
Graphic Color Printer

Copyright ©2003 Canon Inc. all rights reserved.
• Unauthorized transfer or duplication of all or any part of this document is prohibited.
• The content of this document is subject to change without notice.
• Every effort has been made to ensure that the information contained in this guide is
correct. If any error or omission is found, contact us directly or an authorized Canon
representative.
• Canon is not responsible for any damages, direct or indirect, arising from or related to
the use of this printer.
Trademarks
• Canon and the Canon logo are registered trademarks of Canon Inc.
•Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or other countries.
• Apple, AppleTalk, EtherTalk, LocalTalk, and Macintosh are trademarks of Apple
Computer, Inc., in the U.S.A.
• IBM is a trademark of the IBM Corporation in the United States.
• HP is a trademark of Hewlett-Packard, Inc.
• NetWare and Novell are registered trademarks of Novell, Inc. in the United States and
other countries. NDS, NDPS, NLM, and Novell Client are trademarks of Novell, Inc. in
the United States.
• LASER5 is a trademark of LASER5 Corporation.
• Ethernet is a trademark of the Xerox Corporation in the United States.
• Sun, Sun Microsystems, and SunOS are trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the
United States and other countries.
• Adobe and Acrobat are trademarks of Adobe Systems, Inc.
• UNIX is a registered trademark, licensed independently by X/Open Company, Ltd. in
the United States and in other countries.
• Linux is a trademark of Linus Torvalds.
• TurboLinux is a trademark of TurboLinux, Inc.
• Netscape, Netscape Communicator, and Netscape Navigator are trademarks of
Netscape Communications Corporation.
• Red Hat is a trademark of Red Hat Software of the United States.
• Other brand and product names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective companies.
®
, Windows®, Windows NT® and MS-DOS® are registered trademarks of

Notations About Text
Conventions
To ensure the safe and most efficient use of this printer, important
information is provided under the headings listed below. Before you use this
guide, make sure that you understand what these headings mean and
remember the important information described under these headings.
Warning
z Failure to follow these instructions could result in fatal or serious injury.
Always remember and follow the guidelines and advice described under
this heading to ensure your own safety and the safety of other people
working around the printer.
Caution
z Failure to follow these instructions could lead to mistakes in the use of
printer and result in minor injury or serious damage to the printer. Always
remember and follow the guidelines and advice described under this
heading to ensure safe use of the printer.
Important
z Instructions and guidelines for operation of the printer provided under this heading
describe restrictions and other important information which if ignored could cause
minor damage to the printer or other equipment or result in the loss of valuable
data. Always remember and follow the guidelines and advice under this heading to
avoid mistakes in procedure.
Note
z Information under this heading includes tips and hints that will help you avoid
minor problems and use the printer more efficiently.
i
Screen Examples
The screenshots provided as examples in operational procedures may be
slightly different, depending on the operating system in use.
A button or item to press or select in a procedure appears enclosed with a
circular mark in the screen sample. If a procedure requires more
than one button press or selection, all the items are marked, so be sure to
select them as described in the procedure.
3
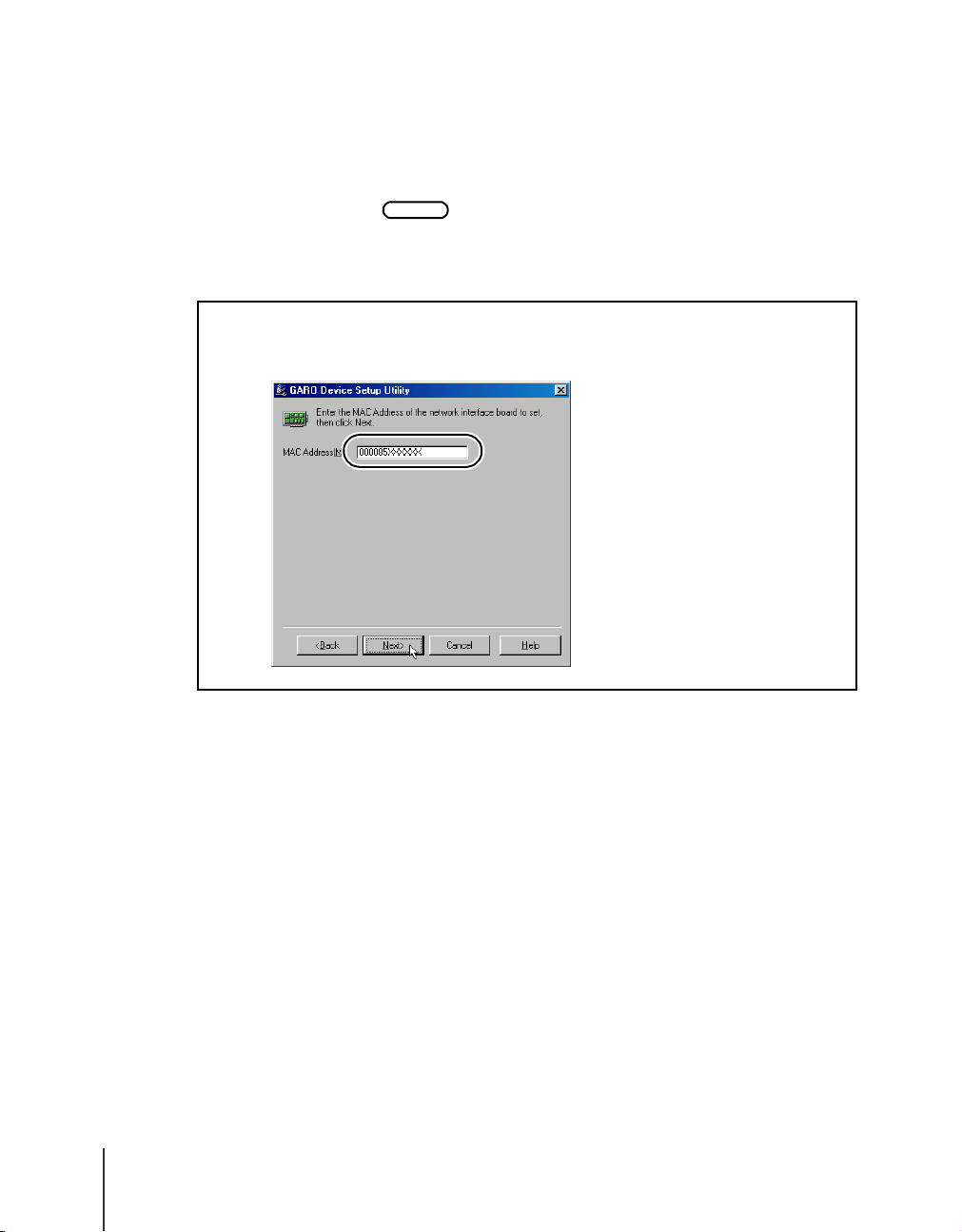
Enter the MAC address into the MAC Address box then click the Next
button.
ii

Abbreviations
Throughout this document the following abbreviations are used in text.
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
•Microsoft
• The term “GARO”, used in the name of this printer driver, is an acronym
Legal Notice
• It is illegal to reproduce currency, bills, negotiable securities and other
®
Windows® Millennium Edition is abbreviated as “Windows
Me”
®
Windows® 98 is abbreviated as “Windows 98”
®
Windows® 95 is abbreviated as “Windows 95”
®
Windows® XP is abbreviated as “Windows XP”
®
Windows® 2000 is abbreviated as “Windows 2000”
®
Windows NT® is abbreviated as “Windows NT”
®
Windows® is abbreviated as “Windows”
for “Graphic Arts Language with Raster Operations”, a printer language
of creating raster images.
documents prohibited by law. Reproduction of such items may be subject
to criminal prosecution.
• It is illegal to reproduce legal certificates, licenses, travel tickets, and
certain public and private documents prohibited from reproduction by
law. Reproduction of such items may be subject to criminal prosecution.
• Please note that intellectual property protected by copyright may not be
reproduced without the express permission of the copyright holder
except for personal or household use under limited circumstances.
iii

