Blamsoft Expanse User Manual
3.0.0 User Manual – Rev A

2
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
Overview
Expanse brings wavetable synthesis in Reason to the next level. At the heart of Expanse are
four wavetable oscillators with waveform modifiers, an additive engine, and modern unison
capabilities. There are two multi-mode filters with tons of modes each offering their own
unique sonic flavor. Three LFOs with many unique waveforms and five powerful graphical
envelopes offer modulation capabilities. The Mod Matrix destinations cover the entire synth.
Six pristine onboard effects allow you to do all your sound design “in the box”. And a flexible
sequencer tops it off. The sound quality of Expanse will make your previous favorite synth cry
as it gathers virtual dust. You will love the experience of creating sounds once you have
learned Expanse’s powerful features.
3
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
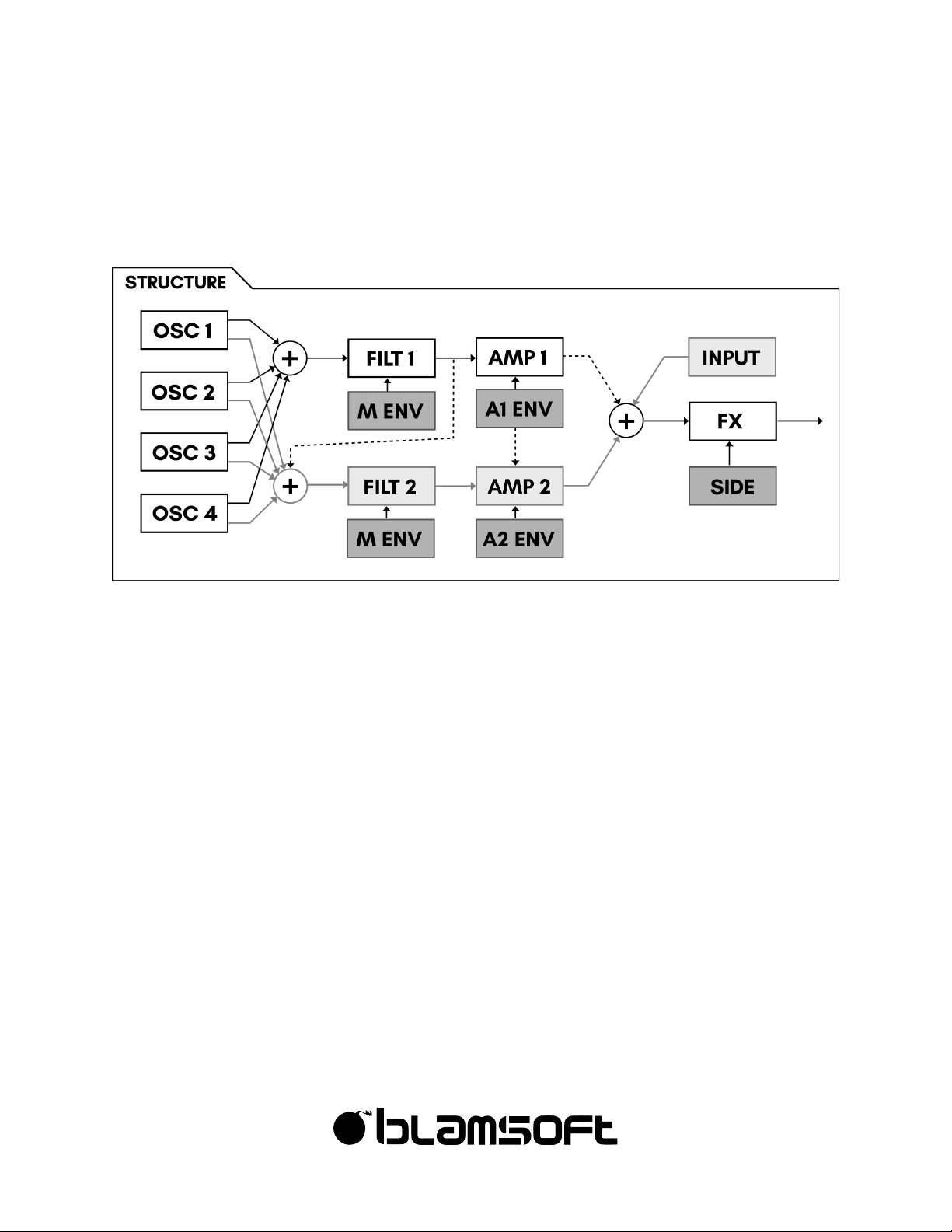
Structure
Knowing the structure is the first step to understanding Expanse.
