Page 1

Engineered Solutions | Access Management System V3.0
Access Management System V3.0
www.boschsecurity.com
u Combines high-end access control features,
performance and availability with intuitive
operation.
u Highly scalable: Up to 200,000 users and 10,000
doors.
Access Management System (AMS) is an access
control system for stand-alone application or for
integration with other systems, such as the Bosch
video management system BVMS.
• As a stand-alone system, it features a simple-to-use
map and alarm viewer for a rapid assessment of all
the devices and entrances on the site.
• As an integrated system, it allows the operator of a
video management system to perform door-related
tasks like video-based ID verification, to grant and
deny access, or to disable doors.
AMS combines the robustness, performance and
features of high-end access control products with a
modern UI that makes it faster to install and configure.
The existing portfolio of Bosch access control devices
can be easily scanned and integrated.
Data privacy and IT security is state-of-the-art, in order
to comply with the latest data-protection regulations.
System overview
Access Management Server
The server is the main component for processing all
data. It coordinates the activities of all the hardware
and software components described below.
u Easy to use: Intuitive GUI and built-in map viewer.
u Easy to configure: Pre-packaged licenses, simple
installation and set-up.
u Comprehensive security management: Integrates
with intrusion and video systems.
Master Access Controller (MAC)
The MAC is an additional security layer to increase
system availability. It holds its own database to
exchange information between AMCs, even if the main
server or the network is down.
Access Modular Controller (AMC)
The AMC is a robust and reliable field controller to
connect to up to 8 doors with readers and door
strikes. With its large on-board memory the AMC can
make autonomous decisions and store hundreds of
thousands of access events, regardless of network
interruptions.
Access Management Database
The SQL server holds all master data (cardholder,
cards, authorizations, schedules, etc.) and also all
access events. The latest version provides encryption
to protect personal information from misuse or theft.
Access Management Dialog Manager
The Dialog Manager is the main user interface for
configuring the system, and for collecting and
maintaining access-related information. In particular,
its personnel dialogs are used for enrolling new
cardholders, and maintaining their access
authorizations and credentials.
Page 2
HR Reception
1
2 3 6
4 5
AMS BVMS
1 2
3
4
5 6
| Access Management System V3.0
2
Access Management Map View
The Map View is a simple-to-use application both to
visualize the overall security situation of the premises,
and zoom into close detail. It displays access
violations, tampering and malfunction alarms, and
allows the sending of commands directly from the
maps themselves.
Access Management BVMS Interface
The seamless integration with BVMS (version 10.1 or
higher) allows the video verification of cardholder
identities from the BVMS operator client: a person
requesting access with a valid card can be manually
verified through camera live stream and the
cardholder’s photo from the database. Camera events
can trigger door actions. Door events can trigger
camera actions.
Access Management Intrusion Interface
Management of up to 25 B and G Series intrusion
panels. Shows area states (e.g. armed, ready to arm),
detector states and intrusion events on Map View.
Allows the sending of commands (e.g. arm, disarm) to
panels.
Access Management SDK
This SDK facilitates the integration of 3rd party
systems with AMS, for instance an Identity
Management or Visitor Management system. A
particular advantage is its ability to re-use 3rd party
integrations initially written for BIS Access Engine.
Access Importer/Exporter
This tool facilitates data import and export from
external systems for 1-time data migration, such as
from Access PE systems, or regular data transfer from
Active Directory via the LDAP protocol.
