Page 1

VEA EL ESPAÑOL EN LA CONTRAPORTADA.
POUR LE FRANÇAIS, VOIR LA COUVERTURE ARRIÈRE.
SAVE THIS MANUAL FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
INSTRUCTIVO DE OPERACIÓN, CENTROS DE SERVICIO Y
PÓLIZA DE GARANTÍA. ADVERTENCIA: LÉASE ESTE
INSTRUCTIVO ANTES DE USAR EL PRODUCTO.
INSTRUCTION MANUAL
FFFFSSSS222211110000LLLLSSSS 11110000”””” TTTTAAAABBBBLLLLEEEE SSSSAAAAWW
WW
Cat.No. FS210LS Form No. 90520749 Rev. 1 AUG. ‘07 Copyright©2007 Black & Decker Printed in China
BEFORE RETURNING THIS PRODUCT FOR ANY
REASON PLEASE CALL 1-800-544-6986
BEFORE YOU CALL, HAVE THE FOLLOWING INFORMATION AVAILABLE, CATALOG NO., TYPE NO., AND DATE CODE . IN MOST
CASES, A BLACK & DECKER REPRESENTATIVE CAN RESOLVE THE PROBLEM OVER THE PHONE. IF YOU HAVE A
SUGGESTION OR COMMENT, GIVE US A CALL. YOUR FEEDBACK IS VITAL TO BLACK & DECKER.
THANK YOU FOR CHOOSING FIRESTORM! GOTO
WWW
.FIRESTORMTOOLS.COM/PRODUCTREGISTRATION
TO REGISTER YOUR NEW PRODUCT
.
Page 2

2
Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury.
Used without the safety alert symbol indicates potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may
result in property damage.
This manual contains information that is important for you to know and understand. This information relates to protecting YOUR SAFETY and PREVENTING EQUIPMENT PROBLEMS. To help you recognize this information, we use the
symbols to the right. Please read the manual and pay attention to these sections.
SAFETY GUIDELINES - DEFINITIONS
GENERAL SAFETY RULES
READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL WARNINGS AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE
USING THIS EQUIPMENT. Failure to follow all instructions listed below, may result in electric shock,
fire, and/or serious personal injury or property damage.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Woodworking can be dangerous if safe and proper operating procedures are not followed. As with all machinery, there
are certain hazards involved with the operation of the product. Using the machine with respect and caution will
considerably lessen the possibility of personal injury. However, if normal safety precautions are overlooked or ignored,
personal injury to the operator may result. Safety equipment such as guards, push sticks, hold-downs, featherboards,
goggles, dust masks and hearing protection can reduce your potential for injury. But even the best guard won’t make
up for poor judgment, carelessness or inattention. Always use common sense
and exercise caution
in the workshop.
If a procedure feels dangerous, don’t try it. Figure out an alternative procedure that feels safer. REMEMBER: Your
personal safety is your responsibility.
Some dust created by power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities contains
chemicals known to cause cancer, birth defects or other reproductive harm. Some examples of these
chemicals are:
• lead from lead-based paints,
• crystalline silica from bricks and cement and other masonry products, and
• arsenic and chromium from chemically-treated lumber (CCA).
Your risk from these exposures varies, depending on how often you do this type of work. To reduce your exposure to these
chemicals: work in a well ventilated area, and work with approved safety equipment, such as those dust masks that are specially
designed to filter out microscopic particles.
• Avoid prolonged contact with dust from power sanding, sawing, grinding, drilling, and other construction activities. Wear protective
clothing and wash exposed areas with soap and water. Allowing dust to get into your mouth, eyes, or lay on the skin may promote
absorption of harmful chemicals.
Use of this tool can generate and/or disperse dust, which may cause serious and permanent respiratory or
other injury. Always use NIOSH/OSHA approved respiratory protection appropriate for the dust exposure. Direct
particles away from face and body.
Wear appropriate hearing protection during use. Under some conditions and duration of use, noise from this
product may contribute to hearing loss.
Page 3

3
GENERAL SAFETY RULES
1. FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY, READ THE INSTRUCTION
MANUAL BEFORE OPERATING THE MACHINE.
Learning the machine’s application, limitations, and
specific hazards will greatly minimize the possibility of
accidents and injury.
2. WEAR EYE PROTECTION. ALWAYS USE SAFETY
GLASSES. Also use face or dust mask if cutting
operation is dusty. Everyday eyeglasses are NOT safety
glasses. USE CERTIFIED SAFETY EQUIPMENT. Eye
protection equipment should comply with ANSI Z87.1
standards, hearing equipment should comply with
ANSI S3.19 standards, and dust mask protection
should comply with MSHA/NIOSH certified respirator
standards. Splinters, air-borne debris, and dust can
cause irritation, injury, and/or illness.
3. WEAR PROPER APPAREL. Do not wear loose
clothing, gloves, neckties, rings, bracelets, or other
jewelry which may get caught in moving parts. Nonslip
footwear is recommended. Wear protective hair
covering to contain long hair.
4. DO NOT USE THE MACHINE IN A DANGEROUS
ENVIRONMENT. The use of power tools in damp or
wet locations or in rain can cause shock or
electrocution. Keep your work area well-lit to prevent
tripping or placing arms, hands, and fingers in danger.
5. MAINTAIN ALL TOOLS AND MACHINES IN PEAK
CONDITION. Keep tools sharp and clean for best and safest
performance. Follow instructions for lubricating and changing
accessories. Poorly maintained tools and machines can further
damage the tool or machine and/or cause injury.
6. CHECK FOR DAMAGED PARTS. Before using the
machine, check for any damaged parts. Check for
alignment of moving parts, binding of moving parts,
breakage of parts, and any other conditions that may
affect its operation. A guard or any other part that is
damaged should be properly repaired or replaced.
Damaged parts can cause further damage to the
machine and/or injury.
7. KEEP THE WORK AREA CLEAN. Cluttered areas and
benches invite accidents.
8. KEEP CHILDREN AND VISITORS AWAY. Your shop is a
potentially dangerous environment. Children and visitors can
be injured.
9. REDUCE THE RISK OF UNINTENTIONAL STARTING.
Make sure that the switch is in the “OFF” position
before plugging in the power cord. In the event of a
power failure, move the switch to the “OFF” position.
An accidental start-up can cause injury.
10. USE THE GUARDS. Check to see that all guards are in
place, secured, and working correctly to prevent injury.
11. REMOVE ADJUSTING KEYS AND WRENCHES
BEFORE STARTING THE MACHINE. Tools, scrap
pieces, and other debris can be thrown at high speed,
causing injury.
12. USE THE RIGHT MACHINE. Don’t force a machine or
an attachment to do a job for which it was not
designed. Damage to the machine and/or injury may
result.
13. USE RECOMMENDED ACCESSORIES. The use of
accessories and attachments not recommended by
Delta may cause damage to the machine or injury to the
user.
14. USE THE PROPER EXTENSION CORD. Make sure
your extension cord is in good condition. When using
an extension cord, be sure to use one heavy enough to
carry the current your product will draw. An undersized
cord will cause a drop in line voltage, resulting in loss of
power and overheating. See the Extension Cord Chart
for the correct size depending on the cord length and
nameplate ampere rating. If in doubt, use the next
heavier gauge. The smaller the gauge number, the
heavier the cord.
15. SECURE THE WORKPIECE. Use clamps or a vise to hold
the workpiece when practical. Loss of control of a
workpiece can cause injury.
16. FEED THE WORKPIECE AGAINST THE DIRECTION OF
THE ROTATION OF THE BLADE, CUTTER, OR ABRASIVE
SURFACE. Feeding it from the other direction will cause
the workpiece to be thrown out at high speed.
17. DON’T FORCE THE WORKPIECE ON THE MACHINE.
Damage to the machine and/or injury may result.
18. DON’T OVERREACH. Loss of balance can make you
fall into a working machine, causing injury.
19. NEVER STAND ON THE MACHINE. Injury could occur if the
tool tips, or if you accidentally contact the cutting tool.
20. NEVER LEAVE THE MACHINE RUNNING UNATTENDED.
TURN THE POWER OFF. Don’t leave the machine until it
comes to a complete stop. A child or visitor could be injured.
21. TURN THE MACHINE “OFF”, AND DISCONNECT THE
MACHINE FROM THE POWER SOURCE before installing
or removing accessories, before adjusting or changing
set-ups, or when making repairs. An accidental start-up
can cause injury.
22. MAKE YOUR WORKSHOP CHILDPROOF WITH
PADLOCKS, MASTER SWITCHES, OR BY
REMOVING STARTER KEYS. The accidental start-up
of a machine by a child or visitor could cause injury.
23. STAY ALERT, WATCH WHAT YOU ARE DOING, AND
USE COMMON SENSE. DO NOT USE THE
MACHINE WHEN YOU ARE TIRED OR UNDER THE
INFLUENCE OF DRUGS, ALCOHOL, OR MEDICATION. A moment of inattention while operating power
tools may result in injury.
24. TAKE PRECAUTIONS AGAINST DUST INHALATION.
The dust generated by certain woods and wood
products can be injurious to your health. Always
operate machinery in well-ventilated areas, and provide
for proper dust removal. Use wood dust collection
systems whenever possible.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE RULES MAY RESULT IN SERIOUS INJURY.
Page 4

4
ADDITIONAL SAFETY RULES FOR
TABLE SAWS
1. DO NOT OPERATE THIS MACHINE until it is
assembled and installed according to the
instructions.
2. OBTAIN ADVICE FROM YOUR SUPERVISOR,
instructor, or another qualified person if you are not
familiar with the operation of this machine.
3. FOLLOW ALL WIRING CODES and recommended
electrical connections.
4. USE THE GUARDS WHENEVER POSSIBLE. Check
to see that they are in place, secured, and working
correctly.
5. KICKBACK IS THE NATURAL TENDENCY OF THE
WORKPIECE TO BE THROWN BACK AT THE
OPERATOR when the workpiece initially contacts the
blade or if the workpiece pinches the blade. Kickback
is dangerous and can result in serious injury.
AVOID KICKBACK by:
A. keeping blade sharp and free of rust and pitch.
B. keeping rip fence parallel to the saw blade.
C. using saw blade guard and spreader for every
possible operation, including all through sawing.
D. pushing the workpiece past the saw blade prior to
release.
E. never ripping a workpiece that is twisted or
warped, or does not have a straight edge to guide
along the fence.
F. using featherboards when the anti-kickback device
cannot be used.
G. never sawing a large workpiece that cannot be
controlled.
H. never using the fence as a guide when
crosscutting.
I. never sawing a workpiece with loose knots or other
flaws.
6. ALWAYS USE GUARDS, SPLITTER, AND ANTI-
KICKBACK FINGERS whenever possible.
7. REMOVE CUT-OFF PIECES AND SCRAPS from the
table before starting the saw. The vibration of the
machine may cause them to move into the saw blade
and be thrown out. After cutting, turn the machine off.
After the blade has come to a complete stop, remove
all debris.
8. NEVER START THE MACHINE with the workpiece
against the blade.
9. NEVER run the workpiece between the fence and a
moulding cutterhead.
10. CUTTING THE WORKPIECE WITHOUT THE USE OF
A FENCE OR MITER GAUGE IS KNOWN AS
“FREEHAND” CUTTING. NEVER perform “free-hand”
operations. Use either the fence or miter gauge to
position and guide the workpiece.
11. HOLD THE WORKPIECE FIRMLY against the miter
gauge or fence.
12. CUTTING COMPLETELY THROUGH THE WORK-
PIECE IS KNOWN AS “THROUGH-SAWING”.
Ripping and cross-cutting are through-sawing
operations. Cutting with the grain (or down the length
of the workpiece) is ripping. Cutting across the grain (or
across the workpiece) is cross-cutting. Use a fence or
fence system for ripping. DO NOT use a fence or fence
system for cross-cutting. Instead, use a miter gauge.
USE PUSH STICK(S) for ripping a narrow workpiece.
13. AVOID AWKWARD OPERATIONS AND HAND
POSITIONS where a sudden slip could cause a hand
to move into the blade.
14. KEEP ARMS, HANDS, AND FINGERS away from the
blade.
15. NEVER have any part of your body in line with the path
of the saw blade.
16. NEVER REACH AROUND or over the saw blade.
17. NEVER attempt to free a stalled saw blade without first
turning the machine “OFF”.
18. PROPERLY SUPPORT LONG OR WIDE workpieces.
19. NEVER PERFORM LAYOUT, assembly or set-up work
on the table/work area when the machine is running.
20. TURN THE MACHINE “OFF” AND DISCONNECT
THE MACHINE from the power source before
installing or removing accessories, before adjusting or
changing set-ups, or when making repairs.
21. TURN THE MACHINE “OFF”, disconnect the machine
from the power source, and clean the table/work area
before leaving the machine. LOCK THE SWITCH IN
THE “OFF” POSITION to prevent unauthorized use.
22. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION regarding the safe
and proper operation of power tools (i.e. a safety
video) is available from the Power Tool Institute,
1300 Sumner Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2851
(www.powertoolinstitute.com). Information is also
available from the National Safety Council, 1121 Spring
Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201. Please refer to the
American National Standards Institute ANSI 01.1
Safety Requirements for Woodworking Machines and
the U.S. Department of Labor OSHA 1910.213
Regulations.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS.
Refer to them often
and use them to instruct others.
READ AND UNDERSTAND ALL WARNINGS AND OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS BEFORE USING
THIS EQUIPMENT. Failure to follow all instructions listed below, may result in electric shock, fire,
and/or serious personal injury or property damage.
Page 5
5
A separate electrical circuit should be used for your machine. This circuit should not be less than #12 wire and should
be protected with a 20 Amp time lag fuse. If an extension cord is used, use only 3-wire extension cords which have 3prong grounding type plugs and matching receptacle which will accept the machine’s plug. Before connecting the
machine to the power line, make sure the switch is in the “OFF” position and be sure that the electric current is of the
same characteristics as indicated on the machine. All line connections should make good contact. Running on low
voltage will damage the machine.
SHOCK HAZARD. DO NOT EXPOSE MACHINE TO RAIN OR OPERATE MACHINE IN DAMP
LOCATIONS.
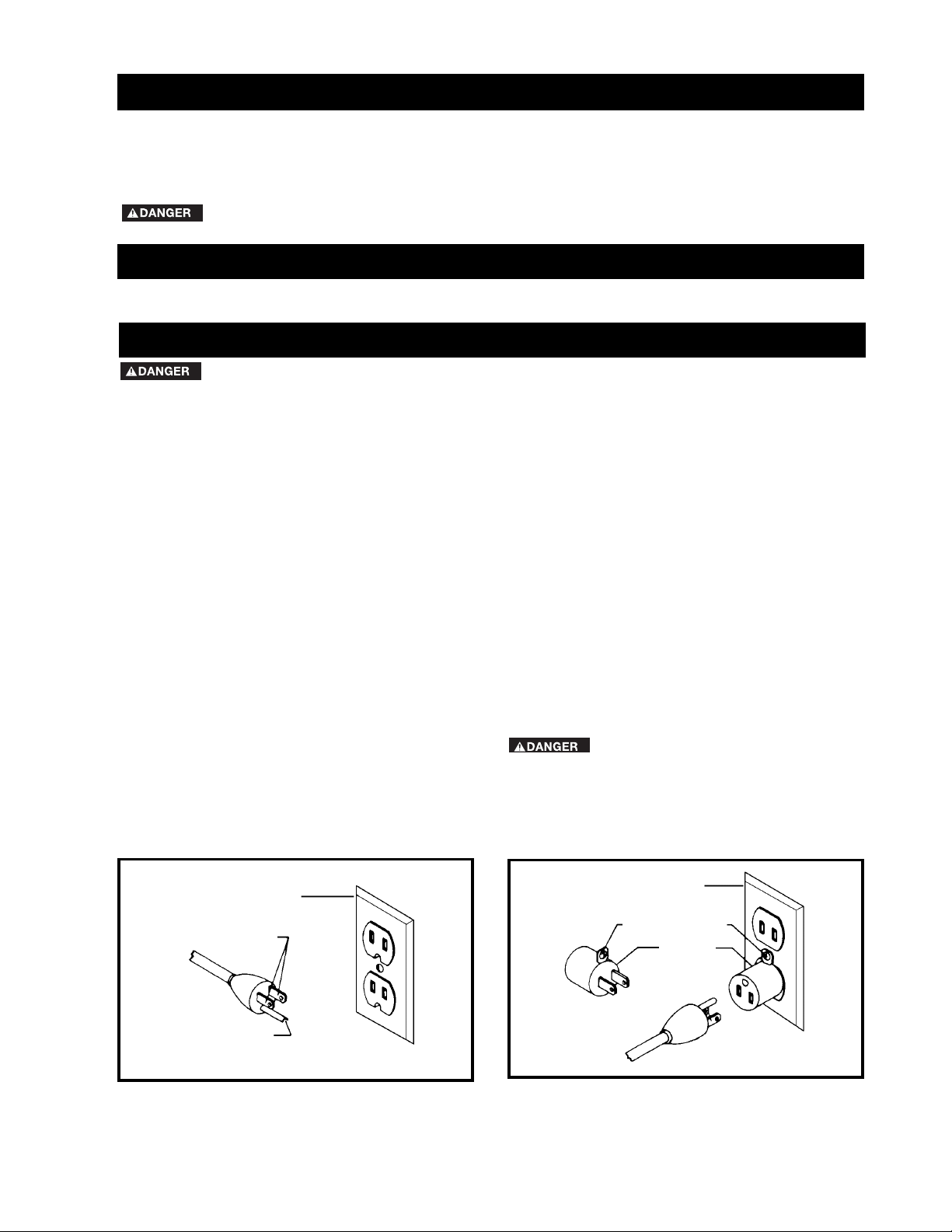
Fig. A Fig. B
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
CURRENT
CARRYING
PRONGS
GROUNDING BLADE
IS LONGEST OF THE 3 BLADES
GROUNDED OUTLET BOX
GROUNDING
MEANS
ADAPTER
2. Grounded, cord-connected machines intended for use
on a supply circuit having a nominal rating less than 150
volts:
If the machine is intended for use on a circuit that has an
outlet that looks like the one illustrated in Fig. A, the
machine will have a grounding plug that looks like the plug
illustrated in Fig. A. A temporary adapter, which looks like
the adapter illustrated in Fig. B, may be used to connect
this plug to a matching 2-conductor receptacle as shown
in Fig. B if a properly grounded outlet is not available. The
temporary adapter should be used only until a properly
grounded outlet can be installed by a qualified electrician.
The green-colored rigid ear, lug, and the like, extending
from the adapter must be connected to a permanent
ground such as a properly grounded outlet box. Whenever
the adapter is used, it must be held in place with a metal
screw.
NOTE: In Canada, the use of a temporary adapter is not
permitted by the Canadian Electric Code.
IN ALL CASES, MAKE CERTAIN THE
RECEPTACLE IN QUESTION IS PROPERLY
GROUNDED. IF YOU ARE NOT SURE HAVE A
QUALIFIED ELECTRICIAN CHECK THE RECEPTACLE.
1. All grounded, cord-connected machines:
In the event of a malfunction or breakdown, grounding
provides a path of least resistance for electric current to
reduce the risk of electric shock. This machine is
equipped with an electric cord having an equipmentgrounding conductor and a grounding plug. The plug must
be plugged into a matching outlet that is properly installed
and grounded in accordance with all local codes and
ordinances.
Do not modify the plug provided - if it will not fit the outlet,
have the proper outlet installed by a qualified electrician.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding
conductor can result in risk of electric shock. The
conductor with insulation having an outer surface that is
green with or without yellow stripes is the equipmentgrounding conductor. If repair or replacement of the
electric cord or plug is necessary, do not connect the
equipment-grounding conductor to a live terminal.
Check with a qualified electrician or service personnel if
the grounding instructions are not completely
understood, or if in doubt as to whether the machine is
properly grounded.
Use only 3-wire extension cords that have 3-prong
grounding type plugs and matching 3-conductor
receptacles that accept the machine’s plug, as shown in
Fig. A.
Repair or replace damaged or worn cord immediately.
POWER CONNECTIONS
MOTOR SPECIFICATIONS
Your machine is wired for 120 volt, 60 HZ alternating current. Before connecting the machine to the power source,
make sure the switch is in the “OFF” position.
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
SHOCK HAZARD. THIS MACHINE MUST BE GROUNDED WHILE IN USE TO PROTECT THE
OPERATOR FROM ELECTRIC SHOCK.
Page 6
FOREWORD
Model FS210LS has big saw capacity at an economical price. It has an extra large, 17 in. x 34 in. aluminum table with
extension and is powered by a heavy-duty 15 amp. motor with a floating jackshaft gear - the most powerful in its class.
This saw is designed to give high quality performance with depth of cut capacity up to 3 in. (76mm) at 90° and 2.5 in.
(63.5mm) at 45° for clean cutting of standard stock sizes. This package includes the saw, a metal stand, rip fence, miter
gage, see-through blade guard with splitter and anti-kickback fingers, table extensions a 10 in. carbide-tipped saw
blade, table insert and blade wrenches.
6
EXTENSION CORDS
Use proper extension cords. Make sure your extension cord is in good condition and is a 3-wire
extension cord which has a 3-prong grounding type plug and matching receptacle which will accept the machine’s
plug. When using an extension cord, be sure to use one heavy enough to carry the current of the machine. An
undersized cord will cause a drop in line voltage, resulting in loss of power and overheating. Fig. C, shows the correct
gauge to use depending on the cord length. If in doubt, use the next heavier gauge. The smaller the gauge number,
the heavier the cord.
Fig. C
MINIMUM GAUGE EXTENSION CORD
RECOMMENDED SIZES FOR USE WITH STATIONARY ELECTRIC MACHINES
Ampere Total Length Gauge of
Rating Volts of Cord in Feet Extension Cord
0-6 120
up to
25 18 AWG
0-6 120 25-50 16 AWG
0-6 120 50-100 16 AWG
0-6 120 100-150 14 AWG
6-10 120
up to
25 18 AWG
6-10 120 25-50 16 AWG
6-10 120 50-100 14 AWG
6-10 120 100-150 12 AWG
10-12 120
up to
25 16 AWG
10-12 120 25-50 16 AWG
10-12 120 50-100 14 AWG
10-12 120 100-150 12 AWG
12-16 120
up to
25 14 AWG
12-16 120 25-50 12 AWG
12-16 120
GREATER THAN 50 FEET NOT RECOMMENDED
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Page 7
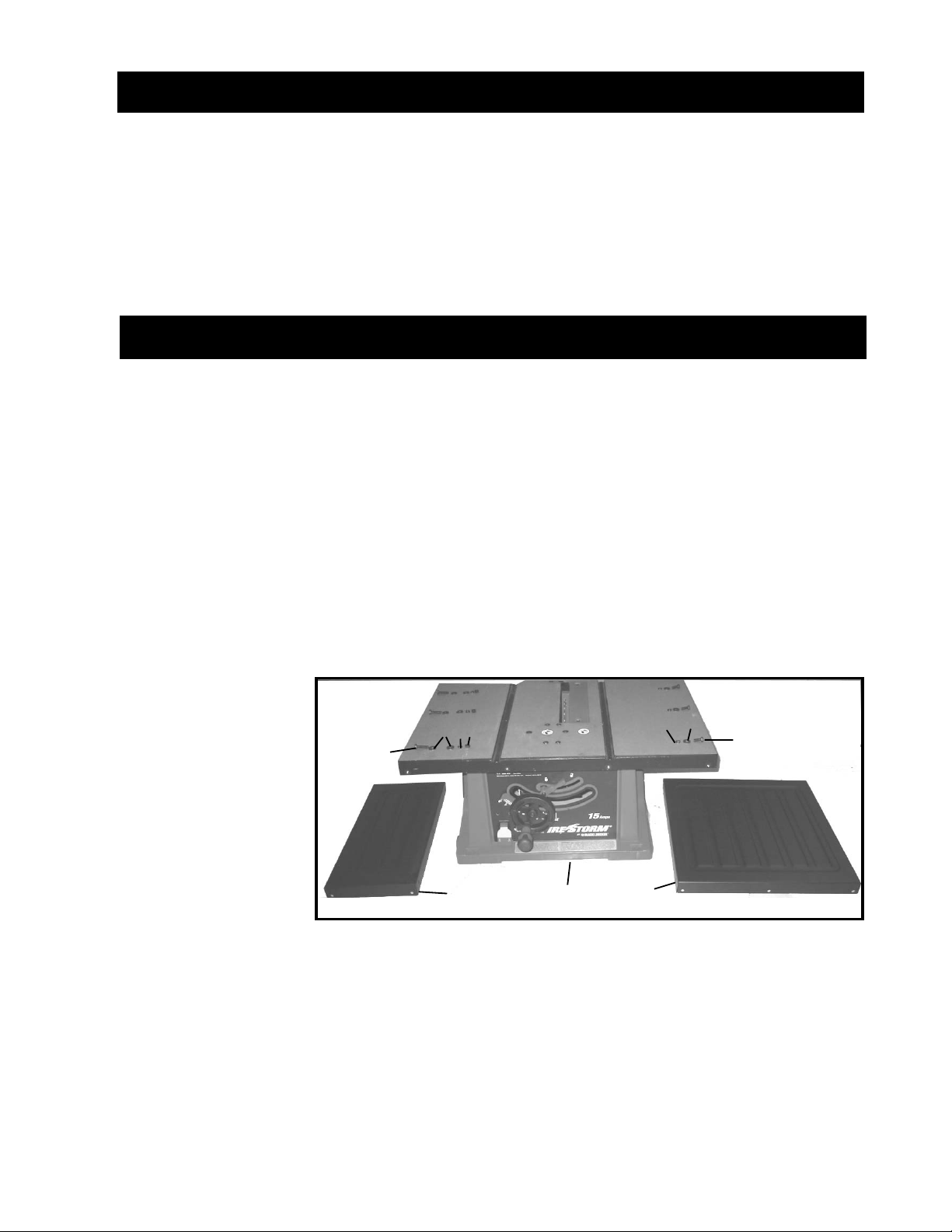
7
Fig. 1
TABLE SAW PARTS
9
2
3
4
5
1- Saw
2- Left Extension Wing
3- 1/4 in.-20X1 in.Hex Head
Screw for Left Extension
Wing (3)
4- 1/4 in. Flat Washer for
Left Extension Wing (6)
5- 1/4 in. Lockwasher for
Left Extension Wing (3)
6- 1/4 in.-20 Hex Nut for Left
Extension Wing (3)
7- Right Extension Wing
8- 1/4 in.-20X5/8 in.Hex
Head Screw for Right
Extension Wing (3)
9- 1/4 in. Flat Washer for
Right Extension Wing (3)
10- 1/4 in. Lockwasher for
Right Extension Wing (3)
7
ASSEMBLY
UNPACKING AND CLEANING
Carefully unpack the machine and all loose items from the shipping container(s). Remove the protective coating from
all unpainted surfaces. This coating may be removed with a soft cloth moistened with kerosene (do not use acetone,
gasoline or lacquer thinner for this purpose). After cleaning, cover the unpainted surfaces with a good quality household
floor paste wax.
NOTICE: THE PHOTO ON THE MANUAL COVER ILLUSTRATES THE
CURRENT PRODUCTION MODEL. ALL OTHER ILLUSTRATIONS CONTAINED
IN THE MANUAL ARE REPRESENTATIVE ONLY AND MAY NOT DEPICT THE
ACTUAL COLOR, LABELING OR ACCESSORIES AND ARE INTENDED TO
ILLUSTRATE TECHNIQUE ONLY.
6
ASSEMBLY TOOLS REQUIRED
ASSEMBLY TIME ESTIMATE
1). Adjustable wrench
2.) 13mm wrench for stand bolts.
3.) 10mm wrench for splitter assembly bolts, rear supports assembly and extension wings assembly.
4.) Slotted screwdriver.
6.) Phillips screwdriver.
5.) Straight edge and/or framing square for adjustments.
2 Hours
7
8
10
1
Page 8
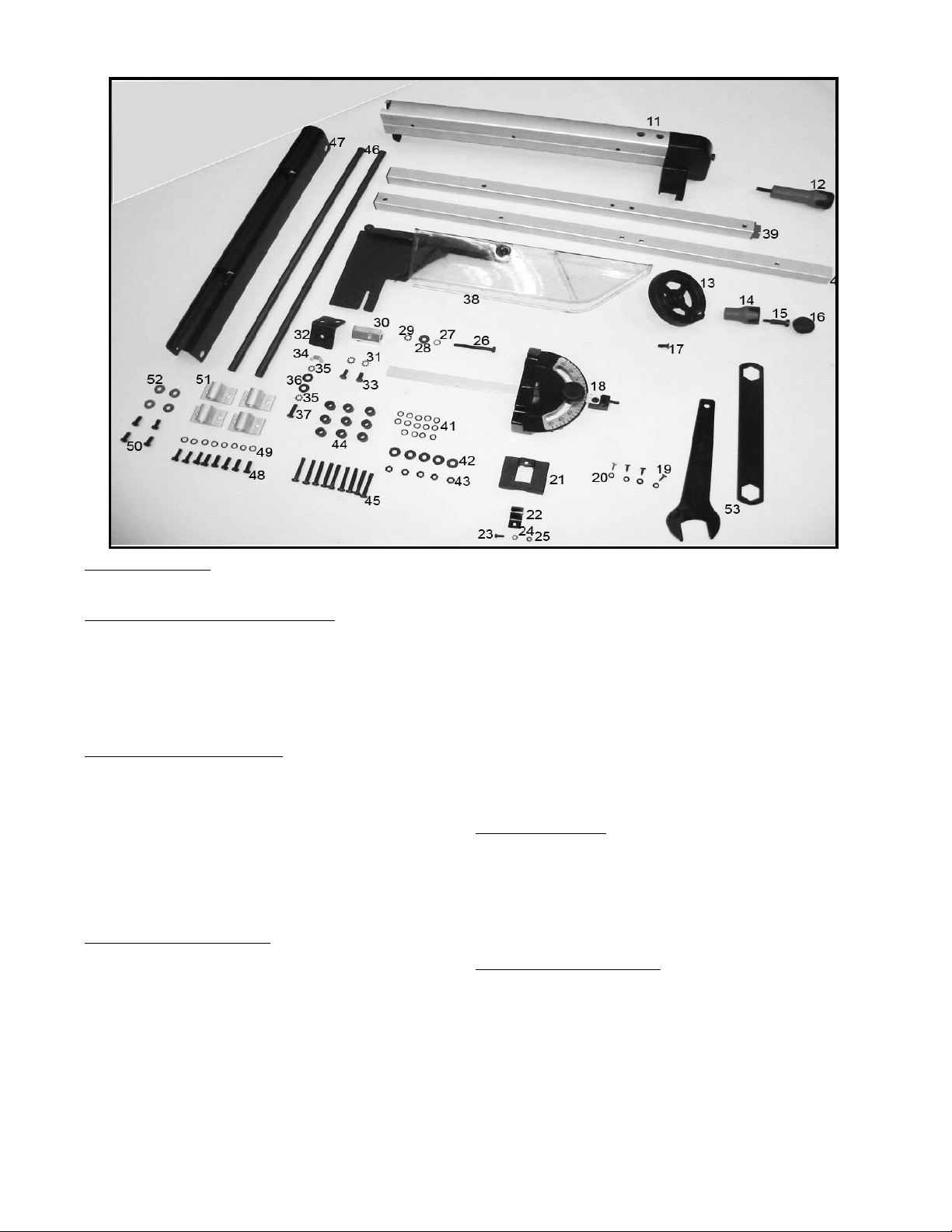
8
Fig. 2
RIP FENCE
P
ARTS
(11,12)
11-Rip Fence
12-Locking Handle for Rip Fence
BLADE RAISING HANDWHEEL P
ARTS
(13,14,15,16,17)
13-Blade Raising and Lowering Handwheel
14-Handle for Blade Raising and Lowering handwheel
15-Screw for Mounting Handwheel Handle
16-Cap for Handle
17-M6X1X12mm Flat Head Screw for Mounting Blade
Raising and Lowering Handwheel
18-Miter Gage
MITER
GAGE
HOLDER
PARTS
(19,20,21,22,23,24,25)
19-M4.2X10mm Pan Head Tap Screws for Mounting
Miter Gage Holder(4)
20-Lockwasher for Mounting Miter Gage Holder(4)
21-Miter Gage Holder
22-Spring Clip for Miter Gage Holder
23-M4X0.7X10mm Pan Head Screw for Miter Gage
Holder
24-3/16 in.External Tooth Lockwasher for Miter Gage
Holder
25-M4X0.7mm Hex Nut for Miter Gage Holder
SPLITTER BRACKET PARTS (26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,
34,35,36,37)
26-1/4-20X2-1/4 in.Long Hex Head Screw for Mounting
Splitter Bracket
27-1/4 in.Internal Tooth Lockwasher for Mounting
Splitter Bracket
28-1/4 in.Flat Washer for Mounting Splitter Bracket
29-1/4 in.External Tooth Lockwasher for Mounting
Splitter Bracket
30-Splitter Bracket
31-1/4 in.External Tooth Lockwasher for Splitter
Bracket(2)
32-Splitter Support Bracket
33-1/4-20X1/2 in.Hex Head Screws for Splitter
Bracket(2)
34-Wing Nut for Mounting Splitter Support Bracket
35-1/4 in.External Tooth lockwasher for Splitter
Bracket(2)
36-1/4 in.Flat washer for Mounting Splitter Support
Bracket(2)
37-M6X1X20mmHex Head Screw for Mounting Splitter
Support Bracket
38-Splitter and Guard Assembly
39-Fence Left Rail
40-Fence Right Rail
FENCE RAIL
PAR
TS
(41,42,43,44,45)
41-M6 Lockwasher for Mounting Fence Rail(14)
42-1/4 in. Flat washer for Mounting Fence Rail(5)
43-1/4 in.-20 Hex Nut for Mounting Rail and Extension
Wings(5)
44-Spacers for Mounting Fence(9)
45-1/4 in.-20X1-1/4 Round Head Screws for Mounting
Fence Rail (9)
OUTFEED SUPPORT
P
ART
S
(46,47,48,49,50,51,52)
46-Rod for Rear Support (2)
47-Rear Support
48-M6X1X15mm Hex Cross Screw for Bracket(8)
49-M6 Lockwasher for Mounting Bracket(8)
50-1/4 in.-20X1/2 in. Hex Head Screw for Rod(4)
51-Bracket(4)
52-1/4 in.Flat Washers for Mounting Rod(4)
53-Wrenches for Blade Changing
Page 9