Oscillators
Four oscillators are mixed together into two parallel signals.
Filters
The parallel signals from the oscillators go to Filter 1 and Filter 2. It is possible to route the
output of Filter 1 into Filter 2.
Envelopes
There are three mod envelopes and two amp envelopes. Each filter’s cutoff frequency is
controlled by one of the envelopes.
LFOs
The three LFOs have their own dedicated modulation targets and can be used as sources in
the Mod Matrix.

4
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
Amps
The filter outputs each go to an amplifier. The amps have their own amp envelopes to control
their gain. It is possible for Amp 1’s Envelope to control Amp 2. When Filter 1 is routed to Filter
2, Amp 1 is not connected.
Mod Matrix
In the Mod Matrix, you can modulate destination parameters using various modulation
sources.
Effects
There are six onboard effects. An external input can be connected to the effects section. A
sidechain input can be connected to the compressor effect.
Sequencers
The Sequencers allows you to create note, gate, and velocity patterns as well as modulation
(CC) patterns.

5
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
Sections
Getting familiar with the overall layout is the second step to learning Expanse.
The blue sections all relate to the oscillators, and the green sections all relate to modulation.
Wavetables
Additive Engine
and Sequencer
Tuning
and
Unison
Mixing
Filters
Mod Envelopes
LFOs Amp Envelopes
Mod Matrix
Effects
Performance, Portamento, and Patches
Mods
6
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
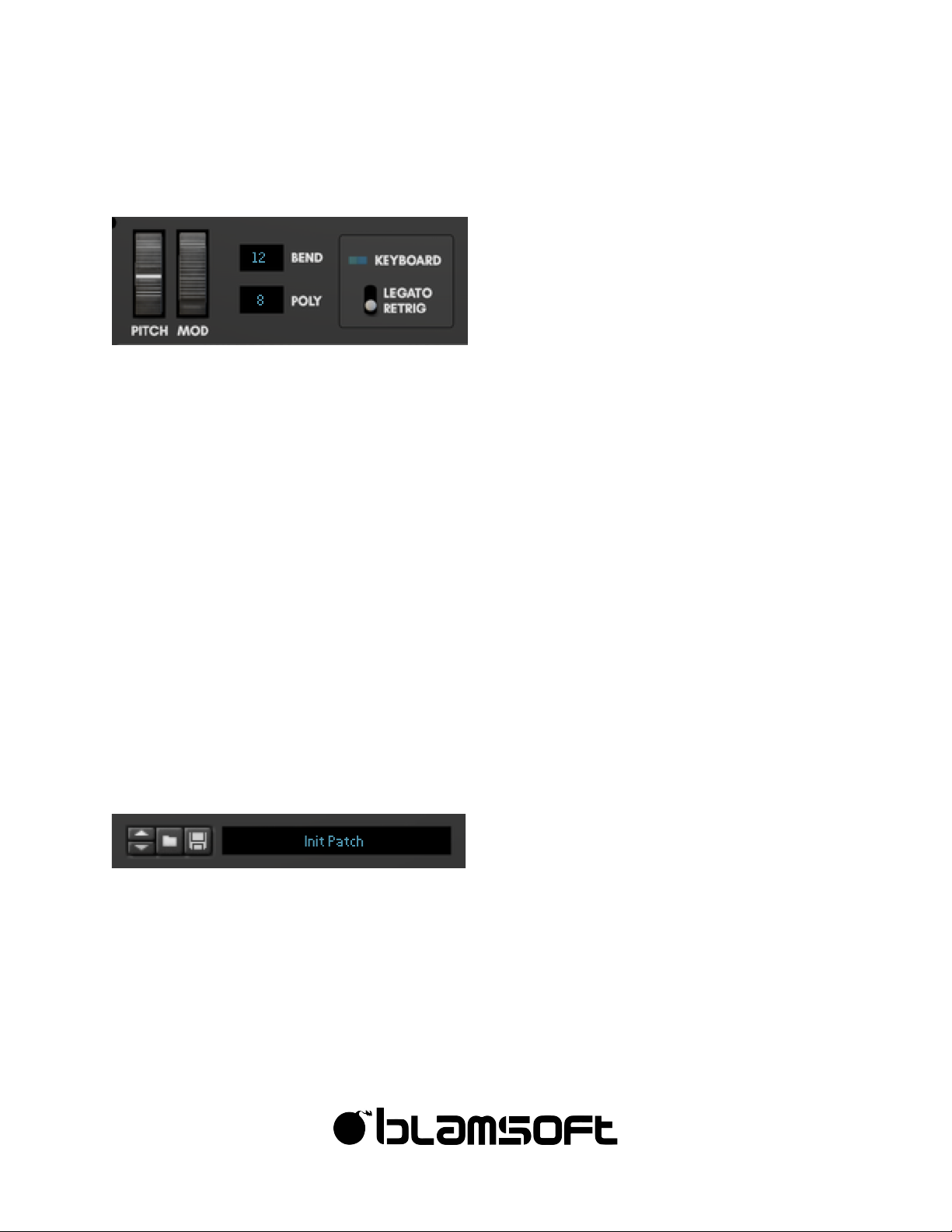
Performance/Polyphony
This upper left section includes parameters found on almost every modern synth.
• Pitch Wheel – Controls the pitch during performance, also is available in the Mod Matrix.
• Mod Wheel – Performance control that is routable in the Mod Matrix
• Polyphony – Adjusts how many simultaneous notes can be played by setting the number
of synth voices. A synth voice is active when its amp envelope is not zero.
• Pitch Bend Range – Adjusts the range of the pitch wheel effect in semitones
• Legato/Retrigger – When set to Legato and polyphony is set to 1, envelopes do not
retrigger if notes are continuously played with no breaks
Tip: You can set the pitch bend range to 0 and use the pitch wheel as a performance
parameter after assigning it in the Mod Matrix.
