Page 1

48DJ,DK,NP034-074
50DJ,DK,DW,DY,NB,NP034-074
Single Package Heating and Cooling Units
Installation, Start-Up and
Service Instructions
CONTENTS
Page
GENERAL ...................................2
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS ...................2
INSTALLATION .............................2-37
Rigging and Unit Placement ..................2
Roof Curb ...................................2
Roof Mount ..................................2
Slab Mount ..................................2
Positioning ..................................3
Field-Fabricated Ductwork ....................6
Condensate Drains ..........................10
Install Outdoor Hoods .......................10
• UNIT SIZES 034 AND 044
• UNIT SIZES 054-074
Outdoor-Air Inlet Adjustments ...............10
• MANUAL OUTDOOR-AIR DAMPER
• ECONOMIZER SETTINGS
Field Wire Routing ..........................17
• UNIT SIZES 034 AND 044
• UNIT SIZES 054-074
Field Electrical Connections .................17
• POWER WIRING
• CONTROL WIRING
Gas Piping (48 Series Units Only) ............36
Installing Flue/Inlet Hoods (48 Series Units
Only) ......................................36
• UNIT SIZES 034 AND 044
• UNIT SIZES 054-074
PRE-START-UP ............................38-41
Unit Preparation ............................38
Compressor Mounting .......................38
Evaporator-Fan Shipping Brackets ...........38
• UNIT SIZES 034 AND 044
• UNIT SIZES 054-074
Internal Wiring ..............................38
Refrigerant Service Valves ...................38
Crankcase Heaters ..........................38
Compressor Oil .............................38
Gas Manifold Pressure (48 Series
Units Only) ................................39
Unit Voltage ................................39
Leak Test and Dehydration ..................39
Evaporator-Fan Belts, Pulleys, and Sheaves ..39
Condenser Fans and Motors .................40
Return-Air Filters ...........................40
Economizer Inlet Screens ...................40
Economizer Dampers .......................40
25% Outdoor-Air Damper ....................40
Initial Check ................................41
START-UP .................................41,42
General .....................................41
Operating Sequences .......................41
• COOLING, UNITS WITHOUT ECONOMIZER
• HEATING, UNITS WITHOUT ECONOMIZER
• COOLING, UNITS WITH ECONOMIZER
Page
• HEATING, UNITS WITH ECONOMIZER
• VENTILATION AIR CIRCULATION (Continuous Fan)
• AUTOMATIC CHANGEOVER USING AUTOMATIC
CHANGEOVER THERMOSTAT
Head Pressure Control ......................42
SERVICE ..................................42-53
Service Access .............................42
• COMPRESSORS
• LIQUID SERVICE VALVES, FILTER DRIERS, AND
SIGHT GLASSES
• EVAPORATOR-FAN MOTORS, PULLEYS, AND
BELTS
• POWER EXHAUST MOTORS, PULLEYS, AND
BELTS
• UNIT CONTROL BOX
• GAS HEAT SECTION (48 Series Units Only)
• MAIN AND PILOT BURNERS (48 Series Units Only)
• FLUE GAS PASSAGEWAYS (48 Series Units Only)
• COMBUSTION AIR BLOWER (48 Series Units Only)
• ECONOMIZER DAMPER MOTOR
• ELECTRIC HEATER CONTROL BOX (50 Series
Units Only)
• HEATER BOX (50 Series Units Only)
• 25% OUTDOOR-AIR DAMPER
• MODULATING POWER EXHAUST DAMPER
MOTOR
• RETURN-AIR FILTERS
• CONDENSER FANS AND FAN MOTORS
• INLET GUIDE VANE MOTOR
Cleaning ....................................45
Lubrication .................................45
• COMPRESSORS
• FAN SHAFT BEARINGS
• INLET GUIDE VANE BEARINGS (Units With
Optional Inlet Guide Vanes)
• FAN MOTOR BEARINGS
• DOOR HINGES
Adjustments ................................46
• EVAPORATOR FAN AND POWER EXHAUST
MOTOR PLATE
• MODULATING POWER EXHAUST DIFFERENTIAL
PRESSURE SWITCH
• INLET GUIDE VANE DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE
SWITCH (Units With Optional Inlet Guide Vanes and
Static Pressure Control)
• BELT INSTALLATION AND TENSIONING
• PULLEY ALIGNMENT
• INSTALLING ALTERNATE MOTOR PULLEY
(Evaporator Fan Only)
• CONDENSER FAN ADJUSTMENT
• 25% OUTDOOR-AIR DAMPER
• REFRIGERANT CHARGE
• PILOT LIGHT OFF (48 Series Units Only)
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 1
Tab 1a 1b
PC 111 Catalog No. 564-818 Printed in U.S.A. Form 48/50D,N-9SI Pg 1 3-96 Replaces: 48DJ,DK-3SI;
48/50NB,NP-1SI; 50DJ,DK-9SI
Page 2

