Page 1

MO0909-EA
Operation Guide 3135 3206
Getting Acquainted
Congratulations upon your selection of this CASIO watch. To get the most out
of your purchase, be sure to read this manual carefully.
Applications
The built-in sensors of this watch measure direction, barometric pressure,
temperature and altitude. Measured values are then shown on the display.
Such features make this watch useful when hiking, mountain climbing, or
when engaging in other such outdoor activities.
• The measurement functions built into this watch are not intended for
taking measurements that require professional or industrial precision.
Values produced by this watch should be considered as reasonable
representations only.
• The Moon phase indicator and tide graph data that appear on the
display of this watch are not intended for navigation purposes. Always
use proper instruments and resources to obtain data for navigation
purposes.
• This watch is not an instrument for calculating low tide and high tide
times. The tide graph of this watch is intended to provide a reasonable
approximation of tidal movements only.
• When engaging in mountain climbing or other activities in which losing
your way can create a dangerous or life-threatening situation, always be
sure to use a second compass to confirm direction readings.
• Note that CASIO COMPUTER CO., LTD. assumes no responsibility for
any damage or loss suffered by you or any third party arising through
the use of this product or its malfunction.
Keep the watch exposed to bright light
Bright light
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
Solar cell
l
l
Warning!
The electricity generated by the solar cell of the
watch is stored by a built-in battery. Leaving or
using the watch where it is not exposed to light
causes the battery to run down. Make sure the
watch is exposed to light as much as possible.
• When you are not wearing the watch on your
wrist, position the face so it is pointed at a
source of bright light.
• You should try to keep the watch outside of
your sleeve as much as possible. Charging is
reduced significantly if the face is covered only
partially.
• The watch continues to operate, even when it is not exposed to light.
Leaving the watch in the dark can cause the battery to run down, which will
result in some watch functions being disabled. If the battery goes dead, you
will have to re-configure watch settings after recharging. To ensure normal
watch operation, be sure to keep it exposed to light as much as possible.
Battery charges in the light. Battery discharges in the dark.
Solar cell
(Converts light to
electrical power.)
• The actual level at which some functions are disabled depends on the
watch model.
• Frequent display illumination can run down the battery quickly and require
charging. The following guidelines give an idea of the charging time
required to recover from a single illumination operation.
Approximately five minutes exposure to bright sunlight coming in through
a window
Approximately 50 minutes exposure to indoor fluorescent lighting
• Be sure to read “Power Supply” for important information you need to
know when exposing the watch to bright light.
If the display of the watch is blank...
If the display of the watch is blank, it means that the watch’s Power Saving
function has turned off the display to conserve power.
• See “Power Saving” for more information.
About This Manual
Module 3135
Bright light
LEVEL 1
LEVEL 2
LEVEL 3
Charge
LEVEL 4
Rechargeable battery
(Light)
Electrical
energy
All
functions
enabled
• Depending on the model of your watch, display
text appears either as dark figures on a light
background (Module 3135), or light figures on a
dark background (Module 3206). All sample
displays in this manual are shown using dark
figures on a light background.
• Button operations are indicated using the
letters shown in the illustration.
• Each section of this manual provides you with
the information you need to perform operations
in each mode. Further details and technical
information can be found in the “Reference”
section.
Dis-
charge
LEVEL 1
LEVEL 2
LEVEL 3
LEVEL 4
Some
functions
disabled
General Guide
• The illustration below shows which buttons you need to press to navigate
between modes.
• In any mode, press L to illuminate the display.
Stopwatch
Mode
Countdown
Timer Mode
▲
▲
World Time Mode
Alarm Mode
▲
Tide/Moon Data
Mode
▲
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
Data Recall
Mode
▲
Timekeeping Mode
Press
D.
▲
▲
Module 3206
• You can use buttons A, B, and C to enter a sensor mode directly from
the Timekeeping Mode or from another sensor mode. To enter a sensor
mode from the Tide/Moon Data, Countdown Timer, Stopwatch, World Time,
Alarm, or Data Recall Mode, first enter the Timekeeping Mode and then
press the applicable button.
Sensor Modes
Press C.
▲
▲
Digital
Compass Mode
Press B.
Thermometer Mode
Press D.
▲
Barometer/
Press A.
▲
Altimeter Mode
1
Page 2
Operation Guide 3135 3206
Timekeeping
Use the Timekeeping Mode to set and view the current time and date.
• In the Timekeeping Mode, an indicator moves along the ring around the
display as seconds advance.
• The tide graph shows tidal movements for the current date in accordance
with the current time as kept in the Timekeeping Mode.
• The Moon phase indicator shows the current Moon phase in accordance
with the current date as kept in the Timekeeping Mode.
• In the Timekeeping Mode, you can press E to toggle the display contents
as shown below.
Day of the Week Screen
Day of week
PM indicator
Press E.
▲
Hour :
Minute
Month – Day
Read This Before You Set the Time and Date!
This watch is preset with a number of city codes, each of which represents
the time zone where that city is located. When setting the time, it is important
that you first select the correct city code for your Home City (the city where
you normally use the watch). If your location is not included in the preset city
codes, select the preset city code that is in the same time zone as your
location.
• Note that all of the times for the World Time Mode city codes are displayed
in accordance with the time and date settings you configure in the
Timekeeping Mode.
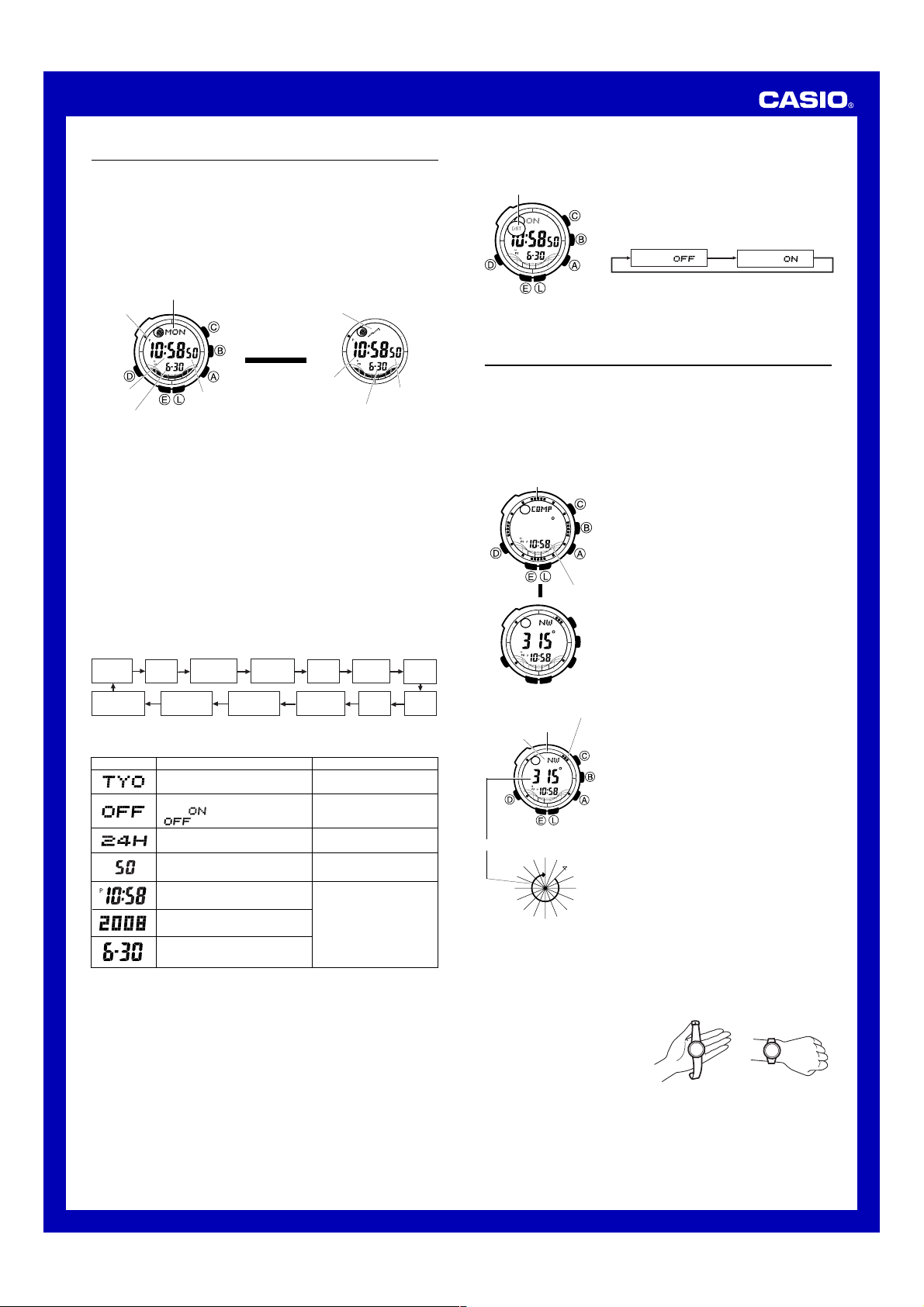
To set the time and date
1. In the Timekeeping Mode, hold down E until the city code starts to flash,
which indicates the setting screen.
2. Use A and C to select the city code you want.
• Make sure you select your Home City code before changing any other
setting.
• For full information on city codes, see the “City Code Table”.
3. Press D to move the flashing in the sequence shown below to select the
other settings.
City Code
Barometric
Pressure Unit
• The following steps explain how to configure timekeeping settings only.
4. When the timekeeping setting you want to change is flashing, use A and/
or C to change it as described below.
DST
Screen
5. Press E to exit the setting screen.
Note
• You also need to enter the Timekeeping Mode in order to configure the
following settings.
Power saving on/off (“To turn Power Saving on and off”)
Temperature, barometric pressure, and altitude units (“To select the
temperature, barometric pressure, and altitude units”)
Daylight Saving Time (DST)
Daylight Saving Time (summer time) advances the time setting by one hour
from Standard Time. Remember that not all countries or even local areas use
Daylight Saving Time.
Second
12/24-Hour
Format
Altitude Unit
Second
Temperature
Unit
To do this:
Change the city code
Toggle between Daylight Saving
Time (
) and Standard Time
(
).
Toggle between 12-hour (
and 24-hour (
24H
Reset the seconds to
12H
) timekeeping.
00
Change the hour or minute
Change the year
Change the month or day
Barometric Pressure
Graph Screen
Barometric
pressure
graph
▲
Hour :
Minute
Month – Day
Minute
Hour
Powe r
Saving
Do this:
Use A (east) and
C(west).