Patches
You can browse the factory sound bank, or save and load your own patches in the upper
middle section.

7
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
Portamento/Volume
The upper left section offers Portamento control and output volume adjustment. Portamento
provides a gliding of pitch between notes.
The Portamento section provides some neat features that aren’t commonly available.
• On/Auto – When set to On, portamento affects every note change. When set to Auto,
portamento only affects legato playing, the first key press does not have portamento.
• Glide/Gliss – When set to Glide, portamento is a typical smooth sliding of pitch. When set
to Gliss, portamento occurs in semitone steps. It is easier to hear this effect at higher
pitches
• Time/Pitch – This affects the speed of the portamento glide. When set to Time, the glide
takes an equal amount of time for all notes. When set to Pitch, the glide time depends on
the distance between notes because the pitch changes at a constant rate.
You most likely are familiar with the volume control. If not, turn it up, see what happens!

Oscillators
Expanse features wavetable oscillators. This type of oscillator is based on a set of
predetermined single-cycle waveforms. Single-cycle means one period of oscillation. A table
consists of 256 single cycle waveforms that can be individually selected using the position
control. There are 67 tables that come in the Expanse sound bank. Wavetables in the Serum-
compatible format can be loaded externally. In addition, wavetables can be created by
sampling an external oscillator at a low pitch. The raw wavetables can be manipulated using
the mods (modifiers), translating them into other unique waveforms that can sound quite
different from the original. Each oscillator has up to 3 modifiers that can be active
simultaneously. An Additive Engine allows you to duplicate the waveform at harmonic
multiples of the original. Unison allows multiple detuned copies of the waveform to be played
simultaneously. Finally, there are mixing controls. The oscillators can be routed to either, or
both, of the two filters.
Selecting Oscillator 1-4
On the far left of the Oscillators section, there are buttons to select oscillator 1, 2, 3, or 4. You
can think of these as pages or tabs. When an oscillator is chosen, the controls (except for the
mix section) change to the selected oscillator.

