
AQUAZONE™
50PTH, PTV, PTD026-072
Two-Stage Water Source Heat Pumps
with PURON® Refrigerant (R-410A)
Installation, Start-Up, and Service Instructions
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1,2
GENERAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-29
Step 1 — Check Jobsite. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
Step 2 — Check Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
• STORAGE
•PROTECTION
•INSPECT UNIT
Step 3 — Locate Unit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
• FIELD CONVERSION OF DISCHARGE AIR
Step 4 — Mount the Unit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
• HORIZONTAL UNIT
• VERTICAL UNITS
Step 5 — Check Duct System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
• SO U N D AT T E N U AT I ON
• EXISTING DUCT SYSTEM
Step 6 — Install Condensate Drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
• HORIZONTAL UNIT
• VERTICAL UNITS
• VENTING
Step 7 — Pipe Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
• WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS
• GROUND-WATER APPLICATIONS
• GROUND-LOOP APPLICATIONS
• INSTALLATION OF SUPPLY AND RETURN HOSE
KIT
Step 8 — Wire Field Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
• POWER CONNECTION
• SUPPLY VOLTAGE
• 208-VOLT OPERATION
• 460-VOLT OPERATION
• WSHP OPEN WIRING
Step 9 — Wire Field Controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
• THERMOSTAT CONNECTIONS
• WATER FREEZE PROTECTION
• AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION
• ACCESSORY CONNECTIONS
• WATER SOLENOID VALVES
Step 10 — Operate ECM Interface Board . . . . . . . . 27
• STANDALONE — NO DDC CONTROLS
• WSHP OPEN CONTROLS
PRE-START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29,30
System Checkout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
FIELD SELECTABLE INPUTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30-33
Complete C Control Jumper Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Deluxe D Control Jumper Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Complete C Control DIP Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Deluxe D Control DIP Switches. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Units with Modulating Hot Water Reheat
(HWR) Option . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
• STANDALONE — NO DDC CONTROLS
• WSHP OPEN CONTROLS
• HWR APPLICATION CONSIDERATIONS
• HWR COMPONENT FUNCTIONS
Deluxe D Control Accessory
Relay Configurations. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Page
START-UP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33-38
Operating Limits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Scroll Compressor Rotation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Unit Start-Up Cooling Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Unit Start-Up Heating Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Unit Start-Up with WSHP Open Controls . . . . . . . . 36
Flow Regulation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Flushing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Antifreeze . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Cooling Tower/Boiler Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Ground Coupled, Closed Loop and Plateframe
Heat Exchanger Well Systems . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
OPERATION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38-42
Power Up Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Units with Aquazone™ Complete C Control . . . . . 39
Units with Aquazone Deluxe D Control. . . . . . . . . . 39
Units with WSHP Open Multiple Protocol. . . . . . . . 39
COMPLETE C AND DELUXE D BOARD
SYSTEM TEST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42,43
Test Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
WSHP Open Test Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Retry Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Aquazone Deluxe D Control LED Indicators . . . . . 43
SERVICE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44,45
Filters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Water Coil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Condensate Drain Pans . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Refrigerant System. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Compressor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Fan Motors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Condensate Drain Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Air Coil Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Condenser Cleaning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Checking System Charge . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Refrigerant Charging. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Air Coil Fan Motor Removal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Replacing the WSHP Open Controller’s
Battery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
TROUBLESHOOTING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45-53
Thermistor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Control Sensors
WSHP Open Controller. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Thermostatic Expansion Valves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Stopped or Malfunctioned ECM Motor. . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Moisture Check. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
APPENDIX A — WSHP OPEN SCREEN
CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54-59
50PTH,PTV,PTD START-UP
CHECKLIST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . CL-1, CL-2
IMPORTANT: Read the entire instruction manual before
starting installation.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment can
be hazardous due to system pressure and electrical
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53500079-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50PT-4SI Pg 1 7-10 Replaces: 50PT-3SI
components. Only trained and qualified service personnel
should install, repair, or service air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions such as cleaning coils and filters and replacing filters. All
other operations should be performed by trained service
personnel. When working on air-conditioning equipment, observe precautions in the literature, tags and labels attached to
the unit, and other safety precautions that may apply.
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, maintenance, or use can cause explosion, fire, electrical shock or
other conditions which may cause personal injury or property
damage. Consult a qualified installer, service agency, or a local
distributor or branch for information or assistance. The
qualified installer or agency must use factory-authorized kits or
accessories when modifying this product. Refer to the individual instructions packaged with the kits or accessories when
installing.
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and work
gloves. Use quenching cloth for brazing operations. Have fire
extinguisher available. Read these instructions thoroughly and
follow all warnings or cautions attached to the unit. Consult
local building codes and the National Electrical Code (NEC)
for special installation requirements.
Understand the signal words — DANGER, WARNING,
and CAUTION. DANGER identifies the most serious hazards
which will result in severe personal injury or death.
WARNING signifies hazards that could result in personal injury or death. CAUTION is used to identify unsafe practices,
which would result in minor personal injury or product and
property damage.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert
symbol ( ). When this symbol is displayed on the unit and in
instructions or manuals, be alert to the potential for personal
injury.
WARNING
Electrical shock can cause personal injury or death. Before
installing or servicing system, always turn off main power
to system. There may be more than one disconnect switch.
Turn off accessory heater power if applicable.
GENERAL
This installation and start-up instructions literature is for
Aquazone™ two-stage water source heat pump systems.
Water source heat pumps (WSHPs) are single-package horizontally and vertically mounted units with electronic controls
designed for year-round cooling and heating. Aquazone
WSHPs are available in the following unit configurations:
• 50PTH unit with horizontal airflow and right, left or back
discharge
• 50PTV unit with vertical airflow and top discharge
• 50PTD unit with vertical airflow and bottom discharge
(downflow)
IMPORTANT: The installation of water source heat pump
units and all associated components, parts, and accessories
which make up the installation shall be in accordance with
the regulations of ALL authorities having jurisdiction and
MUST conform to all applicable codes. It is the responsibility of the installing contractor to determine and comply
with ALL applicable codes and regulations.
INSTALLATION
Step 1 — Check Jobsite —
maintenance instructions are provided with each unit. Before
Installation, operation and
unit start-up, read all manuals and become familiar with the
unit and its operation. Thoroughly check out the system before
operation. Complete the inspections and instructions listed
below to prepare a unit for installation. See Table 1 for unit
physical data.
IMPORTANT: This equipment is designed for indoor
installation ONLY. Extreme variations in temperature,
humidity and corrosive water or air will adversely affect
the unit performance, reliability and service life.
HORIZONTAL UNIT (50PTH) —
ed for indoor installation only. Be sure to allow adequate space
around the unit for servicing. See Fig. 1 for overall unit dimensions. Refer to Fig. 2 for an illustration of a typical horizontal
installation.
VERTICAL AND DOWNFLOW UNITS (50PTV, PTD) —
Vertical units are designed for indoor installations. While vertical units are typically installed in a floor-level closet or a small
mechanical room, the unit access guidelines for these units are
very similar to those described for horizontal units. See Fig. 3
and 4 for overall dimensions. Refer to Fig. 5 for an example of
a typical vertical installation. Refer to Fig. 6 for a sample
downflow installation.
Horizontal units are design-
CAUTION
To avoid equipment damage, do not use these units as a
source of heating or cooling during the construction process. The mechanical components and filters used in these
units quickly become clogged with construction dirt and
debris which may cause system damage.
Step 2 — Check Unit — Upon receipt of shipment at
the jobsite, carefully check the shipment against the bill of
lading. Make sure all units have been received. Inspect the carton or crating of each unit, and inspect each unit for damage.
Ensure the shipping company makes proper notation of any
shortages or damage on all copies of the freight bill. Concealed
damage not discovered during unloading must be reported to
the shipping company within 15 days of receipt of shipment.
NOTE: It is the responsibility of the purchaser to file all
necessary claims with the shipping company.
1. Be sure that the location chosen for unit installation provides ambient temperatures maintained above freezing.
Well water applications are especially susceptible to
freezing.
2. Be sure the installation location is isolated from sleeping
areas, private offices and other acoustically sensitive
spaces.
NOTE: A sound control accessory package may be used
to help eliminate sound in sensitive spaces.
3. Check local codes to be sure a secondary drain pan is not
required under the unit.
4. Be sure unit is mounted at a height sufficient to provide
an adequate slope of the condensate lines. If an appropriate slope cannot be achieved, a field-supplied condensate
pump may be required.
5. Provide sufficient space for duct connection. Do not
allow the weight of the ductwork to rest on the unit.
6. Provide adequate clearance for filter replacement and
drain pan cleaning. Do not allow piping, conduit, etc. to
block filter access.
7. Provide sufficient access to allow maintenance and
servicing of the fan and fan motor, compressor and coils.
Removal of the entire unit from the closet should not be
necessary.
2
8. Provide an unobstructed path to the unit within the closet
or mechanical room. Space should be sufficient to allow
removal of unit if necessary.
9. Provide ready access to water valves and fittings, and
screwdriver access to unit side panels, discharge collar,
and all electrical connections.
10. Where access to side panels is limited, pre-removal of the
control box side mounting screws may be necessary for
future servicing.
STORAGE — If the equipment is not needed immediately at
the jobsite, it should be left in its shipping carton and stored in a
clean, dry area of the building or in a warehouse. Units must be
stored in an upright position at all times. If carton stacking is
necessary, stack units a maximum of 3 high. Do not remove
any equipment from its shipping package until it is needed for
installation.
PROTECTION — Once the units are properly positioned on
the jobsite, cover them with either a shipping carton, vinyl film,
or an equivalent protective covering. Cap open ends of pipes
stored on the jobsite. This precaution is especially important in
areas where painting, plastering, or spraying of fireproof material, etc. is not yet complete. Foreign material that accumulates
within the units can prevent proper start-up and necessitate
costly clean-up operations.
Before installing any of the system components, be sure to
examine each pipe, fitting, and valve, and remove any dirt or
foreign material found in or on these components.
CAUTION
DO NOT store or install units in corrosive environments or
in locations subject to temperature or humidity extremes
(e.g., attics, garages, rooftops, etc.). Corrosive conditions
and high temperature or humidity can significantly reduce
performance, reliability, and service life. Always move
units in an upright position. Tilting units on their sides may
cause equipment damage.
INSPECT UNIT — To prepare the unit for installation, complete the procedures listed below:
1. Compare the electrical data on the unit nameplate with
ordering and shipping information to verify that the
correct unit has been shipped.
2. Do not remove the packaging until the unit is ready for
installation.
3. Verify that the unit’s refrigerant tubing is free of kinks or
dents, and that it does not touch other unit components.
4. Inspect all electrical connections. Be sure connections are
clean and tight at their terminations.
5. Loosen compressor bolts until the compressor rides freely
on springs. Remove shipping restraints.
6. Remove the four
1
/4 in. shipping bolts from compressor
support plate (two bolts on each side) to maximize vibration and sound alternation.
CAUTION
Failure to remove shipping brackets from spring-mounted
compressors will cause excessive noise and could cause
component failure due to added vibration.
7. Remove any blower support cardboard from inlet of the
blower.
8. Locate and verify any accessory kit located in compressor
and/or blower section.
9. Remove any access panel screws that may be difficult to
remove once unit is installed.
Table 1 — Physical Data — 50PTH, PTV, PTD026-072 Units
UNIT 50PTH, PTV, PTD 026 038 049 064 072
COMPRESSOR (1 each) Two- St a g e, Sc r oll
FACTORY CHARGE R-410A (oz) 58 78 81 144 156
ECM FAN MOTOR AND BLOWER
Fan Motor Type VAR VAR VAR VA R VAR
Fan Motor (Hp)
Blower Wheel Size (D x W) (in.) 9 x 7 11 x 10 11x10 11x10 11x10
COAXIAL COIL VOLUME (gal.) .76 .92 1.24 1.56 1.56
WATER CONNECTION SIZE (FPT) (in.)
HWG CONNECTION SIZE (FPT) (in.)
VERTICAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) 28 x 20 28 x 25 32 x 25 36 x 25 36 x 25
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway
(Qty — Size) (in.)
Weight (lb)
Operating 266 327 416 443 443
Packag ed 276 337 426 453 453
HORIZONTAL
Air Coil
Dimensions (H x W) (in.) 18 x 31 20 x 25 20 x 40 20 x 45 20 x 45
Filter Standard — 1-in. Throwaway
(Qty — Size) (in.)
Weight (lb)
Operating 266 327 416 443 443
Packag ed 276 337 426 453 453
LEGEND
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
HWG — Hot Water Generator
VAR — Variable Speed
NOTE: All units have spring compressor mountings, TXV (thermostatic expansion valve) expansion devices, and
1
/2 and 3/4-in. electrical knockouts.
1
/
2
3
/
4
1
/
2
1 — 28 x 24 1 — 28 x 30 2 — 16 x 30
2 — 18 x 18
1
/
2
3
/
4
1
/
2
1 — 12 x 20
1 — 20 x 24
111
111
1
/
2
1 — 18 x 20
1 — 20 x 24
1
/
2
1 — 16 x 30
1 — 20 x 30
2 — 20 x 24 2 — 20 x 24
1 — 16 x 30
1 — 20 x 30
1
/
2
3
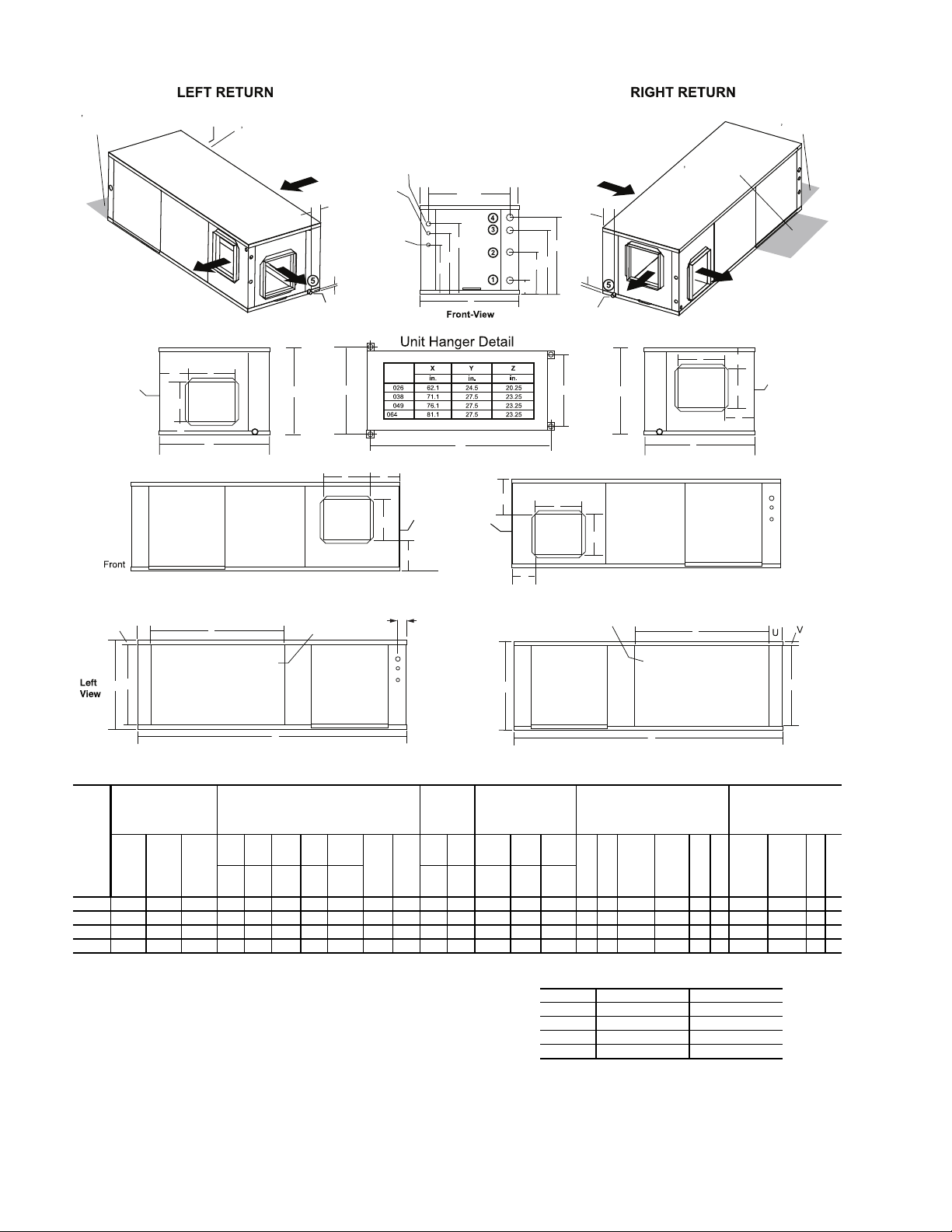
Y Configuration - Left Return/Back Discharge
W Configuration - Left Return/Right Discharge - Air Coil Opening
W Configuration - Left Return/Right Discharge - Air Coil Opening
P Configuration - Right Return/Back Discharge - Air Coil Opening
N Configuration - Right Return/Left Discharge - Air Coil Opening
N Configuration - Right Return/Left Discharge - Air Coil Opening
Left
View
Right
View
Size
Right
View
ASP
BSP
Q
P
O
R
Blower
Outlet
Air Coil Side
C
A
Y
Front
X
Z
C
P
A
R
O
Q
BSP
Left
Discharge
Back
Discharge
Condensate
3/4” FPT
H
CSP
Front
2 Service Access
Right Return
2 Service Access
3.25”
G
F
E
D
CAP
J
K
L
A
Powe r Supply
3/4” Knockout
1/2”
Knockout
Low Voltage
1/2” Knockout
Front
CSP
ASP
Left Return
Right
Discharge
Back
Discharge
Condensate
3/4” FPT
H
2 Service
Access
2 Service Access
Air Coil Side
Blower
Outlet
BSP
P
M
N
O
Blower
Outlet
S
U
V
C
T
B
CSP
Front Front
Air Coil
1.1”
C
Air Coil
ASP
S
B
T
Front
CSP
M
BSP
Blower
Outlet
O
P
N
3.25”
1.6”
, 072
NOTES:
1. Condensate connection is stainless steel
3
/4 in. female pipe thread (FPT).
2. Unit shipped with top and bottom filter rack and is not suitable for duct connection without
additional suppor t.
3. Discharge flange is factory-installed.
4. Hanger kit is factory-installed.
5. Shaded areas are recommended service areas, not required.
6. Discharge can be modified in field. Return cannot be modified.
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
50PTH
UNIT
OVERALL CABINET
(in.)
WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
WATER
CONNEC-
TIONS (in.)
- UNITS
WITH HWR
ELECTRICAL
KNOCKOUTS (in.)
DISCHARGE CONNECTIONS (in.)
DUCT FLANGE INSTALLED
( 0.10 in.)
RETURN CONNECTION
USING AIR COIL
OPENING (in.)
A
WidthBDepthCHeight
123 4 5
Loop
Wate r
FPT
(in.)
HWG
FPT
(in.)
12
J
1
/2-in.
Cond
K
1
/2-in.
Cond
L
3
/4-in.
Cond
M
(LH
rtn)
NOSupply
Height
P
Supply
Width
Q
(RH
rtn)
RSReturn
Width
T
Return
Height
UV
DInE
Out
F
HWG
In
G
HWG
Out
H
Condensate
Loop
in D
Loop
out E
Low
Vol ta ge
Ext
Pump
Power
Supply
026 22.4 62.2 19.3 2.1 10.0 13.9 16.9 3.53/
4
1
/22.1 10.0 3.6 6.1 8.6 3.6 2.0 12.5 15.5 3.6 2.0 33.8 16.2 2.3 1.5
038 25.4 71.2 21.3 3.4 10.8 14.6 18.9 3.43/
4
1
/25.96 13.13 3.4 6.1 8.6 3.1 1.2 19.0 17.5 3.1 1.0 34.8 18.2 3.1 1.5
049 25.4 76.2 21.3 3.4 10.8 15.6 18.9 3.4 11/25.96 13.13 3.6 6.1 8.6 3.1 1.2 19.0 17.5 3.1 1.0 39.8 18.2 3.1 1.5
064,072 25.4 81.2 21.3 3.4 10.8 15.6 18.9 3.4 11/25.96 13.13 3.6 6.1 8.6 3.1 1.2 19.0 17.5 3.1 1.0 44.8 18.2 3.1 1.5
CODE RETURN DISCHARGE
N Right Left
P Right Back
W Left Right
Y Left Back
LEGEND
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
FPT — Female Pipe Thread
HWG — Hot Water Generator
HWR — Hot Water Reheat
Fig. 1 — 50PTH026-072 Dimensional Data
4
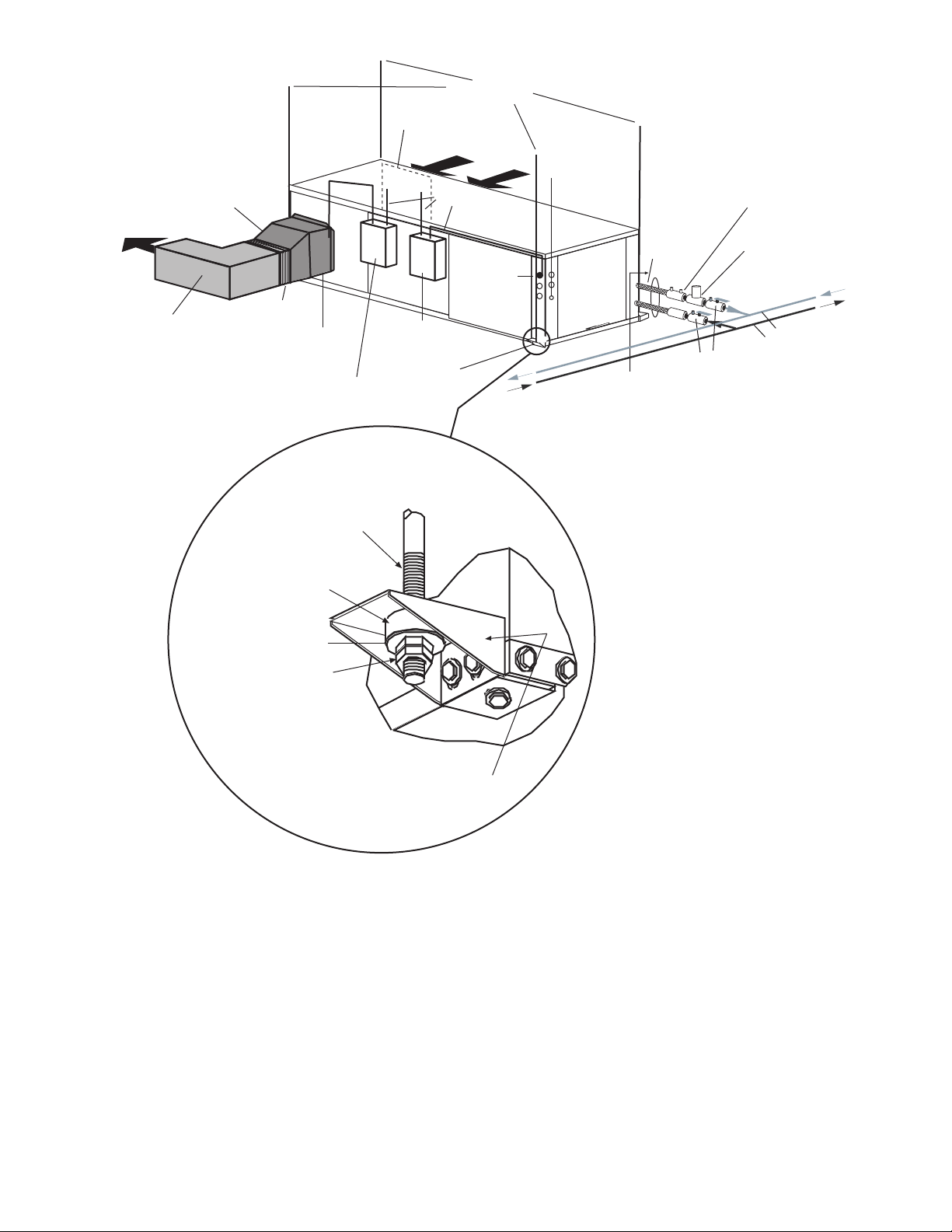
Field-Supplied
Electric Heat
(if applicable)
Filter Access
Integral hanger supportpre-attached in factory
Field-supplied transition to
minimize pressure loss
3/8” threaded rods
(by others)
Return Air
(Ductwork
not shown)
Thermostat
Wiring
Power Wiring
Balancing Valve (fieldinstalled accessory)
Stainless steel
braid hose
with integral
“J” swivel
3/8” Threaded
Rod (by others)
Supply Air
Insulated supply duct with
at least one 90 degree elbow
to reduce air noise
(field-supplied)
Flexible
Connection
Vibration Isolator
(white-compressor end
and red-blower end)
Washer
(by others)
Double Hex Nuts
(by others)
Unit Power
Unit Power
Disconnect
(by others)
Unit Hanger
(factorysupplied)
Low Pressure Drop Water
Control Valve (optional)
(field-installed accessory)
Ball Valve with optional
integral P/T plug (typical for supply
and return piping)
(field-installed accessory)
(field-installed
accessory)
Aux Electric
Heat Disconnect
Water In
Water Out
Building
Loop
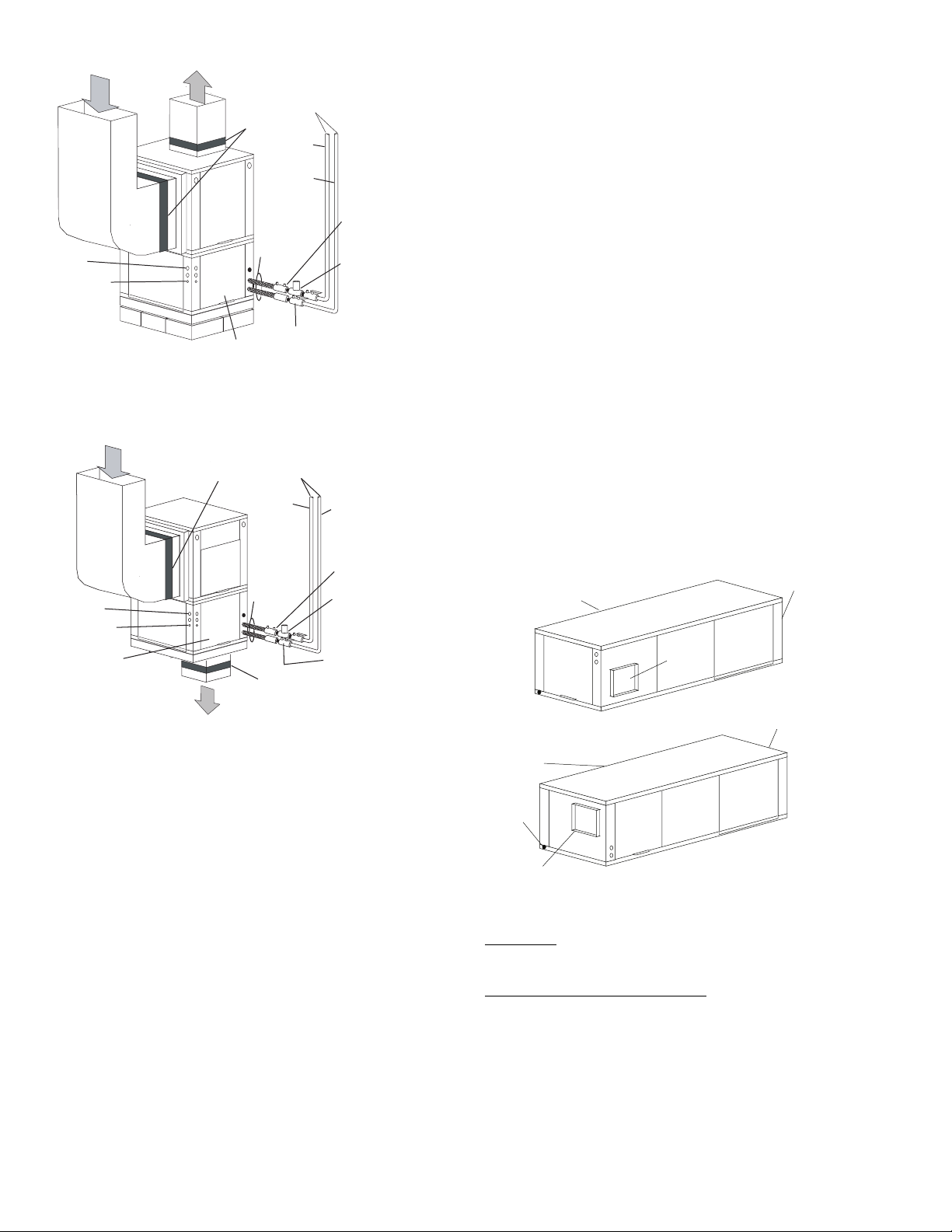
Fig. 2 — Typical Installation — 50PTH Unit
UNIT HANGER ISOLATION DETAIL
5
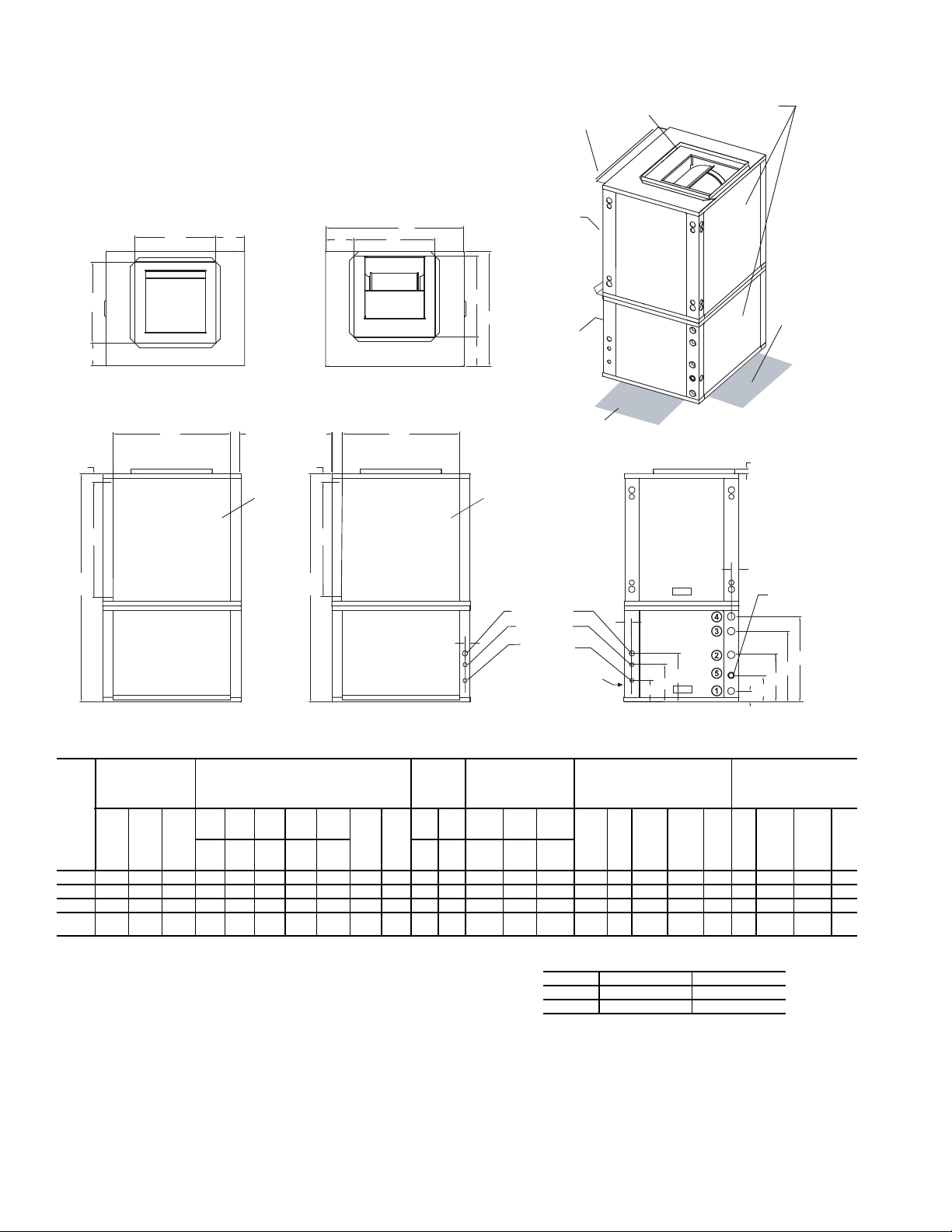
Filter Bracket
NOTES:
1. Condensate connection is stainless steel 3/4 in. female pipe thread (FPT).
2. Unit shipped with top and bottom filter rack and is not suitable for duct connection without
additional support.
3. Discharge flange is field-installed.
4. Shaded areas are recommended service areas, not required.
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
50PTV
UNIT
OVERALL CABINET
(in.)
WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
WATER
CONNEC-
TIONS (in.)
- UNITS
WITH HWR
ELECTRICAL
KNOCKOUTS (in.)
DISCHARGE CONNECTIONS (in.)
DUCT FLANGE INSTALLED
( 0.10 in.)
RETURN CONNECTION
USING AIR COIL OPENING
(in.)
A
WidthBDepthCHeight
123 4 5
Loop
Wate r
FPT
(in.)
HWG
FPT
(in.)
12
J
1
/2-in.
Cond
K
1
/2-in.
Cond
L
3
/4-in.
Cond
M
(LH
rtn)
NOSupply
Width
P
Supply
Depth
Q
(RH
rtn)
RSReturn
Depth
T
Return
Height
U
DInE
Out
F
HWG
In
G
HWG
Out
H
Condensate
Loop
in D
Loop
out E
Low
Vol ta ge
Ext
Pump
Power
Supply
026 22.4 25.6 48.5 2.1 10.0 13.9 16.9 7.8
3
/
4
1
/22.1 10.0 3.6 6.1 8.6 7.2 5.8 14.0 14.0 4.9 2.2 21.1 27.2 1.0
038 25.4 30.6 50.5 3.4 10.8 15.6 18.9 7.83/
4
1
/25.96 13.13 3.6 6.1 8.6 6.4 6.3 18.0 18.0 5.3 2.2 26.1 27.2 1.0
049 25.4 30.6 54.5 3.4 10.8 15.6 18.9 7.8 11/25.96 13.13 3.6 6.1 8.6 6.4 6.3 18.0 18.0 5.3 2.2 26.1 31.2 1.0
064,
072
25.4 30.6 58.5 3.4 10.8 15.6 18.9 7.8 11/25.96 13.13 3.6 6.1 8.6 6.4 6.3 18.0 18.0 5.3 2.2 26.1 35.2 1.0
CODE RETURN DISCHARGE
J Left Top
K Right Top
LEGEND
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
FPT — Female Pipe Thread
HV — High Voltage
HWG — Hot Water Generator
HWR — Hot Water Reheat
LV — Low Voltage
Fig. 3 — 50PTV Dimensional Data
Field-Installed
Discharge Flange
(shipped loose inside
blower section)
Access Panels
Front
O
Q
K - Configuration - Right Return
/Top Discharge
U
T
C
Front
K - Configuration - Right Return -
Air Coil Opening
(Right Side View)
P
Air Coil Side
(Top View)
S
ASP
B
N
R
N
J - Configuration - Left Return
R
P
Air Coil Side
/Top Discharge
(Top View)
S
Front
U
Air Coil
T
C
1.18”
CSP
Back Back Front
J - Configuration - Left Return -
Air Coil Opening
(Left Side View)
O
M
A
Air Coil
Air Coil
Power Supply
3/4”
HV Knockout
1/2”
Knockout
Low Voltage
1/2”
LV Knockout
CSP
2ʼ Service Access
CSP
BSP
CAP
1.63”
J
K
Front View
Isometric View
CAP
L
ASP
ASP
1.00”
1.68”
D
Condensate
3/4” FPT
H
2ʼ Service Access
G
F
E
6
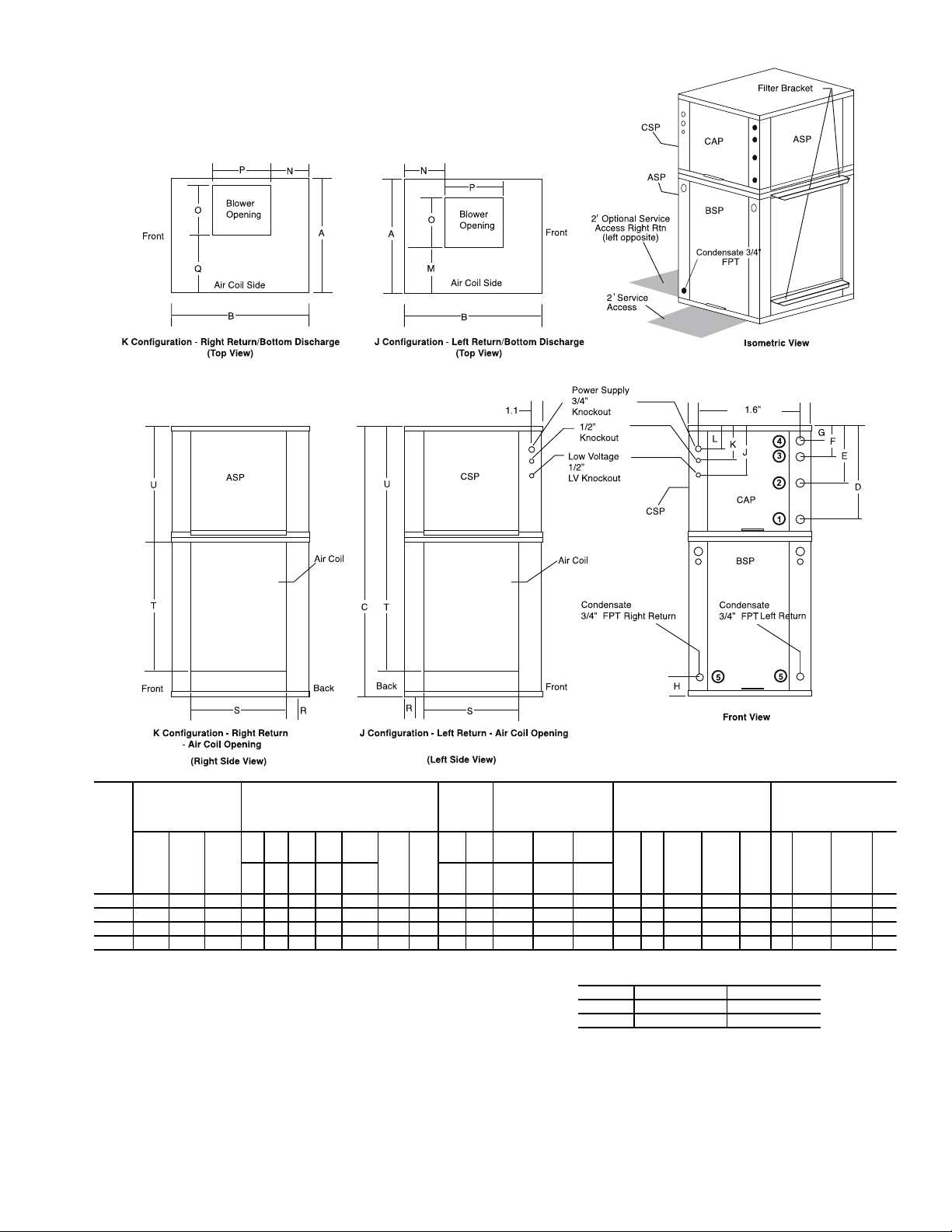
NOTES:
1. Condensate connection is stainless steel 3/4 in. female pipe thread (FPT).
2. Unit shipped with top and bottom filter rack and is not suitable for duct connection without
additional support.
3. Downflow unit does not have discharge flange, and is rated for zero clearance installation.
4. Shaded areas are recommended service areas, not required.
AIRFLOW CONFIGURATION
50PTD
UNIT
OVERALL CABINET
(in.)
WATER CONNECTIONS (in.)
WATER
CONNEC-
TIONS (in.)
- UNITS
WITH HWR
ELECTRICAL
KNOCKOUTS (in.)
DISCHARGE CONNECTIONS (in.)
DUCT FLANGE INSTALLED
( 0.10 in.)
RETURN CONNECTION (in.)
USING AIR COIL OPENING
A
WidthBDepthCHeight
12 3 4 5
Loop
Wate r
FPT
(in.)
HWG
FPT
(in.)
12
J
1
/2-in.
Cond
K
1
/2-in.
Cond
L
3
/4-in.
Cond
M
(LH
rtn)
NOSupply
Width
P
Supply
Depth
Q
(RH
rtn)
RSReturn
Depth
T
Return
Height
U
DInE
Out
F
HWG
In
G
HWG
Out
H
Cond-
ensate
Loop
in D
Loop
out E
Low
Vol t ag e
Ext
Pump
Power
Supply
026 22.4 25.6 52.5 2.1 10.0 13.9 16.9 3.63/
4
1
/22.1 10.0 3.6 6.1 8.6 6.7 8.4 10.1 9.1 10.8 2.2 21.1 27.2 1.0
038 25.4 30.6 54.5 3.4 10.8 15.6 18.9 3.63/
4
1
/25.96 13.13 3.6 6.1 8.6 7.2 9.0 13.4 12.9 10.4 2.2 26.1 27.2 1.0
049 25.4 30.6 58.5 3.4 10.8 15.6 18.9 3.6 11/25.96 13.13 3.6 6.1 8.6 7.2 9.0 13.4 12.9 10.4 2.2 26.1 31.4 1.0
064,072 25.4 30.6 62.5 3.4 10.8 15.6 18.9 3.6 11/25.96 13.13 3.6 6.1 8.6 7.2 9.0 13.4 12.9 10.4 2.2 26.1 35.2 1.0
CODE RETURN DISCHARGE
J Left Bottom
K Right Bottom
LEGEND
ASP — Alternate Service Panel
BSP — Blower Service Panel
CAP — Control Access Panel
CSP — Compressor Service Panel
FPT — Female Pipe Thread
HWG — Hot Water Generator
HWR — Hot Water Reheat
Fig. 4 — 50PTD Dimensional Data
7
• Provide adequate clearance for filter replacement and
Return
Air
Power
Thermostat
Wiring
Compressor
Access Panel
Balancing Valve
(field-installed
accessory)
Low Pressure
Drop Water
Control Valve
(optional)
(field-installed
accessory)
Ball Valve with optional
integral P/T plug
(typical for supply and
return piping) (field-Installed
accessory)
Water
Out
Water
In
Building
Loop
Supply Air
Flexible
Connection
Stainless steel
braid hose
with integral
“J” swivel
(field-installed
accessory)
Return
Air
Power
Thermostat
Wiring
Compressor
Access Panel
Balancing Valve
(field-installed
accessory)
Low Pressure
Drop Water
Control Valve
(optional)
(field-installed
accessory)
Ball Valve with
optional integral
P/T plug (typical for
supply and return
piping)(field-installed
accessory)
Water
Out
Water
In
Building
Loop
Supply Air
Flexible
Connection
Flexible
Connection
Stainless
steel
braid hose
with
integral ”J”
swivel(fieldinstalled
accessory)
NOTE: Ball valve with integral pressure temperature plug recommended.
Fig. 5 — Typical Vertical Installation — 50PTV Unit
NOTE: Ball valve with integral pressure temperature plug recommended.
Fig. 6 — Typical Downflow Installation —
50PTD Unit
Water
Connection End
Supply
Duct
Return Air
Water
Connection End
Drain
Return Air
Discharge Air
Side Discharge
Back Discharge
Fig. 7 — Conversion Right Return,
Side Discharge to Back Discharge
drain pan cleaning. Do not block filter access with piping, conduit or other materials. Refer to Fig. 1, 3, and 4
for dimensional data.
• Provide access for fan and fan motor maintenance and
for servicing the compressor and coils without removing
the unit.
• Provide an unobstructed path to the unit within the closet
or mechanical room. Space should be sufficient to allow
removal of the unit, if necessary.
• In limited side access installations, pre-removal of the
control box side mounting screws will allow control box
removal for future servicing.
• Provide access to water valves and fittings and screwdriver access to the unit side panels, discharge collar and
all electrical connections.
NOTE: Correct placement of the horizontal unit can play an
important part in minimizing sound problems. Since ductwork is normally applied to these units, the unit can be
placed so that the principal sound emission is outside the occupied space in sound-critical applications. A fire damper
may be required by the local code if a fire wall is penetrated.
FIELD CONVERSION OF DISCHARGE AIR — The discharge air of the 50PTH horizontal units can be converted
between side and back discharge in the field. The conversion
process is the same for right and left return configurations. See
Fig. 7 and 8.
NOTE: It is not possible to convert return air between left or
right return models in the field due to refrigerant piping
changes.
Step 3 — Locate Unit — The following guidelines
should be considered when choosing a location for a WSHP:
• Units are for indoor use only.
• Locate in areas where ambient temperatures are between
39 F and 102 F and relative humidity is no greater than
75%.
• Provide sufficient space for water, electrical and duct
• Locate unit in an area that allows easy access and removal
• Allow enough space for service personnel to perform
• Return air must be able to freely enter the space if unit needs
• Install the unit on a piece of rubber, neoprene or other
connections.
of filter and access panels.
maintenance.
to be installed in a confined area such as a closet.
mounting pad material for sound isolation. The pad
should be at least
3
/8 in. [10 mm] to 1/2 in. [13 mm] in
thickness. Extend the pad beyond all four edges of the
unit.
Preparation
— The unit should be on the ground in a well lit
area. Hung units should be taken down to ground level before
converting.
Side to Back Discharge Conversion
1. Remove screws to free the top and discharge panels. Set
screws aside for later use. See Fig. 8.
2. Remove the access panel and set aside.
3. Lift the discharge panel from side of unit and rotate it to
back using care not to damage blower wiring.
4. Check blower wire routing and connections for undue
tension or contact with sheet metal edges. Re-route if
necessary.
8
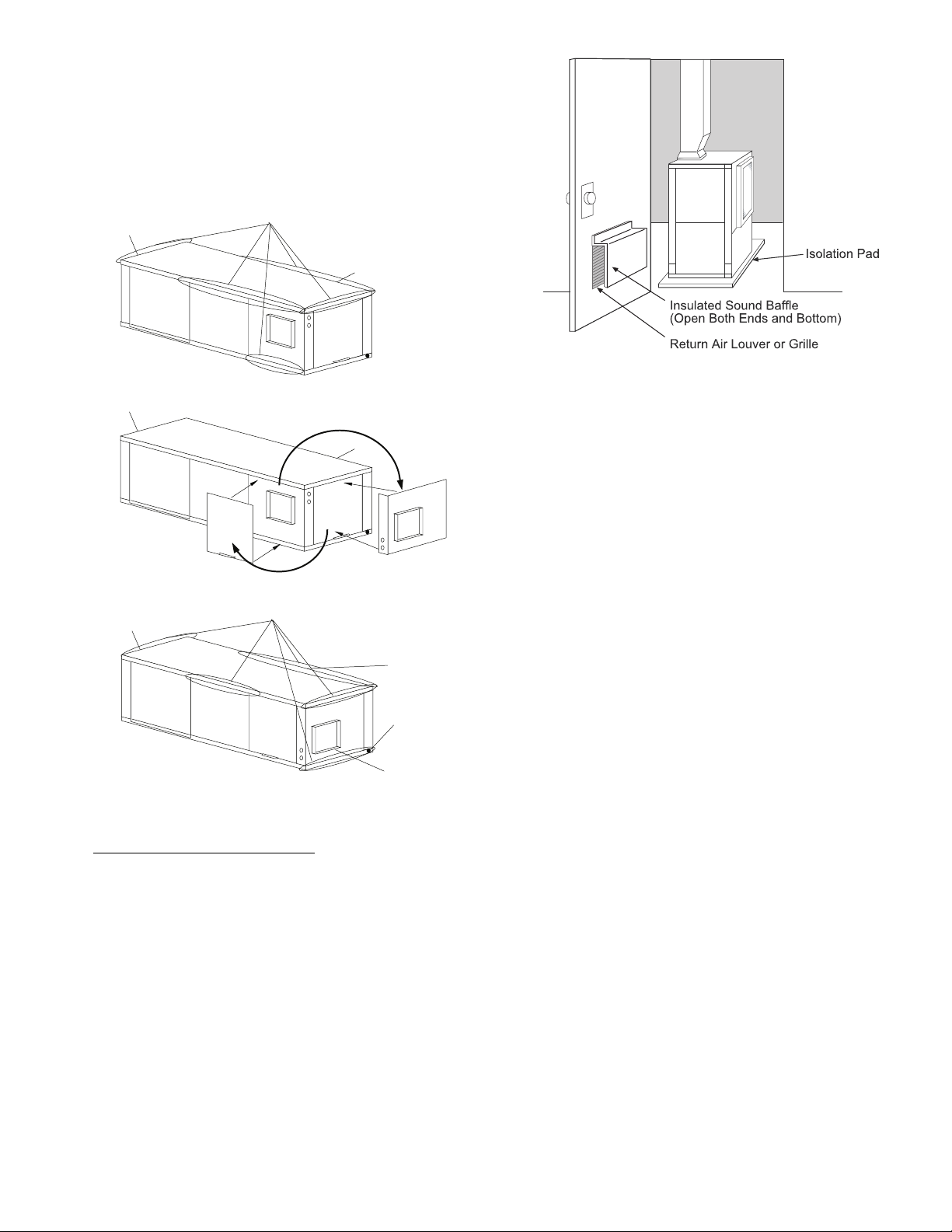
Fig. 9 — 50PTV Units Mounted With
Vibration Absorption Pad
Return Air
Remove Screws
Return Air
Rotate
Move to Side
Side Discharge
Return Air
Discharge Air
Drain
Back Discharge
Replace Screws
Water
Connection End
Water
Connection End
Water
Connection End
Fig. 8 — Conversion Left Return,
Side Discharge to Back Discharge
5. Check refrigerant tubing for contact with other components. Adjust if necessary.
6. Reinstall top panel using screws set aside in Step 1.
NOTE: Location for some screws at bottom of discharge
panel may have to be changed.
7. Manually spin fan wheel to check for obstructions.
Adjust for any obstruction found.
8. Replace access panel.
Back to Side Discharge Conversion
above for Side to Back Discharge Conversion, noting the
panels would be reversed.
— Follow instructions
Step 4 — Mount the Unit
HORIZONTAL UNIT (50PTH) — Horizontal units should
be mounted using the factory-installed hangers. Proper attachment of hanging rods to building structure is critical for safety.
See Fig. 1. Rod attachments must be able to support the weight
of the unit. See Table 1 for unit operating weights.
VERTICAL UNITS (50PTV,PTD) — Vertical and downflow
units are available in left or right return air configurations. See
Fig. 3 and 4. Mount the unit (except 50PTD) on a vibration
absorption pad slightly larger than the entire base to minimize
vibration transmission. It is not necessary to mount the unit on
the floor. See Fig. 9.
NOTE: Some codes require the use of a secondary drain pan
under vertical units. Check local codes for more information.
Step 5 — Check Duct System — Size the duct sys-
tem to handle the design airflow quietly.
NOTE: Depending on the unit, the fan wheel may have a shipping support installed at the factory. This must be removed
before operating unit.
SOUND ATTENUATION — To eliminate the transfer of
vibration to the duct system, a flexible connector is recommended for both discharge and return air duct connections on
metal duct systems. The supply and return plenums should include internal duct liner of fiberglass or be made of duct board
construction to maximize sound attenuation of the blower.
Installing the WSHP unit to uninsulated ductwork in an unconditioned space is not recommended since it will sweat and
adversely affect the unit’s performance.
To reduce air noise, at least one 90-degree elbow could be
included in the supply and return air ducts, provided system
performance is not adversely impacted. The blower speed can
also be changed in the field to reduce air noise or excessive airflow, provided system performance is not adversely impacted.
EXISTING DUCT SYSTEM — If the unit is connected to
existing ductwork, consider the following:
• Verify that the existing ducts have the proper capacity to
handle the unit airflow. If the ductwork is too small, install
larger ductwork.
• Check existing ductwork for leaks and repair as necessary.
NOTE: Local codes may require ventilation air to enter the
space for proper indoor air quality. Hard-duct ventilation
may be required for the ventilating air supply. If hard
ducted ventilation is not required, be sure that a proper air
path is provided for ventilation air to unit to meet ventila-
tion requirement of the space.
Step 6 — Install Condensate Drain
HORIZONTAL UNIT (50PTH) — Slope the unit toward the
drain at
quired pitch, install a condensate at the unit to pump condensate to building drain.
ternal trap is necessary. Install each unit with its own individual
trap and means to flush or blow out the condensate drain line.
Do not install units with a common trap or vent. See Fig. 11 for
typical condensate connections.
NOTE: Never use a pipe size smaller than the connection.
VERTICAL UNITS (50PTV,PTD) — Each unit uses a condensate hose inside all cabinets as a trapping loop, therefore an
external trap is not necessary. See Fig. 12.
1
/4 in. See Fig. 10. If it is not possible to meet the re-
Horizontal units are not internally trapped, therefore an ex-
9
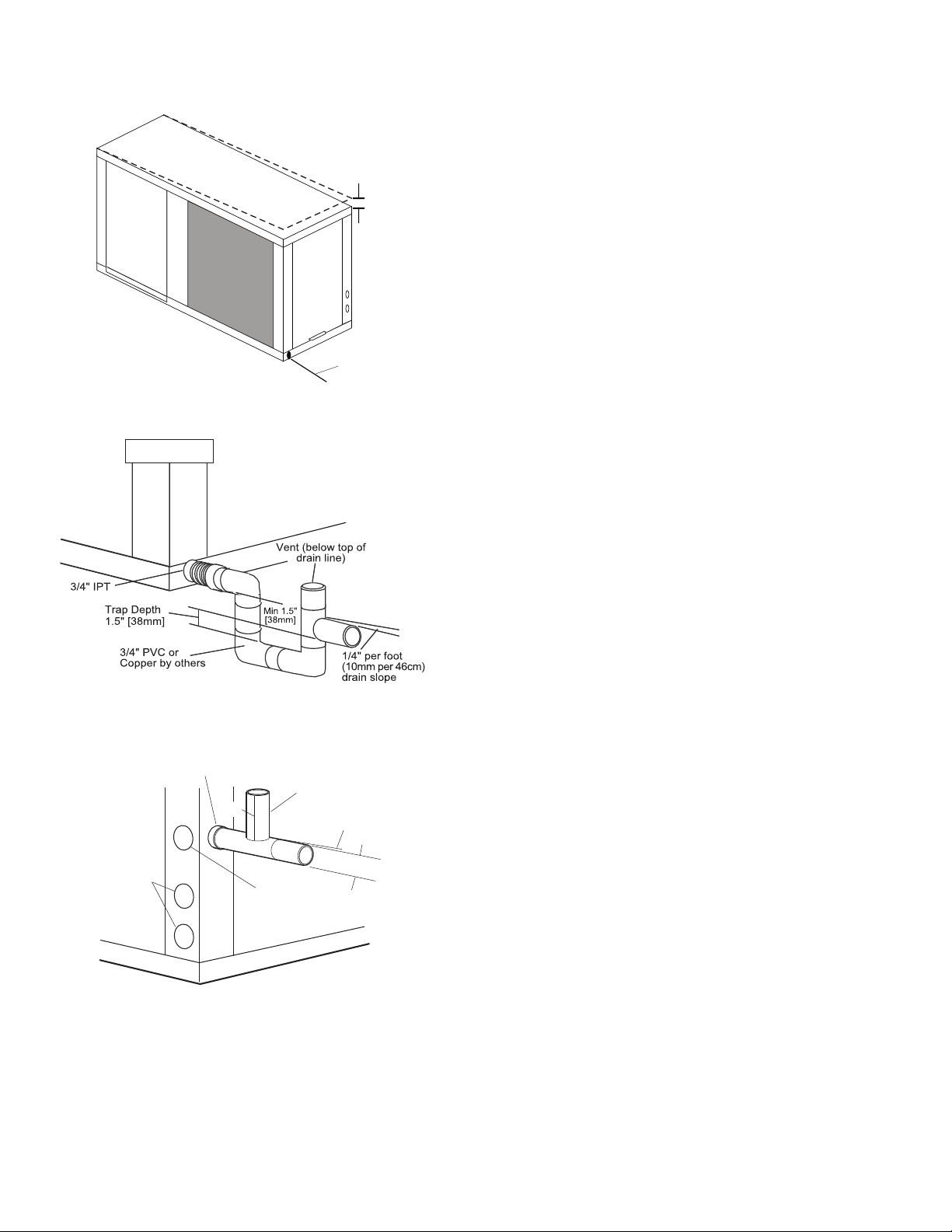
Each unit must be installed with its own individual vent and
NOTE: Trap should be deep enough to offset maximum unit static
difference. A 4-in. trap is recommended.
Fig. 11 — Trap Condensate Drain
Alternate
Condensate
Location
Vent
1/4” per foot
slope to drain
3/4” Copper FPT/PVC
Water
Connections
1/2”
1/2”
3/4” PVC
NOTE: Unit does not need to be sloped toward drain.
Fig. 12 — Vertical Condensate Connection
1/4” Pitch for
Drainage
Drain Connection
Pitch Toward
Drain
Fig. 10 — Horizontal Unit Pitch
means to flush or blow out the condensate drain line. Do not install units with a common trap or vent.
VENTING — Install a vent in the condensate line of any
application that may allow dirt or air to collect in the line. Consider the following:
• Always install a vent where an application requires a long
horizontal run.
• Always install a vent where large units are working against
higher external static pressure and to allow proper drainage
for multiple units connected to the same condensate main.
• Be sure to support the line where anticipated sagging from
the condensate or when “double trapping” may occur.
• If condensate pump is present on unit, be sure drain connections have a check valve to prevent back flow of condensate
into other units.
Step 7 — Pipe Connections — Depending on the
application, there are 3 types of WSHP piping systems to
choose from: water loop, ground-water and ground loop. Refer
to Piping Section of Carrier System Design Manual for additional information.
All WSHP units use low temperature soldered female pipe
thread fittings for water connections to prevent annealing and
out-of-round leak problems which are typically associated with
high temperature brazed connections. Refer to Table 1 for connection sizes. When making piping connections, consider the
following:
• Use a backup wrench when making screw connections to
unit to prevent internal damage to piping.
• Insulation may be required on piping to avoid condensation
in the case where fluid in loop piping operates at temperatures below dew point of adjacent air.
• Piping systems that contain steel pipes or fittings may be
subject to galvanic corrosion. Dielectric fittings may be
used to isolate the steel parts of the system to avoid galvanic
corrosion.
WATER LOOP APPLICATIONS — Water loop applications
usually include a number of units plumbed to a common piping system. Maintenance to any of these units can introduce air
into the piping system. Therefore, air elimination equipment
comprises a major portion of the mechanical room plumbing.
The flow rate is usually set between 2.25 and 3.5 gpm per
ton of cooling capacity. For proper maintenance and servicing,
pressure-temperature (P/T) ports are necessary for temperature
and flow verification.
Cooling tower/boiler systems typically utilize a common
loop maintained at 60 to 95 F. The use of a closed circuit evaporative cooling tower with a secondary heat exchange between
the tower and the water loop is recommended. If an open type
cooling tower is used continuously, chemical treatment and filtering will be necessary.
In addition to complying with any applicable codes, consid-
er the following for system piping:
• Piping systems using water temperatures below 50 F
• Avoid all plastic to metal threaded fittings due to the poten-
• Teflon tape thread sealant is recommended to minimize
• Use backup wrench. Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Flush the piping system prior to operation to remove dirt
GROUND-WATER APPLICATIONS — Typical groundwater piping is shown in Fig. 13. In addition to complying
with any applicable codes, consider the following for system piping:
• Install shut-off valves for servicing.
• Install pressure-temperature plugs to measure flow and
• Connect boiler drains and other valves using a “T” connec-
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Use PVC SCH80 or copper piping material.
NOTE: PVC SCH40 should not be used due to system high
pressure and temperature extremes.
10
1
require
/2-in. closed cell insulation on all piping surfaces to
eliminate condensation.
tial to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
internal fouling of the heat exchanger.
and foreign materials from the system.
temperature.
tor to allow acid flushing for the heat exchanger.
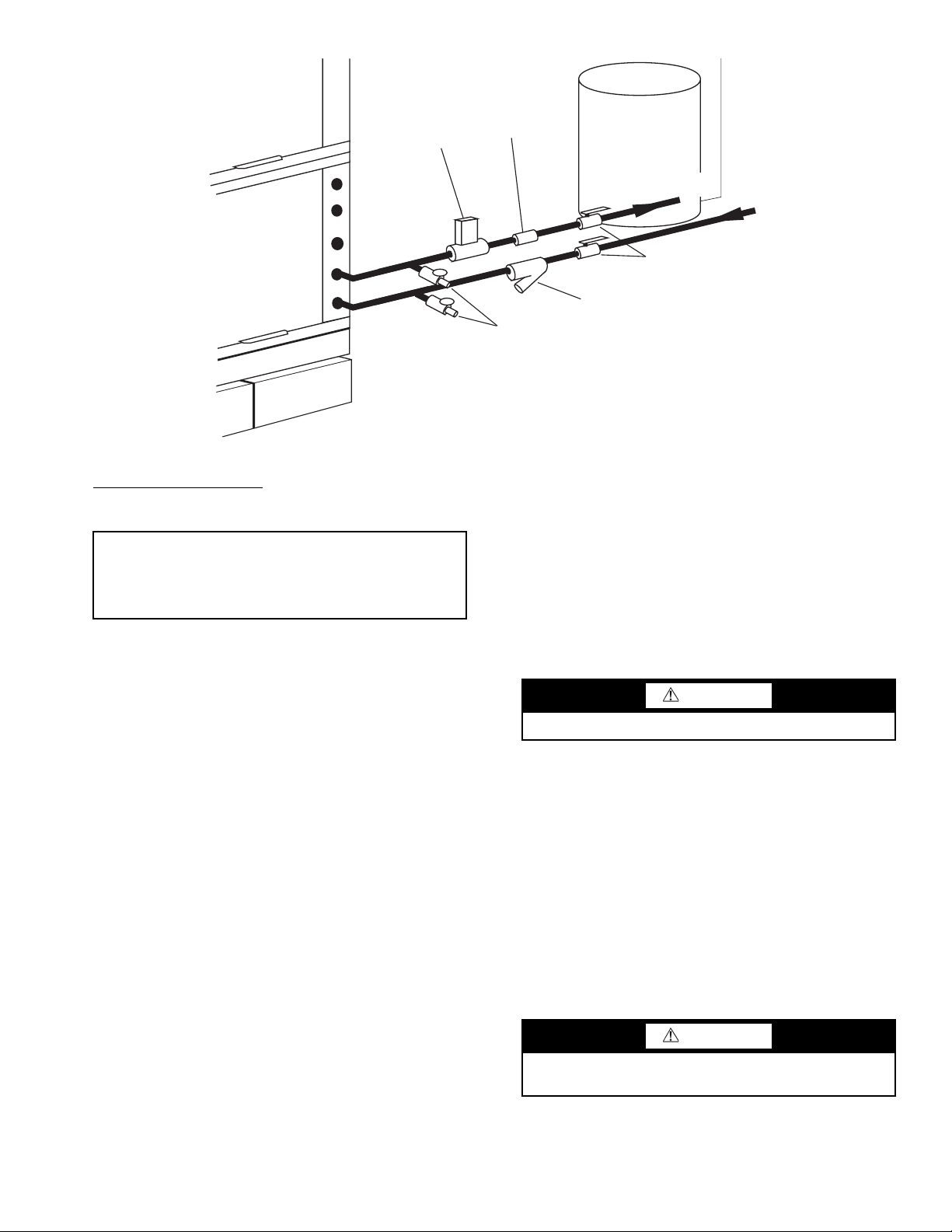
Water Supply and Quantity
Boiler
Drains
(field-installed)
Strainer (field-installed accessory)
(16 to 20 mesh recommended for
filter sediment)
Shut-Off
Valve (field-installed accessory)
Water
Control
Valve
(field-installed
accessory)
Flow
Regulator
(field-installed
accessory)
Pressure
Ta nk
Water Out
Water In
From Pump
Fig. 13 — Typical Ground-Water Piping Installation
— Check water supply. Water
supply should be plentiful and of good quality. See Table 2 for
water quality guidelines.
IMPORTANT: Failure to comply with the above required
water quality and quantity limitations and the closedsystem application design requirements may cause damage
to the tube-in-tube heat exchanger. This damage is not the
responsibility of the manufacturer.
In all applications, the quality of the water circulated
through the heat exchanger must fall within the ranges listed in
the Water Quality Guidelines table. Consult a local water treatment firm, independent testing facility, or local water authority
for specific recommendations to maintain water quality within
the published limits.
GROUND-LOOP APPLICATIONS — Temperatures between
25 and 110 F and a cooling capacity of 2.25 to 3 gpm of flow
per ton is recommended. In addition to complying with any
applicable codes, consider the following for system piping:
• Limit piping materials to only polyethylene fusion in the
buried sections of the loop.
• Do not use galvanized or steel fittings at any time due to
corrosion.
• Avoid all plastic to metal threaded fittings due to the poten-
tial to leak. Use a flange fitted substitute.
• Do not overtighten connections.
• Route piping to avoid service access areas to unit.
• Use pressure-temperature (P/T) plugs to measure flow of
pressure drop.
INSTALLATION OF SUPPLY AND RETURN HOSE
KIT — Follow these piping guidelines.
1. Install a drain valve at the base of each supply and return
riser to facilitate system flushing.
2. Install shutoff/balancing valves and unions at each unit to
permit unit removal for servicing.
3. Place strainers at the inlet of each system circulating
pump.
4. Select the proper hose length to allow slack between connection points. Hoses may vary in length by +2% to –4%
under pressure.
5. Refer to Table 3. Do not exceed the minimum bend radius
for the hose selected. Exceeding the minimum bend radius may cause the hose to collapse, which reduces water
flow rate. Install an angle adapter to avoid sharp bends
in the hose when the radius falls below the required
minimum.
NOTE: Piping must comply with all applicable codes.
Insulation is not required on loop water piping except where
the piping runs through unheated areas or outside the building
or when the loop water temperature is below the minimum expected dew point of the pipe ambient. Insulation is required if
loop water temperature drops below the dew point.
Do not bend or kink supply lines or hoses.
Pipe joint compound is not necessary when Teflon threaded
tape is pre-applied to hose assemblies or when flared-end
connections are used. If pipe joint compound is preferred, use
compound only in small amounts on the male pipe threads of
the fitting adapters. Prevent sealant from reaching the flared
surfaces of the joint.
NOTE: When anti-freeze is used in the loop, assure that it is
compatible with Teflon tape or pipe joint compound employed.
Maximum allowable torque for brass fittings is 30 ft-lb. If a
torque wrench is not available, tighten finger-tight plus one
quarter turn. Tighten steel fittings as necessary.
Optional pressure-rated hose assemblies designed specifically for use with Carrier units are available. Similar hoses can
be obtained from alternate suppliers. Supply and return hoses
are fitted with swivel-joint fittings at one end to prevent kinking during installation.
Backup wrench is required when tightening water connections to prevent water line damage.
Refer to Fig. 14 for an illustration of a supply/return hose
kit. Male adapters secure hose assemblies to the unit and risers.
Install hose assemblies properly and check them regularly to
avoid system failure and reduced service life.
CAUTION
CAUTION
11
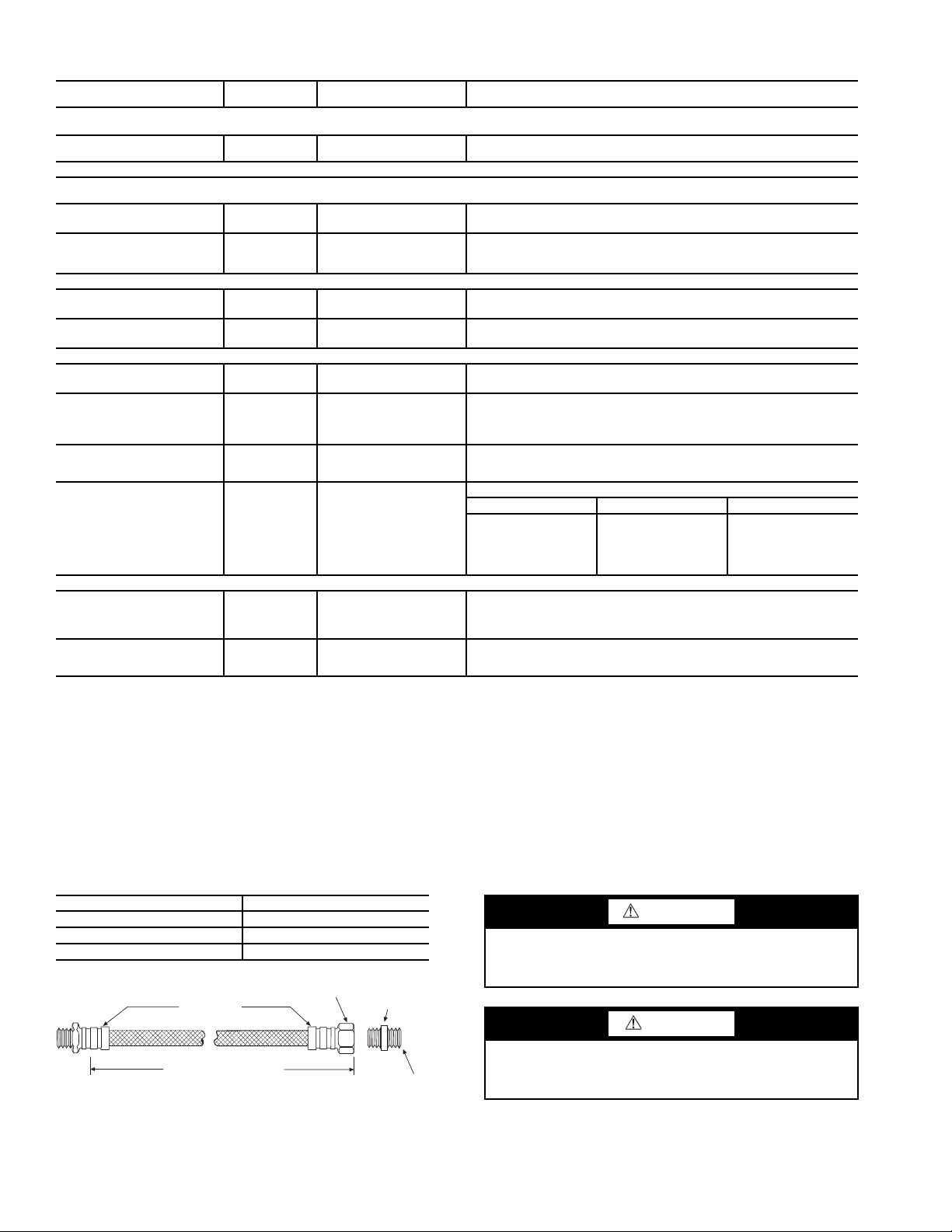
Table 2 — Water Quality Guidelines
Rib Crimped
Length
(2 ft Length Standard)
Swivel
Brass
Fitting
Brass
Fitting
MPT
Fig. 14 — Supply/Return Hose Kit
CONDITION
Scaling Potential — Primary Measurement
Above the given limits, scaling is likely to occur. Scaling indexes should be calculated using the limits below.
pH/Calcium
Hardness Method
Index Limits for Probable Scaling Situations (Operation outside these limits is not recommended.)
Scaling indexes should be calculated at 150 F for direct use and HWG applications, and at 90 F for indirect HX use. A monitoring plan should be
implemented.
Ryznar Stability Index
Langelier Saturation Index
Iron Fouling
2+
(Ferrous)
Iron Fe
(Bacterial Iron Potential)
Iron Fouling
Corrosion Prevention††
pH
Hydrogen Sulfide (H
Ammonia Ion as Hydroxide,
Chloride, Nitrate and Sulfate
Compounds
Maximum Chloride Levels Maximum allowable at maximum water temperature.
Erosion and Clogging
Particulate Size and Erosion
Brackish
HWG — Hot Water Generator
HX — Heat Exchanger
N/A — Design Limits Not Applicable Considering Recirculating
NR — Application Not Recommended
SS — Stainless Steel
*Heat exchanger materials considered are copper, cupronickel, 304 SS
(stainless steel), 316 SS, titanium.
†Closed recirculating system is identified by a closed pressurized piping
system.
**Recirculating open wells should observe the open recirculating design
considerations.
Pota ble Wate r
S)
2
LEGEND
HX
MATERIAL*
All N/A pH < 7.5 and Ca Hardness, <100 ppm
All N/A
All N/A
All N/A
All N/A
All
All N/A
All N/A
Copper N/A
Cupronickel N/A <150 ppm
304 SS N/A <400 ppm
316 SS N/A <1000 ppm
Titanium N/A >1000 ppm
All
All N/A
CLOSED RECIRCULATING† OPEN LOOP AND RECIRCULATING WELL**
6.0 - 7.5
–0.5 to +0.5
<0.2 ppm (Ferrous)
<0.5 ppm of Oxygen
6 - 8.5
<0.5 ppm
<0.5 ppm
75 F (24 C) 100 F (38 C)
NR NR
NR NR
<250 ppm <150 ppm
<550 ppm <375 ppm
>550 ppm >375 ppm
6 - 8.5
Monitor/treat as needed.
<10 ppm of particles and a
maximum velocity of 6 fps.
Filtered for maximum
800 micron size.
If >7.5 minimize steel pipe use.
Based upon 150 F HWG and direct well, 85 F indirect well HX.
2+
If Fe
(ferrous) >0.2 ppm with pH 6 - 8, O2<5 ppm check for iron bacteria.
Minimize steel pipe below 7 and no open tanks with pH <8.
At H
S>0.2 ppm, avoid use of copper and cupronickel piping or HXs.
2
Copper alloy (bronze or brass) cast components are okay to <0.5 ppm.
50 F (10 C)
<20 ppm
<10 ppm (<1 ppm “sandfree” for reinjection) of particles and a maximum velocity
of 6 fps. Filtered for maximum 800 micron size. Any particulate that is not
removed can potentially clog components.
Use cupronickel heat exchanger when concentrations of calcium or sodium chloride are greater than 125 ppm are present. (Seawater is approximately 25,000
ppm.)
††If the concentration of these corrosives exceeds the maximum allowable
level, then the potential for serious corrosion problems exists.
Sulfides in the water quickly oxidize when exposed to air, requiring that no
agitation occur as the sample is taken. Unless tested immediately at the
site, the sample will require stabilization with a few drops of one Molar zinc
acetate solution, allowing accurate sulfide determination up to 24 hours
after sampling. A low pH and high alkalinity cause system problems, even
when both values are within ranges shown. The term pH refers to the acidity, basicity, or neutrality of the water supply. Below 7.0, the water is considered to be acidic. Above 7.0, water is considered to be basic. Neutral water
contains a pH of 7.0.
To convert ppm to grains per gallon, divide by 17. Hardness in mg/l is
equivalent to ppm.
If <–0.5 minimize steel pipe use.
Above this level deposition will occur.
Rotten egg smell appears at 0.5 ppm level.
Table 3 — Metal Hose Minimum Bend Radii
HOSE DIAMETER (in.) MINIMUM BEND RADII (in.)
1
/
2
3
/
4
15
21/
4
1
2
/
2
Step 8 — Wire Field Power Supply
WARNING
To avoid possible injury or death due to electrical shock,
open the power supply disconnect switch and secure it in
an open position during installation.
CAUTION
Use only copper conductors for field-installed electrical
wiring. Unit terminals are not designed to accept other
types of conductors.
All field-installed wiring, including the electrical ground,
MUST comply with the National Electrical Code (NEC) as
well as applicable local codes. In addition, all field wiring must
12
conform to the Class II temperature limitations described in the
NEC.
Refer to unit wiring diagrams Fig. 15-24 for a schematic of
the field connections, which must be made by the installing (or
electrical) contractor. For Deluxe D with WSHP Open controls
3-phase units and Complete C with Open controls single-phase
and 3-phase units contact Application Engineering. Refer to
Table 4 for fuse sizes.
Consult the unit wiring diagram located on the inside of the
compressor access panel to ensure proper electrical hookup.
The installing (or electrical) contractor must make the field
connections when using field-supplied disconnect.
Operating voltage must be the same voltage and phase as
shown in electrical data shown in Table 4.
Make all final electrical connections with a length of flexible conduit to minimize vibration and sound transmission to
the building.
POWER CONNECTION — Make line voltage connection
by connecting the incoming line voltage wires to the line
side of the compressor contactor terminal as shown in
Fig. 25. See Table 4 for amperage ratings to provide correct
wire and maximum overcurrent protection sizing.
SUPPLY VOLTAGE — Operating voltage to unit must be
within voltage range indicated on unit nameplate.
On 3-phase units, voltages under load between phases must
be balanced within 2%. Use the following formula to determine the percentage voltage imbalance:
% Voltage Imbalance
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
Example: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
AB = 452 volts
BC = 464 volts
AC = 455 volts
Average Voltage =
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
=
3
= 457
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage:
(AB) 457 – 452 = 5 v
(BC) 464 – 457 = 7 v
(AC) 457 – 455 = 2 v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
7
457
= 1.53%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is
below the maximum allowable 2%.
Operation on improper line voltage or excessive phase
imbalance constitutes abuse and may cause damage to electrical components.
NOTE: If more than 2% voltage imbalance is present, contact
your local electric utility.
208-VOLT OPERATION — All 208-230 volt units are factory
wired for 208 volts. The transformers may be switched to
230-volt operation by switching the red (208 volt) wire with
the orange (230 volt) wire at the L1 terminal.
460-VOLT OPERATION — Units using 460-v and an ECM
(electronically commutated motor) fan motor, modulating
HWR, and/or internal secondary pump will require a neutral
wire from the supply side in order to feed accessory with
265-v.
Table 4 — 50PTH,PTV,PTD Electrical Data
50PTH,
PTV, PTD
UNITS
026 208/230-1-60 197/254 10.3 52.0 4.3 14.6 17.2 25 0.8 15.4 18.0 25
038
049
064
072 208/230-1-60 197/254 27.2 150.0 7.0 34.2 41.0 60 1.07 35.3 42.1 60
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
RLA — Rated Load Amps
HWR — Hot Water Reheat
V-P H- Hz *
208/230-1-60 197/254 16.7 82.0 4.3 21.0 25.2 40 0.8 21.8 26.0 40
208/230-3-60 197/254 11.2 58.0 4.3 15.5 18.3 25 0.8 16.3 19.1 30
460-3-60 414/506 4.5 29.0 4.1 8.6 9.7 15 0.7 9.3 10.4 15
208/230-1-60 197/254 21.2 96.0 7.0 28.2 33.5 50 1.07 29.3 34.6 50
208/230-3-60 197/254 13.5 88.0 7.0 20.5 23.9 35 1.07 21.6 24.9 35
460-3-60 414/506 6.4 41.0 6.9 13.3 14.9 20 1.07 14.4 16.0 20
208/230-1-60 197/254 25.6 118.0 7.0 32.6 39.0 60 1.07 33.7 40.1 60
208/230-3-60 197/254 17.6 123.0 7.0 24.6 29.0 45 1.07 25.7 30.1 45
460-3-60 414/506 9.0 62.0 6.9 15.9 18.2 25 1.07 17.7 19.2 25
LEGEND *The 460-v units using an ECM (electronically commutated motor) fan
VO LTAGE
MIN/MAX
COMPRESSOR
RLA LRA
FAN
MOTOR
FLA
TOTAL
UNIT FLA
MIN
CIRCUIT
AMPS
motor, modulating HWR, and/or an internal secondary pump will require
a neutral wire from the supply side in order to feed the accessory with
265-v.
MAX
FUSE/
HACR
REHEAT
PUMP
FLA
UNITS WITH HWR
TOTAL
UNIT
FLA
MIN
CIRCUIT
AMP
MAX
FUSE/
HACR
13
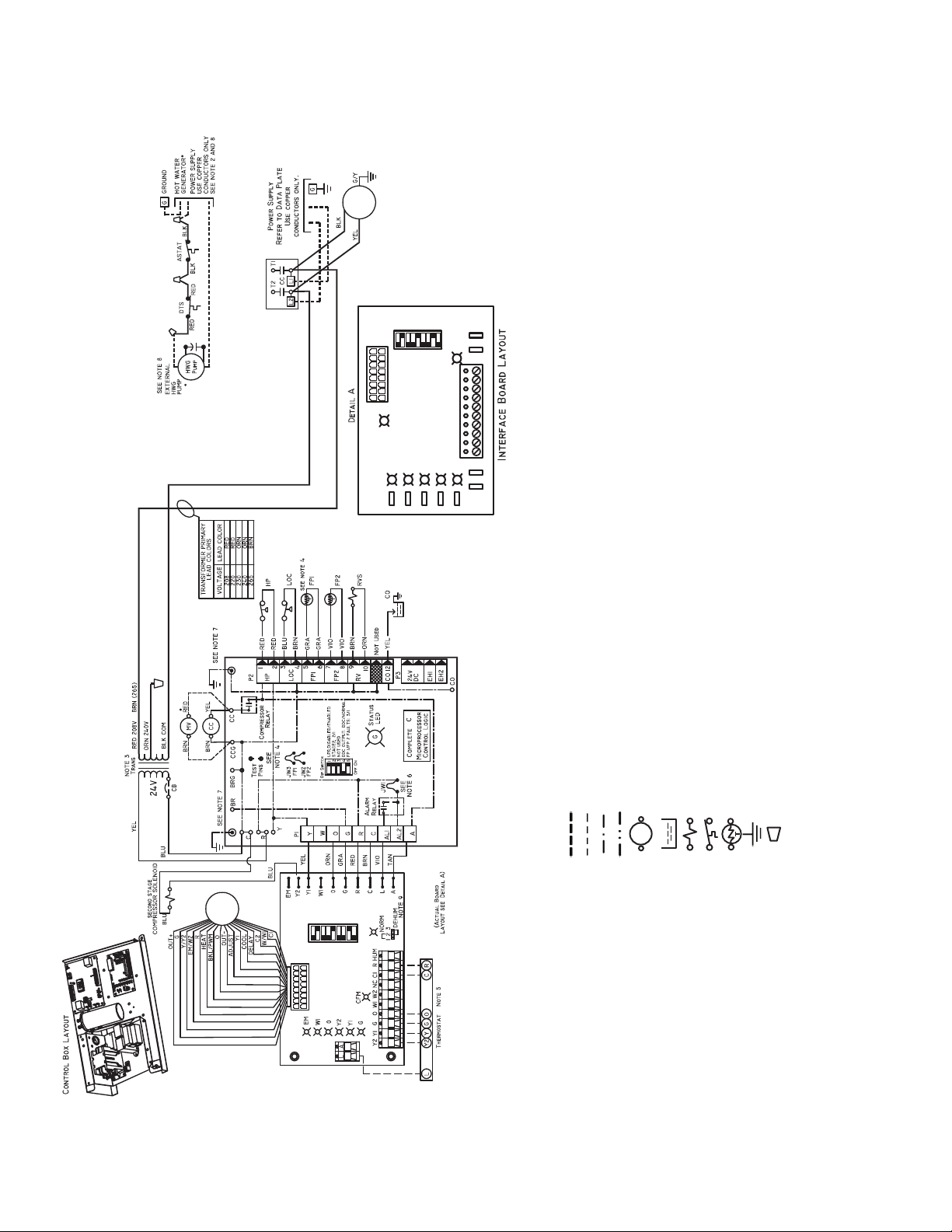
ECM
Y
GGGGR
W
O
Y
2
Y
1
G
R
C
Y
2
Y
1
G
O
W
C
R
D
H
A
L
1
A
A
A
L
1
S
W1
S
W2
S
W3
S
W4
S
W5
S
W6
S
W7
S
W8
S
W9
OF
F
ON
G
D
E
HUM
C
F
M
T
B
1
J1
S
1
BM ECM
ECM
INTERFACE
BOARD
S
W
1
S
W
2
S
W
3
S
W
4
S
W
5
S
W
6
S
W
7
S
W
8
S
W
9
OF
F
ON
S
1
J1
BM ECM
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
DTS — Discharge Temp Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer for 208/230 v will be connected for 208 v operation. For 230 v operation, dis-
connect RED lead at L1 and attach ORN lead to L1. Insulate open end of RED lead. Trans-
former for 220/240 v will be connected for 220 v operation. For 240 v operation, disconnect
RED lead at L1 and attach ORN lead to L1. Transformer is energy limiting or may have cir-
cuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut
JW3 jumper.
5. Typical Aquazone™ thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions
for wiring to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or
greater than unit supply voltage.
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut JW1 jumper and dry contact will be
available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via Complete C board standoffs and screws to control box.
(Ground available from top two standoffs as shown.)
8. Aquastat is field-supplied and must be wired in series with the hot leg to the pump. Aqua-
stat is rated for voltage up to 277 v.
9. Place jumpers on 2 and 3, ECM board, when dehumidification mode is used.
LEGEND
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Fig. 15 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 Units with Complete C Controller, Single Phase (208/230 V)
14
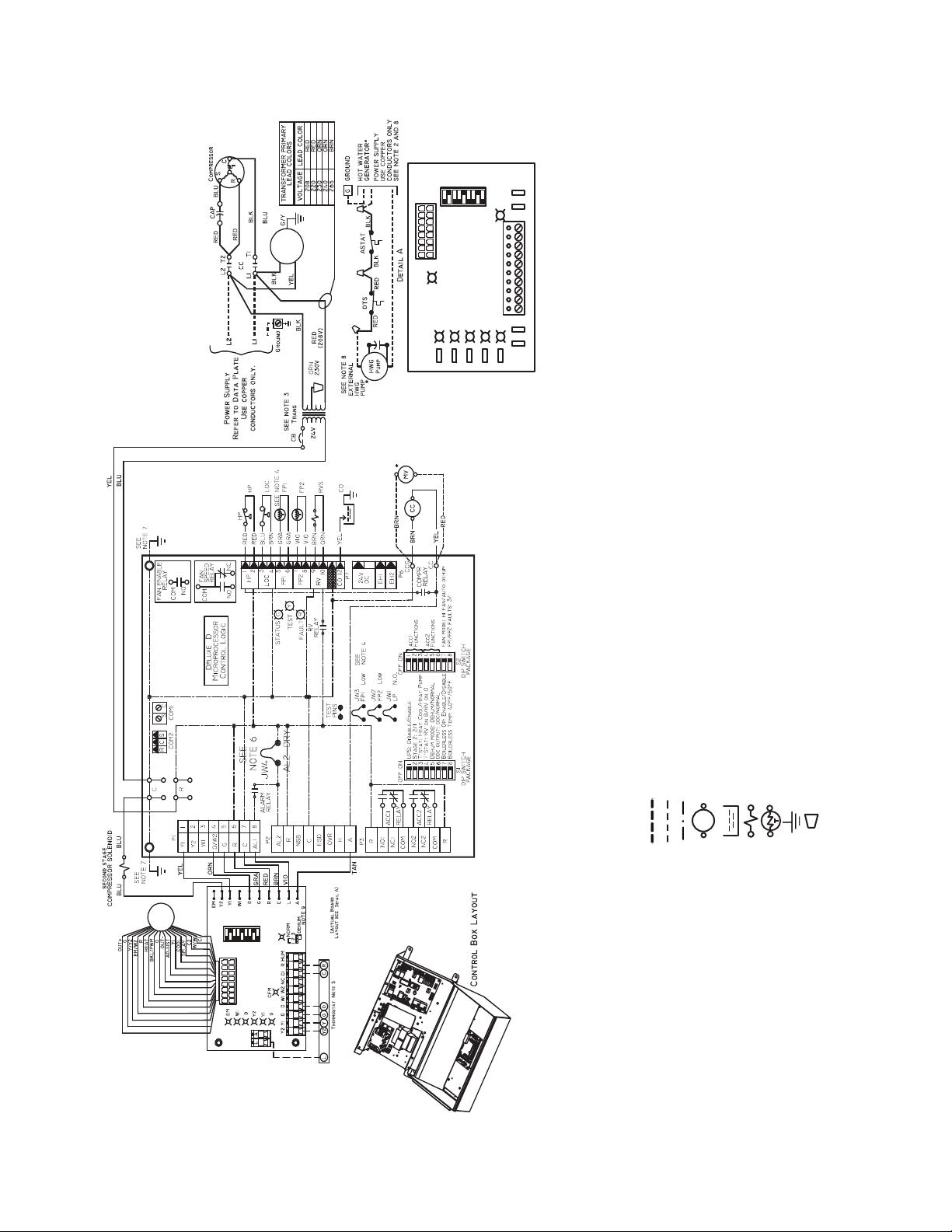
ECM INTERFACE BOARD LAYOUT
Y
GGGGR
W
O
Y2
Y1
G
R
C
Y2
Y1
G
O
W
C
R
DH
AL
1
A
A
AL
1
SW
1
SW
2
SW
3
SW
4
SW
5
SW
6
SW
7
SW
8
SW
9
OFF
ON
G
DEH
UM
C
FM
T
B1
J
1
S
1
BM (ECM)
ECM
INTERFACE
BOARD
SW1
S
W2
S
W3
S
W4
S
W5
S
W6
S
W7
S
W8
S
W9
OFF
O
N
BM
(ECM)
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
CAP — Capacitor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
COMPR — Compressor
DDC — Direct Digital Control
DTS — Discharge Temp Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
NSB — Digital Night Setback
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
LEGEND
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer for 208/230 v will be connected for 208 v operation. For 230 v operation, discon-
nect RED lead at L1 and attach ORN lead to L1. Insulate open end of RED lead. Transformer
for 220/240 v will be connected for 220 v operation. For 240 v operation, disconnect RED
lead at L1 and attach ORN lead to L1. Transformer is energy limiting or may have circuit
breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut
JW3 jumper.
5. Typical Aquazone™ thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for
wiring to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater
than unit supply voltage.
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut AL2 dr y jumper and dry contact will be
available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via Deluxe D board standoffs and screws to control box.
(Ground available from top two standoffs as shown.)
8. Aquastat is field-supplied and must be wired in series with the hot leg to the pump. Aquastat
is rated for voltage up to 277 v.
9. Place jumpers on 2 and 3, ECM board, when dehumidification mode is used.
Fig. 16 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 Units with Deluxe D Controller, Single Phase (208/230 V)
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
15
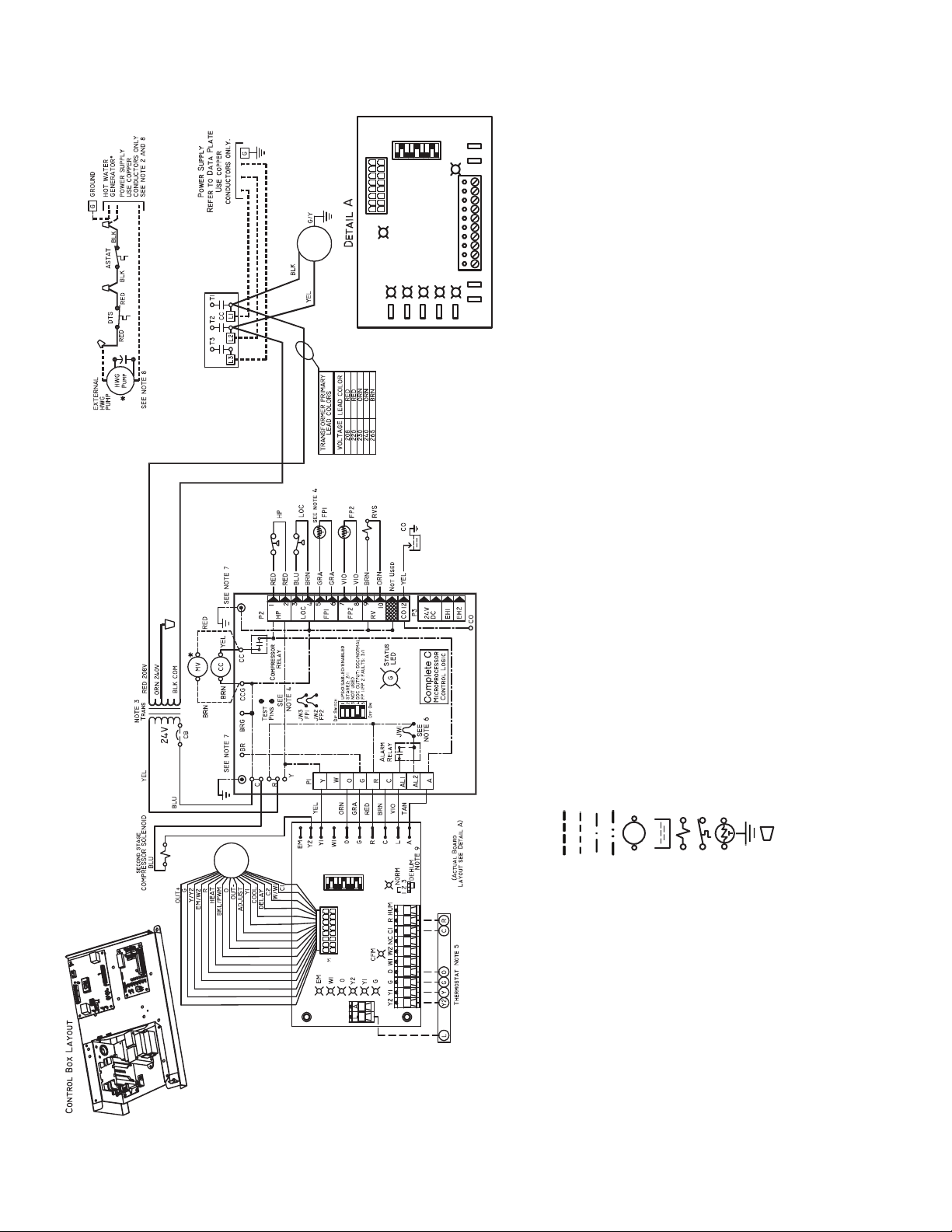
BM (ECM)
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
DTS — Discharge Temp Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer for 208/230 v will be connected for 208 v operation. For 230 v operation, disconnect
RED lead at L1 and attach ORN lead to L1. Insulate open end of RED lead. Transformer for 220/
240 v will be connected for 220 v operation. For 240 v operation, disconnect RED lead at L1 and
attach ORN lead to L1. Transformer is energy limiting or may have circuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3
jumper.
5. Typical Aquazone™ thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for wir-
ing to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit
supply voltage.
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut JW1 jumper and dr y contact will be available
between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via Complete C board standoffs and screws to control box.
(Ground available from top two standoffs as shown.)
8. Aquastat is field-supplied and must be wired in series with the hot leg to the pump. Aquastat is
rated for voltage up to 277 v.
9. Place jumpers on 2 and 3, ECM board, when dehumidification mode is used.
LEGEND
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Fig. 17 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 Units with Complete C Controller, Three Phase (208/230 V)
ON
1
S
J1
Y
W8
W6
W9
W7
W4
W5
W3
W2
W1
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
M
F
C
2
O
W
Y
L1
A
F
HUM
E
OF
D
A
G
A
1
L
A
H
D
R
C
W
O
G
1
Y
2
Y
1
B
T
C
GGGGR
1
R
G
Y
ECM INTERFACE BOARD LAYOUT
BM
(ECM)
N
O
F
OF
W7
W9
W4
W6
W3
W5
W2
W8
SW1
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
S
ECM
INTERFACE
BOARD
16
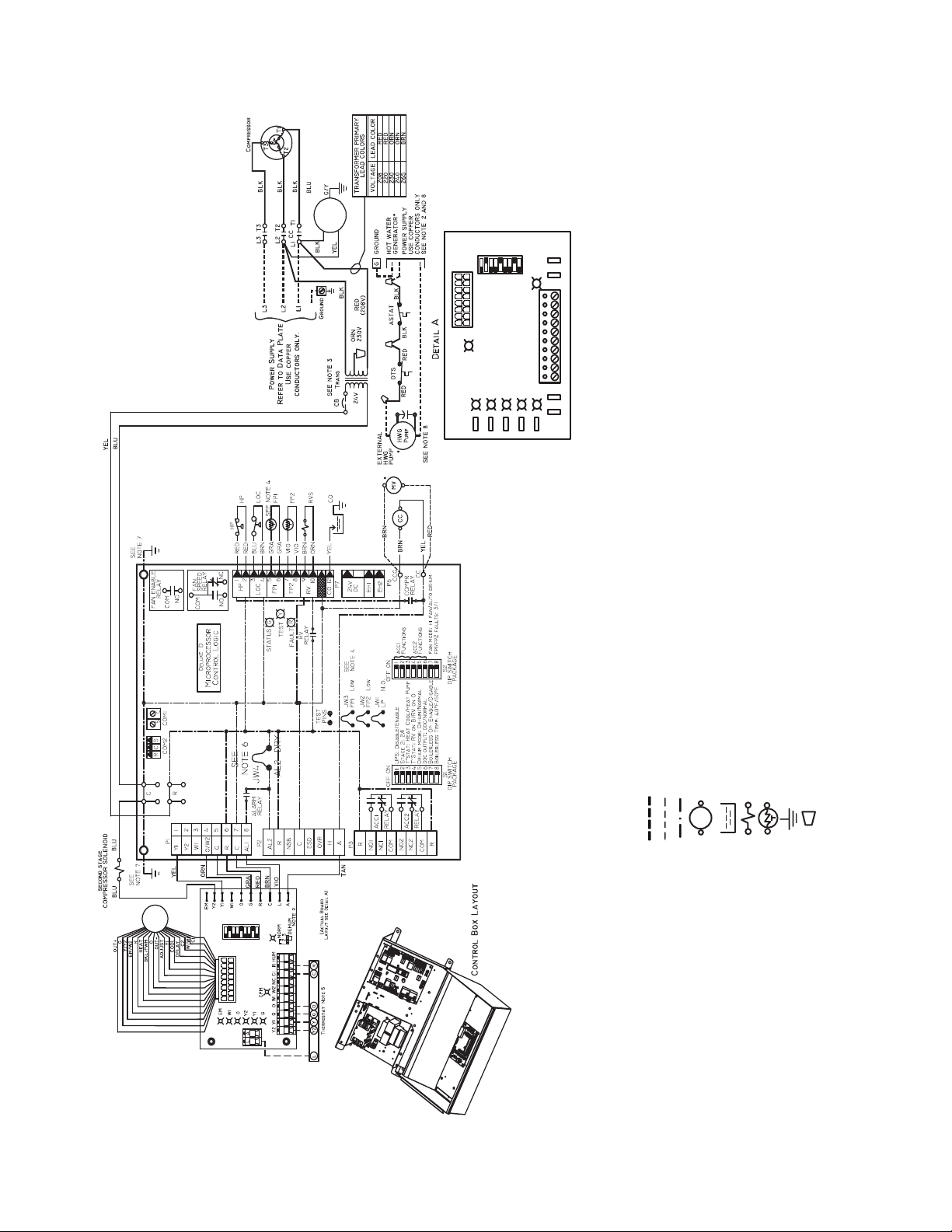
ECM INTERFACE BOARD LAYOUT
Y
GGGGR
W
O
Y2
Y1
G
R
C
Y2
Y1
G
O
W
C
R
DH
AL
1
A
A
AL
1
SW
1
SW
2
SW
3
SW
4
SW
5
SW
6
SW
7
SW
8
SW
9
OFF
ON
G
DEH
UM
C
FM
T
B1
J
1
S
1
BM (ECM)
ECM
INTERFACE
BOARD
SW1
S
W2
S
W3
S
W4
S
W5
S
W6
S
W7
S
W8
S
W9
OFF
O
N
BM
(ECM)
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
COMPR — Compressor
DDC — Direct Digital Control
DTS — Discharge Temp Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
NSB — Digital Night Setback
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
LEGEND
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer for 208/230 v will be connected for 208 v operation. For 230 v operation, dis-
connect RED lead at L1 and attach ORN lead to L1. Insulate open end of RED lead. Trans-
former for 220/240 v will be connected for 220 v operation. For 240 v operation, disconnect
RED lead at L1 and attach ORN lead to L1. Transformer is energy limiting or may have cir-
cuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut
JW3 jumper.
5. Typical Aquazone™ thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions
for wiring to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or
greater than unit supply voltage.
6. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut AL2 dry jumper and dry contact will be
available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via Deluxe D board standoffs and screws to control box.
(Ground available from top two standoffs as shown.)
8. Aquastat is field-supplied and must be wired in series with the hot leg to the pump.
Aquastat is rated for voltage up to 277 v.
9. Place jumpers on 2 and 3, ECM board, when dehumidification mode is used.
Fig. 18 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 Units with Deluxe D Controller, Three Phase (208/230 V)
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
17
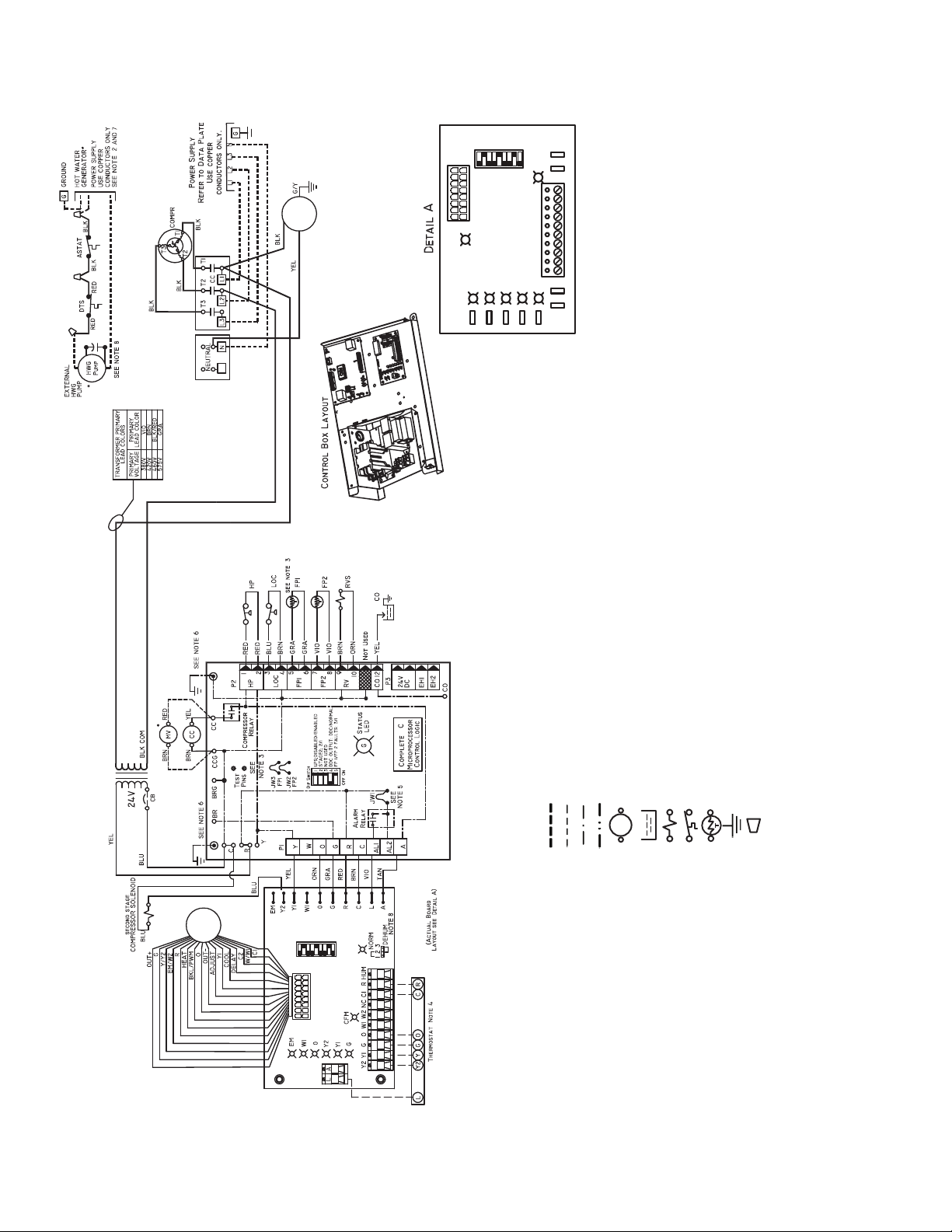
ECM INTERFACE BOARD LAYOUT
Y
GGGGR
W
O
Y
2
Y
1
G
R
C
Y
2
Y
1
G
O
W
C
R
D
H
A
L
1
A
A
A
L
1
S
W1
S
W2
S
W3
S
W4
S
W5
S
W6
S
W7
S
W8
S
W9
OF
F
ON
G
D
E
HUM
C
F
M
T
B
1
J1
S
1
BM (ECM)
ECM
INTERFACE
BOARD
BM
(ECM)
SW1
S
W2
S
W3
S
W4
S
W5
S
W6
S
W7
S
W8
S
W9
OF
F
O
N
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
COMPR — Compressor
DTS — Discharge Temp Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3
jumper.
4. Typical Aquazone™ thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for wir-
ing to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit
supply voltage.
5. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut JW1 jumper and dry contact will be available
between AL1 and AL2.
6. Transformer secondary ground via Complete C board standoffs and screws to control box.
(Ground available from top two standoffs as shown.)
7. Aquastat is field-supplied and must be wired in series with the hot leg to the pump. Aquastat is
rated for voltage up to 277 v.
8. Place jumpers on 2 and 3, ECM board, when dehumidification mode is used.
LEGEND
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Fig. 19 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 Units with Complete C Controller, Three Phase (460 V)
18
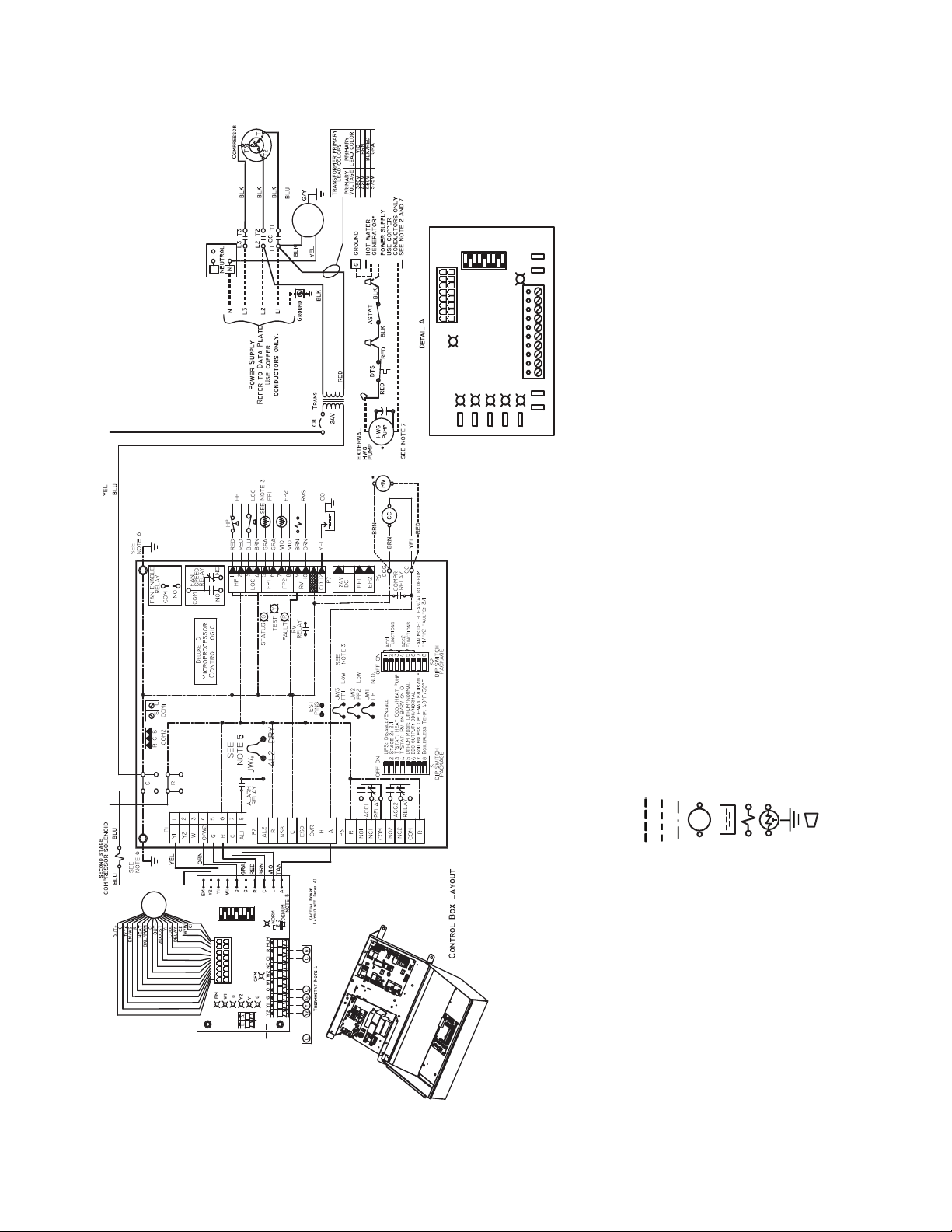
ECM INTERFACE BOARD LAYOUT
Y
GGGGR
W
O
Y2
Y1
G
R
C
Y2
Y1
G
O
W
C
R
DH
AL
1
A
A
AL
1
SW
1
SW
2
SW
3
SW
4
SW
5
SW
6
SW
7
SW
8
SW
9
OFF
ON
G
DEH
UM
C
FM
T
B1
J
1
S
1
BM
(ECM)
ECM
INTERFACE
BOARD
BM
(ECM)
SW1
S
W2
S
W3
S
W4
S
W5
S
W6
S
W7
S
W8
S
W9
OFF
O
N
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
DDC — Direct Digital Control
DTS — Discharge Temp Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Jumper, Alarm
NSB — Digital Night Setback
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
LEGEND
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3
jumper.
4. Typical Aquazone™ thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for wiring
to the unit. Thermostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply
voltage.
5. 24-v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut AL2 dry jumper and dry contact will be available
between AL1 and AL2.
6. Transformer secondary ground via Deluxe D board standoffs and screws to control box. (Ground
available from top two standoffs as shown.)
7. Fan motors are factory wired for medium speed. For high or low speed, remove BLU wire from fan
motor speed tap “M” or “3” and connect to “H” or “2” for high speed or “L” or “4” for low speed.
8. Place jumpers on 2 and 3, ECM board, when dehumidification mode is used.
Fig. 20 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 Units with Deluxe D Controller, Three Phase (460 V)
19
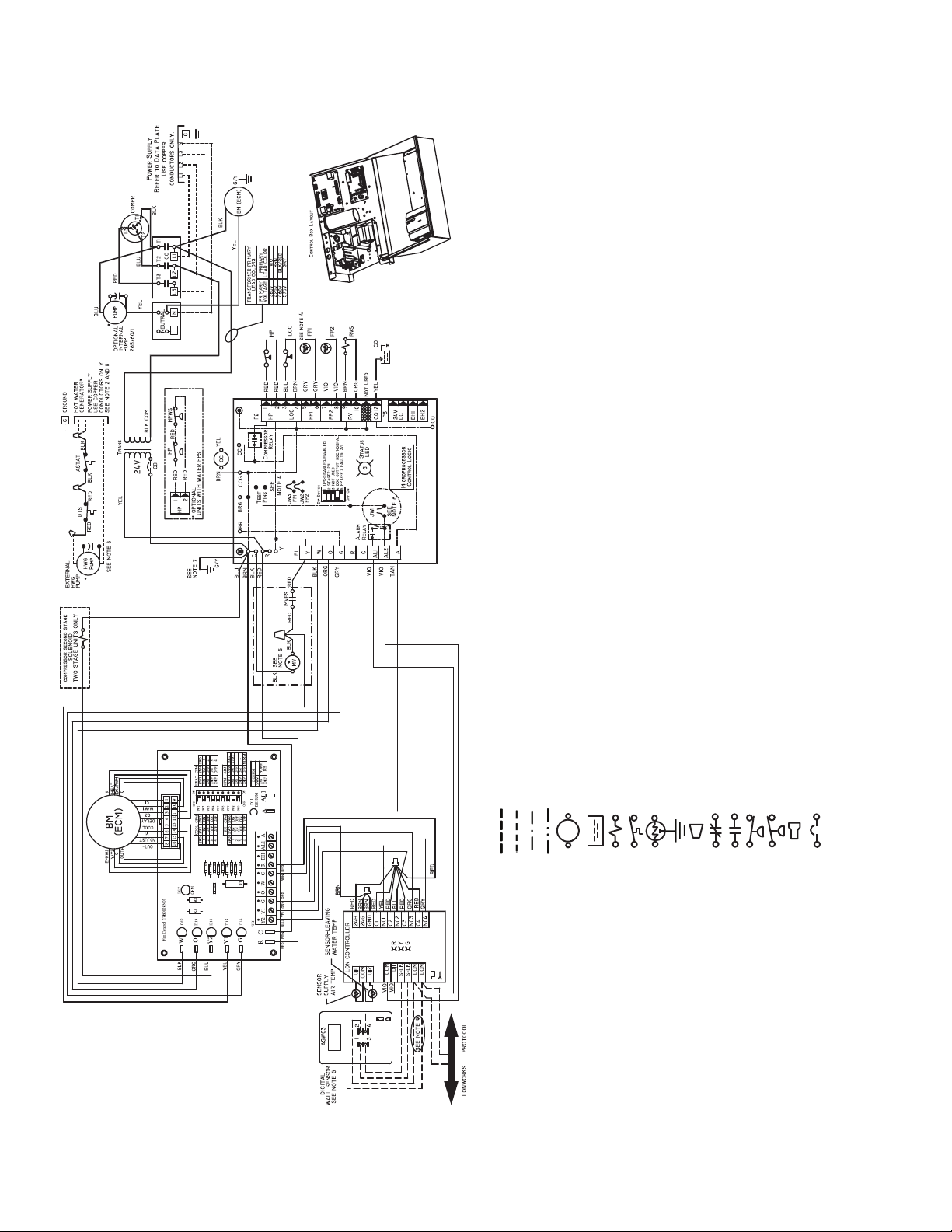
*Optional Wiring.
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
DTS — Discharge Temperature Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High-Pressure Water Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Clippable Field Selection Jumper
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
LON — Local Operating Network
MV — Motorized Valve
MVES — Motorized Valve End Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 460 v (BLK/RED) lead for 460/3/60 units. Transformer is energy limiting or may
have circuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Typical thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for wiring to the unit. Ther-
mostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
6. Factory cut JW1 jumper. Dry contact will be available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via Complete C board standoffs and screws to control box. (Ground
available from top two standoffs as shown.)
8. Aquastat is supplied with unit and must be wired in series with the hot leg to the pump. Aquastat is rated
for voltages up to 277-v.
9. Optional LON wires. Only connect if LON connection is desired at the wall sensor.
10. Fan motors are factory wired for medium speed. For high or low speed, remove BLU wire from fan motor
speed tap “M” and connect to “H” for high speed or “L” for low speed.
11. For low speed, remove BLK wire from BR “6” and replace with RED. Connect BLK and BRN wires
together.
12. For blower motors with leads. For medium or low speed, disconnect BLK wire from BR “6”. Connect BLK
and ORG/PUR wire together. Connect RED for low or BLU for medium to BR “6”.
13. The 460-v units using an ECM (electronically commutated motor) fan motor, modulating HWR, and/or an
internal secondary pump will require a neutral wire from the supply side in order to feed the accessory
with 265-v.
Complete C
a50-8363
LEGEND
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Relay Contacts - N.C.
Relay Contacts - N.O.
Low Pressure Switch
High Pressure Switch
Splice Cap
Circuit Breaker
Fig. 21 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 Units with Complete C and LON Controller, Three Phase (460 V)
20

