Page 1
50LJQ008,012 (50 Hz)
Single-Package Rooftop Heat Pump Units
Installation, Start-Up and Service
Instructions
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS .................. 1
INSTALLATION ............................ 1-16
Step 1 — Provide Unit Support .............. 1
• ROOF CURB
• SLAB MOUNT
Step 2 — Field Fabricate Ductwork ........... 1
Step 3 — Make Field Connection for
Condensate Disposal .........................3
Step 4 — Rig and Place Unit ................. 3
Step 5 — Make Electrical Connections ....... 7
• FIELD POWER SUPPLY
• FIELD CONTROL WIRING
• HEAT ANTICIPATOR SETTINGS
Step 6 — Adjust Indoor-Fan Speed ...........13
START-UP ................................17-19
SERVICE ..................................19-21
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
Installation and servicing of air conditioning equipment
can be hazardous due to system pressure and electrical components. Only trainedandqualified service personnel should
install, repair or service air conditioning equipment.
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance functions of cleaning coils and filters and replacing filters. All
other operations should be performed by trained service personnel. When working on air conditioning equipment, observe precautions in the literature, tags and labels attached
to the unit, and other safety precautions that may apply.
Follow all safetycodes. Wearsafety glasses andwork gloves.
Use quenching cloth for unbrazing operations. Have fire extinguisher available for all brazing operations.
Before performing service or maintenance operations on
unit, turn offmain power switch to unit. Electrical shock
could cause personal injury.
INSTALLATION
Unit is shipped in the vertical configuration. To convert to
horizontal configuration, remove side duct opening covers.
Using the same screws, install covers on vertical duct openings with the insulation-side down. Seals around duct openings must be tight.
IMPORTANT: An external filter kit MUST be used,
or the filters MUST be field-installed outside the unit
on horizontal applications with accessory economizer
or two-position damper. Otherwise, the economizer or
two-position must be partially removed to access the
filters. The area of the field-installed filters should be
equal to the area of the factory-installed filters.
Step 1 — Provide Unit Support
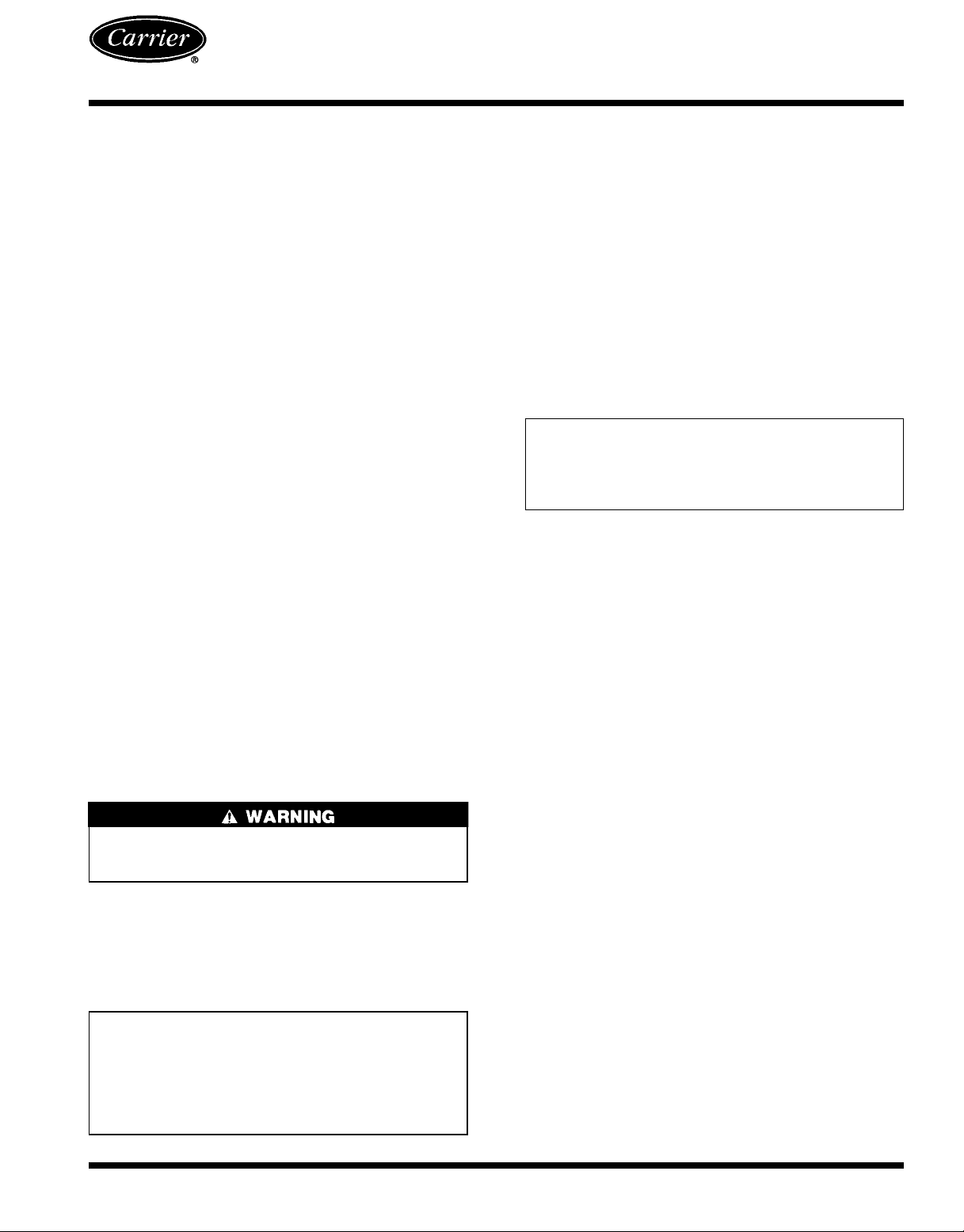
ROOF CURB — Assemble and install accessory roof curb
in accordance with instructions shipped with curb. See
Fig. 1. Install insulation, cant strips, roofing and counter flashing as shown. Ductwork must be attached to curb, not to the
unit. If electric or control power is to be routed through the
curb, attach the accessory thru-the-curb service connection
plates to the roof curb in accordance with the accessory installation instructions. Connection plates must be installed
before unit is set in roof curb.
IMPORTANT: The gasketing of the unit to the roof
curb is critical for a watertight seal. Install gasket supplied with the roof curb as shown in Fig. 1. Improperly applied gasket also can result in air leaks and poor
unit performance.
Curb should be level. Unit leveling tolerances are shown
in Fig. 2. This is necessary for unit drain to function properly. Refer to Accessory Roof Curb Installation Instructions
for additional information as required.
SLAB MOUNT (Horizontal Units Only) — Provide a level
concrete slab that extends a minimum of 152 mm (6 in.) beyond unit cabinet. The slab should be 203 mm (8 in.) thick
with 102 mm (4 in.) above grade. Install a gravel apron in
front of outdoor coil air inlet to prevent grass and foliage
from obstructing airflow. In areas where high snowfall
occurs, increase height of slab to ensure that snow does not
block coil.
NOTE: Horizontal units may be installed on a roof curb if
required.
Step 2 — Field Fabricate Ductwork — On verti-
cal discharge units, secure all ducts to roof curb and building
structure. Do not connect ductwork to unit. For horizontal
applications, field-supplied flanges should be attached to horizontal discharge openings and all ductwork attached to the
flanges. Insulate and weatherproof all external ductwork, joints
and roof openings with counter flashing and mastic in accordance with applicable codes.
Ducts passing through an unconditioned space must be
insulated and covered with a vapor barrier.
If a plenum return is used on a vertical unit, the return
should be ducted through the roof deck to comply with applicable fire codes.
Aminimumclearance to combustibles is not required around
ductwork on vertical discharge units. On horizontal discharge units, a minimum clearance of 25 mm (one in.) is
required for the first 305 mm (12 in.) of ductwork.
Cabinet return-air static shall not exceed −87 Pa
(−.35 in. wg) with economizer or −112Pa (−.45 in. wg) without economizer.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 015-015 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50LJQ-C1SI Pg 1 1-92 Replaces: New
Page 2
ROOF CURB
ACCESSORY
50DJ901371
50DJ901381
‘‘A’’ UNIT SIZE
18-29
[356]
50LJQ008,012
28-09
[610]
UNIT SIZE ‘‘F’’ POWER ‘‘G’’ CONTROL
50LJQ008,012
19 [25] NPT or
29 [51] NPT
NOTES:
1. Roof curb accessory is shipped unassembled.
2. Insulated panels: 25 mm (one in.) thick polyurethane foam, .8 Kg (1
3. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
4. Roof curb: 16-gage steel.
