F-788SG
USER INSTRUCTION
E-IE-444
ENGLISH

Advice and Precautions ............................................................. P.2
How to Use the Slide Cover ...................................................... P.2
Display (2-Line Display) ............................................................. P.3
To Get Start
Power On, Off .......................................................................P.4
Input Capacity ......................................................................P.4
Mode Selection .....................................................................P.5
Display Formals Setting ......................................................P.6
Input Editing .........................................................................P.6
Replay Copy and Multi-statements .......................................P.7
Calculation Stacks ...............................................................P.8
Calculation Accuracy, Input Ranges .....................................P.9
Order of Operations ............................................................P.11
Error Messages and Error Locator...................................... P.12
Before Using the Calculator ...............................................P.13
Basic Calculations
Arithmetic Calculations .......................................................P.14
Memory Calculations ..........................................................P.15
Fraction Operations ............................................................P.16
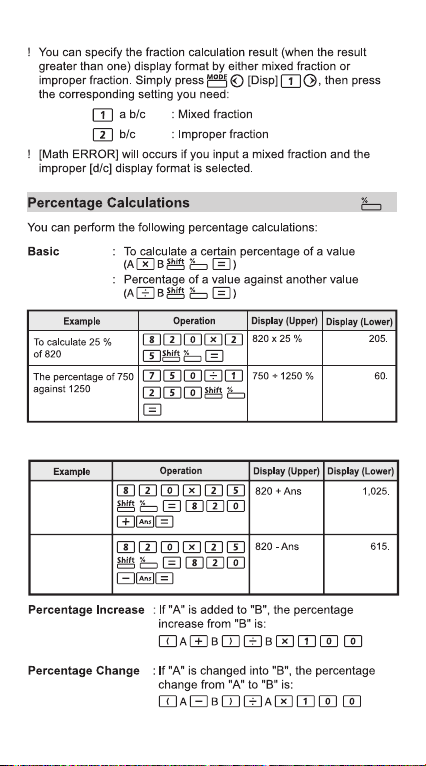
Percentage Calculations .....................................................P.17
Degree-Minutes-Seconds Calculations............................... P.18
Constant Value Calculations............................................... P.19
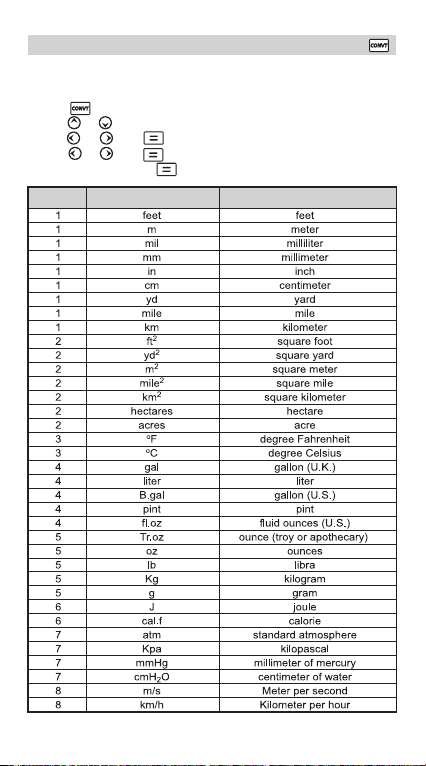
Metric Unit Conversions...................................................... P.23
Engineering Notation Calculations ..................................... P.24
Fix, Sci, Norm, Round ........................................................ P.25
Functional Scientific Calculations
Square, Root, Cube, Cube Root, Power, Power Root,