CONTENTS (cont)
• AUTOMATIC PILOT ADJUSTMENT (48 Series
Units Only)
• GAS VALVE ADJUSTMENT (48 Series Units Only)
• MAIN BURNER ADJUSTMENT (48 Series
Units Only)
Main Burner Removal (48 Series Units Only) ..50
Switch Adjustment .........................50
Refrigerant Feed Components ...............50
Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) .........50
Moisture/Liquid Indicator ....................51
Filter Drier ..................................51
Liquid Line Service Valve ....................51
Compressor Discharge Service Valve ........51
Compressor Suction Service Valve ...........51
Protective Devices ..........................51
• COMPRESSOR PROTECTION
• EVAPORATOR-FAN MOTOR PROTECTION
• CONDENSER-FAN MOTOR PROTECTION
• HIGH- AND LOW-PRESSURE SWITCHES
Relief Devices ..............................51
Control Circuit, 115 V .......................52
Control Circuit, 24 v .........................52
Electric Heat (50 Series Units Only) ..........52
• OVERCURRENT
• OVERTEMPERATURE
Gas Heat (48 Series Units Only) ..............52
• LIMIT SWITCHES
• ROLLOUT SWITCH
TROUBLESHOOTING ......................52-69
Economizer .................................52
• ECONOMIZER MOTOR CHECKOUT
• ECONOMIZER CONTROL BOARD CHECKOUT
Unit Control Board Checkout ................53
• BASIC CHECK
• DETAILED CHECK
START-UP CHECKLIST .....................CL-1
Before performing service or maintenance operations on
unit, turn offmain power switch to unit. Electrical shock
could cause personal injury.
Do not try to light any appliance. Do not touch any electrical switch; do not use any phone in your building.
Immediately call your gas supplier from a neighbor’s
phone. Follow the gas supplier’s instructions. If you cannot reach your gas supplier, call the fire department.
Do not store or use gasoline or other flammable vapors
and liquids in the vicinity of this or any other appliance.
Improper installation, adjustment, alteration, service, or
maintenance can cause injury or property damage. Refer to this manual. For assistance or additional information, consult a qualified installer, service agency, or
the gas supplier.
Disconnect gas piping from 48 Series units when leak
testing at pressures greater than 0.5 psig. Pressures greater
than 0.5 psig will cause gas valve damage resulting in
a hazardous condition. If gas valve is subjected to pressure greater than 0.5 psig, it must be replaced. When
pressure testing field-supplied gas piping at pressures of
0.5 psig or less, the unit connected to such piping must
be isolated by manually closing the gas valve.
GENERAL
This installation instruction contains base unit installation, start-up, and service instructions only. For complete information on PIC (Product Integrated Controls) and variableair volume (VAV) controls and troubleshooting, refer to
appropriate Controls and Troubleshooting literature also enclosed in this literature packet.
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air-conditioning equipment
can be hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only trained and qualified service personnel should
install, repair, or service air-conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions of cleaning coils and filters and replacing filters. All
other operations should be performed by trained service personnel. When working on air-conditioning equipment, observe precautions in the literature, tags and labels attached
to the unit, and other safety precautions that may apply.
Follow all safety codes, including ANSI (American National Standards Institute) Z223.1. Wear safety glasses and
work gloves. Use quenching cloth for unbrazing operations.
Have fire extinguisher available for all brazing operations.
INSTALLATION
Riggingand UnitPlacement —
portation damage. File claim with transportation agency. Do
not drop unit; keep upright. Use spreader bars over unit to
prevent sling or cable damage. Sheets of plywood placed along
the condenser coils will provide additional protection. All
lifting lugs MUST be used when lifting unit. Level by using
unit frame as a reference. See Fig. 1 for information. Unit
and accessory weights are shown in Tables 1A, 1B, and 2.
Weight distribution and center of gravity can be found in
Fig. 2.
Inspect unit for trans-
Roof Curb — Assemble and install as described in in-
structions shipped with the accessory. Accessory roof curb
and information required to field fabricate a roof curb is shown
in Fig. 3A-3C. Install insulation, cant strips, roofing and counter
flashing as required. For unit condensate drains to function
properly, curb must be level or within tolerances shown in
Fig. 3A-3C.
Roof Mount — Check building codes for weight distri-
bution requirements. Unit weight is shown in Tables 1A and
1B. Unit may be mounted on class A, B, or C roofing
material.
Slab Mount — Provide a level concrete slab that ex-
tends beyond unit cabinet at least 6 inches. Make a slab 8 in.
thick with 4 in. above grade. Use gravel apron in front of
condenser coil air inlet to prevent grass and foliage from obstructing airflow.
2
Page 3
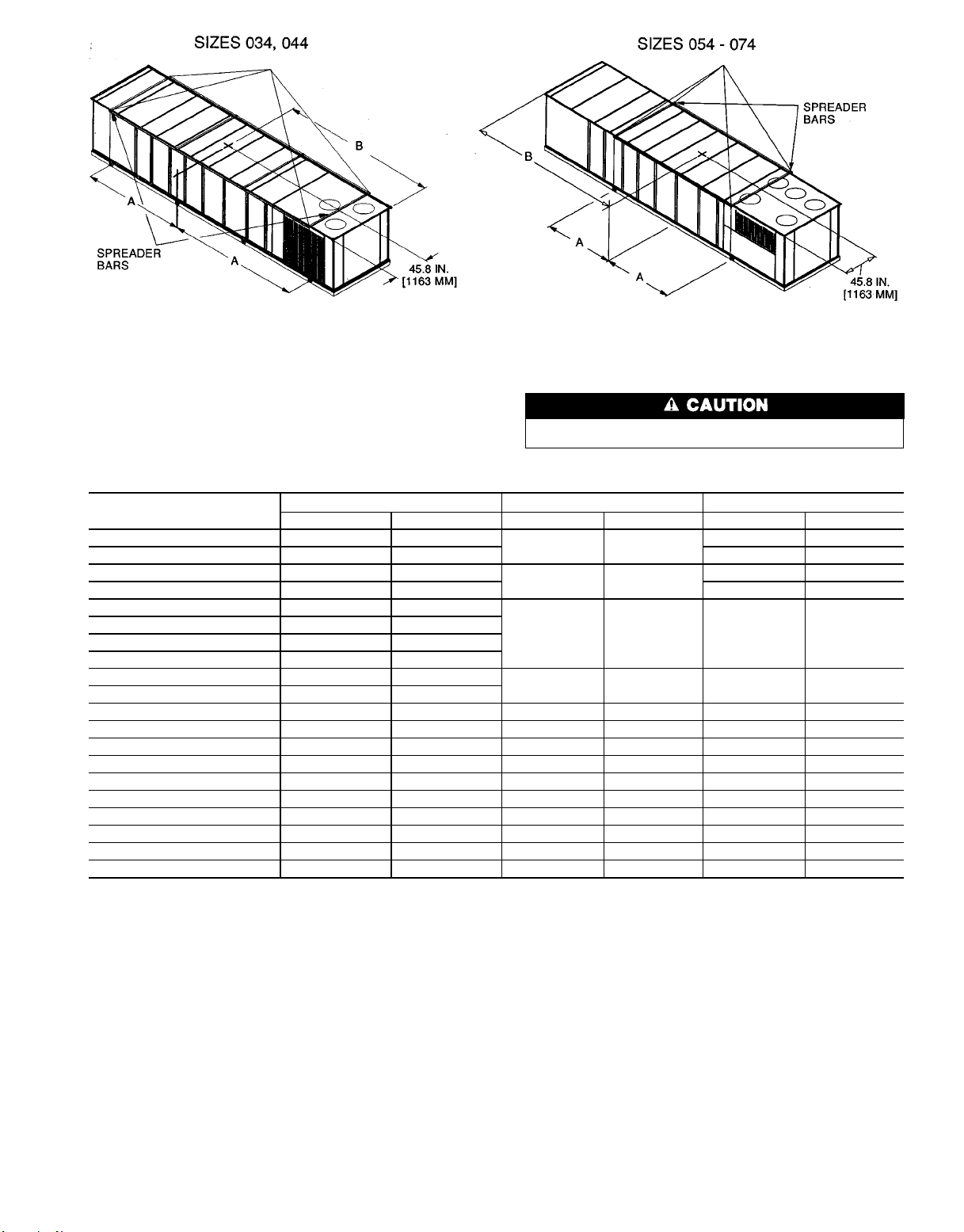
NOTES:
1. Sizes 034,044:Rigwith4 cables and spread with two 95 in. (2413 mm) and
2 8A 1 A8 long spreader bars.
Sizes 054-074:Rigwith 4 cables and spread withfour 95 in. (2413 mm) and
2 8A 1 B 1 A8 long spreader bars.
2. Center of gravity includes economizer.
RIGGING WEIGHTS AND DIMENSIONS
1. All panels must be in place when rigging.
2. Unit is not designed for handling by forklift truck.
UNIT
48DJD,DKD,NPD034 5941 2694.8
48DJE,NPE034 6070 2753.4 110.4 2804
48DJD,DKD,NPD044 6841 3103.1
48DJE,NPE044 6970 3161.6 128.6 3267
48DJD,DKD,NPD054 9230 4186.7
48DJE,NPE054 9350 4241.2
48DJD,DKD,NPD064 9530 4322.8
48DJE,NPE064 9650 4377.2
48DJD,DKD,NPD074 9950 4513.3
48DJE,NPE074 10,080 4572.3
50DJ,DK,NP034 5700 2585.5 84.8 2153 120.8 3067
50DW,DY,NB034 6270 2844.1 76.4 1940 102.5 2604
50DJ,DK,NP044 6350 2880.4 92.6 2353 126.6 3216
50DW,DY,NB044 6920 3138.9 86.0 2185 108.4 2753
50DJ,DK,NP054 8230 3733.1 120.8 3066 126.8 3221
50DW,DY,NB054 8780 3982.6 109.0 2769 109.0 2769
50DJ,DK,NP064 8530 3869.2 120.9 3071 120.9 3071
50DW,DY,NB064 9080 4119.7 120.8 3066 126.8 3221
50DJ,DK,NP074 8960 4064.3 131.7 3345 137.6 3495
50DW,DY,NB074 9500 4309.2 109.0 2769 109.0 2769
*Includes optional economizer.
UNIT WEIGHT* A B
Lb Kg in. mm in. mm
86.0 2185
92.6 2353
121.5 3086 126.8 3221
134.7 3421 134.7 3421
Fig. 1 — Rigging Label
109.4 2780
127.6 3240
If roof curb is not used, support unit with steel beams along
its entire length and then support steel as required.As a minimum, unit must be supported across its width at each lifting
lug location.
Positioning — Provideclearance around and above unit
for airflow,safety,and service access. Do not restrict top (area
above condenser fans) in any way. Allow at least 6 ft on all
sides for rated performance, code compliance, and service.
Do not install unit in an indoor location. Do not locate air
inlets near exhaust vents or other sources of contaminated
air.
On units equipped with or power exhaust option, high velocity air is exhausted out the hoods. Unit should be positioned with at least 10 ft clearance between the exhaust hoods
and any obstruction. Although unit is weatherproof, guard
against water from higher level runoff and overhangs.
3
Page 4
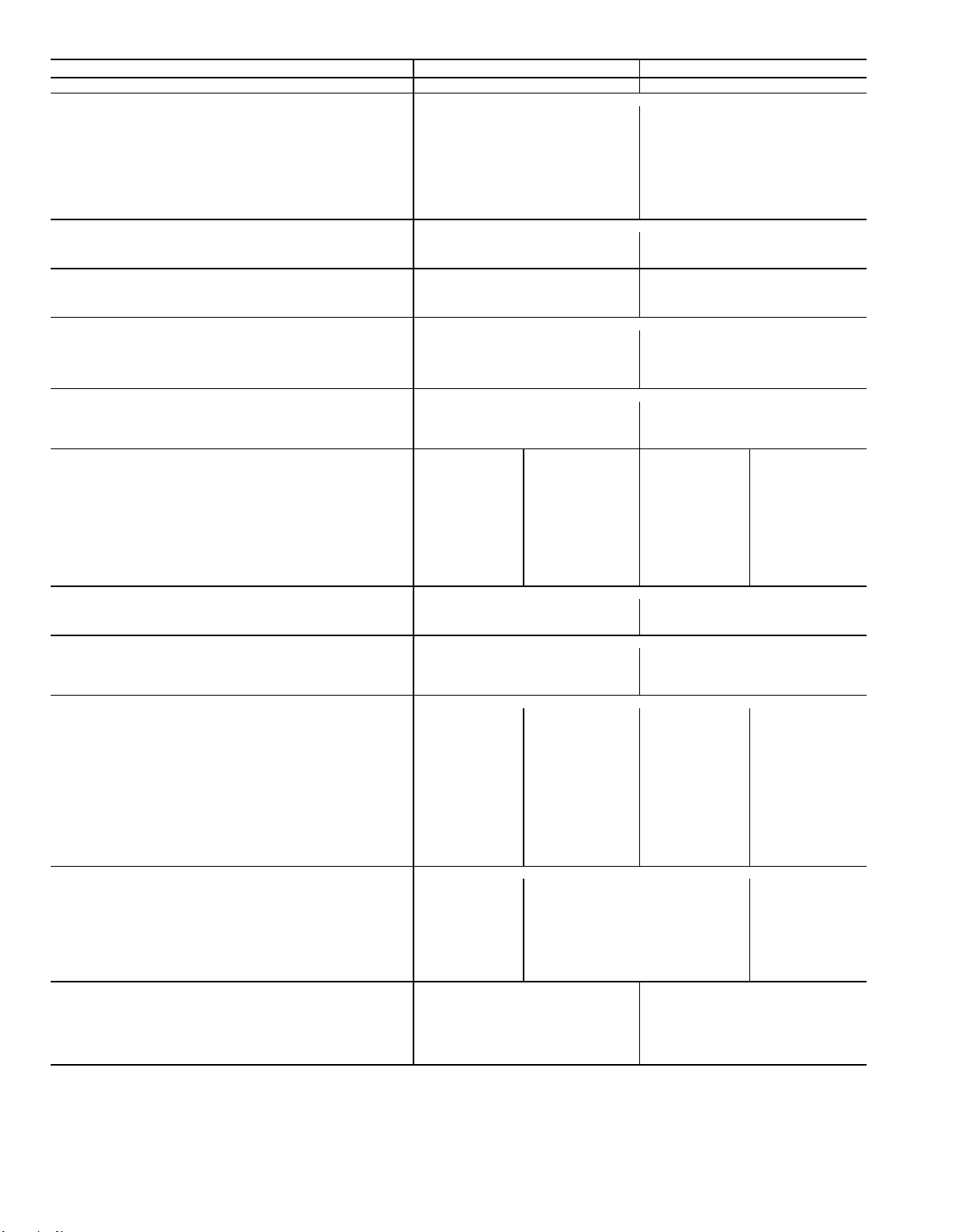
Table 1A — Physical Data; 034, 044 Units
BASE UNIT* 034 044
NOMINAL CAPACITY (tons) 30 40
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)
Base Unit
48 Series, Low Heat 5641 6541
48 Series, High Heat
50 Series, Horizontal Discharge 5970 6620
50 Series, Vertical Discharge 5400 6050
With Economizer
48 Series, Low Heat 5941 6841
48 Series, High Heat 6070 6970
50 Series, Horizontal Discharge 6270 6920
50 Series, Vertical Discharge 5700 6350
COMPRESSORS
Quantity...Type 2...06D 2...06E
Capacity Steps (%) 17, 33, 50, 66, 83, 100 25, 50, 75, 100
Number of Refrigerant Circuits 22
REFRIGERANT
Operating Charge (lb), Sys 1/Sys 2
Without Hot Gas Bypass
With Hot Gas Bypass 31.0/29.0 42.0/40.0
CONDENSER COILS
Quantity 22
Rows...Fins/in.
Aluminum
Copper (Optional) 3...13.7 3...13.7
Total Face Area (sq ft) 37.5 50.0
EVAPORATOR COILS
Quantity
Rows...Fins/in. 3...15.0 3...15.0
Total Face Area (sq ft) 32.1 45.5
Refrigerant Feed Device...No. per Circuit TXV...1 TXV...2
HEATING SECTION (48 Series Units Only) Low Heat High Heat Low Heat High Heat
Number of Heat Exchangers
Input (MBtuh) 264 529 264 529
Output (MBtuh) 211 423 211 423
Temperature Rise Range (F) 0-30 15-45 0-30 15-45
Efficiency (%) 79 79 79 79
Burner Orifice Diameter
Quantity (in. ...drill no.) 6 (.1285...30) 12 (.1285...30) 6 (.1285...30) 12 (.1285...30)
Pilot Orifice Diameter
Quantity (in. ...drill no.) 1 (.076...48) 2 (.076...48) 1 (.076...48) 2 (.076...48)
Firing Stages 2222
Number of Gas Valves
CONDENSER FANS Propeller Type
Quantity...Diameter (in.) 2...30 3...30
Nominal Cfm 18,600 26,000
Motor Hp...Rpm 1.0...1140 1.0...1140
EVAPORATOR FAN Centrifugal 25 x 25 in.
Nominal Cfm 10,500 14,000
Maximum Allowable Cfm 15,000 20,000
Maximum Allowable Rpm 900 900
Shaft Diameter at Pulley (in.) 1
EVAPORATOR-FAN MOTOR AND DRIVE (Any motor available on any unit)
Motor Hp 7.5 10.0 15.0 20.0
Motor Frame Size 213T 215T 254T 256T
Efficiency at Full Load (%)
Standard Efficiency 82.9 85.6 84.5 87.5
High Efficiency† — 89.5 90.0 91.0
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 13.7 13.7 13.7 13.7
Motor Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 34.4 4.3 4.9 5.5
Resulting Fan Rpm 405 510 580 660
Belts Quantity...Model No.
48 Series and 50 Series, Horizontal Discharge 2...BX60 2...5VX630 2...5VX630 2...5VX630
50 Series, Vertical Discharge 2...BX60 2...5VX630 2...5VX630 2...5VX630
Center Distance Range (in.)
48 Series and 50 Series, Horizontal Discharge 17.74...14.30 17.74...14.30 17.63...14.01 17.63...14.01
50 Series, Vertical Discharge 19.86...15.87 19.86...15.87 19.04...15.00 19.04...15.00
OPTIONAL POWER EXHAUST Centrifugal, 15 x 15 in. (Any motor available on any unit)
Quantity...Motor Hp 2...3.0 2...5.0 2...7.5
Motor Frame Size 56HZ 184T 213T
Efficiency at Full Load (%) 81.0 84.0 82.9
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 6.9 6.9 6.9
Motor Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 3.35 4.12 5.0
Shaft Diameter at Pulley (in.) 1
Resulting Fan Rpm 843 1040 1264
Maximum Allowable Rpm 1300 1300 1300
Belts Quantity...No. 2...3VX670 2...3VX670 2...3VX710
FILTERS
Standard Efficiency Throwaway (Standard) 12...20 x 25 x 2 12...20 x 25 x 2
Quantity...Size (in.) 4...16 x 20 x 2 4...16 x 20 x 2
Medium Efficiency (30%) Pleated (Optional) 12...20 x 25 x 2 12...20 x 25 x 2
Quantity...Size (in.) 4...16 x 20 x 2 4...16 x 20 x 2
High Efficiency (90%) Bag Filters with Prefilters (Optional) 6...20 x 24 x 22 6...20 x 24 x 22
Quantity...Size (in.) 6...20 x 20 x 22 6...20 x 20 x 22
612612
1212
3
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
*Data is for all 48 and 50 Series units of the size listed unless otherwise specified.
†Not available on 575-v units.
5770 6670
Semi-Hermetic
29.0/29.0 40.0/40.0
3
⁄8-in. Tube Diameter
3...15.0 3...15.0
1
12
11
⁄
16
⁄
16
⁄2-in. Tube Diameter
13⁄
16
111⁄
16
13⁄
16
4
Page 5
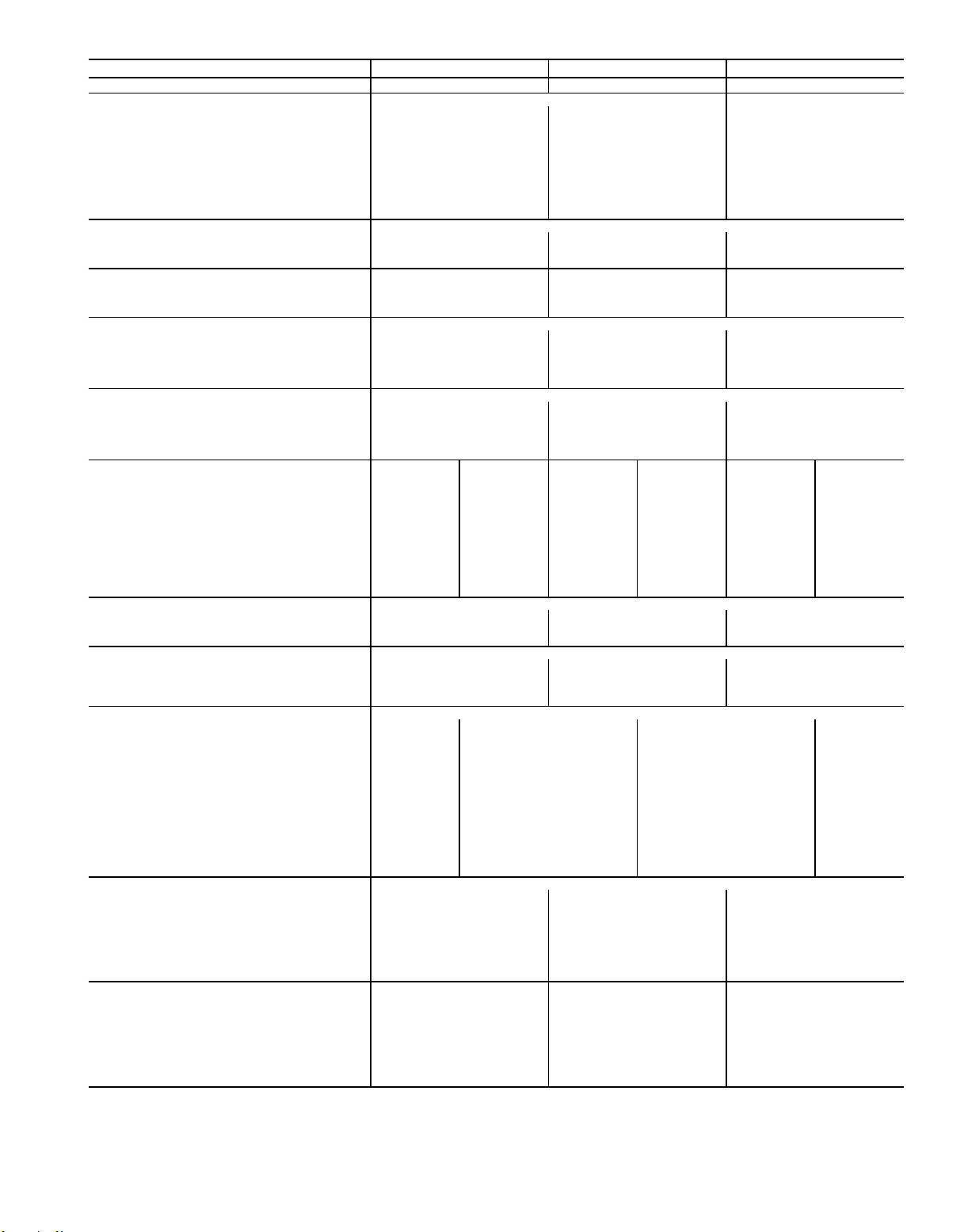
Table 1B — Physical Data; 054-074 Units
BASE UNIT* 054 064 074
NOMINAL CAPACITY (tons) 50 60 75
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)
Base Unit
48 Series, Low Heat 8700 9000 9420
48 Series, High Heat 8820 9120 9550
50 Series, Horizontal Discharge 8250 8550 8970
50 Series, Vertical Discharge 7700 8000 8430
With Economizer
48 Series, Low Heat 9230 9530 9950
48 Series, High Heat 9350 9650 10,080
50 Series, Horizontal Discharge 8780 9080 9500
50 Series, Vertical Discharge 8230 8530 8960
COMPRESSORS Semi-Hermetic
Quantity...Type 2...06E 2...06E 2...06E
Capacity Steps (%) 20, 40, 60, 80, 100 17, 33, 50, 66, 83, 100 14, 28, 43, 71, 85, 100
Number of Refrigerant Circuits 222
REFRIGERANT
Operating Charge (lb), Sys 1/Sys 2
Without Hot Gas Bypass 59.0/44.5 61.0/61.0 70.5/64.5
With Hot Gas Bypass 62.0/44.5 64.0/61.0 73.5/64.5
CONDENSER COILS
Quantity 444
Rows...Fins/in.
Aluminum 2...17.0, 3...17.0 3...17.0 3...17.0
Copper (Optional) 2...15.7, 3...15.7 3...15.7 3...15.7
Total Face Area (sq ft) 72.4 72.4 108.4
EVAPORATOR COILS
Quantity 222
Rows...Fins/in. 3...17.0 4...17.0 4...17.0
Total Face Area (sq ft) 61.5 61.5 61.5
Refrigerant Feed Device...
No. per Circuit
HEATING SECTION (48 Series Units Only) Low Heat High Heat Low Heat High Heat Low Heat High Heat
Number of Heat Exchangers 12 18 12 18 12 18
Input (MBtuh) 540 810 540 810 540 810
Output (MBtuh) 432 648 432 648 432 648
Temperature Rise Range (F) 5-35 15-45 5-35 15-45 5-35 15-45
Efficiency (%) 80 80 80 80 80 80
Burner Orifice Diameter
Quantity (in. ...drill no.) 12 (.1285...30) 18 (.1285...30) 12 (.1285...30) 18 (.1285...30) 12 (.1285...30) 18 (.1285...30)
Pilot Orifice Diameter
Quantity (in. ...drill no.) 2 (.076...48) 3 (.076...48) 2 (.076...48) 3 (.076...48) 2 (.076...48) 3 (.076...48)
Firing Stages 222222
Number of Gas Valves 232323
CONDENSER FANS Propeller Type
Quantity...Diameter (in.) 4...30 4...30 5...30
Nominal Cfm 40,000 40,000 50,000
Motor Hp...Rpm 1.0...1140 1.0...1140 1.0...1140
EVAPORATOR FAN Centrifugal 30 x 27 in.
Nominal Cfm 17,500 21,000 24,500
Maximum Allowable Cfm 25,000 30,000 30,000
Maximum Allowable Rpm 750 750 750
Shaft Diameter at Pulley (in.) 1
EVAPORATOR-FAN MOTOR AND DRIVE (Any motor available on any unit)
Motor Hp 15.0 20.0 25.0 30.0
Motor Frame Size 254T 256T 284T 286T
Efficiency at Full Load (%)
Standard Efficiency 84.5 87.5 87.1 88.3
High Efficiency† 90.0 91.0 91.7 92.4
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 13.7 13.7 13.7 15.5
Motor Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 4.5 5.1 5.5 5.9
Resulting Fan Rpm 555 625 660 700
Belts Quantity...Model No.
48 Series and 50 Series, Horizontal Discharge 2...5VX1120 2...5VX1150 2...5VX1150 2...5VX1180
50 Series, Vertical Discharge 2...5VX1230 2...5VX1230 2...5VX1230 2...5VX1230
Center Distance Range (in.)
48 Series and 50 Series, Horizontal Discharge 48.25...44.00 48.25...44.00 48.50...44.25 48.50...44.25
50 Series, Vertical Discharge 44.25...39.75 44.25...39.75 44.00...40.00 44.00...40.00
OPTIONAL POWER EXHAUST Centrifugal, 18 x 15 in. (Any motor available on any unit)
Quantity...Motor Hp 2...5.0 2...7.5 2...10.0
Motor Frame Size 184T 213T 215T
Efficiency at Full Load (%) 84.0 82.9 85.6
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 10.6 10.6 10.6
Motor Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 4.5 5.0 5.6
Shaft Diameter at Pulley (in.) 1
Resulting Fan Rpm 740 820 920
Maximum Allowable Rpm 925 925 925
FILTERS
Standard Efficiency
Throwaway (Standard) 15...20 x 25 x 2 15...20 x 25 x 2 15...20 x 25 x 2
Quantity...Size (in.) 5...16 x 20 x 2 5...16 x 20 x 2 5...16 x 20 x 2
Medium Efficiency (30%) Pleated (Optional) 15...20 x 25 x 2 15...20 x 25 x 2 15...20 x 25 x 2
Quantity...Size (in.) 5...16 x 20 x 2 5...16 x 20 x 2 5...16 x 20 x 2
High Efficiency (90%) Bag Filters
with Prefilters (Optional) 6...20 x 24 x 22 6...20 x 24 x 22 6...20 x 24 x 22
Quantity...Size (in.) 6...24 x 24 x 22 6...24 x 24 x 22 6...24 x 24 x 22
TXV...2 TXV...2 TXV..2
11
⁄
16
7
⁄
16
TXV — Thermostatic Expansion Valve
*Data is for all 48 and 50 Series units of the size listed unless otherwise specified.
†Not available on 575-v units.
3
⁄8-in. Tube Diameter
1
⁄2-in. Tube Diameter
111⁄
16
17⁄
16
111⁄
17⁄
16
16
5
Page 6
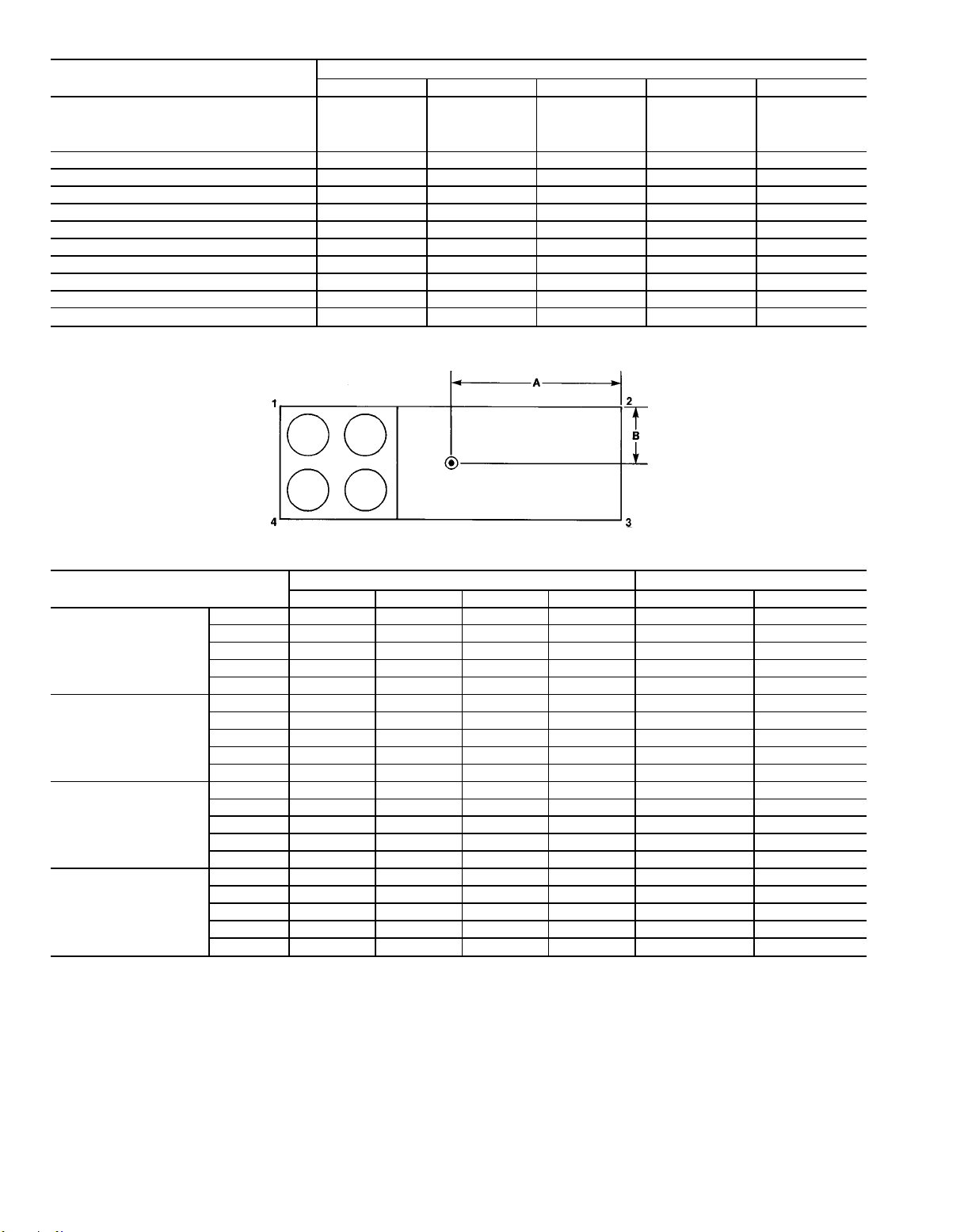
Table 2 — Operating Weights of Options and Accessories
OPTION OR ACCESSORY
Roof Curb
Condenser Section Roof Curb — — 540 540 625
Economizer 300* 300* 530* 530* 530*
Power Exhaust 600* 600* 710* 710* 710*
Barometric Relief 200 200 200 200 200
High-Efficiency Filters 20 20 20 20 20
Bag filters 35 35 40 40 40
Hail Guard 120 150 145 145 210
Copper Condenser Coil Fins 180 235 235 235 420
Electric Heat† 150 150 150 150 150
Inlet Guide Vanes 95 95 115 115 115
*Includes hood.
†50 Series vertical discharge units.
48DJ,DK,NP
50DW,DY,NB
50DJ,DK,NP
034 044 054 064 074
450
450
380
480
480
465
UNIT SIZE
515
560
515
515
560
515
515
560
515
UNIT
034 1754 1213 1216 1758 14- 9 3- 8
044 2035 1382 1385 2039 17- 3 3- 8
48DJD,DKD,NPD
48DJE,NPE
50DW,DY,NB
50DJ,DK,NP
NOTE: Weights include economizer.
054 2334 2276 2281 2339 19- 7 3-10
064 2431 2328 2334 2437 19- 7 3-10
074 2452 2518 2523 2457 21- 0 3-10
034 1781 1251 1253 1785 14- 8 3-10
044 2057 1424 1428 2061 17- 2 3-10
054 2375 2295 2300 2380 19- 7 3-10
064 2393 2373 2378 2506 19- 7 3-10
074 2494 2541 2546 2499 21- 0 3-10
034 1864 1268 1271 1867 13- 3 3-10
044 2070 1387 1389 2074 15-10 3-10
054 2381 2005 2009 2385 19-10 3-10
064 2461 2074 2078 2467 19-10 3-10
074 2551 2194 2199 2556 21- 3 3-10
034 1674 1173 1175 1678 13- 9 3-10
044 1879 1292 1295 1884 16- 3 3-10
054 2090 2021 2025 2094 18- 2 3-10
064 2188 2073 2077 2192 18- 2 3-10
074 2212 2263 2269 2216 21- 3 3-10
UNIT CENTER OF GRAVITYAND CORNER WEIGHTS
CORNER WEIGHT (lb) DIMENSIONS (Ft-in.)
1234 A B
Fig.2—Weight Distribution and Center of Gravity
Field-FabricatedDuctwork — Units are designed for
vertical supply/return only.Field-fabricated ductwork should
be attached to the roof curb. Supply and return duct dimensions are shown in Fig. 3A-3C.
To attach ductwork to roof curb, insert duct approximately 10 to 11 in. up into roof curb. Connect ductwork to
14-gage roof curb material with sheet metal screws driven
from inside of the duct.
Secure all ducts to the building structure, using flexible
duct connectors between roof curb and ducts as required. Ducts
passing through an unconditioned space must be insulated
and covered with a vapor barrier. Outlet grilles must not lie
directly below unit discharge. The return duct must have a
90-degree elbow before opening into the building space if
unit is equipped with power exhaust.
Design supply duct strong enough to handle expected static
pressures.
6
Page 7
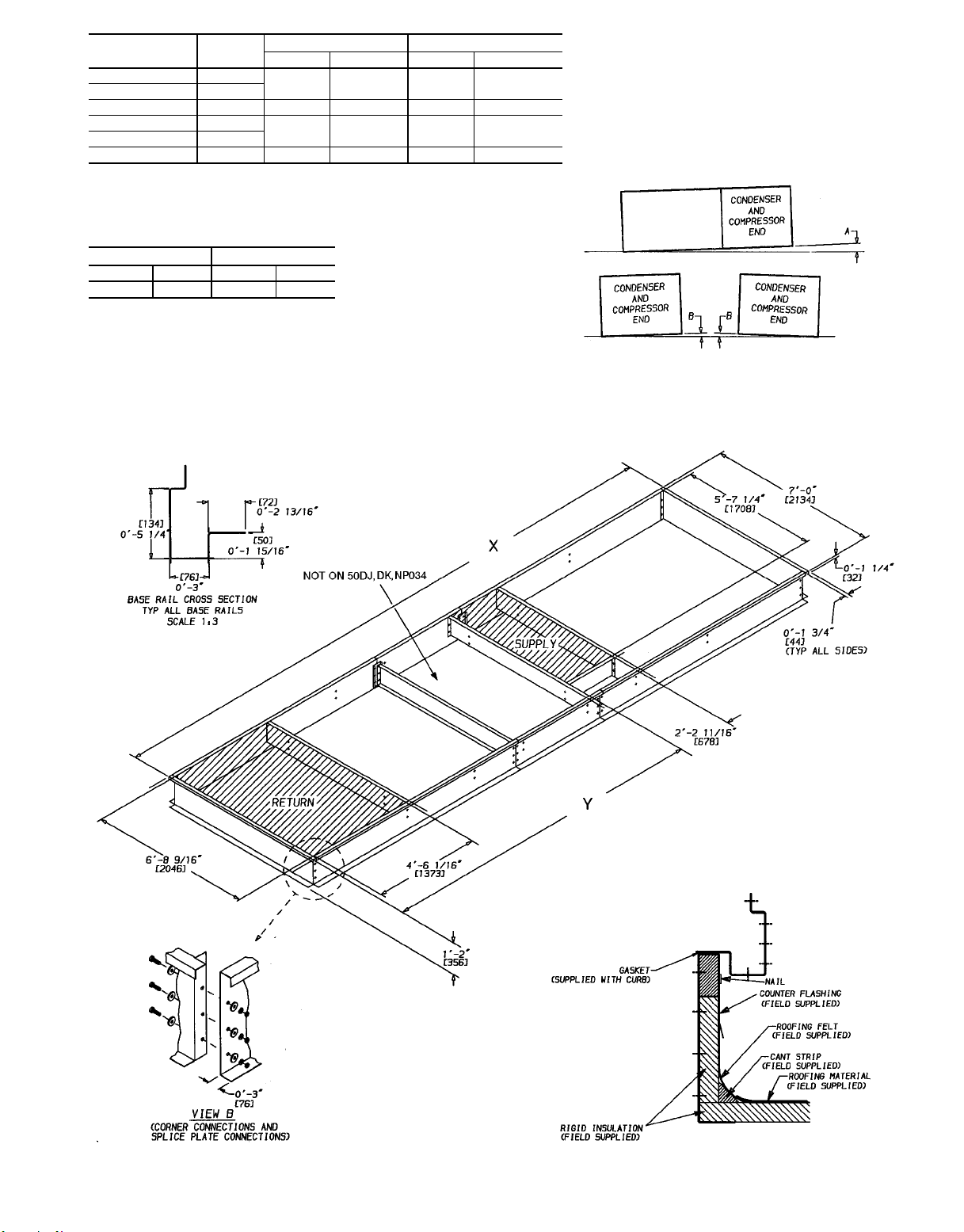
UNIT
MODEL
48DJ,DK,NP 034
50DW,DY,NB 034
UNIT
SIZE
mm ft-in. mm ft-in.
6606 21-8
50DJ,DK,NP 034 6131 20-1
48DJ,DK,NP 044
50DW,DY,NB 044
7825 25-8
50DJ,DK,NP 044 7344 24-1
UNIT LEVELING TOLERANCES
DIMENSIONS*
(degrees and inches)
AB
Deg in. Deg in.
1.0 2.0 .50 .75
*From edge of unit to horizontal.
XY
1
⁄
16
3
⁄
8
1
⁄
16
1
⁄
8
4056 13- 311⁄
3311 10-103⁄
4893 16- 05⁄
4141 13- 71⁄
16
8
8
16
NOTES:
1. Roof curb is shipped unassembled.
2. Roof curb: 14 gage (VA03-56) steel.
3. Dimensions in [ ] are millimeters.
NOTE: To prevent the hazard of stagnant water build-up in the
drain pan of the indoor-air section, unit can only be pitched as
shown.
Fig. 3A — Roof Curb; 034, 044 Units
7
Page 8
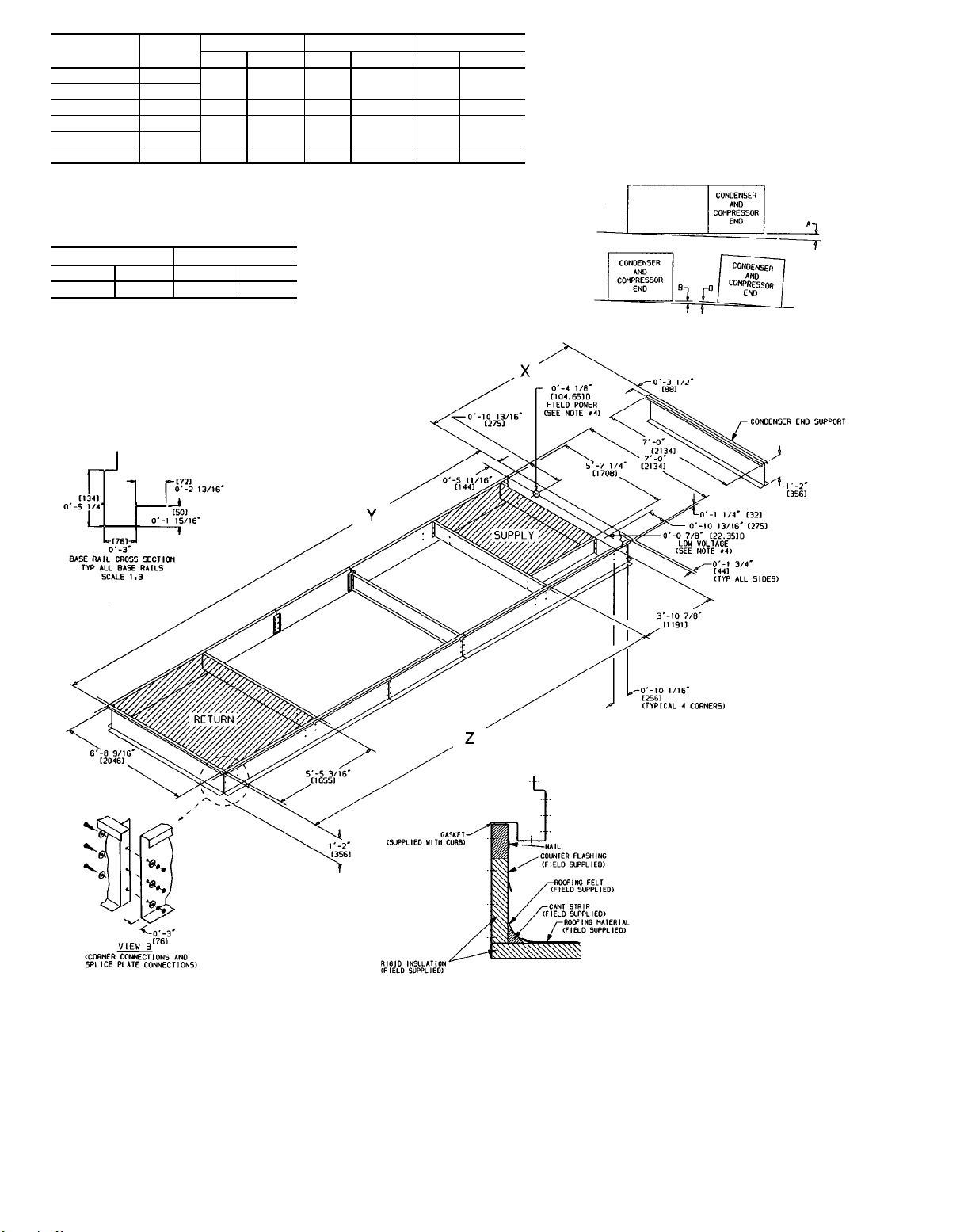
UNIT
MODEL
48DJ,DK,NP 054,064
50DW,DY,NB 054,064
UNIT
SIZE
mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in.
2474 8-1
50DJ,DK,NP 054,064 2458 8-0
48DJ,DK,NP 074
50DW,DY,NB 074
3383 11-1
50DJ,DK,NP 074 3367 11-0
UNIT LEVELING TOLERANCES
DIMENSIONS*
(degrees and inches)
AB
Deg in. Deg in.
1.0 2.0 .50 .75
*From edge of unit to horizontal.
XY Z
3
⁄88476 27-911⁄166965 22-103⁄
3
⁄47444 24-51⁄
3
⁄168476 27-911⁄166965 22-103⁄
9
⁄167444 24-51⁄
16
16
5933 19- 59⁄
5933 19- 59⁄
16
16
16
16
NOTES:
1. Roof curb is shipped unassembled.
2. Roof curb: 14 gage (VA03-56) steel.
3. Dimensions in [ ] are millimeters.
4. Suggested hole location for field wiring
through roof curb (holes to be field drilled).
NOTE: To prevent the hazard of stagnant water build-up in the
drain pan of the indoor-air section, unit can only be pitched as
shown.
Fig. 3B — Roof Curb; 054-074 Units
8
Page 9
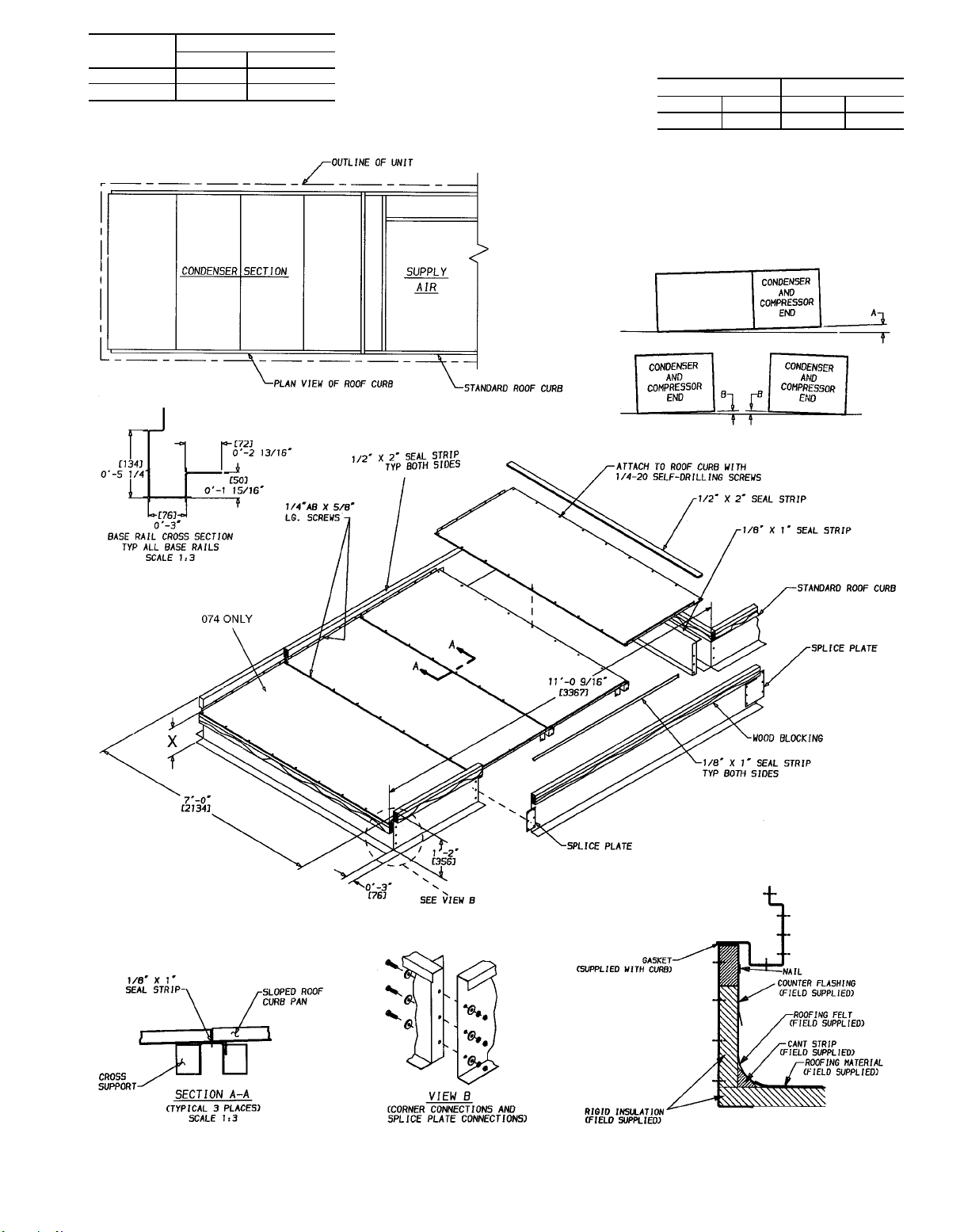
UNIT
SIZE
DIMENSION X
mm Ft-in.
054,064 270 0-10
074 255 0-101⁄
UNIT LEVELING TOLERANCES
DIMENSIONS*
5
⁄
8
16
Deg in. Deg in.
(degrees and inches)
AB
1.0 2.0 .50 .75
*From edge of unit to horizontal.
NOTE: To prevent the hazard of stagnant water
build-up in the drain pan of the indoor-air section,
unit can only be pitched as shown.
Fig. 3C — Condenser Section Roof Curb (054-074 Units Only)
9
Page 10

