Cabletron Systems SmartSTACK 100 ELS100-24TX, SmartSTACK 100 ELS100-24TXM, SmartSTACK ELS100-24TXG, SMARTSTACK ELS100-24 User Manual Addendum

USER’S GUIDE ADDENDUM
SMARTSTACK ELS100-24
FIRMWARE REVISION 2.01
9033194

Cabletron Systems, Inc.
PO Box 5005
Rochester, NH 03866-5005
This addendum is to be used in conjunction with the Installation and User Guide that ships
with the Cabletron SmartSTACK 100 ELS100-24TXG and/or ELS100-24TXM Ethernet
Switches.
This document contains proprietary information that is the property of Cabletron Systems,
Inc. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, translated,
transcribed, or transmitted, in any form, or by any means, manual, electric, electronic, electromagnetic, mechanical, chemical, optical, or otherwise, without prior explicit written permission of Cabletron Systems, Inc. Furthermore, Cabletron Systems, Inc. reserves the right to
revise this publication and to make changes in content from time to time without obligation to
provide notification of such revision or changes.
© Copyright 1999 by Cabletron Systems
All Rights Reserved
Printed in the United States of America
Order Number: 9033194 August 1999
Cabletron Systems, SPECTRUM, LANVIEW
and
SmartSwitch
is a trademark of Cabletron Systems, Inc.
, and
MicroMMAC
are registered trademarks
All other product names mentioned in this manual may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective companies.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
SMARTSTACK ELS100-24 FIRMWARE REVISION 2.01 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
A.1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
A.2 User Interface Menu Hierarchy . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
A.3 SmartTrunking . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
Background . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
A.3.1 Configuring SmartTrunking: User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
A.3.1.1 SmartTrunking Configuration Menu. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
A.3.1.2 Spanning Tree Trunk Configuration Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
A.3.2 Configuring SmartTrunking: Web-Based Management . . . . 11
A.3.2.1 SmartTrunking Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
A.4 Half Duplex Support on 100Base-FX Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
A.5 Read-only Password Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
A.6 Disable Serial Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
A.7 Syslog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
A.7.1 User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
A.8 MIB Enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
A.8.1 802.1p and 802.1Q MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
A.8.2 Interfaces MIB: RFC 2233 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
A.8.3 Cabletron Proprietary MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
A.8.4 SmartTrunking MIB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
A.9 Power Up Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
A.10 Web Management Enable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
9033194 Table Of Contents i