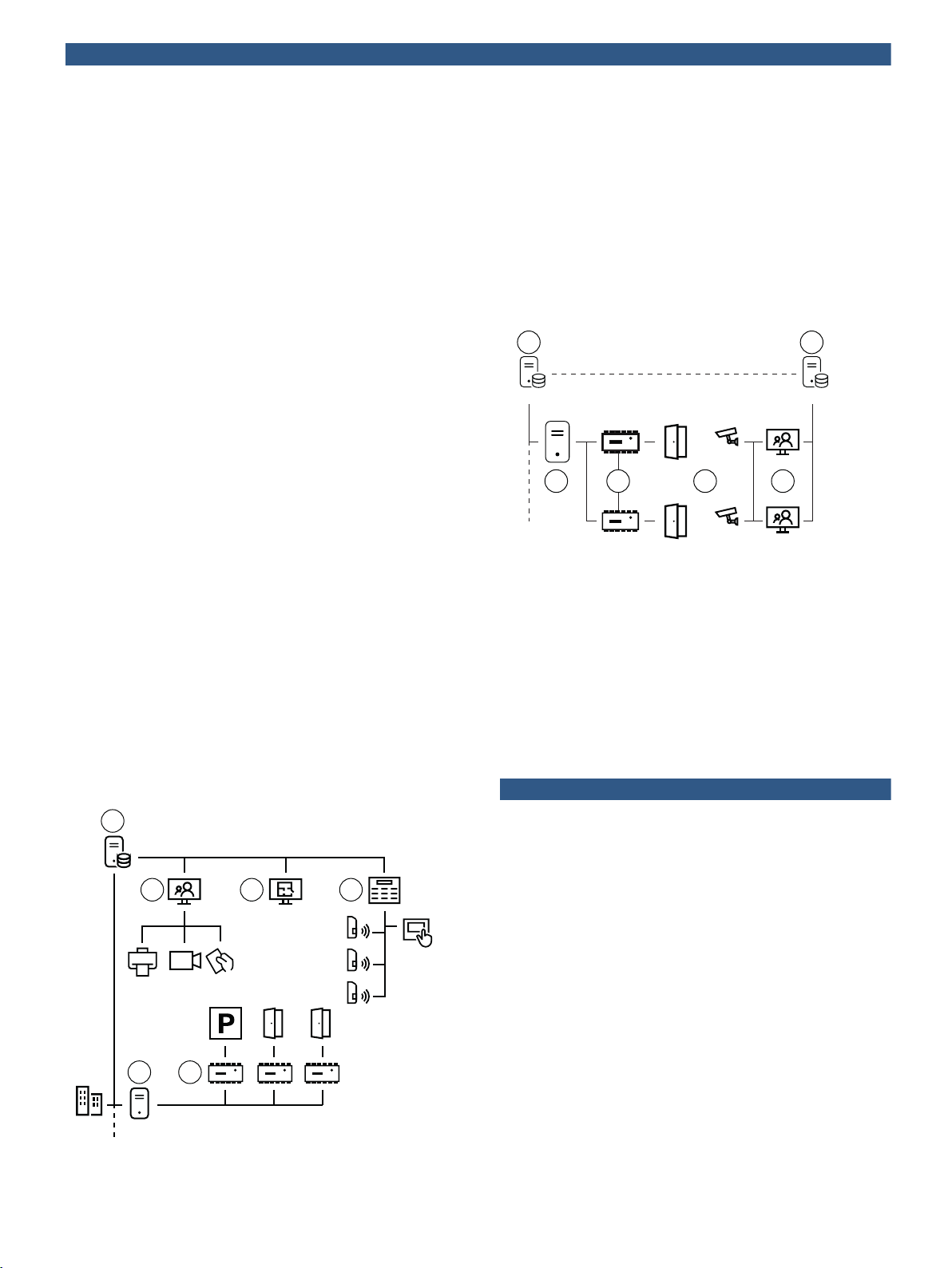
Topology diagrams
The following diagrams illustrate AMS configurations
without and with BVMS.
Stand-Alone topology
(1) AMS server
(2) Client workstation for enrollment
(3) Client workstation for access control and intrusion monitoring
(4) Optional MAC servers (one MAC license is always included, on
the AMS server)
(5) AMCs for parking lot and door control
(6) Intrusion panel with detectors and touch-screen keypad
BVMS Integration
(1) AMS server
(2) BVMS management server or DIVAR IP all-in-one
(3) BVMS Client workstation for access and video management
(4) Optional MAC servers (one MAC license is always included, on
the AMS server)
(5) AMCs
(6) Entrances with cameras
Functions
• Registration of new cardholders:
– Use fully customizable enrollment dialogs to
streamline the process of cardholder enrollment.
