Brinkmann TSF, BFS User Manual

BAS6960
BRINKMANN PUMPS, Inc.
47060 Cartier Drive
Wixom, MI 48393
USA
Phone: +1 248 926 9400 www.brinkmannpumps.com
Fax.: +1 248 926 9405 sales@brinkmannpumps.com
Subject to change without prior notice. Order - No.: BAS6960 ENGLISH
Operating Instructions
BRINKMANN-Screw Pump
BFS / TFS / FFS / BFS-H / TFS-H / BFG / FFG
© Brinkmann Pumpen Edition 03/2020 Page 1 of 15
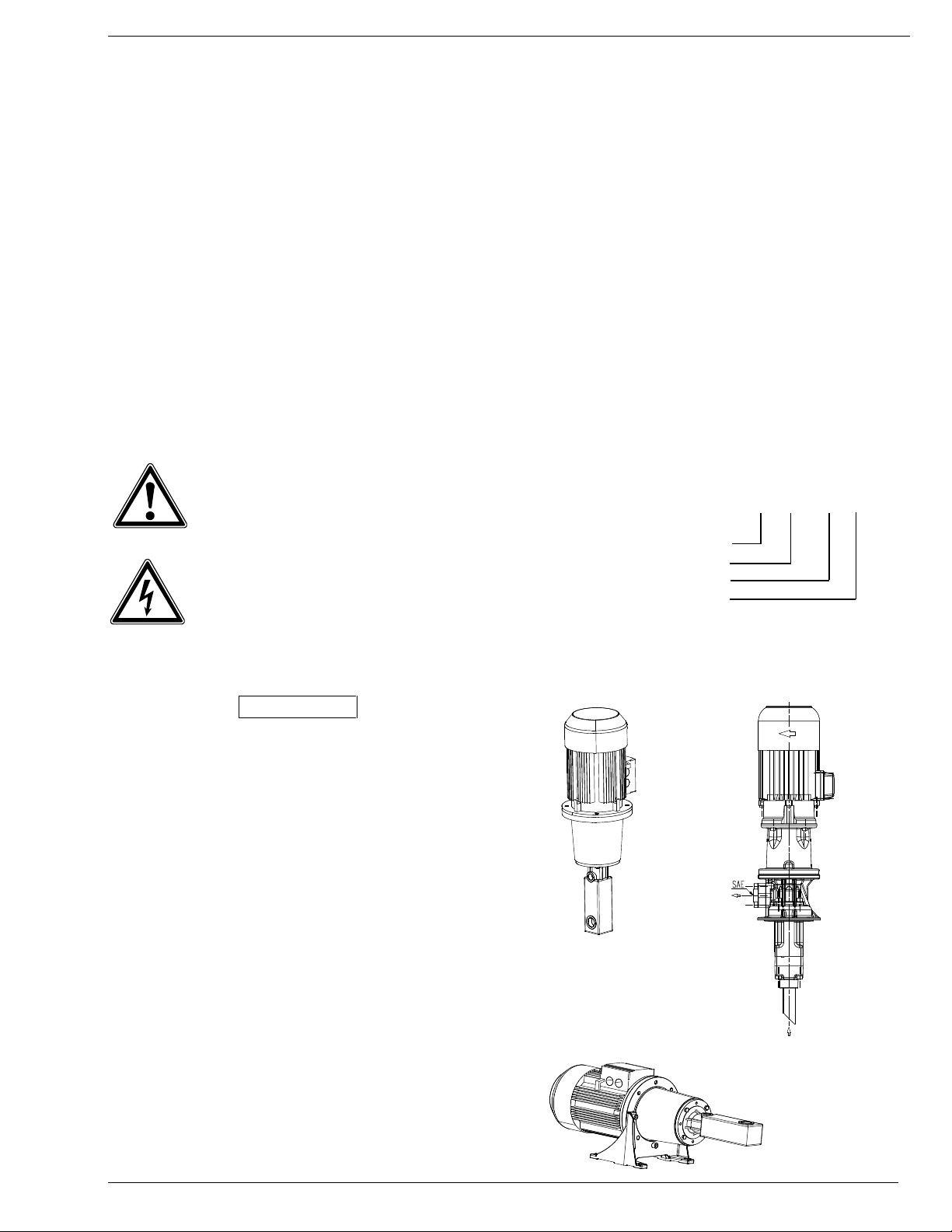
BRINKMANN-Screw Pump Type BFS / TFS / FFS
Contents
1 Indication to the manual .................................... 2
2 Description of product and working principle .. 2-3
3 Safety instructions .......................................... 4-5
4 Transport, and Temporary storage .................... 5
5 Installation / Connection ................................. 6-8
6 Start up / Shut down ....................................... 8-9
7 Operation ........................................................... 9
1 Indication to the manual
This operating manual gives basic instructions which
are to be observed during installation, opera-tion and
maintenance of the pump. It is therefore imperative
that this manual be read by the respon-sible personnel and operator prior to assembly and commissioning. It is always to be kept available at the installation
site.
