Page 1

Financial Calculation (TVM)
Software for the
ALGEBRA FX2.0
1. Before Performing Financial Calculations
2. Simple Interest
3. Compound Interest
4. Cash Flow (Investment Appraisal)
5. Amortization
6. Interest Rate Conversion
7. Cost, Selling Price, Margin
8. Day/Date Calculations
9. Depreciation
10. Bonds
11. TVM Graph
Page 2

2
1. Before Performing Financial Calculations
kk
k TVM Mode
kk
Installing the Financial Application on your ALGEBRA FX2.0 adds a TVM icon to the Main
Menu.
Entering the TVM Mode displays the Financial screen like the one shown below.
Financial 1 screen Financial 2 screen
• 1(SMPL)....Simple interest
• 2(CMPD) ... Compound interest
• 3(CASH)....Cash flow (investment appraisal)
• 4(AMT) ...... Amortization
• 5(CNVT)....Interest rate conversion
• 6(g)1(COST) ... Cost, selling price, margin
2(DAYS) ... Day/date calculations
3(DEPR) ... Depreciation
4(BOND) ... Bonds
5(TVMG) ... TVM (compound interest simulation) graph
Page 3
3
kk
k SET UP Items
kk
uu
u Payment
uu
•{BGN}/{END} ........ Specifies {beginning of the period} / {end of the period} payment
uu
u Date Mode
uu
•{365}/{360} ......... Specifies calculation according to a {365-day} / {360-day} year
uu
u Periods/YR. (Bond)
uu
•{Annual}/{SEMI} ... Indicates an {annual} / {semi-annual} period
Note the following points regarding SET UP screen settings whenever using the Financial Mode.
• Drawing a financial graph while the Label item is turned on, displays the label CASH for the
vertical axis (deposits, withdrawals), and TIME for the horizontal axis (frequency). Axis labels do not appear on the TVM graph.
• The number of display digits applied in the Financial Mode is different from the number of
digits used in other modes. The calculators automatically reverts to Norm 1 whenever you
enter the Financial Mode, which cancels a Sci (number of significant digits) or Eng (engineering notation) setting made in another mode.
kk
k Graphing in the TVM Mode
kk
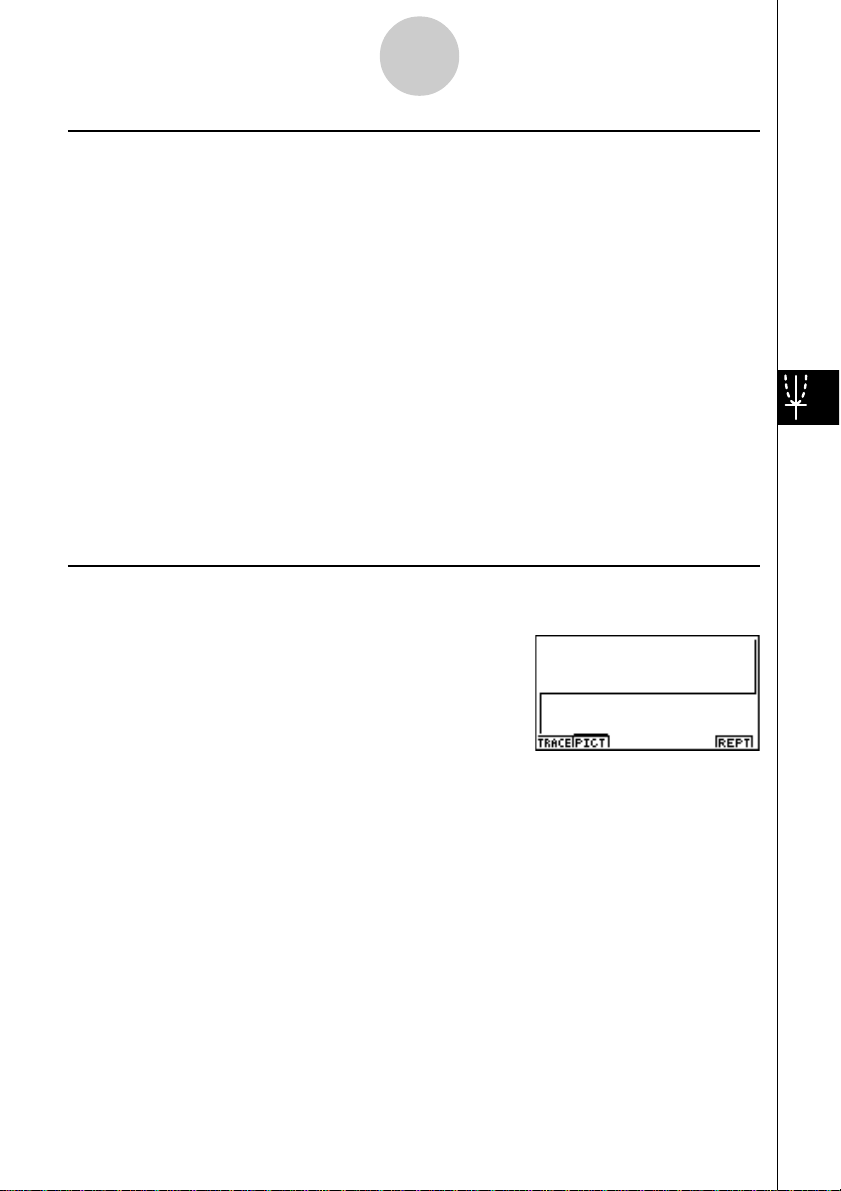
After performing a financial calculation, you can use 6 (GRPH) to graph the results as shown
below.
• Pressing 1 (TRACE) while a graph is on the display activates T race, which can be used to
