Page 1
09DK054-084
HEATING & COOLING
Air-Cooled Condenser Units
50/60 Hz
à
Installation, Start-Up and
Service Instructions
Air-Cooled Packages
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS ...
INSTALLATION .................................................
Step 1 — Complete Pre-Installation
Checks ............................................................................. 1
Step 2 — Rig and Place Unit ..........................................4
• RIGGING
• PLACING THE UNIT
Step 3 — Complete Refrigerant Piping
• GENERAL
• COIL REFRIGERANT PIPING INSTALLATION
• TUBING PACKAGE INSTALLATION
• THREE AND FOUR COIL SPLIT, COIL
CIRCUITING APPLICATIONS; 054-084 UNITS
• REFRIGERANT LINE SIZING
• LIQUID SHUTOFF VALVE AND SIGHT GLASS
• PRESSURE RELIEF
• REFRIGERANT RECEIVER
• LIQUID LIFT
Step 4 — Complete Electrical
Connections..................................................................21
• GENERAL
• FIELD CQNNECTIONS
• MAIN POWER WIRING
• CONTROL CIRCUIT POWER WIRING
• GENERAL WIRING NOTES
• DESCRIPTION OF CONTROLS
Step 5 — Add Accessories as Needed
START-UP..........................................................................29
System Evacuation and
Dehydration ..................................................................29
Charging Procedure........................................................29
Check Operation of Condenser Fan Motor
Controls and Rotation of Fans
SERVICE ......................................................................29-31
Cleaning Condenser Coils
Condenser Fans ..............................................................29
Lubrication
Head Pressure Control ..................................................29
• FAN CYCLING
.......................................................................
........................................
.....................
.....................
................................
SAFETY COIVISIDERATIOIMS
Installing, starting up, and servicing air-conditioning equip
ment can be hazardous due to system pressures, electrical
components, and equipment location (roofs, elevated struc
tures, etc.).
Only trained, qualified installers and service mechanics
should install, start up, and service this equipment (Fig. 1).
Untrained personnel can perform basic maintenance func
tions such as cleaning coils. All other operations should be
performed by trained service personnel.
,.. 1
1-28
28
29
29.
29
7
Fig. 1 — Model 09DK (084 Shown)
When working on the equipment, observe precautions in
the literature and on tags, stickers, and labels attached to
the equipment.
Follow all safety codes. Wear safety glasses and work
gloves. Keep quenching cloth and fire extinguisher nearby
when brazing. Use care in handling, rigging and setting bulky
equipment.
See Tables lA and IB for Physical Data.
ELECTRIC SHOCK HAZARD
Separate power sources (main and control cir
cuit power) are used for these units. Be sure
both main and control circuit powers are dis
connected before servicing.
INSTALLATION
Step 1 — Complete Pre-Installation Checks —
Examine for damage incurred during shipment. File claim
immediately with transit company if damage is found. Ver
ify that the nameplate electrical requirements match the avail
able power supply. Check the shipment for completeness.
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
Book 12 PC 111 Catalog No 530-953 Printed in U.S A Form 09DK-4SI Pg 1 4-93 Replaces: New
Tab 4a
Page 2
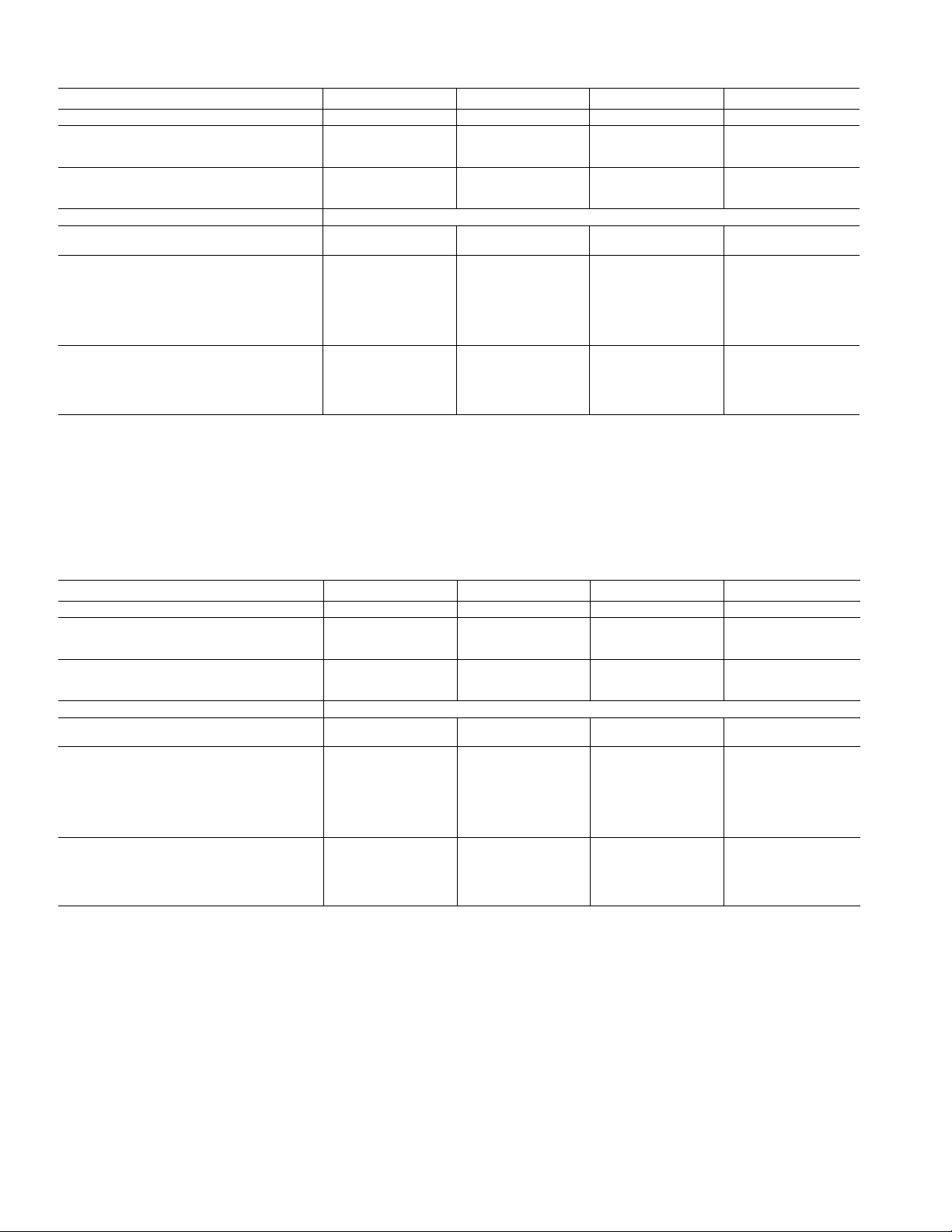
Table IA — Physical Data 60 fìz
English
09DK
NOMINAL TONS
OPERATING WEIGHT-lb
Cu-AI*
Cu-Cut
SHIPPING WEIGHT-lb“
Cu-AI‘
Cu-Cut
054
50
1695
1983
2010
2298 2569 2938 3403
REFRIGERANTS
NOMINAL HEAT REJECTION
(TONS)tt
CONDENSER FANS
No. of Blades
No. of Fans
Fan Diameter-In. 30
AIrflow-cfm
Fan Speed-rpm
Fan Motor-hp 1
CONDENSER COILS
Quantity 4
FIns/in. 17
No. of Rows
Total Face Area (sq ft)
65.8 78.6 95.4 103.5
4 4 4 4
4 4 6 6
35,000
1140 1140
2
80.5
TD — Temperature Difference = Saturated Condensing Temperature - Entering-Air Temperature
‘Copper tubes and aiuminum fins.
TCopper tubes and copper fins.
“Packaging option includes skid and coil protection.
ttNominal heat rejection based on refrigerant R-22, 15° F subcooling, and a 30° F temperature difference (TD).
064
60
1845 2200
2278 2617
2136 2521
R-134A, R-22, R-12, R-500, R-502
30 30 30
35,000 52,000 51,000
1 1 1
4 4 4
17 17 17
3 2
80.5 116.7 1167
074
70
1140 1140
084
80
2421
3099
2725
3
SI
09DK
NOMINAL kW
OPERATING WEIGHT-kg
Cu-AI*
Cu-Cut
SHIPPING WEIGHT-kg“
Cu-AI*
Cu-Cut
REFRIGERANTS
NOMINAL HEAT REJECTION
(kW)tt
CONDENSER FANS
No. of Blades
No. of Fans
Fan DIameter-mm
AIrflow-L/s
Fan Speed-r/s
Fan Motor-kW
CONDENSER COILS
Quantity
FIns/m
No. of Rows
Total Face Area (sq m)
TD — Temperature Difference = Saturated Condensing Temperature - Entering-Air Temperature
‘Copper tubes and aluminum fins.
tCopper tubes and copper fins.
“Packaging option includes skid and coil protection
ttNominal heat rejection based on refrigerant R-22, 8.3° C subcooiing, and a 16.7° C temperature difference (TD).
054 064 074
175.7 210.9 246.0 281.2
769
900
912 969 1144
1042 1165 1333 1544
231.3
4
4
762
16 520
19
.746
4
669
2 3 2 3
7.5
837 998
1033
R-134A, R-22, R-12, R-500, R-502
276 2 335.3
4
4
762 762
16 520 24 540
19 19
.746 .746
• 669 669
4 4 4
75 10.84 10.84
1187
4
6
084
1098
1406
1236
363 8
4
6
762
24 070
19
746
669
Page 3
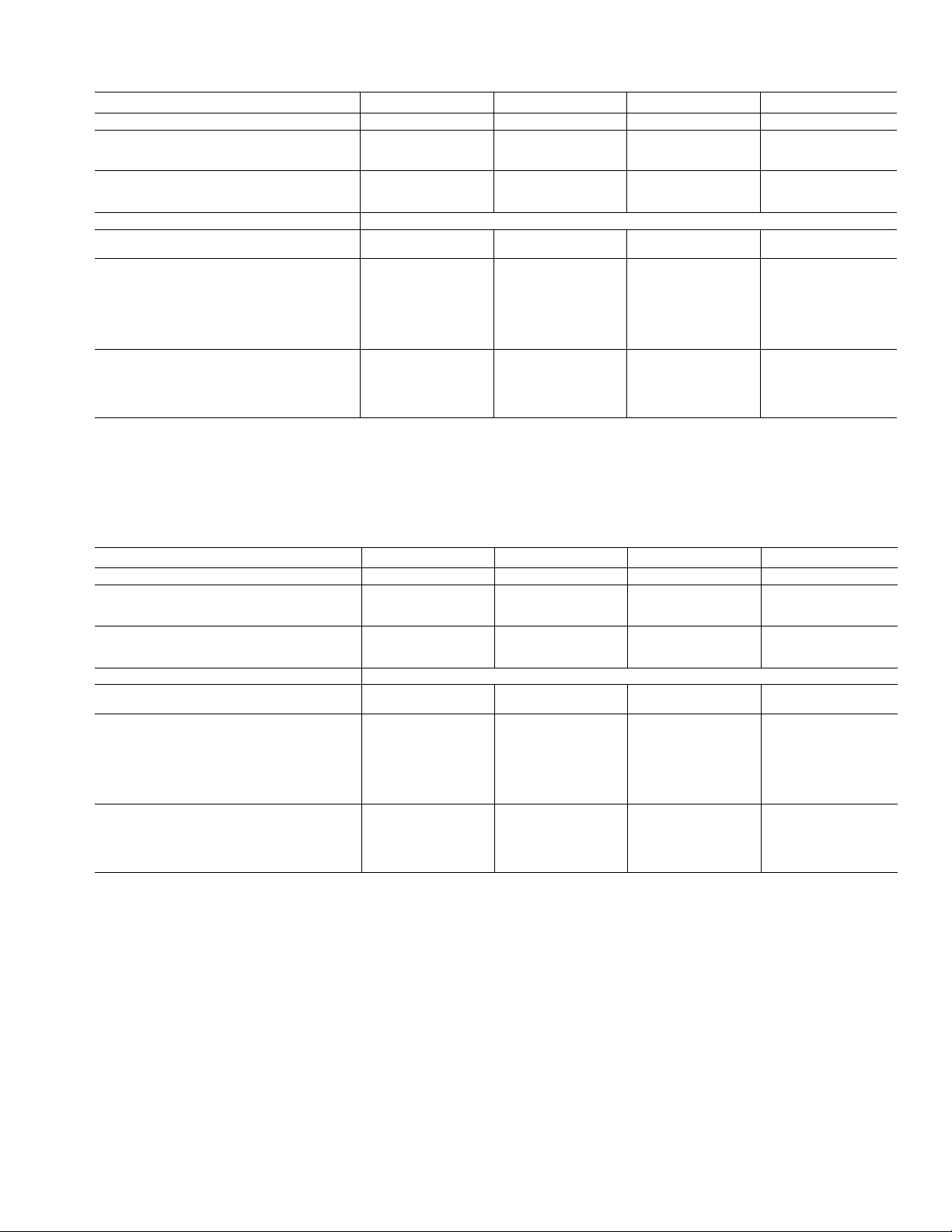
Table 1B — Physical Data 50 Hz
English
09DK
NOMINAL TONS
OPERATING WEIGHT-lb
Cu-AI*
Cu-Cut
SHIPPING WEIGHT-lb"
Cu-AI* 2010
Cu-Cut
REFRIGERANTS
NOMINAL HEAT REJECTION
(TONS)tt
CONDENSER FANS
No. of Blades
No. of Fans
Fan DIameter-ln. 30 30 30 30
AIrflow-cfm
Fan Speed-rpm 950 950 950 950
Fan Motor-hp 1 1
CONDENSER COILS
Quantity
Fins/in.
No. of Rows
Total Face Area (sq ft)
TD — Temperature Difference = Saturated Condensing Temperature - Entering-Air Temperature
'Copper tubes and aluminum fins
tCopper tubes and copper fins.
"Packaging option includes skid and coil protection.
ttNominal heat rejection based on refrigerant R-22, 15° F subcooling, and a 30° F temperature difference (TD).
054 064 074
50 60 70
1695 1845 2200
1983 2278
2298 2569
65.8 78.6
6 6 6 6
4 4 6 6
35,000 35,000 52,000 51,000
4 4 4 4
17 17 17 17
2
80.5 80.5 116.7 1167
2136 2521
R-134A, R-22, R-12, R-500, R-502
3
2617 3099
2938
95 4 103.5
1
2
084
80
2421
2725
3403
1
3
SI
09DK 054 064 074 084
NOMINAL kW
OPERATING WEIGHT-kg
Cu-AI*
Cu-Cut
SHIPPING WEIGHT-kg"
Cu-AI*
Cu-Cut
REFRIGERANTS
NOMINAL HEAT REJECTION
(kW)tt
CONDENSER FANS
No. of Blades
No. of Fans
Fan DIameter-mm 762 762 762 762
AIrflow-L/s 16 520 16 520 24 540 24 070
Fan Speed-r/s 15.8 15.8 15.8 15.8
Fan Motor-kW .746
CONDENSER COILS
Quantity
Fins/m 669 669 669 669
No. of Rows
Total Face Area (sq m)
TD — Temperature Difference = Saturated Condensing Temperature - Entering-Air Temperature
•Copper tubes and aluminum fins
tCopper tubes and copper fins
"Packaging option includes skid and coil protection.
ttNominal heat rejection based on refrigerant R-22, 8 3° C subcooling.
175 7
769 837 998
900 1033
912 969
1042
231.3 276.2 335.3 363.8
6
4
4
2
7.5
and a 16.7° C temperature difference (TD)
210 9 246 0
1165 1333
R-134A, R-22, R-12,R-500, R-502
6 6 6
4 6 6
746 746
4 4
3 2 3
7.5
281 2
1187 1406
1144
10 84 10 84
1098
1236
1544
.746
4
Page 4
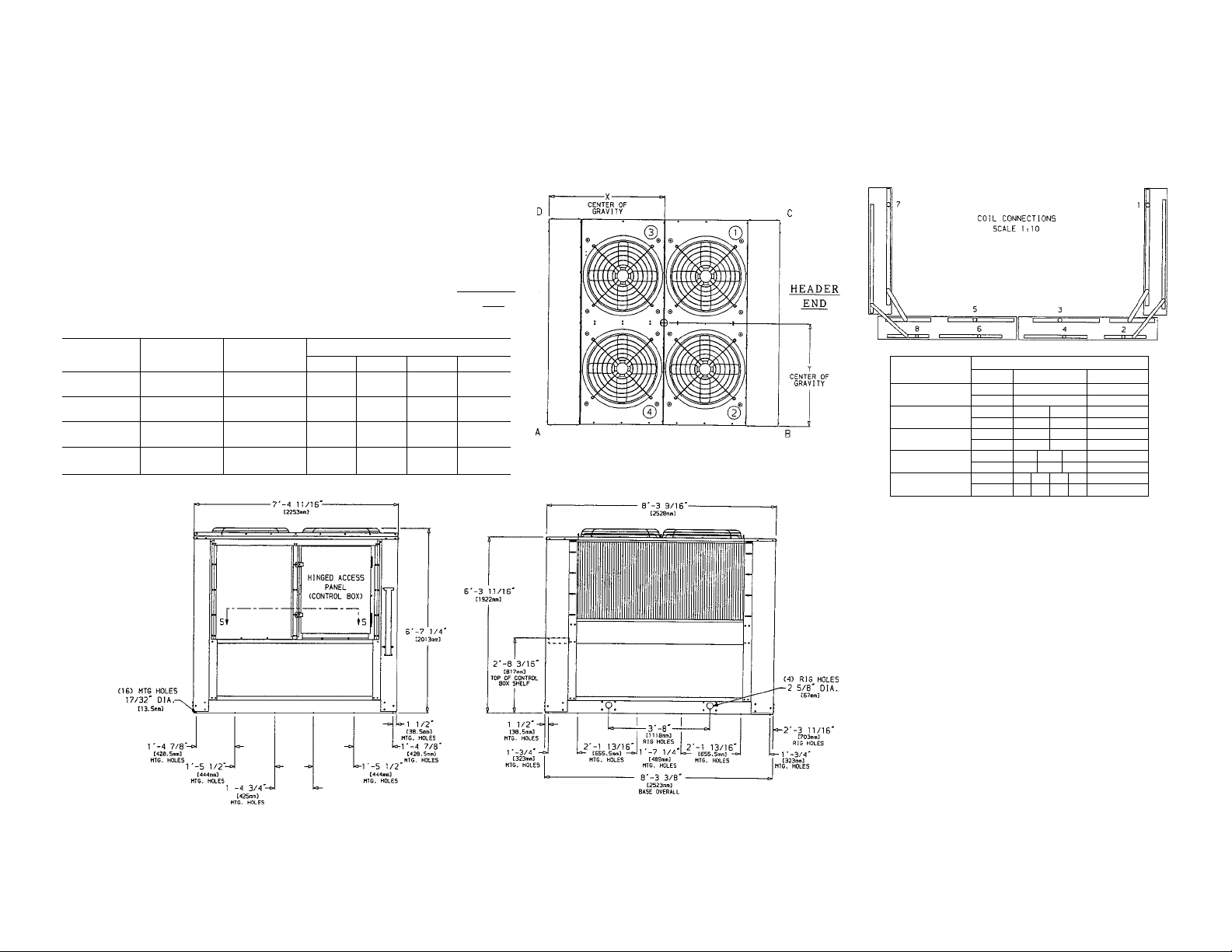
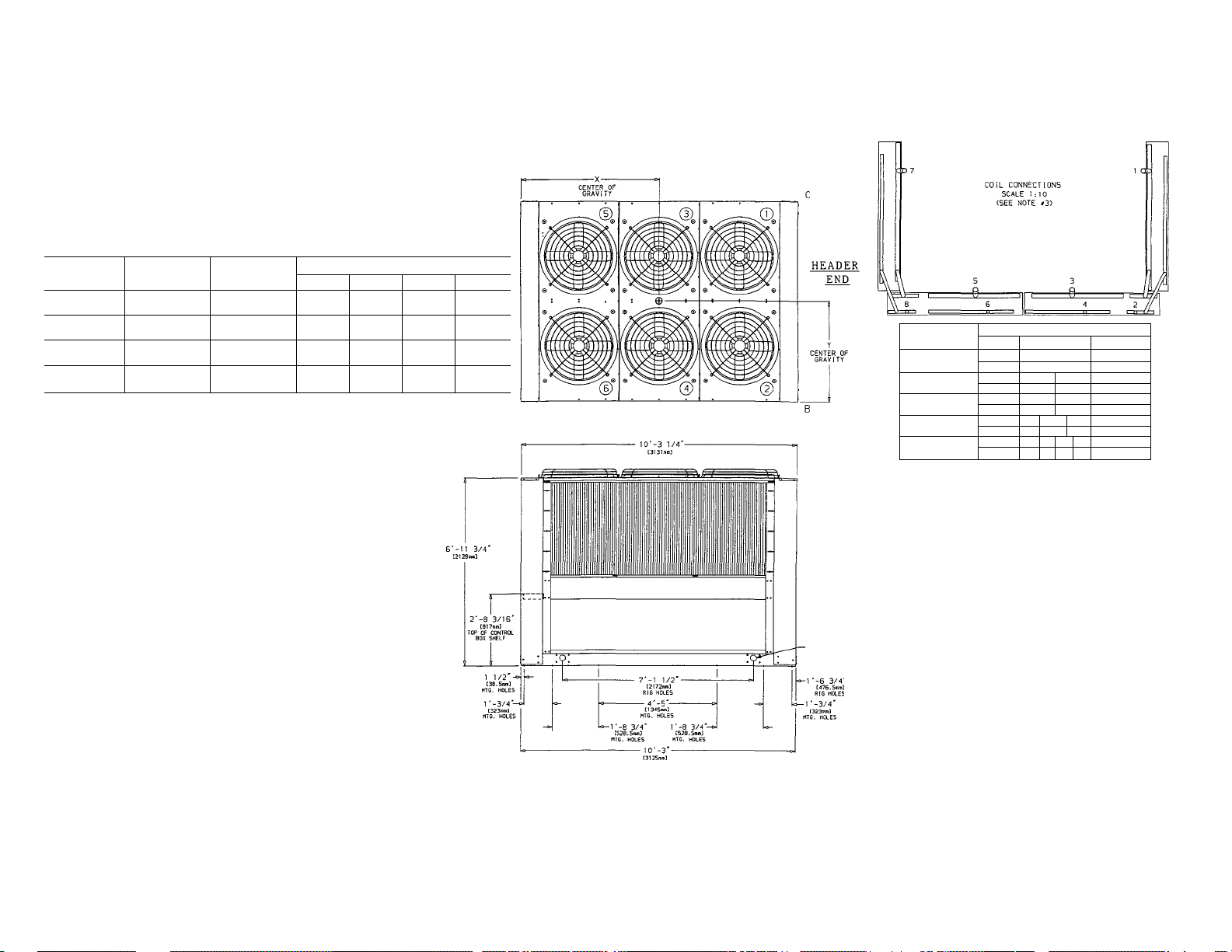
Step 2 — Rig and Place Unit
RIGGING — These units are designed for overhead rig
