
Model 2346
T3 Fiber Optic Modem
User Manual

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
CAUTION!
This product may contain a laser diode emitter operating at a wavelength of 1300 nm - 1600 nm. Use
of optical instruments (for example: collimating optics) with this product may increase eye hazard.
Use of controls or adjustments or performing procedures other than those specified herein may result
in hazardous radiation exposure.
Under normal conditions, the radiation levels emitted by this product are under the Class 1 limits in
21 CFR Chapter 1, Subchapter J.
ATTENCION!
Cet équipement peut avoir une diode laser émettant à des longueurs d'onde allant de 1300nm à
1600nm. L'utilisation d'instruments optiques (par exemple : un collimateur optique) avec cet
équipement peut s'avèrer dangereuse pour les yeux. Procéder à des contrôles, des ajustements ou toute
procédure autre que celles décrites ci-après peut provoquer une exposition dangereuse à des
radiations.
Sous des conditions normales, le niveau des radiations émises par cet équipement est en dessous des
limites prescrites dans CFR21, chapitre 1, sous chapitre J.
NOTICE!
This device contains static sensitive components. It should be handled only with proper Electrostatic
Discharge (ESD) grounding procedures.
NOTE!
Cet équipement contient des composants sensibles aux décharges électro-statiques. Il doit absolument
être manipulé en respectant les règles de mise à la terre afin de prévenir de telles décharges.
2346 T3 Modem
i

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
NOTICE
Canoga Perkins has prepared this users manual for use by customers and Canoga Perkins personnel as
a guide for the proper installation, operation and/or maintenance of Canoga Perkins equipment. The
drawings, specifications and information contained in this document are the property of Canoga
Perkins and any unauthorized use or disclosure of such drawings, specifications and information is
prohibited.
Canoga Perkins reserves the right to change or update the contents of this manual and to change the
specifications of its products at any time without prior notification. Every effort has been made to
keep the information in this document current and accurate as of the date of publication or revision.
However, no guarantee is given or implied that the document is error free or that it is accurate with
regard to any specification.
CANOGA PERKINS CORPORATION
An Inductotherm Company
20600 Prairie Street
Chatsworth, California 91311-6008
Business Phone: (818) 718-6300
(Monday through Friday 7 a.m. - 5 p.m. Pacific Time)
FAX: (818) 718-6312 (24 hrs.)
Web Site: www.canoga.com
Email: fiber@canoga.com
Copyright © 2003 - 2005 Canoga Perkins Corporation
All Rights Reserved
EdgeAccess
Universal Chassis System
2346 T3 Modem
Users Manual
Model Number 2346-UM
Part Number 6912680
Rev. E 01/2008
To reference Technical Advisories and Product Release Notes, go to Canoga Perkins'
website: http://www.canoga.com/
®
ii
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Overview.................................................................................................1-1
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation and Functions..................................................2-1
Set Up and Installation ........................................................................................................................2-1
Power Up and Front Panel Functions..................................................................................................2-3
Alarm Functions..................................................................................................................................2-4
Chapter 3 Software Management...........................................................................3-1
Setting Up for Network Management .................................................................................................3-1
Set Up the Network Management Platform ..................................................................................3-1
Set Up the PC for Terminal Operation.........................................................................................3-1
Management User Interface ................................................................................................................3-2
General Screen Format.................................................................................................................3-2
User Interface Organization.........................................................................................................3-3
Login and Main Menu...................................................................................................................3-3
Manage the 2346.................................................................................................................................3-4
View the Hardware Setup .............................................................................................................3-4
Set the Date and Time...................................................................................................................3-5
Set Up SNMP Access ....................................................................................................................3-5
Manage and Check Traps and Alarms..........................................................................................3-6
Set Up Baud Rates and Modem/SLIP/PPP Parameters ...............................................................3-7
Update Software ...........................................................................................................................3-9
Manage Security................................................................................................................................3-10
Set Up Host Access .....................................................................................................................3-10
Change Your Password...............................................................................................................3-11
Manage the Modem...........................................................................................................................3-11
Set Up Functions and Check Status............................................................................................3-11
Monitor Modem Performance.....................................................................................................3-12
Chapter 4 Maintenance and Troubleshooting ......................................................4-1
General Maintenance...........................................................................................................................4-1
Manage Cable Links..................................................................................................................... 4-1
Check Optical Power Levels.........................................................................................................4-1
Troubleshooting...................................................................................................................................4-2
Check a New Installation..............................................................................................................4-3
Alarms...........................................................................................................................................4-3
Problems With Configuration.......................................................................................................4-4
SW2 (Software Control) Setting Ignored......................................................................................4-4
Problems With Fiber Optics .........................................................................................................4-4
PING.............................................................................................................................................4-4
Loopback.......................................................................................................................................4-5
Chapter 5 Specifications..........................................................................................5-1
2346 Specifications .............................................................................................................................5-1
2346 T3 Modem
iii

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
2346 Models........................................................................................................................................5-2
Appendix A Warranty Information......................................................................A-1
Appendix B Acronym and Abbreviation List...................................................... B-1
Index ......................................................................................................................... I-1
List of Figures
Figure 1. The 2346 Front Panel .........................................................................................................1-1
Figure 2. Switch and Jumper Locations............................................................................................. 2-2
Figure 3. General Screen Format.......................................................................................................3-2
Figure 4. Normal Operation...............................................................................................................4-6
Figure 5. Local Loopback.................................................................................................................. 4-6
Figure 6. Local Bidirectional Loopback............................................................................................ 4-6
Figure 7. Local Loopback at Both Ends ............................................................................................ 4-6
Figure 8. Remote Loopback............................................................................................................... 4-7
Figure 9. Remote Bidirectional Loopback.........................................................................................4-7
List of Tables
Table 1. 2346 LED Functions............................................................................................................ 2-3
Table 2. Main Menu Selections ......................................................................................................... 3-4
Table 3. Hardware Configuration Report .......................................................................................... 3-5
Table 4. Trap Configuration Options.................................................................................................3-6
Table 5. Alarm Output Options..........................................................................................................3-7
Table 6. System Alarms Definitions.................................................................................................. 4-3
iv
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Chapter 1
Overview
The 2346 Managed T3 Fiber Optic Modem converts and extends T3/DS3 signals between devices
located up to 100 Km apart. Use the modem to extend a PBX, router, video codec, M13 multiplexer,
or ATM switch. The 2346 receives and transmits 44.736 Mbps data on single mode or multimode
fiber optic cable.
The 2346 front panel, shown in Figure 1, includes:
• Electrical and optical connectors
• Reset switch
• LEDs for:
• System status
• Configuration
• Electrical signal
• Optical signal
Figure 1. The 2346 Front Panel
The 2346 can be used in a variety of chassis. To install a 2346 in a UCS 1000 or UCS 1001 chassis,
you must use a Model 1230 Bus Access Module (BAM); however, you can install a 2346 directly in a
UCS 1002 or standalone enclosure.
• The UCS 1000 Chassis can hold up to 15 model 1230 BAMs with up to two 2346 modems per
BAM. This allows a total of 30 2346 modems per UCS 1000.
• The UCS 1001 Chassis can hold up to two model 1230 BAMs with up to two 2346 modems per
BAM. This allows a total of four 2346 modems per UCS 1001.
• The UCS 1002 Chassis directly hosts up to fourteen 2346 modems, or thirteen 2346 modems with
the optional Domain Management Module (DMM) installed.
• Each standalone enclosure, such as a Model 1020 or 1030E, holds one 2346 modem.
The 2346 is hot swappable; you can insert or remove it at any time without disrupting the data
transfer of other modules in the chassis.
2346 T3 Modem
1-1

