Canon ColorPASS-Z5000 Owner's Guide
ColorPASS-Z5000
COLOR GUIDE
INCLUDES FIERY® SOFTWARE


Copyright © 2001 Electronics For Imaging and Canon Inc. All rights reserved.
This publication is protected by copyright, and all rights are reserved. No part of it may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means for any purpose
without express prior written consent from Electronics For Imaging, except as expressly permitted herein. Information in this document is subject to change
without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of Electronics For Imaging, Inc.
The software described in this publication is furnished under license and may only be used or copied in accordance with the terms of such license.
Patents: 5,867,179; 5,835,788; 5,666,436; 5,553,200; 5,543,940; 5,537,516; 5,517,334; 5,506,946; 5,424,754; 5,343,311; 5,212,546; 4,941,038; 4,837,722;
4,500,919; D406,117
Trademarks
EFI, the EFI logo, Fiery, the Fiery logo, Fiery Driven, the Fiery Driven logo, EFICOLOR, ColorWise, and Rip-While-Print are trademarks registered in the U.S.
Patent and Trademark Office. Fiery Z4, Fiery X4, Command WorkStation, AutoCal, Starr Compression, Memory Multiplier, NetWise, VisualCal, and Velocity
are trademarks of Electronics For Imaging, Inc.
Canon is a registered trademark of Canon Inc. ColorPASS is a trademark of Canon Inc.
Adobe, the Adobe logo, Adobe Illustrator, PostScript, Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Separator, and Adobe PageMaker are trademarks of Adobe Systems Incorporated,
registered in certain jurisdictions. EPS (Encapsulated PostScript) is a trademark of Altsys Corporation. Apple, the Apple logo, AppleShare, AppleTalk, EtherTalk,
LaserWriter, and Macintosh are registered trademarks, and MultiFinder is a trademark of Apple Computer, Inc. Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, and Windows are
registered trademarks of Microsoft in the US and other countries. QuarkXPress is a registered trademark of Quark, Inc. Times, Helvetica, and Palatino are
trademarks of Linotype AG and/or its subsidiaries. ITC Avant Garde, ITC Bookman, ITC Zapf Chancery, and ITC Zapf Dingbats are registered trademarks of
International Typeface Corporation. Ethernet is a registered trademark of Xerox Corporation. NetWare and Novell are registered trademarks and Internetwork
Packet Exchange (IPX) is a trademark of Novell, Inc. UNIX is a registered trademark of UNIX System Laboratories, a wholly owned subsidiary of Novell, Inc.
PANTONE is a registered trademark of Pantone, Inc. Matchprint is a trademark of Imation Corp.
All other terms and product names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners, and are hereby acknowledged.
Legal Notices
APPLE COMPUTER, INC. (“APPLE”) MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION THE
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, REGARDING THE APPLE SOFTWARE.
APPLE DOES NOT WARRANT, GUARANTEE, OR MAKE ANY REPRESENTATIONS REGARDING THE USE OR THE RESULTS OF THE USE
OF THE APPLE SOFTWARE IN TERMS OF ITS CORRECTNESS, ACCURACY, RELIABILITY, CURRENTNESS, OR OTHERWISE. THE ENTIRE
RISK AS TO THE RESULTS AND PERFORMANCE OF THE APPLE SOFTWARE IS ASSUMED BY YOU. THE EXCLUSION OF IMPLIED
WARRANTIES IS NOT PERMITTED BY SOME STATES. THE ABOVE EXCLUSION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
IN NO EVENT WILL APPLE, ITS DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR ANY CONSEQUENTIAL,
INCIDENTAL OR INDIRECT DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF BUSINESS PROFITS, BUSINESS INTERRUPTION, LOSS OF
BUSINESS INFORMATION, AND THE LIKE) ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE APPLE SOFTWARE EVEN IF APPLE
HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. BECAUSE SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATIONS MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Apple’s liability to you for actual damages from any cause whatsoever, and regardless of the form of the action (whether in contract, tort [including negligence],
product liability or otherwise), will be limited to $50.
Restricted Rights Legends
For defense agencies: Restricted Rights Legend. Use, reproduction, or disclosure is subject to restrictions set forth in subparagraph (c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in
Technical Data and Computer Software clause at 252.227.7013.
For civilian agencies: Restricted Rights Legend. Use, reproduction, or disclosure is subject to restrictions set forth in subparagraph (a) through (d) of the
commercial Computer Software Restricted Rights clause at 52.227-19 and the limitations set forth in Electronics For Imaging’s standard commercial agreement
for this software. Unpublished rights reserved under the copyright laws of the United States.
Printed in the United States of America on recycled paper.
Part Number:
45020175

FCC Information
WARNING: FCC Regulations state that any unauthorized changes or modifications to this equipment not expressly approved by the manufacturer could void
the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
Class A Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, and uses,
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause interference in which case the user will be required to correct the interference
at his own expense.
Industry Canada Class A Notice
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Avis de Conformation Classe A de l’Industrie Canada
Cet appareil numérique de la Classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Certificate by Manufacturer/Importer
This is to certify that the FC07 is shielded against radio interference in accordance with the provisions of VFG 243/1991. The German Postal Services have been
advised that this device is being put on the market and that they have been given the right to inspect the series for compliance with the regulations.
Bescheinigung des Herstellers/Importeurs
Hiermit wird bescheinigt, dass der FC07 im Übereinstimmung mit den Bestimmungen der VFG 243/1991 funkentstört ist. Der Deutschen Bundespost wurde
das Inverkehrbringen dieses Gerätes angezeigt und die Berechtigung zur Überprüfung der Serie auf Einhaltung der Bestimmungen eingeräumt.
RFI Compliance Notice
This equipment has been tested concerning compliance with the relevant RFI protection requirements both individually and on system level (to simulate normal
operation conditions). However, it is possible that these RFI Requirements are not met under certain unfavorable conditions in other installations. It is the user
who is responsible for compliance of his particular installation.
Dieses Gerät wurde sowohl einzeln als auch in einer Anlage, die einen normalen Anwendungsfall nachbildet, auf die Einhaltung der Funkentstörbestimmungen
geprüft. Es ist jedoch möglich, dass die Funkentstörbestimmungen unter ungünstigen Umständen bei anderen Gerätekombinationen nicht eingehalten werden.
Für die Einhaltung der Funkentstörbestimmungen einer gesamten Anlage, in der dieses Gerät betrieben wird, ist der Betreiber verantwortlich.
Compliance with applicable regulations depends on the use of shielded cables. It is the user who is responsible for procuring the appropriate cables.
Die Einhaltung zutreffender Bestimmungen hängt davon ab, dass geschirmte Ausführungen benützt werden. Für die Beschaffung richtiger Ausführungen ist der
Betreiber verantwortlich.
Proprietary Rights
You acknowledge that the Software, Coded Font Programs, Typefaces, Trademarks and accompanying documentation are proprietary to Electronics For Imaging
and its suppliers and that title and other intellectual property rights therein remain with Electronics For Imaging and its suppliers. Except as stated above, this
Agreement does not grant you any right to patents, copyrights, trade secrets, trademarks (whether registered or unregistered), or any other rights, franchises or
licenses in respect of the Software, Coded Font Programs, Typefaces, Trademarks or accompanying documentation. You may not adapt or use any trademark or
trade name which is likely to be similar to or confusing with that of Electronics For Imaging or any of its suppliers or take any other action which impairs or
reduces the trademark rights of Electronics For Imaging or its suppliers. The trademarks may only be used to identify printed output produced by the Coded Font
Programs. At the reasonable request of Electronics For Imaging, you must supply samples of any Typeface identified with a trademark.
Confidentiality
You agree to hold the Software and Coded Font Programs in confidence, disclosing the Software and Coded Font Programs only to authorized users having a need
to use the Software and Coded Font Programs as permitted by this Agreement and to take all reasonable precautions to prevent disclosure to other parties.
Remedies
Unauthorized use, copying or disclosure of the Software, Coded Font Programs, Typefaces, Trademarks or accompanying documentation will result in automatic
termination of this license and will make available to Electronics For Imaging other legal remedies.

