Page 1

INSTALLATION, OPERATION & MAINTENANCE MANUAL (IOM)
MODEL DA0
DIRECT-ACTING, PRESSURE LOADED
PRESSURE REDUCING REGULATOR
for STEAM APPLICATIONS
SECTION I
I. DESCRIPTION AND SCOPE
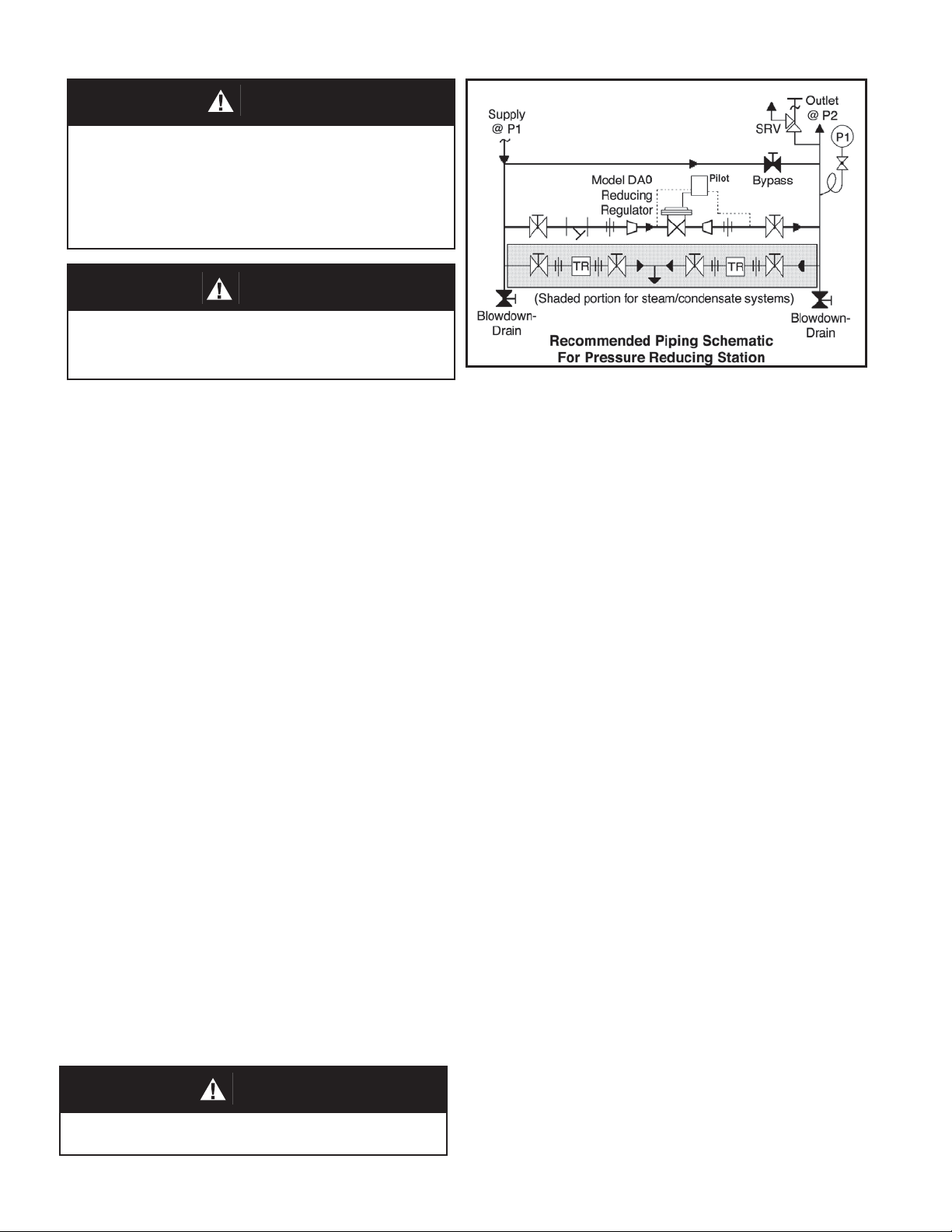
Model DA0 is a pressure reducing regulator used to control downstream (outlet or P2) pressure. Sizes are
1/2" (DN15), 3/4" (DN20), 1" (DN25), 1-1/4" (DN32), 1-1/2" (DN40), 2" (DN50), 3" (DN80) and 4" (DN100). Refer
to Technical Bulletin DA0-TB for design conditions and selection recommendations. (NOTE: This product was
formerly identifi ed as a Model D0; a Model DA0 and D0 are one and the same product.)
This manual does not include instructions related to the various methods of pressure loading a Model DA0
main valve.
SECTION II
II. REFERENCES
Refer to Technical Bulletin DA0-TB and DAG-TB
for tech ni cal specifi cations for this reg u la tor.
