
F-570SG
User instruction
www.canon.com/calcmanual
SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR
E-IE-483
ENGLISH

CONTENTS
Advice and Precautions ............................................................. P.2
How to Use the Slide Cover ...................................................... P.2
Display (2-Line Display) ............................................................. P.3
To Get Start
Power On, Off .......................................................................P.4
Input Capacity ......................................................................P.4
Mode Selection .....................................................................P.5
Display Formals Setting ......................................................P.6
Input Editing .........................................................................P.6
Replay, Copy and Multi-statements ......................................P.7
Calculation Stacks ...............................................................P.8
Calculation Accuracy, Input Ranges .....................................P.9
Order of Operations ............................................................P.11
Error Messages and Error Locator...................................... P.12
Before Using the Calculator ...............................................P.13
Basic Calculations
Arithmetic Calculations .......................................................P.14
Memory Calculations ..........................................................P.15
Fraction Operations ............................................................P.16
Percentage Calculations .....................................................P.17
Degree-Minutes-Seconds Calculations............................... P.18
Constant Value Calculations............................................... P.19
Metric Conversions .............................................................P.23
Engineering Notation Calculations ..................................... P.24
Fix, Sci, Norm, Round ........................................................ P.25
Functional Scientific Calculations
Square, Root, Cube, Cube Root, Power, Power Root,
Reciprocal and Pi................................................................ P.26
Angle Unit Conversion ........................................................P.27
Trigonometry Calculations ..................................................P.27
Logarithm, Natural Logarithm, Antilogarithm and Logab ....P.28
Coordinate Conversion ......................................................P.29
Complex Number Calculations ...........................................P.29
Base-n Calculations and Logical Calculations ....................P.31
Statistical Calculations .............................................................P.33
Standard Deviation ............................................................P.34
Regression Calculations ....................................................P.34
Distribution Calculations .....................................................P.38
Permutation, Combination, Factorials and Random
Number Generation ...........................................................P.39
Equation Calculations............................................................... P.40
Solve Function........................................................................... P.43
CALC Function ..........................................................................P.44
Differential Calculations ...........................................................P.45
Integration Calculations............................................................P.46
Matrix Calculations ...................................................................P.47
Vector Calculations................................................................... P.51
Battery Replacement................................................................. P.55
Specifications ...........................................................................P.56
1
ADVICE AND PRECAUTIONS
This calculator contains precision components such as
LSI chips and should not be used in place subject to
rapid variations in temperature, excessive humidity dirt
or dust, or exposed to direct sunlight.
The liquid crystal display panel is made of glass and
should not be subjected to excessive pressure.
When cleaning the device do not use a damp cloth or a
volatile liquid such as paint thinner. Instead, use only a
soft, dry cloth.
Do not under any circumstances dismantle this device.
If you believe that the calculator is not functioning properly,
either bring or mail the device together with the guarantee
to the service representative of a Canon business office.
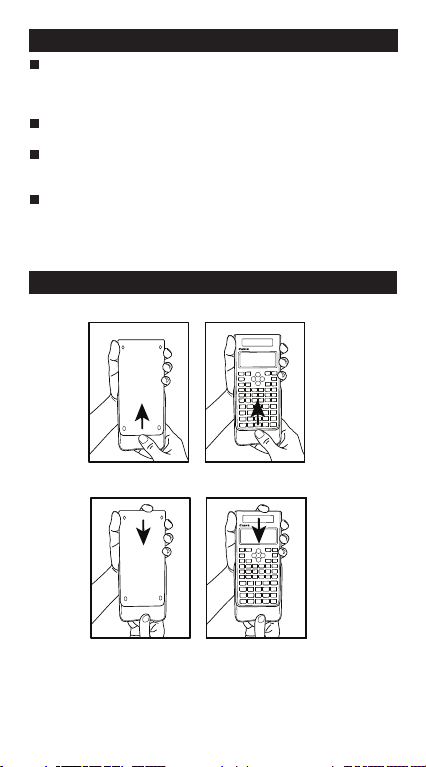
HOW TO USE THE SLIDE COVER
Open or close the cover by sliding as shown in the figure.
F-570SG
OPEN
F-570SG
CLOSE
2
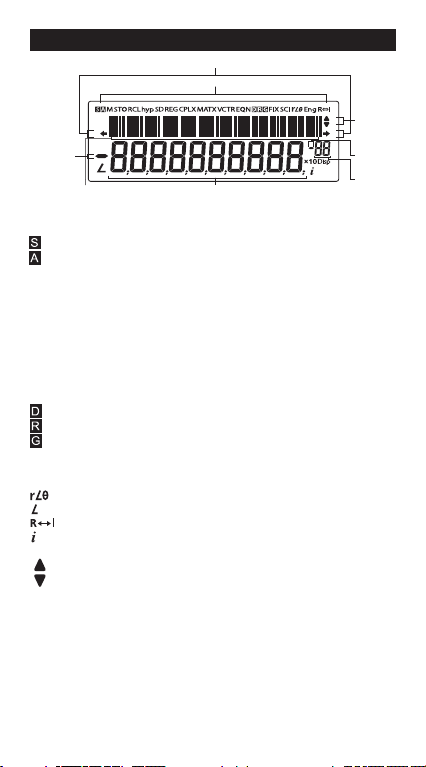
DISPLAY (2-LINE DISPLAY)
Extension mark (Shows the presence of hidden formula)
Status indicators
Mantissa
minus sign
Formula (12 characters)
<Status Indicators>
: Shift key
: Alpha key
M : Independent memory
STO : Store Memory
RCL : Recall Memory
hyp : Hyperbolic key
SD : Statistic Mode
REG : Regression Mode
CPLX : Complex Number Calculation Mode
MATX : Matrix Calculation Mode
VCTR : Vector Calculation Mode
EQN : Equation Calculation Mode
: Degree Mode
: Radian Mode
: Gradient Mode
FIX : Fixed-decimal Setting
SCI : Scientific Notation
Eng : Engineering Notation
: Polar Coordinate
: Angle value
: Switch between Real and Imaginary Number
: Imaginary number
Disp : Multi-statements Display
: Up Arrow
: Down Arrow
Mantissa
Next or
Previous
page
Exponent
minus sign
Exponent
3

