Canon Color Universal Send Kit-Q1 Service Manual
SERVICE
MANUAL
Color Universal
Send Kit-Q1
JANUARY 21, 2009


Application
This manual has been issued by Canon Inc. for qualified persons to learn technical theory, installation, maintenance, and repair
of products. This manual covers all localities where the products are sold. For this reason, there may be information in this
manual that does not apply to your locality.
Corrections
This manual may contain technical inaccuracies or typographical errors due to improvements or changes in products. When
changes occur in applicable products or in the contents of this manual, Canon will release technical information as the need
arises. In the event of major changes in the contents of this manual over a long or short period, Canon will issue a new edition
of this manual.
The following paragraph does not apply to any countries where such provisions are inconsistent with local law.
Trademarks
The product names and company names used in this manual are the registered trademarks of the individual companies.
Copyright
This manual is copyrighted with all rights reserved. Under the copyright laws, this manual may not be copied, reproduced or
translated into another language, in whole or in part, without the written consent of Canon Inc.
COPYRIGHT © 2001 CANON INC.
Printed in Japan
Caution
Use of this manual should be strictly supervised to avoid disclosure of confidential information.

Symbols Used
This documentation uses the following symbols to indicate special information:
Symbol Description
Indicates an item of a non-specific nature, possibly classified as Note, Caution, or Warning.
Indicates an item requiring care to avoid electric shocks.
Indicates an item requiring care to avoid combustion (fire).
Indicates an item prohibiting disassembly to avoid electric shocks or problems.
Indicates an item requiring disconnection of the power plug from the electric outlet.
Indicates an item intended to provide notes assisting the understanding of the topic in question.
Memo
Introduction
REF.
Indicates an item of reference assisting the understanding of the topic in question.
Provides a description of a service mode.
Provides a description of the nature of an error indication.

Introduction
The following rules apply throughout this Service Manual:
1. Each chapter contains sections explaining the purpose of specific functions and the relationship between electrical and mechanical systems with reference to the timing of operation.
In the diagrams, represents the path of mechanical drive; where a signal name accompanies the symbol , the arrow indicates the
direction of the electric signal.
The expression "turn on the power" means flipping on the power switch, closing the front door, and closing the delivery unit door, which results in
supplying the machine with power.
2. In the digital circuits, '1'is used to indicate that the voltage level of a given signal is "High", while '0' is used to indicate "Low".(The voltage value, however, differs from circuit to circuit.) In addition, the asterisk (*) as in "DRMD*" indicates that the DRMD signal goes on when '0'.
In practically all cases, the internal mechanisms of a microprocessor cannot be checked in the field. Therefore, the operations of the microprocessors
used in the machines are not discussed: they are explained in terms of from sensors to the input of the DC controller PCB and from the output of the
DC controller PCB to the loads.
The descriptions in this Service Manual are subject to change without notice for product improvement or other purposes, and major changes will be communicated in the form of Service Information bulletins.
All service persons are expected to have a good understanding of the contents of this Service Manual and all relevant Service Information bulletins and be
able to identify and isolate faults in the machine."


Contents
Contents
Chapter 1 Specifications
1.1 Specifications ............................................................................................................................................. 1- 1
1.1.1 Memory Size and Functional Constraints iPR1135/1125/1110(USA) ..................................................................... 1- 1
1.1.2 SEND Options (USA/EUR/AU)................................................................................................................................ 1- 2
1.1.3 Specifications ..........................................................................................................................................................1- 3
Chapter 2 Functions
2.1 Basic Function ............................................................................................................................................ 2- 1
2.1.1 Authentication at TX ................................................................................................................................................2- 1
2.1.2 Authentication at RX................................................................................................................................................2- 3
2.1.3 Encrypted transmission ...........................................................................................................................................2- 4
2.1.4 Encrypted reception.................................................................................................................................................2- 5
2.1.5 MAC Address Block Function..................................................................................................................................2- 5
2.1.6 URL Send ................................................................................................................................................................2- 6
2.1.7 Setting for communicate SSL ..................................................................................................................................2- 6
2.1.8 i-Fax Divided Data Transmission.............................................................................................................................2- 7
2.1.9 E-Mail Divided Data Transmission ..........................................................................................................................2- 7
2.1.10 E-Mail Divided Data Reception..............................................................................................................................2- 8
2.1.11 USB Deactivation...................................................................................................................................................2- 8
2.1.12 Searchable PDF ....................................................................................................................................................2- 9
2.1.13 Document Orientation Auto Detection ...................................................................................................................2- 9
2.1.14 Document Name OCR...........................................................................................................................................2- 9
2.1.15 Increased Support of File in a Box.......................................................................................................................2- 10
2.1.16 Limit of Reception Length of Extra Long Original ................................................................................................2- 10
2.1.17 Restriction of Paper Type Information Delivery ...................................................................................................2- 10
2.1.18 HDD Data Erase Kit.............................................................................................................................................2- 11
2.1.19 IP Address Range Settings..................................................................................................................................2- 12
2.1.20 Protocol-Related Setup........................................................................................................................................2- 13
2.1.21 RUI Log-in Procedure ..........................................................................................................................................2- 13
2.1.22 cc/bcc Settings.....................................................................................................................................................2- 13
2.1.23 Send to Myself ..................................................................................................................................................... 2- 14
2.1.24 WebDAV Support ................................................................................................................................................2- 14
2.1.25 IPv6 setting display list ........................................................................................................................................2- 15
2.1.26 Encrypted PDF ....................................................................................................................................................2- 15
2.1.27 Digital Signature PDF ..........................................................................................................................................2- 16
2.1.28 Searchable PDF/XPS ..........................................................................................................................................2- 17
2.1.29 Display Host Name(Device Information Delivery Settings)..................................................................................2- 18
2.1.30 Transmission File Format ....................................................................................................................................2- 19
2.1.31 SSOH(Single Sign-On Hybrid).............................................................................................................................2- 20
2.1.32 XPS(XML Paper Specification)............................................................................................................................2- 21
2.1.33 USB Keyboard support ........................................................................................................................................2- 22
Chapter 3 Installation
3.1 Installation procedure .................................................................................................................................3- 1
3.1.1 Overview of the Installation Procedure....................................................................................................................3- 1
3.1.2 Device Signature PDF ............................................................................................................................................. 3- 1
3.1.3 Making SSOH Settings............................................................................................................................................3- 3
3.1.4 User Signature PDF ................................................................................................................................................3- 6
3.1.5 User Signature creation...........................................................................................................................................3- 9

Contents
Chapter 4 Maintenance
4.1 Notes when service .................................................................................................................................... 4- 1
4.1.1 Other Points to Note ................................................................................................................................................4- 1
4.1.2 Recommended setting of system management information....................................................................................4- 1
4.2 Reference matter in market service............................................................................................................ 4- 1
4.2.1 Invalidating the License for Transfer to a Different Device data recovery method ..................................................4- 1
4.2.2 Conditions for Using the RUI ...................................................................................................................................4- 1
4.2.3 Creating SSL Key-Pair and Server Certification ......................................................................................................4- 1
4.2.4 User data Erase of the HDD ....................................................................................................................................4- 4
4.2.5 How to create WebDAV environment for verification...............................................................................................4- 4
4.2.6 IPv6 settings ..........................................................................................................................................................4- 11
4.3 Related Error code ................................................................................................................................... 4- 14
4.3.1 Confirm method of error code ................................................................................................................................4- 14
4.3.2 E-mail Transmission errors ....................................................................................................................................4- 15
4.3.3 I-Fax Transmission errors......................................................................................................................................4- 17
4.3.4 I-Fax Reception errors ...........................................................................................................................................4- 20
4.3.5 SMB Transmission errors ......................................................................................................................................4- 21
4.3.6 FTP Transmission errors .......................................................................................................................................4- 23
4.3.7 NCP Transmission errors.......................................................................................................................................4- 24
4.3.8 Box Transmission errors........................................................................................................................................4- 25
4.3.9 WebDAV Transmission errors ...............................................................................................................................4- 26
4.4 Related Service Mode .............................................................................................................................. 4- 27
4.4.1 Invalidating the License for Transfer to a Different Device (Level 2) .....................................................................4- 27
4.4.2 Related Service Modes List ...................................................................................................................................4- 29
4.4.3 Service mode comparative table............................................................................................................................4- 30

