Brother ST-1150, PT-1160, PT-1250, PT-11Q, PT-1180 Service Manual
...
P-touch
REVISED 1
SERVICE MANUAL
MODEL: PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q
PT-1250/1160
ST-1150(Heavy Duty LabelerTM)

SERVICE MANUAL
MODEL: PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q
PT-1250/1160
ST-1150(Heavy Duty LabelerTM)

© Copyright Brother 2002
All rights reserved.
No part of this publication may be reproduced in any
form or by any means without permission in writing
from the publisher.
Specifications are subject to change without notice.

PREFACE
This publication is a service manual covering the specifications, theory of operation,
disassembly/reassembly procedure, and troubleshooting of the Brother PT-1100/1130
/1170/1180/11Q, PT-1250/1160 and ST-1150.
It is intended for service personnel and other concerned persons to accurately and
quickly provide after-sale service for our PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q, PT1250/1160 and ST-1150.
To perform appropriate maintenance so that the machine is always in best condition
for the customer, the service personnel must adequately understand and apply this
manual.
This manual is made up of three chapters and appendices.
CHAPTER I SPECIFICATIONS
CHAPTER II MECHANISMS
CHAPTER III ELECTRONICS
APPENDICES CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS

CHAPTER I
SPECIFICATIONS

CONTENTS
CHAPTER I SPECIFICATIONS......................................................................... I-1
1.1 MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS ........................................................................ I-1
1.1.1 External Appearance...................................................................................... I-1
1.1.2 Keyboard........................................................................................................ I-1
1.1.3 Display........................................................................................................... I-2
1.1.4 Printing Mechanism ........................................................................................ I-2
1.1.5 Tape Cassette................................................................................................ I-2
1.1.6 Tape Cutter.................................................................................................... I-2
1.2 ELECTRONICS SPECIFICATIONS ...................................................................... I-6
1.2.1 Character Generator....................................................................................... I-6
1.2.2 Power Supply................................................................................................. I-6
1.3 SPECIAL KEY....................................................................................................... I-6
1.3.1 Format ........................................................................................................... I-6
1.3.2 Demonstration Print........................................................................................ I-6
CHAPTER I SPECIFICATIONS
1.1 MECHANICAL SPECIFICATIONS
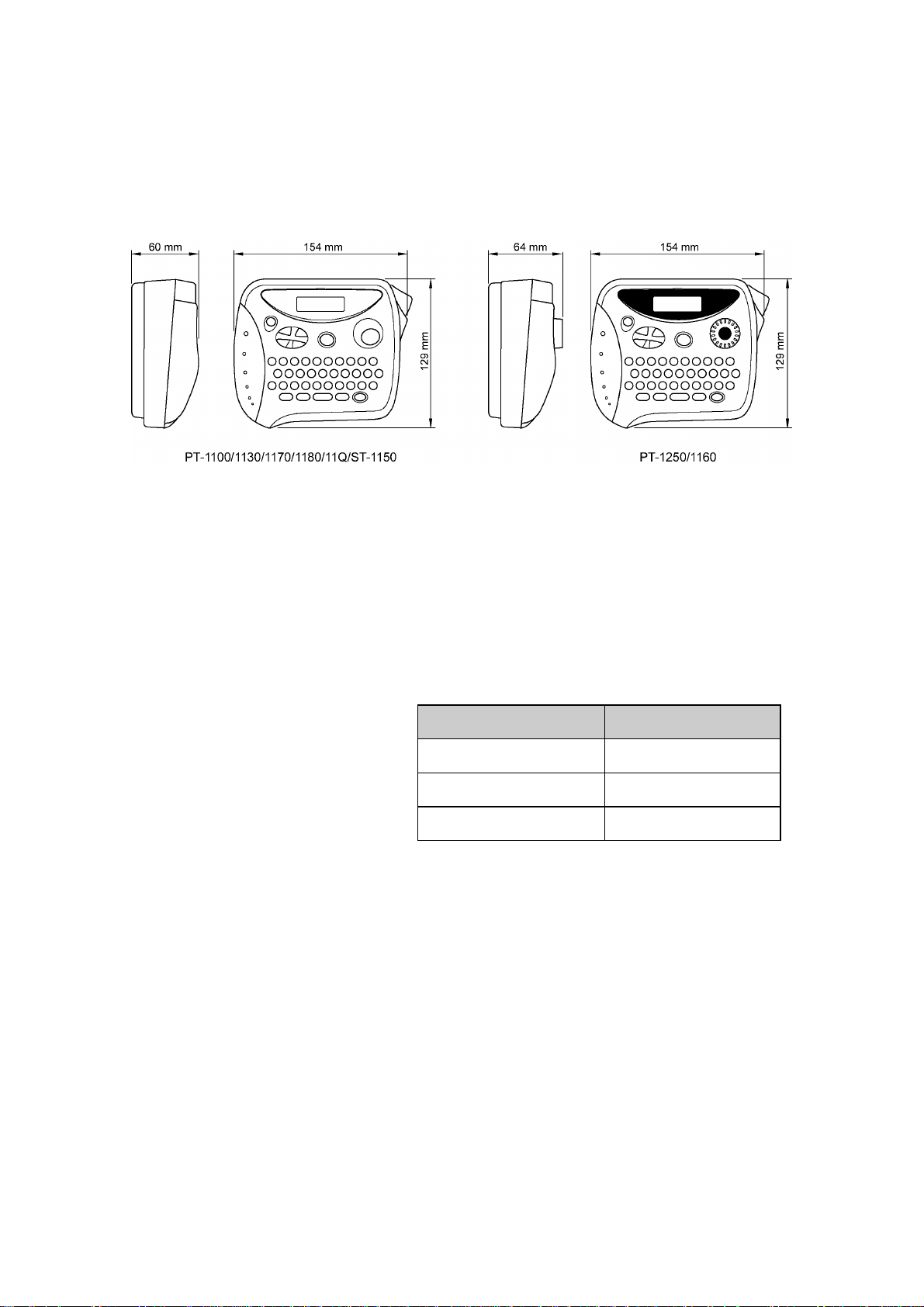
1.1.1 External Appearance
Fig. 1.1-1 External Appearance
(1) Dimensions (W x D x H) 154 x 129 x 60 mm
154 x 129 x 64 mm (PT-1250/1160)
(2) Weight
Machine proper only Approx. 400 g
In package
(PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q/ST-1150)
1.1.2 Keyboard
(1) Entry system Rubber 41 key (PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q/ST-1150)
(2) Number of alphanumeric 30
and symbol keys
(3) Number of function keys 11 (PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q/ST-1150)
(4) Key arrangement See Fig. 1.1-2.
Packaging Weight (g)
Carton with One Unit 670g
Clamshell 650g
Carrying Case 1300g
(including the machine, packing materials and packaged
standard components)
Rubber 40 key and tact switch (PT-1250/1160)
10 (PT-1250/1160)
(including On/Off key, L/R pointing keys must be counted
as one.)
I-1

1.1.3 Display
(1) Display type Liquid crystal display (LCD)
(2) Number of columns 8 columns x 1 row (See Fig. 1.1-2.)
(3) Number of indicators 10 (See Fig. 1.1-2.)