5. Attachductworktocurb (flanges of duct rest on curb).
6. Service clearance 1219 mm (4 ft) on each side.
3
⁄49 [19] NPT 50DJ901311
7. Direction of airflow.
8. Control and power service plates are part of a separately shipped accessory package.
3
⁄4lb) density.
CONNECTOR
PKG. ACC.
Fig. 1 — Roof Curb Dimensions
2
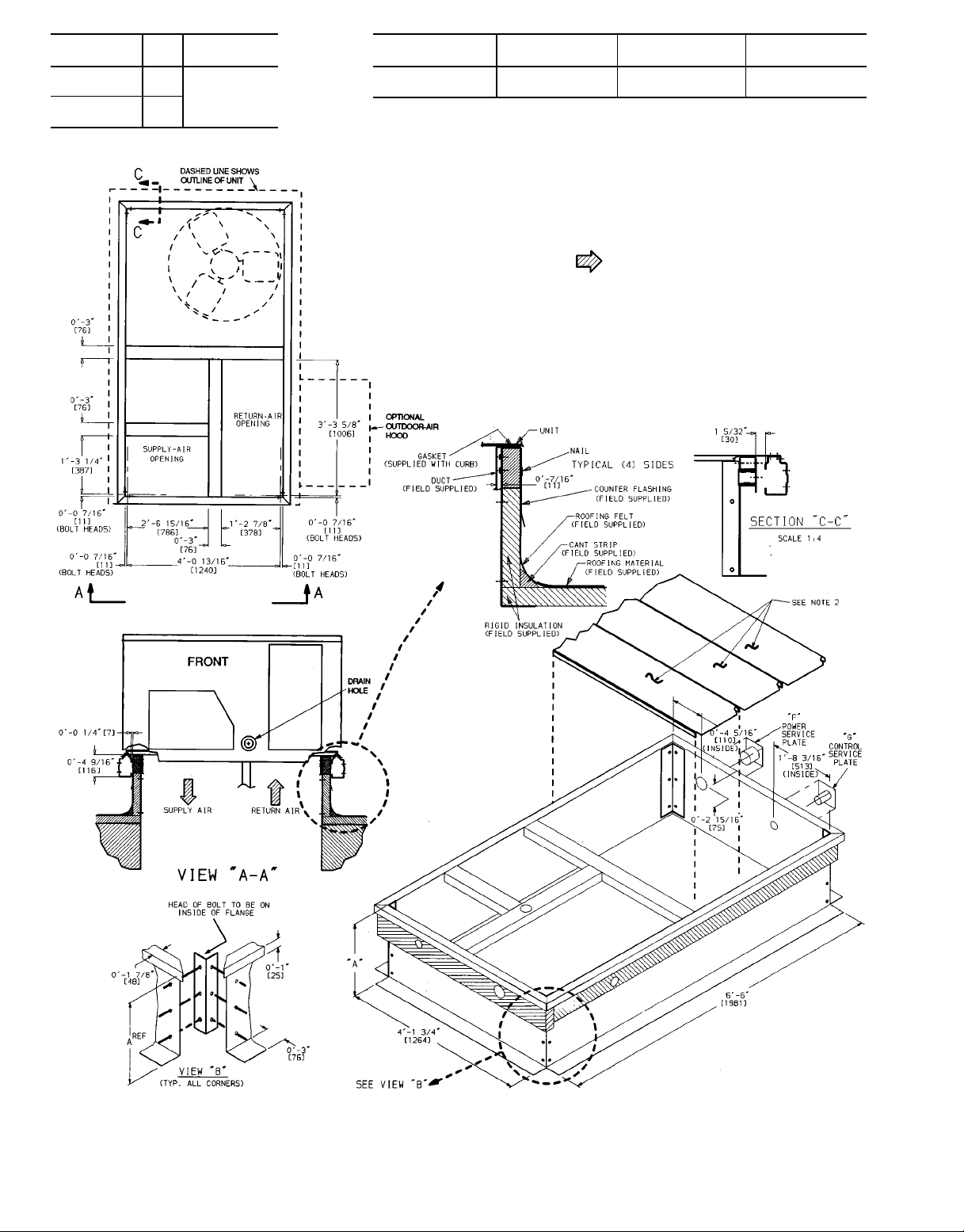
Page 3
MAXIMUM ALLOWABLE DIFFERENCE
A-B B-C A-C
mm in. mm in. mm in.
13 .5 25 1.0 25 1.0
Fig. 2 — Unit Leveling Tolerance
Step 3 — Make Field Connection for CondensateDisposal —
See Fig. 3. A3⁄4-in. FPT connection is located on the side of
the unit. Use a trap at least 100 mm (4 in.) deep, and protect
against freeze-up.
If drain line is run to a drain, pitch line away from unit at
25 mm (one in.) per 3 m (10 ft) of run. Do not use a pipe size
smaller than the unit connection.
Units must have an external trap added.
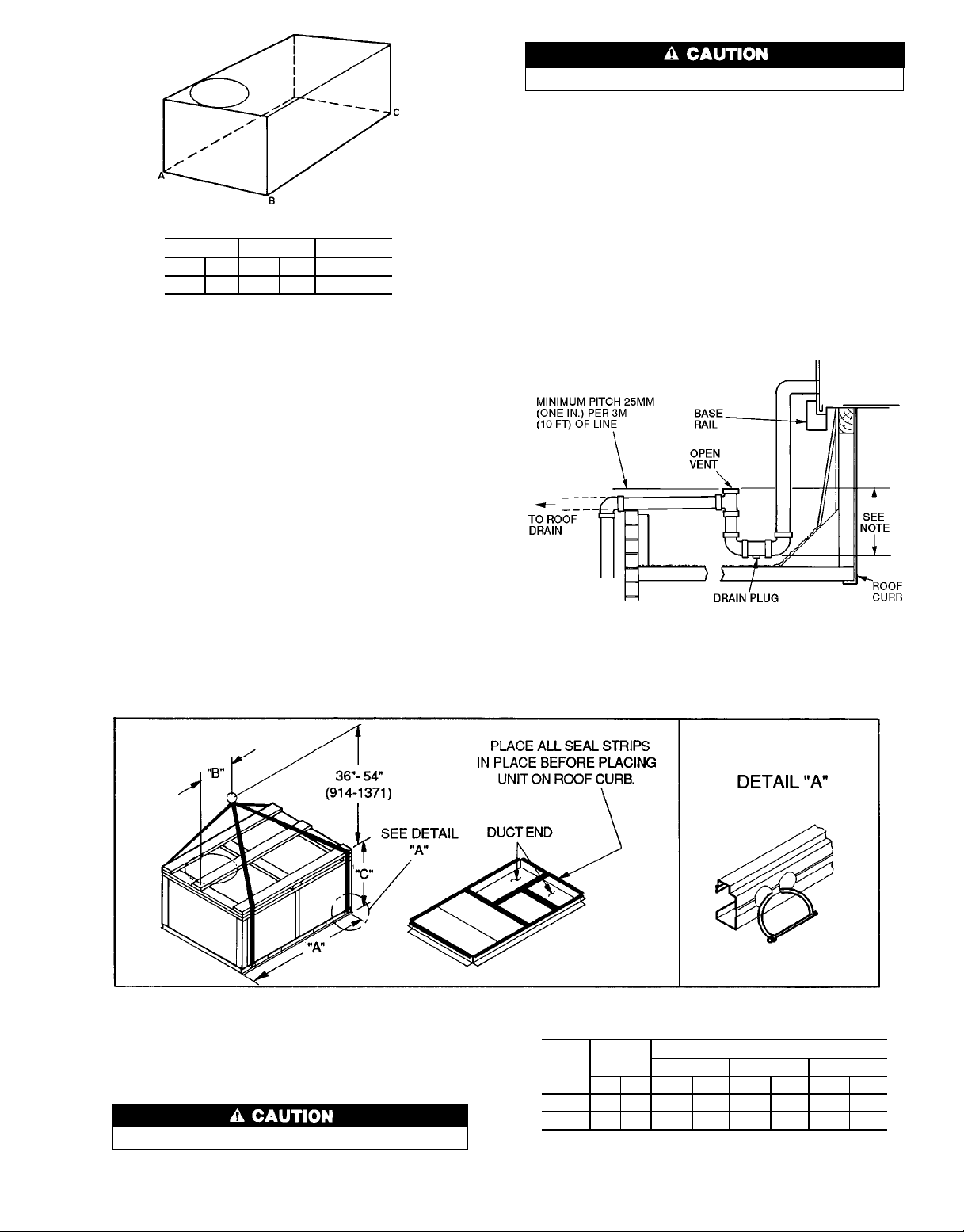
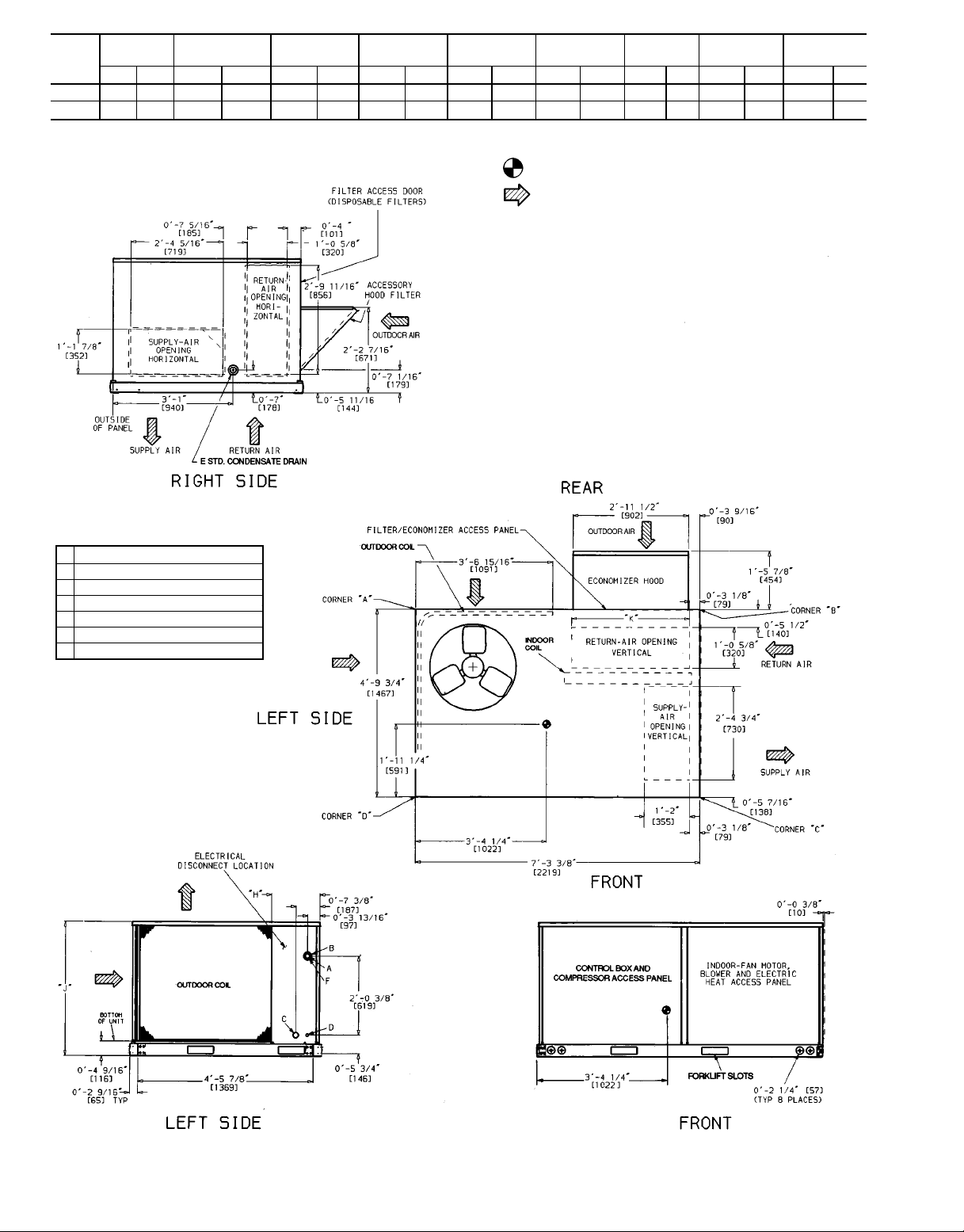
Step4 — Rig andPlace Unit — Inspect unit for trans-
portation damage. File any claim with transportation agency.
Keep unit upright and do not drop. Spreader bars are not
required if top crating is left on unit. Rollers may be used to
move unit across a roof. Level by using unit frame as a reference. See Tables 1A and 1B and Fig. 4 for additional information. Operating weight is shown in Tables 1A and 1B
and Fig. 4.
Lifting holes are provided in base rails as shown in
Fig. 4 and 5. Refer to rigging instructions on unit.
All panels must be in place when rigging.
POSITIONING — Maintain clearance around and above unit
to provide proper air flow and service access. See Fig. 5.
Position unit on roof curb so that the following clearances
are maintained; 6 mm (
1
⁄4in.) clearance between roof curb
and base rails on each side and front of unit: 29 mm (15⁄
in.) clearance between roof curb and rear of unit (see Fig. 1,
section C-C).
Do not install unit in an indoor location. Do not locate
unit air inlet near exhaust vents or other sources of contaminated air.
Although unit is weatherproof, guard against water from
higher level runoff and overhangs.
After unit is in position, remove polyethylene shipping wrapper and rigging skid.
NOTE: Trap should be deep enough to offset maximum unit static
difference. A 100 mm (4 in.) trap is recommended.
Fig. 3 — External Trap Condensate Drain
32
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in ( ) is in millimeters.
2. Hood rigging shackles through holes in base rail, as shown in
detail ‘‘A’’. Holes in base rails are centered around the unit center
of gravity. Use wooden top skid when rigging to prevent rigging
straps from damaging unit.
3. Weightsdonotincludeeconomizer .SeeTables1A and 1B for economizer weights.
All panels must be in place when rigging.
Fig. 4 — Rigging Details
UNIT
50LJQ
008 840 381 87.38 2219 40.25 1022 41.31 1050
012 940 426 87.38 2219 40.25 1022 48.31 1253
MAX
WEIGHT
lb kg in. mm in. mm in. mm
‘‘A’’ ‘‘B’’ ‘‘C’’
DIMENSIONS
3
Page 4
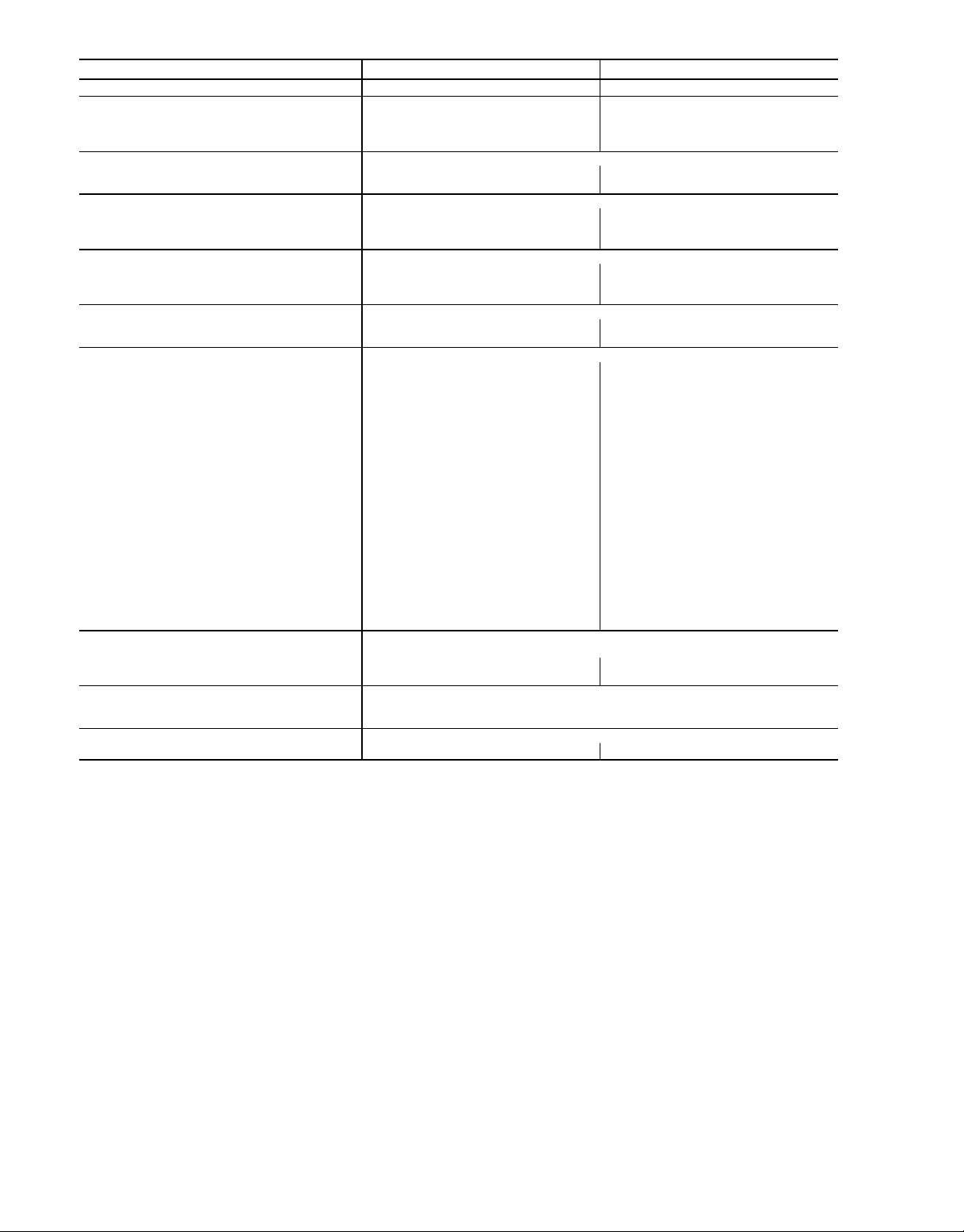
Table 1A — Physical Data (SI)
BASE UNIT 50LJQ 008 012
NOMINAL CAPACITY (kW) 23.2 28.8
OPERATING WEIGHT (kg)
Unit 381 426
With Economizer 401 446
Roof Curb 101 101
COMPRESSOR
Quantity 22
Oil (ml) (each compressor) 1627 2071
REFRIGERANT TYPE
Operating Charge (kg)
Circuit 1 3.7 4.0
Circuit 2 3.2 3.9
OUTDOOR FAN
Quantity...Diameter (mm) 1...660 1...660
Nominal L/s 2900 3260
Motor BkW...r/s .25...16.0 .25...16.0
OUTDOOR COIL
Rows...Fins/m 2...669 2...669
Total Face Area (sq m) 1.9 2.3
INDOOR FAN
Size (mm) 381 x 381 381 x 381
Type Drive Belt Belt
Nominal L/s 1200 1600
Motor BkW per NEC* 1.12 1.50
Maximum Continuous BkW 1.79 2.16
Motor Frame 56 56
Fan r/s Range 10.30-14.70 11.50-15.00
Motor Bearing Type Ball Ball
Maximum Fan r/s 26.7 26.7
Motor Pulley Pitch Diameter
A/B (mm)
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (mm) 140 178
Belt — Type...Length (mm) A...1219 A...1295
Pulley Center Line Distance (mm) 425-489 464-527
Fan Shaft Diameter at Pulley (mm) 25 25
Speed Change per Full Turn of
Movable Pulley Flange (r/s)
Movable Pulley Maximum Full
Turns from Closed Position
Factory Setting — Full Turns Open 55
Factory Speed Setting (r/s) 10.3 11.5
INDOOR COIL Enhanced Copper Tubes, Aluminum Double Wavy Fins,
Rows...Fins/m 3...590 3...590
Total Face Area (sq m) .74 .93
OUTDOOR-AIR INLET SCREENS Cleanable
Quantity...Size (mm)
RETURN-AIR FILTERS Disposable
Quantity...Size (mm)
Enhanced Copper Tubes, Aluminum Fins, Acutrol™ Feed Device
61/86 86/112
.88 .70
55
4...406 x 508 x 50 4...508 x 508 x 50
LEGEND
BkW — Brake Kilowatt
NEC — National Electrical Code (U.S.A. Standard)
*Used to determine wire sizing per NEC.
Hermetic
R-22
Propeller
Centrifugal
Acutrol Feed Device
1...508 x 635 x 25
1...406 x 635 x 25
4
Page 5
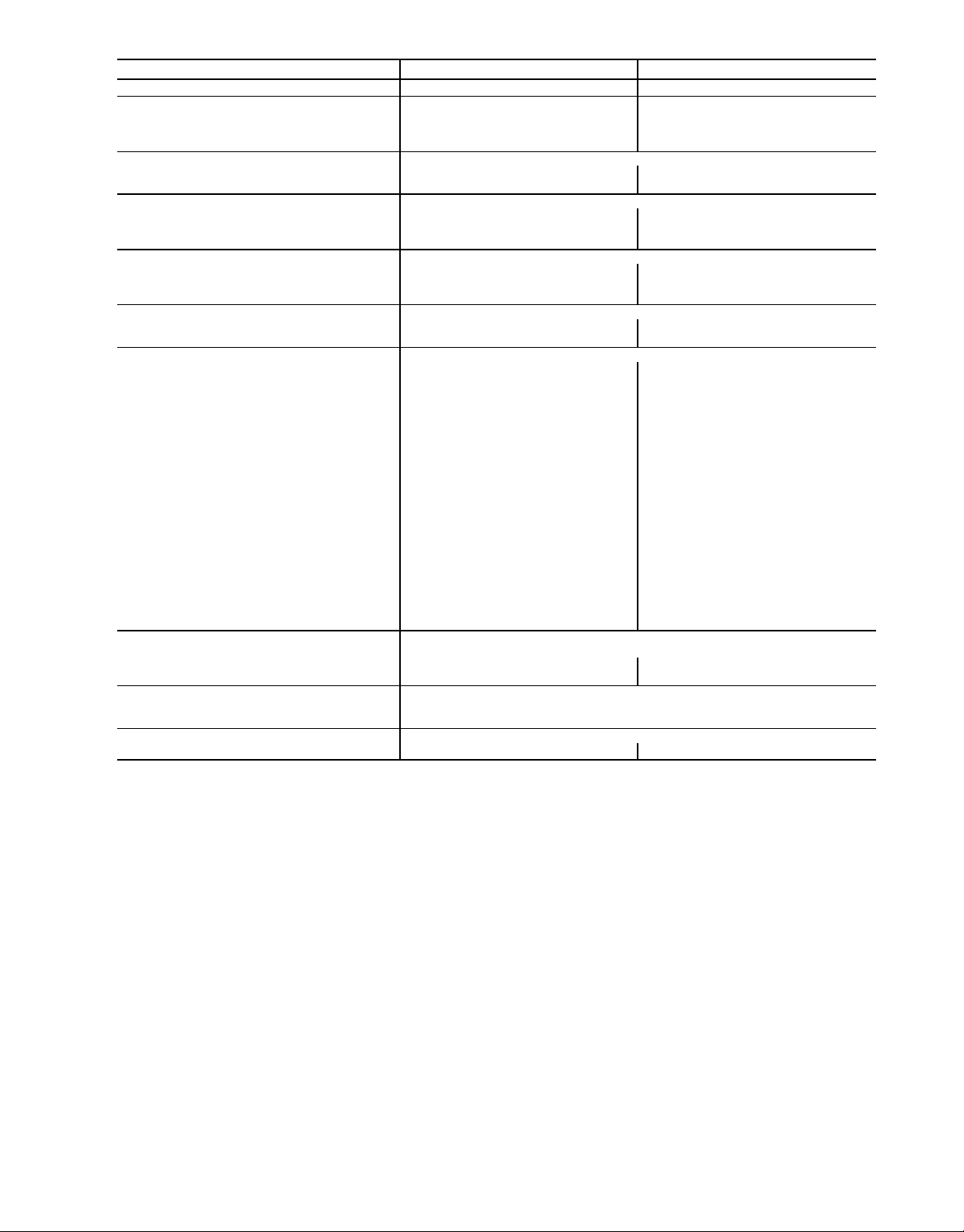
Table 1B — Physical Data (English)
BASE UNIT 50QJ 008 012
NOMINAL CAPACITY (tons) 6.6 8.2
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)
Unit 840 940
With Economizer 884 984
Roof Curb 223 223
COMPRESSOR
Quantity 22
Oil (fluid oz) (each compressor) 55 70
REFRIGERANT TYPE
Operating Charge (lb-oz)
Circuit 1 8-2 8-14
Circuit 2 7-0 8-10
OUTDOOR FAN
Quantity...Diameter (in.) 1...26 1...26
Nominal Cfm 6100 6900
Motor Hp...Rpm
OUTDOOR COIL
Rows...Fins/in. 2...17 2...17
Total Face Area (sq ft) 20.5 25.0
INDOOR FAN
Size (in.) 15x15 15x15
Type Drive Belt Belt
Nominal Cfm 2600 3400
Horsepower per NEC* 1.5 2.0
Maximum Continuous Bhp 2.4 2.9
Motor Frame 56 56