*Optional Wiring.
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
CO — Sensor, Condensate Overflow
DTS — Discharge Temperature Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High-Pressure Water Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW1 — Clippable Field Selection Jumper
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
LON — Local Operating Network
MV — Motorized Valve
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
TRANS — Transformer
LEGEND
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Printed Circuit Trace
Optional Wiring
Relay/Contactor Coil
Condensate Pan
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
Relay Contacts - N.C.
Relay Contacts - N.O.
Low Pressure Switch
High Pressure Switch
Splice Cap
Circuit Breaker
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. Transformer is wired to 460 v (BLK/RED) lead for 460/3/60 units. Transformer is energy limiting or may
have circuit breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides freeze protection for water. When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Typical thermostat wiring shown. Refer to thermostat installation instructions for wiring to the unit. Ther-
mostat wiring must be Class 1 and voltage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
6. Factory cut JW1 jumper. Dry contact will be available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via Deluxe D board standoffs and screws to control box. (Ground avail-
able from top two standoffs as shown.)
8. Aquastat is supplied with unit and must be wired in series with the hot leg to the pump. Aquastat is rated
for voltages up to 277-v.
9. Place jumpers on 2 and 3, ICM board, when dehumidification mode is used.
10. Optional LON wires. Only connect if LON connection is desired at the wall sensor.
11. Blower motor is factory wired for medium and high speeds. For any other combination of speeds, at the
motor attach the BLK wire to the higher of the two desired speed taps and the BLU wire to the lower of
the two desired speed taps.
12. Blower motor is factory wired for high and low speeds. No other combination is available.
13. The 460-v units using an ECM (electronically commutated motor) fan motor, modulating HWR, and/or an
internal secondary pump will require a neutral wire from the supply side in order to feed the accessory
with 265-v.
Fig. 22 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 Units with Deluxe D and LON Controller, Three Phase (460 V)
Deluxe D
HP
LOC
FP1
FP2
RVS
CO
SEE NOTE 4
a50-8364
21