TO GET START
Power ON, OFF
First time operation:
1. Remove the battery insulation tab to load the battery.
2. Press to initialize the calculator.
(Power ON/Clear): Turns on the calculator when it is pressed.
(Power OFF): Turns off the calculator when it is pressed.
Auto Power Off Function:
When the calculator is not used for about 7 minutes, the
calculator will automatically power off. In such a case, pressing
key powers the calculator on again.
Input Capacity
F-570SG allows you to input a single calculation up to 79 steps. One
step is used as each time you press one of the numeric keys,
arithmetic keys, scientific calculation keys or key. , ,
and the direction keys will not use up any step.
Starting from the 72nd step, the cursor changes from [ _ ] to [ ] that
notifying the memory is running low. In case you need to input a
single calculation with more than 79 steps, you should separate your
calculation into two or more segments.
4
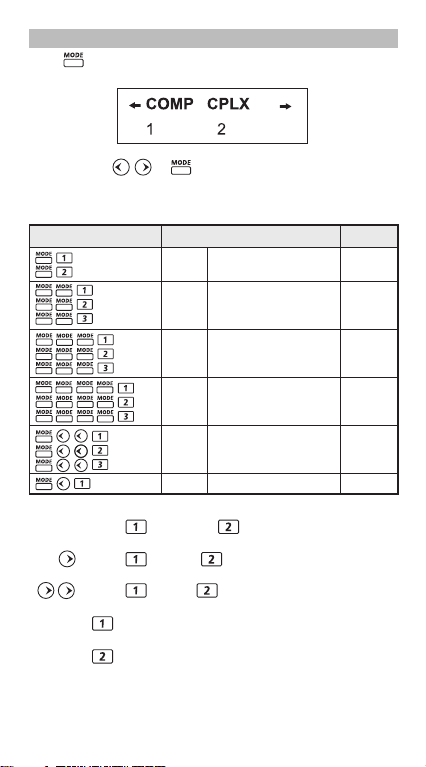
MODE Selection
Press to start the calculation mode selection with the
following display:
When pressing or , you can access the next (or previous
mode selection page.
The following table shows the mode selection menu:
Operation
COMP Normal Calculation
CPLX
SD Statistical Calculation SD
REG Regression Calculation REG
BASE Base-n Calculation d / h / b / o
EQN Equation Calculation EQN
MAT Matrix Calculation MATX
VCT Vector Calculation VCTR
Deg Degree D
Rad Radian R
Fix Fixed-decimal Setting FIX
Sci Scientific Notation SCI
Norm Exponential Notation
Disp*1 Display Setup Selection
*1 Display Setup Selection options
First page : Press [EngON] or [EngOFF] for engineering
: Press [ab/c] or [d/c] to specify mixed fraction or
: Press [Dot] or [Comma] to specify decimal
[Dot] : The decimal point is indicated by dot and
[Comma] : The decimal point is indicated by
symbols on or off.
improper fraction display.
point or 3-digits separator symbols.
the 3-digits separator is indicated by comma.
common and the 3-digits separator is indicated by dot.
Gra Gradient G
Mode
Complex Number Calculation
• To check or clear the calculation mode, refer page13.
Indicator
CPLX
LCD
5
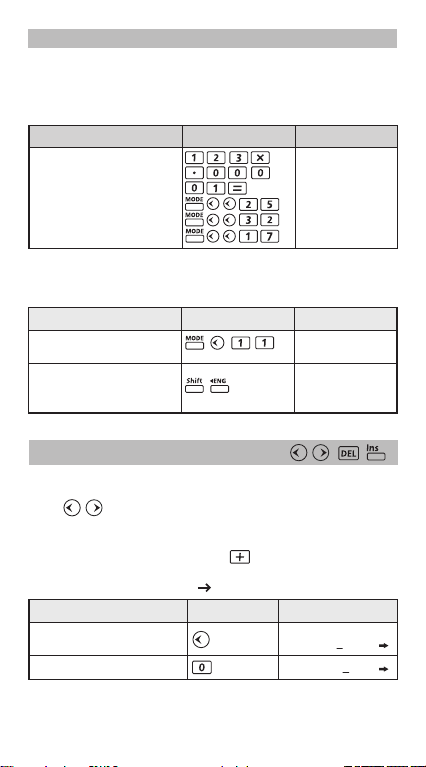
Display Formats Setting
F-570SG can display a result up to 10 digits. Results exceed the digit
limit will be automatically displayed by exponential notation format.
Example : Change the display formats for 1.23 x10
Display Setting Display (Lower)Operation
Default setting :
Norm 1, EngOFF
Scientific Notation : 1.23
"5" significant digits 1.2300 x10
Exponential Notation : Norm 2
Fixed decimal places : "7" 0.0012300
0.00123
* For Norm 1 and Norm 2, refer page 25.
Example : 1.23 x10
–03
= 1.23 m (milli)
Display Setting DisplayOperation
Engineering Symbols : On 123x.00001 m
1.23
Display without engineering
symbols 123x.00001
0.00123
Input Editing
New input begins on the left of the upper (entry) line. As the entries
are more than 12 digits, the line will scroll to the right consecutively.
Press to scroll the cursor within the upper (entry) line and
you can perform input editing as needed.
Example (under editing):
1234567 889900
Replacing an entry (1234567 1234560)
Display Setting Display (Upper)Operation
Press or keep pressing until
"7" blinks 1234567+8899
Replace with "0" 1234560+8899
–03
–03
x10
–03
6
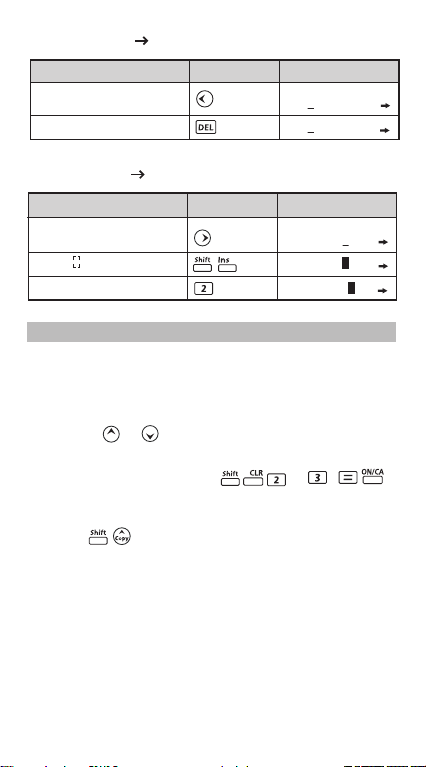
Deletion (1234560 134560 )
Display Setting Display (Upper)Operation
Press or keep pressing until
"2" blinks 1234560+8899
"2" is deleted 134560+88990
Insertion (889900 2889900)
Display Setting Display (Upper)Operation
Press or keep pressing until
"8" blinks 134560+88990
"8" and blinks alternately 134560+88990
Insert "2", "8" still blinking 134560+28899
Replay, Copy and Multi-statements
Replay
• Replay memory capacity is 128 bytes that can store calculation
expressions and results.
• After the calculation is executed, the calculation expression and
its result will be stored in the replay memory automatically.
• Pressing (or ) can replay the performed calculation
expressions and results.
• Replay memory is cleared when you.
i) Initialize calculator setting by (or ) .
ii) Change from one calculation mode to another.
Copy
• Press after replayed the previous calculation
expressions (statements) can make a multi-statement with the
current calculation expression.
7
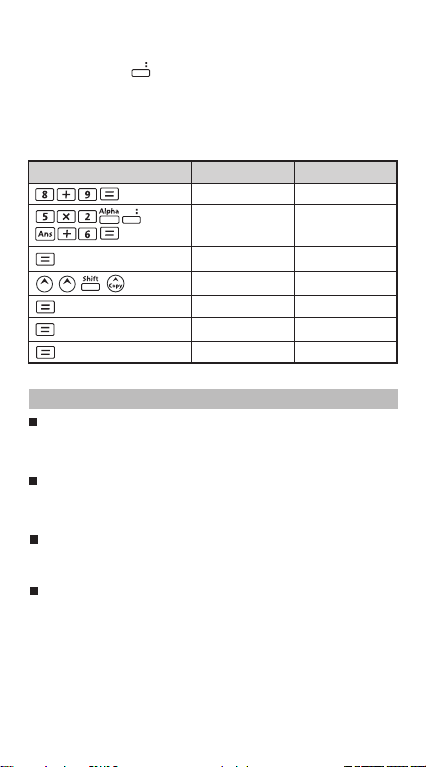
Multi-statements
• You can put two or more calculation expressions together by
using a colon .
• The first executed statement will have [Disp] indicator; and the
[Disp] icon will disappeared after the last statement is being
executed.
Example :
Operation
8 + 9 17.
5 x 2 10.
Display (Lower Line)Display (Upper line)
Disp
Ans + 6 16.
8 + 9 17.
5 x 2 10.
9 : 5 x 2 : Ans + 6
17.
Disp
Disp
Ans + 6 16.
Calculation Stacks
This calculator uses memory areas, called "stacks", to temporarily
store numeric value (numbers) and commands (+ – x ...)
according to their precedence during calculations.
The numeric stack has 10 levels and the command stack has 24
levels. A stack error [Stack ERROR] occurs whenever you try to
perform a calculation that exceeds the capacity of stacks.
Matrix calculations use up to two levels of the matrix stack.
Squaring a matrix, cubing a matrix, or inverting a matrix uses one
stack level.
Calculations are performed in sequence according to "Order of
Operations". After the calculation is performed, the stored stack
values will be released.
8
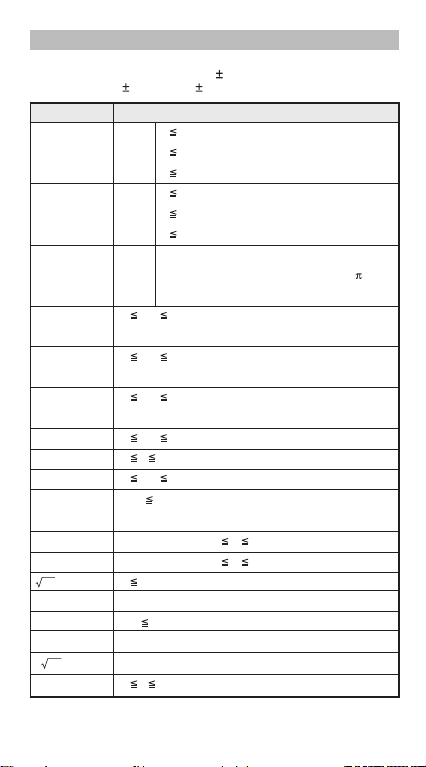
Calculation Accuracy, Input Ranges
Internal digits: Up to 16
Accuracy*: As a rule, accuracy is 1 at the 10th digit.
Output ranges: 1 x 10
–99
to 9.999999999 x 10
99
Function Input Range
sin x Deg 0 | x | <9x10
9
Rad 0 | x | <157079632.7
10
Grad 0 | x | <1x10
cos x Deg 0 | x | <9x10
10
Rad 0 | x | <157079632.7
10
Grad 0 | x | <1x10
tan x Deg Same as sinx, except when | x | =(2n-1)x90
Rad Same as sinx, except when | x | =(2n-1) /2
Grad Same as sinx, except when | x | =(2n-1)100
–1
x 0 | x | 1
sin
–1
x
cos
–1
x 0 | x | 9.999999999x10
tan
99
tanhx
sinhx 0 | x | 230.2585092
coshx
-1
x 0 | x | 4.999999999x10
sinh
cosh-1x 1 x 4.999999999x10
tanh-1x 0 | x | 9.999999999 x10
logx 0< x 9.999999999x10
99
99
–1
99
lnx
x
–9.999999999x1099 x 99.99999999
10
x
–9.999999999x1099 x 230.2585092
e
x 0 x < 1x10
X2 | x | < 1x10
X3 | x | 2.15443469x10
X–1 | x | < 1x10
3
x | x | < 1x10
100
50
33
100
; x≠0
100
X! 0 x 69 (x is an integer)
9
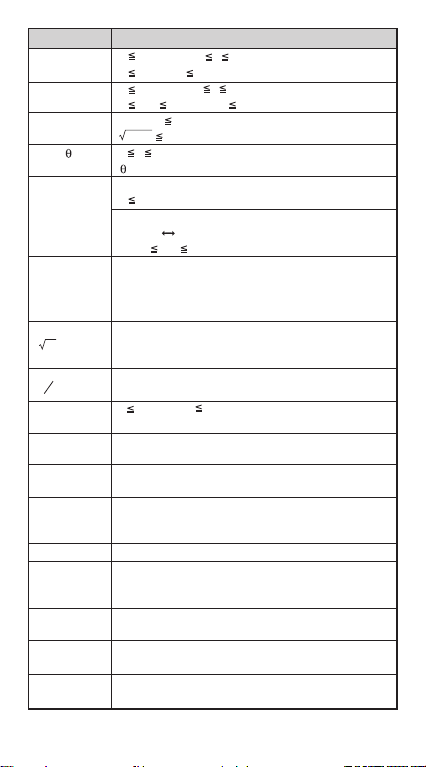
Function Input Range
nPr 0 n < 1x1010, 0 r n (n, r are integers)
1 {n!/(n-r)!}
nCr 0 n <1x1010, 0 r n (n, r are integers)
1 n!/r! 1x10
Pol(x,y) | x |, | y | 9.999999999x10
x2+y2 9.999999999x1099
Rec(r, ) 0 r 9.999999999x10
: Same as sinx, cosx
| a |, b, c < 1x10
˚ ' "
0 b, c
| x |
Decimal Sexagesimal Conversions
<
˚ ' "
0
x>0: –1x10
y
^(x
) x=0: y > 0
x
However: –1x10
y
x
y y=0: x > 0
y
Total of integer, numerator, and denominator must be
b
a
c
10 digits or less (including division marks).
I~Rand(a,b) 0 a<1x10
(a,b should be positive integers or 0)
< 1x10
º0'0"
| x | 999999º59
<0: y=n,m/(2n+1), (m, n are integers),
>0: x≠0, –1x10
<0: x=2n+1,(2n+1)/m (m≠0; m, n are integers)
100
1 x10
100
or 1 n!/(n-r)! < 1x10
100
100
100
< y logx < 100
100
< y log | x | <100
100
< 1/xlog< 100
10
, 0 b<1x10
100
99
99
'59"
10
Rand Result generates a 3 digit pseudo random number
(0.000~0.999)
Single-variable
| x | <1x10
Paired-variable
| x | <1x10
| y | <1x10
ABS | x | <1x10
Positive :
BIN
100
<1x10
<1x10
100
100
100
100
100
|FREQ|
|FREQ|
0~ 0111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
Negative :
1000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000~
1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111
DEC Positive : 0 ~ 2147483647
Negative : –2147483647 ~ –1
OCT Positive : 0 ~ 177 7777 7777
Negative : 200 0000 0000 ~ 377 7777 7777
HEX Positive : 0 ~ 7FFF FFFF
Negative : 8000 0000 ~ FFFF FFFF
10
*For a single calculation, the calculation error is ±1 at the 10th digit.
For exponential display, calculation error is ±1 at the last significant
digit. Errors are cumulative in the case of consecutive calculations,
which can cause them to become larger. (This is also true as internal
consecutive calculations are performed in the case of ^(xy), x y, x!,
nPr, nCr, etc.). In the vicinity of a function's singular point and point of
inflection, errors are cumulative and may become large.
Order of Operations
The calculator will automatically determine the operation priority. This