ging and this method should be used. Lifting holes are pro
vided in the frame base rails which are marked for rigging
(see rigging label on the unit). It is recommended that field
supplied pipes of sufficient length that extend beyond the
frame are passed through the holes. Attach cables, chains,
or straps to both ends of the pipes. Use spreader bars or a
frame to keep the cables, chains, or straps clear of the unit
sides. All cables should run to a central suspension point
so that the angle from the horizontal is not less than
45 degrees. See Fig. 2 and Table 1 for weight distribution
information. Standard coil protection packaging will pro
vide some protection to the unit. Raise and set the unit down
carefully.
Domestic Units With No Overhead Rigging— Standard con
denser packaging consists of coil protection only. Skids are
not provided as part of the standard packaging. If overhead
rigging is not available at the jobsite, place the unit on a
skid or pad by using jacks at the rigging points before drag
ging or rolling. When rolling, use a minimum of 3 rollers.
When dragging, pull the pad or skid. Do not apply pressure
to the unit. Raise from above to lift off the pad or skid
when in final position. See rigging section above for more
information.
Export and Domestic Units With Skids— All export units
are mounted on skids with vertical coil protection. Leave
the unit on the skid until it is in the final position. While on
the skid, the unit can be rolled, dragged or forked; do not
apply force to the unit. Use a minimum of 3 rollers when
rolling, and raise from above to remove the skid when unit
is in the final position. See rigging procedure above for more
information.
A CAUTION
Do not forklift these units unless attached to a skid de
signed for forklifting; damage to unit may occur. If uti
lizing a packaging option which includes a skid, the
forklift truck must have at least a 60-in. (1524 mm)
fork.
PLACING THE UNIT — Locate the condenser where an
adequate supply of inlet outdoor air is available. Do not lo
cate where the possibility of air recirculation exists, such as
under a roof overhang. Also, locate the condenser in an
area free from airborne dirt or other foreign material which
could clog the condenser coils. Refer to Fig. 3 and 4 for
airflow clearances. For multiple units, allow 8 ft (2440 mm)
separation between units for airflow and service. Placement
area must be level and strong enough to support operating
weight of the unit (Fig. 2 and Table 1). It is recommended
to bolt unit securely to pad when unit is positioned and lev
eled. Fasteners for mounting unit are field supplied. If vi
bration isolators are required for a particular installation,
refer to the unit weight distribution data table and diagram
below to help select the proper isolators.
Y - DIMENSION
UNIT 09DK
054
064
074
084
COIL TYPE*
*Cu-AI — Copper Tubes, Aluminum Fins
Cu-Cu — Copper Tubes, Copper Fins.
UNIT 09DK
054
064
074
084
COIL TYPE*
Cu-AI 1695 (769)
Cu-Cu
Cu-AI
Cu-Cu
Cu-AI
Cu-Cu
Cu-AI
Cu-Cu
TOTAL WEIGHT
1983 (900)
1845 (837)
2278 (1033)
2200 (998)
2617 (1187)
2421 (1098)
3099 (1406) 843 (382) 751 (341)
*Cu-AI — Copper Tubes, Aiuminum Fins.
Cu-Cu — Copper Tubes, Copper Fins.
Cu-AI
Cu-Cu
Cu-AI
Cu-Cu
Cu-AI
Cu-Cu
Cu-AI
Cu-Cu
lb (kg)
X- DIMENSION
CENTER OF GRAVITY In. (mm)
X Dimension
48.1 (1222)
48.3 (1227)
48 2 (1224)
44,5 (1232)
56 7 (1440)
57.4 (1458)
57.1 (1450)
581 (1476)
A
452 (205) 425 (193)
524 (238) 497 (225)
489 (222)
598 (271)
618 (280)
722 (328)
673 (305)
Y Dimension
42 7 (1084)
42 9 (1090)
42 8 (1087)
43.1 (1095)
42 5 (1080)
42.8 (1087)
42 6 (1082)
43 0 (1092)
OPERATING CORNER WEIGHTS lb (kg)
B C D
462 (210)
571 (259) 542 (246) 568 (258)
526 (239)
630 (286)
581 (264)
396 (180) 422 (191)
468 (212)
434 (197)
486 (220)
589 (267)
541 (245) 626 (284)
709 (322)
494 (224)
459 (208)
571 (259)
675 (306)
796 (361)
Fig. 2 — Weight Distribution
Page 5
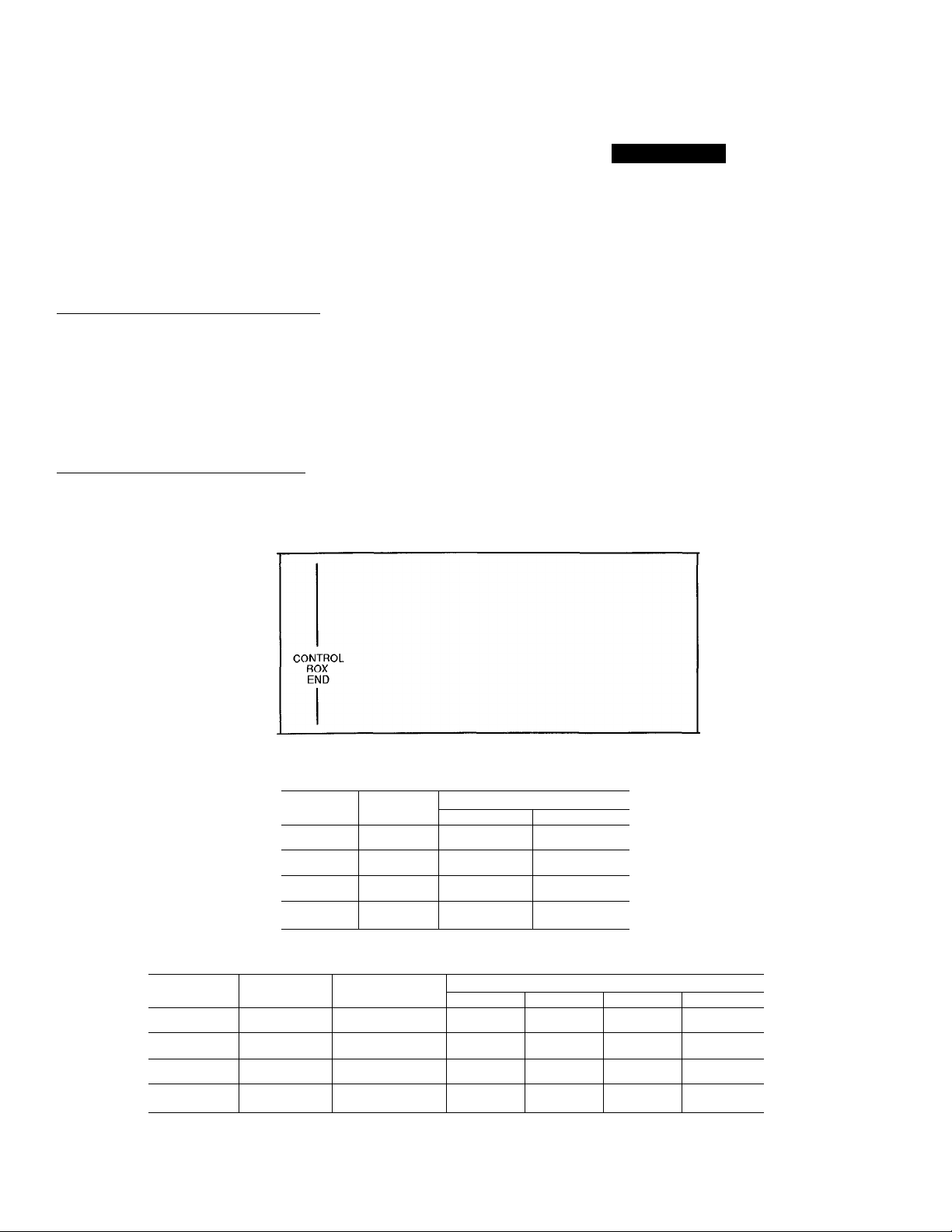
NOTES:
1. The approximate operating weight of the unit is:
09DK-054—
09DK-054-C
09DK-064—
09DK-064-C
2. Unit must have clearances for airflow as follows:
Top — Do not restrict in any way.
Ends — 5 ft [1524 mm]
Sides — 6 ft [1829 mm]
3. All units are shipped with a capacity split tubing kit. This kit may be used by
the field to obtain 100%, 50%/50% and 67%/33% capacity splits. To obtain
a 33%/33%/33% capacity split, coils must be manifolded by the field. Coils'
are factory circuited for a 33%/33%/17%/17% capacity split.
________
-------------
-------------
-------------
► 1695 lb [769 kg]
»■ 1983 lb [900 kg]
»• 1845 lb [837 kg]
»-2278 lb [1033 kg]
CONTROL BOX
END
UNIT
09DK-054—
09DK-054-C
09DK-064—
09DK-064-C
DIMENSION Y DIMENSION X
3'-6 11/16”
[1084 mm]
3'-6 7/8"
[1090 mm]
3'-6 3/4"
[1087 mm]
3’-7 1/8"
[1095 mm]
4'-1/8"
[1222 mm]
4'-5/16"
[1227 mm]
4'-3/16"
[1224 mm]
4'-1/2"
[1232 mm]
OPERATING CORNER WEIGHTS
A B
452 lb
[205 kg]
524 lb
[238 kg]
489 lb
[222 kg]
598 lb
[271 kg]
425 lb
[193 kg]
497 lb
[225 kg]
462 lb
[210 kg]
571 lb
[259 kg]
C
396 lb
[180 kg]
468 lb
[212 kg]
434 lb
[197 kg]
542 lb
[246 kg]
D
422 lb
[191 kg]
494 lb
[224 kg]
459 lb
[208 kg]
568 lb
[258 kg]
CAPACITY SPLIT
100%
50%/50%
67%/33%
33%/33%/33%
33%/33%/17%/17%
HOT GAS
LIQUID
HOT GAS
LIQUID
HOT GAS
LIQUID
HOT GAS 1
LIQUID
HOT GAS 1 7
LIQUID
TYPE
T-A 1/2'-
C224 7rain3
BASE OVERALL
CONNECTIONS
N0.5
1/3.5,7
2,4.6,8
5,7
1/3
2.4
6.8 7/8 I.D.
1.3,5 7
2.4.5 8
7
2 a 4.5
3 5
4
2 8
SIZE
1 1/8’ I.D.
7/8 I.D.
1 1/8' I.D.
1 1/8' I.D.
7/8 1.0.
3,51 1/8' I.D.
7/8 I.D.
1 1/8' I.D.
6 7/8 I.D.
Fig. 3 — Dimensions; 054 and 064 Units
Page 6
NOTES.
1. The approximate operating weight of the unit is:
09DK-074—
09DK-074-C
09DK-084
09DK-084--C
2. Unit must have clearances for airflow as follows:
Top — Do nof restrict in any way.
Ends — 5 ft [1524 mm]
Sides — 6 ft [1829 mm]
3. All units are shipped with a capacity split tubing kit. This kit may be used by
the field to obtain 100%, 50%/50% and 67%/33% capacity splits. To obtain
a 33%/33%/33% capacity split, coils must be manifolded by fhe field. Coils
are factory circuited for a 33%/33%/17%/17% capacity split.
_________
----------------
-----------------
--------------
2200 ib [998 kg]
»2617 ib [1187 kg]
»• 2421 ib [1098 kg]
»-3099 Ib [1406 kg]
09DK-074—
09DK-074-C
09DK-084—
09DK-084-C
Ov
DIMENSION Y
3’-6 1/2"
[1080 mm]
3'-6 13/16"
[1087 mm]
3'-6 5/8"
[1082 mm]
3'-7"
[1092 mm]
П6) MTG HOLES
17/32' DIA.—V
C13.5bb3
r-4 7/8'-
С42В.5в>т:
HT6. HOLES
DIMENSION X
Г-5 1/2'-
C444m}
HTG. HOLES
4'-8 11/16"
[1440 mm]
4'-9 3/8"
[1458 mm]
4'-9 1/8"
[1450 mm]
4'-10 1/8"
[1476 mm]
С22531ПЛ1
Г-4 3/4'-
L425cnir>3
MTG. HOLES
-?'-4 11/16'-
OPERATING CORNER WEIGHTS
A В
618 Ib
[280 kg]
722 Ib
[328 kg]
673 Ib
[305 kg]
843 Ib
[382 kg]
HINGED ACCESS
PANEL
(CONTROL BOX)
526 Ib
[239 kg]
630 Ib
[286 kg]
581 Ib
[264 kg]
751 Ib
[341 kg]
-Г-5 1/2'
C444nti3
MTG. HOLES
C
486 Ib
[220 kg]
589 Ib
[267 kg]
541 Ib
[245 kg]
709 Ib
[322 kg]
»-1 1/2'
[Se.Snnl
MTG. HOLES
• 7/8'
[428.Siw]
MTG. HOLES
D
571 Ib
[259 kg]
675 Ib
[306 kg]
6261b
[284 kg]
796 Ib
[361 kg]
base overall
(4) RIG HOLES
2 5/8' DIA.
СбТтт]
CAPACITY SPLIT
100%
50%/50%
67%/33%
33%/33%/33%
33%/33%/17%/17%
TYPE
HOT GAS 1,3.5.7
LIQUID 2.4.6,8 7/8 I.D.
HOT GAS
LIQUID
HOT GAS
LIQUID 2.4,5 8 7/8 I.D.
HOT GAS 1 7
LIQUID
HOT GAS17
LIQUID 2
CONNECTIONS
N0.5 SIZE
5,7
1.3
2,4 6,8 7/8 I.D.
7
1.3.S
3.5
2
8 4,6 7/8 I.D.
3 5
4
8
• 7'-4 1/2'
[224?готЗ
BASE Overall
1 3/8' I.D.
1 3/8' I.D.
1 3/8' I.D.
1 3/8' I.D.
1 3/8' I.D.
5 7/8 I.D.
Fig. 4 — Dimensions; 074 and 084 Units
Page 7