Fan Rpm Range 622-882 692-896
Motor Bearing Type Ball Ball
Maximum Fan Rpm 1600 1600
Motor Pulley Pitch Diameter
A/B (in.)
Fan Pulley Pitch Diameter (in.) 5.5 7.0
Belt — Type...Length (in.) A...48 A...51
Pulley Center Line Distance (in.) 16.75-19.25 18.25-20.75
Fan Shaft Diameter at Pulley (in.) 11
Speed Change per Full Turn of
Movable Pulley Flange (rpm)
Movable Pulley Maximum Full
Turns from Closed Position
Factory Setting — Full Turns Open 55
Factory Speed Setting (Rpm) 620 690
1
⁄3...960
Enhanced Copper Tubes, Aluminum Fins, Acutrol™ Feed Device
2.4/3.4 3.4/4.4
52 42
55
INDOOR COIL Enhanced Copper Tubes, Aluminum Double Wavy Fins,
Rows...Fins/in. 3...15 3...15
Total Face Area (sq ft) 8.0 10.0
OUTDOOR-AIR INLET SCREENS Cleanable
Quantity...Size (in.)
RETURN-AIR FILTERS
Quantity...Size (in.) 4...16 x 20 x 2 4...20 x 20 x 2
LEGEND
Bhp — Brake Horsepower
NEC — National Electrical Code (U.S.A. Standard)
*Used to determine wire sizing per NEC.
Hermetic
R-22
Propeller
Centrifugal
Acutrol Feed Device
1...20 x 25 x 1
1...16 x 25 x 1
Disposable
1
⁄3...960
5
Page 6
UNIT
50LJQ
STD. UNIT
WEIGHT
Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Ft-in. mm Ft-in. mm Ft-in. mm
ECONOMIZER
WEIGHT
CORNER
WEIGHT ‘‘A’’
CORNER
WEIGHT ‘‘B’’
CORNER
WEIGHT ‘‘C’’
CORNER
WEIGHT ‘‘D’’
008 840 381 44 20 182 83 156 71 231 105 271 123 2-0
012 940 426 44 20 204 93 174 79 259 117 303 137 1-2
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
2. Center of gravity.
3. Direction of airflow.
4. Ductwork to be attached to accessory roof curb only.
5. Minimum clearance (local codes or jurisdiction may prevail):
a. Bottom to combustible surfaces (when not using curb) 25 mm
(one in.).
b. Condenser coil, for proper airflow, 914 mm (36 in.) one side,
305 mm (12 in.) the other. The side getting the greater clearance is optional.
c. Overhead 1524 mm (60 in.) to assure proper outdoor fan
operation.
d. Between units, control box side, 1067 mm (42 in.).
e. Between unit and ungrounded surfaces, control box side, 914
mm (36 in.).
f. Between unit and block or concrete walls and other grounded
surfaces, control box side 1067 mm (42 in.).
g. Horizontal supply and return end, zero mm (zero in.).
6. With the exception of the clearance for the outdoor coil as stated
in notes 5b and c, a removable fence or barricade requires no
clearance.
‘‘H’’ ‘‘J’’ ‘‘K’’
7
⁄8632 3-55⁄161050 2-911⁄16856
7
⁄8378 4-15⁄161253 3-03⁄8924
CONNECTION SIZES
3
⁄89 dia [35] field power supply hole
A 1
1
⁄29 dia [64] power supply knockout
B 2
3
⁄49 dia [44] charging-port hole
C 1
7
⁄89 dia [22] field control wiring hole
D
3
⁄49-14 NPT condensate drain
E
F 29 dia [51] power supply knockout
Fig. 5 — Base Unit Dimensions
6
Page 7
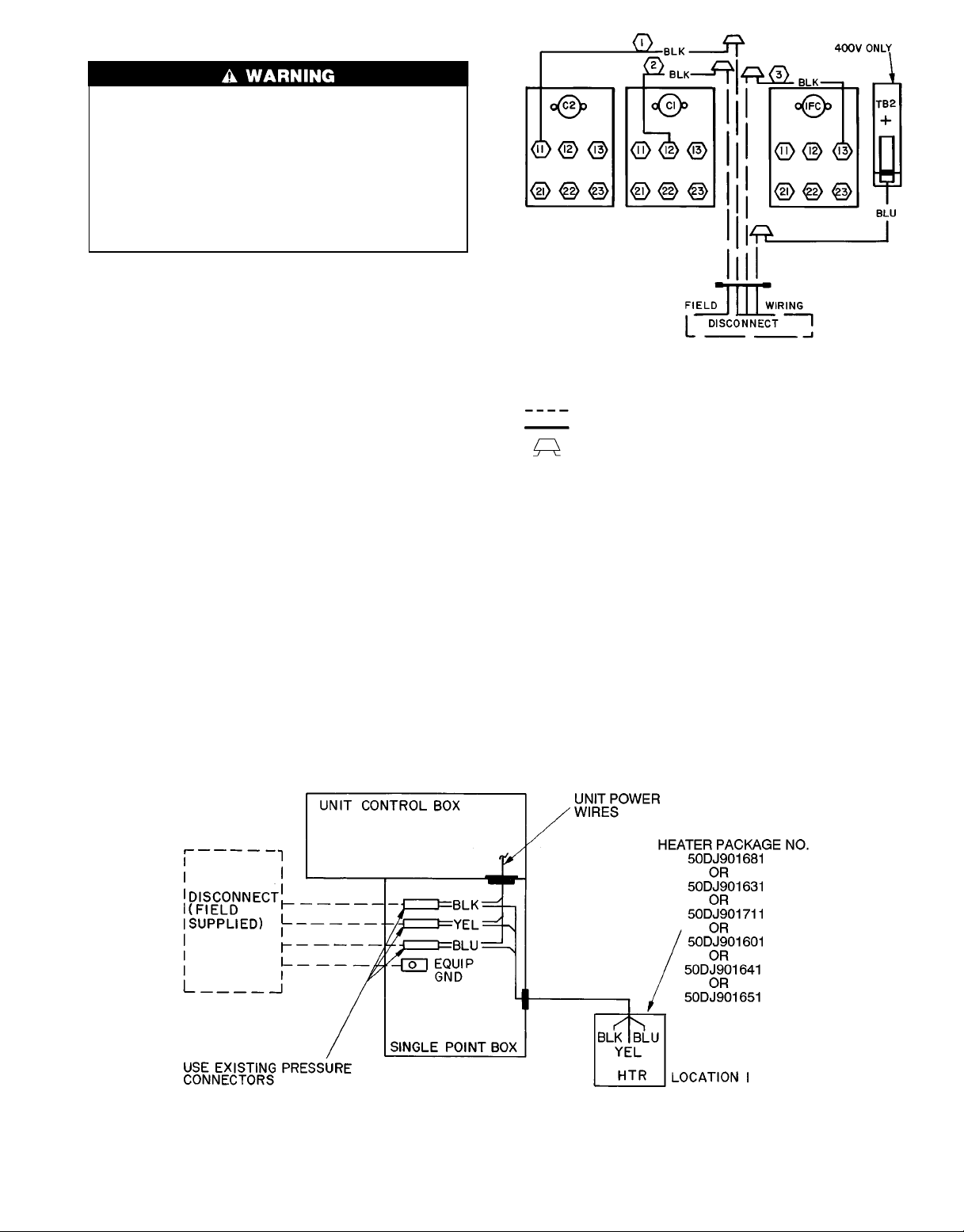
Step 5 — Make Electrical Connections
Unit cabinet must have uninterrupted, unbroken electrical ground to minimize the possibility of personal
injury if an electrical fault should occur. This ground
may consist of electrical wire connected to unit ground
lug in control compartment, or conduit approved for electrical ground when installed in accordance with U.S.A.
National Electrical Code (Ref: ANSI/NFPA 70-1987)
or equivalent local electrical codes. Failure to follow this
warning could result in the installer being liable for personal injury of others.
FIELD POWER SUPPLY — Pigtails are provided for field
wire connections. Use factory-supplied splices or copper/
aluminum connector.
When installing units, provide a disconnect per local codes.
All field wiring must comply with local requirements.
Install conduit through side panel openings. For units without electric heat, install conduit between disconnect and control box. Install power lines to terminal connections as shown
in Fig. 6. For units with electric resistance heat, refer to Table
2 to determine appropriate power wiring figure (Fig.7-13)
and route lines as indicated in appropriate figure.
Voltage to compressor terminals during operation must be
within voltage range indicated on unit nameplate (also see
Table 2). On 3-phase units, voltages between phases must be
balanced within 2% and the current within 10%. Use the formula shown in Table 2, Note 3 to determine the % voltage
imbalance. Operation on improper line voltage or excessive
phase imbalance constitutes abuse and may cause damage to
electrical components. Such operation would invalidate any
applicable Carrier warranty.
When electric heat is installed, remove knockouts for appropriate size conduit from unit block-off panel and single
point box. Install conduit (rigid or electro-metallic tubing)
through conduit drip boot as shown in Fig. 14. Drip boot
eliminates the need for water tight conduit fittings at the single
point box. Refer to Fig. 15 for component locations.
LEGEND
C—Contactor
IFC — Indoor-Fan Contactor
TB — Terminal Block
Field Wiring
Factory Wiring
Splice Connection (Factory Supplied)
Fig. 6 — Power Wiring Connections
LEGEND FOR FIG. 7-13
EQUIP — Equipment
FU — Fuse
GND — Ground
HTR — Heater
TB — Terminal Block
Fig. 7 — Electric Heater Power Wiring Connections — 50LJQ, 220-3-50 and 400-3-50;
Single Point Kit 50DJ902021 and 50DJ902071
7
Page 8
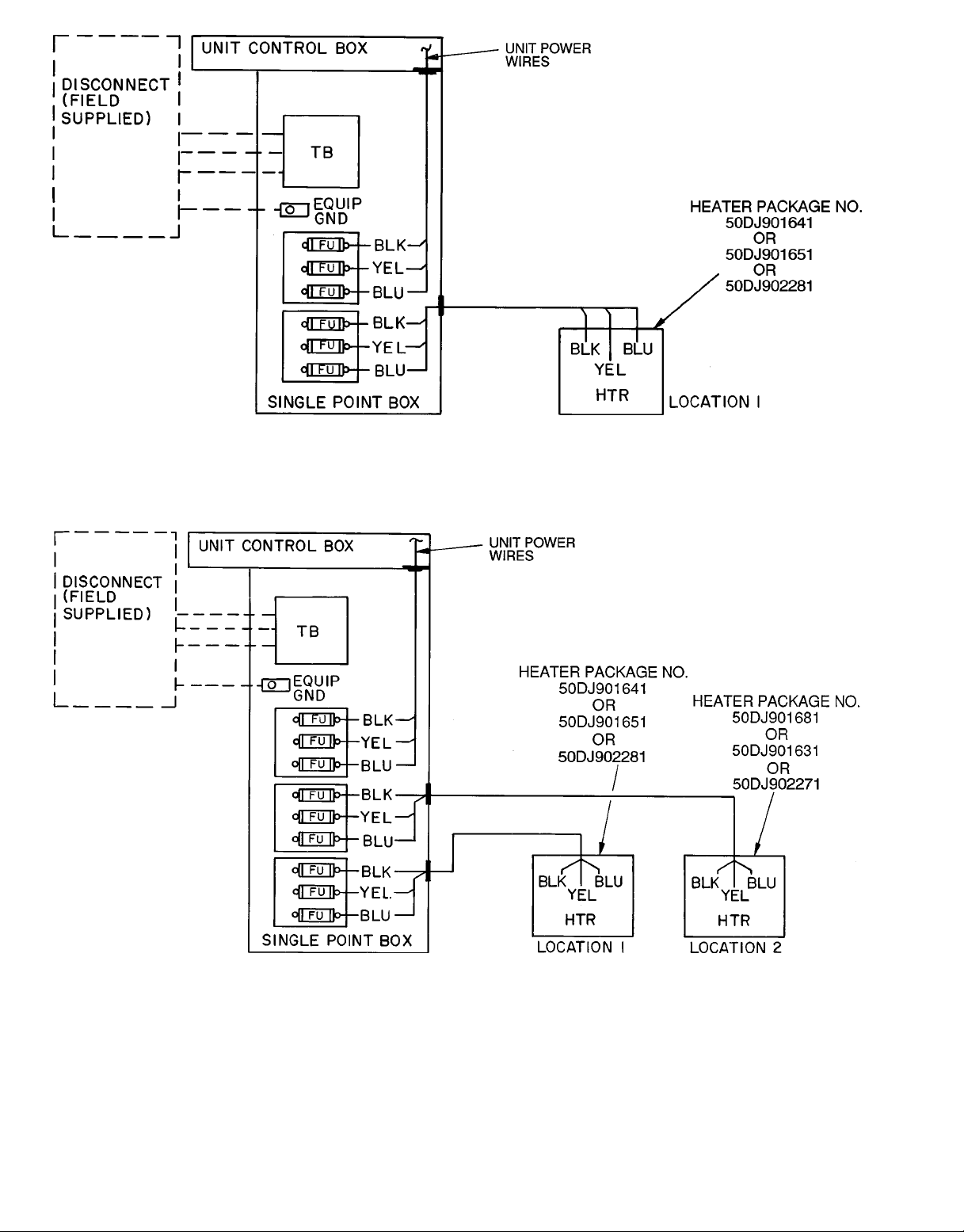
Fig. 8 — Electric Heater Power Wiring Connections — 50LJQ, 400-3-50;
Single Point Kit 50DJ902041 and 50DJ902101
Fig. 9 — Electric Heater Power Wiring Connections — 50LJQ, 400-3-50;
Single Point Kit 50DJ902061 and 50DJ902121
8
Page 9