look up other financial values. In the case of simple interest, for example, pressing e
displays PV, SI, and SFV. Pressing d displays the same values in reverse sequence.
• Zoom, Scroll, and Sketch cannot be used in the Financial Mode.
• Whether you should use a positive or a negative value for the present value (PV) or the
purchase price (PRC) depends on the type of calculation you are trying to perform.
• Note that graphs should be used only for reference purposes when viewing TVM Mode
calculation results.
• Note that calculation results produced in this mode should be regarded as reference values
only.
• Whenever performing an actual financial transaction, be sure to check any calculation results obtained using this calculator with against the figures calculated by your financial institution.
Page 4
4
2. Simple Interest
This calculator uses the following formulas to calculate simple interest.
uu
uFormula
uu
365-day Mode
360-day Mode
SI' =
SI' =
n
365
n
360
× PV × i
× PV × i
i =
i =
I%
100
I%
100
SI : interest
n : number of interest
periods
PV : principal
I% : annual interest
SFV : principal plus interest
SI = –SI'
SFV = –(PV + SI')
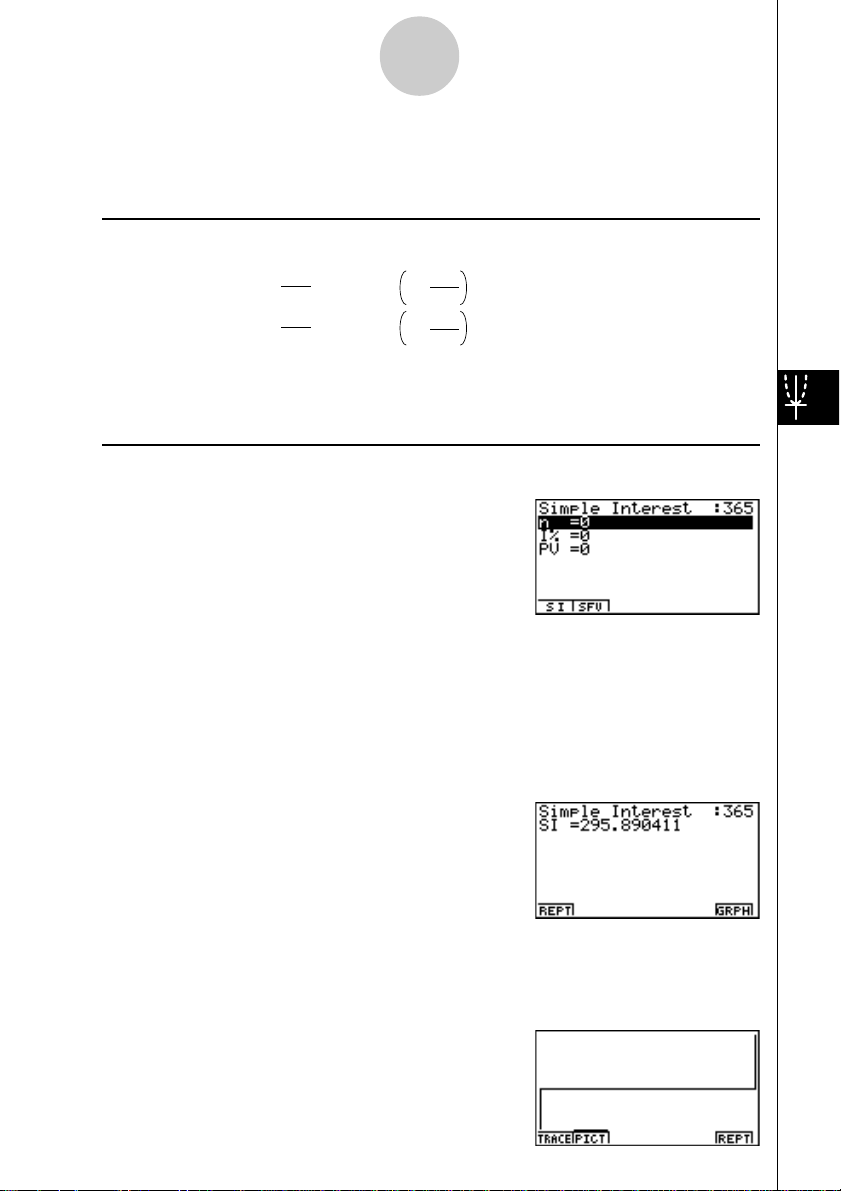
Press 1(SMPL) from the Financial 1 screen to display the following input screen for simple
interest.
• 1(SMPL)
n .................................. number of interest periods (days)
I% ............................... annual interest rate
PV ............................... principal
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
• 1(SI)....... Simple interest
• 2(SFV)... Simple future value
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following function keys to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) ...Parameter input screen
• 6(GRPH)... Draws graph
Page 5
5
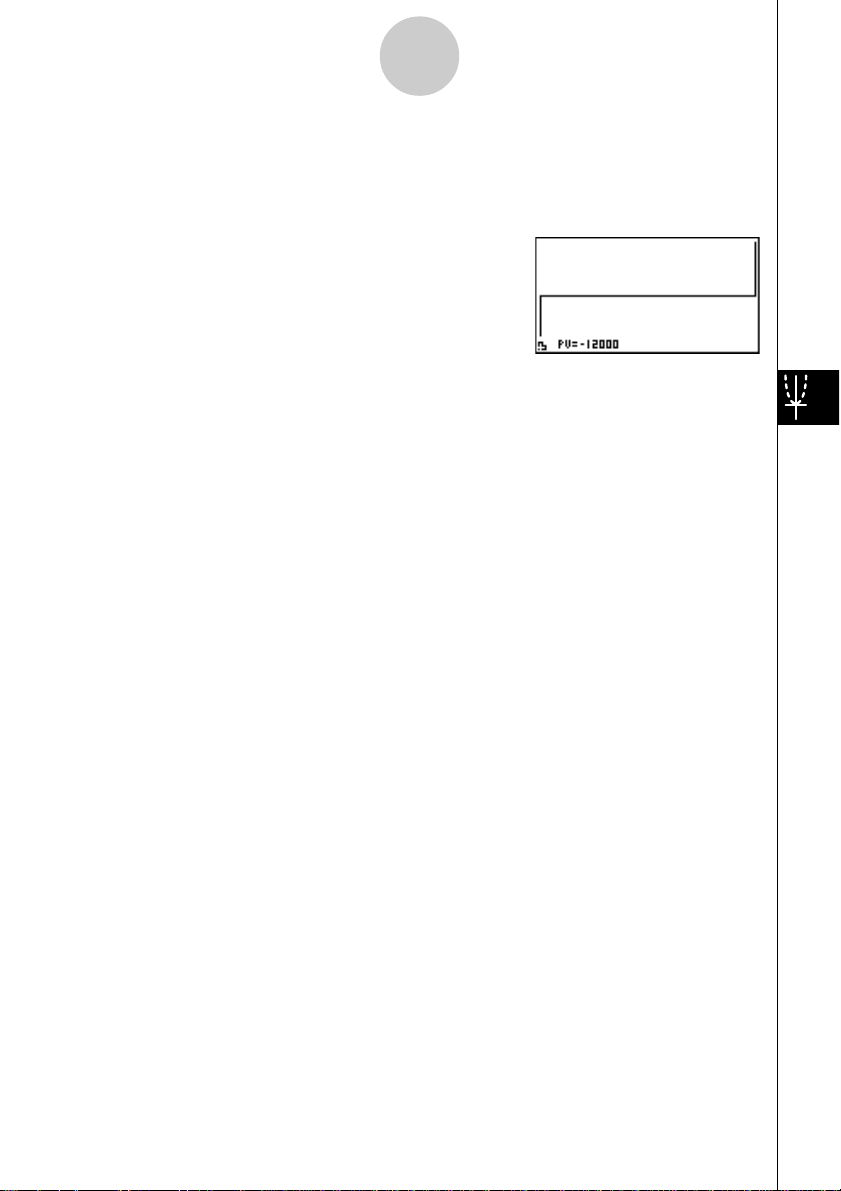
After drawing a graph, you can press 1 (TRACE) to turn on trace and read calculation results
along the graph.
Each press of e while trace is turned on cycles the displayed value in the sequence: present
value (PV) -> simple interest (SI) -> simple future value (SFV). Pressing d cycles in the
reverse direction.
Press i to turn off trace.
Press i again to return to the parameter input screen.
Page 6