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
1-2
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Chapter 2
Hardware Installation and Functions
Before setting up the 2346, make sure the chassis or enclosure is installed and its User Manual is
available for reference. If the system includes an optional DMM and CIM(s), make sure these are
available:
• Serial cable (required to connect to a VT100 type terminal or PC)
• VT100 type terminal or PC to run the User Interface Manager software
• The DMM and CIM manuals
Set Up and Installation
Unpack and inspect all components. Save the shipping carton and packing materials in case you need
to return the equipment to the manufacturer. Appendix A provides information for Return Material
Authorization (RMA).
1. Before inserting the 2346, check the front panel to verify that the 2346 provides the wavelength
that matches its link partner; see Figure 1.
2. Set SW2-1 and 2-2; see Figure 2.
• SW2-1, Line Buildout (LBO): Off (default) for Short LBO, <225 ft (68 m), or On for Long
LBO, >225 ft; when software control is enabled at the Functional Configuration screen,
SW2-1 is ignored.
• SW2-2, Software override: Off (default) is software, On is hardware; set to Hardware in
unmanaged environment, only. For installation in a managed environment where you plan to
use software control (see page 3-11), set SW 2-2 to Off.
Note: If the 2346 was previously installed in a managed environment and set in the User Interface
to software control, follow these steps to set it to hardware control when installing it in an
unmanaged environment:
a. Set SW2-2 to On.
b. Insert the 2346 in a slot with the power on, then remove it.
c. Set SW2-2 to Off.
d. Insert the 2346 in a slot with the power on, then remove it.
e. Set SW2-2 as needed.
3. Set jumper W10 as needed for normal (to NP) or wide pulse (to WP); see Figure 2. NP is the
default.
2346 T3 Modem
2-1
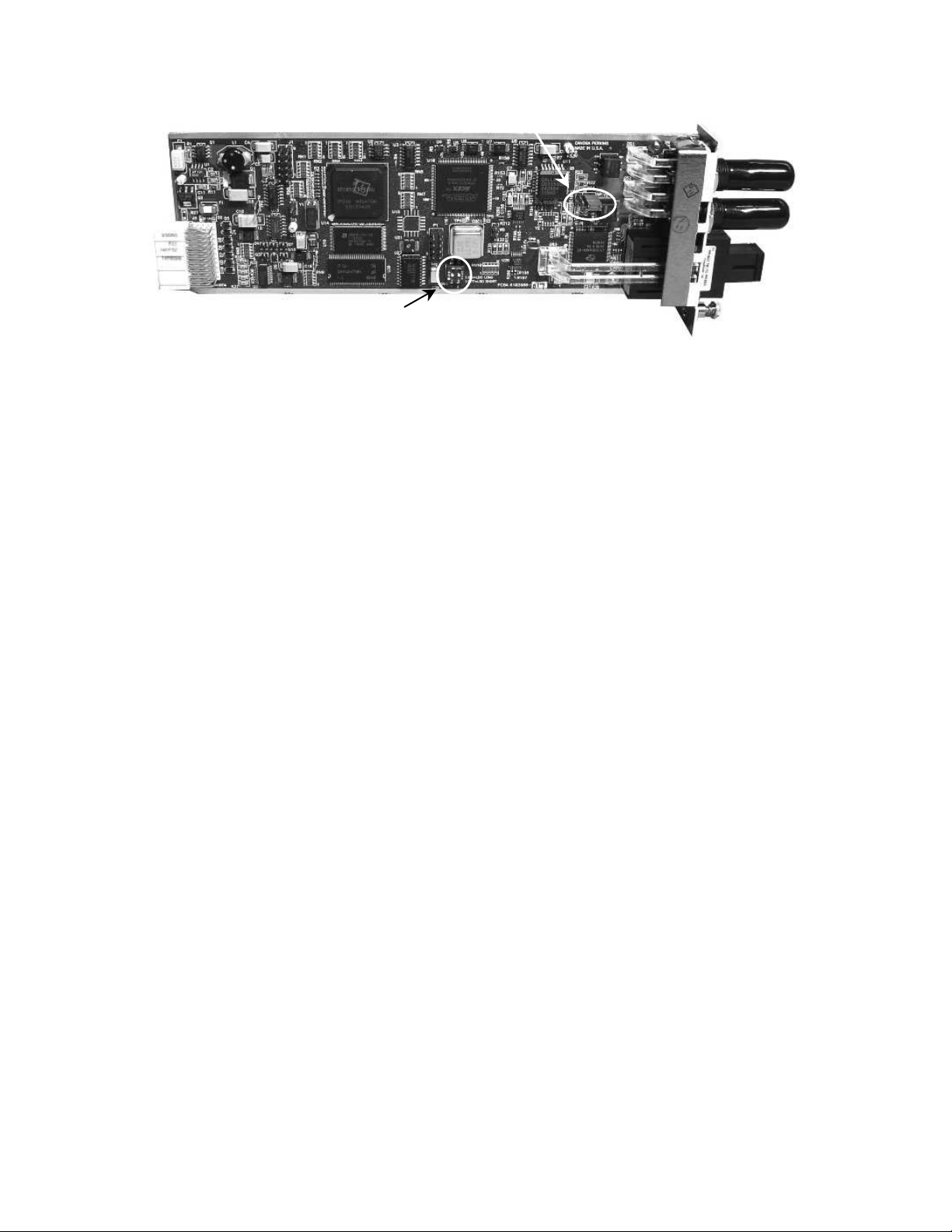
EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
W10
SW2
Figure 2. Switch and Jumper Locations
4. To install a 2346 in a UCS 1000 or 1001 chassis, you must use a Model 1230 BAM; each BAM
can hold up to two 2346 modems. Follow these steps to install the BAM and the 2346:
a. Insert a BAM into an available slot in a UCS 1000 or 1001. Slide the BAM into the rails and
push it firmly into the backplane, then tighten the captive screws. If you encounter
resistance, check that no connector pins are bent.
b. Insert a 2346 into an unused slot in the BAM. Slide the 2346 into the rails and push it firmly
into the backplane, then tighten the captive screw. If you encounter resistance, check that no
connector pins are bent.
5. To install a 2346 directly in a UCS 1002 or standalone enclosure, insert the 2346 into an unused
slot. Slide the 2346 into the rails and push it firmly into the backplane, then tighten the captive
screw. If you encounter resistance, check that no connector pins are bent.
If you encounter more difficulty, contact Canoga Perkins at (818) 718-6300 for technical assistance.
Note: The BAM and 2346 are hot-swappable and can be inserted or removed without disrupting
data transfer in other application modules.
6. If the 2346 is in a standalone enclosure, set the switch on the enclosure for loopback to Normal.
The 2346 uses electrical cables to connect to the local site and fiber optic cables to connect to the
remote modem. Follow these steps to connect the electrical and optical cables:
7. To connect to the local site, plug the BNC cables from the local equipment into the Rx and Tx
connectors using Tx to Rx, and Rx to Tx orientation.
Dirty optical connectors are a common source of link loss or attenuation problems, especially for
single mode fiber (SMF). Clean the connectors before plugging in a cable and whenever there is a
significant or unexplained light loss. To prevent contamination, always install protective dust covers
on unused fiber optic connectors.
8. Wipe the ferrule and the end-face surface of the male fiber coupler with a lint-free isopropyl
alcohol pad from a fiber cleaning kit.
9. Use canned air to blow out any dust from the female fiber coupler.
2-2
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Caution: To avoid damaging the fiber end-surface or connector, use extreme care when
installing or removing cables.
10. Plug in the optical cables:
• If you have a simplex optical connector, use a single strand, single mode fiber cable between
a pair of 2346 modems, one at 1310 nm wavelength and the other at 1550 nm wavelength.
• If you have a duplex connector, use Tx to Rx, and Rx to Tx orientation.
11. Label each cable and connector with a signal name and direction.
12. For cable connections to other modules in the chassis, see the appropriate user manual for details.
13. Measure and record fiber link attenuation and transmission power before starting normal link
traffic in order to identify potential problems with links near the lower limit of receiver
limitations. For details on link attenuation and transmission power, see Chapter 4.
Power Up and Front Panel Functions
During the initial power-up sequence, all LEDs light amber. When start-up is complete and data is
transmitting normally across the link, the STA LED lights green and the CFG/TST, LOS, and CLS
LEDs are off. During normal operation, the LED colors change according to system and port
conditions. The STA and CFG/TST LEDs show the module condition. The LOS and CLS LEDs
show the electrical and optical signal conditions. Table 3 shows the LED states for various
conditions.
Table 1. 2346 LED Functions
LED Status Description
STA Off No power
Green Normal operation
Amber System self-test
Amber blinking Downloading file or in power-up cycle
Red Failed system self-test
CFG/TST Off Normal operation
Red Software or line coding mismatch between local and remote
modems or improperly connected fiber optic cable
Amber Local or local bidirectional loopback
Amber blinking Remote or remote bidirectional loopback
LOS Off Normal operation
Red Local loss of electrical signal
Red blinking Remote loss of electrical signal
CLS Off Normal operation
Red Local loss of optical sync
Red blinking Remote loss of optical sync
2346 T3 Modem
2-3

