Page 1

30GK Series
PRO-DIALOG Control
Air-Cooled Liquid Chillers
50 Hz
Installation, operation and maintenance instructions
1
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 - SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS..................................................................................................................................................4
1.1 - General .................................................................................................................................................................................4
1.2 - Avoiding electrocution.........................................................................................................................................................4
2 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION ......................................................................................................................................................5
2.1 - General .................................................................................................................................................................................5
2.2 - Abbreviations used ...............................................................................................................................................................5
3 - HARDWARE DESCRIPTION....................................................................................................... ...........................................6
3.1 - General .................................................................................................................................................................................6
3.2 - Electronic boards ..................................................................................................................................................................6
3.2.1 - The basic board ............................................................................................................................................................6
3.2.2 - Slave boards .................................................................................................................................................................6
3.2.3 - The user interface.........................................................................................................................................................7
3.2.4 - Connections between boards .......................................................................................................................................7
3.2.5 - Slave board addresses ..................................................................................................................................................7
3.2.6 - Power supply to the boards ..........................................................................................................................................7
3.2.7 - Light emitting diodes on boards ..................................................................................................................................7
3.3 - The controls ..........................................................................................................................................................................7
3.3.1 - Electronic expansion valve (EXV)..............................................................................................................................7
3.3.2 - The head pressure controls ..........................................................................................................................................7
3.3.3 - The evaporator pumps .................................................................................................................................................8
3.3.4 - The condenser pump....................................................................................................................................................8
3.3.5 - Pressure sensors ...........................................................................................................................................................8
3.3.6 - Thermistors ..................................................................................................................................................................8
3.4 - User connections ..................................................................................................................................................................9
4 - SETTING UP PRO-DIALOG PLUS CONTROL .................................................................................................................10
4.1 - Local interface general features..........................................................................................................................................10
4.2 - Unit start/stop control .........................................................................................................................................................11
4.2.1 - Description.................................................................................................................................................................11
4.2.2 - Stopping the unit in local mode ................................................................................................................................. 11
4.2.3 - Starting unit and selecting an operating type.............................................................................................................11
4.3 - Menus .................................................................................................................................................................................12
4.3.1 - Selecting a menu ........................................................................................................................................................12
4.3.2 - Selecting a menu item................................................................................................................................................12
4.3.3 - Modifying the value of a parameter/access to a sub-menu........................................................................................12
4.3.4 - Expand display...........................................................................................................................................................12
4.4 - General menu structure.......................................................................................................................................................13
4.5 - Menu tree structure.............................................................................................................................................................14
4.5.1 - Description of the Information menu.........................................................................................................................15
4.5.2 - Description of the Temperatures menu......................................................................................................................16
4.5.3 - Description of the Pressures menu.............................................................................................................................16
4.5.4 - Description of the Setpoints menu.............................................................................................................................17
4.5.5 - Description of the Inputs menu..................................................................................................................................18
4.5.6 - Description of the Outputs/Tests menu .....................................................................................................................18
4.5.7 - Description of the Configuration menu .....................................................................................................................20
4.5.8 - Description of the Alarms menu ................................................................................................................................25
4.5.9 - Description of the Alarms History menu ...................................................................................................................25
4.5.10 - Runtime menu description .......................................................................................................................................26
The cover photograph is solely for illustration, and forms no part of any offer for sale or any sale contract. The
manufacturer reserves the right to change the design at any time without notice.
2
Page 3

5 - PRO-DIALOG PLUS CONTROL OPERATION .................................................................................................................27
5.1 - Start/stop control ................................................................................................................................................................27
5.2 - Heating/cooling selection ...................................................................................................................................................27
5.3 - Evaporator water pump control ..........................................................................................................................................28
5.4 - Condenser water pump control...........................................................................................................................................28
5.5 - Control interlock contact ....................................................................................................................................................28
5.6 - Evaporator heater control ...................................................................................................................................................28
5.7 - Control point......................................................................................................................................................................28
5.7.1 - Active setpoint ...........................................................................................................................................................28
5.7.2 - Reset...........................................................................................................................................................................28
5.8 - Demand limit ......................................................................................................................................................................29
5.9 - Capacity control ................................................................................................................................................................29
5.10 - Determining the lead circuit............................................................................................................................................29
5.11 - Circuit loading sequence..................................................................................................................................................29
5.12 - Slave compressor start-up sequence ................................................................................................................................30
5.13 - Controlling the EXV ........................................................................................................................................................30
5.14 - Head pressure control on air-cooled units .......................................................................................................................30
5.15 - Head pressure control on water-cooled units...................................................................................................................30
5.16 - Active setpoint selection ..................................................................................................................................................30
5.17 - High pressure load shedding function..............................................................................................................................31
5.18 - Pumping down..................................................................................................................................................................31
5.19 - Master/slave assembly .....................................................................................................................................................31
5.20 - Controlling Pro-Dialog Plus units with a System Manager.............................................................................................31
5.21 - Optional heat reclaim module ..........................................................................................................................................32
6 - DIAGNOSTICS - TROUBLESHOOTING ............................................................................................................................32
6.1 - General ...............................................................................................................................................................................32
6.2 - Displaying alarms ...............................................................................................................................................................32
6.3 - Resetting alarms .................................................................................................................................................................32
6.4 - Alarm codes........................................................................................................................................................................33
3
Page 4

1 - SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
1.1 - General
Installation, start-up and servicing of equipment can be hazardous if factors particular to the installation are not considered:
operating pressures, electrical components, voltages and the
installation site itself (elevated plinths, rooftops and built-up
structures).
IMPORTANT:
Risk of electrocution: Even when the main power isolator or
circuit breaker is off, it is still possible for certain components such as crankcase heaters and trace heaters to be
energised, since they are connected to a separate power source.
Even when the unit is switched off, the power circuit remains
energised, as long as the unit or circuit disconnect is not open.
Refer to the wiring diagram for details.
Only highly trained and qualified installation engineers and
technicians, who are fully trained on the product, are authorised
to install and start up this equipment.
During all servicing operations, it is important to read, understand and follow all the recommendations and instructions
given in the installation and service instructions for the product,
including the tags and labels affixed to the equipment, components and any parts supplied separately, and to comply with all
other relevant safety regulations.
• Apply all safety codes and practices.
• Wear safety glasses and gloves.
• Use the proper tools to move heavy objects. Move units
carefully and set them down gently.
1.2 - Avoiding electrocution
Only personnel qualified in accordance with the recommendations of the IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission)
may be permitted access to electrical components. It is particularly recommended that all sources of electricity to the unit
be shut off before any work is begun. Shut off the main power
supply at the main circuit breaker or isolator.
Attach appropriate safety labels.
Risk of burns: Electrical currents cause components to get
hot either temporarily or permanently. Handle power cables,
electrical cables and conduits, terminal box covers and motor
frames with very great care.
IMPORTANT: This equipment uses and emits electromagnetic
signals. The tests carried out on this product have shown that
it complies with all applicable codes regarding electromagnetic
compatibility.
IMPORTANT : If the boards need to be handled wear antistatic gloves to avoid exposing the electronic components to a
destructive voltage. Only unpack the boards from their antistatic bag when they need to be installed.
4
Page 5

2 - GENERAL DESCRIPTION
2.2 - Abbreviations used
2.1 - General
PRO-DIALOG Plus is a system for controlling units which use
reciprocating compressors*:
• Single or dual circuit
• Air or water-cooled condensers
• Non-reversible heat pumps
• Split systems
* At present only air-cooled models are available.
PRO-DIALOG Plus controls compressor start-up and demand
limits needed to maintain the desired entering or leaving temperature setpoint for water. It automatically sets the position of
the electronic expansion valve (if used) to optimise the evaporator charge. It controls operation of the fans (on air-cooled
units) or water valves (on water-cooled units) to maintain the
correct head pressure in each circuit.
Safety circuits are constantly monitored by PRO-DIALOG
Plus to ensure safe operation of the unit. PRO-DIALOG Plus
also gives access to a Quick Test program covering all inputs
and outputs.
All PRO-DIALOG Plus controls can work in accordance with
three independent modes:
• Local mode: the machine is controlled by commands from
the user interface.
• Remote mode: the machine is controlled by remote
contacts (volt-free contacts, analogue signals).
• CCN mode: the machine is controlled by commands from
the Carrier Comfort Network (CCN). In this case a data
communication cable is used to connect the unit to the
CCN communication bus.
In this manual the circuits are called circuit A and circuit B.
The compressors in circuit A are labelled A1, A2, A3 and A4.
Those in circuit B are labelled B1, B2, B3 and B4. A1 and B1
are the lead compressors.
The following abbreviations are frequently used:
AI - Analogue Input
AO - Analogue Output
CCn - Operating type: CCN
CCN - Carrier Comfort Network.
This is the Carrier communication network
DI - Discrete Input
DO - Discrete Output
EXV - Electronic Expansion Device
LED - Light Emitting Diode
LOFF - Operating type: Local off
L-ON - Operating type: Local operation
MASt - Master unit operating type (master/slave assembly)
RCPM - Reciprocating Compressor Protection Module
rEM - Operating type: by remote control contacts
SCT - Saturated disCharge Temperature
SIO - Standard Input/Output - internal communication bus
linking the basic board to the slave boards
SST - Saturated Suction Temperature
The operating mode must be chosen with the Operating Type
selection button described in section 4.2.1.
When the PRO-DIALOG Plus system operates autonomously
(Local or Remote mode) it retains all of its own control capabilities but does not offer any of the features of the CCN network.
5
Page 6
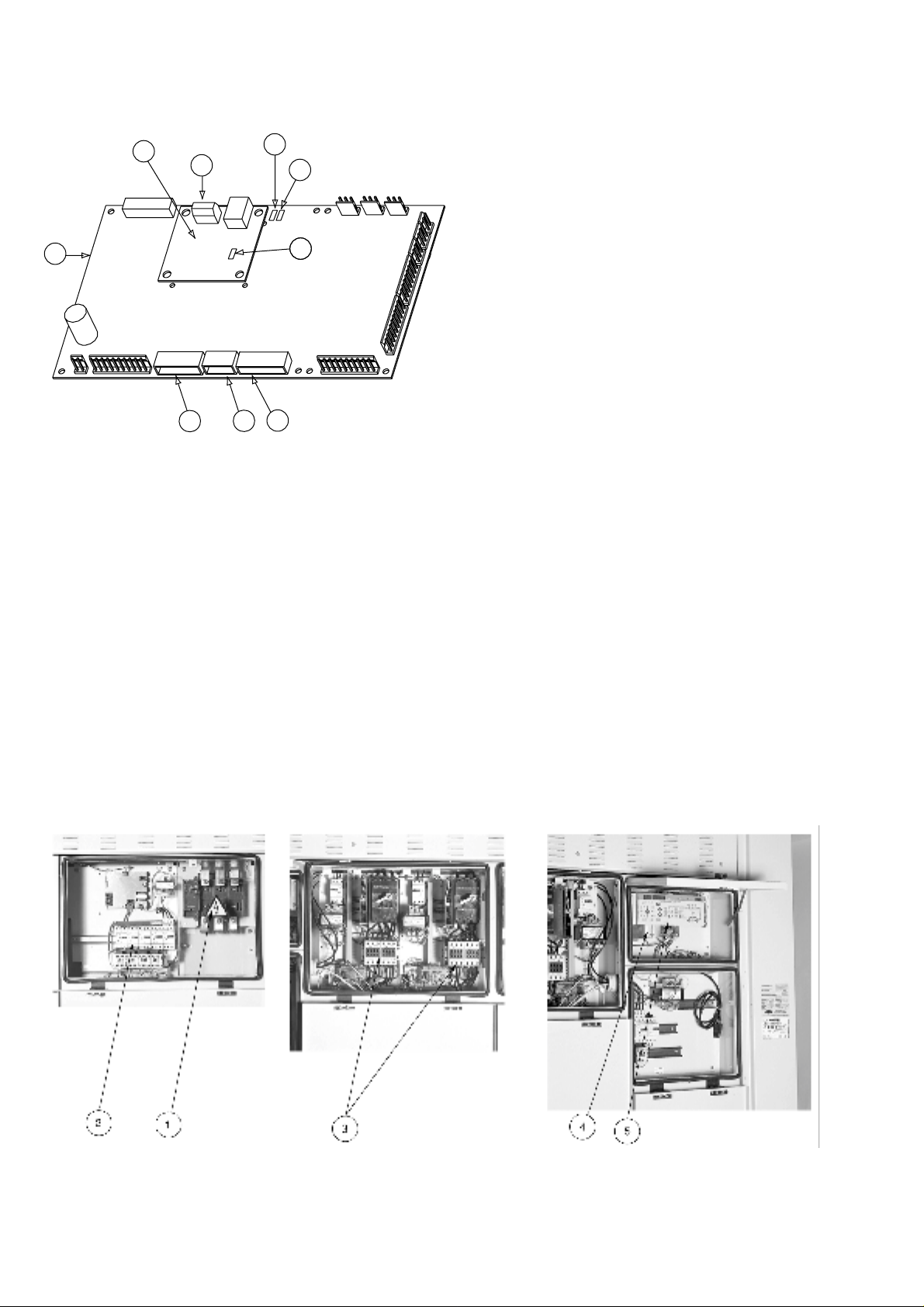
3 - HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
3.1 - General
Control board
9
8
Legend
1 CCN connector
2 Red LED, status of the board
3 Green LED, communication bus SIO
4 Orange LED, communication bus CCN
5 Remote master board customer control connection contacts
6 Remote master board customer control connection signal
7 Remote master board customer report connection contacts
8 Master PD4 basic board
9 CCN/clock board
1
7
2
3
4
5
6
The control system consists of at least a PD4 basic board, a
user interface, a PD4-EXV slave board and, depending on the
application, one or more RCPM compressor boards, 4xDO
boards or 4xAI-2xAO boards and an NRCP-BASE slave board.
Slave boards are connected to the basic board via an internal
communication bus (SIO).
The CCN/clock board is connected and screwed to the master
basic board. It permits communication with elements of the
Carrier Comfort Network via the CCN bus.
The various control components are arranged in modules
within the control cabinet:
• Control module: This comprises the basic board, the
user interface, the EXV control board and option boards,
as well as the customer’s terminal block.
• Start-up module: This consists of the start-up boards,
compressor protection boards, as well as the compressor
circuit breakers and contactors.
• Fan module (air-cooled unit): Consists of one or two
4xDO boards together with the fan circuit breakers and
contactors.
3.2 - Electronic boards
3.2.1 - The basic board
It can be used alone or in conjunction with slave boards. It
holds the program that controls the machine. It continuously
manages the information coming in from the various pressure
and temperature sensors, and communicates with the slave
boards via the SIO bus. It can also communicate with elements
of the Carrier Comfort Network via the CCN bus.
NOTE: After a power cut the unit restarts in the same
operating mode as before the power cut.
3.2.2 - Slave boards
• Compressor board RCPM: This board is used to control
a compressor. Up to eight RCPM boards can be connected
to the basic board.
• 4xDO board: This board can be used to control fan stages.
• PD4-EXV board: This board can control two EXV valves
and two suction temperature sensors.
• 4xAI-2xAO board: This optional board can be used to
read sensors (oil pressure), or to control variable speed
fans (air-cooled units) or the condenser valve (water-cooled
units).
• NRCP-BASE board: This optional board is used to control
the inputs and outputs of the heat reclaim option.
Legend
1 Power supply disconnect switch
2 Fan start-up module
Control box
3 Compressor start-up module
4 Control system
5 User interface
6
Page 7