Condensate Drains — See Fig. 4A-4D and Fig. 5 for
drain locations. The drain assemblies, each consisting of a
10-gage plate with a 11⁄4-in. half coupling welded to it, are
shipped in the unit fan section. Also included are 16-gage
seal plates to cover the drain holes not being used. Open the
access door marked FANSECTION to find the drain assemblies, seal plates, and 4 screws for each mounting taped to
the unit basepan.
After the unit has been set in place on the roof:
1. Select the appropriate drain locations. The 034 units have
6 drain holes (3 per side), and the 044-074 units have 8
drain holes (4 per side). Two holes on each side must be
selected for condensate drains as shown in Fig. 5, and the
remaining holes must be sealed.
2. Remove the drain assemblies and attach them to the bottom of the unit base rails at the preferred drain locations
using the screws provided. See Fig. 6.
NOTE: Use a trap at least 4-in. deep.
3. Cover the remaining drain holes with the seal plates and
screws provided. See Fig. 7.
4. Apply a bead of RTV or similar sealant around the drain
assemblies and seal plates where they attach to the base
rail. See Fig. 8.
NOTE: If unit is slab mounted, holes will need to be drilled
in the side of the base rail and the holes factory-drilled in the
bottom of the base rail will need to be plugged.
Install Outdoor Hoods
UNIT SIZES 034 AND 044
25% Outdoor-Air Hoods (Units Without Economizer
Option)
1. Outdoor-air hoods are shipped bolted to the unit in a shipping position. Remove the 6 screws holding each 25% air
hood shipping cover in place.
2. Replace the 6 screws.
3. Remove the holddown screw from each upper corner of
each hood.
4. Pivot hoods outward (2 hoods total).
5. Install 17 screws around outside of each hood. (Screws
are in the fastener package taped to the basepan inside
the fan section.)
6. Apply a bead of RTV or similar sealant to corner of each
hood at pivot point to prevent water leaks. See Fig. 9.
Economizer Hoods (Units WithEconomizer Option) — Follow the same procedure described in 25% Outdoor-Air Hoods
section above.
UNIT SIZES 054-074
25% Outdoor-Air Hoods — The outdoor-air hoods are fac-
tory installed on the 054-074 units.
Economizer Hoods (Units With Economizer Option)
1. Remove the 6 screws holding each of the 4 economizer
shipping covers in place.
2. Replace the screws.
3. Remove the holddown screw from each upper corner of
each economizer hood.
4. Pivot hoods outward. (There is a total of 4 hoods.)
5. Install 18 screws, (5 each side, 6 top, and 2 bottom), around
the outside of each hood. (Screws are in the fastener package taped to the basepan inside the fan section.)
6. Apply a bead of RTV or similar sealant to corner of economizer hood at pivot point to prevent water leaks. (See
Fig. 9.)
Outdoor-Air Inlet Adjustments
MANUALOUTDOOR-AIRDAMPER (Units WithoutEconomizer Option) —All units except those equipped with a factoryinstalled economizer have a manual outdoor-air damper to
provide ventilation air. This damper can be preset to admit
up to 25% outdoor air into the return-air compartment. To
adjust, loosen the blade limiter screws as shown in Fig. 10
and move the damper to the desired position. Then retighten
the blade limiter screws to secure the damper. See Fig. 10.
(T omake this adjustment, it is necessary to remove the screens
covering the hood opening and make adjustments from inside the hood.)
ECONOMIZER SETTINGS
Enthalpy Sensor (See Fig. 11.) — This sensor is located be-
hind the filters in the end economizer hood (the upper hood
on sizes 054-074). See Fig. 12. For maximum benefit of outdoor air, set enthalpy sensor control to the A setting. At this
setting, when the relative humidity is 50%, and the outdoor
air is below 74 F, the sensor’s relay contacts will be closed.
See Fig. 13 and 14.
NOTE: Enthalpy control setting dial is on the economizer
motor.
Mixed-Air Thermistor (MAT) — This control set point adjustment is on the top of the economizer motor. This motor
is located in the return-air section, and is accessed by opening the access panel marked FILTER SECTION. See
Fig. 15. Set MAT set point adjustment dial to the desired
setting. The factory setting is 55F±5°F;range is 40 to
90 F. The MAT is located on the filter rack.
Damper Vent Position — The position setting adjustment is
located on the cover of the economizer motor. See Fig. 15.
Adjust by setting the fan switch at ON position (continuous
fan operation), and setting the system selector switch to OFF
position. Then turn adjustment screw slowly until the dampers assume the desired vent position. Do not manually operate the damper motor; damage to the motor may result.
Economizer Damper Linkage Adjustment — When replacing economizer damper motors, or if the linkage has come
loose, it is critical that the linkages be adjusted correctly.
They are sensitive, and incorrect adjustment can cause the
motor to stall.
NB,NPUnitMinimum Position Set Point — Minimum economizer position is set using the keypad and display module.
Refer to Control and Troubleshooting literature for more
details.
10
Page 11
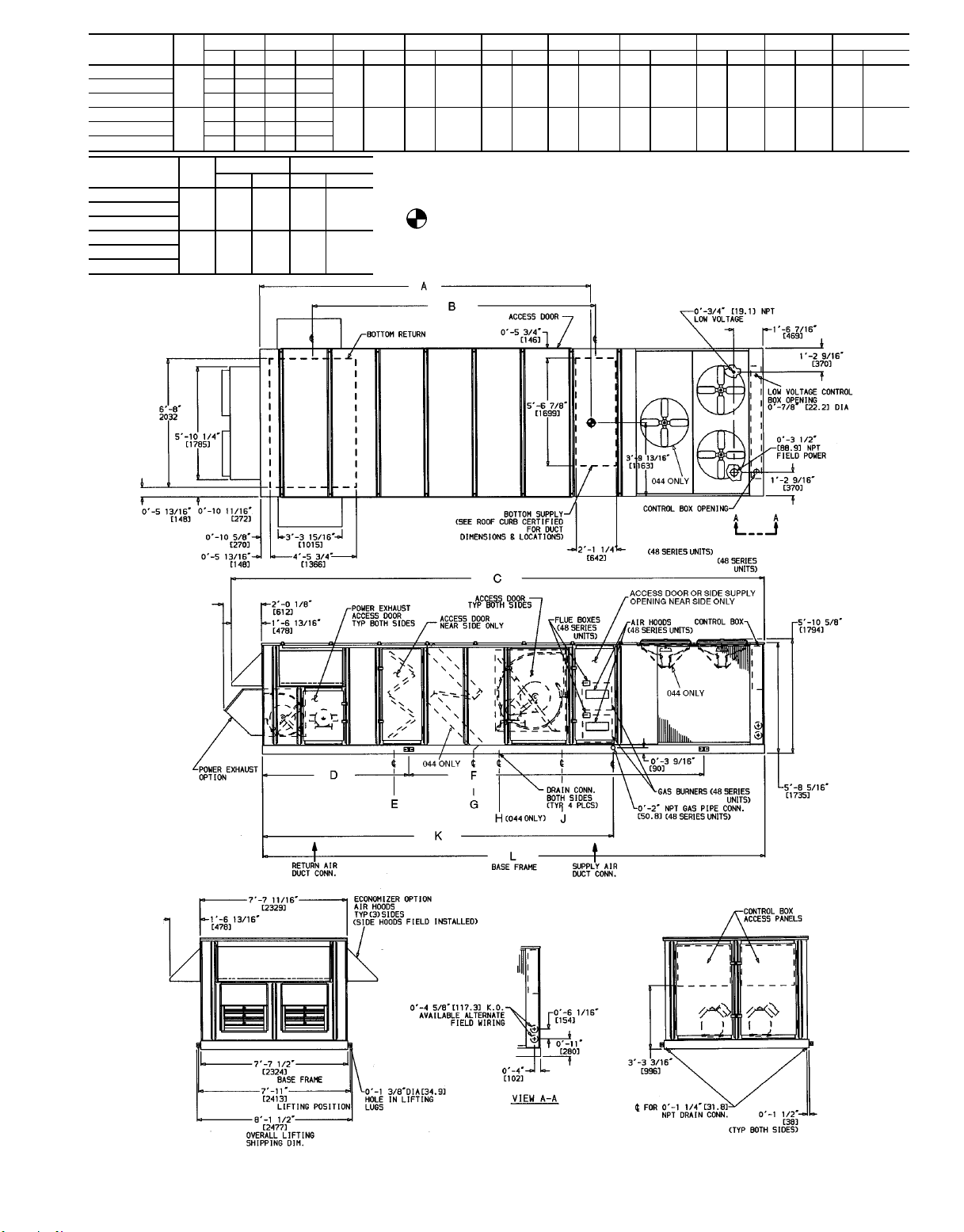
UNIT SIZE
48DJD,DKD,NPD
48DJE,NPE 5770 2617 4474 14-81⁄
WEIGHT A B C D E F G H J
lb kg mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in.
5641 2559 4498 14-9
034
50DW,DY,NB 5970 2708 4044 13-31⁄
48DJD,DKD,NPD
48DJE,NPE 6670 2708 5229 17-17⁄
6541 2967 5255 17-27⁄
044
50DW,DY,NB 6620 3003 4823 15-97⁄
UNIT SIZE
KL
mm ft-in. mm ft-in.
48DJD,DKD,NPD
48DJE,NPE
034 4741 15-6 6797 22-3
50DW,DY,NB
48DJD,DKD,NPD
48DJE,NPE
044 5576 8-3
1
⁄28015 26-39⁄
50DW,DY,NB
1
⁄
8
3662 12-03⁄167278 23-109⁄161709 5-75⁄162216 7- 31⁄44228 13-107⁄162746 9-01⁄8— — 3626 12-109⁄
8
4
8
4497 14-91⁄168496 27-101⁄22328 7-75⁄82091 6-105⁄164706 15-5 3363 11-03⁄83769 12-43⁄84762 15-71⁄
8
8
LEGEND
CONN — Connection
DIM — Dimension
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
5
⁄
8
2. Center ofGravity includeseconomizer.Unit weightdoes
not include economizer.
3. Unit clearances:
Top — Do not restrict condenser fans
16
Control Box End — 68-09
Sides — 68-09
Economizer End — 68-09 (except power exhaustunits 108-09)
Forsmaller service and operational clearances, contact Carrier Product Engineering Department.
4. Vertical discharge ducts designed to be attached to
accessory roof curb. If unit is mounted on dunnage,
support the ducts using cross bracesas doneon the
accessory roof curb.
5. When unit is slab mounted, locate the condensate
drain as low as possible on vertical face of base rail
atthe samelocation asthe standard condensatedrain
(usingfactory suppliedfitting). Plugfactory drilled condensate hole.
16
2
Fig. 4A — Base Unit Dimensional Drawing; 48DJ,DK,NP/50DW,DY,NB034,044 Units
11
Page 12
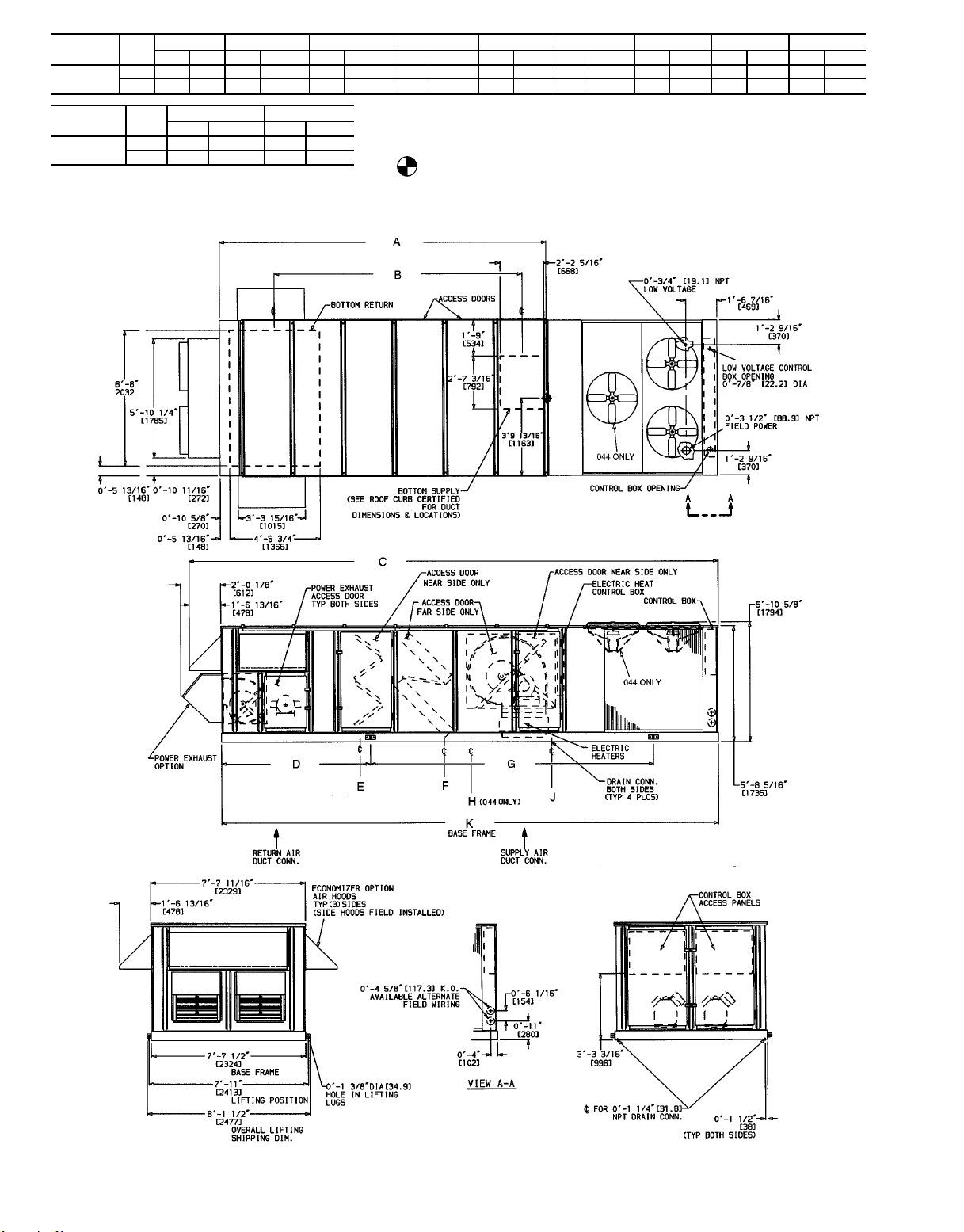
UNIT SIZE
50DJ,DK,NP
UNIT SIZE
50DJ,DK,NP
WEIGHT A B C D E F G H
lb kg mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in.
034 5400 2449 4198 13-9
044 6050 2744 4948 16-2
JK
mm ft-in. mm ft-in.
034 4168 13-8
1
044 4999 16-413⁄167534 24-85⁄
1
⁄42916 9-613⁄166802 22-313⁄161711 5-73⁄82216 7- 31⁄44428 9-01⁄83762 12-43⁄8——
13
⁄163746 12-31⁄28015 26-39⁄162247 7-47⁄162091 6-105⁄163363 11-03⁄84306 14-11⁄23769 12-43⁄
⁄166321 20-87⁄
LEGEND
CONN — Connection
DIM — Dimension
NOTES:
8
1. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
8
2. Center of Gravity includes economizer. Unit
weight does not include economizer.
3. Unit clearances:
Top — Do not restrict condenser fans
Control Box End — 68-09
Sides — 68-09
EconomizerEnd —68-09 (except power exhaust units
108-09)
Forsmaller service and operational clearances, contact Carrier Product Engineering Department.
4. Vertical discharge ducts designed to be attached to
accessory roof curb. If unit is mounted on dunnage,
support the ducts using cross bracesas doneon the
accessory roof curb.
5. When unit is slab mounted, locate the condensate
drain as low as possible on vertical face of base rail
atthe samelocation asthe standard condensatedrain
(usingfactory suppliedfitting). Plugfactory drilled condensate hole.
8
Fig. 4B — Base Unit Dimensional Drawing; 50DJ,DK,NP034,044 Units
12
Page 13
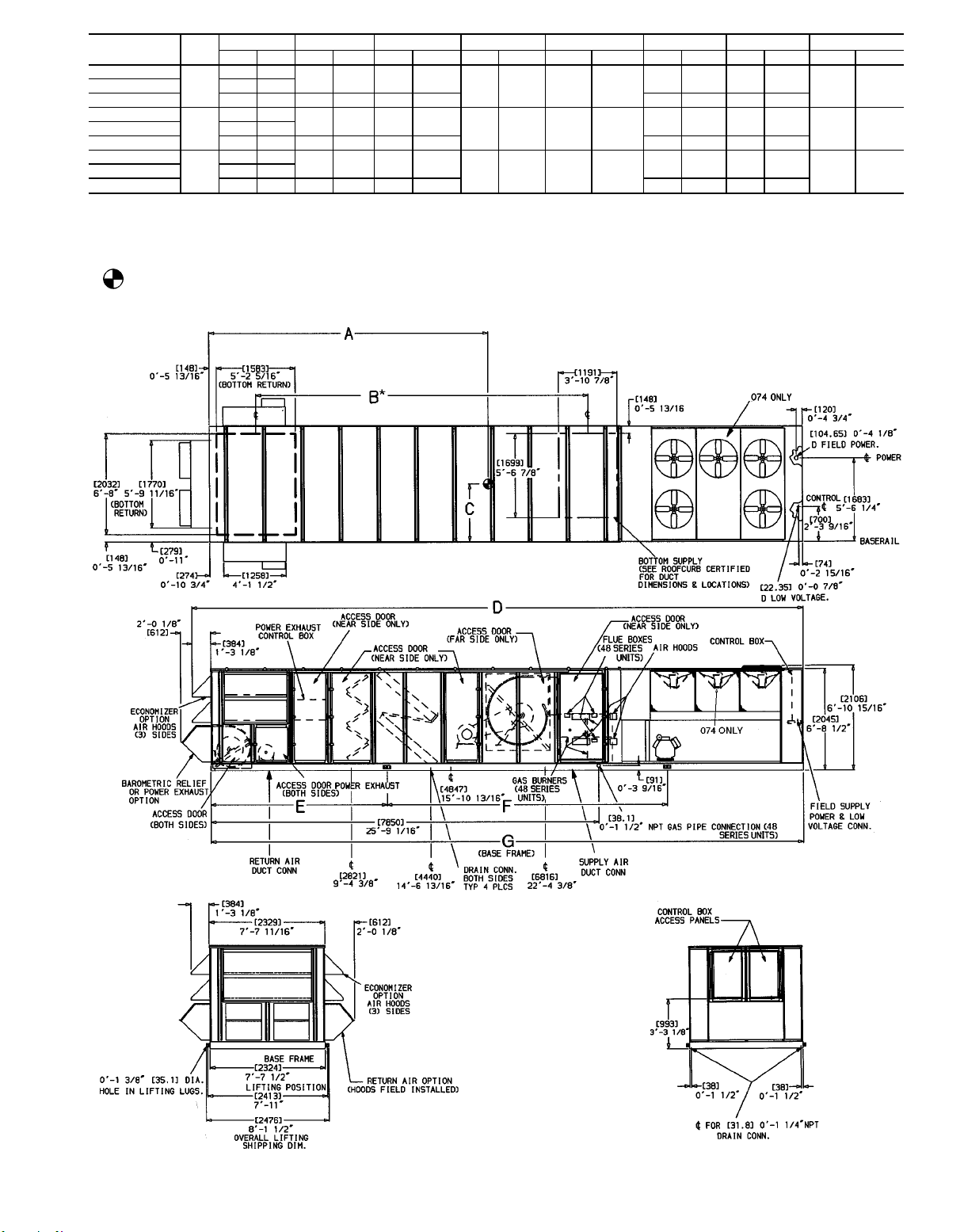
UNIT SIZE
48DJD,DKD,NPD
48DJE,NPE 8820 4000
50DW,DY,NB 8250 3742 6045 19-10 7676 25-2
48DJD,DKD,NPD
48DJE,NPE 9120 4137
50DW,DY,NB 8550 3878 6045 19-10 7676 25-2
48DJD,DKD,NPD
48DJE,NPE 9550 4332
50DW,DY,NB 8970 4069 6477 21-3 7676 25-2
LEGEND
CONN — Connection
DIM — Dimension
*Dimension shown is for 48 series units. On 50 series units, dimension given is measured from
economizer end of unit to drain connection closest to condenser fans.
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
2. Center of Gravity includes economizer. Unit weight does not include economizer.
3. Unit clearances:
Top — Do not restrict condenser fans
Control Box End — 68-09
Sides — 68-09 (except power exhaust units 108-09)
WEIGHT A B C D E F G
lb kg mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in.
054
064
074
8700 3946
9000 4082
9420 4273
5969 19-7 6717 22-0
5969 19-7 6717 22-0
6401 21-0 6717 22-0
7
⁄
16
1163 3-913⁄1611,524 37-911⁄
3
⁄
16
7
⁄
16
1163 3-913⁄1611,524 37-911⁄
3
⁄
16
7
⁄
16
1163 3-913⁄1612,433 40-91⁄
3
⁄
16
2718 8-11 6541 21-51⁄
16
2
11,140 36-69⁄
16
2830 9-33⁄46427 21-1
2718 8-11 6541 21-51⁄
16
2
11,140 36-69⁄
16
2830 9-33⁄46427 21-1
3543 11-71⁄25715 18-9
2
12,049 39-6
3
⁄
8
3694 12-13⁄45563 18-3
Economizer End — 68-09 (except power exhaust units 108-09)
For smaller service and operational clearances, contact Carrier Product Engineering
Department.
4. Verticaldischarge ductsdesigned tobe attachedto accessoryroof curb.If unitis mounted
on dunnage, support the ducts using cross braces as done on the accessory roof curb.
5. When unit is slab mounted, locate the condensate drain as low as possible on vertical
face of base rail at the same location as the standard condensate drain (using factory
supplied fitting). Plug factory drilled condensate hole.
Fig. 4C — Base Unit Dimensional Drawing; 48DJ,DK,NP/50DW,DY,NB054-074 Units
13
Page 14
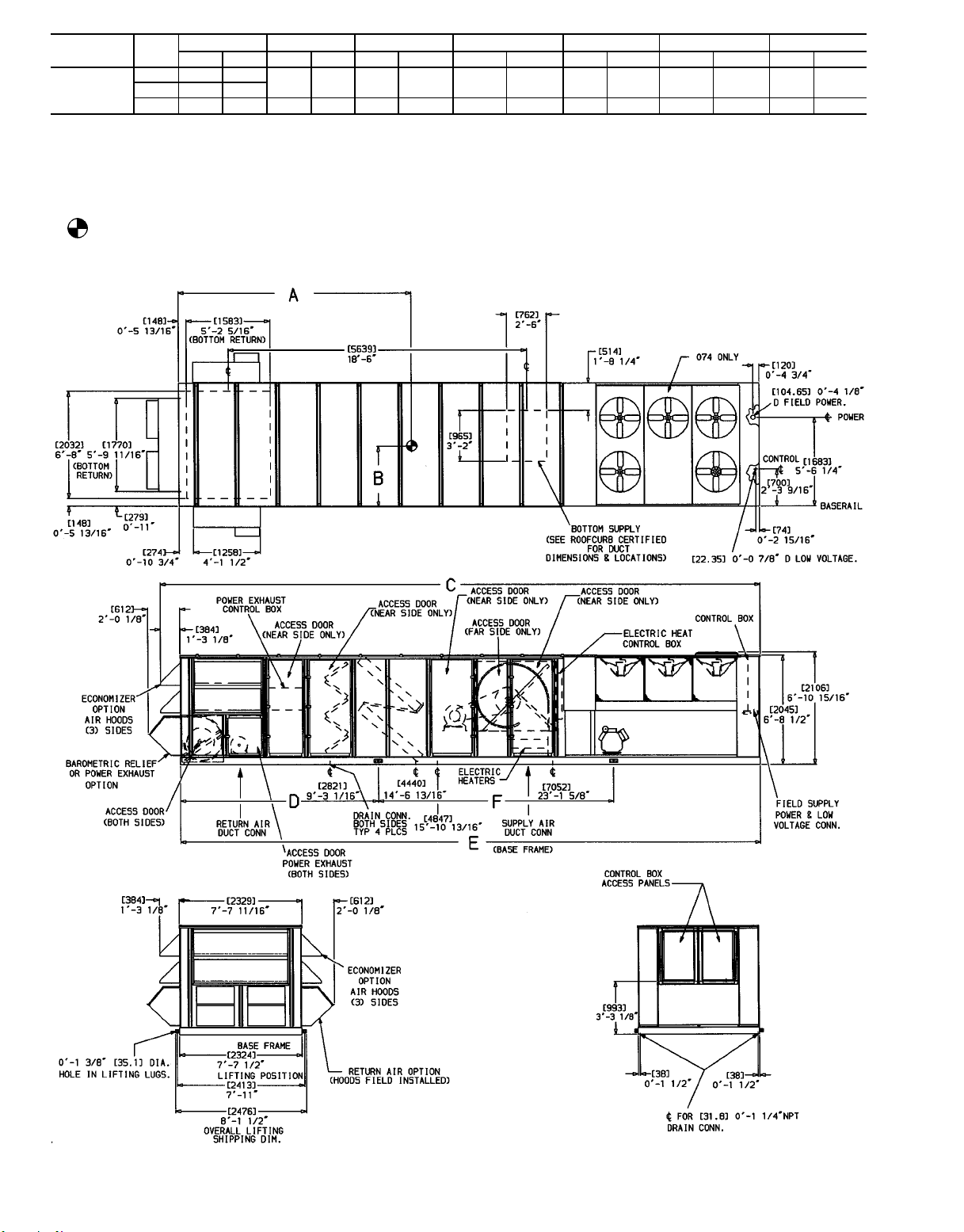
UNIT SIZE
50DJ,DK,NP
054 7700 3493
064 8000 3629
Weight A B C D E F
Lb Kg mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in. mm ft-in.
5537 18-2 1163 3-9
074 8430 3824 5969 21-3 1163 3-9
LEGEND
CONN — Connection
DIM — Dimension
*Dimension shown is for 48 series units. On 50 series units, dimension given
is measured from economizer end of unit to drain connection closest to condenser fans.
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
2. Center of Gravity includes economizer. Unit weight does not include
3. Unit clearances:
economizer.
Top — Do not restrict condenser fans
Control Box End — 68-09
Sides — 68-09 (except power exhaust units 108-09)
13
⁄1610,476 34-47⁄162864 9-43⁄410,092 33-15⁄165347 17-61⁄
13
⁄1611,385 37-41⁄43727 12-23⁄411,001 36-11⁄84483 14-81⁄
Economizer End — 68-09 (except power exhaust units 108-09)
For smallerservice and operational clearances, contactCarrier Product Engineering Department.
4. Verticaldischarge ducts designed to be attached to accessory roof curb. If
unit is mounted on dunnage, support the ducts using cross braces as done
on the accessory roof curb.
5. When unit is slab mounted, locate the condensate drain as low as possible
on vertical face of base rail at the same location as the standard condensate drain (using factory supplied fitting). Plug factory drilled condensate
hole.
2
2
Fig. 4D — Base Unit Dimensional Drawing; 50DJ,DK,NP054-074 Units
14
Page 15
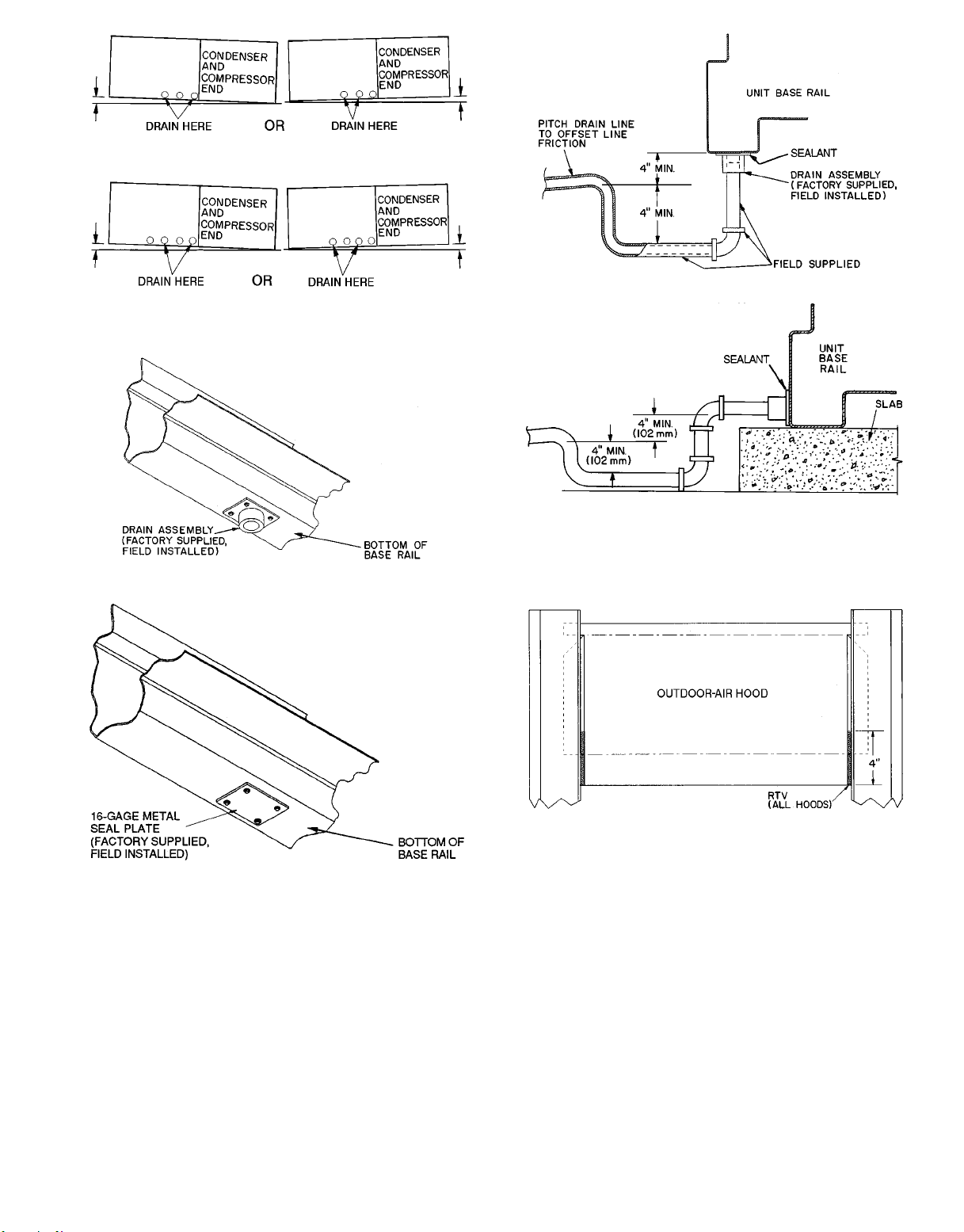
034 UNITS
044-074 UNITS
Fig. 5 — Drain Location Selection
Fig. 6 — Condensate Drain Location
ROOF MOUNT DRAIN
SLAB MOUNT DRAIN
Fig. 8 — Condensate Drain Piping Details
Fig. 7 — Seal Plate Location
Fig. 9 — Outdoor-Air Hood
15
Page 16
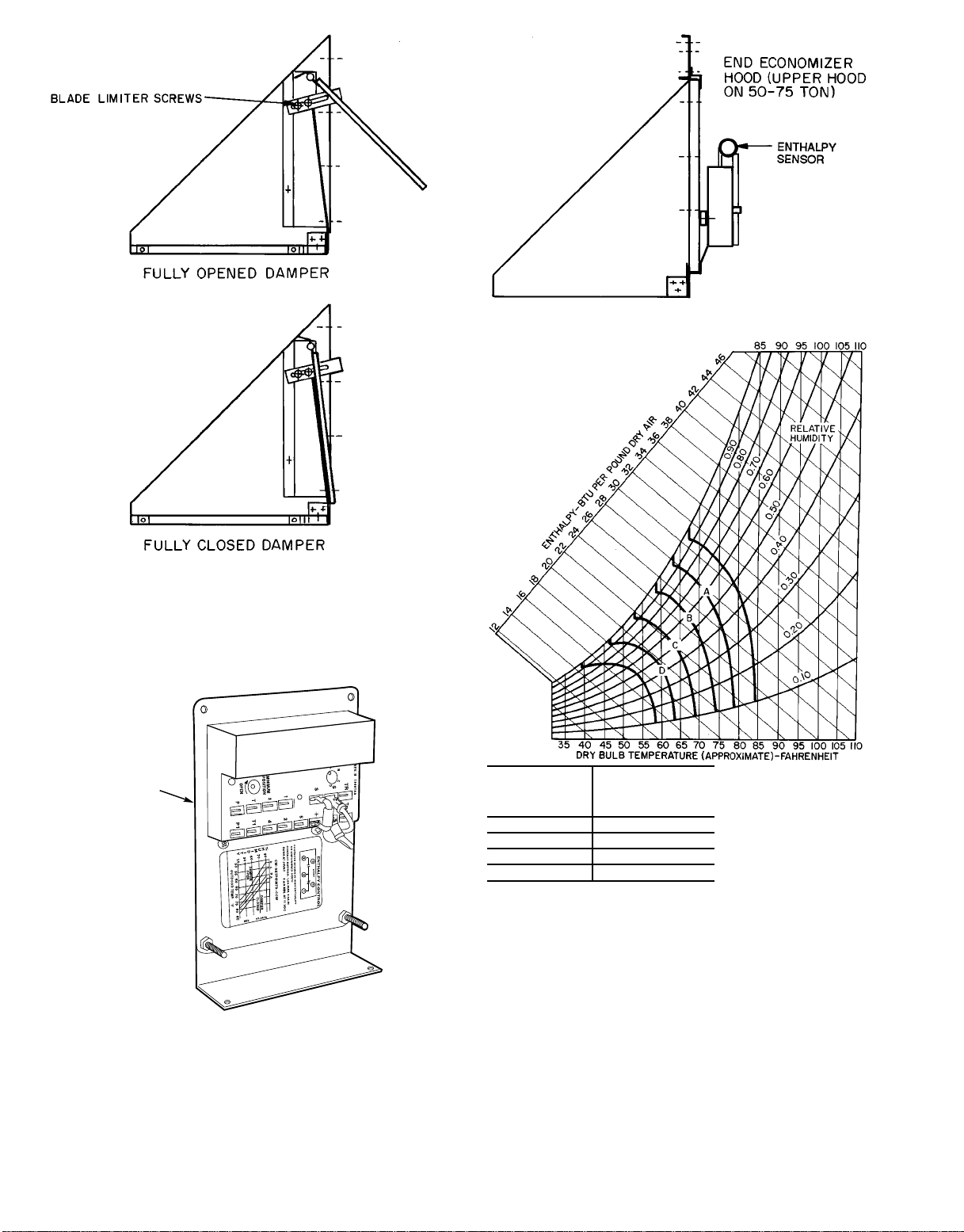
Fig. 12 — Enthalpy Sensor Location
Fig. 10 — Outdoor-Air Damper Adjustments
(Inside of Hood Shown)
ENTHALPY
SENSOR
O
CONTROL
CURVE
A 73
B 68
C 63
D 58
CONTROL
POINT
(Approx Deg)
AT 50% RH
Fig. 13 — Psychrometric Chart for
Enthalpy Control
Fig. 11 — Enthalpy Sensor
16
Page 17
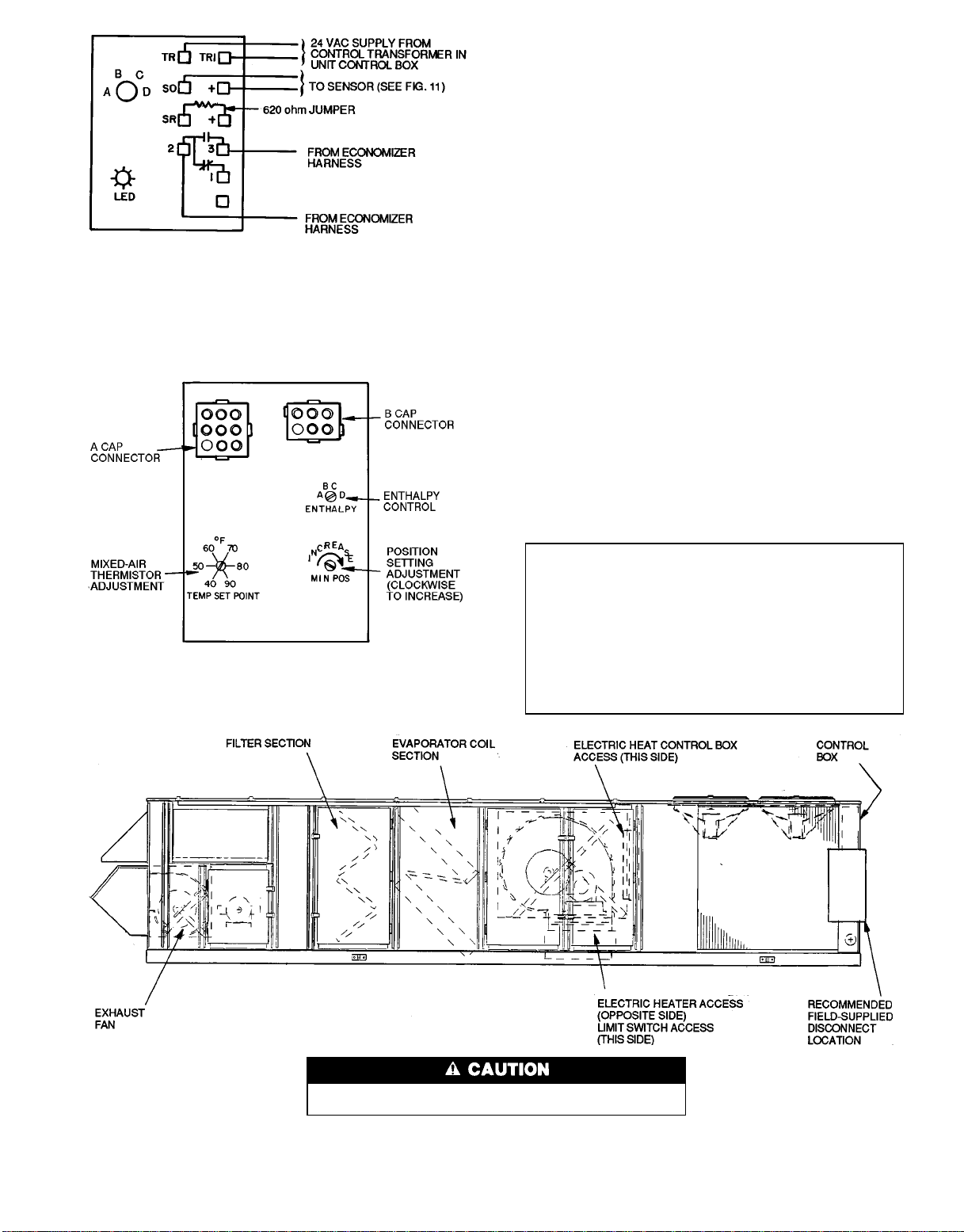
NOTES:
1. Switches shown in high enthalpy state. Terminals 2 and 3 close
on enthalpy decrease.
2. When standard economizer is used with accessory differential enthalpy sensor, set enthalpy control to ‘‘D’’ setting.
Fig. 14 — Wiring Connections for Solid-State
Enthalpy Sensor (HH57AC077)
Fig. 15 — Mixed-Air Thermistor and Economizer
Position Setting Adjustments
(Top of Economizer Motor)
Field Wire Routing
UNIT SIZES 034 AND 044 — Field wiring can be brought
into the unit through the basepan and roof curb or through
the corner post in the side of the unit next to the control box.
A 3-1/2 in. NPT coupling for field power and a 3/4-in.
NPT coupling for 24 v control wiring are provided in the
basepan. There are two 4-5/8 in. knockouts in the corner post
for field power wiring.
If field power wiring is brought through the roof curb, route
wiring out through one of the 4-5/8 in. knockouts to the fieldsupplied disconnect and then back into the unit through the
other knockout. See Fig. 16 for recommended disconnect
location.
If power wiring is brought through the side of the unit,
route wiring from field-supplied disconnect through top
4-5/8 in. knockouts into unit.
If control wiring is to be brought in through the side of the
unit, a 7/8-in. diameter hole must be drilled in the corner
post next to the control box.
UNIT SIZES 054-074 — Field wiring is brought into the
unit through the bottom of the control box. Wiring can be
brought through the roof curb through field-supplied watertight connections. See Fig. 17.
A 4-5/32 in. hole for field power wiring and a 7/8-in. hole
for 24 v control wiring are provided in the bottom of the
control box. Field-supplied couplings must be used when routing wiring into the control box.
See Fig. 17 for recommended disconnect location.
Field Electrical Connections
IMPORTANT: The 48/50DK,DY,NB,NP units generate, use, and can radiate radio frequency energy. If units
are not installed and used in accordance with these
instructions, they may cause radio interference. They
have been tested and found to comply with limits of a
Class A computing device as defined by FCC (Federal
Communications Commission) regulations, Subpart J
of Part 15, which are designed to provide reasonable
protection against such interference when operated in
a commercial environment.
Use care when drilling into corner post to avoid damage to condenser coil.
Fig. 16 — Disconnect Location, 034 and 044 Units
(50 Series Vertical Discharge Unit Shown)
17
Page 18
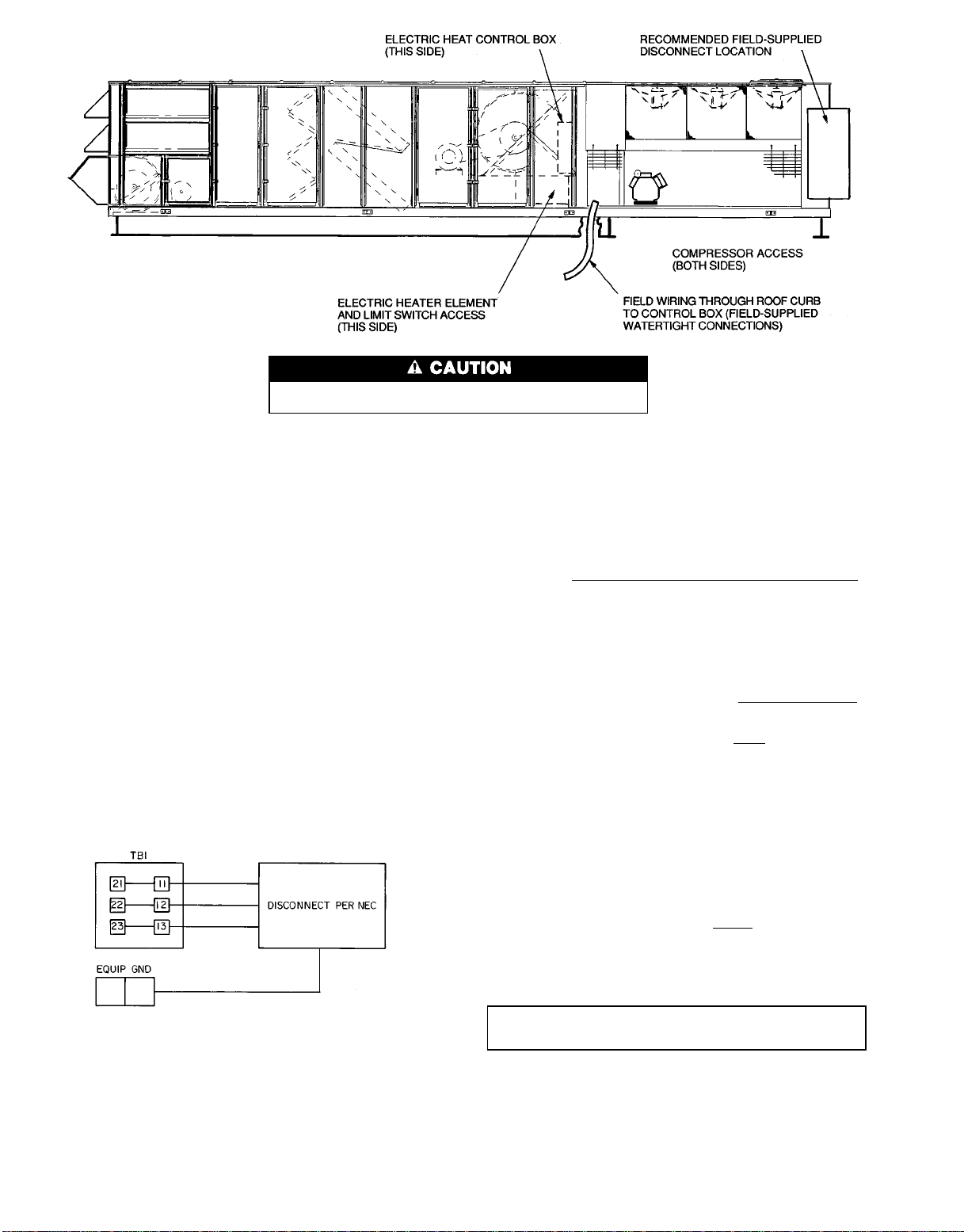
Use care when drilling into corner post to avoid damage to condenser coil.
Fig. 17 — Disconnect Location, 054-074 Units
(50 Series Horizontal Discharge Shown)
POWER WIRING — Units are factory wired for the voltage
shown on the unit nameplate. The main terminal block is
suitable for use with aluminum or copper wires. Maximum
wire size is 3/0 AWG (American Wire Gage).
When installing units, provide a disconnect per NEC
(National Electrical Code) of adequate size (MOCP [Maximum Overcurrent Protection] of unit is on the informative
plate). All field wiring must comply with NEC and all local
codes. Size wire based on MCA (Minimum Circuit Amps)
on the unit informative plate. See Fig. 18 for power wiring
connections to the unit power terminal block and equipment
ground.
Operating voltage to the compressor must be within the
voltage range indicated on the unit nameplate. Voltages between phases must be balanced within 2%, and the current
must be balanced within 10%. See Tables 3-7 for unit electrical data.
LEGEND
EQUIP — Equipment
GND — Ground
NEC — National Electrical Code
TB — Terminal Block
Fig. 18 — Field Power Wiring Connections
Use the following formula to determine the percent
voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
Example: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
452 1 464 1 455
3
1371
=
3
457
=
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage:
(AB) 457 – 452=5v
(BC) 464 – 457=7v
(AC) 457 – 455=2v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent voltage imbalance:
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
7
457
= 1.53%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance
is more than 2%, contact local utility immediately.
Unit failure as a result of operation on improper line voltage or excessive phase imbalance constitutes abuse and may
cause damage to electrical components.
18
Page 19