6
β
β
)
3. Compound Interest
This calculator uses the following standard formulas to calculate compound interest.
uu
uFormula I
uu
PV+PMT u + FV
Here:
(1+ i u S)[(1+ i)n–1] 1
n
i(1+ i)
(1+ i)
= 0
n
i =
I%
100
PV= –(PMT
PMT
V= –
PMT= –
log
n =
(1+ i u S)[(1+ i)n–1]
α
=
=
β
(1+ i)
F(i) = Formula I
F(i)= –
+S [1–(1+ i)
α
u
+ FV
u )
u
+ PV
α
PV + FV
β
u
α
(1+ i S ) PMT–FVi
{ }
(1+ i S ) PMT+PVi
log(1+ i)
n
i(1+ i
1
n
PMT
(1+ i S)[1– (1+ i)
[
–n
] – FV • n(1+ i)
]
ii
PV : present value
FV : future value
PMT : payment
n : number of compound periods
I
%
: annual interest rate
i is calculated using Newton’s Method.
S = 0 assumed for end of term
S = 1 assumed for beginning of term
–n
]
+ (1+ i S)[n(1+ i)
–n–1
–n–1
]
uu
uFormula II (I% = 0)
uu
PV + PMT × n + FV = 0
Here:
PV = – (PMT u n + FV )
FV = – (PMT u n + PV )
Page 7