3.2.3 - The user interface
The user interface is in two parts:
• The main interface: This gives access to all of the
control parameters for the unit. It consists of a 2-digit
primary display block and a secondary 4-digit display
block with 10 LEDs and 5 buttons.
• The summary interface: This gives quick access to just
the main control parameters for the unit. It comprises 12
buttons and 16 LEDs, and includes a schematic diagram
of the unit.
3.2.4 - Connections between boards
The basic board and slave boards communicate with each other
over an internal three-wire RS485 communication bus (SIO
bus). These three wires link all the boards in parallel.
Terminals 1, 2 and 3 on connector J9 (A, B, C are connected
internally) of the basic board are connected to terminals 1, 2
and 3 of terminal J9 of the NRCP-BASE board, terminal J4 of
the PD4-EXV board respectively, except for terminal J3 of the
4xDO and 4xAI-2xAO boards where terminals 2 and 3 are
reversed.
Incorrect connection will render the system inoperative.
3.2.5 - Slave board addresses
Every slave board (except the NRCP-BASE board) has a
unique address controlled by 8 DIP switches. The switch is
disabled when it is in the open position (OPEN or OFF). On
RCPM boards SIO address switch is labelled 'ADDR'.
3.2.7 - Light emitting diodes on boards
All boards continuously check and indicate the proper
operation of their electronic circuits. A light emitting diode
(LED) lights on each board when it is operating properly.
Red LED
• The MAIN red LED flashes at about 2 second intervals to
show that the module is working properly.
• Irregular flashing or no flashing is a sign of a defective
board.
Green LED
(item SIO on the board)
• This LED flashes continuously to show that the board is
communicating correctly over its internal bus.
• If this LED is not flashing, check the wiring of the SIO
bus and the address of the board (slave board only). If the
basic board is not linked to any slave boards, this LED
should not flash.
• If all slave boards indicate a communication fault, check
the SIO bus connection on the basic board. If this
connection is correct and the fault persists, replace the
basic board.
Orange LED - CCN/clock board
• This LED flashes to show that the basic board is communicating via the CCN bus.
NOTE: Any incorrect address will prevent the unit from
starting. Turn off the power before amending the address of
any auxiliary board.
Board addresses
Board Address switch
87654321
PD4-EXV 0 0 011101
4xDO Fan board # 1 0 0 100111
4xDO Fan board # 2 0 0 101011
4xAI-2xAO board # 1 0 0 101111
4xAI-2xAO board # 2 0 1 111000
RCPM # 1 (compressor A1) 1 1 010100
RCPM # 2 (compressor A2) 1 1 011111
RCPM # 2 (compressor A3) 1 1 011001
RCPM # 2 (compressor A4) 1 1 100100
RCPM # 3 (compressor B1) 1 1 101010
RCPM # 4 (compressor B2) 1 1 110101
RCPM # 4 (compressor B3) 1 1 101111
RCPM # 4 (compressor B4) 1 1 110010
3.2.6 - Power supply to the boards
All boards are supplied by a 24 V source, ref erred to earth. In the
event of a power supply interrupt, the unit restarts automatically
without the need for an external command. However, any faults
active when the supply is interrupted are saved and may in
certain cases prevent a circuit or unit from restarting.
NOTE: When connecting the power supply for the boards,
maintain polarity.
3.3 - The controls
3.3.1 - Electronic expansion valve (EXV)
The EXV is used to adjust the refrigerant flow to changes in
the operating conditions of the machine. For this purpose, a
series of calibrated orifices are machined into the wall of the
refrigerant inlet port. As the refrigerant passes through these
orifices, it expands and becomes a bi-phase mixture (liquid and
gas).
T o adjust the refriger ant flow to changes in operating conditions,
a piston moves constantly up or down to vary the cross-section
of the refrigerant path. This piston is driven by an electronically
controlled linear stepper motor. The high degree of accuracy
with which the piston is positioned ensures that the flow of
refrigerant is precisely controlled.
NOTE: The external connector of the EXV must be cleaned
and coated with silicone grease (Part No. 397 EE) to keep out
condensation and prevent corrosion.
3.3.2 - The head pressure controls
The controller can deal with the following:
• in the case of air-cooled units, for each circuit, fan stages
together with, if necessary, a variable speed fan (controlled
by an optional 4xAI-2xAO board)
• in the case of water-cooled units, a water valve. This valve
is controlled by an optional 4xAI-2xAO board which can
deliver a 0-10 V d.c. or 4-20 mA signal, depending on the
configuration.
7
Page 8

3.3.3 - The evaporator pumps
The controller can regulate one or two evaporator pumps, with
automatic changeover between the two pumps.
3.3.4 - The condenser pump
In appropriate cases the controller can regulate a condenser
pump (for water-cooled units or air-cooled units with heat
reclaim option). This control does not require an additional
board.
3.3.5 - Pressure sensors
These are used to measure the following pressures in each
circuit:
• Discharge gas pressure (high pressure type)
• Suction pressure (low pressure type)
• Oil pressure (option)
These electronic sensors deliver 0 to 5 V d.c. to the main board
or to a 4xAI-2xAO slave board. Two sensor versions are used;
one is calibrated for high pressure and the other for low
pressure and oil pressure.
Discharge pressure sensors
These are on the high pressure side of the lead compressor in
each circuit. They replace the usual discharge gas pressure
gauges and can be used to control head pressure or by the high
pressure load shedding option.
Oil pressure sensors
If installed, these sensors are used to measure the compressor
oil pressure on the oil pressure discharge side. The suction
pressure is subtracted from the oil pressure value to arrive at
the differential oil pressure.
Suction pressure sensors
They are located in the low-pressure side of the unit on the lead
compressor of each circuit. The suction pressure sensor reading
is used to control the electronic expansion devices EXV. They
permit replacement of the low-pressure switches, low-pressure
gauges and possibly of the oil pressure safety switch.
3.3.6 - Thermistors
These all have similar characteristics.
Evaporator entering water temperature sensor
The evaporator entering water temperature sensor is installed in
the evaporator wall in the free space at the side of the tube
bundle.
Evaporator leaving water temperature sensor
The evaporator leaving water temperature sensor is installed in
evaporator leaving water piping: The sensor bulb is directly
immersed in the water.
Compressor suction sensor
This is located in the lead compressor of each circuit in the
suction gas line situated between the motor and the cylinders
above the oil pump.
Condenser entering and leaving water temperature sensors
These are used to control the heating capacity on heat pumps.
In cooling only units they have no control function. They are
installed in the common condenser entering and leaving line.
Heat reclaim condenser entering/leaving water temperatures
These sensors measure the entering and leaving water temperatures of heat reclaim condensers and are used on air-cooled
units equipped with the heat reclaim option. If not, they may be
fitted as options. In this case they only have informative
character.
Temperature setpoint reset sensor
This is an optional 0-10 V sensor which can be installed
remotely from the unit. It is used to reset the cooling and
heating setpoint on the unit as a function of either the outdoor
air temperature or ambient room temperature. The sensor is not
supplied by Carrier, and must be configured by the User Menu.
Outdoor temperature sensor
Mounted on the control box. It is used for start-up, setpoint
temperature reset and frost protection control.
Master/slave assembly temperature control
The optional water temperature sensor can be used for master/
slave assembly control.
8
Page 9
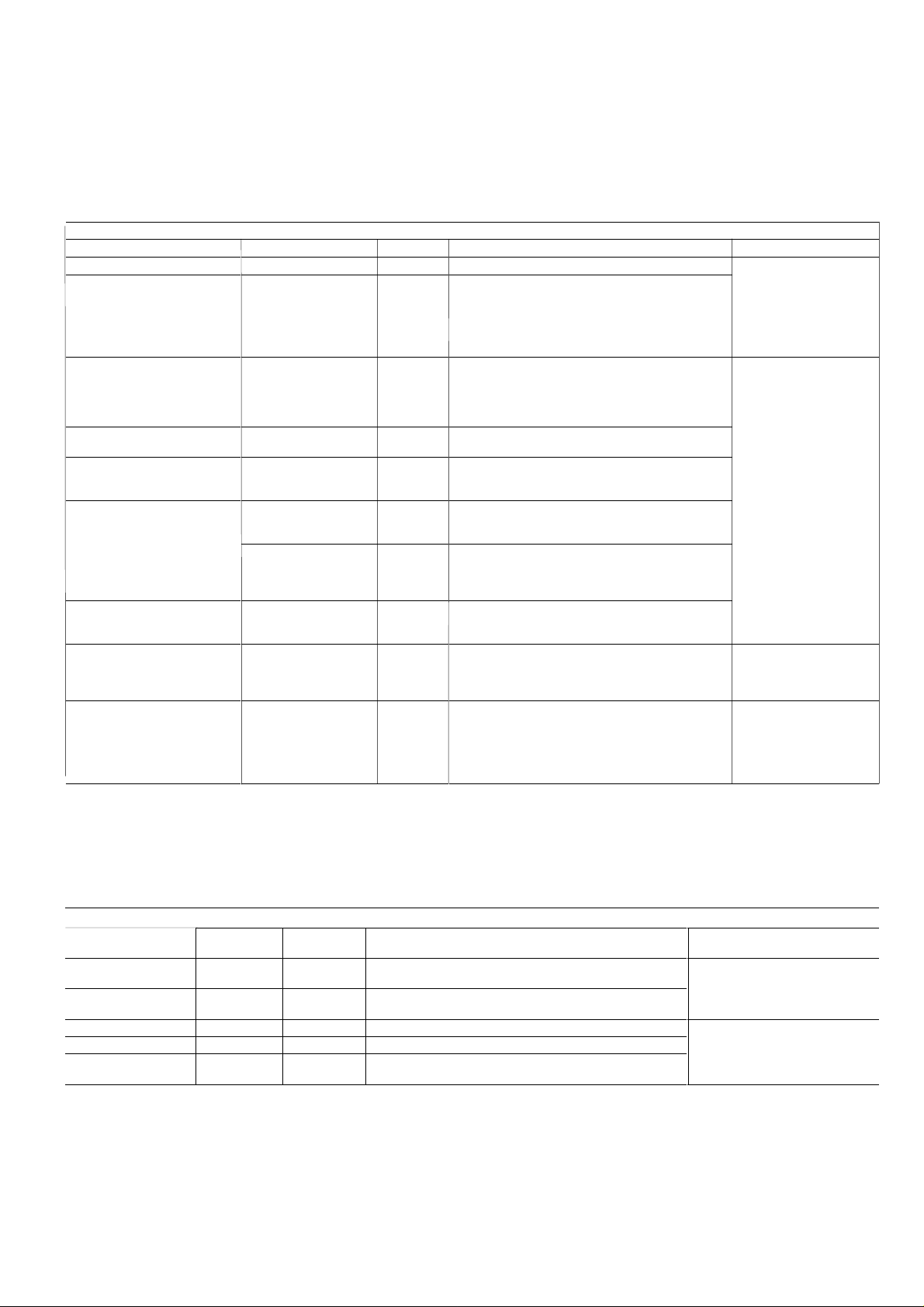
3.4 - User connections
The connections below are available at the customer’s terminal
block. Some of them can only be used in special operating
modes. For further details see the sections that describe the
functions (section 5) and the configurations (section 4.2.1).
NOTE: The bridge between terminals 32, 63 and 65 on the
customer’s terminal block must not be removed.
CONNECTION BLOCK
DESCRIPTION
Alarm relay output, circuit A
Alarm relay output, circuit B
User safety loop and chilled water
pump interlock
Remote start/stop
Remote cooling setpoint selection
Remote heating/cooling control
or
remote heat reclaim control
Demand limit command
0-10 V d.c. setpoint reset or
demand limit entry
Connection to CCN
CONNECTOR/CHANNEL
J3 / CH24
J3 / CH25
J4 / CH15a
J4 / CH11
J4 / CH12
J4 / CH13
J4 / CH13
J4 / CH14
J8 / CH10
J12
TERMINAL
30A - 31A
30B - 31B
34 - 35
32 - 33
65 - 66
63 - 64
63 - 64
73 - 74
71 - 72
1 - 2 - 3
DESCRIPTION
Indicates alarms in circuit A
Indicates alarms in circuit B
This contact is mounted in series with the water flow
control contact. It can be used for any user safety loop
that requires that the unit is shut down, if it is open. The
chilled water pump operation auxiliary contact is
connected between these two terminals.
The remote start/stop command is only used if the unit is
under remote operation control (rEM). See section 4.2.1.
The remote cooling setpoint selection command is only
used if the unit is under remote operation control (rEM).
See section 4.2.1.
The remote heating/cooling control command is only used
if the unit is under remote operation control (rEM). See
section 4.2.1.
The command allows selection of the second condensing
setpoint or of the heat reclaim mode. It is only used if the
unit is under remote operation control (rEM). See section
4.2.1.
This contact permits activating the unit demand limit
function. See section 5.8. This contact is active, whate v er
the operating type.
This 0-10 V d.c. input is used for setpoint reset or unit
demand limit. It is active, whatev er the unit operating type .
This 0-10 V signal can be supplied by a user command or
a 0-10 V temperature sensor.
A RS-485 bus is used for connection to the CCN.
The CCN connector is located on the CCN/clock board
(inserted on the PD4 Basic Board)
- Pin 1: signal +
- Pin 2: ground
- Pin 3: signal -
REMARKS
Volt-free contacts 24 V a.c. 48
V d.c. max, 20 V a.c. or V
d.c., 3 A max, 80 mA min,
external power supply .
Connector: 6 pin WA GO
231-306/026000 pitch 5.08.
24 V a.c., 20 mA
Connector: 10 pin WAGO
734-110, pitch 3.5
Connector: 2 pin WAGO 231302/026000 pitch 5.08
Use of a shielded cable (max.
length: 1000 m)
Shielding: braiding on 95% 100% of the cable surface.
Shielding connection at the
two cable ends.
AVAILABLE TERMINALS
Description
Condenser water flow
switch input
Evaporator 1 and 2 pump
operation input
Evaporator 1 control
Evaporator 2 control
Condenser pump control
Legend
* Associated functions, if selected: automatic changeover, pump 1 and 2; manual or CCN selection; periodical; by default.
Connector/
channel
J5/CH17
J5/CH18
J2/CH19
J2/CH20
J2/CH21
Terminal Description
This contact is used to detect lack of condenser water flow and
shuts down the unit.
This contact is used to detect an evaporator pump operation
fault and switches over to the other evaporator pump*.
This contact permits control of evaporator 1 pump by the unit*.
This contact permits control of evaporator 2 pump by the unit*.
This contact permits control of condenser pump by the unit*.
Remarks
24 V a.c - 20mA
24 V a.c. internal supply.
Max. consumption
- each output: 20 VA/10W
- for all 3: 40 VA/20 W if all are used
9
Page 10
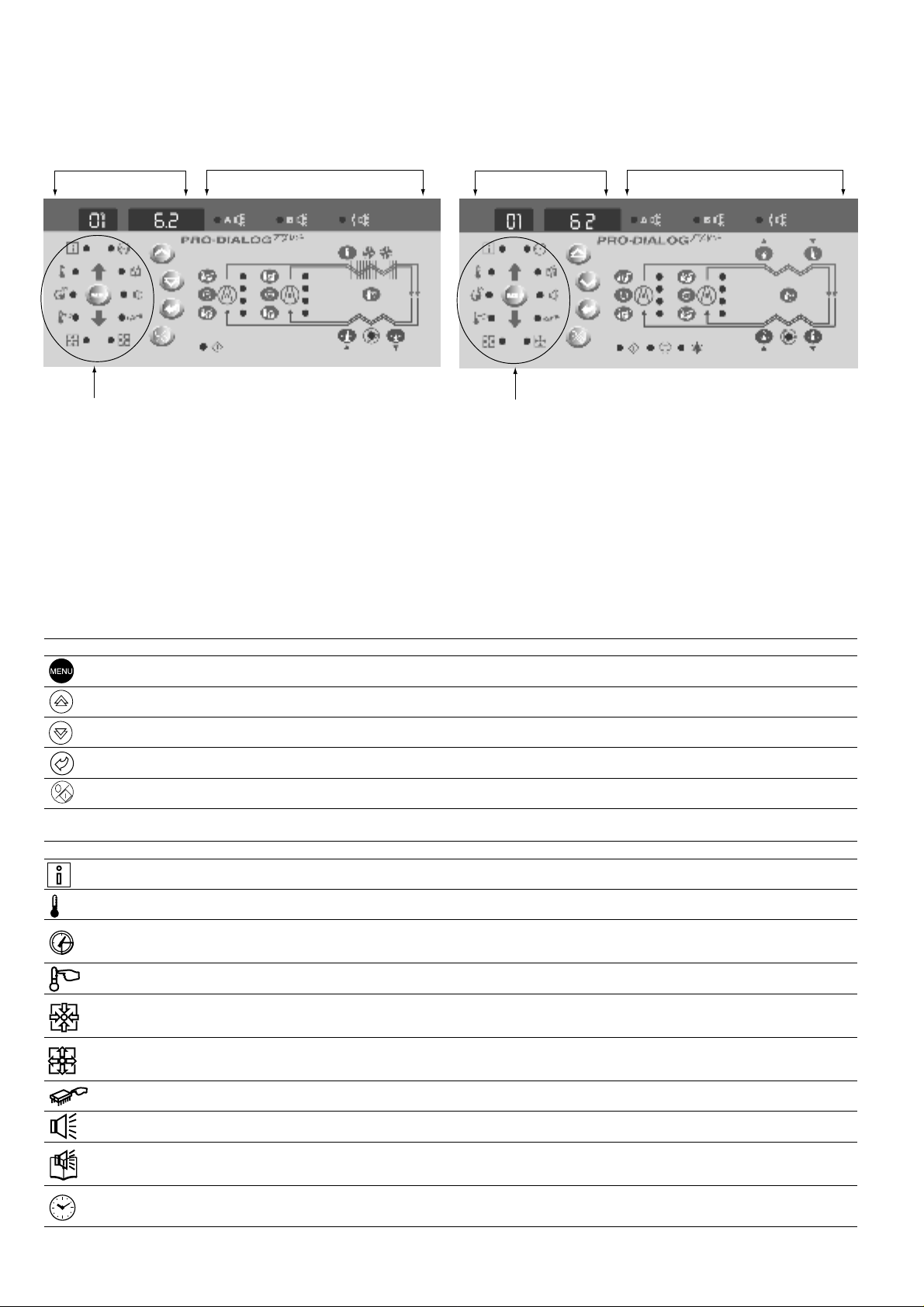
4 - SETTING UP PRO-DIALOG PLUS CONTROL
4.1 - Local interface general features
MAIN INTERFACE SUMMARY INTERFACE
DUAL-CIRCUIT AIR-COOLED
MENU BLOCK
CHILLER INTERFACE
The local interface enables a number of operating parameters to
be displayed and modified.
The interface consists of two distinct parts: the main interface
(left hand section) and the summary interface (right hand
section).
MAIN INTERFACE SUMMARY INTERFACE
DUAL-CIRCUIT WATER-COOLED
MENU BLOCK
CHILLER INTERFACE
Main interface
It gives access to all PRO-DIALOG PLUS data and operating
functions. It consists of:
• A two-digit display showing the number of the item
selected.
• A four-digit display showing the contents of the item
selected.
• LEDs and buttons for unit start/stop, menu selection,
menu item selection and value adjustment.
MAIN INTERFACE
BUTTON NAME DESCRIPTION
Menu Permits the selection of a main menu. Each main menu is represented by an icon. The icon is lit if active.
Up arrow Permits scrolling through the menu items (in the two-digit display). If the modification mode is active this button authorises
Down arrow Permits scrolling through the menu items (in the two-digit display). If the modification mode is active this button authorises
Enter Gives access to the modification mode, validates a modification or displays expanded item description.
Start/stop Authorises start or stop of the chiller in local mode or modification of its operating type.
MAIN INTERFACE MENU LEDS
LED NAME DESCRIPTION
INFORMA TIONS men u Displays the general operating parameters for the unit.
TEMPERATURES menu Displays the unit operating temperatures.
kPa
PRESSURES menu Displays the unit operating pressures.
SETPOINTS menu Displays the unit setpoints and enables them to be modified.
INPUTS menu Displays the status of the unit digital and analogue inputs.
OUTPUTS/TESTS menu Displays the status of the unit outputs and enables them to be tested.
increase of the value of any parameter.
decrease of the value of any parameter.
10
CONFIGURATIONS menu Displays the unit configuration and enables it to be modified.
ALARMS menu Displays active alarms.
ALARMS HISTORY menu Displays the history of the alarms.
OPERATING LOG menu Displays the operating times and number of starts for the unit and the compressors.
Page 11