Step 3 — Complete Refrigerant Piping
GENERAL — All field leak and pressure testing should be
in accordance with local code requirements. If a local code
does not exist, use ASHRAE (American Society of Heat
ing, Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Engineers) Stan
dard 15, Safety Code for Mechanical Refrigeration.
For leak testing procedures, refer to the Carrier’s
“Refrigerant Service Techniques” Book, Form SM-IA.
For any parts that need to be removed, use a mini tubing
cutter. Perform phos-copper brazing on all field-made con
nections while protecting adjacent joints from heat.
Install or replace filter-drier(s). BEFORE CHARGING THE
SYSTEM, INSTALL OR REPLACE THE FILTERDRIER(S) CONNECTED TO THE LIQUID LINE WITHIN
THE INDOOR UNIT(S) TO PREVENT CONTAMINA
TION WITHIN THE SYSTEM.
COIL REFRIGERANT PIPING INSTALLATION - Hot
gas and liquid connections are located on the same end and
are capped from the factory with a heat shrink-type cap,
which provides a clean joint for field piping. The coil cir
cuiting is designed to provide several selections of coil splits
to satisfy various applications (See Table 2), with piping
connections made in the field. In all cases where circuits
are field connected, the piping connections should be made
within the unit cabinet. The hot gas lines should enter and
the liquid lines should leave the condenser at the header
end of the unit.
As a standard item, a tubing package for headering, in
cluding two fan cycle pressure switches (FCPSs) and hard
ware is provided for the 100, 50/50, and 67/33% typical
condenser coil circuiting options. The tubing also provides
the ports for easy FCPS installations. The ports come with
a 1/4 in. male flare fitting and check valve for each FCPS
replacement. Tubing and FCPSs are field installed regard
less of circuiting. Tubing packages are not offered for the
33/33/33% and 33/33/17/17% coil circuiting options; tub
ing for these coil circuit options must be field fabricated
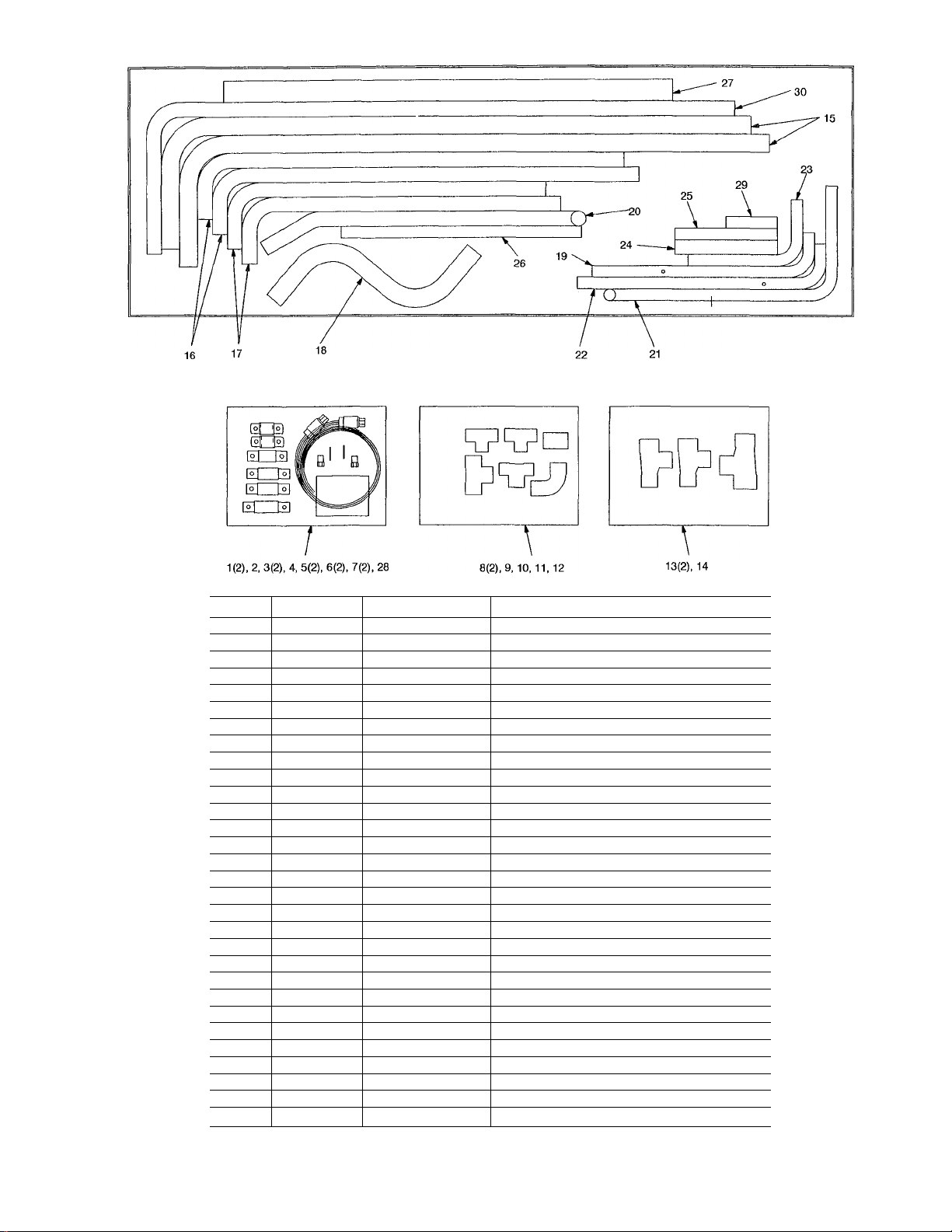
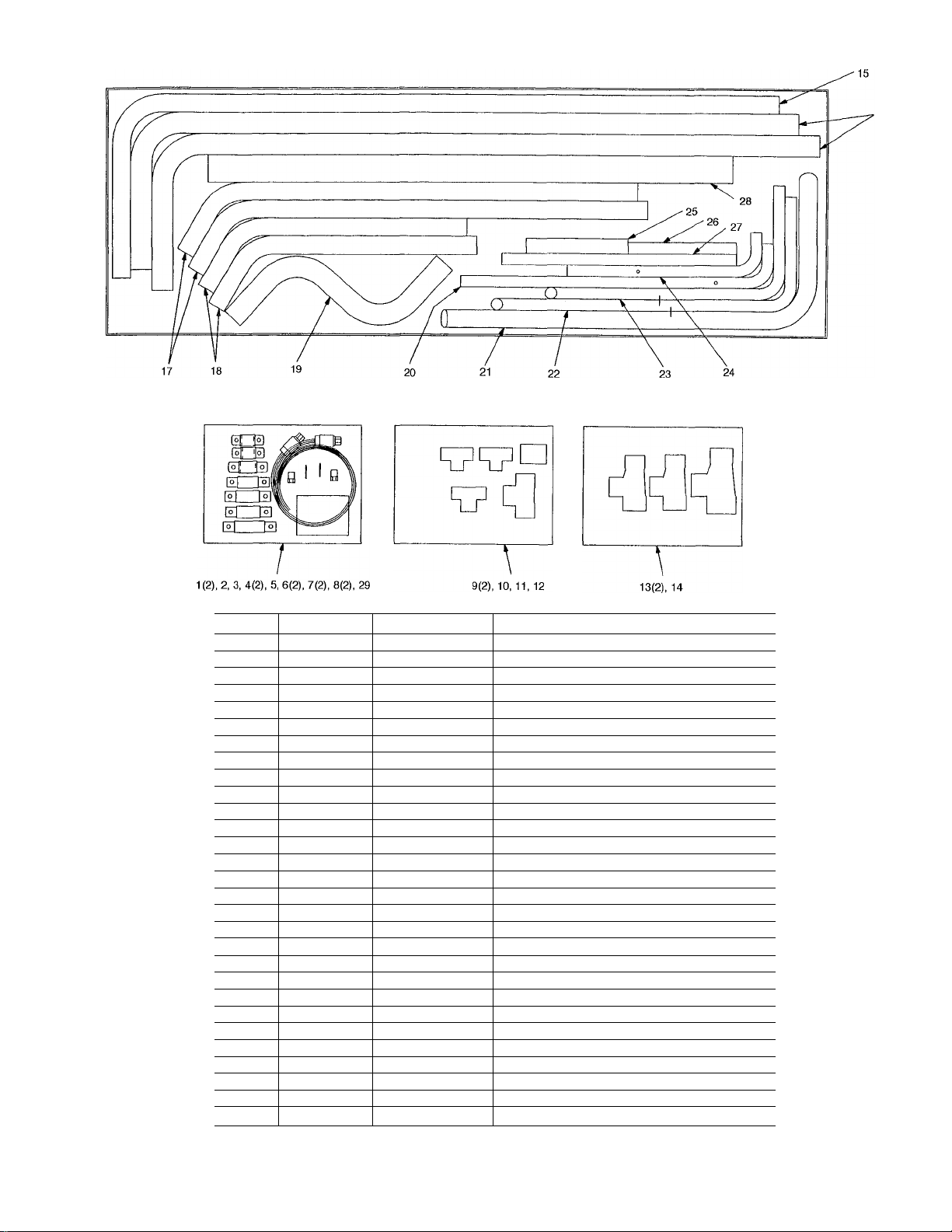
and installed. See Fig. 5 and 6 for tubing package contents.
NOTE: 67/33, 33/33/33 and 33/33/17/17 represent average
coil split combinations. Refer to sections below for actual
values for your particular coil split combination.
IMPORTANT: With the 67/33, 33/33/33, and 33/33/
17/17% capacity split options, 3 or 4 FCPSs are used.
For these applications, an accessory fan control kit is
required. See accessory installation instructions for more
information.
Figure 7 shows a typical piping application for a condenser
with a multiple-split system. Figure 8 shows the typical field
piping arrangements for the 09DK units. See Fig. 9 for coil
connection details. Figures 10 and 11 show typical factory
supplied coil circuiting and typical field installed 67/33%
coil split circuiting respectively.
TUBING PACKAGE INSTALLATION - Before install
ing, inspect the package contents. If any parts are missing
or damaged, file a claim with the shipping company and
notify your Carrier representative. A field supplied 3/8-in.
conduit (Greenfield conduit recommended) is required
according to UL/CSA (Underwriters’ Laboratories/
Canadian Standards Association) code for the FCPS field
wiring. Field supplied 3/8-in. conduit connectors are re
quired for connection to the junction box.
100% Coil Circuiting Applications: 054. 064 Units
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 12 for field piping details
for 100% coil circuiting. Note that tubes 15 and 22 require
cut on the longer leg of the tube. Two 7/8-in. OD tubes,
approximately 3 in. (76.2 mm) long, must be cut from the
remaining tubes (tubes 21, 23, or 25) and brazed between
the tees (item 8) and coil header stubs. The remaining tubes
are not used in this application and may be discarded.
2. Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 2
valve core bodies (item 5) to designated hole locations on
tubes 19 and 22. Insert valve cores (item 6), into valve core
bodies by threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to
3 in.-lb (169.5 to 339 mN-m). Install FCPSl and FCPS2
(item 7) at designated locations on tubes 19 and 22. Cut the
3/8-in. field-supplied FCPS conduit at a desired length to
fit between each FCPS location and the junction box on the
unit. Figure 11 shows a typical installation of the conduit.
Feed FCPS wires through each conduit and secure at the
switch by utilizing each conduit connector. See Fig. 13.
Secure the conduit at the junction box with 3/8-in. fieldsupplied conduit connectors. Wire FCPSl and FCPS2
according to Fig. 14. Clamp hot gas line, tube 27, at the
location specified in Fig. 12 using the 1 5/8-in. clamp
(item 4) and the 2 screws supplied. Clamp the liquid line,
tube 24, using the 1 1/8-in. clamp (item 2) and the 2 screws
provided.
50/50% Coil Circuiting Applications: 054 and 064 units
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 15 for field piping details
for 50/50% coil circuiting. Note that tubes 21 and 22
require cuts on the longer leg of the tubes. Two 7/8-in.
OD tubes, approximately 3 in. (72.6 mm) long, must be
cut from the remaining tubes (21, 25, 26, or 29) and brazed
between the tees (item 8) and coil header stubs. The re
maining tubes are not used in this application and may be
discarded.
2. Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 2
valve core bodies (item 5) to designated hole locations on
tubes 19 and 22. Insert valve cores (item 6) into valve core
bodies by threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to
3 in.-lb (169.5 to 339 mN-m). Install FCPSl and FCPS2
(item 7) at designated locations on tubes 19 and 22. Cut the
field-supplied 3/8-in. FCPS conduit at a desired length to
fit between each FCPS location and the junction box on the
unit. Figure 11 shows a typical installation of the conduit.
Feed FCPS wires through each conduit and secure at the
switch using each conduit connector. See Fig. 13. Secure
the conduit at the junction box with 3/8-in. field-supplied
conduit connectors. Wire FCPSl and FCPS2 according to
Fig. 14. Clamp hot gas lines, tube 15 at the location spec
ified in Fig. 15 using the two 1 3/8-in. clamps (item 3)
and 4 screws provided. Clamp the liquid lines, tubes 21
and 23, using the two 7/8-in. clamps (item 1) and the
4 screws provided.
09DK
054
064 100%
074 100%
084 100%
100% 50/50%
Table 2 — Coil Circuiting Options
09DK CIRCUITING OPTIONS
66/34
50/50%
50/50%
50/50%
66/34
68/32
67/33
34/34/32
34/34/32
32/32/36
33/33/33
34/34/16/16
34/34/16/16
32/32/18/18
33/33/17/17
Page 8
ITEM
QUANTITY NAME
1 2
a
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17 2
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25 1
26
27
28
29
30
Tube Clamp
1
2
1 Tube Clamp
2
2
2
2
1
1
1
1
2
1
2 Discharge Tuba
2
1
1
1
1
1 Liquid Tube
1 Liquid Tube
1
1
1
8
1
1
Tube Clamp
Tube Clamp 1 3/8 in.
Valve Body
Valve Core
Switch Fan cycle pressure switch
Tee
Tee
Tee
Solder Coupling 1 1/8 in.
Elbow, 90 Degree 1 1/8 in
Tee
Tee
Discharge Tube’ 1 1/8 in. CD X 32 11/32 in. Lx 5 1/16 in. W
Discharge Tube
Discharge Tube 1 3/8 in CD
Liquid Tube 7/8 in. CD X 16 13/16 in. L X 3 7/16 in. W
Discharge Tube
Liquid Tube 7/8 in. CD X 17 11/16 in. L
Straight Tube
Straight Tube 7/8 in. CD X 7 3/4 in. L
Straight Tube 7/8 in. OD X 18 1/4 in. L
Straight Tube 1 5/8 in. OD X 34 in. L
Screw 1/4 - 14 X 5/8 in long
Straight Tube 7/8 in OD X 3 7/8 in long
Discharge Tube
DESCRIPTION
7/8 in.
1 1/8 in.
1 5/8 in.
1/4 in. male flare fitting
-
7/8 in. X 7/8 in. X 7/8 in.
1 1/8 in X 1 1/8 in. X 1 1/8 in.
7/8 in. X 7/8 in. X 1 1/8 in.
1 3/8 in. X 1 1/8 in. X 1 1/8 in.
1 5/8 in X 1 3/8 in X 1 3/8 in.
1 3/8 in. CD X 44 23/32 in L x 10 1/16 in. W
1 1/8 in. CD X 24 5/32 in L x 5 1/16 in W
1 1/8 in. CD X 24 1/2 in. L
7/8 in CD X 18 13/16 in L X 3 7/16 in. W
7/8 in. CD x8 11/16 in. Lx 5 1/16 in. W
1 1/8 in. OD X 7 3/4 in. L
1 1/8 in OD X 44 19/32 in. L x 11 9/16 in. W
Fig. 5 — 09DK054,064 Tubing Package Contents
8
Page 9
• 16
ITEM
QUANTITY NAME
1 2
Tube Clamp
2 1 Tube Clamp
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1 Tube Clamp
2
1
2
2
2 Siwitch
2
Tube Clamp
Tube Clamp
Valve Body
Valve Core -
Tee
10 1 Coupling
11 1 Tee
12 1 Tee
13 2 Tee
14 1 Tee
15
16
17 2
18
19
1
2
2
1
Discharge Tube
Discharge Tube
Discharge Tube
Discharge Tube
Discharge Tube
20 1 Liquid Tube
21 1
Discharge Tube
22 1 Liquid Tube
23
24
25
26
1 Liquid Tube
1
1 Straight Tube 1 1/8 in OD X 7 3/4 in L
1 Straight Tube 7/8 in. OD X 8 1/4 in. L
Liquid Tube 7/8 in. OD X 14 13/16 in. L X 3 7/16 in W
27 1 Straight Tube
28
29 8
1 Straight Tube 2 1/8 in OD X 40 in. L
Screw
DESCRIPTION
7/8 in
1 1/8 in.
1 3/8 in
1 5/8 in
2 1/8 in
1/4 in. male flare fitting
Fan cycle pressure switch
7/8 in. X 7/8 in X 7/8 in.
1 3/8 in. X 1 3/8 in.
7/8 in. X 7/8 in. X 1 1/8 in.
1 3/8 in. X 1 3/8 in X 1 3/8 in.
1 5/8 in. X 1 3/8 in. X 1 3/8 in
2 1/8 in X 1 5/8 in X 1 5/8 in
1 3/8 in CD X 50 25/32 in. L x 14 1/8 in. W
1 5/8 in CD X 50 29/32 in. L x 12 1/16 in. W
1 3/8 in CD X 34 1/2 in L X 4 3/4 in. W
1 3/8 in CD X 19 7/8 in. L X 4 3/4 in. W
1 5/8 in CD
7/8 in. OD X 23 13/16 in L X 3 7/16 in. W
1 3/8 in OD X 28 3/8 in. L
7/8 in OD X 23 1/4 in. L (074 Units only)
7/8 in. OD X 18 1/4 in L
7/8 in. OD X 17 7/8 in. L
1/4 in.-14 X 5/8 in long
Fig. 6 — 09DK074,084 Tubing Package Contents
Page 10