Table 3 — Electrical Data, 034 Units
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
187-254 53.2 266.0 53.2 266.0 10.8
CV — Constant Volume
ETL — ETL Testing Laboratory
FLA — Full Load Amps
Hp — Nominal Horsepower
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (for wire sizing)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Electric heat available on 50 Series vertical discharge units.
†108 kW available on CV applications only.
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
LEGEND
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
10.0
15.0
20.0
208/230-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
BASE UNIT
ONLY
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
24.2/
7.5
22.0
30.8/
28.0
46.2/
42.0
59.4/
54.0
154.7/
152.5
161.3/
158.5
176.7/
172.5
191.4/
184.7
200/
200
200/
200
225/
225
250/
225
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 33.4/30.0 — — 188.1/182.5 225/225
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 203.1/196.5 250/225
10.0 33.4/30.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 188.1/182.5 225/225
10.0 33.4/30.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 227.4/255.0 250/300
10.0 33.4/30.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 326.0/368.8 350/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 203.1/196.5 250/225
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 227.4/255.0 250/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 326.0/368.8 350/400
10.0 33.4/30.0 — — 194.7/188.5 225/225
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 209.7/202.5 250/250
10.0 33.4/30.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 194.7/188.5 225/225
10.0 33.4/30.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 235.6/262.5 250/300
10.0 33.4/30.0 88/108 236.6/273.0 334.2/376.3 350/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 209.7/202.5 250/250
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 235.6/262.5 250/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 334.2/376.3 350/400
10.0 33.4/30.0 — — 210.1/202.5 250/250
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 225.1/216.5 250/250
10.0 33.4/30.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 210.1/202.5 250/250
10.0 33.4/30.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 254.9/280.0 300/350
10.0 33.4/30.0 88/108 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 225.1/216.5 250/250
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 254.9/280.0 300/350
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.0 — — 224.8/214.7 250/250
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 239.9/228.7 250/250
10.0 33.4/30.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 224.8/214.7 300/300
10.0 33.4/30.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 271.4/295.0 350/350
10.0 33.4/30.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 239.9/228.7 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 271.4/295.0 350/350
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
NOTES:
1. Electric resistance heaters are rated at 208/240 v, 480 v, or 575 v. To
determine heater capacity (kW) at unit operating voltage, multiply 240 v,
480 v, or 575 v capacity by appropriate multiplier below.
2. Boldface indicates 48 and 50 Series units. All other data is for 50 Series
units only.
FLA
6.0 21.2/20.0 — — 175.9/172.5 225/225
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 154.7/152.5 200/200
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 227.4/255.0 250/300
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 326.0/368.8 350/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 175.9/172.5 225/225
6.0 21.2/20.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 227.4/255.0 250/300
6.0 21.2/20.0 88/108† 236.6/ 273.0 326.0/368.8 350/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 — — 182.5/178.5 225/225
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 161.3/158.5 200/200
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 235.6/262.5 250/300
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 334.2/376.3 350/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 182.5/178.5 225/225
6.0 21.2/20.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 235.6/262.5 250/300
6.0 21.2/20.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 334.2/376.3 350/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 — — 197.9/192.5 250/225
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 176.7/172.5 250/250
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 254.9/280.0 300/350
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 197.9/192.5 250/250
6.0 21.2/20.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 254.9/280.0 300/350
6.0 21.2/20.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 — — 212.6/204.7 250/250
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 191.4/184.7 300/300
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 271.4/295.0 350/350
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
6.0 21.2/20.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 212.6/204.7 300/300
6.0 21.2/20.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 271.4/295.0 350/350
6.0 21.2/20.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
HEATER kW
RATING
240
480
575
Electric heaters are tested and ETL approved at maximum
total external static pressure of 1.9 in. wg.
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
MULTIPLICATION FACTORS
VOLTAGE
DISTRIBUTION
V-3-60
200
208
230
240
440
460
480
550
575
600
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
MULTIPLICATION
FACTOR
0.694
0.751
0.918
1.000
0.840
0.918
1.000
0.915
1.000
1.089
19
Page 20
Table 3 — Electrical Data, 034 Units (cont)
460-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
414-508 28.8 120.0 28.8 120.0 5.4
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
FLA
7.5 11.0 81.2 100
10.0 14.0 84.2 110
15.0 21.0 91.2 110
20.0 27.0 97.2 125
BASE UNIT
ONLY
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
FLA
6.0 9.6 — — 90.8 110
10.0 15.2 — — 96.4 125
15.0 22.0 — — 103.2 125
— — 36 46.3 81.2 100
— — 72 93.0 130.0 150
— — 108† 139.0 187.5 200
6.0 9.6 36 46.3 90.8 110
6.0 9.6 72 93.0 130.0 150
6.0 9.6 108† 139.0 187.5 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 96.4 125
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 130.0 150
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 187.5 200
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 103.2 125
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 130.0 150
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 187.5 200
6.0 9.6 — — 93.8 110
10.0 15.2 — — 99.4 125
15.0 22.0 — — 106.2 125
— — 36 46.3 84.2 110
— — 72 93.0 133.7 150
— — 108† 139.0 191.2 200
6.0 9.6 36 46.3 93.8 110
6.0 9.6 72 93.0 133.7 150
6.0 9.6 108† 139.0 191.2 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 99.4 125
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 133.7 150
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 191.2 200
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 106.2 125
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 133.7 150
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 191.2 200
6.0 9.6 — — 100.8 125
10.0 15.2 — — 106.4 125
15.0 22.0 — — 113.2 125
— — 36 46.3 91.2 125
— — 72 93.0 142.5 175
— — 108† 139.0 200.0 200
6.0 9.6 36 46.3 100.8 125
6.0 9.6 72 93.0 142.5 175
6.0 9.6 108† 139.0 200.0 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 106.4 125
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 142.5 175
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 200.0 200
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 113.2 125
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 142.5 175
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 200.0 200
6.0 9.6 — — 106.8 125
10.0 15.2 — — 112.4 125
15.0 22.0 — — 119.2 125
— — 36 46.3 97.2 150
— — 72 93.0 150.0 200
— — 108† 139.0 207.5 225
6.0 9.6 36 46.3 106.8 150
6.0 9.6 72 93.0 150.0 200
6.0 9.6 108† 139.0 207.5 225
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 112.4 150
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 150.0 200
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 207.5 225
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 119.2 150
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 150.0 200
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 207.5 225
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
20
Page 21
Table 3 — Electrical Data, 034 Units (cont)
575-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
518-632 23.1 96.0 23.1 96.0 4.8
CV — Constant Volume
ETL — ETL Testing Laboratory
FLA — Full Load Amps
Hp — Nominal Horsepower
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (for wire sizing)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Electric heat available on 50 Series vertical discharge units.
†108 kW available on CV applications only.
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
LEGEND
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
BASE UNIT
ONLY
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
7.5 9.0 65.8 80
10.0 11.0 67.8 90
15.0 17.0 73.8 90
20.0 22.0 78.8 100
NOTES:
1. Electric resistance heaters are rated at 208/240 v, 480 v, or 575 v. To
determine heater capacity (kW) at unit operating voltage, multiply 240 v,
480 v, or 575 v capacity by appropriate multiplier below.
2. Boldface indicates 48 and 50 Series units. All other data is for 50 Series
units only.
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 12.2 — — 78.0 100
15.0 18.0 — — 83.8 100
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 78.0 100
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 101.3 110
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 146.2 150
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 83.8 100
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 101.3 110
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 146.2 150
10.0 12.2 — — 80.0 100
15.0 18.0 — — 85.8 100
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 80.0 100
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 103.7 110
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 148.7 150
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 85.8 100
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 103.7 110
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 148.7 150
10.0 12.2 — — 86.0 100
15.0 18.0 — — 91.8 110
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 86.0 100
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 111.2 125
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 156.2 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 91.8 110
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 111.2 125
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 156.2 175
10.0 12.2 — — 91.0 110
15.0 18.0 — — 96.8 110
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 91.0 110
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 117.5 150
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 162.5 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 96.8 110
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 117.5 150
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 162.5 175
HEATER kW
RATING
Electric heaters are tested and ETL approved at maximum
total external static pressure of 1.9 in. wg.
FLA
6.0 7.8 — — 73.6 90
— — 36 36.0 65.8 80
— — 72 72.0 101.3 110
— — 108† 108.0 146.2 150
6.0 7.8 36 36.0 73.6 90
6.0 7.8 72 72.0 101.3 110
6.0 7.8 108† 108.0 146.2 150
6.0 7.8 — — 75.6 90
— — 36 36.0 67.8 90
— — 72 72.0 103.7 110
— — 108† 108.0 148.7 150
6.0 7.8 36 36.0 75.6 90
6.0 7.8 72 72.0 103.7 110
6.0 7.8 108† 108.0 148.7 150
6.0 7.8 — — 81.6 100
— — 36 36.0 73.8 100
— — 72 72.0 111.2 125
— — 108† 108.0 156.2 175
6.0 7.8 36 36.0 81.6 100
6.0 7.8 72 72.0 111.2 125
6.0 7.8 108† 108.0 156.2 175
6.0 7.8 — — 86.6 100
— — 36 36.0 78.8 110
— — 72 72.0 117.5 150
— — 108† 108.0 162.5 175
6.0 7.8 36 36.0 86.6 110
6.0 7.8 72 72.0 117.5 150
6.0 7.8 108† 108.0 162.5 175
MULTIPLICATION FACTORS
240
480
575
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
VOLTAGE
DISTRIBUTION
V-3-60
200
208
230
240
440
460
480
550
575
600
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
MULTIPLICATION
FACTOR
0.694
0.751
0.918
1.000
0.840
0.918
1.000
0.915
1.000
1.089
21
Page 22
Table 4 — Electrical Data, 044 Units
208/230-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
187-254 69.2 345.0 69.2 345.0 16.2
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
FLA
24.2/
7.5
22.0
30.8/
10.0
28.0
46.2/
15.0
42.0
59.4/
20.0
54.0
BASE UNIT
ONLY
196.1/
193.9
202.7/
199.9
218.1/
213.9
231.3/
225.9
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 33.4/30.0 — — 229.5/223.9 250/250
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 244.5/237.9 300/300
250/
250
10.0 33.4/30.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 229.5/223.9 250/250
10.0 33.4/30.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 229.5/255.0 250/300
10.0 33.4/30.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 326.0/368.8 350/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 244.5/237.9 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 244.5/255.0 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 326.0/368.8 350/400
10.0 33.4/30.0 — — 236.1/229.9 300/250
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 251.1/243.9 300/300
250/
250
10.0 33.4/30.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 236.1/229.9 300/250
10.0 33.4/30.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 236.1/262.5 300/300
10.0 33.4/30.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 334.2/376.3 350/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 251.1/243.9 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 251.1/262.5 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 334.2/376.3 350/400
10.0 33.4/30.0 — — 251.5/243.9 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 266.5/257.9 300/300
250/
250
10.0 33.4/30.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 251.5/243.9 300/300
10.0 33.4/30.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 254.9/280.0 300/350
10.0 33.4/30.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 266.5/257.9 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 266.5/280.0 300/350
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.0 — — 264.7/255.9 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 279.7/269.9 300/300
300/
250
10.0 33.4/30.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 264.7/255.9 300/300
10.0 33.4/30.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 271.4/295.0 350/350
10.0 33.4/30.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 279.7/269.9 300/300
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 279.7/295.0 350/350
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
FLA
6.0 21.2/20.0 — — 217.3/213.9 250/250
— — 29/ 35 78.9/ 91.0 196.1/193.9 250/250
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 227.4/255.0 250/300
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 326.0/368.8 350/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 217.3/213.9 250/250
6.0 21.2/20.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 227.4/255.0 250/300
6.0 21.2/20.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 326.0/368.8 350/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 — — 223.9/219.9 250/250
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 202.7/199.9 250/250
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 235.6/262.5 250/300
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 334.2/376.3 350/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 223.9/219.9 250/250
6.0 21.2/20.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 235.6/262.5 250/300
6.0 21.2/20.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 334.2/376.3 350/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 — — 239.3/233.9 300/300
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 218.1/213.9 250/250
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 254.9/280.0 300/350
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 239.3/233.9 300/300
6.0 21.2/20.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 254.9/280.0 300/350
6.0 21.2/20.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
6.0 21.2/20.0 — — 252.5/245.9 300/300
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 231.3/225.9 300/300
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 271.4/295.0 350/350
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
6.0 21.2/20.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 252.5/245.9 300/300
6.0 21.2/20.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 271.4/295.0 350/350
6.0 21.2/20.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
22
Page 23