(4) Character size 5 dots wide by 7 dots high
(5) Field-of-view angle Fixed by a resistor
adjustment
1.1.4 Printing Mechanism
(1) Print method Thermal transfer onto plastic tapes (laminate tape and
(2) Print speed 10 mm/second (Typical)
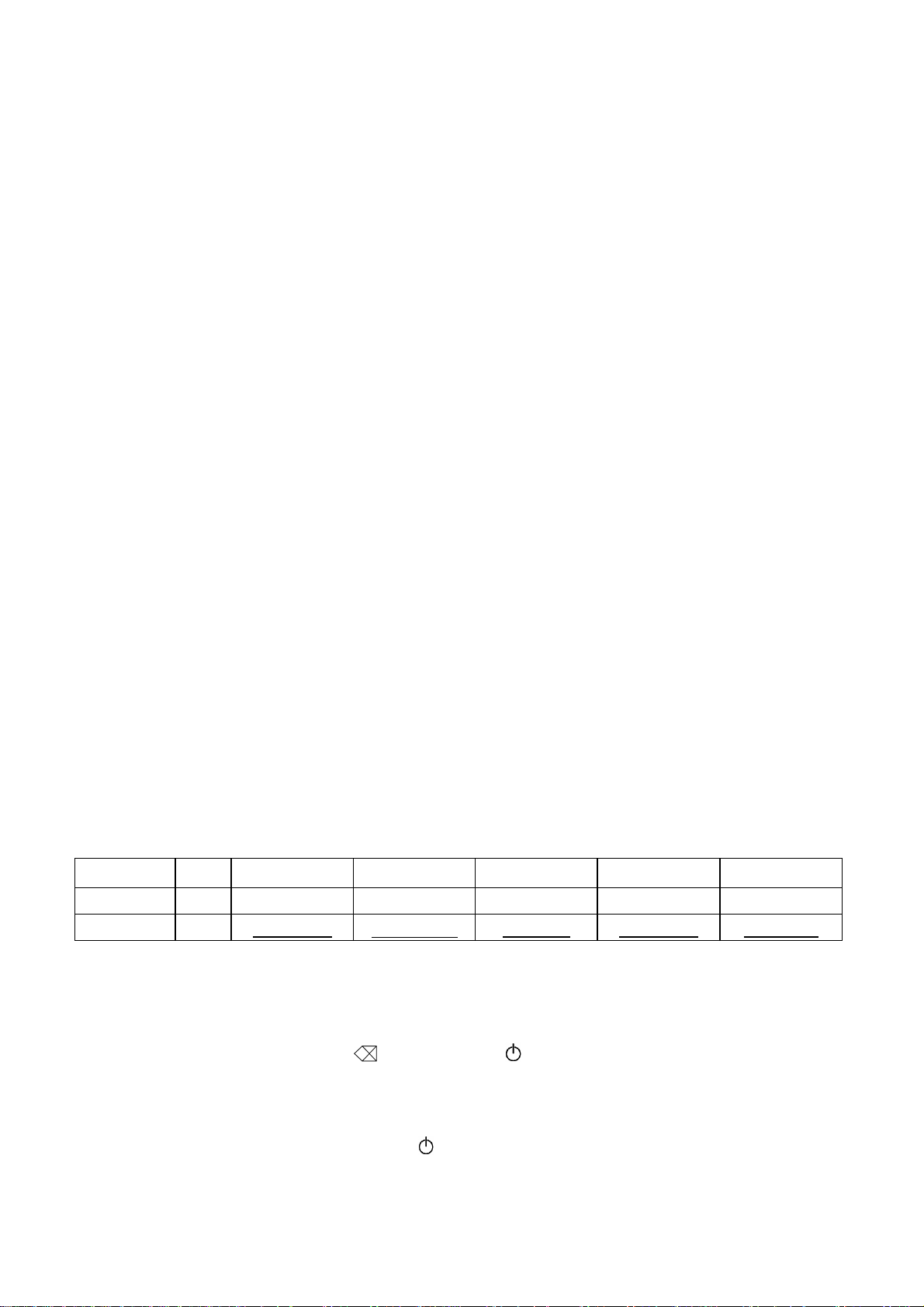
(3) Print head
Type Thermal print head
Heat generator Consists of 64 heating elements vertically aligned
Size of heating element 0.195 mm wide by 0.141 mm high
(4) Character size Ratio Width x height
Standard (Small) size (1) 2.26 x 2.96 mm 16 x 21 dot
Double width (W2) 4.37 x 2.96 mm 31 x 21 dot
Double height (H2) 2.26 x 5.92 mm 16 x 42 dot
Double width and double height (4) 4.37 x 5.92 mm 31 x 42 dot
Quadruple width and double height (8) 8.74 x 5.92 mm 62 x 42 dot
non-laminated tape)
(Fixed print head and tape feeding mechanism)
This part explains the dot size of "H" character as an example in the table above, because the
character size is different by the width of the tape and the character.
1.1.5 Tape Cassette
(1) Cassette Cartridge type (TZ-cassette)
(2) Types of tape cassettes
Laminated tape cassette Laminated tape, ink ribbon, and adhesive base tape
Non-laminated tape cassette Non-laminated tape and ink ribbon
Cloth tape cassette Cloth tape and ink ribbon
(3) Tape size
(4) Tape cassette packed with the machine
1.1.6 Tape Cutter
(1) Tape cutting Manual cutting with the cutter lever
(2) Cutter unit Replaceable by the customer
Width Length
Laminated tape 6, 9, 12 mm 8 m
Non-laminated tape 6, 9, 12 mm 8 m
Cloth tape 12 mm 4 m
Laminated tape cassette containing a 12-mm-wide back ink
ribbon, laminate tape, and adhesive base tape
I-2

Fig. 1.1-2 Key Arrangement (1)
I-3

Fig. 1.1-2 Key Arrangement (2)
I-4

Fig. 1.1-2 Key Arrangement (3)
I-5
1.2 ELECTRONICS SPECIFICATIONS
1.2.1 Character Generator
(1) Internal characters U.K./ FRA/ BEL (PT-1250) 205
GER (PT-1250) 213
U.S.A./ CAN./AUS. 176
(PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q/ST-1150,and
(2) Internal font HELSINKI
(3) Print buffer capacity 55 characters
(4) Phrase memory capacity 300 characters
1.2.2 Power Supply
(1) Power supply Driven by 6 batteries
Optional AC adapter (7VDC, 1.2A) available
* For PT-1180, the power supply is batteries only.
(2) Battery type 6 alkaline batteries (AM4/ LR03)
(3) Service life of batteries Will last through one tape cassette, and then some.
(at room temperature and normal humidity)
(4) Automatic power off Yes (If the machine remains unused for approx. 5 minutes,
it automatically powers itself off.)
(5) Battery indication
1) If the voltage level of the VAD rises over approx. 10.8V, the CPU immediately shuts
down the power.
2) If it drops even more below approx. 5.3V, the CPU displays the message to warn you of
a low battery after completion of printing.
3) If it drops even more below approx. 5.0V, the CPU interrupts the printing and displays
the message to warn you of a very low battery.
4) If it drops below approx. 4.8V, the CPU immediately shuts down the power.
* Displays different for each country when the battery is weak or when the battery
became
empty are indicated below.
* Displays of specification for U.S.A. and for Canada can be switched.
PT-1160/1250 for CAN.)
The optional AC adapter is not available.
UK/BELGIUM FRENCH GERMAN U.S.A./AUSTRALIA CANADA
Battery week 5.3V BATTERY B:V BATTERIE BATTERY PILE!
Battery empty 5.0V BATTERY • B:V ••••• BATTERIE BATTERY • PILE! •••
The underline of eight (8) characters length is drawn for display when the Battery Empty.
1.3 SPECIAL KEY
1.3.1 Format
Push the “Code” key + “BS( )” key + “On/Off ( )” key, when the power is off.
1.3.2 Demonstration Print
Push “Code” key + “D” key. (PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q/ST-1150, and PT-1160/1250 for CAN.)
Push “Code” key + “D” key+ “On/Off ( )” key. (PT-1250 not only for CAN.)
(It is effective when there is not any data in the text.)
I-6

CHAPTER II
MECHANISMS

CONTENTS
CHAPTER II MECHANISM................................................................................ II-1
2.1 THEORY OF OPERATION ................................................................................... II-1
2.1.1 Print Mechanism ............................................................................................ II-1
2.1.2 Platen Roller, (Tape Feed) Sub Roller Setting & Retracting Mechanism......... II-2
2.1.3 Tape & Ribbon Feed Mechanism.................................................................... II-3
2.1.4 Tape Cutter Mechanism ................................................................................. II-5
2.1.5 Cutter Safety Lock Mechanism....................................................................... II-6
2.1.6 Interlock Mechanism of the Roller Holder....................................................... II-7
2.2 DISASSEMBLY & REASSEMBLY ......................................................................... II-8
2.2.1 Disassembly Procedure.................................................................................. II-8
[ 1 ] Removing the cassette cover ASSY, the tape cassette and the batteries..... II-8
[ 2 ] Removing the bottom cover, the cutter case ASSY and the board............... II-9
[ 3 ] Removing the frame ASSY ......................................................................... II-10
[ 4 ] Removing the terminal press cover ............................................................. II-13
[ 5 ] Removing the battery terminals................................................................... II-14
[ 6 ] Removing the sub PCB ............................................................................... II-15
[ 7 ] Removing the main PCB and the rubber 41 key
(PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q/ST-1150).................................................... II-16
[ 8 ] Removing the main PCB, the rubber 40 key and the jog dial
(PT-1250/1160) ........................................................................................... II-17
2.2.2 Reassembly Procedure .................................................................................. II-18
[ 1 ] Installing the rubber 41 key and main PCB (PT-1100/1130/1170/1180/11Q/
ST-1150)..................................................................................................... II-18
[ 2 ] Installing the jog dial, the rubber 40 key and the main PCB
(PT-1250/1160) ........................................................................................... II-19
[ 3 ] Installing the sub PCB ................................................................................. II-20
[ 4 ] Installing the battery terminals..................................................................... II-21
[ 5 ] Installing the terminal press cover ............................................................... II-21
[ 6 ] Installing the frame ASSY............................................................................ II-22
[ 7 ] Installing the cutter case ASSY, board and the bottom cover....................... II-25

[ 8 ] Installing the tape cassette, the batteries, and the cassette cover ASSY...... II-26
[ 9 ] Demonstration print and final check............................................................. II-27
2.3 TROUBLESHOOTING.......................................................................................... II-33
2.3.1 Precautions.................................................................................................... II-33
2.3.2 After Repairing............................................................................................... II-33
2.3.3 Error Message Display ................................................................................... II-34
2.3.4 Troubleshooting Flows.................................................................................... II-35
[ 1 ] Tape feeding failure..................................................................................... II-35
[ 2 ] Printing failure............................................................................................. II-37
[ 3 ] Powering failure (Nothing appears on the LCD) ........................................... II-39
[ 4 ] No key entry possible .................................................................................. II-40
CHAPTER II MECHANISM
2.1 THEORY OF OPERATION
2.1.1 Print Mechanism
(1) Structure of Thermal Head
This machine uses thermal transfer printing. The thermal print head has a heat generator
consisting of 64 heating elements which are vertically aligned as shown in Fig. 2.1-1.