The summary interface (right hand section) includes a mimic
diagram of the unit, together with push-buttons and LEDs. It
gives quick access to the main operating parameters of the unit.
SUMMARY INTERFACE LEDS
LED INDICATION WHEN LIT
Green LED:
The unit is authorised to start or is already running
Red LED:
- Lit: circuit A or unit shut down by alarm
- Flashing: circuit A or unit running with alarm present
Red LED:
- Lit: circuit B or unit shut down by alarm
- Flashing: circuit B or unit running with alarm present
Red LED:
Water flow switch default or user safety lock open.
Green LED:
The evaporator pump is running.
Yellow LEDs:
From top to bottom - start/stop status of compressors A1, A2, A3 and A4
or B1, B2, B3 and B4. Flashing LED indicates that the circuit is in the
protection or defrost mode (A or B).
Green LED:
The unit operates in heating mode.
Green LED:
The unit operates in cooling mode.
The following operating types can be selected using the
Start/Stop button:
OPERATING TYPES
4-DIGIT DISPLA Y DESCRIPTION
LOFF Local Off. The unit is halted in local mode.
L-On Local On. The unit is in local control mode and is authorised
to start.
L-Sc* Local On - timer control. The unit is in local control mode. It
is authorised to start if the period is occupied. If the timer
program for unit operation is unoccupied, the unit remains
shut down until the period next becomes occupied.
CCN* CCN. The unit is controlled by CCN commands.
rEM* Remote. The unit is controlled by remote control contacts.
MAST* Master Unit. The unit runs as a master in a two unit lead/lag
arrangement. This is displayed if the unit is configured for
master/slave control. See section 5.19.
Legend
* Displayed if the configuration requires it.
Section 5.1 gives a more detailed description of the commands to start/stop
the unit, analysed by operating type.
4.2.2 - Stopping the unit in local mode
The unit can be stopped in local mode at any time by pressing
the Start/Stop button.
SUMMARY INTERF A CE PUSH BUTTONS
BUTTON DISPLAY
Blue button: evaporator leaving or entering water temperature in °C
Gray button: outdoor air temperature in °C
Control point (setpoint + reset) in °C
kPa
Press 1: circuit A/B discharge pressure in kPa
Press 2: circuit A/B saturated condensing temperature in °C
kPa
Press 1: circuit A/B suction pressure in kPa
Press 2: circuit A/B saturated suction temperature in °C
Press 1: compressor A1/B1 operating hours in h/10 or h/100
Press 2: compressor A2/B2 operating hours in h/10 or h/100
4.2 - Unit start/stop control
4.2.1 - Description
The unit start/stop can be controlled by one of the following
methods:
• Locally on the actual unit (Local control type)
• By remote control with the aid of user contacts (remote
control type)
• By CCN control with the aid of the CCN (CCN control
type)
The main interface includes a Start/Stop button which can be
used to stop or start the unit in the local operating type or to
select the remote or CCN operating type.
The available operating types are described in the following
table.
TO STOP THE UNIT
BUTTON ACTION 2-DIGIT DISPLAY 4-DIGIT DISPLAY
Press the Start/Stop C LOFF
button for less than
4 seconds (one short
press is enough).
If the button is t LOFF
released, the unit stops
without the need for
further action.
4.2.3 - Starting unit and selecting an operating type
The unit can be started in local mode, or unit operating type
can be changed at any time using the Start/Stop button. In the
example that follows, the unit is stopped (LOFF) and the user
wants to start the unit in local mode.
CHANGING THE OPERATING TYPE
BUTTON ACTION
Continually press the operating type selection
button for more than 4 seconds.
Hold down the Start/Stop button.
The available operating types are displayed
one by one until the button is released.
Release the Start/Stop button if the operating
type you want is displayed (in this example LOn). "C" flashes in the 2-digit display to show
that the controller is awaiting confirmation.
Press the Enter button to confirm the
operating type selected (in this example: LOn). "t" is displayed in the 2-digit display to
indicate the operating type selected. If the
Enter button is not pressed soon enough, the
controller will cancel the change and continue
to use the previous operating type.
2-DIGIT 4-DIGIT
DISPLAY DISPLAY
C LOFF
L-On
L-Sc
rEM
L-On
t L-On
11
Page 12

4.3 - Menus
4.3.1 - Selecting a menu
The MENU button authorises you to select a menu from the 10
main menus that are available. Each time you press this button
one of the 10 LEDs lights up in turn alongside each of the
icons representing a main menu. The active menu is the one
against which the LED is lit. If a menu is empty then its LED
is not lit. To scroll quickly through the menus, hold the MENU
button down.
4.3.2 - Selecting a menu item
The up and down Arrow buttons let you scroll through the
menu items. Menu item numbers are displayed in the two-digit
display. The item number increases or decreases every time
you press the up or down Arrow button. The menu items that are
not in use or incompatible with the configuration are not
displayed. The value or status associated with the active item
is displayed in the four-digit display. To scroll quickly through
the items, hold the up or down Arrow button down.
The following example shows how to access item 3 in the
Pressures menu.
SELECTING A MENU ITEM
OPERA TION PRESS MENU LED ITEM NUMBER
Press the MENU button until the
LED marked PRESSURE lights. 0
Press one of the Arrow buttons 1
until the two-digit display shows 3
(item number 3).
BUTTON 2-DIGIT
kPa
kPa
DISPLAY
0
2
NOTE: The access to a sub-menu may require entering a
password. This is automatically requested. See section 4.5.7.2.
The example below shows how to modify the value of item 1
in the Setpoint menu.
MODIFYING THE V ALUE OF A PARAMETER
OPERA TION PRESS MENU LED ITEM ITEM
button NUMBER NUMBER
2-DIGIT 4-DIGIT
DISPLAY DISPLAY
Hold on the MENU button until 0
the LED for SETPOINT lights.
0
Press one of the Arrow buttons 1
until the two-digit display shows 1
item number 1- cooling setpoint 2).
The value for setpoint 2 is
displayed in the four-digit display 1 6.0
(6.0°C in this example).
Press the Enter button for more
than 2 seconds to enable the
value associated with item 1 to be 1 6.0
modified. The Setpoint men u LED
flashes indicating that modification
mode is active.
Keep pressing the Down Arrow 1 5.9
button until the value 5.7 is
displayed in the four-digit displa y.
The Setpoint menu LED keeps
flashing. 1 5.8
1 5.7
Press the Enter button again to
validate the change. The new
setpoint is 5.7°C. The Setpoint 1 5.7
menu LED stops flashing, indicating that modification mode no
longer applies.
3
4.3.3 - Modifying the value of a parameter/access to a submenu
Press the Enter button for more than 2 seconds to enter the
modification mode or to select a sub-menu. This lets you correct
the value of an item or select a sub-menu with the aid of the up
and down Arrow buttons (if you are authorised to overwrite the
item concerned). When modification mode is activated, the
LED for the main menu to which the item belongs flashes in
menu block. Once the required value is obtained, press the
Enter button again to validate the change or to access the submenu. The LED for the menu to which the item belongs then
stops flashing, indicating that modification mode no longer
applies.
In modification mode, the value to be modified increases or
decreases in steps of 0.1 every time you press the Arrow
buttons. Holding one of these buttons down increases the rate
of increase or decrease.
4.3.4 - Expand display
Pressing the Enter button causes a 23 character text expansion
to be scrolled across the four-digit display. All user menus
provide an expansion of the current displayed parameters. If
the expansion is complete the four-digit display reverts to item
value. This function can be inhibited through the User
Configuration menu.
12
Page 13

4.4 - General menu structure
MAINTENANCE
[MAintEnAnCE]
RUNTIME
ALARMS HISTORY
SUB-MENUS
RUNTIME 2
[RuntiME 2]
RUNTIME 1
[RuntiME 1]
[MAStEr SLAvE]
MASTER/SLAVE
FACTORY
[FACtorY]
SERVICE 3
[SErviCE 3]
SERVICE
[SErviCE]
SERVICE 2
[SErviCE 2]
SERVICE 1
[SErviCE 1]
[brodCASt]
BROADCAST
SUB-SUB-MENUS
NOTE: The items in brackets show what is
displayed on the user interface.
MAIN MENUS
USER
[USEr]
[dAtE]
HOUR + DATE
[HoLidAy]
HOLIDAYS
SCHEDULE 2
[SCHEduLE 2]
SCHEDULE 1
[SCHEduLE 1]
USER 2
[USEr 2]
USER 1
[USEr 1]
[HoLidAy 1]
HOLIDAYS 1
[PEriod 1]
PERIOD 1
[PEriod 1]
PERIOD 1
[HoLidAy 3]
[HoLidAy 2]
HOLIDAYS 3
HOLIDAYS 2
[PEriod 3]
[PEriod 2]
PERIOD 3
PERIOD 2
[PEriod 3]
[PEriod 2]
PERIOD 3
PERIOD 2
SUB-SUB-SUB-MENUS
[HoLidAy 4]
HOLIDAYS 4
[PEriod 4]
PERIOD 4
[PEriod 4]
PERIOD 4
[HoLidAy 5]
HOLIDAYS 5
[PEriod 5]
PERIOD 5
[PEriod 5]
PERIOD 5
[HoLidAy 7]
HOLIDAYS 6
[PEriod 6]
PERIOD 6
[PEriod 6]
PERIOD 6
[HoLidAy 7]
HOLIDAYS 7
[PEriod 7]
PERIOD 7
[PEriod 7]
PERIOD 7
[HoLidAy 8]
HOLIDAYS 8
[PEriod 8]
PERIOD 8
[PEriod 8]
PERIOD 8
- - -
- - -
- - -
[HoLidAy15]
HOLIDAYS 15
[HoLidAy16]
HOLIDAYS 16
STATUS TEMPERATURES PRESSURES SETPOINTS INPUTS OUTPUTS CONFIGURATION ALARMS
13
Page 14

4.5 - Menu tree structure
RUNTIMES
SUB-MENU:
Runtimes 1
ALARMS HIST
Historic alarm code 1
ALARMS
Number of active alarms/
resets
SUB-MENU:
Runtimes 1
SUB-MENU:
Historic alarm code 2
Historic alarm code 3
Active alarm code 1**
Active alarm code 2**
Maintenance--
Historic alarm code 4
Active alarm code 3**
Historic alarm code 5
Active alarm code 4**
-
-
Historic alarm code 6
Historic alarm code 7
Active alarm code 5**--
-
Historic alarm code 8
-
Historic alarm code 9
-
-
-
Historic alarm code 10--
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
NOTE: The items in brackets show what is displayed on the
user interface.
MENU
CONFIG
SUB-MENU:
User Configuration [USEr]
SUB-MENU:
Service Configuration
[SErviCE]
OUTPUTS
Compressor status,
circuit A
Compressor status,
circuit B
INPUTS
Contact 1: remote on/off
Contact 2: remote
setpoint
SETPOINTS
Cooling setpoint 1
Cooling setpoint 2
PRESSURES
Discharge pressure,
circuit A
Suction pressure, circuit
A
SUB-MENU:
Factory Configuration
[FACtorY]--
Capacity reduction
status, circuits A & B
Fan contactor status,
circuit A
Fan contactor status,
Contact 3: remote
heating/cooling
Contact 4: remote heat
reclaim operation
Demand limit selection
Heating setpoint
Condensing setpoint
Heat reclaim setpoint
Oil differential pressure,
compressor A1
Discharge pressure,
circuit B
Suction pressure,
-
-
circuit B
Alarm circuit status,
circuits A & B
EXV position, circuit A
Water flow & customer
interlock control
Evaporator pump fault
detection
Demand limit setpoint
in %
Cooling mode ramp
circuit B
Oil differential pressure,
compressor B1
Oil differential pressure,
compressor A2
-
-
-
EXV position, circuit B
Variable speed fan,
circuit A or cond. water
valve position in %
Variable speed fan,
circuit B or cond. water
Water flow control,
condenser
Control box thermostat
External 0-10 V d.c.
signal--
Heating mode ramp
Cooling - threshold for
zero reset
Cooling - threshold for
max. reset
Oil differential pressure,
compressor A3
Oil differential pressure,
compressor A4
Oil differential pressure,
compressor B2
-
-
valve position in %
Water pump 1 status
Water pump 2 status
Cooling - max. reset
value
Heating - threshold for
zero reset
Oil differential pressure,
compressor B3
Oil differential pressure,
compressor B4
-
-
-
-
Condenser pump status
Evap. heater & heat
reclaim cond. status
Cond. water valve posi-
tion, heat reclaim mode
Solenoid status, heat
-
-
-
-
Heating - threshold for
max. reset
Heating - max. reset
value--
Heat reclaim pressure,
circuit A
Heat reclaim pressure,
circuit B--
-
-
reclaim function
User test interface
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
14
TEMP
STATUS
ITEM
Evaporator water
Default display
0
entering temp.
Evaporator water
leaving temp.
Active modes
1
Condenser water
entering temperature
Condenser water
leaving temperature
Chiller occupied/
unoccupied
Minutes left before
starting
2
3
Heat reclaim water
entering temperature
Heat reclaim water
leaving temperature
Saturated discharge
Cooling/heating
selection
Heat reclaim
selection
Unit capacity in %
4
5
6
temperature, circuit A
Saturated suction
temperature, circuit A
Suction temperature,
Capacity circuit A
in %
Capacity circuit B
7
8
compressor A1
Superheat, circuit A
in %
Present demand
limit in %
9
Saturated discharge
temperature, circuit B
Saturated suction
temperature, circuit B
Suction temperature
compressor B1
Present lag limit in
%
Setpoint in local
control
Setpoint occupied/
unoccupied mode
10
11
12
Superheat, circuit B
Outdoor temperature
Water loop temp.,
master/slave assembly
Active setpoint
Control point
Controlled water
temperature
13
14
15
-
-
-
Condensing point
Heat reclaim
indicator, circuit A
Heat reclaim
16
17
18
indicator, circuit B
Legend
** Displayed if the alarm exists
- Not in use
Page 15