Press A.
Press A.
)
Press A
Use A (+) and C (–).
Day
.
Second
Year
Month
To change the Daylight Saving Time (summer time) setting
DST indicator
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
1. In the Timekeeping Mode, hold down E until
the city code starts to flash, which indicates
the setting screen.
2. Press D and the DST setting screen appears.
3. Use A to cycle through the DST settings in
the sequence shown below.
DST off ( ) DST on ( )
4. When the setting you want is selected, press
E to exit the setting screen.
• The DST indicator appears to indicate that
Daylight Saving Time is turned on.
Digital Compass
A built-in bearing sensor detects magnetic north and indicates one of 16
directions on the display. Direction readings are performed in the Digital
Compass Mode.
• You can calibrate the bearing sensor if you suspect the direction reading is
incorrect.
• See “Using the Digital Compass While Mountain Climbing or Hiking” for
some real-life examples of how to use this feature.
To enter and exit the Digital Compass Mode
12 o’clock position
Two seconds
Current time
▲
To take a direction reading
270°
W
S
W
SW
W
S
180°
W
N
W
W
S
S
North pointer
NNW
NW
E
S
E
SSE
SE
12 o’clock position
Direction
indicator
Angle value (in degrees)
• While the watch is taking compass readings, it displays a direction angle, a
direction indicator, and four direction pointers, all of which change dynamically
when the watch is moved. The direction angle, direction indicator and
direction pointers all disappear from the display after the compass reading
operation is complete. Use the direction indicators imprinted on the bezel to
record the indicated direction. For details, see “Using the Digital Compass
While Mountain Climbing or Hiking”.
Note
• Note that taking a measurement
while the watch is not horizontal
(in relation to the horizon) can
result in large measurement error.
• The margin of error for the angle value and the direction indicator is ±11
degrees. If the indicated direction is northwest (NW) and 315 degrees, for
example, the actual direction can be anywhere from 304 to 326 degrees.
1. While in the Timekeeping Mode or in any of
the other sensor modes, press C to enter the
Digital Compass Mode.
• At this time, the watch will start a Digital
Compass operation. After about two
seconds, letters appear on the display to
indicate the direction that the 12 o’clock
position of the watch is pointing.
•
The direction reading on the display is
updated each second for up to 20 seconds,
after which measurement stops automatically.
2. Press D to return to the Timekeeping Mode.
1. While the watch is in the Digital Compass
Mode, place it on a flat surface, or if you are
wearing the watch, make sure that your wrist
is horizontal (in relation to the horizon).
2. Point the 12 o’clock position of the watch in
the direction you want to measure.
3. Press C to start a Digital Compass
measurement operation.
• After about two seconds, the direction that the
12 o’clock position of the watch is pointing
appears on the display.
• Also, four pointers appear to indicate magnetic
0°
N
N
E
90°
north, south, east, and west.
• After the first reading is obtained, the watch
N
continues to take direction readings
E
NE
automatically each second, for up to 20
E
N
seconds.
E
2
Page 3

Operation Guide 3135 3206
• Any ongoing direction measurement operation is paused temporarily while
the watch is performing an alert operation (daily alarm, Hourly Time Signal,
countdown timer alarm) or while illumination is turned on (by pressing L).
The measurement operation resumes for its remaining duration after the
operation that caused it to pause is finished.
• The following table shows the meanings of each of the direction
abbreviations that appear on the display.
Direction
Meaning
N
E
S
W
• See “Digital Compass Precautions” for other important information about
taking direction readings.
Digital Compass Precautions
This watch features a built-in magnetic bearing sensor that detects terrestrial
magnetism. This means that nor th indicated by this watch is magnetic north,
which is somewhat different from true polar north. The magnetic north pole is
located in northern Canada, while the magnetic south pole is in southern
Australia. Note that the difference between magnetic north and true north as
measured with all magnetic compasses tends to be greater as one gets
closer to either of the magnetic poles. You also should remember that some
maps indicate true north (instead of magnetic north), and so you should make
allowances when using such maps with this watch.
Location
• Taking a direction reading when you are near a source of strong magnetism
can cause large errors in readings. Because of this, you should avoid taking
direction readings while in the vicinity of the following types of objects:
permanent magnets (magnetic necklaces, etc.), concentrations of metal
(metal doors, lockers, etc.), high tension wires, aerial wires, household
appliances (TVs, personal computers, washing machines, freezers, etc.)
• Accurate direction readings are impossible while in a train, boat, air plane,
etc.
• Accurate readings also are impossible indoors, especially inside ferroconcrete structures. This is because the metal framework of such structures
picks up magnetism from appliances, etc.
Storage
• The precision of the bearing sensor may deteriorate if the watch becomes
magnetized. Because of this, you should be sure to store the watch away
from magnets or any other sources of strong magnetism, including:
permanent magnets (magnetic necklaces, etc.) and household appliances
(TVs, personal computers, washing machines, freezers, etc.)
• Whenever you suspect that the watch may have become magnetized,
perform one of the calibration procedures under “Calibrating the Bearing
Sensor”.
Calibrating the Bearing Sensor
You should calibrate the bearing sensor whenever you feel that the direction
readings being produced by the watch are off. There are three different
calibration methods available: magnetic declination correction, bidirectional
calibration, and northerly calibration.
• Magnetic Declination Correction
With magnetic declination correction, you input a magnetic declination
angle (difference between magnetic north and true north), which allows the
watch to indicate true north.
You can perform this procedure when the magnetic declination angle is
indicated on the map you are using.
Note that you can input the declination angle in degree units only, so you
may need to round off the value specified on the map. If your map indicates
the declination angle as 7.4°, you should input 7°. In the case of 7.6° input
8°, for 7.5° you can input 7° or 8°.
• Bidirectional Calibration and Northerly Calibration
Bidirectional calibration and northerly calibration calibrate the accuracy of
the direction sensor in relation to magnetic north.
Use bidirectional calibration when you want to take readings within an area
exposed to magnetic force. This type of calibration should be used if the
watch becomes magnetized for any reason. With northerly calibration, you
“teach” the watch which way is north (which you have to determine with
another compass or some other means).
Important!
• If you want to perform both bidirectional and northerly calibration, be sure
to perform bidirectional calibration first, and then perform northerly
calibration. This is necessary because bidirectional calibration cancels any
existing northerly calibration setting.
• The more correctly you perform bidirectional calibration, the better the
accuracy of the bearing sensor readouts. You should perform bidirectional
calibration whenever you change environments where you use the bearing
sensor, and whenever you feel that the bearing sensor is producing
incorrect readings.
North
East
South
West
Direction
NNE
ESE
SSW
WNW
Meaning
North-
northeast
East-
southeast
South-
southwest
West-
northwest
Direction
NE
SE
SW
NW
Meaning
Northeast
Southeast
Southwest
Northwest
Direction
ENE
SSE
WSW
NNW
Meaning
East-
northeast
South-
southeast
West-
southwest
North-
northwest
To perform magnetic declination correction
1. In the Digital Compass Mode, hold down E
Magnetic declination
angle direction
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
Magnetic
declination
angle value
E: When magnetic north is to the east (east declination)
W: When magnetic north is to the west (west declination)
• You can turn off (OFF) magnetic declination correction (which effectively
makes the magnetic declination angle: 0°) by pressing A and C at the
same time.
• The illustration above, for example, shows the value you should input
and the direction setting you should select when the map shows a
magnetic declination of 1° West.
3. When the setting is the way you want, press E to exit the setting screen.
Precautions about bidirectional calibration
• You can use any two opposing directions for bidirectional calibration. You
must, however, make sure that they are 180 degrees opposite each other.
Remember that if you perform the procedure incorrectly, you will get wrong
bearing sensor readings.
• Make sure that you do not move the watch while calibration of either
direction is in progress.
• You should perform bidirectional calibration in an environment that is the
same as that where you plan to be taking direction readings. If you plan to
take direction readings in an open field, for example, calibrate in an open
field.
for about two seconds until the magnetic
declination angle and magnetic declination
angle direction values start to flash on the
display. This is the setting screen.
2. Use A (+) and C (–) to change the magnetic
declination angle and magnetic declination
angle direction settings.
• You can select a value within the range of
W 90
° to E 90° with these settings.
• The following explains magnetic declination
angle direction settings.
OFF: No magnetic declination correction
performed. The magnetic declination
angle with this setting is 0°.
To perform bidirectional calibration
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
3. Place the watch on a level surface facing any direction you want, and
press C to calibrate the first direction.
•
xxx is shown on the display while calibration is being performed. When
calibration is successful, the display will show
north pointer flashes at the 6 o’clock position. This means that the watch
is ready for calibration of the second direction.
4. Rotate the watch 180 degrees.
5. Press C again to calibrate the second direction.
•
xxx is shown on the display while calibration is being performed. When
calibration is successful, the display will show
Mode (showing the angle value) screen.
xxx appears and then changes to
• If
screen, it means that there is something wrong with the sensor. When
disappears after about one second, try performing the calibration
ERR
again. If
authorized CASIO distributor to have the watch checked.
keeps appearing, contact your original dealer or nearest
ERR
1. In the Digital Compass Mode, hold down E
for about two seconds until the magnetic
declination angle and magnetic declination
angle direction values start to flash on the
display. This is the setting screen.
2. Press D to display the bidirectional
calibration screen.
• At this time, the north pointer flashes at the
12 o’clock position to indicate that the watch
is ready to calibrate the first direction.
OK and x2x, and the
OK and the Digital Compass
(error) on the calibration
ERR
To perform northerly calibration
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
3. Place the watch on a level surface, and position it so that its 12 o’clock
position points north (as measured with another compass).
4. Press C to start the calibration operation.
•
--- is shown on the display while calibration is being performed. When
calibration is successful, the display will show
Mode (with
• If
screen, it means that there is something wrong with the sensor. When
ERR
again. If
authorized CASIO distributor to have the watch checked.
0
--- appears and then changes to
° shown as the angle value).
disappears after about one second, try performing the calibration
keeps appearing, contact your original dealer or nearest
ERR
1. In the Digital Compass Mode, hold down E
for about two seconds until the magnetic
declination angle and magnetic declination
angle direction values start to flash on the
display. This is the setting screen.
2. Press D twice to display the northerly
calibration screen.
• At this time,
display.
-N- (north) appears on the
OK and the Digital Compass
(error) on the calibration
ERR
3
Page 4

Operation Guide 3135 3206
Using the Digital Compass While Mountain Climbing or
Hiking
This section describes three real-life situations where you could use the
watch’s built-in digital compass.