Each heating element is 0.195 mm wide by 0.141 mm high.
Fig. 2.1-1 Heat Generator of Thermal Head
(2) Printing process
When the cylindrical rubber platen roller is pressed against the thermal print head with the
tape* and ink ribbon sandwiched inbetween, the CPU applies electric power to the selected
ones of those 64 heating elements.
* Laminated tape when using laminated tape cassettes.
Non-laminated tape when using non-laminated cassettes.
[For tape cassette except non-laminated thermal film tape cassettes]
If the selected heating element(s) generates heat, the ink on the sandwiched ribbon will be
melted and transferred to the tape, producing a dot(s) on the tape. The ink ribbon and the
tape are advanced and then the next heating cycle is repeated, thus forming a character on
the tape.
[For non-laminated thermal film tape cassettes]
If the selected heating element(s) generates heat, the thermal film tape develops itself to
produce a dot on the tape. The tape is advanced and the next heating cycle is repeated,
thus froming a character on the tape.
(3) Character Formation
While the drive motor (DC motor) feeds the tape and ink ribbon by 0.141 mm for approx
14.0 ms, the thermal head generates heat once. The feed amount of 0.141 mm is smaller
than the width (0.195 mm) of the heating elements so that the heat generated at one
heating cycle will overlap with the next heating cycle. This forms a character having no gap
between adjacent printed dots.
II-1
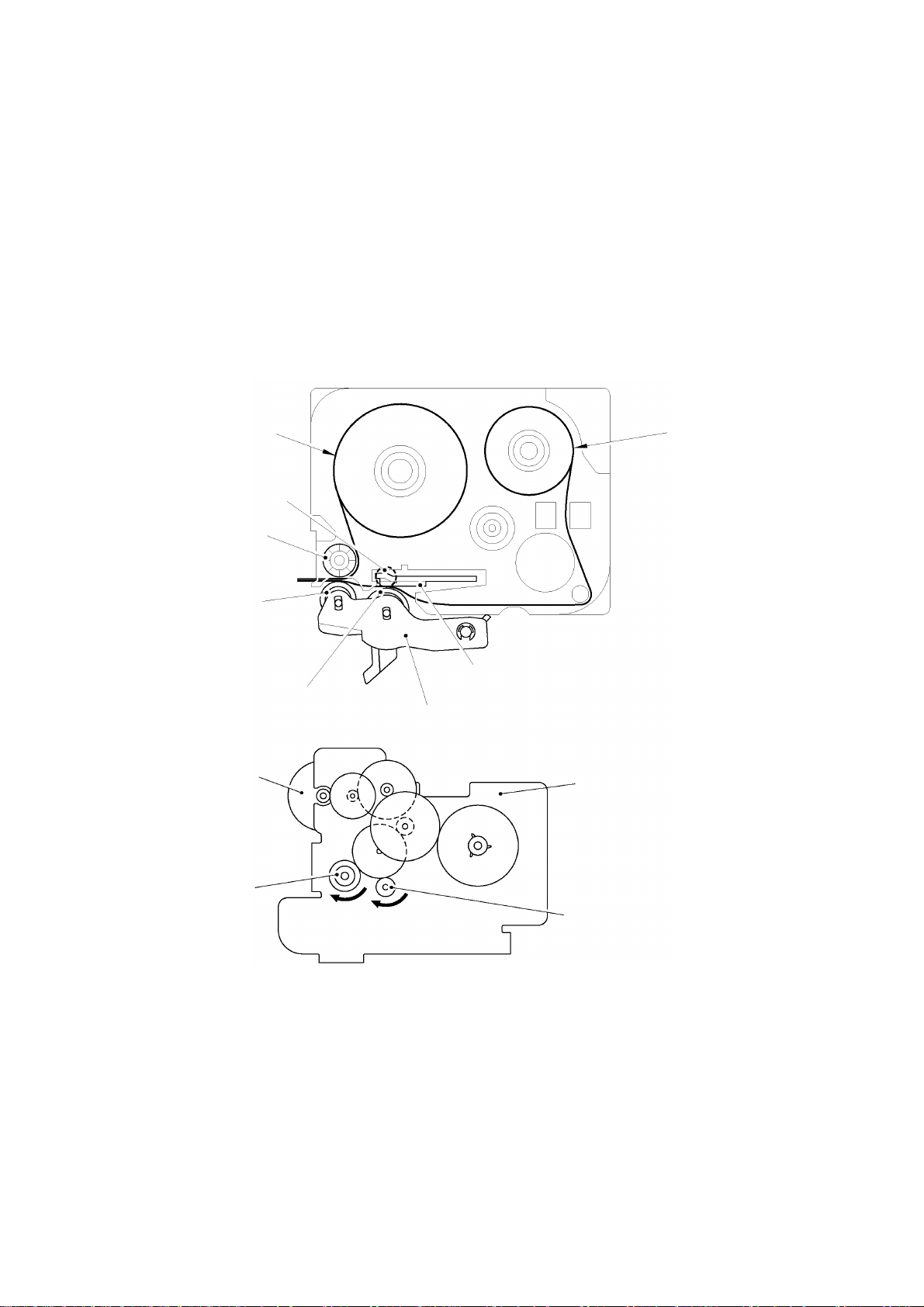
2.1.2 Platen Roller, (Tape Feed) Sub Roller Setting & Retracting Mechanism
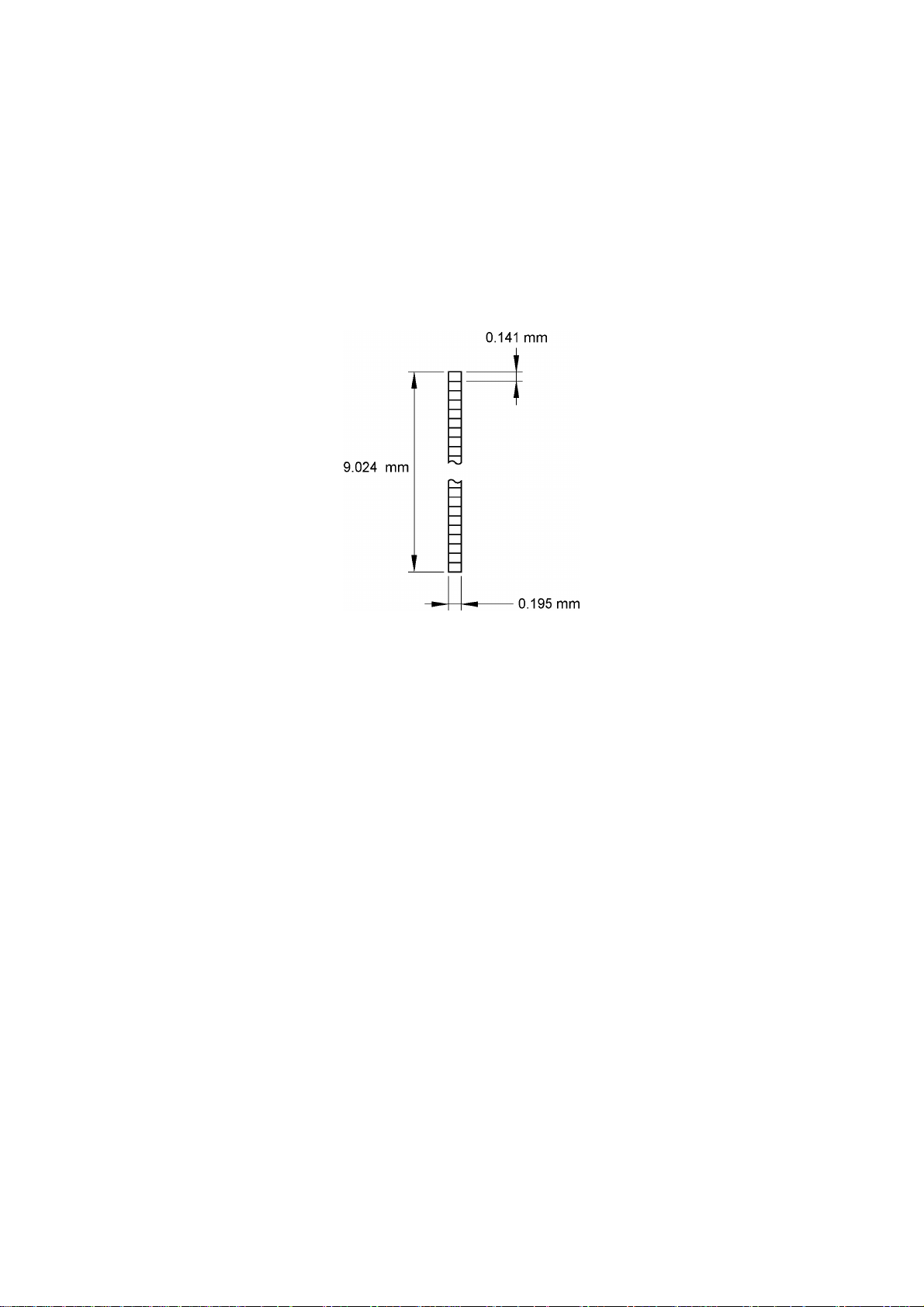
This mechanism consists of the holder cam (cassette cover ASSY) and the roller holder ASSY.