ADDENDUM A. SMARTSTACK ELS100-24
FIRMWARE REVISION 2.01
A.1 Introduction
The Cabletron SmartSTACK ELS100-24 firmware revision 2.01 supports
the following models of the ELS100-24 product family:
ELS100-24TX
•
ELS100-24TXM
•
ELS100-24TXG
•
Firmware revision 2.01 provides the following new features:
SmartTrunking - Allows multiple physical ports of the switch to be
•
aggregated together to form a single logical connection between
network devices.
Half-duplex support on 100Base-FX ports - Enables half duplex
•
operation on 100Base-FX ports.
Read-only password - Adds an additional password option to the
•
user interface (serial console and Telnet) for read-only access.
Disable serial console option - Adds a variable to SNMP allowing the
•
serial console of the switch to be disabled or enabled.
Syslog feature - Allows various types of errors encountered by the
•
switch software to be logged to an external server.
MIB Enhancements
•
- 802.1p and 802.1Q MIB: Adds partial support for the IETF MIBs
for configuring 802.1p (priority) and 802.1Q (VLANs).
- RFC 2233 MIB: Adds support for the Stack Table portion of RFC
2233, extensions to the Interfaces MIB.
- Cabletron MIB Extensions: Adds several new variables to the
Cabletron MIB.
- SmartTrunking MIB: Adds a new proprietary MIB for configuring
SmartTrunking.
The following two features were available in the previous Cabletron
SmartSTACK ELS100-24 firmware version, but were not documented:
Power Up Diagnostics - Allows you to enable a switch functionality
•
self-test upon initialization.
Web Management Enable - Allows you to enable switch
•
management over the web.
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 1
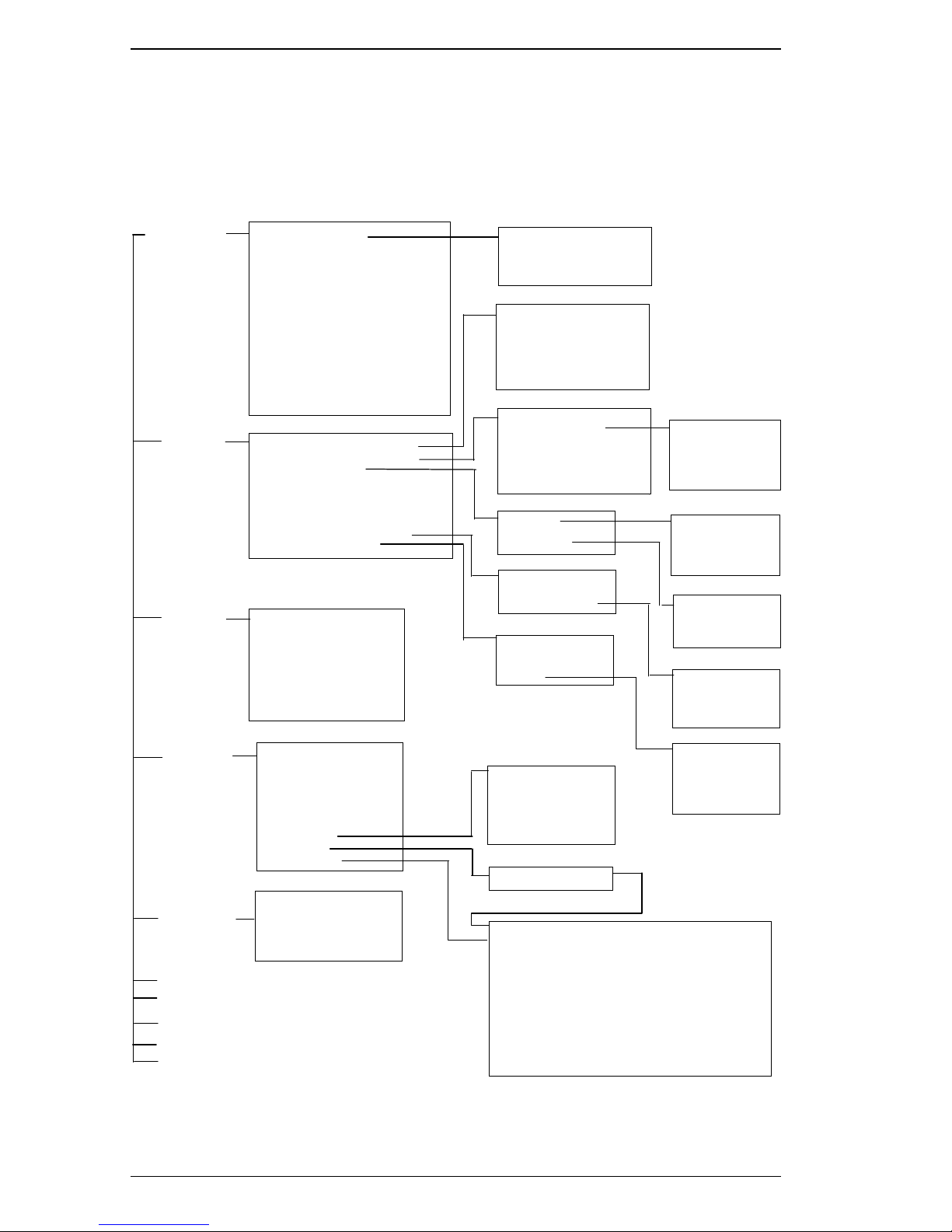
A.2 User Interface Menu Hierarchy
Figure A-1 shows the user interface hierarchy for the Cabletron
SmartSTACK ELS100-24, firmware revision 2.01.
System
Configuration
Menu
Switch
Configuration
Menu
Port Menu
SNMP Configuration Menu
System Name
System Location
System Contact
IP Address
Subnet Mask
Default Gateway
BootP/DHCP Enable
Screen Timeout (minutes)
READ/WRITE Password
READ ONLY Password
Terminal Baud Rate
Power Up Diagnostics
Syslog Server IP Address
Lowest Syslog Severity Level
Web Management Enable
Forwarding Table Configuration Menu
Spanning Tree Configuration Menu
VLAN Configuration Menu
Forwarding Table Aging Time (seconds)
Broadcast Cutoff Rate
Port Mirroring Enable
Mirrored Port Transmit Data Mirror Enable
Mirroring Port Receive Data Mirror Enable
Class of Service Configuration Menu
Trunking Configuration Menu
ID
Port Name
Enable Status
Link Status
Auto Negotiated Status
Full Duplex Status
Speed (10/100Mbps)
Type
Flow Control Status
Configure
SNMP Private Community Name
SNMP Public Community Name
Trap Destination #1-4
Community Name #1-4
Display Table
Make Entry Static
Add Static Entry
Delete Static Entry
Modify Static Entry
Search by Port#
Search by MAC Address
Spanning Tree Protocol Enable
Port Configuration Menu
Hello Time (seconds)
Forward Delay (seconds)
Max Age (seconds)