4.5.1 - Description of the Information menu
INFORMATION MENU [3]
ITEM FORMAT UNITS
0
±nn.n °C
LOFF -
L-On L-Sc CCn rEM MASt -
OFF rEADY dELAY -
StOPPing running triPout OvErridE -
OCCUPIEd UNOCCUPIEd -
COOL HEAT rECLAIM -
ALArM ALErt -
MAStEr SLAvE -
1 [1] nn -
2 [2] -
occu
unoc
Forc
3 nn.n minutes
4 [2] -
HEAt COOL -
5 [2]
YES -
NO 6 Nnn %
7 nnn %
8 [2] nnn %
9 [2] nnn
Forc %
10 nnn %
11 [2] -
SP-1
SP-2
AUtO
12 [2] -
occu
unoc
Forc
13 ±nn.n °C
14 ±nn.n
Forc °C
15 ±nn.n °C
16 ±nn.n °C
Forc °C
17 n
18 n
DESCRIPTION
Automatic display mode. It cycles through the following displays:
1: Controlled water temperature: temperature of the water that the unit tries to maintain at the control point.
2: Unit operating type
Local Off
Local On
Local On - based on unit clock.
CCN Control.
Remote Control
Master unit
3: Unit status
Off: Unit is stopped and not authorised to start.
Ready: Unit is authorised to start
Delay: Unit is in delay at start-up. This delay is active after the unit has been switched on. The delay can be
configured in the User Configuration menu.
Stopping: Unit is currently stopping.
On: Unit is running or authorised to start.
Fault shutdown.
Limit: The operating conditions do not allow total unit operation.
4. Unit occupied/unoccupied status
Occupied: Unit in occupied mode
Unoccupied: Unit in unoccupied mode
5. Heating/cooling operating mode
Cooling: Unit operates in cooling mode
Heating: Unit operates in heating mode
Cooling: Unit is in auto cooling and heat reclaim demand is active
6. Alarm mode
Alarm: Unit is totally stopped because of failure.
Alert: Unit is in failure but not completely stopped.
7. Master/Slave status
Master: The master/slave control is active and the unit is the master
Slave: The master/slave control is active and the unit is the slave
Active mode codes. Each active mode is displayed in turn. This Item is masked when nil. Pressing the enter button when a mode code
is displayed causes a character text expansion to be scrolled accross the four-digit display. See the description in the following table
This item indicates the current chiller occupied/unoccupied mode.
Occupied
Unoccupied
The value is displayed in turn with 'Forc' when the unit is in CCN control and if this variable if forced through CCN.
Start-up delay. This item indicates the minutes left before the unit can be started. This delay at start-up is always active after the unit
has been switched on. The delay can be configured in the User Configuration 1 menu.
Heating/cooling on selection: This item is accessible in read/write, if the unit is in local control mode. It is only displayed, if the unit is
in LOFF, L-On or L-Sc operating type. Displayed for heat pumps.
Heating mode selection
Cooling mode selection
Heat reclaim mode selection: This item is accessible in read/write, if the unit is in local control mode. It is only displayed, if the unit is
in LOFF, L-On or L-Sc operating type. Displayed for air-cooled or water-cooled units with a condenser water valve.
Heat reclaim mode selection, use of heat reclaim condensing setpoint.
Normal cooling mode selection, use of standard condensing setpoint
Total active capacity of unit.
Total active capacity of circuit A.
Total active capacity of circuit B.
Present demand limit. This is the authorised operating capacity of the unit. See section 5.8.
The value is displayed in turn with 'Forc' when the unit is in CCN control and if this variable if forced through CCN.
Present lag chiller demand limit. Displayed when the master/slave control is selected.
Setpoint select in local mode. This point is read/write accessible. Displayed only when the unit is LOFF, L-On or L-Sc operating type.
SP-1 = cooling setpoint 1
SP-2 = cooling setpoint 2
AUtO = active setpoint depends on schedule 2 (setpoint selection schedule). See section 5.7.1 & 4.5.7.6.
Setpoint occupied mode.
Occupied: cooling setpoint 1 is active
Unoccupied: cooling setpoint 2 is active
The value shall be displayed in turn with 'Forc' when the unit is in CCN control and if this variable if forced through CCN.
Active setpoint. This is the current cooling/heating setpoint: it refers to cooling/heating setpoint 1 or 2.
Control point. This is the setpoint used by the controller to adjust the temperature of the leaving or entering water (according to
configuration).
Control point = active setpoint + reset. See section 5.7
The value is displayed in turn with 'Forc' when the unit is in CCN control and if this variable if forced through CCN.
Controlled water temperature. W ater temperature that the unit tries to maintain at the control point.
Condensing setpoint. The value is displayed in turn with 'Forc' if the unit is in CCN mode and this parameter is forced by CCN.
Heat reclaim function indicator, circuit A (see heat reclaim section)
Heat reclaim function indicator, circuit B (see heat reclaim section)
Legend
1 This item is masked when nil.
2 This item is displayed in certain unit configurations only.
3 Access to this menu is read-only except for item 10 that can be forced when the unit is in Local operating type.
15
Page 16

DESCRIPTION OF OPERATING MODES (ITEM 1 OF THE INFORMATION MENU)
MODE # MODE NAME
7 Delay at start-up active
8 2nd cooling setpoint active
9 Setpoint reset active
10 Demand limit active
11 Ramp loading active
12 Low entering water temperature
protection in heating mode
13,14 Low suction temperature protection
15,16 Low discharge superheat protection
17,18 High pressure protection
19,20 Not used
21 Heat reclaim active
22 Evaporator heater active
23 Evaporator pump reversal active
24 Periodic evaporator pump start-up
25 Low night-time capacity
26 Unit under SM control
27 Master/slave link active
DESCRIPTION
The delay at start-up operates after the unit has been switched on. If the delay has not expired, the mode is active.
The delay is configured in the User1 configuration menu.
The second cooling setpoint is active. See section 5.7.1
In this mode, the unit uses the reset function to adjust the leaving or entering water temperature setpoint. See
section 5.7.2.
In this mode, the capacity at which the unit is allowed to operate is limited. See section 5.8.
Ramp loading is active. In this mode, the controlled high or low water temperature value (in °C/min) in heating mode
is limited to a preset value in order to prevent compressor overload. The ramp function must be configured (see
User1 configuration menu). The ramp values can be modified (see setpoint menu).
The unit is in heating mode and the temperature of the evaporator leaving water is lower than the lesser of the two
cooling setpoints. A capacity stage is removed. This mode only applies to heat pumps.
13 = circuit A & 14 = circuit B. Protection for evaporator suction low temperature circuit is active. In this mode, circuit
capacity is not authorised to rise if the unit is in cooling mode, and saturated suction temperature in the circuit is
lower by more than 13°C at the leaving chilled water and lower than the frost protection threshold.
15 = circuit A & 16 = circuit B.
In this mode the circuit capacity is shut down by pumpout and not allowed to restart, when the low superheat alarm
conditions are satisfied. During the shutdown/start-up sequence, mode 15 or 16 is active. See descriptions for
alarms 48 and 49.
17 = circuit A & 18 = circuit B. The circuit is in high pressure protection mode because the HP protection threshold
has been exceeded. The circuit capacity is not authorised to rise and any slave compressor can be stopped in order
to prevent a high pressure break.
Circuit A or circuit B operates in heat reclaim mode and not in standard cooling mode (pumpdown phase is
activated).
Mode active if risk of frost exists.
Two evaporator water pumps installed on the unit and pump reversal is active. See section 5.3
The unit is shut down and is started every day at 14:00 hours for 2 seconds. This function must be configured in the
User1 menu. See sections 5.3 and 4.5.7.3.
Unit capacity is limited. The period when this mode starts, as well as the limited capacity in night-time mode are
controlled in Client1 menu.
Unit is under control of a System Manager (FSM or CSM III).
Unit is connected to a secondary unit by a master slave link and either:
- the unit is configured as a master and this master is operating, or
- the unit is configured as a slave and this slave is operating.
4.5.2 - Description of the Temperatures menu
TEMPERATURES MENU [2]
ITEM FORMAT UNITS COMMENTS
0 ±nn.n °C Evaporator entering water temperature
1 ±nn.n °C Evaporator leaving water temperature
2[1] ±nn.n °C Condenser entering water temperature
3[1] ±nn.n °C Condenser leaving water temperature
4[1] ±nn.n °C Reclaim condenser entering water temperature
5[1] ±nn.n °C Reclaim condenser leaving water temperature
6 ±nn.n °C Saturated discharge temperature circuit A
7 ±nn.n °C Saturated suction temperature circuit A
8 ±nn.n °C Suction temperature compressor A1
9 ±nn.n °C Superheat circuit A
10[1] ±nn.n °C Saturated discharge temperature circuit B
11[1] ±nn.n °C Saturated suction temperature circuit B
12[1] ±nn.n °C Suction temperature compressor B1
13[1] ±nn.n °C Superheat circuit B
14[1] ±nn.n °C Outdoor temperature
15[1] ±nn.n °C Water loop temperature, master/slave assembly
Legend
1 This item is displayed in certain unit configurations only
2 Access to this menu is read-only.
4.5.3 - Description of the Pressures menu
PRESSURES MENU [2]
ITEM FORMAT UNITS COMMENTS
0 nnnn kPa Discharge pressure circuit A
1 nnnn kPa Suction pressure circuit A
2 nnnn kPa Differential oil pressure compressor A1
3 nnnn kPa Discharge pressure circuit B
4 nnnn kPa Suction pressure circuit B
5 nnnn kPa Differential oil pressure compressor B1
6[1] nnnn kPa Differential oil pressure compressor A2
7[1] nnnn kPa Differential oil pressure compressor A3
8[1] nnnn kPa Differential oil pressure compressor A4
9[1] nnnn kPa Differential oil pressure compressor B2
10[1] nnnn kPa Differential oil pressure compressor B3
11[1] nnnn kPa Differential oil pressure compressor B4
12[1] nnnn kPa Pumpdown pressure, heat reclaim, circuit A
13[1] nnnn kPa Pumpdown pressure, heat reclaim, circuit B
Legend
1 This item is displayed in certain unit configurations only.
2 Access to this menu is read-only
16
Page 17

4.5.4 - Description of the Setpoints menu
SETPOINTS MENU [2]
ITEM FORMAT UNITS RANGE
0 ±nn.n °C See table below
1 ±nn.n °C See table below
2 nnn °C See table below
3 [1] nnn °C See table below
4 [1] nnn °C See table below
5 nnn % 0 to 100
6 [1] ±nn.n °C/min 0.1 to 1.1
7 [1] ±nn.n °C/min 0.1 to 1.1
8 [1] ±nn.n [3] See table below
9 [1] ±nn.n [3] See table below
10 [1] ±nn.n °C See table below
11 [1] ±nn.n [3] See table below
12 [1] ±nn.n [3] See table below
13 [1] ±nn.n °C -16 to 16
Legend
1 This item is displayed in certain unit configurations only.
2 All points contained in this table can be modified.
* Those setpoints can be used for entering or leaving water temperature control. By default the unit controls the evaporator entering fluid temperature.
Leaving fluid temperature control requires a parameter modification in the Service Configuration menu.
** These parameters are only accessible when reset based on OAT or delta T has been selected in the User Configuration 1 menu. See section 4.5.7.3.
COMMENTS
This item lets you display and modify Cooling setpoint 1*
This item lets you display and modify Cooling setpoint 2*
This item lets you display and modify Heating setpoint*, only displayed for heat pumps.
This item lets you display and modify the condensing setpoint*. It is used by the control to regulate the fan
stages or a variable-speed fan (air-cooled units) or the condenser water valve control (water-cooled
units), if the unit is not in heat reclaim mode.
This item lets you display and modify the heat reclaim setpoint*. As item 3, this is used for condensing
setpoint control.
Capacity limit setpoint. Limitation by volt-free contact. This item is used to define the maximum capacity
that the unit is authorised to use, if the capacity limit contact activate the limit. See section 5.8.
Cooling ramp loading rate. This parameter is only accessible if the ramp function is validated in the User
Configuration 1 menu. This item refers to the maximum rate of temperature rise in °C in the water heat
exchanger in cooling mode. When capacity loading is effectively limited by the ramp, mode 11 is active.
Heating ramp loading rate. This parameter is only accessible if the ramp function is validated in the User
Configuration 1 menu. This item refers to the maximum rate of temperature drop in °C in the water heat
exchanger in heating mode. When capacity loading is effectively limited by the ramp, mode 11 is active.
Zero reset threshold, cooling mode**
Full reset threshold, cooling mode**
Full reset value, cooling mode**
Zero reset threshold, heating mode**
Full reset threshold, heating mode**
Full reset value, heating mode**
SETPOINT DESCRIPTION CONTROL FOR CONTROL FOR
Cooling Minimum setpoint
- Water 3.3°C 9.3°C
- Medium Brine -10°C-4°C
- Low Brine -20°C -14°C
Maximum setpoint
Heating Maximum setpoint MCT - 4.0 MCT - 10.0
Note:
Three setpoint reset configuration modes can be selected in the Client1 menu:
1 Reset using an external 0-10 V d.c. signal
2 Reset using Delta T
3 Reset by external temperature sensor (air-cooled units only)
The items with zero reset or maximum reset are based on these three modes.
LEAVING WATER ENTERING WATER
17
Page 18

4.5.5 - Description of the Inputs menu
INPUTS MENU [2]
ITEM FORMAT UNITS
0 OPEn/CLoS -
1 OPEn/CLoS -
2[1] OPEn/CLoS -
3[3] OPEn/CLoS -
4 OPEn/CLoS -
5 OPEn/CLoS -
6[1] OPEn/CLoS -
7[1] OPEn/CLoS 8[1] OPEn/CLoS -
9[1] nn.n -
Legend
1 This item is displayed in certain unit configurations only
2 Access to this menu is read-only
* Active in all operating types
See section 3.4
COMMENTS
Remote contact 1 status
This contact is used to start (contact closed) and stop (contact open) the chiller. It is only valid, if the unit is in the remote operating
control (rEM) mode.
Remote contact 2 status
This contact is used to select a cooling only setpoint, if the unit is in cooling mode and in the remote operating control (rEM) type.
Contact open = csp1
Contact closed = csp2
Remote contact 3 status
This contact is used to select the heating or cooling mode, only if the unit is in the remote operating control type.
Contact open: unit in cooling mode
Contact closed: unit in heating mode
Remote contact 4 status
This contact is used to select the second condensing setpoint or the heat reclaim mode (for a heat reclaim unit), only if the unit is in
the remote operating control type.
Contact open = unit uses the normal condensing setpoint and is in normal mode (no heat reclaim)
Contact closed = unit uses the heat reclaim setpoint and is in heat reclaim mode.
Remote contact 5 status*
If this contact is closed, it permits limiting the unit demand, based on the demand limit setpoint, if the demand limit method by
contact has been selected.
Water flow and customer interlock contr ol contact status*
Opening of this contact shuts the unit off or prevents its start-up and generates an alarm. It is used to control the water circulation.
Water pump operation status. If the contact opens when the evaporator pump has received a command to operate, this trips a
pump failure alarm.
Condenser water flow control. Controls the condenser water circulation.
Control box thermostat and phase reversal interlock status*. Opening of this contact shuts the unit off or prevents its start-up
and generates an alarm.
External 0-10 V d.c. signal. This signal from an external source can be used (based on the configuration) for the reset or demand
limit function of the unit.
4.5.6 - Description of the Outputs/Tests menu
4.5.6.1 - General
This menu displays the status of the controller outputs. Moreover, when the machine is fully stopped (LOFF) the outputs
can be activated for manual or automatic tests (the access to the
tests is password controlled).
4.5.6.2 - Menu description
OUTPUTS STATUS AND TESTS MENU [2] [3]
ITEM FORMAT UNITS
0
-
-
-
-
1 [1]
-
-
-
-
2 [1] tEST
-
-
3 [1] tESt
-
-
-
-
DESCRIPTION.
Compressor status
b1 = compressor A1
b2 = compressor A2
b3 = compressor A3
b4 = compressor A4
This item permits display of the compressor status in circuit A. It also permits independent testing. In test mode the direction
arrows permit successive display of 0001, 0010, 0100 and 1000, so as to in turn force authorisation of each output.
Compressor status
b1 = compressor B1
b2 = compressor B2
b3 = compressor B3
b4 = compressor B4
This item permits display of the compressor status in circuit B. It also permits independent testing. In test mode the direction
arrows permit successive display of 0001, 0010, 0100 and 1000, so as to in turn force authorisation of each output.
Capacity reduction status, circuits A & B
b1 = capacity reduction A1
b2 = capacity reduction B1
This item permits display of the capacity reduction status in circuit A. It also permits independent testing.
Fan contactor status/test, circuit A
b1 = fan contactor assembly 1
b2 = fan contactor assembly 2
b3 = fan contactor assembly 3
b4 = fan contactor assembly 4
This item permits display of the fan stages. It also permits independent testing. In test mode the direction arrows permit
successive display of 0001, 0010, 0100 and 1000, so as to in turn force authorisation of each output.
18
Page 19