Contents
Notations About Text . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . i
Conventions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . i
Screen Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .ii
Abbreviations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iii
Legal Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iii
Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . iv
Chapter 1 Before You Begin
Required System Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
System Environment Required for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Using a TCP/IP Network for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Using a NetWare
Using a NetBIOS Network for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Using an AppleTalk Network for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
The Network Environment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Windows Network Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Windows Me, Windows 98, or Windows 95 Computers Only . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows NT Computers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-5
UNIX Server or Linux Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-6
®
NetWare
Macintosh Network Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Example of a Network with Mixed Computers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-8
®
Network for Printing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-7
Chapter 2 TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
Procedures Required for a TCP/IP Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
Setting the Printer IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
Setting the IP Address with GARO Device Setup Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
Setting the IP Address with the ARP/PING Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Setting the IP Address with the Printer Operation Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Setting TCP/IP Protocol for the Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
Setting TCP/IP Protocol with a Web Browser (Remote UI) . . . . . . . . . . . 2-9
Setting TCP/IP Protocol with FTP Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Setting the Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Settings for LPD/RAW Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Windows Me, Windows 98, Windows 95 LPD Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Windows XP, Windows 2000 RAW Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-21
Windows NT 4.0 LPD Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
UNIX LPD Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-26
IPP Connection Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
Windows Me, Windows 98, Windows 95 IPP Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
Windows XP, Windows 2000 IPP Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-29
Setting the Printer for Sharing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-31
Managing the Printer from a Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
Managing the Printer with a Web Browser (Remote UI) . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
Managing the Printer with an FTP Client . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
iv

Managing the Printer with E-mail Notification . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-34
Setting Up the E-mail Notification Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-35
Chapter 3 AppleTalk Network Settings (Macintosh)
Procedures Required for an AppleTalk Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Setting a Macintosh . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Setting the Network Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Mac OS 8.6/9.x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Mac OS X . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Setting the Printer Protocols . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-5
Installing the Printer Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
Chapter 4 NetWare® Settings (Windows)
Procedures Required for a NetWare® Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Setting the Printer Frame Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Setting the frame type with GARO Device Setup Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Setting NetWare® Print Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Types of Print Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Setting Up a NetWare
Using NDS Queue Server Mode/Remote Printer Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Using Bindery Queue Server Mode/Remote Printer Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Setting NetWare® Printer Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
Setting the Computer for NetWare
Connecting to a NetWare® Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-17
Installing the Printer Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-17
Setting the Printer Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-17
®
Server with NWADMIN and PCONSOLE . . . . . 4-8
®
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-17
Chapter 5 NetBIOS/NetBEUI Network Settings (Windows Me/
Windows 98/Windows 95)
Procedures Required for a NetBIOS/NetBEUI Network . . . . . . . . 5-2
Windows Settings for a NetBIOS/NetBEUI Network . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
NetBIOS/NetBEUI Network Connection Methods . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Installing the Printer Driver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Setting the Printer Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting
When You Cannot Use GARO Device Setup Utility . . . . . . . . . . . 6-2
When You Cannot Print . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6-3
Chapter 7 Other Important Information
Initializing Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
List of Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
v

General Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-3
TCP/IP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
®
NetWare
NetBIOS Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
AppleTalk Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-7
Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Software Applications that Use Network Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-8
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
vi
1
Before You Begin
This chapter describes the network, network environment, and
other important information that you should confirm before
you begin.

Required System Environment
This section describes the system environments that are supported by the
network interface board of the printer.
System Environment Required for Printing
The lists below describe the system environments required to support the
network in use.
Using a TCP/IP Network for Printing
z Compatible Operating Systems:
• Windows Me/Windows 98/Windows 95
• Windows NT 4.0
• Windows 2000
• Windows XP
• Solaris Version 1.1.x (SunOS Version 4.1.x) or later
• Solaris Version 2.5.x (SunOS Version 5.5.x) or later
• HP-UX Version 10.x or later
• IBM-AIX Version 4.x or later
• Red Hat Linux 5.2 or later
• Turbo Linux 3.0 or later
Before You Begin
1-2
z Compatible Computers:2
• IBM PC or IBM compatible PC
Important
z If you are using Windows NT 4.0, install Service Pack 6 or later.
Using a NetWare® Network for Printing
z Compatible Servers:
• Novell NetWare
z Compatible Clients:
• Windows Me/Windows 98/Windows 95
• Windows XP Professional
• Windows 2000 Server
• Windows 2000 Professional
• Windows NT Server 4.0
• Windows NT Workstation 4.0
z Compatible Computers:
• IBM PC or IBM PC compatible PC.
®
Version 4.2/5.1