Bridge Priority
SmartTrunking Configuration Menu
VLAN Enable
VLAN Menu
VLAN Port Menu
Class of Service Enable
Priority Threshold
Configure Port Priority
ID
Name
Ports in Trunk
Configure
Port ID
Port Name
Path Cost
Port Priority
Port State
Select Port
ID
VLAN Name
Ports in VLAN
VLAN Egress Ports
Configure
Port ID
Port Name
Type
Modify Port Type
Port ID
Port Name
Priority Default
Configure
Switch
Statistics
Screen
General
Information
Screen
Download Software Menu
Save Current Configuration
Return to Default Configuration
Logout
Reset
ID
Transmitted
Received
Forwarded
Filtered
Dropped
Errored
Switch Summary
Port Statistics
Trunking Statistics
Software Version
Serial Number
Base MAC Address
Up Time (minutes)
Power Up Count
Trunk Number
Frames Transmitted
Frames Received
Frames Forwarded
Frames Filtered
Frames Dropped
Frames Errored
Port #n Statistics
Frames Transmitted Collisions
Frames Received Late Collisions
Frames Forwarded CRC/Alignment Errors
Frames Filtered Undersized Frames
Frames Dropped Oversized Frames
Broadcasts Transmitted Fragments
Broadcasts Received Jabbers
Multicasts Transmitted 64 Byte Frames
Multicasts Received 65 to 127 Byte Frames
Bytes Transmitted 128 to 255 Byte Frames
Bytes Received 256 to 511 Byte Frames
Pause Frames Transmitted 512 to 1023 Byte Frames
Pause Frames Received 1024 to 1518 Byte Frames
Add Ports
Remove Ports
Smart Trunk Name
Protocol Enable
Figure A-1. User Interface Menu Hierarchy
2 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194
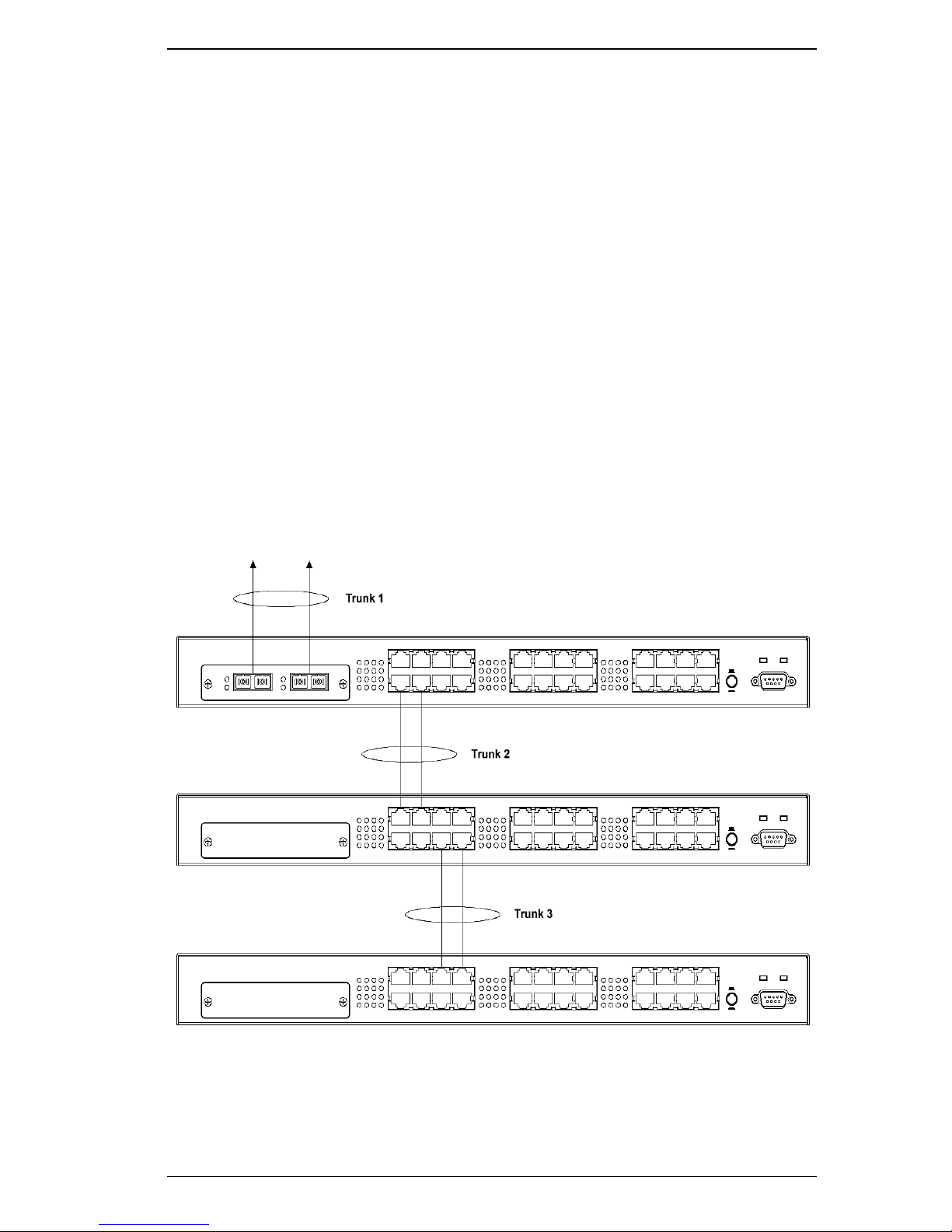
A.3 SmartTrunking
SmartTrunking is a link aggregation feature that allows multiple physical
ports of the switch to be aggregated together to form a single logical
connection between network devices. All physical connections in the
logical connection carry traffic, as compared with previous software
versions in which Spanning Tree would block all traffic on all but one of
the physical connections.
Background
A trunk is a group of ports that perform as a single logical port, connecting
the ELS100-24 switch with another network device. Compared with a
single port, the group of ports in a trunk feature increased bandwidth and
provide a level of connection resiliency - when one physical port link in the
trunk group goes down, the overall connection is not lost. When a port in
a trunk group is removed (link goes down or a cable is severed), traffic on
that port will be redistributed to other ports in the trunk group.
In the example in Figure A-2 below, three switches are connected
(stacked) through a series of trunk groups. Two physical ports are
combined to form each trunk group. The fiber ports in the top switch form
Trunk 1 which carries traffic to the network backbone.
Figure A-2. Trunking Application Example
SmartTrunking uses the DEC Hunt Group protocols - PLAP and LLAP to automatically establish and maintain a trunk connection. Use of these
protocols can be enabled or disabled as desired. When the protocols are
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 3