OUTPUTS STATUS 2 AND TESTS MENU [2] [3] - cont.
ITEM FORMAT UNITS
4 [1] tESt -
-
-
5 tESt
-
-
6 tESt %
7 tESt %
8 [1] tESt %
9 [1] tESt %
10 On -
Stop -
tESt -
FAIL -
Good -
Forc -
11 On -
OFF -
tESt -
FAIL -
Good -
Forc -
12 On -
OFF -
tESt
FAIL
Good
Forc
-
13[1] nn
-
14[1] tESt %
15[1]
-
-
-
-
16 YES
no
tESt
Legend
1 This item is displayed in certain unit configurations only
2 A test is only possible if the units are in local off mode and if all compressors have stopped
3 The password is only valid for the test. 'Test' is displayed during the test, alternating with the item number
DESCRIPTION
Fan contactor status/test, circuit B
b1 = fan contactor assembly 1
b2 = fan contactor assembly 2
b3 = fan contactor assembly 3
b4 = fan contactor assembly 4
This item permits display of the fan stages. It also permits independent testing. In test mode the direction arrows permit
successive display of 0001, 0010, 0100 and 1000, so as to in turn force authorisation of each output.
Alarm command status/test
b1 = alarm circuit A
b2 = alarm circuit B
In test mode the direction arrows permit successive display of 01 and 10, so as to in turn force authorisation of each alarm
output.
EXV position, circuit A
In the test mode the direction arrows permit forcing the valve to its fully open position.
EXV position, circuit B
In the test mode the direction arrows permit forcing the valve to its fully open position.
Variable speed fan, circuit A or condenser water valve position in %
Variable speed fan, circuit B or condenser water valve position in %
Evaporator water pump No. 1 command status. Not displayed if unit does not control a pump.
On: the pump operates
Stop: the pump has stopped
Forc: This item is only displayed if the unit is in local off mode (LOFF). Selecting this item permits energising the pump
without delay and for an unlimited period. The pump continues to operate, until any key on the user interface is pressed: it is
then immediately switched off. If the unit is in CCN control mode, the pump status is displayed alternately with 'Forc' if its
status is forced by CCN.
During the test phase, pump supply is energised for 10 seconds only. When the test has finished, the following display
appears:
- Fail: displayed if the test has failed, because the pump is not started
- Good: displayed if the test succeeds
Evaporator water pump No. 2 command status. Not displayed if unit does not control a pump.
On: the pump operates
Stop: the pump has stopped
Forc: This item is only displayed if the unit is in local off mode (LOFF). Selecting this item permits energising the pump
without delay and for an unlimited period. The pump continues to operate, until any key on the user interface is pressed: it is
then immediately switched off. If the unit is in CCN control mode, the pump status is displayed alternately with 'Forc' if its
status is forced by CCN.
During the test phase, pump supply is energised for 10 seconds only. When the test has finished, the following display
appears:
- Fail: displayed if the test has failed, because the pump is not started
- Good: displayed if the test succeeds
Condenser pump status/test
On: the pump operates
Stop: the pump has stopped
Forc: This item is only displayed if the unit is in local off mode (LOFF). Selecting this item permits energising the pump
without delay and for an unlimited period. The pump continues to operate, until any key on the user interface is pressed: it is
then immediately switched off. If the unit is in CCN control mode, the pump status is displayed alternately with 'Forc' if its
status is forced by CCN.
During the test phase, pump supply is energised for 10 seconds only. When the test has finished, the following display
appears:
- Fail: displayed if the test has failed, because the pump is not started
- Good: displayed if the test succeeds
Evaporator heater and heat reclaim condenser status
b1 = evaporator heater
b2 = heat reclaim condenser heater
Condenser water valve position in heat reclaim mode
Solenoid valve status/test, heat reclaim function
b1 = heat reclaim coil shutoff solenoid valve, circuit A
b2 = heat reclaim coil drain solenoid valve, circuit A
b3 = heat reclaim coil shutoff solenoid valve, circuit B
b4 = heat reclaim coil drain solenoid valve, circuit B
In test mode the direction arrows permit successive display of 0001, 0010, 0100 and 1000, so as to in turn force authorisation
of each output.
Used only for local interface
Cause all diodes and blocks to light up or flash, to verify that they are operating correctly
19
Page 20

4.5.6.3 - Manual tests
This function allows the user to test the outputs individually, if
the machine is completely shut down (LOFF). To carry out a
manual test use the arrow keys to access the output to be tested
and press the Enter key (longer than 2 seconds) to activate the
modification mode. The passwo rd is automatically requested, if it
has not previously been verified . T he Outputs/Test LED on the
user interface begins to flash. Enter the desired test value and
again press Enter to start the test. 'TESt' is displayed on the 4digit display alternately with the value tested. The Outputs/Test
LED stops flashing. Press the Enter key or an arrow key to stop
the test.
4.5.7 - Description of the Configuration menu
4.5.7.1- General
This menu can be used to display and modify all configurations: Factory, Service and User. Only the User Configuration
can be modified by the end-user. The Factory, Service and
master/slave configurations are not described in this document. A configuration can only be modified if the unit is fully
stopped (LOFF).
The menus User 1 [USEr 1] and User 2 [USEr 2] are password-protected. The other menus are directly accessible, except
if item 12 of the User 1 menu (password for all configurations)
has been validated.
4.5.7.2 - Password
A password must be entered in order to access the test function
or to modify a configuration. It is automatically requested, if
necessary: 'EntEr PASS' is displayed on the 4-digit display and
the configuration menu LED flashes, indicating that the modification mode is active. Press the arrow keys until the value '11'
is displayed on the 4-digit display . Press Enter to validate this.
The configuration menu LED stops flashing. If the password is
correct, 'Good' is displayed. If the password is incorrect, 'PASS
incorrEct' is displayed. The User password has a default value
of 11.
This value can be modified through the Service configuration.
The password can be entered if the unit is fully stopped, otherwise 'ACCES dEniEd' (access denied) will be displayed on the
4-digit display. The controller automatically deactivates the
password after 5 minutes without activity (i.e. no buttons
pressed) or after powering up.
SUB-MENU USER CONFIGURATION
USER 1
ITEM
[USER1]
Return to previous menu
0
Circuit selection
1
Circuit capacity increase
2
sequence
Ramp selection*
3
Start-up delay*
4
Water pump selection
5
Water pump changover
6
delay*
Automatic reset
7
selection*
Demand limit selection
8
Voltage corresponding to
9
100% of demand limit
Voltage corresponding to
10
0% of demand limit
Extended display
11
selection
Password for all user
12
configurations
Software version number
13
-
14
-
15
-
16
USER 2
[USER2]*
Return to previous
menu*
Periodic pump startup*
Night mode - start
hour*
Night mode - end
hour*
Night mode - demand
limit in %
Number clock 1*
Number clock 2*
CCN address *
CCN bus*
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
DATE
[dAtE]*
Return to previous
menu
Hour*
Day of the week*
Day and month*
Year*
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SCHEDULE 1
[ScHEduLE 1MEnu]*
Return to previous menu
SUB-MENU:
Period 1 [PErIod 1]
SUB-MENU:
Period 2 [PErIod 2]
SUB-MENU:
Period 3 [PErIod 3]
SUB-MENU:
Period 4 [PErIod 4]
SUB-MENU:
Period 5 [PErIod 5]
SUB-MENU:
Period 6 [PErIod 6]
SUB-MENU:
Period 7 [PErIod 7]
SUB-MENU:
Period 8 [PErIod 8]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SCHEDULE 2
[ScHEduLE 2 MEnu]*
Return to previous
menu
SUB-MENU:
Period 1 [PErIod 1]
SUB-MENU:
Period 2 [PErIod 2]
SUB-MENU:
Period 3 [PErIod 3]
SUB-MENU:
Period 4 [PErIod 4]
SUB-MENU:
Period 5 [PErIod 5]
SUB-MENU:
Period 6 [PErIod 6]
SUB-MENU:
Period 7 [PErIod 7]
SUB-MENU:
Period 8 [PErIod 8]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
HOLIDAYS
[HOLidAy MEnu]*
Return to previous menu
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 1 [HOLidAy 1]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 2 [HOLidAy 2]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 3 [HOLidAy 3]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 4 [HOLidAy 4]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 5 [HOLidAy 5]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 6 [HOLidAy 6]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 7 [HOLidAy 7]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 8 [HOLidAy 8]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 9 [HOLidAy 9]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 10 [HOLidAy 10]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 11 [HOLidAy 11]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 12 [HOLidAy 12]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 13 [HOLidAy 13]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 14 [HOLidAy 14]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 15 [HOLidAy 15]
SUB-MENU:
Holidays 16 [HOLidAy 16]
BROADCAST
[BrodCASt]*
Return to previous menu
Broadcast acknowledger
selection
Broadcast activation
Outdoor temperature
broadcast bus
Outdoor temperature
broadcast element
Start month daylight
saving time
Start day daylight saving
time
Start hour daylight saving
time
Minutes to add
End month daylight saving
time
End day daylight saving
time
End hour daylight saving
time
Minutes to subtract
-
-
-
-
Legend:
*: only displayed if configuration requires.
20
Page 21

CONFIGURATION
USER
[USEr]
USER1
[USEr 1]
USER2
[USEr 2]
SCHEDULE 1
[SCHEduLE 1]*
PERIOD 1
PERIOD 2
PERIOD 3
PERIOD 4
PERIOD 5
PERIOD 6
PERIOD 7
PERIOD 8
SCHEDULE 2
[SCHEduLE 2]*
PERIOD 1
PERIOD 2
PERIOD 3
PERIOD 4
PERIOD 5
PERIOD 6
PERIOD 7
PERIOD 8
HOLIDAYS
[HOLIDAYS]*
HOLIDAY 1
HOLIDAY 2
HOLIDAY 3
HOLIDAY 4
HOLIDAY 5
HOLIDAY 6
HOLIDAY 7
HOLIDAY 8
...
...
...
HOUR + DATE
[dAtE]*
BROADCAST
[broAdCASE]*
SUB-MENU PERIOD CONFIGURATION*
Item PERIOD 1 to 8
[PEriod X MEnu]*
0 Return to previous menu
1 Start of occupied period
2 End of occupied period
3 Selection Monday
4 Selection Tuesday
5 Selection Wednesday
6 Selection Thursday
7 Selection Friday
8 Selection Saturday
9 Selection Sunday
10 Selection holidays
HOLIDAY 15
HOLIDAY 16
SUB-MENU HOLIDAY CONFIGURATION*
Item HOLIDAYS 1 to 16
[HoLidAy X MEnu]*
0 Return to previous menu
1 Start month holidays
3 Start day holidays
4 Number of days, holidays
Legend
*: only displayed if configuration requires.
NOTE: The items in brackets show what is displayed on the
user interface.
21
Page 22

4.5.7.3 - Description of the User 1 Configuration sub-menu
USER 1 CONFIGURATION SUB-MENU [2]
ITEM FORMAT UNITS DEFAULT COMMENTS
0 USEr MEnu - - When selected this item authorises return to the previous menu.
1 [1] 0/1/2 0 Lead circuit selection
2 [1] 0/1 - 0 Circuit capacity increase sequence
3 [1] YES/no - no Ramp loading select. For units with more than one compressor per circuit.
4 1 to 15 min 1 Delay at start-up. This value is reinitialised after power-up or when both circuits are halted by local, remote
5 0/1/2/3/4 - 0 Pump sequence select
6 [1] 24 to 3000 hours 48 Pump changeover delay. Displayed if auto pump sequence is selected. This parameter is used for pump
7 0/1/2/3 - 0 Automatic heating/cooling changeover selection. Permits activation of automatic reset type
8 0/1/2 - 0 Demand limit selection
9 [1] 0 to 10 Volts 0 Voltage corresponding to 100% of the demand limit
10 [1] 0 to 10 Volts 0 Voltage corresponding to 0% of the demand limit
11 «YES/no» - yes Extended menu select
12 «YES/no» -noPassword for all User Configurations
13 nn.n - - Software version number
Legend
1 This item shall be masked when not used.
2 Access to menu is read/write.
0 = automatic based on the number of start-ups and the operating hours of each circuit
1 = lead circuit A
2 = lead circuit B
0 = equal charge for both circuits
1 = priority charge on one circuit
Yes = ramp enabled
No = ramp disabled
This configuration enables the ramp to be activated for heating or cooling (depending on configuration): the
maximum rate (in °C/min) of temperature drop or rise for the heat exchanger water (leaving or entering, upon
configuration). Ramp setting value can be configured in the Setpoint menu.
or CCN command. No compressor will be started up until this pause has expired. However, the evaporator
pump command will be activated immediately. The safety lockout loop will not be checked until the pause has
expired.
0 = no pump
1 = one pump only
2 = two pumps with auto rotation
3 = pump #1 manual select
4 = pump #2 manual select
If the auto sequence is selected, the pump change-over occurs when the rotation delay is elapsed. If the
manual sequence is selected then, the selected pump is used in priority. Change-over occurs if one pump
fails.
auto-rotation: the control tries to limit the pump run time difference to the pump changeover delay value.
Change-over between pumps occurs when this difference becomes greater than the configured pump
changeover delay.
0 = none
1 = 0-10 V d.c. reference voltage
2 = temperature difference
3 = outdoor temperature
0 = demand limit not selected
1 = demand limit by contact
2 = demand limit by external signal 0-10 V d.c.
Yes = menu description available
No = menu description not available
This item authorises activating or inhibiting the menu item expanded display.
Yes = password required for all User Configurations (Date, Time Schedule, Broadcast)
No = password require for User menu only
When this item is validated, the User Password will be required for all configurations accessible by the User.
This item shows the number of the software version used by this controller. Access is read only.
22
Page 23

4.5.7.4 - Description of the User 2 Configuration sub-menu
USER 1 CONFIGURATION SUB-MENU
ITEM FORMAT UNITS DEFAULT COMMENTS
0 USEr 2 Menu When selected this item authorises return to the previous menu.
1[1] YES/no - no Periodic pump quick-start of the water pump(s)
2 [1] n
3 [1] n
4 [1] 0 to 100 % - Night mode demand limit value.
5 [1] 0 or 65 to 99 - 0 Schedule 1 clock number (for unit on/off schedule, see section 4.5.7.6).
6 [1] 0 or 65 to 99 - 0 Schedule 2 clock number (schedule for setpoint selection, see section 4.5.7.6).
7 [1] 1 to 239 - 1 CCN element address.
8 [1] 0 to 239 - 0 CCN bus number.
Legend
*n
n3n4: minutes (00 to 59). Continuous pressing of the Enter key again causes the last two characters to flash so that minutes can be adjusted.
1n2n3 n4
00:00 to 23:59 - 00:00 Authorises entering the time of day at which the night control mode starts. During this period the fan runs at
1n2n3 n4
00:00 to 23:59 - 00:00 Authorises entering the time of day at which the night control mode ends.
: hours (00 to 23). The first time the Enter button is continuously pressed, the first two characters in the 4-digit display flash so that hours can be adjusted.
1n2
Yes = the pump is started periodically when the unit is manually stopped.
No = periodic pump start is disabled
When the unit is manually stopped (e.g. during the winter season) the pump is started each day at 14.00
hours for 2 seconds. If two pumps are available, pump #1 is started on odd days and pump #2 on even days.
Night control mode - start time*
low speed (to reduce fan noise) if permitted by operating conditions, and unit capacity is limited to the
maximum night values.
Night control mode - end time*
Authorises configuration of the maximum capacity authorised during the night mode.
0 = schedule in local operating mode
65 to 99 = schedule in CCN operating mode
0 = schedule in local operating mode
65 to 99 = schedule in CCN operating mode
No two network elements can have the same element number and bus number at the same time.
No two network elements can have the same element number and bus number at the same time.
4.5.7.5 - Description of Date and Time configuration submenu
DATE & TIME CONFIGURATION SUB-MENU
ITEM FORMAT COMMENTS
0 dAtE MEnu When selected this item authorises return to the
1n
2 Current day of week setting.
3n
4 nnnn Current year setting.
1n2n3n4
00:00 to 23:59 n1n2: hours (00 to 23). The first time the Enter button is
«Mo» Monday
«tU» Tuesday
«uE» Wednesday
«tH» Thursday
«Fr» Friday
«SA» Saturday
«Su» Sunday
1n2n3n4
01:01 to 31:12 n1n2:day (01 to 31). The first time the Enter button is
previous menu.
Current time setting.
continuously pressed, the first two characters in the 4digit display flash so that hours can be adjusted.
n3n4: minutes (00 to 59). Continuous pressing of the
Enter key again causes the last two characters to flash
and minutes can be adjusted.
Current day and month setting.
continuously pressed, the first two characters in the 4-
digit display flash so that day can be adjusted.
n3n4:month (01 to 12). Continuous pressing of the
Enter key again causes the last two characters to flash
so that month can be adjusted.
4.5.7.6 - Description of the Time Schedules sub-menus
The control provides two timer programs: time schedule 1 and
time schedule 2.
The first timer program (schedule #1) provides a means to
automatically switch the unit from an occupied mode to an
unoccupied mode: the unit is started during occupied periods.
The second timer program (schedule #2) provides a means to
automatically switch (when auto mode is selected) the active
setpoint from an occupied setpoint to an unoccupied setpoint.
Cooling or heating setpoint 1 is used during occupied periods.
Cooling setpoint 2 is used during unoccupied periods. For
additional information on setpoint activation see section 5.7.1.
Each schedule consists of eight time periods set by the
operator. These time periods can be flagged to be in effect or
not in effect on each day of the week plus a holiday period (see
section 4.5.7.7 on public holidays). The day begins at 00.00
hours and ends at 24.00 hours.
Program is in unoccupied mode unless a schedule time period is
in effect. If two periods overlap and are both active on the same
day, the occupied mode tak es priority o v er the unoccupied per iod.
Each of the eight periods can be displayed and changed with
the aid of a sub-sub-menu. The table below shows how to
access the period configuration. Method is the same for the
time schedule #1 or the time schedule #2.
23
Page 24

