Page 1

PROGRAMMING MANUAL
Digital Storage Oscilloscope
MODEL: 2550 Series (2552, 2553, 2554, 2555, 2556, 2557,
2558, 2559)
Page 2

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Using Status Registers ................................................... 3
About these Commands & Queries ................................ 3
How they are listed? ................................................................................................. 3
How they are described? ........................................................................................... 3
Command Notation .......................................................... 4
Table of Commands & Queries ....................................... 5
Commands & Queries ................................................... 11
Index ............................................................................. 131
2
Page 3

Using Status Registers
A wide range of status registers allows the oscilloscope’s internal processing status to be
determined quickly at any time. These registers and the instrument’s status reporting system are
designed to comply with IEEE 488.2 recommendations. Following an overview, starting this
page, each of the registers and their roles are described.
Related functions are grouped together in common status registers. Some, such as the Status
Byte Register (STB) or the Standard Event Status Register (ESR), are required by the IEEE
488.2 Standard. Other registers are device-specific, and include the Command Error Register
(CMR) and Execution Error Register (EXR). Those commands associated with IEEE 488.2
mandatory status registers are preceded by an asterisk <*>.
About these Commands & Queries
This section lists and describes the remote control commands and queries recognized by the
instrument. All commands and queries can be executed in either local or remote state.
The description for each command or query, with syntax and other information, begins on a new
page. The name (header) is given in both long and short form at the top of the page, and the
subject is indicated as a command or query or both. Queries perform actions such as obtaining
information, and are recognized by the question mark (?) following the header.
How they are listed?
The descriptions are listed in alphabetical order according to their long form. Thus the
description of ATTENUATION, whose short form is ATTN, is listed before that of AUTO
SETUP, whose short form is ASET.
How they are described?
In the descriptions themselves, a brief explanation of the function performed is given. This is
3
Page 4