Reciprocal and Pi................................................................ P.26
Angle Unit Conversion ........................................................P.27
Trigonometry Calculations ..................................................P.27
Logarithm, Natural Logarithm, Antilogarithm and Logab ....P.28
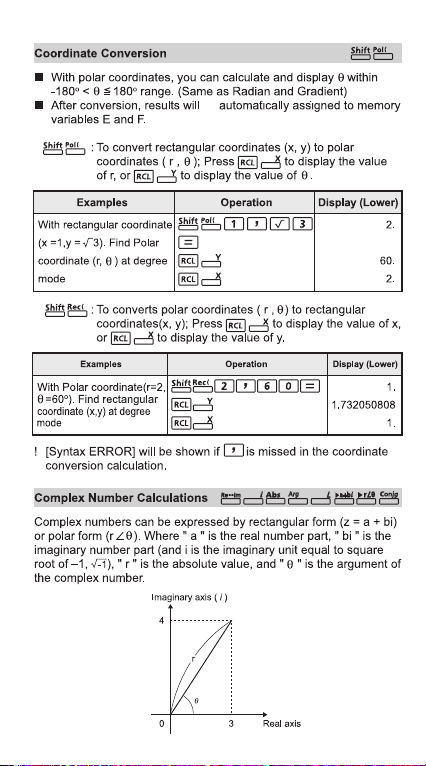
Coordinate Conversion ......................................................P.29
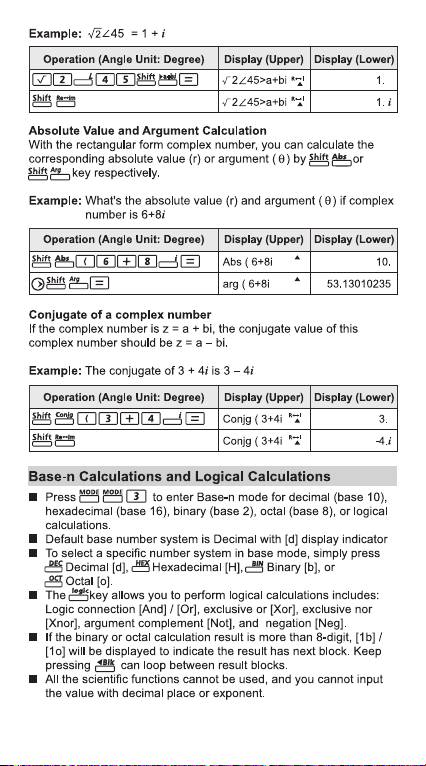
Complex Number Calculations ...........................................P.29
Base-n Calculations and Logical Calculations ....................P.31
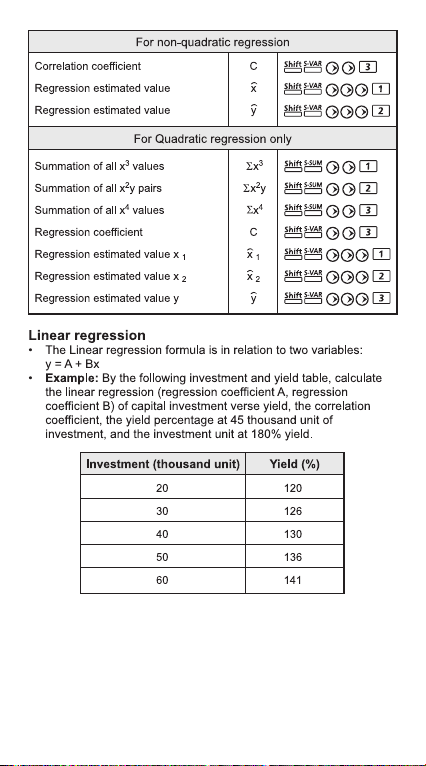
Statistical Calculations .............................................................P.33
Standard Deviation ............................................................P.34
Regression Calculations ....................................................P.34
Distribution Calculations .....................................................P.38
Permutation, Combination, Factorials and Random
Number Generation ...........................................................P.39
Equation Calculations............................................................... P.40
Solve Function........................................................................... P.43
CALC Function ..........................................................................P.44
Differential Calculations ...........................................................P.45
Integration Calculations............................................................P.46
Matrix Calculations ...................................................................P.47
Vector Calculations................................................................... P.51
Battery Replacement................................................................. P.55
Specifications ...........................................................................P.55
1
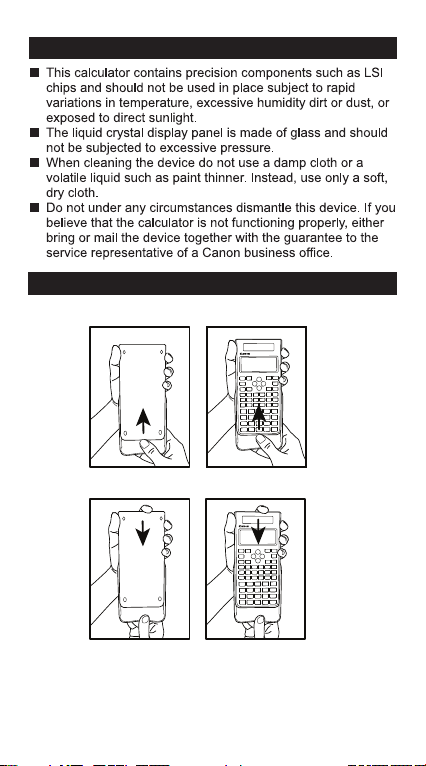
ADVICE AND PRECAUTIONS
HOW TO USE THE SLIDE COVER
Open or close the cover by sliding as shown in the figure.
F-788SG
OPEN
F-788SG
CLOSE
2