Fig. 10 — Electric Heater Power Wiring Connections — 50LJQ, 220-3-50;
Single Point Kit 50DJ902031 and 50DJ902081
Fig. 11 — Electric Heater Wiring Connections — 50LJQ, 220-3-50;
Single Point Kit 50DJ902051 and 50DJ902111
LEGEND FOR FIG. 7-13
EQUIP — Equipment
FU — Fuse
GND — Ground
HTR — Heater
TB — Terminal Block
9
Page 10

Fig. 12 — Electric Heater Power Wiring Connections — 50LJQ, 220-3-50;
Single Point Kit 50DJ902091
Fig. 13 — Electric Heater Power Wiring Connections — 50LJQ, 220-3-50;
Single Point Kit 50DJ902131
LEGEND FOR FIG. 7-13
EQUIP — Equipment
FU — Fuse
GND — Ground
HTR — Heater
TB — Terminal Block
10
Page 11

Table 2 — Electrical Data
UNIT
50LJQ
008
012
VOLTAGE
NOMINAL
V-PH-HZ
220-3-50 198 242 15.3 82.0 1.5 1.5 5.8
400-3-50 360 440 7.7 41.0 1.5 1.5 2.6
220-3-50 198 242 19.6 105.0 1.5 2.0 7.5
400-3-50 360 440 10.4 55.0 1.5 2.0 3.5
RANGE
Min Max RLA LRA FLA Hp FLA
COMPR
(each)
OFM IFM ELECTRIC HEAT POWER SUPPLY
LEGEND
COMPR — Compressor
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
IFM — Indoor-Fan Motor
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
OFM — Outdoor-Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
*Heaters are field-installed only. Heater capacity (kW) is based on
heater voltage of 230 v or 400 v.If power distribution voltage to unit
varies from rated heater voltage, heater kW will vary
accordingly.
†Fuse or HACR circuit breaker.
**Requires 2 heater packages.
NOTES:
1. MCA and MOCP values are calculated in accordance with NEC
(National Electric Code) (U.S.A. Standard), Article 440.
2. Motor RLA and FLA values are established in accordance with UL
(Underwriters’ Laboratories) Standard 465 (U.S.A. Standard).
3. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than 2%.
the % voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance
= 100 x
max voltage deviation from average voltage
Use the following formula to determine
average voltage
ELECTRIC HEAT
Nominal
kW*
— — 41.7 50 — —
9.5 24.7 70.3 80 10 711
14.6 38.0 85.7 90 10 601
22.7 59.0 130.0 150 11 611
29.3 76.2 158.5 175 11 621
38.8 100.9 179.5 200 12 711, 621**
10.5 15.2 21.4 25 7 681
12.5 18.0 44.0 45 7 631
21.0 30.3 59.3 60 8 641
25.0 36.1 66.5 70 8 651
31.5 45.5 78.3 80 9 681, 641**
— — 53.1 60 — —
9.5 24.7 81.6 90 10 711
14.6 38.0 97.1 100 10 601
29.3 76.2 141.3 150 11 621
43.9 114.1 190.9 200 13 601, 621**
10.5 15.2 28.4 35 7 681
12.5 18.0 51.0 60 7 631
21.0 30.3 66.3 70 8 641
25.0 36.1 73.5 80 8 651
31.5 45.5 85.2 90 9 681, 641**
37.5 54.2 96.6 100 9 631, 651**
FLA MCA MOCP†
Example: Supply voltage is 400-3-50.
AB = 393 v
BC = 403 v
AC = 396 v
Average Voltage =
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage.
(AB) 397 − 393=4v
(BC) 403 − 397=6v
(AC) 397 − 396=1v
Maximum deviation is 6 v.
Determine % voltage imbalance.
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x = 1.5%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the
maximum allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is
more than 2%, contact your local electric utility company
immediately.
POWER WIRING
FIG. NO.
= = 397
6
397
ELECTRIC HEAT
PART NO.
50DJ901—
393 + 403 + 396
3
1192
3
11
Page 12