1.1 Identification of safety instructions in the
operating manual
Safety instructions given in this manual noncompliance with which would affect safety are identified by the following symbol
Safety sign according with ISO 3864–B.3.1
or where electrical safety is involved, with
Safety sign according with ISO 3864–B.3.6
Where non-compliance with the safety instructions
may cause a risk to the machine and it’s function the
word
ATTENTION
is inserted.
8 Servicing and Maintenance ............................. 10
9 Trouble shooter’s guide ................................... 11
10 Spare part ....................................................... 12
11 Repair Instructions ..................................... 12-13
12 Disposal .......................................................... 13
13 Terms and Conditions ............................ 14-15
• The medium moves continuously and without
noticeable pulsation toward the pump discharge.
• Proper clockwise rotation must be ensured at all
times. Incorrect counterclockwise rotation will result in dry running and pump damage. Catastrophic failure is possible!
• Screw pumps are self-priming, however, dry
running must be avoided under any circumstances
as it will almost instantly damage the pump and it
might result in catastrophic failure.
• Screw pumps are positive displacement pumps
and must therefore always be used in combination
with a pressure limiting valve or pressure relief
valve.
2.4 Type code structure (example)
High pressure screw pump: BFS 250 S 80 -G
Pump series designation
BFS, TFS or FFS
Pump size
Maximum pressure in bar
Special features
(e.g. with mechanical seal)
2.5 Pump Models
Immersion style
BFS, TFS (-H) pressure outlet above tank plate
2 Description of product and working prin-
ciple
2.1 Scope
Pumping of fluids at high backpressure. The discharge pressure needs to be at least 2 bar higher
than the inlet pressure.
2.2 Application range
• Screw pumps are designed for pumping filtered,
lubricating fluids (Please consult with the manufacturer for specific applications).
• Screw pumps are used in applications where high
pressures and constant flow rates are required
(e.g. general machine design, machine tool industry, etc.)
Operate pump within the design limititations and in
accordance with section 2.6.
2.3 Working principle
• The intermeshing threads of three screw spindles
generate liquid holding chambers.
• The center spindle is driven and all three screw
spindles rotate.
BAS6960 Edition 03/2020 Page 2 of 15
FFS foot mounted inline style
2.6 Limit of Application
Materials
Particle
size
Particle
concentration:
Steel / Forgeable
aluminium alloys
(without Si content) /
GG25
BFG, FFG, BFS,
FFS
< 60 m
< 177 mg/l
Grey cast iron with
hard additives
(e.g. GGV)
BFS, FFS
< 50 m
< 63 mg/l
Ceramic/ corundum
/ hard metal / glass /
CBN Aluminium
alloy with Si parts
BFS, FFS
< 20 m
< 19 mg/l
The particle concentration refers to standardized test.
For additional information please refer to the
filtration diagram in the screw pump catalogue.
ATTENTION
If high pressure screw pumps are to be used
outside of the recommended ranges, a suitable
filter system (e.g. filter bags) must be installed
upstream from the pump or pumps with special
features must be used (e.g., with coated spindles).
If pump failure is caused by excessive wear due
to foreign particles, the warranty is void!
In applications where hard or abrasive particles
are present, the use of coated spindles is highly
recommended.
2.8 Technical data
Detailed technical data can be found in the
screw spindle pump catalogue.