means that algebraic expressions can be entered just as they are
written and the calculation priority is as follows:
1st Priority
2nd
3rd
4th
5th
6th
7th
8th
9th
10th
11th
12th
13th
14th
15th
16th
Recall memory (A - F, X, Y), Rand
Calculation within parentheses ( ).
Function with parentheses that requests the input
argument to the right Pol(, Rec(, Abs(, i~Rand(, logab(,
d/dx, dx, P(, Q(, R(,
Statistic points: Max, Min, Med
Functions that come after the input value preceded by
values, powers, power roots : x
Statistical estimated value calculation:
Percent %, EXP
Engineering symbols (T, G, M, k, m, µ, n, p, f)
metric conversion commands (cm in, etc)
^(, x
Fractions: a b/c, d/c
Prefix symbol: (–) (negative sign),
Base-n symbols (d, h, b, o, Neg, Not)
Multiplication where sign is omitted: Multiplication sign
omitted immediately before , e, variables (2 , 5A,
A, etc.)
Function that come before the input value without
parentheses. sin, cos, tan sin
–1
, cosh–1, tanh–1, log, In, e^, 10^, , 3 , Arg,
tanh, sinh
Conjg, Det, Trn
Permutations, combinations: nPr, nCr
Complex number polar coordinate symbol ( )
Dot: .
Multiplication and division:
Addition and subtraction:
Logical AND (and)
Logical OR, XOR, XNOR (or, xor, xnor)
Calculation ending instruction: =, M+, M– STO(store
memory), r< , a+bi
2
, x3, x–1, x!, ° ' ", °, r, g,
x, y, x1, x2, t
ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ
–1
, cos–1, tan–1, sinh, cosh,
×,
÷
+, –
11
Operations of the same precedence are performed from right to left.
For example: e
performed from left to right
Operations enclosed with parentheses are performed first. When a
calculation contains an argument that is a negative number, the
negative number must be enclosed within parentheses.
Example: (–2)
x
ln 120 ex{ln( 120)}. Other operations are
4
= 16; and –24 = –16
Error Messages and Error Locator
The calculator is locked up while an error message is shown on the
display to indicate the cause of the error.
Press to clear the error, or
Press or to display the calculation with the cursor
positioned under the error and you can correct it accordingly.
Error Message
Math ERROR
Stack ERROR The capacity of the
Syntax ERROR An attempt to perform an
Cause Action
• Calculation result is
outside the allowable
calculation range
• An attempt to perform a
calculation using a value
that exceeds the
allowable input range.
• An attempt to perform an
illogical operation
(division by zero, etc.)
numeric stack or operator
stack is exceeded.
problematic format of the
calculation
12
• Check your input values
and make sure they are
all within the allowable
ranges. Pay special
attention to values in any
memory areas you are
using.
• Press or to display
the calculation with the
cursor located at the
location of the error and
make required corrections.
Simplify the calculation.
The numeric stack has 10
levels and the operator
stack has 24 levels.
Divide your calculation into
two or more separate
parts.
Press or to display
the calculation with the
cursor located at the
location of the error and
make required corrections.
Error Message
Arg ERROR Improper use of an
Dim ERROR • Under Matrix and Vector
Solve ERROR Can’t get the result by
Cause Action
argument.
mode, the dimension
(row, column) over three.
• An attempt to perform an
illegal matrix/vector
operation.
solve function.
Press or to display
the location of the cause of
an error and make required
corrections.
Press or to display
the location of the cause of
an error and make required
corrections.
Press or to display
the location of the cause of
an error and make required
corrections.
Before Using the Calculator
Check the current Calculation Mode
Be sure to check the status indicators that indicate the current
calculation mode (CPLX, SD... etc) and angle unit setting (Deg, Rad
Gra) before starting a calculation.
Return Calculation Mode to the initial setup
You can return the calculation mode to the initial default by pressing
(Mode)
Calculation Mode : COMP
Angle Unit : Deg
Exponential Display Format : Norm 1, Eng Off
Complex Number Display Format : a+bi
Fraction Display Format : a b/c
Decimal Point Character : Dot
, and this action will not clear the variable memories.
Initialize the Calculator
When you are not sure the current calculator setting, you are
recommended to initialize the calculator (calculation mode "COMP",
angle unit "Degree", and clear replay and variable memories) by
performing the following key operations: (All) .
13
BASIC CALCULATIONS
BASIC CALCULATIONS
Press to enter COMP mode as you want to perform
basic calculations.
During the busy calculation, the calculator will display the
message [PROCESSING].
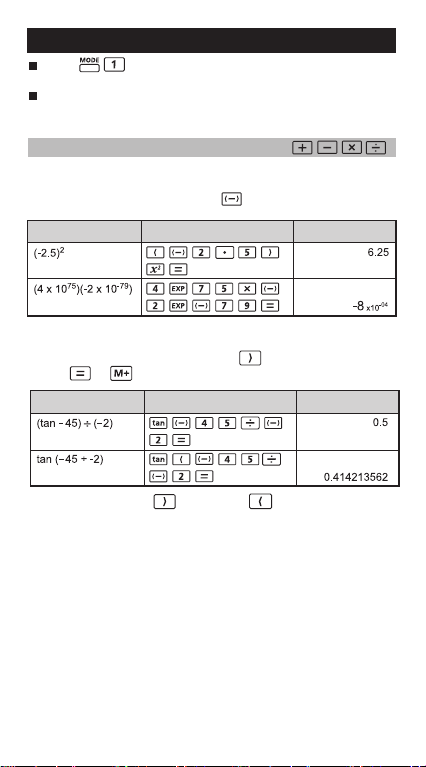
Arithmetic Calculations
•
To calculate the negative values (excludes the negative exponent),
you have to enclose them with parentheses.
• To input the negative vaues, use .
Calculation Expression
• This Calculator supports 24-level of parenthetical expression.
• You can omit the close parentheses as the calculation ends
with or .
Calculation Expression
! When the number of is more than , [SYNTAX Error] will
be shown.
Display (Result)Operation
Display (Result)Operation
14
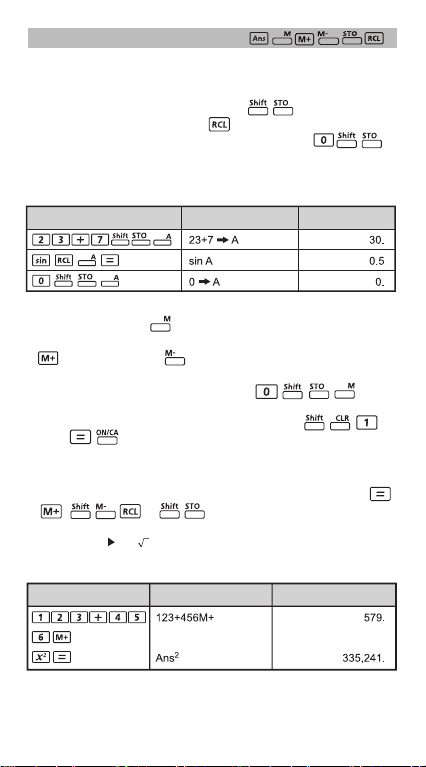
Memory Calculations
Memory Variables
• There are 8 memory variables (A through F, X and Y) which store
data, results, or dedicated values.
To store values into memory by pressing + Memory variable.
•
• To recall memory values, press + Memory variable.
• Memory content can be cleared by simply pressing +
Memory variable.
Example: 23 + 7 (Store to A), calculate sin (memory A), and clear
memory A
Calculation Operation
Independent Memory
•
Independent memory uses the same memory area as variable M.
It is convenient for calculating cumulative total by just pressing
(add to memory) or (subtract from memory); and the
memory contents are retained even when the calculator is turned off.
• To clear independent memory (M), input .
! When you want to clear all memory values, press
(Mcl)
Answer Memory
• The input values or the most recent calculation result will be
automatically stored into Answer Memory whenever you press ,
, , or followed by a memory variables.
• If you continue with pressing an operator key (x2, x3, x-1, x!, %, +,
–, x,
, DRG , ^, x , nPr and nCr), the displayed value will be
÷
changed into [Ans] plus the operator key. Then, you can perform a
new calculation with the latest Answer Memory.
Calculation Operation Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
Display (Upper Line)
Display (Lower Line)
15
• You can recall and use the latest stored Answer Memory by
pressing .
Calculation Operation Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
! Answer Memory is not updated as an error operation had been
performed.
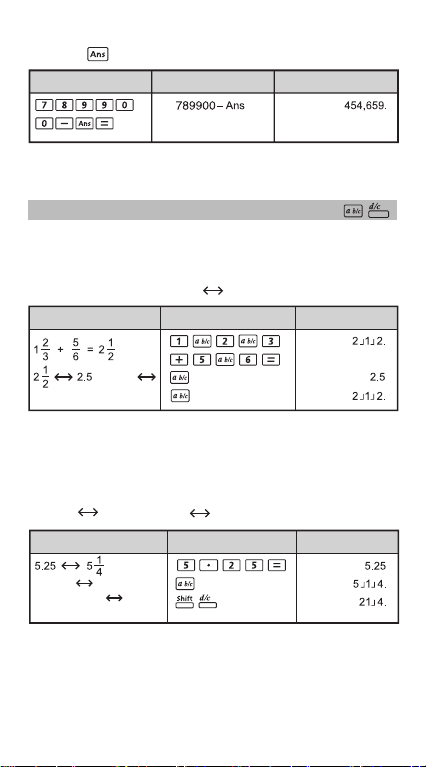
Fraction Operations
The Calculator support Fraction Calculation and the conversions
between Fraction, Decimal point, Mixed fraction and Improper
fraction.
Fraction Calculation, Fraction Decimal point conversion
Example Display (Lower)Operation
(Fraction
Decimal)
• Result will be displayed in decimal format automatically whenever
the total digits of a fractional value (integer + numerator +
denominator + separator marks) exceeds 10.
• As a fraction calculation is mixed with decimal value, the result will
be displayed by decimal format.
Decimal Mixed fraction Improper fraction conversion
Example Display (Lower)Operation
(Decimal Mixed Fraction)
(Mixed Fraction
Improper Fraction)
• Fraction conversion may take as long as two seconds.
16
! You can specify the fraction calculation result (when the result
greater than one) display format by either mixed fraction or
improper fraction. Simply press [Disp] , then
press the corresponding setting you need:
a b/c : Mixed fraction
d/c : Improper fraction
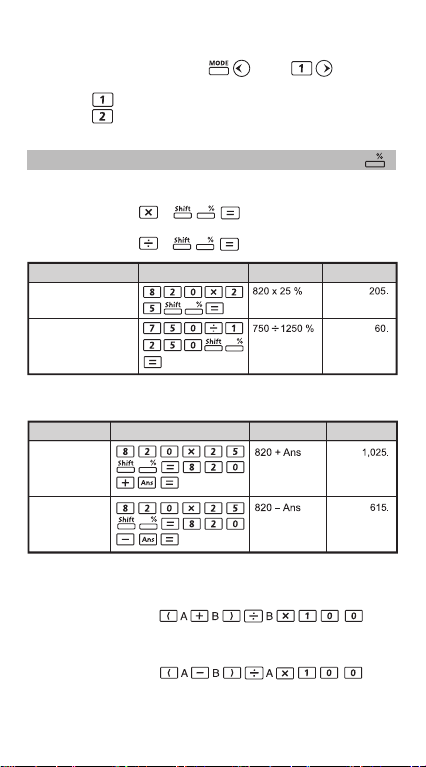
Percentage Calculations
You can perform the following percentage calculations:
Basic : To calculate a certain percentage of a value
(A B ).
: Percentage of a value against another value
(A B ).
Example Display (Lower)Display (Upper)Operation
To calculate 25%
of 820
The percentage of
750 against 1250
Mark up and Discount
Example
820 mark up
25%
820 have 25%
discount
Operation
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
Percentage Increase : If "A" is added to "B", the percentage
Percentage Change : If "A" is changed into "B", the percentage
increase from "B" is:
change from "A" to "B" is:
17