The roller holder ASSY supports the platen roller and the sub roller so that :
Ÿ the platen roller can move perpendicularly to the thermal head and rotate freely and
Ÿ the sub roller can move perpendicularly to the tape feed roller and rotate freely.
By closing the cassette cover ASSY, the holder cam of cassette cover ASSY pushes the roller
holder ASSY toward thermal head side by pushing A face of the roller holder ASSY.
The platen roller is pressed perpendicularly against the thermal head with the tape and ink ribbon
(only the tape when using non-laminated thermal film tape cassettes) sandwiched inbetween under
a uniform load by the roller holder springs (upper and lower). Also, the (tape feed) sub roller is
pressed perpendicularly against the tape feed roller built in the tape cassette with the tape (the
laminate tape and adhesive base tape when using laminated tape cassettes) sandwiched
inbetween by the roller holder springs (upper and lower) and at the same time the (tape feed) sub
roller gear becomes engaged with the tape idle gear.
Opening the cassette cover ASSY, (the holder cam of the cassette cover ASSY is released from
the roller holder ASSY), retracts the roller holder ASSY from the thermal head, providing you with
enough space to replace the tape cassette.
(Tape feed) platen gear
(Tape feed) sub roller gear
Adhesive base tape
Tape cassette
Platen idle gear
Tape feed roller
(Tape feed) sub roller
Holder cam
Roller holder lower spring
Laminate tape
Ink ribbon
Thermal head
Shaft
Roller holder ASSY
Platen roller
A
Roller holder release spring
Roller holder upper spring
(Tape feed) sub roller
Fig. 2.1-2 Platen and (Tape Feed) Sub Roller Setting & Retracting Mechanism
(Top)
Platen roller
II-2
2.1.3 Tape & Ribbon Feed Mechanism
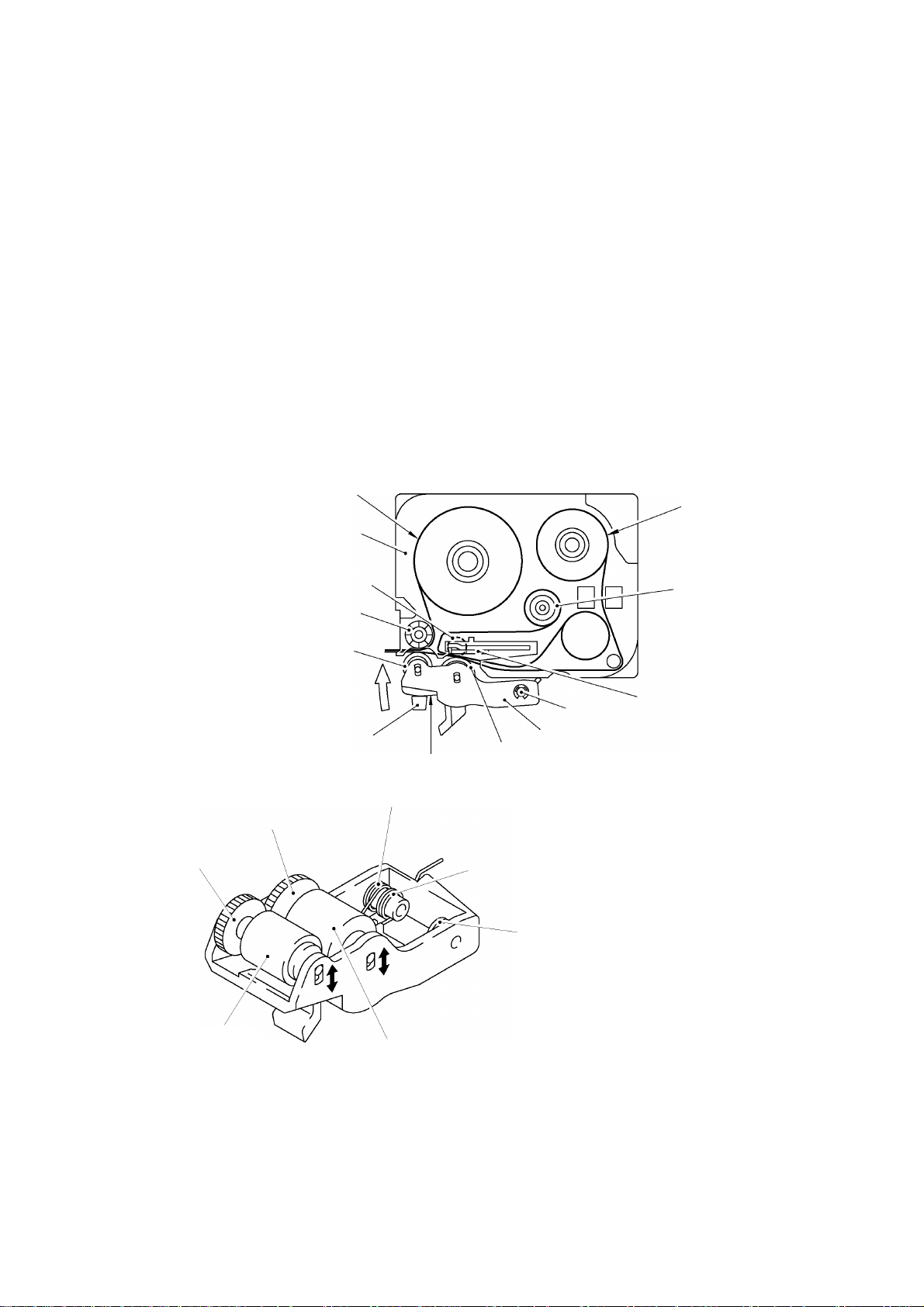
This mechanism consists of a DC motor, gear train, and roller holder ASSY.
(1) Tape Feeding
As the tape feed motor (DC motor) rotates, the rotation is transmitted via the gear train to
the platen idle gear (which rotates both the platen gear) and the tape idle gear (which
rotates the tape feed sub roller).
Accordingly, the sandwiched tape and ink ribbon will be advanced. (When a laminated tape
cassette is mounted, the sandwiched laminate tape, adhesive base tape, and ink ribbon will
be advanced together.)
The feeding amount of the platen is slightly less than that of the tape feed sub roller.
