Page 1

Calculated Industries
Construction
Master III
®
User’s Guide
®
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction...................................................... 3
Key Definitions.................................................. 4
Entering Dimensions........................................13
Entering Square and Cubic Dimensions........... 14
Linear Conversions.......................................... 14
Square and Cubic Conversions........................ 15
Mathematical Operations................................16
Adding Dimensions.......................................... 16
Subtracting Dimensions................................... 17
Multiplying Dimensions...................................17
Dividing Dimensions........................................17
Percentage Calculations...................................18
Memory Functions........................................... 19
Fraction Setting............................................... 20
Linear Dimension Calculations........................ 21
Area Calculations.............................................23
Volume Calculations........................................ 27
Board Feet/Lumber Calculations......................32
Right-Angle Solutions...................................... 34
Hip/Valley Rafters............................................42
Hip/Valley Rafters (Irregular)..........................43
Jack Rafters...................................................... 44
Stair Problems..................................................46
Overflow Indication.........................................49
Accuracy........................................................... 49
Battery and Auto-Shut-Off.............................. 50
Full Reset, All-Clear.........................................50
Appendix A (Area Formulas)............................ 51
Appendix B (Area & Volume Formulas)............ 52
Limited Warranty............................................. 53
Page 3

INTRODUCING:
The Construction Master III
®
Designed for today’s construction professional,
the all-new Construction Master III adds even
more power and ease of use to the already
powerful Construction Master line-up. As with
earlier models, the format of this calculator is so
simple, even the novice user will find it easy to
solve hundreds of dimension-related problems
right in feet, inches and fractions!
■ Add Strings of Dimensions
■ Do Instant Dimensional Conversions
■ Calculate Square & Rectangular Areas
■ Determine Cubic Volumes
■ Complete Metric Conversions
■ Find Circumference and Area of Circles
■ Solve Right-Triangles
■ Find Regular & Irregular Hip/Valley Rafters
■ Solve Jack Rafters Automatically
■ Calculate Stair Risers and Treads
■ Estimate Board Feet & Other Materials
■ And much, much more!
It also works as a standard math calculator
with Memory, Percent, and battery-saving Auto
Shut-Off.
Calculated Industries, Inc.
4840 Hytech Drive • Carson City, NV 89706
1-800-854-8075 • 775-885-4900 • Fax: 775-885-4949
User’s Guide — 3
Page 4

KEY DEFINITIONS
[+] [–] [x]
[÷] [=] Arithmetic operation keys.
[%] Four-function percent key.
0 – 9 Digits used for keying-in numbers.
[ . ] Decimal point.
[Off] Turns all power off. Clears the
display and all values previously
stored in Memory.
[On/C] Turns on power. Pressing once
clears the last entry and the display.
Pressing twice in succession clears
all non-permanent registers.
[M+] Stores any displayed number
(dimensioned or non-dimensioned)
in semi-permanent Memory. Also,
adds any displayed number to any
previously-stored number. Redisplays stored total in format of firstentered dimension. For example,
you can add feet to yards to inches,
and when you press the [Rcl] [M+]
keys, the answer will be displayed
as total feet.
[Rcl]
Recalls and displays the contents of
the semi-permanent Memory or
registers. Pressing [Rcl] twice in a
row displays and clears the Memory.
4 — Construction Master III
®
Page 5

[√ ] This key is used to find the square
root of a number. You must be
careful when entering dimensioned
values because by definition the
square root of a linear dimension
does not exist; therefore the calculator will correctly give you an error if you try to do this.
[Conv] This key, used in conjunction with a
dimension key, converts one dimensioned number to another dimensioned number. The one logistical
limitation is that you must maintain
convention. You cannot convert
from a linear dimension like feet,
for example, to a square or cubic dimension. This violates convention.
Additional [Conv] Key Functions:
When used in conjunction with the following
keys, the [Conv] key gives access to these
additional functions.
[Conv] [√ ] Finds the square (X
Squared) of a number or
dimension. Again, you must
be careful when working with
dimensions because, for example, if you try to square an
already square dimension,
you would bring it to the
fourth power, which does not
work on this calculator.
[Conv] [ ÷ ] Reciprocal, or 1/x function.
2
or X-
User’s Guide — 5
Page 6

[Conv] [ x ] All-Clear, full-reset function
* Pressing [Conv], followed by any of the numbers 2, 4, 8, 1,
3, 6 will set the fraction. Entries other than these will not
change the fraction display.
** This will be the smallest denominator displayed. If,
however, the lowest common denominator is larger than
your preferred setting, the calculator will display this
instead.
*** Upon turning the unit "On," the "fs" symbol will appear
once to indicate a setting other than 1/64ths. If you are
unsure what base was last used, do an All-Clear.
clears Memory and resets all
registers (Jack, Stair, & Fractions) to their default values.
[Conv] [ + ] Pi (π) constant = 3.141593.
[Conv] [ – ] Change sign. Can also be
used to subtract a number
from the semi-permanent
Memory (replaces M-).
[Conv] [ M+ ] Replaces the value stored in
Memory with the value on
the display.
[Conv] [ * ] Fraction Set — This key is
used to semi-permanently set
up the default fractional format of all your answers.**
This preference setting is
cleared by (1) Performing an
All-Clear [Conv][x], or (2)
Replacing it with another
preferred fractional setting,
or (3) By entering a fraction
with a smaller denominator
than your preferred setting.***
6 — Construction Master III
®
Page 7

[Conv] [ 2 ] Fraction set to 1/2’s.
* Successive presses of the Feet key toggles the display
between feet-inch-fraction (if any) and decimal feet
(10ths, 100ths) formats.
** Successive presses of the Inch key toggles the display
between inch-fraction and decimal (10ths, 100ths) inch
formats.
[Conv] [ 4 ] Fraction set to 1/4’s.
[Conv] [ 8 ] Fraction set to 1/8’s.
[Conv] [ 1 ] Fraction set to 1/16’s.
[Conv] [ 3 ] Fraction set to 1/32’s.
[Conv] [ 6 ] Fraction set to 1/64’s.
[Feet] This is an entry and conversion
key. The entry can be in whole or
decimal numbers. This key can also
be used in conjunction with the
[Inch] and [/] keys. Example: To
enter 6 feet 9-1/2 inches, the key sequence is: 6 [Feet] 9 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
This key can also be used with the
[Conv] key to convert any displayed
dimension to feet.*
[Inch] This key is an entry and conversion
key that works the same way as the
[Feet] key described above.** This
key can also be used with the [Conv]
key to convert any dimension value
to inches.
[Yds] Yards — This key is an entry and
conversion key. The entry can be a
whole number or a decimal number.
It will also convert any other displayed dimensioned number to yards
when used with the [Conv] key.
User’s Guide — 7
Page 8

[M] Meters — This is an entry and
conversion key that works in the
same way as the [Yds] key described
above.
[CM] Centimeters — This is an entry
and conversion key used to enter
decimal centimeters or to convert
decimal centimeters from some
other dimensional format when
used in conjunction with the [Conv]
key.
[MM] Millimeters — This is an entry
and conversion key that works in
the same way as the [CM] key described above.
[Cu] Cubic — This definition key is used
in conjunction with a dimension key
(feet, yards, meters, etc.) to enter a
volume measurement. Example: 5
[Cu] [Yds]. Three linear dimensions
multiplied together also equal a
cubic dimension.
[Sq] Square — Similar to the [Cu] key,
this definition key is used in conjunction with a dimension key (feet,
inches, yards, meters, etc.) to enter
an area measurement. Example: 10
[Sq] [Feet]. Also, two linear dimensions multiplied together equal a
square dimension.
8 — Construction Master III
®
Page 9

[/] Fraction Bar — This definition key is
* In order to get a proper conversion, you must convert
from a cubic dimension.
used to define and enter fractions.
Fractions can be both proper (1 or less
— 1/2, 1/8, 1/16) or improper (greater
than 1 — 3/2, 65/64). You enter a
fraction by first entering the
numerator (the part of the fraction
that is above the line) then the [/]
and the denominator (the part below
the line).
For example: To enter 1/2, the key sequence would be 1 [/] 2.
[Bd Ft] Board Feet — This key is an entry
and conversion key for board feet
units of measure. A board foot is a
cubic measurement equal to 144
cubic inches. The entry can be a
whole number or a decimal number.
It will also convert any other displayed cubic dimensioned number
to board feet when used in conjunction with the [Conv] key.*
[Per] Per-Unit — This key is used to
enter the per-unit dollar cost of a
dimensioned value. For example, if
you calculated 35 cubic yards of
concrete, and each yard cost $47,
you would use this key with the
times [x] key as follows:
35 [Cu] [Yds] [x] 47 [Per] [=] $1645
User’s Guide — 9
Page 10

One exception to this key is when
working with board feet: If your
dimension is board feet, the unit
price is entered in the standard
Mbm. (per thousand board foot
measure) format.
[Stair] Using the values entered into Rise
and Run, and the dimension entry
for “Desired Riser Height” (automatically assumed in inches and
permanently stored in Memory),
calculates the following:
1st Press [Stair]: Number of Risers
2nd Press [Stair]: Actual Riser Height
3rd Press [Stair]: Riser Overage/Underage
4th Press [Stair]: Number of Treads
5th Press [Stair]: Actual Tread Width
6th Press [Stair]: Tread Overage/Underage
NOTE: After an All-Clear [Conv][x], the calcu-
lator will default to a “Desired Riser Height” of
7-1/2 Inches. You may enter any “Desired Riser
Height” over this default. For example, enter 8
[Stair] and the calculator will assume an 8 inch
“Desired Riser Height.” You may also recall
what is stored at any time by pressing [Rcl][Stair]
[Circ] Circle — After the entry of the
diameter of a circle (in either
dimensional or non-dimensional
format) pressing [Circ], solves for
the circumference (1st press) and
circle area (2nd press) of a circle.
10 — Construction Master III
®
Page 11