• To set a map and find your current location
Having an idea of your current location is important when mountain
climbing or hiking. To do this, you need to “set the map”, which means to
align the map so the directions indicated on it are aligned with the actual
directions of your location. Basically what you are doing is aligning north on
the map with north as indicated by the watch.
• To find the bearing to an objective
• To determine the direction angle to an objective on a map and head in that
direction
To set a map and find your current location
North indicated
on the map
N
Current
location
N
North indicated by
north pointer
To find the bearing to an objective
N
Objective
Current
location
12 o’clock
N
position
• This will position the map relative to your current location, so the bearing to
your objective is straight ahead of you.
To determine the direction angle to an objective on a map and head
in that direction
N
Objective
Current
location
12 o’clock
N
position
• If you find it difficult to perform the above step while keeping everything
aligned, first move into the correct position (12 o’clock position of the
watch pointed at the objective) without worrying about the orientation of
the map. Next, perform step 1 again to set the map.
1. With the watch on your wrist, position it so the
face is horizontal.
2. In the Timekeeping, Digital Compass,
Barometer/Thermometer, or Altimeter Mode,
press C to take a compass reading.
• The reading will appear on the display after
about two seconds.
3. Rotate the map without moving the watch so
the northerly direction indicated on the map
matches north as indicated by the watch.
• If the watch is configured to indicate
magnetic north, align the map’s magnetic
north with the watch indication. If the watch
has been configured with a declination to
correct to true north, align the map’s true
north with the watch indication.
• This will position the map in accordance
with your current location.
4. Determine your location as you check the
geographic contours around you.
1. Take a compass reading and then set the map
so its northerly indication is aligned with north
as indicated by the watch, and determine your
current location.
• See “To set a map and find your current
location” for information about how to
perform the above step.
2. Set the map so the direction you want to travel
on the map is pointed straight in front of you.
3. With the watch on your wrist, position it so the
face is horizontal.
4. In the Timekeeping, Digital Compass,
Barometer/Thermometer, or Altimeter Mode,
press C to take a compass reading.
• The reading will appear on the display after
about two seconds.
5. Still holding the map in front of you, turn your
body until north as indicated by the watch and
the northerly direction on the map are aligned.
Note
• The following procedure is possible only with a
watch that has a rotary bezel.
1. Take a compass reading and then set the map
so its northerly indication is aligned with north
as indicated by the watch, and determine your
current location.
• See “To set a map and find your current
location” for information about how to
perform the above step.
2. As shown in the illustration to the left, change
your position so you (and the 12 o’clock
position of the watch) are pointed in the
direction of objective, while keeping the map
aligned with the readings being produced by
the watch.
12 o’clock
position
Direction angle of
current reading
4. Rotate the bezel so the “N” (North) indicator on the bezel is aligned with
the north indicator produced by the reading in step 3.
5. To advance to your objective proceed in the direction that 12 o’clock is
pointing.
Note
• When mountain climbing or hiking, conditions or geographic contours may
make it impossible for you to advance in a straight line. If this happens,
return to step 1 and save a new direction to the objective.
3. In the Timekeeping, Digital Compass,
Barometer/Thermometer, or Altimeter Mode,
press C to take a compass reading.
• The compass reading information (angle
value, direction indicator, and four pointers
based on the 12 o’clock position of the
watch) will appear on the display after about
two seconds.
North
pointer
• The compass reading information will
remain on the display for only about 20
seconds after you press C. After that it will
disappear. If you want to re-display the
compass reading information, press C
again to take another reading.
Barometer/Thermometer
This watch uses a pressure sensor to measure air pressure (barometric
pressure) and a temperature sensor to measure temperature.
• You can calibrate the pressure sensor and the temperature sensor if you
suspect that readings are incorrect.
To take barometric pressure and temperature readings
Barometric
pressure graph
Temperature
• The displayed barometric pressure value changes to
a measured barometric pressure falls outside the range of 260 hPa to
1100 hPa (7.65 inHg to 32.45 inHg). The barometric pressure value will
reappear as soon as the measured barometric pressure is within the
allowable range.
• Temperature is displayed in units of 0.1°C (or 0.2°F).
• The displayed temperature value changes to
measured temperature falls outside the range of –10.0°C to 60.0°C (14.0°F
to 140.0°F). The temperature value will reappear as soon as the measured
temperature is within the allowable range.
• In some areas, barometric pressure is expressed in millibars (mb) instead
of hectopascals (hPa). It really makes no difference, because 1hPa = 1mb.
• You can select either hectopascals (hPa) or inchesHg (inHg) as the display
unit for the measured barometric pressure, and Celsius (°C) or Fahrenheit
(°F) as the display unit for the measured temperature value. See “To select
the temperature, barometric pressure, and altitude units”.
• See “Barometer and Thermometer Precautions” for important precautions.
Barometric Pressure Graph
Barometric pressure indicates changes in the atmosphere. By monitoring
these changes you can predict the weather with reasonable accuracy.
This watch takes barometric pressure measurements automatically every two
hours (at the top of each even-numbered hour), regardless of its current
mode. Measurement results are used to produce barometric pressure graph
and barometric pressure differential pointer readings.
The barometric pressure graph shows readings of previous measurements for
up to 20 hours. The horizontal axis of the graph represents time, with each dot
standing for two hours. The rightmost dot represents the most recent reading.
The vertical axis of the graph represents barometric pressure, with each dot
standing for the relative difference between its reading and that of the dots
next to it. Each dot represents 1hPa.
The following shows how to interpret the data that appears on the barometric
pressure graph.
Pressure
differential
pointer
Barometric
pressure
A rising graph generally means improving weather.
A falling graph generally means deteriorating weather.
Pressing B in the Timekeeping Mode or in any
of other sensor modes enters the Barometer/
Thermometer Mode and starts barometric
pressure and temperature measurements
automatically .
• It can take up to four or five seconds for the
barometric pressure reading to appear after
you enter the Barometer/Thermometer Mode.
• Barometric pressure is displayed in units of
1hPa (or 0.05 inHg).
hPa (or inHg) if
xxxx
°C (or °F) if a
xxx.x
4
Page 5

Operation Guide 3135 3206
Note that if there are sudden changes in barometric
pressure or temperature, the graph line of past
measurements may run off the top or bottom of the display.
The entire graph will become visible once barometric
conditions stabilize.
The following conditions cause the barometric pressure
measurement to be skipped, with the corresponding point on
the barometric pressure graph being left blank.
• Barometric reading that is out of range (260 hPa/mb to 1,100 hPa/mb or
7.65 inHg to 32.45 inHg)
• Sensor malfunction
Barometric Pressure Differential Pointer
This pointer indicates the relative difference between the most recent
barometric pressure reading indicated on the barometric pressure graph, and
the current barometric pressure value displayed in the Barometer/
Thermometer Mode.
• Pressure differential is indicated in the range of ±5 hPa, in 1-hPa units.
• The barometric pressure differential pointer is not displayed when the
displayed current barometric value is outside of the allowable measurement
range (260 to 1,100 hPa).
• Barometric pressure is calculated and displayed using hPa as the standard.
The barometric pressure differential also can be read in inHg units as
shown in the illustration.
inHg values
Barometric pressure
differential
Pressure differential
examples in the
illustration are indicated
in 3 hPa/0.1 inHg steps.
About Barometric and Temperature Measurements
• Barometric pressure and temperature measurement operations are
performed as soon as you enter the Barometer/Thermometer Mode. After
that, barometric pressure and temperature measurements are taken every
five seconds.
• You also can perform a barometric pressure and temperature measurement
at any time by pressing B in the Barometer/Thermometer Mode.
hPa values
Current pressure greater
than most recent
measured pressure
Current pressure less
than most recent
measured pressure
Not visible on
the display.
Altimeter
The watch’s altimeter uses a pressure sensor to detect current air pressure,
which is then used to estimate the current altitude based on ISA (International
Standard Atmosphere) preset values. You also can specify a reference
altitude, which the watch will use to calculate your current altitude based on
the value you specify. Altimeter functions also include storage of
measurement data in memory.
Important!
• This watch estimates altitude based on air pressure. This means that
altitude readings for the same location may vary if air pressure changes.
• The semiconductor pressure sensor used by the watch for altitude
measurements also is affected by temperature. When taking altitude
measurements, make sure the watch is not subjected to temperature
changes.
• To avoid the effect of sudden temperature changes during measurement,
keep the watch on your wrist in direct contact with your skin.
• Do not rely upon this watch for altitude measurements or perform button
operations while sky diving, hang gliding, or paragliding, while riding a
gyrocopter, glider, or any other aircraft, or while engaging in any other
activity where there is the chance of sudden altitude changes.
• Do not use this watch for measuring altitude in applications that demand
professional or industrial level precision.
• Remember that the air inside of a commercial aircraft is pressurized.
Because of this, the readings produced by this watch will not match the
altitude readings announced or indicated the flight crew.
How the Altimeter Measures Altitude
The altimeter can measure altitude based on its own preset values, or a
reference altitude specified by you.
When you measure altitude based on preset values
Data produced by the watch’s barometric pressure sensor is conver ted to
approximate altitude based on ISA (International Standard Atmosphere)
conversion values stored in watch memory.
When you measure altitude using a reference altitude specified by you
After you specify a reference altitude, the watch uses that value to convert the
current measured barometric pressure value to altitude.
• When mountain climbing, you can set the
reference value in accordance with a marker
along the way or altitude information from a
map. After that, the altitude readings
produced by the watch will be more accurate
than they would without a reference altitude.
Displaying Your Current Altitude
You can use the procedure described in this section to display your current
altitude. If you leave the watch in the Altimeter Mode, it will update the
displayed altitude value regularly, and indicate reading-to-reading changes in
the altitude graph at the top of the display.
Important!
• The procedure in this section simply displays values indicating your current
altitude, without storing them in watch memory. For information about
recording altitude readings in watch memory, see “Saving Altitude Data”.
A
400
B
To display your current altitude
Current altitude
Altitude
graph
Current time
• Readings are taken at five-second intervals for the first three minutes
after you enter the Altimeter Mode. After that, readings are taken at twominute intervals.
• If you want to restart the altitude measurement operation at any point,
press A.
3. To stop the altitude measurement operation, press D to exit the Altimeter
Mode.
Notes
• Normally, displayed altitude values are based on the watch’s preset
conversion values. You also can specify a reference altitude, if you want.
See “Specifying a Reference Altitude”.
• Altitude is displayed in units of 5 meters (20 feet).
• The measurement range for altitude is –700 to 10,000 meters (–2,300 to
32,800 feet).
