΩ.
68
Page 68

Notes
69
Page 69

Notes
70
 Loading...
Loading...