LEGEND
AL — Alarm Relay Contacts
ASTAT — Aquastat
BM — Blower Motor
BMC — Blower Motor Capacitor
BR — Blower Relay
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Compressor Contactor
DTS — Discharge Temperature Switch
ECM — Electronically Commutated Motor
FP1 — Sensor, Water Coil Freeze Protection
FP2 — Sensor, Air Coil Freeze Protection
HP — High-Pressure Switch
HPWS — High-Pressure Water Switch
HWG — Hot Water Generator
JW — Jumper Wire
LOC — Loss of Charge Pressure Switch
LWT — Leaving Water Temperature
MV — Motorized Valve
MVES — Motorized Valve End Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
P1 — Field Wiring Terminal Block
RH — Relative Humidity
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
SPT — Space Temperature Sensor
TRANS — Transformer
Deluxe D
Field Line Voltage Wiring
Relay Contacts - N.C.
Field Low Voltage Wiring
Relay Contacts - N.O.
Printed Circuit Trace
Low Pressure Switch
Optional Wiring
High Pressure Switch
Relay/Contactor Coil Circuit Breaker
Condensate Float Switch Splice Cap
Solenoid Coil
Temperature Switch
Thermistor
Ground
Wire Nut
* Optional wiring.
NOTES:
1. Compressor and blower motor thermally protected internally.
2. All wiring to the unit must comply with NEC and local codes.
3. 208-240 60 Hz units are wired for 208v operation. For 240v 60 Hz
operation switch RED wire to ORG wire. 2240240v 50 Hz units are
wired for 240v operation. For 220v 50 Hz operation switch ORG
wire to RED. Transformer is energy limiting or may have circuit
breaker.
4. FP1 thermistor provides low temperature protection for water.
When using antifreeze solutions, cut JW3 jumper.
5. Refer to thermostat installation, application and operation manual
for control wiring to the unit. Wire from ECM to “Y” CXM when a
motorized valve is not used. Thermostat wiring must be “Class 1”
and volatage rating equal to or greater than unit supply voltage.
6. 24v alarm signal shown. For dry alarm contact, cut JW1 jumper.
Dry contact will be available between AL1 and AL2.
7. Transformer secondary ground via green wire with yellow stripe
from “C” terminal to control box
8. Aquastat is supplied with unit and must be wired in series with the
hot leg to the pump. Aquastat is rated for voltages up to 277v.
9. For field-installed two-position hot water reheat coils disconnect
wire from terminal W1 and connect to field-supplied hot water
valve.
Fig. 23 — Wiring of 50PTH,PTV,PTD026-072 with Deluxe D and WSHP Open Multiple Protocol Controls (Single-Phase 208-230 V)
a50-8570
22