Example Display (Lower)Display (Upper)Operation
300 is added to 750, (300+750) 75 140.
the percentage
increase of 750 is
25 increased into 30, (30–25) 25x1 20.
the percentage change
of 25 is
Percentage Proportion : the ratio/ percentage of each individual
If A + B + C = D
"A" is a% of "D" where a = x 100%
Examples: To calculate the ratio of each portion as 25+85+90=200
(100%), the ratio of 25 is 12.5%, 85 is 42.5%, 90 is 45%
Operation
* You can store the sum of value into memory variables, then recall
and use the value by pressing or + Memory variable.
portion in a calculation expression.
A
D
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
Degree-Minutes-Seconds Calculations
You can use degrees (hours), minutes and seconds key to perform a
sexagesimal (base-60 notational system) calculation or convert the
sexagesimal value into decimal value.
Degree-Minutes-Seconds Decimal points
Examples Display (Lower)Operation
86o37' 34.2'' 0.7 =
o
123
45'6'' 123o45o6.
o
123
45'6''
123.7516667
123.7516667
o
2.3456 2
20'44'' 2o20o44.16
18

Constant Value Calculations
F-570SG has total 79 constant values, you can enter (or exit) the
constant value selection menu by pressing , the following display
will be shown:
• You can go to the next or previous value selection pages by
pressing or .
• To select a constant value simply press or button. The
selection cursor will shift left or right to underline a constant symbol
and at the same time the display lower line will show the value of
the underlined constant symbol.
• The underlined constant symbol will be selected as you press .
• You can instantly get the constant value if you input the constant
value item number and press when the selection cursor is
underling 0 0.
Operation Display
(menu selection page)
(confirm selection)
19

Scientific Constant Table
NO.
Proton mass
Neutron mass
Electron mass
Muon mass
Bohr radius
Planck constant
Nuclear magneton
Bohr magneton
Fine-structure constant
Classical electron radius
Compton wavelength
Proton gyromagnetic ratio
Proton Compton wavelength
Neutron Compton wavelength
Rydberg constant
(unified) atomic mass unit
Proton magnetic moment
Electron magnetic moment
Neutron magnetic moment
Muon magnetic moment
Faraday constant
Elementary charge
Avogadro constant
Boltzmann constant
Molar volume of ideal gas
Symbol
1.672621777x10
1.674927351 x10
9.10938291x10
-31
1.883531475x10
0.52917721092x10
6.62606957 x10
5.05078353 x10
927.400968 x10
-34
-27
-26
1.054571726 x10
7.2973525698x10
2.8179403267x10
2.4263102389 x10
2.675222005 x10
1.32140985623 x10
1.3195909068x10
10973731.568539
1.660538921 x10
1.410606743x10
-928.476430x10
-26
-0.96623647 x10
-4.49044807 x10
96485.3365
1.602176565x10
6.02214129x10
1.3806488 x10
22.413968 x10
23
-23
-3
UnitValueConstant
-27
-27
-28
-10
-34
-3
-15
-12
8
-15
-15
-27
-26
-26
-26
-19
Molar gas constant
Speed of light in vacuum
First radiationn constant
Second radiation constant hc/k
20
8.3144621
299792458
3.74177153x10
1.4387770 x10
-16
-2