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
Alarm Functions
The 2346 can generate Major and Minor Alarms.
• UCS 1000 and 1001: a BAM is required and holds up to two 2346 modems. On the BAM, the
Status (STA) LED lights green if either 2346 is operating normally. If both modems have errors,
the BAM STA LED lights amber.
• UCS 1001: the alarm outputs are forwarded to the chassis motherboard.
• UCS 1000 and 1002: the alarms are forwarded over the backplane to the CIM and appear on the
Major (MAJ) and Minor (MIN) CIM LEDs and then are forwarded to the DMM for monitoring
and transfer to the Network Manager as traps.
• Model 1020 enclosure: the alarm information is forwarded to the management session.
• Model 1030 enclosure: alarms are not supported.
For details about setting up the Alarms, see Chapter 3; for viewing the Alarm Log, see Chapter 4.
2-4
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Chapter 3
Software Management
You can manage the 2346 through VT100 Terminal Emulation, which is accessible by a Telnet
session, HyperTerminal or similar terminal emulation software, a standard SNMP network manager,
and CanogaView. If the 2346 is in UCS 1000 or 1002 with a CIM within a domain that includes a
DMM, you can access the 2346 through the DMM. If the 2346 is a standalone or in a UCS 1001, you
must access the 2346 directly through the serial port for the enclosure or BAM.
Setting Up for Network Management
Typically, the 2346 runs within the network on an Ethernet connection, communicating with your
Network Management Platform.
Set Up the Network Management Platform
You must run several Management Information Bases (MIBs) on your Network Management
Platform in order to successfully manage this module. Before you start, check that Standard MIB (the
industry-standard mib) is loaded. In addition, download Cp.mib, a private mib that supports all
Canoga Perkins products, available from the Canoga Perkins web site. Go to www.Canoga.com,
click Support, then click Software Download, and follow the prompts on screen.
Set Up the PC for Terminal Operation
Connect the VT100 terminal emulation session to the DMM or directly to a 2346, either standalone or
in a UCS chassis. Setting up the VT100 session depends on which connection, serial port or Ethernet,
you have available for access to the VT100 management program. Canoga Perkins suggests that you
use HyperTerminal for your first session.
You must set up TCP/IP for the DMM or directly-managed 2346 before you can use Telnet; for
details, see the manual for the DMM or go to page 3-7.
Note: For details on the DMM, see the Model 1500 Domain Management Module User Manual (for
UCS 1000) or the Model 1502 Domain Management Module User Manual (for UCS 1002).
These steps briefly describe how to set up your PC for a terminal connection. For details on using
Windows, see your Windows documentation.
1. Turn on your PC.
2. Accessories, the HyperTerminal Folder, and click HyperTerminal.
3. At the Connection Description dialog, select an icon, enter a name for the connection to the
system, and click OK.
4. At the Connect To dialog, pull down the Connect using menu, select the COM port, and
click OK.
2346 T3 Modem
3-1