Using a NetBIOS Network for Printing
z Compatible Operating Systems:
• Windows Me, Windows 98, Windows 95
z Compatible Computers:
• IBM PC or IBM PC compatible PC.
z Required Memory:
• 16MB or more
Important
z If you are using Windows NT 4.0, install Service Pack 6 or later.
Using an AppleTalk Network for Printing
z Compatible Computer
• A Macintosh Series computer equipped with a Power PC processor.
z Compatible Operating Systems
• Mac OS 8.6 or later
• Mac OS x 10.1 or later
z Compatible AppleTalk
• EtherTalk Phase 2
Note
z Required Memory
• 24 MB or more for Mac OS 8.6, 32 MB or more for Mac OS 9
z This printer is not compatible with a Macintosh LocalTalk Network.
Required System Environment
1-3
The Network Environment
Use the diagrams below as reference to determine the type of network where
the printer is connected, and then follow the required procedure.
Windows Network Examples
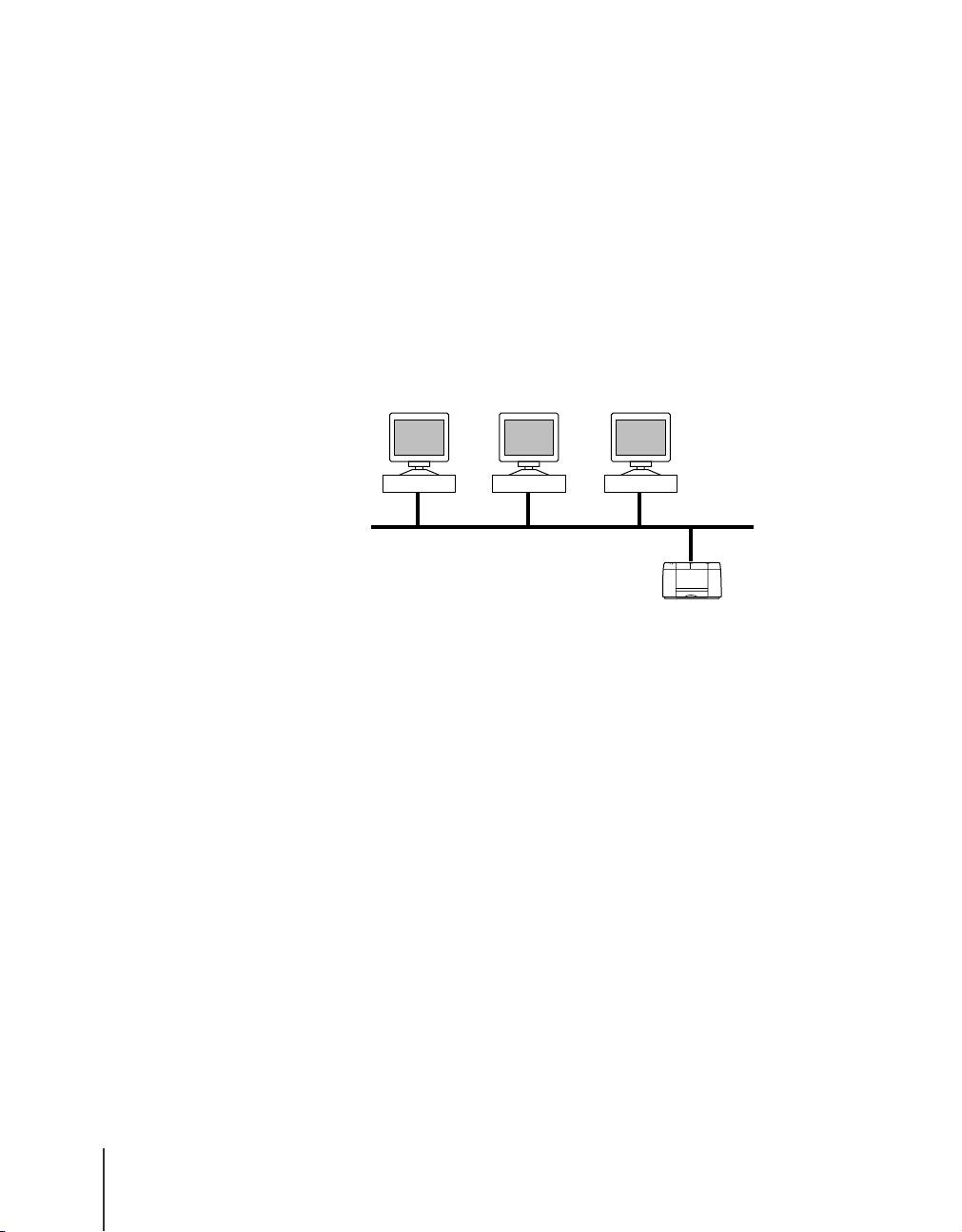
Windows Me, Windows 98, or Windows 95 Computers Only
If the network is like the network environment shown in the illustration
below, you can print with a few simple settings if you use NetBIOS protocol.
By installing Canon LPR Port on each computer, you can also use TCP/IP
protocol.
Windows 98 Windows 95
NetBIOS, TCP/IP
Refer to the following pages for details about the protocols to use.
Windows Me
W2200
Before You Begin
1-4
• Chapter 2 TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
• Chapter 5 NetBIOS/NetBEUI Network Settings (Windows Me/Windows
98/Windows 95)
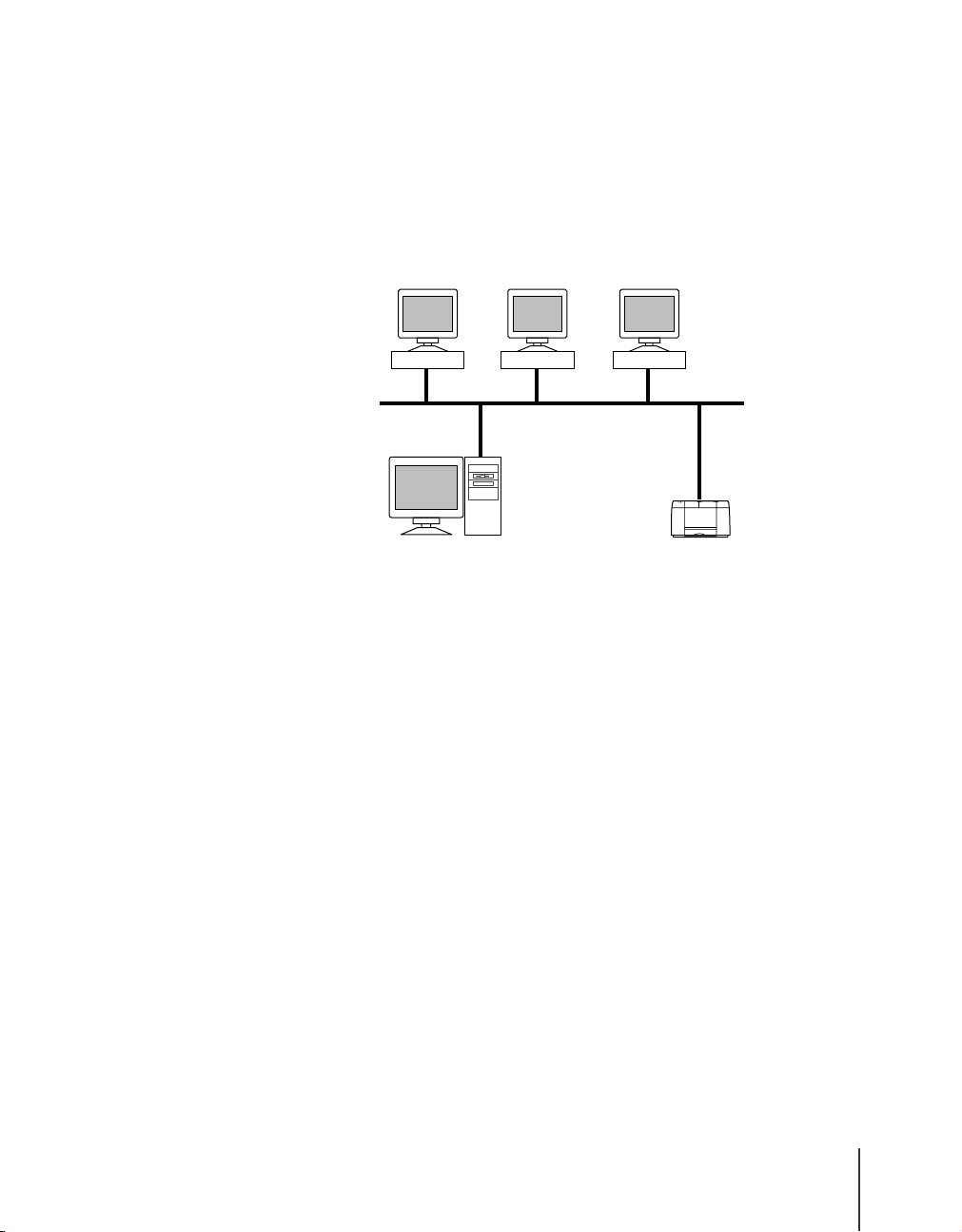
Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows NT Computers
If the network is like the network environment shown in the illustration
below, you can print using the TCP/IP protocol. Computers with Windows
XP, Windows 2000, or Windows NT can use the TCP/IP functions of the
operating system to print. By installing Canon LPR Port on each computer
using Windows Me, Windows 98, or Windows 95, you can also use Canon
LPR port to print.
Windows 98 Windows 95
Windows NT
TCP/IP
Windows 2000
W2200
Refer to the following pages for details about setting procedures.
• Chapter 2 TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
If Windows XP or Windows 2000, Windows NT are used on the network,
you can manage the network printer efficiently by setting up a print server.
For more details about how to set up a print server, see the following section.
• Chapter 2 Setting the Printer for Sharing (Æ P.2-31)
The Network Environment
1-5
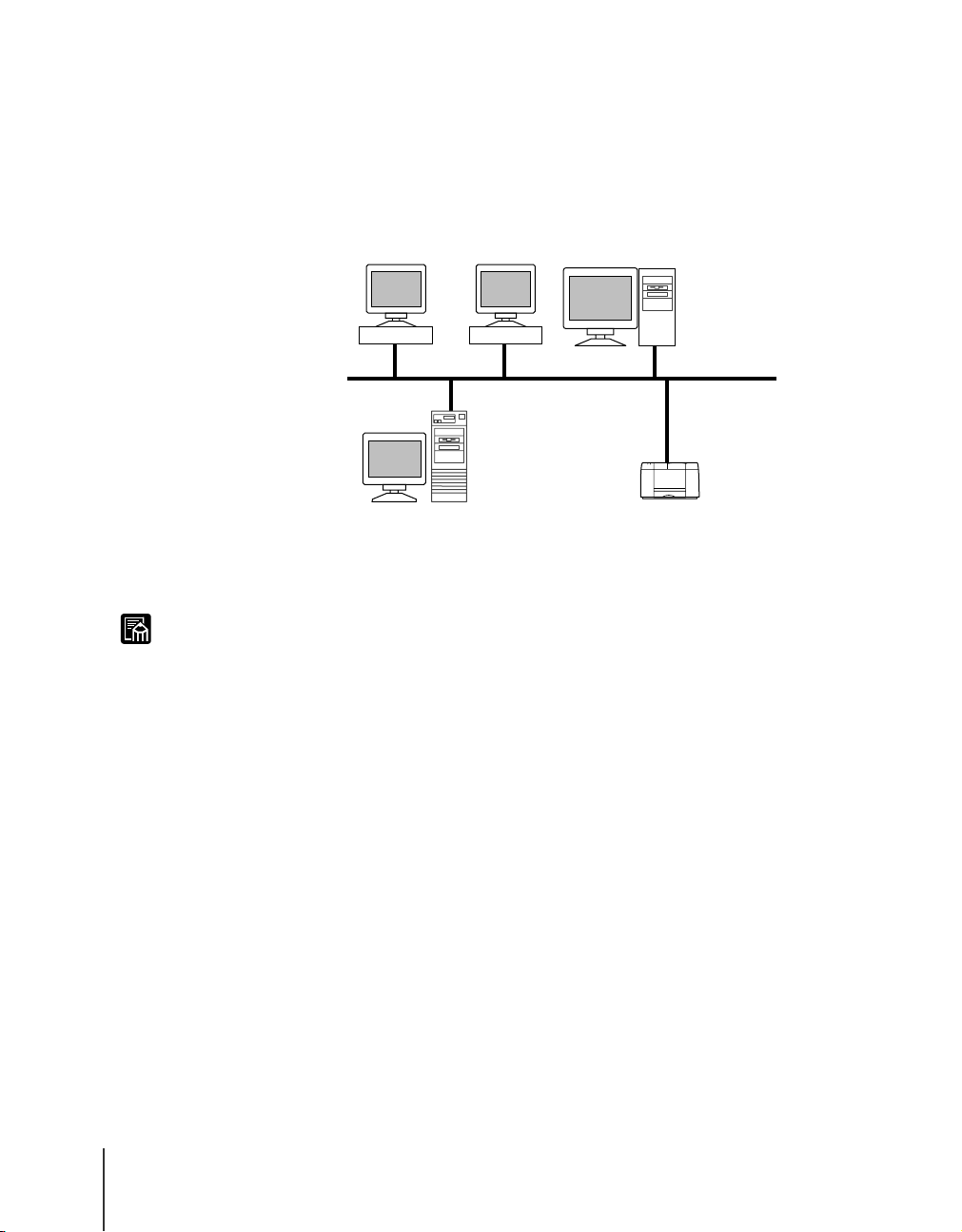