NO.
Stefan-Boltzmann constant
Electric constant
Magnetic constant
Magnetic flux quantum
Standard acceleration of gravity
Conductance quantum
Characteristic impedance of vacuum
Celsius temperature
Newtonian constant of gravitation
Standard atmosphere
Proton g-factor
Planck length
Planck time
Planck mass
Atomic mass constant
Electron volt:
Molar planck constant
Wien displacement lawconstant
Lattice parameter of Si(in vacuum, 22.5▫C)
Hartree energy
Loschmidt constant
Inverse of conductance quantum
Josephson constant
Von Klitzing constant
Thomson cross section
Electron magnetic moment auomaly
Electron g-factor–2(1 + ae)
Electron gyromagnetic ratio
Muon magnetic moment anomaly
Muon g-factor-2
Symbol
UnitValueConstant
Pa
21

NO.
Muon Compton wavelength
Tau Compton wavelength
Tau mass
Shielded proton magnetic moment
moment (H2O, sphere, 25ºC)
Neutron g-factor
Neutron gyromagnetic ratio
Deuteron mass
Deuteron magnetic moment
Helion mass
Shielded helion magnetic
moment (gas, sphere, 25ºC)
Shielded helion gyromagnetic ratio
(gas, sphere, 25ºC)
Molar planck constant
Shielded proton gyromagnetic ratio
(H2O, sphere, 25ºC)
Proton magnetic shielding
correction
sphere, 25ºC)
Symbol
! Constant value cannot perform rounding.
Source: CODATA Internationally 2010
http://physics.nist.gov/constants
UnitValueConstant
22

Metric Conversions
F-570SG has 172 patterns of unit conversions to convert a value to
specified metric units. There are 8 categories including distance, area,
temperature, capacity, weight, energy, pressure and speed.
• Press to enter the conversion menu.
• Press or to select the category .
• Press or then to select the start unit.
• Press or then to select the end unit. You can preview
the value before pressing .
Page UnitSymbol
feet feet
m meter
mil milliliter
mm millimeter
1 in inch
cm centimeter
yd yard
mile mile
km kilometer
ft
yd
m
2 mile
km
hectares hectare
acres acre
3
gal gallon (U.K.)
liter liter
4 B.gal gallon (U.S.)
pint pint
fl.oz fluid ounces (U.S.)
Tr.oz ounce (troy or apothecary)
oz ounces
5 lb libra
Kg kilogram
g gram
J joule
6
cal.f calorie
atm standard atmosphere
Kpa kilopascal
7
mmHg millimeter of mercury
cmH
m/s Meter per second
8
km/h Kilometer per hour
2
square foot
2
square yard
2
square meter
2
square mile
2
square kilometer
o
F degree
o
C degree Celsius
O centimeter of water
2
23

• You can go back to the calculation mode instantly as the key
is pressed within the category selection pages. But after selected
the base conversion unit, , or keys will be invalid.
Example: Convert 10 + (5 ft2 m2) = 10.4645152
Operation Display
(enter the conversion menu)
2
(select ft
)
(convert to m2)
(calculate the answer)
! If the converted result is overflow, [-E-] will be shown in the lower
display. User cannot press to select the over flow value but
following scenario are valid:
Scenario A - Keep selecting the other conversion value by
Scenario B - Clear the screen by and jump out the
Scenario C - Pressing to jump back to previous
pressing or .
selection.
calculation screen.
Engineering Notation Calculations
Following nine symbols can be used when engineering symbols are
turned on by pressing and the LCD will display
[Eng].
Operation UnitUnit
k Kilo 10
M Mega 10
G Giga 10
T Tera 10
m Milli 10
Micro 10
n Nano 10
p Pico 10
f Femto 10
3
6
9
12
-3
-6
-9
-12
-15
24

Example: Convert 0.0007962 second into nano-second =
796200 x 10-9
Operation Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
796,200.
Example: 0.128 gram + 9.3 kilogram = 9300.128 gram
Fix, Sci, Norm, ROUND
You can change the number of decimal point, the number of
significant digits, or the exponential notation criteria by pressing
to the following selection screen:
Press (Fixed Decimal Setting)
Press (Scientific Notation) : [ Sci 0 ~ 9? ] appears on the
Press (Exponential Notation) : [ Norm 1 ~ 2? ] appears. Then,
you can specify the exponential
or .
Norm 1 : Exponential notation is automatically used for integer
values with more than 10 digits and decimal values
with more than two decimal point.
Norm 2 : Exponential notation is automatically used for integer
values with more than 10 digits and decimal values
with more than nine decimal point.
: [ Fix 0 ~ 9? ] appears on the
display. Then, you can specify the
number of decimal places by
pressing ~ .
display. Then, you can specify the
number of significant digits by
pressing ~ .
notation format by pressing
• To clear the setting, refer page 13.
(internal rounding) : Calculate the value or formula result to
decimal, round it off to the significant
decimal place according to the current
specified indication digit setting
(Fix, Sci, Norm).
25

Examples: 57
At default setting. 162.8571429
To fix 4 digits decimal point.
(Internal calculation continues 162.8571
16 digits) 8.1429
162.8571
Perform internal rounding 8.1429
under the specified decimal
setting. 162.8580
To display by 6 digits scientific 1.62858
notation.
Notation format by pressing 162.858
to clear the FIX and Sci
specifications.
÷ 7 x 20 = ??
Operation
Display (Lower)
x10
FUNCTIONAL SCIENTIFIC CALCULATIONS
Press to enter COMP mode for performing functional
scientific calculations.
During the busy calculation, the calculator will display the
message [PROCESSING].
= 3.14159265359
Square, Root, Cube, Cube Root, Power, Power Root,
Reciprocal and Pi
Square Root CubeCube Root
PowerPower Root Reciprocal Pi
Example:
Operation Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
02
Example:
Operation Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
26

Angle Unit Conversion
The calculator default angle unit setting is "Degree". If you need to
change into "Radian" or "Gradient", you can press a number of
times until you reach the setup screen:
Then press the corresponding number key , or for the
angle unit you need. Then the display will show the D , R or G
indicator accordingly.
To convert an angle unit between "Degree", "Radian" and "Gradient",
you can press and the following display menu will be shown:
Then, press , or will convert the displayed value into the
selected angle unit. If you want to indicate the value with other degree
unit after conversion, change the unit using .
Example: Convert 180 degree into radian and gradient
(180
º
Rad
= 200
Gad
)
=
Operation Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
(Radian mode)
(Gradient mode)
Trigonometry Calculations
Before using the trigonometric functions (except hyperbolic
calculations), select the appropriate angle unit (Deg/ Rad/ Gad)
by .
o
90
= ; Radian = 100 Gradient.
27

Trigonometric (sin/ cos/ tan), Inverse Trigonometric
-1
(sin
/ cos-1/ tan-1) Functions
Examples Display (Lower)Operation
Degree Mode
sin 53o 22’ 12” = 0.802505182
0.802505182
.0
cosec x = 1/sinx 1.414213562
o
cosec 45
= 1.414213562
-1
tan
(5/6) = 39.80557109° 39.80557109
Radian Mode
Rad
cos( /6)
0.785398163 0.785398163
1
-1
— =
cos
2
Hyperbolic (sinh/ cosh/ tanh), Inverse Hyperbolic
-1
(sinh
/ cosh-1/ tanh-1) Functions
)daR( 52.0
Examples Display (Lower)Operation
Logarithm, Natural Logarithm,
Antilogarithm and Logab
Examples Display (Lower)Operation
log 255 + ln 3 = 3.505152469
–3
1.2
+ 10
= 15.89871899
e
3.505152469
log
81 – log 1 = 4
3
.0
304520668.0 304520668.0 =
52.0
99817898.51
.4
28

Coordinate Conversion
With polar coordinates, you can calculate and display result
within –180
After conversion, results will automatically assigned to memory
variables E and F.
: To convert rectangular coordinates (x, y) to polar
Degree Mode
With rectangular coordinate 2.
(x =1,y = 3). Find Polar
coordinate (r, ) at degree 60.
mode 2.
o
180o range. (Same as Radian and Gradient)
coordinates ( r , ); Press to display the value
of r, or to display the value of .
Examples
Operation
Display (Lower)
.0
: To converts polar coordinates ( r , ) to rectangular
! [Syntax ERROR] will be shown if is missed in the coordinate
coordinates (x, y); Press to display the value of
x, or to display the value of y.
Examples
With Polar coordinate (r=2,
=60º). Find rectangular
coordinate (x,y) at degree
mode
Operation
conversion calculation.
Display (Lower)
1.732050808
Complex Number
Calculations
Complex numbers can be expressed by rectangular form (z = a + bi)
or polar form (r ). Where " a " is the real number part, " bi " is the
imaginary number part (and i is the imaginary unit equal to square
root of –1,
the complex number.
–1), " r " is the absolute value, and " " is the argument of
Imaginary axis ( i )
Real axis
29
1.
1.