followed by a presentation of the formal syntax, with the header given in Upper-and-LowerCase characters and the short form derived from it in ALL UPPER-CASE characters. Where
applicable, the syntax of the query is given with the format of its response.
sd
Command Notation
The following notation is used in the commands:
< > Angular brackets enclose words that are used as placeholders, of
which there are two types: the header path and the data parameter
of a command.
: = A colon followed by an equals sign separates a placeholder from
the description of the type and range of values that may be used in
a command instead of the placeholder.
{} Braces enclose a list of choices, one of which one must be made.
[ ] Square brackets enclose optional items.
… An ellipsis indicates that the items both to its left and right may be
repeated a number of times.
As an example, consider the syntax notation for the command to set the vertical input sensitivity:
<channel>:VOLT_DIV <v_gain>
<channel> : = {C1, C2, C3, C4}
<v_gain>: = 2 mV to 5 V
The first line shows the formal appearance of the command, with <channel> denoting the
placeholder for the header path and <v_gain> the placeholder for the data parameter specifying
the desired vertical gain value. The second line indicates that one of four channels must be
chosen for the header path. And the third explains that the actual vertical gain can be set to any
value between 2 mV and 5 V.
4
Page 5
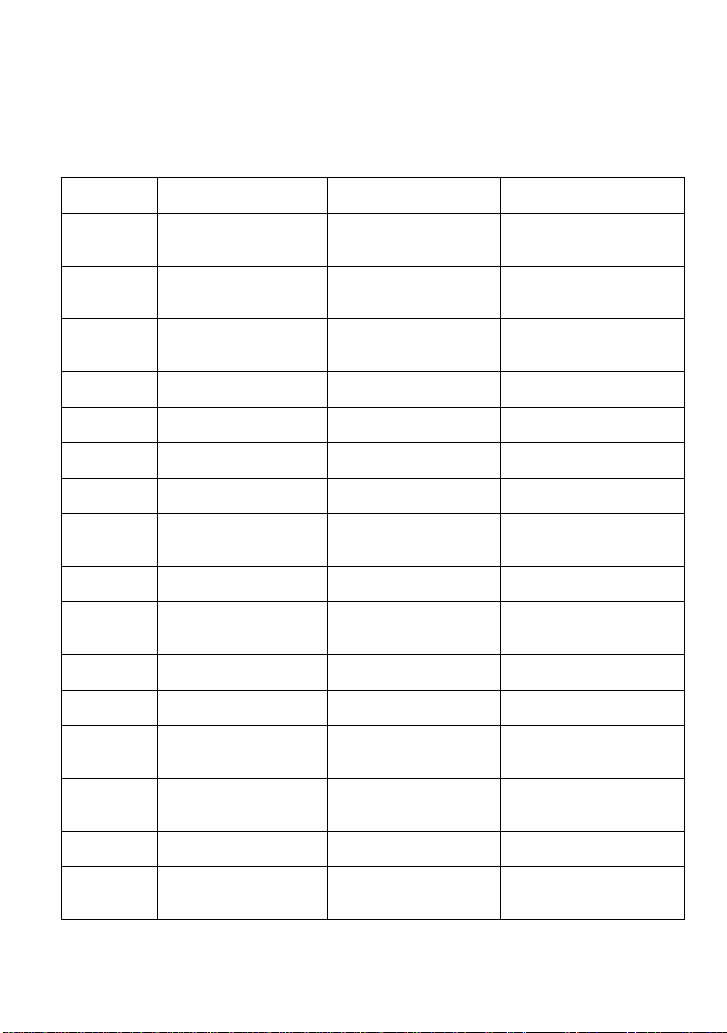
Short Form
Long Form
Subsystem
What the Command or
Query Does
ALST?
ALL_STATUS?
STATUS
Reads and clears
the contents of all
status registers.
ARM
ARM_ACQUISITION
ACQUISITION
Changes acquisition state
from “stopped” to
“single”.
ATTN
ATTENUATION
ACQUISITION
Selects the vertical
attenuation factor of the
probe
ACAL
AUTO_CALIBRATE
MISCELLANEOUS
Enables or disables
automatic calibration.
ASET
AUTO_SETUP
ACQUISITION
Adjusts vertical, time base
and trigger parameters.
AUTTS
AUTO_TYPESET
ACQUISITION
Selects the display type of
automatic setup.
AVGA
AVERAGE_ACQUIRE
ACQUISITION
Selects the average times
of average acquisition.
BWL
BANDWIDTH_LIMIT
ACQUISITION
Enables/disables the
bandwidth-limiting lowpass filter.
BUZZ
BUZZER
MISCELLANEOUS
Controls the built-in
piezo-electric buzzer.
*CAL?
*CAL?
MISCELLANEOUS
Performs complete
internal calibration of the
instrument.
CHDR
COMM_HEADER
COMMUNICATION
Controls formatting of
query responses.
*CLS
*CLS
STATUS
Clears all status data
registers.
CMR?
CMR?
STATUS
Reads and clears the
Command error Register
(CMR).
CONET
COMM_NET
COMMUNICATION
Specifies network
addresses of scope and
printers.
CPL
COUPLING
ACQUISITION
Selects the specified input
channel’s coupling mode.
CRMS
CURSOR_MEASURE
CURSOR
Specifies the type of
cursor/parameter
measurement.
Table of Commands & Queries
5
Page 6
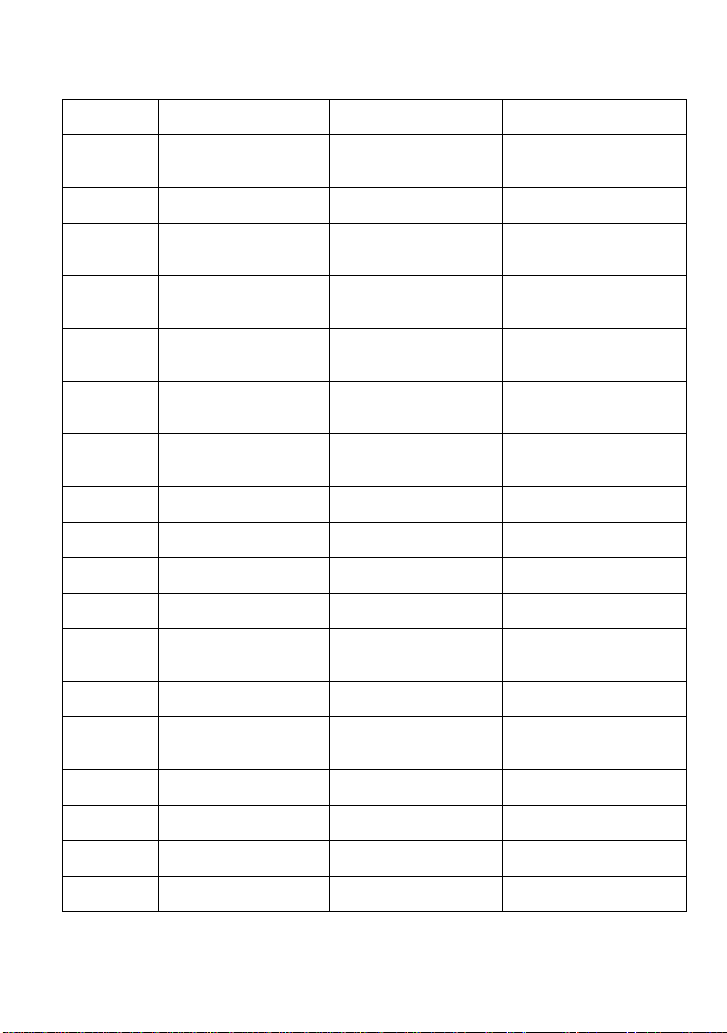
CRST?
CURSOR_SET?
CURSOR
Allows positioning of any
one of eight cursors.
CRVA?
CURSOR_VALUE?
CURSOR
Returns trace values
measured by specified
cursors.
CRAU
CURSOR_AUTO
CURSOR
Changes the cursor mode
to auto mode.
CSVS
CSV_SAVE
SAVE/RECALL
Saves specified waveform
data of CSV format to
USB device.
COUN
COUNTER
FUNCTION
Enables or disables the
cymometer to display on
the screen.
CYMT
CYMOMETER
FUNCTION
Returns the current
cymometer value which
displaying on the screen.
DATE
DATE
MISCELLANEOUS
Changes the date/time of
the internal real-time
clock.
DDR?
DDR?
STATUS
Clears the Device
Dependent Register
(DDR).
DEF
DEFINE?
FUNCTION
Specifies math expression
for function evaluation.
DELF
DELETE_FILE
MASS STORAGE
Deletes files from mass
storage.
DIR
DIRECTORY
MASS STORAGE
Creates and deletes file
directories.
DTJN
DOT_JOIN
DISPLAY
Controls the interpolation
lines between data points.
*ESE
*ESE
STATUS
Sets the Standard Event
Status Enable register
(ESE).
*ESR?
*ESR?
STATUS
Reads, clears the Event
Status Register (ESR).
EXR?
EXR?
STATUS
Reads, clears the
Execution error Register
(EXR).
FLNM
FILENAME
MASS STORAGE
Changes default
filenames.
FRTR
FORCE_TRIGGER
ACQUISITION
Forces the instrument to
make one acquisition.
FVDISK
FORMAT_VDISK
MASS STORAGE
Reads the capability of the
USB device.
FILT
FILTER
FUNCTION
Enables or disables the
filter of specified source.
6
Page 7
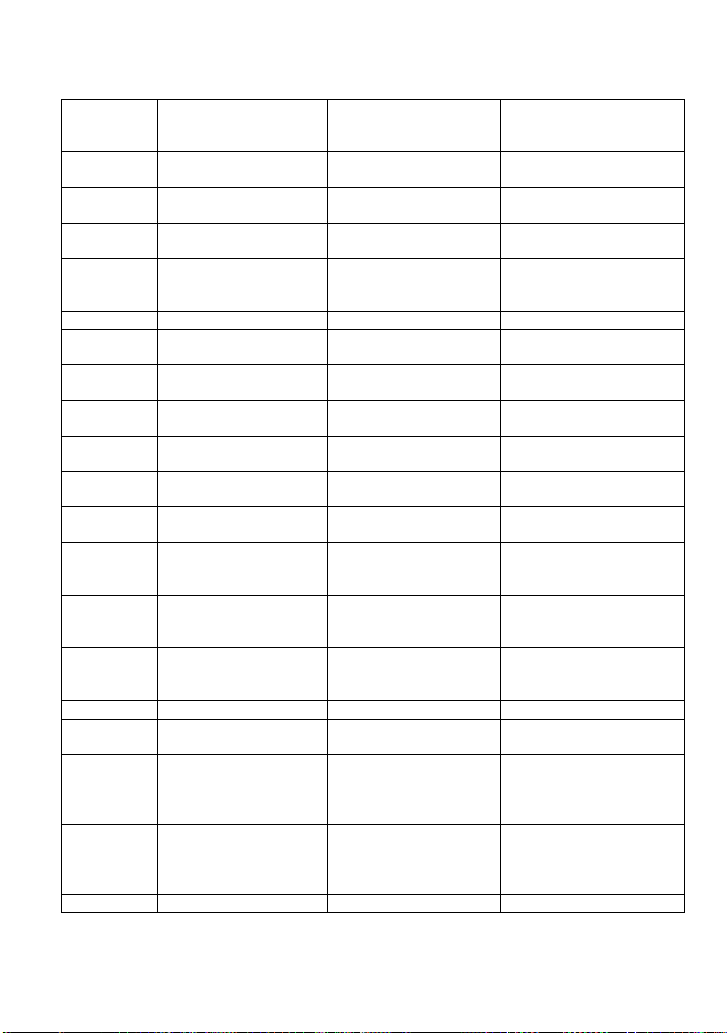
FILTS
FILT_SET
FUNCTION
Selects the type of filter,
and sets the limit value of
filter.
FFTW
FFT_WINDOW
FUNCTION
Selects the window of
FFT.
FFTZ
FFT_ZOOM
FUNCTION
Selects the zoom in/out
times of FFT trace.
FFTS
FFT_SCALE
FUNCTION
Selects the vertical scale
of FFT trace.
FFTF
FFT_FULLSCREEN
FUNCTION
Enables or disables to
display the FFT trace full
screen.
GRDS
GRID_DISPLAY
DISPLAY
Selects the type of grid
GCSV
GET_CSV
WAVEFORMTRANS
Specifies waveform data
of format to controller.
HMAG
HOR_MAGNIFY
DISPLAY
Horizontally expands the
selected expansion trace.
HPOS
HOR_POSITION
DISPLAY
Horizontally positions
intensified zone’s center.
HCSU
HARDCOPY_SETUP
HARD COPY
Configures the hard-copy
driver.
*IDN?
*IDN?
MISCELLANEOUS
For identification
purposes.
INTS
INTENSITY
DISPLAY
Sets the grid or trace/text
intensity level.
ILVD
INTERLEAVED
ACQUISITION
Enables/disables random
interleaved sampling
(RIS).
INR?
INR?
STATUS
Reads, clears INternal
state change Register
(INR).
INVS
INVERT_SET
DISPLAY
Invert the trace or the
math waveform of
specified source.
LOCK
LOCK
MISCELLANEOUS
Lock keyboard
MENU
MENU
DISPLAY
Enables or disables to
display the current menu.
MTVP
MATH_VERT_POS
ACQUISITION
Controls the vertical
position of math
waveform of specified
source.
MTVD
MATH_VERT_DIV
ACQUISITION
Controls the vertical
sensitivity of math
waveform of specified
source.
MEAD
MEASURE_DELY
FUNCTION
Selects the type of delay
7
Page 8
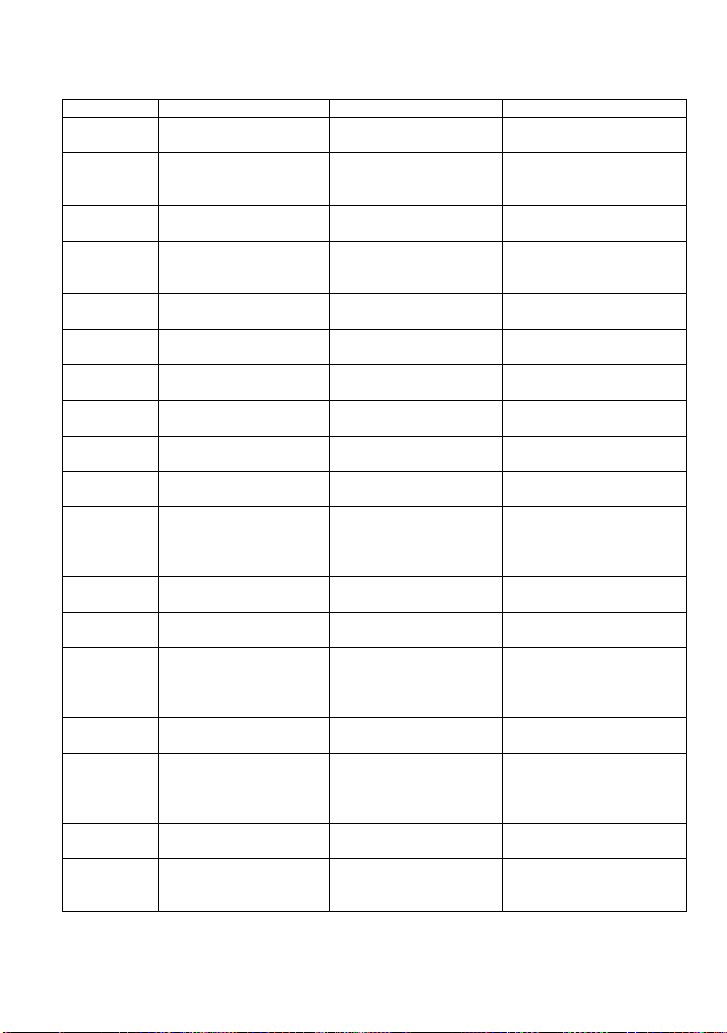
measure.
OFST
OFFSET
ACQUISITION
Allows output channel
vertical offset adjustment.
*OPC
*OPC
STATUS
Sets the OPC bit in the
Event Status Register
(ESR).
*OPT?
*OPT?
MISCELLANEOUS
Identifies oscilloscope
options.
PACL
PARAMETER_CLR
CURSOR
Clears all current
parameters in Custom,
Pass/Fail.
PACU
PARAMETER_CUSTO
M
CURSOR
Controls parameters with
customizable qualifiers.
PAVA?
PARAMETER_VALU
E?
CURSOR
Returns current parameter,
mask test values.
PDET
PEAK_DETECT
ACQUISITION
Switches the peak detector
ON and OFF.
PERS
PERSIST
DISPLAY
Enables or disables the
persistence display mode.
PESU
PERSIST_SETUP
DISPLAY
Selects display persistence
duration.
PNSU
PANEL_SETUP
SAVE/RECALL
Complements the
*SAV/*RST commands.
PFDS
PF_DISPLAY
FUNCTION
Enables or disables to
display the test and the
message options of
pass/fail.
PFST
PF_SET
FUNCTION
Sets the X mask and the Y
mask.
PFSL
PF_SAVELOAD
SAVE/RECALL
Saves or recalls the
created mask setting.
PFCT
PF_CONTROL
FUNCTION
Selects the “operate”,
“output” and the “stop on
output” which are the
options of pass/fail.
PFCM
PF_CREATEM
FUNCTION
Creates the mask of the
pass/fail.
PFDD
PF_DATEDIS
FUNCTION
Return the number of the
pass/fail monitor which
can be displayed on the
screen.
*RCL
*RCL
SAVE/RECALL
Recalls one of five nonvolatile panel setups.
REC
RECALL
WAVEFORMTRANS
Recalls a file from mass
storage to internal
memory.
8
Page 9
RCPN
RECALL_PANEL
SAVE/RECALL
Recalls a front-panel setup
from mass storage.
*RST
*RST
SAVE/RECALL
The *RST command
initiates a device reset.
REFS
REF_SET
FUNCTION
Sets the reference
waveform and its options.
*SAV
*SAV
SAVE/RECALL
Stores current state in nonvolatile internal memory.
SCDP
SCREEN_DUMP
HARD COPY
Causes a screen dump to
controller.
SCSV
SCREEN_SAVE
DISPLAY
Controls the automatic
screen saver.
*SRE
*SRE
STATUS
Sets the Service Request
Enable register (SRE).
*STB?
*STB?
STATUS
Reads the contents of
IEEE 488.
STOP
STOP
ACQUISITION
Immediately stops signal
acquisition.
STO
STORE
WAVEFORMTRANS
Stores a trace in internal
memory or mass storage.
STPN
STORE_PANEL
SAVE/RECALL
Stores front-panel setup to
mass storage.
STST
STORE_SETUP
WAVEFORMTRANS
Controls the way in which
traces are stored.
SAST
SAMPLE_STATUS
ACQUISITION
Return the acquisition
status of the scope
SARA
SAMPLE_RATE
ACQUISITION
Return the sample rate of
the scope
SANU
SAMPLE_NUM
ACQUISITION
Return the number of
sampled points available
from last acquisition and
the trigger position
SKEW
SKEW
ACQUISITION
Sets the skew of specified
trace.
SET50
SETTO%50
FUNCTION
Sets the trigger level of the
trigger source to the centre
of the signal amplitude.
SXSA
SINXX_SAMPLE
ACQUISITION
Sets the type of the
interpolation.
TDIV
TIME_DIV
ACQUISITION
Modifies the time base
setting.
TMPL
TEMPLATE
WAVEFORM
TRANSFER
Produces a complete
waveform template copy.
TRA
TRACE
DISPLAY
Enables or disables the
display of a trace.
*TRG
*TRG
ACQUISITION
Executes an ARM
9
Page 10
command.
TRCP
TRIG_COUPLING
ACQUISITION
Sets the coupling mode of
the specified trigger
source.
TRDL
TRIG_DELAY
ACQUISITION
Sets the time at which the
trigger is to occur.
TRLV
TRIG_LEVEL
ACQUISITION
Adjusts the trigger level of
the specified trigger
source.
TRMD
TRIG_MODE
ACQUISITION
the trigger mode.
TRSE
TRIG_SELECT
ACQUISITION
Selects the condition that
will trigger acquisition.
TRSL
TRIG_SLOPE
ACQUISITION
Sets the trigger slope of
the specified trigger
source.
UNIT
UNIT
ACQUISITION
Sets the unit of specified
trace.
VPOS
VERT_POSITION
DISPLAY
Adjusts the vertical
position of the FFT trace.
VDIV
VOLT_DIV
ACQUISITION
Sets the vertical
sensitivity.
VTCL
VERTICAL
ACQUISITION
Controls the vertical
position of the slope
trigger line.
WF
WAVEFORM
WAVEFORMTRANS
Gets the waveform from
the instrument.
WFSU
WAVEFORM_SETUP
WAVEFORMTRANS
Specifies amount of
waveform data to go to
controller.
WAIT
WAIT
ACQUISITION
Prevents new analysis
until current has been
completed.
XYDS
XY_DISPLAY
DISPLAY
Enables or disables to
display the XY format
10
Page 11