RIGHT ANGLE SOLUTIONS
* While entering 9 [Inch][Pitch] is the same as [.] 75 [Pitch]
(because 9 ÷ 12 = .75), entering 9 [Pitch] will give you the
equivalent of 108 inches of Pitch (as 9 x 12” = 108”) and
you should therefore use caution when entering nondimensioned values for Pitch.
[Pitch] Pitch is the amount of “Rise” in 12
inches of “Run” in a right triangle.
Pitch is most commonly expressed
in inches — i.e., “9 inches of Pitch”
or a “9-in-12 Pitch” — but can be
entered in either decimal (i.e., .75
[Pitch], or 75 [%] [Pitch] for a Percent
Grade) or dimension format.* In
addition, the Pitch can be calculated
given any two sides of a right triangle — Rise, Run or Diagonal.
[Rise] This is the up-side or vertical leg of
a right triangle. This can be entered
or calculated; the latter if you enter
the two other sides or one other
side and the Pitch.
[Run] This is the base-side or horizontal
leg of a right triangle. This can be
entered or calculated; the latter if
you enter the two other sides or one
other side and the Pitch.
[Diag] Diagonal — This is the angled side
or hypotenuse of a right triangle.
While this can be either entered or
computed, it is most often calculated for such applications as
“squaring up a room” or finding a
stringer or rafter length.
User’s Guide — 11
Page 12

[Hip/V] Hip/Valley — Is used to find an
adjacent 45° Hip or Valley rafter off
of a Common rafter. You first solve
for the Common rafter (diagonal)
using either both legs (Rise and
Run) or one leg and the Pitch. You
then press this key to find the adjacent Hip or Valley rafter lengths.
NOTE: To find an “irregular” Hip/Valley (where
the Pitch on both sides is not the same), simply
enter the other roof side’s Pitch directly into the
[Hip/V] key. (For example, enter 9 [Inch] [Hip/V]
or [.] 75 [Hip/V]*). The calculator will then display
the length of the “irregular” Hip/Valley rafter.
[Jack] Calculates jack rafters for regular**
45° Hip/Valley rafters based on the
entry, or previously stored value of
the o.c. (on-center) distance in
inches, the Pitch, and leg (Rise, or
Run). Subsequent presses of [Jack]
will display the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, etc.
jacks until no more remain, and the
calculator will then display “0.”
NOTE: The default for o.c. is 16 inches, which
will remain permanently stored until an entry
replaces it. To set the o.c. to other than 16 inches,
simply enter the number (calculator will automatically assume inches), and immediately press
the [Jack] key (ex. 18 [Jack]). To recall what is
stored, press [Rcl] [Jack] at any time.
* As noted previously, while entering 9 [Inch][Hip/V] is the
same as entering [.] 75 [Hip/V], entering 9 [Hip/V] without
dimensions will give you the equivalent of 108 inches of Pitch,
and you should therefore use caution when using non-dimensioned
Pitch values.
** The built-in Jack rafter function provides jack rafter lengths
only for regular (45°) Hip/Valley rafters (as jack rafter “pairs”
for irregular (non 45°) Hip/Valleys are of unequal lengths).
12 — Construction Master III
®
Page 13

ENTERING DIMENSIONS
When entering dimensioned values, you must
enter the largest dimension first — feet before
inches, inches before fractions. You enter fractions by entering the numerator (value above the
line) then the “/” (fraction bar) key and then the
denominator (value below the line).
Enter the following linear dimensions:
Dimension Keystrokes
5 Feet 5 [Feet]
1/2 Inch 1 [/] 2
5 Feet 1 Inch 5 [Feet] 1 [Inch]
5 Feet 1-1/2 in. 5 [Feet] 1 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
10 Yards 10 [Yds]
17.5 Meters 17.5 [M]
Note: Yards, Meters, Centimeters and Milli-
meters may only be entered as whole values (5
Yards) or decimal values (5.5 Meters), and not
in combination with feet and inches or with
themselves (5 Meters, 2 CM, 8 MM). If a
particular problem contains such a dimension,
you must first convert the yards (or meters) to
“Feet-Inches” and then add dimensions using
the normal process. (See Conversion section.)
User’s Guide — 13
Page 14

ENTERING SQUARE & CUBIC
* A feet-inch dimension cannot be entered directly as a
square, since by definition it is a linear measurement.
However, the area or volume can be found through simple
multiplication. (See Area and Volume examples.)
DIMENSIONS
Enter square & cubic dimensions* in this order:
(1) Numerical Value
(2) Convention — Square or Cubic
(3) Definition — Meters, Yards, Feet, Inches
Enter the following square and cubic dimensions:
Dimension Keystrokes
5 Cubic Yards 5 [Cu] [Yds]
130 Square Feet 130 [Sq] [Feet]
33 Square Meters 33 [Sq] [M]
LINEAR CONVERSIONS
Convert 14 (linear) feet to other linear dimensions:
Keystrokes Display Shows
14 [Feet] . . .
[Conv] [Feet] [Feet] 14 FT 0 IN
[Conv] [Inch] 168 IN
[Conv] [Yds] 4.666667 YDS
[Conv] [M] 4.267209 M
[Conv] [CM] 426.7209 CM
[Conv] [MM] 4267.209 MM
14 — Construction Master III
®
Page 15

SQUARE CONVERSIONS
* OPTIONAL: After the first press of [Conv], you do not have
to press [Conv] again -- just press the next dimension format
you wish to find. You must press [Conv] for your first conversion, however, to use this time-saving method.
** Notice in the last conversion to MM, the answer is
displayed in CM, as it is out of the calculator's normal 7Digit range (See Auto-Range).
Convert 14 square feet to other square dimensions:
Keystrokes Display Shows
14 [Sq] [Feet] . . .
[Conv] [Inch] 2016 SQ IN
[Yds] * 1.555556 SQ YDS
[M] 1.300648 SQ M
[CM] 13006.48 SQ CM
[MM] 1300648. SQ MM
CUBIC CONVERSIONS
Convert 14 cubic feet to other cubic dimensions:
Keystrokes Display Shows
14 [Cu] [Feet] . . .
[Conv] [Inch] 24192 CU IN
[Conv] [Yds] 0.518519 CU YDS
[Conv] [M] 0.396438 CU M
[Conv] [CM] 396438.2 CU CM
[Conv] [MM] 396438.2 CU CM**
User’s Guide — 15
Page 16

MATHEMATICAL OPERATIONS
* The format of the first value you enter determines the format of the answer. However, with the [Conv] key you can
change to any format you desire, provided that you
maintain convention.
Your calculator uses standard chaining logic
which simply means that you enter your first
value, then the operator (+, –, x, ÷), then the
second value and then finally, the Equals sign to
get your answer.
A. 3 [+] 2 [=] 5
B. 3 [–] 2 [=] 1
C. 3 [x] 2 [=] 6
D. 3 [÷] 2 [=] 1.5
This feature also makes the calculator so simple
to use for dimension applications. This is illustrated in the following examples:
Adding Dimensions
Add 7 feet 3-1/2 inches to 11 feet 4 inches:
7 [Feet] 3 [Inch] 1[/] 2
[+] 11 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
[=] 18 FT 7-1/2 IN
Add 11 inches to 2 feet 1 inches:
11 [Inch]
[+] 2 [Feet] 1 [Inch]
[=] 36 IN
Add 2 feet 1 inches to 11 inches:
2 [Feet] 1 [Inch]
[+] 11 [Inch]
[=] 3 FT 0 IN*
16 — Construction Master III
®
Page 17

Subtracting Dimensions
Subtract 3 feet from 11 feet 7-1/2 inches:
11 [Feet] 7 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
[–] 3 [Feet]
[=] 8 FT 7-1/2 IN
Subtract 32 inches from 81 inches:
81 [Inch]
[–] 32 [Inch]
[=] 49 IN
Multiplying Dimensions
Multiply 5 feet 3 inches by 11 feet 6-1/2 inches:
5 [Feet] 3 [Inch]
[x] 11 [Feet] 6 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
[=] 60.59375 SQ FT
Multiply 2 feet 7 inches by 10 (a whole number):
2 [Feet] 7 [Inch]
[x] 10
[=] 25 FT 10 IN
Dividing Dimensions
Divide 30 feet 4 inches by 7 inches:
30 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
[÷] 7 [Inch]
[=] 52 (7-inch segments)
Divide 20 feet 3 inches by 9 (a whole number):
20 [Feet] 3 [Inch]
[÷] 9
[=] 2 FT 3 IN
User’s Guide — 17
Page 18

PERCENTAGE CALCULATIONS
* The Percent key works with dimensions as well.
The Percent key can find a percent of a number,*
add a percent to a number, subtract a percent
from a number or divide a number by a percent.
You do not need to press the Equals key to
complete a percentage calculation.
Computing Percentages
1. Find 18% of 500 feet:
500 [Feet] [x] 18 [%] 90 FT 0 IN
2. Add 10% for waste to 137 square feet:
137 [Sq] [Feet] [+] 10 [%] 150.7 SQ FT
3. Take 20% away from 552 feet 6 inches:
552 [Feet] 6 [Inch] [–] 20 [%] 442 FT 0 IN
4. Divide 350 cubic yards by 80%:
350 [Cu] [Yds] [÷] 80 [%] 437.5 CU YDS
You can also find a percentage by dividing one
number by another. These may also be dimensioned or non-dimensioned numbers, but in such
cases you would not use the Percent key.
1. Find what percent 13 is of 75:
13 [÷] 75 [=] .173333 (or 17.3%)
2. 20 feet 8 inches is what percent of 34 feet 3
7/8 inches?
20 [Feet] 8 [Inch]
[÷] 34 [Feet] 3 [Inch] 7 [/] 8
[=] .602124 (or 60.2%)
18 — Construction Master III
®
Page 19