Type
BFS, TFS, FFS
Mediums
Oils, cooling / cutting oils
coolants
Max. delivery
pressure
870 PSI (60 bar) (BFG, FFG with cast
iron spindle housing)
2175 PSI (150 bar) (2900 PSI (200 bar)
for BFS/FFS1, BFS/FFS2 and
TFS/BFS/FFS3 upon request)
1740 PSI (120 bar) (-H)
Minimum discharge
pressure
Ensure that the discharge pressure is
at least 29 PSI (2 bar) higher than the
inlet pressure
Minimum inlet
pressure
In order to prevent
damage from
cavitation
12 PSI (0.8 bar) absolute, with increased fluid temperature also more,
(Pumps with a flow rate of greater than
210 GPM (800 l/min) have to be
operated in conjunction with a feed
pump > 14.5 PSI (1 bar)).
Kinetic viscosity of
the medium
4.6...200 SSU (1...45 mm2/s (cSt))
higher viscosities upon request
Max. temperature
of medium
140 °F (60°C)
higher temperatures upon request
Max. air content
3 – 5 vol. %
Max. inlet pressure
with mechanical
seal
Execution -G4
< 100 PSI (7 bar)
290 PSI (20 bar)
Concentration of
coolant lubricants
and water soluble
coolants
The fluid must have a minimum lubricity in accordance with industry standards. This corresponds to an approx.
4% concentration equivalent to mineral
oil. A laboratory analysis is available at
the factory.
Minimum flow rate
The minimum flow rate must be large
enough to protect the pump from
overheating. If necessary, consult with
the manufacturer on exact flow rate.
Minimum rpm
25 Hz (1500 rpm), lower rpm are
available upon request. The minimum
rpm depends on the pressure and
medium.
Dry running
The pump MUST never be run dry
without fluid. When testing for the
direction of rotation, bump the pump for
not longer than 1 second.
Cycle times per
hour
Motors less 4.0 HP / 3 kW: up to 200
times per hour.
Motors from 4.0 HP (3 kW) to 5.4 HP
(4.0 kW): up to 40 times per hour.
Motors from 6.7 HP (5.0 kW) to 12 HP
(9 kW): up to 20 times per hour.
Motors from 13.4 HP (10 kW) to 29.5
HP (22 kW): up to 15 times per hour
Increased cycle times are available
upon request.
Maximum fluid
velocity at pump
suction
2 m/s
Installation positions
(Pump must not be installed with motor
facing down)
Piping / Fittings
Pay attention to max. pressure ratings
Ambient temperature
104 °F (40 °C)
Set-up altitude
3280 ft (1000 m)
ATTENTION
The pumps are to be operated within their design
limits. Applications outside of these limits are not
approved. The manufacturer is not responsible for
any damages resulting from use of the pumps in such
applications.
2.7 Important instructions for screw pumps
• Never allow screw pumps to run dry!
• Incorrect rotation will lead to pump dam-
age!
• Sufficient fluid supply must always be ensured!
• Large particles in the coolant fluid may
damage the screw pump!
• The limits for size and concentration of
foreign particles depends on their hardness!
BAS6960 Edition 03/2020 Page 3 of 15
3 Safety instructions
When operating the pump, the safety instructions
contained in this manual, the relevant national accident prevention regulations and any other service
and safety instructions issued by the plant operator
are to be observed.
3.1 Hazards in the event of non-compliance with
the safety instructions
Non-compliance with the safety instructions may
produce a risk to the personnel as well as to the
environment and the machine and results in a loss of
any right to claim damages. For example, noncompliance may involve the following hazards:
• Failure of important functions of the ma-
chines/plant
• Failure of specified procedures of maintenance
and repair
• Exposure of people to electrical, mechanical and
chemical hazards
• Endangering the environment due to hazardous
substances being released
3.2 Unauthorized modes of operation
3.5 Safety instructions relevant for operation
• If hot or cold machine components involve hazards, they must be guarded against accidental
contact.
• Guards for moving parts (e.g. coupling) must not
be removed from the machine while in operation.
• Never subsequently alter any safety devices (e.g.
pressure relief valves)!
• It is necessary to ensure that all safety devices
always work properly!
• Any leakage of hazardous (e.g. explosive, toxic,
hot) fluids (e.g. from the shaft seal) must be
drained away so as to prevent any risk to per-sons
or the environment. Statutory regulations are to be
complied with.
• Hazards resulting from electricity are to be prevented (see for example, the VDE Specifications
and the bye-laws of the local power supply utilities).