CW – Clockwise
CCW – Counter Clockwise
ITA – Inner Trim Assembly
ABBREVIATIONS
IOM-DA0
11-13
SECTION III
III. INSTALLATION
CAUTION
Installation of adequate overpressure pro tec tion is recommended to pro tect the reg u la tor from overpressure and
all down stream equip ment from damage in the event of
regulator failure.
1. Regulator may be rotated around pipe axis 360
degrees. For ease of maintenance, the rec om mend ed position is with the cover dome (25)
up wards.
2. Provide space below, above, and around reg u la-
tor for removal of parts during maintenance.
3. Install block valves and pressure gauges to pro-
vide means for adjustment, operation, bypass,
or removal of the regulator. A pipeline strainer
is recommended before inlet to remove typical
pipe line debris from entering valve and damaging
internal “soft goods”, primarily the dynamic seal.
4. Steam traps should be installed before and after
the regulator to provide proper drainage.
5. Install the regulator with the fl ow in the direction
of the arrow cast or stamped into the body.
6. For best performance, recommend that the piping upstream and downstream of the regulator
be straignt and free from any restrictions, bend,
etd. which can cause turbulence, for a minimun
length of approximately fi fteen to twenty pipe
diameters.
7. Pipe size should be given special consideration,
particularly downstream of the regulator, to
ensure that the steam velocity does not exceed
industry or customer guidelines. Reference
DAG-TB, Table DAG-11 for rec om men da tions
for applying external pressure sensing.
8. External sensing, uses an external control line.
This line is connected from the 1/4" (DN8) NPT
tap on the side of the pilot body to a pressure
tap down stream of the regulator. Use 1/4" or
3/8" (DN8 or 10) outer di am e ter tubing or 3/8"
(DN10) pipe having an inner di am e ter equiv a lent
to Schedule 40 pipe. For condensable vapors (i.e.
steam) slope the external sensing line downward
2 to 5 de grees to outlet piping to prevent water
pock ets, which allows the diaphragm chamber
to always be self draining.
Page 2
CAUTION
DO NOT HYDROSTATIC TEST THROUGH AN IN STALLED
UNIT; ISOLATE REGULATOR FROM TEST. The "OUTLET
RATING" as printed on the name plate is the rec om mend ed
“upper op er at ing limit” for the sens ing di a phragm. Higher
pres sures could cause internal dam age. In ad di tion, note
on the nameplate that the Inlet and Outlet pres sure and
temperature ratings are at different levels.
CAUTION
Installation of adequate overpressure pro tec tion is recommended to pro tect the reg u la tor from over pres sure and
all down stream equip ment from dam age in the event of
regulator failure.
SECTION IV
IV. PRINCIPLE OF OPERATION
1. The pilot receives steam from the upstream tapping
in the side of the main regulator body and passes
it thru to the cover dome. When a loading pressure – P
– is applied into the top of the cover
Load
dome, the outlet controlled pressure – P
balance at approximately .90 – .98 of the loading
pressure - PL. (NOTE: Fluc tu a tions in P1 – Inlet
Pressure will cause a deviation in P2 – Outlet
Pressure due to inverse sym pa thet ic ratio effect.)
See Section VIII.
V. STARTUP
1 Start with the block valves closed.
2. Adjust the loading system pressure control de vice
so that main regulator is trying to be con trolled at 0
psig pressure. (For spring loaded pilots, relax the
range spring compression by turning the adjusting
screw CCW.)
– will
2
SECTION V
2. Movement occurs as pressure variations register
on the stop plate. The registering pressure is the
outlet, P
, or downstream pressure. The loading
2
pressure fl uid op pos es plug move ment. As outlet
pres sure drops, the loading pressure push es the
stop plate down, opening the port; as outlet pres sure increases, the plug pushes up and the port
opening closes.
3. A loss of loading pres sure while inlet pressure is
imposed will cause the regulator to fail close.
4. Crack open the outlet (downstream) block valve
to approximately 10% full open.
5. Slowly open the inlet (upstream) block valve to
about 25% open. Adjust the loading system pres sure control device setpoint pressure upwards
until the main valve is fl owing. Observe the outlet
pressure gauge to ensure not overpressurizing.
3. If it is a “hot” piping system, and equipped with
a bypass valve, slowly open the bypass valve
to preheat the system piping and to allow slow
ex pan sion of the piping. Closely monitor outlet
(down stream) pressure via gauge to ensure not
over-pressurizing. NOTE: If no bypass valve is
in stalled, extra caution should be used in starting
up a cold system; i.e. do everything slowly.
CAUTION
Do not walk away and leave a bypassed reg u la tor unattended!
2
6. Continue to slowly open the inlet (upstream) block
valve until fully open.