DISPLAY (2-LINE DISPLAY)
: Up Arrow
: Down Arrow
3

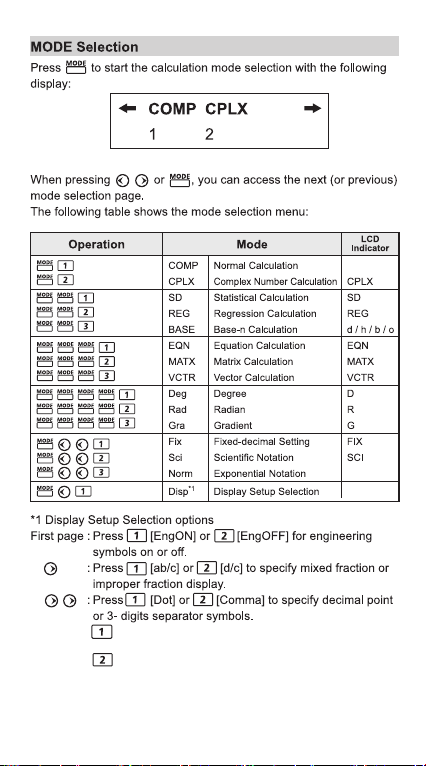
TO GET START
1. Remove the battery insulation tab to load the battery.
2. Press to initialize the calculator.
When the calculator is not used for above 7 minutes, the
calculator will automatically power off. In such a case, pressing
key powers the calculator on again.
F-788SG
Starting from the 72nd step,
4
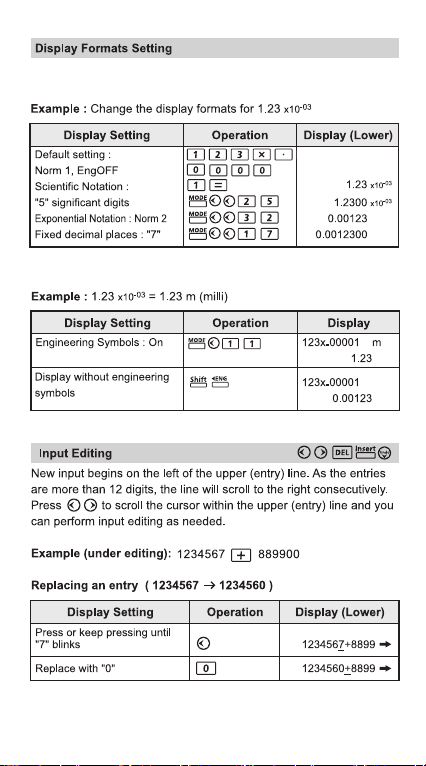
[Dot] : The decimal point is indicated by dot and the
3-digits separator is indicated by comma.
[Comma] : The decimal point is indicated by common
and the 3-digits separator is indicated by dot.
• To check or clear the calculation mode, refer page 13.
5
F-788SG can display a result up to 10 digits. Results exceed the digit limit
will be automatically displayed by exponential notation format.
* For Norm 1 and Norm 2, refer page 25.
6
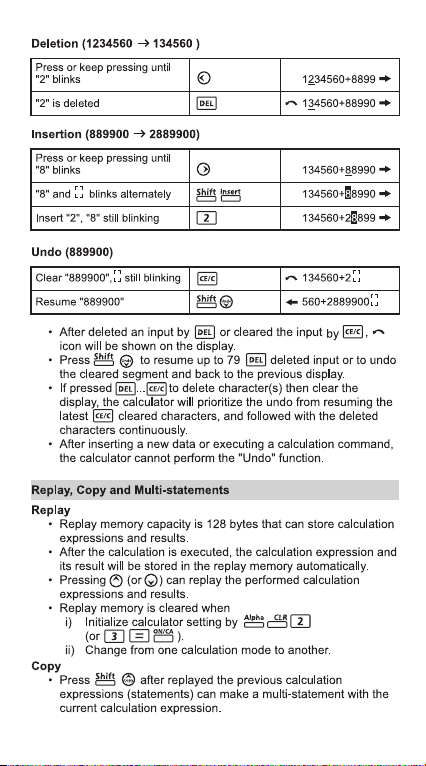
7