As you need to perform the complex number calculation
Press to enter CPLX mode.
Check the current angle unit setting (Deg, Rad, Grad).
The indicator will be shown as the calculation result having
complex numbers. Just press to switch the result
display.
[ ] icon indicate the display result is imaginary number part;
[ ] indicate the display value is the argument value .
But the imaginary numbers will use up replay memory capacity.
Displaying the complex number calculation result
Pressing , following display options will be shown:
a+bi r
1 2
You can set up the complex number calculation result display format
by pressing:
: Rectangular form (Default setting).
: Polar form (the [r ] display indicator will be turned on).
Example: (12+3 ) – (3 + 1 ) = 9 + 2 = 9.219544457 (r)
12.52880771 ( )
Operation (Angle Unit: Degree) Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
(12+3i)-(3+i 9.
(12+3i)-(3+i 2.
(12+3i)-(3+i 12.52880771
(change display value)
(12+3i)-(3+i 9.219544457
Rectangular Form Polar Form Conversion
Press can convert rectangular form complex number into
polar form; whereas press will convert polar form complex
number into rectangular form.
Example: 3 + 4
Operation (Angle Unit: Degree) Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
3 4 3 + 4i > 5
3 + 4i > 53.13010235
= 5 53.13010235
30

Example:
2 45>a+bi 1.
2 45>a+bi 1.
Absolute Value and Argument Calculation
With the rectangular form complex number, you can calculate the
corresponding absolute value (r) or argument ( ) by or
key respectively.
Example: What's the absolute value (r) and argument ( ) if complex
Abs ( 6+8i 10.
Arg ( 6+8i 53.13010235
Conjugate of a complex number
If the complex number is z = a + bi, the conjugate value of this
complex number should be z = a – bi.
2 45 = 1 +
Operation (Angle Unit: Degree) Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
number is 6+8
Operation (Angle Unit: Degree) Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
Example: The conjugate of 3 + 4 is 3 – 4
Operation (Angle Unit: Degree) Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
Conjg ( 3+4i 3.
Conjg ( 3+4i – 4.
Base-n Calculations and Logical Calculations
Press to enter Base-n mode for decimal (base 10),
hexadecimal (base 16), binary (base 2), octal (base 8), or logical
calculations.
Default base number system is Decimal with [d] display indicator
To select a specific number system in base mode, simply press
Decimal [d], Hexadecimal [H], Binary [b], or
Octal [o].
The key allows you to perform logical calculations includes:
Logic connection [And] / [Or], exclusive or [Xor], exclusive nor
[Xnor], argument complement [Not], and negation [Neg].
If the binary or octal calculation result is more than 8-digit, [1b] /
[1o] will be displayed to indicate the result has next block. Keep
pressing can loop between result blocks.
All the scientific functions cannot be used, and you cannot input
the value with decimal place or exponent.
31

Binary Calculation
Example: 10101011 + 1100 – 1001 x 101 10 = 10100001
(at Binary Mode)
Operation Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
10101011+110 10100001.
Octal Calculation
Example: 645 + 321 – 23 x 7 2 = 1064 (at Octal Mode)
645+321-23x7 1064.
Hexadecimal Calculation
Example: (77A6C + D9) x B F = 57C87 (at Hexadecimal Mode)
(77A6C + D9) x B 57C87.
b
o
H
Base-n transformation
12345+b101 12352.
12345+b101 14EA.
12345+b101 11101010.
(go to next block of the result) 12345+b101 10100.
12345+b101 11101010.
o
H
1b
2b
1b
Logical Operation
Examples
(Hexadecimal Mode)
789ABC Xnor 147258 FF93171b.
Display (Lower)Operation
H
Ans Or 789ABC FFFb9FbF.
Neg 789ABC FF876544.
! Beware of the allowable input range of each number system
(page 10).
32
H
H

STATISTICAL CALCULATIONS [SD] [REG]
To enter the standard deviation mode by pressing ,
[SD] indicator lights up. If press , you can enter the
regression mode selection menu. [REG] indicator will be turned on.
Before starting, be sure to clear the statistic memory by pressing
.
Perform the data input (Precautions!).
• In SD mode, store the displayed data by pressing .
• In REG mode, store the x-data and y-data in the form of:
x-data y-data .
• Pressing will input the same data twice.
• Use for same data multiple entries. For example in SD
mode, the data 20 has 8 times will press 20 8 .
• Each time you press to register the input, the number of
data input up to that point is indicated on the display once
(n = the number of input data).
• Press or key during or after data input can display the
data value (x) and data frequency (Freq). Follow with the above
example, press will display [x1 = 20], and press will
display [Freq1= 8].
• To edit the stored data, input the new value during the display
of that data value (x) after pressing or key, and then
press to confirm the edit. But, if you press instead of
,a new data value will be stored.
• Press can delete the data during the display of that
data value (x) after or key is pressed; and the
sequence of the data which following the deleted data will be
shifted up automatically.
• Press key to exit the data value and frequency display,
then you can perform other calculation operations.
• Input data are stored in calculation memory. As the memory full,
[Data Full] will be displayed and you cannot input or perform
any calculation. Press key to perform other calculation
operations.
• After changing into another mode or regression type (Lin, Log,
Exp, Pwr, Inv, Quad), input data will be cleared.
After finishing data entries, you can recall or calculate the
statistical values.
33

Standard Deviation
Press to ender SD mode.
Before starting, be sure to clear the statistical memory by
pressing .
You can recall the following statistical value after input all the
data.
Value OperationSymbol
Square of Sum x
Summation of x x
Number of data sample n
Mean of x x
Population Standard Deviation of x x
Sample Standard Deviation of x x n-1
Example: To calculate x2, x, n, x, x n , and x n-1 of data: 75, 85,
90, 77, 77 in SD mode.
Operation Display (Lower)
n = 5.
(select Scl, clear Stat. memory)
2
n
Display (Upper)
Stat clear 0.
x
x 404.
n 5.
x 80.8
x
x
2
32,808.
n 5.741080038
n-1 6.418722614
Regression Calculations
Press to ender REG mode, then the follow screen
options will be shown:
Lin Log Exp
1 2 3
Press , or for the corresponding regression
[Lin] = Linear regression
[Log] = Logarithmic regression
[Exp] = Exponential regression
34

If follow with or another regression options will be displayed
as follow:
Pwr Inv Quad
1 2 3
You can press , or for the corresponding regression
[Pwr] = Power regression
[Inv] = Inverse regression
[Quad] = Quadratic regression
Before starting, be sure to clear the statistical memory by pressing
.
Input data in the form of x-data y-data . Use
for same data multiple entries.
Press can delete the data during the display of data
value after or key is pressed.
You can recall and use the following regression results:
Value OperationSymbol
Summation of all x2 value x2
Summation of all x value x
Number of data sample n
Summation of all y2 values y2
Summation of all y values y
Summation of all xy pairs xy
Mean of the x values x
Population Standard Deviation of x x n
Sample Standard Deviation of x x
Mean of the y values y
Population Standard Deviation of y y n
Sample Standard Deviation of y y
Regression coefficient A
Regression coefficient B
n-1
n-1
35

For non-quadratic regression
Correlation coefficient r
Regression estimated value x
Regression estimated value y
For Quadratic regression only
Summation of all x
3
values x
3
Summation of all x2y pairs x2y
Summation of all x4 values x
4
Regression coefficient C
Regression estimated value x 1 x
Regression estimated value x 2 x
1
2
Regression estimated value y y
Linear regression
• The Linear regression formula is in relation to two variables:
y = A + Bx
• Example: By the following investment and yield table, calculate
the linear regression (regression coefficient A, regression
coefficient B) of capital investment verse yield, the correlation
coefficient, the yield percentage at 45 thousand unit of
investment, and the investment unit at 180% yield.
Investment (thousand unit) Yield (%)
20 120
30 126
40 130
50 136
60 141
36

Display
Operation
(Upper)
Display (Lower)
Logarithmic, Exponential, Power, and Inverse Regression Formulas
• Loarithmic Regression : y = A + Blnx
• Exponential Regression : y = Ae
• Power Regression : y = Ax
• Invere Regression : y = A+Bx
Quadratic Regression
• The quadratic regression is in relation to the formula:
y = A + Bx + Cx
• Example: ABC company investigated the effectiveness of the
advertisement expenses in coded units, the following data were
obtained:
2
Bx
(lny = lnA + Bx)
B
(lny = lnA + Blnx)
–1
Advertisement expenses: x Effectiveness: y (%)
18 38
35 54
40 59
21 40
19 38
Please calculate the correlation coefficient; use the regression to
estimate the effectiveness (estimate the value of y) if the
advertisement expenses x = 30, and estimate the advertisement
expenses level (estimate the value of x) for the effectiveness
y = 50.
37

Operation
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
Distribution Calculations
After sample data are entered in either Statistic (SD) or
Regression (REG) mode, you can perform the normal distribution
or probability distribution calculation such as P(t), Q(t) and R(t) in
which t is the variate of the probabilistic experiment.
Random variable
Mean of sample
Standard deviation
Press will display the following selection screen.
P( Q( R( t
1 2 3 4
You can press , , or for the corresponding
calculations.
38