7. Continue to slowly open the outlet (downstream)
block valve, especially when the downstream piping system isn’t pressurized. If the outlet (down stream) pressure exceeds the desired pres sure,
close the inlet block valve and go to Step 2. Close
bypass valve approximately 25%, and re peat
pro ce dure.
8. When fl ow is established steady enough that the
outlet (downstream) block valve is fully open, begin
to slowly close the bypass valve if installed.
IOM-DA0
Page 3
9. Develop system fl ow to a level near its expected
normal rate, and reset the regulator set point by
adjusting the loading system pressure control
setpoint to the desired outlet pressure level.
VI. SHUTDOWN
10. Reduce system fl ow to a minimum level and
observe pressure set point. Outlet pressure
will rise from the set point of Step 9 for a Model
DA0. The max i mum rise in outlet pres sure on
de creas ing fl ow should not exceed the 10%. If
it does, consult factory.
SECTION VI
1. Shutoff inlet block valve.
2. Shutoff auxiliary loading pressure source, if sup plied. For spring loaded pilots, relax the range
spring by turning the adjusting screw CCW until
adjusting screw is removed.
3. Allow suffi cient time for the line pressure down-
stream of the inlet block valve to bleed down.
SECTION VII
VII. MAINTENANCE
A. General:
WARNING
SYSTEM UNDER PRESSURE. Prior to per form ing any
maintenance, isolate the reg u la tor from the system and
relieve all pressure. Failure to do so could result in personal injury.
1. The regulator may be serviced without
re mov ing the regulator from pipeline. The
reg u la tor is designed with quick-change trim
to simplify maintenance.
4. Shutoff the outlet block valve.
5. Relieve the trapped upstream and downstream
pressure and loading pres sure.
6. The regulator may now be removed from the
pipe line or disassembled for inspection and pre ven ta tive main te nance while in-line.
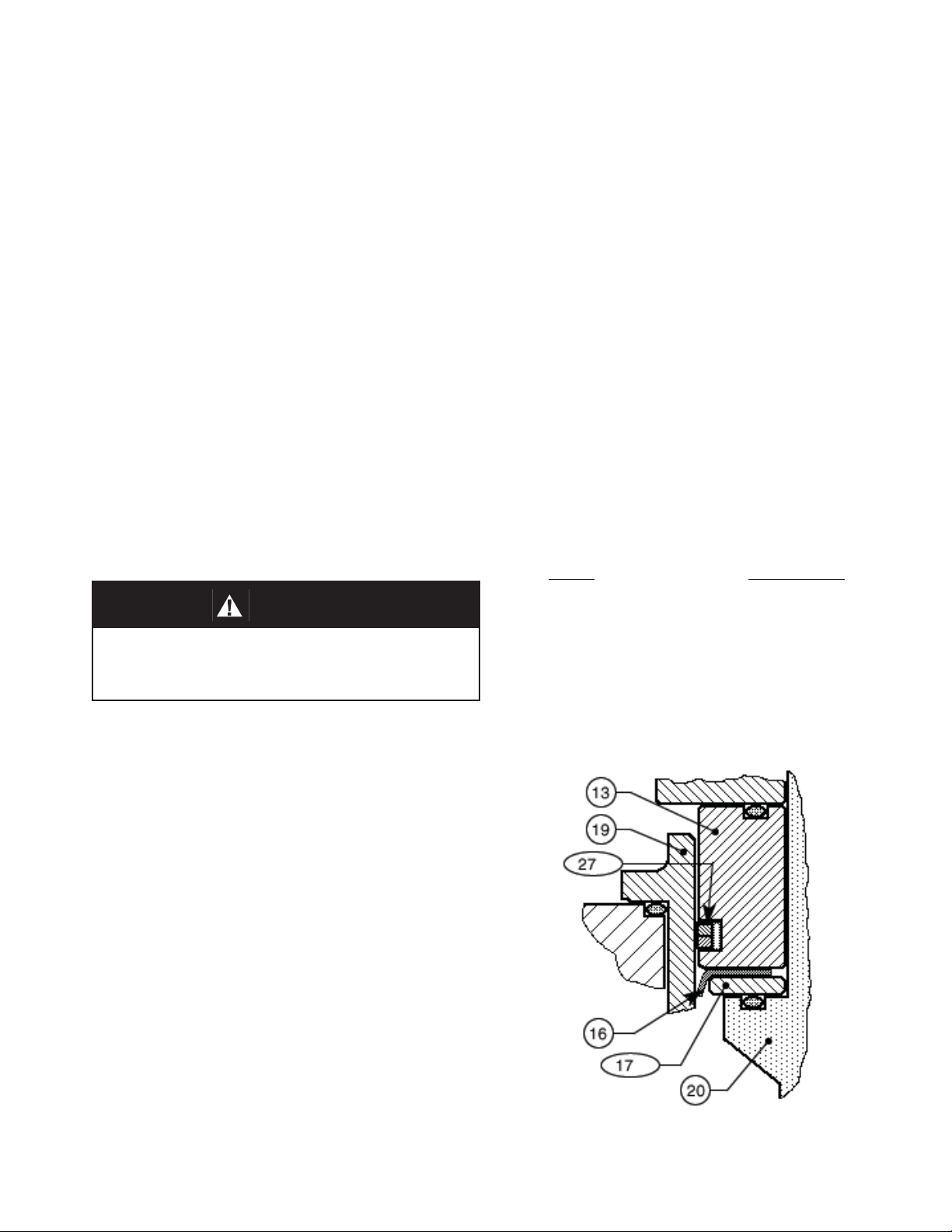
Item No. Part Description
7 ...................................................................................Nut
10 ......................................................................Stop Plate
13 ....................................................Guide Bearing/Piston
14 ...............................Lower and Upper Static Stem Seal
15 ..........................................................Cage O-ring Seal
16 ............................................................................ Wiper
17 ...............................................................Wiper Washer
19 ............................................................................. Cage
20 .............................................................................. Plug
21 ......................................................................Seat Ring
27 ....................................................... Dynamic Side Seal
IOM-DA0
2. Record the nameplate information to req ui si tion repair parts for the regulator. The
in for ma tion should include: size, Product
Code and Serial Number.