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
5. At the COM Properties dialog, on the Port Settings tab, check for these selections:
• Bits per second: 19200 bps
• Data bits: 8
• Parity: None
• Stop bits: 1
• Flow control: None
6. `Click OK. HyperTerminal connects to the system and the VT100 terminal emulation starts.
Management User Interface
The Management User Interface for the 2346 provides screens for setup, monitoring, and diagnostics.
These sections discuss the screens for the 2346, using a Telnet session for access. If you connect
through the DMM in the chassis, see the User Manual for your DMM for details about the DMM
screens.
General Screen Format
A typical screen, shown in Figure 3, includes standard descriptions and reference designations. Use
this and other screens to configure the system, set operational parameters, and verify the system
status. All screens use a common method for navigation.
Chassis and slot information
Model number
Status reports
Change options
Screen navigation
instructions
Messages and
urgent status
Figure 3. General Screen Format
Not all screens and menus provide options that you can change. Some menu items reach screens that
only report status, such as revision numbers, module type, or alarms. On other screens, you can move
through and select options, and enter data.
3-2
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Use these keys to navigate the screens:
• Space bar When a menu item is highlighted, press <Space> to cycle through all options for that
item.
• Tab Press <Tab> to move the highlight to the next column to the right.
• Enter Press <Enter> to select the highlighted option for a menu item.
• Escape Press <Esc> once to cancel changes for the selected item or to return to the previous
screen; press <Esc> two or more times to return to the Main Menu from two or more menu levels
deep.
User Interface Organization
The user interface consists of selectable, nested screens, available in this order:
Main Menu
1. System Configuration
1. Hardware Configuration
2. Functional Configuration
3. Trap Configuration
4. Alarm Output Configuration
5. SNMP Configuration Parameters
8. Host Table
2. Link Error Counters
3. System Alarms
4. Utilities
8. PING Generation
5. Software Upgrade
Login and Main Menu
The first screen is the Login Menu. If this is your initial setup and no password has been set, press
<Enter> at the prompt for the password. Otherwise, type your password and press <Enter>.
After you log in, the Main Menu for the DMM appears. This is the main management screen for the
DMM. For details on all menu options, see the manual for your DMM. From this screen, you can
access the 2346 by either of two methods.
2346 T3 Modem
3-3

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
• To reach the 2346 directly, follow these steps:
a. Type 4, "Manage or access a specific Module," and press <Enter>.
b. Type the slot and chassis numbers with a slash, such as "1/4" for chassis 1, slot 4, and then
press <Enter>.
c. At the Module Menu, type 4, "Access User Interface," then press <Enter> to reach the Main
Menu screen for the 2346.
• To reach the chassis, and then select the 2346, follow these steps:
a. Type 3, "Manage or access a specific Chassis," and press <Enter>, press <Space> to cycle
through the chassis in the domain, and then press <Enter> to select the chassis.
b. At the Chassis Management screen, press <Space> to cycle to the slot number for the 2346,
then press <Enter> to reach the Main Menu screen for the 2346.
Note: In a UCS 1000 chassis, the slots in the BAM appear as A and B for the slot that the BAM is
in.
You can reach all configuration options from the Main Menu; see Table 2.
Table 2. Main Menu Selections
Menu Item Description
1. System Configuration View and set values for the system information and communications
parameters
2. Link Error Counters View number of errors that occur on the link
3. System Alarms View current conditions for local and remote alarms
4. Utilities View and set values for general parameters and run the diagnostic PING
5. Software Update Download and install new firmware
Manage the 2346
You can manage the hardware and software for the module, including communication access.
View the Hardware Setup
To check information about both the local and remote 2346s, including the hardware setup, with
model and serial numbers, and basic system status, go to the Hardware Configuration report. See
Table 3. To view the Hardware Configuration screen, follow these steps:
1. At the Main Menu, type 1, "System Configuration," and press <Enter>.
2. At the System Configuration menu, type 1, "Hardware Configuration," and press <Enter>. The
Hardware Configuration screen appears.
3. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
3-4
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Table 3. Hardware Configuration Report
Item Shows
Chassis/Slot, Type, Temperature Where the modem is installed and status, if available
Modem Model, Type, Revision, Serial No. Data for the modem and optical interface
Power Supply Pri, Sec Type(s) and status for the power supply(s)
Fan Installed Status if a fan is installed
Set the Date and Time
An accurate date and time in the assures accuracy for traps and alarms sent to the system
administrator, as well as for all listed events. If the 2346 is in a system with a DMM, the date and
time for the DMM overrides any date and time set in the 2346.
To set the date and time, follow these steps:
1. At the Main Menu, type
2. At the Utilities menu, type
the current date and time, type the current information in
3. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
4, "Utilities," and press <Enter>; the Utilities menu appears.
1, "Set Date and Time," and press <Enter>, then at the prompt to enter
DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM format.
Set Up SNMP Access
SNMP access is available for a modem in a standalone enclosure, only. To set values for basic
system parameters, including some SNMP parameters, go to the SNMP Configuration Parameters
menu. To access the SNMP Configuration Parameters menu, follow these steps:
1. At the System Configuration menu, type 5, "SNMP Configuration," and press <Enter>. The
SNMP Configuration Parameters screen appears.
2. At the prompt, type the number for an item and follow the prompts on the screen to set values for
these items:
• System Contact: Who is responsible for the 2346, up to 50 characters
• System Name: What you call the 2346, up to 50 characters
• System Location: Where the 2346 is located, up to 50 characters
• Read Community: Name for the people who can view the reports, up to 10 characters;
default is public
• Write Community: Name for the people who can set values for parameters, up to 10
characters; default is public
• SLIP/PPP IP Address: Enter the IP address for access through SLIP or PPP
• Ethernet IP Address: Enter the IP address for access through the Ethernet network
• Ethernet Subnet Mask: Enter the mask that sets the network ID part of the IP address
• Ethernet Default Gateway: Enter the address of the network node that connects to another
network
2346 T3 Modem
3-5