7
PMT = –
n = –
• A deposit is indicated by a plus sign (+), while a withdrawal is indicated by a minus sign (–).
uu
uConverting between the nominal interest rate and effective interest rate
uu
The nominal interest rate (I% value input by user) is converted to an effective interest rate (I%')
when the number of installments per year (P/Y) is different from the number of compound
interest calculation periods (C/Y). This conversion is required for installment savings accounts,
loan repayments, etc.
When calculating n, PV, PMT, FV
The following calculation is performed after conversion from the nominal interest rate to the
effective interest rate, and the result is used for all subsequent calculations.
i = I%'÷100
When calculating I%
After I% is obtained, the following calculation is performed to convert to I%'.
I%' =
PV + FV
n
PV + FV
PMT
[C / Y ]
I%' =
(1+ ) –1
{ }
I%
(1+ ) –1
{ }
100
I%
100 × [C / Y ]
[P / Y ]
[C / Y ]
[P / Y ]
×[C / Y ]×100
×100
P/Y: installment
periods per year
C/Y: compounding
periods per year
P/Y: installment
periods per year
C/Y: compounding
periods per year
The value of I%' is returned as the result of the I% calculation.
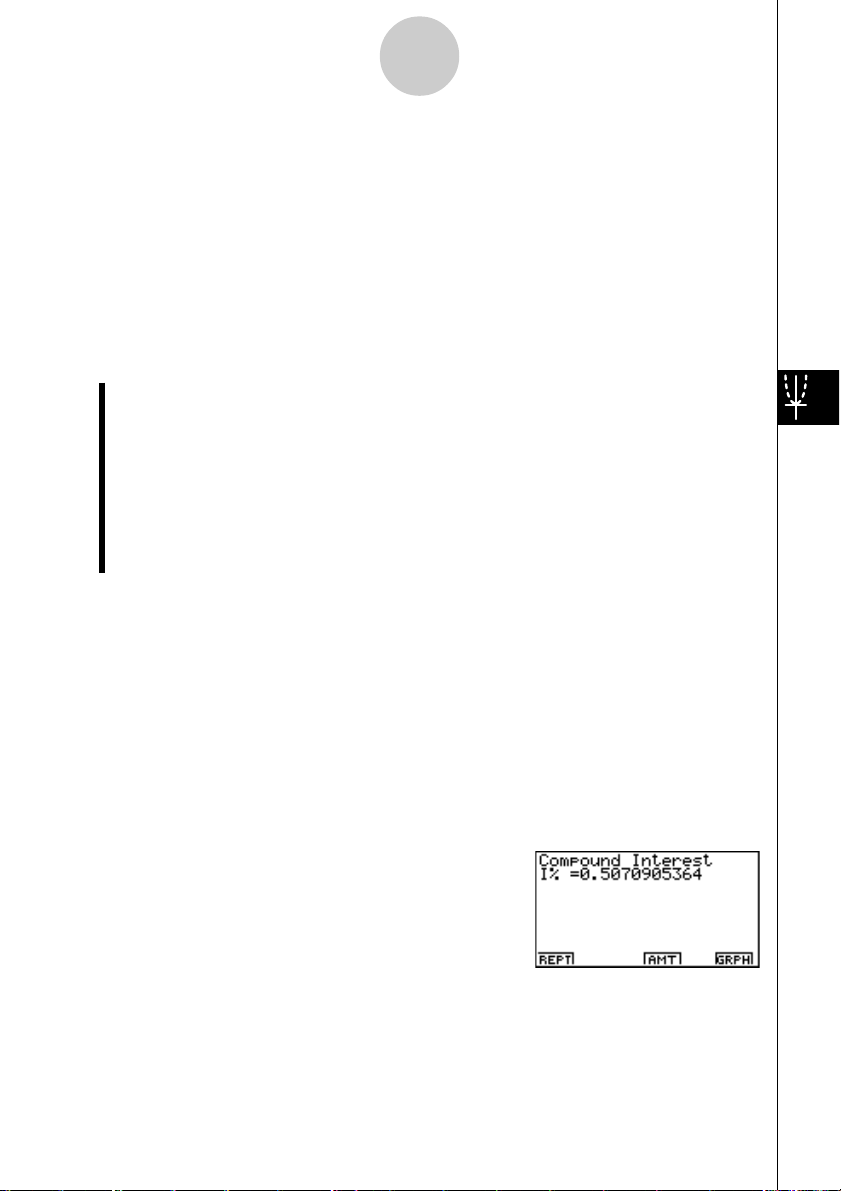
Press 2(CMPD) from the Financial 1 screen to display the following input screen for compound interest.
• 2(CMPD)
Page 8
8
n .................................. number of compound periods
I% ............................... annual interest rate
PV ............................... present value (loan amount in case of loan; principal in case
of savings)
PMT ............................ payment for each installment (payment in case of loan; de-
posit in case of savings)
FV ............................... future value (unpaid balance in case of loan; principal plus
interest in case of savings)
P/Y .............................. installment periods per year
C/Y .............................. compounding periods per year
Inputting Values
A period (n) is expressed as a positive value. Either the present value (PV) or future value
(FV) is positive, while the other (PV or FV) is negative.
Precision
This calculator performs interest calculations using Newton’s Method, which produces approximate values whose precision can be affected by various calculation conditions. Because
of this, interest calculation results produced by this calculator should be used keeping the
above limitation in mind or the results should be verified.
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
• 1(n) ............ Number of compound periods
• 2(I%) ......... Annual interest rate
• 3(PV) ......... Prevent value
• 4(PMT) ...... Payment
• 5(FV) ......... Future value
• 6(AMT) ...... Amortization screen
(Loan: loan amount; Savings: balance)
(Loan: installment; Savings: deposit)
(Loan: unpaid balance; Savings: principal plus interest)
Page 9
9
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following function keys to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) .... Parameter input screen
• 4(AMT) ...... Amortization screen
• 6(GRPH).... Draws graph
After drawing a graph, you can press 1(TRACE) to turn on trace and read calculation
results along the graph.
Press i to turn off trace.
Press i again to return to the parameter input screen.
Page 10