Platen idle gear
Tape feed roller
Transparent laminate tapeAdhesive base tape
(Tape feed) sub roller
DC motor
Tape idle gear
Thermal head ASSY
Platen roller
Roller holder ASSY
Frame
Platen idle gear
Fig. 2.1-3 Tape Feeding Mechanism
II-3
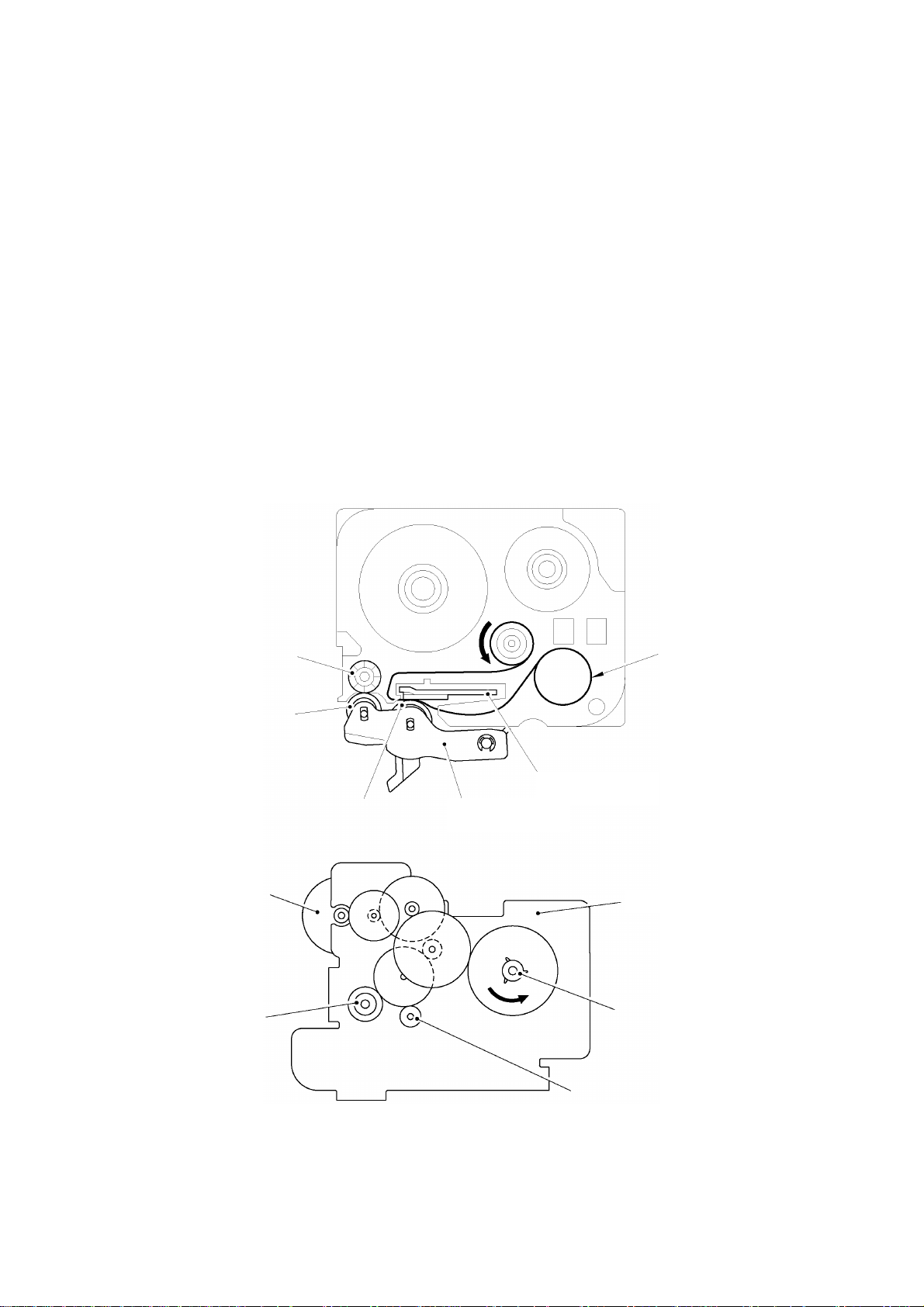
(2) Adhesive Base Tape Feeding (only for laminated tape cassettes)
A laminated tape cassette contains both a transparent laminate tape roll and a separate
adhesive base tape roll.
When a transparent laminate tape and an adhesive base tape pass through the contact
point (between the tape feed roller and (tape feed) sub roller), they are then bonded together
into a single, printed tape. The ink printed on the laminate tape is, therefore, sealed up with
the adhesive base tape.
(3) Ink Ribbon Feeding
As the DC motor rotates, the ribbon drive cam located at the middle of the gear train rotates
counterclockwise. When fitted on the ribbon drive cam, the ribbon take-up roll in the tape
cassette also rotates to take up the ink ribbon.
To apply proper tension to the ink ribbon between the platen roller and the ribbon drive cam,
the feed amount of the ribbon drive cam is slightly greater than that of the platen idle gear.
The difference between the tape feed speeds at the platen roller and at the ribbon drive cam
is absorbed by the clutch spring which is integrated in the ribbon drive cam and allows the
cam to slip.
In this way, the ink ribbon is kept tense, which enables the ribbon to clearly separate from
the tape at the stabilized angle after printing.
Tape feed roller
(Tape feed) sub roller
DC motor
Tape idle gear
Platen roller
Ink ribbon
Thermal head ASSY
Roller holder ASSY
Frame
Ribbon drive cam
Platen idle gear
Fig. 2.1-4 Ribbon Feeding Mechanism
II-4
2.1.4 Tape Cutter Mechanism
The tape cut unit consists from the cutter case ASSY and the board.
Tape that finished printing is fed out from the tape cassette and stops at a point passed between
the cutter case ASSY and the board.
When the cutter lever is pushed at this point, then, the cutter case ASSY (cutter blade) is operated
to cut tape.
Board
Cutter case ASSY
Cutter blade
Fig. 2.1-5 Tape Cutter Mechanism
Tape cassette
Cutter lever
II-5
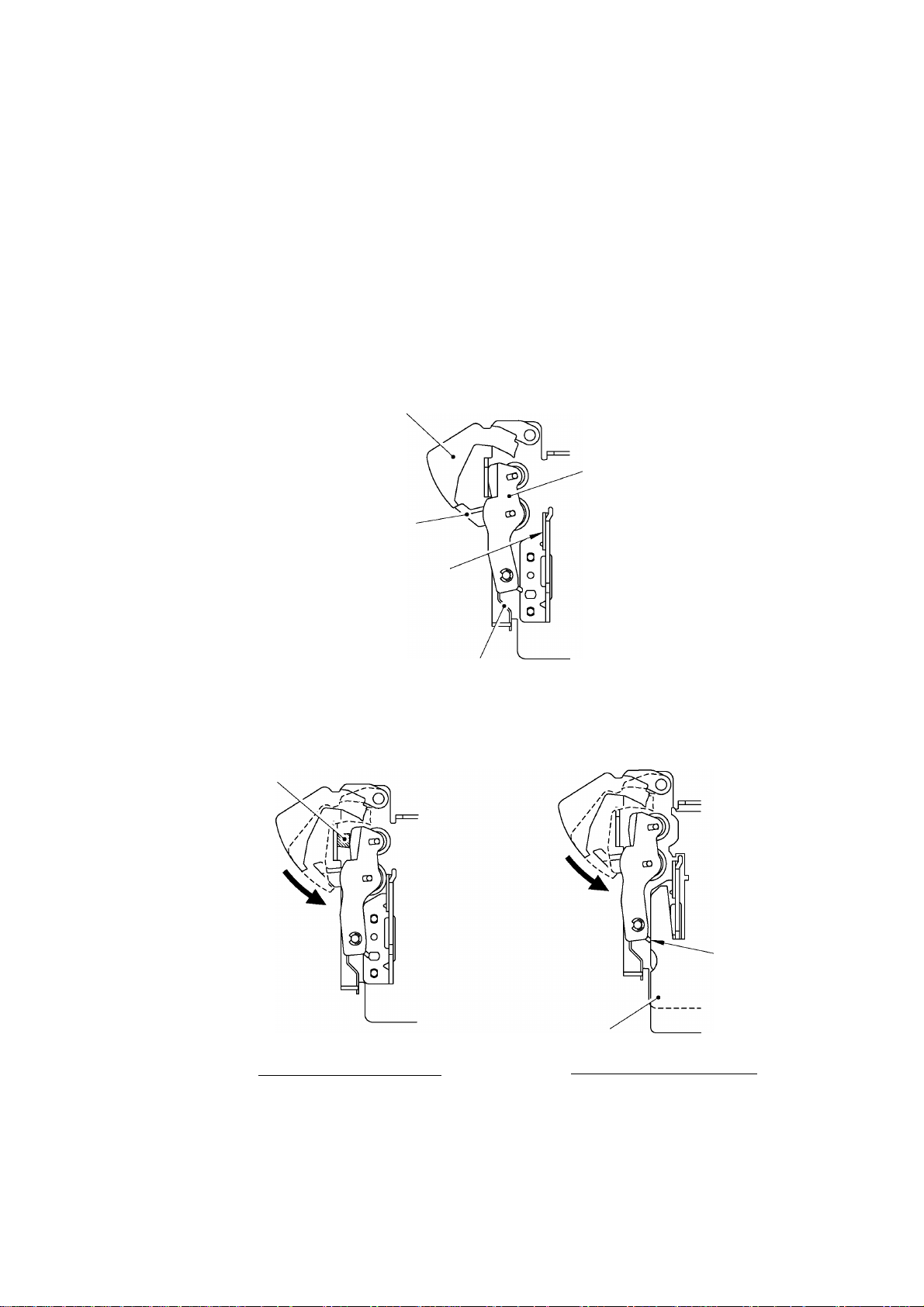
2.1.5 Cutter Safety Lock Mechanism
When the cassette cover ASSY is opened and no tape cassette is loaded, the roller holder ASSY
is retracted from the thermal head with the roller holder release spring (as described in Subsection
2.1.2). In this retracted position, the cutter lever stopper of the roller holder ASSY blocks the end
of the cutter lever, preventing the cutter blade from coming out of the cutter case ASSY for safety,
as shown below.