Limited Warranty And Disclaimer
Electronics For Imaging warrants that, for a period of ninety (90) days from the date of delivery to you, the Software under normal use will perform without
significant errors that make it unusable. Electronics For Imaging’s entire liability and your exclusive remedy under this warranty (which is subject to you returning
ColorPASS to Electronics For Imaging or an authorized dealer) will be, at Electronics For Imaging’s option, to use reasonable commercial efforts to attempt to
correct or work around errors, to replace the Software with functionally equivalent software, or to refund the purchase price and terminate this Agreement. Some
states do not allow limitations on duration of implied warranty, so the above limitation may not apply to you.
Except for the above express limited warranty, Electronics For Imaging makes and you receive no warranties or conditions on the Products, express, implied, or
statutory, and Electronics For Imaging specifically disclaims any implied warranty or condition of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
For warranty service, please contact your authorized service/support center.
EXCEPT FOR THE ABOVE EXPRESS LIMITED WARRANTY, ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING MAKES AND YOU RECEIVE NO WARRANTIES
OR CONDITIONS ON THE SOFTWARE OR CODED FONT PROGRAMS, EXPRESS, IMPLIED, STATUTORY, OR IN ANY OTHER PROVISION
OF THIS AGREEMENT OR COMMUNICATION WITH YOU, AND ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS ANY IMPLIED
WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Electronics For Imaging does not warrant that
the operation of the software will be uninterrupted or error free or that the Software will meet your specific requirements.
Limitation Of Liability
IN NO EVENT WILL ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DAMAGES, INCLUDING LOSS OF DATA, LOST
PROFITS, COST OF COVER OR OTHER SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, CONSEQUENTIAL OR INDIRECT DAMAGES ARISING FROM THE USE OF
THE SOFTWARE, CODED FONT PROGRAMS OR ACCOMPANYING DOCUMENTATION, HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF
LIABILITY. THIS LIMITATION WILL APPLY EVEN IF ELECTRONICS FOR IMAGING OR ANY AUTHORIZED DEALER HAS BEEN ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE. YOU ACKNOWLEDGE THAT THE PRICE OF THE UNIT REFLECTS THIS ALLOCATION OF RISK.
BECAUSE SOME STATES/JURISDICTIONS DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OR LIMITATION OF LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, THE ABOVE LIMITATION MAY NOT APPLY TO YOU.
Export Controls
You agree that you will not export or re-export the Software or Coded Font Programs in any form without the appropriate United States and foreign government
licenses. Your failure to comply with this provision is a material breach of this Agreement.
Government Use
Use, duplication or disclosure of the Software by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subdivision (c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in
Technical Data and Computer Software clause at DFARS 252.227-7013 or in subparagraphs (c) (1) and (2) of the Commercial Computer Software—Restricted
Right Clause at 48 CFR 52.227-19, as applicable.
Third Party Beneficiary
You are hereby notified that Adobe Systems Incorporated, a California corporation located at 345 Park Avenue, San Jose, CA 95110-2704 (“Adobe”) is a thirdparty beneficiary to this Agreement to the extent that this Agreement contains provisions which relate to your use of the Fonts, the Coded Font Programs, the
Typefaces and the Trademarks licensed hereby. Such provisions are made expressly for the benefit of Adobe and are enforceable by Adobe in addition to Electronics
For Imaging.
General
This Agreement will be governed by the laws of the State of California.
This Agreement is the entire agreement held between us and supersedes any other communications or advertising with respect to the Software, Coded Font
Programs and accompanying documentation.
If any provision of this Agreement is held invalid, the remainder of this Agreement shall continue in full force and effect.
If you have any questions concerning this Agreement, please write to Electronics For Imaging, Attn: Licensing Dept. or see Electronics For Imaging’s web site at
www.efi.com.
Electronics For Imaging
303 Velocity Way
Foster City, CA 94404


Contents
Introduction
About the documentation
Key features of ColorWise
Chapter 1: ColorPASS Color Management
Managing color on the ColorPASS
Rendering styles 1-5
RGB Source Profile 1-6
RGB Separation 1-7
CMYK Simulation Profile 1-8
CMYK Simulation Method 1-9
Output Profile 1-9
Pure Black Text/Graphics 1-10
Black Overprint 1-12
Spot Color Matching 1-13
Printer Drivers and Print Options
What a printer driver does 1-14
PostScript printer driver for Windows 95/98/Me, Windows NT 4.0, and Windows 2000 1-15
Adobe PostScript printer driver for Mac OS 1-20
xiii
xv
1-1
1-14
Chapter 2: Simple and Advanced Workflows
Workflow concepts
Short-run printing versus color proofing 2-1
RGB, CMYK, and PANTONE colors 2-2
Desktop versus ColorPASS color management 2-3
Simple workflows
Select your colors wisely 2-4
Select a short workflow 2-5
2-1
2-4

viii Contents
Advanced workflows
Short-run printing examples 2-9
Color proofing examples 2-15
Chapter 3: Color Calibration
Introduction
Understanding calibration
How calibration works 3-3
Scheduling calibration 3-4
Checking calibration status 3-5
Using a spectrophotometer
Setting up the spectrophotometer 3-6
Calibrating the spectrophotometer
Calibrating with ColorWise Pro Tools and DTP41
Using a densitometer 3-24
Setting up the densitometer 3-24
Calibrating the densitometer
Calibrating with ColorWise Pro Tools
Expert Mode 3-33
2-9
3-2
3-2
3-6
3-10
3-16
3-27
3-28
Calibrating from the Control Panel using AutoCal2
Removing calibration 3-37
Chapter 4: ColorWise ProTools
Profile Manager
Setting the default profiles 4-3
Downloading profiles 4-5
Editing profiles 4-7
Managing profiles 4-7
Defining profiles 4-8
3-35
4-1

ix Contents
Color Editor
Editing Profiles 4-12
Undoing simulation edits 4-19
Checking edited profiles 4-21
Color Setup
Setting default ColorWise options 4-23
Chapter 5: Working with Color in Applications
Working with color
Color reference pages 5-2
Office applications
Choosing colors in office applications 5-4
PostScript applications
Choosing colors in PostScript applications 5-5
Default output profile 5-8
CMYK simulation 5-8
Chapter 6: Office Applications
Working with office applications
Defining colors 6-1
Working with imported files 6-1
Selecting options when printing 6-2
Output profiles 6-2
4-12
4-23
5-1
5-3
5-5
6-1

x Contents
Chapter 7: Adobe Photoshop
Photoshop 5.x
Photoshop 5.x color settings 7-1
ColorSync defaults 7-6
Defining colors 7-7
Saving files for importing into other documents 7-7
Selecting options when printing 7-9
Printing tips for advanced users 7-11
Photoshop 4.x
Defining colors 7-13
Saving files for importing into other documents 7-13
Selecting options when printing 7-15
Chapter 8: Page Layout Applications
Working with page layout applications
Defining colors 8-1
Importing images 8-2
CMYK simulation 8-3
Adobe PageMaker 6.5 for Mac OS and Windows
Windows version requirement 8-4
Importing images 8-4
Selecting options when printing 8-5
Optional color management from PageMaker 8-6
7-1
7-13
8-1
8-4
QuarkXPress 4.x for Mac OS and Windows
Importing images 8-7
Selecting options when printing 8-8
Optional color management from QuarkXPress 8-9
QuarkXPress 3.32 for Mac OS and Windows
Windows version requirement 8-9
Importing images 8-9
Selecting options when printing 8-10
8-7
8-9