Chapter 1 Specifications


Contents
Contents
1.1 Specifications .................................................................................................................................................................1-1
1.1.1 Memory Size and Functional Constraints iPR1135/1125/1110(USA)........................................................................................ 1-1
1.1.2 SEND Options (USA/EUR/AU).................................................................................................................................................. 1-2
1.1.3 Specifications ............................................................................................................................................................................... 1-3


1.1 Specifications
Chapter 1
1.1.1 Memory Size and Functional Constraints iPR1135/1125/1110(USA)
System memory (512MB) to upgrade is bundled with imagePRESS Printer Kit-A1.
It is necessary to install imagePRESS Printer Kit-A1 after having installed System memory (512MB) in the main body.
Universal Send Security Feature Set-C1
Universal Send Advanced Feature Set-C1
Color Universal Send Kit-Q1
Remote Operator's Software Kit-A3
Digital User Signature PDF Kit-B1
Encrypted Secure Print Software-C1
512MB
512MB
HDD Data Erase Kit-C1
Access Management System Kit-A2
Secure Watermark-A1
Barcode Printing Kit-D1
HDD Data Encryption Kit-B7
Voice Guidance Kit-E1
IPSec Board-B1
Expansion Bus-F1
REMOVABLE HDD KIT-AA1
imagePRESS Server J200
imagePRESS Server J100
T-1-1
Soft Option
T-1-2
Hard Option
0022-4181
imagePRESS Printer Kit-A1
1GB
1-1
Chapter 1
1.1.2 SEND Options (USA/EUR/AU)
A SEND function may be used to add to the existing transmission functions or to Adobe Acrobat PDF/XML paper specification-related functions.
0020-8026
Individual options are enabled after enabling the SEND transmission function and then obtaining an appropriate license. There is no specific order as to which
license option to enable first. Except for Except for Trace & Smooth, all options may be enabled independently of one another.
SEND Transmission Function
PDF
Compact
Trace
&
Smooth
PDF(OCR)
Encrypted
PDF
Device
Signature
PDF
F-1-1
T-1-3
Digital
Signature
PDF
KIT OPTION
Universal Send Advanced Feature Set PDF(Compact)+PDF(OCR)+Trace&Smooth
Universal Send Security Feature Set Encrypted PDF+Device Signature PDF
The individual option functions are characterized as follows:
PDF/XPS(Compact) It separates a scanned image into a multi-value area and a binary area. It then generates a PDF file at a
PDF/XPS(OCR) The text is extracted by the OCR processing from scanned image. It is not possible to see on PDF though the
Encrypted PDF It enables the use of various security settings of Adobe Acrobat for scanned images (File), limiting various
specific resolution and using a specific method of compression for each of these areas. All this serves to
significantly reduce the size of data. (The reading resolution will be fixed to 300 dpi.)
text data is added to the PDF data. Since text information is retained, the displayed image in Acrobat permits
searches for character strings. This option may also be used for images saved in a Box or transferred using
an iR machine on which it has been enabled.
access attempted by unauthorized users in the absence of an appropriate password.
-Password Required to Open a Document
-Password Required to Change Permission, Allow Printings and Allow Changes
-Enable Accessibility, Copy, Extraction of Images
T-1-4
1-2
Trace&Smooth It turns characters and Line art in a scanned image into outline data.
The outline data can be edited on Illustrator.

Chapter 1
Device Signature PDF/XPS The machine name and information of an MFP machine may be encrypted and attached to the PDF for
Digital User Signature PDF/XPS If the MFP machine is controlled by means of SSOH a user certificate may be associated with a personal ID
display in Acrobat through a signature tab. Signatures may be used in conjunction with a machine certificate
and secret key.
through the RUI. When a scanned image is opened in Acrobat, this function enables the display of encrypted
user information through the signature tab, serving to prevent data manipulation and impersonation.
It is necessary to obtain the certificate from the certificate organization. Please obtain it from VeriSign.
Item on Restriction:
For the electronic signature-attached PDF transmission, user can send with any combination of signature-registering method (device signature, user signature).
User, however, need to take care of the following points to note.
-In the case of selecting multiple signature-registering methods, signature is attached by the order of the following: Device Signature => User Signature.
-In the case of setting multiple signature-registering methods, and opening the signature-attached PDF by Acrobat, only the last-attached signature is valid as a
specification of Acrobat (PDF).
When the signature was added, some changes were generated in PDF.
The signature that proves the state before enters the falsified state.
This is the same meaning as the addition of the change to PDF.
Warning that 'There have been subsequent changes to the document' to the property of the signature.
-To execute user signature, SSOH has to be used.
1.1.3 Specifications
0020-7894
<SEND function basic specifications>
E-mail transmission
- Transmission protocol: SMTP, POP3
- Transmission authentication: SMTP AUTH, POP before SMTP
- Reception authentication: POP3, APOP, POP AUTH
- Encoded transmission: Corresponds to SSL communication in each protocol when SMTP transmission and SMTP and POP reception. (The server side needs to
correspond.)
- Key and certificate: Server certificate that the device has is used when SSL communication.
- Supported formats: TIFF (monochrome), JPEG(color), PDF (monochrome, color), PDF/XPS(high compression)(color), PDF/XPS (OCR) = Searchable PDF, Encrypted PDF, Trace&Smooth PDF, Device Signature PDF/XPS, Digital Signature PDF/XPS.
- PDF files can be split and sent page by page.
- Resolution: 100 X 100, 150 X 150, 200 X 100, 200 X 200, 200 X 400, 300 X 300, 400 X 400, 600 X 600 (dpi)
- Document size: A3 to A5
- Addresses available from LDAP server (e-mail address and FAX telephone number)
Max. number of searching: 2000; The number of broadcasting selection after searching: 64
- No E-mail reception function. Error mails can be printed out.
When broadcasting transmission, display/write all the addresses in the To: field and separate every 100 addresses to send.
I-Fax Tx/ Rx function
- Transmission protocol: SMTP (Tx/ Rx), POP3 (Rx), I-Fax (Simple mode, Full mode)
- Transmission authentication: SMTP AUTH, POP before SMTP
- Reception authentication: POP3, APOP, POP AUTH
- Encoded transmission: Corresponds to SSL communication in each protocol when SMTP transmission and SMTP and POP reception. (The server side needs to
correspond. When the server-less transmission, the encoded transmission is not executed. )
- Key and certificate: Server certificate that the device has is used when SSL communication.
- Supported formats: TIFF (monochrome: MH, MR MMR)
- Resolution: monochrome:200 X 100, 200 X 200, 200 X 400, 300 X 300, 400 X 400, 600 X 600 (dpi)
- Document size: A3, A4
- Reception sizes: A3, A4
- Server-less transmission supported
- Addresses available from LDAP server (e-mail address and FAX telephone number)
Max. number of searching: 2000; The number of broadcasting selection after searching: 64
- When broadcasting transmission, display/write all the addresses in the To: field.
File transmission function
- Transmission protocol: SMB (NetBios over TCP/IP), FTP(TCP/IP), NCP(IPX)
- Supported formats: TIFF (monochrome), JPEG(color), PDF/XPS (OCR), Searchable PDF, Encrypted PDF, Trace&Smooth PDF, Device Signature PDF/XPS,
Digital Signature PDF/XPS.
- PDF files can be split and sent page by page.
- Resolution: 100 X 100, 150 X 150, 200 X 100, 200 X 200, 200 X 400, 300 X 300, 400 X 400, 600 X 600 (dpi)
- Document sizes: A3, A4
- CanonFTP automatically distinguishes responses from the server and switches operation accordingly.
E-mail/I-fax operation confirmed server applications
SMTP server
Sendmail 8.93 or later
Exchange Server 5.5+SP1 or later
Exchange 2000
1-3