enabled, the switch is SmartTrunk-compliant and will automatically
configure to work with Cabletron products such as a Smart Switch Router
(SSR), SmartSwitch, SmartSTACK, etc. When the protocols are disabled,
the switch can be manually configured to interoperate with trunking
implementations used by other vendors.
SmartTrunking support in firmware revision 2.01 follows these
configuration rules:
There can be up to 2 trunk groups configured per switch cluster
•
(group of 8 ports).
Individual trunk groups can be defined only in one cluster, not across
•
clusters.
There can be from 2-8 ports defined per trunk group.
•
There can be up to 6 trunk groups defined per switch.
•
Ports in a trunk group can operate in any combination of speed and
•
duplex mode (10 half with 100 full, for example).
Ports in a trunk group must be in the same VLAN and have the same
•
VLAN mode (hybrid/access).
The Gigabit Ethernet ports on the ELS100-24TXG cannot be
•
trunked.
Further information on SmartTrunking can be found in the
Systems SmartTrunk User’s Guide
Cabletron Systems user manual website at:
http://www.cabletron.com/support/manuals
The implementation of SmartTrunking in firmware version 2.01 on the
ELS100-24 product line differs in several ways from the information
contained in the SmartTrunk User's Guide. The primary differences in the
ELS100-24 implementation are as follows:
Full load balancing of traffic across ports in a trunk is not supported.
•
Unicast traffic is sent to the same port that the destination MAC
address of the packet was learned.
Although it is highly recommended, Spanning Tree does not have to
•
be enabled to use SmartTrunking.
The ports in a trunk are not required to operate in full duplex mode,
•
but can be operated in any combination of half duplex or full duplex.
If a port in a trunk goes down, traffic on that port is redirected onto
•
other links in the trunk whether protocols are enabled or disabled.
If protocols are disabled, inadvertently configuring a user-attached
•
port to a SmartTrunking trunk group will not result in the user losing
network connectivity.
. To examine this guide, see the
Cabletron
The concept of logical ports, each comprised of the physical ports in
•
a trunk group, is not implemented. In both the User Interface and
SNMP, both physical port and trunk numbers can be accessed.
However, port-related configuration features, such as port mirroring,
VLANs, Class of Service, and Spanning Tree, are performed only on
a physical port basis, not a logical port (trunk) basis.
4 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194