xi Contents
Chapter 9: Illustration Applications
Working with illustration applications
Defining colors 9-1
Importing images 9-2
CMYK simulation 9-2
Adobe Illustrator 8.x for Windows and Mac OS
Defining colors 9-3
Importing images 9-3
Optional color management in Illustrator 9-4
Selecting options when printing 9-4
Saving files for importing into other documents 9-5
Macromedia FreeHand 8.x for Windows and Mac OS
Defining colors 9-6
Importing images 9-6
Selecting options when printing from FreeHand 9-7
Saving files for importing into other documents 9-8
Optional color management in FreeHand 9-9
CorelDRAW for Windows and Mac OS
Defining colors 9-9
Importing images 9-9
Selecting options when printing 9-10
Saving files for importing into other documents 9-11
Optional color management in CorelDRAW 9-11
9-1
9-3
9-6
9-9
Appendix A: Desktop Color Primer
The properties of color
The physics of color A-1
CIE color model A-2
Hue, saturation, and brightness A-3
Additive and subtractive color systems A-3
Printing techniques
Halftone and continuous tone devices A-6
A-1
A-5

xii Contents
Using color effectively
A few rules of thumb A-7
Color wheel A-7
Color and text A-8
Raster images and vector images
Optimizing files for processing and printing
Resolution of raster images A-10
Scaling A-12
Appendix B: Color Management
Controlling printed color
Maintaining copier consistency B-2
Print device gamut B-2
Basics of color management
Color conversion B-4
Appendix C: Importing densitometer measurements
Simple ASCII Import File Format (SAIFF)
Example of 1D Status T density for EFI 34 patch page C-2
Example of 1D Status T density for EFI 21 patch page C-2
Example of 1D Status T density for an arbitrary page C-3
A-6
A-9
A-10
B-1
B-3
C-1
Glossary
Bibliography
Index

xiii About the documentation
Introduction
Welcome to the
associated with printing to the ColorPASS-Z5000 Color Server™. It outlines key
workflow scenarios, provides information on calibration and color profiles, and
contains application notes that explain how to print to the ColorPASS-Z5000
Color Server from popular Microsoft Windows and Apple Mac OS applications.
This manual is one book in a set of documentation that also includes manuals for
users and system administrators. All the other manuals should be available at your
site—refer to them for a complete description of your ColorPASS-Z5000
Color Server.
N
:
OTE
The term “ColorPASS” is used in this manual to refer to the ColorPASS-Z5000
Color Server. The ColorPASS supports the CLC5000 color copier. The term “copier”
is used in this manual to refer to this supported device.
Color Guide
. This manual introduces you to the concepts and issues
About the documentation
The
Color Guide
color output of your ColorPASS. Chapter 1 discusses the ColorPASS’s print options
and how to get the best color results, and Chapter 2 describes several effective
workflows. ColorWise Pro Tools™ are discussed in the next two chapters. Chapter 3
covers Calibrator™ and other methods used to calibrate the copier, and Chapter 4
takes you through the features of Profile Manager™, used to manage color profiles on
the ColorPASS, and Color Editor™, which lets you customize simulation and output
profiles. Succeeding chapters offer tips for printing from business and graphics
applications. Finally, the appendixes offer information about color theory and color
management.
is organized to supply you with key information about managing the
Words in bold, for example,
bibliography at the end of this manual provides sources for further investigation of
color printing issues.
output profile
, are terms that appear in the glossary. The

xiv Introduction
Color terms and concepts such as “RGB data,” “color space,” “spot color,” “gamut,”
and “source profile” are used throughout this manual. If you are new to desktop color
or if any terms are unfamiliar, be sure to read Appendixes A and B or check the
glossary.
This manual is part of a set of ColorPASS documentation that also includes the
following manuals for users and system administrators:
• The
Configuration Guide
explains basic configuration and administration of the
ColorPASS for the supported platforms and network environments. It also includes
guidelines for setting up UNIX, Windows NT, and Novell NetWare servers to
provide Adobe PostScript printing services to clients.
•
Getting Started
describes how to install software to enable users to print to the
ColorPASS. Specifically, it describes installation of PostScript printer drivers, printer
description files, and other user software provided on the User Software CD. It also
explains how to connect each user to the network.
• The
Printing Guide
describes the printing features of the ColorPASS for users who
send jobs via remote workstations on the network.
• The
Job Management Guide
explains the functions of the ColorPASS client utilities,
including the Command WorkStation™, and how they can be used to manage jobs.
This book is intended for an operator or administrator, or a user with the necessary
access privileges, who needs to monitor and manage job flow and troubleshoot
problems that may arise.
•
Release Notes
provide last-minute product information and workarounds for some of
the problems you may encounter.

xv Key features of ColorWise
Key features of ColorWise
ColorWise® is the
designed to provide both casual and expert users the best color output for a variety of
purposes. The ColorWise default settings were specifically selected to provide great
out-of-box color from many applications and Windows and Mac OS platforms. This
means that casual users can get good quality output without knowing about or
changing any color settings on the ColorPASS.
To get consistent color you should be sure that the ColorPASS is calibrated on a
regular basis. ColorWise Pro Tools include a simple-to-use calibrator, which allows you
to calibrate using either the scanner that comes with the copier or optional
densitometer (see Chapter 3).
There are a number of features that can be used to modify printing results. Depending
on your particular needs, you can:
• Set the behavior of CMYK printing to emulate DIC, Euroscale, and SWOP
offset press standards
• Match PANTONE colors for the best match when printed using four-color
press conditions or when printed using presses with extra, custom plates
• Select a
printing. CRDs allow for rich, saturated printing of presentation graphics; smooth,
accurate printing of photographs; and relative or absolute colorimetric rendering for
specialized needs
color rendering dictionary
color management system
(CRD), also called a rendering style, for RGB
(CMS) built into the ColorPASS and
• Define the source of incoming RGB color data for better screen matching, and you
can provide for better color conversion of RGB data with no source information
• Define whether RGB data is converted into the full gamut of the copier or whether
it is first converted into the gamut of another device, such as a press standard. This
feature is very helpful for making one device behave like another. It is also useful for
evaluating the appearance of the RGB file under different printing conditions
without having to reprocess the RGB data each time

xvi Introduction
ColorWise offers an open color architecture, letting users customize the ColorPASS to
meet new printing needs as they arise. ColorWise supports ICC profiles, which are
industry standard color profiles that define the color behavior of a device. By
downloading ICC profiles to the ColorPASS, it can simulate a custom press (or
another copier) as well as accurately print colors from a particular monitor or a
particular scanner. In addition, you can create customized ICC profiles for the copier.
ColorWise also lets you use any Status T densitometer by importing data in a standard
file format (see Appendix C). In this case, it is important to note that the quality of the
instrument used will determine the quality of the calibration.