Chapter 1
Domino R4.6 or later
SMTP AUTH-enabled SMTP server
Sendmail 8.12.5 or later + Cyrus SASL API 1.5.28 combination
Exchange Server 5.5+SP1 or later
Exchange 2000
POP server
Qpopper 2.53 or later
Exchange Server 5.5+SP1 or later
Domino R4.6 or later
Exchange 2000
Qpop v4.0.5
POP before SMTP
Sendmail 8.12.5 or later +DRAC 1.11 or later +Qpopper 2.53 or later combinations
POP authentication function-enabled server
Exchange 2000Server: NTLM authentication when the integration authentication operation:
Qpop v4.0.5: STLS, APOP. However, OpenSSL and Popauth need to be installed.
POP authentication function of main PC mail clients
Outlook 2000:NTLM
Outlook Express 6:NTLM
Becky 2.05:APOP
WinBiff 2.42:APOP
Eudora 5.1:STLS, APOP, Kerberos
File transmission operation confirmed operating environments
SMB
Windows Vista
Windows 2000 Professional
Windows XP Home/Professional
Windows Server 2003
RedHat Linux7.2 + Samba2.2/3.0
MacOS 10.2. + Samba2.2/3.0
FTP
Windows 2000 Server + IIS5.0
Windows XP Professional + IIS5.1
Windows Server 2003 + IIS6.0
Windows Vista + IIS7.0
Sun Solaris (SPARC) 2.6 or later
RedHat Linux7.2
Mac OS 10.x.x
NCP
NetWare 3.20
NetWare 4.1, 4.11, 4.2
NetWare 5 +SP1a
NetWare 5.1
WebDAV
Sun Solaris 2.6 or later + Apache2.0
Redhat Enterprise + Apache2.0
Linux AS/ES/WS 4.0 or later + Apache2.0
Windows 2000 Server + Apache2.0
Windows 2000 Professional/Server + IIS5.0
Windows XP Professional + IIS5.1/Apache2.0
Windows Server 2003 + IIS6.0/Apache2.0
Mac OS X + Apache1.3
1-4

Chapter 2 Functions


Contents
Contents
2.1 Basic Function................................................................................................................................................................2-1
2.1.1 Authentication at TX.................................................................................................................................................................... 2-1
2.1.2 Authentication at RX ................................................................................................................................................................... 2-3
2.1.3 Encrypted transmission ................................................................................................................................................................ 2-4
2.1.4 Encrypted reception ..................................................................................................................................................................... 2-5
2.1.5 MAC Address Block Function..................................................................................................................................................... 2-5
2.1.6 URL Send..................................................................................................................................................................................... 2-6
2.1.7 Setting for communicate SSL ...................................................................................................................................................... 2-6
2.1.8 i-Fax Divided Data Transmission ................................................................................................................................................ 2-7
2.1.9 E-Mail Divided Data Transmission ............................................................................................................................................. 2-7
2.1.10 E-Mail Divided Data Reception................................................................................................................................................. 2-8
2.1.11 USB Deactivation ...................................................................................................................................................................... 2-8
2.1.12 Searchable PDF.......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-9
2.1.13 Document Orientation Auto Detection ...................................................................................................................................... 2-9
2.1.14 Document Name OCR ............................................................................................................................................................... 2-9
2.1.15 Increased Support of File in a Box .......................................................................................................................................... 2-10
2.1.16 Limit of Reception Length of Extra Long Original................................................................................................................. 2-10
2.1.17 Restriction of Paper Type Information Delivery ..................................................................................................................... 2-10
2.1.18 HDD Data Erase Kit ................................................................................................................................................................ 2-11
2.1.19 IP Address Range Settings ....................................................................................................................................................... 2-12
2.1.20 Protocol-Related Setup ............................................................................................................................................................ 2-13
2.1.21 RUI Log-in Procedure.............................................................................................................................................................. 2-13
2.1.22 cc/bcc Settings ......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-13
2.1.23 Send to Myself ......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-14
2.1.24 WebDAV Support.................................................................................................................................................................... 2-14
2.1.25 IPv6 setting display list ............................................................................................................................................................ 2-15
2.1.26 Encrypted PDF......................................................................................................................................................................... 2-15
2.1.27 Digital Signature PDF .............................................................................................................................................................. 2-16
2.1.28 Searchable PDF/XPS ............................................................................................................................................................... 2-17
2.1.29 Display Host Name(Device Information Delivery Settings) ................................................................................................... 2-18
2.1.30 Transmission File Format ........................................................................................................................................................ 2-19
2.1.31 SSOH(Single Sign-On Hybrid)................................................................................................................................................ 2-20
2.1.32 XPS(XML Paper Specification) .............................................................................................................................................. 2-21
2.1.33 USB Keyboard support ............................................................................................................................................................ 2-22


