Page 1

Network Attached Storage
TeraStation 5010
User Manual
Please make sure to read this manual before using and follow the procedure. If you have any inquiries about the
product, contact the number on the warranty statement or the packing box. Do not discard this manual, the
warranty statement, or the packing box.
Americas: www.buffaloamericas.com
Europe: www.buffalo-technology.com
Asia Pacific: www.buffalo-asia.com
35021131-05
2016.11
Page 2

Contents
Chapter 1 Getting Started .............................................8
Diagrams ...........................................................................................8
Turning the TeraStation On and Off............................................. 11
Creating an Initialization Drive .................................................... 13
Chapter 2 Configuration ............................................. 15
Setting Up Through Initial Setup Wizard .................................... 15
Opening Advanced Settings ........................................................ 19
Opening Easy Admin .................................................................... 20
Chapter 3 Sharing Files ............................................... 23
Configuring Shared Folders ......................................................... 23
Adding a Shared Folder ........................................................................... 23
Recycle Bin ................................................................................................25
Read-Only Shares .....................................................................................26
Hidden Shares .......................................................................................... 26
Configuring Users ......................................................................... 26
Adding a User ........................................................................................... 26
Importing User Information ....................................................................27
Adding a Group ............................................................................. 28
Configuring Access Restrictions .................................................. 30
Local Users and Groups ...........................................................................30
Active Directory .......................................................................................31
1
Page 3

Chapter 4 Managing Storage...................................... 35
RAID Modes ................................................................................... 35
Working with RAID Arrays ............................................................ 36
Using JBOD ............................................................................................... 36
Changing RAID Mode ..............................................................................37
Configuring a Hot Spare .......................................................................... 38
RMM (RAID Mode Manager) ....................................................................40
RAID Scanning..........................................................................................42
Adding an External Drive ............................................................. 43
Connecting an External Drive ................................................................. 43
Compatibility ...........................................................................................43
Dismounting Drives ...................................................................... 44
Dismounting with the Function Button .................................................44
Dismounting from Settings ....................................................................44
Checking Drives ............................................................................ 45
S.M.A.R.T. ....................................................................................... 46
Formatting Drives ......................................................................... 47
Encrypting Drives .......................................................................... 49
Erasing Data on the TeraStation Completely .............................. 49
Drive Quotas .................................................................................. 50
Quotas for Users .......................................................................................50
Quotas for Groups ...................................................................................50
Size Limits ................................................................................................. 51
Using the TeraStation as an iSCSI Device .................................... 54
Introduction .............................................................................................54
Creating an iSCSI Volume ........................................................................54
Connecting or Disconnecting Volumes .................................................. 56
Using with Multiple Computers .............................................................. 58
2
Page 4

Configuring Access Restrictions .............................................................58
Expanding Volume Sizes .........................................................................62
Deleting Volumes .....................................................................................63
Chapter 5 Backup ........................................................ 65
Back Up from the TeraStation ...................................................... 65
Preparing a Backup Destination ............................................................. 65
Configuring a Backup Job .......................................................................67
Backup Logs .............................................................................................70
Replication ..................................................................................... 72
Preparing a Replication Destination ......................................................73
Configuring a Replication Task ...............................................................73
Synchronizing Between Source and Destination Units Periodically ... 76
Failover .......................................................................................... 77
Usage Restrictions ...................................................................................78
Configuring Failover ................................................................................ 79
Switching to the Backup Unit Manually ................................................. 82
Synchronizing Between Main and Backup Units Periodically..............82
Backing Up Your Mac with Time Machine ................................... 83
Chapter 6 Remote Access ............................................ 89
WebAccess ..................................................................................... 89
FTP .................................................................................................. 91
Cloud Storage ................................................................................ 93
Configuring Cloud Storage .....................................................................93
Uploading Files to Cloud Storage ........................................................... 95
Dropbox Sync ................................................................................ 98
Configuring a New Task ........................................................................... 98
3
Page 5

Changing Dropbox Task Settings .........................................................100
Creating a Shared Link (Windows Only) ...............................................103
Chapter 7 Advanced Features .................................. 104
Email Notification ....................................................................... 104
Sleep Mode .................................................................................. 106
Wake-on-LAN .............................................................................. 107
UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) ......................................... 108
Port Trunking ............................................................................... 110
Offline Files .................................................................................. 111
Accessing from an NFS Client ..................................................... 112
Encrypting Data Transmission ................................................... 115
Encrypting Settings Data ......................................................................115
Encrypting FTP Transfer Data ...............................................................116
SSL Keys ..................................................................................................116
SNMP ............................................................................................ 116
Saving and Applying Settings .................................................... 117
Saving Settings ......................................................................................118
Applying Settings ..................................................................................119
Transferring Another TeraStation's Settings ............................ 120
Creating a Config File (.nas_config) ......................................................120
Transferring Settings .............................................................................121
Restoring Factory Defaults ......................................................... 122
Initializing from Settings ......................................................................122
Initializing with the USB Initialization Drive .......................................122
Resetting the Administrator Password ..................................... 123
Logs .............................................................................................. 124
4
Page 6

Displaying TeraStation's Logs ............................................................... 124
Transferring Logs to the Syslog Server ................................................124
Creating a Link to the Logs in the Shared Folder ................................125
Updating the Firmware ............................................................... 126
Updating Manually ................................................................................126
Updating Automatically ........................................................................127
Sending Usage Feedback ........................................................... 128
Name, Date, Time, and Language .............................................. 129
Beep Alerts .................................................................................. 132
LCD and LEDs ............................................................................... 133
Proxy Server ................................................................................ 134
Jumbo Frames ............................................................................. 135
Changing the IP Address ............................................................ 138
Boot Authentication ................................................................... 140
Note Before Use .....................................................................................140
Important Notice ...................................................................................140
Setting Up the Authentication Server on a Windows PC ....................141
Configuring Boot Authentication on the TeraStation .........................141
If the TeraStation Cannot Be Accessed .................................................143
Chapter 8 Replacing Drives ...................................... 146
LEDs .............................................................................................. 146
Drive Replacement Procedure ................................................... 147
Using JBOD or a Redundant RAID Mode Other Than RAID 0 and
TeraStation Is On .................................................................................... 147
Using a Redundant RAID Mode Other Than RAID 0 and TeraStation Is
Off ...........................................................................................................150
Using RAID 0 ........................................................................................... 150
5
Page 7

Using a Hot Spare ...................................................................................151
Replacing a Non-Malfunctioning Drive ..................................... 151
Chapter 9 Utilities ...................................................... 153
NAS Navigator2 for Windows ..................................................... 153
Mounting as a Network Drive ...............................................................156
Changing the IP Address .......................................................................157
NAS Navigator2 for Mac ............................................................. 158
Mounting as a Network Drive ...............................................................160
Changing the IP Address .......................................................................161
NovaBACKUP ............................................................................... 162
Chapter 10 Appendix ................................................ 163
TeraStation Does Not Boot Properly ......................................... 163
Booting the TeraStation in Emergency Mode ...................................... 163
Power LED Keeps Blinking ....................................................................163
Cleaning the Dustproof Filter .................................................... 164
LCD Panel ..................................................................................... 166
Modes .....................................................................................................166
Errors .......................................................................................................167
Status ......................................................................................................168
Default Settings .......................................................................... 170
Specifications .............................................................................. 170
Chapter 11 Regulatory Compliance Information .... 172
For Customers in the United States ........................................... 172
For Customers in Europe ............................................................ 172
6
Page 8

For Customers in Taiwan ............................................................. 175
7
Page 9

Chapter 1 Getting Started
Diagrams
Depending on the number or type of drives in the unit, the model name will be different. Check the sticker on the
packing box for your unit's model name.
TS5410DN
13456
2 7
11
12
8
9
10
13
19
14
15
16
17
18
20
24 25
26
23
8
Page 10

TS5410RN
13 21 13 22
3456
13
1
10 13 12 15
7 89
TS5210DN
24 25
23
26
14 22 15 20 19 141816 17
1 3456
2 7
11
8
9
19
10
14
12
13
15
23
17
24 25
20
1816
26
1 Power Button ( )
To power on, connect the power cable and wait for 10 seconds, then press the power button. To power off,
press and hold the power button for 3 seconds.
2 Power LED
When the TeraStation is on, the LED glows green.
9
Page 11

3 Info LED
If there is a status message, the amber info LED will light up. Check the LCD panel to see the status message.
4 Error LED
If there is an error, the red error LED will light up. Check the LCD panel to see the error message.
5 LAN1 LED
When LAN port 1 is connected, this LED glows green. It blinks when the connection is active.
6 LAN2 LED
When LAN port 2 is connected, this LED glows green. It blinks when the connection is active.
7 LAN3 LED
When LAN port 3 is connected, this LED glows blue. It blinks when the connection is active.
8 LCD Panel
This display shows the status of many TeraStation settings. It also displays errors and messages when available.
9 Display Button
Switches between the different display modes. Also, if the TeraStation is beeping, press this button to stop it.
10 Function Button
Use this button for dismounting USB devices, rebuilding RAID arrays, configuring failover, stopping the
TeraStation's beeping, and initializing settings using a USB drive.
11 Drive Lock ( )
Open the front panel with the key to replace drives or access the init button.
12 Init Button
Hold down this button with something pointed to initialize the TeraStation's admin username and password,
IP settings, SSL, and service port restriction settings to their factory default values. The effects of this button
can be modified in Settings.
13 Status LEDs
Normally, these LEDs blink green when drives are accessed. If a drive fails, its LED will turn red.
14 Fan
Spins to avoid overheating inside. Do not block the fan.
15 USB 3.0 Port ( )
Compatible Buffalo USB drives, USB flash drives, digital cameras, and USB UPS connections can be connected.
USB hubs are not supported.
16 LAN Port 1 ( )
Use an Ethernet cable to connect this port to your network for communicating at 1000 Mbps.
17 LAN Port 2 ( )
This second Ethernet port may be used for network redundancy or backup for communicating at 1000 Mbps.
You may connect a second TeraStation directly to this port for backup.
18 LAN Port 3 ( )
Use an Ethernet cable to connect this port to your network for communicating at 10 Gbps.
Note: To communicate at 10 Gbps, all network devices must be compatible with 10 GbE.
10
Page 12

19 Power Connector
Use the included power cable to connect to an UPS, surge protector, or outlet.
20 Anti-Theft Security Slot ( )
Use this slot to secure your TeraStation with a cable lock (not included).
21 Serial Number
This sticker shows the TeraStation's serial number.
22 UID Button
Press the UID button on the front or the back of the unit to cycle the blue LED on and off.
23 Link LED
Glows green when the unit is connected to a network.
24 100 Mbps Link LED
Glows amber when the unit is connected to a network at 100 Mbps.
25 1000 Mbps Link LED
Glows green when the unit is connected to a network at 1000 Mbps.
26 10 Gbps Link LED
Glows blue when the unit is connected to a network at 10 Gbps.
Turning the TeraStation On and Off
Note: Do not disconnect or reconnect the internal drives while turning on or off the TeraStation.
Press the power button on the TeraStation to turn it on.
To turn off the TeraStation, press and hold the power button for 3 seconds. Don't unplug the TeraStation without
turning it off first. You can also shut it down and restart it remotely from Settings.
1 Double-click the icon to start NAS Navigator2.
11
Page 13