MEMORY FUNCTIONS
Whenever the [M+] is depressed, the displayed
value will be added to the semi-permanent
Memory. To subtract a value from the Memory,
simply precede [M+] with [Conv] [–] (ex. 10
[Conv] [–] [M+]).
[Rcl] [M+] recalls and displays the total value
stored in Memory. [Rcl] [Rcl] displays and clears
all values stored in Memory without clearing the
display. Turning your calculator [Off] will also
clear the Memory.
The Memory works with dimensioned numbers
as well as non-dimensioned numbers. Convention must be followed when using dimensioned
numbers. This means that you can add or subtract any linear dimensioned number, such as
feet to or from yards, or to or from inches to
meters. You cannot add or subtract a linear dimensioned number to or from a square or cubic
dimensioned number. Of course any squared
number can be added or subtracted to or from
another. This is also true of cubed numbers.
Finally, the Memory function will always
convert the total dimension into the units of the
first dimension entered.
When there is a value other than 0 in the Memory, a small “M” will appear on the left side of
the LCD read-out.
User’s Guide — 19
Page 20

Memory Calculations
* No matter what fraction value you use, the calculator will
always show you the lowest common denominator of your
fraction — i.e., 1/2 not 16/32.
1. 10 [Feet] 5 [Inch] [M+]
5 [Feet] 3 [Inch] 1 [/] 16 [M+]
Recall Memory [Rcl] [M+] 15 FT 8-1/16 IN
Clear Memory [Rcl] [Rcl]
NOTE: After using Memory in a calculation, be sure
to clear the Memory [Rcl] [Rcl] to avoid carrying-over
values from the previous calculation.
2. 105 [Inch] [M+]
45 [Inch] [M+]
37 [Inch] [Conv] [–] [M+]
Recall Memory [Rcl] [M+] 113 IN
Clear Memory [Rcl] [Rcl]
FRACTION SETTING
When you turn on your calculator, it is set to
display values to the nearest 64th of an inch, but
by using the [Conv] key in conjunction with the
number 2, 4, 8, 1, 3, you can change that to show
no lower than 1/2, 1/4, 1/8, 1/16 or 1/32.* The
fraction will remain set until an All-Clear [Conv]
[x] is performed or until you change the Fraction
Set further. You can set the fraction either after
a value is displayed or prior to performing any
calculations.
NOTE: For all the examples in this manual, the
fraction will be set to the default of 64ths.
20 — Construction Master III
®
Page 21

LINEAR DIMENSIONS
Spacing Calculation
— Linear Division
You have a 78 feet 6 inch wall which you want
to divide into five equal spaces for office partitioning. What is the length of each section?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter overall length 78 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
Divide by number of
equal spaces [÷] 5 [=]
Answer: 15 FT 8-13/32 IN
What is it in dec. feet? [Conv] [Feet]
Answer: 15.7 FT
What is it in dec. inches? [Conv] [Inch]
Answer: 188.4 IN
Spacing — Number of Pieces
How many 2 feet 2 inch boards can be cut from
fifteen 10 foot boards?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter length of one
board 10 [Feet]
Divide by smaller cuts [÷] 2 [Feet]
2 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 4.615385 (or 4 whole boards)
Mult. by total number of
10-foot boards 4 [x] 15 [=]
Answer: 60
User’s Guide — 21
Page 22

Calculating the Number
of Studs/Joists/Trusses
Find the number of 16 inch on-center (o.c.)
studs needed for a 18 feet 7-1/2 inch wall.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter length of wall 18 [Feet]
7 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
Divide by o.c. distance [÷] 16 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 13.96875 studs
Add one for each end [+] 1 [=]
Answer: 14.96875 (round to 15)
Similar uses apply to trusses and joists.
Masonry — Estimating Bricks
How many standard bricks (2-1/4” x 3-3/4” x
8”) with 1/2 inch joints are required for a wall
measuring 36 feet 6 inches long and 8 feet high?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter height of wall 8 [Feet]
Divide by brick height [÷] 2 [Inch] 3 [/] 4 [=]
Number high 34.90909
Store in Memory [M+]
Enter length of wall 36 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
Divide by brick length [÷] 8 [Inch] 1 [/] 2 [=]
Number wide 51.52941
Mult. for total bricks [x] [Rcl] [Rcl]* [=]
Answer: 1798.845
Add 5% for spoilage [+] 5 [%]
Answer: 1888.787 (inc. 5% spoilage)
* Be sure to clear Memory before proceeding to next
problem. [Rcl] [Rcl] was used here (instead of [Rcl] [M+])
as it automatically recalls and clears the value in the
Memory.
22 — Construction Master III
®
Page 23

Linear Measurements —
* NOTE: Square and cubic answers are always expressed in
a decimal format.
Window Trim (Multiple Units)
You’re going to have four front windows all
of which measure 4 feet 4 inches by 3 feet 2
inches. How much window trim will you need to
purchase — allowing 20% for cutting and waste?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Multiply length by 2 4 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
[x] 2 [=] 8 FT 8 IN
Store in Memory [M+]
Multiply width by 2 3 [Feet] 2 [Inch]
[x] 2 [=] 6 FT 4 IN
Add into Memory and
recall total for
one window [M+] [Rcl] [Rcl] 15 FT 0 IN
Multiply by 4 [x] 4 [=] 60 FT 0 IN
Add 20% for waste [+] 20 [%]
Answer: 72 FT 0 IN
AREA CALCULATIONS
Area of a Rectangle
What is the area of a room measuring 12 feet 6
inches by 15 feet 8 inches?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter length of room 12 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
Mult. by width [x] 15 [Feet] 8 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 195.8333 SQ FT *
User’s Guide — 23
Page 24

Area of a Square
Using the X-Squared [Conv] [√] key, find the
area of a square with sides of 4 feet 7 inches.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter length of side 4 [Feet] 7 [Inch]
Find square area [Conv] [√]
Answer: 21.00694 SQ FT
Unique Area — Paneling
Typically, paneling is sold in 4 foot by 8 foot
sheets, with the limiting dimensions being the 4
foot width. Find the number of sheets needed for
a room measuring 12 feet 6 inches by 15 feet
(paneling all four walls):
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Find linear feet of
first 2 sides 12 [Feet] 6 [Inch] [x]
2 [=] 25 FT 0 IN
Store in Memory [M+]
Find linear feet of
second 2 sides 15 [Feet] [x]
2 [=] 30 FT 0 IN
Store in Memory [M+]
Recall Memory for
total linear feet [Rcl] [Rcl] 55 FT 0 IN
Divide by total widths [÷] 4 [Feet] [=]
Answer: 13.75 sheets (round up to 14)
24 — Construction Master III
®
Page 25

Area Calculation
— Floor Covering
You have an apartment with two rooms of
carpet that need to be replaced. The room dimensions are as follows: 12 feet 4 inches by 10
feet and 14 feet 8 inches by 16 feet. How many
square yards of carpet are needed and how much
will it cost you if it costs $11.75 per square yard?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find Area of Room 1
Enter length of room 1 12 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
Mult. by width of rm. 1 [x] 10 [Feet] [=]
Answer: 123.3333 SQ FT
Enter in Memory [M+]
Step 2 — Find Area of Room 2
Enter length of room 2 14 [Feet] 8 [Inch]
Mult. by width of rm. 2 [x] 16 [Feet] [=]
Answer: 234.6667 SQ FT
Step 3 — Find Total Area
Enter in memory and
recall total [M+] [Rcl] [Rcl]
Answer: 358 SQ FT
Convert to sq. yards [Conv] [Yds]
Answer: 39.77778 SQ YDS
Estimate dollar cost [x] 11.75 [Per]
Answer: $467.3889
User’s Guide — 25
Page 26

Roof Covering — Shingles
You’re going to use 12 inch wide by 36 inch
long asphalt (strip) shingles with 5 inch weather
exposure. How many shingles are required for
1745 sq. foot roof? (Note: Shingle exposure area
= Exposure x length, and Number of Shingles =
Roof area ÷ shingle exposure area.)
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Find shingle exp. area 5 [Inch] [x] 36 [Inch]
[=] 180 SQ IN
Store in Memory [M+]
Enter surface area 1745 [Sq] [Feet]
Divide by shingle area [÷] [Rcl] [Rcl] [=]
Answer: 1396 shingles
Add 10% for waste [+] 10 [%]
Answer: 1535.6 shingles
Roof Covering — Felt
Roofing felt weighing approximately 15 lbs.
per square, typically comes in rolls 3 feet wide x
144 feet long. If the total roof surface area is 2234
square feet, how many rolls of felt are needed?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Find area of a roll 3 [Feet] [x] 144 [Feet]
[=] 432 SQ FT
Store in Memory [M+]
Enter area to cover 2234 [Sq] [Feet]
Divide by roll area [÷] [Rcl] [Rcl][=]
Answer: 5.171296 Rolls
NOTE: To calculate the Area of other dimensioned
geometric shapes, see Appendix A.
26 — Construction Master III
®
Page 27

VOLUME CALCULATIONS
Volume of a
Rectangular Container
What is the volume of a container 3 feet by 1
foot 9-5/8 inches by 2 feet 4 inches?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter length 3 [Feet]
Multiply by width [x] 1 [Feet] 9 [Inch]
5 [/] 8
Multiply by depth [x] 2 [Feet]
4 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 12.61458 CU FT
Convert to Meters [Conv] [M]
Answer: 0.357207 CU M
Volume of a Cylinder
You want to calculate the circumference and
volume of a cylinder with a diameter 2 feet 4
inches and a height of 4 feet 6 inches.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find circumference and surface area
of circle
Enter diameter 2 [Feet] 4 [Inch]
Find circumference [Circ]
Answer: 7 FT 3-31/32 IN
Find circle area [Circ]
Answer: 4.276057 SQ FT
Step 2 — Multiply for Volume
Multiply by height [x] 4 [Feet] 6 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 19.24226 CU FT
User’s Guide — 27
Page 28