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
• BOOTP Enabled: Enable this if the module needs to obtain its IP address from a BOOTP
server; when the unit has an IP address, disable BOOTP
• Serial Port Config: Set the type of serial port connection: VT100, SLIP, or PPP
• Telnet Timeout: Set the time with no activity until a Telnet connection automatically logs out
3. To return to the System Configuration menu, press <Esc>.
Manage and Check Traps and Alarms
Traps are messages that require management attention and are routed to the Network Manager, but do
not trigger alarms. Conditions that generate an alarm require immediate attention. Enable or disable
traps on the Trap Configuration screen and enable or disable alarms on the Alarm Output
Configuration screen.
Use the Trap Configuration screen to view the current configuration and to enable or disable traps for
the 2346. For a list of events that trigger traps, see Table 4. To set up the traps, follow these steps:
1. At the System Configuration menu, type 3, "Trap Configuration," and press <Enter>.
2. At the Trap Configuration screen, type the number for a trap and press <Enter>. See Table 4.
3. Press <Space> to cycle to Enabled or Disabled and press <Enter>.
4. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
These selections do not affect how the Major and Minor LEDs on the CIM report alarms.
Table 4. Trap Configuration Options
Type of Trap When enabled, sends a Trap if. . .
2) LOS/CLS Loss of Signal (electrical)/Composite Loss of Signal (optical); one or
both received signals fail
3) SQL Squelch occurs (for received signal)
4) Configuration The 2346 is set up incorrectly, including mismatches with other modems
5) Diagnostic Loopback is enabled or disabled
6) Authentication An unauthorized host attempts SNMP access to the 2346
7) Power/Fan Malfunction Power is low or fan is off
8) Cold Start The 2346 is reset by a power failure or forced reset
9) Alarm Input UCS 1001 function; see the UCS 1001 User Manual
10) Security Violation Not used
Use the Alarm Output Configuration screen to view the current configuration and to enable or disable
alarms for the 2346. For a list of events that trigger alarms, see Table 4. To set up the alarms, follow
these steps:
1. At the System Configuration menu, type 4, "Alarm Output Configuration," and press <Enter>.
3-6
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
2. At the Alarm Output Configuration screen, type the number for an alarm and press <Enter>. See
Table 5.
3. Press <Space> to cycle to Enabled or Disabled and press <Enter>.
4. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
These selections do not affect how the CIM Major and Minor LEDs report alarms.
Table 5. Alarm Output Options
Alarm When enabled, sends an alarm if. . .
2) LOS/CLS Loss of Signal (electrical)/Composite Loss of Signal (optical); one or
both received signals fail; default is Off
3) SQL Squelch occurs (for received signal); default is Off
4) Configuration The 2346 is set up incorrectly or the local and remote software versions
do not match; default is Off
5) Power/Fan Power is low or fan is off; default is Minor
6) Power-On Self Test Modem failed when power was turned on; default is Major
7) BERT Bit Error Rate Test (BERT) detects data errors; for details on BERT
results, see page 3-12; default is Off
Note: The Bit Error Rate Test (BERT) sends a continuous 127-bit sequence within the optical data
stream to check for bit errors while the optical signal remains in sync.
Set Up Baud Rates and Modem/SLIP/PPP Parameters
Although the default values for the communication parameters meet requirements for most systems,
you may need to change them for your particular situation.
To reset the VT100 baud rate, follow these steps:
1. At the Main Menu, type
2. At the Utilities menu, type
cycle between 9600 and 19200 bps.
3. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
To access the Modem/SLIP/PPP Configuration menu, follow these steps:
1. At the Main menu, type
4, "Utilities," and press <Enter>.
3, "VT100 Baud Rate," and press <Enter>, then press <Space> to
4, "Utilities," and press <Enter>.
2. At the Utilities menu, type
3. To select the baud rate for the serial port, type
<Enter>, then press <Space> to cycle through the baud rate options; options include 9600, 19200,
38400, 57600, or 115200 bps.
4, "Modem/SLIP/PPP Configuration," and press <Enter>.
4, "Modem/SLIP/PPP Configuration," and press
2346 T3 Modem
3-7

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
4. To enter a new Modem Initialization String, type
default string is "
AT".
5, type the new string, and press <Enter>; the
Note: For details on a different initialization string, see the documentation for your modem.
5. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
Because the DMM defaults to VT100 mode when booting, you cannot see the screens and commands
used to switch to SLIP or PPP mode when you exit VT100 mode. Use a script file to successfully
exit VT100 mode and switch to SLIP or PPP.
1. To create a script on your PC, open Notepad and type the steps you would follow to enter SLIP or
PPP mode. On the last line, press <Space> once to select SLIP mode or twice for PPP mode
proc main
waitfor "Password :"
transmit $PASSWORD, raw
transmit "^M"
transmit "1^M"
transmit "5^M"
transmit "11^M"
transmit " ^M"
endproc
2. Save the Notepad document with a .SCP file extension in the folder where the Dialup Connection
application looks for scripts. The script will be available in the Dialup script menu. This file is
typically in the Windows\System32\ras\ folder.
3. To run the script, reach the Phonebook Entry dropdown menu and select either the PPP or the
SLIP script.
If you do not have a script file, you dial in through a modem, and the networking option is set to
VT100 operation, you will not see the screens, but the 2346 responds to the commands normally.
Follow these steps:
1. Dial in through a modem, then type your user name and password and press <Enter>.
2. Type
3. Type
4. Type
1 and press <Enter>.
5 and press <Enter>.
11 and press <Enter>.
5. Press <Space> once for SLIP mode or twice for PPP mode, then press <Enter> to confirm the
port choice.
The 2346 is ready to run TCP/IP applications.
3-8
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Update Software
Each module in the Universal Chassis System has two flash memory banks that store software:
• The Active Flash Memory holds the software currently in use
• The Inactive Flash Memory holds the new software from a download or the older version of
software
Software is downloaded to the inactive region to avoid disrupting service. Resetting the module and
swapping banks does not affect module operation and is transparent to user traffic.
Use the Software Upgrade report and menu screen to check the current version of the 2346 firmware
and to upgrade software for any module in the domain or a managed module partner, if necessary.
To access the Software Upgrade screen, follow these steps:
1. At the Main Menu, type
5, "Software Upgrade," and press <Enter>.
2. At the Software Upgrade screen, record the numbers for the Active and Inactive Firmware.
3. Access the Canoga Perkins Web site, click Downloads, scroll to the 2346 filename, and compare
the version number listed there with the version numbers you recorded. The 2346 firmware file
name is similar to
23460106.zip, where "2346" indicates the module and "0106" indicates the
version.
Caution: To insure compatibility when a system includes two or more of the same module, you
must upgrade all those modules with the same software.
If the firmware for the 2346 is outdated, Canoga Perkins recommends that you upgrade it.
4. You can download the software through the DMM (for details, see the manual for your DMM) or,
if the 2346 is in a UCS 1001 or a standalone enclosure, follow these steps to start the software
upgrade:
a. Go to the Host Access Table (see page 3-10) and verify that the entry for the host you will
use for the file transfer allows FTP or SFTP access, depending on the method you plan to use.
b. Log in to the FTP or SFTP server from the account that allows access.
Note: You can run only one FTP or SFTP session at a time.
c. Download the new firmware from the Canoga Perkins web site to your TFTP server; put the
firmware in the "
transfer is complete, the file is moved automatically to the "
d. At the Main Menu, type
e. At the Software Upgrade menu, type
/BURNING" directory. For FTP, enable binary transfer mode. When the
/INACTIVE" directory.
5, "Upgrade Software," and press <Enter>.
4, "Get New File with TFTP," and press <Enter>.
f. Follow the prompts on the screen to enter the IP address for the TFTP server and the file
name for the new firmware, then start the upgrade.
2346 T3 Modem
3-9