• The measured altitude may be a negative value in cases where there is a
reference altitude value set or because of certain atmospheric conditions.
• The displayed altitude value changes to
measured altitude falls outside the measurement range. The altitude value
will be displayed again as soon as the measured altitude is within the
allowable range.
• You can change the measurement unit for displayed altitude values to either
meters (m) or feet (ft). See “To select the temperature, barometric pressure,
and altitude units”.
Saving Altitude Data
The watch automatically keeps track of the high altitude achieved to date.
You also can save altitude readings with the touch of a button.
• You can recall and view altitude data using the Data Recall Mode. For
details, see “Recalling Altitude Data”.
Automatic High Altitude Record
Whenever an altitude measurement in the Altimeter Mode is greater than the
currently stored high altitude value, the watch will replace the old value with
the new measurement automatically, along with the reading date and time.
This feature is always enabled and cannot be turned off.
• If the current reading is the same as the existing high altitude value, the
older value will be retained.
Saving an Altitude Reading
Perform the following procedure whenever you want to save an altitude reading.
1. Press A in the Timekeeping Mode or in any
of the other sensor modes to enter the
Altimeter Mode.
• The watch will start altitude measurement
automatically, and display the result.
• It can take up to four or five seconds for the
altitude reading to appear after you enter
the Altimeter Mode.
2. Leave the watch in the Altimeter Mode if you
want the displayed altitude value and the
altitude graph contents to be updated at
regular intervals.
xxxx meters (or feet) if a
To save an altitude reading
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
• Memory can store up to 24 altitude records. Storing a new reading while
there are already 24 in memory will delete the oldest record currently in
memory to make room for the new reading.
1. Press A to enter the Altimeter Mode.
2. Hold down
• At this time the watch will beep and the
3. REC will stop flashing and the watch will
return to the Altimeter Mode automatically
after data save is complete.
A
until REC flashes on the display.
current altitude reading value will be saved
along with the reading date (month - day)
and time.
5
Page 6

Operation Guide 3135 3206
Specifying a Reference Altitude
After you specify a reference altitude, the watch adjusts its air-pressure-toaltitude conversion calculation accordingly. The altitude measurements
produced by this watch are subject to error caused by changes in air
pressure. Because of this, we recommend that you update the reference
altitude whenever one is available during your climb.
To set a reference altitude
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
• Pressing A and C at the same time returns to OFF (no reference
altitude), so the watch performs air pressure to altitude conversions
based on preset data only.
3. Press E to exit the setting screen.
Altitude graph
Altitude
Time
• The horizontal axis represents time, and the flashing dot in the rightmost
column indicates the latest measurement result. For the first three minutes,
each dot represents five seconds. After that, each dot represents two
minutes.
• An out of range measurement result or a measurement error will cause the
column of dots for that measurement to be blank (skipped).
Recalling Altitude Data
In the Data Recall Mode, you can recall and view altitude reading records you
stored in the Altimeter Mode, as well as the high altitude record.
• All of the operations in this section are performed in the Data Recall Mode.
Data Screens
The following explains the contents of each of the screens that appear in the
Data Recall Mode.
Note
• While the altitude record or high altitude screen is displayed, the bottom
part of the display alternates between the measurement date (month and
day) and measurement time, at 1-second intervals.
Altitude
record
indicator
Altitude
To view altitude reading records and the high altitude record
1. Enter the Data Recall Mode.
• After about one second a record with MAX on the top will appear. This is
the high altitude record.
2. Use A (+) and C (–) to scroll through the other altitude reading records.
To delete all altitude data currently in memory
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
1. In the Altimeter Mode, hold down E for about
two seconds until either OFF or the current
reference altitude value starts to flash. This is
the setting screen.
2. Press A (+) or C (–) to change the current
reference altitude value by 5 meters (or 20 feet).
• You can set the reference altitude within the
range of –10,000 to 10,000 meters (–32,800
to 32,800 feet).
The altitude graph shows Altimeter Mode
measurement results.
• The vertical axis of the graph represents
altitude, and each dot stands for 10 meters (40
feet).
Alternates at
1-second intervals.
▲
Measurement time
(Hour : Minute)
1. In the Data Recall Mode, hold down E until
CLR flashes on the display and the watch
beeps twice.
• Releasing E at any time while CLR is
flashing on the display will cancel the delete
operation.
2. Keep E depressed for two seconds.
• The watch will beep to indicate that all of the
altitude data stored in watch memory (including
readings you stored and the high altitude
value) is deleted.
Measurement date
(Month – Day)
▲
Tide/Moon Data
In the Tide/Moon Data Mode, you can see the current tide and the current
date’s Moon phase for your Home City. You can specify a date and view tide
and Moon data for that date.
• See “Moon Phase Indicator” for information about the Moon phase indicator
and “Tide Graph” for information about the tide graph.
• All of the operations in this section are performed in the Tide/Moon Data
Mode.
Tide Data
The Tide Graph that appears first when you enter the Tide/Moon Data Mode
shows the data at 6:00 a.m. for your currently selected Home City on the
current date, according to the Timekeeping Mode. From there you can specify
another date or time.
• If the tide data is not correct, check your Timekeeping Mode settings and
correct them if necessary.
• If you feel that the information shown by the Tide Graph is different from
actual tide conditions, you need to adjust the high tide time. See “Adjusting
the High Tide Time” for more information.
Moon Data
The Moon phase and Moon age information that appears first when you enter
the Tide/Moon Data Mode shows the data at noon for your currently selected
Home City on the current date, according to the Timekeeping Mode. After that
you can specify another date to view data.
• If the Moon data is not correct, check your Timekeeping Mode settings and
correct them if necessary.
• If the Moon phase indicator shows a phase that is a mirror image of the
actual moon phase in your area, you can use the procedure under
“Reversing the Displayed Moon Phase” to change it.
To view Moon Data for a particular date, or Tide Data for a
particular date and time
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
Moon age
Current
tide level
Moon
phase
Current
tide range
2. While the Moon information (Moon age and phase) and tide information
(tide level and tide range for the current date) are displayed, you can press
B (+) to advance the displayed tide range by one hour.
• You also can use A (+) and C (–) to change the date.
• Update of the Moon Phase indicator and the Tide Graph is stopped while
any of the following is occurring.
During button operation
While an alarm is sounding
While a countdown beeper is sounding
During display illumination
During a 2-hour barometric pressure reading operation
Adjusting the High Tide Time
Use the following procedure to adjust the high tide time within a particular
date. You can find out high tide information for your area from a tide table, the
Internet, or your local newspaper.
To adjust the high tide time
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
1. In the Tide/Moon Data Mode, use A (+) and
C (–) to select the date you want.
After you select a date, the watch starts to
•
calculate Moon and tide data for the date you
selected. The calculation operation takes
about 10 seconds, and is indicated by
movement in the Moon Phase indicator and
the Tide Graph on the display. You can use
and C to change to another date while a
calculation operation is in progress.
• After calculation is complete, the Moon
information (Moon age and phase) and tide
information (current tide level and tide
range) will be displayed for the date you
selected.
1. In the Tide/Moon Data Mode, use A (+) and
C (–) to select the date you want.
• After you select a date, the watch starts to
calculate Moon and tide data for the date
you selected. The calculation operation
takes about 10 seconds, and is indicated by
movement in the Moon Phase indicator and
the Tide Graph on the display. You can use
A and C to change to another date while
a calculation operation is in progress.
• After calculation is complete, the Moon
information (Moon age and phase) and tide
information (current tide level and tide
range) will be displayed for the date you
selected.
A
6
Page 7

Operation Guide 3135 3206
Hour
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
Minute
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
• The high tide time setting is not affected by the DST (summer time) setting
of the Timekeeping Mode.
• On some days, there are two high tides. With this watch, you can adjust the
first high tide time only. The second high tide time for that day is adjusted
automatically based on the first high tide time.
Reversing the Displayed Moon Phase
The left-right (east-west) appearance of the Moon depends on whether the
Moon is north of you (northerly view) or south of you (southerly view) as you
view it.
You can use the procedure below to reverse the displayed Moon phase so it
matches the actual appearance of the Moon where you are located.
• To determine the viewing direction of the Moon, use a compass to take a
direction reading of the Moon at its meridian passage.
• For information about the Moon phase indicator, see “Moon Phase
Indicator”.
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
2. While the Moon information (Moon age and
phase) and tide information (current tide level
and tide range) are displayed, hold down E
until the hour digits start to flash. This is the
high tide time hour adjustment screen.
3. Use A (+) and C (–) to change the hour
setting.
4. When the hour is the setting you want, press
D.
• This will cause the minute digits to flash.
5. Use A (+) and C (–) to change the minute
setting.
6. When the minute setting is the way you want,
press E to exit the adjustment screen and
return to the Tide/Moon Data Mode screen.
• Pressing A and C at the same time while the
time adjustment screen is displayed (steps 2
through 5 above) will return the high tide time
to its initial factory default setting.
To reverse the displayed Moon phase
1. In the Tide/Moon Data Mode, hold down E
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
until the hour digits start to flash.
2. Press D twice.
• This will cause the Moon phase indicator to
flash. This is the indicator switching screen.
3. Press A to toggle the Moon phase indicator
between the southerly view (indicated by
) and northerly view (indicated by ).
• Northerly view: Moon is north of you.
• Southerly view: Moon is south of you.
4. When the Moon phase indicator setting is the
way you want, press E to exit the switching
screen and return to the Tide/Moon Data
Mode screen.
Countdown Timer
Seconds
Minutes
Configuring Countdown Timer Settings
The following are the settings you should configure before actually using the
countdown timer.
Countdown start time and reset time
Progress beeper (on/off)
• See “To configure countdown timer settings” for information about setting up
the timer.
• For details about the progress beeper, see “Progress Beeper”.
Reset Time
You can set a “reset time”, which is a kind of alternate countdown start time
you can recall with the press of a button any time a countdown operation is in
progress.
Countdown Timer Beeper Operations
The watch beeps at various times during a countdown so you can keep
informed about the countdown status without looking at the display. The
following describes the types of beeper operations the watch performs during
a countdown.
Current
time
The countdown timer can be set within a range of
one minute to 60 minutes. An alarm sounds when
the timer reaches zero. The press of a button will
start the countdown timer from the currently set
start time, and a progress beeper sounds to keep
you informed of the current status of the
countdown. These features make it possible to
use the watch for yacht racing.
• All of the operations in this section are
performed in the Countdown Timer Mode,
which you enter by pressing D.