1-1 Managing color on the ColorPASS
1
Chapter 1: ColorPASS Color Management
The first part of this chapter describes the options available from the ColorWise color
management system and explains how you can customize the color settings for your
particular needs. It provides descriptions of the preset default settings of ColorWise
and covers additional options for users who need to customize ColorWise.
Beginning on page 1-14 is a detailed explanation of what a PostScript Level 2 or
PostScript 3 printer driver does, as well as information on the capabilities of various
printer drivers and instructions for setting color options with the PostScript drivers for
Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000, Windows 95/98/Me, and Mac OS.
Managing color on the ColorPASS
There are three ways to modify the ColorPASS’s printing behavior. You can:
• Select ColorWise options for an individual print job using menus that appear from
the printer driver.
• Select most ColorWise options as server defaults from ColorPASS Setup or from the
Control Panel, as described in the
all subsequent print jobs unless you override them.
• Select some ColorWise options, particularly default
calibration options, from ColorWise Pro Tools. These options include default
Simulation Profile (see page 1-8), Simulation Method (see page 1-9), Appear in
Driver as (see page 4-9), default Source Profile (see page 1-6), RGB Separation (see
page 1-7), and associated calibration set (see page 3-4).
Configuration Guide
ICC profile
. These defaults will apply to
settings and
Applications can generate color data for the ColorPASS in many different
spaces
. The most common type of color data produced from office applications is
RGB, while prepress applications generally produce CMYK data. Desktop applications
can also generate spot colors such as PANTONE colors. To complicate matters, a
single page may contain a mix of RGB, CMYK, and spot colors. The ColorPASS lets
users control the printing of these mixed-color documents with features that apply
specifically to RGB, CMYK, or spot color data.
color
1-2 ColorPASS Color Management
1
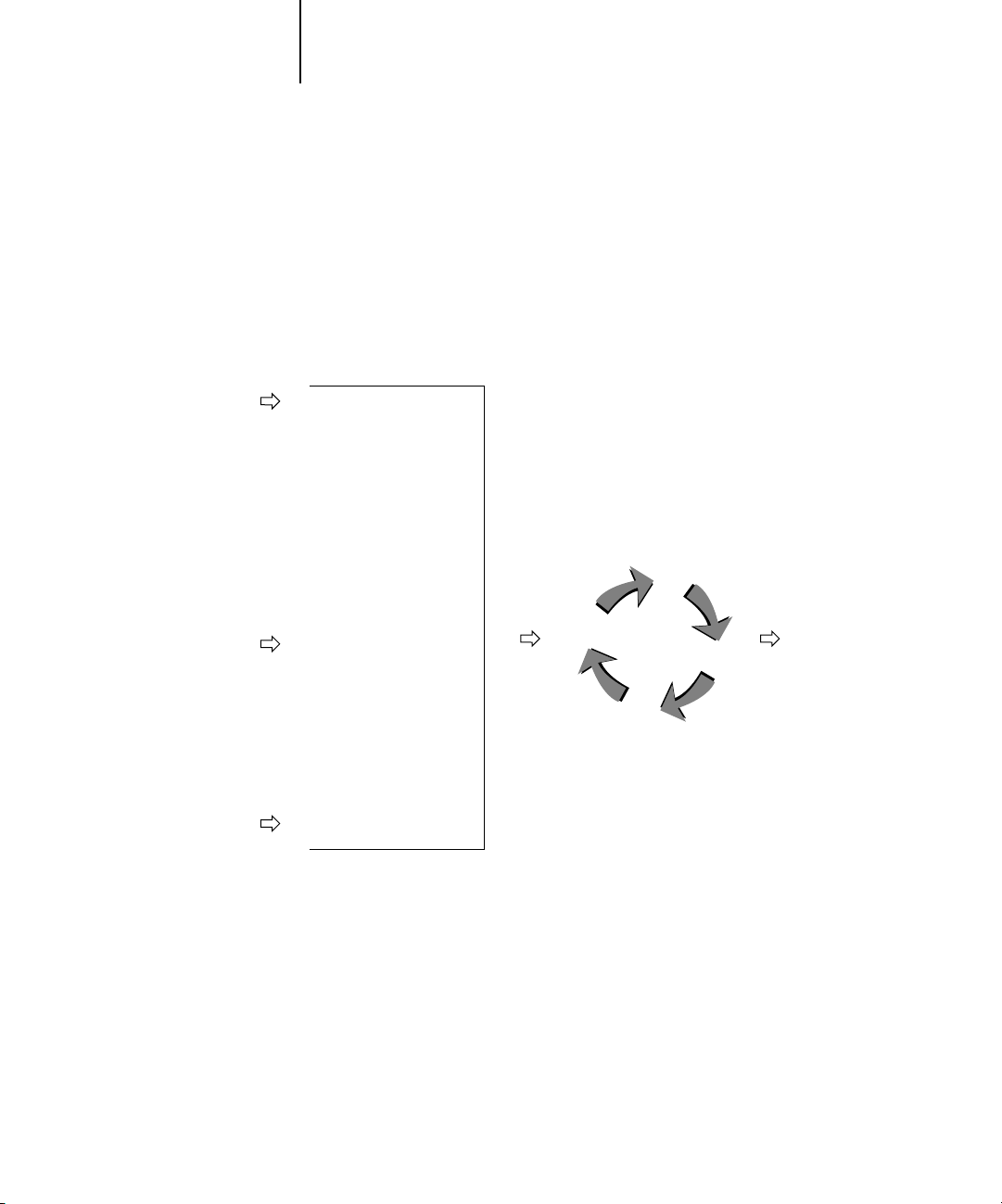
ColorPASS color management generates CMYK data to be sent to the copier;
additional processing may then be performed before printing begins.
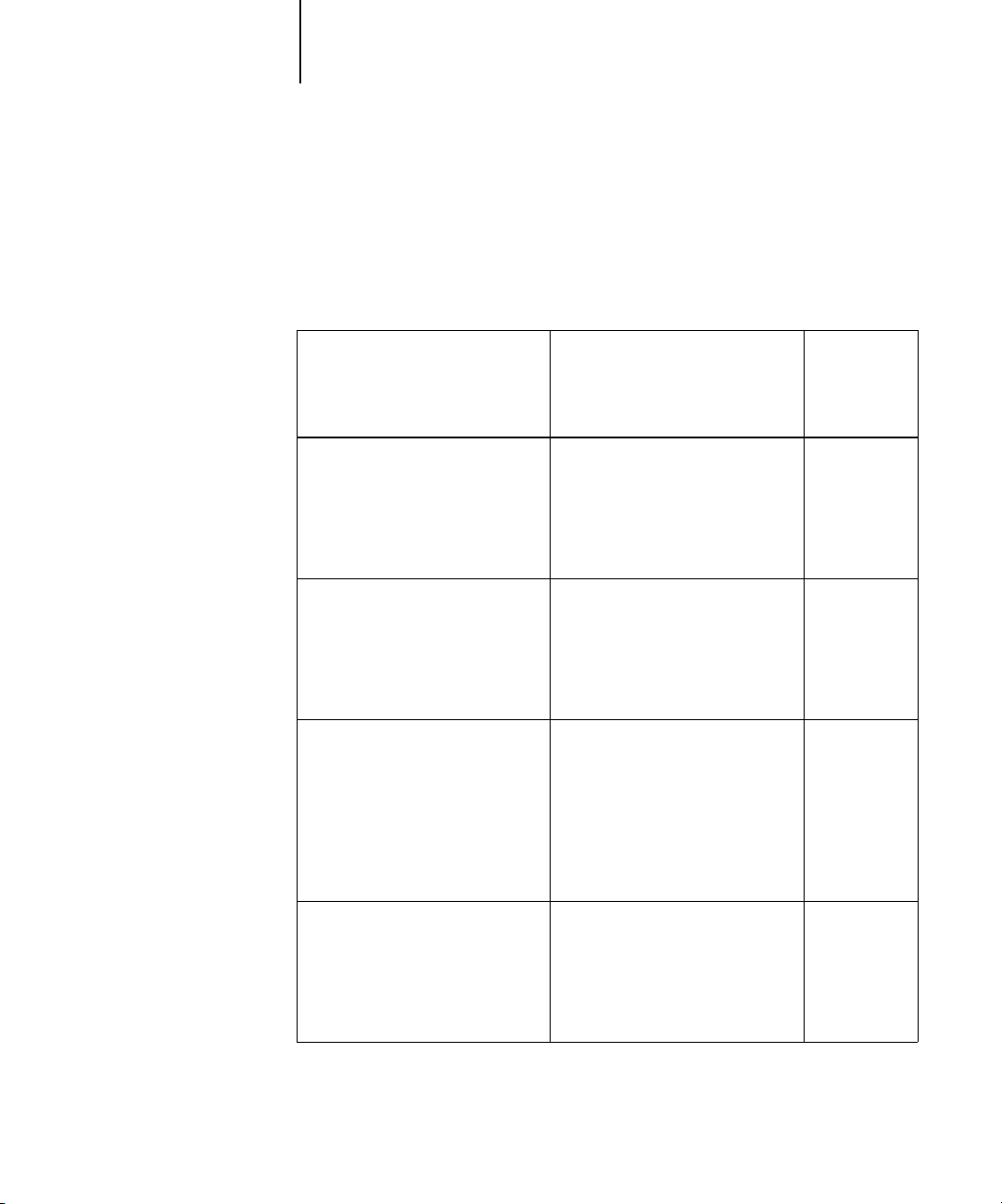
The diagram below illustrates the print options in the ColorPASS color management
process that affect color data conversions. You access these print options when you
send a print job to the ColorPASS. Most of these options and settings are described in
subsequent sections of this chapter.
RGB data
CMYK data
Spot color data
RGB Source Profile
Gamma
Phosphors
White Point
Rendering Style (CRD)
Brightness
Pure Black Text/Graphics
Black Overprint
RGB Separation
Output profile
CMYK Simulation Profile
CMYK Simulation Method
Brightness
Pure Black Text/Graphics
Black Overprint
Combine Separations
Output profile
Spot Color Matching
ColorPASS
color
processor
Color data
sent to
copier
RGB Source Profile is the only color option that applies strictly to RGB color data.
The other options that affect RGB color also affect the more rarely used Lab, XYZ, and
other calibrated color spaces.
OTE
For users who are familiar with PostScript 3.0 color, RGB Source Profile affects
N
:
all CIEBasedABC color spaces (if the source space is RGB). If you send CMYK data to
the ColorPASS in CIEBasedDEFG format, for example, by choosing PostScript Color
Management in Adobe Photoshop, the ColorPASS’s Rendering Style selection—which
normally affects only RGB data—will also affect this CMYK data.
1-3 Managing color on the ColorPASS
1
Settings for the following options can be specified via print options when you send a
job to the ColorPASS. Some can also be set as defaults by the administrator during
ColorPASS Setup. Settings specified via print options override the defaults.
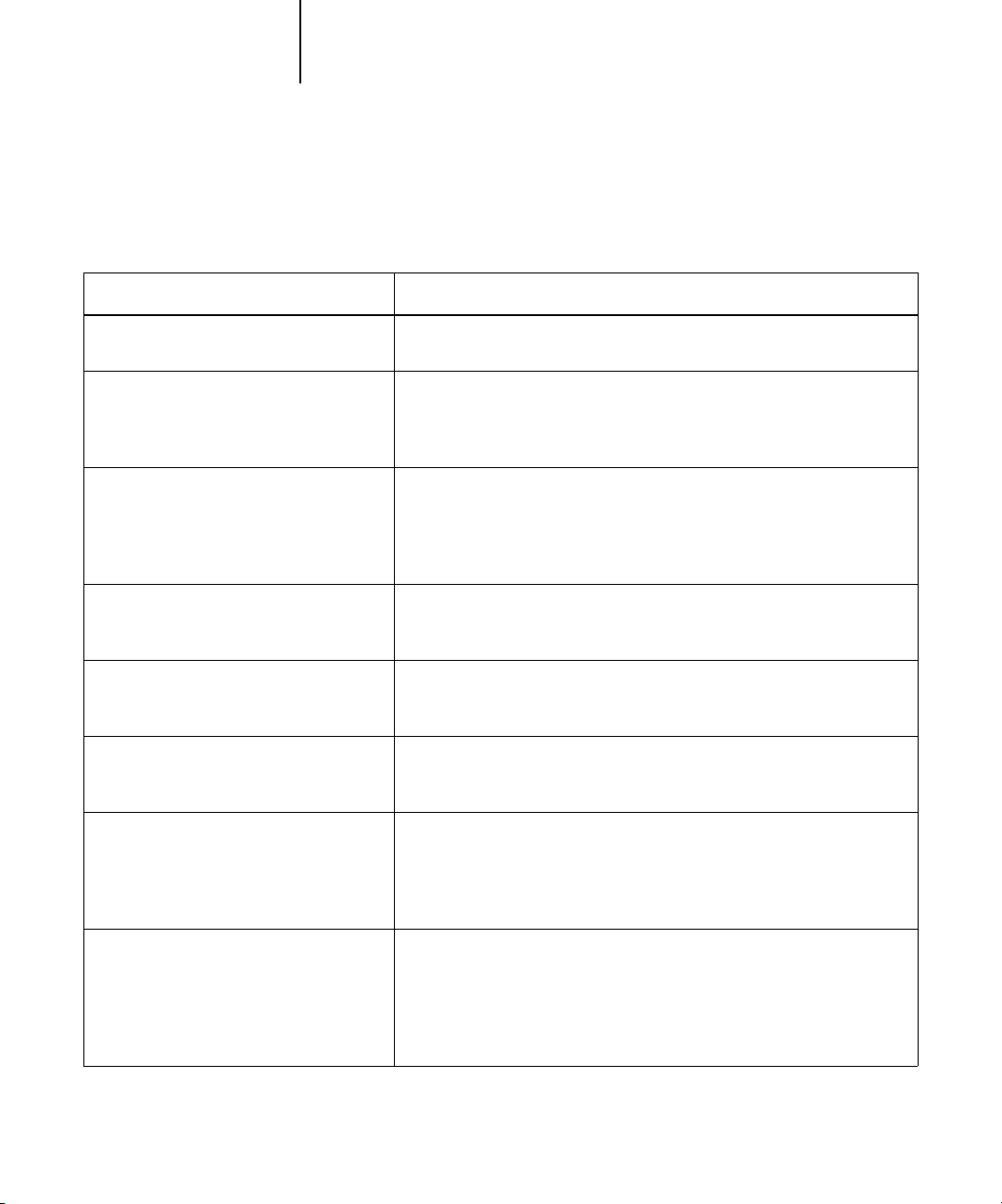
ColorPASS color print option: What it does:
Brightness
85% Lightest to 115% Darkest
Rendering Style
Photographic/Presentation/Relative
Colorimetric/Absolute Colorimetric
(Default set at Setup)
RGB Source Profile
EFIRGB/sRGB (PC)/Apple Standard/Other/
Source 1-10/None
(Default set at Setup or with
ColorWise Pro Tools)
(Other) Gamma
1.0/1.2/1.4/1.6/1.8/2.0/2.2/2.4/2.6/2.8/3.0
(Other) Phosphors
Hitachi EBU/Hitachi-Ikegami/NTSC/
Radius Pivot/SMPTE/Trinitron
(Other) White Point
5000 K (D50)/5500 K/6500 K (D65)/
7500 K/9300 K
RGB Separation
Output/Simulation
Performs a color adjustment on all color channels to make the printed output
lighter or darker.
Applies a ColorPASS color rendering style (CRD) to RGB data (see page 1-5),
or to any incoming data with a PostScript source color space definition,
including CMYK.
Applies an RGB source space definition to RGB data (see page 1-6). If you
choose the Other setting, you can specify particular settings for gamma,
phosphors, and white point. See the corresponding options in this table. This
option, along with Gamma, Phosphors, and White Point, are the only
ColorWise options that affect only DeviceRGB or calibrated RGB color spaces.
Applies the specified gamma value to the RGB source space definition (see
page 1-6). To use this print option, you must choose Other as the RGB Source
setting.
Applies the specified phosphor (monitor type) information to the RGB source
space definition (see page 1-6). To use this print option, you must choose
Other as the RGB Source setting.
Applies the specified white point value to the RGB source color space
definition (see page 1-6). To use this print option, you must choose Other as
the RGB Source setting.
Determines which CMYK color space your original RGB data will be
separated into—CMYK for the copier (Output) or CMYK for a specified
simulation (Simulation) (see page 1-7). It is important to note that when RGB
Separation is set to Simulation, RGB colors are affected by CMYK Simulation
Profile and CMYK Simulation Method.
CMYK Simulation Profile
SWOP-Coated/DIC/Euroscale/Simulation
1-10/Match Copy/None
(Default set at Setup or in
ColorWise Pro Tools)
Adjusts CMYK color data to simulate an offset press standard or a custom
color gamut defined at your site. The Match Copy setting bypasses ColorPASS
calibration to match a copy made from the copier glass. Choosing None
bypasses simulation (see page 1-8).
N
OTE: Some of the Simulation settings have slightly different names depending
on the model of copier.
1-4 ColorPASS Color Management
1
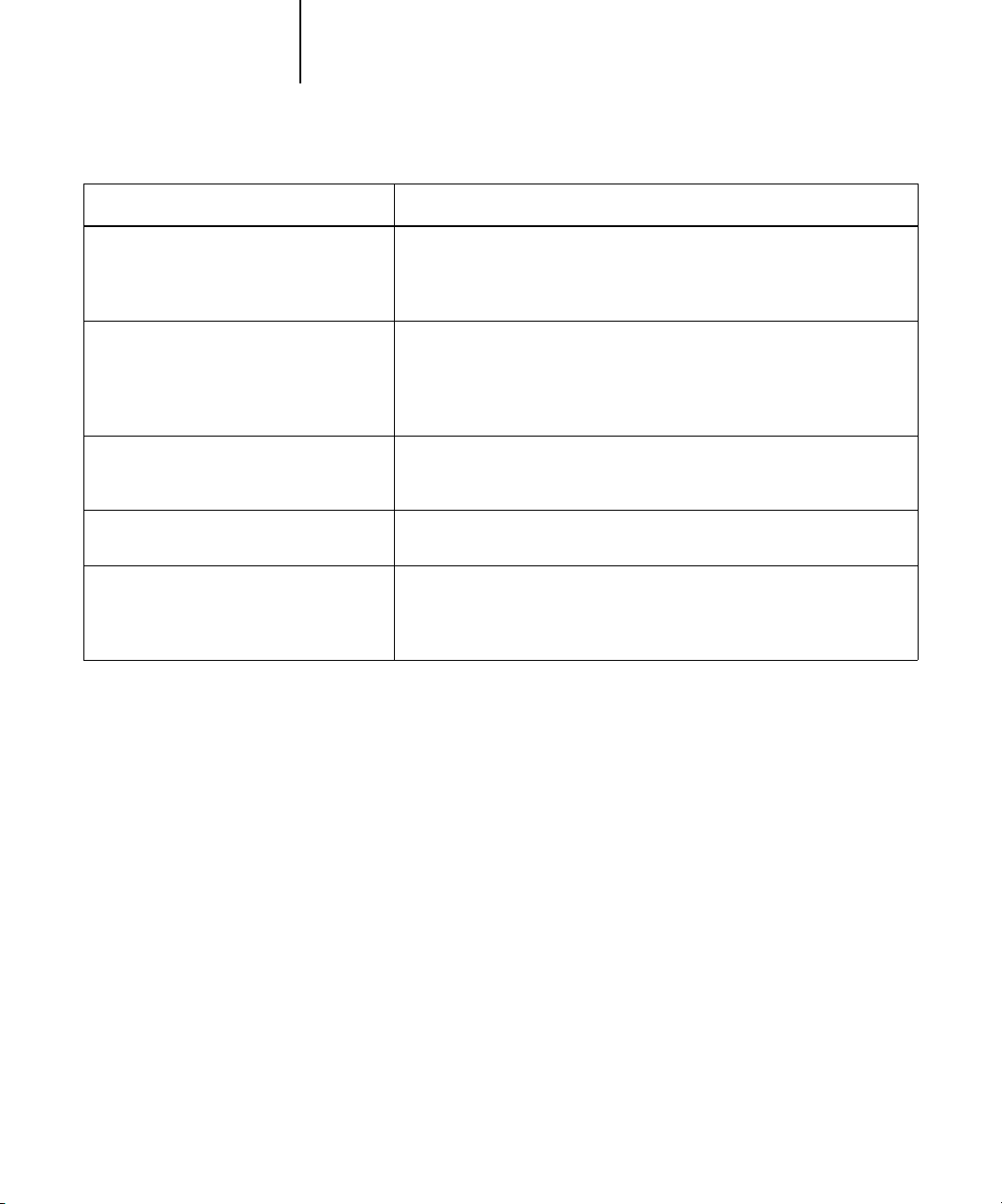
ColorPASS color print option: What it does:
CMYK Simulation Method
Quick/Full
(Default set at Setup or in
ColorWise Pro Tools)
Output Profile
Default output profile/5000 A Fine/5000 A
Coarse/5000 A Off/Output 1-10
(Default set at Setup or in
ColorWise Pro Tools)
Pure Black Text/Graphics
On/Off
(Default set at Setup)
Black Overprint
On/Off (Default set at Setup)
Spot Color Matching
On/Off
(Default set at Setup or with
ColorWise Pro Tools)
Detailed explanations of how these and other settings affect your print jobs are
provided in subsequent sections of this chapter.
Quick simulation applies one-dimensional transfer curves that adjust output
density only. Full simulation applies colorimetric transformations that adjust
hue as well as output density (see page 1-9).
The Output Profile is applied to all data in the print job (see page 1-9).
User-defined output profiles can be downloaded to the ColorPASS with
ColorWise Pro Tools (see Chapter 4).
The On setting optimizes the quality of black text and line art output
(see page 1-10).
The On setting overprints black text placed on colored backgrounds; it
automatically activates the Pure Black Text/Graphics option (see page 1-12).
The On setting enables ColorPASS matching of PANTONE colors; Off
instructs the ColorPASS to match color output to a PANTONE-specified
CMYK combination (see page 1-13).
1-5 Managing color on the ColorPASS
1
Rendering styles
The Rendering Style option specifies a CRD for color conversions. You can modify the
Rendering Style option to control the appearance of images, such as prints from office
applications or RGB photographs from Photoshop. The ColorPASS lets you select
from the four rendering styles currently found in industry standard ICC profiles.
Equivalent
ColorPASS
rendering style:
Best used for:
ICC
rendering
style:
Photographic—Typically results in
less saturated output than
presentation rendering when
printing out-of-gamut colors. It
preserves tonal relationships in
images.
Presentation
colors but does not match printed
colors precisely to displayed colors.
In-gamut colors such as flesh tones
are rendered well, similar to the
Photographic rendering style.
Relative Colorimetric
white-point transformation
between the source and destination
white points. For example, the
bluish gray of a monitor will map to
neutral gray. You may prefer this
style to avoid visible borders when
not printing full-bleed.
Absolute Colorimetric
white point transformation between
the source and destination white
points. For example, the bluish gray
of a monitor will map to a bluish
gray.
—Creates saturated
—Provides
—Provides no
Photographs, including scans and
images from stock photography
CDs.
Artwork and graphs in
presentations. In many cases it can
be used for mixed pages that
contain both presentation graphics
and photographs.
Advanced use when color matching
is important but you prefer white
colors in the document to print as
paper white. It may also be used
with PostScript color management
to affect CMYK data for simulation
purposes.
Situations when exact colors are
needed and visible borders are not
distracting. It may also be used with
PostScript color management to
affect CMYK data for simulation
purposes.
Image,
Contrast, and
Perceptual
Saturation,
Graphics
Same
Same