012207-1BT485BT
LED1
DB
Install BT485 where device is
located at the end of network
segment only.
+ 24vac
(If not installed, it must be connected to DO-5)
DEHUMIDIFY OUTPUT CONTACT (DO-6) (FACTORY OPTION)
FAN SPEED (DO-7) (MED OR LOW)
OA DAMPER (AO-2)
FAN SPEED (DO-8) (HIGH OR FAN ON )
LWT (Input 6)
SAT (LAT) (Input 7)
SPACE CO2
SENSOR
+24vac
4-20mA
+
-
AO1 – Aux Reheat or Cond.
WTR. Loop Econ. (AO 1)
-Gnd
Fan (DO-1) (Fan On or Low Speed)
Aux Heat (DO-2)
Reversing Valve (DO-3)
Comp #2 (DO-4)
Comp #1 (DO-5)
Comp Status (DI-5)
SPT PLUS Sensor
Shown
+12V
Rnet-
Rnet+
Gnd
RED
BLACK
WHITE
GREEN
To WSHP Controller
Rnet Terminals (J13)
FIELD INSTALLED
0
5
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
0
5
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
12
3 45
6
7 8
O
N
1
2 3
4
5
67
8
12
1
2
3
4
123 4
1
2 3
123 45678
GREEN
WHITE
BLACK
RED
Field Installed
J5
J12
J13
J20
J19
J22
J17
J11
J14
To
SPT PLUS
1
2
3
45
6
1
1
10
7
J4
J1 J2
SW3
MSB
LSB
MSTP Baud
9600 19.2k 38.4k 76.8k
SPACE RH
SENSOR
+24vac
4-20mA
+
-
Local Access Port
(FIELD-INSTALLED)
PRIMARY
PRIMARY
CONDENSATE
OVERFLOW SWITCH
REMOTE OCCUPANCY/
FAN STATUS SWITCH
(FIELD-INSTALLED)
NC FIRE/SMOKE
DETECTOR CONTACT
(FIELD-INSTALLED)
Fig. 24 — WSHP Open Control
WSHP Open Inputs and Outputs Table
*These inputs are configurable.
INPUT/OUTPUT TYPE PART NUMBERS TYPE OF I/O
CONNECTION
PIN NUMBERS
CHANNEL
DESIGNATION
Inputs
Space Temperature Sensor SPS, SPPL, SPP Communicating J13, 1 - 4 Local Access Port
Space Relative Humidity 33ZCSENSRH-01 AI (4 - 20mA) J4, 5 and 6 Analog Input 1
Indoor Air Quality 33ZCSENCO2 AI (4 -20mA) J4, 2 and 3 Analog Input 2
Condensate Switch N/A BI (Dry Contacts) J1, 2 Binary Input 3
Stage 1 Compressor Status N/A BI (Dry Contacts) J1, 10 Binary Input 5
Leaving Condenser Water Temperature 10K Type II AI (10K Thermistor) J2, 1 and 2 Analog Input 6
Supply Air Temperature 33ZCSENSAT AI (10K Thermistor) J2, 3 and 4 Analog Input 7
Outputs
Modulating Valve (Auxiliary Heat/Water
Economizer)
N/A AO (0-10Vdc/2 - 10Vdc) J2 4 and 5* Analog Output 1
Outside Air Damper N/A AO (0-10Vdc/2 - 10Vdc) J22 1 and 2* Analog Output 2
Supply Fan On/Low Speed
(3 Speed Only)
N/A BO Relay (24VAC, 1A) J1, 4* Binary Output 1 (G)
Auxiliary Heat or 2-Position Water Loop
Economizer
N/A BO Relay (24VAC, 1A) J1, 5* Binary Output 2
Reversing Valve (B or O Operation) N/A BO Relay (24VAC, 1A) J1, 6* Binary Output 3 (RV)
Compressor 2nd Stage N/A BO Relay (24VAC, 1A) J1, 7 Binary Output 4 (Y2)
Compressor 1st Stage N/A BO Relay (24VAC, 1A) J1, 8 Binary Output 5 (Y1)
Dehumidification Relay N/A BO Relay (24VAC, 1A) J11, 7 and 8 (NO) Binar y Output 6
Fan Speed Medium/Low (3 Speed Only) N/A BO Relay (24VAC, 1A) J11, 5 and 6 (NO)* Binary Output 7
Fan Speed High/Low (3 Speed Only) N/A BO Relay (24VAC, 1A) J11, 2 and 3 (NO)* Binary Output 8
LEGEND
NOTES:
10. Mount the water source heat pump controller in the equipment controls enclosure
with at least two #6 x 1 in. self-tapping screws. Allow adequate clearance for wiring.
11. Verify sensor power and wiring requirements prior to making any terminations. Sen-
sors requiring a separate isolated 24 vac power source will not utilize WSHP termi-
nals J4-1, or 4.
AI — Analog Input
AO — Analog Output
BI — Binary Input
BO — Binary Output
SPT — Space Temperature
Factory Wiring
Field Wiring
a50-8571
23

COMPRESSOR CONTACTOR
Fig. 25 — 50PTH,PTV,PTD Typical Single-Phase Line Voltage Power Connection
LINE
LOAD
CAPACITOR
COMPLETE C CONTROL
TRANSFORMER
WSHP OPEN WIRING — The WSHP Open controller will
be factory mounted to the unit control panel and wired to the
Complete C or Deluxe D control board, however, the system
wiring will need to be completed utilizing WSHP Open controller wiring diagrams and the Third Party Integration (TPI)
Guide. Factory installation includes harness, LWT (leaving
water temperature), supply air, and condensate sensor.
WARNING
Disconnect all power to the unit before performing maintenance or service. Unit may automatically start if power is
not disconnected. Failure to follow this warning could
cause personal injury, death, and/or equipment damage.
Wiring Sensors to Inputs
WSHP Open controller’s inputs. See Table 5.
All field control wiring that connects to the WSHP Open controller must be routed through the raceway built into the corner
post. The raceway provides the UL required clearance between
high and low-voltage wiring.
1. Pass control wires through the hole provided in the corner
post.
2. Feed the wires through the raceway to the WSHP Open
controller.
3. Connect the wires to the removable Phoenix connectors.
4. Reconnect the connectors to the board.
Field-Supplied Sensor Hardware
troller is configurable with the following field-supplied sensors. See Table 5.
Table 5 — Field-Supplied Sensors for
WSHP Open Controller
SENSOR NOTES
Space Temperature Sensor
Indoor Air Quality Sensor
NOTE: BACview6 Handheld or Virtual BACview can be used as the user
interface.
(SPT)
Outdoor Air
Temperature Sensor
(Separate Sensor)
Space Relative
Humidity Sensor
For specific details about sensors, refer to the literature sup-
plied with the sensor.
Wiring a SPT Sensor
ed to a wall-mounted space temperature (SPT) sensor to monitor room temperature using a Molex plug.
The WSHP Open system offers the following SPT sensors.
See Table 6.
— Sensors can be wired to the
— The WSHP Open con-
Field Installed (Must be used with
WSHP Open controller.)
Network Sensor
Required only for demand
control ventilation.
Separate Sensor
— A WSHP Open controller is connect-
ECM CONTROL
BOARD
Table 6 — SPT Sensors
SENSOR
SPT
Standard
SPT Plus SPPL
SPT Pro SPP
SPT Pro
Plus
*The SPT Pro Plus fan speed adjustment has no effect in this application.
PA RT
NUMBER
SPS
SPPF
FEATURES
• Local access port
• No operator control
• Slide potentiometer to adjust set point
• Manual on button to override schedule
• LED to show occupied status
• Local access port
• LCD display
• Manual on button to override schedule
• Warmer and cooler buttons to adjust set point
• Info button to cycle through zone and outside
air temperatures, set points, and local override
time
• Local access port
• LCD display
• Manual on button to override schedule
• Warmer and cooler buttons to adjust set point
• Info button to cycle through zone and outside
air temperatures, set points, and local override
time
• Local access port
• Fan speed*
Wire SPT sensors to the WSHP Open controller’s Rnet
port. An Rnetbus can consist of any of the following combinations of devices wired in a daisy-chain configuration:
• 1 SPT Plus, SPT Pro, or SPT Pro Plus sensor
• 1 to 4 SPT Standard sensors
• 1 to 4 SPT Standard sensors and 1 SPT Plus, SPT Pro, or
SPT Pro Plus sensor
• Any of the above combinations, plus up to 2 BACview
Handheld but no more than 6 total devices
NOTE: If the Rnetbus has multiple SPT Standard sensors, each
sensor must be given a unique address on the Rnetbus. See the
Carrier Open Sensor Installation Guide.
Use the specified type of wire and cable for maximum signal
integrity. See Table 7.
Table 7 — Rnet Wiring Specifications
RNET WIRING SPECIFICATIONS
Description
Conductor 18 AWG
Maximum Length 500 ft
Recommended Coloring
UL Temperature 32 to 167 F
Vo lta ge 300-vac, power limited
Listing UL: NEC CL2P, or better
AWG — American Wire Gage
CMP — Communications Plenum Cable
NEC — National Electrical Code
UL — Underwriters Laboratories
LEGEND
4 conductor, unshielded, CMP,
plenum rated cable
Jacket: white
Wiring: black, white, green, red
6
24

To wire the SPT sensor to the controller:
Fig. 26 — Rnet Cable Wire
a50-8443
–
1. Partially cut , then bend and pull off the outer jacket of
the Rnet cable(s), being careful not to nick the inner
insulation.
2. Strip about
1
/4 in. of the inner insulation from each wire.
See Fig. 26.
OUTER JACKET
.25 IN.
INNER INSULATION
3. Wire each terminal on the sensor to the same terminal on
the controller. See Fig. 15-24. Table 8 shows the recommended Rnet wiring scheme.
Table 8 — Rnet Wiring
WIRE TERMINAL
Red +12-v
Black .Rnet
White Rnet+
Green Gnd
NOTE: The wire should be connected to the terminal shown.
Wiring a Supply Air Temperature (SAT) Sensor — The
SAT sensor is required for reheat applications.
If the cable used to wire the SAT sensor to the controller
will be less than 100 ft, an unshielded 22 AWG (American
Wire Gage) cable should be used. If the cable will be greater
than 100 ft, a shield 22 AWG cable should be used. The cable
should have a maximum length of 500 ft.
To wire the SAT sensor to the controller:
1. Wire the sensor to the controller. See Fig. 15-24.
2. Verify that the Enable SAT jumper is on.
3. Verify that the Enable SAT and Remote jumper is in the
left position.
Wiring an Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) Sensor
— An IAQ
sensor monitors CO2 levels. The WSHP Open controller uses
this information to adjust the outside-air dampers to provide
proper ventilation. An IAQ sensor can be wall-mounted or
mounted in a return air duct. (Duct installation requires an aspirator box assembly.)
The sensor has a range of 0 to 2000 ppm and a linear 4 to
20 mA output. This is converted to 1 to 5 vdc by a 250-ohm,
1
/4 watt, 2% tolerance resistor connected across the zone con-
troller’s IAQ input terminals.
NOTE: Do not use a relative humidity sensor and CO
on the same zone controller if both sensors are powered off the
sensor
2
board. If sensors are externally powered, both sensors may be
used on the same zone controller.
If the cable used to wire the IAQ sensor to the controller
will be less than 100 ft, an unshielded 22 AWG (American
Wire Gage) cable should be used. If the cable will be greater
than 100 ft, a shield 22 AWG cable should be used. The cable
should have a maximum length of 500 ft.
To wire the IAQ sensor to the controller:
1. Wire the sensor to the controller. See Fig. 15-24.
2. Install a field-supplied 250-ohm,
1
/4 watt, 2% tolerance
resistor across the controller’s RH/IAQ and Gnd
terminals.
3. Verify the the RH/IAQ jumper is set to 0 to 5 vdc.
Wiring a Relative Humidity (RH) Sensor
— The RH sensor
is used for zone humidity control (dehumidification) if the
WSHP unit has a dehumidification device. If not, the sensor
only monitors humidity.
NOTE: Do not use a relative humidity sensor and CO
on the same zone controller if both sensors are powered off the
sensor
2
board. If sensors are externally powered, both sensors may be
used on the same zone controller.
If the cable used to wire the RH sensor to the controller will
be less than 100 ft, an unshielded 22 AWG (American Wire
Gage) cable should be used. If the cable will be greater than
100 ft, a shield 22 AWG cable should be used. The cable
should have a maximum length of 500 ft.
To wire the RH sensor to the controller:
1. Strip the outer jacket from the cable for at least 4 inches.
2. Strip
1
/4 in. of insulation from each wire.
3. Wire the sensor to the controller.
Step 9 — Wire Field Controls
THERMOSTAT CONNECTIONS — The thermostat
should be wired directly to the ECM control board. See
Fig. 27.
WATER FREEZE PROTECTION — The Aquazone™ control allows the field selection of source fluid freeze protection
points through jumpers. The factory setting of jumper JW3
(FP1) is set for water at 30 F. In earth loop applications, jumper
JW3 should be clipped to change the setting to 10 F when
using antifreeze in colder earth loop applications. See Fig. 28.
NOTE: The extended range option should be selected
with water temperatures below 60 F to prevent internal
condensation.
AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION — The air coil freeze
protection jumper JW2 (FP2) is factory set for 30 F and should
not need adjusting.
ACCESSORY CONNECTIONS — Terminal A on the control
is provided to control accessory devices such as water valves,
electronic air cleaners, humidifiers, etc. This signal operates
with the compressor terminal. See Fig. 29. Refer to the specific
unit wiring schematic for details.
NOTE: The A terminal should only be used with 24-volt
signals — not line voltage signals.
WATER SOLENOID VALVES — An external solenoid
valve(s) should be used on ground water installations to shut
off flow to the unit when the compressor is not operating. A
slow closing valve may be required to help reduce water
hammer. Figure 29 shows typical wiring for a 24-vac external
solenoid valve. Figures 30 and 31 illustrate typical slow closing
water control valve wiring for Taco 500 Series and Taco ESP
Series valves. Slow closing valves take approximately 60 sec.
to open (very little water will flow before 45 sec.). Once fully
open, an end switch allows the compressor to be energized (only on valves with end switches). Only relay or triac based electronic thermostats should be used with slow closing valves.
When wired as shown, the slow closing valve will operate
properly with the following notations:
1. The valve will remain open during a unit lockout.
2. The valve will draw approximately 25 to 35 VA through
the “Y” signal of the thermostat.
IMPORTANT: Connecting a water solenoid valve can
overheat the anticipators of electromechanical thermostats. Only use relay based electronic thermostats.
25

TYPICAL
WATER
VALVE
C
A
24 VAC
TERMINAL STRIP P2
Fig. 27 — Low Voltage Field Wiring
AQUAZONE CONTROL (Complete C Shown)
Fig. 28 — Typical Aquazone™ Control Board
Jumper Locations
Fig. 29 — Typical Accessory Wiring
a50-8141
a50-7764tf
Fig. 30 — AMV Valve Wiring
C
C
THERMOSTAT
1Y
1
2
3
1Y
AMV
TACO VALVE
HEATER SWITCH
a50-8441
Fig. 31 — Taco SBV Valve Wiring
a50-8442
COMPRESSOR CONTACTOR
LINE
TRANSFORMER
CAPACITOR
LOAD
COMPLETE C CONTROL
W
O
Y2
Y1
G
GGGGR
TB1
CFM
J1
Y
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4
SW5
SW6
SW7
SW8
SW9
OFF
DEHUM
G
S1
ON
Y2
R
C
Y1
THERMOSTAT CONNECTION
DH
R
C
W
G
O
A
A
AL1
AL1
26

–
+
Y
GGGGR
W
O
Y2
Y1
G
R
C
Y2
Y1
G
O
W
C
R
DH
AL1
A
A
AL1
SW1
SW2
SW3
SW4
SW5
SW6
SW7
SW8
SW9
OFF
ON
G
DEHUM
CFM
TB1
J1
S1
THERMOSTAT
INPUT LEDS
CFM COUNTER
1 FLASH PER 100 CFM
ECM MOTOR
LOW VOLTAGE
CONNECTOR
1/4" SPADE
CONNECTIONS
TO COMPLETE C OR
DELUXE D BOARD
THERMOSTAT
CONNECTIONS
DEHUMIDIFICATION
LED
FAN SPEED SELECTION DIP SWITCH
Fig. 32 — ECM Interface Board Physical Layout
Step 10 — Operate ECM Interface Board
STANDALONE — NO DDC CONTROLS — The ECM
fan is controlled by an interface board that converts thermostat
inputs and field selectable cfm settings to signals used by the
ECM (electronically commutated motor) controller. See
Fig. 32.
NOTE: Power must be off to the unit for at least three seconds
before the ECM will recognize a speed change. The motor will
recognize a change in the CFM Adjust or Dehumidification
mode settings while the unit is powered.
There are four different airflow settings from lowest airflow
rate (speed tap 1) to the highest airflow rate (speed tap 4).
Tables 9-13 indicate settings for the ECM interface board, followed by detailed information for each setting.
CAUTION
When the disconnect switch is closed, high voltage is present in some areas of the electrical panel. Exercise caution
when working with energized equipment.
Cooling
mal) cfm for all units with ECM motor. Cooling (normal) setting is used when the unit is not in Dehumidification mode. Tap
1 is the lowest cfm setting, while tap 4 is the highest cfm setting. To avoid air coil freeze-up, tap 1 may not be used if the
Dehumidification mode is selected. See Table 9.
Heating
for 50PTH,PTV,PTD units. Tap 1 is the lowest cfm setting,
while tap 4 is the highest cfm setting. See Table 10.
CFM Adjust
tions. The NORM setting is the factory default position. The +
or – settings adjust the airflow by ±15%. The + or – settings are
used to “fine tune” airflow adjustments. The TEST setting runs
the ECM at 70% torque, which causes the motor to operate
like a standard PSC motor, and disables the cfm counter. See
Tab le 11.
— The cooling setting determines the cooling (nor-
Table 9 — Cooling Settings
TAP SETTING
1 ON ON
2 ON OFF
3 OFF ON
4 OFF OFF
DIP SWITCH
SW1 SW2
— The heating setting determines the heating cfm
Table 10 — Heating Settings
TAP SETTING
1 ON ON
2 ON OFF
3 OFF ON
4 OFF OFF
DIP SWITCH
SW3 SW4
— The CFM Adjust setting allows four selec-
Table 11 — CFM Adjust Settings
TAP SETTING
TEST ON ON
NORM OFF OFF
DIP SWITCH
SW7 SW8
ON OFF
OFF ON
Dehumidification Mode
— The dehumidification mode
setting provides field selection of humidity control. When operating in the normal mode, the cooling airflow settings are determined by the cooling tap setting in Table 12.
Table 12 — Dehumidificaton Mode Settings
TAP SETTING
NORM ON
Dehumid OFF
DIP SWITCH
SW9
When dehumidification is enabled, there is a reduction in
airflow in cooling to increase the moisture removal of the heat
pump. The Dehumidification mode can be enabled in two
ways:
1. Constant Dehumidification mode: When the Dehumidification mode is selected via DIP switch, the ECM will
operate with a multiplier applied to the cooling CFM
settings (approximately 20 to 25% lower airflow). Any
time the unit is running in the Cooling mode, it will operate at the lower airflow to improve latent capacity. The
“DEHUM” LED will be illuminated at all times. Heating
airflow is not affected.
NOTE: Do not select Dehumidification mode if cooling
setting is tap 1.
2. Automatic (humidistat-controlled) Dehumidification
mode: When the Dehumidification mode is selected
via DIP switch AND a humidistat is connected to terminal DH, the cooling airflow will only be reduced when
the humidistat senses that additional dehumidification is
required. The DH terminal is reverse logic. Therefore,
a humidistat (not dehumidistat) is required. The
“DEHUM” LED will be illuminated only when the humidistat is calling for Dehumidification mode. Heating airflow is not affected.
NOTE: Do not select Dehumidification mode if cooling
setting is tap 1.
27