9
Fig. 3
STAND PARTS
53-Leg(4)
54-Top side Bracket(2)
55-Top Front Bracket
56-Top Rear Bracket
57-Bottom side Brackets(2)
58-Bottom Front Brackets(2)
59-Foot(4)
FOR YOUR OWN SAFETY, DO NOT CONNECT THE MACHINE TO THE POWER SOURCE UNTIL
THE MACHINE IS COMPLETELY ASSEMBLED. DO NOT OPERATE THIS MACHINE UNTIL YOU READ AND
UNDERSTAND THE ENTIRE INSTRUCTION MANUAL
53
54
55
56
57
58
60
61
62
63
59
64
65
60-M8X1.25X45mm Hex Head Screw for Leg and
Base(2)
61-M8X1.25X30mm Hex Head Screw for Leg and
Base(2)
62-5/16 in.Hex lock Nut(16)
63-5/16 in.Carriage Bolt(16)
64-M8 Hex Nut(4)
65- M8 Flat washer(8)
Page 10

10
MITER GAGE HOLDER
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM
POWER SOURCE.
1. Assemble spring clip (E) Fig. 4, to the miter gage
holder (A) as shown using a M4x.7x10mm pan head
screw (F), 3/16 in. lockwasher and M4x.7 hex nut.
NOTE: Hex nut (G) Fig. 5, will fit into the recess at the
back of the miter gage holder (A) to keep spring clip (E)
Fig. 4, secured to the miter gage holder.
2. Assemble the miter gage holder (A) Fig. 6, to the left
side of the saw cabinet using the four M4.2x10mm pan
head screws (B) Fig. 7, and 3/16 in. washers (C) from
inside saw cabinet.
3. Fig. 8, illustrates the miter gage (D) inserted into the
miter gage holder when not in use.
Fig. 7
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 8
E
A
F
A
G
A
C
B
D
Page 11

11
STAND ASSEMBLY
1. The stand legs have protrusions which align with the
holes in the top and bottom brackets. Assemble the
stand as shown in Fig. 9A, using 16 carriage bolts and
hex lock nuts. Do not completely tighten the hardware at
this time.
A-Top front bracket (with logo)
B-Top rear bracket
C-Bottom side brackets
D-Bottom front and rear brackets
E-Top side brackets
F-Foot
IMPORTANT: THE TOP, FRONT, AND REAR
BRACKETS (A&B) FIG. 9A, ARE LONGER THAN THE
TOP SIDE BRACKETS (E) FIG. 9A. THE BOTTOM
FRONT AND REAR BRACKETS (D) FIG. 9A, ARE
LONGER THAN THE BOTTOM SIDE BRACKETS (C).
2. Assemble the rubber feet (F) Fig. 9A. NOTE: Each
rubber foot is provided with holes for mounting the
stand to the floor surface if required.
ATTACHING DUST BAG
1. Attach the dust bag to the bag frame and place the
frame of the dust bag inside the saw stand as shown in
Fig. 9B. Refer to the section below to attach this
assembly to the saw.
SAW TO STAND
1. Turn saw table face down on a piece of cardboard to
protect the table surface. Place stand upside down onto
saw and align the four holes in the stand with the
mounting holes in the saw.
2. Using the 2 longer screws for the front, place a M8 flat
washer on a M8X1.25X45mm hex head screw. Insert the
hex head screw through the mounting hole in the saw
and the mounting hole in the stand. Place another M8
flat washer on the hex screw and thread a M8X1.25 hex
nut on the screw and loosely tighten. Repeat this
process to complete another hole in the saw front.
Using the 2 shorter screws for the back, place a M8 flat
washer on a M8X1.25X30mm hex head screw in the
back of saw. Insert the hex head screw through the
mounting hole in the saw and the mounting hole in the
stand. Place another M8 flat washer on the hex screw
and thread a M8X1.25 hex nut on the screw and loosely
tighten. Repeat this process to complete another hole in
the saw back.
3. Then, turn saw table face up, as shown in Fig. 9C
(Saw is shown fully assembled here).
4. Push down on top of the saw so the legs of the stand
adjust to the surface of the floor and tighten all stand
hardware and hardware which secures saw to stand.
Fig. 9A
Fig. 9C
Fig. 9B
C
E
B
D
E
A
C
D
F
Page 12

12
ASSEMBLING BLADE
RAISING AND LOWERING
HANDWHEEL
1. Insert special screw (C) through handle (B) Fig.10 and
assembly handle to handwheel (A) by threading screw
clockwise into handwheel. Then push on handle cover
(D).
2. Fig. 11, illustrates the handle (B) assembled to
handwheel (A).
3. Assemble handwheel (A) Fig. 12, to shaft (B) making
sure the flat on inside of handwheel lines up with flat on
shaft.
4. Fasten handwheel (A) Fig. 13, to shaft (B) Fig. 12,
using a M6x1x12mm flat head screw (C) Fig. 13.
Fig. 10
Fig. 11
Fig. 12
Fig. 13
A
B
A
C
A
B
C
D
Page 13
13
BLADE GUARD AND
SPLITTER ASSEMBLY
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM
POWER SOURCE.
1. IMPORTANT: THE BLADE GUARD AND SPLITTER
ASSEMBLY MUST BE PROPERLY ALIGNED TO THE
SAW BLADE IN ORDER TO PREVENT KICKBACK.
2. Position the blade 90 degrees to the table and lock in
place. Refer to page 18 “Blade Raising and Lowering
Control” and page 19 “Blade Tilting Control”.
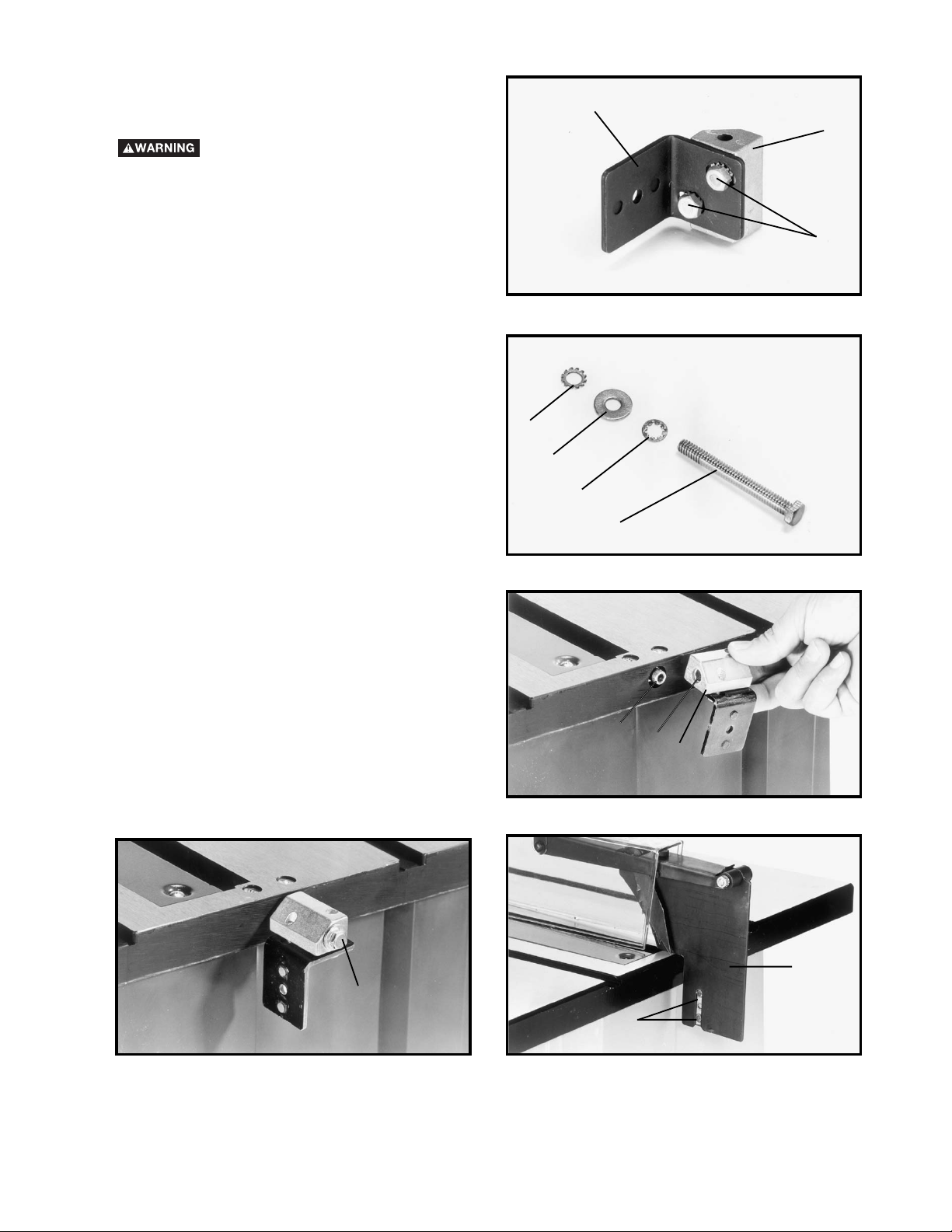
3. Fasten the splitter support bracket (A) Fig. 14, to
splitter bracket (B) using two 1/4-20 x 1/2 in. Hex Head
Screws (C), and two 1/4 in. external tooth lockwashers
as shown. NOTE: Do not completely tighten screws
(C) at this time.
4. Locate the 1/4-20 x 2-1/4 in. hex head screw (G) Fig.
15, and assemble the 1/4 in. internal tooth lockwasher
(O), 1/4 in. flat washer (P) and 1/4 in. external tooth
lockwasher (R) onto screw (G).
5. Position recessed end (E) Fig. 16, of splitter bracket
(B) against end of pivot rod (F) and fasten in place using
assembly from STEP 4 above. NOTE: Do not
completely tighten screw (G) at this time. Assembly
shown in Fig. 17.
6. Position the splitter (H) Fig. 18, on the splitter support
bracket as shown, making certain the two protrusions
(K) on the splitter support bracket are inside the slot of
splitter (H).
Fig. 14
Fig. 15
Fig. 16
Fig. 18Fig. 17
K
H
G
F
E
B
R
P
O
G
A
B
C
Page 14
14
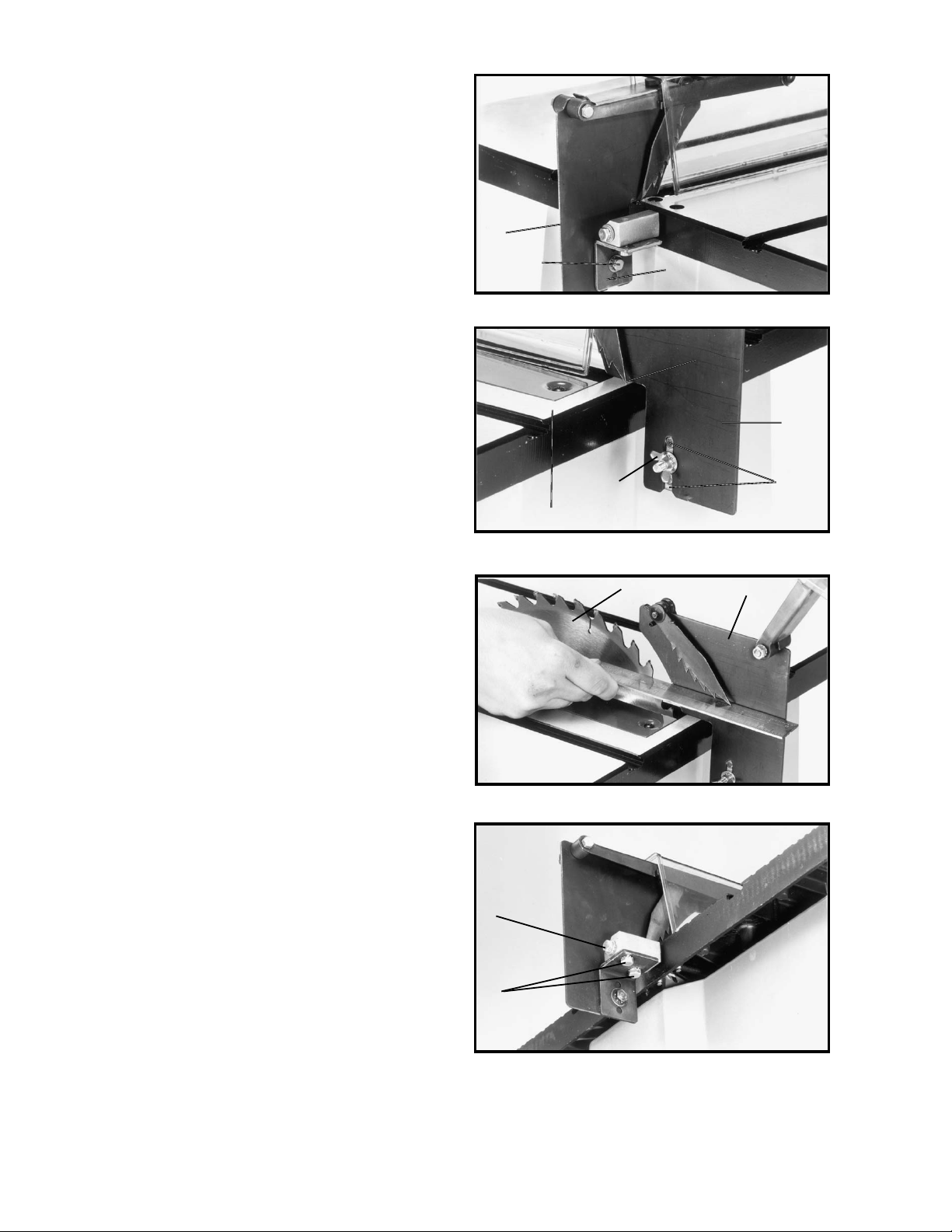
7. Assemble splitter (H) Fig. 19, to splitter support
bracket (B) as shown using M6x1x20mm hex head
screw (L), 1/4 in. external tooth washer, and 1/4 in. flat
washer.
8. Fasten splitter (H) Fig. 20, to splitter support bracket
using 1/4 in. flat washer, 1/4 in. external tooth
lockwasher and M6 wing nut (M). NOTE: Before
tightening wing nut (M) make certain there is at least a
1/8 in. gap between the bottom edge of splitter (N) and
top surface of table (P) and that protrusion “pins” (K) Fig.
20, are inside the slot of splitter assembly (H).
9. Using a straight edge, check to see if the splitter (H)
Fig. 21, is aligned with the saw blade (R). If an
adjustment is necessary, the splitter (H) can be moved
left or right and rotated.
10. When you are certain the splitter is properly aligned
with the saw blade, tighten the two screws (C) Fig. 22,
that fasten the splitter support bracket to the splitter
bracket and tighten screw (G) that fastens the splitter
bracket to the pivot rod.
Fig. 19
Fig. 20
Fig. 21
Fig. 22
C
G
R
H
P
M
K
H
N
H
L
B
Page 15
15
EXTENSION WINGS
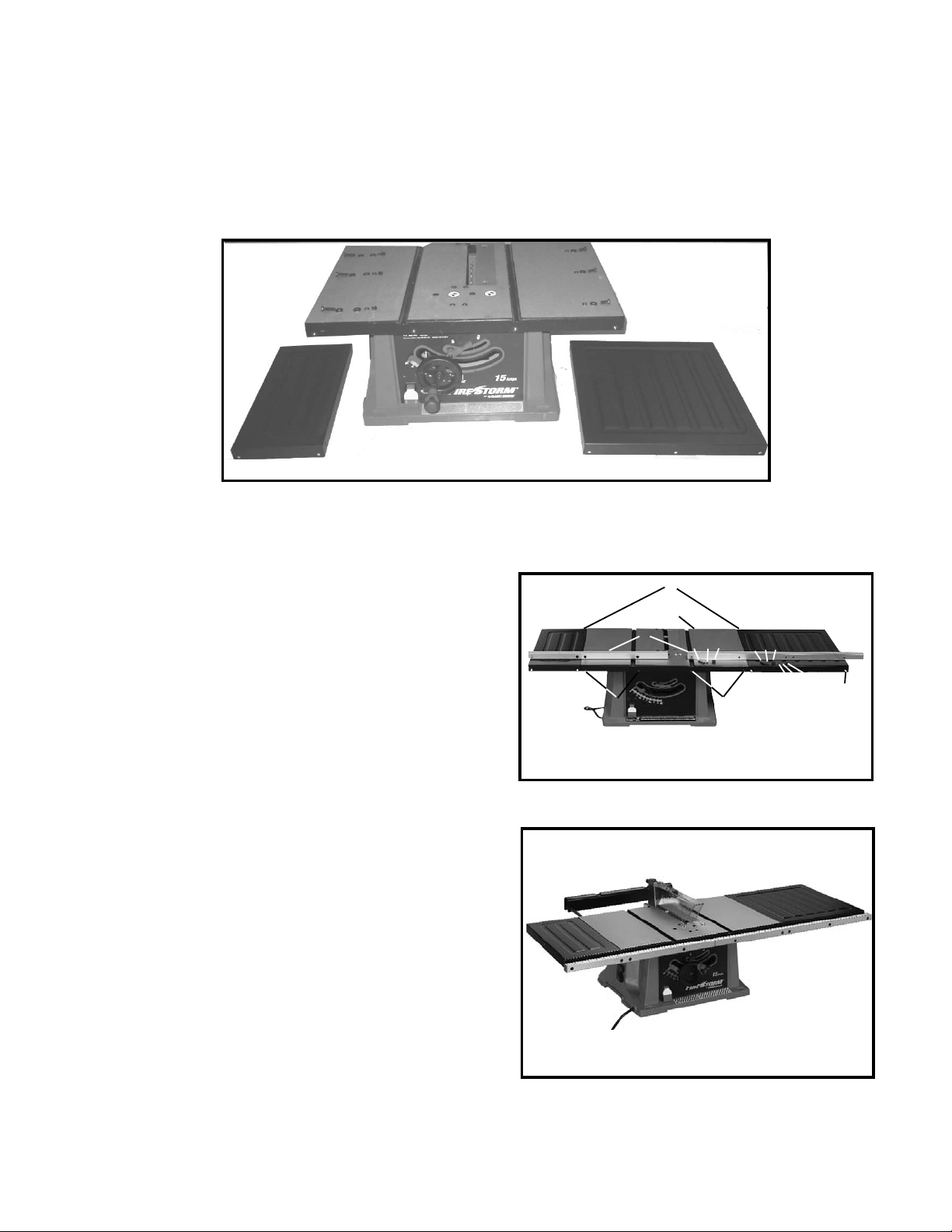
1. Assemble left extension wing (Fig.23), to the saw table using 1/4-20X1 in.hex head screws (3), 1/4 in.flat washers (6),
1/4 in.lockwashers (3),1/4 in.hex nuts (3).
2. Assemble right extension wing into the threaded holes of the saw using 1/4 in.-20X5/8 in. hex head screws (3),
1/4 in. flat washers (3) 1/4 in. lockwashers (3).
3. With a straight edge, make certain the top, front and rear edges of the extension wings are level with the saw table
before tightening three screws which secure extension wing to table.
Fig. 23
GUIDE RAIL TO SAW
1. Holding the guide rail with the larger holes facing you,
loosely fasten guide rails (A) Fig. 24, to the four
threaded holes (B) in saw table (C) using two 1/4-20
x 1-1/4 in. long screws (D), 1/4 in. lockwashers (E), and
spacers (F).
IMPORTANT: Spacers (F) Fig. 24, are positioned
between guide rails (A) and saw table (C).
2. Fasten guide rails (A) Fig. 24, to extension wings
(G) through hole (K) using the 1/4-20 x 1-1/4 in. long
screw (D), 1/4 in. lockwasher (E), spacer (F), 1/4 in. flat
washer (H), 1/4 in. lockwasher (E), and 1/4-20 hex nut
(J). Then tighten all guide rail mounting hardware.
IMPORTANT: Spacer (F) Fig. 24, is positioned
between guide rails (A) and extension wings (G).
3. Fig. 25, illustrates the guide rails properly assembled
to saw table and extension wings.
Fig. 24
Fig. 25
C
A
G
J
E
H
D
E
K
F
B
D
E
F
B
Page 16

16
RIP FENCE
1. Thread the M8x1.25 hex nut (A) Fig. 26,
approximately halfway on the stud of the handle (B).
2. Thread the handle (B) Fig. 26 into the tapped hole
(C) in the fence cam (D). Tighten the hex nut (A) Fig. 26
against the cam (D).
3. Lower rip fence onto table as shown in Fig. 27,
making certain rear clamp hooks over back edge of
table.
4. The rip fence is usually operated on the right hand
side of the saw table. Lift lock handle (B), and position
fence on table. Push downward on handle (B), to lock
fence in place on saw table.
MITER GAGE
The miter gage is shipped completely assembled and is
supplied with a T-slot miter gage bar (A) Fig. 28, that is
inserted into either one of the two T-slotted miter gage
grooves located in the table top, as shown. The T-slot
miter gage prevents the miter gage from falling when it
is extended out beyond the front of the table when
cross-cutting extra wide workpieces.
Fig. 26
Fig. 27
Fig. 28
A
B
B
A
C
D
Page 17
17
OUTFEED SUPPORT
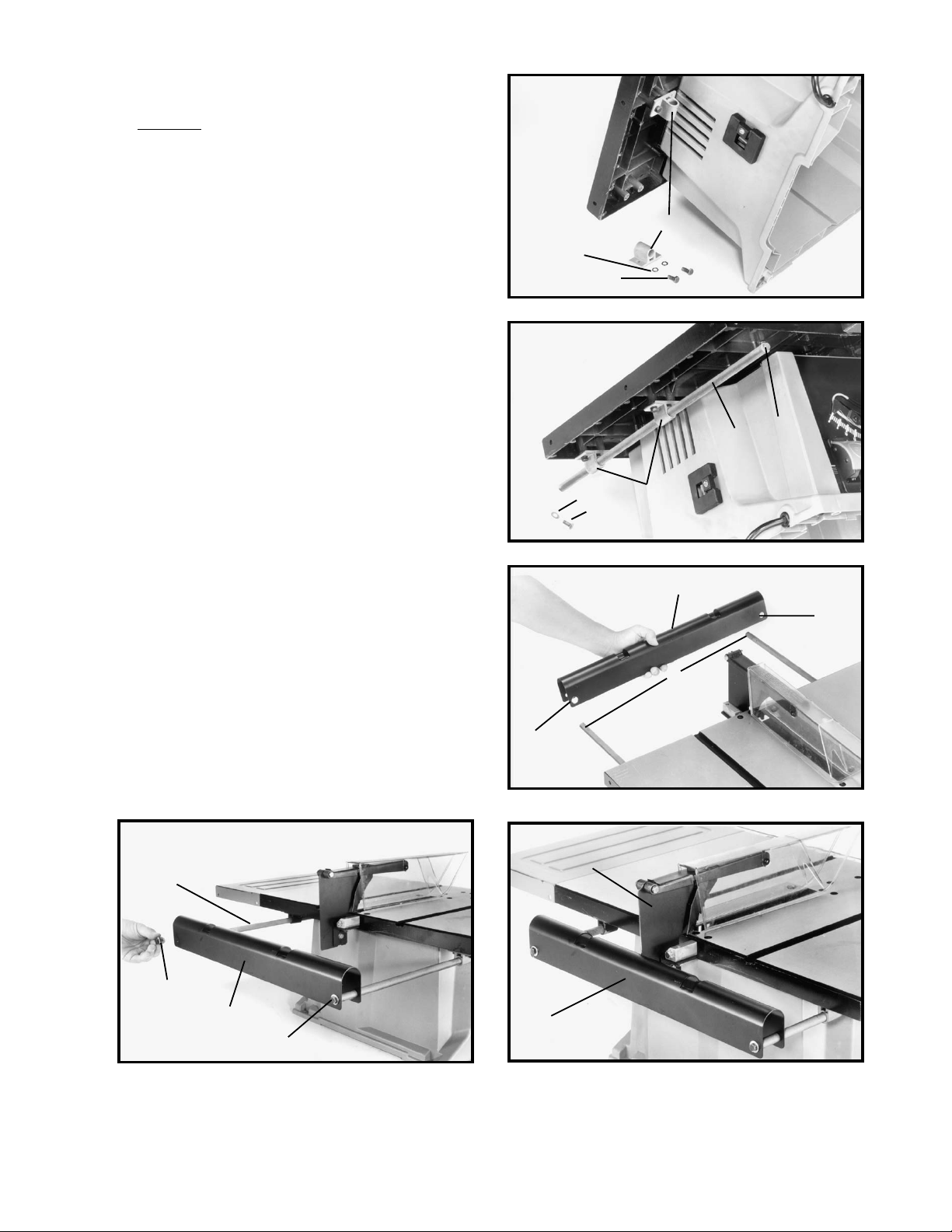
1. LOOSELY fasten both brackets (A) Fig. 29, to the
bottom left side of the saw table as shown, using two
M6x1x15mm phillips hex head screws (B) and M6.1
lockwashers (C). Assemble two remaining brackets to
the bottom right side of saw table in the same manner.
2. Insert rod (D) Fig. 30, through holes in brackets (A) as
shown. Then thread and tighten one 1/4-20x1/2 in. hex
head screw (E) and 1/4 in. flat washer (F) into the front
end of rod (D) as shown at (G). Assemble remaining rod
to the opposite side of saw in the same manner.
3. Insert rods (D) Fig. 31, into larger holes (H) in outfeed
support (J) as shown.
4. Secure outfeed support (J) Fig. 32, to rods (D) using
two 1/4-20x1/2 in. hex head screws and 1/4 in. flat
washers (K) as shown.
5. Push entire outfeed support assembly (J) Fig. 33, in
until it contacts splitter/guard assembly (L) as shown.
Then tighten all outfeed support mounting hardware.
6. Place washer on 1/4-20x1/2 in. hex screw and thread
into the other end of the rods tp prevent them from
coming out of outfeed support brackets.
Fig. 32
Fig. 29
Fig. 30
Fig. 31
Fig. 33
A
B
C
F
E
D
G
A
J
H
H
D
D
K
J
K
L
J
Page 18