A.3.1 Configuring SmartTrunking: User Interface
SmartTrunking can be configured through the user interface.
Ports that are members of a trunk group are indicated as
such by an asterisk ’ * ’ next to the port number on the Port
Menu of the user interface.
A.3.1.1 SmartTrunking Configuration Menu
To configure Trunking, do the following:
Select Switch Configuration Menu from the Main Menu.
1.
Select Trunking Configuration Menu. Figure A-3 shows the Trunking
2.
Configuration menu.
TRUNKING CONFIGURATION Access Control: READ/WRITE
Trunking Enabled Yes
Trunking Protocol Yes
ID NAME PORTS IN TRUNK
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
d. Protocol Enable e. Enable x. Previous Menu
Enter Selection:
Figure A-3. Trunking Configuration Menu
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 5

Table A-1 describes fields and options available in the Trunking
Configuration menu.
Table A-1. Trunking Configuration Menu Description
Fields/Options Description
Trunking Enabled Indicates whether trunking is enabled (Yes) or disabled
(No).
Trunking Protocol Indicates whether trunking protocols are enabled (Yes)
or disabled (No).
ID Lists the trunk group ID number.
Name Lists the trunk group name (1-14 characters).
Ports inTrunk Lists the ports in the trunk group.
Configure Option that allows you to create a new, or configure an
existing, trunk group.
Delete Option that allows you to delete an existing trunk
group.
Select c from the Trunking Configuration menu to configure trunking.
3.
The following message appears:
Enter Trunk Number (1-6):
Enter a trunk group number. In this example, enter the number 1.
4.
Press [Enter].
Figure A-4 shows the Trunk Configuration menu with trunk group number
1.
TRUNK 1 CONFIGURATION Access Control: READ/WRITE
Name
Trunk Status CONNECTED
Trunking Protocol No
PORT ENABLED LINK STATUS
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
a. Add Port(s) b. Remove Port(s) c. Trunk Name
d. Protocol Enable x. Previous Menu
c. Configure d. Delete x. Previous Menu
Enter Selection:
Figure A-4. Trunk Configuration Menu
6 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194

Table A-2 describes the Trunk Configuration menu.
Table A-2. Trunking Configuration Menu Description
Field Description
Name Lists the trunk group name. Use the Trunk Name op-
tion to create a trunk group name (1-14 characters).
Trunk Status Lists the trunk group status: PARTIAL (one or more of
the trunk group ports are linked and one or more are
not linked), CONNECTED (all ports in the trunk group
are linked), DISCONNECTED (no ports in the trunk are
linked).
Trunking Protocol Indicates whether trunking protocols are enabled (Yes)
or disabled (No).
Port Identifies the port by number.
Enabled Indicates whether the port is enabled (Yes) or disabled
(No).
Link Status Indicates port link status: connected or disconnected.
Selection Description
Add Port(s) Allows you to add port(s) to the trunk.
Remove Port(s) Allows you to remove port(s) from the trunk.
Trunk Name Allows you to create a unique trunk group name (1-14
characters).
Protocol Enable Allows you to enable (Yes) or disable (No) the opera-
tion of the trunking protocols on this trunk.
Select a to add ports. The following message appears:
5.
Enter Port Number(s) or Range of Port(s) 1-26:
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 7

In this example, a range of ports is entered to form a trunk group.
6.
Enter
and press [Enter]. Figure A-5 shows the update to the
1-4
screen.
TRUNK 1 CONFIGURATION Access Control: READ/WRITE
Name
Trunk Status CONNECTED
Trunking Protocol No
PORT ENABLED LINK STATUS
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 Yes CONNECTED
2 Yes CONNECTED
3 Yes CONNECTED
4 Yes CONNECTED
a. Add Port(s) b. Remove Port(s) c. Trunk Name
d. Protocol Enable x. Previous Menu
Enter Selection:
Figure A-5. Adding a Range of Ports to a Trunk
To add a trunk name, enter c. The following message appears:
7.
Enter Trunk Name:
Enter a trunk name. In this example, enter
8.
Backbone
and press
[Enter]. This new name appears in the Name field.
Enter x to return to the previous menu. Figure A-6 shows the ports
9.
that have been configured in trunk group 1.
TRUNKING CONFIGURATION Access Control: READ/WRITE
Trunking Protocol No
ID NAME PORTS IN TRUNK
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 Backbone 1-4
c. Configure d. Delete e. Enable x. Previous Menu
Enter Selection:
Figure A-6. Ports Configured in a Trunk Group
To view Trunking Statistics, return to the Main Menu, and select
10.
Switch Statistics, then Trunking Statistics. When displaying statistics
for a trunk group, the statistics are the sum of the statistics for all
physical ports in the trunk group.
8 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194