– Capture both conventional and biometric
characteristics, including photos and signatures.
– Design and produce physical credentials.
– Take advantage of dialogs for the mass import of
stored personnel data.
• Assigning of access authorizations:
– Collect access authorizations into reusable
profiles, and assign these to predefined or
customized personnel types.
• Door functions:
– Use a comprehensive set of template door
models, including elevators and parking lots, to
accelerate the configuration phase of your
project.
– Office mode: unlock doors for free access during
office or shop hours.
– Combat theft and security threats by random
screening of cardholders.
Page 3

3 | Access Management System V3.0
– Verify cardholder identity with biometric checks
at entrances, and with additional video-based ID
verification powered by BVMS.
– Disarm an intrusion area and grant access with a
single card swipe.
– Use the SimonsVoss SmartIntego technology to
enhance your system with card-programmable
remote online doors, as commonly used in hotels,
healthcare, offices and educational
establishments.
• Reporting:
– Take advantage of a large number of predefined
template reports.
• Guard Tours and patrols:
– Define up to 200 guard tours, and monitor up to
8 patrols simultaneously.
• Monitor car parks, visitors, muster points:
– Display customizable summaries of employees
and visitors on site.
– Monitor visiting times, including overstayed visits.
– Monitor the number of available parking spaces.
• Divisions:
– Provide unified access control for a facility that is
shared by any number of independent parties.
– Individual operators can be restricted to manage
only the persons, devices and entrances of those
divisions assigned to them.
• Alarm Monitor, Command & Control:
– The Map View supports up to 1000 maps, which
can be nested to provide both overviews and
close detail.
– Use the Map View to keep control of large
numbers of entrances simultaneously.
– Use the Map View to monitor incoming alarms
and alerts in real time.
AMS does not buffer intrusion alarms that occur
while the network or the system itself is down.
• BVMS and DIVAR IP Integration:
– Video verification at entrances.
– Camera actions (e.g. start recording, pan/tilt/
zoom) triggered by access events (e.g.
unauthorized door opening).
– Door events (e.g. unlock/lock door) triggered by
camera events (e.g. Intelligent Video Analytics).
– Requires version 10.1 or higher.
• Milestone XProtect Integration:
– Use AMS to support XProtect with access events
and alarms for further processing on XProtect
client.
• Intrusion Integration:
– Supports up to 25 Bosch B Series (Bx512) and G
Series (Bx512G) control panels for central user
management and command & control.
– A full contingent of panels provides up to 12,800
intrusion detectors.
• Mobile Device Integration:
– Supports HID Mobile Access (on MIFARE CSN via
NFC and Wiegand) and STid Mobile ID (on
MIFARE CSN via Wiegand and OSDP, NFC and
BLE).
Installation/configuration notes
The following tables illustrate hardware and software
requirements for running AMS.
Server
Supported
operating systems.
Installations on
other operating
systems may
succeed, but are
entirely without
warranty.
Minimum hardware
requirements
Client, including the Map View client
Supported
operating systems.
Installations on
other operating
systems may
succeed, but are
entirely without
warranty.
Minimum hardware
requirements
• Windows Server 2016 (64 bit,
Standard, Datacenter)
• Windows 10, version 1809 (LTSC)
• Ensure that the latest software
updates are installed.
• Note: The default database delivered
with this system is SQL Server 2017
Express edition with advanced services
• Intel i5 processor with at least 4
physical cores
• 8 GB RAM (32 GB recommended)
• 200 GB of free hard disk space (SSD
disks recommended)
• Graphics adapter with
• 256 MB RAM
• A resolution of 1280x1024 (Use the
graphic resolution recommended for
the client if you wish to run the Map
View client on the AMS server).
• At least 32 k colors
• 1 Gbit/s Ethernet card
• A free USB port or network share for
installation files
• Windows 10, version 1809 (LTSC)
• Ensure that the latest software
updates are installed.