1818
STARTING AND STOPPING SAW
The on/off switch (A) Fig. 34 is located on the front of the
saw cabinet. To turn the saw “ON”, move the switch (A)
up to the “ON” position. To turn the saw “OFF”, move the
switch (A) down to the “OFF” position.
MAKE SURE THAT THE SWITCH IS IN
THE “OFF” POSITION BEFORE PLUGGING IN THE
POWER CORD. IN THE EVENT OF A POWER FAILURE,
MOVE THE SWITCH TO THE “OFF” POSITION. AN
ACCIDENTAL START-UP CAN CAUSE INJURY.
LOCKING SWITCH IN THE “OFF”
POSITION
IMPORTANT: When the tool is not in use, the switch
should be locked in the “OFF” position to prevent
unauthorized use. To lock the tool, grasp the switch
toggle (B) and pull it out of the switch (Fig. 35). With the
switch toggle (B) removed, the switch will not operate.
However, should the switch toggle be removed while the
saw is running, the machine can be turned “OFF,” but
cannot be restarted without re-inserting the switch toggle
(B).
BLADE RAISING AND
LOWERING CONTROL
To raise or lower the saw blade, turn handwheel (A) Fig.
36. Turning the handwheel clockwise lowers the blade
and turning the handwheel counterclockwise raises the
blade.
THE BLADE TILTING LOCK HANDLE
(B) FIG. 36, MUST BE LOCKED DURING ALL
CUTTING OPERATIONS.
Fig. 34
Fig. 35
Fig. 36
A
B
A
B
OPERATING CONTROLS AND ADJUSTMENTS
Page 19
19
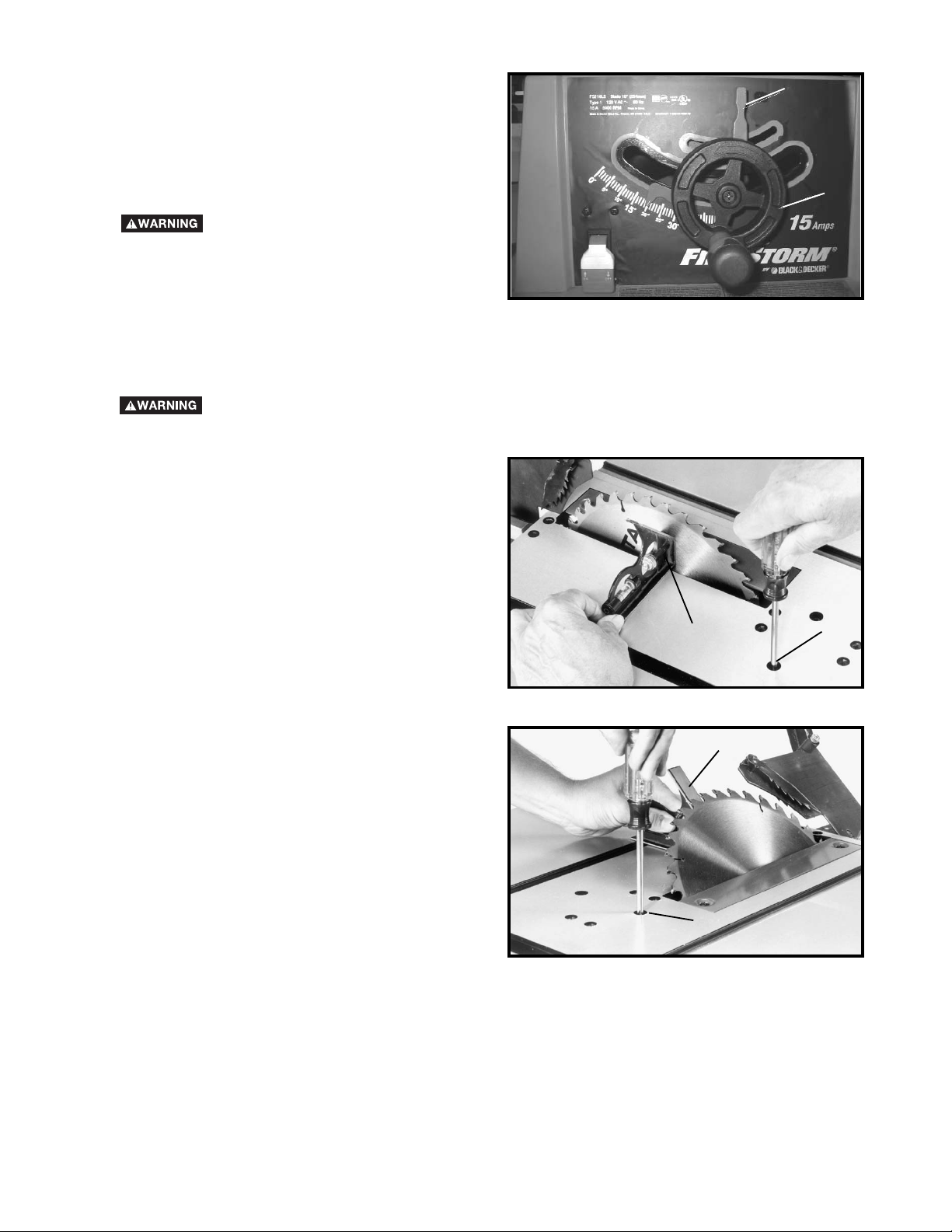
BLADE TILTING CONTROL
To tilt the saw blade, loosen blade tilting lock handle (A)
Fig. 37, move handwheel (B) until the blade is at the
desired angle and tighten lock handle (A). NOTE: The
lock handle (A) is spring-loaded and can be repositioned
by pulling out on the handle (A) and repositioning it on
the serrated stud located underneath the handle.
THE BLADE TILTING LOCK HANDLE
(A) MUST BE LOCKED DURING ALL CUTTING
OPERATIONS.
Fig. 37
ADJUSTING 90 AND 45 DEGREE POSITIVE STOPS
Your saw is equipped with positive stops for rapid and accurate positioning of the saw blade at 90 and 45 degrees to
the table. To adjust the positive stops, proceed as follows:
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER SOURCE.
1. Raise the saw blade to its maximum height.
Fig. 38
Fig. 39
TO ADJUST POSITIVE STOP AT 90
DEGREES
2. Loosen the blade tilting lock handle, move the blade
tilting mechanism as far as possible to the left and
tighten the blade tilting lock handle.
3. Place a square (A) Fig. 38, on the table with one end
of the square against the blade, as shown, and check to
see if the blade is at 90 degrees to the table. If it is not,
loosen screw (B) a few turns and move the blade tilting
mechanism until the blade is at 90 degrees to the table.
Then tighten blade tilting lock handle and tighten screw
(B) until it bottoms.
TO ADJUST POSITIVE STOP AT 45
DEGREES
4. Loosen the blade tilting lock handle, move the blade
tilting mechanism as far as possible to the right and
tighten the blade tilting lock handle.
5. Place a square (A) Fig. 39, on the table with one end
of the square against the blade as shown, and check to
see if the blade is at 45 degrees to the table. If it is not,
loosen screw (C) a few turns and move the blade tilting
mechanism until the blade is at 45 degrees to the table.
Then tighten blade tilting lock handle and tighten screw
(C) until it bottoms.
A
B
A
C
A
B
Page 20
2020
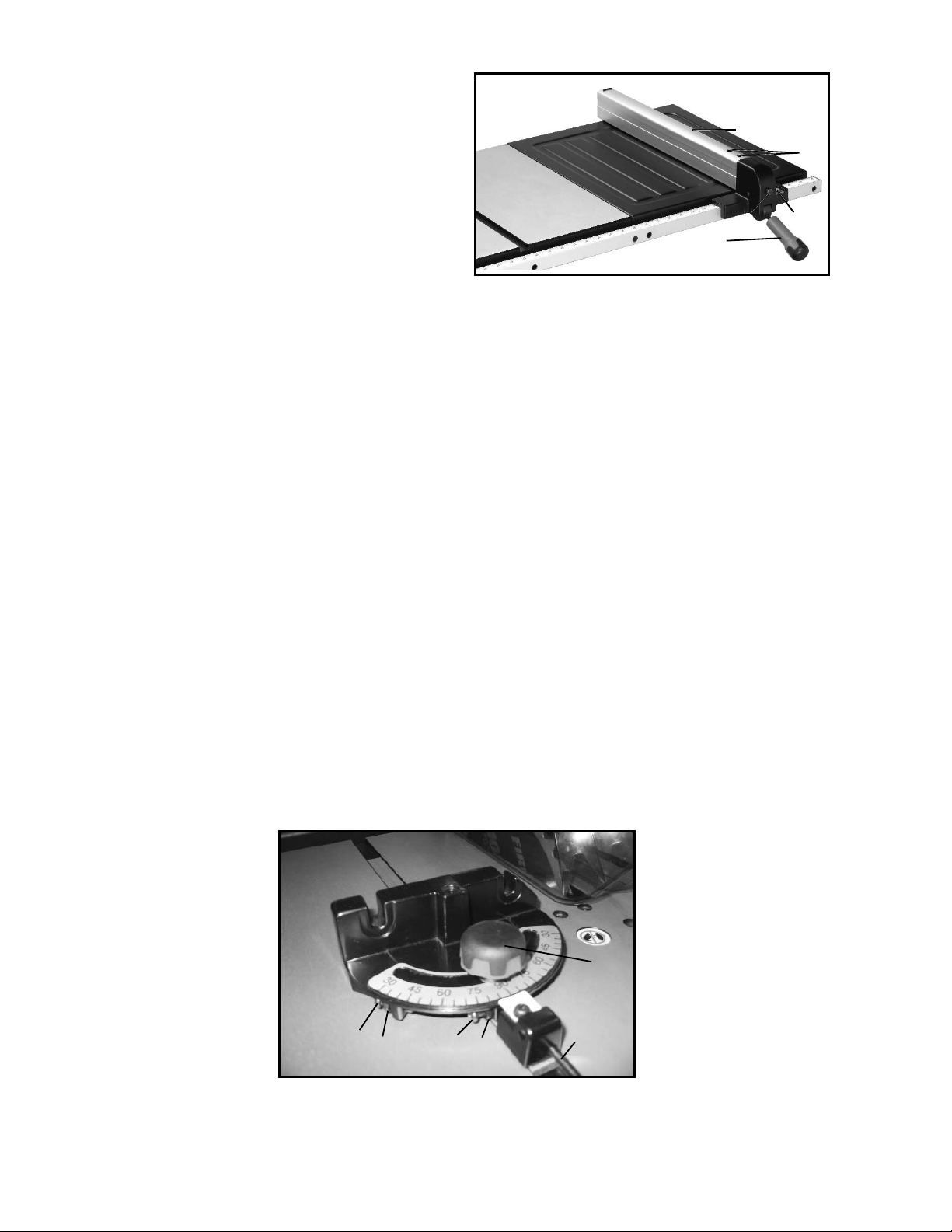
RIP FENCE OPERATION
AND ADJUSTMENTS
1. To move the rip fence (A) Fig. 40, along the table, lift
up fence locking lever (B), slide the fence to the desired
location on the table and push down fence locking lever
(B) to lock the fence in position.
2. A pointer is supplied to indicate the distance the fence
is positioned away from the saw blade. If an adjustment
to the pointer is required, loosen the screw (C) Fig. 40,
that fastens the pointer to the fence bracket and adjust
the pointer accordingly. Then, tighten screw (C).
3.IMPORTANT: THE RIP FENCE MUST BE PROPERLY
ALIGNED TO THE MITER GAGE SLOT IN ORDER TO
HELP PREVENT KICKBACK WHEN RIPPING.
4. The saw blade is set parallel to the miter gage slot at
the factory and the fence must be parallel to the miter
gage slot in order to do accurate work and prevent
kickback when ripping. To check the alignment:
5. Position the fence at one end of the miter gage slot.
Clamp the fence to the table by pushing down the
locking lever. The edge of the fence should then line up
parallel with the miter gage slot.
6. If an adjustment is necessary, proceed as follows:
Fig. 40
MITER GAGE OPERATION AND ADJUSTMENTS
When straight cross-cutting (blade set 90 degrees to the table) the miter gage can be used in either table slot. When
bevel cross-cutting (blade tilted) only use the miter gage in the right table slot where the blade is tilted away from the
miter gage and your hands.
This miter gage is equipped with individually adjustable index stops at 90 degrees and 45 degrees right and left.
Adjustment to the index stops can be made by loosening lock nuts (B) Fig. 41, and tightening or loosening the three
adjusting screws (C) until they contact the other end of stop pin (D) when the miter gage is at 90 and 45 degrees to the
saw blade. Then, tighten lock nuts (B).
To operate the miter gage, simply loosen lock knob (E) Fig. 41, and move the body of the miter gage to the desired
angle. When the stop pin (D) is pushed in, the miter gage body will stop at 90 degrees and 45 degrees right and left.
To rotate the miter gage body past these points, pull out stop pin (D).
Fig. 41
7. Loosen the two 3/16 in. allen head screws (D) Fig. 40,
and lift up locking lever (B). Then while holding the fence
bracket firmly toward the front of the saw, move the rear
end of the fence (A) until it is parallel with the miter gage
slot. Then tighten two screws (D) and push down locking
lever (B).
8. The clamping action of the fence (A) Fig. 40, can be
adjusted by lifting up locking lever (B) and turning screw
(E) clockwise to increase or counterclockwise to
decrease the clamping action of the fence.
C
B
C
B
D
E
C
B
A
D
E
Page 21
21
ADJUSTING BLADE PARALLEL TO
MITER GAGE SLOTS
The blade was adjusted parallel to the miter gage slots
at the factory. In order to insure accurate cuts and help
prevent kickback when cutting, this adjustment should
be rechecked and if necessary, readjusted as follows:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER SOURCE.
2. Raise the blade to its highest position and adjust the
blade so it is 90 degrees to the table.
3. Select a tooth on the saw blade that is set to the left.
Mark this tooth with a pencil or marker.
4. Using a combination square, place the body (A)
Fig. 42, of the square against the miter gage slot and
adjust the blade (B) of the square until it just touches the
marked tooth, as shown.
5. Rotate the blade and check the same marked blade
tooth at the rear of the saw table in the same manner, as
shown in Fig. 43.
6. If the front and back measurements (Figs. 42 and 43)
are not identical, you can adjust the blade. Start by
loosening the nuts below the four screws (C) Fig. 44 on
the table. Then loosen the screws (C). Carefully move
the saw blade until the blade is parallel to the miter
gauge slot. When done, tighten four nuts under the table
and the four screws (C) Fig. 44 securely.
NOTE: If sufficient adjustment cannot be achieved by
loosening screws (C), screws (D) may also be loosened
if absolutely necessary to make the adjustment.
NOTE: Guard has been removed for illustrative
purposes only.
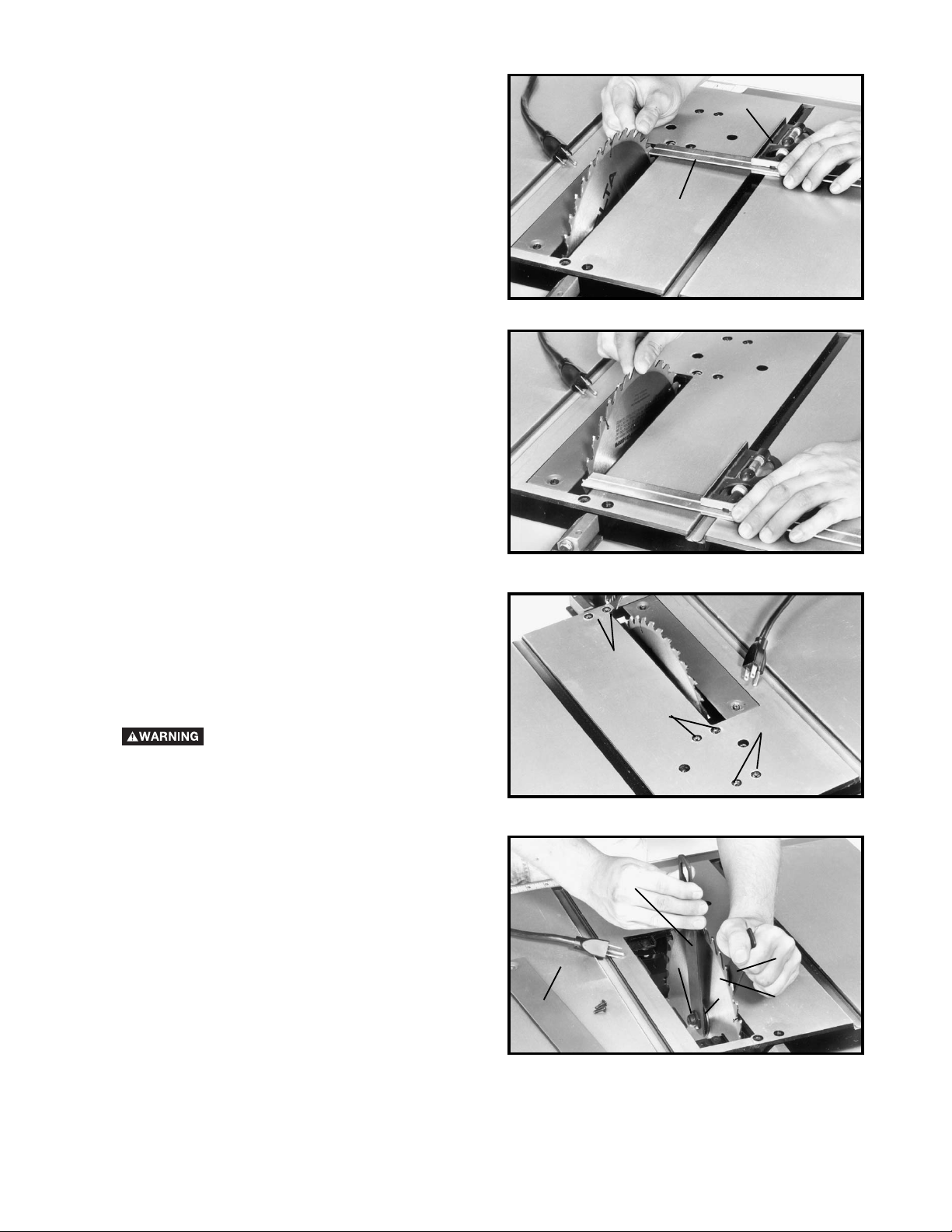
CHANGING THE BLADE
DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER
SOURCE. USE ONLY 10 in. DIAMETER
SAW BLADES RATED FOR 5000 RPM OR HIGHER
WITH 5/8 in. ARBOR HOLES.
1. Raise the saw blade to its maximum height and
remove the table insert (A) Fig. 45.
2. Using the open end wrench (B) Fig. 45, place open
end of wrench on flats on inside blade flange to keep the
saw arbor from rotating and remove arbor nut (C) with
wrench (D). Turn nut (C) counterclockwise to remove.
Remove outside blade flange (E) and saw blade (F).
3. Assemble new blade, making certain teeth of blade
are pointing down at the front of the saw table and
assemble the outside blade flange (E) Fig. 45, and arbor
nut (C). Tighten nut (C) with wrench (D) by turning nut
clockwise while holding arbor steady with other wrench
(B).
4. Replace table insert.
Fig. 42
Fig. 43
Fig. 44
Fig. 45
A
B
C
C
D
A
D
C
E
F
B
Page 22

2222
COMMON SAWING OPERATIONS
CROSS-CUTTING
Cross-cutting requires the use of the miter gage to
position and guide the work. Place the work against the
miter gage and advance both the gage and work toward
the saw blade, as shown in Fig. 46. The miter gage may
be used in either table slot. When bevel cutting (blade
tilted), use the table groove that does not cause
interference of your hand or miter gage with the saw
blade guard.
Start the cut slowly and hold the work firmly against the
miter gage and the table. One of the rules in running a
saw is that you never hang onto or touch a free piece of
work. Hold the supported piece, not the free piece that
is cut off. The feed in cross-cutting continues until the
work is cut in two, and the miter gage and work are
pulled back to the starting point. Before pulling the work
back, it is good practice to give the work a little
sideways shift to move the work slightly away from the
saw blade. Never pick up any short length of free work
from the table while the saw is running. Never touch a
cut-off piece unless it is at least a foot long.
For added safety and convenience the miter gage can
be fitted with an auxiliary wood-facing. This auxiliary
wood-facing can be fastened to the front of the miter
gage by using two wood screws through the slots (A)
Fig. 45, provided in the miter gage body and into the
wood-facing.
NEVER USE THE FENCE AS A CUT-OFF
GAGE WHEN CROSS-CUTTING.
When cross-cutting a number of pieces to the same length,
a block of wood (B) Fig. 46A can be clamped to the fence
and used as a cut-off gage. It is important that this block of
wood always be positioned in front of the saw blade as
shown. Once the cut-off length is determined, secure the
fence and use the miter gage to feed the work into the cut.
This block of wood allows the cut-off piece to move freely
along the table surface without binding between the fence
and the saw blade, thereby lessening the possibility of
kickback and injury to the operator.
WHEN USING THE BLOCK (B) FIG. 46A,
AS A CUT-OFF GAGE, IT IS VERY
IMPORTANT THAT THE REAR END OF THE BLOCK
BE POSITIONED SO THE WORK PIECE IS CLEAR OF
THE BLOCK BEFORE IT CONTACTS THE BLADE.
Common sawing operations include ripping and crosscutting plus a few other standard operations of a fundamental
nature. As with all power machines, there is a certain amount of hazard involved with the operation and use of the
machine. Using the machine with the respect and caution demanded as far as safety precautions are concerned, will
considerably lessen the possibility of personal injury. However, if normal safety precautions are overlooked or
completely ignored, personal injury to the operator can result. The following information describes the safe and proper
method for performing the most common sawing operations.
THE USE OF ATTACHMENTS AND ACCESSORIES NOT RECOMMENDED MAY RESULT IN THE
RISK OF INJURY TO THE USER OR OTHERS.
Fig. 46
Fig. 46A
A
B
Page 23

23
Ripping is cutting lengthwise through a board. The rip
fence (A) Fig. 47 is used to position and guide the work.
One edge of the work rides against the rip fence while
the flat side of the board rests on the table. Since the
work is pushed along the fence, it must have a straight
edge and make solid contact with the table. The saw
blade guard must be used. The guard has anti-kickback
fingers to prevent kickback and a splitter to prevent the
wood kerf from closing and binding the blade.
RIPPING
1. Start the motor and advance the work holding it down
and against the fence. Never stand in the line of the saw
cut when ripping. Hold the work with both hands and
push it along the fence and into the saw blade (Fig. 48).
The work can then be fed through the saw blade with
one or two hands. After the work is beyond the saw
blade and anti-kickback fingers, the hand is removed
from the work. When this is done the work will either
stay on the table, tilt up slightly and be caught by the
end of the rear guard, or slide off the table to the floor.
Alternately, the feed can continue to the end of the table,
after which the work is lifted and brought along the
outside edge of the fence. The cut-off stock remains on
the table and is not touched until the saw blade has
stopped, unless it is a large piece allowing safe removal.
When ripping boards longer than three feet, it is
recommended that outfeed support (B) Fig. 47, should
be extended as far out as possible to keep workpiece
from falling off the saw table.
2. If the ripped work is less than 4 inches wide, a push
stick should always be used to complete the feed, as
shown in Fig. 49. The push stick can easily be made from
scrap material as explained in the section
“CONSTRUCTING A PUSH STICK.”
3. Ripping narrow pieces can be dangerous if not done
carefully. Narrow pieces usually cannot be cut with the
guard in position. If the workpiece is short enough, use a
pushboard. When ripping material under 2 inches in
width, a flat pushboard is a valuable accessory since
ordinary type sticks may interfere with the blade guard.
When using a pushboard, the width of the pushboard
must be added to the width of the rip fence position
setting. A flat pushboard can be constructed as shown in
Fig. 50 and should be used as shown in Fig. 48
NOTE: Some special operations require the addition of
an auxiliary wood facing to the fence, as explained in the
section “USING AUXILIARY WOOD FACING ON THE
RIP FENCE” and use of a push stick.
Fig. 49
Fig. 47
A
Fig. 48
B
Fig. 50
Page 24

24
USING AUXILIARY WOODFACING ON
RIP FENCE
Wood facings (A) Fig. 51 are necessary on some special
operations to one or both sides of the rip fence. The wood
facing is attached to the fence with screws through the
holes in the fence. Most work will require a 3/4 in. stock,
although an occasional job may require 1in. facing.
Fig. 54 Fig. 55
Fig. 53
1. Dadoing is cutting a rabbet or wide groove into the
work. Most dado head sets are made up of two outside
saws and four or five inside cutters, (Fig. 53). Various
combinations of saws and cutters are used to cut
grooves from 1/8 in. to 13/16 in. for use in shelving,
making joints, tenoning, grooving, etc. The cutters are
heavily swaged and must be arranged so that this heavy
portion falls in the gullets of the outside saws, as shown
in Fig. 54. The saw and cutter overlap is shown in Fig. 55,
(A) being the outside saw, (B) an inside cutter, and (C) a
paper washer or washers, used as needed to control the
exact width of groove. A 1/4 in. groove is cut by using
the two outside saws. The teeth of the saws should be
positioned so that the raker on one saw is beside the
cutting teeth on the other saw.
A
B
C
THE BLADE GUARD AND SPLITTER
ASSEMBLY CANNOT BE USED WHEN
DADOING. IT MUST BE REMOVED.
ACCESSORY DADO CUTTERHEAD
Fig. 52
A
Before dadoing, loosen wing nut (A) Fig. 52 and take
off the blade guard and splitter assembly (B). Keep
assembly handy to replace it after dadoing.
B
Fig. 51
A
NOTE: THE MAXIMUM WIDTH DADO CUT FOR THIS
SAW IS 1/2 INCH.
Page 25

25
Fig. 56
Fig. 57
D
E
2. Attach the dado head set (D) Fig. 56, to the saw arbor.
NOTE: THE OUTSIDE ARBOR FLANGE CAN NOT BE
USED WITH THE DADO HEAD SET, TIGHTEN THE
ARBOR NUT AGAINST THE DADO HEAD SET BODY.
DO NOT LOSE THE OUTSIDE ARBOR FLANGE. IT
WILL BE NEEDED WHEN REATTACHING A BLADE TO
THE ARBOR.
THE ACCESSORY DADO HEAD SET
TABLE INSERT (E) FIG. 56, MUST BE
USED IN PLACE OF THE STANDARD TABLE INSERT.
THE BLADE GUARD AND SPLITTER
ASSEMBLY CANNOT BE USED WHEN
DADOING AND MUST BE REMOVED OR SWUNG TO
THE REAR OF THE SAW. AUXILIARY JIGS,
FIXTURES, PUSH STICKS AND FEATHER BOARDS
CAN AND SHOULD BE USED.
3. Fig. 57, shows a typical dado operation using the miter
gage as a guide.
NEVER USE THE DADO HEAD IN A
BEVEL POSITION.
ALWAYS INSTALL BLADE GUARD
AFTER OPERATION IS COMPLETED.
Page 26
2626
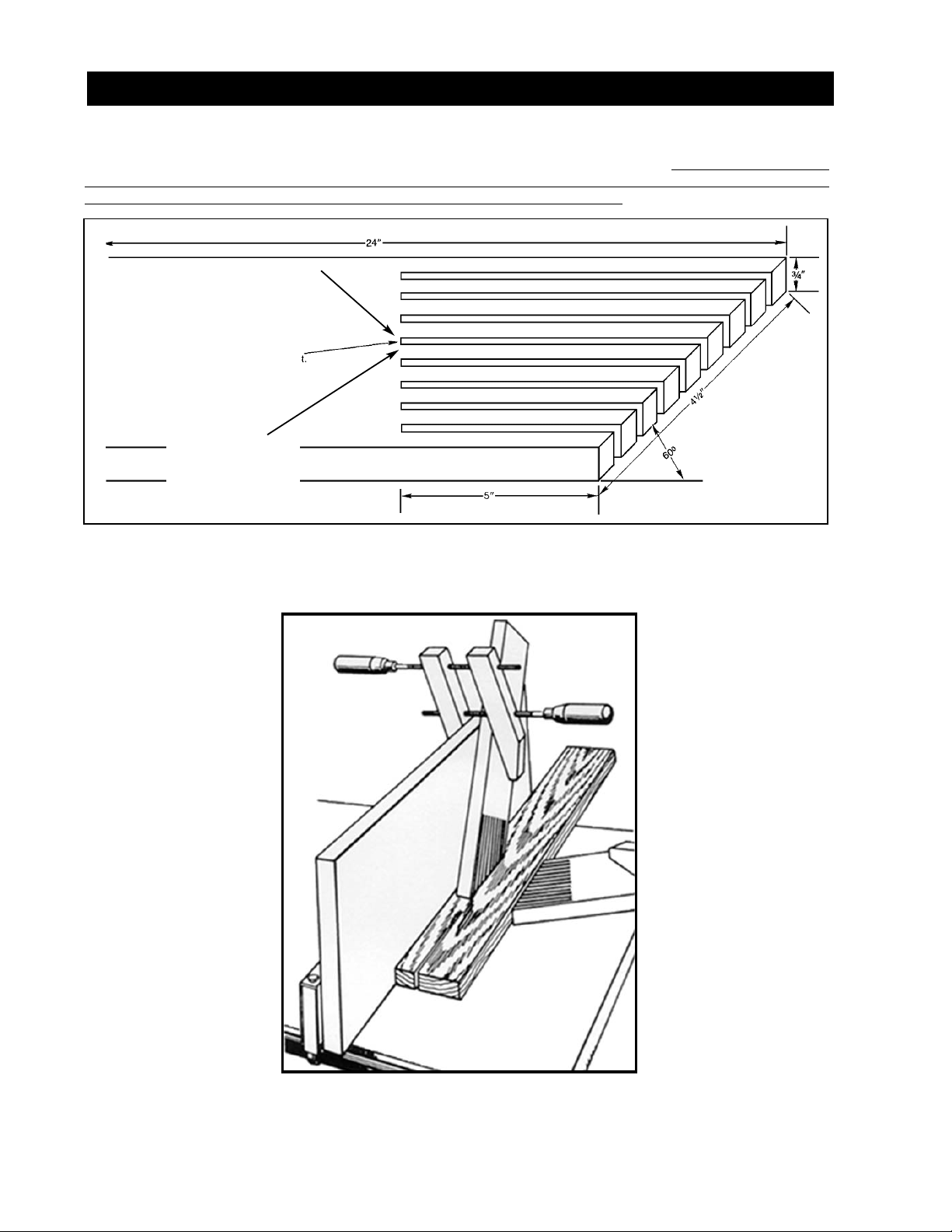
CONSTRUCTING A FEATHERBOARD
Fig. 58, illustrates dimensions for making a typical featherboard. The material which the featherboard is constructed
of, should be a straight piece of wood that is free of knots and cracks. Featherboards are used to keep the work in
contact with the fence and table and help prevent kickbacks. Clamp the featherboards to the fence and table so that
the leading edge of the featherboards will support the workpiece until the cut is completed. Use featherboar
ds for all
non “thru-sawing” operations where the guard and spreader assembly must be removed (see Fig. 59). Always replace
the guard and spreader assembly when the non thru-sawing operation is completed.
Fig. 58
Fig. 59
Kerf should be
about 1/4in.
apart.
LA DISTANCE
ENTRE LES TRAITS
DE SCIE DOIT ÊTRE
D’ENVIRON 6,4 MM
(1/4 PO)
EL CORTE DEBE
ESTAR SEPARADO
POR 6,35 mm (1/4in.)
APROXIMADAMENTE
Page 27

27
BE SURE TO FOLLOW SAFETY RULES AND INSTRUCTIONS
TROUBLE! SAW WILL NOT START
WHAT’S WRONG? WHAT TO DO…
1.Saw not plugged in. 1.Plug in saw.
2.Fuse blown or circuit breaker tripped. 2.Replace fuse or reset
circuit breaker.
3.Cord damaged. 3.Have cord replaced by
authorized service center.
4.Brushes worn out. 4.Have brushes replaced
by authorized service center.
TROUBLE! SAW MAKES UNSATISFACTORY CUTS
WHAT’S WRONG? WHAT TO DO…
1.Dull blade. 1.Replace blade.
2.Blade mounted backwards. 2.Turn blade around.
3.Gum or pitch on blade. 3.Remove blade and
clean with turpentine.
4.Incorrect blade for work being done. 4.Change the blade.
TROUBLE! BLADE DOES NOT COME UP TO SPEED
WHAT’S WRONG? WHAT TO DO…
1.Extension cord too light or too long. 1.Replace with adequate
size cord.
2.Low house current. 2.Contact your electric
company.
TROUBLE! MACHINE VIBRATES EXCESSIVELY
WHAT’S WRONG? WHAT TO DO…
1.Stand on uneven floor. 1.Reposition on flat level
surface.
2.Damaged saw blade. 2.Replace blade.
TROUBLE! DOES NOT MAKE ACCURATE MITER CUTS
WHAT’S WRONG? WHAT TO DO…
1.Miter scale not adjusted correctly. 1.Check and adjust.
2.Blade is not square to fence. 2.Check and adjust.
3.Blade is not perpendicular to table. 3.Check and adjust fence.
4.Workpiece moving. 4.Clamp workpiece to
fence or glue 120 grit
sandpaper to fence with
rubber cement.
TROUBLE! MATERIAL PINCHES BLADE
WHAT’S WRONG? WHAT TO DO…
1.Cutting bowed material. 1. Position bowed material
with concave or hollow side down.
2.Rip fence not parallel to blade. 2. Realign rip fence.
TROUBLE! CANNOT LOCK BLADE INTO BEVEL POSITION
WHAT’S WRONG? WHAT TO DO…
1.Blade tilting lock handle too loose. 1.Remove blade raising and lowering with
handwheel.
2. Remove flat head screw from lock handle.
3. Tighten blade tilting lock handle. The lock
handle (A) is spring-loaded and can be
repositioned by pulling out on the handle (A)
and repositioning it on the serrated stud
located underneath the handle. NOTE: After
tightening, place the handle at the one o’clock
position.
4. Replace the flat head screw.
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
Page 28

28
When ripping work less than 4 inches wide, a push stick should be used to complete the feed and could easily be
made from scrap material by following the pattern shown in Fig. 60.
PUSH STICK
MAKE FROM 1/2in. OR 3/4in.
WOOD OR THICKNESS
LESS THAN WIDTH OF
MAT’L. TO BE CUT
CUT OFF HERE TO
PUSH 1/4in. WOOD
CUT OFF HERE TO
PUSH 1/2in. WOOD
NOTCH TO HELP
PREVENT HAND
FROM SLIPPING
1/2in. SQUARES
CONSTRUCTING A PUSH STICK
Fig. 60
Page 29

29
ACCESSORIES
Recommended accessories for use with your tool are available from your local dealer or authorized service center. If you need
assistance regarding accessories, please call:1-800-544-6986.
The use of any accessory not recommended for use with this tool could be hazardous..
Maintenance
Use only mild soap and damp cloth to clean the tool. Never let any liquid get inside the tool; never immerse any part of the tool into a
liquid.
IMPORTANT: To assure product SAFETY and RELIABILITY, repairs, maintenance and adjustment (other than those listed in this
manual) should be performed by authorized service centers or other qualified service organizations, always using identical
replacement parts.
Service Information
All Black & Decker Service Centers are staffed with trained personnel to provide customers with efficient and reliable power tool
service. Whether you need technical advice, repair, or genuine factory replacement parts, contact the Black & Decker location
nearest you. To find your local service location, refer to the yellow page directory under "Tools—Electric" or call:
1-800-544-6986 or visit www.blackanddecker.com
Full Two-Year Home Use Warranty
Black & Decker (U.S.) Inc. warrants this product for two years against any defects in material or workmanship. The defective product
will be replaced or repaired at no charge in either of two ways.
The first, which will result in exchanges only, is to return the product to the retailer from whom it was purchased (provided that the
store is a participating retailer). Returns should be made within the time period of the retailer’s policy for exchanges (usually 30 to 90
days after the sale). Proof of purchase may be required. Please check with the retailer for their specific return policy regarding
returns that are beyond the time set for exchanges.
The second option is to take or send the product (prepaid) to a Black & Decker owned or authorized Service Center for repair or
replacement at our option. Proof of purchase may be required. Black & Decker owned and authorized Service Centers are listed
under "Tools-Electric" in the yellow pages of the phone directory and on our website www.blackanddecker.com.
This warranty does not apply to accessories. This warranty gives you specific legal rights and you may have other rights which vary
from state to state or province to province. Should you have any questions, contact the manager of your nearest Black & Decker
Service Center. This product is not intended for commercial use.
FREE WARNING LABEL REPLACEMENT: If your warning labels become illegible or are missing, call 1-800-544-6986 for a free
replacement.
Special Warranty Note to Contractors:
FIRESTORMTMbranded products are offered as high end consumer home use tools and carry a HOME USE WARRANTY. These
tools are designed, manufactured and tested to meet or exceed the needs of the do-it-yourselfer in the execution of projects and
repairs in and around the home. With proper use they will provide the home owner with step up power and performance well beyond
their two year warranty. However, if you use tools for a living and use FIRESTORM
TM
branded products or any of Black & Decker’s
other Consumer Home Use tools ON THE JOBSITE you should know that they CANNOT BE COVERED UNDER OUR
WARRANTY.
See ‘Tools-Electric’
– Yellow Pages –
for Service & Sales
Imported by
Black & Decker (U.S.) Inc.,
701 E. Joppa Rd.
Towson, MD 21286 U.S.A.
www.FireStormTools.com
1-800-544-6986
Page 30