2.1 Basic Function
Chapter 2
2.1.1 Authentication at TX
When the mail server is set on the internet, you need to prevent from Third Party Mail Relay that the third party uses the false name. Third Party Mail Relay means
that the third party sends large amount of spam mails using the mail server which other people are operating. If you do not take any measures for this, resources
like server and network lines are exhausted and at the same time, you will get the claim from the user who received the spam mail. As a measure, the authentication
operation when SMTP transmission is prepared.
In case of the inner network (LAN), you can prevent from Third Party Mail Relay by restricting the IP address and the domain name. In order to send from the
outside domain using the mail address or securely use the mail server set on the internet which the provider prepares, the authentication is indispensable at the
transmission. This machine uses two authentication methods, POP Before SMTP and SMTP AUTH and they enable to send i-FAX and e-mail to SMTP server
which requests the sender's authentication.
POP before SMTP
With this method, before SMTP transmission is performed, the POP server is logged into. SMTP transmission can only be continued once the POP server has
confirmed the IP address of the connected client as authorized within a specific period of time. After user authentication is carried out at the POP server, the authenticated client IP address is relayed to the SMTP server, where it is processed. The process requires a certain amount of time. Taking this processing time into
consideration, there is an idle period of 300msec, from POP authentication to the start of SMTP transmission. If a POP before SMTP transmission is generated
during POP reception, POP authentication is made to wait until the reception is finished and then POP authentication and SMTP transmission are performed. Errors
occurring while the POP server is connected are treated as transmission errors.
With regard to the actual programming, all that is necessary is for System Settings > Network Settings > E-Mail/ I-Fax > Authent./ Encryption > POP Authen-
tication bofore Sending to be set to ON.
0020-7895
Related new user error codes are #810 and #813. For details, refer to Troubleshooting.
SMTP AUTH
In SMTP AUTH, user authentication is performed when the SMTP server is connected, so that mail can only be received from registered users. This method was
standardized in March, 1999, as RFC2554. SMTP AUTH uses ESMTP protocol, which is an extension of SMTP, and uses the SASL (Simple Authentication and
Security Layer) authentication mechanism, standardized as RFC2222, to authenticate the user by sending the user name and password information in response to
the server challenge data.
<Authentication mechanisms>
The SMTP server can have multiple authentication mechanisms and the most suitable authentication mechanism is programmed in accordance with the security
policy decided by the SMTP server administrator. The client E-Mail client application selects the authentication algorithm from among the available authentication
mechanisms and performs authentication upon transmission.
This model supports the following five types of authentication mechanism.
CRAM-MD5
Challenge-Response Authentication Mechanism, computed by using the key-protected MD5 algorithm by HMAC-MD5 (RFC2104)
NTLM
Windows NT authentication method
User name must be set in the form 'username@NTdomainname'
E.g.:
Windows2000 or earlier: username\\CANON (domain name may be omitted, depending on the environment)
Windows2000: username@canon.co.jp (domain name may be omitted, depending on the environment)
GSSAPI
Authentication system using Kerberos Version 5 (RFC1510)
User name must be set in the form 'username@realmname'.
username@CANON.CO.JP
(In Exchange2000, realm name = domain name)
PLAIN
Assumes that user name and password are sent as plain text (BASE64 encoded) and the communication packet is encoded. (RFC2595) Allows secure authentication when used in combination with the encoded transmission described later.
LOGIN
Sends the user name and password as plain text (BASE64 encoded). Actual transaction is the same as with PLAIN. Similarly, allows secure authentication when
used in combination with encoded transmission.
<SMTP AUTH transmission operation>
Even if the unit is programmed for transmission with SMTP AUTH, if the mail server does not support SMTP AUTH and the encoding system supported by the
server does not match that supported by this model, SMTP AUTH transmission will not be possible. In that case, even if SMTP AUTH is programmed, transmission
will be by normal SMTP and there will be no transmission error generated. If an unauthenticated mail transmission is attempted to a server that will not allow such
transmission, subsequent SMTP protocols will generate an error in the mail server. Unauthenticated mail can be transmitted to a server that will accept such transmission. These security policies are determined by the server so, even if SMTP AUTH is not programmed, it is impossible to tell whether transmission is possible
without checking with the customer's server administrator.
<Authentication protocol>
Examples of transmission protocol using SMTP AUTH are given below.
The EHLO response from the client tells whether SMTP AUTH is supported by the server and the authentication algorithm being used at that time is described. In
the event that there are multiple authentication algorithms, multiple algorithm names are described. The client selects one of the relayed authentication algorithms
and then relays it on to the server. Server challenge data come from the server and coded data made up from the server challenge data, user name and password are
returned in response for authentication. In general, the authentication algorithm to be used can be selected on the server side and PLAIN and LOGIN authentication
and others which are undesirable from the perspective of security can be blocked by the server setting. (Security policy is determined by the server.)
Server:220 smtp.example.com ESMTP server ready
Client(iR):EHLO ifax.example.com
S: 250-smtp.example.com
S: 250-DSN
S: 250-EXPN
S: 250 AUTH CRAM-MD5 DIGEST-MD5 : <- server declares authentication algorithm
C: AUTH CRAM-MD5 : <- client selects CRAM-MD5
S: 334 : <- server response (subsequently, authentication begins with CRAM-MD5.)
S: PENCeUxFREJoU0NnbmhNWitOMjNGNndAZWx3b29kLmlubm9zb2Z0LmNvbT4=
C: ZnJlZCA5ZTk1YWVlMDljNDBhZjJiODRhMGMyYjNiYmFlNzg2ZQ==
S: 235 Authentication successful.
<Authorisation algorithm selection>
2-1