2 Right-click your TeraStation's icon and select Settings. For macOS, select the TeraStation's icon while holding
down the control key, then select Settings.
3 Enter the username and password, then click OK.
Note: The default username and password are "admin" and "password".
12
Page 14

4 Settings will open.
5 Click at the top-right of Settings and choose Shut Down.
6 Click Yes .
7 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
When all the LEDs on the front of the TeraStation turn off, the shutdown process is complete.
Creating an Initialization Drive
We recommend creating an initialization drive as soon as possible. This USB drive can be used to initialize the
TeraStation's settings to its factory default values, or recover the system if your TeraStation encounters an error that
13
Page 15

prevents the unit from booting. For detailed procedure, refer to the "Creating an Initialization Drive" subsection in
chapter 7.
14
Page 16

Chapter 2 Configuration
Configure and manage your TeraStation using the Settings interface, accessible from a browser window. Open the
interface using the procedure below or type the TeraStation's IP address in the URL field of your browser. Within
Settings, the Easy Admin page gives you quick access to commonly used settings.
Note: Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer 9 or later, and Safari 9 or later are supported. If
you have difficulty viewing Settings, check the following:
• If there are a large number of registered users, groups, or shared folders, use another browser instead of
Internet Explorer.
• If you have a proxy server enabled in the browser settings, disable the proxy server.
• With Internet Explorer, set security to Local intranet. On Windows Server operating systems, higher-level
security is configured by default. Set the security to a lower level temporarily.
• On a Mac, you can also use Bonjour to log in to Settings. Navigate to Bookmarks - Bonjour - TeraStation name
from the menu bar of Safari. If you don't see "Bonjour" in the Bookmarks menu, click Safari - Preferences and
select "Include Bonjour in the Bookmarks menu" under "Advanced".
Setting Up Through Initial Setup Wizard
When you access Settings for the first time, or after initializing the TeraStation's settings, the initial setup wizard will
be displayed. To set up the TeraStation using the wizard, follow the procedure below.
1 Double-click the icon to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Right-click on your TeraStation's icon in NAS Navigator2 and select Settings. For macOS, click your TeraStation's
icon while holding down the control key, then select Settings.
15
Page 17
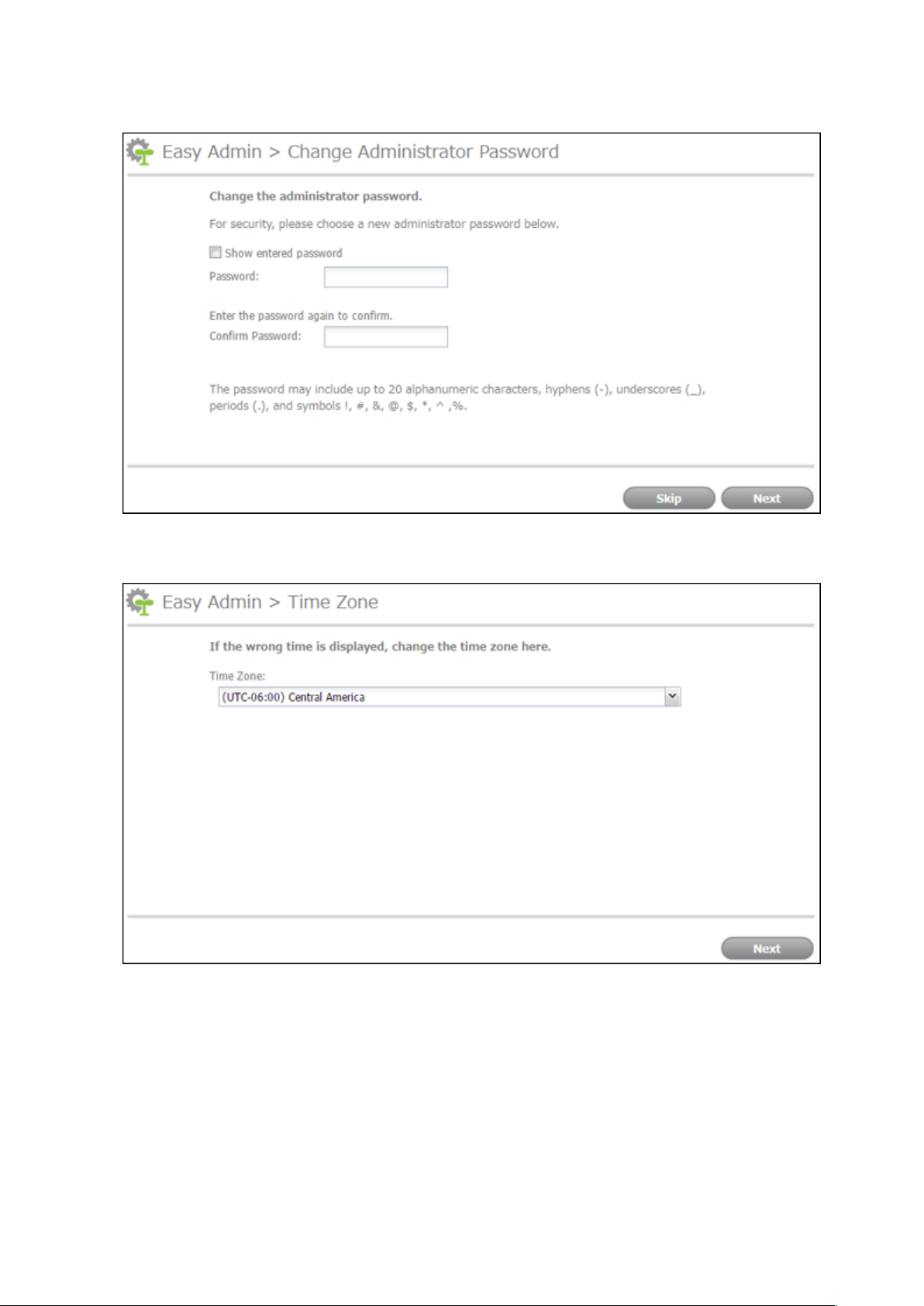
3 The password settings page will be displayed. Enter the desired new administrator password and click Next. If
you click Skip, the administrator password will not change from the default value ("password").
4 The time zone settings page will be displayed. If you need to change the time zone from that which is currently
displayed on the page, select it from the drop-down list and click Next.
16
Page 18
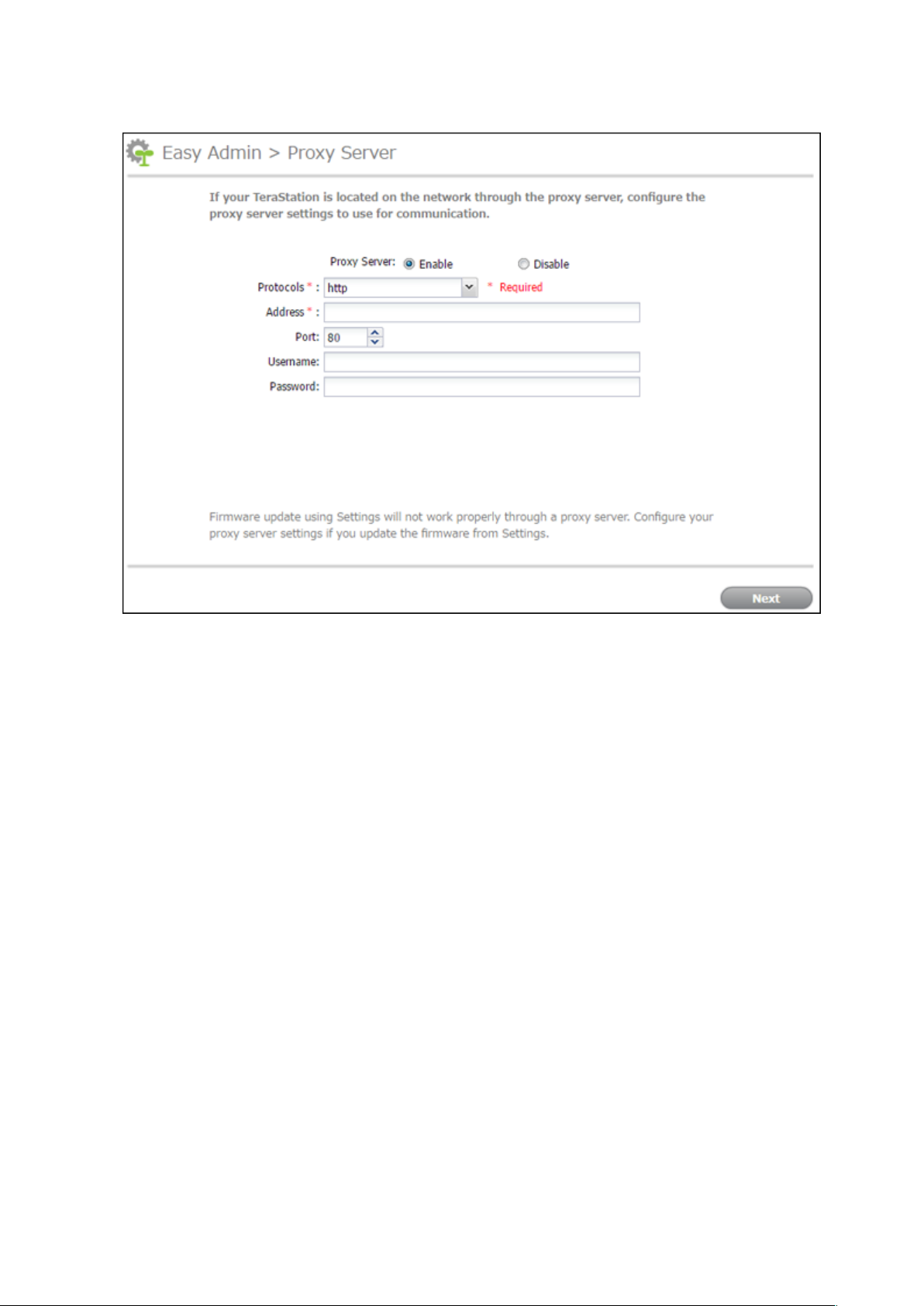
5 The proxy server settings page will be displayed. If you place the TeraStation under a proxy network, set your
proxy settings. Click Next.
6 The RAID settings page will be displayed. To change the RAID mode from the default mode, select the desired
RAID mode and click Next, then click Start in the next page. The "Confirm Operation" screen will open so enter
the confirmation number and click OK. Changing the RAID mode will begin.
17
Page 19

If you want to keep the RAID mode as is, select "Keep current RAID mode" and click Next.
Note: The RAID settings page will not be displayed if using TS5210DN series.
7 The usage feedback settings page will be displayed. If you allow Buffalo to collect your usage and environment
information, select the "Send usage feedback" box. If you don't permit information collection, leave the box
blank and click Next.
18
Page 20