STATUS
ALL_STATUS?, ALST?
Query
Commands & Queries
DESCRIPTION The ALL_STATUS? Query reads and clears the
QUERY SYNTAX ALl_STatus?
RESPONSE FORMAT ALl_STatus
EXAMPLE The following instruction reads the contents of all the
ALST?
RELATED COMMANDS *CLS, CMR? , DDR? ,*ESR? , EXR? , *STB? , URR?
contents of all status registers: STB, ESR, INR,
DDR, CMR, EXR and URR except for the
MAV bit (bit 6) of the STB register. For an
interpretation of the contents of each register,
refer to the appropriate status register.
The ALL_STATUS? Query is useful in a complete
overview of the state of the instrument.
STB,<value>,ESR,<value>,INR,<value>,DDR,<valu
e>,CMR,<value>,EXR,<value>,URR,<value>
<value> : = 0 to 65535
status registers:
Command message:
Response message:
ALST STB, 0, ESR, 52, INR, 5, DDR, 0, CMR, 4,
EXR, 24, URR, 0
11
Page 12

ACQUISITION
ARM_ACQUISITION, ARM
Command
DESCRIPTION The ARM_ACQUISITION command enables the
signal acquisition process by changing the
acquisition state (trigger mode) from “stopped” to
“single”.
COMMAND SYNTAX ARM acquisition
EXAMPLE The following command enables signal acquisition:
Command message:
ARM
RELATED COMMANDS STOP, *TRG, TRIG_MODE, WAIT
12
Page 13

ACQUISITION
ATTENUATION, ATTN
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The ATTENUATION command selects the vertical
attenuation factor of the probe. Values of 1, 5, 10, 50,
100, 500, and 1000 may be specified.
The ATTENUATION? Query returns the
attenuation factor of the specified channel.
COMMAND SYNTAX <channel>: ATTeNuation <attenuation>
<channel> : = {C1, C2, C3, C4}
<attenuation>: = {1, 5, 10, 50, 100, 500, 1000}
QUERY SYNTAX <channel>: ATTeNuation?
RESPONSE FORMAT <channel>: ATTeNuation <attenuation>
EXAMPLE The following command sets to 100 the
attenuation factor of Channel 1:
Command message:
C1:ATTN 100
13
Page 14

AUTO_CALIBRATE, ACAL
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The AUTO_CALIBRATE command is used to enable
or disable the quick calibration of the instrument.
The quick calibration may be disabled by issuing the
command ACAL OFF. Whenever it is convenient, a
*CAL? Query may be issued to fully calibrate the
oscilloscope.
The response to the AUTO_CALIBRATE?
Query indicates whether quick -calibration is enabled.
The command is only used in the CFL series
instrument.
COMMAND SYNTAX Auto_CALibrate <state>
<state> : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX Auto_CALibrate?
RESPONSE FORMAT Auto_CALibrate <state>
EXAMPLE The following instruction disables quick-calibration:
Command message:
ACAL OFF
RELATED COMMANDS *CAL?
14
Page 15

ACQUISITION
AUTO_SETUP, ASET
Command
DESCRIPTION The AUTO_SETUP command attempts to identify
the waveform type and automatically adjusts controls
to produce a usable display of the input signal.
COMMAND SYNTAX AUTO_SETUP
EXAMPLE The following command instructs the oscilloscope
to perform an auto-setup:
Command message:
ASET
RELATED COMMANDS AUTTS
15
Page 16

ACQUISITION
AUTO_TYPESET, AUTTS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The AUTO_TYPESET command selects the
specified type of automatically adjusting which is
used to display.
COMMAND SYNTAX AUTO_TYPESET <type>
<type> : = {SP,MP,RS,DRP,RC}
SP means only one period to be displayed, MP means
multiple periods to be displayed, RS means the
waveform is triggered on the rise side, DRP means
the waveform is triggered on the drop side, and RC
means to go back to the state before auto set.
QUERY SYNTAX AUTO_TYPESET?
RESPONSE FORMAT AUTO_TYPESET <type>
EXAMPLE The following command sets the type of automatic
adjustment to multiple periods:
Command message:
AUTTS MP
RELATED COMMANDS ASET
16
Page 17

ACQUISITION
AVERAGE_ACQUIRE, AVGA
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The AVERAGE_ACQUIRE command selects the
average times of average acquisition.
The response to the AVERAGE_ACQUIRE query
indicates the times of average acquisition.
COMMAND SYNTAX AVERAGE_ACQUIRE <time>
<time> : = {4, 16, 32, 64,128,256}
QUERY SYNTAX AVERAGE_ACQUIRE?
RESPONSE FORMAT AVERAGE_ACQUIRE <time>
EXAMPLE The following turns the average times of average
acquisition 16:
Command message:
AVGA 16
17
Page 18

ACQUISITION
BANDWIDTH_LIMIT, BWL
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION BANDWIDTH_LIMIT enables or disables the
bandwidth-limiting low-pass filter. If the bandwidth
filters are on, it will limit the bandwidth to reduce
display noise. When you turn Bandwidth Limit ON,
the Bandwidth Limit value is set to 20 MHz. It also
filters the signal to reduce noise and other unwanted
high frequency components.
The response to the BANDWIDTH_LIMIT? Query
indicates whether the bandwidth filters are on or off.
COMMAND SYNTAX BandWidth_Limit <channel>, <mode>
[, <channel>, <mode> [, <channel>, <mode>
[, <channel>, <mode>]]]
<channel> : = {C1, C2, C3, C4}
<mode> : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX BandWidth_Limit?
RESPONSE FORMAT BandWidth_Limit <channel>, <mode> [, <channel>,
<mode> [, <channel>, <mode> [, <channel>,
<mode>]]]
EXAMPLE The following turns on the bandwidth filter for all
channels, when Global_BWL is on (as it is by default
The following turns the bandwidth filter on for
Channel 1only:
Command message:
BWL C1, ON
18
Page 19

