Page 1
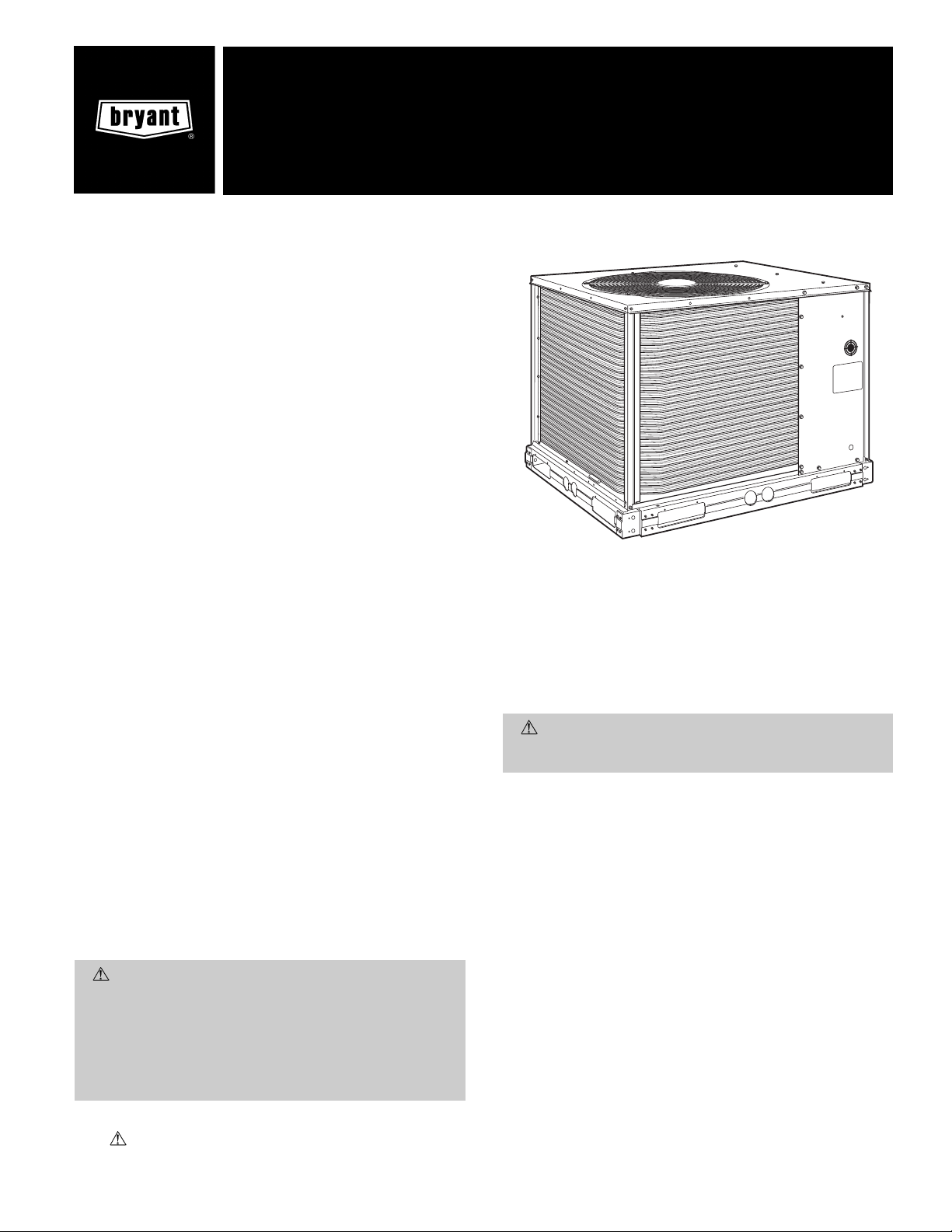
installation, start-up and
service instructions
COMMERCIAL AIR-COOLED
CONDENSING UNITS
IMPORTANT —READ BEFORE INSTALLING
1. Read and become familiar with these installation
instructions before installing this unit (Fig. 1).
2. Be sure the installation conforms to all applicable local
and national codes.
3. These instructions containimportantinformation for the
proper maintenance and repair of this equipment. Retain these instructions for future use.
CONTENTS
Page
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS ....................... 1
INSTALLATION .................................1-9
I. Locate the Unit ............................ 2
II. Rig and Place Unit ......................... 2
III. Compressor Mounting ...................... 2
IV. Unit Refrigerant Piping Connections .......... 2
V. Electrical Connections ...................... 6
VI. Accessory Installation ...................... 9
PRE-START-UP ..................................9
START-UP ..................................... 10
I. Start-Up and Adjustments .................. 10
CARE AND MAINTENANCE ...................... 10
SERVICE .....................................11-13
I. Cleaning ................................ 11
II. Lubrication .............................. 11
III. Condenser-Fan Adjustment ................ 11
IV. Capacity Control .......................... 12
V. Compressor Removal ..................... 12
VI. Crankcase Heater ......................... 12
VII. Refrigerant Charge ........................ 12
VIII. Refrigerant Service Ports ...................12
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE ....................14,15
SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS
WARNING:
ation, service, maintenance, or use can cause explosion, fire, electric shock, or other occurrences which may
injure you or damage your property. Consult a qualified installer or service agency for information or assistance. The qualified installer or agency must use only
factory-authorized kits or accessories when repairing this
product.
Recognize safety information. This is the safety-alert symbol. ( ) When you see this symbol on the unit and in
instructions or manuals, be alert to the potential for personal injury.
Improper installation, adjustment, alter-
569C
576B
Cancels: II 569C-72-3 II 569C-72-4
5/1/99
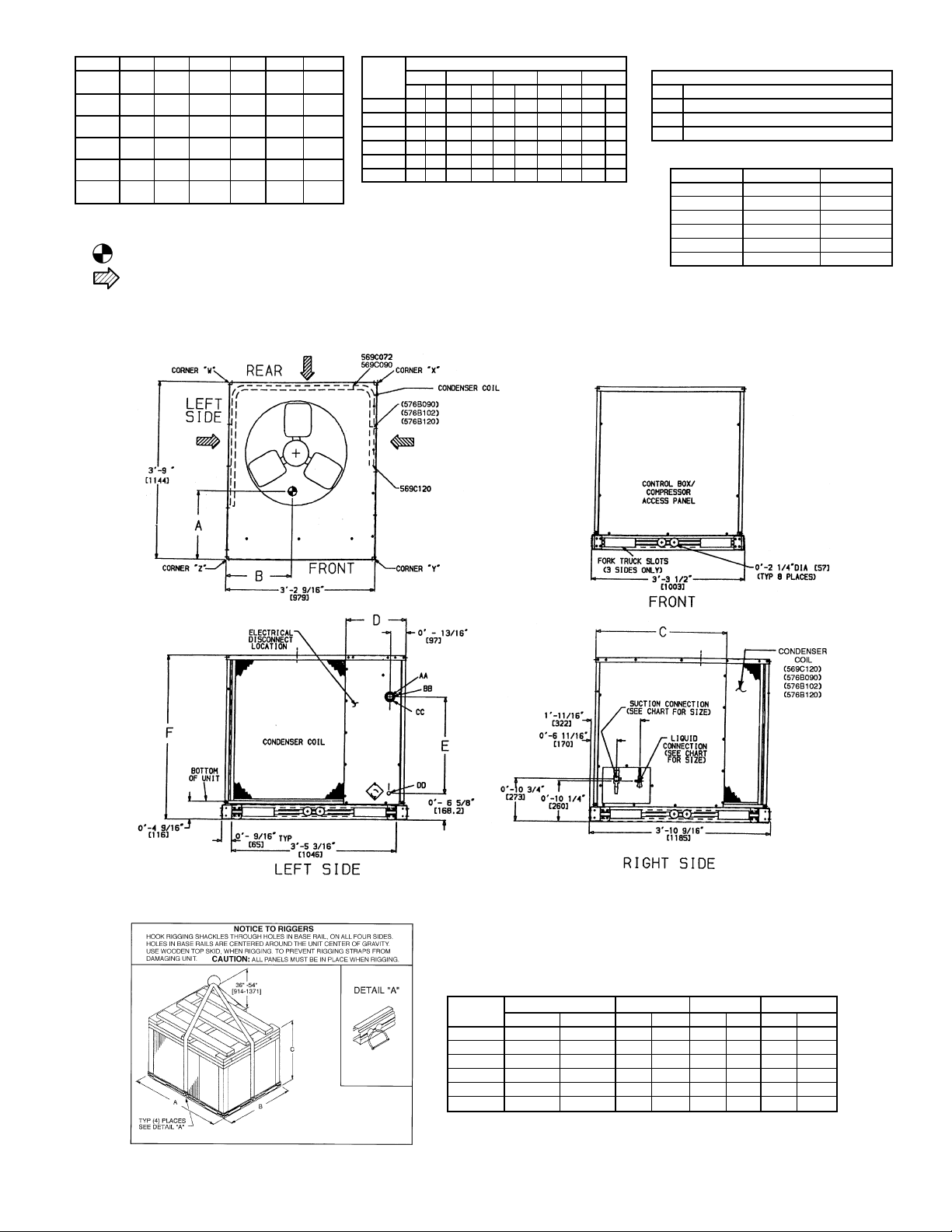
Fig.1—Typical Unit (569C072 Shown)
Understand the signal words — DANGER, WARNING, and
CAUTION. These words are used with the safety-alert symbol. Danger identifies the most serious hazards which will
result in severe personal injury or death. Warning indicates
a condition that could result in personal injury. Caution is
used to identify unsafe practices which would result in minor
personal injury or product and property damage.