Table 4 — Electrical Data, 044 Units (cont)
460-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
414-508 34.6 173.0 34.6 173.0 8.1
CV — Constant Volume
ETL — ETL Testing Laboratory
FLA — Full Load Amps
Hp — Nominal Horsepower
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (for wire sizing)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Electric heat available on 50 Series vertical discharge units.
†108 kW available on CV applications only.
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
LEGEND
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
BASE UNIT
ONLY
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
7.5 11.0 96.9 125
10.0 14.0 99.9 125
15.0 21.0 106.9 125
20.0 27.0 112.9 125
NOTES:
1. Electric resistance heaters are rated at 208/240 v, 480 v, or 575 v. To
determine heater capacity (kW) at unit operating voltage, multiply 240 v,
480 v, or 575 v capacity by appropriate multiplier below.
2. Boldface indicates 48 and 50 Series units. All other data is for 50 Series
units only.
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 128.1 150
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 150.0 200
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 207.5 225
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 134.9 150
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 150.0 200
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 207.5 225
HEATER kW
RATING
240
480
575
Electric heaters are tested and ETL approved at maximum
total external static pressure of 1.9 in. wg.
FLA
6.0 9.6 — — 106.5 125
10.0 15.2 — — 112.1 125
15.0 22.0 — — 118.9 150
— — 36 46.3 96.9 125
— — 72 93.0 130.0 150
— — 108† 139.0 187.5 200
6.0 9.6 36 46.3 106.5 125
6.0 9.6 72 93.0 130.0 150
6.0 9.6 108† 139.0 187.5 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 112.1 125
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 130.0 150
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 187.5 200
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 118.9 150
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 130.0 150
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 187.5 200
6.0 9.6 — — 109.5 125
10.0 15.2 — — 115.1 125
15.0 22.0 — — 121.9 150
— — 36 46.3 99.9 125
— — 72 93.0 133.7 150
— — 108† 139.0 191.2 200
6.0 9.6 36 46.3 109.5 125
6.0 9.6 72 93.0 133.7 150
6.0 9.6 108† 139.0 191.2 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 115.1 125
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 133.7 150
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 191.2 200
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 121.9 150
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 133.7 150
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 191.2 200
6.0 9.6 — — 116.5 150
10.0 15.2 — — 122.1 150
15.0 22.0 — — 128.9 150
— — 36 46.3 106.9 125
— — 72 93.0 142.5 175
— — 108† 139.0 200.0 200
6.0 9.6 36 46.3 116.5 150
6.0 9.6 72 93.0 142.5 175
6.0 9.6 108† 139.0 200.0 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 122.1 150
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 142.5 175
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 200.0 200
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 128.9 150
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 142.5 175
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 200.0 200
6.0 9.6 — — 122.5 150
10.0 15.2 — — 128.1 150
15.0 22.0 — — 134.9 150
— — 36 46.3 112.9 150
— — 72 93.0 150.0 200
— — 108† 139.0 207.5 225
6.0 9.6 36 46.3 122.5 150
6.0 9.6 72 93.0 150.0 200
6.0 9.6 108† 139.0 207.5 225
MULTIPLICATION FACTORS
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
VOLTAGE
DISTRIBUTION
V-3-60
200
208
230
240
440
460
480
550
575
600
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
MULTIPLICATION
FACTOR
0.694
0.751
0.918
1.000
0.840
0.918
1.000
0.915
1.000
1.089
23
Page 24

Table 4 — Electrical Data, 044 Units (cont)
575-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
518-632 26.7 120.0 26.7 120.0 7.2
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
FLA
7.5 9.0 76.3 100
10.0 11.0 78.3 100
15.0 17.0 84.3 110
20.0 22.0 89.3 110
BASE UNIT
ONLY
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
FLA
6.0 7.8 — — 84.1 110
10.0 12.2 — — 88.5 110
15.0 18.0 — — 94.3 110
— — 36 36.0 76.3 100
— — 72 72.0 101.3 110
— — 108† 108.0 146.2 150
6.0 7.8 36 36.0 84.1 110
6.0 7.8 72 72.0 101.3 110
6.0 7.8 108† 108.0 146.2 150
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 88.5 110
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 101.3 110
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 146.2 150
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 94.3 110
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 101.3 110
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 146.2 150
6.0 7.8 — — 86.1 110
10.0 12.2 — — 90.5 110
15.0 18.0 — — 96.3 110
— — 36 36.0 78.3 100
— — 72 72.0 103.7 110
— — 108† 108.0 148.7 150
6.0 7.8 36 36.0 86.1 110
6.0 7.8 72 72.0 103.7 110
6.0 7.8 108† 108.0 148.7 150
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 90.5 110
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 103.7 110
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 148.7 150
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 96.3 110
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 103.7 110
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 148.7 150
6.0 7.8 — — 92.1 110
10.0 12.2 — — 96.5 110
15.0 18.0 — — 102.3 125
— — 36 36.0 84.3 110
— — 72 72.0 111.2 125
— — 108† 108.0 156.2 175
6.0 7.8 36 36.0 92.1 110
6.0 7.8 72 72.0 111.2 125
6.0 7.8 108† 108.0 156.2 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 96.5 110
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 111.2 125
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 156.2 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 102.3 125
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 111.2 125
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 156.2 175
6.0 7.8 — — 97.1 110
10.0 12.2 — — 101.5 125
15.0 18.0 — — 107.3 125
— — 36 36.0 89.3 110
— — 72 72.0 117.5 150
— — 108† 108.0 162.5 175
6.0 7.8 36 36.0 97.1 110
6.0 7.8 72 72.0 117.5 150
6.0 7.8 108† 108.0 162.5 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 101.5 125
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 117.5 150
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 162.5 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 107.3 125
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 117.5 150
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 162.5 175
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
24
Page 25

Table 5 — Electrical Data, 054 Units
208/230-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
187-254 107.7 506.0 74.4 345.0 21.6
CV — Constant Volume
ETL — ETL Testing Laboratory
FLA — Full Load Amps
Hp — Nominal Horsepower
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (for wire sizing)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Electric heat available on 50 Series vertical discharge units.
†108 kW available on CV applications only.
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
LEGEND
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
BASE UNIT
ONLY
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
46.2/
15.0
20.0
25.0
30.0
42.0
59.4/
54.0
74.8/
68.0
88.0/
80.0
276.8/
272.6
290.0/
284.6
305.4/
298.6
318.6/
310.6
350/
350
350/
350
400/
400
400/
400
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 310.2/303.0 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 325.2/316.6 400/400
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 338.4/238.6 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 310.2/303.0 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 310.2/303.0 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 325.2/316.6 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 325.2/316.6 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 338.4/328.6 400/400
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 338.4/328.6 400/400
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 323.4/315.0 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 338.4/328.6 400/400
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 351.6/340.6 450/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 323.4/315.0 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 323.4/315.0 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 338.4/328.6 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 338.4/328.6 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 351.6/340.6 450/400
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 351.6/340.6 450/400
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 338.8/329.0 400/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 353.8/342.6 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 367.0/354.6 450/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 338.8/329.0 400/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 338.8/329.0 450/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 389.3/426.3 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 353.8/342.6 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 353.8/342.6 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 389.3/426.3 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 367.0/354.6 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 367.0/354.6 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 389.3/426.3 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 352.0/341.0 450/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 367.0/354.6 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 380.2/366.6 450/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 352.0/341.0 450/400
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 352.0/341.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.7/441.3 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 367.0/354.6 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 367.0/354.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.7/441.3 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 380.2/366.6 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 380.2/366.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.7/441.3 500/500
NOTES:
1. Electric resistance heaters are rated at 208/240 v, 480 v, or 575 v. To
determine heater capacity (kW) at unit operating voltage, multiply 240 v,
480 v, or 575 v capacity by appropriate multiplier below.
2. Boldface indicates 48 and 50 Series units. All other data is for 50 Series
units only.
FLA
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 276.8/272.6 350/350
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 276.8/280.0 350/350
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 290.0/284.6 350/350
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 290.0/295.0 350/350
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 305.4/298.6 400/400
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 305.4/312.5 450/450
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 389.3/426.3 500/500
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 318.6/310.6 400/400
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 318.6/327.5 500/500
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.7/441.3 500/500
HEATER kW
RATING
240
480
575
Electric heaters are tested and ETL approved at maximum
total external static pressure of 1.9 in. wg.
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
MULTIPLICATION FACTORS
VOLTAGE
DISTRIBUTION
V-3-60
200
208
230
240
440
460
480
550
575
600
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
MULTIPLICATION
FACTOR
0.694
0.751
0.918
1.000
0.840
0.918
1.000
0.915
1.000
1.089
25
Page 26

Table 5 — Electrical Data, 054 Units (cont)
460-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
414-508 50.6 253.0 34.6 173.0 10.8
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
15.0 21.0 129.6 175
20.0 27.0 135.6 175
25.0 34.0 142.6 175
30.0 40.0 148.6 175
BASE UNIT
ONLY
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 15.2 — — 144.8 175
15.0 22.0 — — 151.6 200
20.0 28.0 — — 157.6 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 144.8 175
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 144.8 175
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 200.0 200
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 151.6 200
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 151.6 200
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 200.0 200
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 157.6 200
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 157.6 200
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 200.0 200
10.0 15.2 — — 150.8 200
15.0 22.0 — — 157.6 200
20.0 28.0 — — 163.6 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 150.8 200
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 150.8 200
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 207.5 225
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 157.6 200
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 157.6 200
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 207.5 225
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 163.6 200
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 163.6 200
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 207.5 225
10.0 15.2 — — 157.8 200
15.0 22.0 — — 164.6 200
20.0 28.0 — — 170.6 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 157.8 200
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 158.7 225
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 216.3 250
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 164.6 200
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 164.6 225
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 216.3 250
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 170.6 200
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 170.6 225
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 216.3 250
10.0 15.2 — — 163.8 200
15.0 22.0 — — 170.6 200
20.0 28.0 — — 176.6 225
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 163.8 200
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 166.2 250
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 223.7 250
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 170.6 200
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 170.6 250
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 223.7 250
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 176.6 225
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 176.6 250
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 223.7 250
FLA
— — 36 46.3 129.6 175
— — 72 93.0 142.5 175
— — 108† 139.0 200.0 200
— — 36 46.3 135.6 175
— — 72 93.0 150.0 200
— — 108† 139.0 207.5 225
— — 36 46.3 142.6 175
— — 72 93.0 158.7 225
— — 108† 139.0 216.3 250
— — 36 46.3 148.6 200
— — 72 93.0 166.2 250
— — 108† 139.0 223.7 250
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
26
Page 27

Table 5 — Electrical Data, 054 Units (cont)
575-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
518-632 39.1 176.0 28.8 120.0 9.6
CV — Constant Volume
ETL — ETL Testing Laboratory
FLA — Full Load Amps
Hp — Nominal Horsepower
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (for wire sizing)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Electric heat available on 50 Series vertical discharge units.
†108 kW available on CV applications only.
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
LEGEND
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
BASE UNIT
ONLY
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
15.0 17.0 104.3 125
20.0 22.0 109.3 125
25.0 27.0 114.3 150
30.0 32.0 119.3 150
NOTES:
1. Electric resistance heaters are rated at 208/240 v, 480 v, or 575 v. To
determine heater capacity (kW) at unit operating voltage, multiply 240 v,
480 v, or 575 v capacity by appropriate multiplier below.
2. Boldface indicates 48 and 50 Series units. All other data is for 50 Series
units only.
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
HEATER kW
RATING
240
480
575
Electric heaters are tested and ETL approved at maximum
total external static pressure of 1.9 in. wg.
FLA
10.0 12.2 — — 116.5 150
15.0 18.0 — — 122.3 150
20.0 22.0 — — 126.3 150
— — 36 36.0 104.3 125
— — 72 72.0 111.2 125
— — 108† 108.0 156.2 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 116.5 150
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 116.5 150
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 156.2 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 122.3 150
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 122.3 150
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 156.2 175
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 126.3 150
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 126.3 150
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 156.2 175
10.0 12.2 — — 121.5 150
15.0 18.0 — — 127.3 150
20.0 22.0 — — 131.3 150
— — 36 36.0 109.3 125
— — 72 72.0 117.5 150
— — 108† 108.0 162.5 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 121.5 150
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 121.5 150
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 162.5 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 127.3 150
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 127.3 150
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 162.5 175
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 131.3 150
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 131.3 150
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 162.5 175
10.0 12.2 — — 126.5 150
15.0 18.0 — — 132.3 150
20.0 22.0 — — 136.3 175
— — 36 36.0 114.3 150
— — 72 72.0 123.7 175
— — 108† 108.0 168.7 200
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 126.5 150
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 126.5 175
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 168.7 200
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 132.3 150
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 132.3 175
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 168.7 200
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 136.3 175
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 136.3 175
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 168.7 200
10.0 12.2 — — 131.5 150
15.0 18.0 — — 137.3 175
20.0 22.0 — — 141.3 175
— — 36 36.0 119.3 150
— — 72 72.0 130.0 200
— — 108† 108.0 175.0 225
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 131.5 150
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 131.5 200
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 175.0 225
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 137.3 175
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 137.3 200
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 175.0 225
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 141.3 175
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 141.3 200
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 175.0 225
MULTIPLICATION FACTORS
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
VOLTAGE
DISTRIBUTION
V-3-60
200
208
230
240
440
460
480
550
575
600
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
MULTIPLICATION
FACTOR
0.694
0.751
0.918
1.000
0.840
0.918
1.000
0.915
1.000
1.089
27
Page 28

Table 6 — Electrical Data, 064 Units
208/230-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
187-254 107.7 506.0 107.0 506.0 21.6
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
FLA
46.2/
15.0
42.0
59.4/
20.0
54.0
74.8/
25.0
68.0
88.0/
30.0
80.0
BASE UNIT
ONLY
310.1/
305.9
323.3/
317.9
338.7/
331.9
351.9/
343.9
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 343.5/336.3 450/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 358.5/349.9 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 371.7/361.9 450/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 343.5/336.3 450/400
400/
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 343.5/336.3 450/400
400
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 450/400
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 358.5/349.9 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 358.5/349.9 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 358.5/393.8 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 371.7/361.9 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 371.7/361.9 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 371.7/393.8 450/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 356.7/348.3 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 371.7/361.9 450/450
20.0 61.6/66.0 — — 384.9/373.9 450/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 356.7/348.3 450/450
400/
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 356.7/348.3 450/450
400
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 371.7/361.9 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 371.7/361.9 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 371.7/408.8 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 384.9/373.9 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 384.9/373.9 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 384.9/408.8 450/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 372.1/362.3 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 387.1/375.9 450/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 400.3/387.9 500/450
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 372.1/362.3 450/450
400/
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 372.1/362.3 450/450
400
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 389.3/426.3 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 387.1/375.9 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 387.1/375.9 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 389.3/426.3 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 400.3/387.9 500/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 400.3/387.9 500/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 400.3/426.3 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 385.3/374.3 450/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 400.3/387.9 500/450
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 413.5/399.9 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 385.3/374.3 450/450
450/
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 385.3/374.3 500/500
450
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.7/441.3 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 400.3/387.9 500/450
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 400.3/387.9 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.7/441.3 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 413.5/399.9 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 413.5/399.9 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 413.5/441.3 500/500
FLA
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 310.1/305.9 400/400
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 310.1/305.9 400/400
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 353.5/393.8 400/400
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 323.3/317.9 400/400
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 323.3/317.9 400/400
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 370.0/408.8 450/450
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 338.7/331.9 400/400
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 338.7/331.9 450/450
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 389.3/426.3 500/500
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 351.9/343.9 450/450
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 351.9/343.9 500/500
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.7/441.3 500/500
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
28
Page 29

Table 6 — Electrical Data, 064 Units (cont)
460-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
414-508 50.6 253.0 50.6 253.0 10.8
CV — Constant Volume
ETL — ETL Testing Laboratory
FLA — Full Load Amps
Hp — Nominal Horsepower
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (for wire sizing)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Electric heat available on 50 Series vertical discharge units.
†108 kW available on CV applications only.
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
LEGEND
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
BASE UNIT
ONLY
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
15.0 21.0 145.6 175
20.0 27.0 151.6 200
25.0 34.0 158.6 200
30.0 40.0 164.6 200
NOTES:
1. Electric resistance heaters are rated at 208/240 v, 480 v, or 575 v. To
determine heater capacity (kW) at unit operating voltage, multiply 240 v,
480 v, or 575 v capacity by appropriate multiplier below.
2. Boldface indicates 48 and 50 Series units. All other data is for 50 Series
units only.
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
HEATER kW
RATING
240
480
575
Electric heaters are tested and ETL approved at maximum
total external static pressure of 1.9 in. wg.
FLA
10.0 15.2 — — 160.8 200
15.0 22.0 — — 167.6 200
20.0 28.0 — — 173.6 200
— — 36 46.3 145.6 175
— — 72 93.0 145.6 175
— — 108† 139.0 200.0 200
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 160.8 200
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 160.8 200
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 200.0 200
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 167.6 200
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 167.6 200
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 200.0 200
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 173.6 200
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 173.6 200
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 200.0 200
10.0 15.2 — — 166.8 200
15.0 22.0 — — 173.6 200
20.0 28.0 — — 179.6 225
— — 36 46.3 151.6 200
— — 72 93.0 151.6 200
— — 108† 139.0 207.5 225
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 166.8 200
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 166.8 200
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 207.5 225
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 173.6 200
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 173.6 200
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 207.5 225
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 179.6 225
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 179.6 225
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 207.5 225
10.0 15.2 — — 173.8 200
15.0 22.0 — — 180.6 225
20.0 28.0 — — 186.6 225
— — 36 46.3 158.6 200
— — 72 93.0 158.7 225
— — 108† 139.0 216.3 250
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 173.8 200
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 173.8 225
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 216.3 250
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 180.6 225
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 180.6 225
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 216.3 250
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 186.6 225
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 186.6 225
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 216.3 250
10.0 15.2 — — 179.8 225
15.0 22.0 — — 186.6 225
20.0 28.0 — — 192.6 225
— — 36 46.3 164.6 200
— — 72 93.0 166.2 250
— — 108† 139.0 223.7 250
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 179.8 225
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 179.8 250
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 223.7 250
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 186.6 225
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 186.6 250
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 223.7 250
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 192.6 225
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 192.6 250
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 223.7 250
MULTIPLICATION FACTORS
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
VOLTAGE
DISTRIBUTION
V-3-60
200
208
230
240
440
460
480
550
575
600
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
MULTIPLICATION
FACTOR
0.694
0.751
0.918
1.000
0.840
0.918
1.000
0.915
1.000
1.089
29
Page 30

Table 6 — Electrical Data, 064 Units (cont)
575-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
518-632 39.1 176.0 39.1 176.0 9.6
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
15.0 17.0 114.6 150
20.0 22.0 119.6 150
25.0 27.0 124.6 150
30.0 32.0 129.6 150
BASE UNIT
ONLY
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 12.2 — — 126.8 150
15.0 18.0 — — 132.6 150
20.0 22.0 — — 136.6 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 126.8 150
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 126.8 150
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 156.2 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 132.6 150
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 132.6 150
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 156.2 175
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 136.6 175
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 136.6 175
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 156.2 175
10.0 12.2 — — 131.8 150
15.0 18.0 — — 137.6 175
20.0 22.0 — — 141.6 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 131.8 150
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 131.8 150
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 162.5 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 137.6 175
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 137.6 175
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 162.5 175
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 141.6 175
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 141.6 175
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 162.5 175
10.0 12.2 — — 136.8 175
15.0 18.0 — — 142.6 175
20.0 22.0 — — 146.6 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 136.8 175
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 136.8 175
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 168.7 200
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 142.6 175
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 142.6 175
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 168.7 200
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 146.6 175
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 146.6 175
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 168.7 200
10.0 12.2 — — 141.8 175
15.0 18.0 — — 147.6 175
20.0 22.0 — — 151.6 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 141.8 175
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 141.8 200
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 175.0 225
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 147.6 175
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 147.6 200
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 175.0 225
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 151.6 175
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 151.6 200
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 175.0 225
FLA
— — 36 36.0 114.6 150
— — 72 72.0 114.6 150
— — 108† 108.0 156.2 175
— — 36 36.0 119.6 150
— — 72 72.0 119.6 150
— — 108† 108.0 162.5 175
— — 36 36.0 124.6 150
— — 72 72.0 124.6 175
— — 108† 108.0 168.7 200
— — 36 36.0 129.6 150
— — 72 72.0 130.0 200
— — 108† 108.0 175.0 225
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
30
Page 31

Table 7 — Electrical Data, 074 Units
208/230-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
187-254 107.7 506.0 142.3 690.0 27.8
CV — Constant Volume
ETL — ETL Testing Laboratory
FLA — Full Load Amps
Hp — Nominal Horsepower
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (for wire sizing)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Electric heat available on 50 Series vertical discharge units.
†108 kW available on CV applications only.
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
LEGEND
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
BASE UNIT
ONLY
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
46.2/
15.0
20.0
25.0
30.0
42.0
59.4/
64.0
74.8/
68.0
88.0/
80.0
358.8/
854.6
372.0/
366.6
387.4/
380.6
400.6/
392.6
500/
450
500/
500
500/
500
500/
500
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 392.2/385.0 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 407.2/398.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 420.4/410.6 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 392.2/385.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 392.2/385.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 392.2/393.8 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 407.2/398.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 407.2/398.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 407.2/398.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 420.4/410.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 420.4/410.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 420.4/410.6 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 405.4/397.0 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 420.4/410.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 433.6/422.6 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 405.4/397.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 405.4/397.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.4/408.8 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 420.4/410.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 420.4/410.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 420.4/410.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 433.6/422.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 433.6/422.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 433.6/422.6 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 420.8/411.0 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 435.8/424.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 449.0/436.6 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 420.8/411.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 420.8/411.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 420.8/426.3 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 435.8/424.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 435.8/424.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 435.8/426.3 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 449.0/436.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 449.0/436.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 449.0/436.6 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 — — 434.0/423.0 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 — — 449.0/436.6 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 — — 462.2/448.6 600/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 434.0/423.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 434.0/423.0 500/500
10.0 33.4/30.4 88/108† 236.6/273.0 434.0/441.3 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 449.0/436.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 449.0/436.6 500/500
15.0 48.4/44.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 449.0/441.3 500/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 462.2/448.6 600/500
20.0 61.6/56.0 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 462.2/448.6 600/500
20.0 61.6/66.0 88/108† 236.6/273.0 462.2/448.6 600/500
NOTES:
1. Electric resistance heaters are rated at 208/240 v, 480 v, or 575 v. To
determine heater capacity (kW) at unit operating voltage, multiply 240 v,
480 v, or 575 v capacity by appropriate multiplier below.
2. Boldface indicates 48 and 50 Series units. All other data is for 50 Series
units only.
FLA
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 358.8/354.6 500/450
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 358.8/354.6 500/450
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 358.8/393.8 500/450
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 372.0/366.6 500/500
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 372.0/366.6 500/500
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 372.0/408.8 500/500
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 387.4/380.6 500/500
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 387.4/380.6 500/500
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 389.3/426.3 500/500
— — 29/ 36 78.9/ 91.0 400.6/392.6 500/500
— — 59/ 72 157.7/182.0 400.6/392.6 500/500
— — 88/108† 236.6/273.0 405.7/441.3 500/500
HEATER kW
RATING
240
480
575
Electric heaters are tested and ETL approved at maximum
total external static pressure of 1.9 in. wg.
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
MULTIPLICATION FACTORS
VOLTAGE
DISTRIBUTION
V-3-60
200
208
230
240
440
460
480
550
575
600
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
MULTIPLICATION
FACTOR
0.694
0.751
0.918
1.000
0.840
0.918
1.000
0.915
1.000
1.089
31
Page 32