MISCELLANEOUS
BUZZER, BUZZ
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The BUZZER command enables or disables sound
switch.
The response to the BUZZER? query indicates
whether the sound switch is enabled.
COMMAND SYNTAX BUZZer <state>
<state> : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX BUZZER?
RESPONSE FORMAT BUZZER <state>
EXAMPLE Sending the following code will let the oscilloscope
turn on the sound switch.
Command message:
BUZZ ON
19
Page 20

MISCELLANEOUS
*CAL?
Query
DESCRIPTION The *CAL? query cause the oscilloscope to perform
an internal self-calibration and generates a response.
QUERY SYNTAX *CAL?
RESPONSE FORMAT *CAL <diagnostics>
<diagnostics> : = 0
0 = Calibration successful
EXAMPLE The following instruction forces a self-calibration:
Command message:
*CAL?
Response message:
*CAL 0
RELATED COMMANDS AUTO_CALIBRATE
20
Page 21

COMM_HEADER, CHDR
Command/ Query
DESCRIPTION The COMM_HEADER command controls the way
the oscilloscope formats responses to queries. There
are three response formats: LONG, in which
responses start with the long form of the header word;
SHORT, where responses start with the short form of
the header word; and OFF, for which headers are
omitted from the response and units in numbers are
suppressed.
Unless you request otherwise, the SHORT response
format is used.
This command does not affect the interpretation of
messages sent to the oscilloscope. Headers can be
sent in their long or short form regardless of the
COMM_HEADER setting.
Querying the vertical sensitivity of Channel 1 may
result in one of the following responses:
COMM_HEADER RESPONSE
LONG C1:VOLT_DIV 200E-3 V
SHORT C1:VDIV 200E-3 V
OFF 200E-3
COMMAND SYNTAX Comm_HeaDeR <mode>
<mode> : = {SHORT, LONG, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX Comm_HeaDeR?
RESPONSE FORMAT Comm_HeaDeR <mode>
EXAMPLE The following code sets the response header format
to SHORT:
Command message:
CHDR SHORT
21
Page 22

*CLS
Command
DESCRIPTION The *CLS command clears all the status data
registers.
COMMAND SYNTAX *CLS
EXAMPLE The following command causes all the status data
registers to be cleared:
Command message:
*CLS
RELATED COMMANDS ALL_STATUS, CMR, DDR, *ESR, EXR, *STB, URR
22
Page 23

CMR?
Query
DESCRIPTION The CMR? Query reads and clears the contents of
the Command error Register (CMR) see table
next page---which specifies the last syntax error
type detected by the instrument.
QUERY SYNTAX CMR?
RESPONSE FORMAT CMR <value>
<value> : = 0 to 14
EXAMPLE The following instruction reads the contents of
the CMR register:
Command message:
CMR?
Response message:
CMR 0
RELATED COMMANDS ALL_STATUS? ,*CLS
23
Page 24
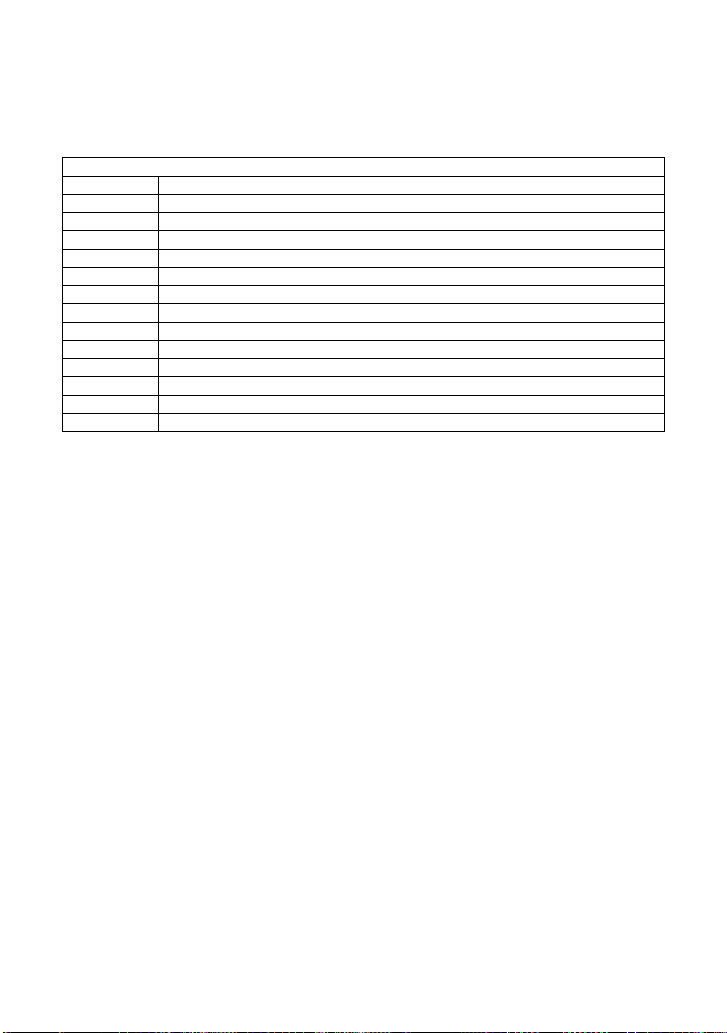
Command Error Status Register Structure (CMR)
Value
Description
1
Unrecognized command/query header
2
Invalid character
3
Invalid separator
4
Missing parameter
5
Unrecognized keyword
6
String error
7
Parameter cannot allowed
8
Command String Too Long
9
Query cannot allowed
10
Missing Query mask
11
Invalid parameter
12
Parameter syntax error
13
Filename too long
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Command Error Status Register Structure (CMR)
24
Page 25

MISCELLANEOUS
COMM_NET, CONET
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The COMM_NET command changes the IP
address of the oscilloscope’s internal network
interface.
The COMM_NET? query returns the IP address
of the oscilloscope’s internal network interface.
COMMAND SYNTAX COMM_NET <ip_add0>, <ip_add1>,
<ip_add2>, <ip_add3>
< ip_add >:= 0 to 255
QUERY SYNTAX COMM_NET?
RESPONSE FORMAT COMM_NET <ip_add0>, <ip_add1>,
<ip_add2>, <ip_add3>
EXAMPLE This instruction will change the IP address to
10.11.0.230:
Command message:
CONET 10,11,0,230
25
Page 26