Chapter 2
Where the SMTP has multiple authentication mechanisms, selection is made in the order of the priority list given below.
1) CRAM-MD5
2) NTLM
3) GSSAPI
4) STARTTLS operation PLAIN
5) STARTTLS operation LOGIN
6) STARTTLS non-operation LOGIN
7) STARTTLS non-operation PLAIN
Authentication methods can be disabled in service mode. When the service mode value is set to '1', the encoding system can be disabled. (The default setting is
all enabled.)
Ordinarily, the default setting is used, but if the server administrator wants to disable a particular encoding system, the settings need to be changed by the service
mode settings.
<SMTP AUTH related user modes>
For the actual SMTP AUTH settings, system administrator settings > network settings > E-Mail/ I-Fax > Authent./ Encryption > SMTP Authentication (SMTP
AUTH) should be set ON and the required user names and passwords for SMTP AUTH need to be entered. If SSL permission, which is the encoded transmission
setting, described later, is ON, with PLAIN and LOGIN authentication, the authentication encoded by the STARTTLS command can be used.
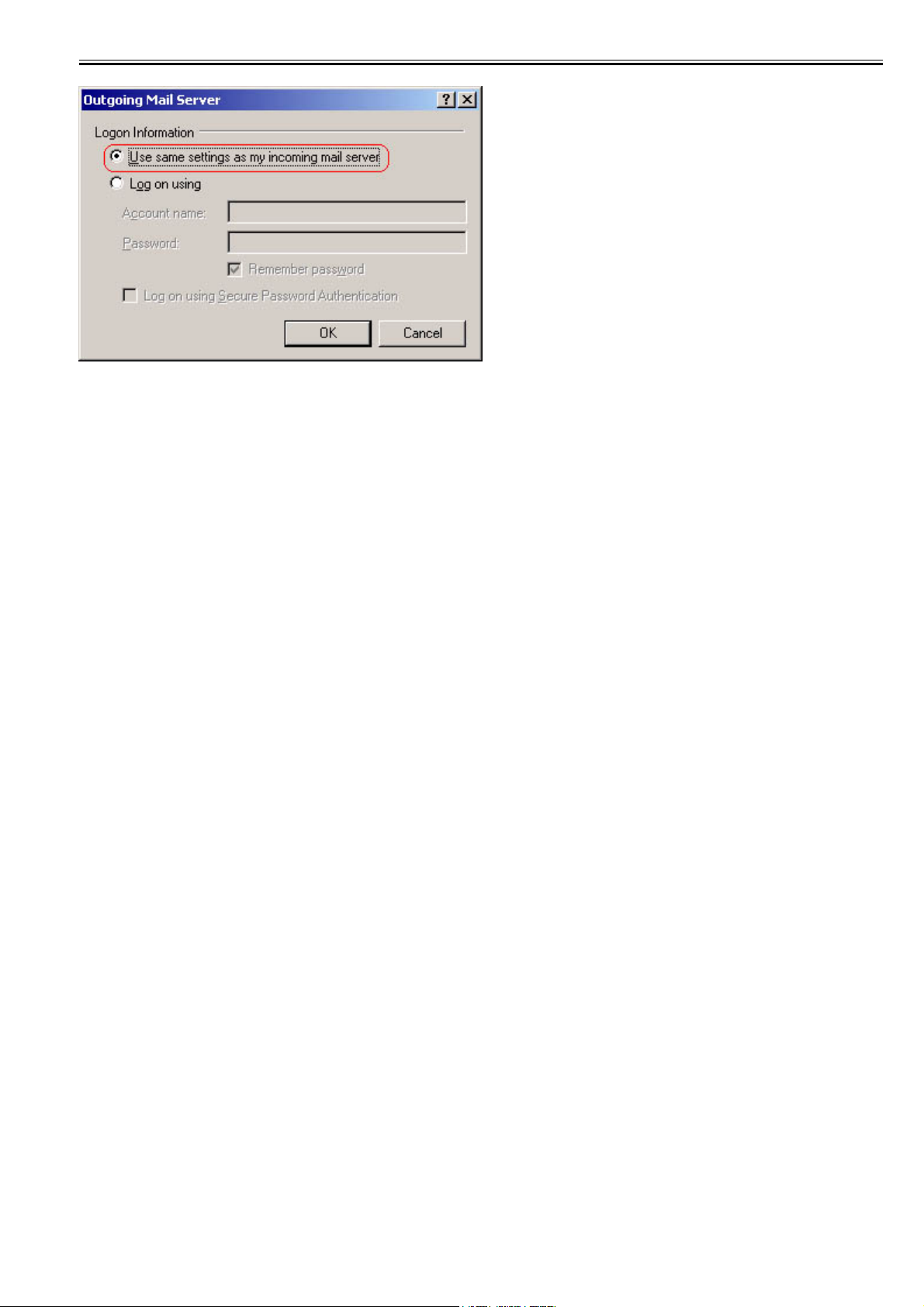
<Outlook Express example>
For reference, this section describes what happens to the Outlook Express settings when using an SMTP server that supports SMTP AUTH. Outlook Express PLAIN
authentication only.
1) From the Outlook Express tools menu, select Accounts. In the example, pop3.canon.com is selected.
2) From Internet Accounts, select the desired account and click on Properties. In the example, the pop3.canon.com server tab has been selected from the Properties
window.
3) Put a check in the 'My server requires authentication' box against the OutGoing mail server.
F-2-1
4) Press the settings button that has been made active.
5) Programme the transmission mail server window's logon information. In the default, 'use same settings as my incoming server' is selected. This setting uses the
POP3 authentication account name and password entered against the reception mail server in the previous window and performs SMTP AUTH operation.
2-2
Chapter 2
F-2-2
If 'Log on using' is selected, the account and password to be used with SMTP AUTH can be specified individually. In that case, if 'Log on using Secue Password
Authentication' is selected, encoding is carried out by TSL(SSL), using the STARTTTLS command.
<SMTP AUTH related user error codes>
The related new user error codes are #839 and #843. For details, refer to the section on Troubleshooting.
2.1.2 Authentication at RX
The username and the password flow by the plaintext in the reception form by past POP3. And POP3 logs in POP server at a short cycle. Therefore, the password
is easily stolen in POP3.
Enable the password to encrypt and to be attested by using APOP and POP AUTH. APOP is defined by RFC1939, and executed with UNIX system POP server,
and POP AUTH is defined by RFC2449, and executed with the MS Exchange server.In addition, if POP server supports the SSL(TLS) encryption by the STLS
instruction, not only the password but also the entire reception packet can be encrypted.
"POP AUTH Method " exists in Aditional Function >Network Settings >E-mail/I FAX >Authent./Encryption , and it is possible to select it from Standard / APOP
/ POP AUTH .
APOP and POP AUTH are executed respectively when APOP and POP AUTH are selected, and when Standard is specified, the authentication by the username
and the password is executed.
Default: It is Standard.
APOP
APOP authentication procedures are as follows.
(1) As a greeting message when connecting to POP server, the server returns the character strings consisting of the time stamp and the host name to the client. The
client links these character strings with the password character strings, and creates the message digest by MD5 from the linked character strings.
(2) With the APOP command, the client returns the message digest created with the user name to the server.
(3) Message digest is created in the POP server with the same algorism. By comparing this created digest and the digest from the client, if both digests are the same,
the password is considered as the correct one.
0020-7897
Greeting message when connecting to the server includes the time stamp, so analyzing is difficult since the created message digest changes every time.
Different from the POP AUTH described later, there is no protocol to check whether or not the server is supporting APOP from the client, so the user have to decide
whether or not APOP is used and set User mode.
If the server does not support APOP and the user uses APOP, an error occurs. When the error occurs at the APOP authentication, "APOP Authentication Error" is
displayed on the status line for certain time.
Following items are the examples of communication.
S: +OK POP3 server ready <1896.697170952@dbc.mtview.ca.us>
C: APOP mrose c4c9334bac560ecc979e58001b3e22fb
S: +OK maildrop has 1 message (369 octets)
C: :
When the server connection, the password "tanstaaf" character strings of the user mrose is linked after "<1896.697170952@dbc.mtview.ca.us>" message. Character
strings of "<1896.697170952@dbc.mtview.ca.us>tanstaaf" is hashed by MD5, then it becomes "c4c9334bac560ecc979e58001b3e22fb".
For actual settings, set as follows. System Settings > Network Settings > E-mail/I-Fax > Authent./ Encryption > POP AUTH Method >APOP.
POP AUTH
POP AUTH uses the authentication mechanism of SASL(Simple Authentication and Security Layer) provided in RFC2222 and conducts the user authentication by
returning the user name and password information as a response to the server challenge and its data from the server. This is standardized as RFC1734 "POP3 AUTHentication command". By the CAPA command extended in RFC2449 "POP3 Extension Mechanism", you can know the capability which the server has, and
SASL authentication algorism which the server supports is included in one capability and returned by the SASL tag.
<Authentication mechanism>
In the POP server, multiple authentication mechanisms can be possessed and the authentication mechanism is set according to the security policy which the server
administrator decides. E-mail client application selects the authentication algorism from the specified authentication algorism and performs the authentication at
the transmission. This device supports the following authentication algorism.
CRAM-MD5
Challenge-Response Authentication Mechanism calculated using MD5 algorism with the key based on the HMAC-MD5 (RFC2104).
Note:
Currently, POP AUTH server in the field are mostly made by Microsoft and NTLM authentication is used. CRAM-MD5 is installed, but there is no server which
the operations are checked, so the evaluation has not performed. For this reason, POP AUTH operations with CRAM-MD5 are not supported.
NTLM
Authentication method of Windows NT
User name has to be set in the form of "User name@ NT domain name".
Example:
Windows2000 or former: User name\\CANON (Domain name can be omitted according to the environment.)
Windows 2000: User name@canon.co.jp (Domain name can be omitted according to the environment.)
2-3