8 The folder path to access shared folders will be displayed and the initial setup will finish.
Opening Advanced Settings
1 Double-click the icon to start NAS Navigator2.
2 Right-click on your TeraStation's icon in NAS Navigator2 and select Settings. For macOS, click your TeraStation's
icon while holding down the control key, then select Settings.
3 Enter the username and password and click OK.
Notes:
• If the time-out period is set to "10 minutes", you will be logged out of Settings after 10 minutes of inactivity.
• Click Secure Connection to log in with an encrypted connection.
19
Page 21

4 Settings will open.
Notes:
• Username/Password Combinations:
Username Password Settings Available
admin password All
guest blank System information (read-only)
If a user is assigned as an administrator, all settings
Your username Your password
• Click to open Easy Admin.
• Click to play a tone from the TeraStation for easy location.
are available. If assigned under another group, only
system information (read-only) is available.
Opening Easy Admin
The Easy Admin page makes it easy to change common settings. Follow the procedure below to open Easy Admin.
1 Double-click the icon to start NAS Navigator2.
20
Page 22

2 Right-click on your TeraStation's icon and choose Settings. For macOS, click the TeraStation icon while holding
down the control key, then select Settings.
3 Click Easy Admin.
21
Page 23

4 The Easy Admin screen will open.
Note: If you click any buttons, you will need to enter a username and password.
22
Page 24
Chapter 3 Sharing Files
Configuring Shared Folders
Adding a Shared Folder
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "Folder Setup".
3 Click Create Folder.
23
Page 25

4 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
Notes:
• Names may contain up to 27 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), and underscores (_). Do not use a symbol
as the first character in a name.
• The description may contain up to 75 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and spaces. Do
not use a symbol or space as the first character.
• You may create up to 400 shared folders.
• If the names of shared folders accessed via AFP and FTP connections contain multibyte characters, configure
the client language in Management - Name/Time/Language to match the characters. If the setting does not
match, the shared folder name will not be displayed correctly.
24
Page 26

• The following characters are handled differently by macOS and Windows. Avoid using these characters when
sharing data between macOS and Windows:
• Windows does not support some characters that macOS and the TeraStation allow. If you create a filename
on a Mac with any of the following characters, it will not display correctly on a Windows computer. You may
have to connect to the TeraStation via AFP in order to display or copy any of the following characters:
? [ ] / \ = + < > ; : " , | *
• Do not use any of the following words for the name of a shared folder as these words are reserved for internal
use by the TeraStation: authtest, global, homes, info, lost+found, lp, msdfs_root, mt-daapd, printers, ram,
spool, usbdisk x (where "x" is a number, for example: usbdisk1)
• Don't use the following unsupported characters in shared folder names, workgroup names, or filenames:
• File and folder names may contain up to 255 single-byte characters.
• Folder and workgroup names whose names contain non-Roman characters may not be displayed correctly.
• If shared folders are accessed from a Mac, information files for the Mac may be generated automatically. Do
not delete these files. If they are deleted using Windows, this may prevent further access from a Mac.
• The TeraStation belongs to the default zone in AppleShare; the zone cannot be specified.
• When files are copied to the TeraStation or to a USB drive connected to the TeraStation, file information such
as date created, date modified, and other date information may be updated or changed.
• During a file transfer, if settings are changed, the file transfer operation may be aborted.
• File copying to the TeraStation is protected by a journaling file system. If the Ethernet cable is disconnected
or a power outage occurs while copying data, the following may occur:
- Preset data such as the TeraStation name, users, and groups may be erased.
- An incomplete file may be copied and the file can no longer be deleted. If this happens, restart the
TeraStation, delete the file, and perform the copy operation again.
Recycle Bin
To protect your data from accidental deletion, you may configure your TeraStation to use a recycle bin instead of
deleting files immediately. The recycle bin will only work with SMB connections. To empty the recycle bin, click File
Sharing - Folder Setup - Empty Recycle Bin in Settings.
Notes:
• You can prevent guests and other users from emptying the trash by navigating to File Sharing - SMB - Recycle
Bin Permissions and select "Administrator only".
• If you use macOS, select "Keep when original file is deleted" for "Mac OS Temp Files" option. If this setting is
changed, files in the recycle bin may be corrupted.
25
Page 27

Read-Only Shares
By default, new shares are set with read and write access, but you may change the attribute to Read only in Attribute.
Read-only shares and HFS Plus-formatted USB drives will have "(Read Only)" added to comments in Explorer.
Note: Configure read-only file attribute in Settings. Configuring them from within Windows is not supported
and may cause unexpected behavior.
Hidden Shares
If hidden shares are enabled, shared SMB folders will not be displayed in Network, and only certain users are allowed
to access them. To hide a shared SMB folder, follow the procedure below.
1 In Settings, navigate to File Sharing - Folder Setup and choose a shared folder or a USB drive to configure
hidden shares.
2 Select the "Hidden share (SMB only)" checkbox and click OK.
Notes:
• If protocols other than "SMB" or "Backup" under "LAN Protocol Support" are enabled, the hidden shares
option will be grayed out and cannot be selected.
• Configure hidden share attribute in Settings. Configuring them from within Windows is not supported and
may cause unexpected behavior.
To access a hidden folder, open File Explorer in your computer and enter "\\TeraStation name\Shared folder name$\"
for the name. For example, if the TeraStation name is "TSXXX001" and the shared folder name is "share", enter "\\
TSXXX001\share$\" to open it.
Configuring Users
Adding a User
Note: The TeraStation can register a maximum 300 of users, which includes the default users "admin" and
"guest".
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "Users".
3 Click Create User.
26
Page 28

4 Enter the desired settings, then click OK.
Notes:
• Usernames may contain up to 128 characters, including hyphens (-), underscores (_), periods (.), !, #, &, @, $, *,
^, and %. Do not use a symbol as the first character.
• The user ID should be a number from 1000 to 1999. Each user ID should be unique. If this field is left blank, a
user ID is assigned automatically.
• Do not duplicate user IDs, group IDs, usernames, or group names. Each should be distinct and unique.
• The description may contain up to 75 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and spaces. Do
not use a symbol or space as the first character.
• Passwords may contain up to 20 alphanumeric characters and the following characters: - _ @ ! # $ % & ' ( ) * + ,
. / ; < > = ? " [ ] ^ { } | ~. Do not use a symbol other than an underscore (_) as the first character.
• Use the same username and password for both Windows and the TeraStation or you may not be able to
access shared folders.
• Do not use any of the following words for a username as these words are reserved for internal use by the
TeraStation: _lldpd, admin, apache, avahi, avahi-autoipd, backup, bin, daemon, ftp, games, gnats, guest, halt,
irc, libuuid, list, lp, mail, man, messagebus, mysql, news, nobody, ntp, openldap, proftpd, proxy, pupet, root,
rpc, rpcuser, snmp, sshd, statd, sync, sys, syslog, uucp, www-data
Importing User Information
You can import users in File Sharing - Users by clicking Import CSV File.
Format for user data: Username (required), password (required), and user description (optional).
Example 1: Importing usernames, passwords, and comments
27
Page 29

username1,password1,comment1
username2,password2,comment2
username3,password3,comment3
Example 2: Importing usernames and passwords
username1,password1,
username2,password2,
username3,password3,
Guidelines:
• Use commas (,) as separators. Do not put spaces before or after commas. If you don't want user descriptions, use
a comma after password at the end.
• If a line has an incorrect format, the user on that line will not be registered.
• If a username already exists, the new user information will overwrite the old information.
• Do not use commas (,) in the username, password, or user description.
Note: Imported users are added to the "hdusers" group automatically.
Adding a Group
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "Groups".
3 Click Add Group.
28
Page 30

4 Enter the desired settings, then click OK.
Notes:
• Group names may contain up to 20 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and periods (.). Do
not use a symbol other than an underscore (_) as the first character.
• Group descriptions may contain up to 75 alphanumeric characters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and spaces.
Do not use a symbol or space as the first character.
• If the group ID field is left blank, a group ID is automatically assigned. Use numbers between 1000 and 1999
to set a group ID manually. Don't use duplicate group IDs.
• You may register up to 300 groups with the TeraStation.
• If you are logged in as a member of the general users group, you can only change your own password. If
you're logged in as an administrator, you can change any settings, including other users' passwords. If you are
logged in as a member of the power users group, you can create and edit shared folders, users, and groups.
• Do not use any of the following words for a group name as these words are reserved for internal use by the
TeraStation: adm, admin, administrator, all, apache, bin, daemon, disk, ftp, ftpuser, guest, halt, hdusers, kmem,
lp, mail, man, mysql, news, nobody, nogroup, none, operator, root, shadow, shutdown, sshd, sync, sys, tty,
users, utmp, uucp, www
29
Page 31

Configuring Access Restrictions
You may restrict access to specific shared folders, including external USB drives.
Notes:
• Access restrictions can be set separately for each shared folder, but not for folders within the shared folders.
• Configure access restrictions through Settings. Configuring access restrictions through Windows is not
supported and may cause unexpected behavior.
• You can also configure users, groups, and shared folders from Easy Admin by clicking Access Restrictions.
• Shared folders with limited access can still be used as backup destinations.
• If you change access restrictions for a user or group while they are accessing files, unexpected behavior may
result.
Local Users and Groups
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "Folder Setup".
3 Click the shared folder that you want to set access restrictions for.
4 Click Edit.
5 Enable "Access Restrictions".
6 Select the level of access for the user or group you added.
30
Page 32

: Read and write access allowed : Read access allowed : Access prohibited
7 Click OK.
Notes:
• The example above shows access restriction by user. To restrict access by group, click the Local Groups tab
and select group permissions.
• If both read-only and read and write permissions are given to a user, the user will have read-only access. The
most restrictive access always applies.
• For an access-restricted shared folder, if you change the access restrictions of all users and groups from read
and write or read only to access prohibited from the user or group list page in Settings, that shared folder can
only be accessed by admin users and groups.
Active Directory
If there is an Active Directory environment, the TeraStation will use account information from the Active Directory
domain controller to set access restrictions for TeraStation's shared folders. There is no need to perform individual
account management for the TeraStation. If multiple TeraStations are installed on the network, the account
information is centrally managed in Active Directory, greatly reducing the operations required for installation and
management.
Notes:
• If usernames or group names from Active Directory include multibyte characters, you will not be able to
configure access restrictions for them.
• The TeraStation supports a domain environment with a maximum of 1000 users and 1000 groups.
1 In Settings, click Network.
2 Click to the right of "Workgroup/Domain".
3 Click Edit.
31
Page 33

4 Select "Active Directory", then click Next.
5 Click Yes .
6 Enter the desired settings, then click OK.
7 Click to the right of "Folder Setup".
32
Page 34