Countdown End Beeper
The watch beeps each second of the final 10 seconds before a countdown
reaches zero, and at zero. The first five beeps (seconds 10 through 6) are
higher pitched than the final five beeps (seconds 5 through 1). The watch
emits a longer beep to signal when the countdown reaches zero.
Progress Beeper
The progress beeper actually includes two beepers: a reset time beeper and
a reset period beeper.
• Note that the reset time beeper and reset period beeper operate only while
the progress beeper is turned on. For more infor mation, see “To turn the
progress beeper on and off”.
Reset Time Beeper
The reset time beeper is similar to the countdown end beeper. The watch
beeps each second of the final 10 seconds before the countdown reaches the
reset time.
Reset Period Beeper
The reset period is in the portion of the countdown between the reset time
and zero. While timing is the reset period, the watch will beep four times at the
top of each minute and 10 seconds before the end of the countdown.
Countdown Timer Examples
Countdown start time: 10 minutes; Reset time: 5 minutes
Progress beeper: On
Reset Period
Start Time Reset Time
10'00"
Reset Time Beeper
Reset Period Beeper
Countdown
End Beeper
0'00"1'00" 0'10"2'00"3'00"4'00"5'00"
0'01"0'02"0'03"0'04"0'05"0'06"0'07"0'08"0'09"0'10" 0'00"
To configure countdown timer settings
1. While the countdown start time is on the
display in the Countdown Timer Mode, hold
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
3. When the setting you want to change is flashing, use A and C to change
it as described below.
Setting
Screen Button Operations
Start Time
Reset Time
4. Press E to exit the setting screen.
• The reset time setting must be less than the countdown start time setting.
down E until the countdown start time setting
starts to flash, which indicates the setting
screen.
• If the countdown start time is not displayed,
use the procedure under “To use the
countdown timer” to display it.
2. Press D to move the flashing in the sequence
shown below to select other settings.
Start
Time
Use A (+) and C (–) to change the setting.
• You can set a start time in the range of 1 to 60
minutes in 1-minute increments.
Use A (+) and C (–) to change the setting.
• You can set a reset time in the range of 1 to 5
minutes in 1-minute increments.
Reset
Time
To turn the progress beeper on and off
Pressing B while the countdown start time is on the display or while a
countdown timer operation is in progress in the Countdown Timer Mode
toggles progress beeper operation on (
displayed) and off ( displayed).
To use the countdown timer
In the Countdown Timer Mode, press A to start
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
To do this:
Stop the countdown operation
Resume a stopped countdown operation
Display the countdown start time
Stop the countdown operation and display the reset
time
Start the countdown from the displayed reset time
the countdown timer.
• The countdown timer measurement operation
continues even if you exit the Countdown Timer
Mode.
• The table below describes button operations
you can perform to control countdown
operations.
Do this:
Press A.
Press A again.
While the countdown is
stopped, press C.
Press C.
Press A.
7
Page 8

Operation Guide 3135 3206
Stopwatch
Hours
1/100 second
Minutes
Seconds
Current time
To measure times with the stopwatch
Elapsed Time
J
AA A A C
Start Stop Re-start Stop Clear
Split Time
AC C A C
JJ J
Start Split Split release Stop Clear
(SPL displayed)
Two Finishes
AC A C C
JJ J
Start Split Stop Split release Clear
First runner
finishes.
Display time
of first runner.
World Time
Current time in the zone
of the selected city code
City code
Timekeeping
Mode time
To toggle a city code time between Standard Time and Daylight
Saving Time
DST indicator
• You cannot toggle between Daylight Saving Time and Standard Time if the
displayed city code is
• Note that the DST/Standard Time setting affects only the currently
displayed city code. Other city codes are not affected.
Alarms
Alarm number
Alarm time
(Hour : Minute)
Current time
The stopwatch lets you measure elapsed time,
split times, and two finishes.
• The display range of the stopwatch is 23 hours,
59 minutes, 59.99 seconds.
• The stopwatch continues to run, restarting from
zero after it reaches its limit, until you stop it.
• The stopwatch measurement operation
continues even if you exit the Stopwatch Mode.
• Exiting the Stopwatch Mode while a split time is
frozen on the display clears the split time and
returns to elapsed time measurement.
• All of the operations in this section are
performed in the Stopwatch Mode, which you
enter by pressing D.
JJ
Second runner
finishes.
World Time displays the current time in 33 cities
(29 time zones) around the world.
• If the current time shown for a city is wrong,
check your Home City time settings and make
the necessary changes.
• All of the operations in this section are
performed in the World Time Mode, which you
enter by pressing D.
Display time of
second runner.
To view the time in another city
In the World Time Mode, use A (east) and C
(west) to scroll through city codes (time zones).
• For full information on city codes, see the “City
Code Table”.
1. In the World Time Mode, use A (east) and C
(west) to display the city code (time zone)
whose Standard Time/Daylight Saving Time
setting you want to change.
2. Hold down E to toggle between Daylight
Saving Time (DST indicator displayed) and
Standard Time (DST indicator not displayed).
• The DST indicator appears on the display
whenever you display a city code for which
Daylight Saving Time is turned on.
UTC.
You can set five independent daily alarms. When
an alarm is turned on, the alarm tone sounds
when the alarm time is reached.
You also can turn on an Hourly Time Signal,
which will cause the watch to beep twice every
hour on the hour.
• The alarm number (AL1 through AL5)
indicates an alarm screen. SIG is shown when
the Hourly Time Signal screen is on the display.
• When you enter the Alarm Mode, the data you
were viewing when you last exited the mode
appears first.
• All of the operations in this section are
performed in the Alarm Mode, which you enter
by pressing D.
J
J
J
To set an alarm time
Alarm on
indicator
On/Off status
2. Hold down E until the hour setting of the alarm time start to flash, which
indicates the setting screen.
• This automatically turns on the alarm.
3. Press D to move the flashing between the hour and minute settings.
4. While a setting is flashing, use A (+) and C (–) to change it.
• When setting the alarm time using the 12-hour format, take care to set
the time correctly as a.m. (no indicator) or p.m. (P indicator).
5. Press E to exit the setting screen.
Alarm Operation
The alarm sounds in all modes at the preset time for about 10 seconds, or
until you stop it by pressing any button.
1. In the Alarm Mode, use A and C to scroll
through the alarm screens until the one whose
time you want to set is displayed.
A
AL1 AL2 AL3
C
SIG AL5 AL4
To test the alarm
In the Alarm Mode, hold down A to sound the alarm.
To turn an alarm and the Hourly Time Signal on and off
1. In the Alarm Mode, use A and C to select an alarm or the Hourly Time
Signal.
2. When the alarm or the Hourly Time Signal you want is selected, press B
to turn it on (
Indicates Hourly Time Signal is ON.
• The alarm on indicator (
are shown on the display in all modes while these functions are turned on.
• If any alarm is on, the alarm on indicator is shown on the display in all
modes.
ON) and off (OF).
Indicates alarm is ON.
) and the Hourly Time Signal on indicator ( )
Illumination
Auto light switch
on indicator
To turn on illumination manually
Press L in any mode to illuminate the display for about one second.
• The above operation turns on illumination regardless of the current auto
light switch setting.
• Illumination is disabled while configuring sensor measurement mode
settings, and during bearing sensor calibration.
About the Auto Light Switch
Turning on the auto light switch causes illumination to turn on, whenever you
position your wrist as described below in any mode.
Note that this watch features a “Full Auto EL Light”, so the auto light switch
operates only when available light is below a certain level. It does not
illuminate the display under bright light.
• The auto light switch is always disabled, regardless of its on/off setting,
when any one of the following conditions exists.
While an alarm is sounding
During sensor measurement
While a bearing sensor calibration operation is being performed in the
Digital Compass Mode
During tide data calculation
Moving the watch to a position that is parallel to the ground and then tilting
it towards you more than 40 degrees causes illumination to turn on.
• Wear the watch on the outside of your wrist.
The display of the watch is illuminated using an
EL (electro-luminescent) panel for easy reading
in the dark. The watch’s auto light switch turns on
illumination automatically when you angle the
watch towards your face.
• The auto light switch must be turned on
(indicated by the auto light switch on indicator)
for it to operate.
• See “Illumination Precautions” for other
important information about using illumination.
Parallel to
ground
l
l
l
l
l
l
More than
40
l
l
l
l
l
°
8
Page 9

Operation Guide 3135 3206
Warning!
• Always make sure you are in a safe place whenever you are reading
the display of the watch using the auto light switch. Be especially
careful when running or engaged in any other activity that can result
in accident or injury. Also take care that sudden illumination by the
auto light switch does not startle or distract others around you.
• When you are wearing the watch, make sure that its auto light switch
is turned off before riding on a bicycle or operating a motorcycle or
any other motor vehicle. Sudden and unintended operation of the auto
light switch can create a distraction, which can result in a traffic
accident and serious personal injury.
To turn the auto light switch on and off
In the Timekeeping Mode, hold down L for about three seconds to toggle the
auto light switch on (A.EL displayed) and off (A.EL not displayed).
• The auto light switch on indicator (A.EL) is on the display in all modes while
the auto light switch is turned on.
• The auto light switch turns off automatically whenever battery power drops
to Level 4.
• Illumination may not turn on right away if you raise the watch to your face
while a barometric pressure or altitude measurement operation is in
progress.
Questions & Answers
Question: What causes incorrect direction readings?
Answer:
• Incorrect bidirectional calibration. Perform bidirectional calibration.
• Nearby source of strong magnetism, such as a household appliance, a
large steel bridge, a steel beam, overhead wires, etc., or an attempt to
perform direction measurement on a train, boat, etc. Move away from large
metal objects and try again. Note that digital compass operation cannot be
performed inside a train, boat, etc.
Question: What causes different direction readings to produce different
Answer: Magnetism generated by nearby high-tension wires is interfering with
Question: Why am I having problems taking direction readings indoors ?
Answer: A TV, personal computer, speakers, or some other object is
Question: How can the barometer be used to predict weather?
Answer: Barometric pressure indicates changes in the atmosphere, and by
Question: How does the altimeter work?
Answer: Generally, air pressure and temperature decrease as altitude
• Note that the following conditions will prevent you from obtaining accurate
results at the same location ?
detection of terrestrial magnetism. Move away from the high-tension
wires and try again.
interfering with terrestrial magnetism readings. Move away from the
object causing the interference or take the direction reading
outdoors. Indoor direction readings are particularly difficult inside
ferro-concrete structures. Remember that you will not be able to take
direction readings inside of trains, airplanes, etc.
monitoring these changes you can predict the weather with
reasonable accuracy. Rising atmospheric pressure indicates good
weather, while falling pressure indicates deteriorating weather
conditions.