8
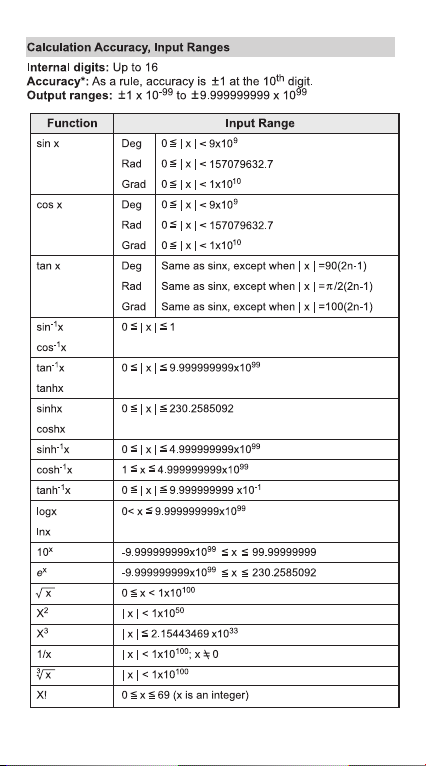
9
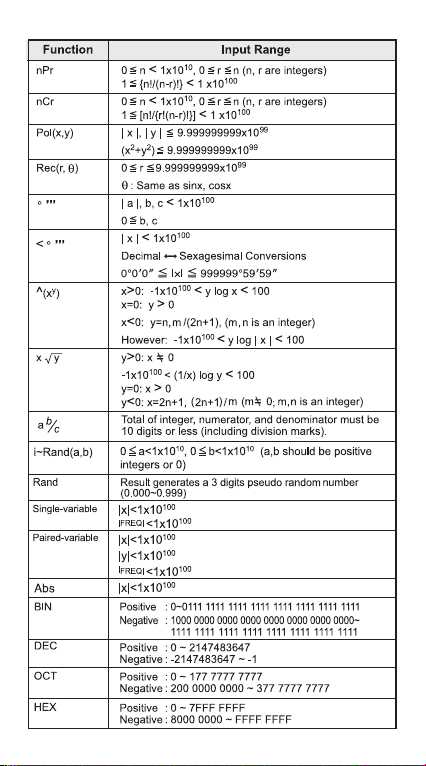
10