PERIOD X CONFIGURATION SUB-MENUS (X = 1 to 8)
ITEM # FORMA T COMMENTS
0 Period X Menu Indicates the period (X) you are going to
1n
2n
3 Mo- 0 or Mo- 1 1 = the period is in effect on Monday.
4 tu- 0 or tu- 1 1 = the period is in effect on Tuesday.
5 UE-0 or UE- 1 1 = the period is in effect on Wednesday.
6 tH- 0 or tH- 1 1 = the period is in effect on Thur sday.
7 Fr-0 or Fr- 1 1 = the period is in effect on Friday.
8 SA- 0 or SA- 1 1 = the period is in effect on Saturday.
9 Su- 0 or Su- 1 1 = the period is in effect on Sunday.
10 Ho- 0 or Ho- 1 1 = the period is in effect on public holidays.
Legend
* n
1n2n3n4
00:00 to 24:00 Authorises entering the time of day at which the
1n2n3n4
00:00 to 24:00 Authorises entering the time of day at which the
: hours (00 to 24). The first time the Enter button is continuously pressed,
1n2
the first two characters in the 4-digit display flash so that hours can be
adjusted.
n3n4: minutes (00 to 59). Continuous pressing of the Enter key again causes
the last two characters to flash so that minutes can be adjusted.
configure. When selected this item authorises a
return to the main menu.
Occupied period - Start time*.
occupied period starts.
Occupied period - End time*.
occupied period ends.
0 = period not in effect on Monday
0 = period not in effect on Tuesday.
0 = period not in effect on Wednesday.
0 = period not in effect on Thursday.
0 = period not in effect on Friday.
0 = period not in effect on Saturday.
0 = period not in effect on Sunday.
0 = period not in effect on public holidays.
Typical timer program:
Time
10
11
12
1
14
1
1
17
1
19
2
21
22
23
24
P1
P1
1
P1
2
4
6
7
8
P3P2P2
P3
P3
P5P4P4P3P2P2
P5P4P4P3P2P2
P5P4P4P3P2P2
P5P4P4P3P2P2
P5P4P4P3P2P2
P4P4P3P2P2
P4P4P3P2P2
P4P4P3P2P2
P4P4P3P2P2
P4P4P3P2P2
HOLSUNSATFRITHUWESTUEMON
MON : Monday
TUE : Tuesday
WED : Wednesday
THU : Thursday
FRI : Friday
SAT : Saturday
SUN : Sunday
HOL : Public holidays
P6P3
Occupied
Unoccupied
4.5.7.7 - Description of the Holidays sub-menus
This function is used to define 16 public holiday periods. Each
period is defined with the aid of three parameters: the month,
starting day and duration of the public holiday period. During
these public holidays the controller will be in occupied or
unoccupied mode, depending on the programmed periods
validated for public holidays (see section 4.5.7.8).
Each of these public holiday periods can be displayed and
changed with the aid of a sub-menu.
ATTENTION: The broadcast function must be activated to
utilise the holiday schedule, even if the unit is running in
stand-alone mode (not connected to CCN). See section
4.5.7.6.
HOLIDAY PERIOD X CONFIGURATION SUB-MENUS (X = 1 to 16)
ITEM # FORMA T COMMENTS
0 HoLidAy X Sub-menu When selected this item authorises a return
to the configuration menu.
1 0 to 12 Start month of public holiday period
0 = period not in use
1 = January, 2 = February, etc.
2 0 to 31 Start day of public holiday period. 0 period
not in use.
3 0 to 99 days Duration of the public holiday period in
days.
NOTE: Typical programming for public holidays:
- A public holiday period lasting 1 day on 20th May, for
instance, is configured as follows: start month = 5, start
day = 20, duration = 1
- A public holiday period lasting 2 day on 25th May, for
instance, is configured as follows: start month = 5, start
day = 25, duration = 2
4.5.7.8 - Description of the Broadcast sub-menu
The controller provides a broadcast configuration menu which
you can use to configure the unit to be the CCN’s broadcaster,
responsible for transmitting the time, outdoor temperature, and
holiday flags to all system elements.
This menu also authorises setting the date to begin and end
daylight saving time . There should be only one broadcaster in a
CCN, so this table should not be configured if any other system
element is acting as broadcaster.
ATTENTION: If the unit operates in standalone mode (not
CCN connected) this menu must be used if the holiday function
is used, or to correct for daylight saving time.
P1: period 1, 0h00, 3h00, Monday
P2: period 2, 7h00, 18h00, Monday and Tuesday
P3: period 3, 7h00, 21h00, Wednesday
P4: period 4, 7h00, 17h00, Thursday and Friday
P5: period 5, 7h00, 12h00, Saturday
P6: period 6, 20h00, 21h00, Public holidays
P7: period 7, Not used in this example
P8: period 8, Not used in this example
Starts at Ends at Active on
24
Page 25

BROADCAST CONFIGURATION SUB-MENU
ITEM # FORMAT COMMENTS
0 broAdCASt MEnu When selected this item authorises a return to the main menu.
1 YES/no Determines whether or not the unit is a broadcast acknowledger when the unit is connected on a CCN network. There must be
2 YES/no This item authorises enabling or disabling the Broadcast function. When it is set to Yes, the control will make a periodic
3 nnn OAT Broadcaster bus number: it is the bus number of the system that has the outside air temperature sensor connected to it.
4 nnn OAT Broadcaster element number: it is the element number of the system element that has the outside air temperature sensor
5nn Daylight saving start month. In this mode you enter the month in which the broadcaster will adjust its time for the start of
6nn Daylight saving start day. In this mode you enter the day on which the broadcaster will adjust its time for the start of daylight
7n
8 nnnn Daylight saving start minutes to add: number of minutes by which the broadcaster will adjust its time for the start of daylight
9nn Daylight saving stop month. In this mode you enter the month in which the broadcaster will adjust its time for the end of
10 nn Daylight saving stop day. In this mode you enter the day on which the broadcaster will adjust its time for the end of daylight
11 n
12 nnnn Daylight saving start minutes to subtract: number of minutes by which the broadcaster will adjust its time for the end of
0 to 239 Used for CCN network function only.
0 to 239 connected to it. Used for CCN network function only.
1 to 12 daylight saving time.
1 to 31 saving time.
1n2n3n4
00:00 to 24:00 adjust its time for the start of daylight saving time.
1 to 1440 minutes saving time.
1 to 12 daylight saving time.
1 to 31 saving time.
1n2n3n4
00:00 to 24:00 will adjust its time for the end of daylight saving time.
1 to 1440 minutes daylight saving time.
only one broadcast acknowledger in a CCN.
Warning: if the unit operates in standalone mode (not CCN connected) this choice must be set to Yes if the holiday function is used
(see section 4.5.7.8) or if you want to configure the daylight saving time function.
broadcast on the CCN. When it is set to No, the control is not the broadcaster and there is no need to configure the other choice in
this table. There must be only one broadcaster in a CCN and this item should not be configured if any other system element is
acting as broadcaster.
Warning: if the unit operates in standalone (not CCN connected) this choice must be set to Yes if the holiday function is used (see
section 4.5.7.8) or if you want to configure the daylight saving time function.
Authorises entering the hours and minutes for saving start. In this mode you enter the time of day when the broadcaster will
n1n2: hours (00 to 24). The first time the Enter button is continuously pressed, the first two characters in the 4-digit display flash so
that hours can be adjusted.
n3n4: minutes (00 to 59). Continuous pressing of the Enter key again causes the last two characters to flash so that minutes can be
adjusted.
Authorises entering the hours and minutes for saving stop. In this mode you enter the time of day when the broadcaster
: hours (00 to 24). The first time the Enter button is continuously pressed, the first two characters in the 4-digit display flash so that hours can be adjusted.
n
1n2
n3n4: minutes (00 to 59). Continuous pressing of the Enter key again causes the last two characters to flash so that minutes can be adjusted.
4.5.8 - Description of the Alarms menu
This menu is used to display and reset up to 5 active alarms. It
also permits alarm reset. If no alarm is active this menu is not
accessible. See section 6 for a complete description of the
alarm codes and alarm reset.
ALARMS MENU
ITEM # FORMAT DESCRIPTION
0 [1] X ALArM X alarms are active
rESEt ALArM Reset of alarms is requested
To reset all active alarms, continuously press the Enter
key. ‘rESET ALArM’ is then displayed. Press the select
key again: all alarms are reset.
1 [1] nn Current alarm code 1*
2 [1] nn Current alarm code 2*
3 [1] nn Current alarm code 3*
4 [1] nn Current alarm code 4*
5 [1] nn Current alarm code 5*
Legend
1 This item is masked when nil
* Pressing the Enter key when alarm code is displayed causes the following
message to be scrolled:
“time of alarm” “date of alarm” “full CCN alarm message”
- “time of alarm”: hh-mm
- “date”: dd-mm
- “full CCN alarm message”: up to 64 characters
4.5.9 - Description of the Alarms History menu
ALARMS HISTORY MENU
ITEM # FORMAT COMMENTS
1 [1] nn Alarm history code 1*
2 [1] nn Alarm history code 2*
3 [1] nn Alarm history code 3*
4 [1] nn Alarm history code 4*
5 [1] nn Alarm history code 5*
6 [1] nn Alarm history code 6*
7 [1] nn Alarm history code 7*
8 [1] nn Alarm history code 8*
9 [1] nn Alarm history code 9*
10 [1] nn Alarm history code 10*
Legend
1 This item is masked when nil
* Pressing the Enter key when alarm code is displayed causes the following
message to be scrolled:
“time of alarm” “date of alarm” “full CCN alarm message”
- “time of alarm”: hh-mm
- “date”: dd-mm
- “full CCN alarm message”: up to 64 characters
25
Page 26

4.5.10 - Runtime menu description
4.5.10.2 - Description of the Runtimes 2 menu
RUNTIMES
RUNTIMES 1
[runtiMES 1]
RUNTIMES 2
[runtiMES 2]
MAINTENANCE
[MAintEnAnCE]
NOTE: The items in brackets show what is displayed on the
user interface.
4.5.10.1 - Description of the Runtimes 1 menu
RUNTIMES MENU [1]
iTEM # FORMAT UNIT COMMENTS
0 - - When selected this item
1 nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Unit operating hours*
2 nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Compressor A1 operating hours*
3 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Compressor A2 operating hours*
4 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Compressor A3 operating hours*
5 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Compressor A4 operating hours*
6 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Compressor B1 operating hours*
7 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Compressor B2 operating hours*
8 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Compressor B3 operating hours*
9 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Compressor B4 operating hours*
10 nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Machine starts*
11 nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Compressor A1 starts*
12 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Compressor A2 starts*
13 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Compressor A3 starts*
14 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Compressor A4 starts*
15 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Compressor B1 starts*
16 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Compressor B2 starts*
17 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Compressor B3 starts*
18 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 -/10 or 100 Compressor B4 starts*
NOTES
1 This item is masked when not used
* Certain values are divided by 10 or by 100, so that number of hours or start-
ups of less then 10 are displayed as 0.
When the value is divided by 10 or by 100 it is displayed in turn with “M 10” or
“M100”.
authorises return to the previous
menu
RUNTIMES MENU [2]
iTEM # FORMAT UNIT COMMENTS
0 - - When selected this item
authorises return to the previous
menu
1 nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Pump #1 operating hours*
2 nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Pump #2 operating hours*
3 [1] nnnn | M 10 | M100 hrs/10 or 100 Condenser pump operating
hours
4 [1] nnnn - Number of start-ups for the
compressor with the highest
number during the last hour
5 nnnn - Average number of compressor
start-ups/hour for the last 24
hours
4.5.10.3 - Maintenance menu description
To be active, the maintenance function must be preset in the
Service configuration.
ITEM # FORMAT DESCRIPTION
0 MAintEnAnCE MEnu When selected this item authorises return to the
previous menu.
1 [1] Accessible with the Service password.
2 [1] For future use
3 [1] For future use
4 [1] ALErt Water loop rate to low
5 [1] nnn/ALErt Next primary pump maintenance operation in nnn
days. 'ALErt' is displayed, when the delay before
maintenance has elapsed.
6 [1] nnn/ALErt Next secondary pump maintenance operation in
nnn days. 'ALErt' is displayed, when the delay
before maintenance has elapsed.
7 [1] nnn/ALErt Next water filter maintenance operation in nnn
days. 'ALErt' is displayed, when the delay before
maintenance has elapsed.
Legend
1 This item is masked when not used.
26
Page 27

5 - PRO-DIALOG PLUS CONTROL OPERATION
5.1 - Start/stop control
The table below summarises the unit control type and stop or
go status with regard to the following parameters.
- Operating type: this is selected using the start/stop button
on the front of the user interface.
- Remote start/stop contacts: these contacts are used when
the unit is in remote operating type (rEM). See sections
3.6.2 and 3.6.3.
- CHIL_S_S: this network command relates to the chiller
start/stop when the unit is in CCN control (CCn). Variable forced to disable: the unit is halted. Variable forced to
Enable: the unit runs in accordance with schedule 1.
- Start/Stop schedule: occupied or unoccupied status of the
unit as determined by the chiller start/stop program
(Schedule #1). Used when the unit is equipped with an
optional CCN/clock board, otherwise the chiller occupied
mode is forced to occupied all the time.
- Master control type. This parameter is used when the
unit is the master unit in a two chiller lead/lag arrangement. The master control type determines whether the unit
is to be controlled locally, remotely or through CCN (this
parameter is a Service configuration).
- CCN emergency shutdown: if this CCN command is
activated, it shuts the unit down whatever the active
operating type.
- General alarm: the unit is totally stopped due to failure.
ACTIVE OPERATING TYPE STATUS OF PARAMETERS CONTROL UNIT
REMOTE MASTER ST AR T/STOP CCN GENERAL
START/STOP CONTROL SCHEDULE EMERGENCY ALARM
LOFF L-ON L-SC rEM CCN MASt CHIL_S_S CONTACT TYPE MODE SHUTDOWN
- - - - - - - - - - Enable - - Off
------- - -. -. - Yes - Off
Active - - - - - - - - - - - Local Off
- - Active - - - - - - Unoccupied - - Local Off
- - - Active - - - Off - - - - Remote Off
- - - Active - - - - - Unoccupied - - Remote Off
- - - - Active - Disable - - - - - CCN Off
- - - - Active - - - - Unoccupied - - CCN Off
- - - - - Active - - Local Unoccupied - - Local Off
- - - - - Active - Off Remote - - - Remote Off
- - - - - Active - - Remote Unoccupied - - Remote Off
- - - - - Active Disable - CCN - - - CCN Off
- - - - - Active - - CCN Unoccupied - - CCN Off
- Active - - - - - - - - Disable No Local On
- - Active - - - - - - Occupied Disable No Local On
- - - Active - - - On - Occupied Dsable No Remote On
- - - - Active - Enable - - Occupied Disable No CCN On
- - - - - Active - - Local Occupied Disable No Local On
- - - - - Active - On Remote Occupied Disable No Remote On
- - - - - Active Enable - CCN Occupied Disable No CCN On
TYPE MODE
5.2 - Heating/cooling selection
On heat pumps, heating/cooling selection can be controlled
differently depending on the active operating type:
• Locally on the unit, using operating types L-C1, L-C2,
LC1r and LC2r (for cooling) and L-H (for heating).
• Remotely using the heat/cool selection volt-free contact
when the unit is in Remote operating type (rEM).
• Via a CCN command when the unit is in CCN operating
type (CCn).
PARAMETER STATUS
ON/OFF
STATUS
Off
On
On
On
On
On
On
CONTROL TYPE
Local
Local
Remote
Remote
CCN
CCN
HEATING/COOLING
SELECTION IN LOCAL MODE
Cooling
Heating
-
-
-
-
The current heat/cool operating mode on the unit is indicated
by item 4 in the Information menu and by the heat/cool LEDs
on the summary interface.
REMOTE HEATING/
COOLING CONTACTS
-
-
Cooling mode
Heating mode
-
-
HC_SEL
-
-
-
-
Cooling
Heating
OPERATING MODE
Cooling
Cooling
Heating
Cooling
Heating
Cooling
Heating
27
Page 28