• Intel i5 or higher
• 8 GB RAM (16 GB recommended)
• 20 GB of free hard disk space
• Graphics adapter
• 256 MB RAM
• To use the AMS Dialog manager, a
resolution of 1280x1024 is sufficient.
• For AMS Map view, a resolution of
1920x1080 (Full HD) is required.
• At least 32 k colors
• DirectX® 11
• 1 Gbit/s Ethernet card
• A free USB port or network share for
installation files
Page 4

4 | Access Management System V3.0
MAC server
Supported
operating systems.
Installations on
other operating
systems may
succeed, but are
entirely without
warranty.
Minimum hardware
requirements
• Windows Server 2016 (64 bit,
Standard, Datacenter)
• Windows 10, version 1809 (LTSC)
• Ensure that the latest software
updates are installed.
• Intel i5 or higher
• 8 GB RAM (16 GB recommended)
• 20 GB of free hard disk space
• Graphics adapter with
• 256 MB RAM
• A resolution of 1280x1024
• At least 32 k colors
• 1 Gbit/s Ethernet card
The complexity of security systems has increased
significantly over the last couple of years. At the same
time, you are still relying on your system to mitigate
security risks. With Bosch Software Assurance, you
can always approach us for help to ensure your system
keeps on running.
You can find the terms and conditions of Bosch
Software Assurance on the Bosch Building
Technologies website: https://
www.boschsecurity.com/xc/en/solutions/
management-software/bosch-software-assurance/
LITE Licensed
number
SDK available ✔
BVMS integration available ✔
Intrusion integration Maximum 25 panels B and G Series
Maximum
number
License bundle PLUS
PLUS Licensed
Number of doors (with 1 or 2
readers):
Number of cards: 2000 200,000
Number of divisions: 1 400
Number of clients
configurable:
Number of MACs 3 10
Number of AMCs Maximum 125 per MAC
Number of authorizations Maximum 1024 per MAC
Number of guard tours 200
SDK available ✔
number
32 512
1 5
Up to 60 (on the network)
recommended for high performance
Maximum
number
Technical specifications
The following tables specify the dimensions of an AMS
access control system from two aspects:
• As per the respective license bundle: LITE, PLUS or
PRO.
• As a maximum, if the necessary licenses are
purchased.
License bundle LITE
LITE Licensed
Number of doors (with 1 or 2
readers):
Number of cards: 1000 200,000
Number of divisions: 1 400
Number of clients
configurable:
Number of MACs 1 1
Number of AMCs Maximum 125 per MAC
Number of authorizations Maximum 1024 per MAC
number
16 144
1 2
Up to 60 (on the network)
recommended for high performance
Maximum
number
BVMS integration available ✔
Intrusion integration Maximum 25 panels B and G Series
License bundle PRO
PRO Licensed
Number of doors (with 1 or 2
readers):
Number of cards: 5000 200,000
Number of divisions: 1 400
Number of clients
configurable:
Number of MACs 5 40
Number of AMCs Maximum 125 per MAC
Number of authorizations Maximum 1024 per MAC
Number of guard tours 200
SDK available ✔
BVMS integration available ✔
number
32 10,000
1 40
Up to 60 (on the network)
recommended for high performance
Maximum
number
Number of guard tours 200
Intrusion integration Maximum 25 panels B and G Series
Page 5

5 | Access Management System V3.0
Languages of the user interface
• AR: Arabic
• DE: German
• EN: English
• ES: Spanish
• FR: French
• HU: Hungarian
• NL: Dutch
• PL: Polish
• PT: Portuguese
• RU: Russian
• TR: Turkish