Closing the cassette cover ASSY or loading a tape cassette release the cutter safety lock
mechanism as follows.
Closing the cassette cover ASSY pivots the roller holder ASSY towards the thermal head so that
the cutter lever stopper does not interfere with the cutter lever.
When a tape cassette is loaded, its outer edge pushes the tab of the roller holder ASSY to pivot
the roller holder ASSY towards the thermal haed so that the cutter lever stopper does not interfere
with the cutter lever.
Cutter lever
Cutter lever stopper of the
roller holder ASSY
Roller holder ASSY
Thermal head
Holder cam (provided on the inside of the
cassette cover ASSY)
Closing the cassette cover
Fig. 2.1-7 Releasing the Cutter Safety Lock Mechanism
Roller holder
release spring
Fig. 2.1-6 Cutter Safety lock Mechanism
Tab of the roller
holder ASSY
Tape cassette
(edge)
Loading the cassette cover
II-6
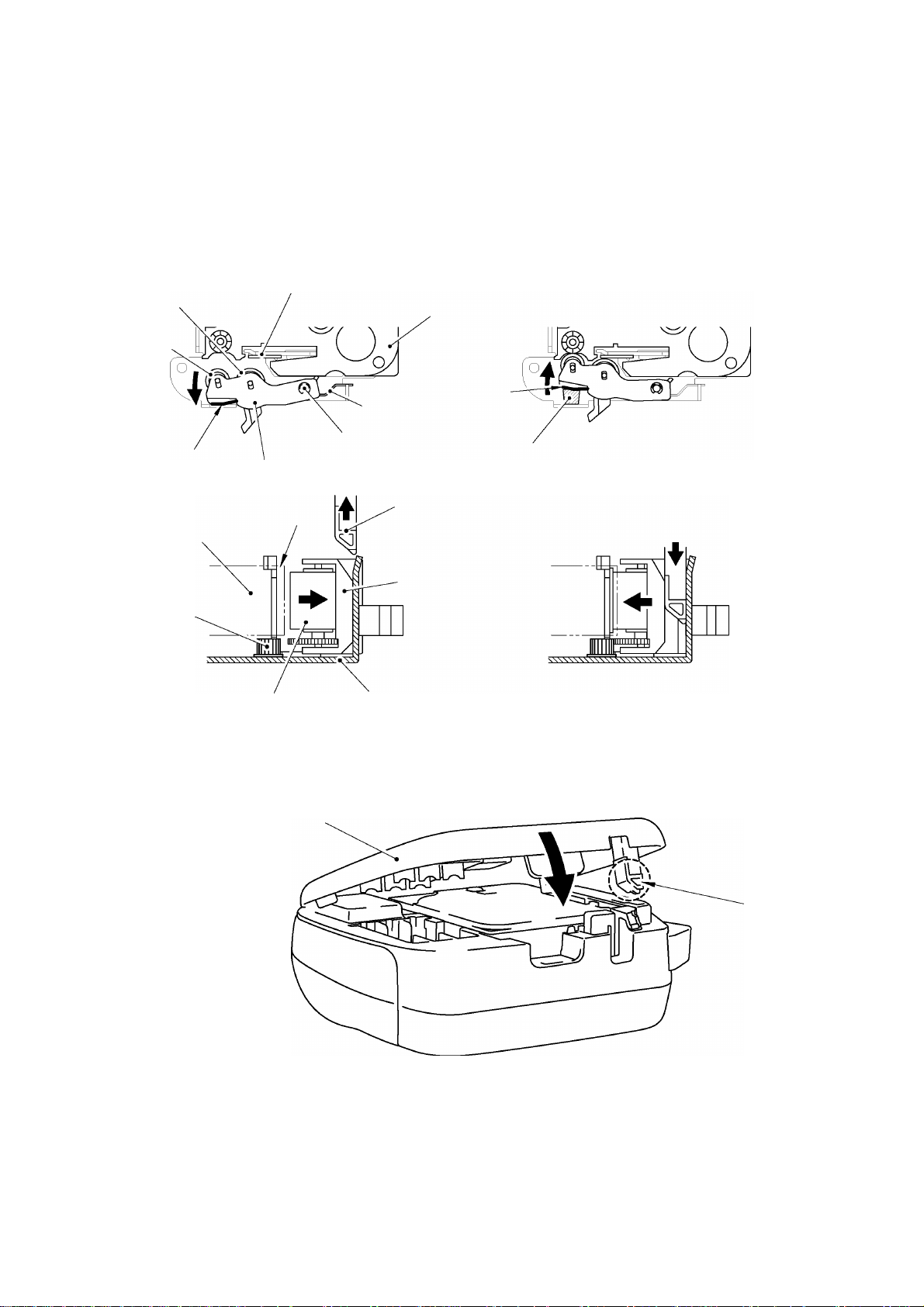
2.1.6 Interlock Mechanism of the Roller Holder
(1) When the cassette case ASSY is opened, then the holder cam attached at back side of
cassette cover is released from surface A. Following to that, the roller holder ASSY is
retracted from the thermal head side with tension of the roller release spring.
(2) When the cassette cover ASSY is closed, then the holder cam located at backside pushes
the thermal head at roller holder ASSY by pressing A surface of the roller holder ASSY.