3. Refer to Section X for recommended repair
parts. Only use original equipment parts
sup plied by Cashco/KM for re build ing or
re pair ing reg u la tors.
4. Owner should refer to owner's procedures
for removal, handling, cleaning and disposal
of nonreuseable parts, i.e. gaskets, etc.
5. The Inner Trim is re moved and replaced in
the body ( 23) as an assemblage of parts.
The Inner Trim Assembly, here in af ter called
ITA, consists of the following parts:
Figure 1: Dynamic Side Seals
3
Page 4
WARNING
SYSTEM UNDER PRESSURE. Prior to per form ing any
maintenance, isolate the reg u la tor from the system and
relieve all pressure. Failure to do so could result in personal injury.
B. Main Valve Disassembly:
1. Shut down system in accordance Section VI.
2. Disconnect the external piping line(s) connecting pilot to main regulator.
3. Though it is possible to disassemble the main
unit while installed in a pipeline, it is rec om mend ed that maintenance be done in a shop
when possible. The descriptions hereafter will
assume shop disassembly. Remove regulator
from pipeline.
4. Place the body in a vise with the cover dome
(25) oriented upwards.
5. Loosen the fl ange bolts (11) and nuts (12)
uniformly and remove.
6. Place matchmarks on body (23) and cover
dome (25) fl anges. Remove cover dome and
gasket (13).
7. Evenly loosen the three cage cap screws
(18) in single revolution increments. NOTE:
Regulator con tains a lower spring (22); the
ITA should rise as the cage cap screws are
evenly backed out. A down wards holding force
should be ap plied to the top of the piston-guide
bearing (13) to pre vent the ITA from pop ping
up as the last threads of the cage cap screws
are backed out.
8. Remove the ITA by pulling up on the plug
(20). Set ITA aside.
9. Remove spring (22) from within the body (23).
10. Remove cage o-ring seal (15).
11. Remove body (23) from vise. Clean all re us able
metal parts according to owner's pro ce dures.
C. Disassembly of the ITA:
1. To disassemble the ITA, hold the lower part
of the plug (20) in a bench vise; Do not hold
on the machined sur face in the plug's (20)
spindle area. NOTE: The spin dle “slides” in
the "pressed-in-place" lower guide bushing
(24) and the surface can not be marred.