P(t): Probability below a
given point x
1 t– u
2
– ( )
1
P(t )= e dt ,
2
2
P(t)
Q(t): Probability below a
given point x and above
the mean
R(t): Probability above a
given point x
Example: Calculate the probability distribution P(t) for the sample
data: 20, 43, 26, 46, 20, 43, 26, 19, 23, 20 when x = 26.
Operation
Q ( t ) = 0.5 – R ( t ),
R ( t ) = 1 – P ( t ),
Display (Upper)
Q(t)
R(t)
Display (Lower)
Permutation, Combination, Factorials and Random
Number Generation
• Permutation : nPr =
• Combination : nCr =
• Factorial : x! = x(x-1)(x-2).....(2)(1)
n!
(n-r)
n!
r!(n-r)
39

Examples Display (Lower)Operation
720.
10P3
10.
5C2
5! 120
Random Number Generation
: To generate a random number between 0.000 and
0.999 ; the result differ each time with the same
possibility of occurrence.
: To generate a random number between two specified
integers. Results differ each time with the same
possibility occurrence within a boundary. The entry is
divided with " , ".
Example: To generate a random number between 0.000 and 0.999;
and generate an integer from range of 1 to 100
Operation
Rand 0.833*
i~Rand(1,100 83.*
Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
* The value is only a sample, results will differ each time.
EQUATION CALCULATIONS
Press to enter the equation mode and the
following selection options will be displayed:
Unknowns?
2 3
By this screen, you can choose for the simultaneous linear equation
solve with either two (2) or three (3) unknowns. Or press or
to display another the options for quadratic (2) or cubic (3) equation:
40

Degree?
2 3
After the equation type is selected, [EQN] indicator lights up. The
following equation solve guiding page sample will be shown if you
specified the equation solve for two (2) or three (3) unknowns
simultaneous linear equation:
Coefficient name
a1?
0.
(Sample display for simultaneous linear
equation solve)
• For quadratic or cubic equation solve, the coefficient name starts
with "a"
• You cannot input complex number as an coefficient
• The calculation starts aftr the last factor ("c2": where the
simultaneous linear equations with two unknows, "d3", where the
simultaneous linear equations with three unknows "c" quadratic
equation and "d" cubic equation) of the specified equation and
then the root of an equation appears.
Variable name
X =
0.
(Sample display for simultaneous linear
equation solve)
• The input display appears by pressing the key, and you can
display or edit the value by pressing the or key. After that,
the last factor is displayed and a calculation is performed again by
pressing to display the root.
• For quadratic or cubic equation, the Variable name starts with "X1".
• Press or key to display the equation solve results.
• If you want to return to the coefficient input screen, simply press
key.
Indicates the direction of
next step or viewing the
other related elements.
Element Value
Indicates the direction of
next step or viewing the
other results.
Result
41

Simultaneous Linear Equations
Two Unknowns Simultaneous Linear Equation:
a
a2x + b2y = c
Three Unknowns Simultaneous Linear Equation:
a1x + b1y + c1z = d
a2x + b2y + c2z = d
a3x + b3y + c3z = d
Example: Solve the simultaneous equation with three unknowns:
2x + 4y – 4z = 20
2x – 2y + 4z = 8
5x – 2y – 2z = 20
Quadratic or Cubic Equations
Quadratic equation : ax2 + bx + c = 0 (a second-order polynomial
Cubic equation : ax3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0 (an equation with cubic
Example: Solve the cubic equation 5x
x + b1y = c
1
1
2
1
2
3
Operation
equation in a single variable x)
polynomial)
Operation
Display (Upper)
3
+ 2x2 – 2x + 1 = 0
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
Display (Lower)
42

SOLVE FUNCTION
You can solve any calculation expression as per your needs in
COMP mode. Simply input the expression with different variables
and press the key.
Example: A cone of height "h" and base is a circular with radius "r",
So, you can replace the variable "V" by A, variable "r" by "B", and
variable "h" by "C".
If the radius is 5cm, cone height is 20cm, calculate the cone volume.
And if the cone volume is 200cm
cone height.
0.
A=(1 3) B
A? 0.
B? 0.
(radius is B = 5cm) C? 0.
(height is C = 20cm) C? 20.
A? 0.
A = 523.5987756
(Calculate with new variables)
C = 47.74648293
! If the expression does not have the equal sign ( = ) and perform
the Solve calculation, the calculator will transform the solution as
zero ( 0 ).
! When the expression cannot be solved, [Solve ERROR] will be
displayed.
the volume of the cone will be in the formula:
1
V = r
3
Operation
(volume is A = 200 cm3)
(radius is B = 2 cm) C? 20.
1
2
h A = B2C
3
3
, with radius 2cm, calculate the
h
s
r
Display (Upper)
A ? 523.5987756
B? 5.
Display (Lower)
2
C 0.
43

CALC FUNCTION
CALC function is deemed to be a memory zone with maximum 79
steps for you to store a single calculation expression which will be
recalled and calculated a number of times by different values.
After input the calculation expression and pressed , the
calculator will request for the current value of your input variables.
Beware that CALC function can only be used in COMP mode or
CPLX mode.
Example: For the equation Y = 5x2 –2x +1, calculate the value of Y if
x = 5 or x = 7.
Operation
Y = 5x
X? 0.
Y = 5x
Y = 5x
! The stored expression will be cleared as you start a new
calculation, change into another mode, or turn off the calculator.
Display (Upper)
2
2
2
Display (Lower)
–2x +1 0.
–2x +1 116.
–2x +1 232.
44

DIFFERENTIAL CALCULATIONS
Press to enter COMP mode for differential calculation.
To perform a differential calculation, you have to input the expression
in the form of:
differential expression a ∆x
• The differential expression must contain the variable x.
• "a" is the differential coefficient.
• "∆x" is the change interval of x (calculation precision).
Example: To determine the derivative at point x = 10, ∆x = 10-8, for
the function f(x) = sin(3x + 30).
Operation
! You can leave out the ∆x in the differential expression and the
calculator will automatically substitute a value for ∆x.
! The smaller the entered value ∆x is, the longer the calculation time
will be and the result is more accurate; the bigger the entered
value ∆x is, the shorter the calculation time will be and the result
will be comparatively less accurate.
! Discontinuous points and extreme changes in the value of x can
cause inaccurate results or errors.
! When performing differential calculation with trigonometric
function, select radian (Rad) as the angle unit setting.
! Logab, i~Rand, Rec( and Pol( functions can’t join to differential
calculation.
! During the busy calculation, the calculator will display the message
[PROCESSING]
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
45

INTEGRATION CALCULATIONS
Press to enter COMP mode for integration calculation.
To perform an integration calculation you are required to input
following elements:
integration expression a b n
• The integration expression has variable x.
• "a" and "b" defining the integration range of the definite integral.
• "n" is the number of partitions (equivalent to N = 2
The integration calculation is based on Simpson’s rule.
As the number of significant digits is increased, internal integration
calculations may take considerable time to complete. For some
cases, even after considerable time is spent for performing a
calculation, the calculation results may be erroneous. Particularly
when significant digits are less than 1, an ERROR might be
occurred.
Example: Perform the integration calculation for
, with n = 4.
3
(5x4 + 3x2 + 2x + 1)dx
2
Operation
Display (Upper)
n
).
Display (Lower)
! The number of partitions (n) have to specify in the range of 1 to 9
integer, any value that out of the setup division range (N=2
n=1~9 integer), [Arg ERROR] will be displayed.
! You can skip the number of partitions entirely and the calculator
will automatically assign an appropriate value on behalf of you.
! The smaller the value of n is, the shorter the calculation time is, but
the result is comparatively less accurate; on the other hand, the
bigger the n is, the longer the calculation time is, and the result is
more accurate.
! When performing integration calculation with trigonometric
function, select radian (Rad) as the angle unit setting.
! Logab, i~Rand, Rec( and Pol( functions can’t join to integration
calculation.
! During the busy calculation, the calculator will display the message
[PROCESSING].
n
, n 0,
46

MATRIX CALCULATIONS
Enter the matrix mode by pressing , and
[MATX] indicator lights up.
Before you start matrix calculations, you have to create one
matrix or maximum three matrices which named A, B, and C at
one time.
The matrix calculation results are stored into MatAns memory
automatically. You can use the matrix MatAns memory for any
subsequent matrix calculations.
Matrix calculation may use up to two levels matrix stack; however,
squaring a matrix, cubing a matrix, or inverting a matrix only use
one stack.
Create a Matrix
1. Press (Dim) to specify the matrix name (A, B or
C), and then specify the dimension (number of rows and number
of columns) of the matrix. The dimension of matrix can be up to
3 x 3.
2. Next, input the value (element) of the matrix according to the
matrix element indictor display, following is a matrix element
indictor example:
MatA23
2 rows and 3 columns
3. Use the cursor keys to move, view or edit the matrix elements.
4. When finished the input, press to exit the matrix creation
screen.
Edit Matrix Elements
1. Press (Edit), then specify the matrix A, B or C for
editing and the corresponding matrix element indicator will be
displayed.
2. Input the new value and press to confirm the edit.
3. When finished the input, press to exit the matrix editing
screen.
47