Simple Concrete Volume
You’re going to form up and pour your own
driveway and you need to calculate the cubic
yards of concrete required for the job accurately.
The measurements are as follows: 36 feet 3 inches by 11 feet 6 inches by 4 inches deep. What’s
the volume of your driveway, and if concrete
costs $55 per yard, how much will your driveway
cost you?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find Volume
Enter length 36 [Feet] 3 [Inch]
Multiply by width [x] 11 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
Multiply by depth [x] 4 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 138.9583 CU FT
Convert to cu. yards [Conv] [Yds]
Answer: 5.146605 CU YDS
Step 2 — Multiply by Cost
Mult. by price per yard [x] 55 [Per]
Answer: $283.0633
Complex Concrete Volume
You’re going to pour an odd-sized patio 4-1/2
inches deep with the dimensions shown below.
First, calculate the total area (by dividing the
drawing into three individual rectangles) and
then determine the total yards of concrete
required for this job.
28 — Construction Master III
®
Page 29
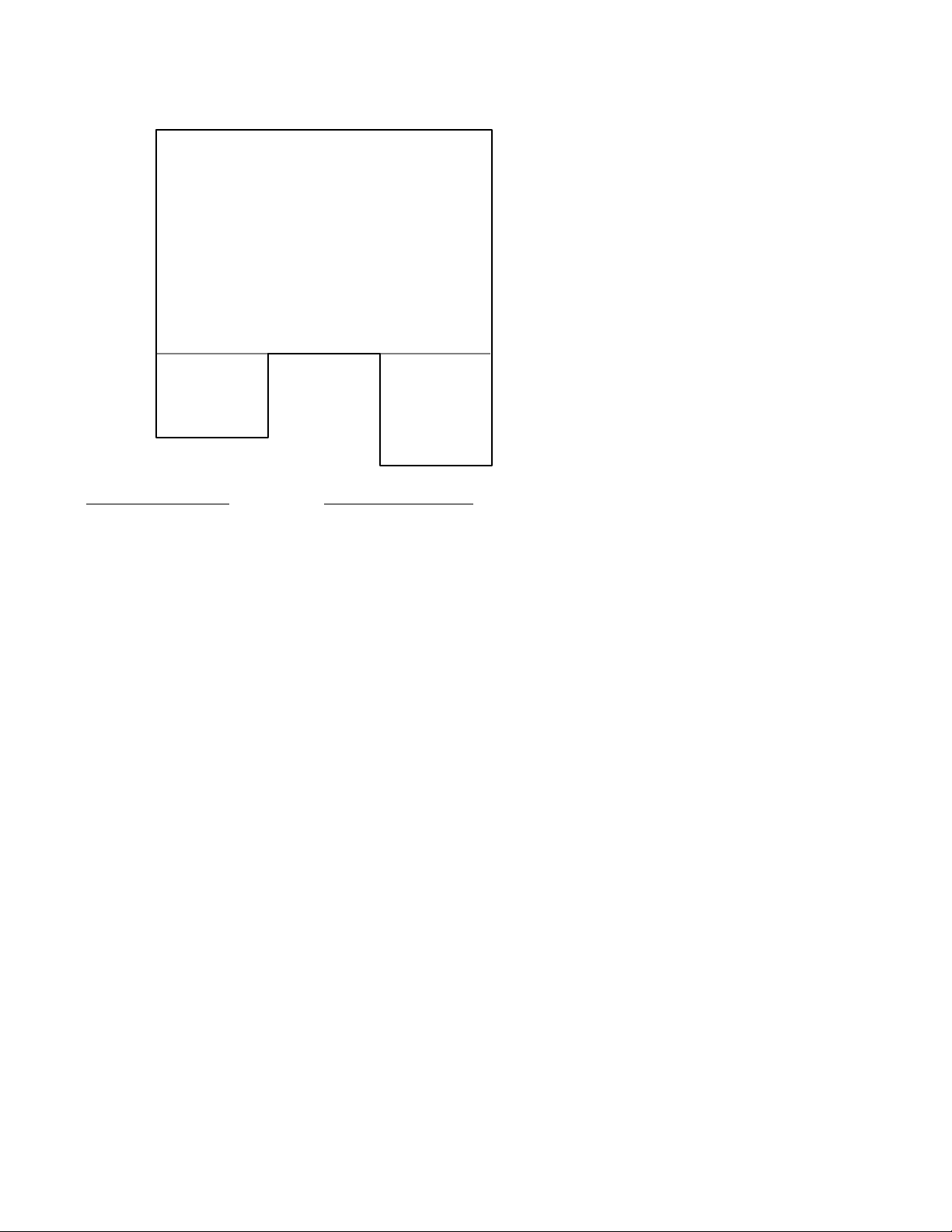
27’ 0”
A
38’ 2”
4’ 2”
B
8’ 6”
9’ 6”
C
9’ 0”
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find Area of Part A
Find length 38 [Feet] 2 [Inch] [–]
4 [Feet] 2 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 34 FT 0 IN
Multiply by width [x] 27 [Feet] [=]
Answer: 918 SQ FT
Enter in Memory [M+]
Step 2— Find Area of Part B
Enter length 4 [Feet] 2 [Inch]
Multiply by width [x] 8 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 35.41667 SQ FT
Add to Memory [M+]
Step 3— Find Area of Part C
Enter length of C 9 [Feet]
Multiply by width [x] 9 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
[=]
Answer: 85.5 SQ FT
Add to Memory [M+]
(continued on next page)
User’s Guide — 29
Page 30

Step 4 — Find Total Area
Recall Memory [Rcl] [Rcl]
Answer: 1038.917 SQ FT
Multiply by depth [x] 4 [Inch] 1 [/] 2 [=]
Answer: 389.5938 CU FT
Convert to yards [Conv] [Yds]
Answer: 14.4294 CU YDS
Concrete Columns
You’re going to pour five columns, each of
which has the following dimensions: Diameter 3
feet 4-1/2 inches, height 11 feet 6 inches. How
many cubic yards of concrete will you need for all
five columns?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find Surface Area of Column
Enter diameter 3 [Feet]
4 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
Find surface area [Circ] [Circ]
Answer: 8.946177 SQ FT
Step 2 — Find Volume
Multiply by height [x] 11 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 102.881 CU FT
Convert to yards [Conv] [Yds]
Answer: 3.810409 CU YDS
Multiply by 5 columns [x] 5 [=]
Answer: 19.05204 CU YDS
30 — Construction Master III
®
Page 31

Single Concrete Footing
Find the number of cubic yards of concrete required for a (16” x 8”) footing that measures 32
feet 7 inches in length.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter length 32 [Feet] 7 [Inch]
Multiply by width [x] 16 [Inch]
Multiply by depth [x] 8 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 28.96296 CU FT
Convert to yards [Conv] [Yds]
Answer: 1.072702 CU YDS
Multiple Footings
Find the total volume of concrete required to
pour five 24” x 12” footings, each 2 feet deep.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find Volume for One Footing
Enter length 2 [Feet]
Multiply by width [x] 24 [Inch]
Multiply by depth [x] 12 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 4 CU FT
Convert to yards [Conv] [Yds]
Answer: .148148 CU YDS
Step 2 — Find for All 5 Footings
Multiply by 5 footings [x] 5 [=]
Answer: 0.740741 CU YDS
NOTE: To calculate the Cubic Volume of other
dimensioned geometric shapes, see Appendix B.
User’s Guide — 31
Page 32

BOARD FEET/LUMBER
2 x 4 x 14
2 x 10 x 16
2 x 12 x 18
Board Feet/Lumber problems can easily be
solved with the Construction Master III’s builtin Board Feet and material estimating program.
Total Board Feet
— Multiple Boards
Calculate the total board feet in the following
boards: 2 by 4 by 14, 2 by 10 by 16, and 2 by 12 by
18. Use the multiplication [x] key to replace “by.”
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Board 2 [x] 4 [x] 14 [Bd Ft]
Answer: 9.333333 BD FT
Enter in Memory [M+]
Enter Board 2 [x] 10 [x] 16 [Bd Ft]
Answer: 26.66667 BD FT
Add to Memory [M+]
Enter Board 2 [x] 12 [x] 18 [Bd Ft]
Answer: 36 BD FT
Add to Memory [M+]
Recall from Memory [Rcl] [M+]
Answer: 72 BD FT
Clear Memory [Rcl] [Rcl]
32 — Construction Master III
®
Page 33