ACQUISITION
COUPLING, CPL
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The COUPLING command selects the
coupling mode of the specified input channel.
The COUPLING? query returns the coupling
mode of the specified channel.
COMMAND SYNTAX <channel>: CouPLing <coupling>
<channel> : = {C1, C2, C3, C4}
<coupling> : = {A1M, A50, D1M, D50, GND}
The A of the <coupling> is alternating current.
The D of the <coupling> is direct current.1M
and 50 is the impedance of input. Some series
(CML) couldn’t have the set of input
impedance.
QUERY SYNTAX <channel>: CouPLing?
RESPONSE FORMAT <channel>: CouPLing <coupling>
EXAMPLE The following command sets the coupling of
Channel 2 to 50 ΩDC:
Command message:
C2: CPL D50
26
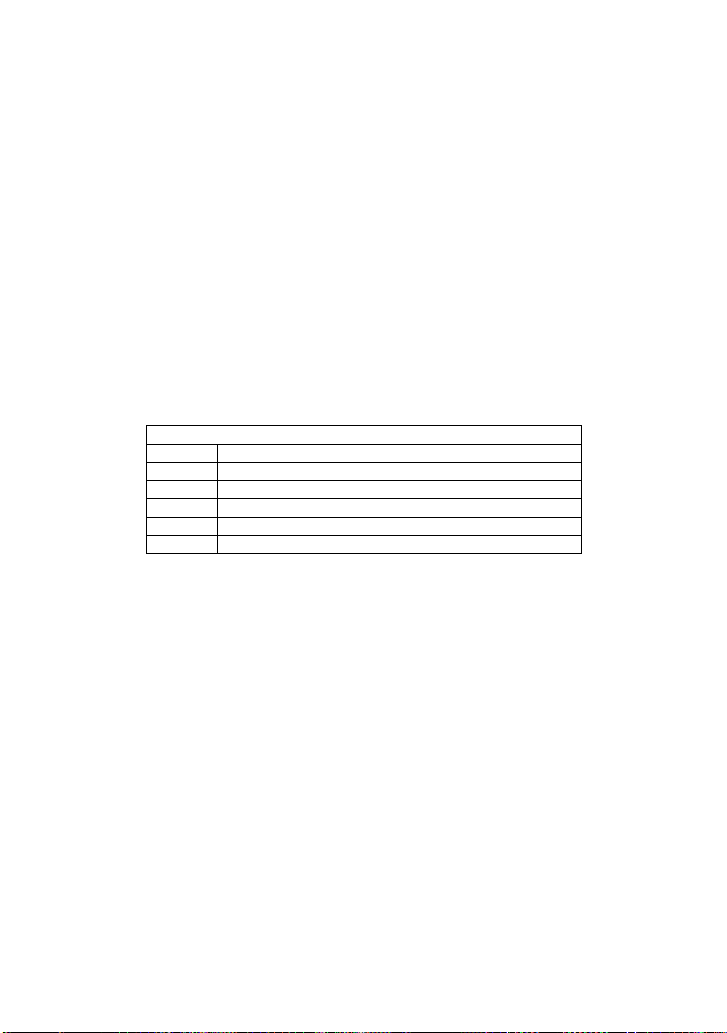
Page 27
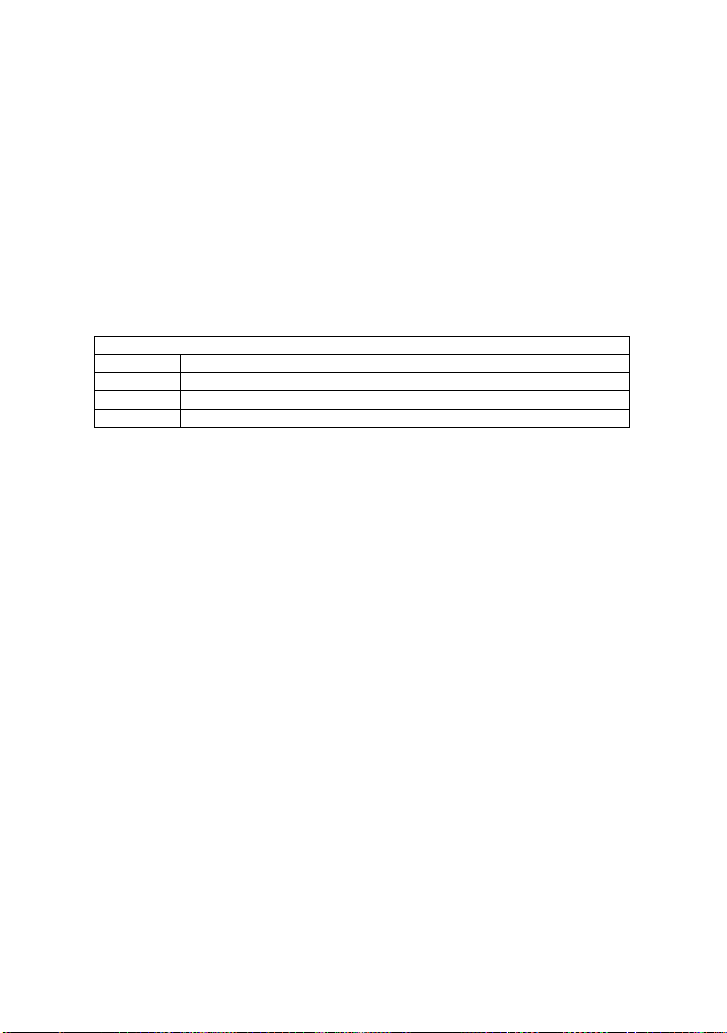
Notation
HREL
Selected tract-cursor mode
VREL
Selected manual-cursor mode and set to voltage type
AUTO
Selected auto mode
OFF
Cursors and parameters off
CURSOR_MEASURE, CRMS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The CURSOR_MEASURE command
specifies the type of cursor or parameter
measurement to be displayed
The CURSOR_MEASURE? query indicates
which cursors or parameter measurements are
currently displayed.
COMMAND SYNTAX CuRsor_MeaSure <mode>
<mode>={ OFF,HREL,VREL,AUTO}
QUERY SYNTAX CuRsor_MeaSure?
RESPONSE FORMAT CuRsor_MeaSure <mode>
EXAMPLE The following command determines cursor
function is turned off:
Command message:
CRMS OFF
RELATED COMMANDS CURSOR_VALUE, PARAMETER_VALUE
27
Page 28
Notation
HREF
The time value of curA under Track cursor mode
HDIF
The time value of curB under Track cursor mode
VREF
The volt-value of curA under manual cursor mode
VDIF
The volt -value of curB under manual cursor mode
TREF
The time value of curA under manual cursor mode
TDIF
The time value of curB under manual cursor mode
CURSOR
CURSOR_SET, CRST
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The CURSOR_SET command allows the user
to position any one of the eight independent
cursors at a given screen location. The
positions of the cursors can be modified or
queried even if the required cursor is not
currently displayed on the screen. When
setting a cursor position, a trace must be
specified, relative to which the cursor will
be positioned.
The CURSOR_SET? Query indicates the
current position of the cursor(s). The values
returned depend on the grid type selected.
COMMANDSYNTAX
<trace>:CuRsor_SeT<cursor>,<position>[,<c
ursor>,<position>,<cursor> ,<position>]
< trace > : = {C1, C2, C3, C4}
<cursor> :
={HREF,HDIF,VREF,VDIF,TREF,TDIF}
<position> : = 0.1 to 11.9(or 17.9) DIV
(horizontal of track, the range of the
value is related to the size of the
screen)
<position>:= -4 to 4 DIV (vertical)
<position>:= -6(or -9) to 6 DIV (horizontal
of manual, the range of the value is
related to the size of the screen)
QUERY SYNTAX <trace>: CuRsor_SeT? [<cursor>, …<cursor>]
28
Page 29

<cursor> :={ HREF, HDIF, VREF, VDIF,
TREF, TDIF}
RESPONSE FORMAT <trace>:CuRsor_SeT <cursor>, <position> [,
<cursor>, <position>, <cursor>, <position>]
EXAMPLE The following command positions the VREF
and VDIF cursors at +3 DIV and −1 DIV
respectively, using C1 as a reference:
Command message:
C1: CRST VREF, 3DIV, VDIF, −1DIV
RELATED COMMANDS CURSOR_MEASURE, CURSOR_VALUE,
PARAMETER_VALUE
29
Page 30
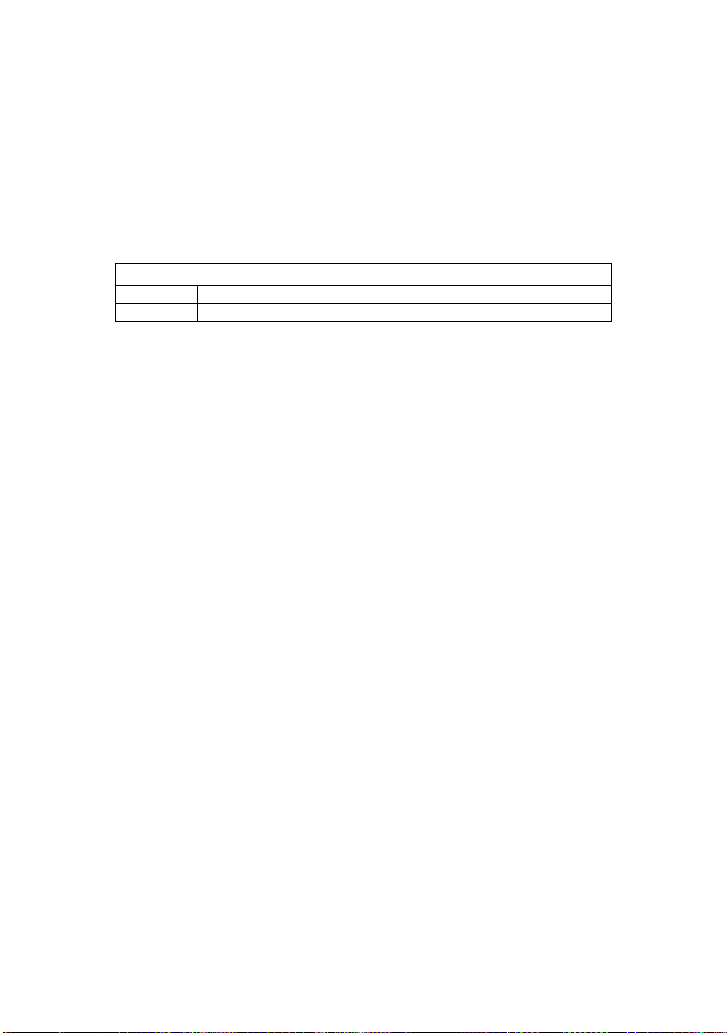
Notation
HREL
the cursor value under track cursor mode
VREL
the dalta volt-value under manual cursor mode
CURSOR
CURSOR_VALUE?, CRVA?
Query
DESCRIPTION The CURSOR_VALUE? Query returns the
values measured by the specified cursors for a
given trace. (The PARAMETER_VALUE?
query is used to obtain measured waveform
parameter values.)
QUERY SYNTAX <trace>: CuRsor_Value? [<mode>,…<mode>]
<trace> : = { C1, C2, C3, C4}
<mode> : = { HREL, VREL }
RESPONSE FORMAT <trace> : CuRsor_Value HREL,
<B->T - A->T>,<B->V - A->V>,<A->T>,
<B->T>,
<(B->V - A->V)/(B->T - A->T)>
<trace> : CuRsor_Value VREL,<delta_vert>
EXAMPLE The following query reads the dalta volt value
under manual cursor mode (VREL) on
Channel 2:
Command message:
C2:CRVA? VREL
Response message:
C2:CuRsor_Value VREL 1.00V
RELATED COMMANDS CURSOR_SET, PARAMETER_VALUE
30
Page 31

CURSOR_AUTO, CRAU
Command
DESCRIPTION The CURSOR_AUTO command changes the
cursor mode to auto mode
COMMAND SYNTAX CRAU
EXAMPLE The following code changes the cursor mode to
auto mode
Command message:
CRAU
31
Page 32