8 Click a shared folder that you want to set access restrictions for.
9 Click Edit.
10 Enable "Access Restrictions".
11 Select the level of access for the user or group.
: Read and write access allowed : Read access allowed : Access prohibited
12 Click OK.
Notes:
• To have the TeraStation join an Active Directory domain, configure it to use a DNS server that can resolve
names for the Active Directory domain.
• After building an Active Directory domain, the administrator password for joining the domain must be
changed at least once, or joining the Active Directory domain will fail.
• The DNS name and NetBIOS name of Active Directory domains should be identical.
• If both read-only and read and write permissions are given, the user will have read-only access. The most
restrictive access setting will apply.
• If there is a difference of more than 5 minutes between the TeraStation's clock and the domain controller's
clock, joining the domain or authenticating domain users and groups may fail. For best results, use an NTP
server to set the time for all network devices.
• To use the TeraStation as a member server in an Active Directory domain, the TeraStation should be logged
in to the domain and accessed from a computer that is not a member of the domain with a valid domain
account.
• If the TeraStation is a member server of an Active Directory domain, you cannot connect as a guest user via
AFP.
• If your TeraStation is a member server in an Active Directory domain and you change the authentication
method to "Workgroup", the account on the domain controller will not be deleted automatically.
• If FTP is enabled, local and domain group access restrictions from the AD network do not work. Use user
access restrictions instead.
33
Page 35

• For an access-restricted shared folder, if you change the access restrictions of all users and groups from read
and write or read only to access prohibited from the user or group list page in Settings, that shared folder can
only be accessed by admin users and groups.
34
Page 36

Chapter 4 Managing Storage
RAID Modes
TeraStations support many types of RAID. The type of RAID arrays available for use depends on how many drives are
installed in your TeraStation.
TeraStation Default RAID Mode Available Modes
TS5410DN, TS5410RN RAID 5 RAID 5, 6, 10, 1, 0, and JBOD
TS5210DN RAID 1 RAID 1, 0, and JBOD
Notes:
• If you change the RAID mode, all data on the array is deleted. This is true for every procedure in this chapter.
Always back up any important data before performing actions that affect your RAID array.
• Drive capacity is shown in Settings in actual gigabytes. The Properties window in Windows may show GiB
instead, which will be a smaller number.
• If the TeraStation is restarted or shut down while changing the RAID mode, the message displayed on the
LCD panel will change from I46 or I47 to I18.
• RAID 5, 6, and 10 are only available for 4-drive models.
RAID 6
RAID 6 arrays are available for TeraStations with 4 or more drives. RAID 6 combines 4 or more drives into a single
array. The usable space is equal to the sum of the capacity of all drives minus the capacity of two drives. For example,
if 4 drives are combined into a RAID 6 array, the usable space is the sum of the capacity of 2 drives. If 2 drives in the
array are damaged, you can recover data by replacing them. If 3 or more drives are damaged, your data is lost.
RAID 5
RAID 5 arrays are available for TeraStations with 3 or more drives. RAID 5 combines 3 or more drives into a single
array. The usable space is equal to the sum of the capacity of the drives minus the capacity of one drive. For
example, if 4 drives are combined into a RAID 5 array, the usable space is the sum of 3 drives. If one drive in the array
is damaged, you can recover data by replacing the damaged drive. If two or more drives are damaged at the same
time, your data is lost.
RAID 10
RAID 10 arrays are available for TeraStations with 4 or more drives. In this mode, mirrored pairs of drives in RAID 1
arrays are combined into a RAID 0 array. The usable space is equal to the capacity of the smallest drive multiplied by
the number of drives divided by 2.
35
Page 37

RAID 1
Combines 2 or more drives into a mirrored array. The available space in the array is the capacity of a single drive.
Identical data is written to each drive. If a drive is damaged, data can be recovered by replacing the damaged drive.
As long as one drive in the array remains undamaged, all data in the array can be recovered.
RAID 0
Combines 2 or more drives into a single array. The usable drive space is the total space of all drives used. This simple
RAID mode offers faster performance than RAID modes that include parity. If a single drive in the array fails, then all
data in the array is lost.
JBOD
This mode uses the drives inside the TeraStation as individual drives. The drive space you can use is the total
capacity of all drives in the TeraStation. If any drive is damaged, then the data on that drive is lost.
Working with RAID Arrays
To change RAID settings, navigate to Storage - RAID in Settings.
Using JBOD
With JBOD, each drive in the TeraStation is addressed separately. To put drives from an array into JBOD, follow the
procedure below.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "RAID".
3 Click the array to delete.
36
Page 38

4 Click Delete RAID Array.
5 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Click OK when finished.
Once JBOD is configured, create shared folders on each drive to use them.
Changing RAID Mode
To change the RAID mode, first put the drives in JBOD.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "RAID".
3 Click the array to delete.
4 Click Delete RAID Array.
5 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Click OK.
37
Page 39

7 Choose a RAID array.
8 Select a RAID mode and the drives to be used, then click Create RAID Array.
9 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
10 Click OK when finished.
Notes:
• You can also configure RAID settings from Easy Admin.
• After changing the RAID mode, create a shared folder.
Configuring a Hot Spare
If you have a hot spare configured and an array fails, the TeraStation immediately switches over to the hot spare. To
use a hot spare, you need an extra drive that's not part of any array and a RAID 1 or RAID 5 array.
38
Page 40

Notes:
• All data on the hot spare drive is deleted when it is configured as a hot spare and again when it changes from
a spare to a drive in the array.
• A hot spare cannot be configured for TeraStation models with only two drives. Use RAID 1 instead.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "RAID".
3 Choose a RAID array.
4 Click Set as a hot spare.
5 Click Yes .
39
Page 41

6 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 Click OK when finished.
Note: To turn the hot spare back into a normal drive, choose Set as a normal drive.
RMM (RAID Mode Manager)
With RMM, you can create or expand a RAID array without erasing the data on the drives.
Changing from JBOD to RAID 1
You must have at least two drives available in JBOD (not in a RAID array) to build the RAID 1 array with RMM.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "RAID".
3 Choose a RAID array.
40
Page 42

4 Set the RAID mode to "RAID 1".
5 Select the "Add a drive to a RAID array with RMM. Your data will be preserved." checkbox.
6 Select the drive whose data will be saved from the drop-down list.
7 Select the drive to add to the RAID array.
8 Click Create RAID Array.
9 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
10 Click OK when finished.
Adding a Drive to an Existing RAID Array
You can add a drive to a RAID 1 or RAID 5 array. Drives in JBOD can be added to the RAID array.
Note: RMM can be used to expand an array by one drive per operation. To expand by two or more drives, RMM
must be performed multiple times.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "RAID".
41
Page 43

3 Choose a RAID array.
4 Select the drive to add to the RAID array.
5 Click Create RAID Array.
6 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 Click OK when finished.
Changing the RAID Mode While Adding a Drive
Select the drive you want to add to the RAID array and choose the mode for the array. Enter the "Confirm Operation"
number and click OK.
RAID Scanning
A RAID scan checks you RAID array for bad sectors and if it finds any, it automatically repairs them. Arrays other than
RAID 0 are supported. For best results, run a RAID scan regularly.
42
Page 44

1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Move the RAID scanning switch to the position to enable RAID scanning.
3 Click to the right of "RAID Scanning".
4 Click Edit.
5 Select when to run the scan and click OK.
Notes:
• Select the "Immediately" checkbox to run a RAID scan immediately.
• To stop a RAID scan, click Cancel RAID Scan.
Adding an External Drive
Connecting an External Drive
Your TeraStation includes USB ports (the number of ports depends on your model), and you can connect external
drives to these ports. Once connected, they appear as shared folders on the TeraStation. Formatted drives are
detected automatically. Unformatted drives should be formatted in Settings.
After a USB drive is recognized, Windows adds "usbdisk x" under the TeraStation in "Network", where "x" is the USB
port where the drive is connected.
Compatibility
The following USB devices are supported by the TeraStation:
• USB storage devices
• Card readers (except for card readers that can recognize two or more memory cards)
Buffalo external USB drives are recommended.
Supported file systems for external drives are below:
43
Page 45

• FAT32
• EXT3
• XFS
• NTFS
• HFS Plus (read-only)
• e xFAT
Connect only one device to each USB port of the TeraStation. Note that only the first partition of a connected USB
drive is mounted. Additional partitions are not recognized.
Notes:
• Backup data from macOS may include characters that cannot be written to FAT16 or FAT32 drives such as
".DS_Store". For best results, reformat the drive before using it as a backup target.
• If your USB 3.0 drive is not reconfigured after rebooting the TeraStation, unplug and reconnect it.
• When copying a file that is over 100 MB to a FAT32-formatted USB drive using File Explorer, an error message
may be displayed. In such a case, use an FTP or SFTP connection to copy the file.
Dismounting Drives
If the TeraStation is powered on, dismount drives (internal and external) before unplugging them. You may
dismount external drives with the function button, or any drive from Settings. If the TeraStation is off, then all drives
are already dismounted and may be unplugged safely.
Note: Do not dismount internal drives while a RAID array is rebuilding or RMM is being configured. If you do,
data on the drives may be lost.
Dismounting with the Function Button
When you press the function button, the TeraStation will beep once. Press and hold the button until the TeraStation
beeps again and the button starts blinking blue. It will take about 6 seconds. When the dismount is finished, the
function button will stop blinking and return to glowing. You may now unplug any USB drives safely.
After 60 seconds, the function button will go out and any drives that have not yet been unplugged will be
remounted.
Dismounting from Settings
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click Drives to dismount an internal drive or USB Drives to dismount an external drive.
44
Page 46

3 Select the drive to dismount and click Dismount Drive.
4 When the following message is displayed, it is safe to unplug the drive.
Note: To remount the drive, unplug it and then plug it back in.
Checking Drives
A drive check tests the data on a drive in the TeraStation or one that is connected via USB for integrity. Errors are
fixed automatically. With large drives, a drive check may run for many hours. Shared folders cannot be accessed
during a drive check. Do not turn off the TeraStation until the drive check is finished. Use the procedure below to run
a drive check.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Select Drives to check an internal drive or USB Drives to check an external drive.
45
Page 47

3 Select the drive or array to test, then click Check Drive.
4 Click Check. You have the option of deleting information files from macOS during the check if desired.
S.M.A.R.T.
S.M.A.R.T. (Self-Monitoring, Analysis, and Reporting Technology) monitors internal drives to detect and report
various indicators of reliability, in the hope of anticipating failures. When a failure is anticipated by S.M.A.R.T., the
user may choose to replace the drive to avoid outages and data loss. Follow the procedure below to check S.M.A.R.T.
information for the TeraStation's internal drives.
Note: S.M.A.R.T. information is only available for internal drives.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "Drives".
46
Page 48

3 Select a drive to check and click S.M.A.R.T.
4 The S.M.A.R.T. information for the drive will be displayed. Different information may be displayed depending
on the brand of drives in your TeraStation. Critical attributes are displayed in bold. Attributes with current value
less than or equal to the threshold value may be significant. If an attribute reports a failure, or has had one in
the past, it will be displayed in the status column.
Formatting Drives
Notes:
• Under some circumstances, data deleted when a drive is formatted can be recovered. To ensure that data is
"gone forever", a format might not be sufficient. See the "Erasing Data on the TeraStation Completely" section
below.
• After a drive is formatted, the "% Used" and "Amount Used" in Settings will not be 0. This is because some
drive space is used for the system area.
47
Page 49