The barometric pressures that you see in the newspaper and on the
TV weather report are measurements corrected to values measured
at 0 m sea level.
increases. This watch bases its altitude measurements on
International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) values stipulated by the
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). These values define
relationships between altitude, air pressure, and temperature.
Altitude Air Pressure Temperature
616 hPa
4000 m
3500 m
3000 m
2500 m
2000 m
1500 m
1000 m
500 m
0 m
14000 ft
12000 ft
10000 ft
8000 ft
6000 ft
4000 ft
2000 ft
0 ft
Source: International Civil Aviation Organization
altitude readings:
When air pressure changes because of changes in the weather
Extreme temperature changes
When the watch itself is subjected to strong impact
701 hPa
795 hPa
899 hPa
19.03 inHg
22.23 inHg
25.84 inHg
About 8 hPa per 100 m
About 9 hPa per 100 m
About 10 hPa per 100 m
About 11 hPa per 100 m
About 12 hPa per 100 m
About 0.15 inHg per 200 ft
About 0.17 inHg per 200 ft
About 0.192 inHg per 200 ft
About 0.21 inHg per 200 ft
–11°C
–4.5°C
2°C
8.5°C
15°C1013 hPa
16.2°F
30.5°F
44.7°F
59.0°F29.92 inHg
About 6.5°C
per 1000 m
About 3.6°F
per 1000 ft
There are two standard methods of expressing altitude: Absolute altitude and
relative altitude. Absolute altitude expresses an absolute height above sea
level. Relative altitude expresses the difference between the height of two
different places.
Height of building 130 m
(relative altitude)
Rooftop at an altitude of
230 m above sea level
(absolute altitude)
Sea Level
Precautions Concerning Simultaneous Measurement of Altitude and
Temperature
Though you can perform altitude and temperature measurements at the same
time, you should remember that each of these measurements requires
different conditions for best results. With temperature measurement, it is best
to remove the watch from your wrist in order to eliminate the effects of body
heat. In the case of altitude measurement, on the other hand, it is better to
leave the watch on your wrist, because doing so keeps the watch at a
constant temperature, which contributes to more accurate altitude
measurements.
• To give altitude measurement priority, leave the watch on your wrist or in
any other location where the temperature of the watch is kept constant.
• To give temperature measurement priority, remove the watch from your
wrist and allow it to hang freely from your bag or in another location where
it is not exposed to direct sunlight. Note that removing the watch from your
wrist can affect pressure sensor readings momentarily.
Power Supply
This watch is equipped with a solar cell and a special rechargeable battery
(secondary battery) that is charged by the electrical power produced by the
solar cell. The illustration shown below shows how you should position the
watch for charging.
Example: Orient the watch so its face is
• The illustration shows how to position a
• Note that charging efficiency drops when
• You should try to keep the watch outside
Important!
• Storing the watch for long periods in an area where there is no light or
• This watch uses a special rechargeable battery to store power produced by
• Never try to remove or replace the watch’s special battery yourself. Use of
• All data stored in memory is deleted, and the current time and all other
• The Home City setting reverts to the initial default of
• Turn on the watch’s Power Saving function and keep it in an area normally
pointing at a light source.
watch with a resin band.
any part of the solar cell is blocked by
clothing, etc.
of your sleeve as much as possible.
Charging is reduced significantly if the
face is covered only partially.
wearing it in such a way that it is blocked from exposure to light can cause
rechargeable battery power to run down. Be sure that the watch is exposed
to bright light whenever possible.
the solar cell, so regular battery replacement is not required. However, after
very long use, the rechargeable battery may lose its ability to achieve a full
charge. If you experience problems getting the special rechargeable battery
to charge fully, contact your dealer or CASIO distributor about having it
replaced.
the wrong type of battery can damage the watch.
settings return to their initial factory defaults whenever battery power drops
to Level 5 and when you have the battery replaced.
whenever the battery power level drops to Level 5 or when you have the
rechargeable battery replaced. If this happens, change the Home City to
the setting you want.
exposed to bright light when storing it for long periods. This helps to keep
the rechargeable battery from going dead.
Solar cell
TYO (Tokyo)
9
Page 10
Operation Guide 3135 3206
Battery Power Indicators
The battery power indicator on the display shows you the current status of the
rechargeable battery’s power.
Battery Power
Level
Indicator
1
2
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
Battery power
indicator
3
(Charge Soon Alert)
4
(Charge Soon Alert)
5
• The flashing LOW indicator at Level 3 tells you that battery power is very
low, and that exposure to bright light for charging is required as soon as
possible.
• At Level 5, all functions are disabled and settings return to their initial
factory defaults. Once the battery reaches Level 2 (indicated by M indicator)
after falling to Level 5, reconfigure the current time, date, and other
settings.
• Display indicators reappear as soon as the battery is charged from Level 5
to Level 2.
• Leaving the watch exposed to direct sunlight or some other very strong light
source can cause the battery power indicator to show a reading temporarily
that is higher than the actual battery level. The correct battery level should
be indicated after a few minutes.
• Performing multiple sensor, illumination, or
beeper operations during a short period may
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
• Even if battery power is at Level 1 or Level 2, the Digital Compass Mode,
Barometer/Thermometer Mode, or Altimeter Mode sensor may be disabled
if there is not enough voltage available to power it sufficiently. This is
indicated by battery indicators (L, M, H) on the display.
• If battery indicators (L, M, H) appears frequently, it probably means that
remaining battery power is low. Leave the watch in bright light to allow it to
charge.
Charging Precautions
Certain charging conditions can cause the watch to become very hot. Avoid
leaving the watch in the areas described below whenever charging its
rechargeable battery. Also note that allowing the watch to become very hot
can cause its liquid crystal display to black out. The appearance of the LCD
should become normal again when the watch returns to a lower temperature.
Warning!
Leaving the watch in bright light to charge its rechargeable battery can
cause it to become quite hot. Take care when handling the watch to
avoid burn injury. The watch can become particularly hot when exposed
to the following conditions for long periods.
• On the dashboard of a car parked in direct sunlight
• Too close to an incandescent lamp
• Under direct sunlight
Charging Guide
After a full charge, timekeeping remains enabled for up to about five months.
• The following table shows the amount of time the watch needs to be
exposed to light each day in order to generate enough power for normal
daily operations.
cause all of the battery indicators (L, M, H) to
flash on the display. Illumination, alarm,
countdown timer alarm, hourly time signal, and
sensor operations will be disabled until battery
power recovers.
After some time, battery power will recover and
battery indicators (L, M, H) will disappear,
indicating that the above functions are enabled
again.
Exposure Level (Brightness)
Function Status
All functions enabled.
All functions enabled.
Illumination, beeper, and
sensor operation disabled.
Except for timekeeping and
the C (charge) indicator, all
functions and display
indicators disabled.
All functions disabled.
Approximate
Exposure Time
Outdoor Sunlight (50,000 lux)
Sunlight Through a Window (10,000 lux)
Daylight Through a Window on a Cloudy Day (5,000 lux)
Indoor Fluorescent Lighting (500 lux)
• For details about the battery operating time and daily operating conditions,
see the “Power Supply” section of the Specifications.
• Stable operation is promoted by frequent exposure to light.
5 minutes
24 minutes
48 minutes
8 hours
Recovery Times
The table below shows the amount exposure that is required to take the
battery from one level to the next.
Exposure Level
(Brightness)
Outdoor Sunlight
(50,000 lux)
Sunlight Through a
Window (10,000 lux)
Daylight Through a
Window on a Cloudy
Day (5,000 lux)
Indoor Fluorescent
Lighting (500 lux)
• The above exposure time values are all for reference only. Actual required
exposure times depend on lighting conditions.
Approximate Exposure Time
Level 5 Level 4 Level 3 Level 2 Level 1
▲
▲
1 hour 14 hours 4 hours
4 hours 68 hours 19 hours
6 hours 137 hours 38 hours
61 hours - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
Reference
This section contains more detailed and technical information about watch
operation. It also contains important precautions and notes about the various
features and functions of this watch.
Moon Phases and Moon Age
The Moon goes through a regular 29.53-day cycle. During each cycle, the
Moon appears to wax and wane as the relative positioning of the Earth,
Moon, and Sun changes. The greater the angular distance between the Moon
and the Sun,* the more we see illuminated.
* The angle to the Moon in relation to the direction at which the Sun is visible
from the Earth.
This watch performs a rough calculation of the current Moon age starting
from day 0 of the moon age cycle. Since this watch performs calculations
using integer values only (no fractions), the margin for error of the displayed
Moon age is ± 1 day.
Moon Phase Indicator
Moon Phase indicator
Module 3135 Module 3206
Moon
Phase
Indicator
Moon Age
Moon Phase
Moon
Phase
Indicator
Moon Age
Moon Phase
Tidal Movements
Tides are the periodic rise and fall of the water of oceans, seas, bays, and
other bodies of water caused mainly by the gravitational interactions between
the Earth, Moon and Sun. Tides rise and fall about every six hours. The Tide
Graph of this watch indicates tidal movement based on the Moon’s transit
over a meridian and the lunitidal interval. The Tide Graph calculates and
graphically represents current tide conditions in your Home City or a port city
in the vicinity of the Home City based on longitudes, lunar day length, and
lunitidal interval preset in watch memory, and on high tide times specified by
you.
Module
3135
Module
3206
Module
3135
Module
3206
The Moon phase indicator of this watch indicates
the current phase of the Moon as shown below. It
is based on the view of the left side of the moon
at meridian transit from the northern hemisphere
of the Earth. If the appearance of the Moon
phase indicator is reversed from the actual Moon
as viewed from your location, you can use the
procedure under “To reverse the displayed Moon
phase” to change the indicator.
(part you cannot see)
Moon phase
(part you can see)
28.7-29.5
1.0-2.7 2.8-4.6 4.7-6.4 6.5-8.3
0.0-0.9
New Moon
8.4-10.1
10.2-12.0 12.1-13.8
First Quarter (Waxing)
13.9-15.7 15.8-17.5 17.6-19.4 19.5-21.2 21.3-23.1 23.2-24.9 25.0-26.8 26.9-28.6
Full Moon
Last Quarter (Waning)
▲
10
Page 11

Operation Guide 3135 3206
Tide Graph
The Tide Graph graphically represents the current tide condition using one of
three patterns that represent spring tide, intermediate tide, and neap tide, as
shown below.