Total Board Feet
— With Dollar Cost
Calculate the total number of board feet if you
ordered 10 of the following board type: 2 by 4 by
14. In addition, if this board cost $250 Mbm., how
much will this order cost?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Board 2 [x] 4 [x] 14 [Bd Ft]
[x]10 [=]
Answer: 93.33333 BD FT
Multiply by unit cost [x] 250 [Per]
Answer: $23.33333
Converting Linear (Running) Feet
— To Board Feet
The perimeter of your foundation is 575 feet 6
inches, and you plan to put a 1 inch by 10 inch sill
plate around it. How many board feet will you
have? And, how much will it cost if this material
costs $125 per thousand board feet?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter perimeter 575 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
Mult. by width of bd. [x] 1 [Inch]
Mult. by length of bd. [x] 10 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 39.96528 CU FT
Convert to board feet [Conv] [Bd Ft]
Answer: 479.5833 BD FT
Multiply by unit cost [x] 125 [Per]
Answer: $59.94792
User’s Guide — 33
Page 34
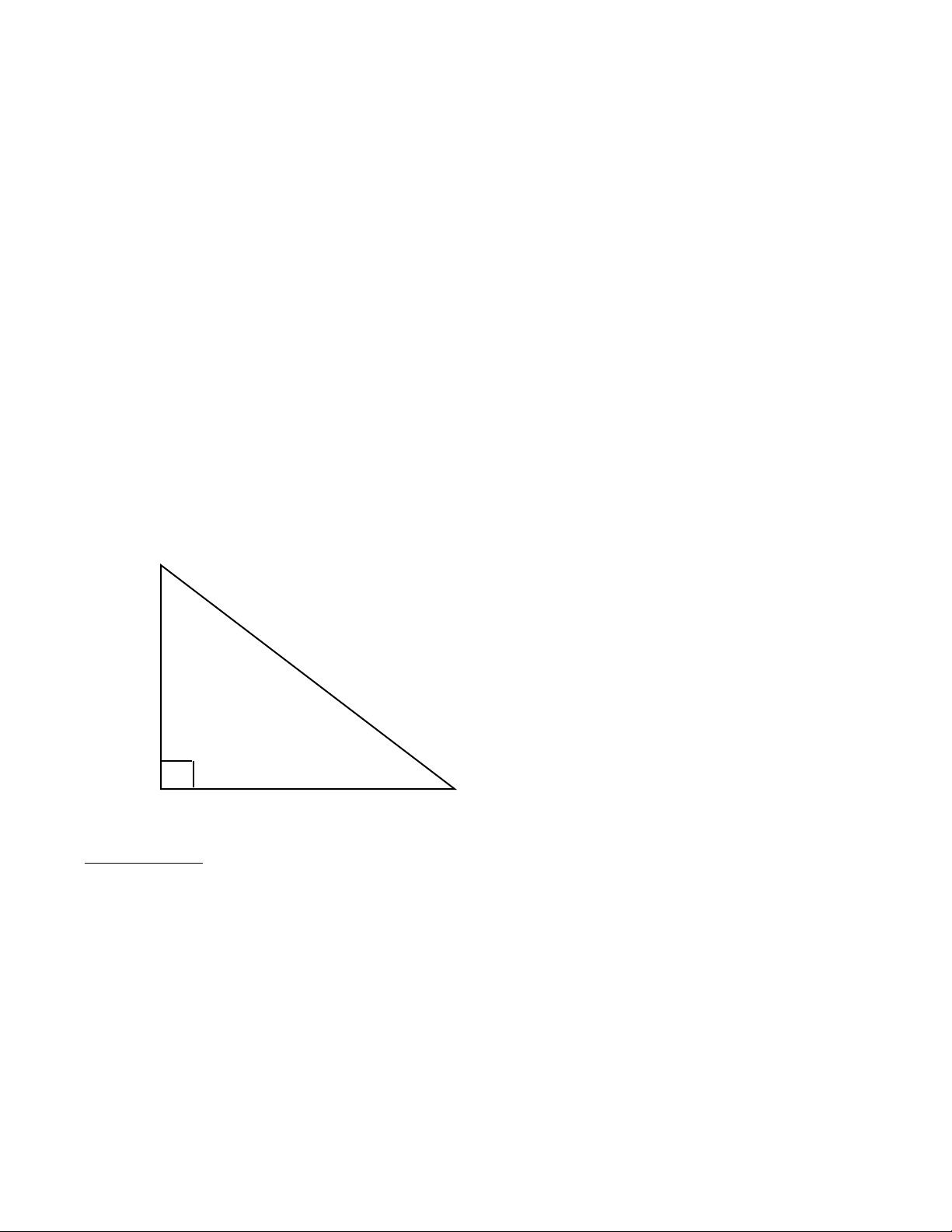
RIGHT-ANGLE SOLUTIONS
Run
* The Pitch or Bevel is defined as the amount of Rise in 12
inches of Run. This is normally expressed in inches. However,
you can enter this in any other dimension format.
** The Tangent of the enclosed angle is defined as the Rise
side divided by the Run side of the triangle and is expressed
as a decimal i.e., in a 3 (rise)-4 (run) -5 (diag) triangle, the
Tan would be 3 ÷ 4 or .75 and would be entered as [.] 75
[Pitch].
Your calculator’s top row of keys provide you
with built-in solutions to right triangles. The
solutions are available in any of the dimensions
offered on the calculator. Thus, you can solve
right triangles directly in feet and inches, decimal
feet, decimal inches, yards, meters, centimeters
or millimeters.
You can solve for any given side if you know:
• Two other sides
• The Pitch or Bevel and one side*
• The Tangent** of the enclosed angle
(entered as Pitch) and one side
Diagonal
Rise
34 — Construction Master III
®
Page 35
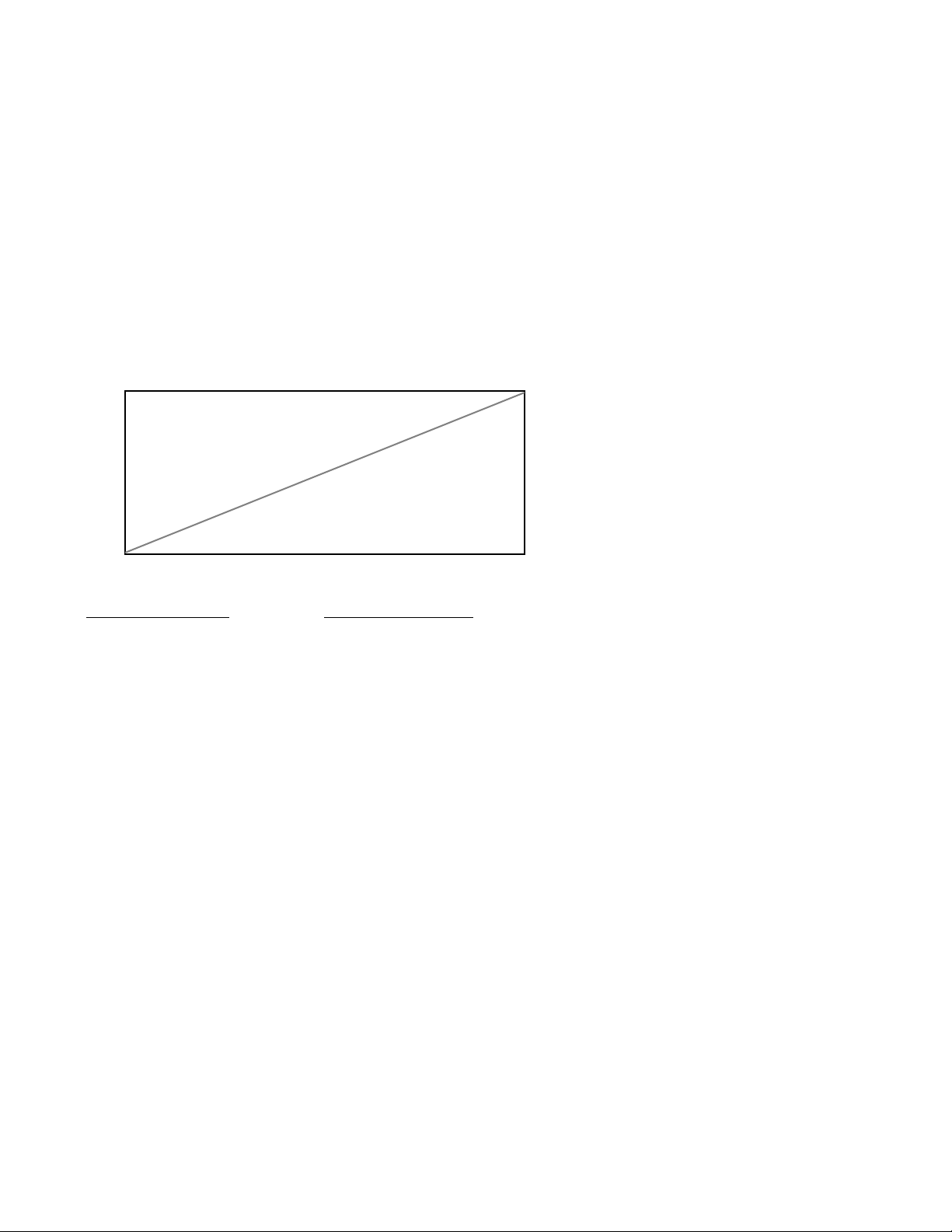
Squaring a Concrete Slab
Assume you want to square up the forms for a
concrete foundation for which you know the dimensions of two sides. The given sides are 45
feet 6 inches and 24 feet 4 inches. In order for the
forms to be square, what should the diagonal
measurement be?
24’ 4”
45’ 6”
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter 1st side as Run 45 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [Run]
Enter 2nd side as Rise 24 [Feet]
4 [Inch] [Rise]
Solve for Diagonal [Diag]
Answer: 51 FT 7–11/64 IN
User’s Guide — 35
Page 36

Area for Roofing Materials
You’re ordering roofing materials for a roof
with a 5-in-12 Pitch, an overall span of 27 feet
and a length of 34 feet 6 inches (across). How
many squares are there?
The three steps to this problem are: (1) Find
the common rafter, (2) Multiply it by the building
length, and (3) Multiply this figure by two since
you’re ordering materials for both sides of the
roof.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find Common Rafter Length
Enter Pitch 5 [Inch] [Pitch]
Find and enter Run 27 [Feet] [÷] 2 [=]
[Run]
Find common rafter [Diag]
Answer: 14 FT 7-1/2 IN
Convert to decimal feet [Feet]
Answer: 14.625 FT
Step 2 — Find Area of One Side
Multiply by length [x] 34 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [=]
Answer: 504.5625 SQ FT
Step 3 — Find Area of Both Sides
Multiply by 2 sides [x] 2 [=]
Answer: 1009.125 SQ FT
Divide by 100 sq. ft.
for roofing squares [÷] 100 [Sq]
[Feet] [=]
Answer: 10.09125 squares
36 — Construction Master III
®
Page 37