UNIX Server or Linux Server
If the network is like the network environment shown in the illustration
below, you can print using TCP/IP protocol. If you print through a UNIX or
Linux server set up as a print server, then the Windows computer can be
released from print job processing much earlier, thus increasing the
efficiency of your system.
Windows 98
Windows 95
TCP/IP
Windows 2000
Note
UNIX Server
W2200
Refer to the following pages for details about setting procedures.
• Chapter 2 TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
z You cannot print directly from a computer running UNIX or Linux.
z You can use NetBIOS in common even in a network environment where there is a
UNIX or Linux computer. In such a case, perform the settings for the protocol to
use.
Before You Begin
1-6
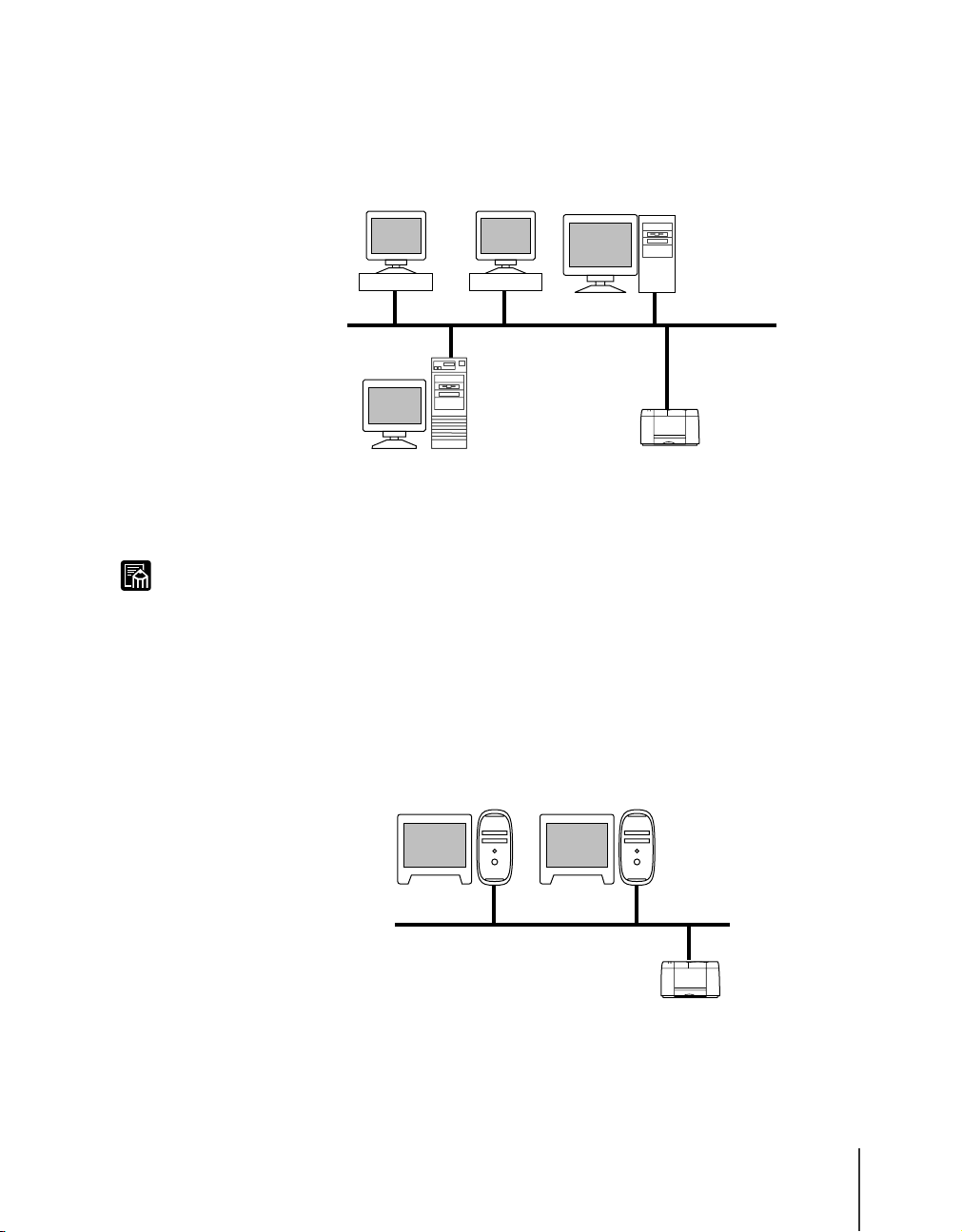
NetWare® server
Note
If the network is like the network environment shown in the illustration
below, you can print using NetWare
®
protocol. NetWare® client software
must be installed on every server computer and client computer.
Windows 98
NetWare
®
Windows 95
Server
Windows 2000
NetWare
®
W2200
Refer to the following pages for details about setting procedures.
• Chapter 4 NetWare
z You can use TCP/IP, AppleTalk or NetBIOS in common even in a network
environment where there is a NetWare
for the protocol to use.
®
Settings (Windows)
®
server. In such a case, perform the settings
Macintosh Network Examples
For a Macintosh computer, the AppleTalk (EtherTalk) protocol is used.
Macintosh
Refer to the following pages for details about setting procedures.
• Chapter 3 AppleTalk Network Settings (Macintosh)
Macintosh
AppleTalk
W2200
The Network Environment
1-7
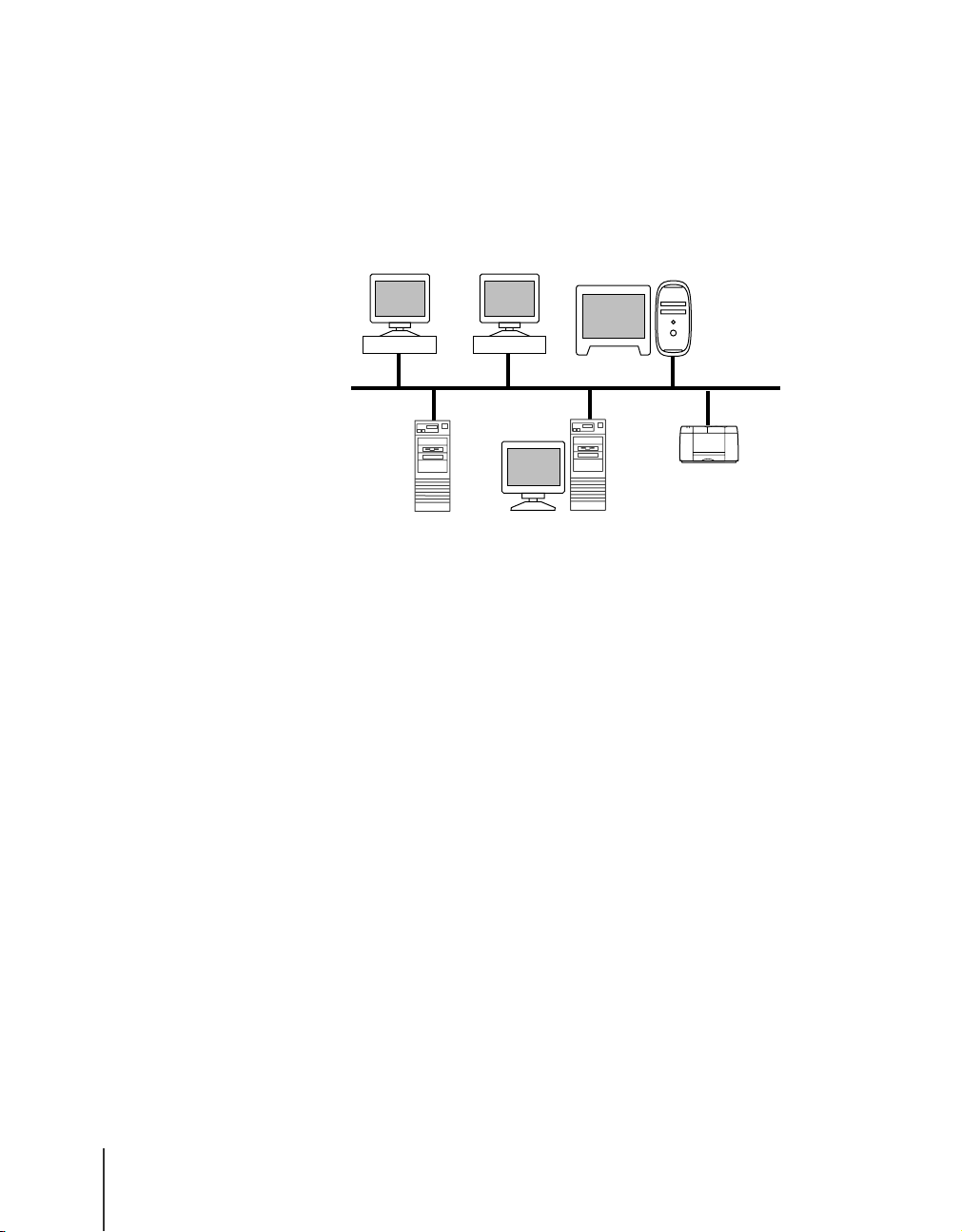
Example of a Network with Mixed Computers
When different computers are used on the same network, the appropriate
procedure must be performed for each computer.
For example, if a Windows 95 and Macintosh are used together, the settings
described above “Windows Network Examples” and “Macintosh Network
Examples” must be performed for each computer.
Windows 98
Windows 95
Macintosh
W2200
Netware Server
Windows 2000
Refer to the following pages for details about protocols.
• Chapter 2 TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
• Chapter 3 AppleTalk Network Settings (Macintosh)
• Chapter 4 NetWare
®
Settings (Windows)
Before You Begin
1-8
2
TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
This chapter describes the setting methods and procedures for
connecting the printer to a TCP/IP network.