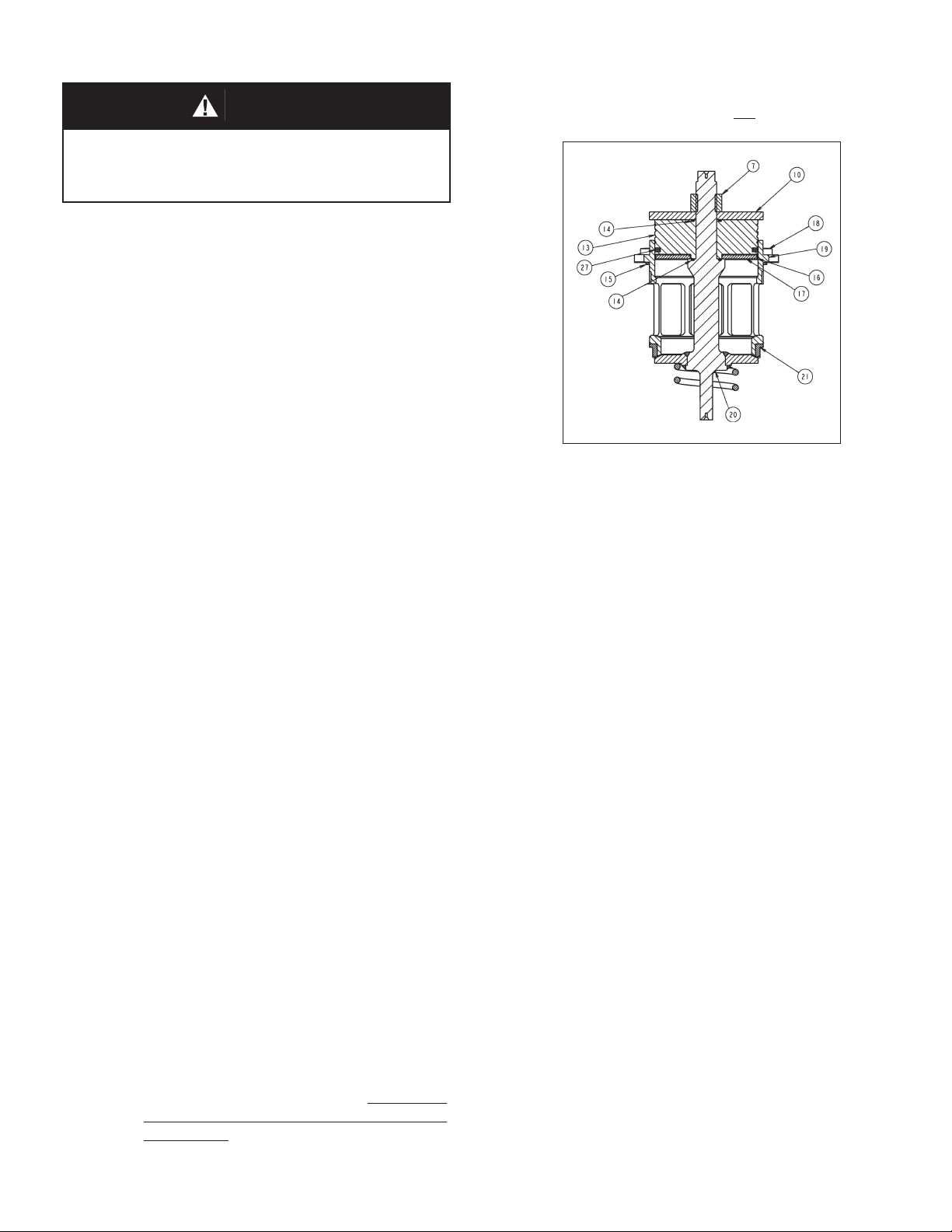
Figure 2: Assembled ITA,
2. Rotate di a phragm lock nut (7) CCW and remove.
3. Remove stop plate (10). Remove ITA from
vise.
4. From below the cage (19) pull the plug (20)
downwards out of the piston-guide bearing
(13) and out thru the bottom of the cage.
5. Remove the piston-guide bearing (13) from
the upper end of cage (19).
6. Examine the dy nam ic side seal (27) mechanism to de ter mine if sig nifi cant leakage was
oc cur ring. If the dy nam ic side seal shows signs
of sig nifi cant leakage, de ter mine if operating
conditions are ex ceed ing pres sure, pres sure
drop, or tem per a ture lim its.
7. Remove top seal (14) and dynamic side seal
(27) and discard. NOTE: Special care should
be taken when using “tools” to remove the
components to ensure that no scratches are
imparted on to any portion of the piston-guide
bearing (13) groove.
8. Remove wiper seal (16)and wiper washer (17)
from within cage (19).
9. Remove lower stem seal (14) from plug (20).
10. Remove seat ring (21) from bottom of cage;
examine for signs of leakage. If seat ring
shows signs of signifi cant leakage, determine
if op er at ing con di tions of pressure, pressure
drop, or temperature are ex ceed ing limits.
4
IOM-DA0
Page 5

11. Clean all reusable metal parts according to
owner's procedures.
D. Inspection of Parts:
1. After inspection remove from the work area
and dis card the old “soft goods” parts (i.e.
o-rings, seals, gaskets, etc.) after in spec tion.
These parts MUST be re placed with fac to ry
supplied new parts.
2. Inspect the metal parts that will be reused. The
parts should be free of surface con tam i nants,
burrs, oxides, and scale. Rework and clean
parts as necessary. Surface con di tions that
affect the regulator performance are stated
below; replace parts that can not be re worked
or cleaned.
2. After re-forming the wiper seal, remove parts
(13, 16, 17) from cage (19) and disassemble
this tem po rary assembly.
Not supplied. Use any
bolt, two washers and
nut of same approximate
hole size.
17
19
16
13
3. QC Requirements:
a. Plug (20);
1. 16 rms fi nish on its seating surface
for tight shutoff.