66/34% Coil Circuiting Applications: 054 and 064 Units
NOTE: To operate the 054 and 064 condenser units with
66/34% coil circuiting, an accessory fan control kit is
required. Refer to fan control kit installation instruc
tions for more information.
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 16 for field piping details
for 66/34% coil circuiting. Note that tube 16 will require
cuts on the longer leg of the tube. Tube 16 will be used in
the two specified locations. A 7/8-in. OD tube, approxi
mately 3 in. (72.6 mm) long, must be cut from the remain
ing tubes (23 or 26) and brazed between the tee (item 8)
and coil header stub. The remaining tubes are not used in
this application and may be discarded.
2. Install Fan-Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 3
valve core bodies (item 5) to designated hole locations on
tubes 19, 21, and 22. Insert valve cores (item 6) into valve
core bodies by threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to
3 in.-lb (169.5 to 339 mN-m). Note that the accessory fan
control kit is required for this coil circuiting. An extra FCPS
and valve assembly is provided with the kit. Install FCPSl,
FCPS2, and FCPS4 (item 7) at designated locations on tubes
19, 21, and 22. Cut the field-supplied 3/8-in. FCPS conduit
at a desired length to fit between each FCPS location and
the junction box on the unit. See Fig. 11 for typical conduit
installation. Feed FCPS wires through each conduit and se
cure at the switch by utilizing each conduit connector. See
Fig. 13. Secure the conduit at the junction box with 3/8-in.,
field-supplied conduit connectors. Wire FCPSl, FCPS2, and
FCPS4 according to Fig. 14 Note that FCPS2 and FCPS4
are wired in parallel. Fan 4 is shared by the 34% and 66%
refrigeration circuit. If either circuit needs the fan to be on,
it will be on. At the location specified in Fig. 16, clamp hot
gas lines, tubes 15 and 30, using a 1 3/8-in. clamp (item 3)
and a 1 1/8-in. clamp (item 2) with the 4 screws supplied.
Clamp the liquid lines, tubes 21 and 25, with 7/8-in. clamps
(item 1) and 4 screws provided.
100% Coil Circuiting Applications: 074 Units
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 17 for field piping details
for 100% coil circuiting. Note that tube 16 requires a cut on
the longer leg of the tube. Two 7/8-in. OD tubes approxi
mately 3 in. (72.6 mm) long, must be cut from the remain
ing tubes (22 or 23) and brazed between the tees (item 9)
and coil header stubs. The remaining tubes are not used and
may be discarded.
2. Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 2
valve core bodies (item 6) to designated hole locations on
tubes 20 and 24. Insert valve cores (item 7) into valve core
bodies by threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to
3 in.-lb (169 to 339 mN-m). Install FCPSl and FCPS2
(item 8) at designated locations on tubes 20 and 24. Cut the
3/8-in. field-supplied FCPS conduit at a desired length to
fit between each FCPS location and the junction box on the
unit. See Fig. 11 for typical conduit installation. Feed FCPS
wires through each conduit and secure at the switch by uti
lizing each conduit connector. See Fig. 13. Secure the con
duit at the junction box with 3/8-in. field-supplied conduit
connectors. Wire FCPSl and FCPS2 according to Fig. 18.
Clamp hot gas line, tube 28, using 2 1/8-in. clamp (item 5)
at the location specified in Fig. 17 with the 2 screws sup
plied. Clamp the liquid line, tube 25, using 1 1/8-in. clamp
(item 2) and the 2 screws provided.
50/50% Coil Circuiting Applications: 074 Units
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 19 for field piping details
for 50/50% coil circuiting. Note that tube 23 will require a
cut, located exactly at the location of the hole in the tube.
Tube 23 will be used in the two locations specified. Two
7/8-in. OD tubes, approximately 3 in. (72.6 mm) long, must
be cut from the remaining tubes (22, 26, or 27) and brazed
between the tees (item 9) and coil header stubs. The re
maining tubes are not used in this application and may be
discarded.
2. Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 2
valve core bodies (item 6) to designated hole locations on
tubes 20 and 24. Insert valve cores (item 7) into valve core
bodies by threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to
3 in.-lb (169.5 to 339 mN-m). Install FCPSl and FCPS2
(item 8) at designated location on tubes 20 and 24. Cut the
3/8-in. field-supplied FCPS conduit at a desired length to
fit between each FCPS location and the junction box on the
unit. See Fig. 11 for typical conduit installation. Feed FCPS
wires through each conduit and secure at the switch by us
ing each conduit connector. See Fig. 13. Secure the con
duit at the junction box with 3/8-in. field-supplied conduit
connectors. Wire FCPSl and FCPS2 according to Fig. 18.
Clamp hot gas line, tube 16, at the location specified in
Fig. 19 using two 1 5/8-in. clamps (item 4) and 4 screws
supplied. Clamp the liquid lines, tubes 23, using the two
7/8-in. clamps (item 1) and the 4 screws provided.
68/32% Coil Circuiting Applications: 074 Units
NOTE: To operate the 074 condenser units with 68/32%
coil circuiting, an accessory fan control kit is required.
See accessory installation instructions for more infor
mation.
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 20 for field piping details
for 68/32% coil circuiting. Note that tubes 17 and 20 re
quire euts on the longer leg of the tubes. Tube 17 will be
used in the two locations specified. Also, a 7/8-in. OD tube,
approximately 3 in. (72.6 mm) long, must be cut from the
remaining tubes (23 or 27) and brazed between the tee
(item 9) and eoil header stub. The remaining tubes are not
used in this application and may be discarded.
2. Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 3
core bodies (item 6) to designated hole locations on tubes
20, 22, and 24. Insert valve cores (item 7) into valve core
bodies by threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to
3 in.-lb (169.5 to 339 mN-m). Note that the accessory fan
control kit is required for this coil circuiting. An extra FCPS
and valve assembly is provided with the kit. Install FCPSl,
FCPS2, and FCPS4 (item 8) at designated locations on tubes
20, 22, and 24. Cut the 3/8-in. field-supplied FCPS conduit
at a desired length to fit between each FCPS location and
the junction box on the unit. See Fig. 11 for typical conduit
installation. Feed FCPS wires through each conduit and se
cure at the switch by utilizing each conduit connector. See
Fig. 13. Secure the conduit at the junction box with 3/8-in.
field-supplied conduit connectors. Wire FCPSl, FCPS2 and
FCPS4 according to Fig. 18. Note that FCPS2 and FCPS4
are wired in parallel. Fan 4 is being shared by the 32% and
68% refrigeration circuit. If either circuit needs the fan to
be on, it will be on. At the location specified in Fig. 20,
clamp hot gas lines, tube 15 with a 1 3/8 in. clamp (item 3)
and tube 16 with a 1 5/8 in. clamp (item 4) with the
4 screws supplied. Clamp the liquid lines, tube 22 with a
7/8 in. clamp (item 1) and tube 25 with a 1 1/8 in. clamp
(item 2) with the 4 screws supplied.
10
Page 11