1-6 ColorPASS Color Management
1
RGB Source Profile
The RGB Source Profile setting allows you to define the characteristics of the RGB
data in your document so that the appropriate color conversion can occur on the
ColorPASS. Commonly used monitor color spaces are available from the driver and
from the ColorWise Pro Tools Profile Manager. In addition, for special needs you can
use ColorWise Pro Tools to download custom monitor or scanner profiles.
When you specify a setting other than None for the RGB Source Profile, the
ColorPASS overrides source color space definitions or profiles that other color
management systems may have specified. For example, if you specified a ColorSync
System Profile on your Mac OS computer, the RGB Source Profile setting overrides it.
In cases where you do not want this setting to override another specified source color
space, choose the None setting.
When you specify a setting other than None for the RGB Source Profile—since the
color space definitions are overridden—the prints from the ColorPASS will be
consistent across platforms. Below are the ColorPASS’s RGB Source Profile options.
• EFIRGB specifies an EFI-defined color space recommended for users who have no
detailed information about their RGB data.
• sRGB (PC) specifies the industry standard definition for a generic Windows PC
monitor.
• Apple Standard specifies the definition of all standard Mac OS computer monitors.
• Other allows you to specify custom RGB source settings. If you choose Other as the
RGB Source setting, you can choose settings for the Gamma, Phosphors, and White
Point options.
• Sources 1-10 specify the definitions you download as RGB source profiles.
(For more information about downloading RGB source profiles, see Chapter 4.)
If you are printing with the PostScript driver for Windows 95/98/Me and have TwoWay Communication enabled, the name of each downloaded profile is represented
in the RGB Source Profile setting pop-up menu. If you are printing with the
AdobePS driver from a Mac OS or Windows NT computer, or the Microsoft
PostScript driver from a Windows 2000 computer, downloaded profiles appear as
Source-1 through Source-10. For more information on Two-Way Communication,
see Getting Started.