WARNING:
nance operations on unit, turn off main power switch
to unit. Electrical shock could cause personal injury.
1. The power supply (volts, hertz, and phase) must correspond to that specified on unit rating plate.
2. The electrical supply provided by the utility must be sufficient to handle load imposed by this unit.
3. Refer to the Locate the Unit section on page 2 and
Fig. 2 and 3 for locations of electrical inlets, required
clearances, and weight distribution based on recommended support points before setting unit in place.
4. This installation must conform with local building codes.
Refer to local plumbing or wastewater codes and other
applicable local codes.
NOTE: When installing any accessory item, see the manufacturer’s installation instructions packaged with the accessory. A qualified agency must use factory-authorized kits or
accessories when modifying this unit.
The 569C072,090, and 120 units use hermetic compressors.
The 576B090,102, and 120 units use semi-hermetic compressors. Refer to Tables 1A and 1B.
Before performing service or mainte-
INSTALLATION
Page 2
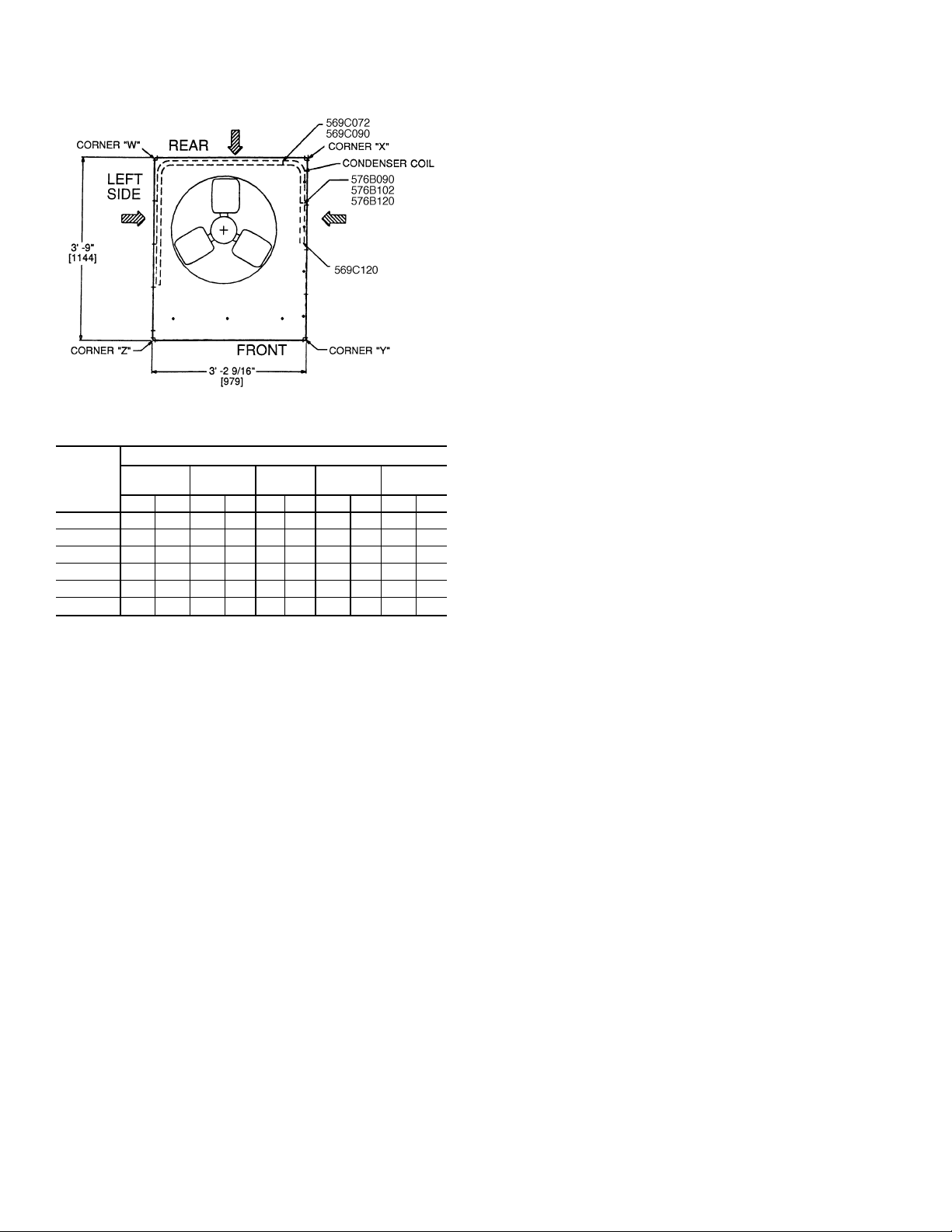
NOTE: If vibration isolators are required for a particular in-
stallation, use corner weight information in Fig. 2 to make
proper selection.
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
2. See Fig. 3 for additional information.
WEIGHT CHART*
UNIT
569C072 340 154 86 39 53 24 77 35 124 56
569C090 370 168 86 39 78 35 99 45 107 49
569C120 395 179 89 40 92 42 109 49 105 48
576B090 510 231 115 52 89 40 133 60 173 87
576B102 564 256 133 50 97 44 141 64 193 88
576B120 564 256 133 60 97 44 141 64 193 88
*Weights are for aluminum coils.
Std Unit
Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg
CornerWCornerXCornerYCorner
Z
Fig.2—Weight Distribution
I. LOCATE THE UNIT
A. Clearance
Maintain clearance around and above unit to provide minimum distance from combustible materials, proper airflow,and
service access. Refer to Fig. 2 and 3.
Minimum clearance (local codes or jurisdiction may prevail):
a. Bottom to combustible surfaces 0 inches.
b. Condenser coil, for proper airflow, 36 in. (914 mm) one side,
12 in. (305 mm) the other. The left or rear side receiving
the greater clearance is optional.
c. Overhead, 60 in. (1524 mm) to ensure proper condenser
fan operation.
d. Between units, control box side, 42 in. (1067 mm) per NEC
(National Electrical Code, U.S.A. Standard).
e. Between unit and ungrounded surfaces, control box side,
36 in. (914 mm) per NEC.
f. Between unit and block or concrete walls and other grounded
surfaces, control box side, 42 in. (1067 mm) per NEC.
Although unit is weatherproof, guard against water from higher
level runoff and overhangs.
Slab-mounted units should be at least 4 in. (102 mm) above
the highest expected water level (flood and runoff). Do not
use the unit if it has been under water.
II. RIG AND PLACE UNIT
Inspect unit for transportation damage. File any claim with
transportation agency. Keep unit upright and do not drop.
Spreader bars are not required if top crating is left on unit.
Rollers may be used to move unit across a roof. Level by using unit frame as a reference. See Tables 1A and 1B and Fig. 4
for additional information. Operating weight is shown in
Tables 1A and 1B.
These units are designed for overhead rigging only. Rig with
packaging assembly and wood bumper strips in place to prevent unit damage by rigging cable. As further protection for
coil faces, plywood sheets may be placed against sides of unit,
behind cables. Run cables to a central suspension point so
that angle from the horizontal is not less than 45 degrees.
Raise and set unit down carefully.
If it is necessary to roll unit into position,mount unit on longitudinal rails, using a minimum of 3 rollers. Apply force to
rails, not unit. If unit is to be skidded into position, place it
on a large pad and drag it by the pad. Do not apply any force
to unit.
Raise from above to lift unit from rails or pad when unit is in
final position.
Lifting holes are provided in base rails as shown in Fig. 4.
Refer to rigging instructions on unit.
IMPORTANT: If unit has forklift protection skids, be sure to
remove forklift protection skids from under unit before setting unit in place.
After unit is in position, remove shipping materials and rigging skids.
III. COMPRESSOR MOUNTING
Compressors are shipped from the factory held down by 4 bolts.
After unit is installed, loosen each bolt until the snubber washer
can be moved with finger pressure (376B units only). See Fig. 5.
IV. UNIT REFRIGERANT PIPING CONNECTIONS
Suction connection is sweat with plastic cap; liquid connection is sweat with plastic cap. Refer to Table 2 for refrigerant
piping sizes. Follow standard piping practices.
A. Size Refrigerant Lines
Consider length of piping required between condensing unit
and evaporator, amount of liquid lift, and compressor oil
return. See Table 3 for design details and line sizing. Refer
to evaporator installation instructions for additional
information.