5.3 - Evaporator water pump control
5.5 - Control interlock contact
The unit can control one or two evaporator water pumps. The
evaporator water pump is turned on when this option is configured (see User configuration) and when the unit is in one of the
on modes described above or in delay mode. Since the minimum
value for the delay at start-up is 1 minute (configurable between 1
and 15 minutes), the pump will run for at least one minute
before the first compressor starts.
The pump is kept running for 20 seconds after the unit goes to
stop mode. The pump keeps working when the unit switches
from heating to cooling mode or vice-versa. It is turned off if
the unit is shut down due to an alarm unless the fault is a frost
protection error.
The pump can be started in particular operating conditions when
the evaporator heater is active. See section 5.19 for the
particular evaporator pump control for the follower unit
(master/slave assembly). If two pumps are controlled and the
reversing function has been selected (see User 1 configuration),
the control tries to limit the pump run time delta to the
configured pump change-over delay. If this delay has elapsed,
the pump reversing function is activated, when the unit is
running. During the reversing function both pumps run together
for two seconds. If a pump has failed and a secondary pump is
available, the unit is stopped and started again with this pump.
This contact can control the status of the water loop. Its
function is to prevent unit start-up, if it is open and if the startup delay has passed. Furthermore, this contact must remain
closed when the unit is not in local off, remote or CCN control
mode. Opening this contact for more than 8 seconds while the
unit is operating, will cause immediate shut-down of the faulty
unit.
5.6 - Evaporator heater control
The evaporator heater can be activated to protect an evaporator
that may be damaged by ice, if the unit is shut down for a long
period at low outdoor air temperature. If the heater is not
sufficient to increase the water temperature, the evaporator
pump can be started.
NOTE: The evaporator heater control parameters may be
modified using the Service Configuration menu.
5.7 - Control point
Control point represents the leaving water temperature that the
unit must produce.
• In cooling mode: control point = active setpoint + reset
• In heating mode: control point = active setpoint - reset
The control provides a means to automatically start the pump
each day at 14.00 hours for 2 seconds when the unit is off. If
the unit is fitted with two pumps, the first pump is started on
odd days and the second pump is started on even days. Starting
the pump periodically for few seconds increases the life-time
of the pump bearings and the tightness of the pump seal.
NOTE: If this function is used, there should not be any
chilled water pump interlock between terminals 34 and 35
(see section 3.4).
5.4 - Condenser water pump control
Only available on water-cooled units and air-cooled units with
heat reclaim.
The condenser pump can be controlled by two modes, depending on the configuration (only accessible by Carrier Service).
1 - Control based on unit start/stop control. In this case it is
controlled in the same way as the evaporator pump.
2 - Control based on compressor status. In this case the pump
is activated at the same time as the first compressor. It
only switches off when no compressor is activated.
5.7.1 - Active setpoint
Two setpoints can be selected as active in cooling mode.
Usually , the second setpoint is used for unoccupied periods or
for ice storage (medium or low brine unit). A single setpoint is
available in heating mode.
Depending on the current operating mode, the active setpoint
can be selected with the operating type selector button, or with
the user’s volt-free contacts, or with network commands (see
section 3.4).
5.7.2 - Reset
Reset means that the active setpoint is modified so that less
machine capacity is required (in cooling mode, the setpoint is
increased, in heating mode it is decreased). This modification is
in general a reaction to a drop in the load. For the Pro-Dialog
Plus control system, the source of the reset can be configured
in the User 1 configuration: it can be based on an external 0-10 V
signal, provided either by the outdoor temperature (that gives a
measure of the load trends for the building) or by the return
water temperature (delta T that gives an average building load).
In response to a drop in the outdoor temperature or to a drop in
delta T, the cooling setpoint is normally reset upwards in order
to optimise unit performance:
28
In both cases the reset parameters, i.e. slope, source and maximum value, are configurable in the Setpoints menu (see section
4.5.4). Reset is a linear function based on three parameters.
• A reference at which reset is zero (outdoor temperature or
delta T - no reset value).
• A reference at which reset is maximum (outdoor
temperature or delta T - full reset value).
• The maximum reset value.
Page 29

5.8 - Demand limit
Generally, demand limit is used by an energy management
system in order to restrict the unit electricity consumption.
NOTE: If the same compressor undergoes too many starts
(per hour) this automatically brings about reduction of
compressor starts, which makes leaving water temperature
control less precise.
The PRO-DIALOG Plus control system for 30GX & 30HX
provides two methods of demand limit:
• By reference to a limiting signal from a user-controlled
volt-free contact: the capacity of the unit cannot exceed
the demand limit setpoint (which can be modified in the
Setpoints menu) when the limit contact is closed.
• By reference to an external 0-10 V d.c. signal: the
capacity of the unit cannot exceed the demand limit
imposed by this external signal. It is a linear function and
its para-meters are configurable in the User1 menu
(voltages at 0% limitation and 100% of limitation). This
function is not available if Reset by reference to an
external 0-10 V d.c. signal has already been selected.
Whatever the method used, demand limit is active in all
operating types: Local, Remote or CCN. However, in
Local operating type, demand limit can be disabled with
keypad commands (see section 4.3.3) and in CCN
operating type, demand limit can be controlled directly
with the aid of CCN commands.
NOTE: A limitation value of 100% means that the unit may
call upon the full array of its capacity stages.
Here is an example of demand limit by an external 0-10 V d.c.
signal. This example assumes that the limitation parameters are
such that at 0 volt the authorised capacity shall be maximum
capacity, and at 10 volts the authorised capacity shall be zero
(this is the default configuration).
Demand limit by 0-10 V d.c. signal
No demand limit
5.10 - Determining the lead circuit
This function commands the start/stop sequence of the two
refrigerant circuits called A and B. The circuit authorised to
start first is the lead circuit. Three methods can be configured
by the user in the Configuration menu:
• Auto mode: the control system determines the lead circuit
so as to equalise the number of starts on each circuit
(value weighted by the operating times of each circuit).
Thus, the circuit with the least number of starts is always
given precedence to start. The lead circuit is stopped last.
This function is only available in two-circuit units.
NOTE: If one circuit has more unloaders than the other, this
circuit is always the lead circuit, independent of the
configuration and the operating hours of the two circuits.
• Circuit A as leader: Circuit A is always the lead circuit.
It is the first to start and the last to stop.
• Circuit B as leader: Circuit B is always the lead circuit.
It is the first to start and the last to stop. This choice is
only available in two-circuit units.
5.11 - Circuit loading sequence
Two circuit loading sequences are available. The choice of
sequence can be configured by the user in the Configuration
menu (see section 4.5.7.3). This function is only available in
two-circuit units.
• Balanced circuit loading: If this sequence is selected, the
control system tries to keep the capacity of circuits A and
B equal as the total load on the unit increases or decreases.
• Loading with priority given to one circuit: If this
sequence is selected, the control system loads the lead
circuit completely before the second circuit starts up. When
there is a demand limit, the second circuit is unloaded first.
Total demand limit
capacity
Maximum permitted
0-10 V dc demand limit
5.9 - Capacity control
This function activates the compressors and capacity unloaders
to keep the entering or leaving water temperature at its
setpoint. The precision with which this is achieved depends on
the capacity of the water loop, the flow rate, the load, and
the number of stages available on the unit.
The control system continuously takes account of the temperature error with respect to the setpoint, as well as the rate of
change in this error and the difference between entering and
leaving water temperatures, in order to determine the optimum
moment at which to add or withdraw a capacity stage.
NOTE: If the unit is air-cooled and if the saturated
condensing temperature of one of the two circuits is lower
than 0°C at the start-up of one circuit, the priority capacity
loading sequence of the circuits is used by the control,
independent of the configuration.
29
Page 30

5.12 - Slave compressor start-up sequence
5.15 - Head pressure control on water-cooled units
Lag compressors are started and stopped in a sequence
designed to equalise their number of start-ups (value weighted
by their operating time).
5.13 - Controlling the EXV
EXVs, if used, control the flow of refrigerant in the evaporator.
They are controlled in order to maintain a constant level of
superheat at the thermistor for the lead compressor inlet gas
(located between the compressor motor and the cylinders).
A thermistor and a pressure sensor, in the lead compressor of
each circuit, are used to measure this superheat. The thermistor
measures the temperature of the superheated gas entering the
cylinders. The pressure sensor measures the suction gas
pressure. The controller converts this value into a saturated
temperature. The difference between the superheated gas
temperature and the saturated temperature is the superheat. The
control system sets the position of the EXV to hold this
superheat at the setpoint configured for the unit.
Since the EXVs are driven by the controller their positions are
always known. During start-up of a circuit its EXV is fully closed
to ensure pump down. After pump down, the system continuously
controls and monitors the valve position. Similarly, on shutdown
of a circuit the EXV is closed again to ensure pumping down.
EXVs are also used to restrict suction temperature, making it
possible to start the unit at higher water and suction temperatures without overloading the compressors. This procedure
controls what is known as Maximum Operating Pressure (MOP).
5.14 - Head pressure control on air-cooled units
There are two methods, configurable only by Carrier Service,
for controlling the condenser fans:
• Controlling condensation by reference to a setpoint
(default): The saturated head pressure is controlled by
reference to a fixed setpoint (user-definable in the Setpoints
menu). This temperature is maintained by cycling fans on
and off, as well as by varying the speed of a fan in
appropriate cases.
• Controlling condensation by reference to the position of
the EXV: The saturated head pressure is controlled by
reference to the position of the EXV and the superheat, by
cycling fans on and off as well as by varying the speed of a
fan in appropriate cases. The control system seeks to keep
the EXVs as wide open as possible whilst maintaining the
correct level of superheat with the fans. When the second
condensing setpoint is selected (reclaim setting), the control
system will automatically revert to controlling by reference
to a setpoint even if control by reference to the EXV has
been selected. The original configuration is reinitialised
when the first condensing setpoint is re-selected.
There are two configurable methods for controlling the condenser water valves (optional):
• Controlling head pressure by reference to a setpoint:
Saturated head pressure is controlled by reference to a userdefinable fixed setpoint. This temperature is maintained by
using the valves to control the flow of water in each condenser circuit.
• Controlling head pressure by reference to the position of
the EXV: Saturated head pressure is controlled by reference
to the position of the EXV and the superheat, by adjusting
the flow of water in each condenser circuit. The valve control
system seeks to keep the EXVs as wide open as possible
whilst maintaining the correct level of superheat. When the
second head pressure setpoint is selected (reclaim setting),
the control system will automatically revert to controlling by
reference to a setpoint even if control by reference to the
EXV has been selected. The original configuration is
reinitialised when the first head pressure setpoint is reselected.
5.16 - Active setpoint selection
Two setpoints can be selected as active in cooling mode, and
one setpoint in heating mode. Usually , the second cooling
setpoint is used for unoccupied periods or for ice storage (brine
unit). Depending on the current operating mode, the active
setpoint can be selected either by choosing the item in the
Information menu. or with the user volt-free contacts, or with
network commands, or by the setpoint time schedule program
(Schedule 2).
The following tables show a summary of the possible selctions
as a function of the control typpes (local, remote or network),
and the parameters below:
• Local setpoint selection: item No. 11 of the Information
Menu permits selection of the active setpoint, if the unit is
in the local operating type.
• Heating/cooling operating mode.
• Control contacts: status of the remote heating and
cooling control contact. This contact is only active, if the
unit is under remote operating control. See section 3.6.6.
• Schedule 2 program status: schedule program for
setpoint selection. See section 4.3.11.6.
NOTE
Certain units can have up to 8 fan stages, of which one per
circuit is a variable-speed fan, depending on their configuration and wiring.
30
Page 31

LOCAL OPERATING MODE
PARAMETER STATUS
HEATING/
COOLING
OPERA TING
MODE
cooling
cooling
heating
holidays
holidays
REMOTE OPERATING MODE
PARAMETER STATUS
HEATING/
COOLING
OPOERA TING
MODE
heating
cooling
cooling
-
-
CCN OPERATING MODE
PARAMETER STATUS
HEA TING/COOLING
OPERATING MODE
cooling
cooling
heating
LOCAL
SETPOINT
SELECTION
sp 1
sp2
auto
auto
CONTROL
CONTACT
sp 1
sp2
holidays
holidays
SCHEDULE 2
PROGRAM STATUS
-
-
occupied
unoccupied
SCHEDULE 2
PROGRAM STATUS
-
-
occupied
unoccupied
SCHEDULE 2
PROGRAM STATUS
occupied
unoccupied
-
ACTIVE SETPOINT
cooling setpoint 1
cooling setpoint 2
heating setpoint
cooling setpoint 1
cooling setpoint 2
ACTIVE SETPOINT
heating setpoint
cooling setpoint 1
cooling setpoint 2
cooling setpoint 1
cooling setpoint 2
ACTIVE SETPOINT
cooling setpoint 1
cooling setpoint 2
heating setpoint
5.17 - High pressure load shedding function
All control commands to the master/slave assembly (start/stop,
setpoint, heating/cooling operation, load shedding, etc.) are
handled by the unit which is configured as the master, and must
therefore only be applied to the master unit. They will be transmitted automatically to the slave unit. The master unit can be
controlled locally, remotely or by CCN commands. Therefor e
to start up the assembly, simply validate the Master operating
type (MASt) on the master unit. If the Master has been configured for remote control then use the remote volt-free contacts
for unit start/stop. The slave unit must stay in CCN operating
type continuously. To stop the master/slave assembly, select
Local Off (LOFF) on the master unit or use the remote voltfree contacts if the unit has been configured for remote control.
One of the functions of the master unit (depending on its configuration) may be the designation, whether the master or slave is
to be the lead machine or the follower . The roles of lead machine
and follower will be reversed when the difference in running
hours between the two units exceeds a configurable value,
ensuring that the running times of the two units are automatically
equalised. The changeover between lead machine and follower
may take place when the assembly is started up, or even whilst
running. The running time balancing function is not active if it
has not been configured: in this case the lead machine is
always the master unit.
This function does not require an additional board. It prevents
high pressure a break on a circuit by the following means:
• Preventing any capacity increase on the circuit once the
high pressure value has reached an initial threshold.
• Shedding one or more capacity stages once a second
protection threshold has been reached.
In the event of capacity stages being shed, no capacity increase
will be authorised on the circuit concerned for a period of 5
minutes.
5.18 - Pumping down
When the lead compressor in each circuit is started or stopped,
that circuit goes through a pumping down cycle to purge the
evaporator and suction line of refrigerant. The maximum
duration of this cycle is 3 minutes.
5.19 - Master/slave assembly
Two PRO-DIALOG Plus units can be linked to produce a master/
slave assembly. The two machines are interconnected over the
CCN bus. All parameters required for the master/slave function
must be configured through the Service configuration menu.
The lead machine will always be started first. When the lead
machine is at its full available capacity, start-up delay (configurable) is initialised on the follower. When this delay has
expired, and if the error on the control point is greater than 1.7°C,
the follower unit is authorised to start and the pump is activated.
The follower will automatically use the master unit active setpoint. The lead machine will be held at its full available capacity for as long as the active capacity on the follower is not
zero. When the follower unit receives a command to stop, its
evaporator water pump is turned off with 20 seconds delay.
In the event of a communication fault between the two units,
each shall return to an autonomous operating mode until the
fault is cleared. If the master unit is halted due to an alarm, the
slave unit is authorised to start without prior conditions.
5.20 - Controlling Pro-Dialog Plus units with a System
Manager
Up to eight PRO-DIALOG Plus units (or System Manager
compatible units) can be controlled by one control module of
the FSM or CSM III type which can handle multi-tasking of
control functions such as starting units in sequence.
Master/slave operation requires the connection of a temperature
probe at the common manifold on each machine, if the heat
exchanger leaving water temperature is controlled.
The master/slave assembly can operate with constant or variable
flow. In the case of variable flow each machine must control its
own water pump and automatically shut down the pump, if the
cooling capacity is zero. For constant flow operation the pumps
for each unit are continuously operating, if the system is operating. The master unit can control a common pump that will be
activated, when the system is started. In this case the slave unit
pump is not used.
31
Page 32