• ZH-CN: Chinese (simplified)
• ZH-TW: Chinese (traditional)
Hardware devices supported
• The Bosch AMC2 family of access controllers
See corresponding datasheets in the product catalogs
at https://www.boschsecurity.com
• Bosch AMC2 extension boards
See corresponding datasheets in the product catalogs
at https://www.boschsecurity.com
• SimonsVoss SmartIntego remote online door
components
• Signotec signature pad
Ordering information
AMS-BASE-LITE30 Lite license
Basic license LITE
Order number AMS-BASE-LITE30
AMS-XCRD-100V30 License for 100 ID cards
License for 100 ID cards
Order number AMS-XCRD-100V30
AMS-XCRD-1KV30 License for 1,000 ID cards
License for 1000 ID cards
Order number AMS-XCRD-1KV30
AMS-XCRD-10KV30 License for 10,000 ID cards
License for 10,000 ID cards
Order number AMS-XCRD-10KV30
AMS-XCRD-50KV30 License for 50,000 ID cards
License for 50,000 ID cards
Order number AMS-XCRD-50KV30
AMS-XDRS-32V30 License for 32 doors
License for 32 doors
Order number AMS-XDRS-32V30
AMS-XDRS-128V30 License for 128 doors
License for 128 doors
Order number AMS-XDRS-128V30
AMS-XDRS-512V30 License for 512 doors
License for 512 doors
Order number AMS-XDRS-512V30
AMS-XOND-25V30 License for 25 remote online doors
License for 25 remote online doors
Order number AMS-XOND-25V30
AMS-BASE-PLUS30 Plus license
Basic license PLUS
Order number AMS-BASE-PLUS30
AMS-BASE-PRO30 Pro license
Basic license PRO
Order number AMS-BASE-PRO30
AMS-XDIV-1V30 License for 1 division
License for 1 additional division
Order number AMS-XDIV-1V30
AMS-XCLI-1V30 License for 1 operator client
License for 1 operator client
Order number AMS-XCLI-1V30
AMS-XCLI-5V30 License for 5 operator clients
License for 5 operator clients
Order number AMS-XCLI-5V30
AMS-XMAC-1V30 License for 1 MAC server
License for 1 MAC server
Order number AMS-XMAC-1V30
AMS-XMAC-5V30 License for 5 MAC servers
License for 5 MAC servers
Order number AMS-XMAC-5V30
AMS-XPAN-1V30 License for 1 intrusion panel
License for 1 intrusion panel
Order number AMS-XPAN-1V30
AMS-XPAN-10V30 License for 10 intrusion panels
License for 10 intrusion panels
Order number AMS-XPAN-10V30
AMS-FUPG-TOPL30 License from Lite to Plus
Upgrade from Lite to Plus
Order number AMS-FUPG-TOPL30
AMS-FUPG-TOPR30 License from Plus to Pro
Upgrade from Plus to Pro
Order number AMS-FUPG-TOPR30
TRA-AMS-CE Training AMS - Expert
Local training for AMS Expert
Order number TRA-AMS-CE
TRA-AMS-EE Training AMS - Expert
Headquarters training for AMS Expert
Order number TRA-AMS-EE
Page 6

6 | Access Management System V3.0
Represented by:
Europe, Middle East, Africa: Germany: North America: Asia-Pacific:
Bosch Security Systems B.V.
P.O. Box 80002
5600 JB Eindhoven, The Netherlands
Phone: + 31 40 2577 284
emea.securitysystems@bosch.com
emea.boschsecurity.com
Bosch Sicherheitssysteme GmbH
Robert-Bosch-Ring 5
85630 Grasbrunn
Germany
www.boschsecurity.com
Bosch Security Systems, LLC
130 Perinton Parkway
Fairport, New York, 14450, USA
Phone: +1 800 289 0096
Fax: +1 585 223 9180
onlinehelp@us.bosch.com
www.boschsecurity.us
Robert Bosch (SEA) Pte Ltd, Security Systems
11 Bishan Street 21
Singapore 573943
Phone: +65 6571 2808
Fax: +65 6571 2699
apr.securitysystems@bosch.com
www.boschsecurity.asia
© Bosch Security Systems 2021 | Data subject to change without notice
76103965835 | en, V4, 22. Jan 2021
 Loading...
Loading...