—2—
Page 3
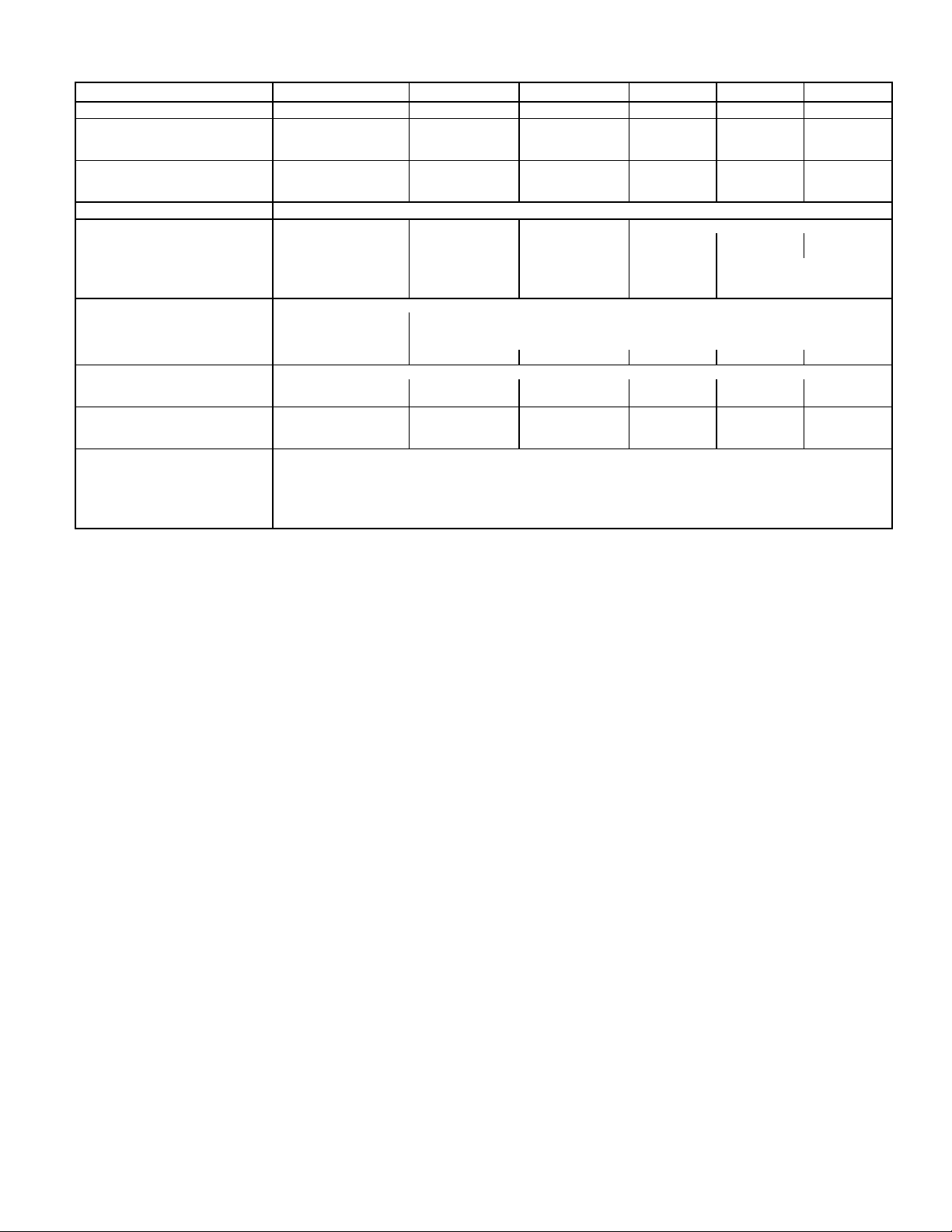
Table 1A — Specifications (English)
UNIT 569C072 569C090 569C120 576B090 576B102 576B120
NOMINAL CAPACITY (Tons) 67
OPERATING WEIGHT (lb)
Aluminum Coils (Standard) 340 370 395 510 564 564
Copper Coils (Optional) 386 438 472 578 632 632
RIGGING WEIGHT (lb)
Aluminum Coils (Standard) 390 420 445 560 614 614
Copper Coils (Optional) 436 488 522 628 682 682
1
⁄
2
10 71⁄
2
81⁄
2
10
REFRIGERANT* R-22
COMPRESSOR Bristol, Reciprocating Copeland, Scroll Copeland, Scroll Reciprocating, Semi-Hermetic
Quantity...Type 1...H26A72Q 1...ZR94KC 1...ZR125KC 1...06DA818 1...06DA824
Quantity Cylinders 2——4 6
Speed (Rpm) 3500 3500 3500 1750 1750
Oil Charge (oz) (ea) 65 85 110 88 128
CONDENSER FAN Propeller; Direct Drive
Quantity...Rpm 1...850 1...1100
Diameter (in.) 26 26
Motor Hp (NEMA)
Nominal Airflow (cfm) 3800 6500 7000 6500 6500 6500
CONDENSER COIL Enhanced Copper Tubes, Aluminum Lanced Fins
Face Area (sq ft) 12.24 15.75 20.5 18.0 18.0 18.0
Storage Capacity (lb)† 11.26 14.88 18.87 16.56 16.56 16.56
CONNECTIONS (sweat)
Suction (in.) 1
Liquid (in.)
CONTROLS
Pressurestat Settings (psig)
High Cutout 426 6 7
Cut-in 320 6 20
Low Cutout 7 6 3
Cut-in 22 6 5
LEGEND
NEMA — National Electrical ManufacturingAssociation
*Unit is factory supplied with holding charge only.
†Storage capacity of condenser coil with coil 80% full of liquid R-22 at
124 F.
1
⁄
3
1
⁄
8
1
⁄
2
11⁄
8
1
⁄
2
NOTE: Unit 576B120 has one step of unloading. Full load is 100% capacity, and one step of unloading is 67% capacity. Unit 576B120 has
the following unloader settings: load is 70 6 1 psig and unload is
60 6 2 psig.
11⁄
8
5
⁄
8
3
⁄
4
11⁄
8
1
⁄
2
11⁄
8
5
⁄
8
1...06DH824
(See Note)
11⁄
8
5
⁄
8
—3—
Page 4
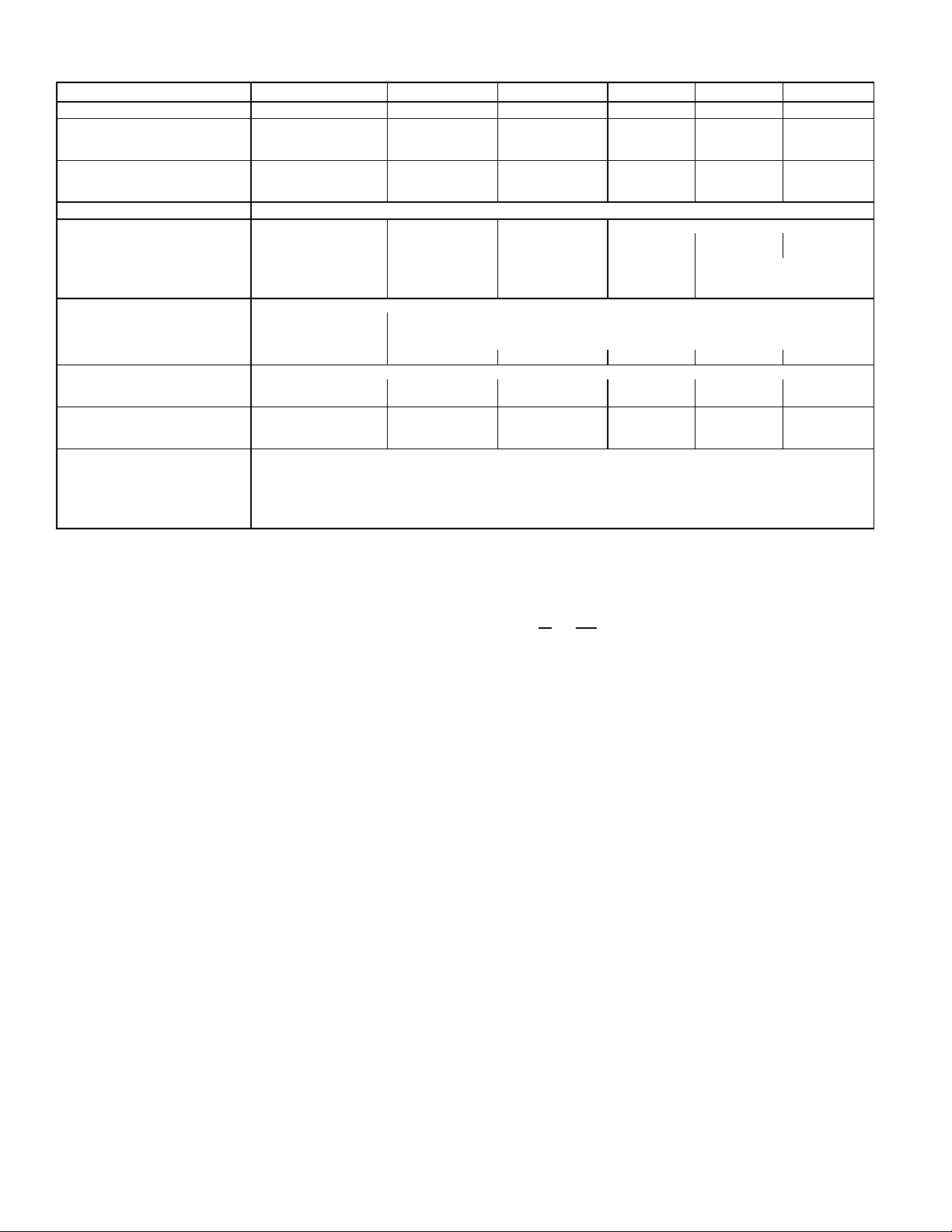
Table 1B — Specifications (SI)
UNIT 569C072 569C090 569C120 576B090 576B102 576B120
NOMINAL CAPACITY (kW) 21 26 35 26 29.9 35
OPERATING WEIGHT (kg)
Aluminum Coils (Standard) 154 168 179 231 256 256
Copper Coils (Optional) 175 199 214 262 287 287
RIGGING WEIGHT (kg)
Aluminum Coils (Standard) 176 191 202 254 279 279
Copper Coils (Optional) 198 221 237 285 309 309
REFRIGERANT* R-22
COMPRESSOR Bristol, Reciprocating Copeland, Scroll Copeland, Scroll Reciprocating, Semi-Hermetic
Quantity...Type 1...H26A72Q 1...ZR94KC 1...ZR125KC 1...06DA818 1...06DA824
Quantity Cylinders 2——4 6
Speed (R/s) 58.4 58.4 58.4 29.2 29.2
Oil Charge (L) (ea) 1.92 2.51 3.25 2.60 3.78
CONDENSER FAN Propeller; Direct Drive
Quantity...R/s 1...14.2 1...18.3
Diameter (mm) 660 660
Motor Hp (NEMA)
Nominal Airflow (L/s) 1800 3050 3300 3050 3050 3050
CONDENSER COIL Enhanced Copper Tubes, Aluminum Lanced Fins
Face Area (sq m) 1.14 1.46 1.90 1.67 1.67 1.67
Storage Capacity (kg)† 5.1 6.75 8.6 7.5 7.5 7.5
CONNECTIONS (sweat)
Suction (in.) 1
Liquid (in.)