10
CF
0
CF
1
CF
2
CF
3
CF
4
CF
5
CF
6
CF
7
4. Cash Flow (Investment Appraisal)
This calculator uses the discounted cash flow (DCF) method to perform investment appraisal
by totalling cash flow for a fixed period. This calculator can perform the following four types of
investment appraisal.
• Net present value (NPV)
• Net future value (NFV)
• Internal rate of return (IRR)
• Pay back period (PBP)
A cash flow diagram like the one shown below helps to visualize the movement of funds.
With this graph, the initial investment amount is represented by CF0. The cash flow one year
later is shown by CF1, two years later by CF2, and so on.
Investment appraisal can be used to clearly determine whether an investment is realizing profits that were originally targeted.
uNPV
1
NPV = CF0 + + + + … +
CF
(1+ i)
CF2
(1+ i)
2
CF3
(1+ i)
3
CFn
(1+ i)
n
i =
I%
100
n: natural number up to 254
uNFV
NFV = NPV × (1 + i )
n
uIRR
1
CF
2
CF
(1+ i)
3
3
CF
(1+ i)
(1+ i)
2
0 = CF0 + + + + … +
In this formula, NPV = 0, and the value of IRR is equivalent to i × 100. It should be noted,
however, that minute fractional values tend to accumulate during the subsequent calculations
performed automatically by the calculator, so NPV never actually reaches exactly zero. IRR
becomes more accurate the closer that NPV approaches to zero.
CF
(1+ i)
n
n
Page 11