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
5. When the file transfer is complete:
a. At the Software Upgrade menu, type
b. Type
6. To update a remote partner, type
and press <Enter>. The 2346 writes the software to the remote partner, which then resets and
starts using the new firmware.
1, "Software Reset," and press <Enter>. The 2346 resets and starts using the new
firmware.
3, "Copy Software from Source modem to Destination modem,"
2, "Swap Bank," and press <Enter>.
Manage Security
To provide system security, the 2346 includes username and password access, as well as SNMP with
Read and write communities and a Host table. To set up values for various security parameters on
your 2346, you must typically have supervisor access.
Set Up Host Access
The SNMP agent allows access to up to 24 Host IP addresses listed in the Host Access Table. Set up
the Host information for access to the 2346 on the Host Access Table screen. When a host attempts
to access the 2346, the IP address is authenticated against the entries on the host table. If a user
attempts SNMP access from a host or network that is not listed in this table, the 2346 rejects that host
and generates an authentication trap. To access the Host Table, follow these steps:
1. At the SNMP Configuration Parameters menu, type
The Host Table screen appears.
2. To add a host, type
parameters:
a. IP Address: for the Host
b. Access Level: Read, Read/Write Read/Trap, or Read/Write/Trap
c. Trap Community: the community name for requests from the host or network
3. To delete a host, type
and press <Enter>. The host table appears again with your changes.
4. To return to the SNMP Configuration Parameters menu, press <Esc>.
1 and press <Enter>, then follow the prompts to enter values for these
2 and press <Enter>, then at the prompt, type the IP Address for that Host
13, "Host Access Table," and press <Enter>.
3-10
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Change Your Password
You can update your password for the 2346 in order to maintain security. You cannot change the
password for any other users, especially those who are not logged in. To update your password,
follow these steps:
1. From the Utilities menu, type
2. To change your password, follow the prompts on the screen.
3. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
2, "Change Password," and press <Enter>.
Manage the Modem
After you set up modem functions, you can monitor those functions and the data transmission.
Set Up Functions and Check Status
You can set up the modem functions and check status on the Functional Configuration screen. To
work with modem functions, follow these steps:
1. At the System Configuration menu, type
2. To set a value for a parameter, type a number and press <Enter>, then follow the prompts on
screen. To move to the next column, for a secondary or remote modem, press <Tab>.
• Software Override: Set to software, following this menu, or hardware, following SW2 for
LBO and software/hardware control (see page 2-1)
• Line Build Out: Set to Off, Short LBO <225 ft (68 m); or On, Long LBO, >225 ft
• Loopback: Set to Norm for normal operation; for details on Loopback and troubleshooting,
see page 4-5
2, "Functional Configuration," and press <Enter>.
3. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
To ensure that both the local and remote modems use compatible configuration options, you can copy
the configuration for the local modem to the remote modem; follow these steps:
1. At the Main menu, type
2. At the Utilities menu, type
on screen to confirm.
3. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
4, "Utilities," and press <Enter>.
7, "Copy Configuration," and press <Enter>, then follow the prompts
2346 T3 Modem
3-11

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
Monitor Modem Performance
You can monitor the performance of both the local and remote modems at the Link Errors report.
The report includes timers and checks for signal errors. In addition, the 2346 uses the Bit Error Rate
Test (BERT), which sends a continuous 127-bit sequence within the optical data stream to check for
bit errors while the optical signal remains in sync. The link Errors screen monitors these conditions:
• Timer: Number of days, hours, minutes, and seconds since the last reset
• Composite LOS Errors (CLS): Number of optical loss of signal errors
• Electrical LOS Errors: Number of electrical loss of signal errors
• Errored Seconds (BPVs): Number of seconds with at least one BiPolar Violation (BPV)
• SQL Rx Errors: Number of received squelch occurrences
• BERT Sync Status: Reports loss if CLS occurs or OK if signal is good
• BERT Sync Count: Number of good to faulty patterns
• BERT Bit Errors: Number of bits with errors in the received pattern
• BERT BER (1E-9): Number of bit errors during this BERT up time
• BERT Up Time: How long BERT is available and running
To view the modem performance, follow these steps:
1. At the Main Menu, type
2. At the Link Error Counters screen, press <Tab> to reset all counters, press <Tab>.
3. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
4, "Link Error Counters," and press <Enter>.
3-12
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Chapter 4
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Well-maintained modules and cabling can help ensure trouble-free operation.
General Maintenance
Well-maintained components and clearly identified cables help assure optimum system operation.
Damaged fiber cables and dirty connectors are a common source of signal loss or attenuation. Single
mode and multimode fiber optics are especially sensitive to contamination. Inspect, clean, and test all
components to maintain optimum performance.
Note: To avoid damage and signal loss, do not over-tighten or force-fit optical connectors.
• To clean the ferrules and end-face surfaces of male fiber couplings, use a lint-free pad saturated
with isopropyl alcohol.
• To clean the female fiber connectors, use canned air.
• To prevent damage and contamination, place protective dust caps on all unused optical
connectors.
Manage Cable Links
Manage the cables to ensure trouble-free operation and maintenance tasks.
• Position and secure the fiber optic cables to prevent excessive bends and damage. Follow the
guidelines for the bend radius for specific fiber cables.
Note: If no minimum bend radius is specified, the typical long-term, low-stress radius is not less
than 15 times the cable diameter (based on Federal Standard FS-1037C).
• Always connect the fiber optic cables in the standard Tx to Rx and Rx to Tx scheme; reversing
this can cause transmission conflicts.
• Label each fiber cable near each end with the signal direction, source, and destination to
minimize connection errors.
Check Optical Power Levels
To ensure the proper performance levels, measure the fiber link loss, or link attenuation, for all fiber
links. Each 2346 is shipped with a document that lists the output power for each laser transmitter. To
determine link attenuation, use either the 2346 Tx source or a hand-held 1310/1550 nm laser source, a
fiber optic test jumper cable (with known loss), and an optical power meter.
Measure optical fiber links at the shortest wavelength of operation to determine the limiting factor in
the loss budget. Each device that transmits to a 2346 has a loss budget that is specified by the
manufacturer and recorded on a data sheet provided with the equipment. That loss budget must be
greater than the total of the measured loss of the fiber link and the attenuation of the 2346.
2346 T3 Modem
4-1