Procedures Required for a TCP/IP Network
Here is a summary of the procedure required to set the printer for use on a
TCP/IP network.
1
Connect the network cable ÆSetup Guide
Follow the instructions in the Setup Guide to connect the network cable.
2
Setting the Printer IP Address ÆP. 2 - 3
Setting the IP address allows setting the printer protocol to enable communication between the
printer and the computer. You can use one of the methods below to set the protocol:
• GARO Device Setup Utility (Canon software application provided with the printer)
• ARP/PING command
• Printer operation panel
3
Setting TCP/IP Protocol for the Printer ÆP. 2 - 9
This procedure selects TCP/IP for the printer protocol. You can use one of the methods below to
set the protocol from the computer.
• Web Browser (Remote UI)
• FTP Client
4
Setting the Computer ÆP. 2 - 1 7
This procedure is performed for each computer to be used for printing.
Important
TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
2-2
z Steps 1, 2, and 3 should be performed by the network system administrator.
z The following print applications can be used to print on a TCP/IP network: LPD,
FTP, RAW (Windows XP, Windows 2000), and IPP (Windows XP, Windows 2000,
Windows Me, Windows 98, Windows 95)

Setting the Printer IP Address
Before setting the printer protocol, you must set the IP address to enable
communication between the printer and the computer. You can use one of the
methods below to set the IP address. Use whichever method is easiest:
• GARO Device Setup Utility (Æ P. 2 - 4 )
• ARP/PING command (Æ P. 2 -6 )
• Printer operation panel (Æ P. 2- 7 )
Important
z When you use the GARO Device Setup Utility to perform the printer network
settings, the subnet mask and gateway address settings are set to 0.0.0.0, so use the
Remote UI or printer operation panel to make the settings for your network.
z If you are using an operating system that is not compatible with the GARO Device
Setup Utility, use another computer on the network, use the ARP/PING command,
or use the printer operation panel to perform the settings.
z The GARO Device Setup Utility must be installed on your computer in order to
use this utility to make the settings. Ask your system administrator to install the
GARO Device Setup Utility on your computer. (Æ Setup Guide)
z Before setting the IP address, confirm that the printer is switched on and connected
to the network.
z The MAC address is required to perform the setting with the GARO Device Setup
Utility or the ARP/PING command. If you need to confirm the MAC address, use
the printer operation panel to print a Status Print or Ext. I/F Print.
1. Press the Online button. The Online lamp switches off.
2. Press the Cancel Job/Utility button.
3. Press or to select Status Print or Ext. I/F Print then press .
z Before setting the IP address, confirm that the printer is switched on and connected
to the network.
z If you are using a DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP server where the IP address is
acquired automatically, use the printer operation panel to select “Automatic” for
the “IP Mode” setting, then select ON for the server in use.
z If you are using a DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP server, selecting the IP address for the
printer is not required. However, the IP address changes every time the printer is
powered on, so in order to access the printer every time the printer is switched on,
the IP address must be checked by Status Print or Ext. I/F Print.
Setting the Printer IP Address
2-3
Setting the IP Address with GARO Device Setup Utility
If you are using Windows, use the GARO Device Setup Utility, the software
utility provided with the printer, to perform the printer network settings.
Note
z If you are using a Macintosh computer, use the printer operation panel to perform
the settings. (Æ Setup Guide)
1
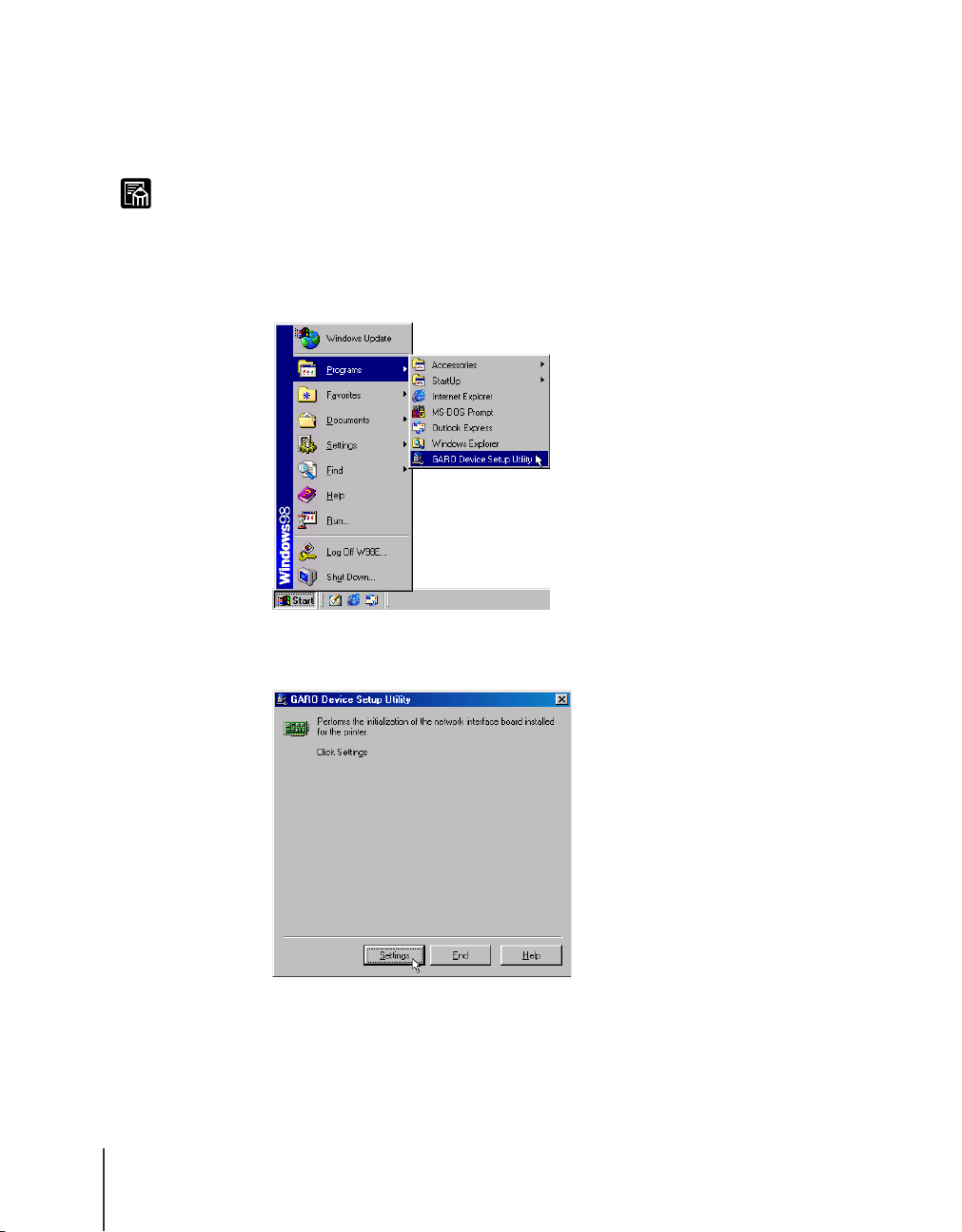
On the desktop, click the Start button, point to Programs, then click
GARO Device Setup Utility.
TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
2-4
2
Click the Settings button.
3
Important
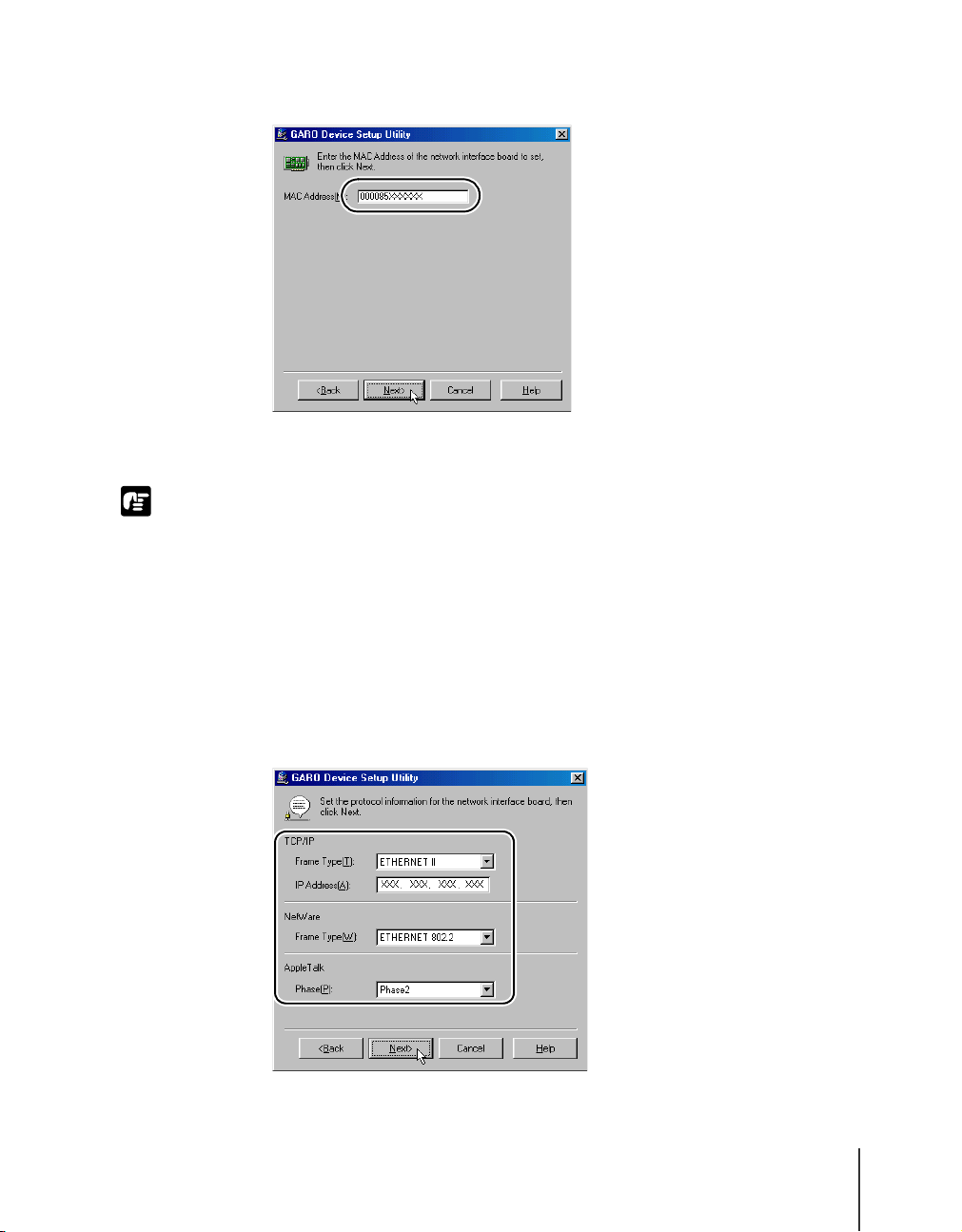
Enter the MAC address into the MAC Address box then click the Next
button.
The utility searches for the printer on the network and when the printer is
found, the protocol settings dialog box opens.
z If the printer cannot be found, make sure that the computer and the printer are in
the same subnet. If you use the GARO Device Setup Utility to perform the settings,
you must make the settings from a computer in the same subnet as the printer.
4
For the TCP/IP Frame Type, select ETHERNET II from the list, enter
the IP address allocated for the printer into the IP Address box, then
click the Next button.
When printing via AppleTalk, select Phase2 for AppleTalk Phase. When
printing with NetWare
®
, select the frame type in use for Frame Type.
Setting the Printer IP Address
2-5