Chapter 2
PLAIN
Authentication method that user name and password are transmitted in plaintext (BASE64 encode) and the packet is encrypted. (RFC2595) By applying with the
later "Encrypted transmission", the authentication is secured.
LOGIN
User name and password are transmitted in plaintext (BASE64 Encode). Actual method of communicating information is same as PLAIN. By applying with the
later "Encrypted transmission", the authentication is secured.
Note:
When SSL is not operated, the authentication of PLAIN and LOGIN is not encrypted, so there is no difference from the authentication of the plaintext USER/
PASS. For this reason, there is no meaning of using POP AUTH. This operation gives misunderstanding that it is encrypted, so operations with POP AUTH are
prohibited.
< POP AUTH reception operations>
Even POP AUTH is set to be used for receiving, if the mail server does not support POP AUTH, the server supporting-authentication method and the device supporting-authentication method are different, the reception with POP AUTH is impossible. In this case, "POP AUTH Encryption Error" is displayed on the status line.
<Authentication protocol example>
Examples of transmission protocol when using POP AUTH are shown below.
With the CAPA response from the client, supporting SASL is informed from the server. At this time, usable authentication algorism is described. If multiple authentication algorisms are possessed, multiple algorism names are described. Client selects one algorism from the authentication algorisms which the server informed and the selected authentication algorism is informed to the server. The server sends the server challenge data, and performs authentication by returning this
data and the encrypted data created from the user name and password as a response. Generally, the authentication algorism can be selected on the server side whether
to be used. If it is not suitable to be used for the security, it can be prohibited by the settings on the server side. (Security policy can be determined by the server.)
Server: +OK POP3 v2001.78 server ready <4a61.3e55cd70@test.canon.co.jp>
Client(iR): CAPA
S: +OK Capability list follows:
S: TOP
S: LOGIN-DELAY 180
S: UIDL
S: STLS
S: USER
S: SASL CRAM-MD5 LOGIN
S: .
C: AUTH CRAM-MD5
S: + PDE5MDQ0LjEwNDU4MTEyMThAYmFiYS5jY20uY2Fub24uY28uanA+
C: ZnJlZCA5ZTk1YWVlMDljNDBhZjJiODRhMGMyYjNiYmFlNzg2ZQ==
S: +OK Authentication successful....
...
<Selection of the authentication algorism>
When SMTP server possesses multiple authentication mechanisms, the authentication method is determined in the following priority order.
1) CRAM-MD5 (Not supported)
2) NTLM
3) PLAIN when STLS (SSL) operation
4) LOGIN when STLS(SSL) operation
From Service mode, you can prohibit the usage of each authentication method. If you set Service mode setting to "1", you can prohibit the usage of the authentication
method. (All defaults: usable)
Usually, the device is used with the default settings, but if the server administrator prohibits the usage of the specific authentication method, you can change the
setting by Service mode.
< POP AUTH-related Addtional Settings>
Actual POP AUTH-related setting is selected in the order of System Settings > Network Settings > E-mail/I-Fax > Authent./ Encryption > POP AUTH, and then
you want to enter the user name and password necessary for POP address and POP password. When enabling "SSL Allow (POP)" (the setting of encryption communication), the encrypted authentication by STLS command can be used at PLAIN and LOGIN authentication.
2.1.3 Encrypted transmission
Transmission packet encryption (SSL)
When Additional Functions > System Settings > Network Settings > E-Mail/ I-Fax > Authnt. /Encryption > allow SSL(SMTP send) is set to ON, and the mail server
supports the SMTP protocol's STARTTLS command, SSL (TLS) is used for transmission packet encryption. Not only the user name and password are encrypted,
but also all of the mail transmission data. Therefore, the transmission speed is slower.
If 'allow SSL(SMTP Semd)' is set to OFF, or the mail server does not support the SMTP protocol's STARTTLS command, the transmission packet is not encrypted.
<STARTTLS command>
STARTTLS is an SMTP command that tells the server that encrypted transmission (SSL/ TLS) is about to start. The command is standardized in RFC2487. Following is an example of the protocol flow during STARTTLS.
The EHLO response from the client declares that STARTTLS is supported from the server. When the client generates the STARTTLS command, the operation is
reprocessed from the starts and negotiation is initiated and the packet data are encrypted.
S: 220 mail.imc.org SMTP service ready
C: EHLO mail.example.com
S: 250-mail.imc.org offers a warm hug of welcome
S: 250-8BITMIME
S: 250-STARTTLS : <- Shows that the server supports STARTTLS.
S: 250 DSN
C: STARTTLS : <- Declares to server that SSL/TLS are to be performed.
S: 220 Go ahead
-- All subsequent transmission packets will be encrypted.
C: <starts TLS negotiation>
C&S: <negotiate a TLS session>
C&S: <check result of negotiation>
C: EHLO mail.example.com
S: 250-mail.imc.org touches your hand gently for a moment
S: 250-8BITMIME
S: 250 DSN
<User error>
Related new user errors are #841 and #842. For details, refer to the section on Troubleshooting.
0020-7898
2-4

Chapter 2
2.1.4 Encrypted reception
There are two types of encrypted reception methods available - encrypted POP and SMTP email receptions.
0020-7899
Encrypted POP Reception
When Allow SSL (POP) control is turned on in Authentication/Encryption Settings window* and the POP server supports STLS command, defined in POP3 protocol, the imageRUNNER/iR can communicate with encrypted packets using SSL (TLS). The communications slows down since not only the user name and password but also the entire communication data for email reception are encrypted. If Allow SSL (POP) control is turned on but the POP server does not support STLS
command of POP3 protocol, it results in an error. If an error occurs in POP SSL communications, the status line displays "SSL Error (POP)."
* Authentication/Encryption Settings window: opens by selecting Additional Functions > System Settings > Network Settings > Email/I-Fax > Authent./ Encryption.
STLS
An extended SMTP command, defined in RFC 2487. RFC 2449 -- POP3 Extension Mechanism -- specifies that STLS must support CAPA command. If a server
supports STLS, it states the support in response to CAPA command.
The following lines exemplify communications when STLS is enabled.
...
S: +OK POP3 v2001.78 server ready <4a61.3e55cd70@test.canon.co.jp>
C: CAPA
S: +OK Capability list follows:
S: TOP
S: LOGIN-DELAY 180
S: UIDL
S: STLS :<-- Indicates the server supports STLS.
S: USER
S: SASL CRAM-MD5 LOGIN
S: .
C: STLS
S: +OK Begin TLS negotiation
<TLS negotiation, further commands are under TLS layer>
S: +OK POP3 v2001.78 server ready 4a61.3e55cd70@test.canon.co.jp
Encrypted SMTP Reception
The iR 2270 and later models support SSL (TLS) encryption for receiving email messages from SMTP servers. To use this feature, a valid server certificate is
required. When SSL or On option is selected for Allow SSL (SMTP Receive)* and the email server supports STARTTLS command, the imageRUNNER/iR can
communicate with encrypted packets using SSL (TLS). When Off option is selected for Allow SSL (SMTP Receive) control, the imageRUNNER/iR does not include STARTTLS in a response for EHLO. The communications slows down since not only the user name and password but also the entire data for email sending
are encrypted. When Off option is selected for Allow SSL (SMTP Receive) or the email server does not support STARTTLS command of SMTP protocol, the
communication packets are not encrypted.
*Allow SSL (SMTP Receive) control: is displayed by selecting Additional Functions > System Settings > Network Settings > Email/I-Fax > Authent./ Encryption.
STARTTLS Command
An extended SMTP command that notifies a start of encrypted communications in SSL/TLS to the SMTP server, defined in RFC 2487.
The following lines exemplify communications when STLS is enabled.
...
S: 220 mail.imc.org SMTP service ready
C: EHLO mail.example.com
S: 250-mail.imc.org offers a warm hug of welcome
S: 250-STARTTLS :<-- Indicates the server supports STARTTLS.
S: 250 DSN
C: STARTTLS : <--Declares the use of SSL/TLS.
S: 220 Go ahead
C: <starts TLS negotiation>
C & S: <negotiate a TLS session>
C & S: <check result of negotiation>
-- The communication packets are encrypted from now on -C: EHLO mail.example.com
S: 250-mail.imc.org touches your hand gently for a moment
S: 250 DSN
C: MAIL FROM <ifax@mail.example.com>
S: 250 Sender OK
...
The client is notified with the response of EHLO that the server supports STARTTLS. When the client issues STARTTLS command, the server and client perform
TLS negotiation and resume communications from the beginning with encrypted packet data.
If SSL option is selected for Allow SSL (SMTP Receive) control and the client carry on communicating in plain text, without using STARTTLS, the imageRUNNER/iR replies "530 Must issue a STARTTLS command first" of SMTP mail command and terminates the SMTP connection with the error. The user interface
indicates "SSL Error (SMTP RX Reject)" in the status line.
If On option is selected for Allow SSL (SMTP Receive) control, the imageRUNNER/iR accepts communications with the client in plain text, without using STARTTLS. If an SSL processing results in an error, for example the imageRUNNER/iR does not feature an encryption algorithm common to the client, the user interface
indicates "SSL Error (SMTP Receive)" and terminates the SMTP connection with the error.
Allow SSL (SMTP Receive) control defaults to Off.
2.1.5 MAC Address Block Function
Receiving MAC Address Settings
0020-7900
Limits network packets to receive by MAC address. To enable this function, select Additional Functions > System Settings > Network Settings > Email/I-Fax >
2-5