Matrix Addition, Subtraction and Multiplication
1 2 3
Example: MatA = , MatB = , MatA x MatB=?
4 5 6
7 8 9
Operation
9 8 7
6 5 4
3 2 1
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
(press left, right, up or down
key to display the result)
48

Obtain the Scalar Product of a Matrix
Each position in the matrix is multiplied by a single value, resulting in
a matrix of the same size. Following procedures show you how to
obtain the scalar product of a matrix with the fixed multiple:
Example: Multiple Matrix C = by 2 <Result: >
Operation
Obtain the Determinant of a Matrix
Following procedures show you how to obtain the determinant of a
square matrix:
Example: Obtain the determinant of Matrix C =
<Result: -471>
Operation
(Dim)
(Matrix C 3x3)
(Input Element)
3 -2
-1 5
Display (Upper)
Display
(Upper)
6 -4
-2 10
Display (Lower)
10 -5 3
-4 9 2
1 7 -3
Display
(Lower)
(DetMatC)
! An error occurs if you obtain the determinant of a non-square
matrix.
49

Transpose a Matrix
Following procedures show you how to transpose a matrix:
9 5
Example: Transpose Matrix B = <Result: >
6 2
8 4
Operation
(Dim)
(Matrix B 3x2) MatB
(Input Element ) MatB
Det Trn 1 2
(Trn MatB) Trn MatB 0.
(press left, right, up or
down key to display the result) MatAns
Invert a Matrix
Following procedures show you how to invert a square matrix:
Example: Inverting Matrix C =
1
< Result:
7
1
14
Operation
(Dim)
(Matrix C 2x2) MatC
(Input Element ) MatC
MatC
-1
(MatC
MatAns
MatAns
MatAns
) MatAns11
8 2
3 6
1
21
4
21
Display (Upper)
0.
11
9.
11
11
Display (Upper)
0.
11
8.
11
-1
0.
12
21
22
9 6 8
5 2 4
Display (Lower)
9.
Display (Lower)
50

Determine the Absolute value of a Matrix
Following procedures show you how to determine the absolute value
of a matrix:
Example: To determine the absolute value of the inverted Matrix C in
the previous example.
Operation
Abs MatAns 0.
MatAns11 1┘7
MatAns12 1┘21
MatAns21 1┘14
MatAns22 4┘21
Display (Upper)
Display (Lower)
VECTOR CALCULATIONS
Enter the vector mode by pressing , and
[VCTR] indicator lights up.
Before you start vector calculations, you have to create one or
more vector which named A, B, or C (maximum three vectors at
one time).
The vector calculation results are stored into VctAns memory
automatically. You can use the vector VctAns memory for any
subsequent vector calculations.
Create a Vector
1. Press (Dim) to specify the vector name (A, B or C),
and then specify the dimension of the vector.
2. Next, input the value (element) of the vector according to the
vector element indictor display, following is a vector element
indictor example:
Element Value
3. Use the cursor keys to move, view or edit the vector elements.
4. When finished the input, press to exit the vector creation
screen.
Edit Vector Elements
1. Press (Edit), then specify the vector A, B or C for
2. Input the new value and press to confirm the edit.
3.
Vector name Dimensions of Vector
VctA1
editing and the corresponding vector element indicator will be
displayed.
When finished the input, press to exit the vector editing screen.
51
0.
Direction indicator, you
can view other elements
at next page.

Vector Addition and Subtraction
Following procedures show you how to add or subtract vectors:
Example: Vector A = (9,5), Vector B = (7,3), Vector A – Vector B =?
Operation
(Create Vector A) VctA(m) m? 0.
(Vector A dimension is 2) VctA
(Input Element) VctA
0.
1
9.
1
(Create Vector B)
VctB
(Input Element) VctB
0.
1
7.
1
VctA - VctB 0.
VctAns
VctAns
! An error occurs if you try to add or subtract vectors whose
dimensions are different from each other. For example Vector A
(a,b,c) cannot add or subtract with Vector B (d,e).
Obtain the Scalar Product of a Vector
Each position in the vector is multiplied by a single value, resulting in
a vector of the same size.
s x VctA(a,b) = VctB(axs, bxs)
Following procedures show you how to obtain the scalar product of a
vector with the fixed multiple.
Example: To Multiply Vector C = (4,5,-6) by 5
Operation
Display (Upper)
(Create Vector C) VctC(m) m? 0.
VctC
(Input Element)
VctC1 4.
5 x VctC 0.
(5 x VctC) VctAns
VctAns
VctAns
Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
2.
1
2.
2
Display (Lower)
0.
1
20.
1
25.
2
-30.
3
52

Calculate the Inner Product of Two Vectors
Following procedures show you how to calculate the inner product of
two vectors.
Example: Calculate the inner product of Vector A and Vector B. As
Vector A = (4,5,-6) and Vector B = (-7,8,9), and the both
vectors are already created in the calculator.
Operation
(Recall
Vector A ) VctA 0.
Dot 1
VctA
VctA
.
(VctA
VctB) VctA . VctB -42.
Calculate the Outer Product of Two Vectors
Following procedures show you how to calculate the outer product of
two vectors.
Example: Calculate the outer product of Vector A and Vector B. As
Vector A = (4,5,-6) and Vector B = (-7,8,9), and the both
vectors are already created in the calculator.
.
.
Operation
(Recall
Vector A ) VctA 0.
VctA x 0.
VctA x VctB 0.
(VctA x VctB) VctAns
VctAns
VctAns
! An error occurs if you try to obtain an inner or outer product of two
vectors whose dimensions are different from each other.
Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
0.
VctB 0.
Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
93.
1
6.
2
67.
3
53

Determine the Absolute value of a Vector
Following procedures show you how to determine the absolute value
(size) of a vector:
Example: To determine the absolute value of the Vector C. As Vector
C = (4,5,-6) and already created in the calculator.
Operation
Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
Abs VctC 0.
Abs VctC 8.774964387
Example: Base on Vector A=(–1, –2, 0) and Vector B=(1, 0, –1),
determine the size of the angle (angle unit: Deg) and the
size 1 vector perpendicular to both A and B.
cos = , whereas = cos
(A • B)
|A||B|
Size 1 vector perpendicular to both A and B=
VctA x VctB
Result: =
|VctA x VctB|
Operation
(VctA
(calculate )
VctA . VctB
| VctA | x | VctB |
(calculate VctA x VctB = (2, -1, 2)) VctAns
(calculate | VctA x VctB |) Abs VctAns 3.
(Create Vector A)
(Input Elements)
(Create Vector B)
(calculate = cos-1 ) cos
VctB1 0.
(Input Elements)
.
VctB) VctA . VctB –1.
(A • B)
–1
|A||B|
A x B
|A x B|
Display (Lower)Display (Upper)
VctA1 0.
VctA1 –1.
VctB1 1.
Ans (Abs Vct
–0.316227766
–1
Ans 108.4349488
2.
1
(Calculate =) VctAns
VctAns
VctAns
1
2
3
54

BATTERY REPLACEMENT
Replace the battery immediately when the display characters are
dim even a darker LCD contrast OR when the following message
appears n the screen. Turn the calculator off and replace the
alkaline bttery immediately.
Please replace the alkaline battery with the following procedures,
1. Press to power off the calculator.
2. Remove the screw that securely fixes the battery cover in place.
3. Remove battery cover.
4.
Remove the old battery with the tip of a ball pen or similar sharp object.
5. Load the new battery with the positive "+" side facing up.
6. Replace the battery cover, screw, and press
the reset button to initialize the calculator.
Caution: Do not use the battery other than the specified
one. Failure to do so may burst the battery, causing
environment contamination or personal injury due to
electrolyte leakage.
Insulate the positive and negative poles of the spent battery
with a tape, follow your local environment regulations and
waste disposal standards, and then dispose the battery.
Battery Cautions
● Keep the battery out of reach of children. If the battery is
swallowed, contact a doctor immediately.
● Misuse of battery may cause leakage, explosion, damages
or personal injury.
● Don’t recharge or disassemble the battery, it could cause a
short circuit.
● Never expose the battery to high temperatures, direct heat,
or dispose by incineration.
55

SPECIFICATIONS
Power Supply : Solar cell and single Alkaline battery
Power Consumption : D.C. 1.5V / 0.1mW
Battery Life : Approximately 3 years
(Base on 1 hour of operation per day)
Auto Power Off : Approx. 7 minutes
Usable Temperature : 0 ~ 40°C
Size : 165 (L) x 80 (W) x 14 (H) mm (body)
168 (L) x 86 (W) x 17.8 (H) mm (with case)
Weight : 89 g (body) / 127 g (with case)
* Specifications are subject to change without notice.
CANON ELECTRONIC BUSINESS MACHINES (H.K.) CO., LTD.
17/F., Tower One, Ever Gain Plaza,
82-100 Container Port Road, Kwai Chung,
New Territories, Hong Kong
CANON MARKETING (MALAYSIA) SDN BHD.
Block D, Peremba Square, Saujana Resort, Section U2,
40150 Shah Alam, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia
(LR44 x 1)
© CANON ELECTRONIC BUSINESS MACHINES (H.K.) CO., LTD. 2016
Made in China / Printed in China
56
PUB NO. E-IE-483
 Loading...
Loading...