COMPRESSORS
SEE NOTE 1
09DK084 UNIT (LOCATED ABOVE OTHER COMPONENTS)
PRESSURE RELIEF DEVICES*
FILTER-DRIERS*
SEE NOTE 4
Fig. 7 — Typical Piping for 09DK Condenser With a Dual Split System
'Field supplied.
NOTES
1. Hot gas lines should rise above refrigerant level in con
denser circuit.
2. Trap should be installed on hot gas lines to prevent
condenser oil and refrigerant vapor migration from ac
cumulating on compressor heads during off cycle.
3. Pitch all horizontal lines downward in the direction of
refrigerant flow.
4. Refer to Carrier System Design Manual, part 3 for proper
piping sizes and design.
MOISTURE
■ INDICATORS*
(SIGHT GLASS)
SEE NOTE 4
Page 12

O-
054,064 Units
..
..........
O
FCPS2■
FCPS2■
FCPS2•
„1..
O
--------
T
1
1
fel-
0
A
' ii
1 FCPS4
34% 66%
li
50% / 50%
--------
100%
i i
r—o--*--o
til
—*-o
FCPS1
FCPS1
FCPS1
FCPS2
FCPS2
t a
34%
FCPS — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
1-0
16%
FCPS4
Fig. 8
1. FCPS1 = Fan cycle pressure switch 1 cycles fan 3 in
response to condensing pressure.
2. FCPS2 = Fan cycle pressure switch 2 cycles fan 4 in
response to condensing pressure.
3. FCPS3 = Fan cycle pressure switch 3 cycles fan 3 in
O— -n
FCPS3
response to condensing pressure.
4. FCPS4 = Fan cycle pressure switch 4 cycles fan 4 in
response to condensing pressure.
5. In the above applications where a fan is being shared by two
different refrigeration circuits, the FCPSs (FCPS1 and 3 or
FCPS2 and 4) are in parallel so that if either circuit needs the
fan to be on, it will be on.
r-0
___a- - --
t- t
s_
FCPS1
ii
16%
Typical Field Piping Arrangements
34%
12
Page 13

074 Units
FCPS2■
FCPS2■
o-
;i
..........
--------------------------
O
--------
— o
I
i i
100%
■ ?—1 ^
lili
ill'
1 1 1 >
1 1 1 >
1 1 1 1
III
ill
1 1 1 1
Jí
--------------------------------------
tij
50% / 50%
1
o
■o
FCPS1
FCPS1
FCPS
FCPS2•
o
FCPS2-
r---0
Î
32%
Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
I I
r
fel.
0
V
1 FCPS4
32%
----------
1
1
1
1
1
1 FCPS4
1 ,
1 /
U !t ii It
32% 36%.
FCPS2 FCPS4
1—0
Í4
itii
68%.
FCPS3 1
|-0
__a.__
\ 1
FCPS3
1
----1
1
1
1
\r\
32%
o
O- -
a_
FCPS1
FCPS1
NOTES:
1 FCPS1 = Fan cycle pressure switch 1 cycles fan 3 in
response to condensing pressure.
2. FCPS2 = Fan cycle pressure switch 2 cycles fan 4 in
response to condensing pressure
3. FCPS3 = Fan cycle pressure switch 3 cycles fan 3 in
response to condensing pressure.
4. FCPS4 = Fan cycle pressure switch 4 cycles fan 4 in
response to condensing pressure
5 In the above applications where a fan is being shared by two
different refrigeration circuits, the FCPSs (FCPS1 and 3 or
FCPS2 and 4) are in parallel so that if either circuit needs the
fan to be on, it will be on
FCPS1
t a ¡i
18%.
18%
Fig. 8 — Typical Field Piping Arrangements (cent)
32%
13
Page 14

084 Units
........O
FCPS2-
FCPS2■
FCPS2 ■
ZI
..........
...................■ T"'"! r—^
O
î
33%
t i U
100%
1 '
1 » •
ill*
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
1 1 ! I
: ! ! !
H
li
50% / 50%
—-O- - L _
ÎÜ
■O
[4
FCPS4
lî il
67%
FCPS1
FCPS1
FCPS1
FCPS2
r---0
FCPS2
Î !i
33%
FCPS — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
1 FCPS1 = Fan cycle pressure switch 1 cycles fan 3 in
response to condensing pressure.
2 FCPS2 = Fan cycle pressure switch 2 cycles fan 4 in
response to condensing pressure
3. FCPS3 = Fan cycle pressure switch 3 cycles fan 3 in
response to condensing pressure.
4. FCPS4 = Fan cycle pressure switch 4 cycies fan 4 in
response to condensing pressure
5. In the above applications where a fan is being shared by two
different refrigeration circuits, the FCPSs (FCPS1 and 3 or
FCPS2 and 4) are in parallel so that if either circuit needs the
fan to be on, it will be on.
FCPS4
O- -1
FCPS3
|-0
î a
17%
__a__
Î !
17%
a_
¡1
FCPS1
33%
Fig. 8 — Typical Field Piping Arrangements (cent)
14
Page 15

LEFTSIDE COILS
RIGHT SIDE COILS
054,064
PERCENT CAPACITY
SPLIT NUMBER
100
50/50
66/34
34/34/32
34/34/16/16
•Connection sizes reflect size of each coil header nozzle.
fA tubing package is factory supplied to facilitate field piping installation for the 100, 50/50 and 66/34 capacity split applications See installation instructions for more
information
LINE TYPE
Hot Gas 1,3,5,7
Liquid 2,4,6,8
Hot Gas
Liquid 2,4/6,8
Hot Gas 1,3,5/7
Liquid 2,4,6/8
Hot Gas
Liquid
Hot Gas
Liquid
COIL CONNECTION
1,3/5,7
1/7/3,5
2/8/4,6
1/7/3/5
2/8/4/6
COIL CONNECTION
in.-ODM*
1 1/8
7/8
1 1/8 1 3/8
7/8 7/8
1 1/8
7/8 7/8
1 1/8
7/8
1 1/8
7/8
TUBING CONNECTION
in. ODMf
1 5/8
1 1/8
1 3/8
(3) 1 1/8
(3) 7/8
074
PERCENT CAPACITY
SPLIT
100
50/50
68/32
32/32/36
32/32/18/18
•Connection sizes reflect size of each coil header nozzle
tA tubing package is factory supplied to facilitate field piping installation for the 100, 50/50 and 68/32 capacity split applications. See installation instructions for more
information.
LINE TYPE
Hot Gas
Liquid
Hot Gas 1,3/5,7
Liquid
Hot Gas 1,3,5/7
Liquid
Hof Gas
Liquid
Hot Gas
Liquid
COIL CONNECTION
NUMBER
1,3,5,7
2,4,6,8
2,4/6,8 7/8
2,4,6/8
1/7/3,5
2/8/4,6
1/7/3/5
2/8/4/6
COIL CONNECTION
in.-ODM* in.-ODMf
1 3/8
7/8 1 1/8
1 3/8 1 5/8
1 3/8 1 5/8 1 3/8
7/8 7/8
1 3/8
7/8
1 3/8
7/8
TUBING CONNECTION
7/8 7/8
2 1/8
(3) 1 3/8
(3) 7/8
084
PERCENT CAPACITY
SPLIT
100
50/50
67/33
33/33/33
33/33/17/17
•Connection sizes reflect size of each coil header nozzle
tA tubing package is factory supplied to facilitate field piping installation for the 100, 50/50 and 67/33 capacity split applications See installation instructions for more
information.
LINE TYPE
Hot Gas
Liquid 2,4,6,8 7/8 1 1/8
Hot Gas 1,3/5,7 1 3/8
Liquid 2,4/6,8
Hot Gas 1,3,5/7 1 3/8
Liquid 2,4,6/8
Hot Gas 1/7/3,5
Liquid 2/8/4,6
Hot Gas
Liquid
COIL CONNECTION
NUMBER in.-ODM*
1,3,5,7 1 3/8
1/7/3/5
2/8/4/6
COIL CONNECTION TUBING CONNECTION
7/8 7/8
7/8
1 3/8
7/8
1 3/8
7/8
in.-ODMt
2 1/8
1 5/8
1 5/8
1 1/8 7/8
(3) 1 3/8
(3) 7/8
Fig. 9 — Coil Connection Data
15
1 3/8
7/8
1 1/8
7/8
1 5/8
7/8
1 5/8
7/8
1 3/8
Page 16