Platen roller
(Tape feed)
sub roller
Tape cassette
Platen idle gear
Thermal head
Tape cassette
A
Roller holder
release spring
Shaft
A
Roller holder ASSY
Platen roller
Thermal head
Holder cam (Cassette
cover ASSY)
Roller holder ASSY
Frame ASSY
Holder cam (Cassette
cover ASSY)
(Roller Holder ASSY retracted) (Roller Holder ASSY engaged)
Fig. 2.1-8 Holder Cam (Cassette Cover ASSY) and Roller Holder ASSY
Cassette cover ASSY
Fig. 2.1-9 Interlock Mechanism of the Roller Holder
II-7
Holder cam
2.2 DISASSEMBLY & REASSEMBLY
2.2.1 Disassembly Procedure
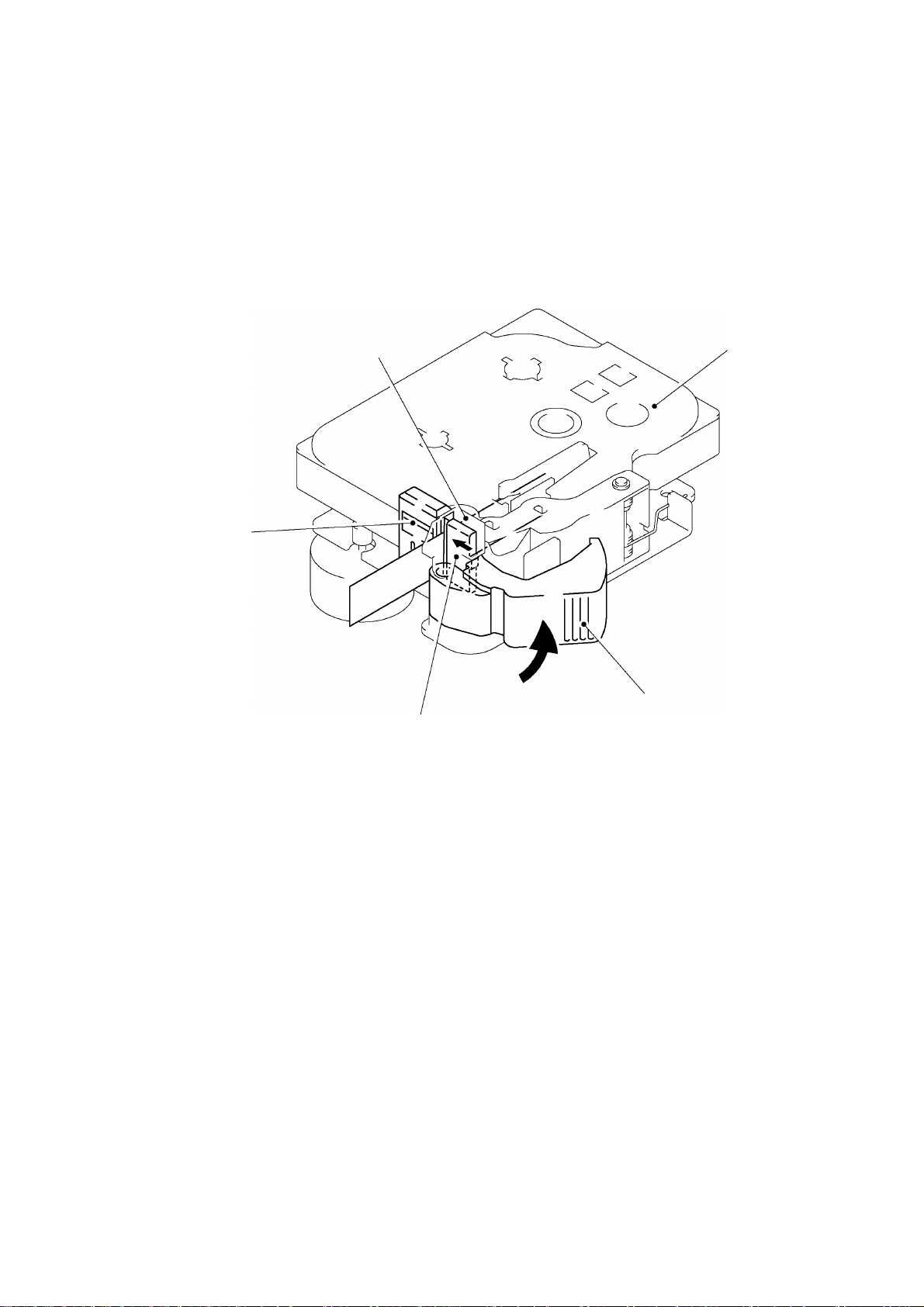
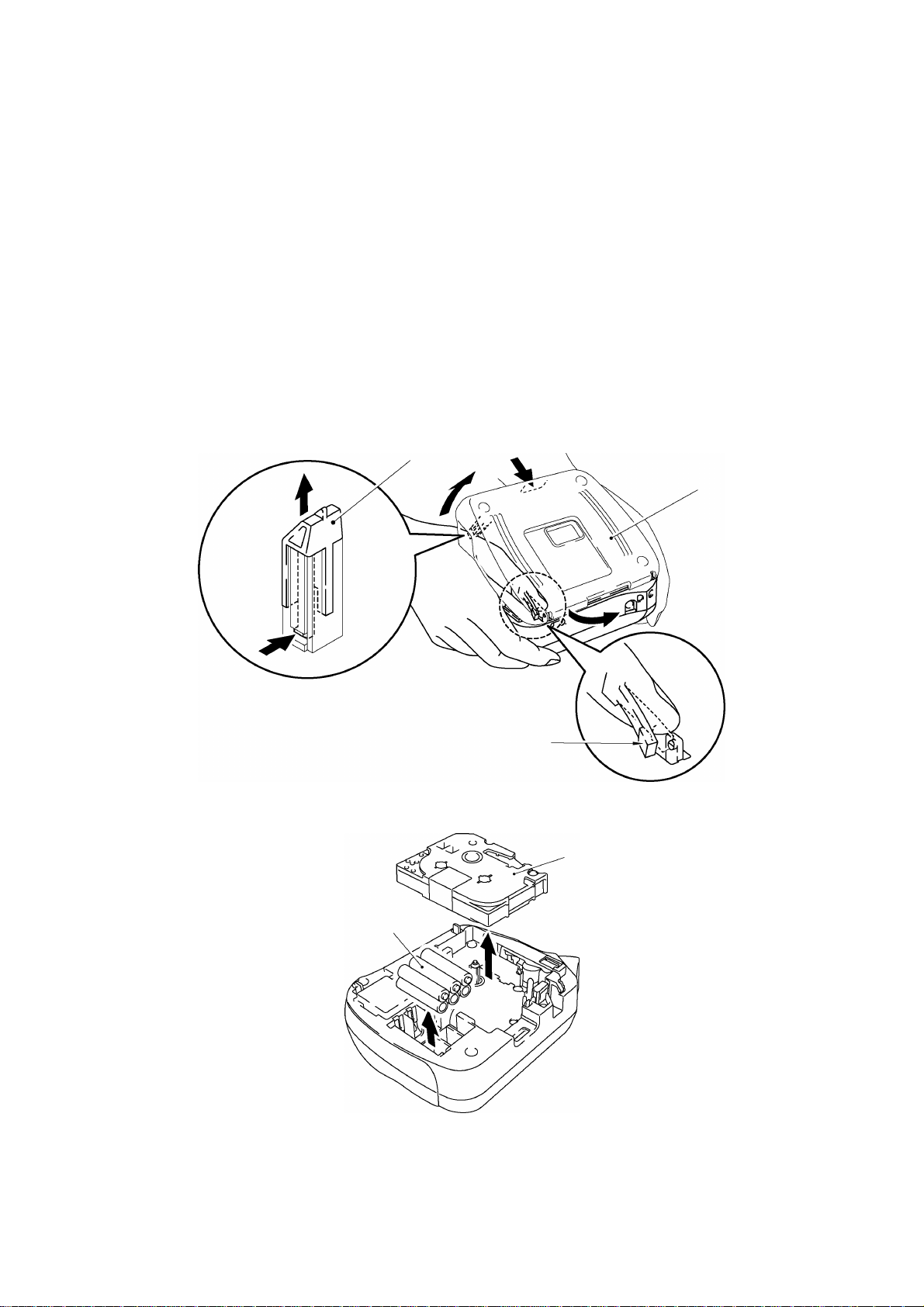
[ 1 ] Removing the cassette cover ASSY, the tape cassette and the batteries
(1) Turn the machine upside down.
(2) Open the cassette cover ASSY by applying the force toward “A” direction.
(3) Push the rib “B” on the holder cam assembled on the cassette cover ASSY to the direction
of the arrow to remove the holder cam from the cassette cover ASSY.
Caution: Never draw out the holder cam. The rib “B” on the holder cam may be damaged.
(4) The cassette cover is removed by applying a force toward “D” direction of the arrow by
pushing the “C” section outward.
(5) Remove the tape cassette.
(6) Remove the batteries.