DISCONNECT
MOUNTING
LOCATION
Fig. 14 — Conduit Installation
EMT OR RIGID
CONDUIT
(FIELDSUPPLIED)
MAIN
CONTROL
BOX
BRACKET AND
CONDUIT DRIP
BOOT
CENTER POST
MANUAL RESET
LIMIT SWITCH
LOCATION
(HIDDEN)
HEATER
COVERS
15 to 23 m (51 to 75 ft), use no. 16 AWG insulated
wire (35 C minimum). For over 23 m (75 ft), use no. 14
AWG insulated wire (35 C minimum). See Table 3 for wire
conversions.
1. If unit is mounted on roof curb and accessory thru-thecurb service plate connection is used, route wire through
connection plate.
2. Pass control wires through the hole provided on unit (see
connection D, Connection Sizes table, Fig. 5).
3. Feed wire through the raceway built into the corner post
to the 24-v barrier located on the left side of the control
box. See Fig. 17. The raceway provides the UL (U.S.A.
Standard) required clearance between high- and lowvoltage wiring.
4. Connect thermostat wires to screw terminals of lowvoltage connector. The connector plugs into the control
board and may be removed to make connection. Plug connector back into the control board after making connection or unit will not operate.
HEAT ANTICIPATORSETTINGS — Set first-stage heat anticipator settings at 1.0. Set second-stage heat anticipator settings at 0.6. For units with optional electric heat,
set anticipator for second stage as shown in Table 4.
HEATER
WIRING
LABEL
HEATER
MOUNTING
BRACKET
SINGLE
POINT
BOX
SINGLE POINT
BOX MOUNTING
SCREWS
CONTROL WIRE
TERMINAL
BLOCK
HEATER
MODULE
(LOCATION 1)
HEATER
MODULE
(LOCATION 2)
Fig. 15 — Component Location
FIELD CONTROL WIRING — Install a Carrier-approved
accessory thermostat assembly according to installation instructions included with the accessory. Locate thermostat assembly on a solid wall in the conditioned space to sense average temperature in accordance with thermostat installation
instructions.
Route thermostat cable or equivalent single leads of colored wire from subbase terminals to low-voltage connections on unit (shown in Fig. 16) as described in Steps 1-4
below.
NOTE: For wire runs up to 15 m (50 ft), use no. 18 AWG
(American Wire Gage) insulated wire (35 C minimum). For
Table 3 — American/European Wire Conversions
AMERICAN EUROPEAN
Industry
Standard Size
18 AWG 0.82 1.0
16 AWG 1.30 1.5
14 AWG 2.08 2.5
12 AWG 3.30 4.0
10 AWG 5.25 6.0
8 AWG 6.36 10.0
6 AWG 13.29 16.0
4 AWG 21.14 25.0
3 AWG 26.65 —
2 AWG 33.61 35.0
1 AWG 42.39 50.0
1/0 AWG 53.49 —
2/0 AWG 67.42 70.0
3/0 AWG 85.00 95.0
4/0 AWG 107.19 120.0
250 kcmil 126.64 150.0
300 kcmil 151.97 —
350 kcmil 177.90 185.0
400 kcmil 202.63 240.0
500 kcmil 253.29 300.0
600 kcmil 303.95 —
LEGEND
AWG — American Wire Gage
kcmil — Thousand Circular Mils
American
Conversion
2
(mm
)
Industry
Standard
Size (mm2)
Table 4 — Unit Voltage
220 400
Heater kW Anticipator Setting Part No. 50DJ901— Heater kW Anticipator Setting Part No. 50DJ901—
9.5 0.3 711 10.5 0.3 681
14.6 0.3 601 12.5 0.3 631
22.7 0.6 611 21.0 0.3 641
29.3 0.6 621 25.0 0.3 651
38.8 0.9 711, 621* 31.5 0.6 681, 641*
43.9 0.9 711, 621* 37.5 0.6 631, 651*
*Requires 2 heater packages.
12
Page 13