5
Confirm the settings then click the Finish button.
The network interface settings are changed.
Note
z The subnet mask and gateway address settings have been set to 0.0.0.0. After
completing the above settings, use the Remote UI or the printer operation panel to
perform the subnet mask and gateway address settings for your network. (Æ P. 2 -9 )
This completes preparation for selecting the printer protocol. Now you are
ready to select the printer protocol. (Æ P.2 - 9 )
Setting the IP Address with the ARP/PING Command
The examples of entries and settings below are for the English operating
system.
1
Start at the MS-DOS prompt or command line.
If you are using UNIX, open the Console screen and log on as a super user.
2
Execute the following commands, and add the static entry to the arp
table.
arp -s <IP address> <MAC address>
Note
TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
2-6
IP address:
Set the IP address assigned to the printer. The IP address consists of four
decimal numbers (within the range 0 to 255) separated by dots.
MAC address:
Set the MAC address of the printer. In the MAC address every two numbers
is separated by a hyphen (-). For UNIX the numbers are separated with a
colon (:).
Windows Sample Entry:
arp -s XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX 00-00-85-XX-XX-XX
UNIX Sample Entry:
arp -s XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX 00:00:85:XX:XX:XX
z If you are using IBM-AIX, enter:
arp -s ether <IP address> <MAC address>

3
Execute the following commands to set the IP address in the network
interface board.
For Windows:
ping <IP address> -l 479
For Solaris 1.x/2.x:
ping -s <IP address> 479
For IBM-AIX:
ping <IP address> 479
For HP-UX:
ping <IP address> 487
For Red Hat Linux/LASER5 Linux:
ping -s <IP address> 479
For TurboLinux:
ping -s <IP address> 480
IP address:
Set the same address entered at Step 2.
Windows Sample:
ping XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX -l 479
Note
z The -l entry is the alphabetic lower case “l” (not the number “1”).
z The subnet mask and gateway addresses are set to 0.0.0.0.
This completes preparation for the protocol setting.
Setting the IP Address with the Printer Operation Panel
1
On the printer operation panel, press the Online button. The Online
lamp goes off.
2
Press the Setup button.
3
Press or to select the following items then press .
Set Interface Æ Ext. Network Æ Set TCP/IP Æ Frame Type
Setting the Printer IP Address
2-7
4
Press or to select “Ethernet II” then press .
5
Press or to select “IP Mode” then press .
6
Select the method for setting the printer IP address. Press or to
select either setting below then press .
Automatic:
Select when the IP address is to be set with DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP.
Manual:
Select when the IP address is to be assigned directly for the printer.
7
If “Automatic” was selected at Step 6, press or to select
“Protocol”, press , then select ON or OFF for DHCP, BOOTP, and
RARP.
If “Manual” was selected at Step 6, press or to select “IP
Setting”, press , then select “IP Address”, “Subnet Mask”, or
“Default G/W”.
Note
8
Important
9
10
z Use the following method to select “IP Address”, “Subnet Mask”, or “Default G/
W”:
1. Press or to select the target field then press .
2. Press or to select the desired number then press .
3. Repeat Step 1 and 2 for all fields.
Press 3 times, press or to select Regis. Settings, then press
.
z In order to save the settings done in Step 4 to Step 7, you must execute “Regis.
Settings”. The selected settings will not be enabled unless they are registered with
“Regis. Settings”.
When you see “Execute?” in the operation panel display, press .
When you see “Registered!” in the operation panel display, press the
Online button. The Online lamp lights.
The printer is ready to print.
TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
2-8