Chapter 2
On for Receiving MAC Address Settings. Up to 100 MAC addresses can be registered to allow communicating with the iR C/Color imageRUNNER. If a conflict
occurs between Receiving MAC Address Settings and IP Address Settings, Receiving MAC Address Settings overrides IP Address Settings.
This function filters packets in the network layer and the reception logs for applications are not recorded.
2.1.6 URL Send
It is function to transmit URL information with E-Mail to be able to refer the image with remote UI. Image preserved in box including fax box instead of transmitting.
The E-mail address where URL is notified can be set by selecting one address or one group address of each box from the address table.
Set the notified mail address by "URL Sending" of "box specification setting."
E-mail automatically notified that the image is stored in the box of the URL sending setting ending is transmitted.
0020-7901
Additional Functions > Mail Box Settings > User Inboxes Settings > User Inbox > URL Send Dettings
F-2-3
2.1.7 Setting for communicate SSL
To communicate SSL, this machine can register the key pair and the certificate. The key pair and the server authentication book self-signed by default have registered as DefaultKey.
The default key used by the following settings can be changed.
- Remote UI
- IPP Print Settings
- Device Information Delivery Settings
- Dept. ID Management Password Confirmation
- E-Mail/I-Fax: Authent./ Encryption Settings
0020-7902
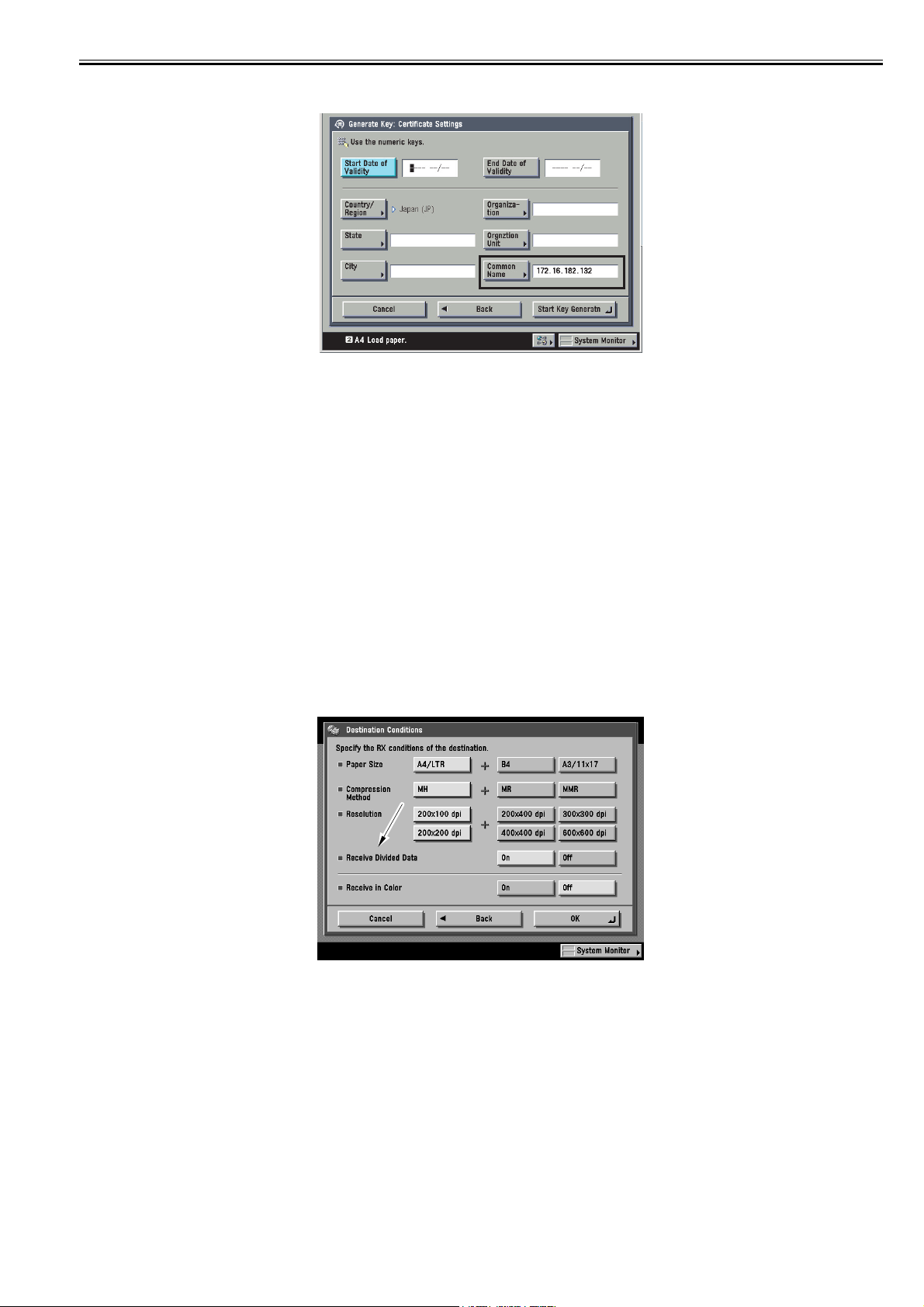
Additional Functions > System Settings > Network Settings > TCP/IP Settings > SSL Settings
F-2-4
In the case of IPPS print from Windows Vista, the Common Name should be the IP address of the host machine when generating SSL key.
Addditional Functions > System Settings > Network Settings > TCP/IP Settings > Certificate Settings > Generate key > Generate SSL Key
2-6
F-2-5
Chapter 2
2.1.8 i-Fax Divided Data Transmission
The mail division mechanism (message/partial) as prescribed by RFC2045 is used to divide mail data for transmission.
If the data of a mail is in excess of the size specified for 'transmission data size upper limit' in user mode, the mail will be transmitted using the specified upper limit.
The order of pages in page-based divided transmission may not be as expected on the receiving side.
A job may make its way between jobs.
In the event of a log mismatch between transmitting and receiving sides, or if the size of the image data per page is in excess of the limit, a solution is offered for
the resulting error.
However, if the communication is by way of a mail server, there will normally be an increase in the mail data size when the server affixes a Received header.
To accommodate the fact, the division is initiated with a safety margin of about 4K bytes at time of transmission.
The transmission is by way of a server, or is a server-less transmission in which IFAX-SZL of service mode is set to '0'.
-the target of transmission is set to 'data size division: ON' in the address book.
-the data size of the transmission mail is in excess of the 'transmission data size upper limit' set in user mode.
-if the transmission is by dividing the data, there will be a serial number affixed to the head of Subject of each mail (e.g., [1/5], [2/5],..., [5/5]).
-mail data will carry 'message/partial' as 'MIME Content Type' to indicate the use of divided transmission.
-there will be indications of 'number', 'total', and 'division ID'.
-'division ID' is a character string made up of the following: date of transmission, time of transmission, 0000 (fixed character string), transmission file number, host
name.
0020-7903
-all units of the same mail will have the same ID'.
ex:
Content-Type: message/partial; number=1; total=3;
id="20041110104508.0000.CanonTxNo.0105@e320g-43-1.ccm.canon.co.jp"
F-2-6
2.1.9 E-Mail Divided Data Transmission
If a value other than '0' is set as the 'transmission data size upper limit' in service mode, the size of data sent for a single mail will be no more than the specified limit.
0020-7904
If the transmission data size is in excess of the setting, the following will be true for models other than the iR C3170/C2570:
-if 'data size division' is enabled (ON) for the target in the address book, data size division transmission will be executed; if disabled (OFF), on the other hand, the
transmission will be by page-based division.
-when division transmission is executed, there will be a serial number affixed to the head of Subject of each mail (e.g., [1/5], [2/5], ..., [5/5]).
-if multiple mails have been transmitted to individual addresses by divided transmission, the transmission results report and the communications management reports will treat them as a single mail.
(1)Data Size Division Transmission
If the size of the mail is in excess of the 'transmission data size upper limit' set in user mode as prescribed for mail division (message/partial) in RFC2045 and
RFC2046, the mail will be transmitted using the upper limit.
If the mailer supports RFC, this function enables merging of received mails.
However, if the communication is by way of a mail server, there will normally be an increase in the mail data size when the server affixes a Received header.
To accommodate the fact, the division is initiated with a safety margin of about 4K bytes at time of transmission.
-mail data will carry 'message/partial' as 'MIME Content Type' to indicate the use of divided transmission.
2-7