When configuring trunk groups, consider the following:
When adding or removing port(s), the following message appears:
•
Enter Port Number(s) or Range of Port(s)
You can enter individual ports, separated by a comma, or a range of
ports separated by a hyphen.
Protocol Enable either enables or disables a proprietary Cabletron
•
protocol to be run by the switch for purposes of automatically
establishing and maintaining a trunk.
If the protocol is enabled, the switch uses the proprietary DEC Hunt
Group protocol to detect when multiple links are established between
two devices, and then automatically set up a trunk. Normally,
Spanning Tree would detect multiple links, and block all but one.
However, with trunking, multiple paths are valid. Protocols should be
enabled when connecting the SmartSTACK switch to other
Cabletron devices, or any other devices using the DEC Hunt Group
protocol.
If the protocol is disabled, trunks should be manually configured
using the user interface, SNMP, or web access.
A.3.1.2 Spanning Tree Trunk Configuration Menu
Trunking operation relative to Spanning Tree can be viewed through the
user interface. To view trunking configuration for Spanning Tree, do the
following:
Select Switch Configuration Menu from the Main Menu.
1.
Select Spanning Tree Configuration Menu.
2.
Select Trunking Configuration Menu.
3.
Figure A-7 shows an example of the Spanning Tree Trunk
Configuration menu.
SPANNING TREE TRUNK CONFIGURATION Access Control: READ/WRITE
TRUNK ID TRUNK NAME PATH COST PORT PRIORITY PORT STATE
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 2 Server3 2 0 DISABLED
3 Backbone 2 0 DISABLED
r. Refresh x. Previous Menu
Enter Selection:
Figure A-7. Spanning Tree Trunk Configuration Menu
Table A-3 describes fields and options available in the Spanning Tree
Trunk Configuration menu.
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9

Table A-3. Spanning Tree Trunk Configuration Menu Description
Field/Option Description
Trunk ID Lists the trunk group ID.
Trunk Name Lists the trunk group name.
Path Cost The contribution of the path through this port when it
is the root port to the total path cost from this bridge
to the root bridge: 10 for 100 Mbps ports, 100 for 10
Mbps ports.
Port Priority The relative priority of the port on the bridge.
Port State The current Spanning Tree state of the port on the
bridge, either: disabled, listening, learning, forwarding, or blocking.
Refresh Refreshes the screen to reflect latest system condi-
tions.
10 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194

A.3.2 Configuring SmartTrunking: Web-Based Management
SmartTrunking can be configured through a web browser-based utility
which allows you to configure and manage Cabletron SmartSTACK
ELS100-24 switches remotely. For more information, see the
WebView, Web-Based Management for the ELS100-24 User Guide.
Cabletron
To
examine this guide, see the Cabletron Systems user manual website at:
http://www.cabletron.com/support/manuals
A.3.2.1 SmartTrunking Configuration
To configure SmartTrunking, do the following:
Select the Switch Configuration link from the Main Menu of Cabletron
1.
Webview.
Select Trunking Configuration menu. Figure A-8 shows the Trunking
2.
Configuration menu.
Figure A-8. Trunking Configuration Menu
To enable SmartTrunking on the switch, select "Yes" from the
3.
Trunking Enable drop-down menu, then select Apply.
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 11

Select Trunking Table Configuration. Figure A-9 shows the Trunking
4.
Table Configuration menu.
Figure A-9. Trunking Table Configuration Menu
To create a new trunk group, select Create New Trunk. Figure A-10
5.
shows the Create New Trunk menu.
Figure A-10. Create New Trunk Menu
Enter the Trunk ID, the Trunk Name, the Trunking Protocol status,
6.
and the ports in the trunk, then select Apply.
12 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194

To modify an existing trunk group, first choose the trunk to modify by
7.
selecting the radio button next to the appropriate trunk on the
Trunking Table Configuration menu (Figure A-9). Then select Modify
Trunk. Figure A-11 shows the Modify Trunk menu.
Figure A-11. Modify Trunk Menu
A.4 Half Duplex Support on 100Base-FX Ports
Half duplex support on 100Base-FX ports of the ELS100-24TXM has
been added in firmware revision 2.01. Previously, only full duplex
operation was supported on 100Base-FX ports. Figure A-12 shows the
Port Configuration menu and the Full Duplex option.
Half Duplex operation is enabled when you set Full Duplex
to No.
PORT 1 CONFIGURATION Access Control: READ/WRITE
a. Port Name Val d’Or
b. Port Enable Yes
c. Flow Control Enable Yes
d. Full Duplex No
e. Port Speed 100
x. Previous Menu
Enter Selection:
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 13
Figure A-12. Port Configuration Menu