11
uu
uPBP
uu
Initial value of N when NPV > 0.
• Press 3 (CASH) from the Financial 1 screen to display the following input screen for Cash
Flow.
• 3(CASH)
I% ............................... interest rate (%)
Csh.............................. list for cash flow
If you have not yet input data into a list, press 5('LIST) and input data into a list.
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
• 1(NPV) ........ Net present value
• 2(IRR) ......... Internal rate of return
• 3(PBP) ........ Pay back period
• 4(NFV) ........ Net future value
• 5('LIST) .... Inputs data from a list
• 6(LIST) ....... Specifies a list for data input
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following function keys to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) .... Parameter input screen
• 6(GRPH) .... Draws graph
Page 12

12
After drawing a graph, you can press 1 (TRACE) to turn on trace and read calculation results
along the graph.
Press i to turn off trace.
Press i again to return to the parameter input screen.
Page 13

13
;;;;;;;;;;;
;;;;;;;;;
;;;;;;;
;;;;;
;;;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;
;;;;;
;;;;;
;;;
;
5. Amortization
This calculator can be used to calculate the principal and interest portion of a monthly installment,
the remaining principal, and amount of principal and interest repaid up to any point.
uu
uFormula
uu
Amount of single payment
;;;
e
;;;
;;;
;;;
;;;
;;;
;;;
;;;
d
12 mn
a: interest portion of installment PM1 (INT)
b: principal portion of installment PM1 (PRN)
c: balance of principal after installment PM2 (BAL)
d: total principal from installment PM1 to payment of installment PM2 (ΣPRN)
e: total interest from installment PM1 to payment of installment PM2 (ΣINT)
*a + b = one repayment (PMT)
a
b
(Number of payments)
c
a : INT
b : PRN
c : BAL
d : Σ PRN = PRN
PM1
e : Σ INT = INT
PM1
BAL0 = PV (INT1 = 0 and PRN1 = PMT at beginning of installment term)
uu
uConverting between the nominal interest rate and effective interest rate
uu
The nominal interest rate (I% value input by user) is converted to an effective interest rate (I%')
for installment loans where the number of installments per year is different from the number of
compound interest calculation periods.
I%' =
PM1
= I BAL
PM1
PM2
PM2
PM2
(1+ ) –1
{ }
PM1–1
× i I × (PMT sign)
= PMT + BAL
= BAL
PM2–1
+ PRN
PM1
+ PRN
PM1
+ INT
I%
100 × [C / Y ]
PM1–1
× i
PM2
PM1+1
PM1+1
+ … + INT
[C / Y ]
[P / Y ]
+ … + PRN
PM2
×100
PM2
Page 14

14
The following calculation is performed after conversion from the nominal interest rate to the
effective interest rate, and the result is used for all subsequent calculations.
i = I%'÷100
Press 4(AMT) from the Financial 1 screen to display the following input screen for interest
rate conversion.
• 4(AMT)
PM1............................. first installment of installments 1 through n
PM2............................. second installment of installments 1 through n
.................................. installments
n
I% ............................... interest rate
PV ............................... principal
PMT ............................ payment for each installment
FV ............................... balance following final installment
P/Y .............................. installments per year
C/Y .............................. compoundings per year
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
• 1(BAL) ........ Balance of principal after installment PM2
• 2(INT) ......... Interest portion of installment PM1
• 3(PRN) ....... Principal portion of installment PM1
• 4(Σ INT) ...... Total interest paid from installment PM1 to installment PM2
• 5(Σ PRN) .... Total principal paid from installment PM1 to installment PM2
• 6(CMPD) .... Compound interest screen
Page 15

15
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following function keys to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) ..... Parameter input screen
• 4(CMPD) .... Compound interest screen
• 6(GRPH) ..... Draws graph
After drawing a graph, you can press 1 (TRACE) to turn on trace and read calculation results
along the graph.
The first press of 1 (TRACE) displays INT and PRN when n = 1. Each press of e shows
INT and PRN when n = 2, n = 3, and so on.
Press i to turn off trace.
Press i again to return to the parameter input screen.
Page 16

16
6. Interest Rate Conversion
The procedures in this section described how to convert between the annual percentage rate
and effective interest rate.
uu
uFormula
uu
APR/100
EFF =
APR =
Press 5(CNVT) in the Financial 1 screen to display the following input screen for interest rate
conversion.
• 5(CNVT)
1+
1+
EFF
100
n
–1 × 100
n
1
n
–1 × n ×100
APR : annual percentage rate (%)
EFF : effective interest rate (%)
n : number of compoundings
n....................................... number of compoundings
I% ............................... interest rate
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
• 1('EFF) ... Converts annual percent rate to effective interest rate
• 2('APR) ... Converts effective interest rate to annual percent rate
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following function key to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) ... Parameter input screen
Page 17