Table 7 — Electrical Data, 074 Units (cont)
460-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
414-508 50.6 253.0 65.4 345.0 13.5
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
15.0 21.0 166.8 225
20.0 27.0 172.8 225
25.0 34.0 179.8 225
30.0 40.0 185.8 250
BASE UNIT
ONLY
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
10.0 15.2 — — 182.0 225
15.0 22.0 — — 188.8 250
20.0 28.0 — — 194.8 250
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 182.0 225
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 182.0 225
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 200.0 225
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 188.8 250
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 188.8 250
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 200.0 250
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 194.8 250
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 194.8 250
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 200.0 250
10.0 15.2 — — 188.0 250
15.0 22.0 — — 194.8 250
20.0 28.0 — — 200.8 250
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 188.0 250
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 188.0 250
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 207.5 250
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 194.8 250
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 194.8 250
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 207.5 250
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 200.8 250
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 200.8 250
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 207.5 250
10.0 15.2 — — 195.0 250
15.0 22.0 — — 201.8 250
20.0 28.0 — — 207.8 250
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 195.0 250
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 195.0 250
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 216.3 250
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 201.8 250
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 201.8 250
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 216.3 250
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 207.8 250
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 207.8 250
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 216.3 250
10.0 15.2 — — 201.0 250
15.0 22.0 — — 207.8 250
20.0 28.0 — — 213.8 250
10.0 15.2 36 46.3 201.0 250
10.0 15.2 72 93.0 201.0 250
10.0 15.2 108† 139.0 223.7 250
15.0 22.0 36 46.3 207.8 250
15.0 22.0 72 93.0 207.8 250
15.0 22.0 108† 139.0 223.7 250
20.0 28.0 36 46.3 213.8 250
20.0 28.0 72 93.0 213.8 250
20.0 28.0 108† 139.0 223.7 250
FLA
— — 36 46.3 166.8 225
— — 72 93.0 166.8 225
— — 108† 139.0 200.0 225
— — 36 46.3 172.8 225
— — 72 93.0 172.8 225
— — 108† 139.0 207.5 225
— — 36 46.3 179.8 225
— — 72 93.0 179.8 225
— — 108† 139.0 216.3 250
— — 36 46.3 185.8 250
— — 72 93.0 185.8 250
— — 108† 139.0 223.7 250
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
32
Page 33

Table 7 — Electrical Data, 074 Units (cont)
575-3-60 (V-Ph-Hz)
COMPR
VOLTAGE
RANGE
518-632 39.1 176.0 52.6 276.0 12.0
CV — Constant Volume
ETL — ETL Testing Laboratory
FLA — Full Load Amps
Hp — Nominal Horsepower
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps (for wire sizing)
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Electric heat available on 50 Series vertical discharge units.
†108 kW available on CV applications only.
NO. 1
RLA LRA RLA LRA
LEGEND
COMPR
NO. 2
OFM IFM
Total
FLA
BASE UNIT
ONLY
Hp FLA MCA MOCP
15.0 17.0 133.8 175
20.0 22.0 138.8 175
25.0 27.0 143.8 175
30.0 32.0 148.8 200
NOTES:
1. Electric resistance heaters are rated at 208/240 v, 480 v, or 575 v. To determine heater capacity (kW) at unit operating voltage, multiply 240 v, 480
v, or 575 v capacity by appropriate multiplier below.
2. Boldface indicates 48 and 50 Series units. All other data is for 50 Series
units only.
EXHAUST
FAN
TotalHpTotal
HEATER kW
RATING
240
480
575
Electric heaters are tested and ETL approved at maximum
total external static pressure of 1.9 in. wg.
FLA
10.0 12.2 — — 146.0 175
15.0 18.0 — — 151.8 200
20.0 22.0 — — 155.8 200
— — 36 36.0 133.8 175
— — 72 72.0 133.8 175
— — 108† 108.0 156.2 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 146.0 175
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 146.0 175
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 156.2 175
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 151.8 200
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 151.8 200
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 156.2 200
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 155.8 200
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 155.8 200
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 156.2 200
10.0 12.2 — — 151.0 200
15.0 18.0 — — 156.8 200
20.0 22.0 — — 160.8 200
— — 36 36.0 138.8 175
— — 72 72.0 138.8 175
— — 108† 108.0 162.5 175
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 151.0 200
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 151.0 200
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 162.5 200
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 156.8 200
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 156.8 200
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 162.5 200
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 160.8 200
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 160.8 200
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 162.5 200
10.0 12.2 — — 156.0 200
15.0 18.0 — — 161.8 200
20.0 22.0 — — 165.8 200
— — 36 36.0 143.8 175
— — 72 72.0 143.8 175
— — 108† 108.0 168.7 200
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 156.0 200
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 156.0 200
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 168.7 200
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 161.8 200
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 161.8 200
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 168.7 200
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 165.8 200
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 165.8 200
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 168.7 200
10.0 12.2 — — 161.0 200
15.0 18.0 — — 166.8 200
20.0 22.0 — — 170.8 200
— — 36 36.0 148.8 200
— — 72 72.0 148.8 200
— — 108† 108.0 175.0 225
10.0 12.2 36 36.0 161.0 200
10.0 12.2 72 72.0 161.0 200
10.0 12.2 108† 108.0 175.0 225
15.0 18.0 36 36.0 166.8 200
15.0 18.0 72 72.0 166.8 200
15.0 18.0 108† 108.0 175.0 225
20.0 22.0 36 36.0 170.8 200
20.0 22.0 72 72.0 170.8 200
20.0 22.0 108† 108.0 175.0 225
MULTIPLICATION FACTORS
ELECTRIC
HEAT*
kW FLA MCA MOCP
VOLTAGE
DISTRIBUTION
V-3-60
200
208
230
240
440
460
480
550
575
600
BASE UNIT WITH
EXHAUST FAN
AND/OR
ELECTRIC HEAT*
MULTIPLICATION
FACTOR
0.694
0.751
0.918
1.000
0.840
0.918
1.000
0.915
1.000
1.089
33
Page 34

CONTROL WIRING — Install a Carrier-approved accessory 24-v thermostat assembly according to the installation
instructions shipped with the accessory. Locate thermostat
assembly to sense average temperature. Route thermostat cable
or equivalent leads of colored wire from subbase terminals
to terminal board (P1). The terminal board (P1) is located on
the constant volume control board on units with no economizer and on the economizer board on units with the economizer option.
Total wire lengths should not exceed the following limits:
50 ft of 18 AWG, 80 ft of 16AWG or 125 ft of 14 AWG.See
Fig. 19 for field wiring connections between the thermostat
and the unit 24-v terminal block. Once wire length from unit
to thermostat is determined, the length should be doubled to
obtain total wire length required. Voltage drop is dependent
on length of current path.
There are no required 115-v field wiring connections, therefore no provisions have been made in the unit for running
115-v wiring. If any of the field-installed options requiring
115-v connections are desired, the unit must be modified in
the field for 115-v wiring.
Options requiring 24-v or 115-v control wiring are listed
below.
Building Pressurization or Smoke Purge Mode — Refer to
appropriate unit Controls and Troubleshooting literature as
necessary for additional information. See Fig. 20 and unit
wiring label for wiring details.
1. Firestat or smoke detector (field-supplied normally-
closed switch 1) — Remove factory-installed jumper wire
and wire a field-supplied firestat or smoke detector contactor between terminals 5 and 6 (034-044 units) or terminals 2 and 3 (054-074 units) on terminal block 2 in the
unit control box.
2. Switch to drive economizer outdoor-air damper fully open
(field-supplied normally-open switch 2) — Wire a fieldsupplied switch between terminals 8 and 9 on economizer motor no. 1. When this switch is manually closed,
it will drive the outdoor-air damper fully open.
3. Switch to disconnect power to economizer motors (field-
supplied normally-closed switch 3) — Wire a fieldsupplied switch between terminal C on the economizer
motor and Plug 8, Pin 2 (PL8-2).
4. Building pressurization switch (field-supplied normally-
open switch 4) — Wire a field-supplied switch between
Fig. 19 — Field Control Thermostat Wiring
TB2 and the C1 connection on the evaporator-fan contactor coil (IFC on unit label diagram).
5. Switch to isolate evaporator-fan motor (field-supplied
normally-closed switch 5).
Modulating Power Exhaust — Wirea field-supplied switch
in series with the black wire removed from TRAN3
primary.
Constant Volume Power Exhaust — Wire a field-supplied
switch in series with the black wire from Plug 7, Pin 1
(PL7-1) to the red wire on economizer motor no. 2 (DMS1
on unit label diagram).
6. Switch to energize power exhaust motor (field-supplied
normally-open switch 6) — Wire a field-supplied switch
from terminal 5 (on 034-044 units) or terminal 2 (054074 units) on terminal block 2 in series with the red wire
from switch 5 to the damper motor switch (DMS1) on
economizer motor no. 2 (or in parallel with SW5).
7. Switch to fully open power exhaust damper (fieldsupplied normally-open switch 7) — Wire a fieldsupplied switch between terminal C and the normallyclosed switch on DPS2.
NOTES AND LEGEND FOR FIG. 20
BUILDING PRESSURIZATION SMOKE PURGE ALARM
Switch 1 Switch 1 Switch 1
Switch 2 Switch 2 Switch 3
Switch 4 Switch 5
Switch 5 Switch 6
Switch 1 — Remove jumper. Firestat or smoke detector —
Switch 2 — Switch to drive economizer outdoor-air damper fully
Switch 3 — Switch to disconnect power to economizer motors.
Switch 4 — Building pressurization switch (energize evaporator-
Switch 5 — Switch to isolate evaporator-fan motor — normally
Switch 6 — Switch to energize power exhaust motors — normally
Switch 7 — Switch to fully open power exhaust damper —
normally closed.
open — normally open.
Drives economizer outdoor-air damper fully closed —
normally closed.
fan motor) — normally open.
closed.
open.
normally open.
Switch 7 (MPE)
LEGEND
C—Contactor
DPS — Differential Pressure Switch
DMS — Damper Motor Switch
ECON — Economizer
IFC — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Contactor
MPE — Modulating Power Exhaust
NC — Normally Closed
NO — Normally Open
PEC — Power Exhaust Contactor Coil
PL — Plug
SW — Switch
TB — Terminal Block
TRAN — Transformer
NOTES:
1. Power exhaust option can be unit mounted on vertical supply/
return units only.
2. is field wiring.
3. is field wiring.
4. Switches 1-7 are field supplied.
5. For building pressurization, field supplied power source mustdrive
room terminals wide open.
34
Page 35

034 AND 044 UNITS
BASE UNIT
054-074 UNITS
BASE UNIT
BASE UNIT
OPTIONAL MODULATING POWER EXHAUST
OPTIONAL NON-MODULATING EXHAUST
Fig. 20 — Field Wiring for Building Pressurization and Smoke Purge
OPTIONAL MODULATING POWER EXHAUST
OPTIONAL NON-MODULATING EXHAUST
35
Page 36

GasPiping (48 SeriesUnits Only)— Unit is equipped
for use with natural gas only. Installation must conform with
local building codes, or in the absence of local codes, with
the National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1.
A 1/8-in. NPT tapping plug, accessible for test gage connection, must be field installed immediately upstream of gas
supply connection to unit, but after manual gas valve. See
Fig. 21. Natural gas pressure at unit gas connection must not
be less than 5 in. wg or greater than 13 in. wg.
Size gas supply piping for 0.5 in. wg maximum pressure
drop. Do not use supply pipe smaller than unit gas
connection.
Disconnect gas piping from unit when leak testing at
pressures greater than 0.5 psig. Pressures greater than
0.5 psig will cause gas valve damage resulting in a hazardous condition. If gas valve is subjected to pressure
greater than 0.5 psig, it must be replaced.
InstallingFlue/Inlet Hoods (48 Series UnitsOnly)
The flue/inlet hoods are shipped in a bag taped to the
—
basepan in the gas section.
UNIT SIZES 034 AND 044 — The 48 series units have 2
inlet hoods, 2 flue hoods, and 2 flue deflector hoods. See
Fig. 22. The 48 series low-heat units have one inlet hood,
one flue hood and one flue deflector hood.
*NPT plug is field supplied.
NOTE: Follow all local codes.
Fig. 21 — Gas Piping Details
Remove shipping block-offsand shipping tape from openings in access panel. Inlet hoods are shipped unassembled
and must be assembled in place. See Fig. 23. The inlet hood
consists of a hood, 2 side plates, and an inlet screen.
Install inlet hoods using screws provided.
NOTE: Hoods must be assembled in place on the access panel.
Flanges on hood and side plates go to the inside of the access panel.
Install inlet screen on each inlet hood using speed clips
and screws provided. Attach flue hoods (see Fig. 24) to access panel using screws provided. Hoods go over each combustion air outlet.
Sub-assemble flue deflector baffle inside the flue deflector
hood as shown in Fig. 25 and 26. Flue deflector baffle must
be assembled and installed on the access panel so that the
holes in the mounting flange are at the bottom. Install flue
deflector hood over flue hoods. Be sure that deflector scoop
is pointed up.
UNIT SIZES 054-074 — The 48 series high-heat units have
2 large inlet hoods, 2 small inlet hoods, 3 flue hoods, and
3 flue deflector hoods. See Fig. 27 and 28. The 48 series
low-heat units have one large inlet hood, 2 small inlet hoods,
2 flue hoods, and 2 flue deflector hoods. (See Fig. 27
and 28).
Remove shipping block-offsand shipping tape from openings in access panels. Inlet hoods are shipped unassembled
and must be assembled in place. See Fig. 23. Inlet hoods
consist of a hood, 2 side plates, and an inlet screen.
Install large and small inlet hoods using screws provided.
NOTE: Hoods must be assembled in place on the access panel.
Flanges on hood and side plates go to the inside of the access panel.
Install inlet screen in each inlet hood using speed clips
and screws provided. Attach flue hoods (see Fig. 24) to access panel using screws provided. Hoods go over each combustion air outlet.
Sub-assemble flue deflector baffle inside flue deflector hood
as shown in Fig. 29. Install flue deflector hoods over flue
hoods. (See Fig. 27.)
NOTE: Be sure deflector hoods are installed as shown and
not upside down. The holes in the mounting flange must be
at the bottom when installed on access panel.
FLUE HOOD AND
FLUE DEFLECTOR
HOOD (48 SERIES
HIGH-HEAT ONLY)
INLET HOOD
(48 SERIES HIGHHEAT ONLY)
FLUE HOOD AND
DEFLECTOR
HOOD
INLET HOOD
Fig. 22 — Flue/Inlet Hood, 034,044 Units
36
INLET HOOD
INLET HOOD
SIDE PLATE
(TYP EACH SIDE)
Fig. 23 — Inlet Hood
Page 37

FLUE AND
FLUE
DEFLECTOR
HOOD
LOCATION
FLUE HOOD
AND FLUE
DEFLECTOR
HOOD
SMALL
INLET
HOOD
Fig. 24 — Flue Hood
FLUE DEFLECTOR
HOOD
FLUE
DEFLECTOR
BAFFLE
(BOTTOM
HOOD ONLY)
FLUE DEFLECTOR
BAFFLE (BOTH HOODS)
Fig. 25 — Flue Deflector Baffles, 034,044 Units
LARGE
INLET
HOOD
LARGE
INLET
HOOD
LOCATION
(48 SERIES,
HIGH-HEAT
ONLY)
Fig. 27 — Flue/Inlet Hood, 054-074 Units
FLUE HOOD AND
FLUE DEFLECTOR
HOOD
SMALL
INLET
HOOD
REMOVED
FLUE AND
FLUE
DEFLECTOR
HOOD
LOCATION
(48 SERIES,
HIGH-HEAT
ONLY)
SMALL INLET
HOOD
TOP
(WHEN
INSTALLED)
FLUE
DEFLECTOR
BAFFLE
FOR BOTTOM
HOOD ONLY
Fig. 26 — Flue Deflector Hood, 034,044 Units
(Assembled)
LARGE INLET
HOOD
Fig. 28 — Flue/Inlet Hood Close-Up
PUSH
BAFFLE
DOWN SO
THESE 2
HOLES
ALIGN
FLUE DEFLECTOR
BAFFLE
TOP (WHEN INSTALLED)
FLUE
DEFLECTOR
HOOD
Fig. 29 — Flue Deflector Baffle, 054-074 Units
(Assembled)
37
Page 38

PRE-START-UP
Unit Preparation —
installed in accordance with these Installation Instructions
and all applicable codes.
Check to see that unit has been
Compressor Mounting — Loosen compressor hold-
down bolts until sidewise movement of the washer under
each holddown bolt head can be obtained. Do not loosen
completely, as bolts are self-locking and will maintain
adjustment.
Evaporator-Fan Shipping Brackets — Evapor-
ator-fan shipping brackets (4 per unit) must be removed from
each corner of the fan sled before starting unit.
UNIT SIZES 034 AND 044
1. To remove brackets, raise fan sled by turning adjusting
bolt counterclockwise until spring is compressed slightly.
2. Remove screws holding shipping bracket to unit cross rail.
3. Remove shipping bracket (top of bracket is slotted so that
it will slide out).
4. After removing all shipping brackets, level fan sled using
the adjusting screws. On all 4 corners, dimension from
cross rail to fan sled should be as shown in Fig. 30.
UNIT SIZES 054-074 — To remove shipping brackets, remove the 6 screws holding each bracket to the cross rail.
There are 8 brackets per unit. See Fig. 30 or 31.
After removing all shipping brackets, level fan sled using
the adjusting screws. On all 4 corners dimension from cross
rail to fan sled should be as shown in Fig. 30 or 31.
Refrigerant Service Valves — All units have a
Schrader-type service port on both suction lines. Be sure that
caps on the ports are tight. All units have discharge and suction service valves on each compressor and a service valve
on each liquid line. Be sure the valves are open before starting unit.
Crankcase Heaters — The crankcase heaters must be
firmly locked into the compressors. The crankcase heaters
are energized when there is power to the unit. Crankcase
heaters must be energized with discharge and suction service valves open for at least 24 hours prior to unit start-up in
orderto remove liquid refrigerant from the compressorcrankcase and to prevent oil foaming.
Compressor Oil — Check that compressor oil is vis-
ible in the sight glass of the compressor.All units are factory
charged with oil. See Table 8. Observe oil level closely at
start-up. If oil level is below the sight glass and cannot be
seen, add oil until the level is approximately 1/4 of sight
glass. See Carrier Standard Service Techniques, Refrigerants section, for procedures to add or remove oil.
Internal Wiring — Check all electrical connections in
the unit control box; tighten as required.
Fig. 30 — Shipping Brackets; 034,044 Units and
50 Series Vertical Discharge 054-074 Units
Fig. 31 — Shipping Brackets; 48 Series 054-074 Units
and 50 Series Horizontal Discharge 054-074 Units
Table 8 — Oil Charge
UNIT SIZE OIL CHARGE (pints)
034 16 ( 8 each circuit)
044 28 (14 each circuit)
054 33 (19 ckt 1, 14 ckt 2)
064 38 (19 each circuit)
074 38 (19 each circuit)
38
Page 39

If oil charge is above sight glass, do not remove any oil
until the compressor crankcase heater has been on for at least
24 hours. When additional oil or a complete charge is needed,
use only Carrier-approved compressor oil.
Approved oils:
Texaco, Inc. ................................................. Capella WF-32
Shrieve Chemical Co. ....................... Zerol 150 (Synthetic)
Witco Co. .......................................................... Suniso 3GS
Do not reuse drained oil and do not use any oil that has
been exposed to the atmosphere.
Gas Manifold Pressure (48 Series Units Only)
Check pressure to ensure it matches the pressure stamped
—
on the valve body. See Gas Valve Adjustment section on
page 50 for more details.
Unit Voltage — Be sure power source agrees with the
unit nameplate rating.
Leak Test and Dehydration — Be sure there are no
refrigerant leaks. All units are shipped with a complete operating charge of R-22 (Tables 1A and 1B) and should be
under sufficient pressure for leak testing after installation. If
there is no system pressure, add refrigerant until a pressure
is observed and then check for leaks. After leaks are repaired, remove and recover refrigerant from the system. For
leak testing procedures, see Carrier Standard Service Techniques, Refrigerants section. Do not use the system compressors to remove refrigerant from the system.
Evaporator-Fan Belts, Pulleys, and Sheaves —
Belts, pulleys, and sheaves are factory installed. All pulleys
are nonadjustable.
See Tables 1A and 1B for fan shaft center distance ranges
and shaft sizes when making selections for field-supplied drives.
See Tables 9A and 9B for a complete listing of fieldsupplied pulleys and belt connections.
Check the lubrication of fan and motor bearings. Bearings
are shipped full of grease for corrosion protection and may
run warm temporarily on start-up until the excess grease has
discharged. Check bearing setscrews for tightness. Also check
the tightness of the setscrews on the fan wheel and on the
fan and motor sheaves. Check fan shaft bearing mountings
for tightness.
Recheck sheave alignment and belt tension. See Adjustments section on page 46 for instructions.
Hand-turn the fan to make sure the fan wheel does not rub
on the fan housing. The fan shaft and motor shaft must be
free wheeling before power is applied to the unit.
Following the necessary electrical checks, check for fan
vibration. If excessive vibration occurs, check for:
• drive misalignment
• mismatched belts
• wheel or sheaves loose on shaft
• loose bearings
• loose mounting bolts
• motor out of balance
• sheaves eccentric or out of balance
• wheel out of balance (replace if necessary)
Table 9A — Field-Supplied Evaporator-Fan Pulley Data, 034,044 Units
IFM
Hp
1
7
10
15
20
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
IFM
RPM
435
500 3.9
590 4.6
⁄
2
650 5.1
720 5.6
820 6.4
500
550
575 4.5
650 5.1
730 5.7
830 6.5 66.0
550
625 4.9
675 5.3
730 5.7
800 6.3
880 6.7 66.0
575
625 4.9
700 5.5
750 5.5
830 6.5
880 6.9 66.0
Grooves
MOTOR PULLEY BLOWER PULLEY BELTS
No.
2BK
2
2 B5V
2 B5V
Type Size (in.)
3.4
BK 3.9 2 B5V 13.6 2 BX 61.8
4.3
B5V
4.3
4.5
No.
Grooves
2 B5V 13.6 2 BX
2 B5V 13.7 2 5VX
2 B5V 13.7 2 5VX
2 B5V 13.7 2 5VX
Type Size (in.) Quantity Type Size (in.)
61.8
64.8
63.0
63.0
63.0
39
Page 40

Table 9B — Field-Supplied Evaporator-Fan Pulley Data, 054-074 Units
IFMHpIFM
RPM
450
470 16.1
485 15.5
15
575 4.5
725 5.7
405
470 16.1
485 15.5
20
575
725 5.7
405
470 16.1
485 15.5
25
575
725 5.7
470
485 15.5
530 3 4.7 3 15.5 3 3
30
600
730 6.5
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
MOTOR PULLEY BLOWER PULLEY
No.
Grooves
Type Size (in.)
2 B5V
3
B5V
2
3
B5V
2
4
B5V
2
No.
Grooves
4.3
4.3 3
4.5
4.3 3
4.5
4.3 4
5.5
BELTS
48 Series and 50 Series
Horizontal Discharge Units
Type Size (in.) Quantity Type Size (in.) Quantity Type Size (in.)
2 B5V
B5V
2 13.7 2 115 2 123660 5.1
B5V
2 13.7 2 B5V 2700 5.5
B5V
2 15.5 2 2660 5.9
18.5
13.7 112650 5.1
18.5
18.5
16.1
2 5VX
3
5VX
3 5VX
4
5VX 118
118
115
123
118 125
123
115
50 Series
Vertical Discharge Units
2 5VX
3
3
4
132
125
123
132
5VX
132
125
5VX
123
5VX 123
Check rotation of wheel with arrow on the fan housing.
Check fan speed with a strobe-type tachometer, or use this
formula:
Fan
Rpm
motor rpm x motor sheave pitch diameter (in.)
=
fan sheave pitch diameter (in.)
(Obtain motor rpm from the fan motor nameplate and read
sheave pitch diameters marked on the fan and motor sheaves.)
Example:
Nameplate motor rpm .................................................. 1760
Motor sheave pitch diameter (in.) .................................. 6.4
Fan sheave pitch diameter (in.) .................................... 12.4
Fan Rpm = = 908 Rpm
1760 x 6.4
12.4
The maximum allowable fan speed for the supply-air fan
is 900 rpm for 034 and 044 units and 750 rpm for 054-074
units. The maximum rpm for the power exhaust is 1300 rpm
for 034 and 044 units and 925 rpm for 054-074 units.
Excessive fan speed may result in condensate carryover from
the evaporator coil, fan motor overload, or wheel failure. See
Table 10 for Air Quantity Limits.
Table 10 — Air Quantity Limits (cfm)
UNIT SIZE MINIMUM MAXIMUM
034 6,000 15,000
044 8,000 20,000
054 10,000 25,000
064 12,000 30,000
074 14,000 30,000
Condenser Fans and Motors — Eachunit has mul-
tiple condenser fans and motors; these are positioned at the
factory.See Fig. 32 for correct location of fan in orifice. Check
that fan propeller rotation is correct; it should be counterclockwise when facing the fans. If fan propeller rotation is
incorrect, switch motor leads.
Return-Air Filters — Check that the correct filters are
installed in the filter rack. See Tables 1A and 1B for quantities and sizes. Access is through the door marked FILTER
SECTION. Do not operate the unit without return-air filters.
Economizer Inlet Screens — Check that they are in
place before operating the unit.
Economizer Dampers — With no power to the unit,
the economizer outdoor-air dampers should be fully closed.
Check by opening the access door marked FILTER SECTION. On units with economizer, be sure economizer minimum position is set at the desired setting. Be sure hood is
installed properly.
25%Outdoor-Air Damper — On units without econo-
mizer, be sure 25% outdoor-air damper is set at the desired
position. Also, be sure hood is installed properly.
40
Page 41