A.5 Read-only Password Protection
Read-only password protection has been added in firmware revision 2.01.
This feature adds an additional password option to the user interface (for
serial console and Telnet) for read-only access. Previously only read/
write password protection was available. To configure read-only
password protection, do the following:
Select System Configuration Menu from the Main Menu (Figure
1.
A-13).
SYSTEM CONFIGURATION Access Control: READ/WRITE
a. SNMP Configuration Menu
b. System Name
c. System Location
d. System Contact
e. IP Address 000.000.000.000
f. Subnet Mask 000.000.000.000
g. Default Gateway 000.000.000.000
h. BootP/DHCP Enable Yes
i. Screen Timeout (minutes) 0
j. READ/WRITE Password
k. READ ONLY Password
l. Terminal Baud Rate 9600
m. Power Up Diagnostics Yes
n. Syslog Server IP Address 000.000.000.000
o. Lowest Syslog Severity Level warning
p. Web Management Enable Yes
x. Previous Menu
Enter Selection:
Figure A-13. System Configuration Menu
Select READ ONLY Password. The following message appears:
2.
Enter New Password:
Enter a password containing six to eight alphanumeric characters
3.
and press [Enter]. The following message appears:
Re-enter New Password:
Enter the password again and press [Enter] to confirm. If the
4.
password is re-entered correctly, the following message appears:
Password Changed
Press any Key to Continue
Refer to the Installation and User Guide, Chapter 3, “
Password Protection
” for more information.
Setting
14 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194

A.6 Disable Serial Console
A new MIB variable was added to the Cabletron proprietary MIB allowing
the serial console of the switch to be disabled or enabled via SNMP.
Previously, the serial console was always enabled. The name of the
variable is SysComPortEnable as shown in the table in A.8.3 Cabletron
Proprietary MIB below.
Make sure the switch IP address is recorded in an easy to
locate place. If the serial console is disabled, and the IP address of the switch is forgotten, the switch cannot be managed.
A.7 Syslog
The syslog capability was added to firmware revision 2.01, enabling the
switch to forward information about errors and other conditions
encountered by the software. If the switch encounters an operational
error, it can be configured to log this occurrence to an external syslog
(UNIX) server.
The web interface can be also be used to configure syslog.
A.7.1 User Interface
The IP address of the external syslog server is configured using the
Syslog Server IP Address option in the System Configuration menu. The
lowest severity condition to report is configured using the Lowest Syslog
Severity Level option in the same menu.
To configure syslog, do the following:
Select System Configuration menu from the Main Menu.
1.
Select Syslog Server IP Address. The following message appears:
2.
Enter Syslog Server IP Address:
In this example, the IP address of 24.1.133.111 is used. Enter the IP
3.
address and press [Enter]. The forwarding address now appears in
the Syslog Server IP Address field (Figure A-14).
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 15

SYSTEM CONFIGURATION Access Control: READ/WRITE
a. SNMP Configuration Menu
b. System Name
c. System Location
d. System Contact
e. IP Address 000.000.000.000
f. Subnet Mask 000.000.000.000
g. Default Gateway 000.000.000.000
h. BootP/DHCP Enable Yes
i. Screen Timeout (minutes) 0
j. READ/WRITE Password
k. READ ONLY Password
l. Terminal Baud Rate 9600
m. Power Up Diagnostics Yes
n. Syslog Server IP Address 024.001.133.111
o. Lowest Syslog Severity Level warning
p. Web Management Enable Yes
x. Previous Menu
Enter Selection:
Figure A-14. Syslog Server IP Address
Select Lowest Syslog Severity Level. Eight different severity level
4.
options are available by selecting o until the desired setting appears.
Table A-4 describes each of these severity levels and conditions. The
higher the severity, the lower the number.
16 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194