UNIT
CONTROL
BOARD
BAT — Battery
C—Contactor
CB — Circuit Breaker
DAT — Discharge-Air Thermistor
EMC/EMFC — Energy Management Closed
EMO/EMFO — Energy Management Open
EQUIP — Equipment
GND — Ground
HR — Heater Relay
IFC — Indoor-Fan Contactor
Fig. 16 — Field Wiring Connections
LEGEND
OFC — Outdoor-Fan Contactor
P—Plug
TB — Terminal Board
TRAN — Transformer
Field Wiring
Factory Wiring
Splice Connection (Factory Supplied)
Tables 5A and 5B show fan rps and rpm at motor pulley
settings. Refer to Tables 6-13 to determine fan speed
settings.
Fan motor pulleys are factory set for speed shown in
Tables 1A and 1B.
RACEWAY
Fig. 17 — Field Control Wiring Raceway
Step 6 — Adjust Indoor-Fan Speed — Adjust in-
door fan speed to meet jobsite conditions.
For units with electric resistance heating, required minimum L/s (cfm) is 1062 (2250) for 50LJQ008 and 1416 (3000)
or 50LJQ012, with the following exceptions.
UNIT
50LJQ
012
UNIT
VOLTAGE
220 50.0
400 50.0
HEATER
kW
UNIT
CONFIG-
URATION
Horizontal
or Vertical
Horizontal
or Vertical
REQUIRED
MINIMUM
L/s Cfm
1534 3250
1605 3400
To change fan speed:
a. Shut off unit power supply.
b. Loosen belt by loosening fan motor mounting nuts. See
Fig. 18.
c. Loosen movable pulley flange setscrew (see Fig. 19).
d. Screw movable flange toward fixed flange to increase speed
and away from fixed flange to decrease speed. Increasing
fan speed increases load on motor. Do not exceed maximum speed specified in Tables 1A and 1B.
e. Set movable flange at nearest keyway of pulley hub and
tighten setscrew (see Tables 1A and 1B for speed change
for each full turn of pulley flange).
To align fan and motor pulleys:
a. Loosen fan pulley setscrews.
b. Slide fan pulley along fan shaft.
c. Make angular alignment by loosening motor from mount-
ing plate.
To adjust belt tension (see Fig. 18):
a. Loosen fan motor mounting bolts.
b. Slide motor mounting plate away from fan scroll for proper
belt tension (13 mm [
1
⁄2-in.] deflection with one finger)
and tighten mounting bolts.
c. Adjust bolt and nut on motor mounting plate to secure
motor in fixed position.
13
Page 14

MOTOR MOUNTING
NUTS AND BOLTS
Fig. 18 — Belt-Drive Motor Mounting
T able 5A — Fan R/s at Motor Pulley Settings (SI)
Fig. 19 — Indoor-Fan Pulley Adjustment
50LJQ
1
0
⁄
2
111⁄2221⁄2331⁄2441⁄25
MOTOR PULLEY TURNS OPEN
008 14.70 14.26 13.82 13.38 12.94 12.50 12.06 11.62 11.18 10.74 10.30
012 15.00 14.65 14.30 13.95 13.60 13.25 12.90 12.55 12.20 1 1.85 11.50
T able 5B — Fan Rpm at Motor Pulley Settings (English)
50LJQ
1
0
⁄
2
008 882 856 830 804 778 752 726 700 674 648 622
012 896 875 855 834 814 794 774 753 733 712 692
MOTOR PULLEY TURNS OPEN
1
1
⁄
2
221⁄2331⁄2441⁄25
14
Page 15

Table 6 — Fan Performance (SI), 50LJQ008 (50 Hz) — Horizontal Discharge Units
AIRFLOW
(L/s)
1100 7.9 0.35 9.4 0.50 10.6 0.68 11.7 0.85 12.7 1.03 13.6 1.25 14.4 1.46 14.9 1.69 15.1 1.92 15.0 2.15
1200 8.3 0.42 9.8 0.59 11.0 0.78 12.0 0.95 13.0 1.15 13.9 1.36 14.8 1.58 15.5 1.82 16.0 2.06 16.4 2.31
1300 8.8 0.51 10.2 0.69 11.3 0.88 12.4 1.08 13.3 1.28 14.2 1.49 15.0 1.72 15.8 1.96 16.5 2.21 17.1 2.47
1400 9.2 0.60 10.6 0.80 11.7 0.99 12.7 1.22 13.7 1.42 14.5 1.63 15.3 1.87 16.1 2.12 16.9 2.38 — —
1500 9.7 0.71 11.0 0.91 12.1 1.12 13.0 1.35 14.0 1.59 14.8 1.81 15.6 2.04 16.4 2.30 — — — —
1600 10.1 0.82 11.3 1.04 12.5 1.28 13.4 1.49 14.3 1.75 15.2 2.00 15.9 2.24 — — — — — —
1700 10.6 0.93 11.8 1.20 12.9 1.44 13.8 1.67 14.7 1.92 15.5 2.20 — — — — — — — —
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (Pa)
Table 7 — Fan Performance (SI), 50LJQ012 (50 Hz) — Horizontal Discharge Units
AIRFLOW
(L/s)
1300 7.6 0.30 8.9 0.41 10.2 0.56 11.1 0.64 12.1 0.77 13.1 0.92 13.9 0.93 14.0 0.52 15.0 1.13 15.6 1.32
1400 8.0 0.40 9.3 0.51 10.5 0.64 11.4 0.75 12.4 0.88 13.3 1.01 14.1 1.11 14.6 0.96 15.4 1.32 16.0 1.42
1500 8.4 0.48 9.6 0.60 10.7 0.72 11.8 0.86 12.7 0.99 13.5 1.12 14.3 1.26 15.1 1.35 15.7 1.49 16.4 1.54
1600 8.8 0.58 10.0 0.69 11.1 0.82 12.1 0.96 12.9 1.10 13.8 1.24 14.5 1.38 15.3 1.54 16.0 1.64 16.7 1.72
1700 9.1 0.69 10.3 0.78 11.3 0.93 12.3 1.07 13.2 1.22 14.0 1.37 14.8 1.52 15.5 1.66 16.3 1.84 17.0 1.95
1800 9.5 0.81 10.7 0.90 11.7 1.05 12.6 1.20 13.5 1.36 14.3 1.52 15.0 1.67 15.8 1.83 16.4 1.99 17.2 2.17
1900 9.9 0.95 11.0 1.02 12.0 1.18 12.9 1.34 13.8 1.50 14.6 1.68 15.3 1.83 16.0 2.00 16.7 2.16 17.3 2.33
2000 10.3 1.11 11.4 1.17 12.3 1.32 13.2 1.48 14.1 1.66 14.9 1.83 15.6 2.01 16.3 2.18 17.0 2.36 17.6 2.53
2100 10.7 1.29 11.8 1.33 12.7 1.47 13.5 1.65 14.4 1.84 15.1 2.00 15.9 2.20 16.6 2.38 — — — —
2200 11.2 1.48 12.1 1.51 13.1 1.64 13.9 1.83 14.6 2.01 15.4 2.20 16.2 2.38 — — — — — —
2300 11.6 1.70 12.5 1.71 13.4 1.83 14.2 2.01 15.0 2.20 15.7 2.41 — — — — — — — —
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (Pa)
Table 8 — Fan Performance (SI), 50LJQ008 (50 Hz) — Vertical Discharge Units
AIRFLOW
(L/s)
1100 8.7 0.42 10.1 0.59 11.1 0.75 12.2 0.93 13.1 1.12 14.0 1.30 14.8 1.51 15.7 1.77 16.4 2.02 17.2 2.35
1200 9.3 0.52 10.5 0.69 11.6 0.87 12.6 1.05 13.5 1.26 14.3 1.46 15.1 1.66 15.9 1.88 16.7 2.14 17.4 2.44
1300 9.8 0.64 11.0 0.81 12.1 1.01 13.0 1.20 13.9 1.41 14.7 1.63 15.5 1.84 16.2 1.98 16.9 2.29 17.6 2.56
1400 10.4 0.77 11.5 0.94 12.6 1.16 13.5 1.37 14.3 1.58 15.1 1.80 15.9 2.04 16.6 2.27 17.3 2.51 — —
1500 11.0 0.92 12.0 1.10 13.0 1.33 13.9 1.56 14.7 1.78 15.5 2.00 16.3 2.25 17.0 2.50 — — — —
1600 11.6 1.08 12.6 1.28 13.5 1.50 14.4 1.76 15.2 2.00 16.0 2.23 16.7 2.47 — — — — — —
1700 12.2 1.26 13.1 1.48 14.0 1.70 14.9 1.97 15.7 2.23 16.4 2.48 — — — — — — — —
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (Pa)
Table 9 — Fan Performance (SI), 50LJQ012 (50 Hz) — Vertical Discharge Units
AIRFLOW
(L/s)
1300 8.4 0.37 9.6 0.51 10.8 0.61 11.7 0.69 12.6 0.81 13.3 0.90 14.3 1.05 15.1 1.27 15.9 1.48 16.7 1.67
1400 8.8 0.46 10.0 0.59 11.1 0.71 12.0 0.82 12.9 0.93 13.7 1.04 14.5 1.17 15.4 1.35 16.2 1.56 16.8 1.75
1500 9.2 0.55 10.4 0.68 11.5 0.81 12.4 0.94 13.2 1.06 14.0 1.19 14.8 1.26 15.6 1.44 16.4 1.62 17.1 1.83
1600 9.7 0.65 10.8 0.79 11.8 0.93 12.8 1.07 13.6 1.19 14.4 1.33 15.1 1.46 15.8 1.59 16.5 1.72 17.3 1.91
1700 10.2 0.75 11.2 0.91 12.2 1.06 13.1 1.20 13.9 1.34 14.7 1.48 15.4 1.63 16.1 1.76 16.7 1.89 17.4 2.04
1800 10.6 0.87 11.7 1.05 12.6 1.20 13.5 1.35 14.3 1.51 15.0 1.65 15.7 1.80 16.4 1.95 17.1 2.10 17.7 2.24
1900 11.1 1.01 12.1 1.19 13.0 1.35 13.9 1.52 14.7 1.68 15.4 1.84 16.1 1.99 16.8 2.14 17.4 2.31 18.0 2.46
2000 11.6 1.16 12.5 1.35 13.4 1.52 14.3 1.69 15.0 1.86 15.8 2.04 16.5 2.21 17.1 2.36 17.7 2.53 — —
2100 12.0 1.32 13.0 1.53 13.8 1.70 14.6 1.88 15.4 2.07 16.1 2.25 16.8 2.43 — — — — — —
2200 12.5 1.50 13.4 1.71 14.3 1.91 15.1 2.09 15.8 2.29 16.5 2.48 — — — — — — — —
2300 13.0 1.70 13.9 1.91 14.7 2.13 15.5 2.31 16.2 2.52 — — — — — — — — — —
r/s — Wheel Speed (Revolutions per Second)
Bkw — Fan Shaft Power (kW)
NOTES:
1. Boldface indicates field-supplied drive required.
2. indicates field-supplied motor and drive required.
3. Maximumusableoutput power (BkW) on the 50LJQ008 unit is1.79
(2.40 Bhp) with standard 1.12 BkW (1.5 hp) motor. The maximum
usable output power (BkW) increases to 2.16 (2.90 Bhp) on the
50LJQ012 unit with standard 1.5 BkW (2 hp) motor. Extensive
50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW r/s BkW
LEGEND
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (Pa)
motor and electrical testing on the Weathermaker I units ensures
that the full power range of the motor can be utilized with confidence. Using the fan motors up to the power ratings shown will
not result in nuisance tripping orprematuremotor failure. Unit warranty will not be affected.
4. Use of field-supplied motor may affect wire sizing. Contact
Carrier representative to verify.
5. Values include losses for filters, unit casings and wet coils.
6. Motor drive range is 10.30 to 14.70 r/s (622 to 882 rpm) on the
50LJQ008and11.50to 15.00 r/s (692 to 896 rpm) on the 50LJQ012.
All other r/s (rpms) will require a field-supplied drive.
15
Page 16