17
7. Cost, Selling Price, Margin
Cost, selling price, or margin can be calculated by inputting the other two values.
uu
uFormula
uu
CST
MRG
100
1–
1–
MRG
100
CST
SEL
CST : cost
SEL : selling price
MRG : margin
×100
CST = SEL
SEL =
1–
MRG(%) =
Press 1(COST) from the Financial 2 screen to display the following input screen.
• 6(g)1(COST)
Cst............................... cost
Sel............................... selling price
Mrg .............................. margin
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
• 1(COST) ...Cost
• 2(SEL) ......Selling price
• 3(MRG) .....Margin
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following function key to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) ... Parameter input screen
Page 18

18
8. Day/Date Calculations
You can calculate the number of days between two dates, or you can determine what date
comes a specific number of days before or after another date.
Press 2(DAYS) from the Financial 2 screen to display the following input screen for day/date
calculation.
• 6(g)2(DAYS)
d1 ................................ date 1
d2 ................................ date 2
D ................................. number of days
• The set up screen can be used to specify either a 365-day or 360-day year for financial
calculations. Day/date calculations are also performed in accordance with the current setting for number of days in the year, but the following calculations cannot be performed
when the 360-day year is set. Attempting to do so causes an error.
(Date) + (Number of Days)
(Date) – (Number of Days)
• The allowable calculation range is January 1, 1901 to December 31, 2099.
To input a date, first highlight d1 or d2. Pressing a number key to input the month causes an
input screen like the one shown below to appear on the display.
Input the month, day, and year, pressing w after each.
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
Page 19

19
• 1(PRD) ...... Number of days from d1 to d2 (d2 – d1)
• 2(d1+D) ..... d1 plus a number of days (d1 + D)
• 3(d1 – D) ... d1 minus a number of days (d1 – D)
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following function key to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) .... Parameter input screen
360-day Date Mode Calculations
The following describes how calculations are processed when 360 is specified for the Date
Mode item in the SET UP screen.
• If d1 is day 31 of a month, d1 is treated as day 30 of that month is used.
• If d2 is day 31 of a month, d2 is treated as day 1 of the following month, unless d1 is day 30.
Page 20

20
9. Depreciation
Any of the following four methods can be used to calculated depreciation.
uu
uStraight-Line Method
uu
The straight-line method calculates depreciation for a given period.
{Y–1}(PV–FV )
SL
SL
SL
1
=
(PV–FV )
j
=
n+1
=
(PV–FV )
u
n 12
n
12–{Y–1}
u
n 12
({Y–1}G12)
Depreciation for an item acquired part way through a year can be calculated by month.
uu
uFixed Percentage Method
uu
Fixed percentage method can be used to calculate depreciation for a given period, or to calculate the depreciation rate.
{Y–1}I%
FP
1
= PV ×
FP
j
= (RDV
n+1
= RDVn ({Y–1}G12)
FP
RDV
1
= PV – FV – FP
RDVj = RDV
100
j–1
+ FV ) ×
j–1
– FP
×
12
I%
100
1
j
SLj : depreciation charge for the jth
year
n : useful life in years
PV : original cost (basis)
FV : scrap value (salvage value)
j : year
Y–1 : number of depreciable months
in first year
FPj : depreciation charge for the jth year
RDVj : remaining depreciable value at the
end of jth year
I
%
: depreciation rate
RDV
n+1
= 0 ({Y–1}G12)
Depreciation for an item acquired part way through a year can be calculated by month.
Page 21

21
12
{Y–1}
n' = n –
n (n +1)
Z =
12
2
(n' integer part +1)(n' integer part + 2*n' fraction part
)
Z' =
SYD
1
=
{Y–1}
12
n
Z
× (PV
– FV )
n'– j+2
Z'
)(PV
– FV – SYD1)( jG1)SYDj = (
RDV
1
= PV – FV – SYD
1
RDVj = RDV
j –1
– SYD
j
n'– (n +1)+2
Z'
)(PV
– FV – SYD1)({Y–1}G12)
12–{Y–1}
12
×SYD
n+1
= (
uu
uSum-of-the-Year's Digits Method
uu
The sum-of-the-year's-digits method calculates depreciation for a given period.
SYDj : depreciation charge for the jth year
RDVj : remaining depreciable value at the
end of jth year
Depreciation for an item acquired part way through a year can be calculated by month.
uu
uDeclining Balance Method
uu
The declining balance method calculates depreciation for a given period.
Y–1I%
DB
1
= PV ×
100n
×
RDV1 = PV – FV – DB
j
= (RDV
DB
RDV
DB
n +1
RDV
j
= RDV
= RDVn
n+1
= 0
j–1
+ FV )
j–1
– DB
j
({Y–1}G12)
({Y–1}G12)
12
1
×
100n
I%
DBj : depreciation charge for the
jth year
RDVj : remaining depreciable
value at the end of jth year
I
%
: factor (%)
Page 22