Table 13 — Blower Performance Data
50PT
UNIT SIZE
026 0.50
038 0.50
049 0.75 1
064 0.75 1
072 0.75 1
MAX ESP
(in. wg)
FAN
MOTOR
(hp)
1
/
2
1
/
2
TAP
SETTING
4 810 950 475 630 740 475 920 1060 475
3 725 850 425 560 660 425 825 950 425
2 620 730 370 490 570 370 710 820 370
1 520 610 300 — — — 600 690 300
4 1120 1400 700 870 1090 700 1120 1400 700
3 1000 1250 630 780 980 630 1000 1250 630
2 860 1080 540 670 840 540 860 1080 540
1 730 900 450 — — — 730 900 450
4 1460 1730 870 1140 1350 870 1560 1850 870
3 1300 1550 780 1020 1210 780 1400 1650 780
2 1120 1330 670 870 1040 670 1200 1430 670
1 940 1120 560 — — — 1010 1200 560
4 1670 2050 1020 1300 1600 1020 1860 2280 1020
3 1500 1825 920 1160 1430 920 1650 2050 920
2 1280 1580 790 1000 1230 790 1430 1750 790
1 1080 1320 660 — — — 1200 1470 660
4 1620 2190 1050 1270 1650 1050 1690 2230 1050
3 1500 1950 980 1170 1520 980 1600 2100 980
2 1400 1830 910 1100 1420 910 1400 1850 910
1 1320 1700 850 — — — 1240 1620 850
COOLING MODE (cfm) DEHUMIDIFICATION MODE (cfm) HEATING MODE (cfm)
Stage 1 Stage 2 Fan Stage 1 Stage 2 Fan Stage 1 Stage 2 Fan
WSHP OPEN CONTROLS — The ECM fan is controlled by
an interface board that converts the fan speed outputs from the
WSHP Open control board to the signal used by the ECM motor (see Fig 35). The indicator LEDs allow the service technician to view the airflow mode that the WSHP Open control is
commanding. The table below indicates the illuminated LEDs
for each fan mode.
ECM INDICATORS LEDs SPEED
G Fan Only
G + Y1 Low Fan
G + Y1 + Y2 Med Fan
G + Y1 +W High Fan
NOTE: Power must be off to the unit for at least three seconds
before the ECM will recognize a speed change. The motor will
recognize a change in the CFM Adjust setting (SW7 and SW8)
while the unit is powered.
The WSHP Open controller provides four different airflow
settings which can be set between the lowest airflow (tap 1) to
the highest airflow (tap 4). The lowest three airflow settings
(Fan Only, Low, and Medium) are set using SW3 and SW 4
while the highest airflow (High) is set independently using
SW5 and SW6. This provides the ability to better adjust the fan
performance of the unit to meet the required load conditions.
Cooling and Heating
— The SW3 and SW4 DIP switch settings determine the fan airflow (cfm) to be used during normal
Fan Only, Cooling, Heating, and Dehumidification modes (see
Table 14A). The fan speed and airflow is independent from the
compressor capacity control. During Fan Only operation, the
fan will operate at the Fan Only airflow value specified in the
table for the appropriate tap setting. Once either cooling or
heating is required and the compressor is energized, the fan
will increase the minimum airflow across the coil to the value
defined by the low fan selection. Coil freeze protection and excessive discharge air temperature protection are integral parts
of the WSHP Open controller function so the fan airflow can
increase to medium or high airflow as required and independent of compressor capacity to prevent excessively hot or cold
supply air temperature and coil freeze-up. The selection of the
high fan airflow setting is independent of the other fan airflow
settings and is defined in Table 14B. The high airflow must be
chosen so that it is equal to or greater than the medium fan airflow. Therefore the tap setting for high fan (SW5 and SW6)
MUST equal or exceed the tap chosen for the SW3 and SW4.
Dehumidification
— When Dehumidification is used, the fan
operates at the airflow setting defined by the Medium Fan airflow setting and the tap position of SW3 and SW4.
CFM Adjust
— The CFM Adjust setting allows the balancer
to fine tune the actual airflow. SW7 and SW8 are used to set
the CFM Adjustment if necessary. The NORM setting is the
factory default. The (+) or (-) settings provide the ability to adjust the airflow by either +15% or -15% as needed. A test position is also provided but should not be used (see Table 11).
28

Table 14A — WSHP Open — Fan Only / Low Fan and Med Fan Airflow
50PT UNIT
SIZE
26 0.5 0.5
38 0.5 0.5
49 0.75 1
64 0.75 1
72 0.75 1
NOTE: Factory default setting shown bold. IMPORTANT: The tap setting for high fan MUST equal or exceed the
MAX
ESP
FAN MOTOR
HP
TAP SETTING
4 OFF OFF 475 920 1050
3 OFF ON 425 825 950
2 ON OFF 370 710 820
1 ON ON 300 600 690
4 OFF OFF 700 1120 1400
3 OFF ON 630 1000 1250
2 ON OFF 540 860 1080
1 ON ON 450 730 900
4 OFF OFF 870 1560 1850
3 OFF ON 780 1400 1650
2 ON OFF 670 1200 1430
1 ON ON 560 1010 1200
4 OFF OFF 1020 1860 2280
3 OFF ON 920 1650 2040
2 ON OFF 780 1430 1750
1 ON ON 660 1200 1470
4 OFF OFF 1050 1600 2230
3 OFF ON 980 1600 2100
2 ON OFF 910 1400 1850
1 ON ON 850 1240 1620
SW 3
(SW 1)
SW 4
(SW 2)
FAN ONLY
tap setting for fan only/low/med fan
COOLING AND
HEATING LOW FAN
COOLING AND
HEATING MED FAN
Table 14B — WSHP Open — High Fan Airflow
50PT UNIT SIZE MAX ESP FAN MOTOR HP TAP SETTING SW 5 SW 6 COOLING AND HEATING HIGH FAN
4 OFF OFF 1060
26 0.5 0.5
38 0.5 0.5
49 0.75 1
64 0.75 1
72 0.75 1
NOTE: Factory default setting shown bold.
IMPORTANT: The tap setting for high fan MUST equal or exceed the
tap setting for fan only/low/med fan
3 OFF ON 950
2 ON OFF 820
1 ON ON 690
4 OFF OFF 1400
3 OFF ON 1350
2 ON OFF 1350
1 ON ON 1350
4 OFF OFF 1850
3 OFF ON 1660
2 ON OFF 1430
1 ON ON 1350
4 OFF OFF 2280
3 OFF ON 2050
2 ON OFF 1750
1 ON ON 1470
4 OFF OFF 2230
3 OFF ON 2100
2 ON OFF 1870
1 ON ON 1670
5. Air is purged from closed loop system.
6. System is balanced as required. Monitor if necessary.
7. Isolation valves are open.
PRE-START-UP
System Checkout —
follow the system checkout procedure outlined below before
starting up the system. Be sure:
1. Voltage is within the utilization range specifications of the
unit compressor and fan motor and voltage is balanced
for 3-phase units.
2. Fuses, breakers and wire are correct size.
3. Low voltage wiring is complete.
4. Piping and system flushing is complete.
When the installation is complete,
8. Water control valves or loop pumps are wired.
9. Condensate line is open and correctly pitched.
10. Transformer switched to lower voltage tap if necessary.
11. Blower rotates freely — shipping support is removed.
12. Blower speed is on correct setting.
13. Air filter is clean and in position.
14. Service/access panels are in place.
15. Return-air temperature is between 40 to 80 F heating and
50 to 110 F cooling.
29

16. Air coil is clean.
17. Control field-selected settings are correct.
AIR COIL — To obtain maximum performance, clean the air
coil before starting the unit. A 10% solution of dishwasher
detergent and water is recommended for both sides of the coil.
Rinse thoroughly with water.
FIELD SELECTABLE INPUTS
Jumpers and DIP (dual in-line package) switches on the
control board are used to customize unit operation and can be
configured in the field.
IMPORTANT: Jumpers and DIP switches should only
be clipped when power to control board has been turned
off.
Complete C Control Jumper Settings
WATER COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP1) LIMIT
SETTING — Select jumper 3 (JW3-FP1 Low Temp) to
choose FP1 limit of either 30 F or 10 F. To select 30 F as the
limit, DO NOT clip the jumper. To select 10 F as the limit, clip
the jumper.
AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP2) LIMIT SETTING — Select jumper 2 (JW2-FP2 Low Temp) to choose
FP2 limit of either 30 F or 10 F. To select 30 F as the limit, DO
NOT clip the jumper. To select 10 F as the limit, clip the
jumper.
ALARM RELAY SETTING — Select jumper 1 (JW1-AL2
Dry) to either connect alarm relay terminal (AL2) to 24 vac (R)
or to remain as a dry contact (no connection). To connect AL2
to R, DO NOT clip the jumper. To set as dry contact, clip the
jumper.
Deluxe D Control Jumper Settings
WATER COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP1) LIMIT
SETTING — Select jumper 3 (JW3-FP1 Low Temp) to
choose FP1 limit of either 30 F or 10 F. To select 30 F as the
limit, DO NOT clip the jumper. To select 10 F as the limit, clip
the jumper.
AIR COIL FREEZE PROTECTION (FP2) LIMIT SETTING — Select jumper 2 (JW2-FP2 Low Temp) to choose
FP2 limit of either 30 F or 10 F. To select 30 F as the limit, DO
NOT clip the jumper. To select 10 F as the limit, clip the
jumper.
ALARM RELAY SETTING — Select jumper 4 (JW4-AL2
Dry) to either connect alarm relay terminal (AL2) to 24 vac (R)
or to remain as a dry contact (no connection). To connect AL2
to R, DO NOT clip the jumper. To set as dry contact, clip the
jumper.
LOW PRESSURE SETTING — The Deluxe D control can
be configured for Low Pressure Setting (LP). Select jumper 1
(JW1-LP Norm Open) for choosing between low pressure
input normally opened or closed. To configure for normally
closed operation, DO NOT clip the jumper. To configure for
normally open operation, clip the jumper.
Complete C Control DIP Switches — The Com-
plete C control has 1 DIP (dual in-line package) switch bank
with five switches labeled SW1. See Fig. 15, 17 , 19, and 21.
PERFORMANCE MONITOR (PM) — The PM is a unique
feature that monitors water temperature and will display a warning when heat pump is beyond typical operating range. Refer to
Control Operation section for detailed information. DIP switch
1 will enable or disable this feature. To enable the PM, set the
switch to ON. To disable the PM, set the switch to OFF.
STAGE 2 — DIP switch 2 will enable or disable compressor
delay. Set DIP switch to OFF for stage 2 in which the compressor will have a 3-second delay before energizing.
NOTE: The alarm relay will not cycle during Test mode if
switch is set to OFF, stage 2.
SWITCH 3 — Not used.
DDC OUTPUT AT EH2 — Switch 4 provides a selection for
Direct Digital Control (DDC) operation. If set to DDC output
at EH2, the EH2 terminal will continuously output the last
fault code of the controller. If the control is set to EH2 Normal,
then EH2 will operate as standard electric heat output. Set the
switch to ON to set the EH2 to normal. Set the switch to OFF
to set the DDC output at EH2.
FACTORY SETTING — Switch 5 is set to ON. Do not
change the switch to OFF unless instructed to do so by the
factory.
Deluxe D Control DIP Switches — The Deluxe D
control has 2 DIP (dual in-line package) switch banks. Each
bank has 8 switches and is labeled either S1 or S2 on the circuit board. See Fig. 16, 18, 20, 22, and 23.
DIP SWITCH BANK 1 (S1) — This set of switches offers
the following options for Deluxe D control configuration:
Performance Monitor (PM)
that monitors water temperature and will display a warning
when heat pump is beyond typical operating range. Set switch 1
to enable or disable performance monitor. To enable the PM, set
the switch to ON. To disable the PM, set the switch to OFF.
Compressor Relay Staging Operation
able or disable compressor relay staging operation. The compressor relay can be set to turn on with stage 1 or stage 2 call
from the thermostat. This setting is used with dual stage units
(units with 2 compressors and 2 Deluxe D controls) or in master/slave applications. In master/slave applications, each compressor and fan will stage according to its switch 2 setting. If
switch is set to stage 2, the compressor will have a 3-second
delay before energizing during stage 2 demand.
NOTE: If DIP switch is set for stage 2, the alarm relay will not
cycle during Test mode.
Heating/Cooling Thermostat Type
lection of thermostat type. Heat pump or heat/cool thermostats
can be selected. Select OFF for heat/cool thermostats. When in
heat/cool mode, Y1 is used for cooling stage 1, Y2 is used for
cooling stage 2, W1 is used for heating stage 1 and O/W2 is
used for heating stage 2. Select ON for heat pump thermostats.
In heat pump mode, Y1 used is for compressor stage 1, Y2 is
used for compressor stage 2, W1 is used for heating stage 3 or
emergency heat, and O/W2 is used for reversing valve (heating
or cooling) depending upon switch 4 setting.
O/B Thermostat Type
pump O/B thermostats. O is cooling output. B is heating output. Select ON for thermostats with O output. Select OFF for
thermostats with B output.
Dehumidification Fan Mode
of normal or dehumidification fan mode. Select OFF for
dehumidification mode. The fan speed relay will remain OFF
during cooling stage 2. Select ON for normal mode. The fan
speed relay will turn on during cooling stage 2 in normal mode.
Output
— Switch 6 provides selection for DDC operation. If
set to DDC output at EH2, the EH2 terminal will continuously
output the last fault code of the controller. If the control is set to
EH2 normal, then the EH2 will operate as standard electric
heat output. Set the switch to ON to set the EH2 to normal. Set
the switch to OFF to set the DDC output at EH2.
Boilerless Operation
erless operation and works in conjunction with switch 8. In
boilerless operation mode, only the compressor is used for
heating when FP1 is above the boilerless changeover temperature set by switch 8 below. Select ON for normal operation or
select OFF for boilerless operation.
— The PM is a unique feature
— Switch 2 will en-
— Switch 3 provides se-
— Switch 4 provides selection for heat
— Switch 5 provides selection
— Switch 7 provides selection of boil-
30

Boilerless Changeover Temperature
— Switch 8 on S1
provides selection of boilerless changeover temperature set
point. Select OFF for set point of 50 F or select ON for set
point of 40 F.
If switch 8 is set for 50 F, then the compressor will be used
for heating as long as the FP1 is above 50 F. The compressor
will not be used for heating when the FP1 is below 50 F and the
compressor will operates in emergency heat mode, staging on
EH1 and EH2 to provide heat. If a thermal switch is being used
instead of the FP1 thermistor, only the compressor will be used
for heating mode when the FP1 terminals are closed. If the FP1
terminals are open, the compressor is not used and the control
goes into emergency heat mode.
DIP SWITCH BANK 2 (S2) — This set of DIP switches is
used to configure accessory relay options. See Fig. 16, 18, 20,
22, and 23.
Switches 1 to 3
— These DIP switches provide selection of
Accessory 1 relay options. See Table 15A for DIP switch
combinations.
Switches 4 to 6
— These DIP switches provide selection of
Accessory 2 relay options. See Table 15B for DIP switch
combinations.
Table 15A — DIP Switch Block S2 —
Accessory 1 Relay Options
ACCESSORY 1
RELAY OPTIONS
Cycle with Fan On On On
Digital NSB Off On On
Water Valve — Slow Opening On Off On
Reheat — Dehumidistat Off On Off
NSB — Night Setback
OAD — Outside Air Damper
NOTE: All other DIP switch combinations are invalid.
OAD On On Off
Reheat — Humidistat Off Off Off
LEGEND
DIP SWITCH POSITION
123
Table 15B — DIP Switch Block S2 —
Accessory 2 Relay Options
ACCESSORY 2
RELAY OPTIONS
Cycle with Compressor On On On
Digital NSB Off On On
Water Valve — Slow Opening On Off On
NSB — Night Setback
OAD — Outside Air Damper
NOTE: All other switch combinations are invalid.
OAD On On Off
LEGEND
DIP SWITCH POSITION
456
Auto Dehumidification Mode or High Fan Mode — Switch 7
provides selection of auto dehumidification fan mode or high
fan mode. In auto dehumidification fan mode, the fan speed
relay will remain off during cooling stage 2 if terminal H is
active. In high fan mode, the fan enable and fan speed relays will
turn on when terminal H is active. Set the switch to ON for auto
dehumidification fan mode or to OFF for high fan mode.
Factory Setting
— Switch 8 is set to ON. Do not change the
switch to OFF unless instructed to do so by the factory.
Units with Modulating Hot Water Reheat
(HWR) Option
STANDALONE — NO DDC CONTROLS — A heat
pump equipped with hot water reheat (HWR) can operate in
three modes: cooling, cooling with reheat, and heating. The
cooling and heating modes are like any other water source heat
pump. The reversing valve ("O" signal) is energized in cooling, along with the compressor contactor(s) and blower relay.
In the heating mode, the reversing valve is deenergized.
Almost any thermostat will activate the heat pump in heating
or cooling modes. The Deluxe D microprocessor board, which
is standard with the HWR option, will accept either heat pump
(Y,O) thermostats or non-heat pump (Y,W) thermostats.
The reheat mode requires either a separate humidistat/
dehumidistat or a thermostat that has an integrated dehumidification function for activation. The Deluxe D board is configured to work with either a humidistat or dehumidistat input to
terminal “H” (DIP switch settings for the Deluxe D board are
shown in Table 16). Upon receiving an “H” input, the Deluxe
D board will activate the cooling mode and engage reheat.
Table 16 — Humidistat/Dehumidistat Logic and
Deluxe D DIP Switch Settings
Sensor 2.1
Humidistat
Dehumidistat Off On Off Standard 24 VAC 0 VAC
2.2 2.3 Logic
Of f O ff O ff Re ve rs e 0 VA C 24 VAC
Reheat
(ON) - H
Reheat
(OFF) - H
Table 17 shows the relationship between thermostat input
signals and unit operation. There are four operational inputs for
single-stage units and six operational inputs for dual-stage
units:
•Fan Only
• Cooling Stage 1
• Cooling Stage 2
• Heating Stage 1
• Heating Stage 2
• Reheat Mode
WSHP OPEN CONTROLS — A heat pump equipped with
the hot water reheat option and the WSHP Open controller,
operates in three modes: Cooling, Heating and Dehumidification. Cooling and Heating modes follow the standard water
source heat pump operation with the reversing valve controlling the operating mode (Heating or Cooling) and the compressor.
The hot water reheat option uses the Deluxe D board and
the optional humidity sensor to provide dehumidification operation that is separate from the standard heating or cooling cycle. The Dehumidification mode is active when the value of the
humidity sensor exceeds the appropriate (occupied or unoccupied) humidity setpoint in the WSHP Open controller. When
this occurs, the WSHP Open controller outputs a signal to the
H terminal of the Deluxe D board which starts dehumidification with hot water reheat. The WSHP Open controller also
sets the fan to operate at the airflow defined by the medium fan
speed and the tap setting of SW3 and SW4. Dehumidification
is ONLY active when neither cooling nor heating is required
and the humidity sensor value exceeds the humidity setpoint.
Also, both the HWR option and the Optional RH sensor must
be set to Enable in the WSHP Open control for dehumidification.
HWR APPLICATION CONSIDERATIONS — Unlike
most hot gas reheat options, the HWR option will operate
over a wide range of entering-water temperatures (EWTs).
Special flow regulation (water regulating valve) is not
required for low EWT conditions. However, below 55 F,
supply-air temperatures cannot be maintained at 72 F
because the cooling capacity exceeds the reheat coil capacity at low water temperatures. Below 55 F, essentially all
water is diverted to the reheat coil (no heat of rejection to
the building loop). Although the HWR option will work fine
with low EWTs, overcooling of the space may result with
well water systems or, on rare occasions, with ground loop
(geothermal) systems (NOTE: Extended range units are
required for well water and ground loop systems). Since
dehumidification is generally only required in cooling, most
31

ground loop systems will not experience overcooling of the
supply-air temperature. If overcooling of the space is a concern (e.g., computer room well water application), auxiliary
heating may be required to maintain space temperature
when the unit is operating in the dehumidification mode.
Water source heat pumps with HWR should not be used as
makeup air units. These applications should use equipment
specifically designed for makeup air.
HWR COMPONENT FUNCTIONS — The proportional
controller operates on 24 VAC power supply and automatically
adjusts the water valve based on the supply-air sensor. The
supply-air sensor senses supply-air temperature at the blower
inlet, providing the input signal necessary for the proportional
control to drive the motorized valve during the reheat mode of
operation. The motorized valve is a proportional actuator/threeway valve combination used to divert the condenser water
from the coax to the hydronic reheat coil during the reheat
mode of operation. The proportional controller sends a signal
to the motorized valve based on the supply-air temperature
reading from the supply air sensor.
The loop pump circulates condenser water through the hydronic reheat coil during the reheat mode of operation (refer to
Fig. 33). In this application, the loop pump is only energized
during the reheat mode of operation. The hydronic coil is utilized during the reheat mode of operation to reheat the air to the
set point of the proportional controller. Condenser water is diverted by the motorized valve and pumped through the hydronic coil by the loop pump in proportion to the control set point.
The amount of reheating is dependent on the set point and how
far from the set point the supply air temperature is. The factory
set point is 70 to 75 F, generally considered "neutral" air.
Deluxe D Control Accessory Relay Configurations — The following accessory relay settings are applica-
ble for Deluxe D control:
CYCLE WITH FAN — In this configuration, the accessory
relay 1 will be ON any time the Fan Enable relay is on.
CYCLE WITH COMPRESSOR — In this configuration, the
accessory relay 2 will be ON any time the Compressor relay is
on.
DIGITAL NIGHT SET BACK (NSB) — In this configuration, the relay will be ON if the NSB input is connected to
ground C.
NOTE: If there are no relays configured for digital NSB, then
the NSB and override (OVR) inputs are automatically configured for mechanical operation.
MECHANICAL NIGHT SET BACK — When NSB input is
connected to ground C, all thermostat inputs are ignored. A
thermostat set back heating call will then be connected to the
OVR input. If OVR input becomes active, then the Deluxe D
control will enter night low limit (NLL) staged heating mode.
The NLL staged heating mode will then provide heating during the NSB period.
WATER VALVE (SLOW OPENING) — If relay is configured
for Water Valve (slow opening), the relay will start 60 seconds
prior to starting compressor relay.
OUTSIDE AIR DAMPER (OAD) — If relay is configured for
OAD, the relay will normally be ON any time the Fan Enable
relay is energized. The relay will not start for 30 minutes following a return to normal mode from NSB, when NSB is no
longer connected to ground C. After 30 minutes, the relay will
start if the Fan Enable is set to ON.
CAUTION
To avoid equipment damage, DO NOT leave system filled
in a building without heat during the winter unless antifreeze is added to system water. Condenser coils never
fully drain by themselves and will freeze unless winterized
with antifreeze.
Table 17 — HWR Operating Modes
MODE
No Demand On/Off Off Off Off Off On/Off Off Off Off Off
Fan Only On/Off On Off Off Off On/Off On Off Off Off
Cooling Stage 1 On On On Off Off On On On Off Off
Cooling Stage 2 On On On On Off On On On On Off
Cooling and Dehumidistat
Dehumidistat Only On/Off Off Off Off On On On On On On
Heating Stage 1 Off On On Off Off Off On On Off Off
Heating Stage 2 Off OnOnOnOffOffOnOnOnOff
Heating and Dehumidistat** Off On On On/Off On Off On On On/Off Off
*Not applicable for single stage units; Full load operation for dual capacity
units.
†Cooling input takes priority over dehumidify input.
†
O G Y1 Y2* H O G Y1 Y2* Reheat
On On On On/Off On On On On On/Off Off
INPUT OUTPUT
**Deluxe D is programmed to ignore the H demand when the unit is in heating
mode.
NOTE: On/Off is either on or off.
32

START-UP
Fig. 33 — HWR Schematic
a50-8145
Water Out
(To Water Loop)
Water In
(From Water Loop)
Mixing Valve
COAX
Evaporator Coil
Reheat
Coil
Refrigerant Out
(Cooling)
Refrigerant In
(Cooling)
Entering Air
Leaving
Air
Internal Pump
NOTE: All components shown are
internal to the heat pump unit.
Use the procedure outlined below to initiate proper unit
start-up.
NOTE: This equipment is designed for indoor installation only.
Operating Limits
ENVIRONMENT — This equipment is designed for indoor
installation ONLY. Extreme variations in temperature, humidity and corrosive water or air will adversely affect the unit performance, reliability and service life.
POWER SUPPLY — A voltage variation of ± 10% of nameplate utilization voltage is acceptable.
UNIT STARTING CONDITIONS — Units start and operate
in an ambient temperature of 45 F with entering-air temperature at 50 F, entering-water temperature at 60 F and with both
air and water at the flow rates used.
NOTE: These operating limits are not normal or continuous
operating conditions. Assume that such a start-up is for the
purpose of bringing the building space up to occupancy temperature. See Table 18 for operating limits.
WARNING
When the disconnect switch is closed, high voltage is present in some areas of the electrical panel. Exercise caution
when working with the energized equipment.
1. Restore power to system.
2. Turn thermostat fan position to ON. Blower should start.
3. Balance airflow at registers.
4. Adjust all valves to the full open position and turn on the
line power to all heat pump units.
5. Operate unit in the cooling cycle first, then the heating
cycle. Refer to Table 18 for unit operating limits. Allow 15 minutes between cooling and heating tests for
pressure to equalize.
NOTE: Two factors determine the operating limits of a unit:
entering-air temperature and water temperature. Whenever any
of these factors are at a minimum or maximum level, the other
two factors must be at a normal level to ensure proper unit
operation. See Table 18.
Table 18 — Operating Limits —
50PTH, PTV, PTD Units
Min. Ambient Air 45 40
Rated Ambient Air 80 70
Max. Ambient Air 100 85
Min. Entering Air 50 40
Rated Entering Air db/wb 80/67 70
Max. Entering Air db/wb 110/83 80
Min. Entering Water 30 20
Normal Entering Water 50-110 30-70
Max. Entering Water 120 90
db — Dry Bulb
wb — Wet Bulb
NOTE: Value in heating column is dry bulb only. Any wet bulb reading is
acceptable.
AIR LIMITS COOLING (F) HEATING (F)
WATER LIMITS
LEGEND
33

Scroll Compressor Rotation — It is important to be
certain compressor is rotating in the proper direction. To
determine whether or not compressor is rotating in the proper
direction:
1. Connect service gages to suction and discharge pressure
fittings.
2. Energize the compressor.
3. The suction pressure should drop and the discharge
pressure should rise, as is normal on any start-up.
If the suction pressure does not drop and the discharge
pressure does not rise to normal levels:
1. Turn off power to the unit. Install disconnect tag.
2. Reverse any two of the unit power leads.
3. Reapply power to the unit and verify pressures are correct.
The suction and discharge pressure levels should now move
to their normal start-up levels.
When the compressor is rotating in the wrong direction, the
unit makes more noise and does not provide cooling.
After a few minutes of reverse operation, the scroll compressor internal overload protection will open, thus activating
the unit lockout. This requires a manual reset. To reset, turn the
thermostat on and then off.
NOTE: There is a 5-minute time delay before the compressor
will start.
Unit Start-Up Cooling Mode
1. Adjust the unit thermostat to the warmest position.
Slowly reduce the thermostat position until the compressor activates.
2. Check for cool air delivery at unit grille a few minutes
after the unit has begun to operate.
3. Verify that the compressor is on and that the water flow
rate is correct by measuring pressure drop through the
heat exchanger using P/T plugs. See Table 19. Check the
elevation and cleanliness of the condensate lines; any
dripping could be a sign of a blocked line. Be sure the
condensate trap includes a water seal.
4. Check the temperature of both supply and discharge
water. Compare to Tables 20-23. If temperature is within
range, proceed. If temperature is outside the range, check
the cooling refrigerant pressures in Tables 20-23.
5. Check air temperature drop across the coil when compressor is operating. Air temperature drop should be
between 15 and 25 F.
Unit Start-Up Heating Mode
NOTE: Operate the unit in heating cycle after checking the
cooling cycle. Allow 5 minutes between tests for the pressure
or reversing valve to equalize.
1. Turn thermostat to lowest setting and set thermostat
switch to HEAT position.
2. Slowly turn the thermostat to a higher temperature until
the compressor activates.
3. Check for warm air delivery at the unit grille within a few
minutes after the unit has begun to operate.
4. Check the temperature of both supply and discharge
water. Compare to Tables 20-23. If temperature is within
range, proceed. If temperature is outside the range, check
the heating refrigerant pressures in Tables 20-23.
5. Once the unit has begun to run, check for warm air delivery at the unit grille.
6. Check air temperature rise across the coil when compressor is operating. Air temperature rise should be between
20 and 30 F after 15 minutes at load.
7. Check for vibration, noise and water leaks.
Table 19 — Water Temperature Change
WATER FLOW RATE (GPM)
For Closed Loop: Ground Source or
Cooling/Boiler Systems at 3 gpm/ton
For Open Loop: Ground Water Systems at
1.5 gpm/ton
Through Heat Exchanger
COOLING
RISE (F)
Min Max Min Max
91248
20 26 10 17
HEATING
DROP (F)
Table 20 — Typical 50PTH,PTV,PTD026 Unit Operating Pressures and Temperatures
ENTERING
WATER
TEMP (F)
(EWT)
30
50
70
90
110
DB — Dry Bulb
HWG — Hot Water Generator
——No heating operation in this temperature range
WATER
FLOW
(Gpm/Ton)
1.5 118-128 159-179 25-30 9-14 16.7-18.7 19-25 73- 83 273-293 6-11 3- 8 5.9- 7.9 16-22
2.25 118-128 146-166 25-30 7-12 12.3-14.3 20-26 75- 85 275-295 6-11 3- 8 4.2- 6.2 17-23
3 118-128 132-152 25-30 7-12 7.9- 9.9 20-26 78- 88 277-297 6-11 3- 8 2.7- 4.7 18-24
1.5 128-138 186-206 18-23 8-13 16.3-18.3 19-25 102-112 302-322 8-12 6-11 8.9-10.9 22-28
2.25 128-138 172-192 18-23 6-11 12.1-14.1 20-26 106-116 303-323 8-12 6-11 6.7- 8.7 23-29
3 128-138 158-178 18-23 6-11 7.8- 9.8 20-26 110-120 305-325 8-12 6-11 4.5- 6.5 23-29
1.5 136-146 281-301 7-12 7-12 15.7-17.7 19-25 128-138 330-350 10-15 8-13 11.3-13.3 27-34
2.25 136-146 267-287 7-12 5-10 11.6-13.6 19-25 134-144 332-352 10-15 8-13 8.5-10.5 28-35
3 136-146 253-273 7-12 4- 9 7.6- 9.6 19-25 141-151 334-354 10-15 8-13 5.8- 7.8 28-35
1.5 139-149 368-388 6-11 7-12 14.9-16.9 18-24 162-172 367-387 14-19 10-15 14.4-16.4 33-41
2.25 139-149 354-374 6-11 5-10 11.0-13.0 18-24 166-176 372-392 15-20 10-15 10.8-12.8 34-42
3 139-149 340-360 6-11 5-10 7.2- 9.2 18-24 171-181 377-397 17-22 10-15 7.1- 9.1 34-42
1.5 143-153 465-485 6-11 7-12 13.9-15.9 17-23 — — — — — —
2.25 143-153 450-470 6-11 5-10 10.2-12.2 17-23 — — — — — —
3 143-153 433-453 6-11 5-10 6.5- 8.5 17-23 — — — — — —
FULL LOAD COOLING WITHOUT HWG ACTIVE FULL LOAD HEATING WITHOUT HWG ACTIVE
Suction
Pressure
LEGEND
(psig)
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Super-
heat
(F)
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Water
Tem p
Rise
(F)
Air
Tem p
Drop (F)
DB
Suction
Pressure
(psig)
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Super-
heat
(F)
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Wate r
Tem p
Drop
(F)
Air
Tem p
Rise (F)
DB
34