1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Select Drives to format an internal drive or USB Drives to format an external drive.
3 Select the drive or array to format, then click Format Drive.
4 Select a format type, then click Format.
5 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Depending on the size and the formatted file system of your drive, the format may take several minutes or
several hours to complete. "Formatting" will be displayed on the LCD panel until the format is complete. Click
OK when finished.
Notes:
• Do not turn off or disconnect power to the TeraStation while formatting a drive.
• For drives of 2.2 TB or larger, make sure that the "GPT partition" checkbox is selected.
48
Page 50

Encrypting Drives
Internal drives (and arrays) can be encrypted with 128-bit AES during formatting. Encrypted drives and arrays are
then readable only from that specific TeraStation. To decrypt a drive or array, clear the "Encryption" checkbox and
format it again.
Erasing Data on the TeraStation Completely
Under some circumstances, data from formatted drives can be recovered. The drive erasure process in this section
does a much more thorough job of erasing data. This procedure is recommended for removing all data from a drive
in a way that makes it nearly impossible to recover with current tools. The TeraStation will then be in the following
state:
• All drives in JBOD
• An empty shared folder on each drive
• All settings returned to their default values
• All logs deleted
If you remove a drive and then erase all data on the TeraStation, the LCD panel will show the E22 error message and
the number of the removed drive. You can still use the TeraStation.
Follow the procedure below to completely and permanently erase all data from your TeraStation.
1 In Settings, click Management.
2 Click to the right of "Restore/Erase".
3 Click Erase TeraStation.
4 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
49
Page 51

5 All data on the TeraStation will be permanently erased.
Drive Quotas
You can set a drive quota to limit drive space for each user or group. You can also set a threshold. If the drive space
exceeds the set threshold, an email notification will be sent. To configure email notifications for drive quota, refer to
the "Email Notification" section in chapter 7.
Notes:
• When using quotas, disable the recycle bin or empty the trash folder often. The limited space includes the
space used for trash.
• Quotas apply per drive or per array. If a quota is set to 1 GB, each array or drive can use a maximum of 1 GB.
• Quotas cannot be set for external drives connected to the TeraStation.
• If both user and group quotas are configured for a user, the most restrictive quota will always apply.
Quotas for Users
Follow this procedure to limit the shared folder drive space available for a user.
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "Users".
3 Select the user whose space will be limited.
4 Enable quotas, choose the maximum space the user will be allowed to use, and click OK.
Note: If you change the primary group, restart the TeraStation to apply the quota settings.
5 Click OK.
Quotas for Groups
Follow the procedure below to limit the space for shared folders that each group can use.
50
Page 52

1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "Groups".
3 Select the group whose space will be limited.
4 Enable quotas, choose the maximum space the group is allowed, and click OK.
5 Click Close.
6 Click to the right of "Users".
7 Select the user who will inherit the group quota settings.
8 Change the user's primary group to the group with the quota, then click OK.
9 Click OK.
Size Limits
If LVM is enabled, volumes can be created with maximum size limits.
Note: When creating a LVM volume, all data in the area where you specified for the LVM volume will be erased.
Before changing any settings, back up any important data.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "LVM".
51
Page 53

3 Select the drive or array where the volume will be located and click Enable LVM.
4 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
5 Click OK.
6 Click Edit under "NAS Volume".
52
Page 54

7 Click Create Volume.
8 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
9 Click OK.
10 Click Close.
11 Click Close.
12 Navigate to File Sharing - Folder Setup.
13 Click Create Folder.
14 Configure the settings.
15 Select the volume that you created and click OK.
53
Page 55

Notes:
• Do not use any of the following words for the name of a volume as these words are reserved for internal use
by the TeraStation: array x, authtest, disk x, global, homes, info, lost+found, lp, mediacartridge x, msdfs_root,
mt-daapd, printers, ram, spool, usbdisk x. Any instances of "x" denote a number (for example: array1 or disk3)
• If an LVM volume could not be mounted, try restarting the TeraStation. If an issue still exists, delete and
recreate the LVM volume. Deleting the LVM volume will erase data on the volume.
Using the TeraStation as an iSCSI Device
Introduction
iSCSI is a protocol for carrying SCSI commands over IP networks. Unlike traditional SAN protocols such as Fibre
Channel, which requires special-purpose cabling, iSCSI can be run over long distances using existing network
infrastructure. Normal Windows formatting such as NTFS is supported.
Differences Between NAS and iSCSI
With iSCSI, the TeraStation is connected to a single computer, such as a server. Other computers on the network
access files on the TeraStation through the computer it's connected to. The TeraStation can be used as a local drive
from Windows Server. Features of Windows Server such as Active Directory can be used normally.
As a NAS, the TeraStation is a server, and computers (including other servers) on the network can access shared
folders on it directly. A separate server is not required, and features such as backup are built-in.
Network Configuration
Use gigabit or faster network equipment with iSCSI. For best results, a dedicated network for iSCSI is recommended,
separate from the regular network. Use fixed IP addresses for storage devices such as the TeraStation.
Connection Tool
The Microsoft iSCSI Software Initiator is already installed on your computer. You don't need to download and install
it.
Creating an iSCSI Volume
To use the TeraStation as an iSCSI drive, create a volume first. Configure the TeraStation as described below.
Notes:
• If the volume settings are changed, all data on the volume will be erased. Before changing any settings, back
up any important data.
• The TeraStation can have up to 255 volumes, but we recommend creating no more than 32. Exceeding this
volume amount may cause irreparable damage to the unit.
• Do not use any of the following words for the name of a volume as these words are reserved for internal use
by the TeraStation: array x, authtest, disk x, global, homes, info, lost+found, lp, mediacartridge x, msdfs_root,
mt-daapd, printers, ram, spool, usbdisk x. Any instances of "x" denote a number (for example: array1 or disk3)
1 In Settings, click Storage.
54
Page 56

2 Move the iSCSI switch to the position to enable iSCSI.
3 Click to the right of "iSCSI".
4 Click Create Volume.
5 Enter a volume name, volume description, drive or array where a volume will be created, and enter a volume
size. Click OK when finished.
55
Page 57

If you enabled LVM for the target drive or array, or selected "File I/O" for the "Backstore" option, the volume size
that you specify here can be changed later. To change the volume size, refer to the "Expanding Volume Sizes"
section below.
6 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
7 Click OK, then Close.
Note: If you click Disable Connection for the selected volume in Storage - iSCSI in Settings, the selected iSCSI
volume can no longer be accessed. If you click Enable Connection, the volume will become accessible from the
iSCSI initiator software.
Connecting or Disconnecting Volumes
Note: By default, the IP address of the TeraStation is automatically assigned from a DHCP server. However, in
this case, if you turn off and restart the TeraStation, the IP address may be changed and the volumes on the
TeraStation may not be accessible. To avoid changing the IP address unexpectedly, using a fixed IP address for
the TeraStation is recommended.
Connecting Volumes
To connect a volume, follow the procedure below.
Note: Do not shut down the TeraStation while connecting to an iSCSI volume. It may cause unexpected data
erasure. Make sure all connections are disconnected before shutdown.
1 In Windows, navigate to Control Panel - Administrative Tools - iSCSI Initiator.
56
Page 58

2 Enter the IP address of the TeraStation into the "Target" box and click Quick Connect.
3 Confirm if the connection is established and click Done.
Connecting a volume is finished.
Formatting Volumes
If using the connected volume for the first time, the volume should be formatted to be used as a local drive. Follow
the procedure below for formatting.
1 In Windows, navigate to Control Panel - Administrative Tools - Computer Management.
2 Click Disk Management.
When the "Initialize Disk" screen is displayed, click OK without changing any settings.
3 Right-click the drive volume that shows the status "Unallocated" and click New Simple Volume from the
displayed menu. Follow the screen to finish formatting.
Formatting a volume is finished. When the formatting process is completed, the drive will be visible as an icon in
Computer or My Computer and can be used as a normal drive on the computer.
Disconnecting a Volume
1 In Windows, navigate to Control Panel - Administrative Tools - iSCSI Initiator.
The status of the connecting volume will be displayed as "Connected" under "Discovered targets".
2 Select a volume to disconnect and click Disconnect.
3 Click Yes .
4 When the volume status is displayed as "Inactive", the disconnection was carried out properly.
57
Page 59

Using with Multiple Computers
If the TeraStation is divided into multiple volumes (or drives), it can be used with multiple computers. However,
multiple computers cannot be accessed from one volume (or one drive) at the same time.
Checking Whether iSCSI Volume is Connected
To check whether an iSCSI volume is connected, navigate to Storage - iSCSI. Current volumes will be listed. If
"Connected" is displayed under "Connection", the volume is currently connected from the client.
Configuring Access Restrictions
A CHAP name and secret can be configured for the entire iSCSI volume or each existing volume. Access restrictions
can be configured so that entering a target CHAP name and secret is required for each connection.
The TeraStation can perform mutual authentication (two-way authentication). Dual passwords ensure that only
authorized client computers can access the volume on the TeraStation.
Follow the procedure below to enable access restrictions.
Configuring Access Restrictions for the Entire TeraStation
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "iSCSI".
3 Click the Security tab.
58
Page 60

4 Click Edit under "Access Control (Target Discovery)".
5 Enable authentication, enter the target CHAP name and secret, and click OK.
Note: To enable mutual authentication in addition to target CHAP name and secret authentication, select the
"Enable mutual authentication" checkbox and enter the initiator CHAP secret.
To search or connect the volume which has mutual authentication enabled from Microsoft iSCSI Initiator,
initiator CHAP secret settings should be configured.
6 Click Close.
Configuring access restrictions for the entire TeraStation is finished.
Connecting Volumes on the Access-Restricted TeraStation
If access restrictions are configured for the entire iSCSI volume, that volume will not be detected by Microsoft iSCSI
Initiator. To connect that volume, the target CHAP name and secret should be authenticated.
59
Page 61

1 Open the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator.
2 Register the initiator CHAP secret to your computer first. If you didn't enable mutual authentication, skip this
step.
Click CHAP in the "Configuration" tab. In the "Initiator CHAP secret" box, enter the configured initiator CHAP
secret and click OK.
3 In the "Discovery" tab, click Discover Portal.
4 Enter the TeraStation's IP address in the "IP address or DNS name" box.
5 Click Advanced.
6 Select the "Enable CHAP log on" checkbox and enter the target CHAP name into the "Name" box and the
target CHAP secret into the "Target secret" box.
If mutual authentication is enabled, select the "Perform mutual authentication" checkbox.
7 Click OK twice.
8 In the "Targets" tab, select the volume from "Discovered targets" and click Connect - OK.
9 If the status of the selected volume is displayed as "Connected" under "Discovered targets", the connection is
established properly.
Accessing the volume on the access-restricted TeraStation is finished.
Configuring Access Restrictions for Individual Volumes
If access restrictions are configured for a volume, that volume cannot be accessed unless the target CHAP name and
secret are authenticated.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "iSCSI".
3 Click the volume to enable access restrictions.
60
Page 62