CONTROLS
Pressurestat Settings (kPa)
High Cutout 2937 6 48
Cut-in 2206 6 138
Low Cutout 48 6 20
Cut-in 152 6 34
LEGEND
NEMA — National Electrical ManufacturingAssociation
*Unit is factory supplied with holding charge only.
†Storage capacity of condenser coil with coil 80% full of liquid R-22 at
51 C.
1
⁄
3
1
⁄
8
1
⁄
2
11⁄
8
1
⁄
2
NOTES:
1. Unit576B120 has one step of unloading. Full load is 100% capacity,
2. Equivalent mm values for connectors are as follows:
11⁄
8
5
⁄
8
and one step of unloading is 67% capacity. Unit 576B120 has the
following unloader settings: load is 483 6 6.9 kPa and unload is
414 6 13.8 kPa.
3
⁄
4
11⁄
8
1
⁄
2
11⁄
8
5
⁄
8
in. mm
1
⁄212.7
5
⁄815.9
11⁄828.6
1...06DH824
(See Note 1)
11⁄
8
5
⁄
8
—4—
Page 5
UNIT DIM. A DIM. B DIM. C DIM. D DIM. E DIM. F
569C072
569C090
569C120
576B090
576B102
576B120
NOTES:
1. Dimensions in [ ] are in millimeters.
1
⁄29 18-23⁄49 —18-21⁄49 18-45⁄169 28-95⁄
18-6
[470.0] [375.0] — [362] [415] [846.5]
18-89 18-6
[508.0] [470.0] — [381] [613] [1052.5]
18-99 18-89 28-09 18-39 28-
[533.4] [508.0] [609.6] [381] [613] [1052.5]
18-69 18-4
[457.2] [425.5] [858.8] [381] [613] [1052.5]
18-79 18-59 28-9
[482.6] [431.8] [858.8] [381] [613] [1052.5]
18-79 18-59 28-9
[482.6] [431.8] [858.8] [381] [613] [1052.5]
1
⁄29 —18-39 28-5⁄169 38-57⁄
5
⁄169 38-57⁄
3
⁄49 28-913⁄169 18-39 28-5⁄169 38-57⁄
13
⁄169 18-39 28-5⁄169 38-57⁄
13
⁄169 18-39 28-5⁄169 38-57⁄
16
9
16
9
16
9
16
9
16
9
16
9
2. Center of Gravity. See chart for dimensions.
3. Direction of Airflow.
4. Minimum clearance (local codes or jurisdiction may prevail):
a. Condenser coil, for proper airflow, 36 in. [914] one side, 12 in. [305]
the other.The left or rear side getting the greater clearance is optional.
b. Overhead, 60 in. [1524] to assure proper condenser fan operation.
UNIT
Std Unit Corner W Corner X Corner Y Corner Z
Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg Lb Kg
569C072 340 154 86 39 53 24 77 35 124 56
569C090 370 168 86 39 78 35 99 45 107 49
569C120 395 179 89 40 92 42 109 49 105 48
576B090 510 231 115 52 89 40 133 60 173 87
576B102 564 256 133 60 97 44 141 64 193 88
576B120 564 256 133 60 97 44 141 64 193 88
*Weights are for aluminum coils.
c. Between units, control box side, 42 in. [1067]
per NEC (National Electrical Code) (U.S.A.
Standard).
d. Between unit and ungrounded surfaces, con-
trol box side, 36 in. [914] per NEC.
e. Betweenunit and block or concrete walls and
other grounded surfaces, control box side,
42 in. [1067] per NEC.
5. With the exception of the clearance for the condenser coil as stated in note 4b, a removable
fence or barricade requires no clearance.
6. Unitsmay be installed on combustible floors made
from wood or Class A, B, or C roof covering
material.
WEIGHT CHART*
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
CONNECTION SIZES
3
AA 1
⁄89 DIA [35] FIELD POWER SUPPLY HOLE
BB 29 DIA [51] POWER SUPPLY KNOCK-OUT
1
⁄29 DIA [64] POWER SUPPLY KNOCK-OUT
CC 2
7
⁄89 DIA [22] FIELD CONTROL WIRING HOLE
DD
SERVICE VALVE CONNECTIONS — 60 Hz
UNIT SUCTION LIQUID
569C072 1
569C090 1
569C120 1
576B090 1
576B102 1
576B120 1
1
⁄89 [28.6]
1
⁄89 [28.6]
1
⁄89 [28.6]
1
⁄89 [28.6]
1
⁄89 [28.6]
1
⁄89 [28.6]
1
⁄29 [12.7]
1
⁄29 [12.7]
5
⁄89 [15.9]
1
⁄29 [12.7]
5
⁄89 [15.9]
5
⁄89 [15.9]
Fig. 3 — Base Unit Dimensions
UNIT
569C072 390 176 45.0 1143 38.5 978 35.5 904
569C090 420 191 45.0 1143 38.5 978 43.5 1105
569C120 445 202 45.0 1143 38.5 978 43.5 1105
576B090 560 254 45.0 1143 38.5 978 43.5 1105
576B102 614 279 45.0 1143 38.5 978 43.5 1105
576B120 614 279 45.0 1143 38.5 978 43.5 1105
*Weights are for aluminum coils.
RIGGING WEIGHT* A B C
lb kg in. mm in. mm in. mm
Fig. 4 — Rigging Label
—5—
Page 6
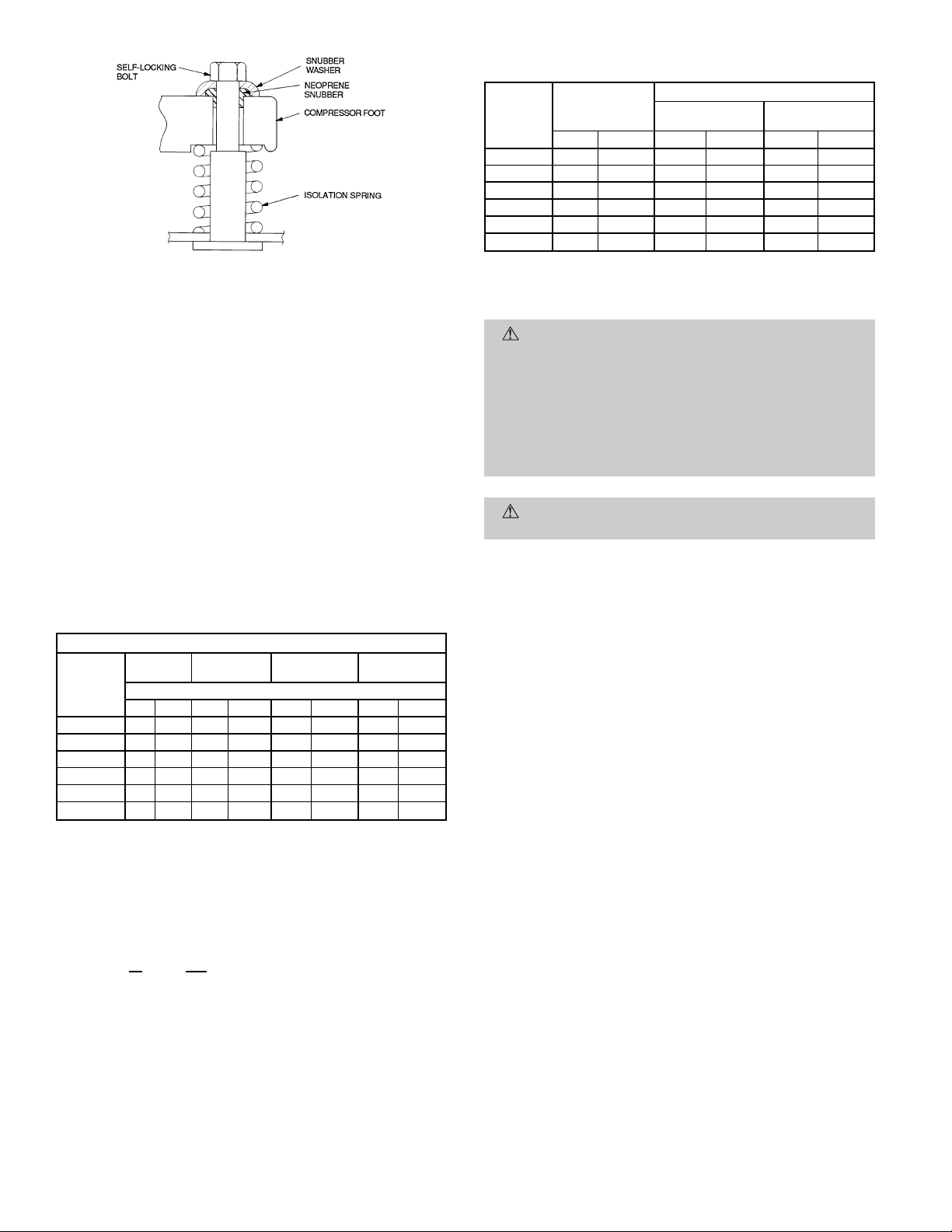
Table 3 — Liquid Line Data
Fig.5—Typical Compressor Mounting (576B Units)
B. Filter Drier and Moisture Indicator
The filter drier is factory installed. Moisture indicator is a
field-installed accessory and should be installed just after liquid line shutoff valve. Do not use a receiver. A receiver is not
supplied with the unit and should not be used.