SAVE/RECALL
CSV_SAVE, CSVS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The CSV_SAVE command selects the specified
option of storing CSV format waveform.
The CSV_SAVE? query returns the option of
storing waveform data of CSV format.
COMMAND SYNTAX CSV_SAVE DD,<DD>,SAVE,<state>
The option DD is the data depth which is saved as.
The option SAVE is that if the waveform data is
stored with parameter.
<DD>:={MAX,DIS} the meaning of MAX is
saved as the maximum data depth. The meaning of
DIS is saved as the date depth which is displayed
on the screen
<save>:= {OFF, ON}
QUERY SYNTAX CSV_SAVE?
RESPONSE FORMAT CSV_SAVE DD, <DD>, SAVE, <state>
EXAMPLE The following command sets the save data depth as
the maximum and “para” save to off
Command message:
CSV_SAVE DD,MAX,SAVE,OFF
32
Page 33

FUNCTION
COUNTER, COUN
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The COUNTER command enables or disables the
cymometer display on the screen of instrument.
The response to the COUNTER? query indicates
whether the cymometer is displayed on the screen
of instrument.
COMMAND SYNTAX COUNTER <state>
< state > : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX COUNTER?
RESPONSE FORMAT COUNTER < state >
EXAMPLE The following command enables the cymometer
display
Command message:
COUN ON
33
Page 34

FUNCTION
CYMOMETER, CYMT
Query
DESCRIPTION The response to the CYMOMETER? query is the
value of the counter which displays on the screen
of the instrument. When the signal frequency is
less than 10Hz, it returns 10Hz.
QUERY SYNTAX CYMOMETER?
RESPONSE FORMAT CYMOMETER <option>
EXAMPLE The following instruction returns the value of
the counter which displays on the screen of the
instrument.
Response message:
CYMT 10Hz
34
Page 35

DATE
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The DATE command changes the date/time of the
oscilloscope’s internal real-time clock.
The command is only used in the CFL series
instrument.
COMMAND SYNTAX DATE <day>, <month>, <year>, <hour>,
<minute>, <second>
<day> : = 1 to 31
<month> : = {JAN, FEB, MAR, APR, MAY,
JUN, JUL, AUG, SEP,OCT, NOV, DEC}
<year> : = 1990 to 2089
<hour> : = 0 to 23
<minute> : = 0 to 59
<second> : = 0 to 59
QUERY SYNTAX DATE?
RESPONSE FORMAT DATE <day>, <month>, <year>, <hour>,
<minute>, <second>
EXAMPLE This instruction will change the date to
NOV. 1, 2009 and the time to 14:38:16:
Command message:
DATE 1, NOV, 2009,14,38,16
35
Page 36

STATUS
DDR?
Query
DESCRIPTION The DDR? Query reads and clears the contents of
the Device Dependent or device specific error
Register (DDR). In the case of a hardware
failure, the DDR register specifies the origin of
the failure.
QUERY SYNTAX DDR?
RESPONSE FORMAT DDR <value>
<value> : = 0 to 65535
EXAMPLE The following instruction reads the contents of
the DDR register:
Command message:
DDR?
Response message:
DDR 0
RELATED COMMANDS ALL_STATUS? ,*CLS
36
Page 37

Function Equations
<source1> + <source2>
Addition
<source1> - <source2>
Subtraction
<source1>*<source2>
Multiplication
<source1>/<source2>
Ratio
FFT(source x)
FFT
FUNCTION
DEFINE, DEF
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The DEFINE command specifies the mathematical
expression to be evaluated by a function.
COMMAND SYNTAX DEFine EQN,’<equation>’
<equation> the mathematical expression
QUERY SYNTAX DEFine?
RESPONSE FORMAT DEFine EQN,'<equation>'
EXAMPLE
Command message:
DEFine EQN,'C1*C2'
37
Page 38

DELETE_FILE, DELF
Command
DESCRIPTION The DELETE_FILE command deletes files
from the currently selected directory on mass
storage.
COMMAND SYNTAX DELete_File DISK, <device>, FILE,
‘<filename>’
<device>:={UDSK}
<filename>:= a file of specified directory and
the specified file should be up to eight characters.
EXAMPLE The following command deletes a front-panel
setup from the directory named SETUP in a
USB memory device:
Command message:
DELF DISK, UDSK, FILE, ‘/ SETUP /001.SET’
RELATED COMMANDS DIRECTORY
38
Page 39

MASS STORAGE
DIRECTORY, DIR
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The DIRECTORY command is used to manage
the creation and deletion of file directories on
mass storage devices. It also allows selection of
the current working directory and listing of
files in the directory.
The query response consists of a double-quoted
string containing a DOS-like listing of the
directory.
COMMAND SYNTAX Directory DISK, <device>, ACTION, <action>,
‘<directory>’
QUERY SYNTAX Directory? DISK, <device> [, ‘<directory>’]
<device>:={UDSK}
<action>:={CREATE, DELETE}
< directory >:= A legal DOS path or filename.
(This can include the ‘/’ character to define the
root directory.)
RESPONSE FORMAT DIRectory DISK, <device> “<directory>”
EXAMPLE The following asks for a listing of the directory of
a USB memory device:
Command message:
DIR? DISK, UDSK
Response message:
DIRectory DISK, UDSK,"A:
BK1000
BK1000AA
BB.SET 2.00 KB
BK00001.SET 2.00 KB
BK00002.SET 2.00 KB
3 File(s), 2 DIR(s)
"
RELATED COMMANDS DELF
39
Page 40

DISPLAY
DOT_JOIN, DTJN
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The DOT_JOIN command controls the
interpolation lines between data points.
COMMAND SYNTAX DoT_JoiN <state>
<state> : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX DoT_JoiN?
RESPONSE FORMAT DoT_JoiN <state>
EXAMPLE The following instruction turns off the
interpolation lines:
Command message:
DTJN OFF
40
Page 41

STATUS
*ESE
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The *ESE command sets the Standard Event
Status Enable register (ESE). This command
allows one or more events in the ESR register
to be reflected in the ESB summary message
bit (bit 5) of the STB register.
COMMAND SYNTAX *ESE <value>
<value> : = 0 to 255
QUERY SYNTAX *ESE?
RESPONSE FORMAT *ESE <value>
EXAMPLE The following instruction allows the ESB bit to
be set if a user request (URQ bit 6, i.e.
decimal 64) and/or a device dependent error
(DDE bit 3, i.e. decimal 8) occurs. Summing
these values yields the ESE register mask
64+8=72.
Command message:
*ESE 72
RELATED COMMANDS *ESR
41
Page 42

STATUS
*ESR?
Query
DESCRIPTION The *ESR? query reads and clears the contents
of the Event Status Register (ESR). The
response represents the sum of the binary
values of the register bits 0 to 7.
QUERY SYNTAX *ESR?
RESPONSE FORMAT *ESR <value>
<value> : = 0 to 255
EXAMPLE The following instruction reads and clears the
contents of the ESR register:
Command message:
*ESR?
Response message:
*ESR 0
RELATED COMMANDS ALL_STATUS, *CLS, *ESE
42
Page 43

Standard Event Status Register (ESR)
Bit
Bit Value
Bit Name
Description
Note
15~8 0 reserved by IEEE 488.2
7
128
PON 1 Power off-to-ON transition as
occurred
(1)
6
64
URQ 1 User Request has been issued
(2)
5
32
CME 1 Command parser Error has been
detected
(3)
4
16
EXE 1 Execution Error detected
(4)
3 8 DDE 1 Device specific Error occurred
(5) 2 4
QYE 1 Query Error occurred
(6) 1 2
RQC 1 Instrument never requests bus control
(7) 0 1
OPC 1 Instrument never requests bus control
(8)
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
43
Page 44

Notes
(1) The Power On (PON) bit is always turned on (1) when the unit is powered up.
(2) The User Request (URQ) bit is set true (1) when a soft key is pressed. An associated register
URR identifies which key was selected. For further details refer to the URR? query.
(3) The CoMmand parser Error bit (CME) is set true (1) whenever a command syntax error is
detected. The CME bit has an associated CoMmand parser Register (CMR) which specifies
the error code. Refer to the query CMR? for further details.
(4) The EXecution Error bit (EXE) is set true (1) when a command cannot be executed due to
some device condition (e.g. oscilloscope in local state) or a semantic error. The EXE bit has
an associated Execution Error Register (EXR) which specifies the error code. Refer to query
EXR? for further details.
(5) The Device specific Error (DDE) is set true (1) whenever a hardware failure has occurred at
power-up, or execution time, such as a channel overload condition, a trigger or a timebase
circuit defect. The origin of the failure may be localized via the DDR? or the self test *TST?
query.
(6) The Query Error bit (QYE) is set true (1) whenever (a) an attempt is made to read data from
the Output Queue when no output is either present or pending, (b) data in the Output Queue
has been lost, (c) both output and input buffers are full (deadlock state), (d) an attempt is
made by the controller to read before having sent an <END>, (e) a command is received
before the response to the previous query was read (output buffer flushed).
(7) The ReQuest Control bit (RQC) is always false (0), as the oscilloscope has no GPIB
controlling capability.
(8) The OPeration Complete bit (OPC) is set true (1) whenever *OPC has been received, since
commands and queries are strictly executed in sequential order. The oscilloscope starts
processing a command only when the previous command has been entirely executed.
44
Page 45

*EXR?
Query
DESCRIPTION The EXR? query reads and clears the contents
of the Execution error Register (EXR). The
EXR register specifies the type of the last
error detected during execution.
QUERY SYNTAX EXR?
RESPONSE FORMAT EXR <value>
<value> : = to
EXAMPLE The following instruction reads the contents
of the EXR register:
Command message:
EXR?
Response message (if no fault):
EXR 0
RELATED COMMANDS ALL_STATUS, *CLS
45
Page 46