Back-Fill on a Slope with Percent
2’3’3’AB??
65%
Grade
of Grade Known
You’ve built 55 linear feet of a three-foot high
retaining wall 3 feet out from the base of a 65%
grade. You plan to back-fill to within 12 inches of
the top of the wall (for a 2’ depth). How many
cubic yards of fill should you have delivered?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Step 1 — Find Volume for Section “A”
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter length 55 [Feet]
Multiply by width [x] 3 [Feet]
Multiply by depth [x] 2 [Feet] [=]
Answer: 330 CU FT
Place in Memory [M+]
Step 2— Find Run and Diagonal of Section “B”
Enter grade as Pitch 65 [%] [Pitch]
Enter height (depth) 2 [Feet] [Rise]
Find Run of “B” [Run]
Answer: 3 FT 0-59/64 IN
Find Diagonal of “B” [Diag]
Answer: 3 FT 8-1/32 IN
Step 3— Find Volume of Triangle “B”
Enter length 55 [Feet]
Mult. by width (run) [x] 3 [Feet] 59 [/] 64
(continued on next page)
User’s Guide — 37
Page 38

COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Mult. by height (depth) [x] 2 [Feet] [=]
Answer: 338.4505 CU FT
Div. by 2 per formula* [÷] 2 [=]
Answer: 169.2253 CU FT
Step 4— Add Volumes of Sections “A” and B”
Add to Value in Mem. [M+]
Recall Total [Rcl] [M+]
Answer: 499.2253 CU FT
Convert to yards [Conv] [Yds]
Answer: 18.48983 CU YDS
Clear Memory [Rcl] [Rcl]
Stair Stringer Length
You have a floor-to-floor Rise of 8 feet 10-3/8
inches and 7-1/2-inch risers. What’s the stringer
length if the Run of the stairway is 10 feet 10
inches?
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Compute Rise of
stringer** 8 [Feet] 10 [Inch]
3 [/] 8 [–]
7 [Inch] 1 [/] 2 [=]
8 FT 2-7/8 IN
Enter as Rise [Rise]
Enter Run 10 [Feet] 10 [Inch]
[Run]
Find stringer length [Diag]
Answer: 13 FT 7-21/64 IN
* Using the formula for Area of a Triangle: 1/2 B x H -- you
multiply the Base (Run) x Height (Rise) and divide by 2 to
find the area of triangle "B."
** Stringer Rule: For stringer calculations, the Rise of the
stairway is the floor-to-floor Rise minus the length of the last
riser.
38 — Construction Master III
®
Page 39
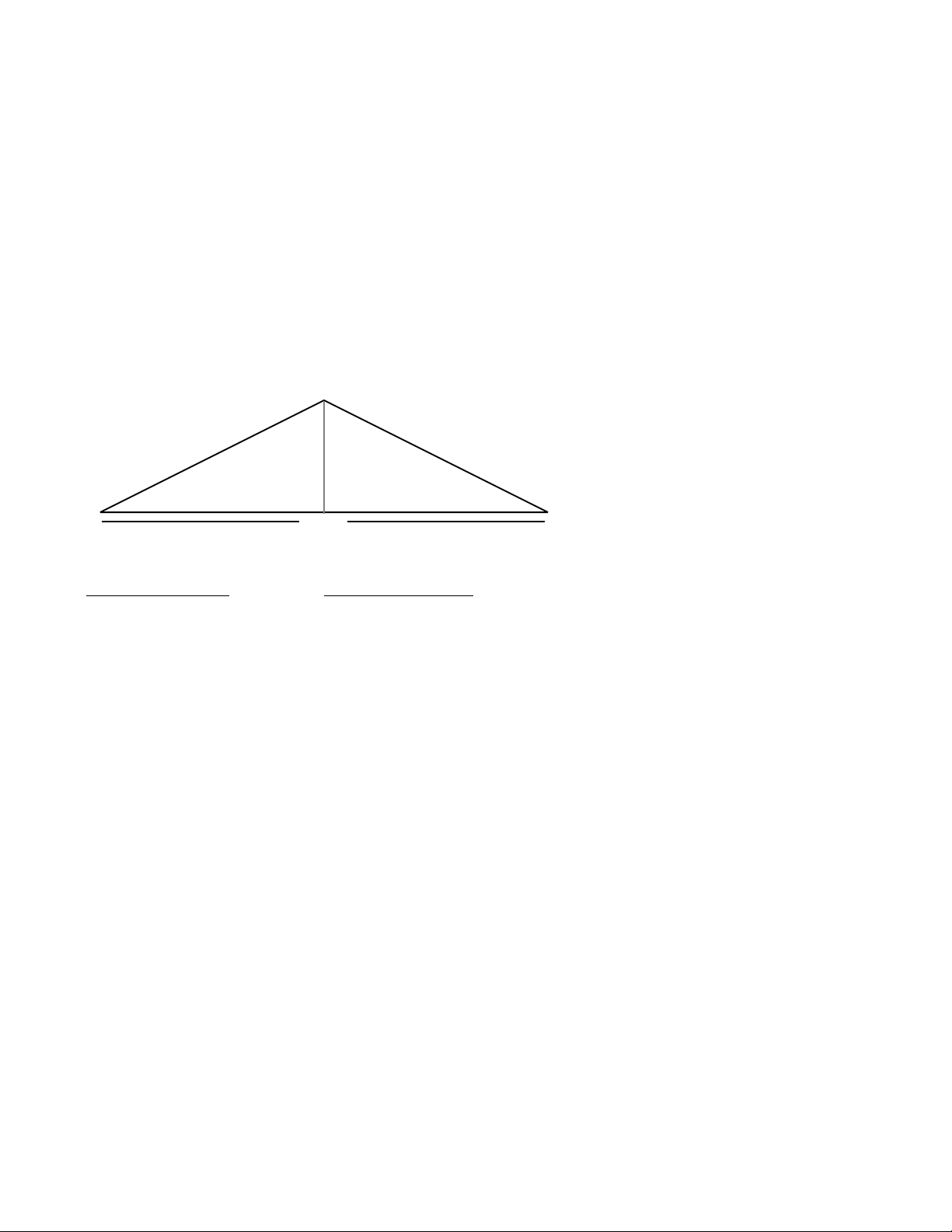
Common Rafter
— Pitch Known
The roof you are working on has a 7-in-12
Pitch, and you know the overall span of the
building is 23 feet 6 inches. What length should
you cut the common rafters (not counting the
overhang or ridge adjustment)?
7/12 Pitch
23’ 6”
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Pitch 7 [Inch] [Pitch]
Calculate Run 23 [Feet] 6 [Inch]
[÷] 2 [=] 11 FT 9 IN
Enter as Run [Run]
Find rafter length [Diag]
Answer: 13 FT 7-15/64 IN
User’s Guide — 39
Page 40

Common Rafter
— Pitch Unknown
You’re unsure of the roof Pitch but know both
the Rise; 6 feet 11-1/2 inches and Run; 14 feet 6
inches. Find the common rafter length. Then
solve for the Pitch.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Rise 6 [Feet] 11 [Inch]
1 [/] 2 [Rise]
Enter Run 14 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [Run]
Find rafter length [Diag]
Answer: 16 FT 1 IN
Find Pitch [Pitch]
Answer: 5-49/64 IN
Computing the Rise Side
of an Angle
Though not commonly asked for, you can
compute the Rise or Run side of a right angle just
as you would the Diagonal. Here, find the Rise
given a 7-in-12 Pitch and a Run of 11 feet 6
inches:
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Pitch 7 [Inch] [Pitch]
Enter Run 11 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [Run]
Find Rise [Rise]
Answer: 6 FT 8-1/2 IN
40 — Construction Master III
®
Page 41

Computing the Rise Side
of an Angle (Diagonal known)
Find the Run and Rise sides of a right angle
with Pitch and Diagonal known. Here, find the
Rise and Run given a 7-in-12 Pitch and a Diagonal of 20 feet 5 inches:
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Pitch 7 [Inch] [Pitch]
Enter Diagonal 20 [Feet]
5 [Inch] [Diag]
Find Rise [Rise]
Answer: 10 FT 3-29/64 IN
Find Run [Run]
Answer: 17 FT 7-5/8 IN
Computing the Run Side
of an Angle
You can also compute the Run side of a right
triangle just as you would the Rise. Here, find
the Run given a 5-in-12 Pitch and a Diagonal of
21 feet 6 inches:
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Pitch 5 [Inch] [Pitch]
Enter Diagonal 21 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [Diag]
Find Run [Run]
Answer: 19 FT 10-5/32 IN
User’s Guide — 41
Page 42