1st Priority
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
6th
7th
8th
9th
10th
11th
12th
13th
14th
15th
Recall memory (A, B, C, D, E, F, 0-9), Rand
Calculation within parentheses ( ).
Function with parenthesis that requests the input
argument to the right Pol(, Rec(, d/dx, dx, sin(, cos(,
tan(, log(, ln(, e^(, 10^(, (,
x2, x3, x–1, x!, ° ’ ”, °, r, g, ^(, x (, Percent %, logab, EXP,
t
a b/c, d/c
Prefix symbol: (–) (negative sign), base-n symbols
(d, h, b, o, Neg, Not) etc.
Statistical estimated value calculation:
Metric conversion commands
Multiplication where sign is omitted: Multiplication sign
omitted immediately before , e, variables (2 , 5A, A,
etc.), functions with parentheses (2 (3), Asin(30), etc.)
Permutations, combinations: nPr, nCr
Complex number polar coordinate symbol (<)
.
Dot:
Multiplication and division:
Addition and subtraction:
Logical AND (and)
Logical OR, XOR, XNOR (or, xor, xnor)
Calculation ending instruction: =, M+, M- STO(store
memory), FMLA, r< , a+bi
3
(, Abs(, i~Rand(, etc.
x, y, x1, x2
ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ
×, ÷
+, –
11
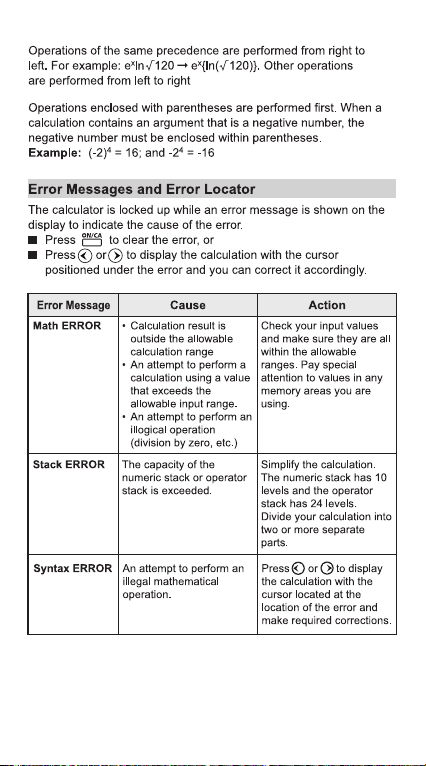
12
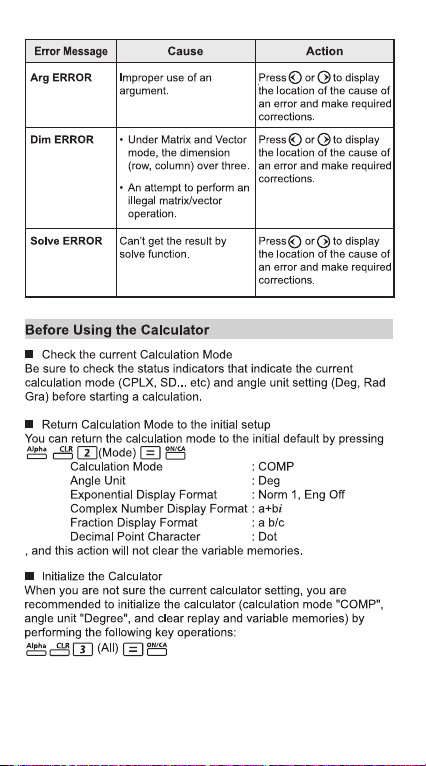
13
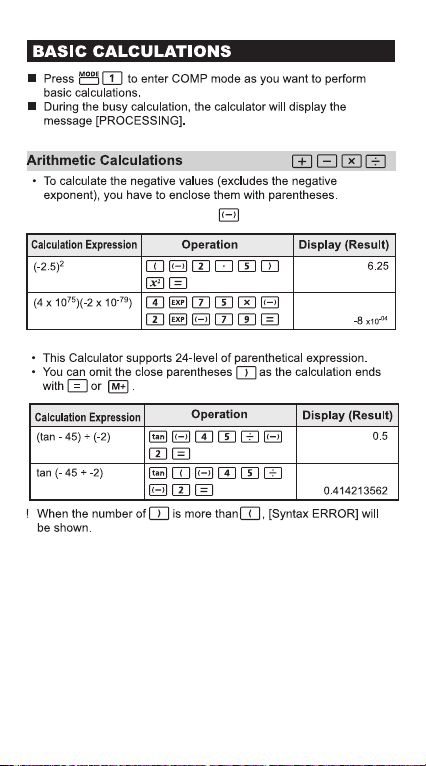
• To input the negative vaues, use .
14
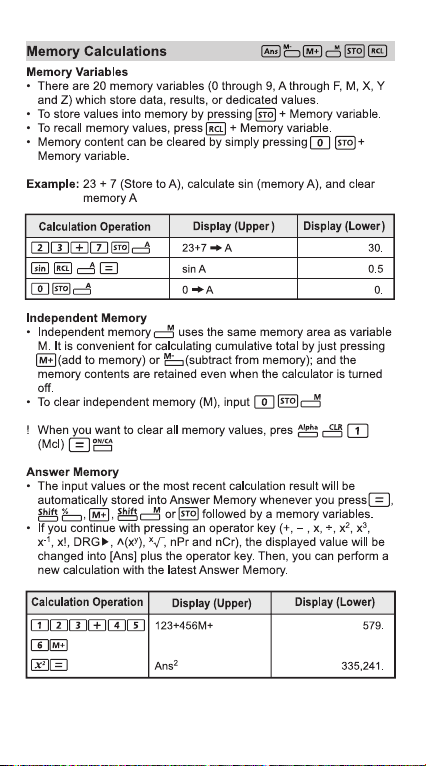
151617
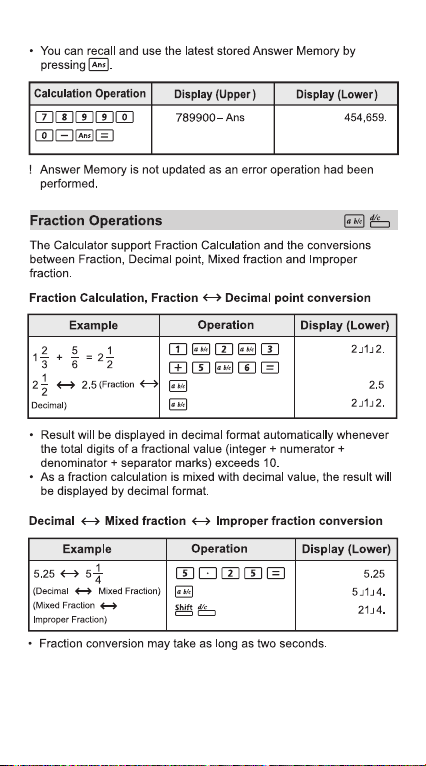
Mark up and Discount
820 mark up
25%
820 have 25%
discount