Execution Error Status Register Structure (EXR)
Value
Description
21
Permission error. The command cannot be executed in local mode.
22
Environment error. The instrument is not configured to correctly process a
command. For instance, the oscilloscope cannot be set to RIS at a slow timebase.
23
Option error. The command applies to an option which has not been installed.
25
Parameter error. Too many parameters specified.
26
Non-implemented command.
32
Waveform descriptor error. An invalid waveform descriptor has been detected.
36
Panel setup error. An invalid panel setup data block has been detected.
50
No mass storage present when user attempted to access it.
53
Mass storage was write protected when user attempted to create, or a file, to delete a
file, or to format the device.
58
Mass storage file not found.
59
Requested directory not found.
61
Mass storage filename not DOS compatible, or illegal filename.
62
Cannot write on mass storage because filename already exists.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
46
Page 47

MASS STORAGE
FILENAME, FLNM
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The FILENAME command is used to change the
default filename given to any traces, setups and
hard copies when they are being stored to a mass
storage device.
COMMAND SYNTAX FiLeNaMe TYPE, <type>, FILE, ‘<filename>’
<type>:={ C1,C2,C3, C4, SETUP,TA, TB, TC,
TD, HCOPY}
<filename> : = an alphanumeric string of up to 8
characters forming a legal DOS filename.
Note: the file’s extension can be specified automatically by the oscilloscope.
QUERY SYNTAX FiLeNaMe? TYPE, <type>
<type> :={ ALL, C1, C2, C3, C4, SETUP, TA,
TB, TC, TD, HCOPY}
RESPONSE FORMAT FiLeNaMe TYPE, <type>, FILE, “<filename>”
[,TYPE, <type>, FILE, “<filename>”...]
EXAMPLE The following command designates channel 1
waveform files to be “TESTWF.DAV”:
Command message:
FLNM TYPE, C1, FILE, ‘TESTWF’
RELATED COMMANDS DIRECTORY, DELETE_FILE
47
Page 48

ACQUISITION
FORCE_TRIGGER, FRTR
Command
DESCRIPTION Causes the instrument to make one acquisition.
COMMAND SYNTAX FoRce_TRigger
EXAMPLE Either of the following pairs of instruction
make one acquisition:
Command message1:
TRMD SINGLE;ARM;FRTR
Command message2:
TRMD STOP;ARM;FRTR
48
Page 49

MASS STORAGE
FORMAT_VDISK, FVDISK
Query
DESCRIPTION The FORMAT_VDISK? query reads the
capability of the USB memory device.
QUERY SYNTAX Format_VDISK?
RESPONSE FORMAT Format_VDISK <capability>
<capability>:= the capability of the USB
memory device.
EXAMPLE The following query reads the capability of the
USB device.
Command message:
Format_VDISK?
Response message:
Format_VDISK 963 MB
49
Page 50

FILTER, FILT
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The FILTER command enables or disables filter of
the specified trace.
The response to the FILTER? query indicates
whether the filter of specified trace is enabled
COMMAND SYNTAX <channel>:FILTER <state>
<channel> : = {C1,C2,C3,C4}
<state> : = {ON,OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX <channel>:FILTER?
RESPONSE FORMAT <channel>:FILTER <state>
EXAMPLE The following command enables the filter of
channel 1:
Command message:
C1:FILT ON
RELATED COMMANDS FILTS
50
Page 51

FILT_SET, FILTS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The FILT_SET command selects the specified type
of filter, and sets the limit value of filter.
The response to the FILT_SET? query indicates
current parameter of the filter
COMMAND SYNTAX <channel>: FILT_SET TYPE,<type>,
<limit>,<limit_value>
<channel> : = {C1,C2,C3,C4}
<type> : = {LP,HP,BP,BR}
LP is lowpass, HP is highpass, BP is bandpass,
BR is bandreject
<limit> : = {UPPLIMIT,LOWLIMIT}
if seted the <limit>,the <type> must be related
QUERY SYNTAX <channel>: FILT_SET?
RESPONSE FORMAT <channel>:FILTER TYPE,<type>,<limit>,
<limit_value >
EXAMPLE The following command changes the type of filter to
bandpass, and sets the upplimit to 200 KHz and the
lowlimit to 100 KHz:
Command message:
C1:FILTS TYPE,BP,
UPPLIMIT,200KHz,LOWLIMIT,100KHz
RELATED COMMANDS FILT
51
Page 52

FFT_WINDOW, FFTW
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The FFT_WINDOW command selects the
window of FFT(Fast Fourier Transform
algorithm).
The response to the FFT_WINDOW? query
indicates current window of FFT
COMMAND SYNTAX FFT_WINDOW <window>
< window > : = {RECT,BLAC,HANN,HAMM}
RECT is short for rectangle.
BLAC is short for Blackman.
HANN is short for hanning.
HAMM is short for hamming,
QUERY SYNTAX FFT_WINDOW?
RESPONSE FORMAT FFT_WINDOW,<window>
EXAMPLE The following command sets the FFT window
to hamming:
Command message:
FFTW HAMM
52
Page 53

FUNCTION
FFT_ZOOM, FFTZ
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The FFT_ZOOM command selects the specified
zoom of FFT.
The response to the FFT_ZOOM? query
indicates current zoom in/out times of FFT
COMMAND SYNTAX FFT_ZOOM <zoom>
< zoom > : = {1,2,5,10}
QUERY SYNTAX FFT_ZOOM?
RESPONSE FORMAT FFT_ZOOM,<zoom>
EXAMPLE The following command sets the zoom factor of
FFT to 1X:
Command message:
FFTZ 1
53
Page 54

FFT_SCALE, FFTS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The FFT_SCALE command selects the specified
scale of FFT(Fast Fourier Transform algorithm).
The response to the FFT_SCALE? query indicates
current vertical scale of FFT waveform.
COMMAND SYNTAX FFT_SCALE <scale>
< scale > : = {VRMS,DBVRMS}
QUERY SYNTAX FFT_SCALE?
RESPONSE FORMAT FFT_SCALE,< scale >
EXAMPLE The following command turns the vertical scale of
FFT to dBVrms:
Command message:
FFTS DBVRMS
54
Page 55

FFT_FULLSCREEN, FFTF
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The FFT_FULLSCREEN command enables or
disables to display the FFT waveform full screen.
The response to the FFT_FULLSCREEN? query
indicates whither the FFT waveform is full screen
displayed.
COMMAND SYNTAX FFT_FULLSCREEN <state>
< state > : = {ON,OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX FFT_FULLSCREEN?
RESPONSE FORMAT FFT_FULLSCREEN < state >
EXAMPLE The following command enables to display the
FFT waveform full screen:
Command message:
FFTF ON
55
Page 56

GRID_DISPLAY, GRDS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The GRID_DISPLAY command selects the
type of the grid which is used to display.
The response to the GRID_DISPLAY? query
indicates current type of the grid
COMMAND SYNTAX GRID_DISPLAY <type>
< type > : = {FULL,HALF,OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX GRID_DISPLAY?
RESPONSE FORMAT GRID_DISPLAY < type >
EXAMPLE The following command changes the type of
grid to full grid:
Command message:
GRID_DISPLAY FULL
56
Page 57

GET_CSV, GCSV
Query
DESCRIPTION The response to the GET_CSV? query
indicates current waveform of CSV format.
The GET_CSV? query have two options to set.
They are the same as the options of CSVS.
QUERY SYNTAX GET_CSV?DD,<DD>,SAVE,<state>
The option DD is the data depth of the CSV
format waveform. The option SAVE is that if
the waveform data have parameters.
<DD>:={MAX,DIS} the meaning of
MAX is that the CSV waveform’s depth is
maximum. The meaning of DIS is that CSV
waveform’s depth is the data which is
displayed on the screen.
<save>:= {OFF,ON}
RESPONSE FORMAT the waveform date of CSV format
EXAMPLE The following command transfers the
waveform data of CSV format to
the controller. It has the maximum depth of
waveform data with parameters information.
Command message:
GET_CSV? DD,MAX,SAVE,ON
57
Page 58

DISPLAY
HOR_MAGNIFY, HMAG
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The HOR_MAGNIFY command horizontally
expands the selected expansion trace by a
specified factor. Magnification factors not
within the range of permissible values will
be rounded off to the closest legal value.
If the specified factor is too large for any of
the expanded traces (depending on their
current source), it is reduced to an
acceptable value and only then applied to
the traces. The VAB bit (bit 2) in the STB
register is set when a factor outside the legal
range is specified.
The HOR_MAGNIFY query returns the
current magnification factor for the
specified expansion function.
COMMAND SYNTAX <exp_trace>: Hor_MAGnify <factor>
<exp_trace>: = {TA, TB, TC, TD}
<factor> : = 1 to 50,000,000 The range of
<factor> it is related to the current timebase
and the range of the timebase
QUERY SYNTAX <exp_trace> : Hor_MAGnify?
RESPONSE FORMAT <exp_trace>: Hor_MAGnify <factor>
EXAMPLE The following instruction horizontally
magnifies Trace A (TA) by a factor of 5:
Command message:
TA: HMAG 5.00
RELATED COMMANDS HPOS
58
Page 59