Computing Roof Pitch
You have a roof where your Rise is 7 feet 101/2 inches and your Run is 13 feet 6 inches.
What’s the Pitch?*
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Rise 7 [Feet] 10 [Inch]
1 [/] 2 [Rise]
Enter Run 13 [Feet]
6 [Inch] [Run]
Find Pitch [Pitch]
Answer: 7 IN
HIP & VALLEY RAFTERS
— (Regular 45-Degree)
You’re working with a 7-in-12 Pitch, and half
your total span is 13 feet 9 inches: (A) Find the
point-to-point length for the common rafter and
(B) Find the length of an adjoining hip (or valley).
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find Common Rafter Length
Enter Run of common 13 [Feet]
rafter 9 [Inch] [Run]
Enter roof Pitch 7 [Inch] [Pitch]
Find common rafter [Diag]
Answer: 15 FT 11-1/64 IN
Step 2 — Find Hip Rafter Length
Find adjacent hip [Hip/V]
Answer: 21 FT 0-27/64 IN
* This could also be solved “long-hand” by directly dividing
the two feet-inch dimensions, and then entering the
resulting answer (.583333) as the Pitch ([=] [Pitch]). Pressing
Pitch again would show the same 7 IN PITCH answer as
shown above.
42 — Construction Master III
®
Page 43
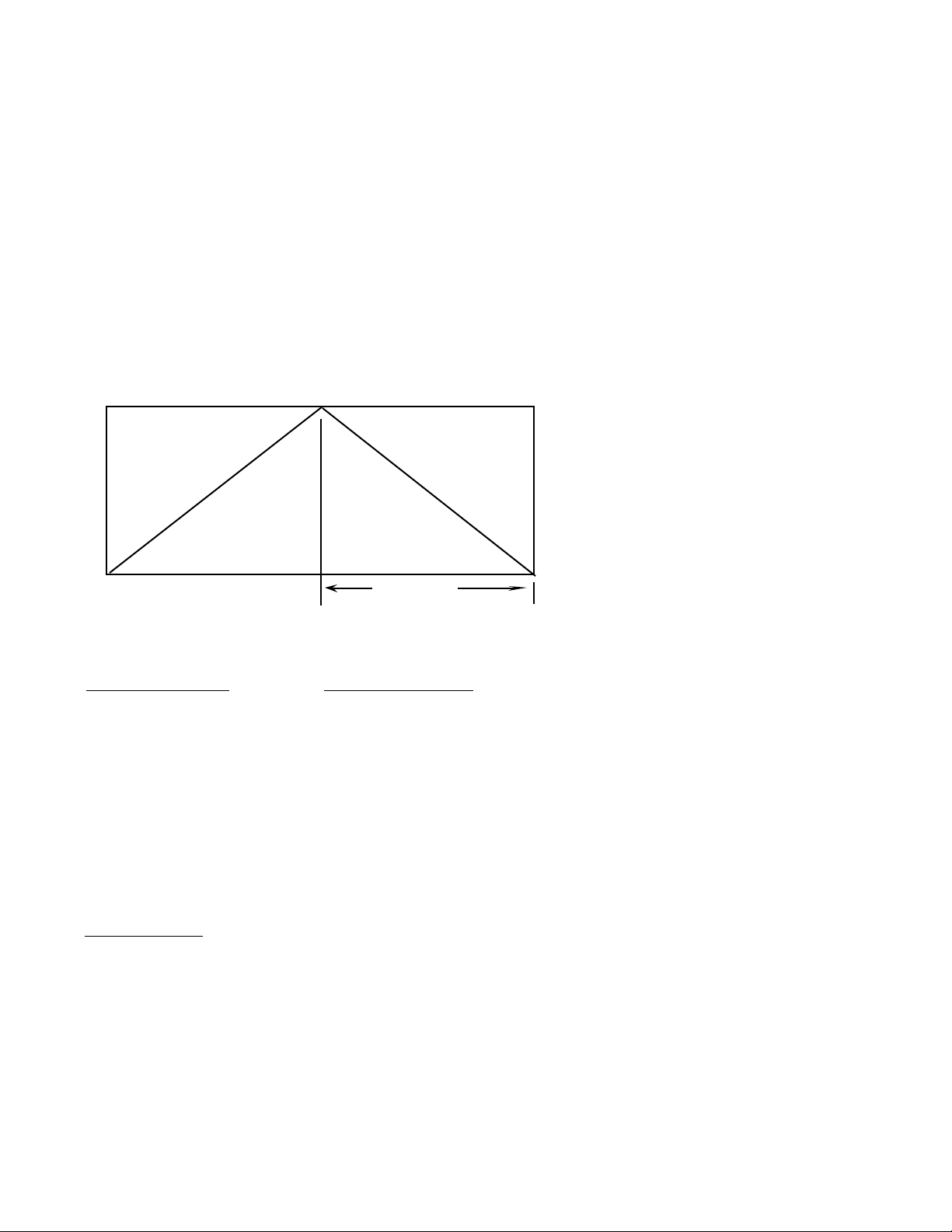
“Bastard” Hip & Valley Rafters
Common
Common
15’ 7”
Answer: 22 FT 7-3/8 IN
* As noted previously, while entering 8 [Inch] [Hip/V] is the
same as entering [.] 667 [Hip/V], entering 8 [Hip/V] without
dimensions will give you the equivalent of 96 inches of
Pitch, and you should therefore use caution when using nondimensioned Pitch values.
— (Irregular Non-45 Degree)
You’re working with a 7-in-12 Pitch and half
your overall span is 15 feet 7 inches. The Pitch of
the irregular side is 8-in-12: (A) Find the pointto-point length for the common rafter and (B)
Find the length of the adjoining “irregular” hip
(or valley).
Irregular
Irregular
hip
hip
Plate
Plate
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Step 1 — Find Common Rafter Length
Enter Run of common 15 [Feet]
rafter 7 [Inch] [Run]
Enter roof Pitch 7 [Inch] [Pitch]
Find common rafter [Diag]
Answer: 18 FT 0-31/64 IN
Step 2 — Find Irregular Hip Rafter Length
Enter “Irreg.” Pitch* 8 [Inch] [Hip/V]
Plate
User’s Guide — 43
Page 44

Hip or Valley, “Jack Rafters”
16”
Jack
Rafters
Plate
— Set at 16” on-center
You’re again working with a 7-in-12 Pitch and
the Run of the common rafter is 20 feet 5 inches.
You want to calculate the length of your jack
rafters at 16 inches o.c.: First, calculate the
common and hip/valley lengths, then the jacks.
Plate
Hip Rafter
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Pitch 7 [Inch] [Pitch]
Enter Run 20 [Feet] 5 [Inch] [Run]
Find Diagonal [Diag]
Answer: 23 FT 7-41/64 IN
Find Hip/Valley [Hip/V]
Answer: 31 FT 2-51/64 IN
Recall 16 inch o.c. [Rcl] [Jack]
Answer: 16 IN JK
Find 1st Jack [Jack]
Answer: 22 FT 1-7/64 IN
Find 2nd Jack [Jack]
Answer: 20 FT 6-19/32 IN
Find 3rd Jack [Jack]
Answer: 19 FT 0-1/16 IN
Etc., Etc.
Repeat, until all jacks are found, or when
calculator displays “0 FT 0 IN.”
44 — Construction Master III
®
Page 45

Hip or Valley, “Jack Rafters”
* You do not need to label the 18 as “inches” — the
calculator will automatically assume an inch format.
— with other than 16” on-center
You’re again working with a 7-in-12 Pitch and
the Run of the common rafter is 30 feet 9 inches.
You want to calculate the length of your jack
rafters at 18 inches o.c. You’ll need to enter 18
inches o.c. into the [Jack] key before you find the
lengths of the jacks:
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Pitch 7 [Inch] [Pitch]
Enter Run of common 30 [Feet] 9 [Inch] [Run]
Enter 18” o.c. * 18 [Jack]
Recall to verify 18” o.c. [Rcl] [Jack]
Answer: 18 IN JK
Find 1st Jack [Jack]
Answer: 33 FT 10-23/64 IN
Find 2nd Jack [Jack]
Answer: 32 FT 1-33/64 IN
Find 3rd Jack [Jack]
Answer: 30 FT 4-43/64 IN
Find 4th Jack [Jack]
Answer: 28 FT 7-27/32 IN
Etc., Etc.
Repeat, until all jacks are found, or when
calculator displays “0 FT 0 IN.”
User’s Guide — 45
Page 46

STAIR PROBLEMS (Risers/Treads)
Solving for Risers Only
— with 7-1/2” Desired Riser Height
If your floor-to-floor drop is 9 feet 5-1/2 inches and your “desired riser height” is 7-1/2 inches, find the number of stair risers, height of the
risers, and any overage/underage remaining.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Rise 9 [Feet] 5 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
[Rise]
Recall desired riser ht. [Rcl] [Stair]
Answer: 7-1/2 IN RISER
Find # of Risers [Stair]
Answer: 15 # RISER
Find actual Riser ht. [Stair]
Answer: 7-9/16 IN RISER
Find underage/overage [Stair]
Answer: – 0-1/16 IN RISER
46 — Construction Master III
®
Page 47

Risers Only — with other than
* You do not need to label the 5.5 as “inches” — the
calculator will automatically assume an inch format.
** OPTIONAL: Unless you plan to use this same Desired Riser
Height (5.5 IN) again, it’s a good idea to do an All Clear
[Conv] [x] to reset to the default settings before going on
to the next problem.
the 7-1/2” Desired Riser Height
You’re building an access stairway for an
elderly client who can’t handle conventionalheight risers. If the total drop is 3 feet 8-3/4
inches and your “desired riser height” is approximately 5-1/2 inches, find the number of stair
risers, actual riser height, and any overage or
underage remaining.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Enter Rise 3 [Feet] 8 [Inch] 3 [/] 4
[Rise]
Enter 5-1/2”riser ht.* 5.5 [Stair]
Recall desired riser ht. [Rcl] [Stair]
Answer: 5-1/2 IN RISER
Find # of Risers [Stair]
Answer: 8 # RISER
Find actual Riser ht. [Stair]
Answer: 5-19/32 IN RISER
Find under/overage [Stair]
Answer: 0 IN RISER
Clear Stair setting [Conv] [x]**
User’s Guide — 47
Page 48

Risers & Treads — with 7-1/2”
* OPTIONAL: It’s a good idea to do an All Clear [Conv] [x]
to reset to the default settings before starting a new
problem.
Desired Riser Height
Your “desired riser height” is the default 7-1/2
inches, and you want to calculate the number of
stair risers, riser height, the overage/underage
of risers, number of treads, width of treads, and
underage/overage of treads. (For this problem
you’ll need the rise and run of the stair.) The
rise of the stair is 28 feet 5-1/2 inches, the run of
the stair is 35 feet 6 inches.
COMMENTS KEYSTROKES
Clear calculator [On/C] [On/C]
Do All Clear [Conv] [x]*
Enter Rise 28 [Feet] 5 [Inch] 1 [/] 2
[Rise]
Enter Run 35 [Feet] 6 [Inch] [Run]
Recall desired riser ht. [Rcl] [Stair]
Answer: 7-1/2 IN RISER
Convert to 1/16’s [Conv] 1
Find # of Risers [Stair]
Answer: 46 # RISER
Find actual Riser ht. [Stair]
Answer: 7-7/16 IN RISER
Find under/overage [Stair]
Answer: 0-5/8 IN RISER
Find # of Treads [Stair]
Answer: 45 # TREAD
Find Tread width [Stair]
Answer: 9-7/16 IN TREAD
Find under/overage [Stair]
Answer: – 1-5/16 IN TREAD
48 — Construction Master III
®
Page 49