Setting TCP/IP Protocol for the Printer
To set the TCP/IP protocol on the computer to be used, you can use one of
the software applications listed below. Use whichever method is easiest:
• Web Browser (Remote UI) (Æ P.2 - 9 )
• FTP Client (Æ P. 2- 15 )
Setting TCP/IP Protocol with a Web Browser (Remote UI)
1
Start the Web Browser, enter the following URL for the Address, then
press the Enter key.
http://<Printer IP address or name>/
Example: http://XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX/
Important
z For the Web Browser, use Netscape Navigator/Communicator 4.04 or later, or use
Internet Explorer 4.01SP1 or later. However, Netscape Navigator Version 6 or later
is not compatible.
z If you are using TurboLinux 4.0, you cannot use Netscape Communicator 4.08 to
set this printer. Use another version of a Web Browser.
z A connection through a Proxy Server cannot be used. If you are using a network
environment with a Proxy Server, use the “Proxies” server setting in the Web
Browser to add the printer IP address to the “Exceptions” text box (the address not
used by the Proxy Server). (Performing this setting may differ, depending on the
network environment.)
z Use the Web Browser to enable JavaScript and Cookie so these features can be
used.
z If more than one Remote UI is being used, then the most recently used settings
remain enabled. Starting and using only one Remote UI at a time is recommended.
Note
z If you have started the Remote UI with the printer name, confirm that the DNS
environment and the board DNS settings are executed correctly.
z If the Raw mode or NetBEUI print history is displayed when the Remote UI starts,
the Document Name and User information cannot be acquired. Therefore, only the
following are displayed: “Unidentified” and Raw TCP” for the Document Name
and User settings in the Raw mode, “Unidentified” and “LSLM_USER” for the
Document Name and User settings for NetBEUI.
Setting TCP/IP Protocol for the Printer
2-9
2
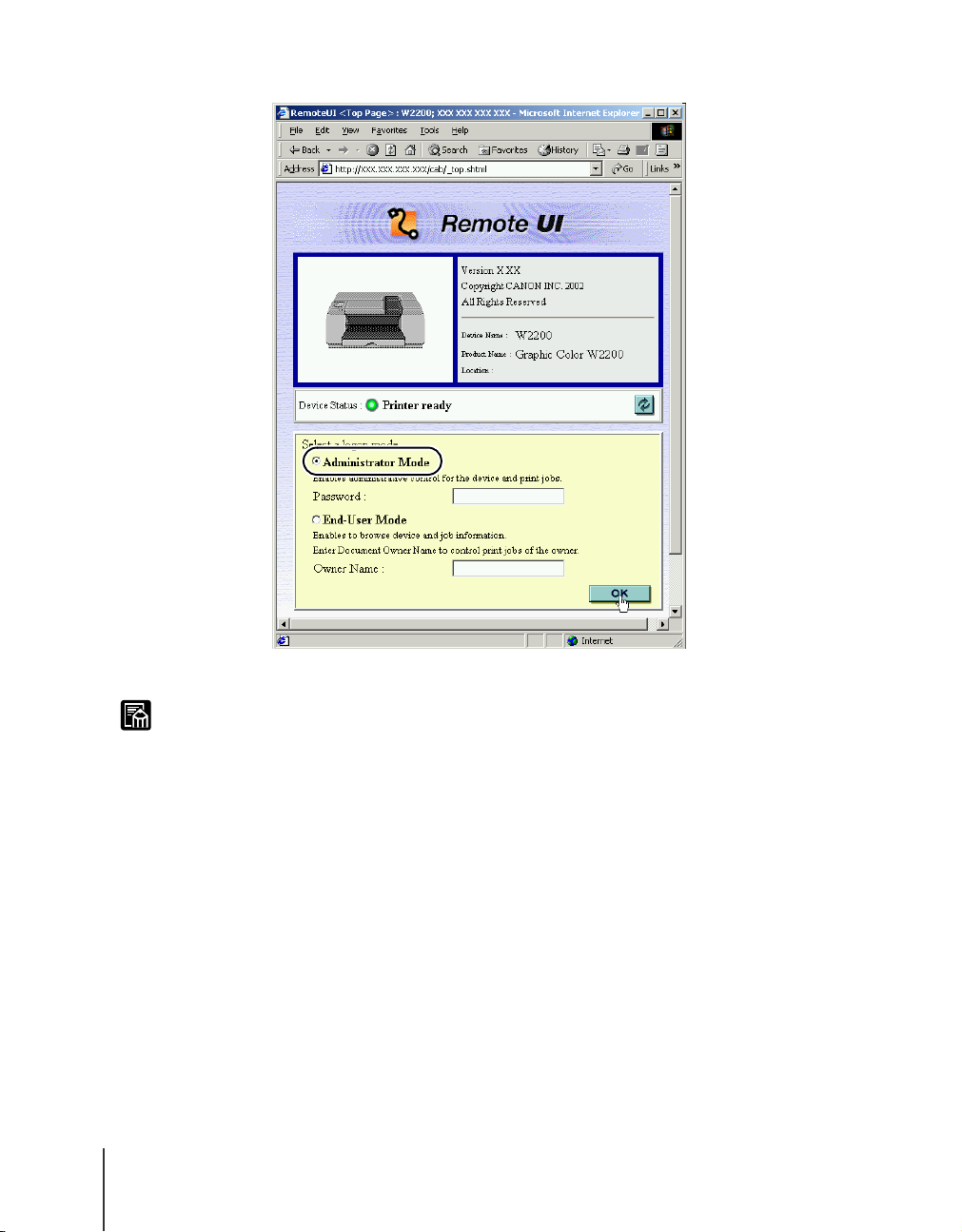
Click and select Administrator Mode then click the OK button.
2-10
The Remote UI starts.
Note
z If a password has been set for the printer, enter the password and click the OK
button. If no password has been set, then a password entry is not required.
TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
3
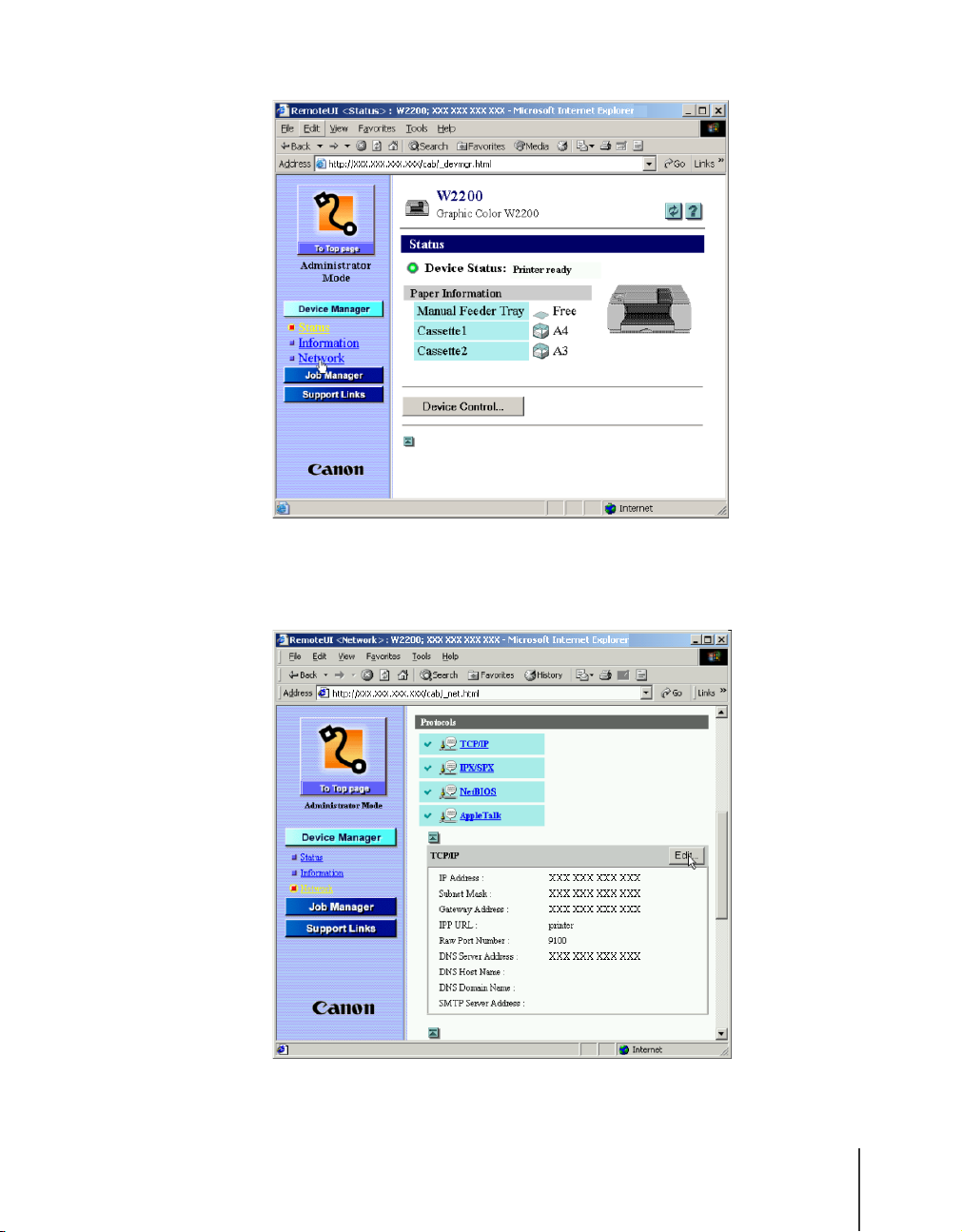
From the Device Manager menu on the left, select Network.
The Network page opens.
4
To the left of TCP/IP, click the Edit button.
The Edit TCP/IP Protocol settings page opens.
Setting TCP/IP Protocol for the Printer
2-11
Note
5
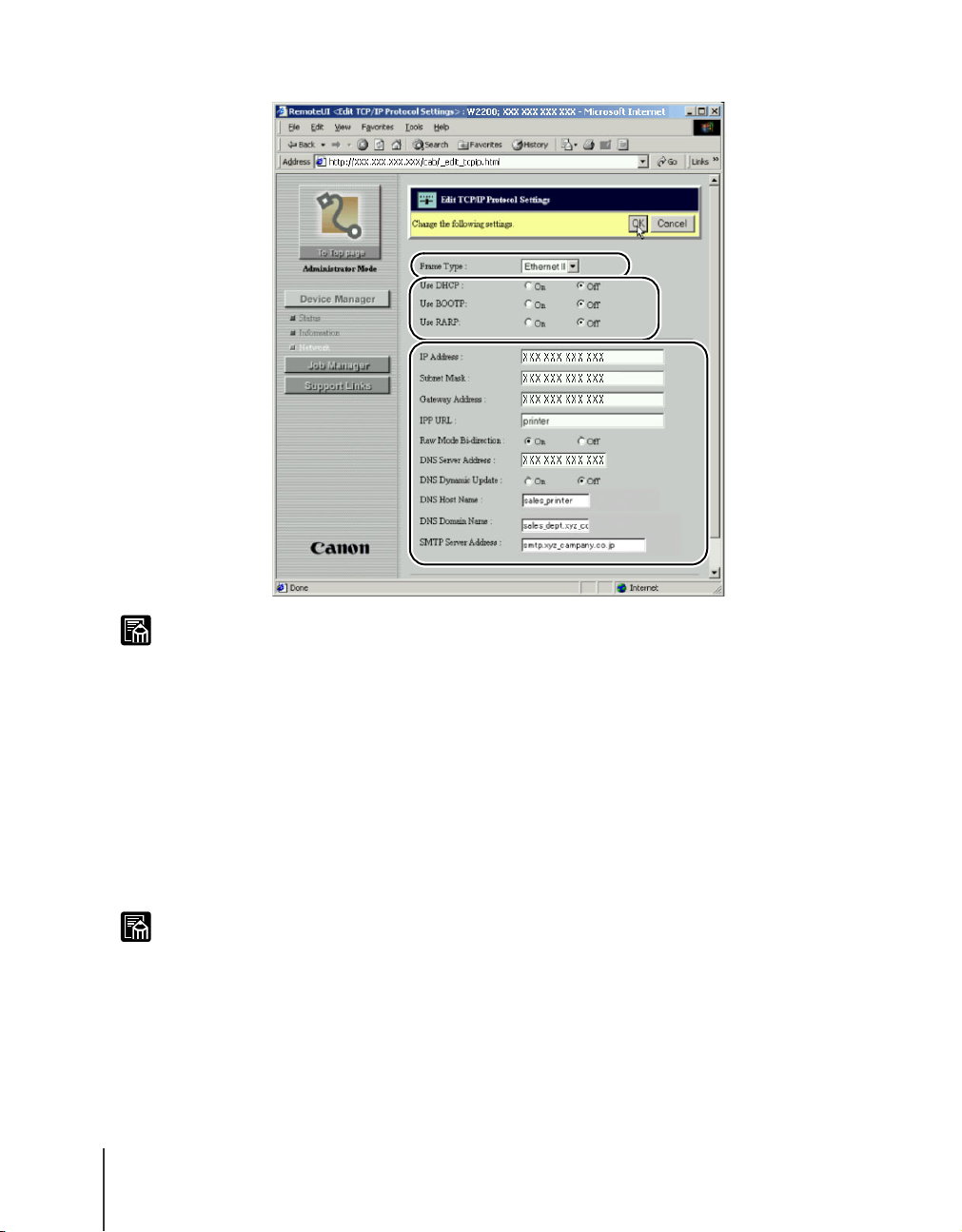
Click the Frame Type list box and select Ethernet II.
z If you select Disabled, the network interface board will no longer be recognized on
the TCP/IP network.
z To use the printer with “Disabled” specified, perform the IP address setting
described in “Setting the Printer IP Address” (Æ P.2 -3 )
2-12
6
Select the method for setting the printer IP address.
To set the IP address, first click all the buttons off.
If the IP address is to be acquired automatically, click on the button for the
method to be used: DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP.
Note
z If you select DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP to select the IP address, make sure that the
IP address can be set by DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP at power on after a reset. After
confirming which setting can be used, the IP address is assigned. If the check box
for DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP is clicked off, the check is not performed with that
function. If none of these methods can be used, perform the IP address setting then
enter the IP address into the “IP Address” text box.
TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)