100% Coil Circuiting Applications: 084 Units
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 21 for field piping details
for 100% coil circuiting. Note that tubes 16 and 20 require
a cut on the longer leg of the tubes. Two 7/8-in. OD tubes,
approximately 3 in. (72.6 mm) long, must be cut from the
remaining tubes (22 or 23) and brazed between the tees
(item 9) and coil header stubs. The remaining tubes are not
used in this application and may be discarded.
2. Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 2
valve core bodies to designated hole locations on tubes 20
and 24. Insert valve cores into valve core bodies by thread
ing into place and tightening to 1 5 to 3 in.-lb (169.5 to
339 mN-m) Install FCPSl and FCPS2 at designated loca
tions on tubes 20 and 24. Cut the 3/8-in. field-supplied FCPS
conduit at a desired length to fit between each FCPS loca
tion and the junction box on the unit. See Fig. 11 for typ
ical conduit installation. Feed FCPS wires through each conduit
and secure at the switch by utilizing each conduit connec
tor. See Fig. 13. Secure the conduit at the junction box
with 3/8-in. field-supplied conduit connectors. Wire FCPSl
and FCPS2 according to Fig. 18. At the location specified
in Fig. 21, clamp hot gas line, tube 28, using 2 1/8-in.
clamp and 2 screws provided. Clamp the liquid line, tube
25, using 1 1/8-in. clamp and 2 screws provided.
50/50% Coil Circuiting Applications: 084 Units
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 22 for field piping details
for 50/50% coil circuiting. Note that tube 20 requires a cut
on the longer leg of the tube. Tube 23 will require a cut
located exactly at the location of the hole in the tube, and
will be used at the two locations specified. Two 7/8-in. OD
tubes, approximately 3 in. (72.6 mm) long, must be cut
from the remaining tubes (22, 26, and 27) and be brazed
between the tees (item 9) and coil header stubs. The re
maining tubes are not used in this application and may be
discarded.
2. Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 2
valve core bodies (item 6) to designated hole locations on
tubes 20 and 24. Insert valve cores (item 7) into valve core
bodies by threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to
3 in.-lb (169.5 to 339 mN-m). Install FCPSl and FCPS2
(item 8) at designated locations on tubes 20 and 24. Cut the
3/8-in. field-supplied FCPS conduit at a desired length to
fit between each FCPS location and the junction box on the
unit. See Fig. 11 for typical conduit installation. Feed FCPS
wires through each conduit and secure at the switch by us
ing each conduit connector. See Fig. 13. Secure the con
duit at the junction box with 3/8-in. field-supplied conduit
connectors. Wire FCPSl and FCPS2 according to Fig. 18.
At the location specified in Fig. 22, clamp hot gas line,
tube 16, using two 1 5/8-in. clamps and 4 screws provided.
Clamp the liquid lines, tubes 23, using two 7/8-in. clamps
(item 1) and 4 screws provided.
Fig. 10 — Typical Factory-Supplied Coil Circuiting,
09DK054-084 Units (084 Shown)
CONDUITS
Fig. 11 — Typicai Coil Circuiting for 09DK054-084
Units (67/33% Split Option; 084 Unit Shown)
16
Page 17

6113?)% Coil Circuiting Applications: 084 Units
NOTE: To operate 084 condenser units with 67/33% coil
circuiting, an accessory fan control kit is required.
See accessory installation instructions for more
information.
1. Piping — Refer to Fig. 9 and 23 for field piping details
for 67/33% coil circuiting. Note that tubes 17 and 20
require a cut on the longer leg of the tubes. Tube 17 will
be used in the two locations specified. Also, a 7/8-in. OD
tube, approximately 3 in. (72.6 mm) long must be cut from
the remaining tubes (22 or 27) and brazed between the tee
(item 9) and coil header stub. The remaining tubes are not
used in this application and may be discarded.
2 Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Braze 3
valve core bodies (item 6) to designated hole locations on
tubes 20, 23, and 24. Insert valve cores (item 7) into valve
core bodies by threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to
3 in.-lb (169.5 to 339 mN-m). Note that the accessory
fan control kit is required for this coil circuiting. An extra
FCPS and valve assembly is provided with the kit. Install
FCPSl, FCPS2, and FCPS4 (item 8) at designated loca
tions on tubes 20, 23, and 24. Cut the 3/8-in. field-supplied
FCPS conduit at a desired length to fit between each FCPS
location and the junction box on the unit. See Fig. 11 for
typical conduit installation. Feed FCPS wires through each
conduit and secure at the switch by utilizing each conduit
connector. See Fig. 13. Secure the conduit at the junction
box with 3/8-in. field-supplied conduit connector. Wire FCPSl,
FCPS2, and FCPS4 according to Fig. 18. Note that FCPS2
and FCPS4 are wired in parallel. Fan 4 is shared by the
33% and 67% refrigeration circuit. If either circuit needs
the fan to be on, it will be on. At the location specified in
Fig. 23, clamp hot gas lines, tube 15 with a 1 3/8-in. clamp
(item 3) and tube 16 with a 1 5/8-in. clamp (item 4) with
the 4 screws supplied Clamp the liquid lines, tube 23 with
a 7/8-in. clamp (item 1) and tube 25 with a 1 1/8-in. clamp
(item 2) with 4 screws supplied.
THREE AND FOUR COIL SPLIT, COIL CIRCUITING
APPLICATIONS; 054-084 UNITS
NOTE: To operate 054-084 condenser units with the 3
and 4 coil split coil circuiting, the fan control kit is re
quired. See accessory installation instructions for more
information.
1. Piping — Piping is not provided in the tubing package
for these coil circuiting options. Tubing is field fabricated
and installed, according to the coil circuiting shown in
Fig. 8. For pipe sizing information, refer to Refrigerant Line
Sizing, page 18. To secure the piping, it should be routed
to the brackets supplied on the unit.
100%
FCPS — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
Fig. 12 — 100% Coil Circuiting; 054 and 064 Units
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in ( ) are in millimeters
2. See Fig 5 for tubing package contents.
17
Page 18

2. Install Fan Cycle Pressure Switches and Clamps — Four
FCPSs should be used. Locate holes, valve core assem
blies, and FCPS’s 1, 2, 3, and 4 at the specified locations.
See Fig. 8. Insert valve cores into valve core bodies by
threading into place and tightening to 1.5 to 3 in.-lb (169.5
to 339 mN-m). The additional two FCPSs and valve core
assemblies are provided with the accessory fan control kit.
Cut the 3/8-in. field-supplied FCPS conduit at a desired length
to fit between each FCPS location and the junction box on
the unit. See Fig. 11 for typical conduit installation. Feed
FCPS wires through each conduit and secure at the switch
by utilizing each conduit connector. See Fig. 13. Secure
the conduit at the junction box with 3/8-in. field-supplied
conduit connectors. Wire the FCPSs according to Fig. 14
and 18. Note that FCPS2 and 4 and FCPSl and 3 are wired
in parallel. Fans 3 and 4 are being shared by two different
refrigeration circuits. If either refrigeration circuit needs the
fan to be on, it will be on. Clamp all lines to brackets sup
plied on the unit.
REFRIGERANT LINE SIZING - Sizing depends on length
of lines between various sections of the refrigerant system.
See Fig. 9 for coil connection details. Consider the amount
of liquid lift and drop in the system as well as proper com
pressor oil return. See Liquid Lift section for more infor
mation. Consult Carrier System Design Manual, Part 3, or
Carrier E20-II Refrigerant Piping Computer Program for proper
piping sizes and design
LIQUID SHUTOFF VALVE AND SIGHT GLASS - A
shutoff valve is not supplied with 09DK condensers. It is
strongly recommended that a full line size liquid shutoff
valve be field supplied near condenser to allow for servic
ing parts of the refrigerant circuit A field-supplied mois
ture indicating sight glass is recommended for use in charg
ing and servicing the system. Refer to Fig. 7.
PRESSURE RELIEF - The ASHRAE Standard 15, Safety
Code for Mechanical Refrigeration states; “Every refriger
ating system shall be protected by a pressure relief device
or some other means designed to safely relieve pressure due
to fire or other abnormal conditions ” Since 09DK con
densers do not have pressure relief devices, one must be
field supplied and installed just before the liquid line ser
vice valve. (See Fig. 7.) When the split coil is used with
multiple systems, each system must have its own pressure
relief.
Procedure for Using the Refrigerant Receiver — See
Fig. 24.
1. During normal operation — Valve A is open and valves
B and C are closed. Receiver is isolated from the
system.
2. For servicing — Valves A and C are closed and valve B
is open. Run unit until all the refrigerant is in the re
ceiver and then close valve B. Unit is now ready for ser
vicing.
3. To resume operation — Leave valve A closed and open
valves B and C. Run unit until the stored refrigerant is
drawn into the system. To completely remove the re
frigerant from the receiver, throttle valve B while noting
condition of refrigerant in the liquid line sight glass; also,
watch the suction pressure. A sudden surge of bubbles
in the sight glass and a rapid decrease in suction pres
sure indicates that all the refrigerant has been withdrawn
from the receiver. Immediately close valves B and C
and then open valve A. The unit should now be ready
for normal operation, with the receiver isolated from the
system. The system should be charged to a clear sight
glass when under normal operation.
LIQUID LIFT — Amount of liquid lift available before re
frigerant flashing occurs depends on amount of liquid sub
cooling in the system.
All 09DK condensers have positive subcooling when ap
plied with optimum charge. With subcooling, it is possible
to overcome an appreciable friction drop and/or static head
(due to elevation of the liquid metering device above the
condenser).
When 09DK condensers are applied with minimum charge,
no positive subcooling in condenser is realized; therefore,
if subcooling is required it must be obtained by external
means such as a liquid suction interchanger.
The average amount of liquid lift available is shown in
Table 3 for refrigerants R-22, R-502, and R-134A. Avail
able subcooling is greatly reduced when R-12 and R-500
are used in these units. It is recommended that the evapo
rator be at the same level as the condenser, or lower.
1/4 SAE FLARE WITH
56 (14 2) HEX
REFRIGERANT RECEIVER — A refrigerant receiver is
not furnished with 09DK condensers and is not recom
mended for normal applications as its use will be detrimen
tal to the desired effects of subcooling. However, if a par
ticular application requires a receiver to increase refrigerant
holding capacity of the condenser, a receiver can be used.
When a receiver is to be used year-round, it should be in
stalled indoors. Carrier recommends the following installa
tion in such a case (see Fig 24): locate valves on each side
of the receiver so receiver may be isolated from system for
normal operation.
SAE — Society of Automotive Engineers
Fig. 13 — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
18
CONDUIT
CONNECTOR
Page 19

09DK05^.054 POWER SCHEMATIC
09Dk:054.064 standard control schematic
nOO% 8 50X/50X CAPACITY SPLITS)
ir FW CONTROI. (IT IS USED. SEE FW CONTRa CIt (tCCESSOAri SOOUTIC
09DIC054.064 FAN CONTROL KIT CACCESSOftYJ SCHEMATIC
C67X/33X.33X/33X/33X g 33X/33X/17X/17% CAPACITY SPLITS)
l2Xi CDNIML VCL1ACE Oi«.r>
o
2
09PK054.064 COMPONENT ARRANGEMENT
& cSl
& cui
(D>®®
oO o
M2 №1
®®<32)
o
0 0
0U2 Ml
o>
o
NOTES.
1
Units are factory wired for a 50%/50% capacity split. If 100% capacity is required, con
nect the factory-supplied jumpers from TB2-1 to TB3-1 and from TB2-2 to TB3-2.
2. When a fan control kit is used, the jumper from TB2-1 to TB3-1 and from TB2-2 to TB3-2
must be connected. The fan control kit is factory wired for 67%/33% capacity split. If a
33%/33%/33% capacity split is required, remove the jumper from TB4-1 to TB5-1 and
from TB4-2 to TB5-2. If a 33%/33%h 7%/17% capacity split is required, remove the jump
ers from TB4-1 to TB5-1 to TB7-1 and from TB4-2 to TB5-2 to TB7-2.
3. On fan control kits, 208/230 v units are factory wired for 230 v power supply. For 208 v
power supply, connect yellow wire to terminal marked H2.
4. Terminal blocks TB2, TB3, TB4, TBS, TB6 and TB7 are for external field control connec
tions. Control connections are to be class 1 wiring, 14 AWG copper conductors only.
5. Wiring for field power supply must be rated 75° C minimum. Use copper, copper-clad
aluminum, or aluminum conductors. Maximum incoming wire size for each terminal block
IS 2/0.
6. Replacement of factory wires must be with 105° C wire or its equivalent.
7. Factory wiring is in accordance with National Electrical Code (NEC). Field modifications
or additions must be in compliance with all applicable codes.
8. Fan motors are thermally protected. Three-phase motors are protected against primary
single phasing conditions.
9. Line numbers on the left side of the label diagrams indicate the contact number. The
numbers on the right side of label diagrams match the contacts with their corresponding
coils. A plain number indicates normally open contacts. An underlined number indicates
normally closed contacts.
Fig. 14 — Wiring Diagram and Component Arrangement; 054 and 064 Units
dXJKD
<D®<D
O
o
o0
□= C
CONTRCC RELIT
outrr TERnlNii.
’ EOUIRHENT
FAN COKTACIOA
FAN CTCLINC FRESSURE S
FACJ9ST INSIALLEB »Hi
NOIOfi NASTER SENSOR
PRINAftr
SCCCMOAAT
TERNiNAL eiOCi:
TRV6FCFUCR
r~l TERNINAL 8L0CC CC»»«C1ICN
O "*»F£D TERNINAl
O LMURCED TERnlNAL
Page 20

50 / 50%
FCPS — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
Fig. 15 — 50/50% Coil Circuiting; 054 and 064 Units
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in ( ) are in millimeters
2 See Fig. 5 for tubing package contents.
FCPS — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
Fig. 16 — 66/34% Coil Circuiting; 054 and 064 Units
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in ( ) are in millimeters
2. See Fig 5 for tubing package contents
20
Page 21