Fig. 32 — Condenser-Fan Adjustment
Initial Check
IMPORTANT: Do not attempt to start unit, even momentarily,until all items on the Start-Up Checklist and
the following steps have been completed.
1. Verify unit has been installed per the Installation section
of this literature.
2. Certify that all auxiliary components (sensors, controls,
etc.) have been installed and wired to the control boxes
per these instructions, the Controls and Troubleshooting
literature (DK,DY,NB,NP units only), and the unit wiring
label diagrams.
3. Verify that pressure hoses (static, duct, etc.) are properly
attached, routed, and free from pinches or crimps that may
affect proper control operation.
4. Set any control configurations that are required (fieldinstalled accessories, etc.). The unit is factory configured
for all appropriate factory-installed options with the applicable controls programmed to the default values. See
unit Controls and Troubleshooting literature for applicable configuration values.
5. Enter unit set points (if applicable). The unit is shipped
with the set point default values shown in the Controls
and Troubleshooting literature (as applicable). If a different set point is required, change per the example shown
under Set Point Function section in appropriate unit Controls and Troubleshooting literature.
6. Configure schedule subfunctions (if applicable): occupied, unoccupied, and holiday periods. See Schedule Function section in Controls and Troubleshooting literature for
details on setting periods.
7. Verify that control time periods programmed meet current requirements.
8. Check all electrical connections to be sure they are tight.
START-UP
General
1. Put the ON/OFF switch in the ON position. Close the control circuit breaker (CCB), which will energize the control circuit and the crankcase heaters.
2. For PIC and VAV units, refer to Controls and Troubleshooting literature for quick test details.
3. Complete Pre-Start-Up section items and Start-Up Checklist.
Operating Sequences — Base unit operating se-
quences are presented below.Referto unit Controls and Troubleshooting literature for details on VAV and PIC controls operation.
COOLING, UNITS WITHOUT ECONOMIZER — Unit
power on, system selector switch set at COOL or AUTO.
position, fan switch set at AUTO. position.
On a call for cooling,Y1 on the thermostat subbase closes,
energizing compressor no. 1 as first stage of cooling. (Compressor no. 1 is always the larger of the 2 unit compressors.)
If cooling load cannot be satisfied with only first-stage cooling, Y2 on the thermostat will close, energizing compressor
no. 2.
Condenser fans are energized with compressor no. 1. The
no. 1 fan runs continuously while the unit is on mechanical
cooling; the no. 2 fan is cycled on and off in response to
outdoor ambient temperature for head pressure control. Check
cooling effects at a setting below room temperature. Reset
thermostat at a setting above room temperature. Compressors will shut off.
HEATING, UNITS WITHOUT ECONOMIZER
48 Series Low-Heat Units — Unit power on, thermostat sys-
tem switch set at HEAT or AUTO. position, and fan switch
set at AUTO. position.
First-stage thermostat (W1) calls for heat. Time-delay relay (built into constant volume control board), controlling
evaporator fan, begins timer sequence (55 ± 10-second delay). Induced-draft contactor closes and induced-draft motor
starts.
Centrifugal switch closes. Pilot valve opens, allowing gas
to flow to first-stage pilot. Spark ignitor ignites pilot flame.
Sensor detects flame, energizes main gas valve coil and main
gas valve opens. Gas flows to main burners and first-stage
burners ignite. Spark ignitor shuts off and pilot remains on.
The spark ignitor will continue to spark for 90 seconds
until pilot flame is sensed. If the pilot fails to ignite or the
sensor fails to detect flame, the pilot valve closes and the
spark ignitor shuts off for 300 seconds (5 minutes). During
this time the induced draft motor remains on to purge any
unburnt gas from the combustion tubes. This ignition sequence will repeat indefinitely.
When time-delay sequence is complete, time-delay relay
closes and evaporator-fan motor starts.
When additional heat is needed on 034,044 units, W2 is
energized and a second coil in the main gas valve is energized.This brings on an additional stage of heat. When secondstage thermostat is satisfied, the second-stage gas valve coil
is deenergized.
When additional heat is needed on 054-074 units, W2 is
energized,and pilot valve number 2 opens. Gas flows to secondstage pilot, and spark ignitor ignites pilot flame. Sensor detects flame, energizes the main gas valve coil, and main gas
valve number 2 opens. Gas flows to main burners and secondstage burners ignite. Second-stage spark ignitor shuts off.When
second-stage thermostat is satisfied, the second-stage gas valve
coil is deenergized.
41
Page 42

When the first-stage thermostat is satisfied, first-stage main
gas valve and the pilot valve close. Induced-draft motor shuts
off.Time-delay relay (built into constant volume control board)
opens and timer sequence begins. When sequence is complete (after 110 ± 5 seconds) evaporator-fan motor shuts off.
48 Series High-Heat Units — Unit power on, thermostat system switch set at HEAT or AUTO. position, and fan switch
set at AUTO. position.
First-stage thermostat (W1) calls for heat. Time-delay relay (built into constant volume control board), controlling
evaporator fan, begins timer sequence (approximately 55 ±
10-second delay).
When time-delay sequence is complete, time-delay relay
closes and evaporator fan starts.
When evaporator fan starts, airflow switch closes, closing
induced draft contactor, and induced draft motor starts.
Centrifugal switch closes. Pilot valve opens, allowing gas
to flow to first-stage pilot. Spark ignitor ignites pilot flame.
Sensor detects flame, energizes main gas valve coil, and main
gas valve opens. Gas flows to main burners and first-stage
burners ignite. Spark ignitor shuts off and pilot remains on.
The spark ignitor will continue to spark for 90 seconds
until pilot flame is sensed. If the pilot fails to ignite or the
sensor fails to detect flame, the pilot valve closes and the
spark ignitor shuts off for 300 seconds (5 minutes). During
this time the induced draft motor remains on to purge any
unburnt gas from the combustion tubes. This ignition sequence will repeat indefinitely.
When additional heat is needed, W2 is energized. Pilot
valve no. 2 opens, allowing gas to flow to second-stage pilot. Spark ignitor ignites pilot flame. Sensor detects flame,
energizes main gas valve coil, and main gas valve no. 2 opens.
Gas flows to main burners and second-stage burners ignite.
Second-stage spark ignitor shuts off. When the second-stage
thermostat is satisfied, W2 is deenergized and the second
induced-draft motor and gas valve are shut off.
When the first-stage thermostat is satisfied, first-stage main
gas valve and the pilot valve close. Induced draft motor shuts
off.Time-delay relay (built into constant volume control board)
opens and timer sequence begins. When sequence is complete (after 110 ± 5 seconds) evaporator-fan motor shuts off.
50 Series Units — Unit power on, system selector switch
set at HEAT position, fan switch set at AUTO. position.
On a call for heating, W1 on the thermostat closes, and
evaporator fan and the first stage of electric heat are energized. On a further drop in room temperature, W2 on the
thermostat closes, energizing the second stage of electric heat.
NOTE: Units equipped with low electric heat option have
only one stage. Reset thermostat to a setting below room
temperature. Electric heat and evaporator fan shut off.
COOLING, UNITS WITH ECONOMIZER — With subbase switch set at COOL position and fan switch set at AUTO.
position, evaporator fan is energized when Y1 on thermostat
closes. If enthalpy is below setting on enthalpy switch, the
economizer outdoor-air dampers will modulate open to satisfy the cooling requirement. If outdoor air alone will not
meet the cooling requirements, Y2 on the thermostat will
close energizing compressor no. 1 to work in conjunction
with the modulating economizer to meet the cooling requirement. While the unit is operating using outdoor air, compressor no. 2 cannot be energized. If enthalpy is above setting on enthalpy switch, the economizer outdoor-air dampers
move to the minimum (ventilation) position, and condenser
fan numbers 1 and 2 cycle on and off as described in Cooling, Units Without Economizer section on page 41.
NOTE: If fan switch is ON position and the room thermostat
is satisfied, the outdoor-air dampers move to the minimum
position.
HEATING, UNITS WITH ECONOMIZER — Operation is
the same as described in Heating, Units Without Economizer sections on page 41, except that the outdoor-air dampers move to the minimum position on a call for heat.
VENTILATION-AIR CIRCULATION (Continuous Fan) —
Turnunit power on. Set system selector switch at OFF,HEAT,
or COOL position, and set fan switch at ON position.
Evaporator-fan contactor is energized through the switch
on the thermostat and the evaporator fan runs continuously.
The damper moves to the minimum position.
AUTOMATIC CHANGEOVER USING AUTOMATIC
CHANGEOVER THERMOSTAT — Turn unit power on. Set
system selector switch at AUTO. position.
When the temperature of the conditioned space rises to
the cooling selector lever setting, unit automatically switches
from heating to cooling mode. When the temperature of the
conditioned space falls to the heating selector switch setting,
unit automatically changes from cooling to heating mode.
The thermostat is interlocked so that cooling and heating systems do not operate at the same time.
Head Pressure Control — All units have a fan cy-
cling thermostat which cycles the no. 2 condenser fan. This
switch opens at 60F±3°Fandcloses at 70F±3°F.This
allows the unit to operate down to 45 F outdoor ambient
temperature.
NOTE:Accessory−20 F Low Ambient Kit is available, which
allows mechanical cooling to −20 F outdoor ambient. See
accessory installation instructions for mounting and operation details.
SERVICE
ServiceAccess —
through clearly labeled hinged access doors. These doors are
not equipped with tiebacks, so if heavy duty servicing is needed,
either remove them or prop them open to prevent accidental
closure.
Each door is held closed with 3 latches. The latches are
secured to the unit with a single 1/4-in. 220 x 1/2-in. long
bolt. See Fig. 33.
To open, loosen the latch bolt using a 7/16-in. wrench.
Pivot the latch so it is not in contact with the door. Open the
door. To shut, reverse the above procedure.
NOTE: Disassembly of the top cover may be required under
special service circumstances. It is very important that the
orientation and position of the top cover be marked on the
unit prior to disassembly. This will allow proper replacement of the top cover onto the unit and prevent rainwater
from leaking into the unit.
IMPORTANT:After servicing is completed, make sure
door is closed and relatched properly,and that the latches
are tight. Failure to do this can result in water leakage
into the indoor-air section of the unit.
COMPRESSORS
Sizes 034 and 044 —Access to the compressors is through
the doors on the condenser end of the unit. This door also
provides access to the discharge and suction service valves,
the crankcase heaters, and the high- and low-pressure switches.
Compressor no. 1 is always the compressor on the left when
facing main control box.
Sizes 054-074 — The oil pump end (compressor access) of
each compressor is readily accessible from sides of unit as
shown in Fig. 17. Access the motor end of the compressor
through the condenser end of the unit or by removing
compressor.
All unit components can be reached
42
Page 43

Fig. 33 — Door Latch
LIQUID SERVICEVALVES,FILTER DRIERS, AND SIGHT
GLASSES
Sizes 034 and 044 — Access to these components is through
the access panel on the right side of the unit. See Fig. 34.
There is also a Schrader port in each suction line that is accessible through this same panel. When charging unit, route
service line through the round holes and replace panel to minimize air bypass.
Sizes 054-074 — Access to these components is from the
side of the unit as shown in Fig. 34.
EVAPORATOR-FAN MOTORS, PULLEYS, AND BELTS
— Access to these components is through the 2 doors labeled FAN SECTION on each side of the unit.
POWER EXHAUST MOTORS, PULLEYS, AND BELTS
— Access to these components is through the door below
the side economizer hoods on either side of the unit. See
Fig. 35 and 36.
UNITCONTROLBOX—Access to this component is through
the doors marked ELECTRICAL SECTION on the condenser end of the unit (when facing the condenser coil).
GAS HEAT SECTION (48 Series Units Only) — Access to
the gas heat section is through the door labeled HEAT SECTION on the left side of the unit (when facing condenser
end). See Fig. 37 and 38.
All gas system components are in the gas section.
MAIN AND PILOT BURNERS (48 Series Units Only) —
At the beginning of each heating season, inspect for deterioration due to corrosion or other causes. Observe the pilot
and main burner flames and adjust if necessary. See Automatic Pilot Adjustment or Main Burners Adjustment Section
on pages 49 and 50.
FLUE GAS PASSAGEWAYS (48 Series Units Only) — The
flue collector box and heat exchanger cells may be inspected
by removing the combustion air blower(s), flue box cover,
and main burner assembly. See Fig. 39 and 40. If cleaning
is required, remove heat exchanger baffles through the flue
box and clean all parts with a wire brush. When replacing
heat exchanger baffles,be sure to replace screw through clamp
on baffle retaining rod into the vestibule plate.
Fig. 35 — Modulating Power Exhaust Damper
Motor Access, 034 and 044 Units
Fig. 36 — Modulating Power Exhaust Motor
Access, 054-074 Units
COMBUSTION AIR BLOWER (48 Series Units Only) —
Clean periodically to assure proper airflow and heating efficiency.Inspect blower wheel every fall and periodically during the heating season. For first heating season, inspect blower
wheel bimonthly to determine proper cleaning frequency. If
cleaning is required, remove blower assembly from unit and
then disassemble and clean. See Fig. 41.
Fig. 34 — Typical Filter Drier and Liquid Service
Valve Access
43
Page 44

NOTE: High heat consists of sections 1 and 2.
Low heat consists of section 1 only.
Fig. 37 — Gas Section Detail, 48 Series 034 and
044 Units
Fig.39 — BurnerSection Detail (48 Series Units Only)
NOTE: High heat consists of sections 1-3.
Low heat consists of section 1 and 2 only.
Fig. 38 — Gas Section Detail, 48 Series 054-074 Units
ECONOMIZER DAMPER MOTOR — On units so equipped,
the economizer motor is located in the mixing box section.
Access to it is through the doors labeled FILTER SECTION
on the sides of the unit.
ELECTRIC HEATER CONTROLBOX(50Series Units Only)
— Access to the electric heater control box is through the
door on the right side of the unit next to the condenser section. See Fig. 16 and 17.
The electric heater control box contains:
• power terminal block HTB, HTB1, HTB2 (not used on all
voltages)
Fig. 40 — Flue Box Assembly, 48 Series Units Only
(Shown with Burner Assembly)
Fig. 41 — Combustion Blower Removal
• fuse blocks FB1, FB2, etc.
• fuses FU (3 per fuse block)
• heater contactors HC1, HC1A, etc.
• plug No. 20 (PL20)
HEATER BOX (50 Series Units Only) —Access to the heater
box is through the door on the left side (sizes 034 and 044)
or right side (sizes 054-074) of the unit next to the condenser section. See Fig. 16 and 17. See Fig. 42 for heater
box contents.
44
Page 45

NOTE: Only the heater element contactors are located in the
heater box. The heaters are located in the unit airstream.
25% OUTDOOR-AIR DAMPER — Access to adjust the
damper is through the hoods. Remove filters to gain access
into unit to adjust linkage arms.
MODULATING POWER EXHAUST DAMPER MOTOR
— The modulating power exhaust damper motor is located
in the return-air end of the unit.
On unit sizes 034 and 044, it is accessed by removing the
access panel on the left-hand corner post. See Fig. 35.
IMPORTANT:When replacing panel, be sure to properly secure it in order to prevent water from being drawn
into the unit.
On unit sizes 054-074, the motor is accessed through the
small door below the side economizer hoods on the left side
of the unit. See Fig. 36.
RETURN-AIR FILTERS—Access to these filters is through
the door marked FILTER SECTION. Filters in upper and
lower bag filter tracks can only be removed from the left
side of the unit (when facing condenser end).
CONDENSER FANS AND FAN MOTORS — Remove the
wire fan guard on top of the unit to gain access to the condenser fans and motors.
INLET GUIDE VANE MOTOR — The inlet guide vane motor is located on the evaporator-fan sled on the side opposite
the fan motor. See Fig. 43. Access is through the door labeled FAN SECTION on the left side of the unit.
Cleaning — Inspect unit at the beginning of each heating
and cooling season and during each season as operating conditions may require.
Clean condenser coil with a vacuum cleaner, fresh water,
compressed air, or a bristle brush (not wire). Coil cleaning
should be a part of the planned maintenance program. Clean
evaporator coil with a stiff bristle brush (not wire), vacuum
cleaner, or compressed air.
Check and clean condensate drain annually at the start of
the cooling season.
Replace return-air filters at the start of each heating and
cooling season or as often as necessary during each season,
depending on operating conditions. See Tables 1A and 1B
for filter types, quantities, and sizes.
1. Remove economizer outdoor-air filters from the hoods by
removing the filter retainers.
2. Clean filters with steam or hot water and mild detergent.
3. Reinstall filters in hoods after cleaning. Never replace clean-
able filters with throwaway filters.
Lubrication
COMPRESSORS — Each compressor is correctly charged
at the factory. Refer to 06D and 06E Compressor Service
Manuals if additional information regarding compressor lubrication system is required. See Compressor Oil section on
page 38 and Table 8.
FAN SHAFT BEARINGS — Lubricate fan shaft bearings at
least once a year with suitable bearing grease. Extended grease
lines are provided on pulley side of blower. Typical lubricants are given below:
MANUFACTURER LUBRICANT
Texaco Regal AFB-2*
Mobil Mobilplex EP No. 1
Sunoco Prestige 42
Texaco Multifak 2
*Preferred lubricant because it contains rust and oxidation inhibitors.
INLET GUIDE VANE BEARINGS (Units With Optional
Inlet Guide Vanes) — These bearings are oil impregnated.
Lubricate annually with a few drops of nondetergent
SAE 20 oil.
F ANMOTOR BEARINGS — The condenser- and evaporatorfan motors have sealed bearings so no field lubrication is
required.
DOOR HINGES — All door hinges should be lubricated at
least once a year.
C—Contactor
FB — Fuse Block
FU — Fuse
HC — Heat Element Contactor
HTB — Heater Terminal Block
PL — Plug Assembly
LEGEND
Fig. 42 — Typical Electric Heat Control Box
Fig. 43 — Inlet Guide Vane Motor
45
Page 46

Adjustments
EVAPORATOR FAN AND POWER EXHAUST MOTOR
PLATE — Adjust using a15⁄16-in. wrench on the adjusting
bolts:
1. Loosen holddown bolts. (See Fig. 44.)
2. Turn the adjusting bolts to move the motor mounting plate
toward or away from the fan to loosen or tighten the belts.
Make the same number of turns to each bolt.
3. Retighten holddown bolts.
MODULATING POWER EXHAUST DIFFERENTIAL
PRESSURE SWITCH — On 034,044 units, the differential
pressure switch is located in the auxiliary control box. The
auxiliary control box is mounted in the corner next to the
power exhaust motor door. To gain access to the auxiliary
control box, remove the auxiliary control box cover. When
replacing the auxiliary control box cover, be sure to secure
the cover properly in order to prevent water from being drawn
into the auxiliary control box.
On 054-074 units, the differentialpressure switch is mounted
below the auxiliary control box next to the access door labeled FILTER SECTION.
INLET GUIDE VANE DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE
SWITCH (Units With Optional Inlet Guide Vanesand Static
Pressure Control) — On 034,044 units, the inlet guide vane
differentialpressure switch is located in the auxiliary control
box. The auxiliary control box is mounted in the corner of
the unit under the side air hood that is next to the access
door marked FILTER SECTION. To gain access to the auxiliary box, remove the auxiliary control box cover.When replacing the auxiliary control box cover, be sure to secure the
cover properly in order to prevent water from being drawn
into the auxiliary control box.
On 054-074 units, the inlet guide vane differential pressure
switch is mounted on an upright located behind the evaporatorfan motor. See Fig. 43.
BELT INSTALLATION AND TENSIONING
IMPORTANT: When installing or replacing belts, always use a complete set of new, matched belts to prevent potential vibration problems. Mixing belts often
results in premature breakage of the new belts.
1. Turn off unit power.
2. Adjust motor plate so belts can be installed without stretching over the grooves of the pulley. (Forcing the belts can
result in uneven belt stretching and a mismatched set of
belts.)
3. Before tensioning the belts, equalize belt slack so that it
is on the same side of the belt for all belts. Failure to do
so may result in uneven belt stretching.
4. Tighten belts using the motor plate adjusting bolts.
5. Adjust until proper belt tension (1/2-in. deflection with
one finger) is obtained. Be sure to adjust both adjusting
bolts the same number of turns.
NOTE: Check the tension at least twice during the first
day of operation, as there is normally a rapid decrease in
tension until the belts have run in. Check tension
periodically thereafter and keep it at the recommended
tension.
With the correct belt tension, belts may slip and squeal
momentarily on start-up. This slippage is normal and disappears after wheel reaches operating speed. Excessive belt
tension shortens belt life and may cause bearing and shaft
damage.
Fig. 44 — Motor Plate Adjustment
PULLEY ALIGNMENT — For proper belt life, the motor
and fan pulleys must be properly aligned. To check, first turn
off unit power. Place a straightedge against the motor and
fan pulleys. See Fig. 45. If the pulleys are properly aligned,
the straightedge should be parallel to the belts.
If they are not parallel, check that the motor shaft and fan
shaft are parallel. If they are not, adjust the motor plate adjusting bolts until they are.
After verifying that the shafts are parallel, loosen the setscrews on the motor pulley. Move pulley on the shaft until
the pulleys are parallel. To move the sheave on the shaft,
loosen the belts. If necessary,blowersheave can also be moved
on the shaft.
INSTALLING ALTERNATE MOTOR PULLEY (Evaporator Fan Only) — On all units, the alternate motor pulley is
field-supplied. To install the alternate pulley:
1. Turn off unit power.
2. Loosen belts using motor adjusting bolts until belts can
be removed without stretching them over the grooves of
the pulley.
3. Remove belts.
4. Loosen setscrews on motor pulley.
5. Slide pulley off motor shaft. Make sure setscrews on new
pulley are loose.
6. Slide new pulley onto fan shaft and align it with the fan
pulley as described in Pulley Alignment section above.
7. Tighten setscrews.
8. Install belts and tension properly as described in Pulley
Alignment section above.
CONDENSER FAN ADJUSTMENT
1. Turn off unit power.
2. Remove fan guard and loosen fan hub setscrew.
3. See Fig. 32 and adjust fan height using a straight edge
laid across the fan deck.
4. Tighten setscrew and replace rubber hubcap to prevent
hub from rusting to the motor shaft. Fill hub recess with
Permagum if hub has no rubber hubcap.
5. Replace fan guard.
46
Page 47

Fig. 45 — Pulley Alignment
Fig. 46 — Charging Chart, 034 Units; System 1,
One Condenser Fan Running
25% OUTDOOR-AIR DAMPER — See Manual OutdoorAir Damper section on page 10 for adjustment details.
REFRIGERANT CHARGE — All units are shipped with a
complete operating charge of R-22. See unit nameplate and
Tables 1A and 1B for amount of charge. When adding a complete charge, evacuate system using standard evacuating procedures and weigh in the specified amount of charge. All
units have charging charts for each refrigerant circuit. See
Fig. 46-59.
PILOT LIGHT OFF (48NP Units Only) — If pilots do not
light as described in Heating section on page 41, be sure that
pilot orifice is unobstructed, then check for spark ignitor malfunctions as follows:
1. Turn offthe control circuit breaker (CCB) to shut offcontrol supply power to ignitor control pack (ICP).
3
2. Check that spark gap is
⁄8in. 61⁄32inch.
3. Check that ICP is securely grounded.
4. Check that the high-voltage lead is securely connected
between the ICP and the electrode body.
5. Turn on CCB to restore power to ICP. Check that 24 v is
supplied to terminal TH of the ICP.
6. Check unit label diagram for correct terminal usage if any
wires are removed.
Fig. 47 — Charging Chart, 034 Units; System 1,
All Condenser Fans Running
Fig. 48 — Charging Chart, 034 Units; System 2,
One Condenser Fan Running
47
Page 48

Fig. 49 — Charging Chart, 034 Units; System 2,
All Condenser Fans Running
Fig. 52 — Charging Chart, 044 Units; System 2,
One Condenser Fan Running
Fig. 50 — Charging Chart, 044 Units; System 1,
One Condenser Fan Running
Fig. 51 — Charging Chart, 044 Units; System 1,
All Condenser Fans Running
Fig. 53 — Charging Chart, 044 Units; System 2,
All Condenser Fans Running
Fig. 54 — Charging Chart, 054 Units; System 1,
All Condenser Fans Running
48
Page 49

Fig. 55 — Charging Chart, 054 Units; System 2,
All Condenser Fans Running
Fig. 58 — Charging Chart, 074 Units; System 1,
All Condenser Fans Running
Fig. 56 — Charging Chart, 064 Units; System 1,
All Condenser Fans Running
Fig. 57 — Charging Chart, 064 Units; System 2,
All Condenser Fans Running
Fig. 59 — Charging Chart, 074 Units; System 2,
All Condenser Fans Running
AUTOMATIC PILOTADJUSTMENT(48 Series Units Only)
1. Set system selector switch at OFF position to shut offunit.
Turn off power to unit.
2. Remove screw cap cover on pilot gas valve to expose
adjusting screw.
3. To ensure that main burners do not ignite, remove wire
from gas valve terminal 2. Tape wire. Do not allow wire
to be grounded.
4. Turnon power to unit. Set system selector switch to HEAT
position and set thermostat to a setting that will call for
heat. Pilot ignites.
5. Witha small screwdriver, turn adjustment screw until flame
fully engulfs sensor.
6. Replace cap on pilot gas valve. Turn off power to unit.
Return valve(s) to original position.
7. Check for proper burner operation by cycling the burners. Wait 30 seconds between burner cycles.
8. Check that all panels are closed securely before leaving
the unit.
49
Page 50

GAS VALVEADJUSTMENT (48 Series Units Only) — The
gas valve opens and closes in response to the thermostat or
limit control. When power is supplied to valve terminal 3
(D1 on low heat), the pilot valve opens to the preset position. When power is supplied to terminal 2 (W1 on low heat),
the main valve opens to its preset position.
The regulator factory manifold pressure setting 2.9 in. wg
and is stamped on the valve body.
Manifold pressure is the pressure at the factory-supplied
pressure tap on the manifold downstream of the gas valve.
This is not the same as the pressure at the tap on the gas
valve body.Always use the tap on the manifold to read manifold pressure.
To adjust regulator:
1. Set thermostat at setting for no call for heat.
2. Turn main gas valve to OFF position.
3. Install a suitable pressure measuring device.
4. Set main gas valve to ON position.
5. Set thermostat to call for high fire (W2).
6. Remove screw cap or plastic cover covering the regula-
tor adjustment screw.
7. Turn adjustment screw clockwise to increase pressure or
counterclockwise to decrease pressure.
8. Once desired pressure is established, remove pressure-
measuring device and replace screw cap.
MAIN BURNERS ADJUSTMENT (48 Series Units Only)
— Main burners are factory set and should require no adjustment. However, if burner adjustment is necessary:
1. Perform Automatic Pilot Adjustment (page 49).
2. Turn gas valve to ON position. Allow unit to operate at
least 15 minutes with heat section access panel closed.
3. Open heat section access panel.
4. Loosen primary air shutter and adjust to a minimum open-
ing of
5
⁄8inch.
5. Retighten primary air shutter and close access panel.
To check ignition of main burners and fan switch operation, move thermostat dial above and below room temperature several times, pausing at least one minute between cycles.
1. Remove top cover from motor to gain access to motor
terminals and cam adjustments.
2. Disconnect controller from motor.Connect RED, WHITE,
and BLUE terminals on the 135-ohm manual potentiometer to corresponding RED, WHITE, and BLUE terminals on the motor. Connect 24-vac power to Terminals 1
and 2. See Fig. 60.
3. Adjust the 135-ohm potentiometer so that the motor shaft
turns to the position where auxiliary equipment is to be
switched.
1
4. Adjust auxiliary cam by inserting a
⁄8-in. straight blade
screwdriver into slot on cam and moving TOP of screwdriver to the right or left. See Fig. 61.
5. To close auxiliary switch RED and BLUE contacts as the
motor travels open (energizing the power exhaust motor), the switch differential can only be 10 degrees on both
switches.Toadjust either cam, perform the following steps:
a. If RED and BLUE contacts are open, rotate the cam
counterclockwise until the contacts close.
b. If the RED and BLUE contacts are closed, rotate the
cam clockwise until the contacts open.
Refrigerant Feed Components — Each refrigerant
circuit (2 per unit) has all the necessary refrigerant controls.
Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) — On size
034, each circuit has one. On size 044, each circuit has 2.
The superheat is nonadjustable. On sizes 054-074, each circuit has 2 TXVs on which superheat may be adjusted if absolutely necessary.
The TXV is set to maintain 10 to 13 F superheat leaving
the evaporator coil. It controls the flow of refrigerant to the
evaporator coils.
Main Burner Removal (48 Series Units Only)
NOTE: For high-heat units, the side posts must be removed
before the burner assembly can be removed.
1. Shut off main gas valve.
2. Shut off power to unit.
3. Unplug PL9 (and PL10 on high-heat) and all sensor and
ignitor wires.
4. Disconnect gas connection(s) from between gas valve(s)
and field-supplied piping. See Fig. 37 and 38.
5. Remove 2 screws securing burner assembly to unit.
6. Slide burner assembly from unit.
Switch Adjustment — All units with an economizer
have an auxiliary switch located on the economizer damper
motor. This switch is factory set to prevent the power exhaust from operating when the economizer damper is less
than 50% open. If other than the factory setting is desired,
follow the steps below.
Do not turn motor shaft by hand or with a wrench. Damage to the gear train will result.
Fig. 60 — Auxiliary Switch Stroke Adjustment
50
Page 51