9
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
Wavetable
The current waveform for the oscillator is shown on the left side of the Oscillators section.
Keep in mind that this display shows the effect of Mods and the Additive Engine. You don’t
necessarily see the wavetable raw waveform.
• Position – Position moves through the individual frames of the table. If you’re not familiar
with wavetables, you can think of it as adjusting the waveform shape.
• Random – This determines how random the starting phase of the oscillator waveform will
be. This is usually not noticeable unless you are using a unison density of more than 1.
When using unison, you can turn Random down to create a Laser Zap effect.
• Noise – This control cross-fades the oscillator waveform with white noise.
• Sample Browser – You can browse for one of the wavetables included in the sound bank
Wavetables folder, load your own Serum-compatible wavetable, or create a wavetable by
sampling a synth. See the Wavetables section for more details.
• Import setting – This can be set to spectral morph, crossfade, or off. This setting only
applies when there are less than 256 frames in a wavetable. See the Wavetables section
for more details.
Mods
The Mods (modifiers) transform the raw waveform from the wavetable. The three Mods
process the waveform in order (except for when using the post settings).
10
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
• Mod Selection – Selects one of the Mod algorithms
• Amount – Controls how much the Mod affects the waveform or a key parameter of the
Mod
• Pre/Post Harmonics – When Post is enabled, the Mod processes the waveform after the
Additive Engine
There are a wide variety of Mods to choose from:
Off
No modification
FM
Frequency Modulation
PD
Phase Distortion
RM
Ring Modulation
Sync
Hard Sync
Inv
Invert part of the waveform
Rev
Reverse part of the waveform
Dec
Sample rate reduction (decimation)
Quan
Quantization (bit depth reduction)
Clip
Apply gain and hard clip
Fold
Apply gain and foldback
Sat
Apply gain and saturate
Pinch
Inverse saturation
Gate
Zeroes out part of the waveform like a PWM
Juno
Zeroes out parts of the waveform like a PWM at 2x frequency
Mirror
Reversing Sync
Zoom
Zooms into the beginning part of the waveform
Wrap
Apply gain and wrap around from top to bottom
LP
Low pass filter
HP
High pass filter
Phase
Adjusts phase, effectively rotates waveform
In
Contracts waveform toward the center
Out
Expands waveform toward the edges
Sine
Applies a sine amplitude shaper
Odd
Keeps odd harmonics
11
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
Even
Keeps even harmonics
Pluck (Mod 3)
Creates a Karplus-Strong pluck. Oscillator noise amount is useful with this
mode.
FM Routing
(Mod 3)
Creates an inter-oscillator frequency modulation connection
RM Routing
(Mod 3)
Creates an inter-oscillator ring modulation connection
Additive Engine
The Additive Engine duplicates and layers the base waveform at harmonic frequencies.
Commonly, in additive synthesis the base waveform is a sine wave. In Expanse, the base
waveform is the wavetable raw waveform with Mods applied (except for when Mods are
configured as post-Additive). You can edit the layering by dragging the bars in the display.
The bars above the middle adjust the magnitude of the waveform at that frequency. The bars
below the middle adjust the phase. The light gray bars represent octaves. For more details,
see the Additive Engine Theory section.
Ctrl/Cmd click, Shift drag
The harmonic bars can be reset to default or adjusted more precisely using the standard
Reason modifier keys.
Copy, Paste, and Reset
By using alt-click on the display, you have the option of copying or resetting all the oscillator
settings (except for the wavetable). Copy copies the settings from the current oscillator to the
12
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
clipboard. Paste transfers the settings from the clipboard into the current oscillator. Reset sets
the current oscillator settings to their default values.