30
SSSSCCCCIIIIEEEE ÀÀÀÀ TTTTAAAABBBBLLLLEEEE DD
DDEEEE 222255554444
MM
MM
MM
MM
((((11110000
PPPPOO
OO)))) FFFFSSSS222211110000LLLLSSSS
CONSERVER CE MODE D’EMPLOI POUR UN USAGE ULTÉRIEUR.
AVANT DE RETOURNER CE PRODUIT POUR QUELQUE RAISON QUE CE SOIT,
COMPOSER LE NUMÉRO
SUIVANT : 1 800 544-6986
MERCI D’A
MERCI D’A
VOIR CHOISI FIREST
VOIR CHOISI FIREST
ORM ! VISITEZ
ORM ! VISITEZ
WWW
WWW
.FIREST
.FIREST
ORMT
ORMT
OOLS.COM/PRODUCTREGISTRA
OOLS.COM/PRODUCTREGISTRA
TION
TION
POUR ENREGISTRER VOTRE NOUVEAU PRODUIT
POUR ENREGISTRER VOTRE NOUVEAU PRODUIT..
MODE D’EMPLOI
Page 31

31
Indique une situation dangereuse imminente qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, causera la mort ou des graves
blessures.
Indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, pourrait causer la mort ou de
graves blessures.
Indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle n’est pas évitée, pourrait causer des
blessures mineures ou modérées.
Utilisé sans le symbole d’alerte à la sécurité, indique une situation potentiellement dangereuse qui, si elle
n’est pas évitée, peut se solder par des dommages à la propriété
Ce mode d’emploi contient de l’information qu’il est important de connaître et de comprendre. Cette information
concerne VOTRE SÉCURITÉ et vise à ÉVITER TOUT PROBLÈME D’ÉQUIPEMENT. Pour vous aider à reconnaître ces
informations, nous utilisons les symboles à droite. Veuille lire le mode d’emploi et porter une attention accrue à ces
sections.
LIGNES DIRECTRICES EN MATIÈRE DE SÉCURITÉ —
DÉFINITIONS
ATTENTION
ATTENTION
AVERTISSEMENT
Certaines poussières produites par les activités de ponçage, de sciage, de meulage, de perçage et
autres activités de construction peuvent contenir des produits chimiques pouvant causer le cancer,
des anomalies congénitales ou d’autres problèmes liés aux fonctions reproductrices. Voici quelques exemples de ces
produits chimiques :
• le plomb contenu dans les peintures à base de plomb;
• la silice cristalline de la brique, du ciment et d’autres produits de maçonnerie; et
• l’arsenic et le chrome provenant du bois traité chimiquement.
Les risques reliés à l’exposition à ces poussières varient selon la fréquence à laquelle l’utilisateur travaille avec ce type de
matériaux. Pour réduire l’exposition à ces produits chimiques, travailler dans un endroit bien ventilé et porter un équipement
de sécurité approuvé comme un masque antipoussières conçu spécialement pour filtrer les particules microscopiques.
• Éviter le contact prolongé avec les poussières produites par les activités de ponçage, sciage, meulage, perçage et autres
activités de construction. Porter des vêtements de protection et laver les parties du corps exposées avec une solution d’eau et
de savon. Le fait de laisser la poussière pénétrer dans la bouche et les yeux ou de la laisser reposer sur la peau, peut
promouvoir l’absorption de produits chimiques nocifs.
l’utilisation de cet outil peut produire et/ou propulser des poussières qui pourraient causer des
problèmes respiratoires graves et permanents, ou d’autres problèmes médicaux. Toujours porter un
appareil respiratoire approuvé par la NIOSH/OSHA pour se protéger de la poussière. Diriger les particules loin du visage et du
corps.
porter une protection auditive appropriée pour utiliser l’appareil. Dans certaines conditions et selon la durée
d’utilisation, le bruit provoqué par ce produit peut contribuer à une perte auditive.
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
ATTENTION
RÈGLES GÉNÉRALES DE SÉCURITÉ
LIRE ATTENTIVEMENT TOUTES LES MISES EN GARDE ET DIRECTIVES
D’UTILISATION AVANT D’UTILISER CET ÉQUIPEMENT. À défaut de suivre les directives
sous-mentionnées, un choc électrique, un incendie, des dommages ou une blessure corporelle grave
pourraient survenir.
AVERTISSEMENT
DIRECTIVES DE SÉCURITÉ IMPORTANTES
Le travail du bois peut être dangereux si des procédures de sécurité et d’utilisation ne sont pas suivies. Comme avec
tout équipement, l’utilisation du produit comporte certains dangers. En utilisant cette machine avec toute la prudence
requise, le risque de blessures corporelles en sera considérablement réduit. Au contraire, si les mesures de sécurité
normales ne sont pas respectées ou sont ignorées, l’opérateur de l’outil peut être blessé. L’utilisation d’équipement de
sécurité comme des pare-mains, des poussoirs, des dispositifs d’ancrage, des planches en éventail, des lunettes de
sécurité, des masques antipoussières, des protecteurs auditifs peut réduire le risque de blessure. Cependant, même
la meilleure des protections ne compense pas pour un faible jugement, une imprudence ou de l’inattention. T
oujours
fair
e pr
euve de jugement et être prudent dans l’atelier. Si une procédure semble dangereuse, ne pas l’essayer.
Rechercher une procédure alternative qui semble plus sécuritaire. RAPPEL : votre sécurité personnelle est de votre
responsabilité.
Page 32

32
1. POUR SA PROPRE SÉCURITÉ, LIRE LE MODE
D’EMPLOI AVANT D’UTILISER L’OUTIL. L’apprentissage
de l’utilisation de cet outil, des restrictions, et des risques
qui lui sont propres réduit grandement la possibilité
d'accidents et de blessures.
2. PORTER UNE PROTECTION OCULAIRE. TOUJOURS
PORTER DES LUNETTES DE SÉCURITÉ. Utiliser
également un masque facial ou anti-poussière si
l’opération de découpe génère de la poussière. Les
lunettes de vue ne constituent PAS des lunettes de
sécurité. UTILISER UN ÉQUIPEMENT DE SÉCURITÉ
HOMOLOGUÉ. Votre protection oculaire doit être
conforme aux normes ANSI Z87.1, vos protecteurs auditifs
aux normes ANSI S3.19, et votre masque anti-poussières
aux normes homologuées MSHA/NIOSH. Les éclats de
bois, débris en suspension dans l’air, et poussières
peuvent provoquer des irritations, blessures et/ou
maladies.
3. PORTER LES VÊTEMENTS APPROPRIÉS. Ne pas
porter de vêtement ample, ni gant, ni cravates, ni bague,
ni bracelet, ni autre bijou, car ces derniers pourraient
s’enchevêtrer dans des pièces mobiles. Le port de
chaussures antidérapantes est recommandé. Se couvrir
les cheveux s’ils sont longs.
4. NE PAS UTILISER CET OUTIL DANS UN
ENVIRONNEMENT DANGEREUX. L'utilisation d'outils
électriques dans des endroits humides ou mouillés ou
sous la pluie peut provoquer un choc électrique ou
l'électrocution. Tenir la zone de travail bien éclairée pour
éviter de trébucher ou de mettre vos bras, mains et doigts
en danger.
5. CONSERVER TOUS LES OUTILS ET MACHINES DANS
LE MEILLEUR ÉTAT POSSIBLE. S’assurer que vos outils
sont aiguisés et propres afin d’optimiser sécurité et
performance. Suivre les consignes de graissage et de
changement d’accessoires. Les outils et machines mal
entretenus peuvent s'endommager davantage et/ou
provoquer des blessures.
6. VÉRIFIER QUE LES PIÈCES NE SONT PAS
ENDOMMAGÉES. Avant d’utiliser la machine, vérifier
qu'aucune pièce n'est endommagée. Vérifier l’alignement
des pièces mobiles, la présence de grippage des pièces
mobiles, de bris de pièces et tout autre problème pouvant
nuire au fonctionnement de l’outil. Un dispositif de
protection ou toute autre pièce qui pourrait être
endommagé(e) doit être réparé(e) ou remplacé(e)
correctement. Les pièces endommagées peuvent
contribuer à endommager davantage l'appareil et/ou
provoquer des blessures.
7. GARDER LA ZONE DE TRAVAIL PROPRE. Les zones et
établis encombrés sont souvent des causes d’accidents.
8. ÉLOIGNER LES ENFANTS ET LES VISITEURS. L'atelier
représente un environnement potentiellement dangereux.
Les enfants et les visiteurs peuvent être blessés.
9. RÉDUIRE LE RISQUE DE DÉMARRAGE ACCIDENTEL.
S’assurer que l’interrupteur se trouve sur la position d’arrêt
avant de brancher le cordon d’alimentation. En cas de
panne de courant, mettre l’interrupteur sur la position
d’arrêt. Un démarrage accidentel peut provoquer des
blessures.
10. UTILISATION DES DISPOSITIFS DE PROTECTION.
Vérifier que tous les dispositifs de protection sont en
place, fixés, et qu’ils fonctionnent correctement afin de
réduire tout risque de blessure.
11. RETIRER LES CLÉS ET LES CLÉS DE RÉGLAGE.
AVANT LE DÉMARRAGE DE L'APPAREIL. Des outils,
chutes, et autres débris peuvent être projetés à grande
vitesse, provoquant des blessures.
12. UTILISATION DE L’OUTIL APPROPRIÉ. Ne pas forcer un
appareil ou un accessoire pour accomplir un travail pour
lequel il n'est pas conçu. Cela pourrait endommager
l'appareil et/ou causer des blessures.
13. UTILISATION DES ACCESSOIRES RECOMMANDÉS.
L'utilisation d'accessoires non recommandés par Delta
pourrait endommager l'appareil ou blesser l'utilisateur.
14. UTILISER LA RALLONGE APPROPRIÉE. S'assurer que
la rallonge est en bon état. En utilisant une rallonge,
s'assurer d'utiliser une rallonge assez lourde pour le
transport du courant nécessaire au fonctionnement du
produit. Une rallonge sousdimensionnée provoquera une
chute de tension menant ainsi à une perte de courant et
une surchauffe. Se reporter au tableau des rallonges
électriques pour connaître le calibre approprié à utiliser
selon la longueur de la rallonge et l’intensité nominale de
la plaque signalétique. En cas de doute, utiliser le calibre
suivant le plus gros. Plus le numéro de calibre est petit,
plus la rallonge est lourde.
15. FIXER LA PIÈCE. Utiliser des pinces ou un étau pour
maintenir la pièce lorsque c’est possible. La perte de
contrôle d'une pièce peut provoquer des blessures.
16. ACHEMINER LA PIÈCE À CONTRE-COURANT DU
SENS DE ROTATION DE LA LAME, DE LA FRAISE, OU
DE LA SURFACE ABRASIVE. En l'acheminant à
contresens, la pièce sera projetée à grande vitesse.
17. NE PAS FORCER LA PIÈCE SUR L'APPAREIL.Cela
pourrait endommager l'appareil et/ou causer des
blessures.
18. NE PAS TROP TENDRE LES BRAS. Une perte
d’équilibre peut vous faire tomber sur une machine en
fonctionnement provoquant ainsi des blessures.
19. NE JAMAIS SE TENIR DEBOUT SUR L'APPAREIL. Si
l’outil bascule, ou si vous touchez accidentellement l’outil
de coupe, vous pouvez être blessé.
20. NE JAMAIS LAISSER LA MACHINE FONCTIONNER
SANS SURVEILLANCE. ÉTEINDRE L’APPAREIL. Ne
pas laisser l'appareil tant qu’il ne soit pas complètement
arrêté. Un enfant ou un visiteur pourrait être blessé.
21. ÉTEINDRE L'APPAREIL ET COUPER LE COURANT
avant d'installer ou de retirer des accessoires, avant tout
réglages ou modifications de celles-ci ou lors de
réparation. Un démarrage accidentel peut provoquer des
blessures.
22. METTRE L'ATELIER À L'ÉPREUVE DES ENFANTS
AVEC DES CADENAS, DES INTERRUPTEURS
PRINCIPAUX OU EN RETIRANT LES CLÉS DE
DÉMARRAGE. Le démarrage accidentel d'un appareil par
un enfant ou par un visiteur peut causer des blessures.
23. DEMEURER VIGILANT, SURVEILLER LE TRAVAIL
EFFECTUÉ, ET FAIRE PREUVE DE JUGEMENT. NE
PAS UTILISER L'APPAREIL EN CAS DE FATIGUE OU
SOUS L’INFLUENCE DE DROGUES, D'ALCOOL, OU
DE MÉDICAMENTS. Un moment d'inattention, en utilisant
des outils électriques, peut se solder par des blessures.
24. PRENDRE DES MESURES PRÉVENTIVES CONTRE
L’INHALATION DE POUSSIÈRES. La poussière produite
par certains bois et produits en bois peut nuire à votre
santé. Toujours utiliser l’équipement dans des endroits
bien aérés et veiller à le dépoussiérer correctement.
Utiliser des systèmes de dépoussiérage lorsque c’est
possible.
RÈGLES GÉNÉRALES DE SÉCURITÉ
NÉGLIGER DE SUIVRE CES RÈGLES RISQUE D’ENTRAÎNER DES BLESSURES GRAVES.
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 33

33
CONSERVER CES DIRECTIVES.
Les consulter souvent et les utiliser pour donner des directives aux autres.
1. NE PAS UTILISER CET OUTIL AVANT qu'il ne soit
assemblé et installé conformément aux instructions.
2. CONSULTER LE SUPERVISEUR, instructeur, ou autre
personne qualifiée si vous n'êtes pas familiarisé avec le
fonctionnement de cet outil.
3. SUIVRE TOUS LES CODES DE CÂBLAGE et les
connexions électriques recommandées.
4. UTILISER LES DISPOSITIFS DE PROTECTION
CHAQUE FOIS QUE POSSIBLE. Vérifier qu’ils sont
bien en place et fixés et fonctionnent correctement.
5. LE REBOND EST LA TENDANCE NATURELLE DE LA
PIÈCE DE REVENIR VERS L'OPÉRATEUR lorsque la
pièce entre en contact pour la première fois avec la lame
ou si la pièce pince la lame. L'effet de rebond est
dangereux et peut se solder par de graves blessures.
POUR ÉVITER L’EFFET DE REBOND :
A. maintenir la lame affûtée et libre de rouille et de résine.
B. garder le guide longitudinal parallèle à la lame de la scie.
C. utiliser le dispositif de protection de lame et dispositif
d'écartement pour toutes les opérations possibles, y
compris pour tous les débitages complets.
D. pousser la pièce au-delà de la lame de scie avant de
dégager.
E. ne jamais scier en long une pièce qui est tordue ou
voilée, ou qui n'a pas de bord droit pour glisser le long du
guide.
F. utiliser des planches en éventail lorsqu'on ne peut pas
utiliser les dispositifs anti-effet de rebond.
G. ne jamais scier une grande pièce qui ne peut pas être
contrôlée.
H. ne jamais utiliser le guide comme guide longitudinal pour
le tronçonnage.
I. ne jamais scier une pièce avec des n?uds détachés ou
autres défauts.
6. TOUJOURS UTILISER DES PARE-MAINS, UN
COUTEAU SÉPARATEUR ET DES DOIGTS ANTIEFFET DE REBOND si possible.
7. DÉGAGER LA TABLE DES PIÈCES COUPÉES ET
CHUTE avant de démarrer la scie. La vibration de
l'appareil pourrait les entraîner vers la lame de scie et les
projeter Après la coupe, éteindre la machine. Une fois la
lame complètement immobilisée, enlever tous les débris.
8. NE JAMAIS DÉMARRER L'APPAREIL avec la pièce
contre la lame.
9. NE JAMAIS acheminer la pièce entre le guide et la fraise
à moulurer.
10. LA COUPE DE PIÈCE SANS GUIDE OU DE JAUGE À
ONGLET EST CONNUE SOUS LE NOME DE COUPE
« À MAINS LIBRES ». NE JAMAIS effectuer d’opération
« à mains libres ». Utiliser soit le guide ou la jauge à
onglet pour positionner et guider le travail.
11. TENIR SOLIDEMENT LA PIÈCE contre la jauge à
onglet ou le guide.
12. LA COUPE D'UNE PIÈCE DE PART ET D'AUTRE
EST CONNUE COMME UN « DÉBITAGE COMPLET ».
Le sciage en long et le tronçonnage sont des opérations
de débitage complet. La coupe dans le sens du grain
(ou le long de la pièce) est un sciage en long. La coupe
à contrefil (ou en sens transversal) est un tronçonnage.
Utiliser un guide ou un système de guide pour le sciage
en long. NE PAS utiliser un guide ou un système de
guide pour le tronçonnage. Utiliser plutôt une jauge à
onglet. UTILISER UN (DES) POUSSOIR(S) pour scier
en long une pièce étroit.
13. ÉVITER LES OPÉRATIONS MALADROITES
ET ÉVITER DE PLACER LES MAINS À UN ENDROIT
où un glissement soudain pourrait amener la main sur
la lame.
14. GARDER LES BRAS, LES MAINS, ET LES DOIGTS
éloignés de la lame.
15. NE JAMAIS laisser de partie du corps dans le passage
de la lame de scie.
16. NE JAMAIS S'INCLINER AUTOUR ou au-dessus de la
lame de scie.
17. NE JAMAIS tenter de débloquer une lame coincée sans
éteindre l'appareil au préalable.
18. SOUTENIR CORRECTEMENT LES PIÈCES
LONGUES OU LARGES.
19. NE JAMAIS EFFECTUER D'OPÉRATIONS DE
TRAÇAGE, d'assemblage, ou de réglage sur la
table/l'espace de travail lorsque l'appareil est en
marche.
20. ÉTEINDRE L'APPAREIL ET COUPER LE COURANT
avant d'installer ou de retirer des accessoires, avant
tout réglages ou modifications de celles-ci ou lors de
réparation
21. ÉTEINDRE L'APPAREIL
ET couper le courant, et
nettoyer la table/l'espace de travail avant de quitter la
machine. VERROUILLER L'INTERRUPTEUR EN
POSITION « D’ARRÊT » pour éviter toute utilisation
non autorisée.
22. DES INFORMATIONS SUPPLÉMENTAIRES à propos
de l'utilisation sans danger et appropriée des outils
électriques (p. ex. une vidéo sur la sécurité) sont
disponibles auprès du Power Tool Institute, 1300
Sumner Avenue, Cleveland, OH É.-U. 441152851(www.powertoolinstitute.com). Des informations
sont également disponibles auprès du National Safety
Council, 1121Spring Lake Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201,
É.-U. Se reporter à la norme ANSI 01.01 de l'American
National Standards Institute concernant les machines
de travail du bois, ainsi que la réglementation OSHA
1910.213 du département américain du travail.
RÈGLES DE SÉCURITÉ SUPPLÉMENTAIRES POUR
LES SCIES DE TABLE
LIRE ATTENTIVEMENT TOUTES LES MISES EN GARDE ET DIRECTIVES D’UTILISATION
AVANT D’UTILISER CET ÉQUIPEMENT. À défaut de suivre les directives sous-mentionnées, un choc
électrique, un incendie, des dommages ou une blessure corporelle grave pourraient survenir.
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 34

34
Un circuit électrique séparé doit être utilisé pour l’appareil. Ce circuit doit utiliser un câble de calibre 12 au minimum et
doit être protégé par un fusible temporisé de 20 A. Si vous utilisez une rallonge, n’utiliser que des rallonges à 3 fils
pourvues d’une fiche de mise à la terre à 3 broches et une prise correspondant à la fiche de l’appareil. Avant de
brancher la machine sur le secteur, s’assurer que l’interrupteur est en position d’arrêt et veiller à ce que le courant
électrique ait bien les mêmes caractéristiques que celles indiquées sur la machine. Tous les branchements doivent
établir un bon contact. Si la machine fonctionne à basse tension, elle peut être endommagée.
RISQUE DE CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE. NE PAS EXPOSER L’APPAREIL À LA PLUIE NI L’UTILISER DANS
UN ENDROIT HUMIDE.
2. Pour les machines mises à la terre et branchées à un
cordon d’alimentation utilisées sur un circuit
d’alimentation de régime nominal inférieur à 150 V :
Si la machine est utilisée sur un circuit dont la prise de
courant ressemble à celle de la fig. A, la machine aura
alors une fiche de mise à la terre semblable à celle de la
fig. A. Un adaptateur temporaire, qui ressemble à celui
de la fig. B, peut être utilisé pour connecter cette fiche à
une prise à 2 conducteurs, comme le montre la fig. B, s’il
n’existe aucune prise de courant correctement mise à la
terre. L’adaptateur temporaire ne doit être utilisé que
jusqu’à ce qu’un électricien qualifié puisse installer une
prise électrique correctement mise à la terre. La patte
rigide verte, la cosse et tout élément semblable sortant
de l’adaptateur doivent être correctement branchés à
une masse permanente comme une boîte de sortie mise
à la terre. Chaque fois que l’adaptateur est utilisé, il doit
être maintenu en place par une vis métallique.
REMARQUE : au Canada, l’utilisation d’un adaptateur
temporaire n’est pas autorisée par le Code électrique
canadien.
DANS TOUS LES CAS, S’ASSURER
QUE LA PRISE DE COURANT EN QUESTION EST
CORRECTEMENT MISE À LA TERRE. EN CAS DE
DOUTE, DEMANDER À UN ÉLECTRICIEN
PROFESSIONNEL DE VÉRIFIER LA PRISE.
1. Pour tous les appareils mis à la terre, branchés à un
cordon d’alimentation :
En cas de défaillance ou de panne, la mise à la terre
permet un cheminement de moindre résistance pour le
courant électrique afin de réduire le risque de choc
électrique. Cette machine est munie d’un cordon
d’alimentation doté d’un conducteur de mise à la terre
d’équipement et d’une fiche de mise à la terre. La fiche
doit être branchée sur une prise de courant
correspondante qui est installée et mise à la terre
conformément à tous les codes et à toutes les
ordonnances à l’échelle locale.
Ne pas modifier la fiche fournie; si elle ne s’insère pas
dans la prise de courant, faire installer une prise
appropriée par un électricien professionnel.
Si le conducteur de mise à la terre d’équipement n’est
pas correctement connecté, ceci peut provoquer un
choc électrique. Le conducteur de mise à la terre
d’équipement est le conducteur avec isolation qui a une
surface extérieure verte avec ou sans rayures jaunes. S’il
est nécessaire de faire réparer ou remplacer le cordon
électrique ou la fiche, ne pas connecter le conducteur de
mise à la terre d’équipement à une borne sous tension.
Vérifier auprès d’un électricien ou d’un personnel de
réparation professionnels si les directives de mise à la
terre ne sont pas parfaitement comprises, ou en cas de
doute sur le fait que la machine soit correctement mise à
la terre ou non.
Utiliser uniquement une rallonge à 3 fils pourvue d’une
fiche de mise à la terre à 3 lames et une prise à 3
conducteurs correspondant à la fiche de la machine,
comme le montre la fig. A.
Réparer ou remplacer immédiatement le cordon s’il est
endommagé ou usé.
CONNEXIONS ÉLECTRIQUES
CARACTÉRISTIQUES TECHNIQUES DU MOTEUR
L’appareil est conçu pour être alimenté par un courant alternatif de 120 volts et 60 Hz. Avant de brancher l’appareil à
la source d’alimentation, s’assurer que l’interrupteur est en position d’arrêt.
DIRECTIVES DE MISE À LA TERRE
RISQUE DE CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE. CET APPAREIL DOIT ÊTRE MIS À LA TERRE LORS DE SON
UTILISATION AFIN DE PROTÉGER L’UTILISATEUR CONTRE TOUT CHOC ÉLECTRIQUE.
Fig. A
Fig. B
PRISE ÉLECTRIQUE MISE
À LA TERRE
LAMES
CONDUCTRICES
LA LAME DE MISE A LA TERRE EST LA PLUS
LONGUE DES TROIS LAMES
PRISE ÉLECTRIQUE MISE À LA
TERRE
MOYEN DE MISE À
LA TERRE
ADAPTATEUR
Page 35

35
RALLONGES
Utiliser les rallonges appropriées S’assurer que la rallonge est en bon état et qu’il s’agit d’une rallonge à
3 fils avec une fiche de mise à la terre à 3 broches et prise de courant compatible avec la fiche de l’appareil. Lorsque
qu’une rallonge est utilisée, s’assurer d’en utiliser une de calibre suffisamment élevé pour assurer le transport du
courant de l’appareil. Une rallonge sousdimensionnée provoquera une chute de tension menant ainsi à une perte de
puissance et une surchauffe. Fig. C montre le calibre correct à utiliser selon la longueur de la rallonge. En cas de doute,
utiliser le calibre suivant le plus gros. Plus le numéro de calibre est petit, plus le cordon est lourd.
Fig. C
ATTENTION
RALLONGE DE CALIBRE MINIMUM
CALIBRES RECOMMANDÉS POUR UNE UTILISATION AVEC DES MACHINES
ÉLECTRIQUES D’ÉTABLI
Intensité Longueur totale Calibre de
nominale Volts du cordon en pieds la rallonge
0-6 120
jusqu’à
25 18 AWG
0-6 120 25-50 16 AWG
0-6 120 50-100 16 AWG
0-6 120 100-150 14 AWG
6-10 120
jusqu’à
25 18 AWG
6-10 120 25-50 16 AWG
6-10 120 50-100 14 AWG
6-10 120 100-150 12 AWG
10-12 120
jusqu’à
25 16 AWG
10-12 120 25-50 16 AWG
10-12 120 50-100 14 AWG
10-12 120 100-150 12 AWG
12-16 120
jusqu’à
25 14 AWG
12-16 120 25-50 12 AWG
12-16 120
SUPÉRIEURE À 50 PIEDS
NON RECOMMANDÉE
AVANT-PROPOS
Le modèle FS210LS de Delta dispose d’une scie haute capacité à un prix abordable. Il également comporte une table
extra-large en aluminium de 52 x 104 cm (17 x 34 po) avec rallonges et est doté d’un moteur de 15 ampères de type
industriel avec arbre de renvoi flottant : le plus puissant de sa catégorie. La scie de table est conçue pour vous offrir une
performance de haute qualité avec une profondeur de coupe jusqu’à 76 mm (3 po) à 90°, et 63,5 mm (2,5 po) à 45°,
pour une coupe nette des pièces de dimension standard. L’ensemble comprend la scie, un socle en métal, un guide
longitudinal, un guide d’onglet, un protège-lame transparent avec couteau séparateur et doigts antirecul, des rallonges
de table, une lame de scie de 254 mm (10 po), un insert de table et des clés pour la lame.
DESCRIPTION FONCTIONNELLE
Page 36

36
Fig. 1
PIÈCES DE LA SCIE DE TABLE
9
2
3
4
5
1– Scie
2– Rallonge gauche
3– (3) vis à tête hexagonale de
6,4 mm - 20 x 25,4 mm (1/4 po
- 20 x 1 po) pour la rallonge
gauche
4– (6) rondelles plates de 6,4
mm (1/4 po) pour la rallonge
gauche
5– (3) rondelles de blocage de
6,4 mm (1/4 po) pour la rallonge
gauche
6– (3) écrous hexagonaux de
6,4 mm (1/4 po) - 20 pour la
rallonge gauche
7– Rallonge droite
8– (3) vis à tête hexagonale de
6,4 mm - 20 x 15,8 mm (1/4 po
- 20 x 5/8 po) pour la rallonge
droite
9– (3) rondelles plates de
6,4 mm (1/4 po) pour la rallonge
droite
10– (3) rondelles de blocage de
6,4 mm (1/4 po) pour la rallonge
droite
ASSEMBLAGE
DÉSEMBALLAGE ET NETTOYAGE
Désemballer soigneusement la machine et toutes les pièces de ou des emballages d’expédition. Retirer le revêtement
protecteur de toutes les surfaces non peintes. Le revêtement peut être retiré avec un chiffon doux humidifié avec du
kérosène (ne pas utiliser d’acétone, d’essence ou de diluant à laque). Après le nettoyage, couvrir les surfaces non
peintes d’une cire à parquets d’usage domestique de bonne qualité.
AVIS : LA PHOTO DE LA COUVERTURE DU MODE D’EMPLOI ILLUSTRE LE
MODÈLE DE PRODUCTION ACTUEL. LES AUTRES ILLUSTRATIONS DE CE
MODE D’EMPLOI NE SONT PRÉSENTES QU’À TITRE INDICATIF ET IL EST
POSSIBLE QUE LA COULEUR, LES ÉTIQUETTES, OU LES ACCESSOIRES,
QUI ONT UNIQUEMENT POUR BUT D’ILLUSTRER LA TECHNIQUE,
DIFFÈRENT DES CARACTÉRISTIQUES RÉELLES DE CE MODÈLE.
6
OUTILS NÉCESSAIRES POUR L’ASSEMBLAGE
DURÉE ESTIMÉE POUR L’ASSEMBLAGE
1). Clé ajustable
2.) Clé de 13 mm pour les boulons du socle.
3.) Clé de 10 mm pour les boulons de l’ensemble du couteau séparateur, l’ensemble des traverses arrières et de
l’ensemble des rallonges de table.
4.) Tournevis à fente.
6.) Tournevis cruciforme.
5.) Règle droite et/ou équerre de charpente pour les réglages.
2 heures
7
8
10
1
Page 37

37
Fig. 2
PIÈCE DU GUIDE LONGITUDINAL
(11,12)
11– Guide longitudinal
12– Poignée de verrouillage du guide longitudinal
PIÈCES DU VOLANT DE RELÈVEMENT DE LA LAME
(13,14,15,16,17)
13– Volant d’abaissement et de relèvement de la lame
14– Poignée du volant d’abaissement et de relèvement
de la lame
15– Vis pour l’assemblage de la poignée du volant
16– Capuchon pour poignée
17– Vis à tête plate M6X1X12 m pour l’assemblage du
Volant d’abaissement et de relèvement de la lame
18– Guide d’onglet
PIÈCES DU POR
TE-GUIDE D’ONGLET
(19,20,21,22,23,24,25)
19– (4) vis d’assemblage à tête cylindrique à dépouille
M4,2X10 mm pour l’assemblage du porte-guide
d’onglet
20– (4) rondelles de blocage pour l’assemblage du
porte-guide d’onglet
21– Porte-guide d’onglet
Attache à ressort du porte-guide d’onglet
23– Vis à tête cylindrique à dépouille M4X0,7X10 mm
pour le porte-guide d’onglet
24– Rondelle à denture extérieure de 4,8 mm (3/16 po)
pour le porte-guide d’onglet
25– Écrou hexagonal M4X0,7 mm pour le porte-guide
d’onglet
PIÈCES DU SUPPOR
T DU COUTEAU SÉPARATEUR
(26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37)
26– Vis à tête hexagonale longue de 6,4 mm - 20 x 57,2
mm (1/4 po - 20 x 2 1/4 po) pour l’assemblage du
support du couteau séparateur
27– Rondelle à denture intérieure de 6,4 mm (1/4 po)
pour l’assemblage du support du couteau séparateur
28– Rondelle plate de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) pour
l’assemblage du support du couteau séparateur
29– Rondelle à denture extérieure de 6,4 mm (1/4 po)
pour l’assemblage du support du couteau séparateur
30– Support du couteau séparateur
31– (2) rondelles à denture extérieure de 6,4 mm (1/4
po) pour le support du couteau séparateur
32– Support du couteau séparateur
33– (2) vis à tête hexagonale de 6,4 mm - 20 x 12,7 mm
(1/4 po - 20 x 1/2 po)
34– Écrou papillon pour l’assemblage du support du
couteau séparateur
35– (2) rondelles à denture extérieure de 6,4 mm (1/4
po) pour le support du couteau séparateur
36– (2) rondelles plates de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) pour
l’assemblage du support du couteau séparateur
37– Vis à tête hexagonale M6X1X20 mm pour
l’assemblage du support du couteau séparateur
38– Ensemble du couteau séparateur et protège-lame
39– Barre de guidage gauche du guide
40– Barre de guidage droite du guide
PIÈCES DES BARRES DE GUIDAGE DU GUIDE
(41,42,43,44,45)
41– (14) rondelles de blocage M6 pour l’assemblage de
la barre de guidage du guide longitudinal
42– (5) rondelles plates de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) pour
l’assemblage de la barre de guidage du guide longitudinal
43– (5) écrous hexagonaux de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) - 20
pour l’assemblage de la barre de guidage du guide
longitudinal
44– (9) cales pour l’assemblage du guide longitudinal
45– (9) vis à tête ronde de 6,4 mm - 20 x 31,2 mm (1/4
po - 20 x 1 1/4 po) pour l’assemblage de la barre de
guidage du guide longitudinal
PIÈCES DE L
’APPUI ARRIÈRE
(46,47,48,49,50,51,52)
46– (2) tiges pour la traverse arrière
47– Traverse arrière
48– (8) vis à tête hexagonale M6X1X15 mm cruciforme
pour les traverses
49– (8) rondelles de blocage M6 pour l’assemblage des
traverses
50– (4) vis à tête hexagonale de 6,4 mm - 20 x 12,7 mm
(1/4 po - 20 x 1/2 po) pour les tiges
51– (4) traverses
52– (4) rondelles plates pour
53– Clés pour les changements de lame
Page 38