Table 21 — Typical 50PTH,PTV,PTD038 Unit Operating Pressures and Temperatures
ENTERING
WATER
TEMP (F)
(EWT)
30
50
70
90
110
DB — Dry Bulb
HWG — Hot Water Generator
——No heating operation in this temperature range
WATER
FLOW
(Gpm/Ton)
1.5 120-130 156-176 25-30 9-14 22.1-24.1 18-24 69- 79 293-313 7-12 14-19 8.9-10.9 17-23
2.25 119-129 148-168 25-30 8-13 16.8-18.8 19-25 73- 83 297-317 7-12 14-19 6.7- 8.7 18-24
3 119-129 138-158 25-30 8-13 10.5-12.5 19-25 76- 86 300-320 7-12 14-19 4.5- 6.5 19-25
1.5 129-139 225-245 15-20 10-15 21.9-23.9 18-24 96-106 322-342 10-15 17-22 12.2-14.2 23-29
2.25 128-138 211-231 15-20 9-14 16.1-18.1 19-25 100-110 326-346 10-15 17-22 9.3-11.3 24-30
3 128-138 197-217 15-20 9-14 10.3-12.3 19-25 105-115 331-351 10-15 17-22 6.4- 8.4 24-30
1.5 136-146 302-322 9-14 13-18 21.5-23.5 18-24 123-133 352-372 11-16 19-24 15-17 28-35
2.25 135-145 283-303 9-14 12-17 15.8-17.8 19-25 129-139 358-378 11-16 19-24 11.6-13.6 29-36
3 135-145 265-285 9-14 12-17 10.0-12.0 19-25 135-145 364-384 11-16 19-24 8.2-10.2 30-37
1.5 140-150 390-410 7-12 13-18 20.5-22.5 17-23 157-167 390-410 13-18 18-23 21-23 36-44
2.25 140-150 369-389 8-13 8-13 14.9-16.9 17-23 169-179 399-419 13-18 16.5-21.5 15.5-17.5 37-45
3 140-150 349-369 8-13 8-13 9.3-11.3 17-23 181-191 408-428 14-19 15-20 10.5-12.5 39-47
1.5 145-155 488-508 7-12 13-18 19.0-21.0 17-23 — — — — — —
2.25 145-155 467-487 8-13 8-13 14.0-16.0 17-23 — — — — — —
3 145-155 447-467 8-13 8-13 9.0-11.0 17-23 — — — — — —
FULL LOAD COOLING WITHOUT HWG ACTIVE FULL LOAD HEATING WITHOUT HWG ACTIVE
Suction
Pressure
(psig)
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Super-
heat
(F)
LEGEND
Table 22 — Typical 50PTH,PTV,PTD049 Unit Operating Pressures and Temperatures
ENTERING
WATER
TEMP (F)
(EWT)
30
50
70
90
110
DB — Dry Bulb
HWG — Hot Water Generator
——No heating operation in this temperature range
WATER
FLOW
(Gpm/Ton)
1.5 112-122 187-207 22-27 14-19 20.7-22.7 18-24 66- 76 286-306 7-12 8-13 8-10 18-24
2.25 111-121 167-187 22-27 12-17 15.5-17.5 18-24 69- 79 289-309 7-12 9-14 6- 8 19-25
3 111-121 147-167 23-28 11-16 10.2-12.2 18-24 72- 82 292-312 7-12 9-14 4- 6 19-25
1.5 125-135 242-262 13-18 10-15 20.9-22.9 19-25 93-103 314-334 8-13 10-15 11.5-13.5 23-29
2.25 123-133 224-244 13-18 9-14 15.6-17.6 19-25 98-108 320-340 8-13 10-15 8.7-10.7 24-30
3 122-132 205-225 14-19 7-12 10.2-12.2 19-25 103-113 326-346 8-13 10-15 5.9- 7.9 25-31
1.5 133-143 310-330 8-13 8-13 20.5-22.5 19-25 123-133 344-364 9-14 9-14 15-17 28-35
2.25 132-142 290-310 8-13 7-12 15.2-17.2 19-25 130-140 354-374 9-14 9-14 11.5-13.5 29-36
3 131-141 270-290 9-14 5-10 9.9-11.9 19-25 137-147 361-381 9-14 9-14 7.9- 9.9 30-37
1.5 138-148 396-416 7-12 7-12 19.2-21.2 18-24 165-175 390-410 13-18 8-13 19.6-21.6 37-45
2.25 137-147 374-394 7-12 6-11 14.3-16.3 18-24 175-185 401-421 15-20 8-13 15-17 38-46
3 136-146 352-372 7-12 4- 9 9.3-11.3 18-24 185-195 413-433 17-22 8-13 10.3-12.3 39-47
1.5 144-154 497-517 7-12 5-10 18.0-20.0 17-23 — — — — — —
2.25 143-153 472-492 7-12 4- 9 13.3-15.3 17-23 — — — — — —
3 142-152 447-467 7-12 3- 8 8.5-10.5 17-23 — — — — — —
FULL LOAD COOLING WITHOUT HWG ACTIVE FULL LOAD HEATING WITHOUT HWG ACTIVE
Suction
Pressure
(psig)
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Super-
heat
(F)
LEGEND
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Water
Tem p
Rise
(F)
Water
Tem p
Rise
(F)
Air
Tem p
Drop (F)
DB
Air
Tem p
Drop (F)
DB
Suction
Pressure
(psig)
Suction
Pressure
(psig)
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Super-
heat
(F)
Super-
heat
(F)
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Wate r
Tem p
Drop
(F)
Wate r
Tem p
Drop
(F)
Air
Tem p
Rise (F)
DB
Air
Tem p
Rise (F)
DB
Table 23 — Typical 50PTH,PTV,PTD064,072 Unit Operating Pressures and Temperatures
ENTERING
WATER
TEMP (F)
(EWT)
30
50
70
90
110
DB — Dry Bulb
HWG — Hot Water Generator
——No heating operation in this temperature range
WATER
FLOW
(Gpm/Ton)
1.5 117-127 170-190 27-32 15-20 18.2-20.2 17-23 66- 76 282-302 10-16 9-14 8-10 19-25
2.25 116-126 143-163 28-33 13-18 12.6-14.6 17-23 69- 79 285-305 10-16 9-14 6- 8 19-25
3 115-125 135-155 29-34 12-17 7.0- 9.0 17-23 72- 82 289-309 10-16 10-15 4- 6 20-26
1.5 128-138 238-258 16-21 14-19 20.5-22.5 21-27 90-100 310-330 11-17 12-17 11.3-13.3 24-30
2.25 126-136 222-242 21-26 13-18 14.9-16.9 21-27 95-105 313-333 11-17 12-17 8.5-10.5 25-31
3 125-135 205-225 26-31 12-17 9.2-11.2 21-27 99-109 316-336 11-17 12-17 5.7- 7.7 26-32
1.5 135-145 315-335 10-15 14-19 21.0-23.0 22-28 115-125 337-357 12-18 14-19 14-16 28-35
2.25 134-144 296-316 12-17 13-18 15.5-17.5 22-28 120-130 341-361 12-18 14-19 10.6-12.6 29-36
3 133-143 276-296 15-20 11-16 10.0-12.0 22-28 126-136 345-365 12-18 15-20 7.3- 9.3 30-37
1.5 139-149 408-428 10-15 15-20 20.1-22.1 21-27 157-167 390-410 15-20 14-19 18.2-20.2 37-45
2.25 138-148 386-406 10-15 13-18 14.8-16.8 21-27 161-171 394-414 15-20 14-19 13.9-15.9 38-46
3 138-148 364-384 10-15 11-16 9.5-11.5 21-27 166-176 398-418 15-20 15-20 9.6-11.6 39-47
1.5 144-154 515-535 8-13 14-19 19.0-21.0 20-26 — — — — — —
2.25 143-153 493-513 8-13 13-18 14.0-16.0 20-26 — — — — — —
3 142-152 469-489 8-13 12-17 9.0-11.0 20-26 — — — — — —
FULL LOAD COOLING WITHOUT HWG ACTIVE FULL LOAD HEATING WITHOUT HWG ACTIVE
Suction
Pressure
(psig)
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Super-
heat
(F)
LEGEND
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Water
Tem p
Rise
(F)
35
Air
Tem p
Drop (F)
DB
Suction
Pressure
(psig)
Discharge
Pressure
(psig)
Super-
heat
(F)
Sub-
cooling
(F)
Wate r
Tem p
Drop
(F)
Air
Tem p
Rise (F)
DB

Unit Start-Up with WSHP Open Controls —
Fig. 34 — BACview6 Display Interface
a50-8444
*Sponsored by ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air Conditioning Engineers).
The WSHP Open is a multi-protocol (default BACnet*) controller with extensive features, flexible options and powerful
capabilities. The unit comes from the factory pre-programmed
and needs minimal set up to function in a BAS (Building
Automation System) system or provide additional capabilities
to Carrier's WSHP product line. Most settings on the controller
have factory defaults set for ease of installation. There are a
few settings that must be configured in the field and several
settings that can be adjusted if required by unique job conditions. Refer to Appendix A — WSHP Open Screen Configuration. In order to configure the unit, a BACview
required. See Fig. 34.
NOTE: If the WSHP Open control has lost its programming,
all display pixels will be displayed on the SPT sensor. See the
WSHP Third Party Integration Guide.
When the unit is OFF, the SPT sensor will indicate OFF.
When power is applied, the SPT sensor will indicate temperature in the space at 78 F.
To start-up a unit with WSHP Open controls:
1. To plug in the BACview
6
handheld display into a SPT
sensor, point the two ears on the connector up and tilt the
bottom of the plug toward you. Insert the plug up into the
SPT sensor while pushing the bottom of the plug away
from you.
2. BACview
6
should respond with "Establishing Connection." The Home screen will then appear on the display
showing operating mode and space temperature. Press
any button to continue.
See Appendix A — WSHP Open Screen Configuration
for the hierarchal structure of the WSHP Open controller.
All functions of the controller can be set from the Home
screen.
3. When the Login is requested, type 1111 and push the OK
softkey. The Logout will then be displayed to indicate the
password was accepted.
4. To set the Clock if it is not already displayed:
a. Select System Settings from the Home screen, then
press Clockset.
b. Scroll to hour, minute and second using the arrow
keys. Use the number keypad to set actual time.
c. Scroll to day, month and year using arrow keys.
Use number keypad to set date.
5. To set Daylight Savings Time (DST):
a. Push the DST softkey. The display will indicate
02:00:060 which is equal to 2:00AM.
6
display is
b. To program the beginning and end dates, scroll
down to the beginning month and press the enter
key. The softkeys (INCR and DECR) will activate
to increment the month in either direction, Jan,
Feb, March, etc.
c. Use number keys to select the day of month and
year.
d. Push the OK softkey to finalize the data.
6. To view configuration settings:
a. Select the Config softkey.
b. Select the Service Config softkey. Scroll through
the factory settings by using the up and down
arrow keys. See below for factory settings.
Only the following settings will need to be
checked.
• # of Fan Speeds — This should be set to "1" for
units with PSC motors and set to "3" for units with
ECM motors.
• Compressor Stages — This should be set to "1."
• Factory Dehumidification Reheat Coil — This
should be set to "none" unless the modulating hot
water reheat option is supplied in the unit, then set
to "installed."
• The condenser water limit needs to be verified
depending on design parameters and application,
whether geothermal or boiler/tower.
7. To view unit configuration settings:
a. Select the Unit Configuration softkey, then select
Unit.
b. Scroll through the unit settings by using the up and
down arrow keys. Unit settings include:
• Fan Mode: Default Continuous
• Fan Delay:
• Minimum SAT Cooling: Default 50 F
• Maximum SAT Heating: Default 110 F
• Filter Service Alarm: Must be set from 0 to 9999 hr
8. To set local schedules:
a. Select the Schedule softkey from the Configuration
screen, then press enter.
b. Select Weekly, then press enter (7 schedules
available).
c. Select day and press enter.
d. Press enter again and select ADD or DEL (DECR
or INCR) set schedule.
e. Enter ON/OFF time, then press continue.
36

f. Press OK to apply and save to a particular day of
the week.
g. Continue to add the same or different schedule spe-
cific days of the week.
To add exceptions to the schedule:
i. Press Add softkey.
ii. Select exception type from following:
• Date
• Date Range
• Week-N-Day
• Calender Reference
9. Go back to Home Screen.
10. Remove BACview
6
cable from SPT sensor by reversing
the process in Step 1.
11. Perform system test.
Flow Regulation — Flow regulation can be accom-
plished by two methods. Most water control valves have a flow
adjustment built into the valve. By measuring the pressure drop
through the unit heat exchanger, the flow rate can be determined. See Table 24. Adjust the water control valve until the
flow of 1.5 to 2 gpm is achieved. Since the pressure constantly
varies, two pressure gages may be needed in some
applications.
Table 24 — Coaxial Water Pressure Drop
UNIT 50PTH, PTV,
PTD
026
038
049
064,072
GPM
4.0 1.5 1.3 1.1 1.0
6.0 3.1 2.6 2.3 2.1
7.0 4.1 3.4 3.0 2.7
8.0 5.1 4.3 3.8 3.4
4.0 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6
6.0 2.6 2.5 2.3 2.1
8.0 4.5 4.2 4.0 3.7
9.0 5.7 5.2 4.8 4.4
5.5 1.1 0.9 0.8 0.7
8.3 2.2 2.1 2.0 1.8
11.0 3.9 3.6 3.2 3.1
12.0 4.5 4.2 3.8 3.5
7.0 0.5 0.3 0.2 0.1
10.5 1.9 1.8 1.7 1.6
14.0 3.9 3.5 3.2 2.9
15.0 4.8 4.3 3.9 3.5
WATER TEMPERATURE (F)
30 F 50 F 70 F 90 F
Pressure Drop (psi)
An alternative method is to install a flow control device.
These devices are typically an orifice of plastic material designed to allow a specified flow rate that are mounted on the
outlet of the water control valve. Occasionally these valves
produce a velocity noise that can be reduced by applying some
back pressure. To accomplish this, slightly close the leaving
isolation valve of the well water setup.
WARNING
the water level in the flush cart tank to drop below the
pump inlet line in order to prevent air from filling the line.
3. Maintain a fluid level in the tank above the return tee in
order to avoid air entering back into the fluid.
4. Shutting off the return valve that connects into the flush
cart reservoir will allow 50 psig surges to help purge air
pockets. This maintains the pump at 50 psig.
5. To purge, keep the pump at 50 psig until maximum
pumping pressure is reached.
6. Open the return valve to send a pressure surge through
the loop to purge any air pockets in the piping system.
7. A noticeable drop in fluid level will be seen in the flush
cart tank. This is the only indication of air in the loop.
NOTE: If air is purged from the system while using a
10 in. PVC flush tank, the level drop will only be 1 to
2 in. since liquids are incompressible. If the level drops
more than this, flushing should continue since air is still
being compressed in the loop. If level is less than 1 to
2 in., reverse the flow.
8. Repeat this procedure until all air is purged.
9. Restore power.
Antifreeze may be added before, during, or after the flushing process. However, depending on when it is added in the
process, it can be wasted. Refer to the Antifreeze section for
more detail.
Loop static pressure will fluctuate with the seasons. Pressures will be higher in the winter months than during the warmer months. This fluctuation is normal and should be considered
when charging the system initially. Run the unit in either
heating or cooling for several minutes to condition the loop to a
homogenous temperature.
When complete, perform a final flush and pressurize the
loop to a static pressure of 40 to 50 psig for winter months or
15 to 20 psig for summer months.
After pressurization, be sure to remove the plug from the
end of the loop pump motor(s) to allow trapped air to be
discharged and to ensure the motor housing has been flooded.
Be sure the loop flow center provides adequate flow through
the unit by checking pressure drop across the heat exchanger.
Compare the results to the data in Table 24.
Antifreeze — In areas where entering loop temperatures
drop below 40 F or where piping will be routed through areas
subject to freezing, antifreeze is needed.
Alcohols and glycols are commonly used as antifreeze
agents. Freeze protection should be maintained to 15 F below
the lowest expected entering loop temperature. For example, if
the lowest expected entering loop temperature is 30 F, the
leaving loop temperature would be 22 to 25 F. Therefore, the
freeze protection should be at 15 F (30 F – 15 F = 15 F).
IMPORTANT: All alcohols should be pre-mixed and
pumped from a reservoir outside of the building or
introduced under water level to prevent fuming.
To avoid possible injury or death due to electrical shock,
open the power supply disconnect switch and secure it in
an open position before flushing system.
Flushing — Once the piping is complete, units require final
purging and loop charging. A flush cart pump of at least 1.5 hp
is needed to achieve adequate flow velocity in the loop to purge
air and dirt particles from the loop. Flush the loop in both directions with a high volume of water at a high velocity. Follow the
steps below to properly flush the loop:
1. Verify power is off.
2. Fill loop with water from hose through flush cart before
using flush cart pump to ensure an even fill. Do not allow
Calculate the total volume of fluid in the piping system. See
Table 25. Use the percentage by volume in Table 26 to determine the amount of antifreeze to use. Antifreeze concentration
should be checked from a well-mixed sample using a hydrometer to measure specific gravity.
FREEZE PROTECTION SELECTION — The 30 F FP1
factory setting (water) should be used to avoid freeze damage
to the unit.
Once antifreeze is selected, the JW3 jumper (FP1) should
be clipped on the control to select the low temperature (antifreeze 13 F) set point to avoid nuisance faults.
37

Table 25 — Approximate Fluid Volume (gal.)
per 100 Ft of Pipe
PIPE DIAMETER (in.) VOLUME (gal.)
Copper 14.1
Rubber Hose 13.9
Polyethylene
LEGEND
IPS — Internal Pipe Size
SCH — Schedule
SDR — Standard Dimensional Ratio
NOTE: Volume of heat exchanger is approximately 1.0 gallon.
1.25 6.4
1.5 9.2
3
/4 IPS SDR11 2.8
1 IPS SDR11 4.5
11/4 IPS SDR11 8.0
1
/2 IPS SDR11 10.9
2 IPS SDR11 18.0
11/4 IPS SCH40 8.3
11/2 IPS SCH40 10.9
2 IPS SCH40 17.0
Table 26 — Antifreeze Percentages by Volume
MINIMUM TEMPERATURE FOR
ANTIFREEZE
Methanol (%) 25 21 16 10
100% USP Food Grade
Propylene Glycol (%)
Ethenol 29 25 20 14
FREEZE PROTECTION (F)
10 15 20 25
38 30 22 15
Cooling Tower/Boiler Systems — These systems
typically use a common loop temperature maintained at 60 to
95 F. Carrier recommends using a closed circuit evaporative
cooling tower with a secondary heat exchanger between the
tower and the water loop. If an open type cooling tower is used
continuously, chemical treatment and filtering will be necessary.
Ground Coupled, Closed Loop and Plateframe
Heat Exchanger Well Systems — These systems al-
low water temperatures from 30 to 110 F. The external loop
field is divided up into 2 in. polyethylene supply and return
lines. Each line has valves connected in such a way that upon
system start-up, each line can be isolated for flushing using
only the system pumps. Locate air separation in the piping system prior to the fluid re-entering the loop field.
OPERATION
Power Up Mode —
inputs, terminals and safety controls are checked for normal
operation.
NOTE: The compressor will have a 5-minute anti-short cycle
upon power up.
The unit will not operate until all the
Units with Aquazone™ Complete C Control
STANDBY — Y and W terminals are not active in Standby
mode, however the O and G terminals may be active, depending on the application. The compressor will be off.
COOLING — Y and O terminals are active in Cooling mode.
After power up, the first call to the compressor will initiate a
5 to 80 second random start delay and a 5-minute anti-short
cycle protection time delay. After both delays are complete, the
compressor is energized.
NOTE: On all subsequent compressor calls the random start
delay is omitted.
HEATING STAGE 1 — Terminal Y is active in heating
stage 1. After power up, the first call to the compressor will
initiate a 5 to 80 second random start delay and a 5-minute
anti-short cycle protection time delay. After both delays are
complete, the compressor is energized.
NOTE: On all subsequent compressor calls the random start
delay is omitted.
HEATING STAGE 2 — To enter Stage 2 mode, terminal W is
active (Y is already active). Also, the G terminal must be
active or the W terminal is disregarded. The compressor relay
will remain on and EH1 is immediately turned on. EH2 will
turn on after 10 minutes of continual stage 2 demand.
NOTE: EH2 will not turn on (or if on, will turn off) if FP1 temperature is greater than 45 F and FP2 is greater than 110 F.
LOCKOUT MODE — The status LED will flash fast in
Lockout mode and the compressor relay will be turned off
immediately. Lockout mode can be “soft” reset via the Y input
or can be “hard” reset via the disconnect. The last fault causing
the lockout is stored in memory and can be viewed by entering
test mode.
LOCKOUT WITH EMERGENCY HEAT — While in Lockout mode, if W becomes active, then Emergency Heat mode
will occur.
EMERGENCY HEAT — In Emergency Heat mode, terminal
W is active while terminal Y is not. Terminal G must be active
or the W terminal is disregarded. EH1 is immediately turned
on. EH2 will turn on after 5 minutes of continual emergency
heat demand.
Units with Aquazone Deluxe D Control
EXTENDED COMPRESSOR OPERATION MONITOR —
If the compressor has been on for 4 continuous hours the control will automatically turn off the compressor relay and wait
the short cycle time protection time. All appropriate safeties,
including the low-pressure switch, will be monitored. If all
operations are normal and the compressor demand is still present, the control will turn the compressor back on.
STANDBY/FAN ONLY — The compressor will be off. The
Fan Enable, Fan Speed, and reversing valve (RV) relays will be
on if inputs are present. If there is a Fan 1 demand, the Fan
Enable will immediately turn on. If there is a Fan 2 demand,
the Fan Enable and Fan Speed will immediately turn on.
NOTE: DIP switch 5 on S1 does not have an effect upon Fan 1
and Fan 2 outputs.
HEATING STAGE 1 — In Heating Stage 1 mode, the Fan
Enable and Compressor relays are turned on immediately.
Once the demand is removed, the relays are turned off and the
control reverts to Standby mode. If there is a master/slave or
dual compressor application, all compressor relays and related
functions will operate per their associated DIP switch 2 setting
on S1.
HEATING STAGE 2 — In Heating Stage 2 mode, the Fan
Enable and Compressor relays are remain on. The Fan Speed
relay is turned on immediately and turned off immediately
once the demand is removed. The control reverts to Heating
Stage 1 mode. If there is a master/slave or dual compressor
application, all compressor relays and related functions will
operate per their associated DIP switch 2 setting on S1.
HEATING STAGE 3 — In Heating Stage 3 mode, the Fan
Enable, Fan Speed and Compressor relays remain on. The EH1
output is turned on immediately. With continuing Heat Stage 3
demand, EH2 will turn on after 10 minutes. EH1 and EH2 are
turned off immediately when the Heating Stage 3 demand is removed. The control reverts to Heating Stage 2 mode.
The output signal EH2 will be off if FP1 is greater than 45 F
AND FP2 (when shorted) is greater than 110 F during Heating
Stage 3 mode. This condition will have a 30-second recognition time. Also, during Heating Stage 3 mode, EH1, EH2, Fan
Enable, and Fan Speed will be ON if G input is not active.
EMERGENCY HEAT — In Emergency Heat mode, the Fan
Enable and Fan Speed relays are turned on. The EH1 output is
turned on immediately. With continuing Emergency Heat demand, EH2 will turn on after 5 minutes. Fan Enable and Fan
Speed relays are turned off after a 60-second delay. The control
reverts to Standby mode.
38

Output EH1, EH2, Fan Enable, and Fan Speed will be ON if
the G input is not active during Emergency Heat mode.
COOLING STAGE 1 — In Cooling Stage 1 mode, the Fan
Enable, compressor and RV relays are turned on immediately.
If configured as stage 2 (DIP switch set to OFF) then the compressor and fan will not turn on until there is a stage 2 demand.
The Fan Enable and compressor relays are turned off immediately when the Cooling Stage 1 demand is removed. The control reverts to Standby mode. The RV relay remains on until
there is a heating demand. If there is a master/slave or dual
compressor application, all compressor relays and related functions will track with their associated DIP switch 2 on S1.
COOLING STAGE 2 — In Cooling Stage 2 mode, the Fan
Enable, compressor and RV relays remain on. The Fan Speed
relay is turned on immediately and turned off immediately
once the Cooling Stage 2 demand is removed. The control
reverts to Cooling Stage 1 mode. If there is a master/slave or
dual compressor application, all compressor relays and related
functions will track with their associated DIP switch 2 on S1.
NIGHT LOW LIMIT (NLL) STAGED HEATING — In NLL
staged Heating mode, the override (OVR) input becomes active and is recognized as a call for heating and the control will
immediately go into a Heating Stage 1 mode. With an additional 30 minutes of NLL demand, the control will go into Heating
Stage 2 mode. With another additional 30 minutes of NLL
demand, the control will go into Heating Stage 3 mode.
Units with WSHP Open Multiple Protocol —
The WSHP Open multi-protocol controller will control mechanical cooling, heating and waterside economizer outputs
based on its own space temperature input and set points. An
optional CO
space can maximize the occupant comfort. The WSHP Open
controller has its own hardware clock that is automatically set
when the heat pump software is downloaded to the board. Occupancy types are described in the scheduling section below.
The following sections describe the functionality of the WSHP
Open multi-protocol controller. All point objects referred to in
this sequence of operation will be referenced to the objects as
viewed in the BACview
SCHEDULING — Scheduling is used to start/stop the unit
based on a time period to control the space temperature to specified occupied heating and cooling set points. The controller is
defaulted to control by occupied set points all the time, until either a time schedule is configured with BACview
tant, i-Vu
able the BAS (Building Automation System) on/off point. The
local time and date must be set for these functions to operate
properly. The occupancy source can be changed to one of the
following:
Occupancy Schedules
until a time schedule has been configured using either Field
Assistant, i-Vu Open, BACview
tem to enable/disable the BAS on/off point. The BAS point can
be disabled by going to Config, then Unit, then Occupancy
Schedules and changing the point from enable to disable then
clicking OK.
NOTE: This point must be enabled in order for the i-Vu Open,
Field Assistant, or BACview
schedule to the controller.
Schedule_schedule
schedule configured and stored in the unit. The schedule is
accessible via the BACview
Field Assistant control system. The daily schedule consists of a
start/stop time (standard or 24-hour mode) and seven days of
the week, starting with Monday and ending on Sunday. To
enter a daily schedule, navigate to Config, then Sched, then
enter BACview
schedule_schedule. From here, enter either a Weekly or Exception schedule for the unit.
IAQ (indoor air quality) sensor mounted in the
2
6
handheld user interface.
6
®
Open, or a third party control system to enable/dis-
, Field Assis-
— The controller will be occupied 24/7
6
or a third party control sys-
6
control system to assign a time
— The unit will operate according to the
6
Handheld tool, i-Vu Open, or
6
Admin Password (1111), then go to
Occupancy Input Contact
— The WSHP Open controller has
the capability to use an external dry contact closure to determine the occupancy status of the unit. The Occupancy Schedules will need to be disabled in order to utilize the occupancy
contact input.
NOTE: Scheduling can only be controlled from one source.
BAS (Building Automation System) On/Off
— A BAS
system that supports network scheduling can control the unit
through a network communication and the BAS scheduling
function once the Occupancy Schedules have been disabled.
NOTE: Scheduling can either be controlled via the unit or the
BAS, but not both.
INDOOR FAN — The indoor fan will operate in any one of
three modes depending on the user configuration selected.
Fan mode can be selected as Auto, Continuous, or Always
On. In Auto mode, the fan is in intermittent operation during
both occupied and unoccupied periods. Continuous fan mode
is intermittent during unoccupied periods and continuous during occupied periods. Always On mode operates the fan continuously during both occupied and unoccupied periods. In the
default mode, Continuous, the fan will be turned on whenever
any one of the following is true:
• The unit is in occupied mode as determined by its occu-
pancy status.
• There is a demand for cooling or heating in the unoccu-
pied mode.
• There is a call for dehumidification (optional).
When power is reapplied after a power outage, there will be
a configured time delay of 5 to 600 seconds before starting the
fan. There are also configured fan delays for Fan On and Fan
Off. The Fan On delay defines the delay time (0 to 30 seconds;
default 10) before the fan begins to operate after heating or
cooling is started while the Fan Off delay defines the delay
time (0 to 180 seconds; default 45) the fan will continue to operate after heating or cooling is stopped. The fan will continue
to run as long as the compressors, heating stages, or the dehumidification relays are on. If the SPT failure alarm or condensate overflow alarm is active; the fan will be shut down immediately regardless of occupancy state or demand.
Automatic Fan Speed Control
— The WSHP Open controller
is capable of controlling up to three fan speeds using the ECM
(electronically commutated motor). The motor will operate at
the lowest speed possible to provide quiet and efficient fan operation with the best latent capability. The motor will increase
speed if additional cooling or heating is required to obtain the
desired space temperature set point. The control increases the
motor's speed as the space temperature rises above the cooling
or below the heating set point. The amount of space temperature increase above or below the set point required to increase
the fan speed is user configurable in the set point.
The Low Fan speed range is configured by the width of the
Yellow (for cooling) and Light Blue (for heating) setpoint
bands. The fan will operate at low speed as long as the space
temperature remains within the yellow or light blue band
range. The Medium Fan speed range is determined by the Orange and Dark Blue setpoint band. The fan will operate at medium speed when the space temperature enters this range. If the
space temperature rises or falls into the red range, the fan will
operate at High Fan speed.
As the temperature returns toward setpoint, a configurable
hysteresis is used to prevent the fan from changing speeds erratically. The default value is 0.5° F (shown above).
Also, the control will increase the fan speed as the Supply
Air Temperature approaches the configured Minimum or Maximum SAT limits.
Fan Speed Control (During Heating)
— Whenever heat is required and active, the control continuously monitors the supply-air temperature to verify it does not rise above the config-
39

ured maximum heating SAT limit (110 F default). As the SAT
approaches this value, the control will increase the fan speed as
required to ensure the SAT will remain within the limit. This
feature provides the most quiet and efficient operation by operating the fan at the lowest speed possible.
Fan Speed Control (During Cooling)
cal cooling is required and active, the control continuously
monitors the supply-air temperature to verify it does not fall below the configured minimum cooling SAT limit (50 F default).
As the SAT approaches this value, the control will increase the
fan speed as required to ensure the SAT will remain within the
limit. The fan will operate at lowest speed to maximize latent
capacity during cooling.
COOLING — The WSHP Open controller will operate one or
two stages of compression to maintain the desired cooling set
point. The compressor outputs are controlled by the PI (proportional-integral) cooling loop and cooling stages capacity algorithm. They will be used to calculate the desired number of
stages needed to satisfy the space by comparing the space temperature (SPT) to the appropriate cooling set point. The water
side economizer, if applicable, will be used for first stage cooling in addition to the compressor(s). The following conditions
must be true in order for the cooling algorithm to run:
• Cooling is set to Enable.
• Heating mode is not active and the compressor time
guard has expired.
• Condensate overflow input is normal.
• If occupied, the SPT is greater than the occupied cooling
set point.
• Space temperature reading is valid.
• If unoccupied, the SPT is greater than the unoccupied
cooling set point.
• If economizer cooling is available and active and the
economizer alone is insufficient to provide enough cooling.
• OAT (if available) is greater than the cooling lockout
temperature.
If all the above conditions are met, the compressors will be
energized as required, otherwise they will be deenergized. If
cooling is active and should the SAT approach the minimum
SAT limit, the fan will be indexed to the next higher speed.
Should this be insufficient and if the SAT falls further (equal to
the minimum SAT limit), the fan will be indexed to the maximum speed. If the SAT continues to fall 5 F below the minimum SAT limit, all cooling stages will be disabled.
During Cooling mode, the reversing valve output will be
held in the cooling position (either B or O type as configured)
even after the compressor is stopped. The valve will not switch
position until the Heating mode is required.
The configuration screens contain the minimum SAT
parameter as well as cooling lockout based on outdoor-air
temperature (OAT) Both can be adjusted to meet various
specifications.
There is a 5-minute off time for the compressor as well as a
5-minute time delay when staging up to allow the SAT to
achieve a stable temperature before energizing a second stage
of capacity. Likewise, a 45-second delay is used when staging
down.
After a compressor is staged off, it may be restarted again
after a normal time-guard period of 5 minutes and if the supply-air temperature has increased above the minimum supplyair temperature limit.
The WSHP Open controller provides a status input to moni-
tor the compressor operation. The status is monitored to determine if the compressor status matches the commanded state.
This input is used to determine if a refrigerant safety switch or
other safety device has tripped and caused the compressor to
stop operating normally. If this should occur, an alarm will be
generated to indicate the faulted compressor condition.
— Whenever mechani-
HEATING — The WSHP Open controller will operate one or
two stages of compression to maintain the desired heating set
point. The compressor outputs are controlled by the heating PI
(proportional-integral) loop and heating stages capacity algorithm. They will be used to calculate the desired number of
stages needed to satisfy the space by comparing the space temperature (SPT) to the appropriate heating set point. The following conditions must be true in order for the heating algorithm to
run:
• Heating is set to Enable.
• Cooling mode is not active and the compressor time
guard has expired.
• Condensate overflow input is normal.
• If occupied, the SPT is less than the occupied heating set
point.
• Space temperature reading is valid.
• If unoccupied, the SPT is less than the unoccupied heating set point.
• OAT (if available) is less than the heating lockout
temperature.
If all the above conditions are met, the heating outputs will
be energized as required, otherwise they will be deenergized. If
the heating is active and should the SAT approach the maximum SAT limit, the fan will be indexed to the next higher
speed. Should this be insufficient, and the SAT rises further
reaching the maximum heating SAT limit, the fan will be
indexed to the maximum speed. If the SAT still continues to
rise 5 F above the maximum limit, all heating stages will be
disabled.
During Heating mode, the reversing valve output will be
held in the heating position (either B or O type as configured)
even after the compressor is stopped. The valve will not switch
position until the Cooling mode is required.
The configuration screens contain the maximum SAT
parameter as well as heating lockout based on outdoor-air
temperature (OAT); both can be adjusted to meet various
specifications.
There is a 5-minute off time for the compressor as well as a
5-minute time delay when staging up to allow the SAT to
achieve a stable temperature before energizing a second stage
of capacity. Likewise, a 45-second delay is used when staging
down.
After a compressor is staged off, it may be restarted again
after a normal time-guard period of 5 minutes and if the supply-air temperature has fallen below the maximum supply air
temperature limit.
The WSHP Open controller provides a status input to moni-
tor the compressor operation. The status is monitored to determine if the compressor status matches the commanded state.
This input is used to determine if a refrigerant safety switch or
other safety device has tripped and caused the compressor to
stop operating normally. If this should occur, an alarm will be
generated to indicate the faulted compressor condition. Also, if
auxiliary heat is available (see below), the auxiliary heat will
operate to replace the reverse cycle heating and maintain the
space temperature as required.
AUXILIARY HEAT — The WSHP Open controller can control a two-position, modulating water, or steam valve connected to a coil on the discharge side of the unit and supplied by a
boiler or a single-stage ducted electric heater in order to maintain the desired heating set point. Should the compressor capacity be insufficient or a compressor failure occurs, the auxiliary
heat will be used. Unless the compressor fails, the auxiliary
heat will only operate to supplement the heat provided by the
compressor if the space temperature falls more than one degree
below the desired heating set point (the amount is configurable). The heat will be controlled so the SAT will not exceed
the maximum heating SAT limit.
40