NOTE: Unit is shipped with R-22 holding charge. System pressure must be relieved before removing caps. Recover refrigerant prior to brazing.
Pass nitrogen or other inert gas through piping while brazing to prevent formation of copper oxide.
Install field-supplied thermostatic expansion valve(s) in evaporator section. It is recommended that a field supplied liquid line solenoid be positioned in the main liquid line (near
the evaporator coil). It should be wired to close when compressor stops to minimize refrigerant migration during the
‘‘OFF’’ cycle.
Table 2 — Refrigerant Piping Sizes
LINEAR LENGTH OF PIPING — FT (M)
0-25
UNIT
(0-7.6)
LSLSLSLS
569C072
1
⁄211⁄
569C0901⁄211⁄
569C1205⁄811⁄
576B0901⁄211⁄
576B1025⁄811⁄
576B1205⁄811⁄
LEGEND
L—Liquid Line S—Suction Line
NOTES:
1. Pipe sizes are based on a 2° F (1° C) loss for liquid and suction
lines.
2. Pipe sizes are based on the maximum linear length shown for each
column, plus a 50% allowance for fittings.
3. Chargeunits with R-22 in accordance with unit installation instructions.
4. Line size conversion to mm is:
in. mm
1
⁄
2
5
⁄
8
1
1
⁄
8
13⁄
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
12.7
15.9
28.6
34.9
25-50
(7.6-15.2)
Line Size (in. OD)
1
⁄211⁄
⁄211⁄
⁄813⁄
⁄211⁄
⁄811⁄
⁄811⁄
8
8
8
8
8
8
1
5
1
5
5
50-75
(15.2-22.9)
1
⁄
2
11⁄
5
⁄
8
11⁄
5
⁄
8
13⁄
5
⁄
8
11⁄
5
⁄
8
13⁄
5
⁄
8
13⁄
8
8
8
8
8
8
75-100
(22.9-30.5)
1
⁄
2
11⁄
5
⁄
8
13⁄
5
⁄
8
13⁄
5
⁄
8
13⁄
5
⁄
8
13⁄
5
⁄
8
13⁄
8
8
8
8
8
8
LIQUID LINE
Max Allowable
Temp Loss
UNIT
MAX
ALLOWABLE
LIQUID LIFT
Max Allowable
Pressure Drop
Ft M psi kPa F C
569C072 86 26.2 7 48.3 2 1
569C090 60 18.3 7 48.3 2 1
569C120 70 21.3 7 48.3 2 1
576B090 60 18.3 7 48.3 2 1
576B102 65 19.8 7 48.3 2 1
576B120 65 19.8 7 48.3 2 1
NOTE: Values shown are for units operating at 45 F (7.2 C) saturated
suction and 95 F (35 C) entering air.
V. ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS
WARNING:
The unit cabinet must have an uninterrupted, unbroken electrical ground to minimize the possibility of personal injury if an electrical fault should
occur. This ground may consist of electrical wire connected to the unit ground lug in the control compartment or conduit approved for electrical ground when
installed in accordance with the NEC and local electrical codes. Failure to adhere to this warning could result in personal injury.
CAUTION:
Failure to follow these precautions could
result in damage to the unit being installed:
A. Field Power Supply (Fig. 6-8)
1. Make all electrical connections in accordance with NEC
ANSI/NFPA (American National Standards Institute/
National Fire ProtectionAssociation) 70, latest edition,
and local electrical codes governing such wiring. Refer
to unit wiring diagram.
2. Use only copper or copper-clad conductor fan connections between field-supplied electrical disconnect switch
and unit. DO NOT USE ALUMINUM WIRE. Maximum
wire size is no. 2 AWG (American Wire Gage).
3. Voltage to compressor terminals during operation must
be within voltage range indicated on unit nameplate (also
see Table 4). On 3-phase units, voltages between phases
must be balanced within 2% and the current within 10%.
Use the formula shown inTable 4, Note 2, to determine
the percent voltage imbalance. Operation on improper
line voltage or excessive phase imbalance constitutes abuse
and may cause damage to electrical components. Such
operation would invalidate any applicable warranty.
4. Insulate low-voltage wires for highest voltage contained within conduit when low-voltage control wires are
run in same conduit as high-voltage wires.
5. Donot damage internal components when drilling through
any panel to mount electrical hardware, conduit, etc.
—6—
Page 7

All units except 208/230-v units are factory wired for the voltage shown on the nameplate. If the 208/230-v unit is to be
connected to a 208-v power supply, the transformer must be
rewired by moving the black wire from the 230-v orange wire
on the transformer and connecting it to the 200-v red wire
from the transformer. The end of the orange wire must then
be insulated.
Refer to unit label diagram for additional information. Pigtails are provided for field wire connections. Use factorysupplied splices or UL (Underwriters’Laboratories) approved
copper/aluminum connector.
When installing units, provide a disconnect per NEC.
All field wiring must comply with NEC and local
requirements.
Install field wiring as follows:
1. Install conduit through side panel openings.
2. Install power lines to terminal connections as shown in
Fig. 6.
B. Control Voltage Connections
Install an accessory thermostat assembly according to installation instructions included with the accessory. Locate thermostat assembly on a solid wall in the conditioned space to
sense average temperature in accordance with thermostat
installation instructions.
Route thermostat cable or equivalent single leads of colored
wire from subbase terminals to low-voltage connections on
unit (shown in Fig. 7) as described in Steps 1 through 4
below.
NOTE: Refer to Table 5 for wire conversion information.
NOTE: For wire runs up to 50 ft (15.2 m), use no. 18 AWG
(0.82 mm) insulated wire (35 C minimum). For 50 to 75 ft
(15.2 to 22.9 m), use no. 16 AWG (1.30 mm) insulated wire
(35 C minimum). For over 75 ft (22.9 m), use no. 14 AWG
(2.08 mm) insulated wire (35 C minimum). All wire larger
than no. 18 AWG (0.82 mm) cannot be directly connected to
the thermostat and will require a junction box and splice at
the thermostat.
1. Connect thermostat wires to screw terminals of low voltage connection board.
2. Pass the control wires through the hole provided in the
corner post. See Fig. 8.
3. Feed wire through raceway built into the corner post
and into the 24-v thermostat connection board. The 24-v
thermostat connection is located on the left side of the
low voltage connection compartment. The raceway provides the UL required clearance between the high- and
low-voltage wiring.
4. Total combined amperage draw of the field-installed liquid line solenoid valve and indoor fan contactor must
not exceed 22 va. If the specified va must be exceeded,
use a remote relay to switch the load.
LEGEND
C—Contactor
NEC — National Electrical Code (U.S.A. Standard)
Field Wiring
Factory Wiring
Splice Connection (Factory Supplied)
Fig. 6 — Power Wiring Connections
AHA — Adjustable Heat Anticipator
C—Contactor, Compressor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CC — Cooling Compensator
CLO — Compressor Lockout
HPS — High-Pressure Switch
IFC — Indoor (Evaporator) Fan Contactor
Fig.7—Typical Control Wiring Connections (569C Shown)
LEGEND
LLSV — Liquid Line Solenoid Valve
LPS — Low-Pressure Switch
TB — Terminal Block
TC — Thermostat-Cooling
TDR — Time-Delay Relay
TH — Thermostat-Heating
TRAN — Transformer
Terminal (Marked)
Splice
Factory Wiring
Field Control Wiring
To Indicate Common Potential Only,
Not To Represent Wiring
—7—
Page 8

Table 4 — Electrical Data
UNIT
569C072
569C090
569C120
576B090
576B102
576B120
CSA — Canadian Standards Association
FLA — Full Load Amps
HACR — Heating, Air Conditioning and Refrigeration
LRA — Locked Rotor Amps
MCA — Minimum Circuit Amps
MOCP — Maximum Overcurrent Protection
NEC — National Electrical Code (U.S.A. Standard)
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
RLA — Rated Load Amps
UL — Underwriters’ Laboratories
NOTES:
1. In compliance with NEC requirements for multimotor and combination load equipment (refer to NEC Articles 430 and 440), the overcurrent protective device for the unit shall be fuse or HACR breaker.