18

F-788SG
19

NO.
Symbol
1.672621777x10
1.674927351 x10
9.10938291x10
-31
1.883531475x10
0.52917721092x10
6.62606957 x10
5.05078353 x10
927.400968 x10
1.054571726 x10
7.2973525698x10
UnitValueConstant
-27
-27
-28
-10
-34
-27
-26
-34
-3
20
2.8179403267x10
2.4263102389 x10
2.675222005 x10
1.32140985623 x10
1.3195909068x10
10973731.568539
1.660538921 x10
1.410606743x10
-928.476430x10
-26
-0.96623647 x10
-4.49044807 x10
96485.3365
1.602176565x10
6.02214129x10
1.3806488 x10
22.413968 x10
23
-23
-3
8.3144621
299792458
3.74177153x10
1.4387770 x10
-16
-2
-15
-12
8
-15
-15
-27
-26
-26
-26
-19

21Pa22

Metric Unit Conversions
F-788SG has 172 patterns of unit conversions to convert a value to
specified metric units. There are 8 categories including distance, area,
temperature, capacity, weight, energy, pressure and speed.
• Press to enter the conversion menu.
• Press or to select the category .
• Press or then to select the start unit.
• Press or then to select the end unit. You can preview the
value before pressing .
Page UnitSymbol
23

(enter the conversion menu)
2
(select ft
)
(convert to m2)
(calculate the answer)
24

• To clear the setting, refer page 13.
25

162.8571429
162.8571
8.1429
162.8571
8.1429
162.8580
1.62858×
162.858
02
10
Square Root CubeCube Root
PowerPower Root Reciprocal Pi
26

selected angle unit. If you want to indicate the value with other degree
unit after conversion, change the unit using .
27

sin 53o 22’ 12” = 0.802505182
cosec x = 1/sinx 1.414213562
o
cosec 45
= 1.414213562
-1
tan
(5/6) = 39.80557109° 39.80557109
Rad
cos( /6)
0.785398163 0.785398163
1
-1
— =
cos
2
0.802505182
)daR( 52.0
.0
.0
304520668.0 304520668.0 =
52.0
log 255 + ln 3 = 3.505152469
-3
1.2
+ 10
= 15.89871899
e
3.505152469
log
81 – log 1 = 4
3
99817898.51
.4
28
be
29

3031323334




35
36

37

After sample data are entered in either Statistic (SD) or
Regression (REG) mode, you can perform the normal distribution
or probability distribution calculation such as P(t), Q(t) and R(t) in
which t is the variate of the probabilistic experiment.
• “t” is a parameter when the normal distribution is standardized. “t”
can be found from the statistical result.
38

39

Equation Calculations
Press to enter the equation mode and the
following selection options will be displayed:
Unknowns?
2 3
By this screen, you can choose for the simultaneous linear equation
solve with either two (2) or three (3) unknowns. Or, press or
to display another the options for quadratic (2) or cubic (3) equation:
40

Degree?
2 3
After the equation type is selected, [EQN] indicator lights up. The
following equation solve guiding page sample will be shown if you
specified the equation solve for two (2) or three (3) unknowns
simultaneous linear equation:
Coefficient name
a1?
0.
(Sample display for simultaneous linear equation solve)
• For quadratic or cubic equation solve, the coefficient name starts
with "a"
• You cannot input complex number as an coefficient
• The calculation starts after the last factor ("c2": where the
simultaneous linear equations with two unknowns, "d3": where the
simultaneous linear equations with three unknowns, "c": quadratic
equation and "d": cubic equation) of the specified equation and
then the root of an equation appears.
Variable name
X =
0.
(Sample display for simultaneous linear equation solve)
• The input display appears by pressing the key, and you can
display or edit the value by pressing the or key. After that, the
last factor is displayed and a calculation is performed again by
pressing to display the root.
• For quadratic or cubic equation, the Variable name starts with
"X1".
• Press or key to display the equation solve results.
• If you want to return to the coefficient input screen, simply press
key.
Indicates the direction of
next step or viewing the
other related elements.
Element Value
Indicates the direction of
next step or viewing the
other results.
Result
41