Auxiliary Modulating Hot Water/Steam Heating Reheat
— The control can modulate a hot water or steam valve connected to a coil on the discharge side of the unit and supplied
by a boiler in order to maintain the desired heating set point
should the compressor capacity be insufficient or a compressor
failure occurs. Unless a compressor fault condition exists, the
valve will only operate to supplement the heat provided by the
compressor if the space temperature falls more than one degree
below the desired heating set point. The valve will be controlled so the SAT will not exceed the maximum heating SAT
limit.
Two-Position Hot Water/Steam Heating Reheat
— The con-
trol can operate a two-position, NO or NC, hot water or steam
valve connected to a coil on the discharge side of the unit and
supplied by a boiler in order to maintain the desired heating set
point should the compressor capacity be insufficient or a compressor failure occurs. Unless a compressor fault condition exists, the valve will only open to supplement the heat provided
by the compressor if the space temperature falls more than one
degree below the desired heating set point. The valve will be
controlled so the SAT will not exceed the maximum heating
SAT limit. The heat stage will also be subject to a 2-minute
minimum OFF time to prevent excessive valve cycling.
Single Stage Electric Auxiliary Heat
— The control can operate a field-installed single stage of electric heat installed on
the discharge side of the unit in order to maintain the desired
heating set point should the compressor capacity be insufficient
or a compressor failure occurs. Unless a compressor fault condition exists, the heat stage will only operate to supplement the
heat provided by the compressor if the space temperature falls
more than one degree below the desired heating set point. The
heat stage will be controlled so the SAT will not exceed the
maximum heating SAT limit. The heat stage will also be subject to a 2-minute minimum OFF time to prevent excessive
cycling.
INDOOR AIR QUALITY (IAQ) AND DEMAND CONTROLLED VENTILATION (DCV) — If the optional indoor air quality sensor is installed, the WSHP Open controller
can maintain indoor air quality via a modulating OA damper
providing demand controlled ventilation. The control operates
the modulating OA damper during occupied periods. The control monitors the CO
set points, adjusting the ventilation rate as required. The control
level and compares it to the configured
2
provides proportional ventilation to meet the requirements of
ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and
Air Conditioning Engineers) specifications by providing a base
ventilation rate and then increasing the rate as the CO
level in-
2
creases. The control will begin to proportionally increase ventilation when the CO
point and will reach the full ventilation rate when the CO
level rises above the start ventilation set
2
level
2
is at or above the maximum set point. A user-configurable minimum damper position ensures that proper base ventilation is
delivered when occupants are not present. The IAQ configurations can be accessed through the configuration screen. The
following conditions must be true in order for this algorithm to
run:
• Damper control is configured for DCV.
• The unit is in an occupied mode.
• The IAQ sensor reading is greater than the DCV start
control set point.
The control has four user adjustable set points: DCV start
control set point, DCV maximum control set point, minimum
damper position, and DCV maximum damper position.
Two-Position OA Damper
— The control can be configured
to operate a ventilation damper in a two-position ventilation
mode to provide the minimum ventilation requirements during
occupied periods.
DEHUMIDIFCATION — The WSHP Open controller will
provide occupied and unoccupied dehumidification only on
units that are equipped with the modulating hot water reheat
(HWR) option. This function requires an accessory space relative humidity sensor. When using a relative humidity sensor to
control dehumidification during occupied or unoccupied times,
the dehumidification set points are used accordingly. When the
indoor relative humidity becomes greater than the dehumidification set point, a dehumidification demand will be acknowledged. Once acknowledged, the dehumidification output will
be energized, bringing on the supply fan (medium speed), mechanical cooling, and the integral hot water reheat coil. The
controls will engage Cooling mode and waste heat from the
compressor cooling cycle will be returned to the reheat coil simultaneously, meaning that the reversing valve is causing the
compressor to operate in the Cooling mode. During Cooling
mode, the unit cools, dehumidifies, and disables the HWR coil;
however, once the call for cooling has been satisfied and there
is still a call for dehumidification, the unit will continue to operate using the reheat mode and HWR coil.
WATERSIDE ECONOMIZER — The WSHP Open controller has the capability of providing modulating or two-position
water economizer operation (for a field-installed economizer
coil mounted to the entering air side of the unit and connected
to the condenser water loop) in order to provide free cooling
(or preheating) when water conditions are optimal. Water economizer settings can be accessed through the equipment status
screen. The following conditions must be true for economizer
operation:
• SAT reading is available.
• LWT reading is available.
• If occupied, the SPT is greater than the occupied cooling
set point or less than the occupied heating set point and
the condenser water is suitable.
• Space temperature reading is valid.
• If unoccupied, the SPT is greater than the unoccupied
cooling set point or less than the unoccupied heating set
point and the condenser water is suitable.
Modulating Water Economizer Control
— The control has
the capability to modulate a water valve to control condenser
water flowing through a coil on the entering air side of the unit.
Cooling — The purpose is to provide an economizer cooling
function by using the water loop when the entering water loop
temperature is suitable (at least 5 F below space temperature).
If the water loop conditions are suitable, then the valve will
modulate open as required to maintain a supply-air temperature
that meets the load conditions. Should the economizer coil capacity alone be insufficient for a period greater than 5 minutes,
or should a high humidity condition occur, then the compressor
will also be started to satisfy the load. Should the SAT approach the minimum cooling SAT limit, the economizer valve
will modulate closed during compressor operation.
Heating — Additionally, the control will modulate the water
valve should the entering water loop temperature be suitable
for heating (at least 5 F above space temperature) and heat is
required. The valve will be controlled in a similar manner except to satisfy the heating requirement. Should the economizer
coil capacity alone be insufficient to satisfy the space load conditions for more than 5 minutes, then the compressor will be
started to satisfy the load. Should the SAT approach the maximum heating SAT limit, the economizer valve will modulate
closed during compressor operation.
Two-Position Water Economizer Control
— The control has
the capability to control a NO or NC, two-position water valve
to control condenser water flow through a coil on the entering
air side of the unit.
Cooling — The purpose is to provide a cooling economizer
function directly from the condenser water loop when the entering water loop temperature is suitable (at least 5 F below
space temperature). If the optional coil is provided and the water loop conditions are suitable, then the valve will open to pro-
41

vide cooling to the space when required. Should the capacity
be insufficient for a period greater than 5 minutes, or should a
high humidity condition occur, then the compressor will be
started to satisfy the load. Should the SAT reach the minimum
cooling SAT limit, the economizer valve will close during
compressor operation.
Heating — Additionally, the economizer control will open the
water valve should the entering water loop temperature be suitable for heating (at least 5 F above space temperature) and
heat is required. The valve will be controlled in a similar manner except to satisfy the heating requirement. Should the coil
capacity be insufficient to satisfy the space load for more than
5 minutes, then the compressor will be started to satisfy the
load. Should the SAT reach the maximum heating SAT limit,
the economizer valve will close during compressor operation.
DEMAND LIMIT — The WSHP Open controller has the
ability to accept three levels of demand limit from the network.
In response to a demand limit, the unit will decrease its heating
set point and increase its cooling set point to widen the range in
order to immediately lower the electrical demand. The amount
of temperature adjustment in response is user adjustable for
both heating and cooling and for each demand level. The response to a particular demand level may also be set to zero.
CONDENSER WATER LINKAGE — The control provides optimized water loop operation using an universal controller (UC) open loop controller. Loop pump operation is automatically controlled by WSHP equipment occupancy schedules, unoccupied demand and tenant override conditions.
Positive pump status feedback prevents nuisance fault trips.
The condenser water linkage operates when a request for condenser water pump operation is sent from each WSHP to the
loop controller. This request is generated whenever any WSHP
is scheduled to be occupied, is starting during optimal start (for
warm-up or pull down prior to occupancy), there is an unoccupied heating or cooling demand, or a tenant pushbutton override. At each WSHP, the water loop temperature and the loop
pump status is given. The WSHP will NOT start a compressor
until the loop pumps are running or will shutdown the compressors should the pumps stop. This prevents the WSHP from
operating without water flow and thus tripping out on refrigerant pressure, causing a lockout condition. The WSHP Open
controller control will prevent this from occurring. Also, the
loop controller can be configured to start the pumps only after a
configurable number of WSHPs are requesting operation (from
1-"N"). This can be used to prevent starting the entire loop operation for only one WSHP. Meanwhile, the WSHPs will not
operate if the loop pump status is off and therefore the WSHP
compressor will not run.
COMPLETE C AND DELUXE D BOARD
SYSTEM TEST
Test mode provides the ability to check the control operation in a timely manner. The control enters a 20-minute test
mode by momentarily shorting the test terminals. All time delays are sped up 15 times. The following operations are common to both Complete C and Deluxe D controls.
Test Mode — To enter Test mode, cycle the fan 3 times
within 60 seconds. The LED will flash a code representing the
last fault when entering the Test mode. The alarm relay will
also power on and off during Test mode. See Tables 27 and 28.
To exit Test mode, short the terminals for 3 seconds or cycle
the fan 3 times within 60 seconds.
NOTE: The flashing code and alarm relay cycling code will
both have the same numerical label. For example, flashing
code 1 will have an alarm relay cycling code 1. Code 1 indicates the control has not faulted since the last power off to
power on sequence.
Table 27 — Complete C Control Current LED
Status and Alarm Relay Operations
LED STATUS DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION ALARM RELAY
On
Off
Slow Flash Fault Retry Open
Fast Flash Lockout Closed
Slow Flash Over/Under Voltage Shutdown
Flashing Code 1 Test Mode — No fault in memory Cycling Code 1
Flashing Code 2
Flashing Code 3
Flashing Code 4
Flashing Code 5
Flashing Code 6
Flashing Code 7
Flashing Code 8 Test Mode — PM in memory Cycling Code 8
Flashing Code 9
LEGEND
CO — Condensate Overflow
FP — Freeze Protection
HP — High Pressure
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
LP — Low Pressure
PM — Performance Monitor
NOTES:
1. Slow flash is 1 flash every 2 seconds.
2. Fast flash is 2 flashes every 1 second.
3. EXAMPLE: “Flashing Code 2” is represented by 2 fast flashes followed by
a 10-second pause. This sequence will repeat continually until the fault is
cleared.
Normal Mode Open
Normal Mode with
PM Warning
Complete C Control is
non-functional
Test Mode —
HP Fault in memory
Test Mode —
LP Fault in memory
Test Mode —
FP1 Fault in memory
Test Mode —
FP2 Fault in memory
Test Mode —
CO Fault in memory
Test Mode — Over/Under
shutdown in memory
Test Mode — FP1/FP2
Swapped Fault in memory
Cycle
(closed 5 sec.,
open 25 sec.)
Open
Open,
(Closed after
15 minutes)
Cycling Code 2
Cycling Code 3
Cycling Code 4
Cycling Code 5
Cycling Code 6
Cycling Code 7
Cycling Code 9
Table 28 — Complete C Control LED Code and
Fault Descriptions
LED
CODE
1 No fault in memory There has been no fault since
2 High-Pressure Switch HP switch opens instantly
3 Low-Pressure Switch LP switch opens for
4 Freeze Protection Coax
— FP1
5 Freeze Protection Air Coil —
FP2
6 Condensate overflow Sense overflow (grounded) for
7
(Autoreset)
FP — Freeze Protection
HP — High Pressure
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
LP — Low Pressure
PM — Performance Monitor
Over/Under Voltage
Shutdown
8 PM Warning Performance Monitor Warning
9 FP1 and FP2
Thermistors are swapped
LEGEND
FAULT DESCRIPTION
the last power-down to powerup sequence
30 continuous seconds before
or during a call (bypassed for
first 60 seconds)
FP1 below Temp limit for
30 continuous seconds
(bypassed for first 60 seconds of
operation)
FP2 below Temp limit for
30 continuous seconds
(bypassed for first 60 seconds of
operation)
30 continuous seconds
"R" power supply is <19VAC or
>30VAC
has occurred.
FP1 temperature is higher than
FP2 in heating/test mode, or
FP2 temperature is higher than
FP1 in cooling/test mode.
42

WSHP Open Test Mode — To enter WSHP Open test
mode, navigate from the BACview
6
home screen to the configuration screen. Choose the service screen and enable unit test.
The controller will then test the following:
FAN TEST — Tests all fan speeds, sequences fan from low to
high, and operates each speed for one minute. Resets to disable
on completion.
COMPRESSOR TEST — Tests compressor cooling and
heating operation. Sequences cooling stage 1 then cooling
stage 2 followed by heating stage 2 then reduces capacity to
heating stage 1. Operates for 1 minute per step.
DEHUMIDIFICATION TEST — Tests dehumidification
mode. Operates for 2 minutes.
AUXILIARY HEATING TEST — Tests auxiliary heat.
Sequences fan on and enables heating coil for 1 minute.
H
O ECONOMIZER TEST — Tests entering/returning
2
water loop economizer operation. Sequences fan and opens
economizer water valve for one minute.
OPEN VENT DAMPER 100% TEST — Tests outside air
(OA) damper operation.
PREPOSITION OA DAMPER — Prepositions OA damper
actuator to set proper preload.
NOTE: The auxiliary heating test, H
vent damper 100% test, and preposition OA damper features
O economizer test, open
2
will not be visible on the screen unless configured.
Once tests are complete, set unit test back to disable. Unit will
automatically reset to disable after 1 hour.
Retry Mode — In Retry mode, the status LED will start to
flash slowly to signal that the control is trying to recover from
an input fault. The control will stage off the outputs and try to
again satisfy the thermostat used to terminal Y. Once the thermostat input calls are satisfied, the control will continue normal
operation.
NOTE: If 3 consecutive faults occur without satisfying the
thermostat input call to terminal Y, the control will go into
lockout mode. The last fault causing the lockout is stored in
memory and can be viewed by entering Test mode.
Aquazone™ Deluxe D Control LED Indicators —
STATUS LED — Status LED indicates the current status or
mode of the D control. The Status LED light is green.
TEST LED — Test LED will be activated any time the D
control is in test mode. The Test LED light is yellow.
FAULT LED — Fault LED light is red. The fault LED will
always flash a code representing the last fault in memory. If
there is no fault in memory, the fault LED will flash code 1 and
appear as one fast flash alternating with a 10-second pause.
See Table 29.
There are 3 LED indicators on the Deluxe D control:
Table 29 — Aquazone Deluxe D Control Current LED Status and Alarm Relay Operations
DESCRIPTION
Normal Mode On Off Flash Last Fault Code in Memory Open
Normal Mode with PM On Off Flashing Code 8
Deluxe D Control
is non-functional
Tes t M od e — On Flash Last Fault Code in Memory Cycling Appropriate Code
Night Setback Flashing Code 2 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
ESD Flashing Code 3 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
Invalid T-stat Inputs Flashing Code 4 — Flash Last Fault Code in Memory —
No Fault in Memory On Off Flashing Code 1 Open
HP Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 2 Open
LP Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 3 Open
FP1 Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 4 Open
FP2 Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 5 Open
CO Fault Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 6 Open
Over/Under Voltage Slow Flash Off Flashing Code 7 Open (closed after 15 minutes)
HP Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 2 Closed
LP Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 3 Closed
FP1 Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 4 Closed
FP2 Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 5 Closed
CO Lockout Fast Flash Off Flashing Code 6 Closed
CO — Condensate Overflow HP — High Pressure
ESD — Emergency Shutdown LP — Low Pressure
FP — Freeze Protection PM — Performance Monitor
STATUS LED
(Green)
Off Off Off Open
LEGEND NOTES:
TEST LED
(Yellow)
FAULT LED (Red) ALARM RELAY
Cycle (closed 5 sec,
open 25 sec, …)
1. If there is no fault in memory, the Fault LED will flash code 1.
2. Codes will be displayed with a 10-second Fault LED pause.
3. Slow flash is 1 flash every 2 seconds.
4. Fast flash is 2 flashes every 1 second.
5. EXAMPLE: “Flashing Code 2” is represented by 2 fast flashes
followed by a 10-second pause. This sequence will repeat continually until the fault is cleared.
43

SERVICE
Perform the procedures outlined below periodically, as
indicated.
WARNING
To prevent injury or death due to electrical shock or contact
with moving parts, open unit disconnect switch before servicing unit.
IMPORTANT: When a compressor is removed from this
unit, system refrigerant circuit oil will remain in the compressor. To avoid leakage of compressor oil, the refrigerant
lines of the compressor must be sealed after it is removed.
IMPORTANT: All refrigerant discharged from this unit
must be recovered without exception. Technicians must follow industry accepted guidelines and all local, state and federal statutes for the recovery and disposal of refrigerants.
IMPORTANT: To avoid the release of refrigerant into the
atmosphere, the refrigerant circuit of this unit must only be
serviced by technicians who meet local, state and federal
proficiency requirements.
Filters — Filters must be clean for maximum performance.
Inspect filters every month under normal operating conditions.
Replace when necessary.
IMPORTANT: Units should never be operated without
a filter.
Water Coil — Keep all air out of the water coil. Check
open loop systems to be sure the well head is not allowing air
to infiltrate the water line. Always keep lines airtight.
Inspect heat exchangers regularly, and clean more frequently if the unit is located in a “dirty” environment. Keep the heat
exchanger full of water at all times. Open loop systems should
have an inverted P trap placed in the discharge line to keep
water in the heat exchanger during off cycles. Closed loop
systems must have a minimum of 15 psig during the summer
and 40 psig during the winter.
Check P trap frequently for proper operation.
CAUTION
To avoid fouled machinery and extensive unit clean-up,
DO NOT operate units without filters in place. DO NOT
use equipment as a temporary heat source during
construction.
Condensate Drain Pans — Check condensate drain
pans for algae growth twice a year. If algae growth is apparent,
consult a water treatment specialist for proper chemical treatment. Applying an algaecide every three months will typically
eliminate algae problems in most locations.
Refrigerant System — Verify air and water flow rates
are at proper levels before servicing. To maintain sealed circuitry integrity, do not install service gages unless unit operation
appears abnormal.
Check to see that unit is within the superheat and subcooling temperature ranges shown in Tables 20-23. If the unit is not
within these ranges, recover and reweigh in refrigerant charge.
Compressor — Conduct annual amperage checks to en-
sure that amp draw is no more than 10% greater than indicated
on the serial plate data.
Fan Motors — All units have lubricated fan motors. Fan
motors should never be lubricated unless obvious, dry
operation is suspected. Periodic maintenance oiling is NOT
recommended as it will result in dirt accumulating in the excess
oil and cause eventual motor failure. Conduct annual dry operation check and amperage check to ensure amp draw is no
more than 10% greater than indicated on serial plate data.
Condensate Drain Cleaning — Clean the drain line
and unit drain pan at the start of each cooling season. Check
flow by pouring water into drain. Be sure trap is filled to maintain an air seal.
Air Coil Cleaning — Remove dirt and debris from evap-
orator coil as required by condition of the coil. Clean coil with
a stiff brush, vacuum cleaner, or compressed air. Use a fin
comb of the correct tooth spacing when straightening mashed
or bent coil fins.
Condenser Cleaning — Water-cooled condensers may
require cleaning of scale (water deposits) due to improperly
maintained closed-loop water systems. Sludge build-up may
need to be cleaned in an open water tower system due to
induced contaminants.
Local water conditions may cause excessive fouling or
pitting of tubes. Condenser tubes should therefore be cleaned at
least once a year, or more often if the water is contaminated.
Proper water treatment can minimize tube fouling and
pitting. If such conditions are anticipated, water treatment
analysis is recommended. Refer to the Carrier System Design
Manual, Part 5, for general water conditioning information.
CAUTION
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and rubber
gloves when using inhibited hydrochloric acid solution.
Observe and follow acid manufacturer’s instructions.
Clean condensers with an inhibited hydrochloric acid solution. The acid can stain hands and clothing, damage concrete,
and, without inhibitor, damage steel. Cover surroundings to
guard against splashing. Vapors from vent pipe are not harmful,
but take care to prevent liquid from being carried over by the
gases.
Warm solution acts faster, but cold solution is just as effective if applied for a longer period.
GRAVITY FLOW METHOD — Do not add solution faster
than vent can exhaust the generated gases.
When condenser is full, allow solution to remain overnight,
then drain condenser and flush with clean water. Follow acid
manufacturer’s instructions. See Fig. 35.
FORCED CIRCULATION METHOD — Fully open vent
pipe when filling condenser. The vent may be closed when
condenser is full and pump is operating. See Fig. 36.
Regulate flow to condenser with a supply line valve. If
pump is a nonoverloading type, the valve may be fully closed
while pump is running.
For average scale deposit, allow solution to remain in condenser overnight. For heavy scale deposit, allow 24 hours.
Drain condenser and flush with clean water. Follow acid manufacturer’s instructions.
44

Checking System Charge — Units are shipped with
Fig. 35 — Gravity Flow Method
FILL CONDENSER WITH
CLEANING SOLUTION. DO
NOT ADD SOLUTION
MORE RAPIDLY THAN
VENT CAN EXHAUST
GASES CAUSED BY
CHEMICAL ACTION.
PAIL
FUNNEL
CONDENSER
PAIL
3’ TO 4’
VENT
PIPE
5’ APPROX
1”
PIPE
SUCTION
PUMP
SUPPORT
TANK
FINE MESH
SCREEN
RETURN
GAS VENT
PUMP
PRIMING
CONN.
GLOBE
VALV ES
SUPPLY
1” PIPE
CONDENSER
REMOVE WATER
REGULATING VALVE
Fig. 36 — Forced Circulation Method
full operating charge. If recharging is necessary:
1. Insert thermometer bulb in insulating rubber sleeve on
2. Connect pressure gage to discharge line near compressor.
3. After unit conditions have stabilized, read head pressure
4. From standard field-supplied Pressure-Temperature chart
5. Read liquid line temperature on thermometer; then
6. Compare the subcooling temperature with the normal
liquid line near filter drier. Use a digital thermometer for
all temperature measurements. DO NOT use a mercury
or dial-type thermometer.
on discharge line gage.
NOTE: Operate unit a minimum of 15 minutes before
checking charge.
for R-410A refrigerant, find equivalent saturated condensing temperature.
subtract from saturated condensing temperature. The difference equals subcooling temperature.
temperature listed in Tables 20-23. If the measured liquid
line temperature does not agree with the required liquid
line temperature, ADD refrigerant to raise the temperature or REMOVE refrigerant (using standard practices) to
lower the temperature (allow a tolerance of ± 3° F).
Refrigerant Charging
WARNING
To prevent personal injury, wear safety glasses and gloves
when handling refrigerant. Do not overcharge system —
this can cause compressor flooding.
NOTE: Do not vent or depressurize unit refrigerant to atmosphere. Remove and recover refrigerant following accepted
practices.
Air Coil Fan Motor Removal
CAUTION
Before attempting to remove fan motors or motor mounts,
place a piece of plywood over evaporator coils to prevent
coil damage.
Disconnect motor power wires from motor terminals before
motor is removed from unit.
1. Shut off unit main power supply.
2. Loosen bolts on mounting bracket so that fan belt can be
removed.
3. Loosen and remove the 2 motor mounting bracket bolts
on left side of bracket.
Slide motor/bracket assembly to extreme right and lift out
through space between fan scroll and side frame. Rest motor on
a high platform such as a step ladder. Do not allow motor to
hang by its power wires.
Replacing the WSHP Open Controller’s Battery — The WSHP Open controller’s 10-year lithium
CR2032 battery provides a minimum of 10,000 hours of data
retention during power outages.
NOTE: Power must be ON to the WSHP Open controller
when replacing the battery, or the date, time and trend data will
be lost.
1. Remove the battery from the controller, making note of
the battery's polarity.
2. Insert the new battery, matching the battery's polarity
with the polarity indicated on the WSHP Open controller.
TROUBLESHOOTING
When troubleshooting problems with a WSHP, consider the
following:
Thermistor — A thermistor may be required for single-
phase units where starting the unit is a problem due to low
voltage. See Fig. 37 for thermistor nominal resistance.
Control Sensors — The control system employs 2 nom-
inal 10,000 ohm thermistors (FP1 and FP2) that are used for
freeze protection. Be sure FP1 is located in the discharge fluid
and FP2 is located in the air discharge. See Fig. 38.
45

WSHP Open Controller — With the WSHP Open con-
0.0
10.0
20.0
30.0
40.0
50.0
60.0
70.0
80.0
90.0
0.0 20.0 40.0 60.0 80.0 100.0 120.0 140.0
Temperature (degF)
Resistance (kOhm)
Fig. 37 — Thermistor Nominal Resistance
SUCTION
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE
COAX
EXPANSION
VALV E
FP2
FP1
LIQUID
LINE
WATER IN
WATER OUT
CONDENSATE
OVERFLOW
(CO)
AIR COIL
FREEZE
PROTECTION
WATER
COIL
PROTECTION
THERMISTOR
(°F)
(°F)
AIR
COIL
AIRFLOW
AIRFLOW
LEGEND
Fig. 38 — FP1 and FP2 Thermistor Location
COAX — Coaxial Heat Exchanger
Airflow
Refrigerant Liquid Line Flow
troller option, the 100 most recent alarms can be viewed using
the BACview
To view the alarms:
1. Navigate to the Alarm Status screen from the Home
screen using the arrow softkeys. The screen will display
the current alarm status, either normal or Alarm, and allow for scrolling through the unit’s alarm status.
2. From the Alarm Status screen, press the Alarm softkey to
view the 100 most recent alarms which are labeled with
date and time for easy reference.
NOTE: Active faults can be viewed by scrolling down,
these faults indicate a possible bad sensor or some condition which may not merit an alarm.
3. To view alarms which have been corrected, scroll down
through the Alarm screen to Return Top Normal screen.
NOTE: Alarms are automatically reset once alarm condition has been corrected.
See Table 32 for possible alarm cause and solution.
6
alarm status and alarm history.
Thermostatic Expansion Valves — Thermostat-
ic expansion valves (TXV) are used as a means of metering the
refrigerant through the evaporator to achieve a preset superheat
at the TXV sensing bulb. Correct superheat of the refrigerant is
important for the most efficient operation of the unit and for the
life of the compressor.
Packaged heat pumps typically use one bi-flow TXV to meter refrigerant in both modes of operation. When diagnosing
possible TXV problems it may be helpful to reverse the refrigerant flow to assist with the diagnosis.
Geothermal and water source heat pumps are designed to
operate through a wide range of entering-water temperatures
that will have a direct effect on the unit refrigerant operating pressures. Therefore, diagnosing TXV problems can be
difficult.
TXV FAILURE — The most common failure mode of a TXV
is when the valve fails while closed. Typically, a TXV uses
spring pressure to close the valve and an opposing pressure,
usually from a diaphragm, to open the valve. The amount of
pressure exerted by the diaphragm will vary, depending on the
pressure inside of the sensing bulb. As the temperature of and
pressure within the bulb decreases, the valve will modulate
closed and restrict the refrigerant flow through the valve. The
result is less refrigerant in the evaporator and an increase in the
superheat. As the temperature at the bulb increases the diaphragm pressure will increase, which opens the valve and
allows more refrigerant flow and a reduction in the superheat.
If the sensing bulb, connecting capillary, or diaphragm
assembly are damaged, pressure is lost and the spring will force
the valve to a closed position. Often, the TXV will not close
completely so some refrigerant flow will remain, even if inadequate flow for the heat pump to operate.
The TXV sensing bulb must be properly located, secured,
and insulated as it will attempt to control the temperature of the
line to which it is connected. The sensing bulb must be located
on a dedicated suction line close to the compressor. On a packaged heat pump, the bulb may be located almost any place on
the tube running from the compressor suction inlet to the
reversing valve. If the bulb is located on a horizontal section, it
should be placed in the 10:00 or 2:00 position for optimal
performance.
CAUTION
Use caution when tightening the strap. The strap must be
tight enough to hold the bulb securely but caution must be
taken not to over-tighten the strap, which could dent, bend,
collapse or otherwise damage the bulb.
46

The bulb must be secured to the pipe using a copper strap.
The use of heat transfer paste between the bulb and the pipe
will also help ensure optimum performance.
The bulb must also be properly insulated to eliminate any
influence on valve operation by the surrounding conditions.
Cork tape is the recommended insulation as it can be molded
tight to the bulb to prevent air infiltration.
Causes of TXV Failure
failure are:
1. A cracked, broken, or damaged sensing bulb or capillary
can be caused by excessive vibration of the capillary during shipping or unit operation.
If the sensing bulb is damaged or if the capillary is
cracked or broken, the valve will be considered failed and
must be replaced. Replacement of the TXV “power head”
or sensing bulb, capillary, diaphragm assembly is possible on some TXVs. The power head assembly screws
onto most valves, but not all are intended to be replaceable. If the assembly is not replaceable, replace the entire
valve.
2. Particulate debris within the system can be caused by several sources including contaminated components, tubing,
and service tools, or improper techniques used during
brazing operations and component replacement.
Problems associated with particulate debris can be compounded by refrigerant systems that use POE (polyol ester oil). POE oil has solvent-like properties that will clean
the interior surfaces of tubing and components. Particulates can be released from interior surfaces and may migrate to the TXV strainer, which can lead to plugging of
the strainer.
3. Corrosive debris within the system may happen after a
failure, such as a compressor burn out, if system was not
properly cleaned.
4. Noncondensables may be present in the system. Noncondensables includes any substance other than the
refrigerant or oil such as air, nitrogen, or water. Contamination can be the result of improper service techniques,
use of contaminated components, and/or improper evacuation of the system.
Symptoms
and will include one or more of the following:
• Low refrigerant suction pressure
• High refrigerant superheat
• High refrigerant subcooling
• TXV and/or low pressure tubing frosting
• Equalizer line condensing and at a lower temperature than
the suction line or the equalizer line frosting
• FP1 faults in the heating mode in combination with any of
the symptoms listed above
• FP2 faults in the cooling mode in combination with any of
the symptoms listed above. Some symptoms can mimic a
failed TXV but may actually be caused be another problem.
Before conducting an analysis for a failed TXV the follow-
ing must be verified:
• Confirm that there is proper water flow and water temperature in the heating mode.
• Confirm that there is proper airflow and temperature in the
cooling mode.
• Ensure coaxial water coil is clean on the inside; this applies
to the heating mode and may require a scale check.
• Refrigerant may be undercharged. To verify, subcooling and
superheat calculations may be required.
— The symptoms of a failed TXV can be varied
— The most common causes of TXV
Diagnostics
a TXV has failed. The following tools may be required for
testing:
1. Refrigerant gage manifold compatible with the refriger-
2. Digital thermometer, preferably insulated, with wire leads
3. Refrigerant pressure-temperature chart for the refrigerant
To determine that a TXV has failed, verify the following:
• The suction pressure is low and the valve is non-responsive.
The TXV sensing bulb can be removed from the suction
line and warmed by holding the bulb in your hand. This
action should result in an increase in the suction pressure
while the compressor is operating. The sensing bulb can
also be chilled by immersion in ice water, which should
result in a decrease in the suction pressure while the
compressor is operating. No change in the suction pressure would indicate a nonresponsive valve.
• Simultaneous LOW suction pressure, HIGH refrigerant
subcooling and HIGH superheat.
• LOW suction pressure, LOW subcooling and HIGH superheat may indicate an undercharge of refrigerant. HIGH subcooling and LOW superheat may indicate an overcharge of
refrigerant. The suction pressure will usually be normal or
high if there is an overcharge of refrigerant.
• LOW suction pressure and frosting of the valve and/or
equalizer line may indicate a failed valve. However, these
symptoms may also indicate an undercharge of refrigerant.
Calculate the subcooling and superheat to verify a failed
valve or refrigerant charge issue.
Repair
—Several tests may be required to determine if
ant in the system
that can be connected directly to the tubing
used
WARNING
Puron® refrigerant (R-410A) operates at higher pressure
than R-22, which is found in other WSHPs. Tools such as
manifold gages must be rated to withstand the higher pressures. Failure to use approved tools may result in a failure
of tools, which can lead to severe damage to the unit, injury
or death.
WARNING
Most TXVs are designed for a fixed superheat setting and
are therefore considered non-adjustable. Removal of the
bottom cap will not provide access for adjustment and can
lead to damage to the valve or equipment, unintended venting of refrigerant, personal injury, or possibly death.
CAUTION
Always recover the refrigerant from the system with suitable approved tools, recovery equipment, and practices
prior to attempting to remove or repair any TXV.
CAUTION
Use caution when tightening the strap. The strap must be
tight enough to hold the bulb securely but caution must be
taken not to over-tighten the strap, which could dent, bend,
collapse or otherwise damage the bulb.
47

CAUTION
Puron® refrigerant (R-410A) requires the use of synthetic
lubricant (POE oil). Do not use common tools on systems
that contain R-22 refrigerants or mineral oil. Contamination and failure of this equipment may result.
IMPORTANT: Repair of any sealed refrigerant system
requires training in the use of refrigeration tools and procedures. Repair should only be attempted by a qualified service technician. A universal refrigerant handling certificate
will be required. Local and/or state license or certificate
may also be required.
See Tables 30-32 for additional troubleshooting
IMPORTANT: Due to the hygroscopic nature of the
information.
POE oil in Puron refrigerant (R-410A) and other environmentally sound refrigerants, any component replace-
ment must be conducted in a timely manner using
caution and proper service procedure for these types of
refrigerants. A complete installation instruction will be
included with each replacement TXV/filter drier assembly. It is of critical importance these instructions are
Disconnect power from unit before removing or replacing
connectors, or servicing motor. Wait 5 minutes after disconnecting power before opening motor.
carefully understood and followed. Failure to follow
these instructions can result in a system that is contaminated with moisture to the extent that several filter drier
replacements may be required to properly dry the
system.
Table 30 — ECM Troubleshooting
FAULT DESCRIPTION SOLUTION
Motor rocks slightly when
starting
Motor will not start No movement Check power at motor.
Motor rocks Check for loose or non-compliant motor mount.
Motor oscillates up and down
while being tested off of blower
Motor starts, but runs erratically Varies up and down or intermittent Check line voltage for variation or “sag.”
“Hunts” or “puffs” at high cfm
(speed)
Stays at low cfm despite system
call for cool or heat cfm
Stays at high cfm Check to see if “R” is missing/not connected at motor.
Blower will not shut off Check to see if there is current leakage from controls into G, Y, or W. Check for Triac switched
Excessive noise Noisy blower or cabinet Determine if it’s air, cabinet, duct, or motor noise.
“Hunts” or “puffs” at high cfm
Evidence of moisture Motor failure or malfunction has
(speed)
occurred and moisture is present
Evidence of moisture present
inside air mover
This is normal start-up for ECM.
Check low voltage (24-vac R to C) at motor.
Check low voltage connections (G,Y, W, R, C) at motor.
Check for unseated pins in connectors on motor harness. See Fig. 39.
Test with a temporary jumper between R and G.
Check motor for tight shaft.
Perform motor/control replacement check.
Run moisture check. See Moisture Check section in Troubleshooting.
Make sure blower wheel is tight on shaft.
Perform motor/control replacement check.
It is normal for motor to oscillate with no load on shaft.
Check low voltage connections (G,Y, W, R, C) at motor, unseated pins in motor harness
connectors. See Fig. 39.
Check “Bk” for erratic cfm command (in variable speed applications).
Check system controls, thermostat.
Perform moisture check. See Moisture Check section in Troubleshooting.
If removing panel or filter reduces “puffing,” reduce restriction or reduce maximum airflow.
Check low voltage (thermostat) wires and connections.
Verify fan is not in delay mode. Wait until delay is complete.
Check to see if “R” is missing/not connected at motor.
Perform motor/control replacement check.
Verify fan is not in delay mode. Wait until delay is complete.
Perform motor/control replacement check.
thermostat or solid state relay.
Check for loose blower housing, panels, etc.
If high static is creating high blower speed, check for air whistling through seams in ducts,
cabinets, or panels.
If high static is creating high blower speed, check for cabinet/duct deformaton.
If removing panel or filter reduces “puffing,” reduce restriction or reduce maximum airflow.
Replace motor and perform moisture check. See Moisture Check section in Troubleshooting.
Perform moisture check. See Moisture Check section in Troubleshooting.
CAUTION
48

Fig. 39 — ECM Pin Connectors
a50-8448
49

Stopped or Malfunctioned ECM Motor — Refer
Fig. 40 — ECM Troubleshooting Flow Diagram
a50-8447
to Fig. 40 to determine the possible cause of a stopped or malfunctioned ECM motor. Follow the instructions in the boxes.
50