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
Note: For accurate results, warm up each unit for at least 30 minutes before checking power levels.
The transmission laser in a 2346 turns on automatically when the chassis receives power.
To measure the output power, follow these steps:
1. Clean the connectors on the fiber optic test cable before plugging it in to the Tx connector on
the 2346.
2. Warm up each component for at least 30 minutes.
3. Set the optical power meter to the proper wavelength.
4. Wait two or three minutes for the power reading to stabilize, and then read the output power.
5. Subtract out the test cable loss, then record the power level and compare it to the value on the
performance sheet for that particular 2346. Measurement tolerance is +/- 0.5 dBm.
Note: When referencing optical power levels with numerical values less than zero, the reading
closer to zero is the greater value; for example, -17 dBm is greater than -20 dBm.
6. If the reading is incorrect, repeat the measurement with a different test cable. If the power level is
still not within range, call Technical Support.
If you know the link attenuation, subtract that value from the 2346 Tx output value to determine the
power expected at the remote cable end, which is the input power at the remote receiver, and skip this
section. Otherwise, continue these steps to use the 2346 to measure the link attenuation.
7. At the local site, connect the fiber link cable to Tx on the 2346.
8. At the remote site, set the optical power meter to the proper wavelength and connect it to the fiber
link cable.
9. Record the optical power level and compare it with the sensitivity level listed on the data sheet
for the link fiber type.
10. Subtract the remote power level from the value for the transmitter output power at the local site.
The result provides the link loss, in dB. This power level must not exceed the limit for Rx
sensitivity listed on the data sheet for the remote unit.
Note: If you cannot determine the Rx sensitivity, contact Canoga Perkins Technical Support
Department for assistance.
11. Repeat this process at the other site.
Troubleshooting
This section describes fault conditions and corrective action. As a rule, whenever there is a
significant signal loss, check the fiber path and the minimum bend radius for potential problems.
Remove and inspect the cable connectors, being careful not to damage the fiber end-face surface or
the connector housing. Clean all optical connectors before reinstalling them.
4-2
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
The front panel LEDs show both normal and fault conditions. Typically, if a LED is steady red, the
fault is in the local 2346; if it blinks red, the fault is in the remote modem. Additional information
about fault conditions appears in the System Alarms and System Configuration screens. To aid
troubleshooting, Table 1 lists the functions of the front panel LEDs. For details on the LED status
during normal start-up and operation, see Chapter 2.
Additional information about fault conditions appears in the System Alarms, Hardware
Configuration, and Functional Configuration screens.
Check a New Installation
On new installations, make sure that all steps in Chapter 2 are complete, then make these checks:
• The STA LED is green
• The fiber type (multimode or single mode) matches the 2346 optical mode
• All fiber cabling is of the same type; do not mix multimode and single mode cables
• The fiber optic cable is within the specifications and loss budget of the optic interface module
• The line length between the 2346 and the remote link does not exceed the allowable loss
budget or overdrive limit
• All host modules in the link are turned on
• All fiber cables are connected Tx to Rx and Rx to Tx
Alarms
The System Alarms screen reports alarms and faults on the 2346. To view current alarm status,
follow these steps:
1. From the Main Menu, type 3, Alarms, and press <Enter>. The System Alarms report appears.
2. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
Table 6. System Alarms Definitions
Item Reports. . .
Configuration Errors If the local and remote modems have incompatible set ups,
including software version
Fiber/Electrical Loss of Signal If optical or electrical loss of signal occurs
SQL Rx If squelch occurs
Chassis Management OK if 2346 is in managed chassis or N/A if in standalone
Alarm Relay Inputs Loss if CLS occurs or OK if signal is good; UCS 1001, only
Power Supply Primary/Secondary Function of main/second power supply
Chassis Temperature Excessive temperature
Fan Failure
Power-On Self Test OK or faulty hardware or software
2346 T3 Modem
4-3

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
Problems With Configuration
If a configuration error appears and you have difficulty isolating the fault, you can reset all
configurable settings to default except for the time and date, password, BOOTP setting, and Telnet
timeout. You can then restart your configuration process. To update reset to default, follow these
steps:
1. At the Main menu, type
2. At the Utilities menu, type
the prompts on the screen.
3. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
4, "Utilities," and press <Enter>.`
6, "Reset Configuration To Default," press <Enter>, and then follow
SW2 (Software Control) Setting Ignored
If the 2346 was installed in a UCS 1000 or 1002 and set in the User Interface to software control, it
ignores the line buildout switch setting when placed in a UCS 1001 or Model 1030. For details on
setting the 2346 to hardware control before installing, see Chapter 2.
Problems With Fiber Optics
If the CLS LED lights Red or the System Alarms screen shows a Fiber Loss of Signal, inspect and
clean the cables and connectors, then replace any damaged fiber. Retest the 2346 after cleaning.
PING
Use the PING Generation screen to test the connection to a specific IP address; follow these steps:
1. From the Main Menu, type
2. From the Utilities menu, type
3. At the prompt, type the IP address to PING and press <Tab>.
4. At the prompt, type the number of times to send a PING, from 1 to 256, or type
continuously every 3 seconds, and press <Enter>.
"
PING response received..." indicates a good connection;
TIMEOUT: Unable to reach [IP address]..." indicates a faulty connection.
"
5. To stop the PING and return to the Utilities menu, press <Esc>.
4-4
3, Diagnostics, and press <Enter>.
8, PING Generation, and press <Enter>.
2346 T3 Modem
0 to PING

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Loopback
Use loopback to diagnose a fault on the optical link, either on a modem or with a cable. The 2346
supports both local and remote loopback in one or both directions. Set loopback either in software for
a managed 2346 or at the loopback function switch on a standalone enclosure See Figures 4
through 9.
• Local loopback returns the received electrical signal to the local site and ignores the received
optical signal; turn on Local Loopback at the local modem. The remote modem returns All Ones
to the remote site. Faulty data can indicate that the local 2346 is faulty.
• Remote loopback returns the received optical signal to the remote modem and ignores the
received electrical signal; turn on Remote Loopback at the local modem. The remote modem
returns All Ones to the remote site. Faulty data can indicate that either the fiber optic cable link
or the remote 2346 is faulty.
• Bi-directional loopback returns the received electrical signal to its local site and the received
optical signal to the modem that sent it; turn on Local loopback at one modem and Remote
Loopback at the other modem. Faulty data can isolate the faulty equipment to indicate that either
the fiber optic link or a 2346 is faulty.
To set up the software and start or stop loopback, follow these steps:
1. From the Main Menu, type
2. At the System Configuration menu, type
Functional Configuration screen appears.
3. Enable Software Override, if needed. Type
between Enabled and Disabled, and press <Enter> to select Enabled. To move to the next
column fo r a remote modem, press <Tab>.
4. To set and start Loopback, type
options. To move to the next column for a remote modem, press <Tab>. When you finish
making selections, press <Enter>; loopback starts.
5. To stop Loopback, type
the next column for a remote modem, press <Tab>. When you finish making selections, press
<Enter>; loopback ends.
6. To return to the Main Menu, press <Esc>.
Alternately, if the 2346 is in a standalone enclosure that includes loopback support, such as a 1020,
you can set the Loopback function switch on the front panel for local or remote loopback; for details,
see the manual for the enclosure.
1, "System Configuration," and press <Enter>.
2, "Functional Configuration," and press <Enter>. The
1 and press <Enter>, then press <Space> to cycle
3 and press <Enter>, then press <Space> to cycle through the
3 and press <Enter>, then press <Space> to cycle to Norm. To move to
2346 T3 Modem
4-5