2. No major defects on bottom guide
spin dle.
b. Cage (19);
1. 16 rms fi nish on cylinder bore. No
“ledges” formed due to wear from
moving dynamic side seal (27) or
wiper seal (16).
c. Lower guide bushing (24) (non-re place-
able):
1. 16 rms fi nish in bore.
2. Max 0.015 inch (0.38 mm) clearance
be tween plug (20) spindle and lower
guide bushing (24).
4. Staging Material for Reassembly.
a. Inspect and clean parts, as necessary,
from the spare parts kit.
b. Lay out all the regulator parts and check
against the bill of material.
E. Reassembly of the ITA:
1. When replacing the wiper seal (16), the replacement wiper seal (16) is “pre-formed”.
It may, however, require re-forming. Under
normal circumstances, this step may not be
required. If needed, reform the wiper seal
(16) by press ing the temporary assembly of
parts into the cage (19) backwards as shown
in Figure 3. The wiper seal (16) is best left in
this position overnight (minimum of two (2)
hours) prior to fi nal re as sem bly.
Figure 3: Temporary Wiper Seal Assembly
3. Place wiper washer (17) into “cup” of wiper
seal (16). Holding these parts between thumb
and forefi nger, in sert into cage (19) at an ap-
proximate 45° angled approach with wiper
washer (17) on bottom, wiper seal (16) on
top with turned-down lip of wiper seal en ter ing cage fi rst. Rotate wiper seal and wiper
washer to a level po si tion approximately half
way down into cage. Allow wiper washer to
rest on bottom of cage.
4. Stretch the corrugated, metal, piston ring
en er giz er of the dynamic seal (27) over the
lower cir cum fer ence of piston-guide bearing
(13). Using thumbs, work the energizer into
the bearing groove.
5. Carefully stretch and slip one of the piston
ring seals over the lower circumference of
pis ton-guide bearing (13), taking care not to
“cut” the piston ring seal. Using thumbs, work
the piston ring seal into the groove of the
bearing. Repeat this procedure with a second
piston ring seal. NOTE: A piston ring as sem bly
(PRA) (27), consists of one metal corrugated
energizer and two piston ring seals
6. Position piston-guide bearing (13) over and
into upper end of cage (19) until the lower
piston ring seal touches the upper lip of the
cage. While gently applying force to press the
piston-guide bearing into the cage, si mul ta neous ly use fi n gers to lightly circumferentially
press the fi rst piston ring seal inwards into
the piston-guide bearing groove until the fi rst
IOM-DA0
5
Page 6

piston ring seal “slips inside” the cage (19).
Repeat process for second piston ring seal .
7. Place properly oriented seat ring (21) onto its
shoul der at the lower end of cage (19).
8. Install new lower stem o-ring seal (14) into
groove of plug (20).
into the body (23). To secure cap screws tight,
rotate cap screws CW in equal increments in
one-half revolution increments to pull down
the ITA evenly, taking care NOT TO “AN GLE”
the ITA in the BODY. Torque cap screws to
13-15 ft-lbs (17.6-20.3 N-m).
6. Install new gasket (37) onto body (23) fl ange.
9. Insert plug (20) upwards through lower end
of cage (19) and through the center hole in
piston-guide bearing (13), wiper washer (17)
and wiper seal (16). Hold plug (20) and cage
(19) assembly together.
10. Place the second new upper stem o-ring seal
(14) into groove of guide bearing (13). Position
stop plate (10) on top of stem seal and guide
bearing.
11. Thread nut (10) over the upper end of plug
(20) and tighten hand tight.
12. Place this assembly of parts into vise, use the
"fl ats" on the lower part of the plug to secure
tight. Use torque value as follows:
Body Size
in (DN)
1/2" - 1" (15 - 25) 60 - 70 (81 - 95)
1 1/4" - 2" (32 - 50) 120 - 130 (163 - 176)
2 1/2" - 4" (65 - 100) 110 - 120 (149 - 163)
Torque Value
Ft-lbs (N-m)
13. This completes ITA reassembly.
7. Aligning matchmarks and fl ange bolt holes,
place cover dome (25) onto body (23).
8. Install all fl ange bolts (11) and nuts (12) with
nameplate (99) located under one bolt head..
9. Tighten the body bolting (11,12) evenly in
an alternating cross pattern in one revolution
increments to the following torque values:
Body Size
in (Dn)
1/2" - 2" (15 - 50) 30 - 35 (41 - 47)
2 1/2" - 4" (65 - 100) 45 - 50 (61 - 69)
Torque Value
Ft-lbs (N-m)
G. Pressure Testing:
1. If a hydrostatic pressure test is performed,
pressure must be applied to all three of cover
dome (25), inlet and outlet of body at the same
level.
DO NOT HYDROSTATICALLY TEST WITH-
OUT COVER DOME PRESSURIZED. NOT
AD HER ING WILL DO PHYSICAL DAMAGE
TO INTERNALS THAT COULD REN DER
THE UNIT IN OP ER A BLE.