4 Enable authentication, enter a target CHAP name and secret, and click OK.
Note: To enable mutual authentication, select the "Enable" checkbox to the right of "Mutual Authentication"
and enter the initiator CHAP secret.
5 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Click OK, then Close.
Configuring access restrictions for each iSCSI volume is finished.
Connecting to Individual Volumes that are Access-Restricted
1 Open the Microsoft iSCSI Initiator.
2 Register the initiator CHAP secret to your computer first. If you didn't enable mutual authentication, skip this
step.
Click CHAP in the "Configuration" tab. In the "Initiator CHAP secret" box, enter the configured initiator CHAP
secret and click OK.
3 In the "Discovery" tab, click Discover Portal.
4 Enter the TeraStation's IP address in the "IP address or DNS name" box.
5 Click Advanced.
6 Select the "Enable CHAP log on" checkbox and enter the target CHAP name into the "Name" box and the
target CHAP secret into the "Target secret" box.
If mutual authentication is enabled, select the "Perform mutual authentication" checkbox.
7 Click OK twice.
61
Page 63

8 In the "Targets" tab, select the volume from "Discovered targets" and click Connect.
9 Click Advanced.
10 Select the "Enable CHAP log on" checkbox and enter the target CHAP name into the "Name" box and the
target CHAP secret into the "Target secret" box.
If mutual authentication is enabled, select the "Perform mutual authentication" checkbox.
11 Click OK twice.
12 If the status of the selected volume is displayed as "Connected" under "Discovered targets", the connection is
established properly.
Accessing the access-restricted volume is finished.
Expanding Volume Sizes
The volume size of the existing volumes can be expanded after they are created.
Notes:
• Expanding the volume size may erase all data in the volume depending on the formatting type. Back up the
data before expanding the volume size is recommended.
• To expand the volume size, the volume should be have "File I/O" selected for the "Backstore" option, or was
created in a drive or array with LVM enabled.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "iSCSI".
3 Select the volume to expand.
62
Page 64

4 Enter the desired volume size to add and click OK.
5 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Click OK, then Close.
Expanding the volume size is finished.
Deleting Volumes
To delete an existing volume, follow the procedure below.
Note: Deleting a volume will erase all data on the volume. Back up the data before deleting the volume.
1 In Settings, click Storage.
2 Click to the right of "iSCSI".
63
Page 65

3 Select the volume to delete and click Delete Volume.
4 Confirm that the volume is correctly selected on the screen and click OK.
5 The "Confirm Operation" screen will open. Enter the confirmation number, then click OK.
6 Click OK.
7 Click Close.
Deleting the volume is finished.
64
Page 66

Chapter 5 Backup
Back Up from the TeraStation
You can back up TeraStation folders to:
• A different folder on the TeraStation
• Another LinkStation on the network
• Another TeraStation on the network
You can also configure backup jobs from Easy Admin.
Note: For best results, using LAN port 3 to connect a backup device is recommended.
Preparing a Backup Destination
First, configure a folder as a backup destination.
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "Folder Setup".
3 Choose the folder to set as a backup destination.
4 Click Edit.
5 Under "LAN Protocol Support", select the "Backup" checkbox and click OK.
Note: If a backup access password is configured for the shared folder, that folder will not show up as a target
for the backup source or destination when configuring a backup job on another LinkStation or TeraStation. To
configure a backup access password, enter it into the "Backup Access Password" box. Leave this box blank if you
don't want a backup access password.
Backing Up to a LinkStation or TeraStation on Another Network When Connected
via VPN
You can back up to a LinkStation or TeraStation on another network as long as the two networks are connected by a
VPN. Follow this procedure to enter the IP address or hostname of the destination LinkStation or TeraStation.
If your setup meets the requirements below, you don't have to configure these settings:
• The source and destination TeraStations are on the same network.
• No backup access password is set for the destination TeraStation.
• No TeraStation from outside the subnet or connected by a VPN is used.
65
Page 67

1 In Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of "Backup".
3 Click List of LinkStations and TeraStations.
66
Page 68

4 Click Add under "Off-Subnet Devices", enter the IP address or hostname of the destination LinkStation or
TeraStation, and click Close.
Notes:
• To back up data between LinkStations or TeraStations on a network using jumbo frames, make sure that
both devices are configured to use identical (or similar) Ethernet frame sizes. If Ethernet frame sizes are
significantly different, the backup job may not be properly performed. In such a case, select the default frame
size (1500 bytes).
• You can also specify hostname by a fully qualified domain name (FQDN).
• Windows-based TeraStations with multibyte characters in the hostname may not be detected as a backup
destination, and folders in these devices cannot be used as backup destination folders.
Configuring a Backup Job
1 In Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of "Backup".
67
Page 69

3 Click Create New Job.
Note: Up to 8 backup jobs can be configured.
4 Select backup settings such as date and time to run.
The following types of backup jobs may be selected:
68
Page 70

Type Files included
All files in the source will be backed up to the destination. You can specify
how many backup versions to keep from 1–400, or select "Unlimited" to keep
Normal backup
Overwrite (incremental)
Overwrite (differential)
Management backup
all backups until the drive is full. If a specific number of backup versions is
specified, the backup destination folder should be on the same TeraStation
that the backup job is configured from, or on an external USB drive attached
to that TeraStation.
The first time the backup job runs like a normal backup. In subsequent
backups, files added to the source as well as files deleted from the source are
kept in the backup folder.
The first backup job runs like a normal backup. As each additional backup
job runs, files are added to and deleted from the backup folder. The backup
destination folder is always the same size as the backup source folder.
Each time a backup is executed, management information is stored, and
only files that have changed are copied or deleted. Data is retrieved from the
previous backup file for files that were not changed. This is useful for making
backups with limited space or for referencing status at a particular point in
time (for use for data snapshot applications). The destination folder for a
management backup should be a local folder on this TeraStation or on a USB
drive attached to it. The destination folder will be set to read-only. Do not use
folders from drives formatted with FAT.
You can specify how many backup versions to keep from 1–400, or select
"Unlimited" to keep all backups until the drive is full. The backup destination
folder should be on the same TeraStation that the backup job is configured
from, or on an external USB drive attached to that TeraStation.
5 Click Add.
6 Click Browse under "Backup Source Folder Name".
7 Select the shared folder that will be the backup source, then click OK.
8 Click Browse under "Backup Destination Folder Name".
69
Page 71

9 Select the backup destination and click OK.
10 Click OK. Jobs added to "Backup List" are displayed.
11 Click Close.
Backup Logs
The following backup error codes may be recorded in the backup log. Read the description and try the respective
corrective actions for the error.
Code Description Corrective Action Log Example
rsync error: errors
selecting input/
output files, dirs (code
3) at main.c(634)
[Receiver=3.1.0]
Can't write to backup
destination(target
disk is broken?).
rsync error: error
starting client-server
protocol (code 5) at
main.c(1504)
rsync error: error in
socket IO (code 10)
at clientserver.c(128)
[sender=3.1.0pre1]
rsync error: error
in file IO (code 11)
at receiver.c(389)
[receiver=3.1.0]
Code 3
Code 5
Code 10
Code 11
The backup destination USB
drive could not be found.
The backup destination shared
folder could not be found.
The Ethernet cable was
disconnected from the backup
source TeraStation when the
backup job started.
The drive capacity of the
backup destination TeraStation
became full.
Verify that the backup destination
USB drive is connected to the
TeraStation properly.
Verify that the Ethernet cable is surely
connected and that the hub or other
devices on the network are turned on.
Reconnect the Ethernet cable.
Delete unnecessary files and folders.
70
Page 72

Code Description Corrective Action Log Example
Code 12
Code 14
Code 22
Code 20
Code 23
Code 23
Could not communicate
between backup source and
destination TeraStations.
The settings of the TeraStation
were changed while the
backup job was running.
Insufficient memory on the
TeraStation was not enough
so that the backup job did not
run.
The connection was
disconnected while the
backup job was running.
Invalid characters were used in
the filename or folder name of
the backup destinations.
The backup destination files
were updated while the
backup job was running.
4 GB or more files were backed
up to the FAT32-formatted USB
drive.
The TeraStation backed up the
data to the FAT32-formatted
USB drive, then the upper- or
lowercases of filename and
folder name on the backup
source TeraStation were
changed.
Verify that the Ethernet cable is surely
connected and that the hub or other
devices on the network are turned on.
Do not change the settings while the
backup job is running. If changed, the
connection is temporarily terminated
and the backup job will fail.
Reduce the number of backup
destination files or disable any other
functions running at the same time.
Do not change the settings while the
backup job is running. If changed, the
connection is temporarily terminated
and the backup job will fail.
Change the filename or folder
name using compatible characters.
Available characters are described in
the "Adding a Shared Folder" section
in chapter 3.
Do not overwrite the backup
destination files while the backup job
is running. If updated, the backup
destination files will not be backed up
and the backup job will fail.
Reduce the file size to 4 GB or less or
change the file system to one other
than FAT32. Refer to the "Adding an
External Drive" section in chapter 4
for the compatible file systems.
Do not change the upper- or
lowercase of filenames and folder
names on the backup source
TeraStation if the backup destination
USB drive is formatted to FAT32. Linux
on the TeraStation is case-sensitive
but FAT isn't, so the same filename
and folder name that only differs
in upper- or lowercase will not be
identified and treated as the same file
or folder. To back up properly, using
XFS or ext3 is recommended.
rsync error: error in
rsync protocol data
stream (code 12) at
io.c(515)
ERROR: out of
memory in flist_
expand
rsync error: error
allocating core
memory buffers
(code 22) at util.c(120)
[sender=2.6.8]
rsync: fork failed in
do_recv: Cannot
allocate memory (12)
rsync error: error
in IPC code (code
14) at main.c(655)
[receiver=2.6.8]
rsync error: received
SIGINT, SIGTERM, or
SIGHUP (code 20) at
rsync.c(242)
rsync error: some
files could not be
transferred (code 23)
at main.c(702)
rsync error: some
files could not be
transferred (code 23)
at main.c(702)
71
Page 73

Code Description Corrective Action Log Example
Code 24
Code 30
B14
B101
B102
B103
B104
B105
B106
B107
The backup destination files
were updated while the
backup job was running.
The Ethernet cable was
disconnected from the
backup source or destination
TeraStations while the backup
job was running.
Insufficient TeraStation
memory.
The backup destination
TeraStation does not exist.
The backup source folders on
the backup source TeraStation
do not exist.
The backup destination folders
on the backup destination
TeraStation do not exist.
The drives were not
recognized.
The file systems of the USB
drive are not supported.
The device files such as "/dev/
null" etc. does not exist.
Do not overwrite the backup
destination files while the backup job
is running. If updated, the backup
destination files will not be backed up
and the backup job will fail.
Reconnect the Ethernet cable.
Restart the TeraStation and try again. -
Verify that the backup destination
TeraStation is turned on, the Ethernet
cables are connected properly,
and the hostname of the backup
destination TeraStation is not
changed.
Verify that the backup destination
folders on the backup destination
TeraStation exist in the shared folder
list and the backup destination
folders are configured for backup
from Settings.
Verify that the backup source folders
on the backup source TeraStation
exist in the shared folder list.
Verify that the backup destination
folders on the backup destination
TeraStation exist in the shared folder
list.
Verify that the drives are recognized
properly from Settings. If you
configure the "usbdisk" folders for
the backup source or destinations,
confirm if these folders exist in the
shared folder list.
Verify that the USB drive are
formatted to the compatible file
systems. If you configure the
management backup in the backup
job, FAT format cannot be used for the
backup destination.
Restart the TeraStation and try again. -
rsync warning:
some files vanished
before they could be
transferred (code 24)
at main.c
rsync error: timeout
in data send/receive
(code 30) at io.c(195)
[sender=3.1.0]
-
-
-
-
-
-
Replication
Replication copies all data from a share to a share on a different TeraStation. This is an easy way to configure a
reliable system to provide data protection in the event your main TeraStation fails. To configure replication, connect
an Ethernet cable to the LAN port of each TeraStation and follow the procedure below.
72
Page 74