38
Fig. 3
PIÈCES DU SOCLE
53– (4) pattes
54– (2) traverses supérieures latérales
55– Traverse supérieure avant
56– Traverse supérieure arrière
57– (2) traverses inférieures latérales
58– (2) traverses inférieures avant
59– (4) pieds
POUR VOTRE PROPRE SÉCURITÉ, NE PAS BRANCHER L’APPAREIL À UNE SOURCE
D’ALIMENTATION JUSQU’À CE QU’IL SOIT ENTIÈREMENT ASSEMBLÉ. Ne pas utiliser le présent appareil avant
d’avoir lu et compris le mode d’emploi dans son intégralité.
53
54
55
56
57
58
60
61
62
63
59
64
65
60– (2) vis à tête hexagonale M8X1,25X45 mm
pour patte et base
61– (2) vis à tête hexagonale M8X1,25X30 mm
pour patte et base
62– (16) écrous hexagonaux à embase de 7,9 mm
(5/16 po)
63– (16) boulons de carrosserie de 7,9 mm (5/16
po)
64– (4) écrous hexagonaux M8
65– (8) rondelles plates M8
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 39

39
PORTE-GUIDE D’ONGLET
DÉBRANCHER L’APPAREIL DE LA SOURCE D’ALIMENTATION.
1. Assembler l’attache à ressort (E) fig. 4, au porte-guide d’onglet (A) comme indiqué avec une vis cylindrique à
dépouille (F) M4x0,7x10 mm, un contre-écrou 4,8 mm (3/16 po) et un écrou hexagonal M4x0,7. NOTE : l’écrou
hexagonale (G) fig. 5, s’ajustera dans le retrait à l’arrière du porte-guide d’onglet (A) pour fixer solidement l’attache à
ressort (E) fig. 4, au porte-guide d’onglet.
2. Assembler le porte-guide d’onglet (A) fig. 6, au côté gauche de l’armoire de la scie à l’aide de vis à tête cylindrique
à dépouille (B) fig. 7 et de rondelles (C) de 4,8 mm (3/16 po) à partir de l’intérieur de l’armoire.
3. Fig. 8 illustre le guide d’onglet (D) inséré dans le porte-guide d’onglet lorsque inutilisé.
AVERTISSEMENT
ASSEMBLAGE DU SOCLE
1. Les pattes du socle comportent des saillies qui s’aligneront avec les trous dans les traverses supérieures et
inférieures. Assembler le socle comme l’illustre la fig. 9A, à l’aide de 16 boulons de carrosserie et écrous hexagonaux
à embase. Ne pas serrer complètement la boulonnerie pour le moment.
A– Traverse supérieure avant (avec le logo)
B– Traverse supérieure arrière
C– Traverses inférieures latérales
D– Traverses inférieures avant et arrière
E– Traverses supérieures latérales
F– Pied
IMPORTANT : les traverses supérieures, avant et arrière (A et B) fig. 9A, sont plus longues que les traverses
supérieures latérales (E) fig. 9A. Les traverses inférieures avant et arrière (D) fig. 9A, sont plus longues que les
traverses inférieures latérales (C).
2. Assembler les pieds en caoutchouc (F) fig. 9A. REMARQUE : chaque pied de caoutchouc est doté de trous pour
fixer le socle au plancher si nécessaire..
RACCORD DU SAC À POUSSIÈRE
1. Fixer le sac à poussière à sa structure puis insérer celle-ci dans le socle de la scie comme indiqué à la fig. 9B. Se
reporter à la rubrique ci-dessous pour fixer l’ensemble du sac à la scie.
FIXATION DE LA SCIE SUR LE SOCLE
1. Tourner la table de la scie face en bas sur un morceau de carton pour protéger la surface de la table. Placer le socle
tête en bas sur la scie et aligner les quatre trous du socle avec les trous de montage de la scie.
2. Utiliser les deux plus longues vis pour l’avant, enfiler une rondelle plate M8 sur la vis à tête hexagonale M8x1,25x45
mm. Insérer la vis à tête hexagonale dans le trou de montage de la scie et dans le trou de montage du socle. Placer
une autre rondelle plate M8 sur la vis à tête hexagonale et enfiler un écrou hexagonal M8x1,25 sur la vis puis visser
sans serrer trop fort. Répéter l’assemblage pour l’autre trou de l’avant de la scie.
Utiliser les deux vis les plus courtes pour l’arrière, enfiler une rondelle plate M8 sur une vis à tête hexagonale
M8X1,25X30 mm à l’arrière de la scie. Insérer la vis à tête hexagonale dans le trou de montage de la scie et dans le
trou de montage du socle. Placer une autre rondelle plate M8 sur la vis à tête hexagonale et enfiler un écrou hexagonal
M8x1,25 sur la vis puis visser sans serrer trop fort. Répéter l’assemblage pour l’autre trou à l’arrière de la scie.
3. Puis remettre la scie de table sur ses pieds comme illustrée à la fig. 9C (la scie est illustrée ici entièrement
assemblée).
4. Pousser sur le dessus de la scie pour que les pattes du socle s’ajustent à la surface du plancher puis serrer toute
la boulonnerie du socle et la boulonnerie de fixation de la scie au socle.
ASSEMBLAGE DE LA LAME
VOLANT d’abaissement et de
RELÈVEMENT
1. Insérer la vis spéciale (C) dans la poignée (B) fig. 10 puis visser la vis en sens horaire pour assembler la poignée sur
le volant (A). Puis enfoncer le capuchon de la poignée (D).
Page 40

40
2. La fig. 11 illustre la poignée (B) assemblée sur le volant (A).
3. Assembler le volant (A) fig. 12, sur l’arbre (B) tout en s’assurant que le méplat de l’intérieur du volant s’aligne avec
le méplat de l’arbre.
4. Fixer le volant (A) fig. 13, à l’arbre (B) fig. 12, avec une vis à tête plate M6x1x12 mm (C) fig. 13.
ENSEMBLE DE PROTÈGE-LAME
ET COUTEAU SÉPARATEUR
DÉBRANCHER L’APPAREIL DE LA SOURCE D’ALIMENTATION.
1. IMPORTANT : POUR EMPCHER TOUT REBOND OU RECUL, L’ENSEMBLE DU PROTÈGE-LAME ET
COUTEAU SÉPARATEUR DOIT ÊTRE CORRECTEMENT ALIGNÉ AVEC LA LAME DE LA SCIE.
2. Positionner la lame à angle droit (90°) par rapport à la table puis la verrouiller en place. Consulter la page 42 «
Commande d’abaissement et de relèvement de la lame » et la page 42 « Commande d’inclinaison de la lame ».
3. Fixer le support du couteau séparateur (A) fig. 14, au support du couteau (B) à l’aide de deux vis à tête hexagonale
6,4 mm - 20 x 12,7 mm (1/4 po - 20 x 1/2 po) (C) et deux rondelles à denture extérieure de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) comme
illustré. REMARQUE : ne pas serrer complètement les vis (C) à ce moment.
4. Localiser la vis à tête hexagonale 6,4 mm - 20 x 57,2 mm (1/4 po - 20 x 2 1/4 po) (G) fig. 15, et enfiler une rondelle
à denture intérieure (O) de 6,4 mm (1/4 po), une rondelle plate (P) de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) et une rondelle à denture
extérieure (R) de 6,4 mm (1/4 po)sur la vis (G).
5. Positionner l’extrémité en retrait (E) fig. 16, du support du couteau séparateur (B) contre l’extrémité de la tige pivot
(F) puis la fixer en utilisant l’assemblage de l’ÉTAPE 4 ci-dessus. REMARQUE : ne pas serrer complètement la vis
(G) à ce moment. Ensemble illustré à la fig. 17.
6. Positionner le couteau séparateur (H) fig. 18, sur le support comme indiqué tout en s’assurant que les deux saillies
(K) du support sont à l’intérieur de la rainure du couteau séparateur (H).
7. Assembler le couteau séparateur (H) fig. 19, au support (B) comme indiqué à l’aide d’une vis à tête hexagonale
M6x1x20 mm (L), d’une rondelle à denture extérieure de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) et une rondelle plate de 6,4 mm (1/4 po).
8. Fixer le couteau séparateur (H) fig. 20, au support avec une rondelle plate de 6,4 mm (1/4 po), une rondelle à denture
extérieure de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) et un écrou papillon M6 (M). REMARQUE : Avant de serrer l’écrou papillon (M), s’assurer
d’avoir un jeu d’au moins 3,2 mm (1/8 po) entre le bord inférieur du couteau séparateur (N) et la surface supérieure de
la table (P) et que les saillies de type « goujons » (K) 15, soient à l’intérieur de la rainure de l’assemblage du couteau
séparateur (H).
9. Utiliser une règle droite pour voir si le couteau séparateur (H) Fig. 21, est aligné avec la lame de la scie (R). Si un
réglage est nécessaire, il est possible de déplacer et de tourner le couteau séparateur (H) vers la droite ou la gauche.
10. Lorsque le couteau séparateur est correctement aligné avec la lame de la scie, serrer les deux vis (C) fig. 22, qui
fixent le support du couteau séparateur et serrer la vis (G) qui fixe le support du couteau séparateur à la tige pivot.
RALLONGES
1. Assembler la rallonge gauche (fig. 23) à la table de la scie avec trois vis à tête hexagonale 6,4 mm - 20 x 25,4 mm
(1/4 po - 20 x 1 po), six rondelles plates de 6,4 mm (1/4 po), trois contre-écrous et trois écrous hexagonaux.
2. Assembler la rallonge droite aux trous filetés de la scie à l’aide de trois vis à tête hexagonale 6,4 mm - 20 x 15,8
mm (1/4 po - 20 x 5/8 po), trois rondelles plates de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) et trois contre-écrous de 6,4 mm (1/4 po).
3. À l’aide d’une règle droite, s’assurer que les bords supérieurs, avant et arrière des rallonges sont à niveau avec la
table de la scie avant de serrer les trois vis qui fixe solidement les rallonges à la table.
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 41

41
ASSEMBLAGE DE LA BARRE DE GUIDAGE À LA SCIE DE TABLE
1.Tenir la barre de guidage avec les grands trous face à vous. Serrer lâchement les barres de guidage (A) fig. 24, au
quatre trous filetés (B) de la table de la scie (C) avec deux longues vis (D) de 6,4 m - 20 x 31,2 mm (1/4 po - 20 x 1 1/4
po) (D), des contre-écrous (E) et des cales (F).
IMPORTANT : les cales (F) fig. 24, sont insérées entre les barres de guidage (A) et la table de la scie (C).
2. Fixer les barres de guidage (A) fig. 24, aux rallonges (G) par les trous (K) avec la longue vis (D) de 6,4 mm - 20 x 31,2
mm (1/4 po - 20 x 1 1/4 po), on contre-écrou (E) de 6,4 mm (1/4 po), une cale (F), une rondelle plate (H) de 6,4 mm (1/4
po), un contre-écrou (E) de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) et un écrou hexagonal (J) de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) - 20 puis serrer toute la
visserie d’assemblage de la barre de guidage.
IMPORTANT : la cale (F) fig. 24, est insérée entre les barres de guidage (A) et les rallonges (G).
3. La fig. 25 illustre les barres de guidage correctement assemblées à la table de la scie et aux rallonges.
GUIDE LONGITUDINAL
1. Enrosque la M8x1.25 tuerca de cierre (A) Fig. 26 aproximadamente a la mitad del camino sobre el gorrón de la
agarradera (B).
2. Enrosque la tuerca de cierre (B) Fig. 26 dentro del agujero roscado (C) en la leva de la guía (D). Apriete la tuerca de
cierre (A) Fig. 26 contra la leva (D).
3. Le guide longitudinal est généralement utilisé sur le côté droit de la table de la scie. Soulever la poignée (B) et
positionner le guide sur la table. Abaisser la poignée (B) pour verrouiller le guide en place sur la table de la scie.Fig. 27
GUIDE D’ONGLET
Le guide d’onglet est expédié entièrement assemblé et est doté d’une barre à rainurer en T (A) fig. 28, qui s’insère dans
l’une ou l’autre des deux rainures, pour le rainurage en T, logées sur le dessus de la table comme indiqué. Le guide
d’onglet pour rainurage en T empêche celui-ci de tomber lorsqu’il dépasse l’avant de la table lors de coupe de pièces
extra-large.
APPUI ARRIÈRE
1. Fixer LÉGÈREMENT les deux supports (A) fig. 29, au côté gauche inférieur de la table de la scie comme indiqué,
avec deux vis à tête hexagonale cruciformes M6x1x15 mm (B) et des contre-écrous M6,1 (C). Assembler les deux
autres traverses du côté inférieur droit de la lame de la scie de la même manière.
2. Insérer la tige (D) fig. 30, dans les trous des supports (A) comme indiqué. Puis visser et serrer la vis à tête hexagonale
(E) 6,4 mm - 20 x 12,7 mm (1/4 po - 20 x 1/2 po) et enfiler une rondelle plate (F) de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) sur l’extrémité
avant de la tige (D) comme indiqué en (G). Assembler l’autre tige sur le côté opposé de la scie de la même manière.
3. Insérer les tiges (D) fig. 31, dans les grands trous (H) de l’appui arrière (J) comme illustré.
4. Fixer solidement l’appui arrière (J) fig. 32, aux tiges (D) avec deux vis à tête hexagonale 6,4 mm - 20 x 12,7 mm (1/4
po - 20 x 1/2 po) et rondelles plates de 6,4 mm (1/4 po) (K) comme indiqué.
5. Pousser sur tout l’ensemble de l’appui arrière (J) fig. 33, jusqu’à ce qu’il touche l’ensemble protège-lame et couteau
séparateur (L) comme indiqué. Puis serrer toute la quincaillerie de fixation de l’appui arrière.
6. Enfiler une rondelle sur la vis à tête hexagonale de 6,4 mm - 20 x 12,7 mm (1/4 po - 20 x 1/2 po) et visser l’autre
extrémité des tiges pour les empêcher de sortir des supports de l’appui arrière.
DÉMARRAGE ET ARRÊT DE LA SCIE
L’interrupteur marche/arrêt (A) fig. 34 est logé à l’avant de l’armoire de la scie. Pour mettre la scie sous tension,
déplacer l’interrupteur (A) vers le haut en position de marche. Pour l’éteindre, déplacer l’interrupteur (A) vers le bas à
la position d’arrêt.
UTILISATION DES COMMANDES ET RÉGLAGES
Page 42

42
S’ASSURER QUE L’INTERRUPTEUR SE TROUVE SUR LA POSITION D’ARRÊT AVANT DE
BRANCHER LE CORDON D’ALIMENTATION. EN CAS DE PANNE DE COURANT, METTRE
L’INTERRUPTEUR SUR LA POSITION D’ARRÊT. UN DÉMARRAGE ACCIDENTEL PEUT
PROVOQUER DES BLESSURES.
VERROUILLER L’INTERRUPTEUR EN POSITION D’ARRÊT
IMPORTANT : lorsque l’outil est inutilisé, l’interrupteur doit être verrouillé en position d’arrêt afin d’empêcher
toute utilisation non autorisée. Pour ce faire, saisir la bascule de l’interrupteur (B) et la retirer de l’interrupteur (fig.
35). Une fois la bascule (B) de l’interrupteur retirée, l’interrupteur ne fonctionnera pas. Cependant, si la bascule de
l’interrupteur est retirée tandis que la scie est en marche, il sera possible d’éteindre l’outil et non de le redémarrer
sans réinsérer la bascule de l’interrupteur (B).
COMMANDE D’ABAISSEMENT ET DE RELÈVEMENT DE LA LAME
Pour abaisser ou relever la lame de la scie, tourner le volant (A) fig. 36. Le tourner en sens horaire abaisse la lame et
le tourner dans le sens antihoraire la relève.
LA POIGNÉE DE BLOCAGE D’INCLINAISON DE LA LAME (B) FIG. 36, DOIT ÊTRE
VERROUILLÉE PENDANT TOUTES LES OPÉRATIONS DE COUPE.
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
COMMANDE D’INCLINAISON DE LA LAME
Pour incliner la lame de la scie, desserrer la poignée de blocage (A) Fig. 37, tourner le volant (B) jusqu’à ce que la lame
soit à l’angle souhaité puis resserrer la poignée de blocage (A). REMARQUE : la poignée de blocage (A) est à ressort
et se déplace en retirant la poignée (A) et en la repositionnant sur le goujon à crans d’arrêt situé directement sous la
poignée.
LA POIGNÉE DE BLOCAGE D’INCLINAISON DE LA LAME (A) DOIT ÊTRE VERROUILLÉE
PENDANT TOUTES LES OPERATIONS DE COUPE.
RÉGLAGES DES BUTÉES POSITIVES À 90 ET 45 DEGRÉS
La scie est dotée de butées fixes pour un positionnement rapide et précis de la lame de la scie à 90 et 45 degrés par
rapport à la table. Pour ajuster les butées fixes, procéder comme suit :
DÉBRANCHER L’APPAREIL DE LA SOURCE D’ALIMENTATION.
1. Lever la lame de la scie à sa hauteur maximum.
RÉGLAGE D’UNE BUTÉE FIXE À 90 DEGRÉS
2. Desserrer la poignée de blocage de l’inclinaison de la lame, déplacer le mécanisme d’inclinaison de la lame le plus
à gauche possible, et serrer la poignée de blocage de l’inclinaison de la lame.
3. Placer une équerre (A) fig. 38, sur la table avec une de ses extrémités
contre la lame comme illustré et vérifier que la lame est perpendiculaire par rapport à la table. Si ce n’est pas le cas,
desserrer la vis (B) de quelques tours, puis déplacer le mécanisme d’inclinaison de la lame jusqu’à ce que la lame soit
à 90° par rapport à la table. Puis serrer la poignée de blocage de l’inclinaison de la lame et serrer la vis (B) jusqu’à ce
qu’elle vienne en butée.
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 43

43
RÉGLAGE D’UNE BUTÉE FIXE À 45 DEGRÉS
4. Desserrer la poignée de blocage de l’inclinaison de la lame, déplacer le mécanisme d’inclinaison de la lame le plus
à droite possible, et serrer la poignée de blocage de l’inclinaison de la lame.
5. Placer une équerre (A) fig. 39, sur la table, une de ses extrémités contre la lame comme illustré et vérifier que la lame
est à 45° par rapport à la table. Si ce n’est pas le cas, desserrer la vis (C) de quelques tours, puis déplacer le
mécanisme d’inclinaison de la lame jusqu’à ce que la lame soit à 45° par rapport à la table. Puis serrer la poignée de
blocage de l’inclinaison de la lame et serrer la vis (C) jusqu’à ce qu’elle vienne en butée.
UTILISATION ET RÉGLAGE DU GUIDE LONGITUDINAL
1. Pour déplacer le guide longitudinal (A) fig. 40, le long de la table, relever le levier de blocage du guide (B), glisser le
guide sur la table à l’endroit souhaité, puis abaisser le levier de blocage du guide (B) pour le bloquer dans cette
position.
2. Un pointeur est fourni pour indiquer la distance entre le guide et la lame de la scie. Si le pointeur nécessite un
réglage, desserrer la vis (C) fig. 40, qui fixe le pointeur au support du guide et le régler selon le besoin. Puis resserrer
la vis (C).
3. IMPORTANT : LE GUIDE LONGITUDINAL DOIT ÊTRE CORRECTEMENT ALIGNÉ AVEC LA RAINURE DU
GUIDE D’ONGLET POUR ÉVITER L’EFFET DE REBOND EN SCIANT EN LONG.
4. La lame de scie est installée parallèlement à la rainure du guide d’onglet en usine. Le guide doit être parallèle à la
rainure du guide d’onglet afin d’assurer une précision de travail et d’éviter l’effet de rebond lors d’une opération de
sciage en long. Pour vérifier l’alignement :
5. Positionner le guide à l’une des extrémités de la rainure du guide d’onglet. Fixer le guide à la table en abaissant le
levier de blocage. Le bord du guide devrait alors être parallèle à la rainure du guide d’onglet.
6. Si un réglage s’avère nécessaire, procéder comme suit :
7. Desserrez les deux vis à tête à six pans creux de 47 mm (3/16 po) (D) fig. 40, et relevez le levier de blocage (B). Puis
tenir le support du guide bien fermement vers l’avant de la scie et déplacer l’arrière du guide (A) jusqu’à ce qu’il soit
parallèle à la rainure du guide d’onglet. Puis serrer deux vis (D) puis abaisser le levier de blocage (B).
8. Régler le serrage du guide (A) fig. 40, en relevant le levier de blocage (B) et en tournant la vis (E) en sens horaire
pour augmenter ou dans le sens antihoraire pour réduire le serrage du guide.
UTILISATION ET RÉGLAGES DU GUIDE D’ONGLET
Pour tronçonner droit (la lame est à 90° par rapport à la table), le guide d’onglet peut être utilisé dans l’une des deux
rainures de la table. Pour tronçonner en biseau (lame inclinée), utiliser le guide d’onglet dans la rainure droite de la table
uniquement, de sorte que la lame soit inclinée loin du guide d’onglet et de vos mains.
Le guide d’onglet est muni de butées réglables individuellement à 90 et 45 degrés à droite et à gauche. Desserrer les
contre-écrous pour régler les butées (B) fig. 41, et serrer ou desserrer les trois vis de réglage (C) jusqu’à ce qu’elles
touchent l’autre extrémité du goujon d’arrêt (D) lorsque le guide d’onglet est à 90 et 45 degrés par rapport à la lame
de la scie. Puis serrer les contre-écrous (B).
Pour utiliser le guide d’onglet, desserrer simplement le bouton de verrouillage (E) fig. 41, et pivoter le corps du guide
d’onglet à l’angle souhaité. Lorsque le goujon d’arrêt (D) est enfoncé, le corps du guide d’onglet s’arrêtera à 90 et 45
degrés à droite et à gauche. Pour pivoter le corps du guide d’onglet au-delà de ces limites, retirer le goujon d’arrêt (D).
RÉGLAGE DE LA LAME EN PARALLÈLE AUX RAINURES DU GUIDE
D’ONGLET
À l’usine, la lame a été réglée parallèlement aux rainures du guide d’onglet. Pour garantir une précision de coupe et
éviter l’effet de rebond, revérifier ce réglage et réajuster au besoin comme suit :
Page 44

44
1. DÉBRANCHER L’APPAREIL DE LA SOURCE D’ALIMENTATION.
2. Relever la lame au maximum et la régler de sorte qu’elle se trouve à 90° par rapport à la table.
3. Sélectionner une dent de la lame qui se trouve sur la gauche. Marquer cette dent à l’aide d’un crayon ou d’un
marqueur.
4. À l’aide d’une équerre combinée, positionner le corps (A) Fig. 42, de l’équerre contre la rainure du guide d’onglet
et ajuster la lame (B) de l’équerre jusqu’à ce qu’elle touche la dent marquée comme indiquée.
5. Tourner la lame et vérifier la même dent de lame marquée à l’arrière de la table de scie de la même manière comme
indiqué à la fig. 43.
6. Si les mesures (fig. 42 et 43) ne sont pas identiques à l’avant et à l’arrière, il est possible d’ajuster la lame.
Commencer en desserrant les écrous sous les quatre vis (C) fig. 44, sur la table. Puis desserrer les vis (C). Déplacer
soigneusement la lame de la scie jusqu’à ce qu’elle soit parallèle à la rainure du guide d’onglet. Puis serrer fermement
quatre écrous sous la table ainsi que les quatre vis (C) fig. 44.
REMARQUE : s’il n’est pas possible d’effectuer un réglage suffisant en desserrant les vis (C), les vis (D) peuvent
également se desserrer pour effectuer le réglage si absolument nécessaire.
REMARQUE : le dispositif de protection a été retiré uniquement pour illustrer le procédé.
CHANGEMENT DE LA LAME
DÉBRANCHER L’APPAREIL DE LA SOURCE D’ALIMENTATION. UTILISER UNIQUEMENT DES
LAMES DE SCIE DE 254 MM (10 PO) PRÉVUES POUR 5 000 TR/MIN OU PLUS AVEC UN ALÉSAGE
DE 15,8 MM (5/8 PO).
1. Relever la lame de la scie au maximum puis retirer l’insert de table (A) fig. 45.
2. À l’aide de la clé à fourche (B) fig. 45, positionner l’extrémité ouverte de la clé sur les méplats de la bride interne
de la lame pour empêcher la rotation de l’arbre de la scie puis retirer l’écrou de l’arbre (C) avec la clé (D). Tourner
l’écrou (C) en sens antihoraire pour le retirer. Retirer la bride externe de la lame (E) et la lame de la
scie (F).
3. Assembler la nouvelle lame, s’assurer que les dents pointent vers le bas à l’avant de la table de la scie et assembler
la bride externe de la lame (E) fig. 45, et l’écrou d’arbre (C). Serrer l’écrou (C) avec la clé (D) en tournant l’écrou en sens
horaire tout en maintenant l’arbre fixe avec l’autre clé (B).
4. Replacer l’insert de la table.
Les opérations courantes de sciage comprennent le sciage en long et le tronçonnage, ainsi que quelques autres
opérations standard de nature fondamentale. Comme pour tout appareil électrique, le fonctionnement et l’utilisation de
l’appareil comporte un certain nombre de risques. En utilisant l’appareil avec toute la prudence requise en ce qui
concerne les mesures de sécurité, le risque de blessures corporelles en sera considérablement réduit. Au contraire, si
les mesures de sécurité normales ne sont pas respectées ou complètement ignorées, l’opérateur de l’outil peut être
blessé. Les informations suivantes décrivent la méthode sûre et correcte à suivre pour exécuter les opérations de sciage
les plus courantes.
L’UTILISATION D’ACCESSOIRES NON RECOMMANDÉS POURRAIT SE SOLDER PAR UN
RISQUE DE BLESSURES POUR L’UTILISATEUR OU POUR D’AUTRES.
TRONÇONNAGE
Le tronçonnage nécessite l’utilisation du guide d’onglet pour positionner et guider l’ouvrage. Placer la pièce contre le
guide d’onglet et pousser le guide et la pièce en direction de la lame de la scie comme indiqué à la fig. 46. Le guide
d’onglet peut servir dans l’une ou l’autre rainure de la table. Pour une coupe en biseau (lame inclinée), utiliser la rainure
de la table qui ne crée pas l’interférence entre la main ou le guide d’onglet et le protège-lame de la scie.
Commencer lentement la découpe et tenir fermement la pièce contre le guide d’onglet et la table. L’une des règles
relatives à l’utilisation d’une scie consiste à ne jamais se cramponner ou toucher une pièce d’ouvrage qui n’est pas
fixée. Tenir la pièce supportée, et non la pièce coupée mobile. L’avance pour le tronçonnage se poursuit jusqu’à ce
que la pièce soit coupée en deux, et que le guide d’onglet et la pièce reviennent au point de départ. Avant de tirer la
pièce vers l’arrière, il est conseillé d’imprimer un petit mouvement sur le côté, à la pièce, pour l’éloigner de la lame de
la scie. Ne jamais ramasser sur la table une pièce de courte longueur alors que la scie est en marche. Ne jamais
toucher une pièce coupée à moins qu’elle ne fasse au moins 300 mm (1 pi) de long.
AVERTISSEMENT
OPÉRATIONS COURANTES DE SCIAGE
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 45

45
Pour une sécurité accrue et plus de commodité, ajouter au guide d’onglet un parement auxiliaire en bois Fixer le
parement en bois à l’avant du guide d’onglet en insérant deux vis à bois dans les trous (A) fig. 46, à cet effet sur le
corps du guide d’onglet et dans le parement en bois.
NE JAMAIS UTILISER LE GUIDE COMME JAUGE DE COUPE POUR LES OPÉRATIONS DE
TRONÇONNAGE.
Pour tronçonner plusieurs pièces de même longueur, fixer un bloc de bois (B) fig. 46A sur le guide et l’utiliser comme jauge
de coupe. Il est important de toujours positionner ce bloc de bois devant la lame de la scie comme indiqué. Après avoir
déterminé la longueur de coupe, fixer solidement le guide et utiliser du guide d’onglet pour acheminer la pièce de coupe. Ce
bloc de bois permet à la pièce coupée de se déplacer librement le long de la surface de la table sans se coincer entre le guide
et la lame de la scie, ce qui réduit donc la possibilité d’effet de rebond et de blessure pour l’opérateur de la scie.
LORS DE L’UTILISATION DU BLOC (B) FIG. 46A, COMME JAUGE DE COUPE, IL EST TRÈS IMPORTANT
DE POSITIONNER L’EXTRÉMITÉ ARRIÈRE DU BLOC DE SORTE QUE LA PIÈCE SOIT À L’ÉCART DU BLOC AVANT
QU’ELLE N’ENTRE EN CONTACT AVEC LA SCIE.
SCIAGE EN LONG
La coupe d’une planche dans sa longueur est connue sous le nom de sciage en long. Utiliser le guide longitudinal (A)
fig. 47, pour positionner et guider la pièce. L’un des bords de la pièce vient s’appuyer contre le guide longitudinal
tandis que le côté plat de la planche repose sur la table. Étant donné que la pièce est poussée le long du guide, il doit
avoir un bord droit et bien toucher la table. Utiliser le protège-lame de la scie. Il est muni de doigts anti-effet de rebond
afin d’empêcher l’effet de rebond, et d’un couteau séparateur pour empêcher le trait de scie de se fermer et de coincer
la lame.
1. Démarrer le moteur et avancer la pièce en l’appuyant contre le guide. Ne jamais se mettre dans la trajectoire de la
scie lors d’une opération de sciage en long. Tenir la pièce des deux mains et la pousser le long du guide et vers la
lame de la scie (fig. 48). La pièce peut être guidée sous la lame de la scie avec une ou deux mains. Une fois que la
pièce au-delà de la lame de la scie et des doigts anti-effet de rebond, retirer la main de la pièce. Une fois la coupe
effectuée, il est possible de laisser la pièce sur la table, de l’incliner légèrement et de la saisir par l’extrémité du
protège-lame arrière, ou de la faire tomber de la table, sur le sol. Alternativement, il est possible de continuer de guider
la pièce vers l’extrémité de la table, après quoi il faut la déplacer pour la placer le long du bord extérieur du guide. La
pièce coupée doit rester sur la table, et ne doit pas être touchée jusqu’à ce que la lame se soit immobilisée, à moins
qu’il ne s’agisse d’une grosse pièce pouvant être retirée en toute sécurité. Pour scier en long des planches de plus
d’un mètre (trois pieds) de long, on recommande d’utiliser un appui arrière (B) fig. 47, qui s’étend aussi loin que
possible pour empêcher la pièce de tomber de la table de la scie.
2. Si la pièce mesure moins de 101 mm (4 pouces) de largeur, toujours utiliser un poussoir pour terminer
l’acheminement comme indiqué à la fig. 49. Le poussoir se fabrique facilement de matériau de rebut selon l’explication
de la rubrique « FABRICATION D’UN POUSSOIR ».
3. Il peut être dangereux de scier des pièces étroites en long si cette opération n’est pas réalisée avec prudence. Les
pièces étroites ne peuvent généralement pas être coupées lorsque le protège lame est en place. Si la pièce est assez
petite, utiliser un poussoir. Pour scier en long des pièces de moins de 51 mm (2 po) de largeur, un poussoir plat peut
être un accessoire très utile étant donné que des bâtons ordinaires peuvent interférer avec le protège-lame. En cas
d’utilisation d’un poussoir, il faut ajouter la largeur du poussoir à la largeur du guide longitudinal pour le réglage de la
position. Fabriquer un poussoir plat comme illustré à la fig. 50 l’utiliser comme indiqué à la fig. 48
REMARQUE : certaines opérations spéciales exigent l’ajout d’un parement en bois face au guide, selon l’explication
de la section « UTILISATION DU PAREMENT EN BOIS AUXILIAIRE FACE AU GUIDE LONGITUDINAL » et
l’utilisation d’un poussoir.
UTILISATION DU PAREMENT EN BOIS AUXILIAIRE AVEC LE GUIDE
LONGITUDINAL
Pour certaines opérations spéciales, il est nécessaire de placer des planches de repères (A) fig. 51 sur un côté du guide, ou
sur les deux. Fixer la planche de repère sur le guide en mettant des vis dans les trous du guide. La plupart du temps, une
pièce de 19 mm (3/4 po) sera nécessaire, parfois 25,4 mm (1 po).
FRAISE ACCESSOIRE À RAINURER
REMARQUE : LA LARGEUR MAXIMUM DE RAINURAGE EST DE 12,7 mm (1/2 po) POUR CETTE SCIE.
L’ENSEMBLE PROTÈGE-LAME/COUTEAU SÉPARATEUR NE PEUT PAS ÊTRE UTILISÉ POUR
LES RAINURAGES. IL DOIT ÊTRE RETIRÉ.
Avant de rainurer, desserrer l’écrou à oreilles (a) fig. 52 et retirer l’ensemble pare-main/couteau séparateur (B).
Garder l’ensemble sous la main pour le replacer après le rainurage.
AVERTISSEMENT
ATTENTION
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 46