Moisture Check — To perform moisture check:
• Check that connectors are orientated “down” (or as recommended by equipment manufacturer).
• Arrange harnesses with “drip loop” under motor.
• Check if condensate drain is plugged.
• Check for low airflow (too much latent capacity).
• Check for undercharged condition.
• Check and plug leaks in return ducts, cabinet.
Table 31 — Good Practices
DO DO NOT
Check motor, controls wiring, and connections thoroughly before replac-
Automatically assume the motor is bad.
ing motor.
Orient connectors down so water cannot get in. Install “drip loops.” Locate connectors above 7 and 4 o’clock positions.
Use authorized motor and control model numbers for replacement. Replace one motor or control model number with another (unless
replacement is authorized).
Keep static pressure to a minimum by:
• Using high efficiency, low-static filters.
• Keeping filters clean.
• Designing ductwork for minimum static and maximum comfort.
• Improving ductwork when replacement is necessary.
Use high pressure drop filters.
Use restricted returns.
Size equipment wisely. Oversize system then compensate with low airflow.
Check orientation before inserting motor connectors. Plug in power connector backwards.
Force plugs.
Table 32 — WSHP Troubleshooting
Main Power Problems X X Green Status LED Off Check line voltage circuit breaker and disconnect.
HP Fault — Code 2
High Pressure
LP/LOC Fault — Code 3
Low Pressure/Loss of
Charge
FP1 Fault — Code 4
Water Freeze Protection
FP2 Fault — Code 5
Air Coil Freeze Protection
Condensate Fault —
Code 6
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
RV — Reversing Valve
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
FAULT HEATING COOLING POSSIBLE CAUSE SOLUTION
Check for line voltage between L1 and L2 on the contactor.
Check for 24 vac between R and C on controller.
Check primary/secondary voltage on transformer.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Bring water temperature within design parameters.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
Dirty air coil — construction dust etc.
External static too high. Check blower performance per Tables 9-13.
Tables 20-23.
Plugged strainer or filter. Clean or replace.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Clip JW2 jumper for antifreeze (10F) use.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower performance per Tables 9-13.
parameters.
Normal airside applications will require 30 F only.
Check slope of unit toward outlet.
Poor venting. Check vent location.
LEGEND
X Reduced or no water flow in cooling Check pump operation or valve operation/setting.
X Water temperature out of range in
X Reduced or no airflow in heating Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
X Air temperature out of range in heating Bring return-air temperature within design parameters.
X X Overcharged with refrigerant Check superheat/subcooling vs typical operating condition per
X X Bad HP switch Check switch continuity and operation. Replace.
X X Insufficient charge Check for refrigerant leaks.
X Compressor pump down at start-up Check charge and start-up water flow.
X Reduced or no water flow in heating Check pump operation or water valve operation/setting.
X Inadequate antifreeze level Check antifreeze density with hydrometer.
X Improper freeze protect setting (30F
X Water temperature out of range Bring water temperature within design parameters.
X X Bad thermistor Check temperature and impedance correlation.
X X Bad thermistor Check temperature and impedance correlation.
X X Blocked drain Check for blockage and clean drain.
X X Improper trap Check trap dimensions and location ahead of vent.
cooling
vs 10F)
X Reduced or no airflow in cooling Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
X Air temperature out of range Too much cold vent air. Bring entering air temperature within design
X Improper freeze protect setting (30F
vs 10F)
X Poor drainage Check for piping slope away from unit.
X Moisture on sensor Check for moisture shorting to air coil.
51

Table 32 — WSHP Troubleshooting (cont)
FAULT HEATING COOLING POSSIBLE CAUSE SOLUTION
Over/Under Voltage —
Code 7 (Auto Resetting)
Performance Monitor —
Code 8
FP1 and FP2 Thermistors
— Code 9
No Fault Code Shown X X No compressor operation See Scroll Compressor Rotation section.
Swapped Thermistor —
Code 9
Unit Short Cycles X X Dirty air filter Check and clean air filter.
Only Fan Runs X X Thermostat position Ensure thermostat set for heating or cooling operation.
Only Compressor Runs X X Thermostat wiring Check G wiring at heat pump. Jumper G and R for fan operation.
Unit Does Not Operate in
Cooling
Insufficient Capacity/
Not Cooling or Heating
Properly
LEGEND
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
RV — Reversing Valve
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
X X Under voltage Check power supply and 24 vac voltage before and during operation.
Check power supply wire size.
Check compressor starting.
Check 24 vac and unit transformer tap for correct power supply voltage.
X X Over voltage Check power supply voltage and 24 vac before and during operation.
X Heating mode FP2>125F Check for poor airflow or overcharged unit.
X Cooling mode FP1>125F OR
FP2<40F
X FP1 temperature is higher
X X Compressor overload Check and replace if necessary.
X X Control board Reset power and check operation.
X X FP1 and FP2 swapped Reverse position of thermistors.
X X Unit in 'Test Mode' Reset power or wait 20 minutes for auto exit.
X X Unit selection Unit may be oversized for space. Check sizing for actual load of space.
X X Compressor overload Check and replace if necessary.
X X Unit locked out Check for lockout codes. Reset power.
X X Compressor overload Check compressor overload. Replace if necessary.
X X Thermostat wiring Check Y and W wiring at heat pump. Jumper Y and R for compressor
X X Fan motor relay Jumper G and R for fan operation. Check for line voltage across BR
X X Fan motor Check for line voltage at motor. Check capacitor.
X X Dirty filter Replace or clean.
X Reduced or no airflow in heating Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
X X Leaky ductwork Check supply and return air temperatures at the unit and at distant duct
X X Low refrigerant charge Check superheat and subcooling per Tables 20-23.
X X Restricted metering device Check superheat and subcooling per Tables 20-23. Replace.
X X Thermostat improperly located Check location and for air drafts behind thermostat.
X X Unit undersized Recheck loads and sizing check sensible cooling load and heat pump
X X Scaling in water heat exchanger Perform condenser cleaning.
X X Inlet water too hot or cold Check load, loop sizing, loop backfill, ground moisture.
than FP2 temperature.
X FP2 temperature is higher
than FP1 temperature.
X Reversing valve Set for cooling demand and check 24 vac on RV coil and at control.
X Thermostat setup Check for 'O' RV setup not 'B'.
X Thermostat wiring Check O wiring at heat pump. Jumper O and R for RV coil 'Click'.
X Reduced or no airflow in cooling Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
X Defective reversing valve Set for cooling demand and check 24 vac on RV coil and at control.
Check 24 vac and unit transformer tap for correct power supply voltage.
Check for poor water flow or airflow.
Swap FP1 and FP2 thermistors.
Swap FP1 and FP2 thermistors.
operation in Test mode.
Check Y and W wiring at heat pump. Jumper Y and R for compressor
operation in test mode.
contacts.
Check fan power enable relay operation (if present).
If RV is stuck, run high pressure up by reducing water flow and while
operating, engage and disengage RV coil voltage to push valve.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower performance per Tables 9-13.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower performance per Tables 9-13.
registers if significantly different, duct leaks are present.
If RV is stuck, run high pressure up by reducing water flow and while
operating, engage and disengage RV coil voltage to push valve.
capacity.
52

Table 32 — WSHP Troubleshooting (cont)
FAULT HEATING COOLING POSSIBLE CAUSE SOLUTION
High Head Pressure X Reduced or no airflow in heating Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower performance per Tables 9-13.
X Reduced or no water flow in
cooling
X Inlet water too hot Check load, loop sizing, loop backfill, ground moisture.
X Air temperature out of range in
X X Unit overcharged Check superheat and subcooling. Reweigh in charge.
X X Noncondensables in system Remove refrigerant, evacuate system and charge unit.
X X Restricted metering device Check superheat and subcooling per Tables 20-23. Replace.
Low Suction Pressure X Reduced water flow in heating Check pump operation or water valve operation/setting.
X Water temperature out of range Bring water temperature within design parameters.
X X Insufficient charge Check for refrigerant leaks.
Low Discharge Air
Temperature in Heating
High Humidity X Too high airflow Check blower performance per Tables 9-13
Low Refrigerant Suction
Pressure
High Refrigerant Superheat X X Insufficient refrigerant charge Locate and repair leak.
High Refrigerant
Subcooling
TXV and/or Low Pressure
Tubing Frosting
Equalizer Line Condensing
or Frosting
X Too high airflow Check blower performance per Tables 9-13.
X Poor performance See “Insufficient Capacity.”
X Normal operation Check/compare with unit Installation Manual for typical operating temper-
X Reduced water flow Check pump operation.
X Water temperature out of range Bring water temperature within proper range.
X Scaling in water to refrigerant
X X Return air temperature below
X X Insufficient refrigerant charge Locate and repair leak.
X X Improperly located TXV sensing
X X Failed or restricted metering
X X Improperly located TXV sensing
X X Failed or restricted metering
X X Excessive refrigerant charge Remove refrigerant as needed.
X X Failed or restricted metering
X Normal operation May occur when entering water temperature is close to minimum.
X X Insufficient refrigerant charge Locate and repair leak.
X X Failed or restricted metering
X X Failed or restricted metering
heating
X Scaling in water heat exchanger Perform condenser cleaning.
X Reduced airflow in cooling Check for dirty air filter and clean or replace.
X Air temperature out of range Too much cold vent air. Bring entering air temperature within design
X Unit oversized Recheck loads and sizing check sensible cooling load and heat pump
heat exchanger
X Reduced airflow Check for dirty air filter.
minimum
X Supply air bypassing to return air
stream (zone systems).
bulb
device
bulb
device
device
device
device
LEGEND
LED — Light-Emitting Diode
RV — Reversing Valve
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
Check pump operation or valve operation/setting.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate. See Tables 19 and 24.
Bring return-air temperature within design parameters.
Plugged strainer or filter. Clean or replace.
Check water flow adjust to proper flow rate.
Check fan motor operation and airflow restrictions.
External static too high. Check blower performance per Tables 9-13.
parameters.
capacity.
atures and pressures chart.
Check strainer or filter.
Improper flow regulator.
Conduct water quality analysis.
Check for dirty air coil.
Check fan motor operation.
External static pressure exceeds fan operating parameters.
Space temperature too cold.
Excessive fresh air.
Check for leaking ductwork.
Locate bulb on suction line between reversing valve and compressor.
Failed TXV power head, capillary or sensing bulb.
Plugged TXV strainer.
Locate bulb on suction line between reversing valve and compressor.
Failed TXV power head, capillary or sensing bulb.
Plugged TXV strainer.
Failed TXV power head, capillary or sensing bulb.
Plugged TXV strainer.
Failed TXV power head, capillary or sensing bulb.
Plugged TXV strainer.
Failed TXV power head, capillary or sensing bulb.
Plugged TXV strainer.
53

APPENDIX A — WSHP OPEN SCREEN CONFIGURATION
SCREEN NAME POINT NAME
Operating Mode
SPT F Displays SPT
SAT F Displays SAT
Condenser Leaving
Temperature
Condenser Entering
Temperature
Fan
Equipment
Status
Alarm Status
Sensor
Calibration
BAS — Building Automation System
DCV — Demand Controlled Ventilation
IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
OAT — Outdoor Air Temperature
RH — Relative Humidity
SAT — Supply Air Temperature
SPT — Space Temperature
TPI — Third Party Integration
Compressor Capacity 0 - 100% Displays compressor capacity
Damper Position 0 - 100%
O Economizer 0 - 100% Displays position of economizer valve
H
2
Auxiliary Heat 0 - 100%
Space RH 0 - 100%
Dehumidification Inactive/Active
IAQ CO
2
SPT Alarm Status
Alarming SPT F
SPT Alarm Limit F
SPT Sensor Alarm
Status
IAQ Alarm Status Normal/Alarm Current IAQ/ventilation condition
Compressor Alarm
Status
SAT Alarm Status Normal/Alarm Current SAT condition
Condensate Overflow
Alarm Status
Condenser Water Tem-
perature Alarm Status
Filter Alarm Status Normal/Alarm Current filter condition
Space RH Alarm Status Normal/Alarm Current space RH condition
OAT Alarm Status Normal/Alarm
Airside Linkage Status Normal/Alarm Current linkage status if enabled
Condenser Water
Linkage
SAT
SAT Offset X -9.9 - 10.0 F 0 F Used to correct sensor reading
Leaving Condenser
Water Temperature
Leaving CW Offset X -9.9 - 10.0 F 0 F Used to correct sensor reading
Rnet Sensor
Temperature
Rnet Offset X -9.9 - 10.0 F 0 F Used to correct sensor reading
RH % Displays Space RH value
RH Sensor Offset X -15% - 15% 0 % Used to correct sensor reading
LEGEND
PASSWO RD
LEVEL
No Password
Required
No Password
Required
Admin Password
level access only
EDITABLE RANGE DEFAULT NOTES
Off, Fan Only, Economize,
Cooling, Heating, Cont Fan,
Test, Start Delay, Dehumidify
F
F
Off/Low Speed/
Medium Speed
High Speed/On
0 - 9999 ppm Displays the space CO2 level
Normal/Alarm
Normal/Alarm
Normal/Alarm Current compressor condition
Normal/Alarm
Normal/Alarm
Normal/Alarm Current linkage status if enabled
F Display SAT
F
F Displays SPT
Displays unit operating mode
Displays leaving condenser
water temperature
Displays entering condenser
water temperature (Value
will not update when compressor
Displays current damper position
(Viewable only if Ventilation DMP
reheat valve (Viewable only if Leaving
Air Auxiliary Heat Type = 2 position,
Displays space RH% (Viewable only if
Displays if dehumidification is active
Dehumidification Reheat = Installed)
exceeded the alarm limit (when SPT
Displays the SPT alarm limit that was
exceeded; causing the alarm condition
(when SPT alarm above is in Alarm)
SPT sensor - ALARM is displayed
should the sensor fail to communicate
Current status of the condensate
is operating)
Displays fan speed status
Type = 2 position or DCV)
Displays position of auxiliary
1 stage Elect or Modulating)
Humidity Sensor = Installed)
(Viewable only if Factory
Displays current space
temperature condition
Displays the SPT that
alarm above is in Alarm)
Displays the status of the Rnet
with the control module
drain (overflow switch)
Current status of the
condenser water
Current status of the OAT
broadcast function
Displays Leaving Condenser
Water Temperature
54

APPENDIX A — WSHP OPEN SCREEN CONFIGURATION (cont)
SCREEN NAME POINT NAME
Operating Mode
Fan Operating Mode Auto/Continuous/Always On
Occupancy Status Unoccupied/Occupied Displays the current occupancy status
Occupancy Control
Outside Air
Temperature
SPT F Displays SPT
SPT Status
SPT Sensor Status Inactive/Connected
Condensate Overflow Normal/Alarm
Cooling Set Point F
Unit
Maintenance
System Settings
Occupancy
Maintenance
Schedule
Configuration
BAS — Building Automation System
DCV — Demand Controlled Ventilation
IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
OAT — Outdoor Air Temperature
RH — Relative Humidity
SAT — Supply Air Temperature
SPT — Space Temperature
TPI — Third Party Integration
Heating Set Point F
Set Point Adjustment F
Auxiliary Heat Control
Set Point
O Economizer
H
2
Control Set Point
Calculated IAQ/
Ventilation Damper
position
Active Compressor
Stages
SAT F Displays SAT
Reset Filter Alarm X No/Yes
Overflow Contact Closed/Open
Occupancy Contact Closed/Open
BAS/Keypad Override X
OAT Input N/A / Network
BACnet X See TPI
Keypad Configuration X Mapping
Password X Changes password
Network X See TPI
BACnet Time Master X See TPI
Clock Set X Changes clock/time setting
Override Schedules
Pushbutton Override Inactive/Active Occupied
Keypad Override
Schedules Inactive/Active Occupied
Occupancy Contact Inactive/Active Occupied
BAS on/off Inactive/Active Occupied
Local Occupancy
Schedules
Local Holiday
Schedules
Local Override
Schedules
BACnet Occupancy
Schedules
LEGEND
PASSWORD
LEVEL
No Password
required
No Password
required
User/Admin
Password level
access
EDITABLE RANGE DEFAULT NOTES
Off, Fan Only,Economize,
Cooling, Heating, Cont Fan, Test,
Start Delay, Dehumidify
Always Occupied/Local Schedule/
BACnet Schedule/BAS Keypad/
Occupied Contact/Holiday Schedule/
Override Schedule/Pushbutton
Override/Unoccupied None
F
Normal/Above Limit/Below
Limit/Sensor Failure
F
F
%
0/1/2
Inactive/Occupied/
Unoccupied
Inactive/Active Occupied
Inactive/Active Occupied/Active
Unoccupied
X Disable/Enable Enable
X Disable/Enable Disable
X Disable/Enable Disable
X Disable/Enable Disable
Inactive
Displays unit operating mode
Displays how the fan is configured
Displays OAT (Viewable only if OAT
Displays the connection status
being used for heating control
Displays the offset values from the Rnet
user set point adjustment that is being
applied to the configured set points
Displays the calculated set point being
used for auxiliary heating control
Displays the calculated set point being
Displays the ventilation damper
position calculated by the DCV control
Displays the actual number of
Used to reset the filter alarm timer after
the filter has been cleaned or replaced
Displays the state of the condensate
Displays the state of the external/
remote occupancy input switch contact
Provides capability to force the
occupied or unoccupied mode
Displays if an OAT value is being
Used to display the active and
inactive occupancy control inputs
Used to define which occupancy inputs
to operate
Displays the origin of the
occupancy control
is a network broadcast)
Displays the SPT status
of the Rnet sensor
Displays the status of the
condensate overflow
Displays the actual set point
being used for cooling control
Displays the actual set point
used for economizer control
compressor stages operating
overflow switch contact
equipment to operate in an
received from the Network
are used to determine
occupancy mode.
55

APPENDIX A — WSHP OPEN SCREEN CONFIGURATION (cont)
SCREEN NAME POINT NAME
Occupied Heating
Occupied Cooling X 55 - 99 F 76 F
Unoccupied Heating X 40 - 90 F 55 F
Unoccupied Cooling X 55 - 99 F 90 F
Effective Heating
Set Point
Effective Cooling
Set Point
Optimal Start
Configuration
Occupied RH
Set Points
Configuration
Schedule
Weekly Schedule
Configuration
Schedule
Exception
Schedules 1 - 12
LEGEND
BAS — Building Automation System
DCV — Demand Controlled Ventilation
IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
OAT — Outdoor Air Temperature
RH — Relative Humidity
SAT — Supply Air Temperature
SPT — Space Temperature
TPI — Third Party Integration
Set Point
Unoccupied RH
Set Point
DCV CTRL Start
Set Point
DCV Max CTRL
Set Point
Start Time
End Time X 00:00 - 24:00 18:00
Mon X No/Yes Yes
Tu e X N o /Ye s Ye s
Wed X No/Yes Yes
Thur X No/Yes Yes
Fri X No/Yes Yes
Sat X No/Yes No
Sun X No/Yes No
Start Month
Start Day X 0 - 31 0
Start Time X 00:00 - 23:59 0:00
End Month X 0 - 12 0
End Day X 0 - 31 0
End Time X 00:00 - 24:00 0:00
PASSWORD
LEVEL
User/Admin
Password level
access
User/Admin
Password level
access
User/Admin
Password level
access
EDITABLE RANGE DEFAULT NOTES
X 40 - 90 F 72 F
X0 - 10 F
X0 - 10 F
X 0 - 100% 65%
X 0 - 100% 90%
X 0 - 9999 ppm 500 ppm
X 0 - 9999 ppm 1050 ppm
X 00:00 - 23:59 06:00
X0 - 120
Defines the Occupied
Heating Set Point
Defines the Occupied
Cooling Set Point
Defines the Unoccupied
Heating Set Point
Defines the Unoccupied
Cooling Set Point
Takes into effect bias (maximum
allowable set point deviation)
Takes into effect bias (maximum
allowable set point deviation)
Uses historical data to calculate
ramp up time so as to be at set point
at occupied/unoccupied time
Defines the control set point used
during occupied periods (Viewable
only if Humidity Sensor = Installed/
Determines when to start
Dehumidification when occupied)
Defines the control set point used
during unoccupied periods
(Viewable only if Humidity Sensor =
Installed/Determines when to start
Dehumidification when unoccupied)
Defines the control set point used to
start increasing ventilation during
occupied periods (Viewable only if
Ventilation DMP Type = DCV)
Defines the control set point
used to define where the ventilation
will reach its maximum limit during
occupied periods (Viewable only if
Ventilation DMP Type = DCV/Used
to determine DCV ending control
Defines the start time for an
Defines the ending time of an
Determines if this day is included
Determines if this day is included
Determines if this day is included
Determines if this day is included
Determines if this day is included
Determines if this day is included
Determines if this day is included
Defines the start month of this
Defines the start day of this holiday
Determines the start time for this
Defines the month to end this
Defines the day to end this holiday
Determines the time to end this
point)
occupied period
occupied period
in this schedule
in this schedule
in this schedule
in this schedule
in this schedule
in this schedule
in this schedule
hoilday schedule
schedule
schedule
hoilday schedule
schedule
schedule
56

APPENDIX A — WSHP SCREEN OPEN CONFIGURATION (cont)
SCREEN NAME POINT NAME
Fan Mode
Fan On Delay X 0 - 30 sec 10 sec
Fan Off Delay X 0 - 180 sec 45 sec
Heating Enable X Disable/Enable Enable
Cooling Enable X Disable/Enable Enable
Minimum SAT in
Configuration
Unit
Configuration
Configuration
Service
Test
LEGEND
BAS — Building Automation System
DCV — Demand Controlled Ventilation
IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
OAT — Outdoor Air Temperature
RH — Relative Humidity
SAT — Supply Air Temperature
SPT — Space Temperature
TPI — Third Party Integration
Cooling
Maximum SAT in
Heating
Damper Ventilation
Positio n
DCV Maximum Vent
Positio n
Filter Alarm Timer X 0 - 9999 hrs 0 hrs Disables Filter Alarm if set to 0
Pushbutton Override X Disable/Enable Enable Enables Override Feature on Rnet sensor
SPT Sensor Set Point
Adjustment
Lockout Cooling if
OAT <
Lockout Heating if
OAT >
Power Fail Restart
Delay
Occupancy Schedules X Disable/Enable Enable Enables unit occupied
Set Point Separation X 2 - 9 F 4 F
Test Mode
Fan Test X Disable/Enable Disable
Fan Speed
Compressor Test X Disable/Enable Disable
Dehumidification Test X Disable/Enable Disable
Testing Compressor
Aux Heating Test X Disable/Enable Disable
O Economizer Test X Disable/Enable Disable
H
2
Preposition OA
Damper
Open Vent
Damper 100%
SAT F Displays SAT
LCWT F
PASSWORD
LEVEL
Admin Password
level access only
Admin Password
level access only
EDITABLE RANGE DEFAULT NOTES
Auto= Intermittant operation during both
occupied and unoccupied periods/
X
X40 - 60 F50 F
X 80 - 140 F 110 F
X 0 - 100% 100%
X 0 - 100% 100%
X Disable/Enable Enable
X -65 - 80 F -65 F
X 35 - 150 F 150 F
X 0 - 600 sec 60 sec Delay before equipment starts
X Disable/Enable Disable
X Disable/Enable Disable
X Disable/Enable Disable Used to test OA damper operation
Auto/Continuous/
Always On
Off/Low Speed/Medium
Speed/High Speed/On
Inactive/Heating/Cooling/
Dehumidify/TimeGard
Wait
Continuous
Continuous = Intermittant during unoccupied
periods and continuous during occupied
periods/Always on = fan operates
continuously during both occupied and
unoccupied periods
Defines the delay time before the fan begins
to operate after heating or cooling is started
Defines the amount of time the fan will
continue to operate after heating or
cooling is stopped
Provides capability to manually
disable heating operation
Provides capability to manually
disable cooling operation
Defines the minimum acceptable operating
temperature for the Supply Air
Defines the maximum acceptable operating
temperature for the Supply Air
Normally set to 100% if 2 position damper
type or set to minimum ventilation position if
Usually set at 100% - Used to limit maximum
Enables Set Point adjustment capability
Cooling is locked out when OAT is less than
configured value and OAT is actively being
Heating is locked out when OAT is greater
than configured value and OAT is actively
Used to enable test mode. Will automatically
Used to test all fan speeds. Sequences fan
from low to high and operates each speed for
1 minute. Resets to disable on completion
Used to test compressor cooling and heating
operation. Sequences cooling stage 1, then
stage 2, then heating stage 2 and reduces
capacity to stage 1. Operates for 1 minute per
Used to test entering/return air water loop
economizer coil operation. Sequences fan on
and opens economizer coil water valve for 1
minute. Resets to disable on completion
damper type = DCV
damper opening in DCV mode
on Rnet Sensor
broadcast
being broadcast
Used to enforce minimum
set point separation
reset to disable after 1 hour
Displays current fan operation
step. Resets to disable on completion.
Used to test dehumification mode -
Operates for 2 minutes. Resets to
disable on completion.
Displays compressor test mode
Used to test auxiliary heat.
Sequences fan on and enables
heating coil for 1 minute. Resets to
disable on completion
Used to preposition OA damper
actuator to set proper preload
Displays Leaving Condenser
Water Temperature
57

APPENDIX A — WSHP SCREEN OPEN CONFIGURATION (cont)
SCREEN NAME POINT NAME
# of Fan Speeds
G Output Type X Fan On/Fan Low Fan On
Compressor Stages X One Stage/Two Stages One Stage
Reversing Valve Type X O type output/B type output O type
Leaving Air Auxiliary
Heat Type
Entering Air Water
Economizer Type
2-Position Water
Val ve Type
Modulating Water
Val ve Type
Ventilation Damper
Ty pe
Damper Actuator Type X (0-10 volt)/(2-10 volt) 0-10 volt
Configuration
Service
Configuration
LEGEND
BAS — Building Automation System
DCV — Demand Controlled Ventilation
IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
OAT — Outdoor Air Temperature
RH — Relative Humidity
SAT — Supply Air Temperature
SPT — Space Temperature
TPI — Third Party Integration
Humidity Sensor X None/Installed None
Factory Dehumidifica-
tion Reheat Coil
Occupancy
Input Logic
Condensate Switch
Alarm Delay
Condensate Switch
Alarm State
Minimum Condenser
Water Temperature in
Heating
Maximum Condenser
Water Temperature in
Heating
Minimum Condenser
Water Temperature in
Cooling
Maximum Condenser
Water Temperature in
Cooling
IAQ sensor
minimum input
IAQ sensor
maximum input
IAQ sensor
minimum output
IAQ sensor
maximum output
PASSWORD
LEVEL
Admin Password
level access only
EDITABLE RANGE DEFAULT NOTES
X 1,2,3 3
X
X None/2-Position/Modulating None
X Normally Closed/Normally Open
X Normally Closed/Normally Open
X None/2-Position/DCV None
X None/Installed None
X Occupied Open/Occupied Closed
X 5 - 600 seconds 10 sec
X Alarm OPEN/Alarm CLOSED
X25 - 60 F60 F
X 65 - 100 F 90 F
X30 - 60 F60 F
X 85 - 120 F 95 F
X 0 - 5 ma 4 ma
X 5 - 20 ma 20 ma
X 0 - 9999 ppm 0 ppm
X 0 - 9999 ppm 2000 ppm
None/2-Position HW/1 Stage
Electric/Modulating HW
None
Normally
Closed
Normally
Closed
Occupied
CLOSED
Alarm
CLOSED
Used to set number of
fan motor speeds
When set to Fan On, G output is
energized when ever any fan speed
is active (required for ECM and Fan
control board). When set to Fan
Low, output is only energized for
Set to Installed if factory-installed
Used to determine external occu-
pancy switch contact occupied state
Delay before equipment alarms on
acceptable water loop temperature
acceptable water loop temperature
acceptable water loop temperature
acceptable water loop temperature
Maximum output current (mA) for
Corresponding value in ppm for
Corresponding value in ppm for
Low Speed
Defines the number of
stages of compression
Determines reversing valve
signal output type
Determines Auxiliary
Reheat Coil Type
Determines Entering Air
Economizer Coil Type
Determines type of 2-position
water valve used
Determines type of modulating
water valve used
Determines type of ventilation
damper control to be used
Used to determine ventilation
damper output signal range
(closed - open)
Set to Installed if humidity
sensor is present
dehumidification reheat coil
is present
high condensate level
Determine Alarm state of
condensate switch input
Determines the minimum
to start heating
Determines the maximum
to start heating
Determines the minimum
to start cooling
Determines the maximum
to start cooling
Minimum output current (mA)
for IAQ sensor
IAQ sensor
minimum output current
maximum output current
58

APPENDIX A — WSHP SCREEN OPEN CONFIGURATION (cont)
SCREEN NAME POINT NAME
SPT Occupied Alarm
Hysteresis
SPT Alarm Delay X 0 - 30 min per degree 10 min
SPT Unoccupied Low
Alarm Temperature
SPT Unoccupied High
Alarm Temperature
SAT Low SAT
Alarm Limit
SAT High SAT
Alarm Limit
Condensate Overflow
Alarm Delay
Space Humidity Occupied
High Alarm Limit
Configuration
Alarm
Configuration
Configuration
Linkage
BAS — Building Automation System
DCV — Demand Controlled Ventilation
IAQ — Indoor Air Quality
OAT — Outdoor Air Temperature
RH — Relative Humidity
SAT — Supply Air Temperature
SPT — Space Temperature
TPI — Third Party Integration
Space Humidity Alarm
Delay
Space Humidity Unoccu-
pied High Alarm Limit
IAQ/Ventilation Occupied
High Alarm Limit
IAQ/Ventilation
Alarm Delay
Rnet Sensor SPT Alarm X Ignore/Display Ignore
Rnet Sensor SAT Alarm X Ignore/Display Ignore
Rnet Sensor Compressor
Lockout Alarm
Rnet Sensor Condenser
Water Temperature Alarm
Rnet Sensor Condensate
Overflow Alarm
Rnet Sensor Dirty
Filter Alarm
Rnet Sensor Space
High Humidity Alarm
Loop Control Network
Number
Loop Control Network
Address
Number of Linked Heat
Pumps
LEGEND
PASSWO RD
LEVEL
Admin Password
level access only
EDITABLE RANGE DEFAULT NOTES
Defines the hysteresis applied above
X2 - 20 F5 F
X 35 - 90 F 45 F
X 45 - 100 F 95 F
X 15 - 90 F 45 F
X 90 - 175 F 120 F
X 5 - 600 sec 10 sec
X 45% - 100% 100%
X 0 - 30 min per % RH 5 min
X 45% - 100% 100%
X 0 - 9999 ppm 1100 ppm
X 0.1 - 1.0 min per ppm 0.25 min
X Ignore/Display Display
X Ignore/Display Display
X Ignore/Display Display
X Ignore/Display Display
X Ignore/Display Ignore
the cooling and below the heating set
points before an alarm condition will
Used to calculate the delay time before
an alarm is generated after the alarm
Defines the fixed unoccupied
Defines the fixed unoccupied
Defines the fixed minimum
Defines the fixed maximum
Defines the delay time before an alarm
is generated after the alarm condition
Defines the fixed occupied
high space RH alarm limit
Used to calculate the delay time before
an alarm is generated after the alarm
Defines the fixed unnoccupied
high space RH alarm limit
Defines the fixed occupied high
space IAQ/Ventilation alarm limit
Used to calculate the delay time before
an alarm is generated after the alarm
Determines if the SPT alarm is
displayed on the local Rnet sensor
Determines if the SAT alarm is
displayed on the local Rnet sensor
Determines if the Compressor Lockout
alarm is displayed on the local Rnet
Determines if the Condenser Water
Temperature alarm is displayed on the
Determines if the Condensate
Overflow alarm is displayed on the
Determines if the Dirty Filter alarm is
displayed on the local Rnet sensor
Determines if the High Space
RH alarm is displayed on the
occur
condition occurs
ow SPT alarm limit
high SPT alarm limit
SAT alarm limit
SAT alarm limit
occurs
condition occurs
condition occurs
sensor
local Rnet sensor
local Rnet sensor
local Rnet sensor
See TPI
See TPI
See TPI
59



Copyright 2010 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53500079-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50PT-4SI Pg 62 7-10 Replaces: 50PT-3SI

50PTH,PTV,PTD
START-UP CHECKLIST
CUSTOMER:___________________________ JOB NAME: _______________________________________
MODEL NO.:___________________________ SERIAL NO.:____________________ DATE:_________
I. PRE-START-UP
DOES THE UNIT VOLTAGE CORRESPOND WITH THE SUPPLY VOLTAGE AVAILABLE? (Y/N)
HAVE THE POWER AND CONTROL WIRING CONNECTIONS BEEN MADE AND TERMINALS
TIGHT? (Y/N)
HAVE WATER CONNECTIONS BEEN MADE AND IS FLUID AVAILABLE AT HEAT EXCHANGER?
(Y/N)
HAS PUMP BEEN TURNED ON AND ARE ISOLATION VALVES OPEN? (Y/N)
HAS CONDENSATE CONNECTION BEEN MADE AND IS A TRAP INSTALLED? (Y/N)
IS AN AIR FILTER INSTALLED? (Y/N)
II. START-UP
IS FAN OPERATING WHEN COMPRESSOR OPERATES? (Y/N)
IF 3-PHASE SCROLL COMPRESSOR IS PRESENT, VERIFY PROPER ROTATION PER INSTRUCTIONS.
(Y/N)
UNIT VOLTAGE — COOLING OPERATION
PHASE AB VOLTS PHASE BC VOLTS PHASE CA VOLTS
(if 3 phase) (if 3 phase)
PHASE AB AMPS
PHASE BC AMPS PHASE CA AMPS
(if 3 phase) (if 3 phase)
CONTROL VOLTAGE
IS CONTROL VOLTAGE ABOVE 21.6 VOLTS? (Y/N) .
IF NOT, CHECK FOR PROPER TRANSFORMER CONNECTION.
TEMPERATURES
FILL IN THE ANALYSIS CHART ATTACHED.
COAXIAL HEAT
EXCHANGER
COOLING CYCLE:
FLUID IN
FFLUID OUT F PSI FLOW
HEATING CYCLE:
FLUID IN
FFLUID OUT F PSI FLOW
AIR COIL COOLING CYCLE:
AIR IN
HEATING CYCLE:
AIR IN
FAIR OUT F
FAIR OUT F
CL-1

HEATING CYCLE ANALYSIS
a50-8449
SUCTION
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE
COAX
EXPANSION
VALVE
°F
°F
AIR
COIL
°F
PSI
FLUID OUT
FLUID IN
°F
PSI
°F
LIQUID LINE
PSI
°F
SAT
LOOK UP PRESSURE DROP IN TABLES 20-23
TO DETERMINE FLOW RATE
a50-8450
PSI
SAT
°F
AIR
COIL
°F
°F
LIQUID LINE
COOLING CYCLE ANALYSIS
EXPANSION
VALVE
°F
FLUID IN
°F
PSI
COAX
FLUID OUT
°F
PSI
LOOK UP PRESSURE DROP IN TABLES 20-23
TO DETERMINE FLOW RATE
SUCTION
COMPRESSOR
DISCHARGE
HEAT OF EXTRACTION (ABSORPTION) OR HEAT OF REJECTION =
FLOW RATE (GPM) x TEMP. DIFF. (DEG. F) x FLUID FACTOR* =
(Btu/hr)
SUPERHEAT = SUCTION TEMPERATURE – SUCTION SATURATION TEMPERATURE
=
(DEG F)
SUBCOOLING = DISCHARGE SATURATION TEMPERATURE – LIQUID LINE TEMPERATURE
=
*Use 500 for water, 485 for antifreeze.
Copyright 2010 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 04-53500079-01 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50PT-4SI Pg CL-2 7-10 Replaces: 50PT-3SI
(DEG F)
CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
 Loading...
Loading...