• The pumps’ stability against falling over is not
ensured unless it is properly mounted onto the
tank or to the floor.
• The female threads on the motor MUST NOT be
used to lift the entire pump and motor assembly.
• Pump may not be used in potentially explosive
environments!
• Pump and discharge piping are not designed to
hold any weight and may not be used as a step
ladder.
3.3 Remaining Risk
Risk of Injury!
Risk of squeezing or crushing body parts when
installing or removing the pump exists. Proper and
secured lifting tools must be used.
Risk of burns!
The pump must have cooled down sufficiently prior to
commencing any repair, maintenance or installation.
3.4 Qualification and training of operating per-
sonnel
The personnel responsible for operation, maintenance, inspection and assembly must be adequately
qualified. Scope of responsibility and supervision of
the personnel must be exactly defined by the plant
operator. If the staff does not have the necessary
knowledge, they must be trained and instructed,
which may be performed by the machine manufacturer or supplier on behalf of the plant operator.
Moreover, the plant operator is to make sure that the
contents of the operating manual are fully understood
by the personnel.
3.6 Safety instructions relevant for maintenance, inspection and assembly work
Any work on the machine shall only be performed
when it is at a standstill, it being imperative that the
procedure for shutting down the machine described in
this manual be followed.
Pumps and pump units which convey hazardous
media must be decontaminated.
On completion of work all safety and protective
facilities must be re-installed and made operative
again.
Prior to restarting the machine, the instructions listed
under “Start up” are to be observed.
3.7 Signs on the pump
It is imperative that signs affixed to the machine, e.g.
• arrow indicating the direction of rotation
• symbols indicating fluid connections
be observed and kept legible.
BAS6960 Edition 03/2020 Page 4 of 15

3.8 Unauthorized alterations and production of
Drawing 1
spare parts
Any modification may be made to the machine only
after consultation with the manufacturer. Using spare
parts and accessories authorized by the manufacturer is in the interest of safety. Use of other parts may
exempt the manufacturer from any liability.
4 Transport and Temporary Storage
Protect pumps against damage during transportation.
The pumps may only be transported lying flat and
must be secured on the motor side as well as on the
pump side.
Store pumps protected from moisture in an enclosed
location. Prevent foreign bodies from entering the
pump.
Keep the storage temperature above freezing
Pumps are factory preserved.
If storage exceeds 6 months, the preservation should
be checked and reapplied if applicable.
Pumps that have been immersed or have been
running must be cleaned and preserved prior to
storage. This applies especially to water based fluids!
4.1 Pump Preservation
4.1.1 Draining pump
Pumps with mechanical seal –G or axial thrust
–A:
6. Place pump on a work bench (7) horizontally
with the threaded port facing up. The flange (8)
may not touch the surface. See picture 1.
7. Plug outlet port (5) with a sealing plastic cap.
8. Turn the motor shaft as quickly as possible
counterclockwise. This will allow for the remaining fluid to drain from the adjacent cavities
(6).
9. Repeat steps 1-8 until no more fluid drains.
4.1.2 Pump preservation
Interior Preservation
1. Outlet (5) and inlet port (3) should be open.
2. Place pump on a work bench (7) horizontally
with the threaded port facing up. The flange (8)
may not touch the surface.
3. Pour preservation agent (spray oil) into the inlet
port (3) and turn motor (1) shaft clockwise until
it becomes visible at the outlet port and the fluid
level of the oil is above the lowest point of the
labyrinth seal area.
Pumps with mechanical seal –G or axial thrust
–A:
4. Plug outlet port (5) with a sealing plastic cap.
5. Turn motor shaft (1) clockwise as quickly as
possible by hand in order for the preservation
agent to enter into the adjacent cavities (6).
1. Separate pump and motor.
2. Clean the pump body thoroughly
3. Outlet (5) and Inlet port should be open.
4. Stand pump up with the coupling (2) facing up
tilting it in direction of the inlet port (3).
5. Turn motor shaft (1) counterclockwise. Keep
pump tilted until it is completely drained.
Exterior Preservation
6. Preserve all unpainted metal components
Drain excess preserving agent and plug outlet and
inlet ports with plastic caps.
Collect draining coolant and oil and dispose in ac-
cordance with applicable local laws and regulations!
BAS6960 Edition 03/2020 Page 5 of 15
 Loading...
Loading...