Table 3 — Available Liquid Lift Ft (m)
REFRIGERANT R-22
UNIT
054
09DK
NOTES:
1 The liquid lift data allows for a 7 psi (48 kpa) drop for liquid line
accessories, and a 2° F (1.rC), iiquid line ioss with maximum
change.
2. Temperature difference = Saturated condensing temperature (en
tering) — Entering-air temperature (dry buib) in degree F (° C)
3. The liquid iift data is based on 15° F (8 3° C) subcooiing, 95 F
(35 C) entering-air temperature, and a 50/50% capacity split appiication Subcooling based on condenser subcooling = Satu
rated condensing temperature entering - Actual temperature leaving
the coii
064
074
084
Temperature Difference F (C)
20
30
(16.7)
(11.1)
50
60
(15 2)60(18.3)
(18.3)
41
(12 5)31(9.5)
44
(13.4)34(10.4)
51
(15.6)41(12.5)51(15.6)
R-502 R-134A
20
30
(16.7)20(11.1)
(11.1)
44
(13.4)
41
(12.5)
44
(13.4)28(8.5)18(5.5)7(2.1)
(10.7)22(6.7)
25
(7 6)
35
(8.8)26(7.9)
(6.1)6(1.8)
29
20
30
(16.7)
10
(3 1)
Example: Supply voltage is 240-3-60.
AB = 243 V
BC = 236 V
AC = 238 V
Average Voltage
243 -F 236 -f 238
^ 717
3
= 239 V
Determine maximum deviation from average voltage:
(AB) 243 - 239 = 4 V
(BC) 239 - 236 = 3 V
(AC) 239 - 238 = 1 V
Maximum deviation is then 4 v. To determine the percent
voltage imbalance:
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x----------
4
239
= 1.7%
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory since it is
below the maximum allowable of 2%.
Step 4 — Complete Electrical Connections
GENERAL — Verify nameplate electrical requirements match
available power supply. Voltage at condenser must be within
the minimum and maximum shown in Table 4 and phases
must be balanced within 2%. Contact local power company
for line voltage corrections. Never operate a motor where a
phase imbalance in supply voltage is greater than 2%.
Use the following formula to determine the percent voltage
imbalance:
max voltage deviation
% Voltage _ from average voltage
Imbalance ^ average voltage
IMPORTANT: If supply voltage phase imbalance is
more than 2%, contact your local electric utility com
pany immediately.
Condenser operation on improper line voltage or exces
sive phase imbalance may be considered abuse and any re
sulting damage may not be covered by Carrier warranty.
All wiring must be in accordance with local or NEC
(National Electrical Code) regulations.
FIELD CONNECTIONS - Refer to Table 4 and Fig. 14,
18, and 25 for field wiring details.
100%
Fig. 17 - 100% Coil Circuiting; 074 Units
21
Page 22

09DK074.0B4 POWER SCHEMATIC
090K074.084 FAN CONTROL KIT CACCESSORY^ SCHEMATIC
C67X/33-4.33X/33X/33X g 33X/33X/1 7X/1 7% CAPACITY SPLITS)
09DK074.0B4 COMPONENT ARRANGEMENT
Ni
to
FIELD COKlAa.
COMCTIWS CN.T
09DK074.084 STANDARD CONTROL SCHEMATIC
(^00% 8 50X/50X CAPACITY SPLIT53
[|F PM nwrttx Ell IS USED. SEE PM CMTUX Ell (UCESSOftr) SCICIUtK)
FUSTE»
- BBN TO FNI cowccT Piuo Fca aeovtsoHz)
- «CES50BT
«-.JL
(H5V CWiaOL YOtTIGE 0*T
—©
----------------------------------------------------
230V CONTROL ONLY
-----------»-------
-HI —O FC3
NOTES:
1. Units are factory wired for a 50%/50% capacity split. If 100% capacity is required, con
nect the factory-supplied jumpers from TB2-1 to TB3-1 and from TB2-2 to TB3-2.
2. When a fan control kit is used, the jumper from TB2-1 to TB3-1 and from TB2-2 to TB3-2
must be connected. The fan control kit is factory wired for 67%/33% capacity split, if a
33%/33%/33% capacity split is required, remove the jumper from TB4-1 to TB5-1 and
from TB4-2 to TB5-2. If a 33%/33%/17%/17% capacity split Is required, remove the jump
ers from TB4-1 to TB5-1 to TB7-1 and from TB4-2 to TB5-2 to TB7-2.
3. On fan control kits, 208/230 v units are factory wired for 230 v power supply. For 208 v
power supply, connect yellow wire to terminal marked H2.
^S0D
---
4. Terminal blocks TB2, TB3, TB4, TBS, TB6 and TB7 are for external field control connec
tions. Control connections are to be class 1 winng, 14 AWG copper conductors only.
5. Wiring for field power supply must be rated 75° C minimum. Use copper, copper-clad
aluminum, or alurTwnum conductors. Maximum incoming wire size for each terminal block
IS 2/0.
6. Replacement of factory wires must be with 105° C wire or its equivalent.
7. Factory wiring is in accordance with National Electncal Code (NEC). Field modifications
or additions must be in compliance with all applicable codes.
8. Fan motors are thermally protected. Three phase motors are protected against primary
single phasing conditions.
9. Line numbers on the left side of the label diagrams indicate the contact number. The
numbers on the nght side of label diagrams match the contacts with their corresponding
coils. A plain number indicates normally open contacts. An underlined number indicates
normally closed contacts.
Fig. 18 — Wiring Diagram and Component Arrangement; 074 and 084 Units
FN, 3S §
1
HNinOL BOX
(D<D(Z>
0X2)0
(KCESSoen
Jn C
©o®
o o
FIELD CCmaOL PI
0 o o
o
o o
CONTROL EIT 0W.T)
|o
>m TE>MBlTL(lf SKITCK
COKTOOL RELIT
DLPTIT TERXINIL
' EauiPHENT
FIN CCMTICTOR
FICTWT II6IILLED S>1l<
lEmiNiL euXE
®®®
®®®
o
o
r~l TEftBlNAl ÍL0CE CC*»«CTIi»l
C
O
Page 23

50 / 50%
FCPS — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
Fig. 19 — 50/50% Coil Circuiting; 074 Units
32 / 68%
Page 24

100%
50 / 50%
FCPS — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
Fig. 22 — 50/50% Coil Circuiting; 084 Units
24
Page 25

33 / 67%
1 Dimensions in ( ) are in millimeters.
2 See Fig. 6 for tubing package contents.
A — Bypass valve
B — Receiver inlet valve
C — Receiver outlet valve
Fig. 24 — Piping for Optional Receiver
Fig. 23 — 67/33% Coil Circuiting; 084 Units
25
Page 26

09DK
054
-500 208/230-3-60
-600 460-3-60
-100 575-3-60
-200
-900
064
-500
-600
-100 575-3-60 518
-200 380-3-60
-900 380/415-3-50
074
-500 208/230-3-60 187
-600
-100
-200
-900
NAMEPLATE
V-PH-HZ
380-3-60 342
380/415-3-50
208/230-3-60
460-3-60
460-3-60 414
575-3-60 518
380-3-60
380/415-3-50 342
084
-500 208/230-3-60
-600 460-3-60
-100 575-3-60 518
-200
-900
380-3-60
380/415-3-50
Control Circuit Information
09DK
CONTROL POWER
ALL
UNITS
-500
-600
-100 115-1-60
-200
-900
V-PH-HZ
115-1-60 103
115-1-60 103 127
230-1-60
230-1-50 207 253
Table 4 — 09DK Electrical Data
SUPPLY VOLTAGE*
Min
187
414
518
342
187
414
342
342 440
342
187
414
342
342
SUPPLY
VOLTAGE*
103 127
207
OVERCURRENT
PROTECTION
127
253
Max
254
508
632 14.5
418
440
254
508
632
418
254 34 0
508
632 21.3
418
440
254 34.0
508
632
418
440
MCA MOCP NO. FANS
23.2 25 4
11.7
166
128
23.2 25
11 7 15 4
14.5 15
166 20
128 15
17.1 20 6 93 (1,2) 2.8 (3-6) 2.7
24.4 25 6 93 (1-6)3 9
18.8 20 6 9.3 (1-6)3 0
17.1 20
21 3
24 4
188 20
AMPS
10
10
10
10
10
FAN MOTORS
Total Kw
6.2 (1,2) 5.5 (3,4) 5.4
15 4
15 4
20 4
15 4
4 6.2 (1,2) 5 5 (3,4) 5 4
4 62
4 6.2 (1-4) 3.9
4 6.2 (1-4) 3.0
35 6 93 (1,2) 5.5 (3-6) 5.4
25 6 93
35 6 9.3 (1,2) 5.5 (3-6) 5 4
25 6 9.3 (1-6) 3.4
25
LEGEND
FLA
— Full Load Amps
MCA
— Minimum Circuit Amps; Used for wire sizing
6 93 (1,2)2 8(3-6) 2.7
6
6 93 (1-6) 3.0
(Complies with NEC Sectien 430-24)
6.2
6.2
62
62
62
9.3 (1-6) 3.9
(Fan no.)
FLA for ea. fan
(1,2) 2.8 (3,4) 2.7
(1-4) 3.4
(1-4) 3.9
(1-4) 3.0
(1,2) 2.8 (3,4)2 7
(1-4) 3.4
(1-6)3 4
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
NEC — National Electrical Code
'Units are suitable for use on electrical systems where voltage sup
plied to the unit terminals is within listed minimum and maximum
limits.
NOTES:
1. Maximum allowable phase imbalance: Voltage ± 2%; Amps ± 10%
2. Maximum incoming wire size for power circuit is 2/0 max
3. Control Circuit: Uses no. 8 screws for wire connections at the ter
minal block.
4. 100 va is required for the 09DK054-084 control circuit
26
Page 27

NOTES:
1. Factory wiring is in accordance with National Electrical Code (NEC),
field modifications or additions must be in compliance with all ap
plicable codes.
2. Wiring for field power supply must be rated 75 C minimum. Use
copper, copper-clad aluminum, or aluminum conductors. Maxi
mum incoming wire size for each terminal block is 2/0.
3. Terminal blocks TB2, TBS, TB4, TBS, TB6, and TB7 are for
external field control connections. Control connections are to be
class 1 wiring.
4. Replacement of factory wires must be with type 105 C wire or its
equivalent.
5. Units are factory wired for a 50%/50% capacity split. If 100% ca
pacity is required, connect the factory-supplied jumpers from TB2-1
to TB3-1 and from TB2-2 to TB3-2.
6. If a fan control kit is to be used, the jumper from TB2-1 to TB3-1
and the jumper from TB2-2 to TB3-2 must be connected. The
fan control kit is factory wired for a 67%/33% capacity split. If a
33%/33%/33% capacity split is required, remove the jumper from
TB4-1 to TB5-1 and from TB4-2 to TB5-2. If a 33%/33%/17%/17%
capacity split is required, remove the jumpers from TB4-1 to TB5-1
to TB7-1 and from TB4-2 to TB5-2 to TB7-2.
K)
CONTROL BOX
STANDARD UNITS
Fig. 25 — Field Wiring; 054-084 Units
UNITS WITH FAN CONTROL LIT tACCESSORV)
CONTROL BOX
Page 28

MAIN POWER WIRING — These units must have ade
quate overcurrent protection, fuses, or HACR (Heating, Air
Conditioning and Refrigeration) breakers, according to the
national and applicable local codes.
For field power connections, all main power wiring en
ters the unit through a factory-punched access hole under
the control box. Two access holes are provided, the larger
should be used for 208/230 v applications. See Fig. 26.
Wiring must be rated at 75 C minimum. Use copper, copperclad aluminum, or aluminum conductors. Field power sup
ply connections are made at terminal block 1 (TBl). Max
imum incoming wire size for each terminal connection on
TBl is 2/0, and all power wiring must comply with appli
cable local and national codes. Refer to the unit power cir
cuit information to determine incoming wire sizes. (See
Table 4.) Refer to Table 5 for American and European wire
conversion information.
CONTROL CIRCUIT POWER WIRING - Provide a sep
arate single phase power source for each control circuit (de
pending on the coil refrigerant circuit split), with the re
quired overcurrent protection (fuses or circuit breakers). See
Table 4 for control circuit overcurrent protection amps.
For field control circuit connections, units are factory wired
for a 50/50% capacity split and would utilize terminal blocks
2 and 3 (TB2 and TB3). TB2 will control fans 1, 3, and 5;
TB3 will control fans 2, 4, and 6. Fans 5 and 6 are on 074
and 084 units only. If 100% condenser application is re
quired, connect the factory supplied jumpers from TB2-1 to
TB3-1 and from TB2-2 to TB3-2, and bring incoming con
nections to either TB2 or TB3. Factory-punched access holes
under the control box are provided for the incoming wires.
See Fig. 26 for access hole details. Terminal block connec
tions utilize no. 8 screws. Wiring must be class 1, 14 AWG
(American Wire Gage) copper conductors only. Power re
quired for control circuits is 100 va. See Table 4 for control
circuit voltage data.
GENERAL WIRING NOTES
1. Power entry is at one end only.
2. Fan motors are thermally protected. Three-phase motors
are protected against primary single-phasing conditions.
3. Replacement of factory wires must be with appliance
wiring material, rated 105 C, or its equivalent.
4 Factory wiring is in accordance with NEC. Field mod
ifications or additions must be in compliance with all
applicable codes.
DESCRIPTION OF CONTROLS - The condenser units
utilize a dual voltage control scheme: a 3-phase power cir
cuit for the fan system operation and a single-phase control
circuit voltage for fan cycling control. The number of con
trol circuit voltages will depend on the coil split application
used. See head pressure control description in the service
section for a detailed description of the controls function.
Table 5 — American/European Wire Conversions
AMERICAN EUROPEAN
Industry
Standard Size
18 AWG 0.82
16 AWG 1 30 1.5
14 AWG 2.08 2.5
12 AWG 3 30 40
10 AWG 5 25
8 AWG 6.36 100
6 AWG 13.29 16.0
4 AWG 21.14 25.0
3 AWG 26.65
2 AWG 33.61 35 0
1 AWG 42.39 50.0
1/0 AWG 53.49
2/0 AWG 67.42 70.0
3/0 AWG 85.00 95.0
4/0 AWG 107.19 120.0
250 kcmil 126 64
300 kcmil 151 97
350 kcmil 177 90
400 kcmil 202 63
500 kcmil 253 29
600 kcmil 303 95 —
LEGEND
AWG — American Wire Gage
kcmil — Thousand Circular Mils
American
Conversion
(mm^)
Industry
Standard
Size (mm^)
1.0
60
—
—
150.0
—
185 0
240 0
300 0
Step 5 — Add Accessories As Needed — The
following accessories are available for the 09DK054-084
condensers: fan sound reduction kit, condenser coastal coil
filter, security grille package, condenser coil hail guard pack
age, accessory control transformer, Motormaster® III de
vice, Motormaster III Relay/Sensor Kit, and accessory fancontrol kit. Winter Start and any special electrical interlock
must be considered separately. Refer to installation instruc
tions furnished with each accessory for more information.
2 13/32"
Fig. 26 — Power Wiring Access Holes; 054-084 Units
28
Page 29