Tide Name Graph Description
Spring Tide
Intermediate Tide
Neap Tide
•
The Tide Graph flashes as shown below to indicate the tide range.
l
l
l
l
l
•
The segments on either end of the Tide Graph flash during high tide.
Lunitidal Interval
Theoretically, high tide is at the Moon’s transit over the meridian and low tide
is about six hours later. Actual high tide occurs somewhat later, due to factors
such as viscosity, friction, and underwater topography. Both the time
differential between the Moon’s transit over the meridian until high tide and
the time differential between the Moon’s transit over the meridian until low tide
are known as the “lunitidal interval”.
Auto Return Features
• The watch returns to the Timekeeping Mode automatically if you do not
perform any button operation for two or three minutes in the Tide/Moon
Data, Alarm, Data Recall, Digital Compass, or Barometer/Thermometer
Mode.
• If you do not perform any button operation while in the Altimeter Mode, the
watch returns to the Timekeeping Mode automatically after nine or 10
hours.
• If you leave a screen with flashing digits on the display for two or three
minutes without performing any operation, the watch exits the setting
screen automatically.
Initial Screens
When you enter the World Time or Alarm Mode, the data you were viewing
when you last exited the mode appears first.
Scrolling
The A and C buttons are used on the setting screen to scroll through data
on the display. In most cases, holding down these buttons during a scroll
operation scrolls through the data at high speed.
Sensor Malfunction Indicator
Subjecting the watch to strong impact can cause sensor malfunction or
improper contact of internal circuitry. When this happens,
appear on the display and sensor operations will be disabled.
ERR appears while a measurement operation is being performed in a
• If
sensor mode, restart the measurement. If
again, it can mean there is something wrong with the sensor.
• Even if battery power is at Level 1 or Level 2, the Digital Compass Mode,
Barometer/Thermometer Mode, or Altimeter Mode sensor may be disabled
if there is not enough voltage available to power it sufficiently. In this case,
ERR will appear on the display. This does not indicate malfunction, and
sensor operation should resume once battery voltage returns to its normal
level.
ERR keeps appearing during measurement, it could mean there is a
• If
problem with the applicable sensor.
Whenever you have a sensor malfunction, be sure to take the watch to
your original dealer or nearest authorized CASIO distributor as soon as
possible.
Large difference between
high tide and low tide. Occurs
a few days before and after a
New Moon and Full Moon.
Medium difference between
high tide and low tide.
Small difference between
high tide and low tide. Occurs
a few days before and after
the first quarter and last
quarter of a half moon.
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
High tideHigh tide Low tide
ERR appears on the display
ERR
(error) will
Button Operation Tone
Mute indicator
The button operation tone sounds any time you
press one of the watch’s buttons. You can turn the
button operation tone on or off as desired.
• Even if you turn off the button operation tone,
the alarm, Hourly Time Signal, and Countdown
Timer Mode alarm all operate normally.
To turn the button operation tone on and off
In any mode (except when a setting screen is on
the display), hold down D to toggle the button
operation tone on (
displayed).
• Since the D button also is the mode change button, holding it down to turn
the button operation on or off also causes the watch’s current mode to
change.
• The
indicator is displayed in all modes when the button operation tone is
turned off.
Power Saving
Elapsed Time in
Dark
60 to 70 minutes
(Display Sleep)
6 or 7 days
(Function Sleep)
• Wearing the watch inside the sleeve of clothing can cause it to enter the
sleep state.
• The watch will not enter the sleep state while the digital time is between
6:00 AM and 9:59 PM. If the watch is already in the sleep state when the
digital time reaches 6:00 AM, however, it will remain in the sleep state.
• The watch will not enter the sleep state while it is in the Digital Compass,
Barometer/Thermometer, Altimeter, Countdown Timer, or Stopwatch Mode.
When the watch is left in any mode besides the Countdown Timer and
Stopwatch Mode, it will return to the Timekeeping Mode automatically after
a specific amount of time. Then if left in the dark for the elapsed time
indicated in the table above, the watch will enter the sleep state.
When turned on, Power Saving enters a sleep
state automatically whenever the watch is left for
a certain period in an area where it is dark. The
table below shows how watch functions are
affected by Power Saving.
• There actually are two sleep state levels:
“display sleep” and “function sleep”.
Display
Blank, with
PS flashing
Blank, with
flashing
PS not
not displayed) and off (
Operation
Display is off, but all functions are
enabled.
All functions are disabled, but
timekeeping is maintained.
To recover from the sleep state
Perform any one of the following operations.
• Move the watch to a well-lit area. It can take up to two seconds for the
display to turn on.
• Press any button.
• Angle the watch towards your face for reading.
To turn Power Saving on and off
1. In the Timekeeping Mode, hold down E until
the city code starts to flash, which indicates
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
Power Saving on
indicator
Timekeeping
• Resetting the seconds to 00 while the current count is in the range of 30 to
59 causes the minutes to be increased by 1. In the range of 00 to 29, the
seconds are reset to
• With the 12-hour format, the P (PM) indicator appears on the display for
times in the range of noon to 11:59 p.m. and no indicator appears for times
in the range of midnight to 11:59 a.m.
• With the 24-hour format, times are displayed in the range of 0:00 to 23:59,
without any indicator.
• The 12-hour/24-hour timekeeping format you select in the Timekeeping
Mode is applied in all modes.
• The watch’s built-in full automatic calendar makes allowances for different
month lengths and leap years. Once you set the date, there should be no
reason to change it except when battery power drops to Level 5.
• The times for the Timekeeping Mode and all the city codes of the World
Time Mode are calculated in accordance with each city’s UTC offset.
• The UTC offset is a value that indicates the time difference between a
reference point in Greenwich, England and the time zone where a city is
located.
the setting screen.
2. Press D nine times until the Power Saving
on/off screen appears.
3. Press A to toggle Power Saving on (
off (
OFF).
4. Press E to exit the setting screen.
• The Power Saving on indicator (PS) is on the
display in all modes while Power Saving is
turned on.
00
without changing the minutes.
ON) and
11
Page 12
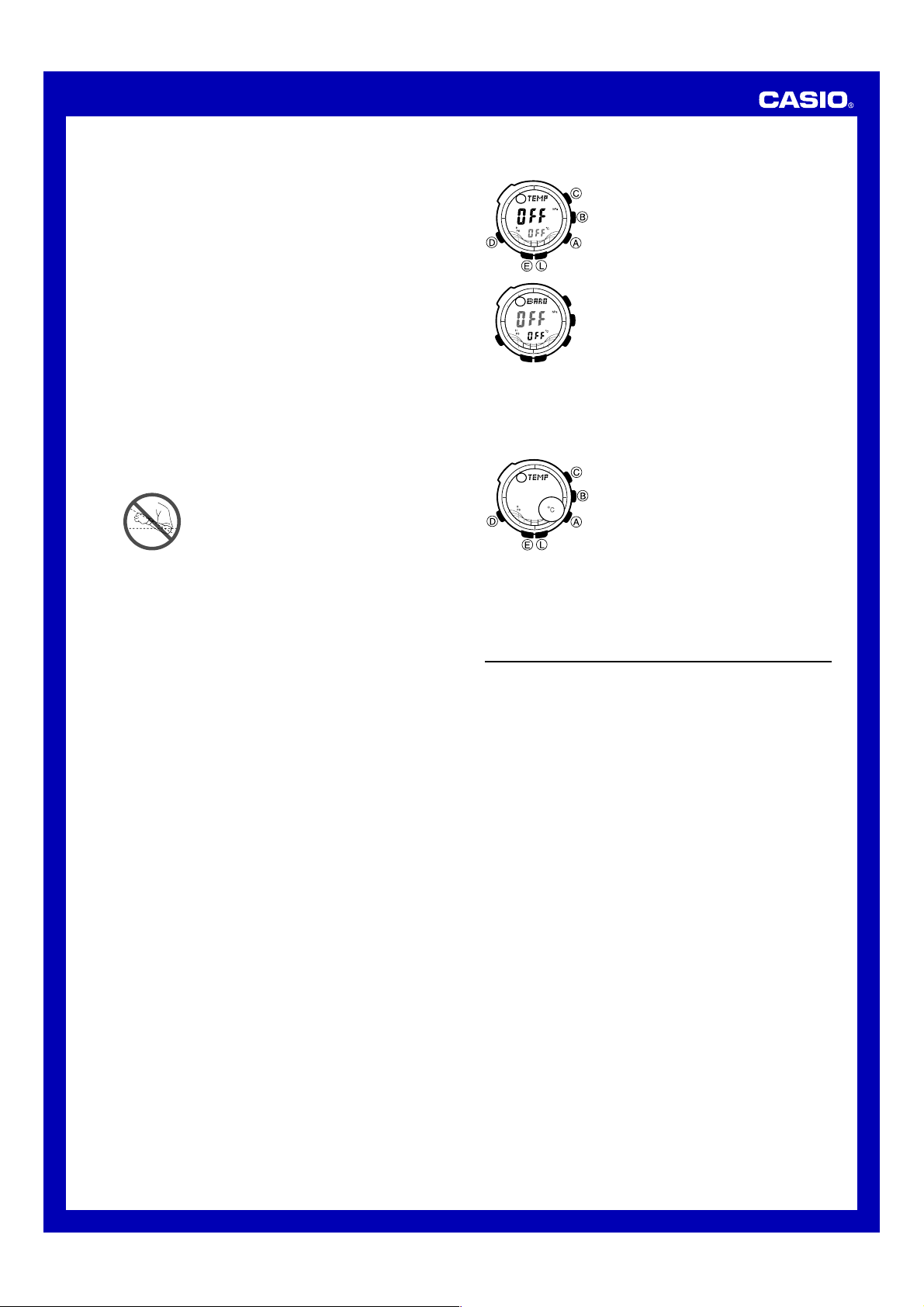
Operation Guide 3135 3206
• The letters “UTC” is the abbreviation for “Universal Time Coordinated”,
which is the world-wide scientific standard of timekeeping. It is based upon
carefully maintained atomic (cesium) clocks that keep time accurately to
within microseconds. Leap seconds are added or subtracted as necessary
to keep UTC in sync with the Earth’s rotation.
Illumination Precautions
• The electro-luminescent panel that provides illumination loses power after
very long use.
• Illumination may be hard to see when viewed under direct sunlight.
• Illumination turns off automatically whenever an alarm sounds.
• The watch may emit an audible sound whenever the display is illuminated.
This is due to vibration of the EL panel used for illumination, and does not
indicate malfunction.
• Frequent use of illumination runs down the battery.
Auto light switch precautions
• The auto light switch is turned off automatically whenever battery power is
at Level 4.