OVERFLOW INDICATION
When you make an incorrect entry, or the answer is beyond the range of the calculator, it will
display the word “Error.” To clear an error
condition you must hit the [On/C] button twice. At
this point you must determine what caused the
error and re-key the problem. An “error”
condition will also occur if you enter a mathematical impossibility such as division by zero.
Auto-Range — If an “overflow” is created
because of an input and calculation with small
units that are out of the standard 7-digit range
of the display, the answer will be automatically
expressed in the next larger units (instead of
showing “Error”) — i.e., 10,000,000 MM cannot
be displayed because it is out of the 7-digit
display, so 1,000,000 CM will be displayed
instead. This auto-ranging also applies to other
dimension units, such as inches to feet, and feet
to yards, etc.
ACCURACY
Your calculator has an eleven digit display.
This is made up of seven digits (normal display)
and four digits for the fraction.
Standard Display — In a standard calculation, each calculation is carried out internally to 9 digits and is rounded to a 7-digit
standard display. A 5/4 rounding technique
is used to add 1 to the least significant digit
in the display if the next non-displayed digit
is five or more. If this digit is less than five,
no rounding occurs.
User’s Guide — 49
Page 50

Fractional Display — Two digits are allowed for the numerator and another two
for the denominator. The largest proper
fraction allowed would be 99/99. The calculator will also handle improper fractions
i.e., 24/16. Once an operation takes place,
the improper fraction is divided out and is
reduced to its lowest form. Any fraction may
be entered as above. However, once a
problem is entered and operated upon, the
fraction will be rounded and displayed to the
nearest 1/64.
BATTERY & AUTO SHUT-OFF
Your calculator is powered by a single 3-Volt
Lithium CR-2032 battery. This should last upwards of 800 hours of actual use (1 year plus for
most people). Should the display become very
weak or erratic, replace the battery.*
Your calculator is designed to shut itself off
after about 8-12 minutes of non-use. Note:
Values in Memory or shown on the display will
be cleared.
FULL RESET, ALL-CLEAR
Your calculator is equipped with a special
two-key sequence — [Conv] [x] — to clear all
memory registers to their initial default values.
EXTREME CAUTION SHOULD BE USED AS
ALL STORED VALUES WILL BE ALTERED.
STEPS KEYSTROKES DISPLAY
Clear calculator [Conv] [x] 0.
* WARNING: Please use caution when disposing of your old
batteries as they contain hazardous chemicals.
50 — Construction Master III
®
Page 51

Appendix A
AREA FORMULAS
Your new calculator can perform these helpful
formulas -- right in feet, inches and fractions --
to provide even more useful solutions to your
dimensional problems.*
w
l
Rectangle
Area = lw
b
a
Triangle
Area = ab
1
2
Square
Area = a
a
a2r
Circle
Circumference = 2πr
Area = πr
b
a
Ellipse
Area = πab
* For calculations involving cubed variables (i.e., r3), use the
x2 key to raise it to the second power, then multiply the
result by itself once more to achieve the desired
exponential value. For example, to find 23 press: 2 [Conv]
[√] = 4 [x] 2 gives you 8.
2
User’s Guide — 51
Page 52
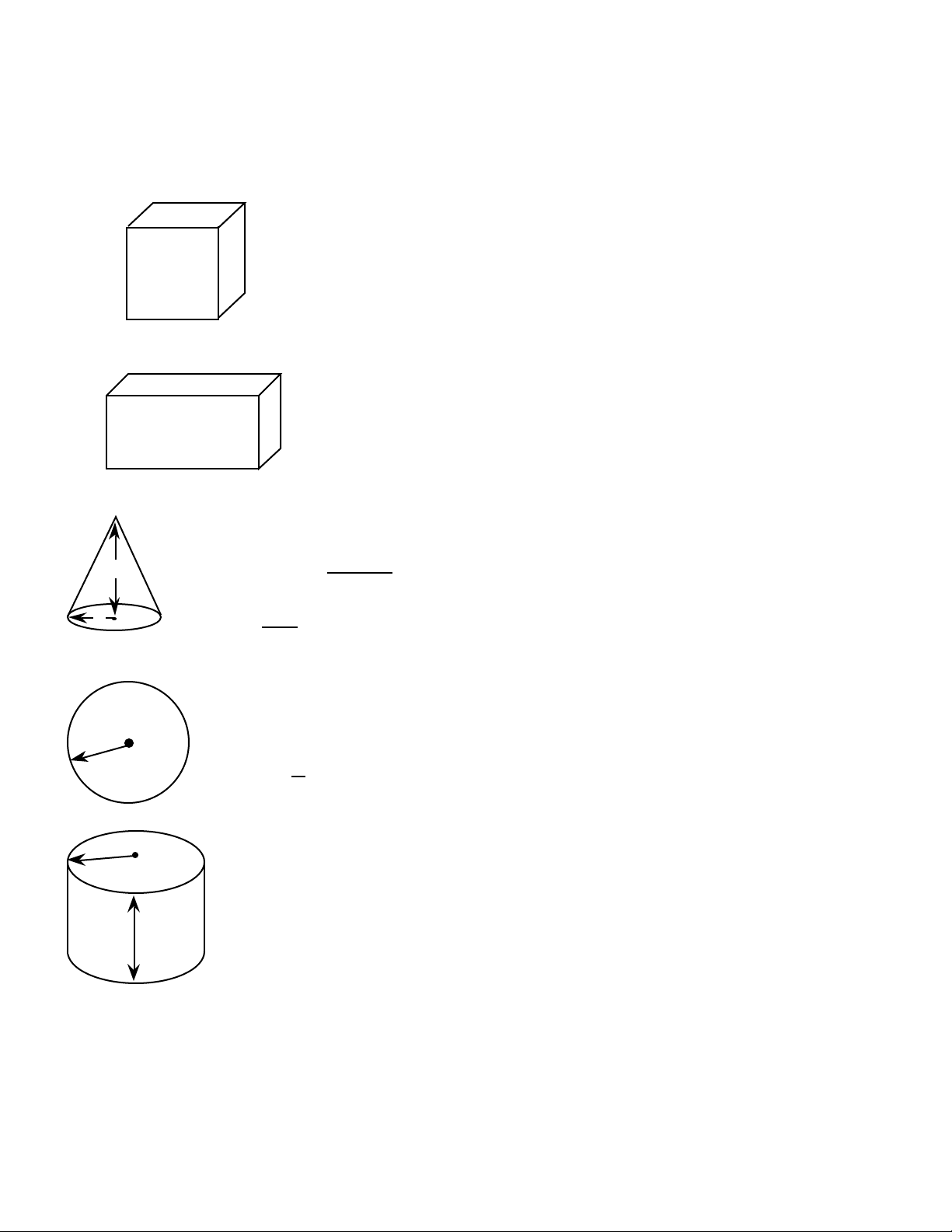
Appendix B
AREA & VOLUME FORMULAS
w
l
Surface area = 2hw + 2hl + 2lw
Volume = l x w x h
r
2
Cone
Surface area = πr r + h (+πr if you add the base)
Volume = πr h
r
√
2
3
Cylinder
Surface area = 2πrh + 2πr
Volume = πr h
h
a
2
3
a
Cube
a
Surface area = 6a
Volume = a
h
h
Sphere
Rectangle Prism
2 2 2
Surface area = 4πr
4
Volume = πr
3
3
r
2
52 — Construction Master III
®
2
Page 53

LIMITED WARRANTY
This product, except the battery and case, is
warranted by Calculated Industries, Inc. (CII), to
the original purchaser to be free from defects in
material and workmanship under normal use for
a period of one (1) year from the date of purchase. During the warranty period, and upon
proof of purchase, the calculator will be repaired
or replaced (with the same or similar model at
CII’s option), without charge for either parts or
labor at the CII repair center listed below.
The purchaser shall bear all shipping, packing
and insurance costs to the repair center — c.o.d.
returns will not be accepted. In addition, the
purchaser must include $5.95 for return shipping
and handling.
The warranty will not apply to this product if
it has been misused, abused or altered. Without
limiting the foregoing, leakage of battery, bending or dropping the unit, or visible cracking of
the LCD display are presumed to be defects resulting from misuse or abuse.
Neither this warranty nor any other warranty
express or implied, including implied warranties
of merchantability, shall extend beyond the warranty period. No responsibility is assumed for
any incidental or consequential damages, including but without limiting the same, to the mathematical accuracy of the product, keystroke procedures or example material offered. The keystroke procedures and pre-programmed material are sold on an “as is” basis. The entire risk
as to their quality and performance is with the
user.
User’s Guide — 53
Page 54

Some states do not allow limitations on how
long an implied warranty lasts and some states
do not allow the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so that the
above limitations or exclusions may not apply to
you. This warranty gives you specific legal rights
which vary from state to state and country to
country.
LOOKING FOR NEW IDEAS
Calculated Industries, a leading manufacturer
of special function calculators and digital measuring instruments, is always looking for new
product ideas in these areas.
If you have one, or if you have any suggestions for improvements to this product or its
User’s Guide, please call or write our Product
Development Department. Thank you.
Calculated Industries, Inc.
4840 Hytech Drive
Carson City, NV 89706 U.S.A.
1-800-854-8075 • 775-885-4900 • Fax: 775-885-4949
Page 55

Construction Master III® is a registered
trademark of Calculated Industries, Inc.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Calculated Industries® is also
a registered trademark.
Designed in the United States of America
by Calculated Industries, Inc.
© 1999, Calculated Industries, Inc.
CM3-Man. v1.0
 Loading...
Loading...