Simultaneous Linear Equations
Two Unknowns Simultaneous Linear Equation:
a
a2x + b2y = c
Three Unknowns Simultaneous Linear Equation:
a
a2x + b2y + c2z = d
a3x + b3y + c3z = d
Example: Solve the simultaneous equation with three unknowns:
2x + 4y – 4z = 20
2x – 2y + 4z = 8
5x – 2y – 2z = 20
Quadratic or Cubic Equations
Quadratic equation : ax2 + bx + c = 0 (a second-order polynomial
Cubic equation : ax
Example: Solve the cubic equation 5x
x + b1y = c
1
1
Operation
Operation
1
2
x + b1y + c1z = d
1
2
3
Display (Upper)
equation in a single variable x)
3
+ bx2 + cx + d = 0 (an equation with cubic
polynomial)
3
+ 2x2 – 2x+1 = 0
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
Display (Lower)
42

SOLVE FUNCTION
You can solve any calculation expression as per your needs in
COMP mode. Simply input the expression with different variables
and press the key.
Example: A cone of height "h" and base is a circular with radius "r",
the volume of the cone will be in the formula:
So, you can replace the variable "V" by A, variable "r" by "B", and
variable "h" by "C".
If the radius is 5cm, cone height is 20cm, calculate the cone volume.
And if the cone volume is 200cm
cone height.
3
1
V = r2h A = B2C
1
3
3
, with radius 2cm, calculate the
h
s
r
Operation
! If the expression does not have the equal sign ( = ) and perform
calculation, the calculator will transform the solution as zero ( 0 ).
!
When the expression cannot be solved, [Solve ERROR] will be
displayed.
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
the Solve
43

CALC FUNCTION
CALC function is deemed to be a memory zone with maximum 79
steps for you to store a single calculation expression which will be
recalled and calculated a number of times by different values.
After input the calculation expression and pressed , the
calculator will request for the current value of your input variables.
Beware that CALC function can only be used in COMP mode or
CPLX mode.
Example: For the equation Y = 5x
x = 2 or x = 7.
Operation
! The stored expression will be cleared as you start a new
calculation, change into another mode, or turn off the calculator.
2
–2x +1, calculate the value of Y if
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
44

DIFFERENTIAL CALCULATIONS
Press to enter COMP mode for differential calculation.
To perform a differential calculation, you have to input the expression
in the form of:
differential expression a x
• The differential expression must contain the variable x.
• "a" is the differential coefficient.
• " x" is the change interval of x (calculation precision).
-8
Example: To determine the derivative at point x = 10, x = 10
the function f(x) = sin(3x + 30).
Operation
! You can leave out the x in the differential expression and the
calculator will automatically substitute a value for x.
! The smaller the entered value x is, the longer the calculation time
will be and the result is more accurate; the bigger the entered
value x is, the shorter the calculation time will be and the result
will be comparatively less accurate.
! Discontinuous points and extreme changes in the value of x can
cause inaccurate results or errors.
! When performing differential calculation with trigonometric
function, select radian (Rad) as the angle unit setting.
b, i–Rand, Rec ( and Pol ( functions can’t join to differential
! Log
a
calculation.
! During the busy calculation, the calculator will display the message
[PROCESSING]
Display (Upper)
, for
Display (Lower)
45

INTEGRATION CALCULATIONS
Press to enter COMP mode for integration calculation.
To perform an integration calculation you are required to input
following elements:
• The integration expression has variable x.
• "a" and "b" defining the integration range of the definite integral.
• "n" is the number of partitions (equivalent to N = 2
The integration calculation is based on Simpson’s rule.
As the number of significant digits is increased, internal integration
calculations may take considerable time to complete. For some
cases, even after considerable time is spent for performing a
calculation, The calculation precision may be low. Particularly
when significant digits are less than 1, an ERROR might be
occurred.
Example: Perform the integration calculation for
, with n = 4.
integration expression a b n
3
(5x4 + 3x2 + 2x + 1)dx
2
Operation
Display (Upper)
n
).
Display (Lower)
! The number of partitions (n) have to specify in the range of 1 to 9
integer, any value that out of the setup division range (N=2
n=1~9 integer), [Arg ERROR] will be displayed.
! You can skip the number of partitions and the calculator will
automatically assign an appropriate value on behalf of you.
! The smaller the value of n is, the shorter the calculation time is, but
the result is comparatively less accurate; on the other hand, the
bigger the n is, the longer the calculation time is, and the result is
more accurate.
! When performing integration calculation with trigonometric
function, select radian (Rad) as the angle unit setting.
b, i–Rand, Rec ( and Pol ( functions can’t join to integration
! Log
a
calculation.
! During the busy calculation, the calculator will display the message
[PROCESSING].
n
, n 0,
46