Note
z The check to determine whether DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP can be used requires
about 1 or 2 minutes to execute. Clicking off the check boxes for a method that
cannot be used is recommended.
z In order to have DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP assign the IP address, the DHCP,
BOOTP, or RARP must be booted.
7
Enter the IP Address, Subnet Mask, and Gateway Address in the
appropriate text box.
For the “IP Address” enter the IP address of the printer. For “Subnet Mask”
and “Gateway Address” enter the settings for the TCP/IP network.
z When using DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP you cannot select more than one. The value
acquired from DHCP, BOOTP, or RARP is used.
8
Below the IPP URL text box, click the Raw Mode Bi-direction button
on. Normally this setting does not need to be changed.
9
Perform the DNS settings.
In the DNS Server Address text box, enter the IP address of the DNS server.
Next, in the DNS Domain Name text box, enter the assigned domain name
of the printer.
Example: sales_dept.xyz_company.co.jp
Note
z DNS can be used for this printer in the following cases:
• When the dynamic update function is enabled by clicking DNS Dynamic
Update on (see Step 10 below).
• After the name of the SMTP server has been specified with the entry in the
SMTP Server Address box (see Step 11 below).
10
When the dynamic update function is used for DNS, click the DNS
Dynamic Update check box on and set the following items:
DNS Host Name: Enter the host name of the printer.
(Example: sales_printer)
DNS Domain Name: Enter the assigned domain name of the printer.
(Example: sales_dept.xyz_company.co.jp)
Setting TCP/IP Protocol for the Printer
2-13

Note
Note
z The DNS dynamic update function automatically registers the printer IP address,
as well as the specified DNS Host Name and Domain Name on the DNS Server.
z This function is used for a DNS server that can be automatically updated, i.e. for a
Dynamic DNS Server.
z By using LPR to set the DNS Host Name and DNS Domain Name, the printer can
be used without a fixed IP address.
11
To have the e-mail function notify the user about the printer status
when paper jams or other problems occur, enter the IP address of the
e-mail server into the SMTP Server Address.
z This setting requires some preliminary detailed settings. (Æ “Managing the Printer
with E-mail Notification”, P.2-34)
12
Press the OK button.
13
From the Device Manager menu on the left, select Network, then click
the Reset button.
The new settings are enabled when the network interface board is re-started.
2-14
This completes the printer protocol settings.
TCP/IP Network Settings (Windows)
 Loading...
Loading...