F. Main Reassembly:
1. Place body (23) in a vise.
2. Lower spring (22) into the body (23) and
center around the bushing.
3. Position the cage o-ring seal (15) down in
the body groove.
4. With the ITA held manually in the closed po si tion, carefully insert ITA into body (23). NOTE:
Lower spring (22) must be compressed to allow the cap crews (18) to engage the threads
in the body.
5. Properly align all three cage bolt holes with
holes in the body. There is only one circumferential location pos si ble for this align ment.
Use hand to apply downward force to the top
of the cage (19) until the ITA is lowered suf fi cient ly to engage the cage cap screws (18)
6
Figure 4: Location of Auxiliary Ports
IOM-DA0
Page 7

2. Inboard Leakage Test.
a. Release all loading pressure in cover
dome.
b. Pressurize inlet to 30 psig (2.1 Barg) with
air, GN
.
2
c. Tube outlet to a beaker of water to ob serve
number of escaping gas bubbles.
Inboard leakage path may be via plug/seat or
dynamic side seal.
3. Pressure Containment Test.
a. Pressurize inlet to 200 psig (13.8 Barg)
and outlet and cover dome to 150 psig
(10.3 Barg) with air or GN
.
2
b. Spray liquid lead detector and check all
ex ter nal leak points; i.e. plugged con nec tions, and fl ange bolting.
4. Excessive leakage will require disassembly,
examination of sealing elements, correction
of problem, reassembly and retesting.
IOM-DA0
7
Page 8

VIII. PRESSURE LOADING
SECTION VIII
1. Loading pressure can be supplied using various
schemes. Please reference LOADING SYSTEMS
on web-site for the schematics of these various
schemes, including:
• pressure unloading using BPV
• pressure loading using PRV
• pressure loading using pilot
• pressure loading using I/P transducer
LOADING PRESSURE FOR
MODEL DA0
APPLIED PRESSURES
2. The Model DA0 exhibits a deviation in outlet
controlled pressure when the inlet pressure var ies; this “effect” is identifi ed as ISR – Inverse
Sympathetic Ratio. Its relative pressure effect
can be calculated from the following equation.
ISR FACTOR
BODY SIZE
in (DN)
1/2" - 1" (15 - 25) 3.0
1 1/4" - 1 1/2" (32 - 40) 4.0
2" (50) 2.0
2 1/2" - 4" (65 - 100) 5.4
ISR – %
PISTON SPRING
LOWER PISTON
SPRING RANGE
psig (Barg)
none (none) 0 (0) 0 (0)
2 - 5 (.14 - .34) 3 (.21) 2 (.14)
1 - 2 (.07 - .14) 1 (.07) 1 (.07)
4 - 10 (.28 - 6.9) 6 (.41) 4 (.28)
SIZE / ORIENTATION – S/O Factor
Body Size
in (DN)
1/2" - 1" (15 - 25) 1 -1
1 1/4" - 1 1/2" (32 - 40) 2 -2
2" (50) 2.5 -2.5
2 1/2" - 3" (65 - 80) 3 -3
4" (100)
P
= ISR Effect +
LOAD
Compression Effect Spring Preload Orientation Effect
Lower Piston Spring + Lower Piston Spring + Body Size
∆P Piston
Spring
psig (Barg)
Cover Dome
on Top
LVPS
psig
(Barg)
Orientation
Cover Dome
on Bottom
4-4
Req'd
C
P
= P2 + [ISR x (P1 – P2)] +
Load
V
C
V
Max
x ∆P
Piston Spr. + LVPS + S/O
Factor
Figure 8: Loading Pres sure Formula
8
IOM-DA0
Page 9

SECTION IX
IX. TROUBLE SHOOTING GUIDE
When trouble shooting this regulator there are many possibilities as to what may be causing problems. Many times, the regulator itself is not defective, but one or more of the accessories may be. Sometimes the pro cess may be causing diffi culties.
The key to effi cient trouble shooting is information and communication. The customer should try to be as precise as possible
in their explanation of the problem, as well as their understanding of the application and operating con di tions.
It is imperative the following information be provided by the customer:
• Fluid (with fl uid properties) • Range of outlet pressure
• Range of fl ow rate • Range of fl uid temperature
• Range of inlet pressure • Range of ambient temperature
Pressure readings should be taken at every location where pressure plays a role - i.e., regulator inlet (as close as possible to
inlet port), regulator outlet (as close as possible to outlet port), etc.
Following are some of the more common complaints along with possible causes and remedies.
1. Erratic regulation, instability or hunting.
Possible Causes Remedies
A. Sticking of internal parts. A. Remove internals, clean, and if necessary, replace.
B. Oversized regulator.
B. Check actual fl ow conditions; resize regulator for min i mum and maxi-
mum fl ow; if necessary, replace with smaller size regulator.