1-7 Managing color on the ColorPASS
1
• None instructs the ColorPASS to allow the RGB sources you defined elsewhere, such
as in the application, to be used. When you set RGB Source to None, the
appearance of colors will not be independent of the file type. For example, RGB EPS
files will look different from RGB TIFF files.
With RGB Source set to None, PostScript RGB data that contains a source color
space definition is converted using the CRD specified by the Rendering Style option
(see page 1-5). NonPostScript RGB data and PostScript RGB data that does not
contain a source color space definition is converted using a general undercolor
removal conversion method.
RGB Separation
The RGB Separation option determines how RGB colors (as well as Lab and XYZ
colors) are converted to CMYK. The name of this option is meant to be descriptive,
since the option defines the color spaces that will be used by the ColorPASS to
“separate” the RGB data into CMYK values.
The two choices available for this option determine whether RGB data is converted
into the full gamut of the copier (Output) or whether it is first converted into the
gamut of another digital printer or a press standard (Simulation). This feature is
helpful for making one device behave like another for RGB data. For example, if a
high-quality ICC profile is available for another print device, the copier can simulate
the behavior of that device.
RGB Separation is also useful for prepress applications. For example, it lets you
experiment with the appearance of an RGB scan under different press printing
conditions without having to convert the RGB data to CMYK data for each printing
condition. When the desired printing condition is found, you can then convert the file
to CMYK, if desired, using the same CMYK simulation profile that was used during
the experimentation.
NOTE: The RGB Separation print option should be used in conjunction with the
Output Profile or CMYK Simulation Profile print options.
•
Output converts all RGB colors into the CMYK color space of your copier (when the
Output Profile option is set to Printer’s default), or a customized CMYK color space
for your copier (when the Output Profile option is set to Output 1-10).