22
Press 3(DEPR) from the Financial 2 screen to display the following input screen for depreciation.
Depreciation for an item acquired part way through a year can be calculated by month.
• 6(g)3(DEP)
n .................................. useful life in years
I% ............................... depreciation rate/factor
PV ............................... original cost (basis)
FV ............................... scrap value (salvage value)
j ................................... year
Y–1.............................. number of depreciable months in first year
•Parameters can be displayed as integer or decimal values only. Inputting a fraction causes it
to be converted to a decimal value.
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
• 1(SL).......... Straight-Line Method
• 2(FP) ......... 1.Fixed Percentage Method
............ 2.Depreciation ratio
• 3(SYD)....... Sum-of-the-Year's Digits Method
• 4(DB) ......... Declining Balance Method
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following functions key to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) .... Parameter input screen
• 6(TABL) ..... Calculation result table
Page 23

23
The following function keys are on the calculation result table screen.
• 1(REPT) .... Parameter input screen
• 6(GRPH) .... Draws graph
After drawing a graph, you can press 1 (TRACE) to turn on trace and read calculation results
along the graph.
Press i to turn off trace.
Press i again to return to the parameter input screen.
Page 24

24
10. Bonds
The bond calculation function calculates the price and yield of a bond.
uu
uFormula
uu
D
Issue date
: price per $100 of face value
PRC
A B
Purchase date Coupon Payment dates
Redemption date
CPN : annual coupon rate (%)
YLD : yield to maturity (%)
A : accrued days
M : number of coupon payments per year (1=annual, 2=semi annual)
N : number of coupon payments between settlement date and maturity date
RDV : redemption price or call price per $100 of face value
D : number of days in coupon period where settlement occurs
B : number of days from settlement date until next coupon payment date = D – A
INT : accrued interest
CST : price including interest
• Less than six months to redemption
CPN
RDV +
PRC = – ()
B MYLD/100
1+ ( × )
D
• Six months or more to redemption
RDV
PRC = +
YLD/100
(1+ )
M
–
DA M
×
CPN
INT =
M
(N–1+B/D )
CPN
×
DA M
N
Σ
k=1
YLD/100
(1+ )
CPN
M
M
(K–1+B/D )
–
DA M
CST = PRC + INT
×
CPN
Page 25

25
Press 4(BOND) from the Financial 2 screen to display the following input screen for band
calculation.
• 6(g)4(BOND)
d1 ................................ purchase date
d2 ................................ redemption date
RDV ............................ redemption price or call price per $100 of face value
CPN ............................ annual coupon rate (%)
PRC ............................ price per $100 of face value
YLD ............................. yield to maturity (%)
To input a date, first highlight d1 or d2. Pressing a number key to input the month causes an
input screen like the one shown below to appear on the display.
Input the month, day, and year, pressing w after each.
After configuring the parameters, press one of the function keys noted below to perform the
corresponding calculation.
• 1(PRC) ... Price per $100 of face value
• 2(YLD) ... Yield to maturity
Page 26

26
•An error (Ma ERROR) occurs if parameters are not configured correctly.
Use the following functions key to maneuver between calculation result screens.
• 1(REPT) ... Parameter input screen
• 5(MEMO) ... Screen of various bond calculation values*
• 6(GRPH) ... Draws Graph
Pressing5 (MEMO) displays various bond calculation values, like those shown here.
*The interest payment date is calculated from d2 when 365 is specified for the Date Mode item
in the SET UP screen.
• w~w
• 6(GRPH)
After drawing a graph, you can press 1 (TRACE) to turn on trace and read calculation results
along the graph.
Press i to turn off trace.
Press i again to return to the parameter input screen.
Page 27

27
11. TVM Graph
The TVM Graph lets you assign two of the five parameters (n, I%, PV, PMT, FV) to the x-axis
and y-axis of a graph, and plot changes in y as the value of x changes.
Press 5(TVM) from the Financial 2 screen to display the following input screen for TVM
Graph.
• 6(g)5(TVM)
After configuring the parameters, press the function keys noted below to assign parameters to
the x-axis and y-axis.
• 1(X) ... Assigns highlighted parameter to the x-axis
• 2(Y) ... Assigns highlighted parameter to the y-axis
After making the required settings, draw the graph.
• 6(GRPH) ... Draws graph
After drawing a graph, you can press 1 (TRACE) to turn on trace and read calculation results
along the graph.
Press i to turn off trace.
Pressing 6 (Y-CAL) after drawing a graph displays the screen shown below.
Inputting an x-axis value on this screen and pressing w displays the corresponding y-axis
value.
Press i again to return to the parameter input screen.
•Calculation may take some time to perform when you specify I% as the y-axis parameter.
 Loading...
Loading...