2. Downstream pressure will not reach desired setting.
Possible Causes Remedies
A. Supply pressure is down (confi rm on pressure
gauge.
B. Undersized regulator. B. Check actual fl ow conditions; resize regulator for min i mum and maxi-
C. Pressure loading system pressure restricted. C1. Clean restriction or bleed orifi ces.
D. Faulty loading pressure control device. D. Replace/repair loading pressure control device.
A. Increase supply pressure.
mum fl ow; if necessary, replace with larger regulator.
C2. Clean fi lter(s).
C3. Clean loading pressure control device.
6. Leakage at body/cover fl ange.
Possible Causes Remedies
A. Body bolts not torqued properly. A. Torque to proper value (see Section VII, F-11).
B. Pressures may be too high. B. Consult factory.
7. Leakage across seat.
Possible Causes Remedies
A. Contamination (debris) in regulator. A. Remove internals, clean, & replace sealing and seating elements. *
B. Oversized regulator; valve plug operates
directly next to seat.
* Seat leakage may be diagnosed when a failure of the dynamic side seal has occurred. Inspect both potential internal leak paths.
B. Check actual fl ow conditions; resize regulator for minimum and maxi-
mum fl ow; if necessary, replace with smaller size regulator.
IOM-DA0
9
Page 10

SECTION X
X. ORDERING INFORMATION
NEW REPLACEMENT UNIT vs PARTS "KIT" FOR FIELD REPAIR
To obtain a quotation or place an order, please retrieve the Serial Number and Product Code that was stamped on
the metal name plate and attached to the unit. This information can also be found on the Bill of Material ("BOM"),
a parts list that was provided when unit was originally shipped. (Serial Number typically 6 digits). Product Code
typical format as follows: (last digit is alpha character that refl ects revision level for the product).
–
–
7
NEW REPLACEMENT UNIT:
Contact your local Cashco, Inc., Sales Rep re sen ta tive with the Serial Number and Product code.
With this information they can provide a quotation
for a new unit including a complete description,
price and availability.
CAUTION
Do not attempt to alter the original construction of any
unit without assistance and approval from the factory. All
purposed changes will require a new name plate with appropriate ratings and new product code to accommodate
the recommended part(s) changes.
PARTS "KIT" for FIELD REPAIR:
Contact your local Cashco, Inc., Sales Rep re sen ta tive with the Serial Number and Product code.
Identify the parts and the quantity required to repair
the unit from the "BOM" sheet that was provided
when unit was originally shipped.
NOTE: Those part numbers that have a quantity indicated
under "Spare Parts" in column "A” refl ect minimum
parts required for inspection and rebuild, - "Soft
Goods Kit". Those in column “B” include minimum
trim replacement parts needed plus those "Soft
Goods" parts from column "A".
If the "BOM" is not available, refer to the crosssectional drawings included in this manual for part
identifi cation and selection.
A Local Sales Representative will provide quotation
for appropriate Kit Number, Price and Availability.
The contents of this publication are presented for informational purposes only, and while every effort has been made to ensure their accuracy, they are not to be
construed as warranties or guarantees, express or implied, regarding the products or services described herein or their use or applicability. We reserve the right to
modify or improve the designs or specifi cations of such product at any time without notice.
Cashco, Inc. does not assume responsibility for the selection, use or maintenance of any product. Responsibility for proper selection, use and maintenance of any
Cashco, Inc. product remains solely with the purchaser.
10
IOM-DA0
Page 11

Figure 5
Item No. Description
7 Nut
10 Stop Plate
11 Cap Screws
12 Nuts
13 Guide Bearing
14 * Seal
15 * Cage Seal
16 * Wiper Seal
17 Washer
18 Cage Cap Screws
19 Cage
IOM-DA0
Item No. Description
20 * Plug
21 * Seat
22 Spring
23 Body
24 Body Bushing
25 Cover Dome
27 * Dynamic Seal (see Figure 1)
37 * Gasket
90 Washer (on 1/2"- 2" sizes below No.7)
* Recommended Repair Parts.
11
Page 12

Cashco, Inc.
P.O. Box 6
Ellsworth, KS 67439-0006
PH (785) 472-4461
Fax. # (785) 472-3539
www.cashco.com
email: sales@cashco.com
Printed in U.S.A. DA0-IOM
Cashco GmbH
Handwerkerstrasse 15
15366 Hoppegarten, Germany
PH +49 3342 4243135
Fax. No. +49 3342 4243136
www.cashco.com
Email: germany@cashco.com
Cashco do Brasil, Ltda.
Al.Venus, 340
Indaiatuba - Sao Paulo, Brazil
PH +55 11 99677 7177
Fax. No.
www.cashco.com
Email: brazil@cashco.com
 Loading...
Loading...