46
1. Le rainurage consiste à couper une feuillure ou une rainure large dans la pièce. La plupart des ensembles à rainurer
sont constitués de deux lames externes et de quatre ou cinq couteaux internes (fig. 53). De nombreuses combinaisons
de lames et couteaux sont utilisées pour couper des rainures de 3,2 mm (1/8 po) à 20,6 mm (13/16 po) pour des
étagères, pour réaliser des assemblages, tenonnage, rainurage, etc. Les couteaux sont très estampés et doivent être
placés de sorte que cette partie estampée se trouve au niveau des dents des lames externes, comme le montre la fig.
54. La fig. 55 montre la superposition de la lame et du couteau (A) est la lame externe, (B) est un couteau interne, et (C)
est un ou des joints en papier utilisés au besoin pour contrôler la largeur exacte de la rainure. Une rainure de 6,4 mm
(1/4 po) est coupée à l’aide des deux lames externes. Les dents des scies doivent être positionnées de sorte que le
rabot de l’une des lames se trouve à côté de la dent coupante de l’autre lame.
2. Fixer l’ensemble à rainurer (D) fig. 56, sur l’arbre de la scie.
REMARQUE : LA BRIDE D’AXE EXTERNE NE PEUT PAS ÊTRE UTILISÉE AVEC L’ENSEMBLE À
RAINURER, RESSERRER L’ÉCROU D’ARBRE CONTRE LE CORPS DE L’ENSEMBLE À RAINURER.
NE PAS PERDRE LA BRIDE D’AXE EXTERNE. ELLE SERA NÉCESSAIRE POUR FIXER À NOUVEAU
UNE LAME SUR L’AXE.
L’INSERT DE TABLE POUR L’ENSEMBLE À RAINURER ACCESSOIRE (E) FIG. 56, DOIT ÊTRE
UTILISÉ AU LIEU DE L’INSERT DE TABLE STANDARD.
L’ENSEMBLE PROTÈGE-LAME/COUTEAU SÉPARATEUR NE PEUT PAS ÊTRE UTILISÉ POUR LE RAINURAGE
ET DOIT ÊTRE RETIRÉ OU BASCULÉ À L’ARRIÈRE DE LA SCIE. UTILISER ÉGALEMENT DES SERRE-JOINTS,
FIXATIONS, POUSSOIRS ET PLANCHES EN ÉVENTAILS SUPPLÉMENTAIRES.
3. La fig. 57 illustre une opération courante de rainurage avec utilisation du guide d’onglet comme guide.
NE JAMAIS UTILISER LA TÊTE À RAINURER EN POSITION DE BISEAU.
TOUJOURS RÉINSTALLER LE PROTÈGE-LAME APRÈS AVOIR TERMINÉ L’OPÉRATION.
AVERTISSEMENT
AVERTISSEMENT
ATTENTION
ATTENTION
CONSTRUCTION D’UNE PLANCHE EN ÉVENTAIL
La fig. 58 illustre les dimensions utilisées pour la fabrication d’une planche en éventail typique. Utiliser une pièce de
bois droite exempte de n?uds et de fissures pour la fabrication de la planche en éventail. Les planches en éventail sont
utilisées pour maintenir la pièce en contact avec le guide et la table et d’éviter les effets de rebond. Fixer les planches
en éventail sur le guide et la table de sorte que le bord d’attaque des planches en éventail soutienne la pièce tout au
long de la coupe. Utiliser des planches en éventail pour toutes les opérations, hors débitage complet, pour lesquelles
l’ensemble protège-lame/dispositif d’écartement doit être retiré (voir fig. 59). Toujours replacer l’ensemble protège-
lame/dispositif d’écartement lorsque l’opération (hors débitage complet) est terminée.
Page 47

47
SUIVRE LES RÈGLES ET CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ
PROBLÈME ! LA SCIE NE DÉMARRE PAS
QUEL EST LE PROBLÈME ? QUE FAIRE…
1.Scie non branchée. 1.Brancher la scie.
2.Fusible grillé ou disjoncteur déclenché.2.Remplacer le fusible ou réinitialiser le disjoncteur.
3.Cordon endommagé. 3.Faire remplacer le cordon par un centre de réparation agréé.
4.Brosses usées. 4.Faire remplacer les brosses par un centre de réparation agréé.
PROBLÈME ! LES DÉCOUPES EFFECTUÉES PAR LA SCIE NE SONT PAS SATISFAISANTES
QUEL EST LE PROBLÈME ? QUE FAIRE…
1.Lame émoussée. 1.Remplacer la lame.
2.Lame montée à l’envers. 2.Inverser la lame.
3.Gomme ou résine sur la lame. 3.Retirer la lame et la nettoyer avec de la térébenthine.
4.Lame inadéquate pour le travail 4.Changer la lame.
effectué.
PROBLÈME ! LA LAME N’ATTEINT PAS SON PLEIN RÉGIME
QUEL EST LE PROBLÈME ? QUE FAIRE…
1.La rallonge est trop légère ou 1.La remplacer par une rallonge de taille adéquate.
trop longue.
2.Courant domestique trop faible. 2.Contacter votre fournisseur d’électricité.
PROBLÈME ! LA MACHINE VIBRE DE MANIÈRE EXCESSIVE
QUEL EST LE PROBLÈME ? QUE FAIRE…
1.Socle sur un plancher inégal. 1.Le repositionner sur une surface plane.
2.Lame de scie endommagée. 2.Remplacer la lame.
PROBLÈME ! LES COUPES À ONGLET MANQUENT DE PRÉCISION
QUEL EST LE PROBLÈME ? QUE FAIRE…
1.L’échelle d’onglet n’est pas 1.Vérifier et régler.
correctement réglée.
2.La lame n’est pas d’équerre par 2.Vérifier et régler.
rapport au guide.
3.La lame n’est pas perpendiculaire 3.Vérifier et régler le guide.
à la table
4.La pièce à couper se déplace. 4.La fixer au guide ou coller du papier abrasif de calibre
120 sur le guide à l’aide de colle de caoutchouc.
PROBLÈME ! LE MATÉRIAU PINCE LA LAME
QUEL EST LE PROBLÈME ? QUE FAIRE…
1.Découpe de matériau arqué. 1. Positionner le matériau arqué avec le côté concave ou creux vers le bas.
2.Le guide longitudinal n’est pas 2. Réaligne le guide longitudinal.
parallèle à la lame.
PROBLÈME ! IMPOSSIBLE DE BLOQUER LA LAME EN BISEAU
QUEL EST LE PROBLÈME ? QUE FAIRE…
1.La poignée de blocage 1.Retirer le volant d’abaissement et de relèvement de la lame.
d’inclinaison de la lame est trop lâche. 2. Déposer la vis à tête plate de la poignée de blocage.
3. Serrer la poignée de blocage d’inclinaison de la lame. La poignée de
blocage (A) est à ressort et se déplace en tirant sur la poignée (A)
et en la repositionnant sur le goujon à crans d’arrêt logé sous la poignée.
REMARQUE : Une fois serrée, positionner la poignée à une heure.
4. Remettre la vis à tête plate.
GUIDE DE DÉPANNAGE
Page 48

48
Poussoir
Pièce en bois de 12,7
mm (1/2 po) ou 19 mm
(3/4 po) ou d'une
épaisseur inférieur
e à la
lar
geur de la pièce à
couper
Couper ici pour une pièce de
6,4 mm (1/4 po)Couper ici pour
une pièce de 6,4 mm (1/4 po)
Encoche pour
empêcher la main de
glisser
Carrés de 12,7
mm (1/2 po)
Pour scier en long un ouvrage de moins de 10,2 cm (4 po) de large, utiliser un poussoir pour terminer la coupe. Il est
facile de fabriquer un poussoir avec des déchets de découpe en suivant le modèle indiqué à la fig. 60.
Fig. 59
Couper ici pour une pièce
de 6,4 mm (1/4 po)Couper
ici pour une pièce de 12,7
mm (1/2 po)
« FABRICATION D'UN POUSSOIR »
Page 49

49
ACCESSOIRES
Les accessoires recommandés pouvant être utilisés avec l’outil sont disponibles auprès de votre distributeur local ou centre de
réparation autorisé. Pour tout renseignement concernant les accessoires, composer le : 1-800-544-6986
l’utilisation de tout accessoire non recommandé avec l’outil pourrait s’avérer dangereuse.
Entretien
N’utiliser qu’un détergent doux et un chiffon humide pour nettoyer l’outil. Ne jamais laisser de liquide pénétrer dans l’outil et
n’immerger aucune partie de l’outil dans un liquide.
IMPORTANT : pour garantir la SÉCURITÉ et la FIABILITÉ du produit, les réparations, l’entretien et le réglage (autre que ceux
énumérés dans ce mode d’emploi) doivent être réalisés par un centre de réparation autorisé ou tout autre centre de réparation
professionnel, et les des pièces de rechange identiques doivent être utilisées.
Information sur les services
Black & Decker dispose d'un réseau complet composé de centres de service et de centres autorisés situés partout en Amérique du
Nord. Tous les centres de service Black & Decker sont dotés de personnel qualifié en matière d'outillage électrique; ils sont donc en
mesure d'offrir à leur clientèle un service efficace et fiable. Pour obtenir un conseil technique ou une pièce d'origine ou pour faire
réparer un outil, on peut communiquer avec le centre Black & Decker le plus près. Pour obtenir le numéro de téléphone, consulter les
pages jaunes sous la rubrique "Outils - électriques" ou composer le 1 800 544-6986 (1-800-54-HOW-TO)
www.blackanddecker.com.
Garantie complète de deux ans pour usage résidentiel
Black & Decker (U.S.) Inc. garantit ce produit pour une période de deux ans contre tout défaut de matériel ou de fabrication. Le
produit défectueux sera remplacé ou réparé sans frais, suivant l’une des deux méthodes suivantes.
La première méthode consiste en un échange seulement. On doit retourner le produit au détaillant qui l’a vendu (pourvu qu’il s’agisse
d’un détaillant participant), en respectant les délais stipulés dans sa politique relative aux échanges (normalement de 30 à 90 jours
après la vente). Une preuve d’achat peut être requise. On doit vérifier la politique de retour du détaillant pour tout produit retourné
après le délai prescrit pour les échanges.
La deuxième méthode consiste à apporter ou à envoyer le produit (prépayé) à un centre
Black & Decker ou à un centre de service autorisé aux fins de réparation ou de remplacement, selon notre choix. Une preuve d’achat
peut être requise. Les centres
Black & Decker et les centres de service autorisés sont répertoriés dans les pages jaunes sous la rubrique «Outils - électriques».
Cette garantie ne s’applique pas aux accessoires. Elle confère des droits légaux particuliers à l’acheteur, mais celui-ci pourrait aussi
bénéficier d’autres droits variant d’un territoire à l’autre.
Toute question doit être adressée au gérant du centre Black & Decker le plus près.
Ce produit n’est pas destiné à un usage commercial.
Remplacement gratuit de l’étiquette d’avertissement : En cas de perte ou d’endommagement des étiquettes d’avertissement,
composer le 1 800 544-6986 afin d’en obtenir de nouvelles sans frais.
Remarque à l’intention des entrepreneurs concernant la garantie
spéciale
Les produits de marque FIRESTORM
MC
sont des outils hauts de gamme destinés aux consommateurs et comportent une GARANTIE
POUR USAGE RÉSIDENTIEL. Ces outils sont conçus, fabriqués et mis à l’essai en vue de répondre aux besoins du bricoleur, ou de
les dépasser, lorsque ce dernier réalise des projets ou effectue des réparations à
l’intérieur ou à l’extérieur de sa résidence. Utilisés correctement, ces outils procurent à
l’utilisateur un rendement et une puissance supérieurs qui excèdent de loin la période de garantie de deux ans. Par contre, tout outil
utilisé à des fins commerciales ou tout produit de marque FIRESTORM
MC
ou tout autre produit Black & Decker destiné aux
consommateurs et réservé à un usage résidentiel, utilisé dans le cadre d’une ACTIVITÉ RELIÉE AU TRAVAIL, N’EST PAS
COUVERT PAR LAPRÉSENTE GARANTIE.
Imported by / Importé par
Black & Decker Canada Inc.
100 Central Ave.
Brockville (Ontario) K6V 5W6
Voir la rubrique “Outils électriques”
des Pages Jaunes
pour le service et les ventes.
AVERTISSEMENT
Page 50

50
SSSSIIIIEEEERR
RR
RR
RRAAAA
DD
DDEEEE
MM
MMEEEESSSSAAAA FFFFSSSS222211110000LLLLSSSS
222255554
444 MM
MM
MM
MM ((((11110000””””))))
CONSERVE ESTE MANUAL PARA FUTURAS CONSULTAS
ANTES DE DEVOL
ANTES DE DEVOL
VER ESTE PRODUCTO POR CUALQUIER MOTIVO, LLAME AL
VER ESTE PRODUCTO POR CUALQUIER MOTIVO, LLAME AL
(55) 5326-7100
(55) 5326-7100
¡GRACIAS POR ELEGIR FIRESTORM! VAYA A WWW.FIRESTORMTOOLS.COM/
PRODUCTREGISTRATION
PARA REGISTRAR SU NUEVO PRODUCTO.
MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIONES
Page 51

51
IIndica una situación de peligro inminente, que si no se evita, provocará la muerte o lesiones graves.
Indica una situación de peligro potencial, que si no se evita, provocará la muerte o lesiones graves.
Indica una situación de peligro potencial, que si no se evita, provocará lesiones leves o moderadas.
Utilizado sin el símbolo de alerta de seguridad, indica una situación de peligro potencial, que si no se evita, puede
provocar daños en la propiedad
DEFINICIONES DE LAS NORMAS DE SEGURIDAD
Algunas partículas originadas al lijar, aserrar, amolar, taladrar y realizar otras actividades de
construcción contienen productos químicos que producen cáncer, defectos de nacimiento y otros
problemas reproductivos. Algunos ejemplos de estos productos químicos son:
• el plomo de las pinturas de base plomo,
• la sílice cristalina de ladrillos, cemento y otros productos de mampostería, y
• el arsénico y el cromo de la madera con tratamiento químico (CCA).
El riesgo derivado de estas exposiciones varía según la frecuencia con la que se realice este tipo de trabajo. Para reducir la
exposición a estos productos químicos: se recomienda trabajar en áreas bien ventiladas y usar equipos de seguridad
aprobados, como las máscaras para polvo especialmente diseñadas para filtrar las partículas microscópicas.
• Evite el contacto prolongado con las partículas de polvo originadas al lijar, aserrar, esmerilar, taladrar y realizar demás actividades
de la construcción. Use indumentaria protectora y lave las áreas expuestas con agua y jabón. Evite que el polvo entre en la boca
y en los ojos o se deposite en la piel, para impedir la absorción de productos químicos nocivos.
el uso de esta herramienta puede generar o dispersar partículas de polvo, que pueden causar lesiones
respiratorias permanentes y graves u otras lesiones. Use siempre protección respiratoria aprobada por
NIOSH/OSHA (Instituto Nacional de Salud y Seguridad Ocupacional de EE.UU./Administración de la Salud y Seguridad
Ocupacional de EE.UU.) apropiada para la exposición al polvo. Aleje la cara y el cuerpo del contacto con las partículas.
utilice la protección auditiva apropiada durante el uso. En determinadas condiciones y según el período de
uso, el ruido provocado por este producto puede originar pérdida de audición.
Es importante que usted conozca y comprenda la información incluida en este manual. Esta información se relaciona con la
protección de SU SEGURIDAD y la PREVENCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS CON EL EQUIPO. Para ayudarlo a reconocer esta información,
utilizamos los símbolos que se incluyen a la derecha. Lea el manual y preste atención a estas secciones.
NORMAS GENERALES DE SEGURIDAD
LEA Y COMPRENDA TODAS LAS ADVERTENCIAS Y LAS INSTRUCCIONES DE
OPERACIÓN ANTES DE UTILIZAR ESTE EQUIPO. El incumplimiento de cualquiera de las
instrucciones enumeradas a continuación puede provocar descarga eléctrica, incendio o lesiones
personales graves o daños a la propiedad.age.
INSTRUCCIONES IMPORTANTES SOBRE SEGURIDAD
El trabajo de carpintería puede ser peligroso si no se siguen procedimientos operativos seguros y adecuados. Al igual
que con cualquier máquina, el uso de este producto implica determinados riesgos. Si utiliza la máquina con la
precaución necesaria, reducirá considerablemente la posibilidad de lesiones personales. No obstante, si no se presta
la debida atención a las medidas normales de seguridad o se las ignora, el operador puede lesionarse. El uso del
equipo de seguridad, como protectores, varas para empujar, plantillas de guía, tablas de canto biselado, anteojos,
máscaras para polvo y protección auditiva puede reducir las posibles lesiones personales. Pero ni siquiera el mejor
protector puede compensar una mala decisión, un descuido o la falta de atención. Utilice siempr
e el sentido comú
n y
tenga pr
ecaución en el taller. Si un procedimiento parece peligroso, no lo intente. Busque un procedimiento alternativo
que le parezca más seguro. RECUERDE: su seguridad personal es su responsabilidad.
Page 52

52
1. PARA SU PROPIA SEGURIDAD, LEA EL MANUAL DE
INSTRUCCIONES ANTES DE UTILIZAR LA MÁQUINA. Al
aprender la aplicación, las limitaciones y los peligros
específicos de la máquina, se minimizará enormemente la
posibilidad de accidentes y lesiones.
2. UTILICE PROTECCIÓN PARA LOS OJOS. SIEMPRE USE
ANTEOJOS DE SEGURIDAD. Utilice también máscaras
faciales o para polvo si el corte produce polvillo. Los
anteojos de uso diario NO son anteojos de seguridad.
UTILICE UN EQUIPO DE SEGURIDAD CERTIFICADO. El
equipo de protección para los ojos debe cumplir con las
normas del ANSI Z87.1, el equipo de protección auditiva
debe cumplir con las normas del ANSI S3.19 y la protección
de la máscara para polvo debe cumplir con las normas
certificadas de protección para la respiración
MSHA/NIOSH. Las astillas, los desechos transportados por
el aire y el polvo pueden provocar irritación, lesiones y
enfermedades.
3. USE INDUMENTARIA ADECUADA. No use ropa holgada,
guantes, corbatas, anillos, pulseras u otras joyas que
podrían engancharse en las piezas móviles. Se recomienda
usar calzado antideslizante. Use una cubierta protectora del
pelo para sujetar el pelo largo.
4. NO UTILICE LA MÁQUINA EN UN ENTORNO
PELIGROSO. La utilización de herramientas mecánicas en
lugares húmedos o mojados, o en la lluvia, puede causar
descargas eléctricas o electrocución. Mantenga bien
iluminada el área de trabajo para evitar tropezar o poner en
peligro los brazos, las manos y los dedos.
5. MANTENGA TODAS LAS HERRAMIENTAS Y MÁQUINAS
EN CONDICIONES ÓPTIMAS. Mantenga las herramientas
afiladas y limpias para lograr el mejor y más seguro
rendimiento. Siga las instrucciones de lubricación y cambio
de accesorios. Las herramientas y las máquinas mal
mantenidas pueden dañar más la herramienta o la máquina
y/o causar lesiones.
6. COMPRUEBE SI HAY PIEZAS DAÑADAS. Antes de
utilizar la máquina, compruebe si hay piezas dañadas.
Compruebe la alineación de las piezas móviles, si las piezas
móviles se atascan, si hay piezas rotas y toda otra situación
que podría afectar su funcionamiento. Un protector o
cualquier otra pieza que presente daños debe repararse o
reemplazarse apropiadamente. Las piezas dañadas pueden
causar daños adicionales a la máquina y/o lesiones.
7. MANTENGA LIMPIA EL ÁREA DE TRABAJO. Las áreas y
los bancos desordenados invitan a que se produzcan
accidentes.
8. MANTENGA ALEJADOS A LOS NIÑOS Y A LOS
VISITANTES. El taller es un entorno potencialmente
peligroso. Los niños y los visitantes pueden sufrir lesiones.
9. REDUZCA EL RIESGO DE UN ARRANQUE NO
INTENCIONADO. Asegúrese de que el interruptor esté en
la posición de apagado antes de enchufar el cable de
alimentación. En caso de un apagón, mueva el interruptor a
la posición de apagado. Un arranque accidental podría
causar lesiones.
10. UTILICE LOS PROTECTORES. Asegúrese de que todos
los protectores estén colocados en su sitio, sujetos
firmemente y funcionando correctamente para prevenir
lesiones.
11. QUITE LAS LLAVES DE AJUSTE Y DE TUERCA ANTES
DE ARRANCAR LA MÁQUINA. Las herramientas, los
pedazos de desecho y otros residuos pueden salir
despedidos a alta velocidad, causando lesiones.
12. UTILICE LA MÁQUINA ADECUADA. No fuerce una
máquina o un aditamento a hacer un trabajo para el que no
se diseñó. El resultado podría ser daños a la máquina y/o
lesiones.
13. UTILICE ACCESORIOS RECOMENDADOS. La utilización
de accesorios y aditamentos no recomendados por Delta
podría causar daños a la máquina o lesiones al usuario.
14. UTILICE EL CORDÓN DE EXTENSIÓN ADECUADO.
Asegúrese de que el cordón de extensión esté en buenas
condiciones. Cuando utilice un cordón de extensión,
asegúrese de utilizar un cordón que sea lo suficientemente
pesado como para llevar la corriente que su producto tome.
Un cordón de tamaño insuficiente causará una caída de la
tensión de la línea, lo cual producirá una pérdida de
potencia y recalentamiento. Consulte el Cuadro de
cordones de extensión para obtener el tamaño correcto
dependiendo de la longitud del cordón y la capacidad
nominal en amperios indicada en la placa de
especificaciones. En caso de duda, utilice el próximo calibre
más grueso. Cuanto más pequeño sea el número de calibre,
más pesado será el cordón.
15. SUJETE FIRMEMENTE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO. Utilice
abrazaderas o un tornillo de carpintero para sujetar la pieza
de trabajo cuando resulte práctico. La pérdida de control de
una pieza de trabajo puede causar lesiones.
16. HAGA AVANZAR LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO CONTRA EL
SENTIDO DE ROTACIÓN DE LA HOJA, EL CORTADOR O
LA SUPERFICIE ABRASIVA. Si la hace avanzar desde el
otro sentido, el resultado será que la pieza de trabajo salga
despedida a alta velocidad.
17. NO FUERCE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO SOBRE LA
MÁQUINA. El resultado podría ser daños a la máquina y/o
lesiones.
18. NO INTENTE ALCANZAR DEMASIADO LEJOS. Una
pérdida del equilibrio puede hacerle caer en una máquina en
funcionamiento, causándole lesiones.
19. NO SE SUBA NUNCA A LA MÁQUINA. Se podrían
producir lesiones si la herramienta se inclina o si usted hace
contacto accidentalmente con la herramienta de corte.
20. NO DEJE NUNCA DESATENDIDA LA MÁQUINA
CUANDO ESTÉ EN MARCHA. APÁGUELA. No deje la
máquina hasta que ésta se detenga por completo. Un niño
o un visitante podría resultar lesionado.
21. APAGUE LA MÁQUINA Y DESCONÉCTELA DE LA
FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN antes de instalar o quitar
accesorios, antes de ajustar o cambiar configuraciones o al
realizar reparaciones. Un arranque accidental puede causar
lesiones.
22. HAGA SU TALLER A PRUEBA DE NIÑOS CON
CANDADOS E INTERRUPTORES MAESTROS O
QUITANDO LAS LLAVES DE ARRANQUE. El arranque
accidental de una máquina por un niño o un visitante podría
causar lesiones.
23. MANTÉNGASE ALERTA, FÍJESE EN LO QUE ESTÁ
HACIENDO Y USE EL SENTIDO COMÚN. NO UTILICE LA
MÁQUINA CUANDO ESTÉ CANSADO O BAJO LA
INFLUENCIA DE DROGAS, ALCOHOL O MEDICAMENTOS. Un momento de distracción mientras se estén
utilizando herramientas mecánicas podría causar lesiones.
24. TOME PRECAUCIONES CONTRA LA INHALACIÓN DE
POLVO. El polvo generado por determinadas maderas y
productos para madera puede ser perjudicial para su salud.
Siempre opere la máquina en áreas con buena ventilación y
encárguese de eliminar el polvo adecuadamente. Utilice un
sistema de recolección de polvo, cuando esto sea posible.
NORMAS GENERALES DE SEGURIDAD
LA FALTA DE CUMPLIMIENTO DE ESTAS NORMAS PUEDE PROVOCAR LESIONES
GRAVES.
INSTRUCCIONES IMPORTANTES SOBRE SEGURIDAD
Page 53