Compressor Discharge Service Valve — Each
compressor has one.
Compressor Suction Service Valve — Each com-
pressor has one.
Protective Devices
COMPRESSOR PROTECTION
Overcurrent — Each compressor has one manual reset, cali-
brated trip, magnetic circuit breaker. Do not bypass connections or increase the size of the circuit breaker to correct trouble.
Determine the cause and correct it before resetting the breaker.
Overtemperature — Each 06D compressor has an internal
protector to protect it against excessively high discharge gas
temperatures. Each 06E compressor has an external discharge gas thermostat. See Fig. 62. They will reset, but the
circuit will automatically be locked out by the control board.
Unit must be manually reset by interrupting control power.
Crankcase Heater — Each compressor has a crankcase heater
to prevent absorption of liquid refrigerant by oil in the crankcase when the compressor is idle. Since 115-v power for the
crankcase heaters is drawn from the unit control circuit, main
unit power must be on for the heaters to be energized.
IMPORTANT:After a prolonged shutdown or service
job, energize the crankcase heaters for 24 hours before
starting the compressor.
Fig. 61 — Auxiliary Switch Adjustment
Moisture/Liquid Indicator — A clear flow of liquid
refrigerant indicates sufficient charge in the system. Bubbles
indicate undercharged system or the presence of noncondensables. Moisture in the system measured in parts per million (ppm) changes the color of the indicator:
Green — moisture below 45 ppm (dry)
Chartreuse — 45 to 130 ppm (caution!)
Yellow — moisture above 130 ppm (wet)
Change filter driers at the first sign of moisture in the sys-
tem. See Carrier Charging Handbook for more information.
IMPORTANT: Unit must be in operation at least
12 hours before moisture indicator can give an accurate reading. With unit running, indicating element must
be in contact with liquid refrigerant to give a true
reading.
Filter Drier — Replace whenever the moisture/liquid in-
dicator shows moisture in the system.
Liquid Line Service Valve — Located immediately
ahead of the filter drier, this valve has a 1/4-in. flare connection for field charging. With the liquid circuit shut, the
compressor can be used to pump the refrigerant down into
the high side. The refrigerant can then be stored there by
closing the compressor discharge valve.
Compressor Lockout — If any of the safeties (compressor
internal thermostat [06D compressors only], high-pressure,
or low-pressure) trip, or if there is a loss of power to the
compressors, the compressors will be locked out. To reset
DJ,DW units, manually move the thermostat setting. To reset DK,DY,NB,NP units, consult the controls and troubleshooting literature for the appropriate unit for details.
EVAPORATOR-FANMOTOR PROTECTION — A manual
reset, calibrated trip, magnetic circuit breaker protects against
overcurrent. Do not bypass connections or increase the size
of the breaker to correct trouble. Determine the cause and
correct it before resetting the breaker.
CONDENSER-FAN MOTOR PROTECTION — Each
condenser-fan motor is internally protected against overtemperature. They are also protected against a severe overcurrent condition by manual reset, calibrated trip, magnetic
circuit breakers on a common circuit. As with the circuit breakers, do not bypass connections or increase breaker size to
correct trouble. Determine the cause and correct it before
resetting the breaker.
HIGH-AND LOW-PRESSURE SWITCHES — See Fig. 62
for compressor mounting locations. Settings for these switches
are shown in Table 11. If either switch trips, that refrigerant
circuit will be automatically locked out by the controls. To
reset, interrupt control power.
NOTE: When a pressure transducer is used, the low pressure trip point is the same as the low-pressure switch.
Relief Devices — All units have relief devices to pro-
tect against damage from excessive pressures (i.e., fire). These
devices protect the high and low side.
51
Page 52

Fig. 62 — Typical Compressor Overtemperature,
High- and Low-Pressure Switch Locations
Table 11 — Pressure Switch Settings (psig)
SWITCH CUTOUT CUT-IN
High 426 6 7 320 6 20
Low 27 6 46767
Fig. 63 — Location of Rollout Switch Capillary Tube
ECONOMIZER MOTOR CHECKOUT — The motor may
be checked out separately from the control board. See
Table 12 for motor checkout. To check out the motor, apply
24 VAC power to terminals T0 and T2 of the control board.
NOTE: The connections to motor terminals T1 and R must
remain in place.
Table 12 — Economizer Motor Checkout
Control Circuit, 115 V — This control circuit is pro-
tected against overcurrent by a 5-amp circuit breaker.Breaker
can be reset. If it trips, determine cause of trouble before
resetting.
Control Circuit, 24 V — This control circuit is pro-
tected against overcurrent by a 3.2-amp circuit breaker.Breaker
can be reset. If it trips, determine cause of trouble before
resetting.
Electric Heat (50 Series Units Only)
OVERCURRENT — Heaters are protected by fuses in the
power circuit, located in the heater control box. As with circuit breakers, determine the cause of fuses tripping before
replacing them. Do not replace with larger fuses. All fuses
are 60 amp.
OVERTEMPERATURE — Heaters are protected by limit
switches mounted in the heater box. They reset automatically once they cool.
Gas Heat (48 Series Units Only)
LIMIT SWITCHES — The maximum supply-air temperature is controlled by a limit switch located in the gas section.
The limit is designed to trip at 100 F above the maximum
temperature rise shown in Tables 1A and 1B.
When the limit trips, the gas valve is deenergized. Once
the unit cools, the gas valve is reenergized.
ROLLOUT SWITCH — This switch senses any flame or
excessive heat in the main burner compartment and deenergizes the gas valve. If this occurs, the gas heating system
is locked out until the rollout switch is reset manually. Reset
by pressing the button on the rollout switch. See Fig. 39.
When the rollout switch trips, it likely indicates a flue blockage. Inspect the unit for any obstruction in the flue system,
for holes on the flue box, or for a defective centrifugal switch
or loose combustion blower. See Fig. 63 for proper location
of the rollout capillary.
TROUBLESHOOTING
Economizer —
electronic control board mounted on the back of the cover
plate of the economizer motor with the adjustments and electrical plugs accessible through the top of the cover.The economizer control is factory wired to the terminals on the motor.
All potentiometers and adjustments are a part of the control
board.
The economizer control consists of an
MOTOR
TEST
A Remove wire connected to
B Remove wire connected to
PROCEDURE EXPECTED RESULT
terminal W on the motor.
terminal B on the motor,
leaving W wire disconnected (Test A).
AND RESPONSE
Motor drives open. If not,
replace the motor.
Motor drives closed. If not,
replace the motor.
CONTROL BOARD CHECKOUT — To check out the control board motor, conduct the following 4 tests.
Test 1:
1. Apply 24 VAC power to terminals T0 and T2 of control
board.
2. Remove mixed air sensor connected between terminals
S1 and S2.
3. Remove outdoor-air enthalpy sensor between terminals
11 and SO.
4. Refer to Table 13.
Table 13 — Economizer Control Board Checkout,
Test 1
MOTOR
TEST
A Turn minimum position
B Turn minimum position
PROCEDURE EXPECTED RESULT
potentiometer fully
counterclockwise.
potentiometer fully
clockwise.
AND RESPONSE
Motor drives closed. If not,
check minimum position
jumper between
terminals Z and Y, and
check terminal W and T1
connections to motor.
Motor drives open. If not,
check terminal B and R
connections to the motor.
Test 2:
1. Apply 24 VAC power to terminals T0 and T2 of the control board.
2. Apply 24 v between terminals 1 and T2, and jumper terminal T0 to terminal 1.
3. Remove the mixed-air sensor connected between terminals S1 and S2, and replace it with a 5490-ohm resistor.
4. Remove outdoor-air enthalpy sensor between terminals
11 and SO, and replace it with a 1.2 kOhm resistor.
5. Turn the minimum position potentiometer fully counterclockwise.
6. Refer to Table 14.
52
Page 53

Table 14 — Economizer Control Board Checkout,
Test 2
Table 16 — Economizer Control Board Checkout,
Test 4
MOTOR
TEST
A Turn enthalpy set point
B Turn enthalpy set point
PROCEDURE EXPECTED RESULT
potentiometer to the
A position.
potentiometer to the
D position.
AND RESPONSE
1. The relays energize. If not,
check return enthalpy resistor. If resistor is o.k.,
control board is faulty.
2. Motor drives open. If relays energize, but motor
does not drive open, the
control board is faulty.
1. The relays deenergize. If
not, control board is faulty.
2. Motor drives closed. If relays deenergize by motor
does not drive closed, the
control board is faulty.
Test 3:
1. Apply 24 VAC power to terminals T0 and T2 of the control board.
2. Apply 24 v between terminals 1 and T2, and jumper terminal T0 to terminal 1.
3. Remove the mixed-air sensor connected between terminals S1 and S2, and replace it with a 5490-ohm resistor.
4. Remove outdoor-air enthalpy sensor between terminals
11 and SO, and replace it with a 1.2 kOhm resistor.
5. Turn the minimum position potentiometer fully counterclockwise.
6. Turn enthalpy set point potentiometer to the A setting.
7. Refer to Table 15.
Table 15 — Economizer Control Board Checkout,
Test 3
MOTOR
TEST
A Turn mixed-air potenti-
B Turn mixed-air
C Turn mixed-air potenti-
PROCEDURE EXPECTED RESULT
ometer to the midpoint
position.
potentiometer fully
counterclockwise.
ometer fully clockwise.
AND RESPONSE
Motor should drive to midstroke with the set point set
between 60 and 70 F. If not,
the control board is faulty.
Motor drives open, If not, the
control board is faulty.
Motor drives closed. If not,
the control board is faulty.
Test 4
Refer to Table 16 for the correct procedure for test 4.
UnitControl BoardCheckout — The following tools
are required to perform the troubleshooting tasks detailed in
this section:
• 1.5-v battery
• 2 sets of jumper wires with alligator clips
• Multimeter
• T oggleswitchwith 14-in. wires terminated with1⁄4-in. spade
connectors
Read these instructions completely before attempting to
troubleshoot the control board. Failure to follow the steps
precisely could result in damage to unit, personal injury, or death.
The control board checkout procedure consists of 2 parts:
A basic check to verify availability of 24 and 115 v to the
control board and a detailed check of each circuit within the
board.
MOTOR
TEST
A (Outdoor-
Air Sensor)
B (Indoor-
Air Sensor)
PROCEDURE EXPECTED RESULT
1. Connect the enthalpy
sensor terminal 1 to
terminal 1 on the motor.
2. Connect the positive terminal of a DC milliammeter to terminal S of
the sensor.
3. Connect the negative
terminal of a DC milliammeter to terminal S
the enthalpy board.
1. Connect the enthalpy
sensor terminal 1 to
terminal 1 on the motor.
2. Connect the positive terminal of a DC milliammeter to terminal S of
the sensor.
3. Connect the negative
terminal of a DC milliammeter to terminal S
the enthalpy board.
O
R
AND RESPONSE
Milliammeter reading
should be between
3 and 24 mA if the
sensor is operating
correctly. If the reading is 0 mA, the
sensor is either
wired backward or is
defective.
of
Milliammeter reading
should be between
3 and 24 mA if the
sensor is operating
correctly. If the reading is 0 mA, the
sensor is either
wired backward or is
defective.
of
BASIC CHECK — Refer to Fig. 64 for control board component identification.
NOTE: All plugs (except P1) are labeled for easy identification. Plug P1 can be identified by its orange color.
1. Turnunitpower off.Disconnect plug P1 from control board.
2. Turn unit power on and check voltage across Pin R and
Pin C at plug P1. If voltage reads 18 to 30 v, skip to
Step 5.
3. Turn unit power off. Disconnect plug P3.
4. Turn unit power on and measure voltage across wires on
plug P3, Pins 1 and 2 (wires coming from the unit). If
voltage reads 18 to 30 v, there is either a bad connection
between plug P3 and control board, or the control board
is defective. Verify the connection at this point and proceed to Step 5. If there is no voltage, check the circuit
breaker and transformer in the 24-v control circuit of the
unit.
5. Turn unit power off and disconnect plug P4 from the control board.
6. Switch scale on meter to read 115 v.
7. Turn unit power on and check voltage across Pin 6 on
plug 4 and unit ground (wires coming from the unit). If
voltage reads 104 to 122 v, there is adequate power available to the board. Verify connection at this point and proceed to Step 8. If there is no voltage, check the circuit
breaker and transformer in the 115-v control circuit of
the unit.
8. After verifying that 24-v and 115-v supply power is available to the control board, turn unit power off and reconnect plugs P1, P3, and P4. Proceed to Detailed Check section
below.
DETAILED CHECK
NOTE: Plug P1 must be disconnected in order to perform
any of the troubleshooting steps detailed in this section. To
save time, reconnect plug P1 only after you have completed
all of the required troubleshooting.
53
Page 54

LEGEND
CLO — Compressor Lockout
P—Plug
SC — Safety Circuit
Fig. 64 — Control Board Component Arrangement
Symptom: Evaporator fan will not operate.
1. Turn unit power off and disconnect plug P1 from the control board.
2. Install a jumper across Pin R and Pin G at plug P1 on the
control board.
3. Turn unit power on and check if the indoor (evaporator)
fan contactor (IFC) coil has been pulled in. If the contactor has not been pulled in, check the voltage across the
IFC coil. If there is voltage at this point, the IFC contactor is defective. If there is no voltage, proceed to
Step 4.
4. Turn unit power off and disconnect plug P4 from the control board.
5. Turn unit power on and check for continuity across
Pin 6 and Pin 3 at plug P4 on the control board. If there
is no continuity, the board is defective. Replace control
board. If there is continuity, then there is a bad connection between the board and plug P4. Correct the
connection.
6. Turn unit power off. Reconnect plug P1 (if troubleshooting is complete) and plug P4.
Symptom: Condenser fan no. 1 will not operate.
1. Turn unit power off. Disconnect plugs P1 and P3 from
the control board.
2. Check for continuity between Pin 8 at plug P3 on the control board and Pin Y1 at plug P1 on the control board. If
there is no continuity, the board is defective. If there is
continuity, either the connection is bad between plug P3
and the control board or the problem is external to the
board. Reconnect plug P1 (if troubleshooting is complete) and plug P3 to the board.
Symptom: Condenser fan no. 2-5 will not operate.
1. Check operation of condenser fan no. 1. If fan no. 1 operates properly, the problem is external to the board.
Symptom: Compressor no. 1 will not operate.
1. Turn unit power off. Disconnect the 2 wires attached to
the terminals marked SC1.
2. Check continuity between the 2 wires. If there is no
continuity, the problem is external to the control board
(possibly the pressure switches). If there is continuity,proceed to Step 3.
3. Reconnect the wires removed in Step 1.
4. Withthe unit power still of f,disconnectplug P1 from control board. Install a jumper wire across Pin R and Pin Y1
at plug P1 on the control board.
5. Connect a voltmeter across the coil for compressor
no. 1 contactor.
6. Energize unit and monitor the voltage for a few
seconds.
IMPORTANT: Do not run compressor too long.
7. a. If proper voltage is indicated at the contactor, but con-
tactor fails to close, replace contactor.
b. If voltage is indicated for a few seconds (i.e., the con-
tactor momentarily pulls in and is then deenergized),
the compressor lockout (CLO) logic has shut down
the unit. This is an indication that the board is not sensing proper compressor current, or that one of the safeties has tripped. Proceed to Step 8 to verify compressor lockout logic operation.
54
Page 55

c. If proper voltage is indicated at the contactor and con-
tactor closes, the board is operating properly.
8. To verify compressor lockout logic:
a. Disconnect CLO sensor wires connected to CLO1 at
the control board. Check wires for continuity. If there
is no continuity, replace the sensor.
b. Connect the multimeter to read voltage between
Pin X at plug P1 and ground.
c. Turn unit power on and check the multimeter. Within
a few seconds the meter should indicate 24 v. If it does
not, the control board is defective and must be
replaced.
d. Turn unit power off. Use a toggle switch to connect a
fresh 1.5-v battery to the terminals marked CLO1 as
shown in Fig. 65.
The negative (−Ve) pole of the battery must be connected to the inner terminal, and the positive (1Ve)
pole must be connected to the outer terminal as shown
in Fig. 65.
e. Turn unit power on and use the toggle switch to make
and break the connection between the outer CLO1 terminal and the positive (1Ve) pole of the battery.
f. If the multimeter shows 24 v when the battery is dis-
connected and no voltage when the battery is connected, the CLO logic is good. If the multimeter shows
no change, the CLO logic is defective and the board
must be replaced.
Symptom: Compressor no. 2 will not operate.
1. Be sure unit power is off.Disconnect the 2 wires attached
to the terminals marked SC2.
2. Check continuity between the 2 wires. If there is no continuity, the problem is external to the control board (possibly the pressure switches). If there is continuity,proceed
to Step 3.
3. Reconnect the wires removed in Step 1.
4. Withunit power still off,disconnect plug P1 from the control board and install jumper wire across Pins R and Y2
at plug P1.
5. Connect a voltmeter across the coil for compressor
no. 2 contactor.
6. Energize unit and monitor the voltage for a few
seconds.
IMPORTANT: Do not run compressor too long.
7. a. If proper voltage is indicated at the contactor, but con-
tactor fails to close, replace contactor.
b. If voltage is indicated for a few seconds (i.e., the con-
tactor momentarily pulls in and is then deenergized),
the Compressor Lockout (CLO) logic has shut down
the unit. This is an indication that the board is not sensing proper compressor current, or that one of the safeties has tripped. Proceed to Step 8 to verify compressor lockout logic operation.
c. If proper voltage is indicated at the contactor and con-
tactor closes, the board is operating properly.
8. To verify compressor lockout logic:
a. Disconnect CLO sensor wires connected to CLO2 at
the control board. Check wires for continuity. If there
is no continuity, replace the sensor.
b. Connect the multimeter to read voltage between
Pin X on plug P1 and ground.
c. Turn unit power on and check the multimeter. Within
a few seconds the meter should indicate 24 v. If it does
not, the control board is defective and must be
replaced.
d. Turn unit power off. Connect a fresh 1.5-v battery to
terminals marked CLO2 as shown in Fig. 65.
The negative (−Ve) pole of the battery must be connected to the inner terminal, and the positive (±Ve)
pole must be connected to the outer terminal as shown
in Fig. 65.
e. Turn unit power on. Make and break the connection
between the outer CLO2 terminal and the positive (±Ve)
pole of the battery.
f. If the multimeter shows 24 v when the battery is dis-
connected and no voltage when the battery is connected, the CLO logic is good. If the multimeter shows
no change, the CLO logic is defective and the board
must be replaced. Remove all jumpers and replace all
plugs except plug P1. (Replace plug P1 only if no further troubleshooting is required.)
Symptom: First or second stage of heating will not operate.
1. Turn unit power off. Disconnect plugs P1 and P3.
2. Check continuity between Pin W1 at plug P1 and Pin 5
at plug P3. If there is continuity, the board is good and
the problem is either the connection at P3, or external to
the control board. If there is no continuity, the control
board is defective and must be replaced.
3. Check continuity between Pin W2 at plug P1 and Pin 7
at plug P3. If there is continuity, the board is good and
the problem is either at the connection at plug P3 or external to the board. If there is not continuity, the board is
defective and must be replaced. Reconnect plug P3 to the
control board. (Reconnect plug P1 only if no further troubleshooting is required.)
Symptom: Evaporator fan will not energize on a call for heat.
1. Turn unit power off. Disconnect plug P1 and plug P4.
2. Install jumper wire between Pin R and Pin W1 at plug
P1.
3. Turn unit power on. Check for continuity between Pin 6
and Pin 3 at plug P4 on control board.
4. If there is no continuity between these points, the board
is defective and must be replaced.
NOTE: The control board (part number HK37AA001) has
no time delay.
5. If there is continuity between these points, the problem is
at the connection at plug P4 or external to the control
board.
6. Turn unit power off. Reconnect plugs P1 and P4.
55
Page 56

LEGEND
CLO — Compressor Lockout
P—Plug
SC — Safety Circuit
Fig. 65 — Compressor Lockout Connections
56
Page 57

LEGEND FOR FIG. 66-73
ACC — Accessory
BP — Building Pressure
C—Contactor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CCB — Control Circuit Breaker
CF — Check Filter Switch
CLO — Compressor Lockout
COM — Common
COMM — Communication Plug
COMP — Compressor
COND — Condenser
CR — Control Relay
CS — Centrifugal Switch
CV — Constant Volume
DP — Duct Pressure
DPT — Discharge Pressure Transducer
DSIO — High-Voltage Relay Module
DU — Dummy
EC — Enthalpy Control
EQUIP — Equipment
FS — Fan Status Switch
FU — Fuse
GND — Ground
GR — Gas Relay
HHR — Hydronic Humidifier Relay
HIR — Heat Interlock Relay
HPS — High-Pressure Switch
HR — Heater Relay
HSIO — Keypad and Display Module
HV — High Voltage
HYD — Hydronic
I—Ignitor
ICP — Ignitor Control Pack
IDC — Induced Draft Contactor
IDM — Induced Draft Motor
IFC — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Contactor
IFCB — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Circuit Breaker
IFM — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Motor
IGV — Inlet Guide Vanes
IGVM — Inlet Guide Vanes Motor
LPS — Low-Pressure Switch
LS — Limit Switch
LSR — Limit Switch Relay
MG — Main Gas
MGV — Main Gas Valve
MM — Head Control Pressure Device
MPER — Modulating Power Exhaust Relay
MV — Main Valve
NC — Normally Closed
NO — Normally Open
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
PCB — Power Exhaust Circuit Breaker
PEC — Power Exhaust Contactor
PEDM — Power Exhaust Damper Motor
PEM — Power Exhaust Motor
PG — Pilot Gas
PGV — Pilot Gas Valve
PIC — Processor-Integrated Controls
P, PL — Plug
PS — Power Supply (5 VDC)
PSIO — Processor Module
PV — Pilot Valve
PWR — Power
RES — Resistor
RFC — Return Fan Contactor
RFDM — Return Fan Damper Motor
RS — Rollout Switch
SEN,SN — Sensor
SPT — Suction Pressure Transducer
SW — Switch
TB — Terminal Block
TDO — Timed Discrete Output
TH — Thermostat
TRAN — Transformer
VLV — Valve
Field Wiring
Factory Wiring
57
Page 58

Fig. 66 — Gas Heat Sections; 48DJ,NP034,044 Units
58
Page 59

59
Fig. 67 — Gas Heat Sections; 48DJ,NP054-074 Units
Page 60

60
Fig. 68 — Gas Heat Section; 48DK034,044 Units
Page 61

61
Fig. 69 — Gas Heat Section; 48DK054-074 Units
Page 62

62
Fig. 70 — Typical Wiring Schematic; 48/50DJ,50DW Units (054-074 Shown)
Page 63

63
Fig. 70 — Typical Wiring Schematic; 48/50DJ,50DW Units (054-074 Shown) (cont)
Page 64

64
Fig. 71 — Typical Wiring Schematic; 48/50DK,50DY Units (054-074 Shown)
Page 65

65
Fig. 71 — Typical Wiring Schematic; 48/50DK,50DY Units (054-074 Shown) (cont)
Page 66

66
Fig. 72 — Typical Control Wiring Schematic; 48/50NP,50NB Units (054-074 Shown)
Page 67

67
Fig. 72 — Typical Control Wiring Schematic; 48/50NP,50NB Units (054-074 Shown) (cont)
Page 68

Fig. 72 — Typical Control Wiring Schematic; 48/50NP,50NB Units (054-074 Shown) (cont)
68
Page 69

69
Fig. 73 — Typical Power Wiring Schematic; 48/50NP,50NB Units (054-074, 208/230 and 460 v Shown)
Page 70

PACKAGED SERVICE TRAINING
Our packaged service training programs provide an excellent way to increase your knowledge of the
equipment discussed in this manual. Product programs cover:
• Unit Familiarization • Maintenance
• Installation Overview • Operating Sequence
A large selection of product, theory, and skills programs is available. All programs include a video
cassette and/or slides and a companion booklet. Use these for self teaching or to conduct full training
sessions.
For a free Service Training Material Catalog (STM), call 1-800-962-9212. Ordering instructions are
included (U.S.A. and Canada only).
Copyright 1996 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 1
Tab 1a 1b
PC 111 Catalog No. 564-818 Printed in U.S.A. Form 48/50D,N-9SI Pg 70 3-96 Replaces: 48DJ,DK-3SI;
48/50NB,NP-1SI; 50DJ,DK-9SI
Page 71

Page 72

START-UP CHECKLIST
MODEL NO.:
DATE:
SERIAL NO.:
TECHNICIAN:
PRE-START-UP:
M VERIFY THAT ALL PACKING MATERIALS HAVE BEEN REMOVED FROM UNIT
M LOOSEN ALL SHIPPING HOLDDOWN BOLTS AND REMOVE SHIPPING BRACKETS PER INSTRUCTIONS
M VERIFY INSTALLATION OF ECONOMIZER HOOD
M VERIFY INSTALLATION OF EXHAUST HOOD
M VERIFY THAT CONDENSATE CONNECTION IS INSTALLED PER INSTRUCTIONS
M VERIFY THAT ALL ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS AND TERMINALS ARE TIGHT
M CHECK GAS PIPING FOR LEAKS (48 SERIES UNITS ONLY)
M CHECK THAT INDOOR-AIR FILTER IS CLEAN AND IN PLACE
M VERIFY THAT UNIT IS LEVEL
M CHECK FAN WHEEL AND PROPELLER FOR LOCATION IN HOUSING/ORIFICE, AND VERIFY SET SCREW
IS TIGHT
M VERIFY THAT FAN SHEAVES ARE ALIGNED AND BELTS ARE PROPERLY TENSIONED
START-UP
ELECTRICAL
SUPPLY VOLTAGE L1-L2
L2-L3 L3-L1
COMPRESSOR AMPS — COMPRESSOR NO. 1 L1 L2 L3
— COMPRESSOR NO. 2 L1 L2 L3
SUPPLY FAN AMPS EXHAUST FAN AMPS
ELECTRIC HEAT AMPS L1 L2 L3
TEMPERATURES
OUTDOOR-AIR TEMPERATURE
RETURN-AIR TEMPERATURE
COOLING SUPPLY AIR
F DB (Dry-Bulb)
FDB F WB (Wet-Bulb)
F
GAS HEAT SUPPLY AIR
(48 SERIES UNITS ONLY)
F
ELECTRIC HEAT SUPPLY AIR
(IF UNIT IS SO EQUIPPED)
F
PRESSURES
GAS INLET PRESSURE (48 SERIES UNITS ONLY)
IN. WG
GAS MANIFOLD PRESSURE
(48 SERIES UNIT ONLY) VALVE NO. 1
REFRIGERANT SUCTION CIRCUIT NO. 1
REFRIGERANT DISCHARGE CIRCUIT NO. 1
IN. WG VALVE NO. 2 IN. WG
PSIG CIRCUIT NO. 2 PSIG
PSIG CIRCUIT NO. 2 PSIG
CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE
M VERIFY REFRIGERANT CHARGE USING CHARGING CHARTS ON PAGES 47-49
GENERAL
M ECONOMIZER MINIMUM VENT AND CHANGEOVER SETTINGS TO JOB REQUIREMENTS
Copyright 1996 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 1 1
Tab 1a 1b
PC 111 Catalog No. 564-818 Printed in U.S.A. Form 48/50D,N-9SI CL-1 3-96 Replaces: 48DJ,DK-3SI;
48/50NB,NP-1SI; 50DJ,DK-9SI
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Loading...
Loading...