2. Unbalanced 3-Phase Supply Voltage
Never operate a motor where a phase imbalance in supply voltage is
greater than 2%.
voltage imbalance.
= 100 x
NOMINAL VOLTAGE
(V-Ph-Hz)
208/230-3-60 187 254 21.8 142 1.9 25.6 35
460-3-60 414 508 9.6 72 1.0 12.9 15
575-3-60 518 632 7.6 58 1.9 11.4 15
220-3-50 198 242 19.0 142 1.0 25.6 35
400-3-50 360 440 9.5 72 1.0 12.9 15
208/230-3-60 187 254 28.8 195 3.8 39.8 45
460-3-60 414 508 14.7 95 1.9 20.3 20
575-3-60 518 632 10.8 80 1.9 15.4 15
220-3-50 198 242 28.8 195 1.5 37.5 45
400-3-50 360 440 14.7 90 1.5 19.9 20
208/230-3-60 187 254 37.8 239 3.1 46.2 60
460-3-60 414 508 17.2 125 1.4 22.7 30
575-3-60 518 632 12.3 80 1.4 19.3 25
220-3-50 198 242 37.8 239 1.4 46.2 60
400-3-50 360 440 17.2 114 1.4 22.7 30
208/230-3-60 187 254 31.5 160 3.1 42.5 50
380-3-60 342 418 19.0 75 2.2 26.0 35
460-3-60 414 508 15.7 80 1.4 21.0 25
575-3-60 518 632 12.6 64 1.4 17.2 20
220-3-50 198 253 31.5 160 1.4 42.5 50
400-3-50 342 460 15.7 80 1.4 21.0 25
208/230-3-60 187 254 39.7 198 3.1 52.7 70
380-3-60 342 418 24.0 93 2.2 32.2 40
460-3-60 414 508 19.9 99 1.4 26.3 35
575-3-60 518 632 15.9 79 1.4 21.3 25
220-3-50 198 253 39.7 198 1.4 52.7 70
400-3-50 342 460 19.9 99 1.4 26.3 35
208/230-3-60 187 254 39.7 198 3.1 52.7 70
380-3-60 342 418 24.0 93 2.2 32.2 40
460-3-60 414 508 19.9 99 1.4 26.3 35
575-3-60 518 632 15.9 79 1.4 21.3 25
220-3-50 198 253 39.7 198 1.4 52.7 70
400-3-50 342 460 19.9 99 1.4 26.3 35
LEGEND
Use the following formula to determine the percent
max voltage deviation from average voltage
average voltage
VOLTAGE RANGE COMPRESSOR OFM POWER SUPPLY
Min Max RLA LRA FLA MCA MOCP
Example: Supply voltage is 460-3-60.
(AB) 457 - 452=5v
(BC) 464 - 457=7v
(AC) 457 - 455=2v
Maximum deviation is 7 v.
Determine percent voltage imbalance
% Voltage Imbalance = 100 x
This amount of phase imbalance is satisfactory as it is below the maximum allowable 2%.
IMPORTANT: If the supply voltage phase imbalance is more than 2%,
contact your local electric utility company immediately.
3. The 575-v units are CSA only.
4. The 380-v units are
AB = 452 v
BC = 464 v
AC = 455 v
Average Voltage =
7
= 1.53%
457
not
UL or CSA listed.
452 + 464 + 455
3
1371
=
3
= 457
—8—
Page 9

PRE-START-UP
Fig. 8 — Field Control Wiring Raceway
(576B Unit Shown)
Table 5 — American/European Wire Conversions
AMERICAN EUROPEAN
Industry
Standard Size
18 AWG 0.82 1.0
16 AWG 1.30 1.5
14 AWG 2.08 2.5
12 AWG 3.30 4.0
10 AWG 5.25 6.0
8AWG 6.36 10.0
6AWG 13.29 16.0
4AWG 21.14 25.0
3AWG 26.65 —
2AWG 33.61 35.0
1AWG 42.39 50.0
1/0 AWG 53.49 —
2/0 AWG 67.42 70.0
3/0 AWG 85.00 95.0
4/0 AWG 107.19 120.0
250 kcmil 126.64 150.0
300 kcmil 151.97 —
350 kcmil 177.90 185.0
400 kcmil 202.63 240.0
500 kcmil 253.29 300.0
600 kcmil 303.95 —
LEGEND
AWG — American Wire Gage
kcmil — Thousand Circular Mils
American
Conversion
2
(mm
)
Industry
Standard
Size (mm2)
VI. ACCESSORY INSTALLATION
At this time any required accessories should be installed on
the unit. Refer to Table 6 for available accessories. Control
wiring information is provided in the unit wiring book.
Table 6 — Accessory List
ACCESSORY
Gage Panel
Winter-Start Relay Package
Weatherprobe™ II Low Ambient Kit
Hail Guard Package (072)
Hail Guard Package (090,102,120)
Thermostats
Subbase
WARNING:
Failure to observe the following warn-
ings could result in serious personal injury:
1. Follow recognized safety practices and wear protective goggles when checking or servicing refrigerant system.
2. Do not operate compressor or provide any electric
power to unit unless compressor terminal cover is
in place and secured.
3. Do not remove compressor terminal cover until all
electrical sources have been disconnected.
4. If refrigerant leak is suspected around compressor terminals, recover refrigerant whenever possible and relieve all pressure from system before
touching or disturbing anything inside terminal box.
5. Never attempt to repair soldered connection while
refrigerant system is under pressure.
6. Do not use torch to remove any component. System contains oil and refrigerant under pressure.
To remove a component, wear protective goggles
and proceed as follows:
a. Shut off electrical power to unit.
b. Recover refrigerant. Relieve all pressure from
system.
c. Cut component-connecting tubing with tubing
cutter and remove component from unit.
d. Carefully unsweat remaining tubing stubs when
necessary. Oil can ignite when exposed to torch
flame.
Proceed as follows to inspect and prepare the unit for initial
start-up:
1. Field electrical power source must agree with unit nameplate rating.
2. Check voltage imbalance as shown in Table 4, Note 2.
3. Check that all internal wiring connections are tight and
that all barriers, covers, and panels are in place.
4. Ensure all service valves are open. On 576B units, be
sure all compressor service valves are backseated.
5. Verify thatcompressor holddown boltshave been loosened and that flat/snubber washers can be rotated by
applying finger pressure (snug, but not tight).
6. On 569C and 576Bunits, verify compressor crankcase
heater is securely in place.Crankcase heater must operate for a least 24 hours before start-up.
7. Note that compressor oil level is visible in the sight
glass (576B units only).
8. Check for leaks in refrigerant system by using soap
bubbles and/or electronic leak detector.
9. Check that liquid line solenoid valve is located at evaporator coil as shown in Filter Drier and Moisture Indicator section, page 6.
10. Check that both outdoor and indoor units are properly
mounted in accordance with installation instructions
and applicable codes.
—9—
Page 10

START-UP
I. START-UP AND ADJUSTMENTS
CAUTION:
in the Pre-Start-Up section before starting the unit.
Do not jumper any safety devices when operating the
unit.
Do not operate the compressor when the outdoor tem-
perature is below 25 F (24 C) (unless accessory low ambient kit is installed).
A. Checking Cooling Control Operation
Start and check the unit for proper cooling control operation
as follows:
1. Place room thermostat SYSTEM switch in OFF position. Observe that blower motor starts when FAN switch
is placed in ON position and shuts down when FANswitch
is placed in AUTO. position.
2. Place SYSTEM switch in COOL position and FAN switch
in AUTO. position. Set cooling control below room temperature. Observe that compressor and condenser- and
evaporator-fan motors start. Observe that cooling cycle
shuts down when control setting is satisfied.
B. Unit Controls
All units have the following internal-protection controls:
Compressor Overload
This overload interrupts power to the compressor when
either the current or internal motor winding temperature become excessive, and automatically resets when the internal
temperature drops to a safe level. This overload may require
up to 60 minutes (or longer) to reset. If the internal overload
is suspected of being open, disconnect the electrical power to
the unit and check the circuit through the overload with an
ohmmeter or continuity tester.
Time Guardt II Device
The unit is equipped with accessory Time Guard II recycle
timer. The device will cause a 5-minute delay between compressor starts.
Cycle-LOC™ Device
When high-pressure or low-pressure fault occurs, the Cycle-
LOC device will protect the system by not allowing the compressor to start.
Low-Pressure/Loss of Charge Switch (LPS)
When the liquid line pressure drops below 7 psig (48 kPa),
the LPS opens 24-v power to the compressor contactor and
stops the compressor. When the pressure reaches 22 psig
(152 kPa), the switch resets and the compressor is allowed to
restart.