1-8 ColorPASS Color Management
1
• Simulation converts all RGB colors into the CMYK color space for a specified
simulation (make sure to select the desired simulation with the CMYK Simulation
Profile print option).
CMYK Simulation Profile
The CMYK Simulation Profile print option allows you to print press proofs or
simulations. This setting specifies the offset press standard or other color printing
device that you want to simulate. This option affects CMYK data only.
With the Windows 95/98/Me printer driver, you can also view an unlimited number
of custom Quick and Full simulations created using ColorWise Pro Tools. On
Windows NT, Windows 2000, and Mac OS computers, you can view up to 10 Quick
and 10 Full custom simulations. The number of custom simulations is limited by the
disk space on the ColorPASS.
If you are printing with the PostScript driver for Windows 95/98/Me and have TwoWay Communication enabled, the name of each downloaded or custom profile is
represented in the CMYK Simulation Profile setting pop-up menu. If you are printing
with the AdobePS driver from a Mac OS or Windows NT computer, or the Microsoft
PostScript driver from a Windows 2000 computer, downloaded or custom profiles
appear as Simulation-1 through Simulation-10. For more information on Two-Way
Communication, see Getting Started.
The CMYK Simulation Profile setting you should specify depends on the press
standard for which the CMYK data was separated.
• For images that were separated using a custom separation (such as a separation
produced with an ICC profile), choose the corresponding profile on the ColorPASS
with the CMYK Simulation Profile setting.
• For images that were separated for SWOP, choose SWOP as the CMYK Simulation
Profile setting.
NOTE: To properly simulate a printed image that was separated through the use of an
ICC profile, the same profile must be present on the ColorPASS. For more
information about downloading ICC profiles to the ColorPASS, see “Downloading
profiles” on page 4-5.

1-9 Managing color on the ColorPASS
1
• The Match Copy setting bypasses ColorPASS calibration to simulate the color of a
copy produced by the copier. Use this setting when you print images scanned with
the Fiery Scan plug-in set to Match Copy.
CMYK Simulation Method
The CMYK Simulation Method setting specifies the quality of simulation to perform.
• Quick applies one-dimensional transfer curves that adjust output density only.
• Full provides a more complete and accurate simulation by applying colorimetric
transformations that adjust hue as well as output density. The Full Simulation
option also maintains the integrity of the black channel by adjusting it
independently. This is especially important for images separated using an optimized
black generation (UCR/GCR) setting, either from a scan or from within an
application such as Photoshop.
Output Profile
The output profile is applied to all data in the print job, so make sure the selected
profile is right for your job. The default output profile consists of both a profile for
your copier, describing its color characteristics, and a calibration target that describes
the expected behavior of the copier.
The output profiles provided with the ColorPASS correspond to one of several
different gradation smoothing calibration sets. You should select an output profile
based on the desired gradation smoothing property, which determines the amount of
smoothing the ColorPASS applies to your print job to eliminate banding. Coarse
provides more gradation smoothing than Fine. There are two sets of output profiles, A
and B, which you can calibrate for different paper stocks. The output profiles 5000 A
Fine, 5000A Coarse, 5000 A Off, 5000 B Fine, 5000 B Coarse, and 5000 B Off
correspond to the gradation smoothing property, respectively.
In certain cases you may wish to customize the default output profile using the
ColorWise Pro Tools Color Editor to achieve particular color effects (see page 4-12). If
so, the new customized output profile is applied to all data in the print job. Changing
only the output profile does not affect its associated calibration target (since the target
is based on a copier model). If you wish, you can edit D-Max values of the calibration
target separately (see page 4-7).