Table 10 — Fan Performance (English), 50LJQ008 (50 Hz) — Horizontal Discharge Units
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
2200 459 0.42 549 0.62 625 0.83 691 1.06 753 1.31 805 1.58 842 1.87 857 2.16 851 2.45 823 2.70
2400 482 0.50 569 0.71 645 0.95 708 1.18 768 1.40 824 1.72 872 2.01 909 2.32 931 2.64 935 2.96
2600 507 0.59 592 0.82 663 1.08 727 1.32 784 1.58 839 1.87 891 2.17 936 2.49 973 2.82 999 3.16
2800 533 0.71 615 0.95 683 1.20 747 1.49 802 1.75 855 2.04 906 2.35 954 2.67 997 3.01 1034 3.36
3000 559 0.83 637 1.09 704 1.35 765 1.66 823 1.94 872 2.22 921 2.54 969 2.88 1014 3.22 — —
3200 585 0.96 660 1.24 727 1.52 785 1.83 841 2.15 892 2.45 939 2.76 984 3.10 ————
3400 610 1.10 682 1.41 750 1.72 806 2.01 860 2.36 912 2.69 958 3.01 1002 3.34 ————
3600 636 1.25 707 1.60 772 1.93 828 2.23 880 2.57 930 2.95 978 3.29 ——————
3800 661 1.41 733 1.82 795 2.15 852 2.48 901 2.80 949 3.20 — ———————
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
Table 11 — Fan Performance (English), 50LJQ012 (50 Hz) — Horizontal Discharge Units
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
3000 484 0.55 560 0.70 631 0.87 690 1.03 747 1.20 800 1.38 850 1.52 879 1.38 925 1.81 964 1.92
3200 505 0.66 579 0.81 646 0.98 708 1.16 761 1.34 812 1.51 862 1.71 908 1.85 944 2.01 984 2.09
3400 527 0.78 599 0.93 664 1.11 724 1.30 775 1.48 827 1.67 873 1.85 920 2.07 963 2.21 1001 2.31
3600 548 0.92 619 1.05 680 1.24 738 1.43 794 1.64 840 1.83 888 2.04 931 2.23 976 2.47 1017 2.62
3800 571 1.08 639 1.19 698 1.39 756 1.60 810 1.81 856 2.02 901 2.23 945 2.44 986 2.65 1029 2.89
4000 593 1.25 659 1.35 717 1.56 773 1.78 823 1.98 875 2.22 915 2.42 960 2.65 1000 2.87 1039 3.10
4200 616 1.45 680 1.53 737 1.74 789 1.95 841 2.18 889 2.41 934 2.65 972 2.87 1015 3.12 1053 3.34
4400 639 1.67 701 1.73 757 1.92 807 2.16 858 2.41 903 2.62 951 2.89 990 3.12 1028 3.36 — —
4600 662 1.91 722 1.95 777 2.13 827 2.38 874 2.62 921 2.87 965 3.11 1008 3.39 ————
4800 686 2.17 744 2.20 797 2.36 846 2.62 891 2.85 938 3.14 980 3.37 ——————
5000 710 2.45 766 2.47 816 2.61 866 2.86 910 3.12 934 3.39 — ———————
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
Table 12 — Fan Performance (English), 50LJQ008 (50 Hz) — Vertical Discharge Units
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
2200 503 0.50 585 0.71 653 0.92 716 1.15 772 1.38 824 1.63 884 1.95 934 2.30 916 2.64 1019 3.09
2400 534 0.61 613 0.84 677 1.06 738 1.30 794 1.55 844 1.81 892 2.08 944 2.40 987 2.76 1039 3.20
2600 565 0.74 639 0.97 703 1.20 761 1.46 816 1.74 866 2.01 913 2.29 957 2.58 1004 2.91 1050 3.31
2800 597 0.89 665 1.12 731 1.40 786 1.66 839 1.93 889 2.23 935 2.52 978 2.62 1019 3.13 1061 3.47
3000 629 1.06 694 1.29 759 1.59 812 1.88 862 2.15 911 2.46 957 2.78 1000 3.09 1040 3.41 — —
3200 662 1.25 724 1.50 785 1.80 840 2.11 887 2.41 934 2.71 980 3.04 1022 3.38 ————
3400 696 1.46 756 1.73 811 2.02 868 2.37 914 2.69 959 3.00 1003 3.32 ——————
3600 729 1.69 787 1.98 839 2.27 894 2.64 942 2.99 984 3.32 ————————
3800 763 1.95 819 2.27 869 2.56 920 2.92 970 3.31 — —————————
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
Table 13 — Fan Performance (English), 50LJQ012 (50 Hz) — Vertical Discharge Units
AIRFLOW
(Cfm)
3000 532 0.64 605 0.81 670 0.97 725 1.12 778 1.28 825 1.43 874 1.60 926 1.82 974 2.11 1012 2.36
3200 557 0.75 628 0.93 690 1.10 746 1.28 796 1.44 844 1.61 888 1.70 934 1.94 988 2.18 1025 2.47
3400 583 0.88 651 1.06 711 1.25 767 1.44 815 1.61 863 1.79 907 1.97 947 2.14 991 2.32 1038 2.57
3600 609 1.01 674 1.22 732 1.42 787 1.61 836 1.80 880 1.98 926 2.18 966 2.36 1004 2.54 1045 2.74
3800 535 1.16 698 1.39 755 1.59 808 1.80 857 2.01 901 2.20 943 2.39 985 2.60 1023 2.79 1059 2.98
4000 662 1.33 722 1.57 778 1.78 829 2.01 878 2.22 922 2.44 962 2.63 1003 2.84 1042 3.06 1078 3.26
4200 689 1.52 746 1.77 801 1.99 851 2.23 898 2.45 943 2.69 983 2.91 1021 3.11 1060 3.34 — —
4400 715 1.72 772 1.99 825 2.22 873 2.46 919 2.71 963 2.94 1004 3.19 1042 3.41 ————
4600 742 1.94 797 2.22 848 2.48 896 2.72 940 2.98 984 3.22 1025 3.48 ——————
4800 770 2.18 823 2.46 872 2.75 919 3.00 963 3.27 — —————————
5000 797 2.44 849 2.73 897 3.04 943 3.30 ————————————
Rpm — Wheel Speed (Revolutions per Minute)
Bhp — Fan Shaft Power (Brake Horsepower)
NOTES:
1. Boldface indicates field-supplied drive required.
2. indicates field-supplied motor and drive required.
3. Maximumusable output power (Bhp) on the50LJQ008 unit is 2.40
(1.79 BkW) with standard 1.5hp (1.12 BkW) motor. The maximum
usable output power (Bhp) increases to 2.90 Bhp (2.16
BkW) on the 50LJQ012 unit with standard 2 hp (1.5 BkW) motor.
0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2.0
Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp Rpm Bhp
LEGEND
EXTERNAL STATIC PRESSURE (in. wg)
Extensive motor and electrical testing ontheWeathermakerI units
ensures that the full power range of the motor can be utilized with
confidence. Using the fan motors up to the power ratings shown
will not result in nuisance tripping or premature motor failure. Unit
warranty will not be affected.
4. Use of field-supplied motor may affect wire sizing. Contact
Carrier representative to verify.
5. Values include losses for filters, unit casings, and wet coils.
6. Motor drive range is 622 to 882 rpm (10.30 to 14.70 r/s) on the
50LJQ008and692to896rpm (11.50to 15.00 r/s) on the 50LJQ012.
All other rpms (r/s) will require a field-supplied drive.
16
Page 17