Notes:
• For best results, use static IP addresses and LAN port 3 for connecting both replication TeraStations (source
and destination).
• Replication source data is copied to the replication destination folder with a differential overwrite. Any data
that is not in the replication source will be overwritten.
Preparing a Replication Destination
First, configure a folder as a replication destination.
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "Folder Setup".
3 Choose the folder to set as a replication destination.
4 Click Edit.
5 Under "LAN Protocol Support", select the "Backup" checkbox and click OK.
Note: Do not configure a backup access password for the shared folders. Folders with a backup access password
set cannot be selected as replication destinations.
Configuring a Replication Task
1 In Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of "Replication".
73
Page 75

3 Click Edit.
4 Click Add.
5 Click Browse under "Replication Source".
74
Page 76

6 Select the shared folder that will be the replication source, then click OK.
7 Click Browse under "Replication Target".
8 Select the shared folder that will be the replication destination, then click OK.
9 Click OK.
10 Click Ye s.
Notes:
• During setup, you may choose to encrypt and/or compress replication data. Encrypted data will be
transferred securely on the network. Compressed data will ease network loading and is recommended for
75
Page 77

slow or heavily loaded network connections. Either will increase the CPU load on the source TeraStation.
Encrypted and compressed data will be decrypted and decompressed on the destination TeraStation.
• A maximum of 64 shared folders can be configured for replication.
• Replication can also be used to copy all data from a share to a share on an attached external drive. Format
the drive with ext3 or XFS before using it for replication. Drives with FAT32 partitions are not supported with
replication.
• You can select the first and second level of shared folders and USB drives connected to the TeraStation as the
replication source. Folders whose names contain more than 80 alphanumeric characters or "@" cannot be
selected.
As the replication destination, you can select the first level of shared folders, USB drives, and on/off-subnet
NASs shared folders.
• Don't use the same TeraStation for both failover and replication, or replication and Time Machine.
• Don't configure replication from one source folder to multiple destination folders.
• If a network problem causes a replication error, unsynced data may be shown as "0" even though replication
is incomplete. Click Resync to recover from the replication error. All files from the source folder will be copied
to the destination folder.
Synchronizing Between Source and Destination Units Periodically
To copy files that are saved via other file sharing protocols such as AFP or FTP to the replication destination regularly,
configure "Periodic Sync" from Settings. Follow the procedure below.
1 In Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of "Replication".
76
Page 78

3 Click Periodic Sync.
4 Select "Daily" or "Weekly" from the "Schedule" drop-down list. If "Daily" is selected, configure the sync period. If
"Weekly" is selected, specify the week days and the sync period.
5 When the configuration is finished, click OK.
Failover
With failover, two TeraStations are connected to the network for redundancy. If an issue renders the main
TeraStation inaccessible, operation automatically switches to the backup TeraStation.
Data on both TeraStations stays up-to-date.
BackupMain
Switches automatically if failure occurs.
Failover will activate during any of the following situations:
• The backup TeraStation cannot detect the main TeraStation within a specified time
77
Page 79

If the backup TeraStation has not received a packet from the main TeraStation within a specified time, the backup
TeraStation considers the main TeraStation to have failed. By default, it will try 5 times and wait 60 seconds. If this
is triggered by accident, reconfigure failover from the main TeraStation.
• Errors
Failover will occur if any of the following errors occur:
E12 (cooling failure), E14 (cannot mount RAID array), E16 (drive not found), E22 (cannot mount drive), E30 (drive
failure)
Notes:
• Only use identical model and capacity TeraStations for failover. If the capacity of the main TeraStation is larger
than that of the backup TeraStation, an I33 replication error will occur.
• All drive bays of a TeraStation should be occupied if it will be used for failover. Failover will not work if a drive
is missing from any bay.
Usage Restrictions
Functional Restrictions
Failover is not available when any of the following functions are enabled:
Replication, sleep mode, encrypted drive volume, LVM volume, iSCSI volume, port trunking, cloud storage, Dropbox
Sync, hot spare, access restrictions by Active Directory domain
Setting Restrictions
The following functions will not be available while failover is enabled:
Initializing settings, changing the RAID settings, formatting drives, iSCSI volume, changing the backup unit's
settings, turning the TeraStation on and off, updating the firmware.
While failover is enabled, shutdown, power-on, and firmware update operations can be made available by
temporarily changing the TeraStation to maintenance mode. Maintenance mode can be enabled or disabled at
Backup - Failover in the main TeraStation's Settings. Click Maintenance mode to enable maintenance mode, or click
Cancel maintenance mode to disable maintenance mode.
To update the firmware while in maintenance mode, the main TeraStation can be updated from Settings, but the
backup TeraStation cannot. Download the firmware updater from the Buffalo website for the backup TeraStation
and try updating the firmware through it.
Non-Transferable Settings
The settings below are not copied from the main TeraStation to the backup TeraStation. Make a note of the original
settings so that they can be configured manually if failover errors.
WebAccess*, UPS synchronization, SNMP (when using SNMPv3), the backup job settings either if specifying shared
folders on the backup TeraStation or USB drives as the backup destination, and USB drives' shared folder settings
* After failover, re-register your BuffaloNAS.com account for WebAccess on the new main TeraStation if LAN port 1 is
assigned a new static IP address or using DHCP. If the new main TeraStation inherits the original static IP address for
LAN port 1, WebAccess settings will be transferred and you will not need to reconfigure it.
Using with UPS
Once failover is configured, you cannot set up a UPS for the backup TeraStation. Configure your UPS before
configuring failover. UPS recovery can be configured for both the main and backup TeraStations. However, the UPS
settings of the main TeraStation will not be copied to the backup TeraStation.
78
Page 80

If the backup TeraStation is configured to sync with the UPS connected to the main TeraStation, and the main
TeraStation becomes unavailable, the backup TeraStation will not be able to detect a power outage. In this case,
move the UPS cable from the main TeraStation to the backup TeraStation and reconfigure the UPS link settings.
Configuring Failover
Use the same LAN ports for transferring data and it is recommended that both TeraStations are configured with
static IP addresses for the purposes of failover. It is also recommended to use LAN port 3 for failover. This section
explains using an example with LAN ports 1 and 3.
Using the Same LAN Port for Both Failover and Connecting to the Network
Using this setup, if the main TeraStation fails, the backup TeraStation will replace it completely. The backup
TeraStation will be updated over normal network traffic.
LAN port 3
(Static IP)
Main
Network
LAN port 3
(Static IP)
Backup
Using Different LAN Ports for Connecting to the Network and Failover
With this setup, the backup TeraStation and main TeraStation are connected by a second Ethernet cable connecting
their LAN 3 ports. Updating is done over this dedicated network path, so updates are quicker and don't interfere
with normal network traffic.
LAN port 3
LAN port 1
(Static IP)
Main
Network
LAN port 1
(Static IP)
Backup
(Static IP)
LAN port 3
(Static IP)
• LAN Port 1 for Alive Check and LAN Port 3 for Failover
Select the IP address labeled "(LAN1)" for the LAN port setting of "IP Settings for File Sharing" and select "(LAN3)"
for "Backup LAN Port" in Settings.
• LAN Port 3 for Both Alive Check and Failover
Select the IP address labeled "(LAN3)" for the LAN port settings both "IP Settings for File Sharing" and "Backup
LAN Port" in Settings.
79
Page 81

Configuration
1 In Settings for the main TeraStation, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of "Failover".
3 Click Configure Failover.
80
Page 82

4 Select a TeraStation to be the backup destination device and enter its administrator username and password
(the username is "admin", the password is "password" by default).
5 Select the LAN port to be used for sharing files and enter a virtual IP address and subnet mask.
About Virtual IP Address:
A virtual IP address is an IP address that will be used for file sharing while failover is configured. By assigning
a different IP address from the one to be assigned to the LAN port, you can access the TeraStation for sharing
files, as well as open Settings using the virtual IP address. This IP address will be inherited to the backup
TeraStation when failover occurs, so you can access the backup TeraStation even if you don't know the backup
TeraStation's static IP address.
Configure an unused IP address for the virtual IP; make sure it uses the same segment as the main and backup
TeraStations.
6 Select the LAN port to be used for transferring data via failover, then click Continue.
7 If the administrator username and password is correct, the backup TeraStation will beep. Press and hold the
function button to accept the settings from the main TeraStation. When you press the function button, the
backup TeraStation will stop beeping. Hold it down until the backup TeraStation beeps again.
8 The I51 message will display on the LCD panel and NAS Navigator2 for both TeraStations. Wait until
initialization finishes. Failover is configured after it finishes and the I51 message disappears.
Notes:
• If replication is configured for more than one folder, initialize the TeraStation before configuring failover.
• The main TeraStation cannot be used as the backup location for Time Machine.
• Do not use the same TeraStation for both failover and replication, or failover and Time Machine.
• If email notification is enabled and failover occurs, navigate to Management - Email Notification - Edit in the
main TeraStation's Settings and click OK.
• Ethernet frame size settings for main and backup TeraStations should be 1500 bytes. To change the Ethernet
frame size, navigate to Network - IP Address - Edit, and change the Ethernet frame size to "1500" bytes.
• Files whose filenames contain more than 80 alphanumeric characters will not be backed up.
• If the I33 error message appears on the LCD panel, navigate to Backup - Replication and click Resync.
81
Page 83

• If failover occurs unexpectedly due to issues such as network problems, even if neither TeraStation has failed,
log in to both the main and backup TeraStations' Settings interface, reset the failover settings, and configure
it again.
• The RAID array on the backup TeraStation may be reconfigured and resynchronized as part of the failover
configuration process. This is expected behavior and not an error.
Switching to the Backup Unit Manually
If "Switch to backup unit manually" is selected in the Advanced Settings tab on Settings, the backup TeraStation
will not replace the main TeraStation if the main TeraStation fails. To have the backup TeraStation replace the main
TeraStation, you can either:
• Log in to Settings for the backup TeraStation and click Set as Main Unit.
• Or, press and hold down the function button on the backup TeraStation.
Synchronizing Between Main and Backup Units Periodically
To copy files that are saved via other file sharing protocols such as AFP or FTP to the backup TeraStation regularly,
configure "Periodic Sync" from Settings. Follow the procedure below.
1 In Settings for the main TeraStation, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of "Failover".
3 Click the Periodic Sync tab.
82
Page 84