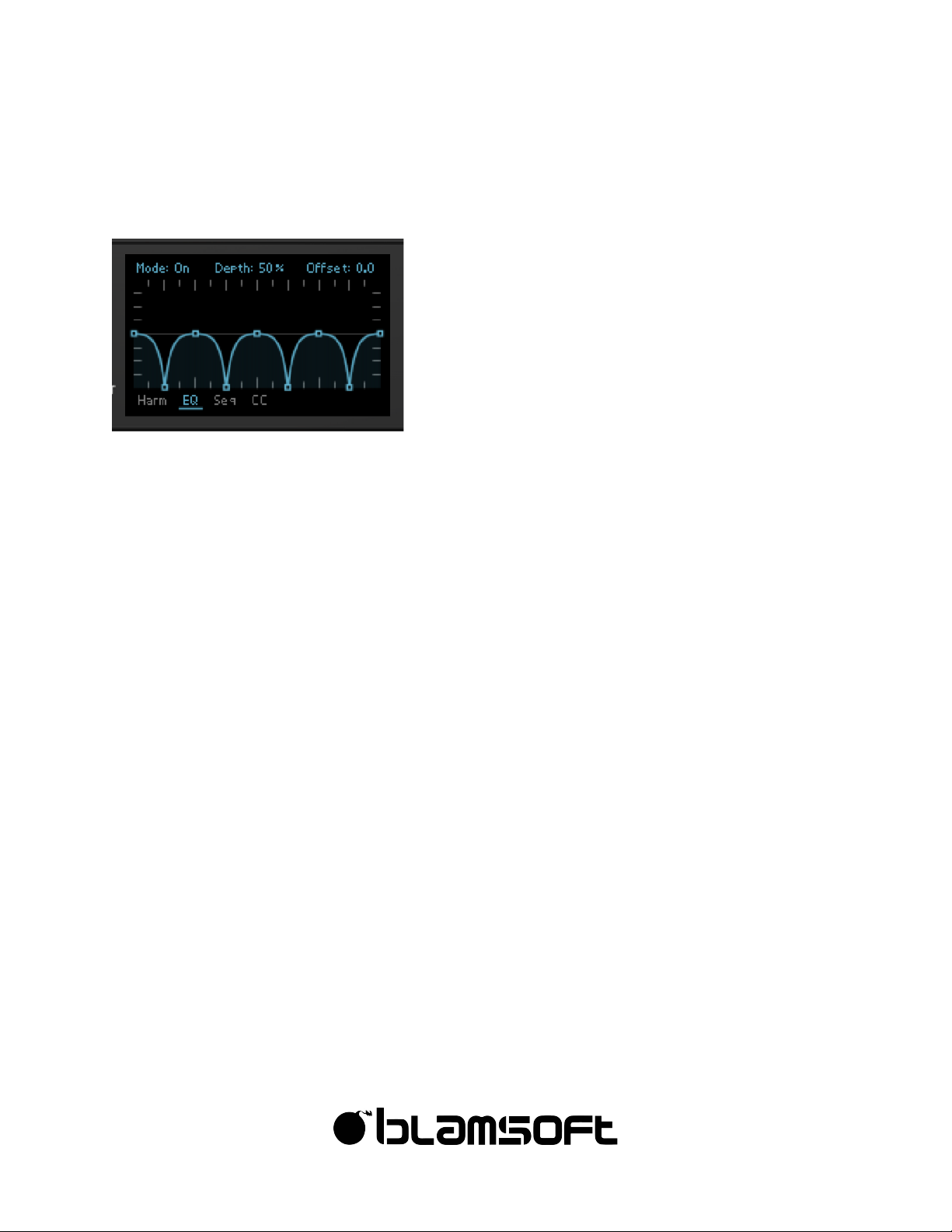
Spectral EQ
The Spectral EQ allows you to shape the spectrum of the oscillator. You can draw curves using
the editor, creating your own filter curve. Here is a summary:
• Double-click to add or remove points
• Drag the segments to adjust the curve
• Shift drag to snap to a horizontal increment
• Ctrl/Cmd drag to snap to a vertical increment
• You can snap to both a horizontal and vertical increment using both Shift and Ctrl/Cmd
• Shift drag on a curve adjusts the two adjacent points
The EQ has Offset (frequency in octaves) and Depth (gain) settings with modulation capability
for each. You can route Keyboard to EQ Offset to achieve a consistent mod across the
keyboard. There are presets in an Alt-click menu.