START-UP
IMPORTANT:Energizecrankcase heaters 24 hours prior
to base unit start-up to remove entrapped refrigerant
from the oil. Heaters are energized as long as there is
power to the unit.
Unit Preparation — Make sure that unit has been in-
stalled in accordance with these installation instructions and
applicable codes.
Return-Air Filters — Make sure correct filters are in-
stalled in unit (see Tables 1A and 1B). Do not operate unit
without return-air filters.
Compressor Mounting — Compressors are inter-
nally spring mounted. Do not loosen or remove compressor
holddown bolts.
Internal Wiring — Check all electrical connections in
unit control boxes; tighten as required.
Refrigerant Service Ports — Each refrigerant sys-
tem has 3 Schrader-type service gage ports: one on the suction line, one on the liquid line and one on the compressor
discharge line. Be sure that caps on the ports are tight.
Cooling — To start unit, turn on main power supply. Set
system selector switch at COOL position and fan switch at
AUTO. position. Adjust thermostat to a setting below room
temperature. Compressor starts on closure of contactor.
Check unit charge. Refer to Refrigerant Charge section on
page 20.
Reset thermostat at a position above room temperature.
Compressor will shut off.
TO SHUT OFF UNIT — Set system selector switch at OFF
position. Resetting thermostat at a position above room temperature shuts unit off temporarily until space temperature
exceeds thermostat setting.
Heating — To start unit, turn on main power supply.
Set thermostat at HEATposition and a setting above room
temperature, fan at AUTO. position.
First stage of thermostat energizes Compressor no. 1 and
Compressor no. 2; second stage energizes the electric heat
(where applicable). Check heating effectsat air supply grille(s).
If unit does not energize, reset limit switch (located on
indoor-fan scroll) by depressing button located between terminals on the switch.
TO SHUT OFF UNIT — Set system selector switch at OFF
position. Resetting heating selector lever below room temperature will shut unit off temporarily until the space temperature falls below thermostat setting.
Safety Relief — A soft-solder joint at the suction line
fitting provides pressure relief under abnormal temperature
and pressure conditions.
Ventilation (Continuous Fan) — Set fan and sys-
tem selector switches at ON and OFF positions, respectively. Indoor fan operates continuously to provide constant
air circulation.
Operating Sequence (See Fig. 20)
COOLING — With accessory economizer — Upon a re-
quest for cooling from the space thermostat, terminals Y1
and G will be energized with 24 v.As a result, the indoor-fan
contactor (IFC), indoor-fan motor (IFM), and reversing valve
solenoids (RVS1 and RVS2) will be energized and the
economizer damper blade will open to minimum position.
Note that if the indoor fan is on when the space thermostat
calls for cooling, terminal G is already energized and the
economizer damper blade is at minimum position.
If the outdoor-air temperature is below the outdoor-airthermostat (OAT) setting, then the position of the damper blade
will be determined by the temperature of the discharge air as
sensed by the discharge-air thermistor (DAT). The damper
blade will slide open for 5 seconds, and rest for 30 seconds
until the proper discharge-air temperature is obtained. The
damper blade will modulate to different positions to maintain this discharge-air temperature.
If the thermostat calls for a second stage of cooling
by supplying 24 v to Y2, the outdoor-fan contactor (OFC)
and Compressor contactor no. 1 (C1) will be energized,
which will bring on the outdoor fan and Compressor no. 1,
respectively.
When the thermostat is satisfied, Y2 will be deenergized
first, which will deenergize the outdoor fan and Compressor
no. 1. When the indoor fan is deenergized, the economizer
will return to a fully closed position.
If the outdoor-air temperature is above the OAT setting,
the economizer will move to the minimum position and the
unit will operate as described in Cooling, Units Without
Accessory Economizer section below.
Without accessory economizer — Upon a request for cooling from the space thermostat, terminals Y1 and G will be
energized with 24 v. As a result, the indoor-fan contactor
(IFC), outdoor-fan contactor (OFC) and Compressor contactor no. 1 (C1) will be energized, which in turn will energize the indoor fan, outdoor fan and Compressor no. 1,
respectively.
If the space thermostat calls for a second stage of cooling
by supplying 24 v to Y2, Compressor contactor no. 2 (C2)
will be energized, thus energizing Compressor no. 2.
When the space thermostat is satisfied, Y2 will be deenergized first, which will deenergize Compressor no. 2.
Upon a further drop in space temperature, Y1 will be deenergized which will deenergize Compressor no. 1, and the
outdoor and indoor fans.
HEATING — Upon a request for heating from the space thermostat, terminal W1 will be energized with 24 v. On units
with economizer, the economizer damper blade will move to
minimum position regardless of the outdoor-air temperature, and the unit will operate as described in Cooling, Without Accessory Economizer section above. The IFC, OFC,
C1 and C2 will be energized. The reversing valves switch
position and the indoor fan, outdoor fan, Compressor no. 1,
and Compressor no. 2 are energized.
If the space temperature continues to fall while W1 is energized, W2 will be energized with 24 v, and the heater contactor(s) (HC) willbe energized, which will energize the electric
heater(s).
When the space thermostat is satisfied, W2 will be deenergized first, and the electric heater(s) will be
deenergized.
Upon a further rise in space temperature, W1 will be deenergized,and the reversing valve solenoids (RVS1and RVS2)
will be energized. On units with economizer, the economizer damper blade will move to the fully closed position.
DEFROST — When the temperature of the outdoor coil drops
below 28 F as sensed by the defrost thermostat (DFT2) and
the defrost timer is at the end of a timed period
(adjustable at 30, 50 or 90 minutes). RVS1 and RVS2 are
energized and the OFC is deenergized. This switches the
17
Page 18

NOTES:
1. In heating mode, economizer damper blade will move to the minimum position, and unit will operate as described for units without
economizer, regardless of outdoor air temperature.
2. The temperatures given in the graph are for demonstration purposes only and may vary depending on which thermostat is used.
LEGEND
C—Contactor
HC — Heater Contactor
IFC — Indoor-Fan Contactor
OAT — Outdoor-Air Thermostat
OFC — Outdoor-Fan Contactor
RVS — Reversing Valve Solenoid
W—Heating Stage
X—Contact Energized
Y—Cooling Stage
UNITS WITH ECONOMIZER
AVERAGE OUTDOOR-AIR TEMPERATURE GREATER THAN OAT SETTING
Thermostat Demand G Y1 Y2 W1 W2 C1 C2 IFC OFC RVS1 RVS2 HC
Second Stage Cooling XX X X X X X X X
First Stage Cooling XX X X X X X
Deadband (Offset)
First Stage Heating XXXX
Second Stage Heating XXXXX X
AVERAGE OUTDOOR-AIR TEMPERATURE LESS THAN OAT SETTING, BUT GREATER THAN −2 C (28 F)
Thermostat Demand G Y1 Y2 W1 W2 C1 C2 IFC OFC RVSI RVS2 HC
Second Stage Cooling XXX X X X X X
First Stage Cooling XX X X X
Deadband(Offset)
First Stage Heating XXXX
Second Stage Heating XXXXX X
UNITS WITHOUT ECONOMIZER
AVERAGE OUTDOOR-COIL TEMPERATURE LESS THAN −2C (28 F)
Thermostat Demand G Y1 Y2 W1 W2 C1 C2 IFC OFC RVSI RVS2 HC
Second Stage Cooling XX X X X X X X X
First Stage Cooling XX X X X X X
Deadband (Offset)
First Stage Heating XXXX
Second Stage Heating XXXXX X
AVERAGE OUTDOOR-COIL TEMPERATURE GREATER THAN −2 C (28 F)
Thermostat Demand G Y1 Y2 W1 W2 C1 C2 IFC OFC RVSI RVS2 HC
Second Stage Cooling XX X X X X X X X
First Stage Cooling XX X X X X X
Deadband (Offset)
First Stage Heating XXXX
Second Stage Heating XXXXX X
Fig. 20 — Typical Operating Sequence
18
Page 19

position of the reversing valves and shuts off the outdoor
fan. The electric heaters (if installed) will be energized. On
units with economizer,the economizer damperblade will move
to the fully closed position.
The unit continues to defrost until the coil temperature as
measured by DFT2 reaches 65 F or the duration of defrost
cycle completes a 10-minute period.
During the defrost mode, if circuit 1 defrosts first, RVS1
will oscillate between heating and cooling modes until the
defrost mode is complete.
At the end of the defrost cycle, the electric heaters (if installed) will be deenergized; the reversing valves switch and
the outdoor-fan motor will be energized. On units with economizer, the economizer damper blade will move to the minimum position. The unit will now operate in the heating mode.
If the space thermostat is satisfied during a defrost cycle,
the unit will continue in the defrost mode until the time or
temperature constraints are satisfied.
SERVICE
When servicing unit, shut off all electrical power to unit
to avoid shock hazard or injury from rotating parts.
Cleaning — Inspect unit interior at the beginning of each
heating and cooling season and as operating conditions
require.
Fig. 21 — Cleaning Outdoor Coil
INDOOR COIL
1. Turn unit power off. Remove indoor coil access panel.
2. If accessory economizer is installed, remove economizer
by disconnecting Molex plug and removing economizer
mounting screws. Refer to Accessory Economizer Installation Instructions for more details.
3. Slide filters out of unit.
4. Clean coil using a commercial coil cleaner or dishwasher
detergent in a pressurized spray canister.Washboth sides
of coil and flush with clean water. For best results, backflush toward return-air section to remove foreign
material.
5. Flush condensate pan after completion.
6. Reinstall economizer and filters.
7. Reconnect wiring.
8. Replace access panels.
OUTDOOR COIL — Inspect coil monthly. Clean outdoor
coil annually, and as required by location and outdoor air
conditions.
2-Row Coils— Clean coil as follows:
1. Turn off unit power.
2. Remove top panel screws on outdoor-coil end of unit.
3. Remove outdoor-coil corner post. See Fig. 21. To hold
top panel open, place coil corner post between top panel
and center post. See Fig. 22.
4. Remove device holding coil sections together at return
end of outdoor coil. Carefully separate the outer coil section 75 to 100 mm (3 to 4 in.) from the inner section. See
Fig. 23.
5. Use a water hose or other suitable equipment to flush down
between the 2 coil sections to remove dirt and debris. Clean
the outer surfaces with a stiff brush in the normal manner.
Fig. 22 — Propping Up Top Panel
Fig. 23 — Separating Coil Sections
6. Reposition the outer coil panel section and remove the
coil corner post from between the top panel and center
post. Secure the sections together.
7. Install the coil corner post, coil center post and replace
all screws.
19
Page 20

CONDENSATE DRAIN — Check and clean each year at
start of cooling season. In winter, keep drain dry or protect
against freeze-up.
FILTERS — Clean or replace at start of each heating and
cooling season, or more often if operating conditions require
it. Replacement filters must be same dimensions as original
filters.
OUTDOOR-AIR INLET SCREENS — Clean screens with
steam or hot water and a mild detergent. Do not use disposable filters in place of screens.
Lubrication
COMPRESSORS — Each compressor is charged with correct amount of oil at the factory.
FAN-MOTOR BEARINGS — Fan motor bearings are of
the permanently-lubricated type. No further lubrication is
required. No lubrication of outdoor- or indoor-fan motors is
required.
Outdoor-Fan Adjustment (Fig. 24)
Refrigerant Charge — Amount of refrigerant charge
is listed on the unit nameplate (also refer to Tables 1A and
1B). Refer to Carrier Standard Service Techniques Manual,
Chapter 1, Refrigerants section.
Unit panels must be in place when unit is operating dur-
ing charging procedure.
LOW CHARGE HEATING OR NO CHARGE — Use stand-
ard evacuating techniques. After evacuating system, weigh
in the specified amount of refrigerant (refer to Tables 1A and
1B).
LOW CHARGE COOLING — Use Cooling Charging Chart,
Fig. 25 and 26. Vary refrigerant until the conditions of the
chart are met. Note the charging chart is different from type
normally used. Chart is based on charging the units to the
correct superheat for the various operating conditions. Accurate pressure gage and temperature sensing device are required. Connect the pressure gage to the service port on the
suction line. Mount the temperature sensing device on the
suction line and insulate is so that outdoor ambient temperature does not affect the reading. Indoor-air L/s (cfm) must be
within the normal operating range of the unit.
TO USE COOLING CHARGING CHART— Take the outdoor ambient temperature and read the suction pressure gage.
Refer to chart to determine what suction temperature should
be. If suction temperature is high, add refrigerant. If suction
temperature is low, carefully blow some of the charge. Recheck the suction pressure as charge is adjusted.
Example: (Fig. 26) (Circuit 1)
Outdoor Temperature ....................29C(85F)
Suction Pressure ...................483kPa(70psig)
Suction Temperature should be .............7C(46F)
(Suction Temperature may vary ± 3° C (5° F)
Fig.24 — Outdoor-Fan Adjustment
1. Shut off unit power supply.
2. Remove outdoor-fan assembly (grille, motor,motor cover
and fan) and loosen fan hub setscrews.
3. Adjust fan height as shown in Fig. 24.
4. Tighten setscrews and replace outdoor-fan assembly.
If Chargemastert charging device is used, temperature and
pressure readings must be accomplished using the charging
chart.
20
Page 21

Fig. 25 — Cooling Charging Charts, 50LJQ008
Fig. 26 — Cooling Charging Charts, 50LJQ012
21
Page 22

Page 23

Page 24

Copyright 1992 Carrier Corporation
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Catalog No. 015-015 Printed in U.S.A. Form 50LJQ-C1SI Pg 24 1-92 Replaces: New
 Loading...
Loading...