START-UP
System Evacuation and Dehydration — Refer
to GTAC II, Module 4, “Dehydration for Proper Evacua
tion and Dehydration techniques.”
Charging Procedure — Charge to a clear sight glass.
Refer to GTAC II, Module 5 “Charging, Recovery, Recy
cling, and Reclamation” for proper charging techniques.
Add 10 lbs (4.5 kg) of R-22 over clear sight glass to flood
subcooler sections of the condenser coils. This 10 lbs
(4.5 kg) is added to the total unit charge, and must be pro
portioned by the percentage of circuits when multiple cir
cuits are employed. For example, in Table 2, add .67 x
10 lbs (4.5 kg) (approximately 6.7 lbs [3.0 kg]) for the 67%
circuit. Refer to Table 6 for condenser coil refrigerant
circuit data.
Check Operation of Condenser Fan Motor Con
trols and Rotation of Fans — Rotation should be
clockwise as viewed from top of unit.
A CAUTION
Before starting unit, be sure wire fan guards are
secured in place over each fan; personal injury may
result.
SERVICE
Cleaning Condenser Coils — Clean coils with a vac
uum cleaner, fresh water, compressed air, or a bristle brush
(not wire). Units installed in corrosive environments should
have coil cleaning as a part of a planned maintenance sched
ule. In this type of application, all accumulations of dirt
should be cleaned off the coil.
A CAUTION
Do not use high-pressure water or air. Damage to fins
may result.
Condenser Fans — Each fan is supported by a formed
wire mount bolted to the fan deck and covered with a wire
guard. The exposed end of the fan motor shaft is protected
by grease. If the fan motor must be removed for service or re
placement, be sure to grease fan shaft, and reinstall fan guard.
For proper performance, fan should be 7/8 in. (22 mm) be
low the top of the venturi on the fan deck for 60 Hz units,
and 1/2 in. (13 mm) to top of the fan hub for 50 Hz units.
Tighten set screws to 15 ± 1 ft-lbs (20 ±1.3 N-m). Fig
ure 27 shows the proper position of the mounted fan.
IMPORTANT: Check for proper fan rotation (clock
wise viewed from above). If rotation needs to be re
versed on one motor, disconnect main power supply
and switch motor leads at the fan contactor. If rota
tion needs to be reversed on all motors, disconnect
main power supply and switch two leads at TBl.
rated condenser temperature minus entering outdoor-air tem
perature) and decreases with decreased temperature differ
ence. A drop in entering outdoor-air temperature results in
a lower saturated condensing temperature. When outdoorair temperature drops below the minimum temperatures listed
in Table 7 for standard units, additional head pressure con
trol is required.
Model 09DK units have fully automatic intermediateseason head pressure control through condenser fan cycling
using electromechanical fan cycling controls. Standard head
pressure controls will control the 100 and 50/50% con
denser capacity applications. Head pressure can also be con
trolled by fan cycling controls supplemented by the acces
sory Motormaster® III solid-state head pressure controller.
See Motormaster III installation instructions for more infor
mation. Other circuit split applications (67/33, 33/33/33,
33/33/17/17% capacity splits) will require the accessory fan
control kit which includes a control panel and additional
fan cycling pressure switches. See fan control installation
instructions for more information.
In the standard control scheme, fans 1 and 2 will be on
when there is a call for cooling from the respective coil cir
cuits. Fans 1 and 2 are non-cycling. On 054 and 064 units,
fans 3 and 4 will be controlled by using a fan cycling pres
sure switch on each of the primary coil circuits in response
to condensing pressure. On 074 and 084 units, fans 3 and 4
will also be controlled using a fan cycling pressure switch
in each of the primary coil circuits in response to condens
ing pressure. Fans 5 and 6 will be controlled by using two
air temperature switches, which respond to the outdoor am
bient temperature. The air temperature switches are located
on the control box shelf. For temperature and pressure set
ting details, see Table 8.
With respect to the fan cycling pressure switch control,
fans 3 and 4 are on above 260 ± 15 psig (1793 ± 103 kPa)
and off below 160 ± 10 psig (1103 ± 69 kPa). If pressure
is rising between 160 psig (1103 kPa) and 260 psig
(1793 kPa), fans 3 and 4 are off. If pressure is reducing
from 260 psig (1793 kPa) to 160 psig (1103 kPa) fans 3 and
4 are on. With respect to the air temperature switch control
on the 074 and 084 condensers, below 70 ± 3° F
(21.1 ± 1.7° C) outdoor ambient, fans 5 and 6 are off; above
80 ± 3° F (26.7 ± 1.7° C) fans 5 and 6 are on. Between
70 F (21.1 C) and 80 F, (26.7 C) whether fans 5 and 6 are
on or off depends on whether temperature is rising or fall
ing. If the temperature is rising from 70 F (21.1 C) to 80 F
(26.7 C), fans 5 and 6 are off. If the temperature is falling
from 80 F (26.7 C) to 70 F (21.1 C), fans 5 and 6 are on.
TOP OF VENTURI
ON FAN DECK
TOP OF VENTURI
ON FAN DECK
L
HUB
ALL 50-Hz
UNITS
ALL 60-Hz
UNITS
Lubrication — Fan motors have permanently lubricated
bearings.
Head Pressure Control — Reduce condensing capac
ity under low ambient temperature conditions. See Fan
Cycling section below.
FAN CYCLING — Efficient operation of evaporator ther
mostatic expansion valves require a 90 F (32 C) minimum
saturated condensing temperature when compressors are op
erating at 100% capacity, 80 F (27 C) for 75% compressor
capacity, and 70 F (21 C) for 50 and 25% compressor
capacity.
The capacity of an air-cooled condenser increases with
increased temperature difference (defined as entering satu
NOTE: Fan rotation is ciockwise as viewed from top of unit
Fig. 27 — Condenser Fan Adjustment
29
Page 30

UNIT
COIL
No. of Ckts
Cap. (% Ckt)
REFRIGERANT
Min Chg/Ckt
Oper Chg/Ckt
Vol/Ckt
STORAGE CAPACITY
R-12
R-22
R-500
R-502
R-134A
Table 6 — Condenser Coil Refrigerant Circuit Data
09DK054 09DK064
2 2
34 16
7 51
16 53
8.83
19.45
013
0.46
13 46
29.64
12.31
27.11
11.61
25.56
12.89
28.37
13.46
29 64
3.61
7.64
4 08
8.99
0 21
6 22
13 69
5.69
12 52
5 36
11.81
5.95
13.11
6.22
13.69
006
kg
lb
kg
lb
cu ft
kg
lb
kg
lb
kg
lb
kg
lb
kg
lb
2
50
10.98
24.17
12 92
28 44
019
0.68
19.67
43.33
18 00
39.63
16.97
37.37
18.84
41.48
19.73
43.33
1
66
14 45
31 81
17.00
37.42
.025
0.89
25.90
57.02
23.69
52.16
22.34
49 16
24.79
54.59
25.9
57 02
2
50
16.48
36.28
19.38
42.68
029
1.01
29.19
64.28
26.77
58.94
25.09
55 24
27.89
61.40
29.19
64 28
1 2
66 34
21.68
47.74
25.51
56 17
.037
1.32
38.42
84 59
35 23
77 56
33.02
72 70
36.70
80.80
38.42
84 59
11.27
24.81
13.26
29.19
.02
0.69
19 97
43.97
18 31
40 31
17.16
37.78
19.08
42.00
19.97
43 97
2
16
5.21
11.46
6.13
13.49
.009
0.32
9.22
20.31
8.46
18 62
7.93
17 46
8.81
19 40
9 22
20 31
UNIT
COIL
No. of Ckts
Cap. (% Ckt)
REFRIGERANT
Min Chg/Ckt
Oper Chg/Ckt
Vol/Ckt
STORAGE CAPACITY
R-12
R-22
R-500
R-502
R-134A
NOTE: Storage capacity calculated for 80% liquid,
kg
lb
kg
lb
cu ft
kg
lb
kg
lb
kg
lb
kg
lb
kg
lb
2
50
15 91
35.04
18.73
41.23
.028
0 97
28.53
62.82
26.10
57 46
24 61
54.18
27 31
60 14
28.53
62.82
1
68
21.61
47.58
25 43
55 98
037
1 32
38.74
85.30
35 44
78.03
33.42
73 58
37.09
81.66
38.74
85.30
09DK074
10.22
22.50
26.47
36.89
2
32 18
12.02
.018
0 62
18.32
40.33
16.75
15 80
34 78
17.54
38 61
18.32
40.33
2
5.70
12 54
6.70
14.76
.010
0.35
10.21
22.49
9 34
20.57
8.81
19 40
9.78
21.53
10.21
22.49
2 1
50
23 87
52 22
28.08
61.83
.041
1.46
43.26
95.25
39.51
87.00
37.24
82.00
41.33
91.00
43.26
95.25
09DK084
67 33
31.84
70.11
37.46
82.48
.055
1.95
57.63
127 00
52.68
116 00
49.65
109.33
55.11
121.33
57.68
127.00
2
15.90
35.00
18.70
41.18
.028
0.97
28 84
63 50
26.34
58.00
24.83
54 67
27 55
60.67
28.84
63.50
2
17
7.97
17.55
9.39
20 65
.014
0 49
14.42
31.75
13.17
29 00
12 41
27 33
13.78
30.33
14.42
31.75
30
Page 31

Table 7 — Minimum Outdoor-Air Operating
Temperature
English
COMPRESSOR CAPACITY (%)*
TD
100 1 75 1 50 1 25
°F
30
25
20
30
25
20
30
25
20
Minimum Outdoor-Air
Temperature ° F
29
38
47
12
22
-20 -20
31
34
40
47
19
25
38
42
46
22
29
36
-20
31
-20
51
53
56
43
47
51
09DK—
All
Sizes
054,
064
074,
084
HEAD
PRESSURE
CONTROL
FCPSs and
Motormaster®
III
FCPSst
2 Fans
FCPSst
2 Fans
ATSs
2 Fans
SI
HEAD
All
064
084
PRESSURE
CONTROL
FCPSs and
Motormaster
III
FCPSst
2 Fans
FCPSst
2 Fans
ATSs
2 Fans
LEGEND
09DK—
Sizes
054,
074,
ATS — Air Temperature Switch
FCPS — Fan Cycling Pressure Switch
TD — Temperature Difference = Saturated Condensing
'Interpolation permitted.
tAdditional FCPSs needed for 67/33, 33/33/33, and 33/33/17/17%
capacity split applications
NOTES:
1. Fans or the 09DK054-084 units are controlled by ATSs and FCPSs.
2 Minimum outdoor temperatures are determined for indoor and out
Temperature Entering - Entering-Air Temperature
See Table 8 for more details.
door unit combinations of the same capacity.
COMPRESSOR CAPACITY (%)*
TD
100 1 75 1 50 1 25
°C
Minimum Outdoor-Air
Temperature ° C
16.7
13.9
11 1
16.7
139
11 1
167
139
11 1
-29
-11
-29 -29 -29
-2
3
8
-6
-1
1
4
8
-7
-4
-1
11
3
6
12
8
13
-6
-2
2
6
8
11
Table 8 — Fan Cycling Controls Temperature/
Pressure Settings
English
UNIT 09DK—
054,064
074,084
FCPS
OPENS AT 160
±10 psig
CLOSES AT 260
±15 psig
FM 3,4'
FM 3,4'
CLOSES AT 80 ± 3° F
ATS
OPENS AT 70 ± 3° F
—
FM 5,6t
SI
FCPS
UNIT 09DK— ± 69 kPa OPENS AT 21.1 ± 1.7°C
054,064
074,084 FM 3,4*
ATS — Air Temperature Switch
FCPS — Fan Cycle Pressure Switch
FM — Fan Motor
'Fan motors 3 and 4 are each controlled by a FCPS for 100 and
50/50% capacity split applications. For other capacity split options,
the accessory fan control kit must be used and additional FCPS's
are required. See accessory fan control kit installation instructions
for more information
fFan motors 5 and 6 are each controlled by an ATS.
OPENS AT 1103 ATS
CLOSES AT 1793
± 103 kPa
FM 3,4*
LEGEND
CLOSES AT 26.7 ± 1.7° C
FM 5,6t
...
31
Page 32

PACKAGED SERVICE TRAINING
Our packaged service training programs provide an excellent way to increase your knowledge of the
equipment discussed in this manual. Product programs cover:
• Unit Familiarization • Maintenance
• Installation Overview • Operating Sequence
A large selection of product, theory, and skills programs is available. All programs include a video
cassette and/or slides and a companion booklet. TJse these for self teaching or to conduct full training
sessions.
For a free Service Training Material Catalog (STM), call 1-800-962-9212. Ordering instructions are
included.
Copyright 1993 Carrier Corporation
Book 12 PC 111 Catalog No. 530-953 Printed in U.S A. Form 09DK-4SI Pg 32 4-93 Replaces: New
Tab 4a
Manufacturer reserves the right to discontinue, or change at any time, specifications or designs without notice and without incurring obligations.
 Loading...
Loading...