13
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
Tuning/Unison
The oscillators have basic tuning controls combined with advanced unison features. The basic
tuning controls are:
• Fine – Fine tune in the range of -0.5 to 0.5 semitones.
• Semi – Semitone offset of -11 to +11 semitones
• Octave – Octave offset of -3 to +3 octaves
Unison creates multiple copies of the oscillator waveform that are slightly out of tune with one
another. By adjusting these out of tune waveform copies, you can create thick sounds with a
wide stereo field. The unison controls are:
• Tuning – This controls the intonation spacing of waveform copies. The single note settings
use various math equations to determine the spacing. The choices are Cubic, Squared,
Exponential, Linear, Logarithmic, and Square Root. As the setting is moved from Cube
towards Square Root, the spacing goes from clustered near the root pitch to widely
spaced away from the root pitch. There are also dual note settings that allow some
waveforms to play a fourth, fifth, or octave interval from the fundamental pitch.
• Density – This sets the number of simultaneous waveforms that are playing
• Blend – When Density is odd there is always a root pitch waveform playing. This
determines the volume mix of the root pitch versus the other copies. When Density is
even, this determines the volume mix of the two waveforms nearest to the root pitch
versus the other copies.
• Detune – This setting controls how far in pitch the waveform copies are from the root
pitch
• Spread – Each waveform copy has its own panning. As this control is turned up, the
panning of the waveform copies is spread across the stereo field.

14
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
There are also two tuning controls in the main display.
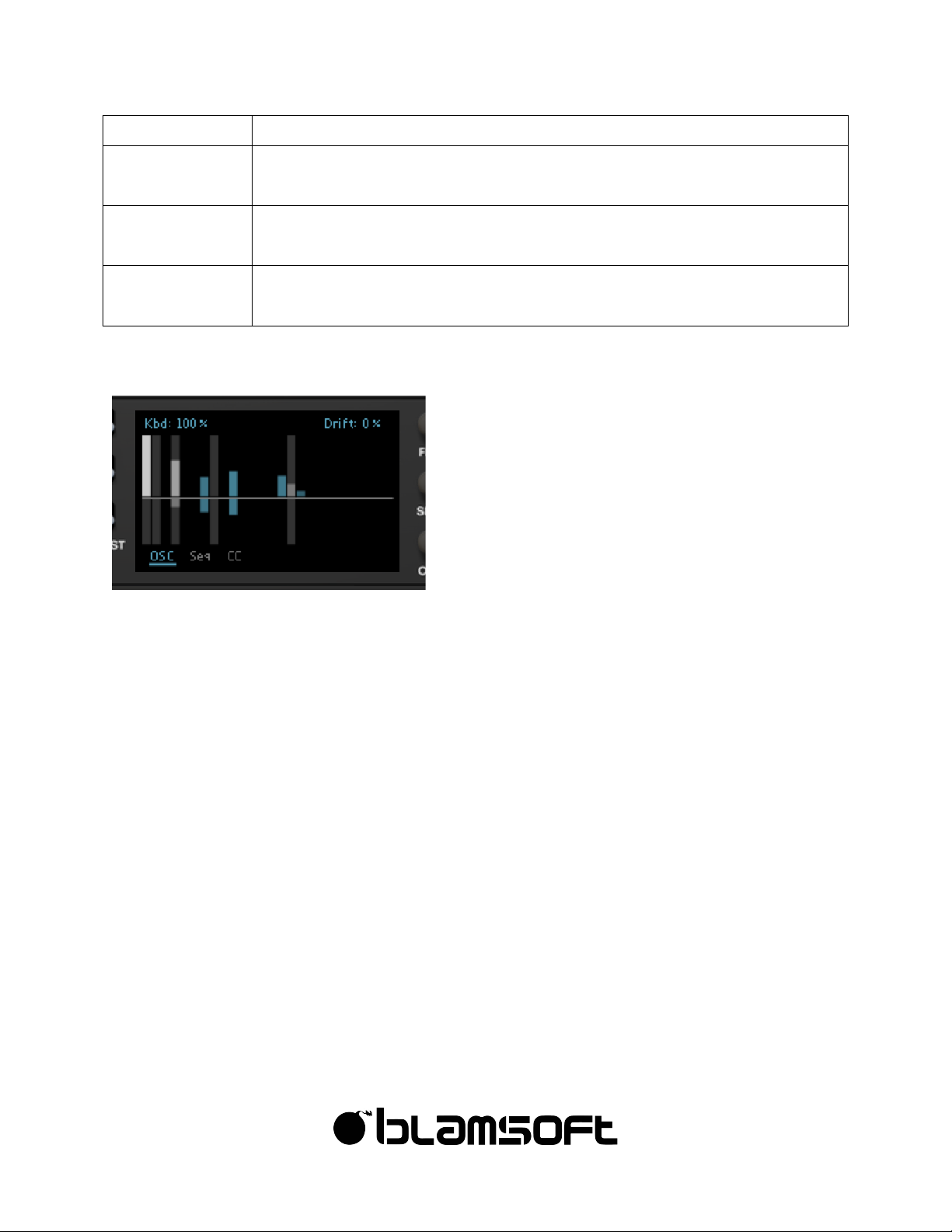
• Keyboard Tracking – This setting controls much the oscillator tracks the keyboard notes,
from not tracking to tracking exactly at 100%.