Table A-4. Syslog Severity Level Descriptions
Severity Level Condition
emergency (0) System is unusable.
alert (1) Action must be taken immediately.
critical (2) Action must be taken immediately.
error (3) Displays an error message.
warning (4) Action must be taken to prevent performance degra-
dation.
notice (5) Normal condition. Signification of a potential error
condition.
info (6) Informational. No action required.
debug (7) Displays a debug-level message.
A.8 MIB Enhancements
The following subsections describe MIB enhancements that have been
provided in firmware revision 2.01.
A.8.1 802.1p and 802.1Q MIB
Support for portions of the IETF 802.1p (priority) and 802.1Q (VLANs)
MIBs has been added.
IEEE 802.1p MIB - The IEEE 802.1p MIB is an extension to the
•
Bridge MIB defined by RFC 1493. This extension is used to manage
priority and multicast filtering as defined by IEEE 802.1D-1998. The
ELS100-24 switch supports only the portion of this MIB that is used
to manage traffic classification and priority configuration.
IEEE 802.1Q MIB - The IEEE 802.1Q MIB is an extension to the
•
Bridge MIB defined by RFC 1493. This extension is used to manage
802.1Q tagged VLANs as defined by IEEE 802.1Q-1998. The
ELS100-24 supports only the portion of this MIB that is relevant to its
capabilities.
A.8.2 Interfaces MIB: RFC 2233
RFC 2233 defines extensions to the Interfaces group of MIB-II. The 2.01
firmware revision for the ELS100-24 switch adds support for only a portion
of these extensions, specifically the Stack Table. This table is used to
map the physical ports of a switch with the logical trunk group to which
they belong.
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 17

A.8.3 Cabletron Proprietary MIB
Three new MIB objects were added to the Cabletron Proprietary MIB in
firmware revision 2.01. The following is a description of these variables
presented as a supplement to Table 5-1 in the Installation and User
Guide.
Variable Description
SysSyslogServer The IP address of the Syslog server.
SysLowestSyslogSeverity The least severe Syslog severity level sent to the Sys-
log server. All the logs with the same or higher severity
will be delivered. The greater the severity, the lower the
number.
SysComPortEnable Enable/disable status of the serial communications
port.
18 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194
A.8.4 SmartTrunking MIB
Support for the Cabletron SmartTrunking MIB was added in firmware
revision 2.01. Table A-5 describes the variables contained in the MIB.
Table A-5. SmartTrunking MIB Variables
Variable Description
TrunkGlobalStatus The global state of trunking capability for the switch,
either True or False.
TrunkConfigTable Trunk group configuration table indexed by
TrunkIndex.
TrunkIndex Trunk group number or index.
TrunkConfigName The trunk group’s name, used for informational pur-
poses.
TrunkConfigProtocol The trunking protocol in use, either no protocol or
DEC Hunt Group.
TrunkConfigLoadBal ance
TrunkIfIndex The index in the Interfaces MIB that is associated
TrunkRowStatus Variable used to create and delete trunk group inter-
TrunkConnectionTable Trunk group connection table indexed by ifIndex
Tr u nkPo rtRe mote IfInd ex
TrunkLLAPRequirement Indicates whether this managed entity requires the
TrunkMaxTrunks The maximum number of trunks that can be config-
TrunkFlowDiagnostic
Table
The type of load balance algorithm applied to this
trunk group (this variable is not applicable since the
ELS100-24 trunking implementation does not support load balancing).
with the trunk group.
faces in the TrunkConfigTable.
used to describe how local interfaces in a trunk
group are connected to remote interfaces.
The ifIndex of the interface at the other end of this
port in the trunk group link.
LLAP protocol updates to perform the trunking function.
ured on the switch.
Table indexed by TrunkIndex and ifIndex which provides a means to programmatically evaluate the
load balancing of a trunk group.
TrunkFlowDiagnos ticInstalledFlows
9033194 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 19
A counter of the flows installed on this port since it
was first operational.

The Power Up Diagnostics and Web Management Enable features in the
user interface were available prior to Cabletron SmartSTACK ELS100-24
firmware revision 2.01, but were not documented in the Installation and
User Guide. These features are documented in the following two sections.
A.9 Power Up Diagnostics
The Power Up Diagnostics feature allows you to enable or disable
diagnostics software to be run every time the switch is initialized. The
diagnostics software tests switch components to determine if the switch
is fully operational before completing boot up.
Select System Configuration menu from the Main Menu of the user
1.
interface.
Select Power Up Diagnostics to toggle between enable (Yes) and
2.
disable (No).
A.10 Web Management Enable
The Web Management Enable feature allows you to enable or disable the
capability to configure and manage the switch over the web.
Select System Configuration menu from the Main Menu of the user
1.
interface.
Select Web Management Enable to toggle between enable (Yes)
2.
and disable (No).
20 SmartSTACK ELS100-24 Firmware Revision 2.01 9033194
 Loading...
Loading...