MATRIX CALCULATIONS
Enter the matrix mode by pressing , and [MATX]
indicator lights up.
Before you start matrix calculations, you have to create one
matrix or maximum three matrices which named A, B, and C at
one time.
The matrix calculation results are stored into MatAns memory
automatically. You can use the matrix MatAns memory for any
subsequent matrix calculations.
Matrix calculation may use up to two levels matrix stack; however,
squaring a matrix, cubing a matrix, or inverting a matrix only use
one stack.
Create a Matrix
1. Press (Dim) to specify the matrix name (A, B or C),
and then specify the dimension (number of rows and number of
columns) of the matrix. The dimension of matrix can be up to
3 x 3.
2. Next, input the value (element) of the matrix according to the
matrix element indictor display, following is a matrix element
indictor example:
M a t A
23
2 rows and 3 columns
3. Use the cursor keys to move, view or edit the matrix elements.
4. When finished the input, press to exit the matrix creation
screen.
Edit Matrix Elements
1. To edit the element saved in the matrix memory, press
(Edit), then specify the matrix A, B or C for editing and the
corresponding matrix element indicator will be displayed.
2. Input the new value and press to confirm the edit.
3. When finished the input, press to exit the matrix editing
screen.
47

Matrix Addition, Subtraction and Multiplication
1 2 3
Example: MatA = , MatB = , MatA x MatB=?
Operation
(press left, right, up or down
key to display the result)
! Matrices which will be added, subtracted or multiplied must be in
the same size. An error occurs if you try to add, subtract or multiply
matrices whose dimensions are different from each other. For
example, you cannot add or subtract a 2 x 3 to a 2 x 2 matrix.
4 5 6
7 8 9
9 8 7
6 5 4
3 2 1
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
48

49

50

VECTOR CALCULATIONS
51

52

53

54

BATTERY REPLACEMENT
and replace the alkaline battery immediately.
Please replace the alkaline battery with the following procedures,
Caution: Do not use the battery other than the specified one. Failure
to do so may burst the battery, causing environment
contamination or personal injury due to electrolyte leakage.
Insulate the positive and negative poles of the spent battery with
a tape, follow your local environment regulations and waste
disposal standards, and then dispose the battery.
Cautions!
Keep the battery out of reach of children. If the battery is
swallowed, contact a doctor immediately.
Misuse of battery may cause leakage, explosion, damages
or personal injury.
Don’t recharge or disassemble the battery, it could cause a short circuit.
Never expose the battery to high temperatures, direct heat,
or dispose by incineration.
55

SPECIFICATIONS
Power Suppl
Power Consumption: D.C. 1.5V / 0.1mW
Battery Life
Auto Power Off
Usable
Size : 165 (L) x 80 (W) x 14 (H) mm (body)
168 (L) x 86.3 (W) x 17.8 (H) mm (with case)
Weight : 89 g
* Specifications are subject to change without notice
CANON ELECTRONIC BUSINESS MACHINES (H.K.) CO., LTD.
17/F., Tower One, Ever Gain Plaza, 82-100 Container Port Road,
Kwai Chung, New Territories, Hong Kong
CANON MARKETING (MALAYSIA) SDN BHD.
Block D, Peremba Square, Saujana Resort, Section U2,
40150 Shah Alam, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
y
: Solar cell and a single Alkaline battery (LR44 x 1)
:
Approximately 3 years
(Base on 1 hour of operation per day)
:
T
emperature: 0 ~ 40oC
Approx. 7 minutes
/ 124 g (include cover)
© CANON ELECTRONIC BUSINESS
MACHINES (H.K.) CO., LTD. 2012
E-IE-444
56
PRINTED IN CHINA
 Loading...
Loading...