5.21 - Optional heat reclaim module
6 - DIAGNOSTICS - TROUBLESHOOTING
Change-over procedure from cooling mode to heat reclaim
mode:
• Start-up of the condenser pump
• Verification of the condenser flow switch control contact.
If this remains open after one minute of condenser pump
operation, the circuit remains in cooling mode and alarm
79 for circuit A (alarm 80 for circuit B) will be activated.
• As soon as the saturated condensing temperature reaches
30°C, the pumpdown sequence is activated.
• Pumpdown: closing of the cooling mode coil shutoff valve.
Opening of the drain valve, closing of the EXV valve.
• When the pumpdown pressure reaches the end of the
pumpdown threshold, the pumpdown valve is closed and
the heat reclaim function is effective.
6.1 - General
The PRO-DIALOG Plus control system has many fault tracing
aid functions. The local interface and its various menus give
access to all unit operating conditions. The test function makes
it possible to run a quick test of all devices on the unit. If an
operating fault is detected, an alarm is activated and an alarm
code is stored in the Alarm menu.
6.2 - Displaying alarms
The alarm LEDs on the summary interface (see section 4.1)
give a quick display of the status of each circuit and the unit as
a whole.
• A flashing LED shows that the circuit is operating but
there is an alarm.
• A steady LED shows that the circuit has been shut down
due to a fault.
The Alarm menu on the main interface displays up to 5 fault
codes that are active on the unit.
6.3 - Resetting alarms
When the cause of the alarm has been corrected the alarm can
be reset, depending on the type, either automatically on return
to normal, or manually when action has been taken on the unit.
Alarms can be reset even if the unit is running.
This means that an alarm can be reset without stopping the
machine. In the event of a power supply interrupt, the unit
restarts automatically without the need for an external command. However, any faults active when the supply is interrupted are saved and may in certain cases prevent a circuit or a
unit from restarting.
A manual reset must be run from the main interface using the
following procedure:
RESET OF ACTIVE ALARMS
OPERATION ITEM NUMBER ITEM VALUE PRESS MENU
Hold down the MENU
button until the LED 0
for alarms lights. The
4-digit display shows 0 2 ALArM
the number of active
alarms (2 in this
example).
Press the Enter button 0 rESEt ALArM
until "rESEt ALARrM"
is shown in the 4-digit
display.
Press the Enter button 0 Good
again to validate the then, 2 AL
reset. "Good" is dis- then, no ALArM
played for 2 seconds
then, "2 ALArM" and
then, "no ALArM".
2-DIGIT DISPLAY 4-DIGIT DISPLAY BUTTON LED
32
Page 33

6.4 - Alarm codes
The following list gives a complete description of each alarm
code and its possible cause.
ALARM CODE DESCRIPTIONS
Code Alarm name Description Action Pumpdown Reset type Probable cause
1 Evaporator leaving water thermistor fault Thermistor outside range Unit shut down Yes Auto Thermistor or wiring fault or
2 Evaporator entering water thermistor fault Ditto Unit shut down Yes Auto Ditto
3 Condenser leaving water thermistor fault Ditto Heating mode: Unit shut down, Yes Auto Ditto
4 Condenser entering water thermistor fault Ditto Heating mode: Unit shut down, - Auto Ditto
5 Heat reclaim entering water thermistor fault Ditto Unit with heat recalaim option: - Auto Ditto
6 Heat reclaim leaving water thermistor fault Ditto None - Auto Ditto
7 Outdoor temperature sensor fault Ditto Reset: normal setpoint used. - Auto, if temp. mea- Thermistor faulty
8 CHWS (master/slave) fluid thermistor fault Ditto Deactivated - Ditto Themistor faulty
9 Suction thermistor fault, compressor A1 Ditto Circuit A shut down Yes Auto Ditto
10 Suction thermistor fault, compressor B1 Ditto Circuit B shut down Yes Auto Ditto
11 External 0-10 V dc signal fault Reset signal outside range Reset: normal setpoint used No Auto Signal incorrect, wiring error
12 Discharge pressure sensor fault, circuit A Voltage transmitted by incorrect sensor Circuit A shut down Yes Auto Sensor fault or wiring error
13 Discharge pressure sensor fault, circuit B Ditto Circuit B shut down Yes Auto Ditto
14 Suction pressure sensor fault, circuit A Ditto Circuit A shut down No Auto Ditto
15 Suction pressure sensor fault, circuit B Ditto Circuit B shut down No Auto Ditto
16 Oil pressure sensor fault, compressor A1 Ditto Circuit A shut down No Auto Ditto
17 Oil pressure sensor fault, compressor B1 Ditto Circuit B shut down No Auto Ditto
18 Oil pressure sensor fault, compressor A2 Ditto Compressor A2 shut down - Auto Ditto
19 Oil pressure sensor fault, compressor B2 Ditto Compressor B2 shut down - Auto Ditto
20 Oil pressure sensor fault, compressor A3 Ditto Compressor A3 shut down - Auto Ditto
21 Oil pressure sensor fault, compressor B3 Ditto Compressor B3 shut down - Auto Ditto
22 Oil pressure sensor fault, compressor A4 Ditto Compressor A4 shut down - Auto Ditto
23 Oil pressure sensor fault, compressor B4 Ditto Compressor B4 shut down - Auto Ditto
24 Pumpdown pressure sensor fault, circuit A Ditto If circuit is in heat reclaim - Auto, if press. mea-
25 Pumpdown pressure sensor fault, circuit B Ditto Ditto - Ditto Ditto
26 Loss of communication with compressor board A1 Communication with the compressor Circuit A shut down No Auto Wiring fault, faulty module,
27 Loss of communication with compressor board A2 Ditto Compressor A2 shut down No Auto Ditto
28 Loss of communication with compressor board A3 Ditto Compressor A3 shut down No Auto Ditto
29 Loss of communication with compressor board A4 Ditto Compressor A4 shut down No Auto Ditto
30 Loss of communication with compressor board B1 Ditto Circuit B shut down No Auto Ditto
31 Loss of communication with compressor board B2 Ditto Compressor B2 shut down No Auto Ditto
32 Loss of communication with compressor board B3 Ditto Compressor B3 shut down - Auto Ditto
33 Loss of communication with compressor board B4 Ditto Compressor B4 shut down - Auto Ditto
34 Loss of communication with EXV board Ditto Unit shut down No Auto Wiring bus faulty, incorrect
35 Loss of communication with NRCP board The board does not respond Unit shut down, if heat reclaim mode No Auto, if board is NRCP board faulty
36 Loss of communication with fan board 1 Ditto Unit shut down, if the number of No Auto Wiring bus faulty, incorrect
37 Loss of communication with fan board 2 Ditto Circuit B shut down No Auto Ditto
38 Loss of communication with 4xAI - 2xAO board 1 Ditto Unit shut down or no action No Auto Ditto, depending on
39 Loss of communication with 4xAI - 2xAO board 2 Ditto Compressors or circuit shut down No Auto Ditto, depending on
40 Pumpdown fault, circuit A End of pumpdown conditions not Circuit A shut down No Manual EXV or sensor faulty
41 Pumpdown fault, circuit B Ditto Circuit B shut down No Manual Ditto
42 Evaporator frost protection Unit operating: units shut down if Unit shut down No Auto first time, Low water flow or
43 Low evaporator water flow rate. Unit shut down No Manual Water pump faulty
44 Low suction temperature, circuit A Circuit operating: saturated suction Circuit A shut down No Manual Low charge, filter dirty
45 Low suction temperature, circuit B Ditto Circuit B shut down No Manual Ditto
46 High suction overheat, circuit A EXV fully open Circuit A shut down Yes Manual Ditto
47 High suction overheat, circuit B Ditto Circuit B shut down Yes Manual Ditto
48 Low suction overheat, circuit A EXV in min. position, and circuit Circuit A shut down Yes Manual EXV or thermistor or
board is lost incorrect module address
satisfied
temp. < defrost threshold. then manual thermistor defective
Unit shut down: if temp < threshold
and evaporator heater on for more
than 10 mins.
temp. < defrost threshold and < leaving ot thermistor faulty
water -16°C for more than 10 mins.
superheat below superheat setpoint transducer defective
-5.5 K, saturated suction temp. above
MOP for 5 mins.
if control on leaving water.
Cooling mode: no action
if control on entering water.
Cooling mode: no action
heat reclaim mode shut down,
unit changes over to standard
cooling mode. If not: no action
Limitation or reset deactivated. sured by sensor
Limitation or reset deactivated
mode, it goes to cooling mode. sured by sensor
If not, no action returns to normal
is selected again detected
fan stages per circuit is less than 3. address or board faulty
If not, circuit A shut down
returns to normal
bad connection
address or board faulty
configuration
configuration
33
Page 34

ALARM CODE DESCRIPTIONS
Code Alarm name Description Action Pumpdown Reset type Probable cause
49 Low suction overheat, circuit B Circuit B shut down Yes Manual Ditto
50 Low oil pressure, compressor A1 Oil pressure < min. threshold Circuit A shut down No Manual Compressor, crankcase
51 Low oil pressure, compressor B1 Ditto Circuit B shut down No Manual Ditto
52 Low oil pressure, compressor A2 Ditto Compressor A2 shut down Manual Ditto
53 Low oil pressure, compressor B2 Ditto Compressor B2 shut down Manual Ditto
54 Low oil pressure, compressor A3 Ditto Compressor A3 shut down Manual Ditto
55 Low oil pressure, compressor B3 Ditto Compressor B3 shut down Manual Ditto
56 Low oil pressure, compressor A4 Ditto Compressor A4 shut down Manual Ditto
57 Low oil pressure, compressor B4 Ditto Compressor B4 shut down Manual Ditto
58 Evaporator water flow control fault 1. Interlock not closed before end Unit shut down. No Manual Evaporator water flow fault
59 Low pressure fault, circuit A Circuit operating, and suction pressure Circuit A shut down No Auto first time, Low refrigerant charge, EXV
60 Low pressure fault, circuit B Ditto Circuit B shut down No Ditto Ditto
61 Repeated high pressure load sheds, circuit A More than 6 successive capacity load None No Auto Transducer faulty, condenser
62 Repeated high pressure load sheds, circuit B Ditto Ditto Ditto Ditto
63 High pressure switch not reset or reverse compressor The high pressure switch has not been Circuit A shut down No Manual The high pressure switch has
rotation, circuit A reset after a high pressure cut-out, not been reset, poor electrical
64 High pressure switch not reset or reverse compressor Ditto Circuit B shut down No Manual Ditto
rotation, circuit B
65 Control box thermostat fault Sensor overheat Unit shut down Manual Control box poorly
66 Loss of communication with System Manager Units controlled by SM, and Unit operates in autonomous mode Auto CCN network fault
67 Loss of communication with the master or slave Master/slave connection interrupted Unit operates in autonomous mode Auto CCN network fault
68 Master/slave configuration error Poor master/slave configuration Master/slave control not allowed Auto/manual in Master/slave configuration
69 Initial factory configuration necessary All factory parameters are at zero Unit prevented from starting Auto No factory configuration
70 Poor factory configuration. Poor factory configuration Ditto Ditto Factory configuration error
1. Compr. A3 configured and A2 absent
2. Compr. A4 configured and A2 or A3 absent
3. No lead compr. in circuit B
4. Compr. B3 configured and B2 absent
5. Compr. B4 configured and B2 or B3 absent
6. Difference of compressors in circ. A and B too high
7. Fan configured for a water-cooled condenser
8. No fans configured
9. Heat reclaim option configured, and heat reclaim
sensors not configured
71 CCN/Clock Board fault The CCN/Clock Board is no longer Unit shut down No Auto, if the board CCN/Clock Board faulty
72 Emergency stop An emergncy stop commend has been Unit shut down No CCN CCN network command
73 Pump No. 1 fault Evaporator water pump operating Unit shut down No Manual Pump overheat or poor
74 Pump No. 2 fault Ditto Unit shut down No Manual Ditto
75 Condenser anti-freeze protection, circuit A Saturated temperature is under the Unit shut down. Condenser pump No Auto Discharge pressure trans-
76 Condenser anti-freeze protection, circuit B Ditto Ditto No Auto Ditto
77 Lack of water flow, condenser Water flow switch (water-cooled units) Unit shut down No Manual Condenser pump, low water
78 Condenser water flow fault, heat reclaim mode Ditto Units stays in cooling mode No Manual Ditto
of start-up delay Pump shut down
2. Pump shut down for 2 mins
and water flow contact closed
below permitted threshold for more then manual* faulty or filter dirty
than 3 mins.
sheds in the circuit due to exceeded ent. air temp., evaporator ent.
high pressure water temp. too high, cond.
or the lead compressor does not work connection of lead compr.
communication with the module over
2 mins. faulty
beween the two units for more than
2 mins.
case of heating/ fault
cooling fault
detected is again detected
transmitted by the CCN network.
contact open, when the pump has pump connection
received a commmand to operate.
frost cut-out point started, if unit is shut down ducer faulty, refrigerant leak,
not closed for 1 min. flow, water flow switch
heater, pressure sensor or
EXV faulty, refrigerant
charge too high, low oil
charge
blocked or fan flow rate too
low
ventilated
or low cond. water temp.
79 Heat reclaim mode fault, circuit A More than two consecutive pumpdown Circuit A stays in cooling mode No Manual Leak or heat reclaim or drain
80 Heat reclaim mode fault, circuit B Ditto Circuit B stays in coolng mode No Manual Ditto
81 High pressure fault, circuit A Circuit operating and discharge pressure Unit shut down No Manual, the high Fan circuit fault, air or
82 High pressure fault, circuit B Ditto Ditto No Ditto Ditto
83 Maintenance alert A maintenance alert is active None Manual
1. Charge too low
2. Water loop too low
3. Air filter maintenance delay elapsed
4. Pump 1 maintenance delay elapsed
5. Pump 2 maintenance delay elapsed
6. Water filter maintenance delay elapsed
sequences not successful solenoid shut-off valve fault
exceeds the high pressure cut-out point pressure command condenser temperature too
must be reset high
manually by the
button on the HP
pressure switch
34
Page 35

6.4.1 - Compressor faults
6.4.1.1 - General
Each compressor is protected against multiple faults by two
DGT (only for units with low-temperature option):
The discharge gas thermostat detects and protects the
compressor against abnormally high discharge temperatures.
digital inputs located on the control board. If one of these
inputs opens, it causes an immediate shutdown on the
compressor without any action from the basic board.
Starter Guard:
This board patented by Carrier (also called AM board)
monitors both the compressor regime and the status of its
6.4.1.2 - Compressor protection devices
On PRO-DIALOG Plus units, compressors are individually
crankcase heaters which ensure correct lubrication when the
compressor starts.
protected by the following devices connected to the digital
inputs on the compressor control board:
ALARM CODE DESCRIPTIONS
Code Alarm name Action Pumpdown Reset type Probable cause
101 DGT fault, compressor A1 Circuit A shut down No Manual Hot gas thermostat contact open
102 Starter Guard fault compressor A1 Circuit A shut down No Ditto Crankcase heater fault and open motor current
201 DGT fault, compressor A2 Compressor A2 shut down Ditto Hot gas thermostat contact open
202 Starter Guard fault compressor A 2 Compressor A2 shut down Ditto Crankcase heater fault and open motor current
301 DGT fault, compressor A3 Compressor A3 shut down Ditto Hot gas thermostat contact open
302 Starter Guard fault compressor A 3 Compressor A3 shut down Ditto Crankcase heater fault and open motor current
401 DGT fault, compressor A4 Compressor A4 shut down Ditto Hot gas thermostat contact open
402 Starter Guard fault compressor A 4 Compressor A4 shut down Ditto Crankcase heater fault and open motor current
501 DGT fault, compressor B1 Circuit B shut down No Ditto Hot gas thermostat contact open
502 Starter Guard fault compressor B1 Circuit B shut down No Ditto Crankcase heater fault and open motor current
601 DGT fault, compressor B2 Compressor B2 shut down Ditto Hot gas thermostat contact open
602 Starter Guard fault compressor B 2 Compressor B2 shut down Ditto Crankcase heater fault and open motor current
701 DGT fault, compressor B3 Compressor B3 shut down Ditto Hot gas thermostat contact open
702 Starter Guard fault compressor B3 Compressor B3 shut down Ditto Crankcase heater fault and open motor current
801 DGT fault, compressor B4 Compressor B4 shut down Ditto Hot gas thermostat contact open
802 Starter Guard fault compressor B4 Compressor B4 shut down Ditto Crankcase heater fault and open motor current
fault detection board contact
fault detection board contact
fault detection board contact
fault detection board contact
fault detection board contact
fault detection board contact
fault detection board contact
fault detection board contact
35
Page 36

36
Order No. 13040-76, 05.2000. Supersedes order No.: New Manufactured by: Carrier S.A., Montluel, France.
Manufacturer reserves the right to change any product specifications without notice. Printed in the Netherlands on totally chlorine-free paper.
 Loading...
Loading...