53
NORMAS DE SEGURIDAD ADICIONALES PARA LAS
SIERRAS DE MESA
1. NO UTILICE ESTA MÁQUINA hasta que esté
completamente montada e instalada de acuerdo con las
instrucciones.
2. OBTENGA ASESORAMIENTO de su supervisor, instructor
u otra persona calificada si no está completamente
familiarizado con la utilización de esta máquina.
3. SIGA TODOS LOS CÓDIGOS DE CABLEADO y las
conexiones eléctricas recomendadas.
4. UTILICE LOS PROTECTORES SIEMPRE QUE SEA
POSIBLE. Asegúrese de que estén colocados en su sitio,
sujetos firmemente y funcionando correctamente.
5. EVITE EL RETROCESO:
A. manteniendo la hoja afilada y libre de herrumbre y
resina.
B. manteniendo el tope-guía para cortar al hilo paralelo a la
hoja de sierra.
C. utilizando el protector de la hoja de sierra y el separador
para todas las operaciones posibles, incluyendo el
aserrado pasante.
D. empujando la pieza de trabajo más allá de la hoja de
sierra antes de soltarla.
E. no cortando nunca al hilo una pieza de trabajo que esté
torcida o combada, o que no tenga un borde recto
para guiarla a lo largo del tope-guía.
F. utilizando tablas de canto biselado cuando no pueda
utilizarse el dispositivo antirretroceso.
G. no aserrando nunca una pieza de trabajo grande que no
pueda ser controlada.
H. no utilizando nunca el tope-guía como guía cuando se
realicen cortes transversales.
I. no aserrando nunca una pieza de trabajo que tenga
nudos sueltos u otros defectos.
6. UTILICE SIEMPRE LOS PROTECTORES, EL
SEPARADOR Y LOS DEDOS ANTIRRETROCESO,
excepto cuando se indique otra cosa en el manual.
7. RETIRE LAS PIEZAS CORTADAS Y LOS RESIDUOS de
la mesa antes de arrancar la sierra. La vibración de la
máquina puede hacer que dichas piezas y residuos se
muevan hacia la hoja de sierra y salgan despedidos.
Después de realizar el corte, apague la máquina. Cuando la
hoja se haya detenido completamente, retire todos los
residuos.
8. NUNCA ARRANQUE LA MÁQUINA con la pieza de
trabajo contra la hoja.
9. SUJETE FIRMEMENTE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO contra el
calibre de ingletes o el tope-guía.
10. NUNCA haga pasar la pieza de trabajo entre el tope-guía
y una fresa de moldurar.
11. NUNCA realice operaciones "a pulso". Utilice el tope-guía
o el calibre de ingletes para posicionar y guiar la pieza de
trabajo.
12. UTILICE UNO O VARIOS PALOS DE EMPUJAR para
cortar al hilo una pieza de trabajo estrecha.
13. EVITE LAS OPERACIONES DIFÍCILES Y LAS
POSICIONES DIFÍCILES DE LAS MANOS en las que un
resbalón repentino podría hacer que una mano se mueva
hacia la hoja.
14. MANTENGA LOS BRAZOS, LAS MANOS Y LOS DEDOS
alejados de la hoja.
15. NUNCA haga que alguna parte de su cuerpo esté en línea
con la trayectoria de la hoja de sierra.
16. NUNCA PONGA LAS MANOS ALREDEDOR de la hoja de
sierra ni sobre ella.
17. NUNCA intente soltar una hoja de sierra parada sin apagar
primero la máquina.
18. SOPORTE APROPIADAMENTE las piezas de trabajo
LARGAS O ANCHAS.
19. NUNCA REALICE TRABAJO DE INSTALACIÓN,
MONTAJE o preparación en la mesa/área de trabajo
cuando la máquina esté en marcha.
20. APAGUE LA MÁQUINA Y DESCONÉCTELA de la fuente
de alimentación antes de instalar o quitar accesorios,
antes de ajustar o cambiar las preparaciones o al hacer
reparaciones.
21. APAGUE LA MÁQUINA, desconéctela de la fuente de
alimentación y limpie la mesa/área de trabajo antes de
dejar la máquina. BLOQUEE EL INTERRUPTOR EN LA
POSICIÓN DE APAGADO para impedir el uso no
autorizado.
22. HAY DISPONIBLE INFORMACIÓN ADICIONAL
RELACIONADA CON LA UTILIZACIÓN SEGURA y
apropiada de esta herramienta a través del Instituto de
Herramientas Mecánicas, Power Tool Institute, 1300
Summer Avenue, Cleveland, OH 44115-2851. También hay
información disponible a través del Consejo Nacional de
Seguridad, National Safety Council, 1121 Spring Lake
Drive, Itasca, IL 60143-3201. Sírvase consultar los
Requisitos de Seguridad para Máquinas de Elaboración
de la Madera ANSI 01.1 del Instituto Nacional Americano
de Normas (American National Standards Institute) y las
normas OSHA 1910.213 del Departamento de Trabajo de
los EE.UU.
GUARDE ESTAS INSTRUCCIONES.
Refiérase a ellas con frecuencia y utilícelas para adiestrar a otros.
LEA Y COMPRENDA TODAS LAS ADVERTENCIAS Y LAS INSTRUCCIONES DE OPERACIÓN ANTES
DE UTILIZAR ESTE EQUIPO. EL INCUMPLIMIENTO DE CUALQUIERA DE LAS INSTRUCCIONES
ENUMERADAS A CONTINUACIÓN PUEDE PROVOCAR DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA, INCENDIO O
LESIONES PERSONALES GRAVES O DAÑOS A LA PROPIEDAD.
Page 54
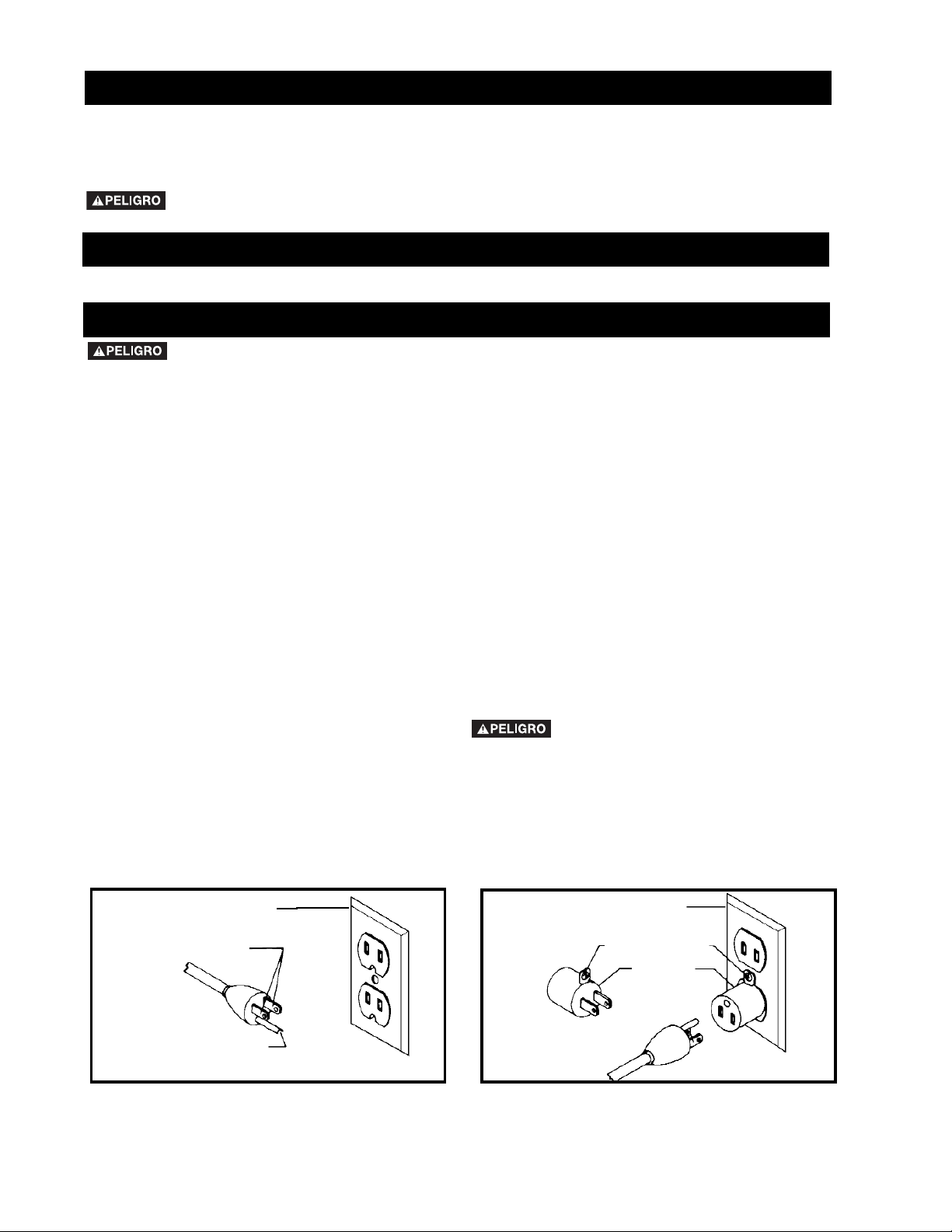
54
Fig. A
Fig. B
CAJA DE TOMACORRIENTE A
TIERRA
PATAS DE
CONDUCCIÓN DE
CORRIENTE
LA PATA A TIERRA ES LA MÁS
LARGA DE LAS 3
MEDIOS DE CONEXIÓN
A TIERRA
ADAPTADOR
CAJA DE TOMACORRIENTE A
TIERRA
1. Todas las máquinas a tierra, conectadas por cables:
En caso de un mal funcionamiento o falla, la conexión a tierra
proporciona un trayecto de la menor resistencia posible, para
reducir el riesgo de que la corriente ocasione una descarga
eléctrica. Esta máquina está equipada con un cable eléctrico
que tiene un conductor y un enchufe para poner el equipo a
tierra. El enchufe se debe utilizar con un tomacorriente
adecuado que haya sido instalado correctamente y
conectado a tierra de acuerdo con todos los códigos y las
ordenanzas locales.
No cambie el enchufe suministrado; si no se adapta
apropiadamente al tomacorriente, solicite a un electricista
calificado que instale el tomacorriente correcto.
Como consecuencia de una conexión inadecuada del
conductor a tierra del equipo, puede generarse riesgo de
descargas eléctricas. El conductor a tierra del equipo es el
que tiene un aislante de color verde en la superficie externa,
con o sin bandas amarillas. Si fuera necesario reparar o
reemplazar el cable eléctrico, no conecte el conductor a tierra
del equipo a una terminal de baja tensión.
Llame a un electricista calificado o al personal de
mantenimiento para que verifiquen las conexiones si no
comprende completamente las instrucciones de conexión a
tierra o si duda de que la máquina esté conectada a tierra
correctamente.
Utilice solamente cables prolongadores de 3 conductores que
tengan enchufes a tierra de 3 patas y tomacorrientes de 3
conductores que se adapten al enchufe de la máquina, como
se muestra en la Fig. A.
Repare o reemplace los cables dañados o gastados
inmediatamente.
2. Máquinas conectadas por cable a tierra, diseñadas
para utilizarse en un circuito de suministro con un índice
nominal menor a 150 voltios:
Si la máquina está diseñada para utilizarse en un circuito
que no posee un tomacorriente similar al que ilustra la
Fig. A, tendrá un enchufe a tierra parecido al que ilustra
la Fig. A. Puede utilizar un adaptador temporal similar al
adaptador ilustrado en la Fig. B para conectar este
enchufe al tomacorriente de 2 conductores
correspondiente, como se muestra en la Fig. B, si no
dispone de un tomacorriente con una buena conexión a
tierra. El adaptador temporal únicamente debe usarse
hasta tanto un electricista calificado haya instalado un
tomacorriente conectado a tierra correctamente. La
oreja, la lengüeta, o algo semejante, de color verde que
sale del adaptador debe estar conectada a tierra en
forma permanente por medio de una caja de
tomacorriente conectada a tierra correctamente. Cuando
se utilice el adaptador, debe estar fijo con un tornillo de
metal.
NOTA: En Canadá,el Código Eléctrico Canadiense no
permite el uso de un adaptador temporal.
EN TODOS LOS CASOS, ASEGÚRESE DE
QUE EL TOMACORRIENTE EN CUESTIÓN ESTÉ
CONECTADO A TIERRA CORRECTAMENTE. SI NO
ESTÁ SEGURO, CONTRATE A UN ELECTRICISTA
CALIFICADO PARA QUE VERIFIQUE EL
TOMACORRIENTE.
Debe utilizar un circuito eléctrico independiente para su máquina. Este circuito no debe ser menor a un cable Nº 12 y debe estar
protegido con un fusible de acción retardada de 20 amperios. Si utiliza un cable prolongador, debe ser únicamente de 3
conductores, que tenga enchufe a tierra de 3 patas y tomacorrientes correspondientes que acepten el enchufe de la máquina. Antes
de conectar la máquina a la línea eléctrica, asegúrese de que el interruptor esté en la posición de “APAGADO” (OFF) y que la
corriente eléctrica tenga las mismas características que indica la máquina. Todas las conexiones a la línea deben hacer un buen
contacto. La máquina se dañará si está funcionando con bajo voltaje.
RIESGO DE DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA. NO EXPONGA LA MÁQUINA A LA LLUVIA NI LA UTILICE EN
LUGARES HÚMEDOS.
La máquina está cableada para corriente alterna de 120 V., 60 Hz. Antes de conectar la máquina a la fuente de
alimentación, asegúrese de que el interruptor esté en la posición de apagado.
RIESGO DE DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA. ESTA MÁQUINA DEBE ESTAR CONECTADA A TIERRA MIENTRAS
ESTÉ EN USO, PARA PROTEGER AL OPERADOR DE UNA DESCARGA ELÉCTRICA.
CONEXIONES ELÉCTRICAS
ESPECIFICACIONES DEL MOTOR
INSTRUCCIONES DE CONEXIÓN A TIERRA
Page 55

55
CORDÓN DE EXTENSIÓN DE CALIBRE MÍNIMO
TAMAÑOS RECOMENDADOS PARA USO CON MÁQUINAS ELÉCTRICAS ESTACIONARIAS
Capacidad Longitud Total Del Calibre Del Cordon
Nominal En Voltios Cordon De Extensión
Amperios En Pies
0-6 120
Hasta
25 18 AWG
0-6 120 25-50 16 AWG
0-6 120 50-100 16 AWG
0-6 120 100-150 14 AWG
6-10 120
Hasta
25 18 AWG
6-10 120 25-50 16 AWG
6-10 120 50-100 14 AWG
6-10 120 100-150 12 AWG
10-12 120
Hasta
25 16 AWG
10-12 120 25-50 16 AWG
10-12 120 50-100 14 AWG
10-12 120 100-150 12 AWG
12-16 120
Hasta
25 14 AWG
12-16 120 25-50 12 AWG
12-16 120
NO SE RECOMIENDA LONGITUDES MAYOR DE 50 PIES
CABLES PROLONGADORES
Use los cables prolongadores apropiados. Asegúrese de utilizar un cable prolongador en buenas
condiciones y de que sea uno de 3 conductores con enchufe a tierra de 3 patas y el tomacorriente correspondiente
que se adapte al enchufe de la máquina. Cuando utilice un cable prolongador, compruebe que tenga la capacidad
para conducir la corriente de la máquina. Un cable de menor capacidad provocará una disminución en el voltaje de la
línea, que producirá pérdida de potencia y sobrecalentamiento. La Fig. C muestra el calibre correcto que debe
utilizarse de acuerdo con la longitud del cable. En caso de duda, utilice el calibre inmediatamente superior. Cuanto
menor sea el número de calibre, más grueso será el cable.
Fig. C
INTRODUCCIÓN
El modelo FS210LS posee una gran capacidad de sierra a un precio económico. Posee una mesa de aluminio extra
grande de 431,8 mm x 863,6 mm (17" x 34") con extensión y alimentada por un motor para trabajo pesado de 15 amp.
con engranaje de contraeje flotante, el más potente de su clase. Esta sierra está diseñada para brindar un rendimiento
de alta calidad con una capacidad de profundidad de corte de hasta 76 mm (3") a 90° y 63,5 mm (2.5") a 45° para un
corte limpio de tamaños de material estándar. Este paquete incluye la sierra, una base de metal, una guía de corte
longitudinal, calibrador de inglete, una guarda de hoja transparente con hendedor y seguro antirretroceso, extensiones
de la mesa, una hoja de sierra con punta de carburo de 254 mm (10”), inserto para mesa y llaves para cambio de hoja.
DESCRIPCIÓN DE LAS FUNCIONES
Page 56

56
PARTES DE LA SIERRA DE MESA
9
2
3
4
5
1- Sierra
2- Base de extensión izquierda
3-Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal 1/4"20X1” para la base de extensión
izquierda (3)
4- Arandela plana de 6,35 mm (1/4")
para la base de extensión izquierda (6)
5- Arandela de bloqueo de 6,35 mm
(1/4") para la base de extensión
izquierda (3)
6- Tuerca hexagonal de
1/4"-20 para la base de
extensión izquierda (3)
7- Base de extensión derecha
8- Tornillo de cabeza
hexagonal 1/4"-20X5/8” para
la base de extensión
derecha (3)
9- Arandela plana de
6,35 mm (1/4") para la base
de extensión derecha (3)
10- Arandela de bloqueo de
6,35 mm (1/4") para la base
de extensión derecha (3)
ENSAMBLAJE
DESEMBALAJE Y LIMPIEZA
Desembale cuidadosamente la máquina y todos los elementos sueltos del o los contenedores de envío. Quite el
recubrimiento protector de todas las superficies sin pintura. Puede quitarlo con un trapo suave humedecido con
queroseno (no utilice acetona, gasolina ni solvente de barniz para este fin). Luego de limpiar, cubra las superficies sin
pintura con cera en pasta de buena calidad que se utiliza para los pisos del hogar.
AVISO: LA FOTO EN LA TAPA DEL MANUAL ILUSTRA EL MODELO
FABRICADO EN LA ACTUALIDAD. TODAS LAS DEMÁS ILUSTRACIONES QUE
APARECEN EN EL MANUAL SON SOLAMENTE REPRESENTATIVAS Y
PUEDEN MOSTRAR UN COLOR, ETIQUETAS Y ACCESORIOS DIFERENTES A
LOS REALES Y TIENEN EL ÚNICO PROPÓSITO DE ILUSTRAR EL
PROCEDIMIENTO.
6
HERRAMIENTAS NECESARIAS PARA EL ENSAMBLAJE
TIEMPO APROXIMADO PARA EL ENSAMBLAJE
1). Llave ajustable
2.) Llave de 13 mm para los pernos de soporte.
3.) Llave de 10 mm para los pernos de ensamble del hendedor, ensamble de los soportes traseros y el ensamble de las
bases de extensión.
4.) Destornillador de cabeza plana.
6.) Destornillador Phillips.
5.) Escuadra de borde recto y/o de encuadre para los ajustes.
2 horas
7
8
10
1
Fig. 1
Page 57

57
Fig. 2
P
ARTES DE LA GUÍA DE CORTE LONGITUDINAL
(11,12)
11- Guía de corte longitudinal
12- Mango de bloqueo para la guía de corte longitudinal
PAR
TES DEL VOLANTE PARA ELEVAR LA HOJA
(13,14,15,16,17)
13- Volante para elevar y bajar la hoja
14- Mango del volante para elevar y bajar la hoja
15- Tornillo para montar el mango del volante
16- Tapa para el mango
17- Tornillo de cabeza plan M6 X 1 X 12 mm para montar
el volante para elevar y bajar la hoja
18- Calibrador de inglete
PAR
TES DEL SUJETADOR DEL CALIBRADOR DE
INGLETE (19,20,21,22,23,24,25)
19- Tornillos de cabeza troncocónica M4, 2 X 10 mm
para montar el sujetador del calibrador de inglete (4)
20- Arandela de bloqueo para montar el sujetador del
calibrador de inglete (4)
21- Sujetador del calibrador de inglete
22- Pinza de resorte para el sujetador del calibrador de
inglete
23- Tornillo de cabeza troncocónica M4 X 0,7 X 10 mm
para el sujetador del calibrador de inglete
24- Arandela de bloqueo de diente externo de 4,763 mm
(3/16”) para el sujetador del calibrador de inglete
25- Tuerca hexagonal M4 X 0,7 mm para el sujetador del
calibrador de inglete
PARTES DE LA ABRAZADERA DEL HENDEDOR
(26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37)
26- Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal largo 1/4-20X2-1/4”
para montar la abrazadera del hendedor
27- Arandela de bloqueo de diente interno de 6,35 mm
(1/4”) para montar la abrazadera del hendedor
28- Arandela plana de 6,35 mm (1/4”) para montar la
abrazadera del hendedor
29- Arandela de bloqueo de diente externo de 6,35 mm
(1/4”) para montar la abrazadera del hendedor
30- Abrazadera del hendedor
31- Arandela de bloqueo de diente externo de 6,35 mm
(1/4”) para la abrazadera del hendedor (2)
32- Abrazadera para el soporte del hendedor
33- Tornillos de cabeza hexagonal de 1/4-20 X 1/2”
para la abrazadera del hendedor (2)
34- Tuerca mariposa para montar la abrazadera para el
soporte del hendedor
35- Arandela de bloqueo de diente externo de 6,35 mm
(1/4”) para la abrazadera del hendedor (2)
36- Arandela plana de 6,35 mm (1/4”) para montar la
abrazadera para el soporte del hendedor (2)
37- Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal M6 X 1 X 20 mm para
montar la abrazadera para el soporte del hendedor
38- Ensamble de guarda y hendedor
39- Riel de guía izquierdo
40- Riel de guía derecho
P
AR
TES DEL RIEL DE GUÍA
(41,42,43,44,45)
41- Arandela de bloqueo M6 para montar el riel de guía
(14)
42- Arandela plana de 6,35 mm (1/4”) para montar el
riel de guía (5)
43- Tuerca hexagonal de 1/4”-20 para montar el riel y
las bases de extensión (5)
44- Espaciadores para montar la guía (9)
45- Tornillos de cabeza redonda de 1/4”-20X1-1/4 para
montar el riel de guía (9)
PARTES DEL SOPORTE DE AVANCE DE SALIDA
(46,47,48,49,50,51,52)
46- Varilla para el soporte trasero (2)
47- Soporte trasero
48- Tornillo de cruz hexagonal de M6 X 1 X 15 mm
para la abrazadera (8)
49- Arandela de bloqueo M6 para montar la abrazadera
(8)
50- Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal de 1/4”-20 X 1/2”
para la varilla (4)
51- Abrazadera (4)
52- Arandelas planas de 6,35 mm (1/4”) para montar la
varilla (4)
53- Llaves para cambiar las hojas
Page 58

58
Fig. 3
PARTES DE LA BASE
53- Pata (4)
54- Abrazadera lateral superior (2)
55- Abrazadera frontal superior
56- Abrazadera trasera superior
57- Abrazaderas superiores laterales (2)
58- Abrazaderas frontales inferiores (2)
59- Pie (4)
POR SU PROPIA SEGURIDAD, NO CONECTE LA MÁQUINA A LA FUENTE DE ALIMENTACIÓN HASTA QUE
ESTÉ ARMADA COMPLETAMENTE. NO OPERE ESTA MÁQUINA HASTA QUE HAYA LEÍDO Y
COMPRENDA TODO EL MANUAL DE INSTRUCCIONES
53
54
55
56
57
58
60
61
62
63
59
64
65
60- Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal M8 X 1,25 X 45 mm
para la pata y la base (2)
61- Tornillo de cabeza hexagonal M8 X 1,25 X 30 mm
para la pata y la base (2)
62- Tuerca de bloqueo hexagonal de 7,93 mm (5/16")
(16)
63- Perno de cabeza de hongo de 7,93 mm (5/16")
(16)
64- Tuerca hexagonal M8 (4)
65- Arandela plana M8 (8)
SUJETADOR DEL CALIBRADOR DE INGLETE
DESCONECTE LA MÁQUINA DE LA FUENTE DE ENERGÍA.
1. Ensamble la pinza de resorte (E), Fig. 4, al sujetador del calibrador de inglete (A) como se muestra, utilizando un
tornillo de cabeza troncocónica M4 x 0,7 x 10 mm (F), una arandela de bloqueo de 4,763 mm (3/16") y una tuerca
hexagonal M4 x 0,7. NOTA: la tuerca hexagonal (G), Fig. 5, encajará en la cavidad en la parte posterior del sujetador
del calibrador de inglete (A) para fijar la pinza de resorte (E), Fig. 4, al sujetador del calibrador de inglete.
2. Ensamble el sujetador del calibrador de inglete (A), Fig. 6, al lado izquierdo del gabinete de la sierra con los cuatro
tornillos de cabeza troncocónica M4 0,2 x 10 mm (B), Fig. 7 y las arandelas de 4,763 mm (3/16") (C) desde el interior
del gabinete de la sierra.
3. La Fig. 8, ilustra el calibrador de inglete (D) insertado en el sujetador del calibrador de inglete cuando no se utiliza.
Page 59

59
ENSAMBLAJE DE LA BASE
1. Las patas de la base poseen protuberancias que deben alinearse con los orificios en las abrazaderas superiores e
inferiores. Ensamble la base como se muestra en la Fig. 9A, con 16 pernos de soporte y tuercas de bloqueo
hexagonales. No ajuste el equipo por completo en este momento.
A- Abrazadera delantera superior (con logotipo)
B- Abrazadera trasera superior
C- Abrazaderas laterales inferiores
D- Abrazaderas delanteras y traseras inferiores
E- Abrazaderas laterales superiores
F- Pie
IMPORTANTE: LAS ABRAZADERAS DELANTERAS Y TRASERAS SUPERIORES (A Y B), FIG. 9A, SON MÁS
LARGAS QUE LAS ABRAZADERAS LATERALES SUPERIORES (E), FIG. 9A. LAS ABRAZADERAS DELANTERA Y
TRASERA INFERIORES (D), FIG. 9A, SON MÁS LARGAS QUE LAS ABRAZADERAS LATERALES INFERIORES (C).
2. Ensamble las patas de goma (F), Fig. 9A. NOTA: cada pata de goma viene provista con orificios para montar la base
a la superficie del piso, si fuera necesario.
INSERCIÓN DE LA BOLSA RECOLECTORA DE POLVO
1. Conecte la bolsa recolectora de polvo al marco de la bolsa y coloque el marco de la bolsa recolectora de polvo
dentro de la base de la sierra como se muestra en la Fig. 9B. Consulte la sección a continuación sobre cómo insertar
este ensamble a la sierra.
SIERRA A LA BASE
1. De vuelta a la mesa de la sierra en un trozo de cartón para proteger la superficie de la mesa. Invierta la base sobre
la sierra y alinee los cuatro orificios de la base con los orificios de montaje en la sierra.
2. Con los 2 tornillos más largos para la parte delantera, coloque una arandela plana M8 en un tornillo de cabeza
hexagonal M8X1,25X45 mm. Inserte el tornillo de cabeza hexagonal a través del orificio de montaje en la sierra y el
orificio en la base. Coloque otra arandela plana M8 en el tornillo de cabeza hexagonal y enrosque una tuerca hexagonal
M8 x 1,25 en el mismo y ajuste sin excesiva firmeza. Repita este proceso para completar otro orificio en la parte
delantera de la sierra.
Con los 2 tornillos más cortos para la parte trasera, coloque una arandela plana M8 en un tornillo de cabeza hexagonal
M8 X 1,25 X 30 mm en la parte posterior de la sierra. Inserte el tornillo de cabeza hexagonal a través del orificio de
montaje en la sierra y el orificio en la base. Coloque otra arandela plana M8 en el tornillo de cabeza hexagonal y
enrosque una tuerca hexagonal M8 x 1,25 en el mismo y ajuste sin excesiva firmeza. Repita este proceso para
completar otro orificio en la parte posterior de la sierra.
3. A continuación, gire la mesa de la sierra hacia arriba, como se muestra en la Fig. 9C (La sierra se muestra totalmente
ensamblada en esta figura).
4. Presione la parte superior de la sierra de modo que las patas de la base se ajusten a la superficie del piso y ajuste
todo el equipo de montaje de la base y el equipo de montaje que fija la sierra a la base.
ENSAMBLADO DE LA HOJA
VOLANTE PARA ELEVAR Y BAJAR
1. Inserte el tornillo especial (C) a través del mango (B), Fig. 10, y ensamble el mango al volante (A) enroscando el
tornillo en el sentido de las agujas del reloj en el volante. A continuación, presione la cubierta del mango (D).
2. La Fig. 11, ilustra el mango (B) ensamblado en el volante (A).
3. Ensamble el volante (A), Fig. 12, al eje (B) y asegúrese de que la parte plana dentro del volante esté alineada con la
parte plana en el eje.
4. Ajuste el volante (A), Fig. 8, al eje (B), Fig. 12, con un tornillo de cabeza plana M6 x 1 x 12 mm (C), Fig. 13.
ENSAMBLE DE LA GUARDA DE LA HOJA Y DEL HENDEDOR
DESCONECTE LA MÁQUINA DE LA FUENTE DE ENERGÍA.
1. IMPORTANTE: EL ENSAMBLE DE LA GUARDA DE LA HOJA Y DEL hendedor DEBE ESTAR
CORRECTAMENTE ALINEADO A LA HOJA DE LA SIERRA PARA PREVENIR EL RETROCESO.
2. Coloque la hoja a 90 grados de la mesa y trábela en el lugar. Consulte la página 63, “Control de elevación y descenso
de la hoja” y la página 63, “Control de inclinación de la hoja”.
Page 60

60
3. Ajuste la abrazadera para el soporte del hendedor (A), Fig. 14, a la abrazadera del hendedor (B) con dos tornillos
de cabeza hexagonal 1/4-20 x 1/2" (C) y dos arandelas de bloqueo de diente externo de 6,35 mm (1/4") como se
muestra. NOTA: no ajuste completamente los tornillos (C) en este momento.
4. Ubique el tornillo de cabeza hexagonal 1/4-20 x 2-1/4" (G), Fig. 15, y ensamble la arandela de bloqueo de diente
interno de 6,35 mm (1/4") (O), la arandela plana de 6,35 mm (1/4") (P) y la arandela de bloqueo de diente externo de
6,35 mm (1/4") (R) en el tornillo (G).
5. Coloque el extremo embutido (E), Fig. 16, de la abrazadera del hendedor (B) contra el extremo de la barra giratoria
(F) y ajuste en su lugar utilizando el ensamble del PASO 4 anterior. NOTA: no ajuste completamente el tornillo (C)
en este momento. El ensamble se muestra en la Fig. 17.
6. Posicione el hendedor (H), Fig. 18, en la abrazadera para el soporte del hendedor como se muestra y asegúrese de
que las dos protuberancias (K) de la abrazadera para el soporte del hendedor estén dentro de la ranura del hendedor (H).
7. Ensamble el hendedor (H), Fig. 19, a la abrazadera para el soporte del hendedor (B), como se muestra con un
tornillo de cabeza hexagonal M6 x 1 x 20 mm (L), la arandela de diente externo de 6,35 mm (1/4") y la arandela plana
de 6,35 mm (1/4").
8. Ajuste el hendedor (H), Fig. 20, a la abrazadera para el soporte del hendedor con una arandela plana de 6,35 mm
(1/4"), una arandela de diente externo de 6,35 mm (1/4")" y una tuerca mariposa M6 (M). NOTA: antes de ajustar la
tuerca mariposa (M) asegúrese de que haya un espacio de al menos 3,175 mm (1/8") entre el extremo inferior del
hendedor (N) y la superficie superior de la mesa (P) y que las "clavijas" de las protuberancias (K), Fig. 20, estén dentro
de la ranura del ensamble del hendedor (H).
9. Con un borde recto, verifique si el hendedor (H) Fig. 21, está alineado a la hoja de la sierra (R). Si fuera necesario
realizar un ajuste, el hendedor (H) se puede rotar y mover hacia la izquierda o la derecha.
10. Cuando esté seguro de que el hendedor está alineado correctamente a la hoja de la sierra, ajuste los dos tornillos
(C), Fig. 22, que ajustan la abrazadera del soporte del hendedor a la abrazadera del hendedor y ajuste el tornillo (G)
que ajusta la abrazadera del hendedor a la barra giratoria.
BASES DE EXTENSIÓN
1. Ensamble la base de extensión, (Fig. 23), a la mesa de la sierra con los tornillos de cabeza hexagonal 1/4-20 X 1”(3),
las arandelas planas de 6,35 mm (1/4”) (6), las arandelas de bloqueo de 6,35 mm (1/4”) (3), las tuercas hexagonales
de 1/4” (3).
2. Ensamble la base de extensión derecha en los orificios enroscados de la sierra con los tornillos de cabeza
hexagonal de 1/4”-20 X 5/8” (3), arandelas planas de 6,35 mm (1/4”) (3) y arandelas de bloqueo de 6,35 mm (1/4”) (3).
3. Con un borde recto, asegúrese de que los extremos superior, delantero y trasero de las bases de extensión estén
nivelados con la mesa de la sierra antes de ajustar los tres tornillos que fijan la base de extensión a la mesa.
RIEL DE GUÍA A LA SIERRA
1. Sujetando el riel de guía con los orificios más grandes hacia usted, ajuste sin demasiada firmeza los rieles de
guía (A), Fig. 24, a los cuatro orificios enroscados (B) en la mesa de la sierra (C) con dos tornillos largos de 1/4-
20 x 1-1/4" (D), arandelas de bloqueo 1/4" (E) y espaciadores (F).
IMPORTANTE: los espaciadores (F), Fig. 24, están posicionados entre los rieles de guía (A) y la mesa de la
sierra (C).
2. Ajuste los rieles de guía (A), Fig. 24, a las bases de extensión (G) a través del orificio (K) con el tornillo largo de
1/4-20 x 1-1/4” (D), la arandela de bloqueo de 6,35 mm (1/4”) (E), el espaciador (F), la arandela plana de 6,35 mm
(1/4”) (H), la arandela de bloqueo de 6,35 mm (1/4”) (E) y la tuerca hexagonal de 1/4-20 (J). A continuación, ajuste todo
el equipo de montaje del riel de guía.
IMPORTANTE: el espaciador (F), Fig. 24, está entre los rieles guía (A) y las bases de extensión (G).
3. La Fig. 25, ilustra los rieles de guía ensamblados correctamente a la mesa de la sierra y las bases de extensión.
Page 61

61
GUÍA DE CORTE LONGITUDINAL
1. Visser l’écrou hexagonal M8x de 1,25 (A) fig. 26 à mi-chemin sur le goujon de la poignée (B).
2. Fixer la poignée (B) fig. 26 dans le trou fileté (C) de la came du guide. Serrer l'écrou hexagonal (A) fig. 26
contre la came (D).
3. Baje la guía de corte longitudinal a la mesa como se muestra en la Fig. 27, y asegúrese de que la abrazadera trasera
se enganche en el extremo posterior de la mesa.
4. La guía de corte longitudinal generalmente se instala generalmente del lado derecho de la mesa de la sierra. Levante
el mango de bloqueo (B) y posicione la guía en la mesa. Presione hacia bajo el mango (B) para bloquear la guía en su
lugar en la mesa de la sierra.
CALIBRADOR DE INGLETE
El calibrador de inglete se envía completamente ensamblado y se proporciona con una barra de calibrador de inglete
con una ranura en forma de T (A), Fig. 28, que se inserta en cualquiera de las dos ranuras del calibrador de inglete en
forma de T ubicadas en la parte superior de la mesa, como se ilustra. El calibrador de inglete con ranura en forma de
T evita que el calibrador de inglete se extienda más allá del frente de la mesa al cortar transversalmente piezas de
madera muy anchas.
SOPORTE DE AVANCE DE SALIDA
1. Ajuste sin demasiada firmeza ambas abrazaderas (A), Fig. 29, al lado inferior izquierdo de la mesa de la sierra como
se muestra con dos tornillos de cabeza hexagonal phillips M6 x 1 x 15 mm (B) y arandelas de bloqueo M6 0,1 (C).
Ensamble las dos abrazaderas restantes al lado inferior derecho de la mesa de la sierra de la misma manera.
2. Inserte la varilla (D), Fig. 30, a través de los orificios en las abrazaderas (A), como se muestra. A continuación,
enrosque y ajuste un tornillo de cabeza hexagonal 1/4-20 x 1/2" (E) y una arandela plana de 1/4" (F) en el extremo
delantero de la varilla (D) como se muestra en (G). Ensamble la varilla restante en el lado opuesto de la sierra de la
misma manera.
3. Inserte las varillas (D), Fig. 31, en los orificios más grandes (H) en el soporte de avance de salida (J) como se
muestra.
4. Fije el soporte de avance de salida (J), Fig. 32, a las varillas (D) con dos tornillos de cabeza hexagonal 1/4-20 x 1/2"
y arandelas planas de 6,35 mm (1/4") (K) como se muestra.
5. Empuje todo el ensamble de soporte de avance de salida (J), Fig. 33, hacia adentro hasta que entre en contacto
con el ensamble del hendedor/guarda (L) como se muestra. A continuación, ajuste todo el equipo de montaje del
soporte de avance de salida.
6. Coloque la arandela en el tornillo hexagonal de 1/4-20 x 1/2” y enrosque en el otro extremo de la varillas para evitar
que se salgan de las abrazaderas del soporte de avance de salida.
ENCENDIDO Y APAGADO DE LA SIERRA
El interruptor de encendido/apagado (A), Fig. 34, está ubicado en la parte delantera del gabinete de la sierra. Para
“ENCENDER” la sierra, mueva el interruptor (A) hacia arriba hasta la posición de “ENCENDIDO” (ON). Para
“APAGAR” la sierra, mueva el interruptor (A) hacia abajo hasta la posición de “APAGADO” (OFF).
ASEGÚRESE DE QUE EL INTERRUPTOR ESTÉ EN LA POSICIÓN DE “APAGADO” (OFF) ANTES
DE ENCHUFAR EL CABLE DE ALIMENTACIÓN. EN CASO DE UN CORTE DE CORRIENTE, MUEVA EL
INTERRUPTOR A LA POSICIÓN DE “APAGADO” (OFF). UN ARRANQUE ACCIDENTAL PODRÍA CAUSAR LESIONES.
BLOQUEO DEL INTERRUPTOR EN LA POSICIÓN DE “APAGADO” (OFF)
IMPORTANTE: Cuando no utilice la herramienta, bloquee el interruptor en la posición de "APAGADO" para
prevenir el uso no autorizado. Para bloquear la herramienta, tome la palanca del interruptor (B) y hale del interruptor
hacia afuera (Fig. 35). Al quitar la palanca del interruptor (B), éste no operará. Sin embargo, si se extrajera la palanca
del interruptor mientras la sierra está funcionando, la máquina se puede "APAGAR", pero no se puede volver a
encender sin reinsertar la palanca del interruptor (B).
CONTROLES DE OPERACIÓN Y AJUSTES
Page 62