4 Click Edit.
5 Select "Daily" or "Weekly" from the "Schedule" drop-down list. If "Daily" is selected, configure the sync period. If
"Weekly" is selected, specify the week days and the sync period.
6 When the configuration is finished, click OK.
Backing Up Your Mac with Time Machine
Time Machine is a backup program included with macOS. Configure your TeraStation as shown to use Time Machine.
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
83
Page 85

2 Move the AFP switch to the position to enable AFP.
3 Click to the right of "Folder Setup".
4 Choose a shared folder as your backup destination for Time Machine.
5 Click Edit.
6 Under "LAN Protocol Support", select the "AFP (Mac)" checkbox and click OK.
7 Click OK.
8 Click Close.
9 Click Backup.
10 Click to the right of "Time Machine".
11 Click Edit.
12 Click Browse.
84
Page 86

13 Select the shared folder that you set in the previous step, then click OK.
14 Click OK.
15 Click OK.
16 Move the Time Machine switch to the position to enable Time Machine.
17 On the Mac, open System Preferences.
85
Page 87

18 Click Time Machine.
86
Page 88

19 Click Select Backup Disk.
20 Select the TeraStation, then click Use Disk.
87
Page 89

21 Enter a username and password with the rights to access the shared folder of the TeraStation, then click
Connect.
Note: If access restrictions are not configured on the destination share, log in with the administrator account.
The default username and password for the administrator account are "admin" and "password". If access
restrictions are configured, log in with an account with write privileges.
22 Time Machine will count down from 120 seconds, and the backup will begin.
88
Page 90

Chapter 6 Remote Access
WebAccess
WebAccess is a software utility for accessing the files in the shared folder of your TeraStation from your computer
or mobile devices through the Internet. Be careful when configuring WebAccess. Certain settings can make the
files in the shared folder available to anyone on the Internet, without any access restrictions.
Notes:
• You can also configure WebAccess from Easy Admin.
• WebAccess supports downloading up to 60,000 files at a time. Attempting to download up to 60,000 files at a
time may result in unexpected behavior.
1 In Settings, click File Sharing.
2 Click to the right of "WebAccess".
3 Click Edit.
89
Page 91

4 Configure the desired settings, then click OK.
• You may use the BuffaloNAS.com server as a DNS server, or disable it to use a different DNS server.
• Choose a "BuffaloNAS.com Name" and "BuffaloNAS.com Key" for your WebAccess account. Names and keys
may use 3 to 20 alphanumeric characters, underscores (_), and hyphens (-).
• If "Exclusive Session" is enabled, multiple users cannot be logged in to WebAccess at the same time. Only
the last login will be active.
• Enter a time in minutes (1 to 120, or "Unlimited") before inactive users are logged out of WebAccess.
5 Click OK.
6 Move the WebAccess switch to the position to enable WebAccess.
7 Click to the right of "Folder Setup".
8 Select a shared folder to publish.
Notes:
• For best results, create a new dedicated share for WebAccess.
• When accessing shared folders through WebAccess from a remote location, a username and password
may be required for certain operations. For best results, create a user account with permissions on the
WebAccess share before using WebAccess.
9 Click Edit.
10 Under "LAN Protocol Support", check "WebAccess" and click OK.
Notes:
• The following levels of security are available:
"Allow anonymous" - Anyone can access (view) shared folders.
90
Page 92

"Allow all groups and users" - All groups and users registered on the LinkStation or TeraStation can use
WebAccess.
"Use inherited folder permissions" - Users and groups have the same access permissions with WebAccess that
they do locally. If access restrictions are not set for the shared folder, then this option will not be shown.
• When a user or group can access a folder through WebAccess depends on a combination of WebAccess
settings and the shared folder's settings.
WebAccess permissions Allow anonymous
Folder setup
Folder attribute
Not logged in R R - - - User with read and
write access
User with read-only
WebAccess
account
R: Read only, R/W: Read and write, -: No access
There are many ways to access WebAccess folders depending on your device.
• From a computer, supported browsers include Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Google Chrome, Internet Explorer 9 or
later, Safari 9 or later.
Instructions: http://buffalonas.com/manual/en/
• To access from an iOS device, install the "WebAccess i" application from the App Store.
Instructions: http://buffalonas.com/manual/i/en/
• To access from an Android device, install the "WebAccess A" application from Google Play.
Instructions: http://buffalonas.com/manual/a/en/
• To access from a Windows Phone, install "WebAccess" from the Windows Phone Store.
Instructions: http://buffalonas.com/manual/wp/en/
access
Group with read and
write access
Group with read-only
access
Other users R/W R R/W R - -
Read
and
write
R/W R R/W R R/W R
R/W R R/W R R R
R/W R R/W R R/W R
R/W R R/W R R R
Read
only
Allow all groups
and users
Read
and
write
Read
only
Use inherited
folder permissions
Read
and
write
Read
only
FTP
By default, the TeraStation's shares are only accessible by users connected to the same network or router as the
TeraStation. The optional FTP server allows users outside the local network to access the TeraStation.
Note: FTP is intended for users who already have FTP client software and have experience with it.
1 In Settings, move the FTP switch to the position to enable FTP.
2 Click to the right of "Folder Setup".
3 Choose a folder to enable remote FTP access on.
91
Page 93

4 Click Edit.
5 Select read-only or read and write for the shared folder's attribute; under "LAN Protocol Support", select the
"FTP" checkbox and click OK.
Accessing the TeraStation with an FTP Client
• To access the TeraStation via FTP, configure your FTP client software with the following settings:
Hostname: IP address of the TeraStation
Username: The TeraStation's username
Password: The TeraStation's password
Port: 21
• Shared folders connected by FTP are available from the "/mnt" directory. The default locations are:
For a RAID mode other than RAID 1 (two arrays):
/mnt/array1/share
/mnt/usbdisk1
/mnt/usbdisk2
/mnt/usbdisk3 (if your TeraStation has 3 USB ports.)
For RAID 1 (two arrays):
/mnt/array1/share
/mnt/array2/share2
/mnt/usbdisk1
/mnt/usbdisk2
/mnt/usbdisk3 (if your TeraStation has 3 USB ports.)
For JBOD:
/mnt/disk1/share
/mnt/disk2/share2
/mnt/disk3/share3
/mnt/disk4/share4
/mnt/usbdisk1
/mnt/usbdisk2
/mnt/usbdisk3 (if your TeraStation has 3 USB ports.)
Accessing the TeraStation with an Anonymous User
• To allow anonymous access to your FTP share, disable access restrictions.
• To access the TeraStation via anonymous FTP, configure your FTP client software with the following settings:
Hostname: IP address of the TeraStation
Username: anonymous
Password: any character string
Port: 21
*If the TeraStation joins a domain, anonymous users cannot access it.
Notes:
• If a file was created or copied by AFP, you may not be able to delete it using an FTP connection. If this occurs,
use an SMB or AFP connection instead to delete the file.
• For FTP connections, make sure that the total filename including directory path is 250 single-byte characters
or less.
*
92
Page 94

Cloud Storage
The TeraStation supports Amazon S3, a fee-based online storage service provided by Amazon, and other cloud
storage services that share the Amazon S3 API. Follow the procedure below to configure your TeraStation to use
with your cloud storage service:
Note: Set the TeraStation's time settings to the correct time. Using NTP is recommended. To configure NTP
settings on the TeraStation, refer to the "Name, Date, Time, and Language" section in chapter 7.
Configuring Cloud Storage
1 In Settings, click Web Services.
2 Click to the right of "Cloud Storage".
3 Click Add.
93
Page 95

4 Select the service name from the drop-down list. Enter the bucket name, access key ID, and secret access key;
select the storage class and the connection protocol, then click OK.
5 Enter a shared folder name to use with the cloud storage service and click OK.
94
Page 96

6 Under "LAN Protocol Support", select the "Backup" checkbox and enter the desired shared folder settings. Click
OK.
7 Click OK.
8 Click Close.
Note: Do not configure a folder that is created through the procedure above as replication destination folder.
Uploading Files to Cloud Storage
To upload files to cloud storage, using backup job is recommended.
1 In Settings, click Backup.
2 Click to the right of "Backup".
95
Page 97

3 Click Create New Job.
4 Select backup settings such as date and time to run.
5 Click Add.
96
Page 98

6 Click Browse under "Backup Source Folder Name".
7 Select the shared folder that uploaded files will be saved to, then click OK.
8 Click Browse under "Backup Destination Folder Name".
9 Select the shared folder created from the "Configuring Cloud Storage" section above, then click OK.
10 Click OK. Tasks added to "Backup List" are displayed.
11 Click Close.
97
Page 99

Notes:
• If a shared folder created through this process is configured to use NFS, it cannot be mounted from an NFS
client.
• Files cannot be uploaded to this shared folder using WebAccess.
• If using the cloud storage through a proxy server, click Proxy Settings. In the displayed page, you can select
if using the configured settings or setting identical proxy server. If using the identical proxy server, select
"New settings" and enter the proxy server name, port number, username, and password. Ask your network
administrator for detailed proxy server settings.
• To use after the network was temporarily disconnected, click Reconnect.
• If a file is added to the bucket from a folder other than the TeraStation's remote replication folder, it may take
more than an hour for the file to appear in the TeraStation's remote replication folder. However, when a file is
added to the TeraStation's remote replication folder, it immediately appears in the bucket.
• If you enter an incorrect bucket name and then cancel editing the cloud storage service settings, that wrong
bucket name may still accidentally be registered. If this happens, reconfigure the cloud storage service
settings correctly starting from step 4.
• Be careful with existing files in the destination folder, as files with the same name will be overwritten even if
copied files are older.
• If you copy a file to the remote folder using File Explorer or a backup process, the file will also be uploaded
sequentially to the cloud storage bucket. This second uploading process will start in the background during
the first copying process and will not be visible. If you shut down or restart the TeraStation immediately after
copying a file to the remote folder, the file may not be uploaded to the bucket. Try copying the file again if
this occurs.
• If you encounter any upload or download errors, click Error Log. The log will display the filename and
operation during which the error occurred.
• If uploading fails, try copying the file again. If it still fails, click Reconnect or set the cloud storage switch to off
and on again, then restart the cloud storage service.
• If transferring or accessing 1 TB or more files from cloud storage, make sure there is enough free space on
the TeraStation for temporary file caching. For example, when uploading 1 TB of files to cloud storage, it is
recommended to keep at least 2 TB of free space available.
Dropbox Sync
The TeraStation supports syncing with Dropbox, the online cloud service. Once connected, you can share
TeraStation files via Dropbox (or Dropbox files via TeraStation). To link your TeraStation with your Dropbox account,
follow the procedure below.
Note: To use Dropbox Sync, you need a Dropbox account and an available empty Dropbox folder. If you don't
have a Dropbox account, or if you need to create a new empty Dropbox folder, refer to the Dropbox website.
Configuring a New Task
1 In Settings, click Web Services.
2 Move the Dropbox Sync switch to the position to enable Dropbox Sync.
98
Page 100

3 Click to the right of "Dropbox Sync".
4 Click Add.
5 Click View Dropbox Authentication Page.
6 The authentication site that is offered by Dropbox will be displayed. Log in to the website with your Dropbox
account, then click Allow.
99
 Loading...
Loading...