1-10 ColorPASS Color Management
1
You can also use ColorWise Pro Tools’ Profile Manager to download your own output
profile to the ColorPASS (see page 4-5). Downloaded output profiles are at first
associated with the calibration target that is tied to the default output profile. As
mentioned above, you can edit calibration target D-Max values separately.
If you are printing with the PostScript driver for Windows 95/98/Me and have TwoWay Communication enabled, the name of each downloaded or custom profile is
represented in the Output Profile setting pop-up menu. If you are printing with the
AdobePS driver from a Mac OS or Windows NT computer, or the Microsoft
PostScript driver from a Windows 2000 computer, downloaded or custom profiles
appear as Output-1 through Output-10. For more information on Two-Way
Communication, see Getting Started.
Pure Black Text/Graphics
The Pure Black Text/Graphics option affects the printout for black text and vector
graphics on a page. Under most circumstances it is preferable to leave this option set to
the On position. When Pure Black Text/Graphics is on, black colors generated by
applications are printed using 100 percent black-only toner (for example,
RGB = 0, 0, 0; CMYK = 0%, 0%, 0%, 100%; or K = 100%). This means the black
text and line art will not exhibit halftone artifacts and will not be misregistered, since
there is only one toner used. In addition, this setting eliminates blasting. This option
is automatically set to On when the Black Overprint option is set to On.
For some jobs it is preferable to turn this option Off, for example, if the page includes
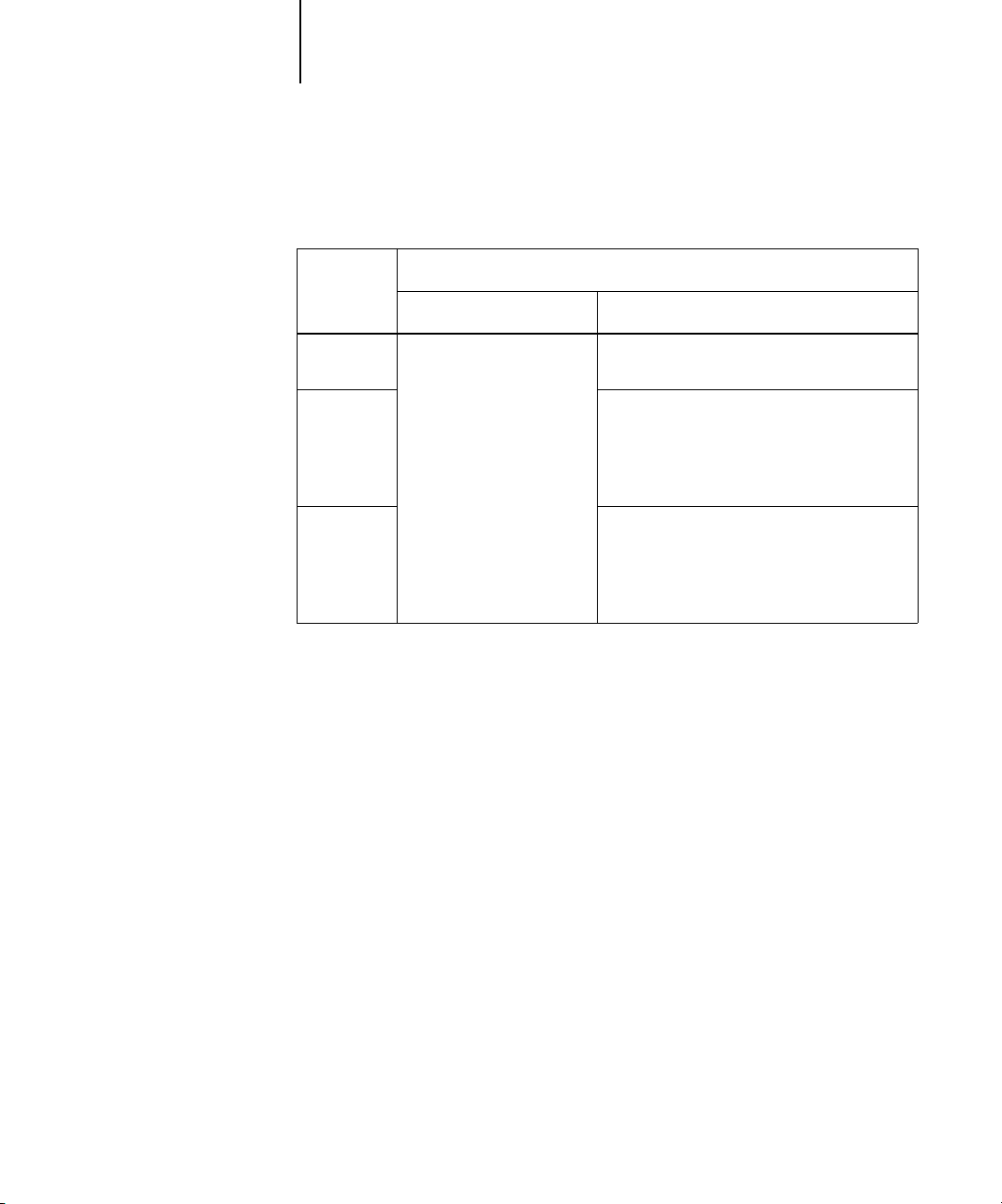
gradient fills that use black. The table below describes the behavior of the Pure Black
Text/Graphics option with black data defined in different color spaces.
1-11 Managing color on the ColorPASS
1
NOTE: The Pure Black Text/Graphics option can be used only when printing
composites, not when printing separations.
Input
black color
RGB
CMYK
Spot
NOTE: PostScript applications, such as QuarkXPress, may convert elements defined as
RGB = 0, 0, 0 to four-color CMYK black before sending the job to the ColorPASS.
These elements are not affected by the Pure Black Text/Graphics option. See the
application notes for details. Also, black text and line art defined as RGB = 0, 0, 0 in
office applications (such as Microsoft Word) are converted to single-color black
(CMYK = 0%, 0%, 0%, 100%) by the Microsoft PostScript Level 3 driver for
Windows 2000. To print this single-color black at the maximum toner density of the
copier, set the Pure Black Text/Graphics option to On.
On Off
Prints 100% black
Pure Black Text/Graphics
With the default profile, prints a rich black
using all toners.
Prints only with black toner, because CMYK
simulations preserve the black channel. The
actual amount of toner used depends on the
current simulation and the calibration state
of the copier.
Prints only with black toner, because spot
color simulations preserve the black channel.
The actual amount of toner used depends on
the current simulation and the calibration
state of the copier.

1-12 ColorPASS Color Management
1
Black Overprint
The Black Overprint option lets you specify whether or not black text, defined as
RGB = 0, 0, 0, or as CMYK = 0%, 0%, 0%, 100%, overprints colored backgrounds.
• On—Black text overprints colored backgrounds, eliminating white gaps and
reducing halo effects or misregistration of colors. Setting Black Overprint to On
automatically activates the Pure Black Text/Graphics option.
• Off—Black text knocks out colored backgrounds.
NOTE: PostScript applications may perform their own black overprint conversions
before sending the print job to the ColorPASS.
One example of how you might use this setting is with a page that contains some black
text on a light blue background. The background blue color is CMYK = 40%, 30%,
0%, 0% and the black text is CMYK = 0%, 0%, 0%, 100%.
• With Black Overprint On, the final text portions of the page are overprinted, or
combined with the underlying colors. This results in CMYK = 40%, 30%, 0%,
100% for the color used for the text. There is no transition in the cyan and magenta
toners, and the quality of the output is improved since it will not show artifacts near
the edges of the text. The option also works with text defined in the RGB color
space, that is RGB = 0, 0, 0.
• With Black Overprint Off, the border of the text is on an edge that has cyan and
magenta toners on one side (outside the text) and black toner on the other side
(inside the text). On many devices, this transition causes visible artifacts because of
the practical limitations of the copier.

1-13 Managing color on the ColorPASS
1
Spot Color Matching
The Spot Color Matching option provides automatic matching of PANTONE colors
with their best CMYK equivalents.
• On—The ColorPASS uses its built-in table to generate the closest CMYK matches of
PANTONE colors your copier can produce. (New tables are generated when you
add new output profiles.)
• Off—The ColorPASS uses the CMYK equivalents defined by your application to
print PANTONE colors.
For jobs that include PANTONE spot colors, set Spot Color Matching to On unless
you are printing press simulations. In that case, set Spot Color Matching to Off and
choose the appropriate CMYK Simulation setting (see page 1-8).
NOTE: You can use the Spot Color Matching option only when printing composites,
not when printing separations.
Spot Color Matching and the PANTONE Coated Color Reference
The PANTONE Coated Color Reference (described on page 5-7) prints differently
depending on the Spot Color Matching setting.
• On—The ColorPASS uses its built-in table to generate the best matches of the
PANTONE colors that your copier can produce. The PANTONE number is
printed below each swatch.
• Off—The ColorPASS prints swatches using the CMYK values recommended by
Pantone (and used by applications that provide PANTONE color libraries). The
CMYK values used to generate the color, as well as the PANTONE number of the
color, are printed below each swatch. These CMYK values are printed through the
selected CMYK Simulation and Output Profile settings.

1-14 ColorPASS Color Management
1
Printer Drivers and Print Options
This section describes the role of the printer driver and explains how to use Windows
and Mac OS printer drivers for ColorPASS printing.
NOTE: The term “PostScript” by itself is used to refer to Adobe PostScript Level 2
or later.
What a printer driver does
To take full advantage of the features of the ColorPASS, your print jobs must be sent as
PostScript data. Since most applications cannot generate PostScript data directly, it is
the function of a printer driver to interpret instructions from the application and
convert them to PostScript data.
A PostScript printer driver also allows you to select print options specific to your
copier. To do this, the printer driver must be matched with a PostScript printer
description file (PPD) for your ColorPASS. The PPD contains information about the
particular features supported by the ColorPASS and the copier. The PPD can be
thought of as the lines of PostScript code in the file that are device-specific. When you
print a job, the printer driver lets you choose among features by displaying print
options.
A few PostScript applications can send PostScript data directly to the copier and
present print options within the application interface. Even these applications,
however, require that you use a PostScript printer driver.
Your ColorPASS user software includes Adobe PostScript printer drivers for
Windows 95/98/Me, Windows NT 4.0, and Mac OS and the Microsoft PostScript
printer driver for Windows 2000. These are the recommended printer drivers for
printing to the ColorPASS. (See Getting Started for information on installing printer
drivers.)
It is recommended that you set the print options initially in ColorPASS Setup (see the
Configuration Guide). This provides you with a default configuration that is
appropriate for most ColorPASS print jobs.
 Loading...
Loading...