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
A
Figure 4. Normal Operation
Figure 5. Local Loopback
Fiber Link
IS
Figure 6. Local Bidirectional Loopback
Figure 7. Local Loopback at Both Ends
4-6
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Figure 8. Remote Loopback
Figure 9. Remote Bidirectional Loopback
2346 T3 Modem
4-7

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
4-8
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Chapter 5
Specifications
See also the specifications for the chassis or standalone enclosure.
2346 Specifications
Data Rates: 44.736 Mbps
Physical Specifications
Dimensions 3.0"H x 1.0"W x 9.0"D (76.2 mm x 25.4 mm x 228.6 mm)
Weight: 0.3 lb. (0.136 Kg)
Operating Temperature, rackmount 0° to 50° C
Operating Temperature, standalone 0° to 50° C
Operating Humidity: Up to 90% (non-condensing)
Copper Connectors: BNC
Optical Connectors: ST or SC
Regulatory Compliance
• ETL, ETLc (UL 60950/CSA C22.2 No. 60950)
• EN 60950, EN 60825-1
• FCC Part 15B (U.S.)/ICES-003 (CAN)
• EN 55022, EN 55024
• EN 61000-3-2
• EN 61000-3-3
• NEBS Level 3 Tested and Certified
• CE Mark
EIA-232 Pinout
Pin Number Signal Name Source I/O
1 RI DCE Output
2 DCD DCE Output
3 DTR DCE Input
4 SIG GND
5 RXD DCE Output
6 TXD DCE Input
7 CTS DCE Output
8 RTS DCE Input
2346 T3 Modem
5-1

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
2346 Models
Model Fiber Optic Option
2346-1121 1310 nm MM ST, 11 dB
2346-1321 1310 nm SM ST, 10 dB
2346-1331 1310 nm SM ST 26 dB
2346-1531 1550 nm SM ST 30 dB
2346-1124 1310 nm MM SC 11 dB
2346-1324 1310 nm SM SC 10 dB
2346-1334 1310 nm SM SC 26 dB
2346-1534 1550 nm SM SC 30 dB
2346-1374 Single Fiber 1310 nm SM SC 40 Km
2346-1584 Single Fiber 1550 nm SM SC 40 Km
2346-1354 Single Fiber 1310 nm SM SC 20 Km
2346-1564 Single Fiber 1550 nm SM SC 20 Km
2346-1070 CWDM 1470 nm SM 22 dB SC
2346-1071 CWDM 1490 nm SM 22 dB SC
2346-1072 CWDM 1510 nm SM 22 dB SC
2346-1073 CWDM 1530 nm SM 22 dB SC
2346-1074 CWDM 1550 nm SM 22 dB SC
2346-1075 CWDM 1570 nm SM 22 dB SC
2346-1076 CWDM 1590 nm SM 22 dB SC
2346-1077 CWDM 1610 nm SM 22 dB SC
EIA-232 Pinout
Pin Number Signal Name Source I/O
1 RI DCE Output
2 DCD DCE Output
3 DTR DCE Input
4 SIG GND
5 RXD DCE Output
5-2
6 TXD DCE Input
7 CTS DCE Output
8 RTS DCE Input
2346 T3 Modem

EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Appendix A
Warranty Information
Current Warranty information is available on-line in the Client Login Area of the Canoga Perkins
web site (www.canoga.com) or by contacting Technical Support at 800-360-6642 (voice) or
fiber@canoga.com (email).
2346 T3 Modem
A-1


EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
Appendix B
Acronym and Abbreviation List
AMI Alternate Mark Inversion
B3ZS Bipolar 3-Zero Substitution
BAM Bus Access Module
CIM Chassis Interconnect Module
DMM Domain Management Module
LNK Link
MM Multimode
MMF Multimode Fiber
SMF Single Mode Fiber
SM Single Mode
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol
UCS Universal Chassis System
2346 T3 Modem
B-1

EdgeAccess® Universal Chassis System
B-2
2346 T3 Modem

Index
EdgeAccess Universal Chassis System
A
Alarm Configuration screen, 3-6
alarms, 2-4
B
baud and Modem/SLIP/PPP, 3-7
C
change Password, 3-11
copy configuration, 3-11
D
Domain Management Module menu, 3-4
E
Edit Host Access screen, 3-10
F
Functional Configuration screen, 3-11
H
Hardware Configuration report, 3- 5
host access, 3-10
I
IP address, Host, 3-10
L
LEDs and functions, 2-3
Link Error Counters screen, 3-12
loopback for troubleshooting, 4-5
M
maintaining
cables and connectors, 4-1
optical power and link loss, 4-1
mibs, network managment, 3-1
modem functions set up, 3-11
N
network managment mibs, 3-1
P
PING Generation screen, 4-4
R
remote configuration, 3-11
reset and swap firmware, 3-10
S
screen
Alarm Configuration, 3-6
Domain Management Module menu, 3-4
Edit Host Access screen, 3-10
Functional Configuration, 3-11
Link Error Counters, 3-12
PING Generation, 4-4
SNMP Configuration, 3-5
Software Upgrade, 3-9
Trap Configuration, 3-6
security
host access, 3-10
password, 3-11
set Date and Time, 3-5
set up
baud and Modem/SLIP/PPP, 3-7
modem functions, 3-11
SNMP Configuration screen, 3-5
software download, FTP or SFTP, 3-9
Software Upgrade screen, 3-9
software version, 3-9
T
Trap Configuration screen, 3-6
troubleshooting
and loopback, 4-5
and PING, 4-4
and reset to default, 4-4
U
Utilties menu, 3-5, 3-7, 3-11, 4-4
2346 T3 Modem
I-1

CANOGA PERKINS CORPORATION
20600 Prairie Street
Chatsworth, California 91311-6008 USA
Phone: (818) 718-6300 FAX: (818) 718-6312
Web Site: www.canoga.com
Email: fiber@canoga.com
 Loading...
Loading...