PT2002008
“B”
Holder cam
Fig. 2.2-1 Removing the Cassette Cover
“A”
“C”
Tape cassette
Cassette cover ASSY
“D”
Batteries
Fig. 2.2-2 Removing the Tape Cassette and Batteries
II-8
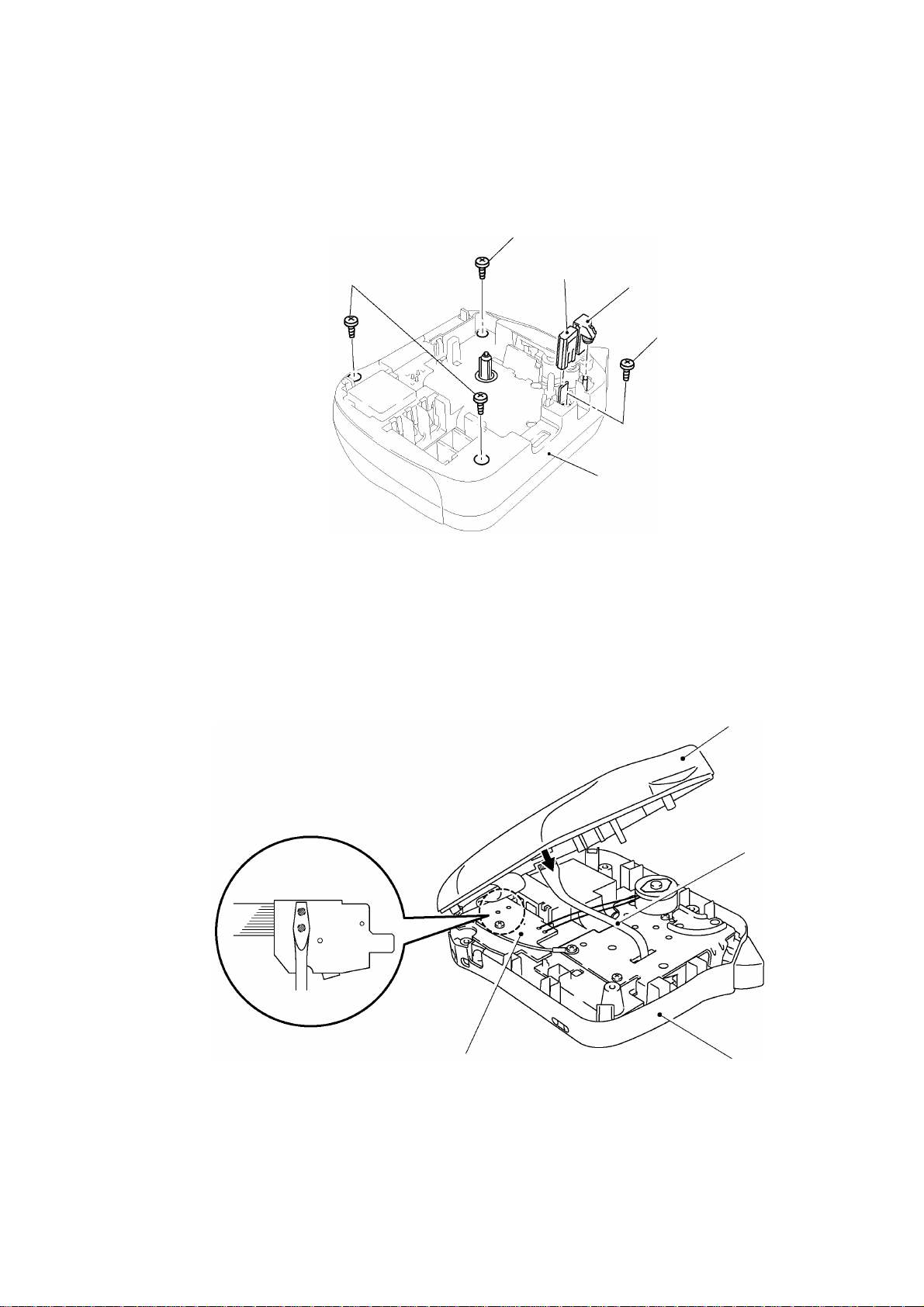
[ 2 ] Removing the bottom cover, the cutter case ASSY and the board
(1) Place the machine upside down.
(2) Pull out the cutter case ASSY and the board from the frame.
(3) Remove the four screws, then the bottom cover and the upper cover are able to be
separated.
Screw
Screws
Board
Cutter case ASSY
Screw
Bottom cover
Fig. 2.2-3 Removing the Bottom Cover, Cutter Case ASSY and the Board (1)
(4) Open the upper cover to the left as shown below.
(5) Discharge the condenser (C1) on the sub PCB ASSY with tool like a screwdriver.
(6) Disconnect the thermal head flat cable from the main PCB.
Note: Discharge without fail before disconnecting the thermal flat cable, otherwise the electronic
part such as LSI or others should be damaged.
Upper cover
Sub PCB
Fig. 2.2-4 Removing the Bottom Cover, Cutter Case ASSY and the Board (2)
II-9
Thermal head flat cable
Bottom cover
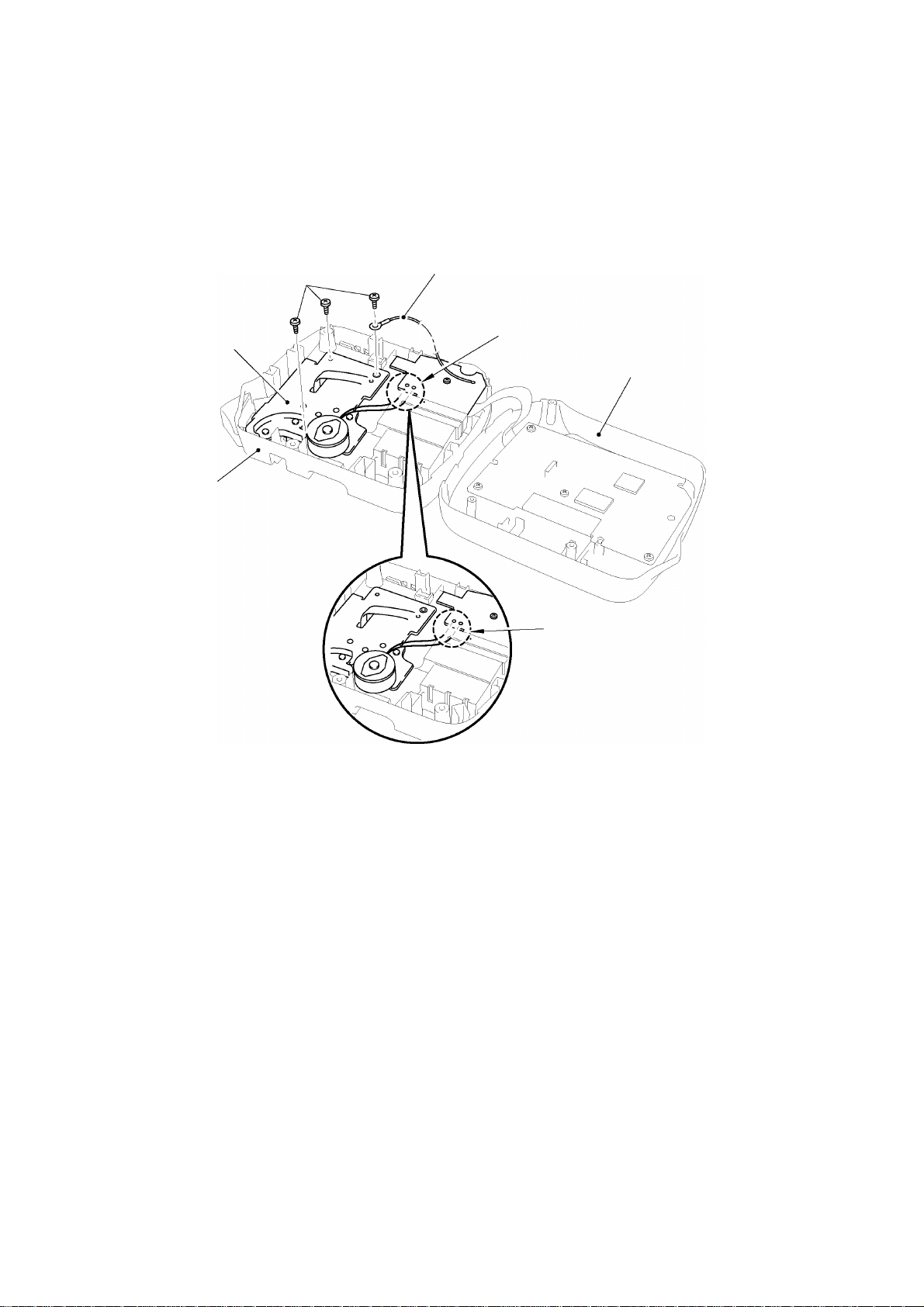
[ 3 ] Removing the frame ASSY
(1) Remove the two motor harnesses from the sub PCB by melting the solder.
(2) Remove the three screws and remove the frame ASSY from the bottom cover.
Note: The cutter lever will be disconnected from the cutter lever shaft of the frame Assy at this
point.
Frame ASSY
Bottom cover
Screws
FG harness
Melting the solder
Upper cover
Melting the solder
Fig. 2.2-5 Removing the Frame ASSY
II-10
 Loading...
Loading...