• Wearing the watch on the inside of your wrist, movement of your arm, or
vibration of your arm can cause frequent activation of the auto light switch
and illumination of the display. To avoid running down the battery, turn off
the auto light switch whenever engaging in activities that might cause
frequent illumination of the display.
• Note that wearing the watch under your sleeve while the auto light switch is
turned on can cause frequent illumination of the display and can run down
the battery.
More than 15 degrees
too high
• Static electricity or magnetic force can interfere with proper operation of the
auto light switch. If illumination does not turn on, try moving the watch back
to the starting position (parallel with the ground) and then tilt it back towards
your face again. If this does not work, drop your arm all the way down so it
hangs at your side, and then bring it back up again.
• Under certain conditions, illumination does not turn on until about one
second after you turn the face of the watch towards you. This does not
necessarily indicate malfunction.
• You may notice a very faint clicking sound coming from the watch when it is
shaken back and forth. This sound is caused by mechanical operation of
the auto light switch, and does not indicate a problem with the watch.
Barometer and Thermometer Precautions
• The pressure sensor built into this watch measures changes in air
pressure, which you can then apply to your own weather predictions. It is
not intended for use as a precision instrument in official weather prediction
or reporting applications.
• Sudden temperature changes can affect pressure sensor readings.
• Temperature measurements are affected by your body temperature (while
you are wearing the watch), direct sunlight, and moisture. To achieve a
more accurate temperature measurement, remove the watch from your
wrist, place it in a well ventilated location out of direct sunlight, and wipe all
moisture from the case. It takes approximately 20 to 30 minutes for the
case of the watch to reach the actual surrounding temperature.
Pressure Sensor and Temperature Sensor Calibration
The pressure sensor and temperature sensor built into the watch are
calibrated at the factory and normally require no further adjustment. If you
notice serious errors in the pressure readings and temperature readings
produced by the watch, you can calibrate the sensor to correct the errors.
Important!
• Incorrectly calibrating the barometric pressure sensor can result in incorrect
readings. Before performing the calibration procedure, compare the
readings produced by the watch with those of another reliable and accurate
barometer.
• Incorrectly calibrating the temperature sensor can result in incorrect
readings. Carefully read the following before doing anything.
Compare the readings produced by the watch with those of another
reliable and accurate thermometer.
If adjustment is required, remove the watch from your wrist and wait for 20
or 30 minutes to give the temperature of the watch time to stabilize.
• Illumination may not turn on if the face of the
watch is more than 15 degrees above or below
parallel. Make sure that the back of your hand
is parallel to the ground.
• Illumination turns off in about one second, even
if you keep the watch pointed towards your
face.
To calibrate the pressure sensor and the temperature sensor
1. Press B to enter the Barometer/
Thermometer Mode.
2. In the Barometer/Thermometer Mode, hold
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
• Pressing A and C at the same time returns to the factory calibration
(OFF).
4. Press E to return to the Barometer/Thermometer Mode screen.
down E for about two seconds until either
OFF or the reference temperature value starts
to flash. This is the setting screen.
• If you want to calibrate the barometric
pressure sensor, press D to move the
flashing to the middle display area. This is
the pressure sensor calibration screen.
• At this time, OFF or the barometric pressure
value should be flashing on the display.
3. Use A (+) and C (–) to set the calibration
value in the units shown below.
Temperature 0.1°C (0.2°F)
Barometric Pressure 1 hPa (0.05 inHg)
• “OFF” is displayed while the reference
temperature value and barometric pressure
value are zero (0).
To select the temperature, barometric pressure, and altitude units
1. Enter the Timekeeping Mode.
2. Hold down E until the city code starts to
flash, which indicates the setting screen.
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
l
4. Press A to change the unit setting.
• Each press of A changes the selected unit setting as shown below.
Temperature
Altitude m and ft
Barometric Pressure hPa and inHg
5. After the settings are the way you want, press E to exit the setting screen.
3. Use D to select the setting screen for the unit
you want to change.
• See step 3 under “To set the time and date”
for information about how to scroll through
setting screens.
°
C and °F
Specifications
Accuracy at normal temperature: ±20 seconds a month
Timekeeping: Hour, minute, second, p.m. (P), month, day, day of the week
Time format: 12-hour and 24-hour
Calendar system: Full Auto-calendar pre-programmed from the year
2000 to 2099
Other: 2 display formats (Day of the Week, Barometric Pressure Graph);
Home City code (can be assigned one of 33 city codes); Standard
Time / Daylight Saving Time (summer time)
Digital Compass: 20 seconds continuous measurement; 16 directions;
Angle value 0° to 359°; Four direction pointers; Calibration
(bidirectional, northerly); Magnetic declination correction
Barometer:
Measurement and display range:
260 to 1,100 hPa (or 7.65 to 32.45 inHg)
Display unit: 1 hPa (or 0.05 inHg)
Measurement timing: Daily from midnight, at two hour intervals (12 times
per day); Ever y five seconds in the Barometer/Thermometer Mode
Other: Calibration; Manual measurement (button operation); Barometric
pressure graph
Thermometer:
Measurement and display range: –10.0 to 60.0°C (or 14.0 to 140.0°F)
Display unit: 0.1°C (or 0.2°F)
Measurement timing: Every five seconds in the Barometer/Thermometer
Mode
Other: Calibration; Manual measurement (button operation)
Altimeter:
Measurement range: –700 to 10,000 m (or –2,300 to 32,800 ft.) without
reference altitude
Display range: –10,000 to 10,000 m (or –32,800 to 32,800 ft.)
Negative values can be caused by readings produced based on a
reference altitude or due to atmospheric conditions.
Display unit: 5 m (or 20 ft.)
Current Altitude Data: 5-second interval for first 3 minutes followed by 2-
minute interval for next 9 or 10 hours
Altitude Memory Data: 24 altitude records and one high altitude record
Altitude records: Pressing a button records the current altitude value,
along with the date (month-day) of the reading.
High altitude record: Automatically records the highest altitude value
measured in the Altimeter Mode to date, along with the date (month-
day) of the reading.
Other: Reference altitude setting; Altitude graph
12
Page 13
Operation Guide 3135 3206
Bearing Sensor Precision:
Direction: Within ±10°
Values are guaranteed for a temperature range of –10°C to 40°C (14°F
to 104
°
F).
North pointer: Within ±2 digital segments
Pressure Sensor Precision:
Conditions
Fixed
temperature
Effect of
variable
temperature
• Values are guaranteed for a temperature range of –10°C to 40°C (14°F to
104°F).
• Precision is lessened by strong impact to either the watch or the sensor,
and by temperature extremes.
Temperature Sensor Precision:
±2°C (±3.6°F) in range of –10°C to 60°C (14.0°F to 140.0°F)
Tide/Moon Data:
Moon phase indicator for specific date; Tide level for specific date and time
Other: High tide time adjustment; Moon phase reversal
Countdown Timer:
Measuring unit: 1 second
Countdown range: 60 minutes
Setting ranges: Countdown start time (1 to 60 minutes, 1-minute increments);
Reset time (1 to 5 minutes, 1-minute increments)
Other: Progress beeper
Stopwatch:
Measuring unit: 1/100 second
Measuring capacity: 23:59' 59.99''
Measuring modes: Elapsed time, split time, two finishes
Alarms: 5 Daily alarms; Hourly time signal
World Time: 33 cities (29 time zones)
Other: Daylight Saving Time/Standard Time
Illumination: EL Backlight (electro-luminescent panel); Auto Light Switch
Other: Battery power indicator; Power Saving; Low-temperature resistance
(Altitude)
0 to 6000 m
0 to 19680 ft.
6000 to 10000 m
19680 to 32800 ft.
0 to 6000 m
0 to 19680 ft.
6000 to 10000 m
19680 to 32800 ft.
(Full Auto EL Light operates only in the dark)
(–10°C/14°F); Button operation tone on/off
Altimeter Barometer
± (altitude differential × 3%
+ 30 m) m
± (altitude differential × 3%
+ 100 ft.) ft.
± (altitude differential × 3%
+ 45 m) m
± (altitude differential × 3%
+ 150 ft.) ft.
± 80 m every 10°C
± 264 ft. every 50°F
± 120 m every 10°C
± 396 ft. every 50°F
± (pressure differential × 3%
+ 3 hPa) hPa
± (pressure differential × 3%
+ 0.0885 inHg) inHg
± 6 hPa every 10°C
± 0.177 inHg every 50°F
Power Supply: Solar cell and one rechargeable battery
Approximate battery operating time: 5 months (from full charge to
Level 4) under the following conditions:
• Watch not exposed to light
• Internal timekeeping
• Display on 18 hours per day, sleep state 6 hours per day
• 1 illumination operation (1.5 seconds) per day
• 10 seconds of alarm operation per day
• 10 digital compass operations per week
•
10 hours of altimeter measurement at 2-minutes interval, once per month
• 2 hours of barometric pressure measurement per day
Frequent use of illumination runs down the battery. Particular care is
required when using the auto light switch.
20 months when the watch is left in the sleep state (display off) after a
full charge.
City Code Table
City
Code GMT Differential
CCS*
• Based on data as of December 2008.
• The rules governing global times (GMT differential and UTC offset) and
* In December 2007, Venezuela changed its offset from –4.0 to –4.5. Note
City
Pago Pago
PPG
Honolulu
HNL
Anchorage
ANC
Los Angeles
LAX
Denver
DEN
Chicago
CHI
New York
NYC
Caracas
Rio De Janeiro
RIO
Fernando de
FEN
Noronha
Praia
RAI
UTC
London
LON
Pari s
PA R
Berlin
BER
Athens
ATH
Cairo
CAI
Jerusalem
JRS
summer time are determined by each individual country.
however, that this watch displays an offset of –4.0 (the old offset) for the
CCS (Caracas, Venezuela) city code.
UTC Offset/
–11
–10
–9
–8
–7
–6
–5
–4
–3
–2
–1
–
0
+1
+2
City
JED
THR
DXB
KBL
KHI
DEL
DAC
BKK
SEL
TYO
ADL
SYD
City
Jeddah
Tehran
Dubai
Kabul
Karachi
Delhi
Dhaka
Yangon
Bangkok
Hong Kong
Seoul
Tokyo
Adelaide
Sydney
Noumea
Wellington
Code GMT Differential
RGN
HKG
NOU
WLG
UTC Offset/
+3
+3.5
+4
+4.5
+5
+5.5
+6
+6.5
+7
+8
+9
+9.5
+10
+11
+12
13
 Loading...
Loading...