62
CONTROL DE ELEVACIÓN Y DESCENSO DE LA HOJA
Para elevar o bajar la hoja de la sierra, gire el volante (A), Fig. 36. Si gira el volante en el sentido de las agujas del reloj,
la hoja descenderá y si lo gira en el sentido contrario a las agujas del reloj, la hoja se elevará.
EL MANGO DE BLOQUEO DE INCLINACIÓN DE LA HOJA (B), FIG. 36, DEBE ESTAR
TRABADO DURANTE TODAS LAS OPERACIONES DE CORTE.
CONTROL DE INCLINACIÓN DE LA HOJA
Para inclinar la hoja de la sierra, afloje el mango de bloqueo de inclinación (A), Fig. 37, mueva el volante (B) hasta que
la hoja esté en el ángulo deseado y ajuste el mango de bloqueo (A). NOTA: el mango de bloqueo (A) funciona a resorte
y se puede volver a colocar sacándolo del mango (A) y colocándolo en la clavija dentada debajo del mango.
EL MANGO DE BLOQUEO DE INCLINACIÓN DE LA HOJA (A) DEBE ESTAR TRABADO
DURANTE TODAS LAS OPERACIONES DE CORTE.
AJUSTE DE TOPES POSITIVOS A 90 Y 45 GRADOS
La sierra está equipada con topes positivos para un posicionamiento rápido y exacto de la hoja de la sierra a 90 y 45
grados de la mesa. Para ajustar los topes positivos, proceda de la siguiente forma:
DESCONECTE LA MÁQUINA DEL SUMINISTRO DE ENERGÍA.
1. Eleve la hoja de la sierra a la altura máxima.
AJUSTAR UN TOPE POSITIVO A 90 GRADOS
2. Afloje el mango de bloqueo de inclinación de la hoja, mueva el mecanismo de inclinación de la hoja hacia la
izquierda, tan lejos como sea posible, y ajuste el mango de bloqueo de inclinación de la hoja.
3. Coloque una escuadra (A), Fig. 38, en la mesa con un extremo contra la hoja, como se muestra, y verifique si la
hoja está a 90 grados de la mesa. De lo contrario, afloje el tornillo (B) algunas vueltas y mueva el mecanismo de
inclinación de la hoja hasta que ésta quede a 90 grados de la mesa. A continuación, ajuste el mango de bloqueo de
inclinación de la hoja y ajuste el tornillo (B) hasta que llegue al fondo.
AJUSTAR UN TOPE POSITIVO A 90 GRADOS
4. Afloje el mango de bloqueo de inclinación de la hoja, mueva el mecanismo de inclinación de la hoja hacia la
derecha, tan lejos como sea posible, y ajuste el mango de bloqueo de inclinación de la hoja.
5. Coloque una escuadra (A), Fig. 39, en la mesa con un extremo contra la hoja como se muestra y verifique si la hoja
está a 45 grados en la mesa. De lo contrario, afloje el tornillo (C) algunas vueltas y mueva el mecanismo de inclinación
de la hoja hasta que ésta quede a 45 grados de la mesa. A continuación, ajuste el mango de bloqueo de inclinación
de la hoja y ajuste el tornillo (C) hasta que llegue al fondo.
OPERACIÓN DE LA GUÍA DE CORTE LONGITUDINAL Y AJUSTES
1. Para mover la guía de corte longitudinal (A), Fig. 40, a lo largo de la mesa, levante la palanca de bloqueo de la guía
(B), deslice la guía a la ubicación deseada en la mesa y presione la palanca de bloqueo de la guía (B) para trabar la
guía en su lugar.
2. Se proporciona un indicador para verificar la distancia entre la guía y la hoja de la sierra. Si se necesita ajustar el
indicador, afloje el tornillo (C), Fig. 40, que ajusta el indicador al soporte de la guía y ajuste el indicador como
corresponde. A continuación, ajuste el tornillo (C).
3. IMPORTANTE: LA GUÍA DE CORTE LONGITUDINAL DEBE ESTAR CORRECTAMENTE ALINEADA A LA
RANURA DEL CALIBRADOR DE INGLETE PARA EVITAR EL RETROCESO AL CORTAR
LONGITUDINALMENTE.
Page 63

63
4. La hoja de la sierra viene instalada de fábrica en forma paralela a la ranura del calibrador de inglete y la guía debe
estar en paralelo a la ranura del calibrador de inglete para poder realizar un trabajo exacto y evitar el retroceso al cortar
longitudinalmente. Para verificar la alineación:
5. Coloque la guía en un extremo de la ranura del calibrador de inglete. Asegure la guía a la mesa empujando la
palanca de bloqueo hacia abajo. El extremo de la guía debe estar alineado en forma paralela a la ranura del calibrador
de inglete.
6. Si es necesario realizar un ajuste, realice el siguiente procedimiento:
7. Afloje los dos tornillos de cabeza Allen de 4,8 mm (3/16 pulg.) (D) Fig. 40 y levante la palanca de bloqueo (B).
Mientras sostiene el soporte de la guía firmemente hacia el frente de la sierra, mueva la parte posterior de la guía (A)
hasta que quede paralela a la ranura del calibrador de inglete. Ajuste los dos tornillos (D) y empuje la palanca de
bloqueo hacia abajo (B).
8. La acción de sujeción de la guía (A), Fig. 40, puede ajustarse si levanta la palanca de bloqueo (B) y gira el tornillo
(E) en el sentido de las agujas del reloj para aumentar la acción de sujeción de la guía o en el sentido contrario de las
agujas del reloj para disminuirla.
AJUSTES Y OPERACIÓN DEL CALIBRADOR DE INGLETE
Para el corte transversal recto (con la hoja a 90 grados de la mesa), se puede utilizar el calibrador de inglete en
cualquiera de las ranuras de la mesa. Para el corte transversal biselado (hoja inclinada) sólo use el calibrador de inglete
en la ranura derecha de la mesa cuando la hoja esté inclinada lejos del calibrador de inglete y de sus manos.
El calibrador de inglete viene con topes indicadores regulables en forma individual a 90 grados y 45 grados a derecha
e izquierda. Puede ajustar los topes indicadores si afloja las tuercas de bloqueo (B), Fig. 41, y ajusta o afloja los tres
tornillos de ajuste (C) hasta que entren en contacto con el otro extremo de la clavija del tope (D) cuando el calibrador
de inglete esté a 90 y 45 grados de la hoja de la sierra. A continuación, ajuste las tuercas de bloqueo (B).
Para operar el calibrador de inglete, simplemente afloje la perilla de bloqueo (E), Fig. 41, y mueva el cuerpo del
calibrador de inglete al ángulo deseado. Al presionar la clavija del tope (D), el cuerpo del calibrador de inglete se
detendrá a 90 grados y a 45 grados a la derecha y a la izquierda. Para girar el cuerpo del calibrador de inglete más allá
de estos puntos, presione la clavija del tope hacia afuera (D).
AJUSTE DE LA HOJA EN PARALELO A LAS RANURAS DEL CALIBRADOR DE
INGLETE
La hoja viene instalada de fábrica en forma paralela a las ranuras del calibrador de inglete. Para garantizar cortes
precisos y prevenir el retroceso durante el corte, este ajuste debe verificarse nuevamente y, de ser necesario,
reajustarse de la siguiente manera:
1. DESCONECTE LA MÁQUINA DEL SUMINISTRO DE ENERGÍA.
2. Eleve la hoja hasta la posición más alta y ajústela de modo que quede a 90 grados de la mesa.
3. Seleccione un diente de la sierra que esté hacia la izquierda. Marque este diente con un lápiz o un rotulador.
4. Con una escuadra de combinación, coloque el cuerpo (A), Fig. 42, de la escuadra contra la ranura del calibrador de
inglete y ajuste la hoja (B) de la escuadra hasta que toque el diente marcado, como se muestra.
5. Gire la hoja y verifique el diente de la hoja marcada en la parte posterior de la mesa de la sierra de la misma forma,
como se muestra en la Fig. 43.
6. Si las mediciones delanteras y posteriores (Figs. 42 y 43) no son idénticas, puede ajustar la hoja. Comience
aflojando las tuercas debajo de los cuatro tornillos (C), Fig. 44, en la mesa. Luego afloje los tornillos (C). Mueva con
cuidado la hoja de la sierra hasta que quede paralela a la ranura del calibrador de inglete. Una vez hecho esto, ajuste
con firmeza las cuatro tuercas debajo de la mesa y los cuatro tornillos (C), Fig. 44.
NOTA: si no se puede obtener una regulación suficiente al aflojar los tornillos (C), también puede aflojar los tornillos (D)
si es absolutamente necesario para realizar el ajuste.
NOTA: la guarda se ha extraído con fines ejemplificativos solamente.
CAMBIO DE LA HOJA
DESCONECTE LA MÁQUINA DEL SUMINISTRO DE ENERGÍA. USE SOLAMENTE HOJAS DE
254 MM (10") DE DIÁMETRO CON ORIFICIOS PARA EL EJE DE 15,9 MM (5/8"), CON UNA
VELOCIDAD DE 5000 RPM O MAYOR.
1. Eleve la hoja de la sierra a la altura máxima y extraiga el inserto para mesa (A), Fig. 45.
2. Con la llave abierta (B), Fig. 45, colóquela en las partes planas en el interior de la brida de la hoja para evitar que el
eje de la sierra gire y retire la tuerca del eje (C) con la llave (D). Gire la tuerca (C) en el sentido contrario a las agujas del
reloj para extraerla. Quite la brida externa de la hoja (E) y la hoja de la sierra (F).
3. Ensamble la hoja nueva, asegúrese de que los dientes de la hoja apunten hacia abajo en la parte delantera de la
mesa de la sierra y ensamble la brida externa (E), Fig. 44, y la tuerca de eje (C). Ajuste la tuerca (C) con la llave (D)
girándola en el sentido de las agujas del reloj mientras sujeta el eje inmóvil con la otra
llave (B).
4. Vuelva a colocar el inserto para mesa.
Page 64

64
OPERACIONES MÁS COMUNES DE CORTE CON SIERRA
Las operaciones comunes de corte con sierra incluyen los cortes longitudinales y transversales, además de algunas
otras operaciones estándar fundamentales. Como sucede con todas las máquinas eléctricas, hay un determinado
margen de peligro relacionado con el funcionamiento y el uso de la máquina. El uso de la máquina de conformidad con
las medidas de seguridad, y con la precaución que éstas exigen, disminuirá considerablemente la posibilidad de
lesiones personales. No obstante, si no se presta la debida atención a las medidas de seguridad normales o se las
ignora por completo, el operador puede lesionarse. La siguiente información describe el método adecuado y seguro de
realizar las operaciones más comunes de corte con sierra.
EL USO DE SUPLEMENTOS Y ACCESORIOS NO RECOMENDADOS PUEDE PROVOCAR
RIESGOS DE LESIONES AL USUARIO O A OTRAS PERSONAS.
CORTE TRANSVERSAL
El corte transversal requiere el uso de un calibrador de inglete para guiar y ubicar la pieza de trabajo. Coloque la pieza
contra el calibrador de inglete y lleve el calibrador y la pieza hacia la hoja de la sierra, como muestra la Fig. 46. El
calibrador de inglete se puede usar en cualquiera de las dos ranuras de la mesa. Cuando realice un corte biselado
(con la hoja inclinada), utilice la ranura de la mesa que no interfiera con su mano o el calibrador de inglete con la guarda
de la hoja de la sierra.
Comience el corte lentamente y sostenga el trabajo con firmeza contra el calibrador de inglete y la mesa. Una de las
reglas para el funcionamiento de una sierra es que nunca debe tocar o colgarse de una pieza de trabajo suelta.
Sostenga la parte apoyada, no la parte suelta que se corta. La alimentación en el corte transversal continúa hasta que
el trabajo se corte en dos, y tanto el calibrador de inglete como el trabajo se vuelvan a colocar en el punto inicial. Antes
de eso, es aconsejable correr la pieza de trabajo un poco hacia un lado para alejarla ligeramente de la hoja de la sierra.
Nunca tome ningún trozo pequeño que quedó suelto en la mesa mientras la sierra está en funcionamiento. Nunca
toque una pieza cortada a menos que tenga por lo menos
30 cm (un pie) de longitud.
Para mayor seguridad y conveniencia, el calibrador de inglete puede ajustarse con un revestimiento de madera
auxiliar. Este revestimiento de madera auxiliar puede sujetarse al frente del calibrador de inglete con dos tornillos para
madera a través de las ranuras (A), Fig. 45, provistas en el cuerpo del calibrador y del revestimiento de madera.
NUNCA USE LA GUÍA COMO UN CALIBRADOR PARA EL CORTE TRANSVERSAL.
Cuando corte transversalmente un número de piezas de la misma longitud, puede fijar un bloque de madera (B), Fig. 46A, a
la guía y utilizarlo como calibrador de corte. Es importante que este bloque de madera siempre esté ubicado delante de la
hoja de la sierra como se muestra en la ilustración. Una vez determinada la longitud del corte, asegure la guía y utilice el
calibrador de inglete para introducir el trabajo en el corte. Este bloque de madera permite que la pieza cortada se mueva
libremente a lo largo de la superficie de la mesa sin quedar atascada entre la guía y la hoja de la sierra; de este modo, la
posibilidad de retroceso y lesiones al operador es menor.
CUANDO UTILICE EL BLOQUE (B), FIG. 46A, COMO CALIBRADOR DE CORTE, ES MUY
IMPORTANTE QUE EL EXTREMO POSTERIOR DEL BLOQUE ESTÉ UBICADO DE MODO QUE
LIBERE LA PIEZA DE TRABAJO ANTES DE QUE ÉSTA ENTRE EN CONTACTO CON LA HOJA.
CORTE LONGITUDINAL
El corte longitudinal se realiza a lo largo de una tabla. La guía de corte longitudinal (A), Fig. 47, se utiliza para posicionar
y guiar el trabajo. Un borde del trabajo corre contra la guía de corte longitudinal mientras que el lado plano de la tabla
descansa sobre la mesa. Debido a que el trabajo es empujado a lo largo de la guía, debe tener un borde recto y un
contacto firme con la mesa. Se debe usar la guarda de la hoja de la sierra. La guarda tiene seguros antirretroceso para
prevenir el retroceso y un hendedor para evitar que el corte de la madera se cierre y atasque la hoja.
1. Encienda el motor y haga avanzar el trabajo, sosteniéndolo hacia abajo y contra la guía. Nunca
se pare en la línea
de corte de la sierra mientras realiza el corte longitudinal. Sostenga el trabajo con ambas manos y empújelo a lo largo
de la guía y hacia la hoja de la sierra (Fig. 48). Luego puede introducirlo en la hoja de la sierra con una o ambas manos.
Después de que el trabajo pasó la hoja de la sierra y los seguros antirretroceso, retire la mano. Una vez terminado
esto, el trabajo quedará en la mesa, apenas inclinado y atrapado por el extremo de la guía posterior, o se deslizará de
la mesa al piso. Alternativamente, la alimentación puede continuar hasta el final de la mesa y después de eso, se
levanta el trabajo y se lo lleva junto al borde externo de la guía. El material cortado permanece en la mesa y no debe
tocarse hasta que se haya detenido la hoja de la sierra, a menos que la pieza sea grande y permita una remoción sin
peligro. Cuando se cortan longitudinalmente tablas de más de 90 cm (3 pies) de largo, se recomienda extender lo más
posible el soporte de avance de salida (B), Fig. 47, para evitar que la sierra se caiga de la mesa de la sierra.
2. Si el trabajo cortado longitudinalmente tiene menos de 10 cm (4 pulgadas) de ancho, siempre debe usarse una vara
para empujar completamente la alimentación, como se muestra en la Fig. 49. La vara para empujar puede realizarse
fácilmente a partir de material de desecho, según se explica en la sección “CONSTRUCCIÓN DE UNA VARA PARA
EMPUJAR".
3. El corte longitudinal de piezas angostas puede resultar peligroso si no se hace con cuidado. Generalmente, las
piezas angostas no pueden cortarse con la guarda en su lugar. Si la pieza de trabajo es muy corta, utilice una tabla
para empujar. Cuando corta material de un ancho menor a 5 cm (2 pulgadas), una tabla plana para empujar es un
accesorio provechoso, dado que las varas comunes pueden interferir con la guarda de la hoja. Cuando use una tabla
para empujar, se debe sumar el ancho de ésta al ancho de la configuración de la posición de la guía de corte
longitudinal. Una tabla plana para empujar puede construirse como se ve en la Fig. 50 y debe utilizarse como se
muestra en la Fig. 48.
Page 65

65
NOTA: algunas operaciones especiales requieren que se incorpore a la guía un revestimiento de madera auxiliar, como
se explica en la sección “UTILIZACIÓN DE UN REVESTIMIENTO DE MADERA EN LA GUÍA DE CORTE
LONGITUDINAL”, y el uso de una vara para empujar.
UTILIZACIÓN DE UN REVESTIMIENTO DE MADERA EN LA GUÍA DE CORTE
LONGITUDINAL
Los revestimientos de madera (A) Fig. 51, son necesarios en algunas operaciones especiales en uno o ambos lados de la
guía de corte longitudinal. El revestimiento de madera se sujeta a la guía con tornillos a través de los orificios de la guía. La
mayoría de los trabajos necesitarán material de 19,05 mm (3/4”), aunque algún trabajo eventual podría requerir un
revestimiento de 25,4 mm (1”).
CABEZAL PORTACUCHILLA ACCESORIO PARA RANURAS
NOTA: EL ANCHO MÁXIMO DE CORTE DE RANURAS PARA ESTA SIERRA ES DE 12,7 MM (1/2 PULGADA).
EL ENSAMBLE DE LA GUARDA DE LA HOJA Y EL HENDEDOR NO PUEDE SER UTILIZADO AL
REALIZAR RANURAS. DEBE EXTRAERSE.
Antes de ranurar, afloje la tuerca de mariposa (A), Fig. 52, y quite el conjunto de protector de la hoja y separador (B).
Tenga a mano el conjunto para colocarlo de nuevo después de ranurar.
1. Cortar ranuras consiste en realizar un rebajo o surco ancho en la pieza de trabajo. La mayoría de los juegos de
cabezales para ranuras están compuestos de dos sierras externas y cuatro o cinco cuchillas internas, (Fig. 53). Se
utilizan diversas combinaciones de sierras y cuchillas para cortar ranuras de 3,17 mm a 20,63 mm (1/8" a 13/16")
aproximadamente para la instalación de estantes y la realización de uniones, espigas, ranuras, etc. Las cuchillas son
muy dentadas y deben estar dispuestas de tal modo que la porción pesada caiga dentro de los pasos de las sierras
externas, como se muestra en la Fig. 54. La superposición de la sierra y la cuchilla se distingue en la Fig. 55, siendo
(A) la sierra externa, (B) una cuchilla interna y (C) una arandela o arandelas de papel, usadas según sea necesario para
controlar el ancho exacto de la ranura. Para cortar una ranura de 6,35 mm (1/4”) aproximadamente se utilizan dos
sierras externas. Los dientes de las sierras deben estar ubicados de manera que el rastrillador de una sierra quede
junto a los dientes de corte de la otra sierra.
2. Sujete el juego de cabezales para ranuras (D) Fig. 56, al eje de la sierra.
NOTA: LA BRIDA EXTERNA DEL EJE NO PUEDE UTILIZARSE CON EL JUEGO DE CABEZALES PARA RANURAS;
AJUSTE LA TUERCA DEL EJE CONTRA EL CUERPO DEL JUEGO DE CABEZALES PARA RANURAS. NO PIERDA
LA BRIDA EXTERNA DEL EJE. SERÁ NECESARIA AL REAJUSTAR UNA HOJA AL EJE.
EL INSERTO PARA MESA DEL JUEGO DE CABEZALES PARA RANURAS (E) FIG. 56, DEBE
UTILIZARSE EN LUGAR DEL INSERTO ESTÁNDAR.
EL ENSAMBLE DE GUARDA DE LA HOJA Y HENDEDOR NO PUEDE UTILIZARSE CUANDO SE
REALICEN CORTES DE RANURAS Y SE DEBE EXTRAER O LLEVAR HACIA LA PARTE
POSTERIOR DE LA SIERRA. ADEMÁS, SE DEBEN USAR BARRAS, ACCESORIOS, VARAS PARA EMPUJE Y
TABLAS DE CANTO BISELADO.
3. La Fig. 57 muestra una operación típica de corte de ranura con el calibrador de inglete como guía.
NUNCA UTILICE EL CABEZAL PARA RANURAS EN LA POSICIÓN DE BISELADO.
SIEMPRE INSTALE LA GUARDA DE LA HOJA LUEGO DE QUE HAYA FINALIZADO LA
OPERACIÓN.
Page 66

66
CONSTRUCCIÓN DE UNA TABLA DE CANTO BISELADO
La Fig. 58 ilustra las dimensiones para realizar una tabla de canto biselado típica. El material de la tabla de canto
biselado debe ser una pieza de madera recta que no tenga nudos ni grietas. Las tablas de canto biselado se utilizan
para mantener el trabajo en contacto con la guía y la mesa y para prevenir retrocesos. Sujete la tabla de canto biselado
a la guía y la mesa de modo que el borde guía de la tabla de canto biselado sostenga la pieza de trabajo hasta que se
complete el corte. Utilice tablas de canto biselado para todas las operaciones que no sean longitudinales o
transversales, donde el ensamble de guar
da y esparcidor debe extraerse (vea la Fig. 59). Siempre vuelva a colocar el
ensamble de guarda y esparcidor cuando la operación haya finalizado.
ASEGÚRESE DE SEGUIR LAS REGLAS E INSTRUCCIONES DE SEGURIDAD
PROBLEMA: LA SIERRA NO ENCIENDE
¿QUÉ SUCEDE? QUÉ HACER…
1. La sierra no está enchufada. 1. Enchufe la sierra.
2. Fusible quemado o interruptor 2. Reemplace el fusible o reinicie el
automático activado. interruptor automático.
3. Cable dañado. 3. Lleve al centro de mantenimiento autorizado para que le
cambien el cable.
4. Cepillos gastados. 4. Lleve al el centro de mantenimiento
autorizado para que le cambien los cepillos.
PROBLEMA: la sierra realiza cortes no satisfactorios
¿QUÉ SUCEDE? QUÉ HACER…
1. Hoja sin filo. 1. Reemplace la hoja.
2. Hoja montada al revés. 2. Gire la hoja.
3. Depósitos de goma o grumos 3. Retire la hoja y limpie con aguarrás.
de resina sobre la hoja.
4. Hoja incorrecta para el trabajo 4. Cambie la hoja.
que se realiza.
PROBLEMA: ! : LA HOJA NO ALCANZA VELOCIDAD
¿QUÉ SUCEDE? QUÉ HACER…
1. Cable prolongador demasiado 1. Reemplácelo por un cable de tamaño adecuado.
liviano o demasiado largo.
2. Baja corriente en el hogar. 2. Comuníquese con la empresa de energía eléctrica.
PROBLEMA: LA MÁQUINA VIBRA EXCESIVAMENTE.
¿QUÉ SUCEDE? QUÉ HACER…
1. La base está sobre un piso disparejo. 1. Reubique sobre una superficie plana.
2. Hoja de sierra dañada. 2. Reemplace la hoja.
PROBLEMA: NO REALIZA CORTES DE INGLETE PRECISOS
¿QUÉ SUCEDE? QUÉ HACER…
1. La escala de inglete no está 1. Verifíquela y ajústela.
correctamente regulada.
2. La hoja no está en escuadra con 2. Verifíquela y ajústela.
la guía.
3. La hoja no está perpendicular a 3. Verifique y ajuste la guía.
la mesa
4. La pieza de trabajo se mueve. 4.Sujete la pieza de trabajo a la guía o adhiera un papel de lija número
120 a la guía con cemento para caucho.
.
PROBLEMA: EL MATERIAL MUERDE LA HOJA
¿QUÉ SUCEDE? QUÉ HACER…
1. Corte de material curvado. 1. Posicione el material curvado
con el lado cóncavo o hueco hacia abajo.
2. La guía de corte longitudinal no 2. Vuelva a alinear la guía de corte longitudinal.
está paralela a la hoja.
PROBLEMA: NO SE PUEDE BLOQUEAR LA HOJA EN LA POSICIÓN DE BISELADO
¿QUÉ SUCEDE? QUÉ HACER…
1. El mango de bloqueo de inclinación 1. Retire la elevación y el descenso de la hoja con el volante.
de la hoja está demasiado suelto.
2. Retire el tornillo de cabeza plana del mango de bloqueo.
3. Ajuste el mango de bloqueo de inclinación de la hoja. El mango de bloqueo (A)
funciona a resorte y puede cambiar de posición si se desliza el mango hacia afuera
(A) y se vuelve a posicionar en la clavija dentada ubicada debajo del mango.
NOTA: después de ajustar, coloque el mango en la posición hacia abajo.
4. Vuelva a colocar el tornillo de cabeza plana.
GUÍA DE DETECCIÓN DE PROBLEMAS
Page 67

67
CORTE AQUI PARA EMPUJAR
†MADERA DE 1/4" (6.4 mm)
CORTE AQUI PARA EMPUJAR
†MADERA DE 1/2" (12.7 mm)
MUESCA PARA AYUDAR
A PREVENIR QUE LA
MANO SE RESBALE
CUADROS DE 1/2"
(12.7 mm)
VARA DE EMPUJE
HAGASE DE MADERA DE 1/2" O 3/4"
(12.7 ó 19 mm) O UN ESPESOR
MENOR QUE LA ANCHURA DEL
MATERIAL A SER CORTADO.
Cuando realice un corte longitudinal en una pieza con un ancho menor a 10 cm (4 pulgadas), puede utilizar una vara para
empujar a fin de completar la introducción en la hoja. Esta vara se puede hacer fácilmente con material de desecho, siguiendo
la ilustración de la Fig. 60.
Fig. 59
CONSTRUCCIÓN DE UNA VARA PARA EMPUJAR
Page 68

68
ACCESORIOS
Los accesorios que se recomiendan para la herramienta están disponibles en su distribuidor local o en el centro de mantenimiento
autorizado. Si necesita ayuda con respecto a los accesorios, llame al: (55)5326-7100.
el uso de accesorios no recomendados para utilizar con esta herramienta puede resultar peligroso.
Mantenimiento
Para limpiar la herramienta, sólo utilice jabón suave y un paño húmedo. Nunca permita que penetre líquido dentro de la herramienta y
nunca sumerja ninguna de las piezas en un líquido.
IMPORTANTE: para garantizar la SEGURIDAD y CONFIABILIDAD del producto, las reparaciones, el mantenimiento y los ajustes (los
que no estén enumerados en este manual) se deben realizar en los centros de mantenimiento autorizados o en otras organizaciones
de mantenimiento calificadas, utilizando siempre piezas de repuesto idénticas.
Información de mantenimiento
Black & Decker ofrece una amplia red de puntos de servicio propios y autorizados en toda Norteamérica. Todos los Centros de
mantenimiento de Black & Decker cuentan con personal altamente capacitado dispuesto a brindar a todos los clientes un servicio
eficiente y confiable en la reparación de herramientas eléctricas.
Si necesita consejo técnico, reparaciones o piezas de repuesto originales de fábrica, póngase en contacto con el centro de
mantenimiento de Black & Decker más cercano a su domicilio.
Para ubicar a su servicio local, consulte “Herramientas eléctricas” (Tools-Electric) en la sección amarilla, o llame al: (55)5326-7100
www.blackanddecker.com
Garantía completa de dos años para uso en el hogar
Black & Decker (EE.UU.) Inc. ofrece una garantía de dos años por cualquier defecto del material o de fabricación de este producto. El
producto defectuoso se reparará o reemplazará sin costo alguno de una de las siguientes maneras:
La primera opción, el reemplazo, es devolver el producto al comercio donde se lo adquirió (siempre y cuando se trate de un comercio
participante). Las devoluciones deben realizarse conforme a la política de devolución del comercio (generalmente, entre 30 y 90 días
posteriores a la venta). Le pueden solicitar comprobante de compra. Consulte en el comercio acerca de la política especial sobre
devoluciones una vez excedido el plazo establecido.
La segunda opción es llevar o enviar el producto (con flete pago) a un Centro de mantenimiento propio o autorizado de
Black & Decker para su reparación o reemplazo según nuestro criterio. Le pueden solicitar comprobante de compra. Encontrará una
lista de los centros de mantenimiento autorizados y de propiedad de Black & Decker en "Herramientas eléctricas" en las páginas
amarillas de la guía telefónica.
Esta garantía no se extiende a los accesorios. Esta garantía le concede derechos legales específicos que pueden variar según el
estado. Ante cualquier inquietud, comuníquese con el Centro de mantenimiento de Black & Decker más cercano.
Este producto no es para uso comercial.
REEMPLAZO GRATUITO DE LAS ETIQUETAS DE ADVERTENCIA: Si sus etiquetas de advertencia se vuelven ilegibles o faltan,
llame al (55)5326-7100 para que se le reemplacen gratuitamente.
Nota especial sobre la GARANTÍA a contratistas:
Los productos de marca FIRESTORMTMson herramientas de uso doméstico de calidad e incluyen una GARANTÍA POR USO
DOMÉSTICO. Estas herramientas han sido diseñadas, fabricadas y probadas para satisfacer y superar las necesidades de los
aficionados a trabajos independientes, en la ejecución de proyectos y la realización de reparaciones en toda la casa. Si las utiliza
correctamente, le proporcionarán potencia y rendimiento superiores mucho después de los dos años de garantía. Sin embargo, si
usted utiliza las herramientas para trabajar y usa productos de marca FIRESTORM
TM
o cualquier otra herramienta Black & Decker
para uso doméstico en sitios de trabajo, debe saber que NO ESTARÁN CUBIERTAS POR NUESTRA GARANTÍA.
CULIACAN, SIN
Av. Nicolás Bravo #1063 Sur
(667) 7 12 42 11
Col. Industrial Bravo
GUADALAJARA, JAL
Av. La Paz #1779
(33) 3825 6978
Col. Americana Sector Juarez
MEXICO, D.F.
Eje Central Lázaro Cardenas
No. 18
(55) 5588 9377
Local D, Col. Obrera
MERIDA, YUC
Calle 63 #459-A
(999) 928 5038
Col. Centro
MONTERREY, N.L.
Av. Francisco I. Madero
No.831
(81) 8375 2313
Col. Centro
PUEBLA, PUE
17 Norte #205
(222) 246 3714
Col. Centro
QUERETARO, QRO
Av. Madero 139 Pte.
(442) 214 1660
Col. Centro
SAN LUIS POTOSI, SLP
Av. Universidad 1525
(444) 814 2383
Col. San Luis
TORREON, COAH
Blvd. Independencia, 96 Pte.
(871) 716 5265
Col. Centro
VERACRUZ, VER
Prolongación Díaz Mirón #4280
(229)921 7016
Col. Remes
VILLAHERMOSA, TAB
Constitución 516-A
(993) 312 5111
Col. Centro
PARA OTRAS LOCALIDADES LLAME AL: (55) 5326 7100
Para reparación y servicio de sus herramientas eléctricas, favor de dirigirse al Centro de Servicio más
cercano:
SECCI N
AMARILLA
Si funciona…
y funciona muy bien.
Para servicio y ventas consulte
“HERRAMIENTAS ELECTRICAS”
en la sección amarilla.
IMPORTADOR: BLACK & DECKER S.A. DE C.V.
BOSQUES DE RADIATAS NO. 42
BOSQUES DE LAS LOMAS, 05120 MEXICO,
D.F.
TEL (55)5326-7100
ESPECIFICACIONES
120V
60 Hz
15 A
1674 W
 Loading...
Loading...