High-Pressure Switch (HPS)
When the refrigerant high-side pressure reaches 426 psig
(2937 kPa), the HPS opens 24-v power to the compressor contactor and stops the compressor. When the pressure drops to
320 psig (2206 kPa), the switch resets and the compressor is
allowed to restart.
C. Sequence of Operation
At start-up, the thermostat calls for cooling. When all safety
devices are satisfied, the compressor contactor (fan contactor) will energize causing the compressor and outdoor (condenser) fan motor to operate.Terminal 9G9 at thethermostat
is also energized, allowing the field-supplied and -installed
(24v) indoor (evaporator) fan contactor to function. A fieldsupplied and -installed liquid line valve (connected between
Complete the required procedures given
Terminals G and C) will also open, allowing the system to
function in cooling. As cooling demand is satisfied, the thermostat contacts break, deenergizing the contactor causing the
system to shut off. The liquid line solenoid (LLS) valve closes,
minimizing the potential for refrigerant migration at this time.
The compressor does not restart until the thermostat again
calls for cooling. If a demandfor cooling occurs within 5minutes after the thermostat is satisfied, the system will not restart due to the feature of Time Guard II device. After the
5-minute time period, the system will restart as normal upon
thermostat demand.
The system is protected with a Cycle-LOC device so that the
compressor will not start if a high-pressure or low-pressure
fault occurs. To reset the Cycle-LOC device, set the thermostat to eliminate the cooling demand then return to the original set point. This should be done only once, and if system
shuts down due to the same fault, determine the problem before attempting to reset the Cycle-LOC device.
The crankcase heaters must be energized for a minimum of
24 hours before starting a 569C and 576B unit.
D. Oil Charge
576B Units
Allow unit to run for about 20 minutes. Stop unit and check
compressor oil level.Add oil only if necessary to bring oil into
view in sight glass. Use only approved compressor oil.
Approved oils are:
Suniso 3GS
WF32-150
If oil is added, run unit for an additional 10 minutes. Stop
unit and check oil level. If level is still low, add oil only after
determining that piping system is designed for proper oil return and that system is not leaking oil.
569C Units
The 569C units do not have a sight glass and are factory charged
with the correct amount of oil.
All Units
Do not reuse drained oil or use any oil that has been exposed
to the atmosphere. Procedures for adding or removing oil are
given in the Standard Service Techniques Manual, Chapter 1,
Refrigerants.
CARE AND MAINTENANCE
To ensure continuing high performance and to minimize the
possibility of premature equipment failure, periodic maintenance must be performed on this equipment. This cooling unit
should be inspected at least once each year by a qualified service person.
NOTE TO EQUIPMENT OWNER: Consult your local dealer
about the availability of a maintenance contract.
WARNING:
nance on this equipment requires certain expertise,
mechanical skills, tools, and equipment. If you do not
possess these, do not attempt to perform any maintenance on this equipment other than those procedures
recommended in the User’sManual. FAILURE TO HEED
THIS WARNING COULD RESULT IN SERIOUS PERSONAL INJURYAND POSSIBLEDAMAGE TO THIS
EQUIPMENT.
The ability to properly perform mainte-
—10—
Page 11

SERVICE
WARNING:
When servicing unit, shut off all electrical power to unit to avoid shock hazard or injury from
rotating parts.
I. CLEANING
Inspect unit interior at the beginning of each cooling season
and as operating conditions require.
A. Condenser Coil
Inspect coil monthly. Clean condenser coil annually, and as
required by location and outdoor-air conditions.
Clean coil as follows:
1. Turn off unit power.
2. Remove and save top panel screws on condensing unit.
3. Remove condenser coil corner post. See Fig. 9. To hold
top panel open, place coil corner postbetween top panel
and side panel. See Fig. 10.
4. Remove bracket holding coil sectionstogether at return
end of condenser coil. Carefully separate the outer coil
section 3 to 4 in.(75 to 100 mm) from the inner coil section. See Fig. 11.
5. Use a water hose or other suitable equipment to flush
down between the 2 coil sections to remove dirt and
debris. Clean the outer surfaces with a stiff brush in the
normal manner.
6. Reposition the outer coil section, attach the bracket removed in Step 4, and remove the coil corner post from
between the top panel and side panel. Secure the sections together. Install the coil corner post and replace
all screws (removed in Step 2).
Fig. 10 — Propping Up Top Panel
II. LUBRICATION
A. Compressors
Each compressor is charged withthe correct amount of oil at
the factory. Refer to the Oil Charge section on page 10 for additional information.
B. Fan Motor Bearings
Fan motor bearings are of the permanently-lubricated type.
No further lubrication is required.
Fig. 9 — Cleaning Condenser Coil
Fig. 11 — Separating Coil Sections
III. CONDENSER-FAN ADJUSTMENT (Fig. 12)
1. Shut off unit power supply.
2. Removecondenser-fan assembly (grille, motor,motor cover,
and fan).
3. Loosen fan hub setscrews.
4. Adjust fan height as shown in Fig. 12.
5. Tighten set screws.
6. Replace condenser-fan assembly.
NOTE: Fan height adjustments are as follows:
UNIT in. mm
569C072 4.50 114
All Units
(except 569C072)
6.42 163
Fig. 12 — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Adjustment
—11—
Page 12

IV. CAPACITY CONTROL (576B120 Only)
Asuction pressure-actuated unloader controls 2 cylinders and
provides capacity control. Unloaders are factory set (see
Table 1A or 1B), but may be field adjusted:
A. Control Set Point
The control set point (cylinder load point) is adjustable from
0 to 85 psig (586 kPa). To adjust, turn control set point adjustment nut (Fig. 13) clockwise to its bottom stop. In this
position, set point is 85 psig (586 kPa). Then, turn adjustment counterclockwise to desired control set point. Every full
turn counterclockwise decreases set point by 7.5 psig (51.7 kPa).
B. Pressure Differential
The pressure differential (difference between cylinder load and
unload points) is adjustable from 6 to 22 psig (41.4 to 152 kPa).
To adjust, turn pressure differential adjustment screw (Fig. 13)
counterclockwise to its back stop position. In this position,
differential is 6 psig (41.4 kPa). Then, turn adjustment screw
clockwise to desired pressure differential. Every full turn clockwise increases differential by 1.5 psig (10.3 kPa).
Fig. 13 — Compressor Capacity Control Unloader
V. COMPRESSOR REMOVAL
See Tables 1A and 1B for compressor information.
Follow safety codes and wear safety glasses and work gloves.
1. Shut off power to unit. Remove unit access panel (front
of unit).
2. Remove refrigerant from system using refrigerant removal methods described in GTACII, Module 5, Charging, Recovery, Recycling, and Reclamation.
3. Disconnect compressor wiring at compressor terminal
box.
4. Remove bolts from suction flange and discharge service valve (576B Units).
CAUTION:
compressor may cause higher levels of vibration when
unit is restored to service.
5. Remove crankcase heater from compressor base (576B
units only).
6. Remove compressor holddown bolts.
7. Remove compressor from unit.
Excessive movement of copper lines at
8. Clean system. Add new liquid line filter drier.
9. Install new compressor in unit.
10. Connect suction and discharge lines to compressor.Ensure that compressor holddown bolts are in place.
11. Connect wiring.
12. Install crankcase heater.
13. Evacuate and recharge unit, per Step VII.
14. Restore unit power.
VI. CRANKCASE HEATER (Except 569C072)
The crankcase heater prevents refrigerant migration and compressor oil dilution during shutdownwhen compressor is not
operating.
Close both compressor service valves if applicable when crankcase heater is deenergized for more than 6 hours.
VII. REFRIGERANT CHARGE
Unit panels must be in place when unit is operating during
charging procedure. Unit is shipped with a holding charge
only. Weighin 7 lbs (3 kg) of R-22 to start unit. Refer to GTACII,
Module 5, Charging, Recovery, Recycling, and Reclamation
for additional information.
See Troubleshooting Guide on page 14 for additional
information.
A. Low Charge Cooling
Using Cooling Charging Charts, Fig. 14 and 15, vary refrigerant until the conditions of the appropriate chart are met.
Note the charging charts are different from type normally used.
The charts are based on charging the units to the correct subcooling for the various operating conditions. Accurate pressure gage and temperature sensing device are required. Connect the pressure gage to the service port on the liquid line
service valve. Mount the temperature sensing device on the
liquid line, close the liquid line service valve, and insulate it
so that outdoor ambient temperature does not affect the reading. Indoor-air cfm must be within the normal operating range
of the unit.
Operate unit a minimum of 15 minutes. Ensure that temperature and pressure have stabilized. Plot liquid pressure
and temperature on chart and add or reduce charge as required. Do not vent refrigerant to the atmosphere. Recover
any excess charge. Operate the unit until the system stabilizes.Adjust charge to conform with charging chart, using liquid pressure and temperature to read chart.
B. Refrigerant Leaks
Proceed as follows to repair a refrigerant leak and to charge
the unit:
1. Locate the leak and ensure that refrigerant system pres-
sure has been relieved.
2. Repair leak following accepted practices.
NOTE: Install a new filter drier in the liquid line whenever
the system has been opened for repair.
3. Add a small charge of R-22 refrigerant vapor to system
and leak-test unit.
4. Evacuate refrigerant system if additional leaks are not
found.
5. Charge unit with R-22 refrigerant.
NOTE: Do not vent refrigerant to the atmosphere. Recover
any excess charge.