Chapter 2
-there will be indications of 'number', 'total', and 'division ID'.
-'division ID' is a character string made up of the following: date of transmission, time of transmission, 0000 (fixed character string), transmission file number, host
name.
-all units of the same mail will have the same ID'.
ex:
Content-Type: message/partial; number=1; total=3;
id="20041110104508.0000.CanonTxNo.0105@e320g-43-1.ccm.canon.co.jp"
(2)Page-Based Division Transmission
The attached image data is divided with reference to page breaks within the 'transmission data size upper limit' specified in user mode, transmitting it by dividing
it into multiple mails.
If Multi Page TIFF or PDF is selected, multiple pages up to the specified upper limit will be transmitted as a single Multi Page TIFF or PDF file.
If transmission is by collecting multiple files inside a Box, the transmission will be as a single job, increasing the possibility of its being divided.
If the size of the attached image data for a single page is in excess of the setting, the transmission will be handled as an error, ending the ongoing transmission.
If the setting is '0', no division of the data will occur, and all data will be transmitted as a single mail regardless of its size.
Default maximum data size is 3MByte.
Example of Divided Transmission for Multiple Files
When using PDF transmission of the following 3 files:
-file A, consisting of 5 pages
-file B, consisting of 6 pages
-file C, consisting of 2 pages
In keeping with the setting for divided transmission, the mail will be divided as follows, converted into PDF files, and transmitted as 3 mails:
-mail 1, consisting of 1 through 5 pages of file A + 1st page of file B (as PDF file)
-mail 2, consisting of 2 through 6 pages of file B + 1st page of file C (as PDF file)
-mail 3, consisting of 2 pages of file C (as PDF file)
F-2-7
2.1.10 E-Mail Divided Data Reception
The following takes place in response to an incoming divided mail:
The divided mail (message/partial) will be temporarily stored in 'divided data reception box' inside the System Box; once all divisions are available, merging is
initiated.
As in the case of a normal mail, the result of merging will be printed, transferred, or stored in the System Box.
If a length of time is specified for 'divided reception time-out', and such a time passes, as many divided mails as possible are merged and the result will be printed
as soon as data is enough to make up a single page.
If the data is not enough to make up a single page, such information as on To, From, and Subject provided as part of the main Header will be printed.
A mail for which a time-out condition has occurred and mail units with the same ID will be removed, ending the job as an error (code #848).
The mails that are stored in 'division data reception box' may be manually removed.
If a check mark is put for 'print at time of deletion', an attempt for merging will be made, and printing occurs if possible. This operation will be identified by error
0020-7905
code #99.
2.1.11 USB Deactivation
This feature sets permissions for using the USB device/host interface.
USB Device On/Off
When USB is connected with iR and PC is printed, it uses it with the USB device.
iR rectangular connector on A side is done.
This parameter is located under the System Settings. With this parameter, the USB device interface can be turned on or off (the factory preset is on).
On: normal operation
Off: both raw mode and USB's 1284.4 mode operations stop
The plug-and-play function is also disabled because the device does not respond to Device-ID requests.
Changes to the on/off setting take effect the next time the device is restarted.
0020-7906
USB Host On/Off
When IC card reader etc. are connected with iR, it uses it with the USB host.
It connects it with the flat type connector of iR.
This parameter is located under the System Settings. With this parameter, the USB device interface can be turned on or off (the factory preset is on).
On: normal operation
Off: operation stops
The plug-and-play function is also disabled because the device does not respond to Device-ID requests.
Changes to the on/off setting take effect the next time the device is restarted.
Note that this parameter is used to disable all devices that can be connected to the USB host, including IC cards and other authorization tokens, keyboards, and
USB keys.
Location of Parameters
Under Additional Functions,
2-8

Chapter 2
System Settings > Network Settings > USB Settings
Use USB device
Use USB host
These parameters cannot be accessed from remote user interfaces.
Operation when updating firmware using USB memory
The USB host is always enabled when update firmware is selected in Service Mode.
After the update is completed and the device restarted, the state of the USB host is again dependent on the value of the System Settings parameter.
2.1.12 Searchable PDF
A searchable PDF file consists of pages of scanned images that have been put through OCR processing. The test data is extracted, and is laid over the original images
in the form of invisible text so that a search may be run for a particular segment of the data. A search in a PDF file requires a PDF browser application (e.g., Adobe
Acrobat, Adobe Reader). Or, Windows' search function may be used to look for a string of characters. Here again, the target of transmission must be an e-mail
address or a file server. To make use of this function, PDF (OCR) is specified when selecting the file format on the Transmission screen. A PDF file that will be
generated in response will consist of the following:
0022-6564
-Imaging Block
Transmission from a Box as well as reception transfer is also supported.
Supported Languages
Japanese, Latin 1, Latin 2, Estonian, Lithuanian, Russian, Greek
The characters that may be read by OCR are limited to those in English and the display character set of the UI, and then other characters will not be extracted.
Recognized Fonts
Japanese Mincho/Gothic
English Helvetica, Courier New, Times New Roman
Characters in a font other than the foregoing may show a drop in the rate of recognition.
Recognized Characters
Japanese: JIS non-Kanji, JIS Level 1, JIS No. 2 (547 characters), Roman numerals, circled numerals
English: alphabet characters, numerals, symbols (52 + 10 + 30), Euro symbol
Others: specific characters unique to English and some languages
The characters must be black on a white background to be recognized.
Recognized Character Size
Japanese: 8 to 48 pt (300 dpi)
A higher point size applies to 2-byte characters.
English: 6 to 72 pt (300 dpi)
If smaller than the lowest point size, the rate of recognition is likely to drop appreciably.
Limitations on Characters
Japanese:6000 characters (approx.) or less on a page
English:for a single character area, 130 characters or less per line, 100 lines or less
Characters outside the foregoing limitations will not be processed by OCR.
Characters Tending to Cause OCR Failure
-on an original with a complicated layout
-on an original with excessive noise
-on an original scanned in photo mode
-on an original scanned at an appreciable angle (slant)
2.1.13 Document Orientation Auto Detection
Document orientation auto detection is available when PDF (OCR) is selected. When a PDF (OCR) file is sent to an e-mail address or a file server, the result of
OCR processing is used to identify the orientation of the original (with reference to the orientation of characters), and the file is sent after automatically rotating the
image, if necessary, so that the user need not concern himself with the orientation of the document for transmission. It is important to bear in mind, however, that
any of the following types of documents may be transmitted in the wrong orientation:
- whose characters are at an angle (+/-3 deg or more)
- which contains white characters against black background, uncommon font, or handwritten characters
- whose text is not at 300 dpi and is not between 10 and 20 pt
- whose characters per page are appreciably limited in number (ideally, there must be 50 characters or more)
0020-7909
Memo:
A document may not fall under the foregoing types, but may still be transmitted in the wrong orientation. If wrong orientation is too frequent, disable the function.
2.1.14 Document Name OCR
The file name OCR function is available when PDF (OCR) is selected. When a PDF (OCR) file is sent to an e-mail address or a file server, a file name will be
assigned with reference to the result of OCR processing. When transmission is executed with the File Name OCR button checked (part of transmission settings),
as many characters as specified in Additional Functions will be collected from the head of the text block on the first page and used as the name of the file. A maximum of 24 characters may be used, and it may be combined with a name that has separately been assigned. All characters that follow the initial 24 will be cut out
0020-7910
of the name.
Memo:
If the setting Additional Functions>Common Settings>Langage Switch is set to [ON] , 2-byte characters will not be collected for the file name. If a name must
include a 2-byte character, be sure to set the setting to [OFF].
2-9
 Loading...
Loading...