• Drift – Drift creates instability in the oscillator tuning, this can be used subtly to give an
analog feel or more drastically to make an oscillator unpredictably out of tune. Note, this
setting is most effective with low density settings and more than one oscillator in the mix.
Mixing
The four oscillators can be mixed without using the oscillator pages. Each oscillator has its own
controls.
• Pan – Adjusts the pan of the oscillator from left to right
• Mix – Sets the volume level of the oscillator
• F1-F2 – Adjusts the mix of the oscillators into Filter 1 or Filter 2. When turned all the way to
the left, the oscillator goes 100% into Filter 1 and 0% into Filter 2. When in the middle, the
oscillator goes 50% into Filter 1 and 50% into Filter 2. When turned all the way to the right,
the oscillator goes 0% into Filter 1 and 100% into Filter 2.
• Solo – Allows you to solo a single oscillator and mute the others
15
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
Wavetables
Using the browser, you can load wavetables into Expanse’s oscillators. You are not limited to
the wavetables provided by Blamsoft. Wavetables in a Serum-compatible format can be
directly loaded into Expanse. You can also make your own Serum-compatible wavetables
using Serum or other audio software, or programming environments that offer wav file
output. The format is as follows.
- 2048 samples per single-cycle
- Maximum of 256 frames (positions), less than 256 frames will be morphed or
crossfaded according to the import setting.
- For example, a 256 frame wavetable has exactly 524288 samples. If you use a powerful
audio editor, such as Audacity, you can see the exact number of samples in the file.
You load any sample into Expanse and it will do its best to create a wavetable. Low notes with
a steady pitch work best.
Import Setting
When there are less than 256 frames in the Serum-compatible wavetable, extra frames are
created that make a smooth transition between original frames. You can also limit the number
of frames that are used so a jumpy wavetable can be made smooth. The Spectral Morph

16
©"2016"Blamsoft,"Inc."All"rights"reserved."
settings results in a smooth transition of frequency domain components, Crossfade results in a
smooth transition in the time domain, or Off provides no transitions.
Sampling an Oscillator
You can sample an oscillator to create a wavetable. Expanse processes an audio sample and
extracts the periodic waveforms present in the file. For Expanse to do this well, there are some
things you can do to help. Here is the procedure for creating a wavetable, other settings will
work but not in all cases.
1 Create a steady pitched note on the oscillator you want to sample. Low notes are best.
These are the ideal notes.
Sample Rate
Note
44100
F0 – MIDI Note 17
88200
F1 – MIDI Note 29
96000
Gb/F#1 – MIDI Note 30
176400
F2 – MIDI Note 41
192000
Gb/F#2 – MIDI Note 42
2 Make the clip several seconds long, it is recommended to use at least 10 seconds.
3 Use “Bounce in place” and “Bounce clips to new samples” to quickly create a sample
that can be loaded into Expanse.
See the Creating Wavetables tutorial on the Blamsoft website for more details.
 Loading...
Loading...