VIII. REFRIGERANT SERVICE PORTS
Each unit has 3service ports: one on the suction line, one on
the liquid line, and one on the compressor discharge line. Be
sure caps on the ports are tight.
—12—
Page 13

Fig. 14 — Cooling Charging Chart — 569C072
Fig. 15 — Cooling Charging Chart — 569C090,120
and 576B090,102,120
—13—
Page 14

SYMPTOM CAUSE REMEDY
Compressor does not run —
Contactor open
Power off. Restore power.
Fuses blown. Replace with correct fuses after finding cause
Transformer open/shorted. Replace transformer if primary windings are
Thermostat circuit open. Check thermostat setting.
Low-pressure switch open. Check for refrigerant undercharge or system
High-pressure switch open. Check for refrigerant over charge or
Connections loose. Tighten all connections.
Compressor motor thermostat open. Check for excessive motor temperature.
Compressor does not run —
Contactor closed
Compressor leads loose, broken. Check connections with power off.
Single phasing. Replace blown fuse.
Compressor internal overload open. Allow compressor motor windings to cool down to reset
Compressor cycles on highpressure switch —
Condenser fan on
High-pressure switch faulty. Replace switch.
Airflow restricted. Dirty coil. Remove obstruction, clean condenser coil.
Air recirculating. Clear airflow area.
Noncondensables in system. Recover, evacuate and recharge as required. Refer to
Refrigerant overcharge. Recover as required.
Refrigerant system restrictions. Check or replace filter drier, expansion
Compressor cycles on highpressure switch —
Condenser fan off
Fan slips on shaft. Tighten fan hub screws.
Motor not running. Check power and capacitor
Motor bearings seized. Replace motor.
Motor overload open. Check overload rating. Check for
Motor burned out, windings open. Replace motor.
Compressor cycles on lowpressure switch —
Evaporator fan running
Filter drier plugged. Replace filter drier.
Expansion valve power head
defective.
Low refrigerant charge. Find leak, repair, evacuate system, and recharge.
Expansion valve restricted/plugged. Remove and replace expansion valve.
Airflow restricted —
Low suction pressure
Evaporator coil iced up. Check refrigerant charge.
Evaporator coil dirty. Clean coil fins.
Indoor-air filter dirty. Clean or replace filters.
Indoor-air dampers closed. Check damper operation and position.
Indoor (evaporator) fan stopped —
Low suction pressure
Electrical connections loose. Tighten all connections.
Fan relay defective. Replace relay.
Motor overload open. Check power supply.
Motor defective. Replace motor.
Fan belt broken or slipping. Replace or tighten belt.
Compressor runs but
cooling insufficient —
Suction pressure low
Refrigerant charge low. Add charge.
Head pressure low. Check refrigerant charge.
Indoor-air filters dirty. Clean or replace filters.
Expansion valve power head
defective.
Expansion valve restricted/plugged. Remove and replace expansion valve.
Evaporator coil partially iced. Check low-pressure setting.
Evaporator airflow restricted. Remove obstruction.
Compressor runs but
cooling insufficient —
Suction pressure high
Heat load excessive. Check for open doors or windows.
NOTE: See Fig. 16 and 17 for component arrangements.
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
and correcting.
receiving power and no output.
leak.
obstruction of outdoor airflow.
overload. Determine cause for overload opening.
Carrier GTAC-II, Module 5, Charging, Recovery,
Recycling, and Reclamation.
valve, etc.
fan blade obstruction.
Replace power head.
Replace power head.
1
⁄3and3⁄4hp motor.
—14—
Page 15

LEGEND FOR FIG. 16 AND 17
C—Contactor, Compressor
CAP — Capacitor
CB — Circuit Breaker
CH — Crankcase Heater
CLO — Compressor Lockout
COMP — Compressor Motor
COTP — Compressor Temperature Protection
EQUIP — Equipment
GND — Ground
HPS — High-Pressure Switch
LPS — Low-Pressure Switch
NEC — National Electrical Code
OFC — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Contactor
OFM — Outdoor (Condenser) Fan Motor
OL — Overload Relay
QT — Quadruple Terminal
TB — Terminal Block
TDR — Time-Delay Relay
TRAN — Transformer
Terminal (Marked)
Terminal (Unmarked)
Terminal Block
Factory Wiring
Field Power Wiring
Fig. 16 — Typical 569C Wiring Schematic and Component Arrangement
Fig. 17 — Typical 576B Wiring Schematic and Component Arrangement
—15—
Page 16

Page 17

Page 18

Copyright 1999 Bryant Heating & Cooling Systems CATALOG NO. 5356-902
Page 19

START-UP CHECKLIST
I. PRELIMINARY INFORMATION
OUTDOOR: MODEL NO. SERIAL NO.
INDOOR: AIR HANDLER MANUFACTURER
MODEL NO. SERIAL NO.
ADDITIONAL ACCESSORIES
II. PRE-START-UP
OUTDOOR UNIT
IS THERE ANY SHIPPING DAMAGE?
IF SO, WHERE:
WILL THIS DAMAGE PREVENT UNIT START-UP? (Y/N)
CHECK POWER SUPPLY. DOES IT AGREE WITH UNIT? (Y/N)
HAS THE GROUND WIRE BEEN CONNECTED? (Y/N)
HAS THE CIRCUIT PROTECTION BEEN SIZED AND INSTALLED PROPERLY? (Y/N)
ARE THE POWER WIRES TO THE UNIT SIZED AND INSTALLED PROPERLY? (Y/N)
HAVE COMPRESSOR HOLDDOWN BOLTS BEEN LOOSENED (Snubber washers are snug, but not tight)?
(Y/N)
(Y/N)
CONTROLS
ARE THERMOSTAT AND INDOOR-FAN CONTROL WIRING
CONNECTIONS MADE AND CHECKED? (Y/N)
ARE ALL WIRING TERMINALS (including main power supply) TIGHT? (Y/N)
HAS CRANKCASE HEATER BEEN ENERGIZED FOR 24 HOURS? (Y/N)
INDOOR UNIT
HAS WATER BEEN PLACED IN DRAIN PAN TO CONFIRM PROPER DRAINAGE? (Y/N)
ARE PROPER AIR FILTERS IN PLACE? (Y/N)
HAVE FAN AND MOTOR PULLEYS BEEN CHECKED FOR PROPER ALIGNMENT? (Y/N)
DO THE FAN BELTS HAVE PROPER TENSION? (Y/N)
HAS CORRECT FAN ROTATION BEEN CONFIRMED? (Y/N)
PIPING
IS LIQUID LINE SOLENOID VALVE LOCATED AT THE EVAPORATOR COIL AS REQUIRED? (Y/N)
HAVE LEAK CHECKS BEEN MADE AT COMPRESSOR, CONDENSER, EVAPORATOR,
TXVs (Thermostatic Expansion Valves), SOLENOID VALVES, FILTER DRIERS, AND FUSIBLE PLUGS
WITH A LEAK DETECTOR? (Y/N)
LOCATE, REPAIR,AND REPORTANY LEAKS.
CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE CUT ALONG DOTTED LINE
ARE ALL 576B COMPRESSOR SERVICE VALVES FULLY OPENED (BACKSEATED)?
(Y/N)
HAVE LIQUID LINE SERVICE VALVE AND SUCTION LINE SERVICE VALVE BEEN OPENED? (Y/N)
IS THE OIL LEVEL IN COMPRESSOR CRANKCASE ON 576B UNIT IN VIEW IN THE COMPRESSOR SIGHT GLASS?
(Y/N)
CHECK VOLTAGE IMBALANCE
LINE-TO-LINE VOLTS: AB
(AB + AC + BC)/3 = AVERAGE VOLTAGE =
MAXIMUM DEVIATION FROM AVERAGE VOLTAGE =
VOLTAGE IMBALANCE = 100 X (MAX DEVIATION)/(AVERAGE VOLTAGE) =
IF OVER 2% VOLTAGE IMBALANCE, DO NOT ATTEMPT TO START SYSTEM!
CALL LOCAL POWER COMPANY FOR ASSISTANCE.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
VAC VBC V
V
V
%
—CL-1—
Page 20

III. START-UP
CHECK EVAPORATOR-FAN SPEEDAND RECORD.
CHECK CONDENSER-FAN SPEED AND RECORD.
AFTER AT LEAST 15 MINUTES RUNNING TIME, RECORD THE FOLLOWING MEASUREMENTS:
OIL PRESSURE (576B only)
SUCTION PRESSURE
SUCTION LINE TEMP
DISCHARGE PRESSURE
DISCHARGE LINE TEMP
ENTERING CONDENSER-AIR TEMP
LEAVING CONDENSER-AIR TEMP
EVAP ENTERING-AIR DB (dry bulb) TEMP
EVAP ENTERING-AIR WB (wet bulb) TEMP
EVAP LEAVING-AIR DB TEMP
EVAP LEAVING-AIR WB TEMP
COMPRESSOR AMPS (L1/L2/L3) / /
HAS REFRIGERANT CHARGE BEEN ADJUSTED PER UNIT CHARGING CHART?
NOTES:
Copyright 1999 Bryant Heating & Cooling Systems CATALOG NO. 5356-902
—CL-2—
 Loading...
Loading...