DISPLAY
HOR_POSITION, HPOS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The HOR_POSITION command horizontally
positions the geometric center of the intensified
zone on the source trace. Allowed positions range
from division -9 to 9. If this would cause the
horizontal position of any expanded trace to go
outside the left or right screen boundaries, the
difference of positions is adapted and then applied
to the traces.
The VAB bit (bit 2) in the STB register is set if a
value outside the legal range is specified.
The HOR_POSITION query returns the position
of the geometric center of the intensified zone on
the source trace.
COMMAND SYNTAX <exp_trace>: Hor_POSition <hor_position>
<exp_trace>: = {TA, TB, TC, TD}
<hor_position>: = -9 to 9 DIV(The range of the
value is related to the size of the screen). the range
of the <hor_position> is related to the
magnification factors of command HMAG. While
the range after magnifying beyond the screen
could display, it will be adjusted to the proper
value.
QUERY SYNTAX <exp_trace>: Hor_POSition?
RESPONSE FORMAT <exp_trace>: Hor_POSition <hor_position>
EXAMPLE The following instruction positions the center of
the intensified zone on the trace currently viewed
by Trace A (TA) at division 3:
Command message:
TA: HPOS 3
RELATED COMMANDS HMAG
59
Page 60

HARD COPY
HARDCOPY_SETUP, HCSU
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The HARDCOPY_SETUP command
configures the instrument’s hard-copy driver.
COMMAND SYNTAX HCSU PSIZE, <page_size>,
ISIZE, <image_size>,
FORMAT, <format>, BCKG,
<bckg>, PRTKEY, <printkey>
<page_size> :={ DEFAULT}
<printkey>:={SAVE,PRINT}
<format> : = {PORTRAIT, LANDSCAPE}
<bckg> : = {BLACK, WHITE}
<image_size>:={DEFAULT,A4,LETTER}.
QUERY SYNTAX HCSU?
RESPONSE FORMAT HCSU PSIZE, <page_size>, ISIZE,
<image_size>, FORMAT, <format>, BCKG,
<bckg>, PRTKEY, <printkey>
EXAMPLE The following example selects PORTRAIT
format, sets the size of the image to “6*8CM”:
Command message:
HCSU ISIZE, 6*8CM, FORMAT,
PORTRAIT
RELATED COMMANDS SCDP
60
Page 61

MISCELLANEOUS
*IDN?
Query
DESCRIPTION The *IDN? query is used for identification
purposes``. The response consists of four
different fields providing information on the
manufacturer, the scope model, the serial
number and the firmware revision level.
QUERY SYNTAX *IDN?
RESPONSE FORMAT *IDN SIGLENT, <model>, <serial_number>,
<firmware_level>
<model> : = A eleven characters model
identifier
<serial_number> : = A 14-digit decimal code
<firmware_level> : = similar to k.xx.yy.zz
EXAMPLE This example issues an identification request
to the scope:
Command message:
*IDN?
Response message:
*IDN
B&K Precision, 2553,SN#,
3.01.01.22
61
Page 62

INTENSITY, INTS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The INTENSITY command sets the intensity
level of the grid or the trace.
The intensity level is expressed as a
percentage (PCT). A level of 100 PCT
corresponds to the maximum intensity whilst
a level of 0 PCT sets the intensity to its
minimum value.(The minimum value of the
trace is 30 PCT)
The response to the INTENSITY? Query
indicates the grid and trace intensity levels.
COMMAND SYNTAX INTenSity GRID, <value>, TRACE, <value>
<value> : = 0(or 30) to 100 [PCT]
Note 1: Parameters are grouped in pairs. The
first of the pair names the variable to be
modified, whilst the second gives the new
value to be assigned. Pairs may be given in
any order and be restricted to those variables
to be changed.
Note 2: The suffix PCT is optional.
QUERY SYNTAX INTenSity?
RESPONSE FORMAT INTenSity TRACE, <value>, GRID, <value>
EXAMPLE The following instruction enables remote
control of the intensity, and changes the grid
intensity level to 75%:
Command message:
INTS GRID, 75
62
Page 63

ACQUISITION
INTERLEAVED, ILVD
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The INTERLEAVED command enables or
disables random interleaved sampling (RIS)
for timebase settings where both single shot
and RIS mode are available.
The response to the INTERLEAVED? Query
indicates whether the oscilloscope is in RIS
mode.
COMMAND SYNTAX InterLeaVeD <mode>
<mode> : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX InterLeaVeD?
RESPONSE FORMAT InterLeaVeD <mode>
EXAMPLE The following instructs the oscilloscope to use
RIS mode:
Command message:
ILVD ON
RELATED COMMANDS TIME_DIV, TRIG_MODE
63
Page 64

Internal State Register Structure (INR)
Bit
Bit
Value
Description
15…14
0 Reserved for future use
13
8192 1 Trigger is ready
12
4096 1 Pass/Fail test detected desired outcome
11
2048 1 Waveform processing has terminated in Trace D
10
1024 1 Waveform processing has terminated in Trace C
9
512 1 Waveform processing has terminated in Trace B
8
256 1 Waveform processing has terminated in Trace A
7
128 1 A memory card, floppy or hard disk exchange has been detected
6
64
1
Memory card, floppy or hard disk has become full in “AutoStore
Fill” mode
5
32 0 Reserved for LeCroy use
4
16 1 A segment of a sequence waveform has been acquired
3 8 1
A time-out has occurred in a data block transfer
2 4 1
A return to the local state is detected
1 2 1
A screen dump has terminated
0 1 1
A new signal has been acquired
STATUS
INR?
Query
DESCRIPTION The INR? query reads and clears the contents of
QUERY SYNTAX INR?
the INternal state change Register(INR). The
INR register (table below) records the
completion of various internal operations and
state transitions.
Note : This command only supports 0 bit and 13
bit.
RESPONSE FORMAT INR <value>
EXAMPLE If we send INR? query after have triggered
INR?
<value> : = 0 to 65535
the INR register:
Command message1:
64
Page 65

Response message1:
INR 8913
If we send INR? query while the instrument
didn’t trigger, the INR register:
INR?
Command message2:
Response message2:
INR 8912
If we send INR? query after have sent a INR?
query and the mode of the instrument is STOP
The INR register:
INR?
Command message3:
Response message3:
INR 0
If we send INR? query while there is no and
then make the instrument triggered. Finally we
send another INR? query
the INR register:
INR?
Command message4:
Response message4:
INR 1
RELATED COMMANDS ALL_STATUS? ,*CLS
65
Page 66

DISPLAY
INVERTSET, INVS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The INVERTSET command inverts the
specified traces or the waveform of math.
The response to the INVERTSET? query
indicates whether the specified waveform is
invert.
COMMAND SYNTAX <trace>:INVERTSET < state >
< trace > : = {C1,C2,C3,C4,MATH}
< state >:= {ON,OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX <trace>:INVERTSET?
RESPONSE FORMAT <trace>:INVERTSET < state >
EXAMPLE The following instruction inverts the trace of
channel 1:
Command message:
C1:INVS ON
66
Page 67

MISCELLANEOUS
LOCK, LOCK
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The LOCK command enables or disables the
panel keyboard of the instrument.
When any command or query is executed in
either local or remote state, the functions of
the panel keys except “FORCE” are not
available. W hen the panel keyboard of the
instrument is locked , press “FORCE” key can
enable the panel keyboard function.
The LOCK? query returns the status of the
panel keyboard of the instrument.
COMMAND SYNTAX LOCK < status >
<status>:= {ON,OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX LOCK?
RESPONSE FORMAT LOCK < status >
EXAMPLE The following instruction enables the
functions of the panel keys:
Command message:
LOCK ON
67
Page 68

DISPLAY
MENU, MENU
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The MENU command enables or disables to
display the menu.
The response to the MENU? query indicates
whether the menu is displayed.
COMMAND SYNTAX MENU < status >
<status>:= {ON,OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX MENU?
RESPONSE FORMAT MENU < status >
EXAMPLE The following instruction enables the display
of the menu:
Command message:
MENU ON
68
Page 69

ACQUISITION
MATH_VERT_POS, MTVP
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The MATH_VERT_POS command controls
the vertical position of the math waveform
with specified source.
The FFT waveform isn’t included. But we
have another command which called VPOS to
control its vertical position.
The response to the MATH_VERT_POS?
query indicates the value of the vertical
position of the math waveform.
COMMAND SYNTAX MATH_VERT_POS <position>
<position>:= the position is related to the
position of the screen center. For example, if
we set the position of MTVP to 25. The math
waveform will be displayed 1 grid up to the
vertical center of the screen. Namely one grid
is 25.
QUERY SYNTAX MATH_VERT_POS?
RESPONSE FORMAT MATH_VERT_POS < position >
EXAMPLE The following instruction changes the vertical
position of the math waveform to 1 grid up to
the screen vertical centre:
Command message:
MTVP 25
69
Page 70

ACQUISITION
MATH_VERT_DIV, MTVD
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The MATH_VERT_DIV command controls
the vertical sensitivity of the math waveform
of specified source. We can only set the value
of existing
The FFT waveform isn’t included.
The response to the MATH_VERT_DIV?
query indicates the specified scale of math
waveform of specified source.
COMMAND SYNTAX MATH_VERT_DIV < scale >
< scale >:= 1PV/div ~ 100V/div.
QUERY SYNTAX MATH_VERT_DIV?
RESPONSE FORMAT MATH_VERT_DIV < scale >
EXAMPLE The following instruction changes the vertical
sensitivity of the math waveform of specified
source to 1V/div:
Command message:
MTVD 1V
70
Page 71

FUNCTION
MEASURE_DELY, MEAD
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The MEASURE_DELY command selects the
type of delay measure.
The response to the MEASURE_DELY?
query indicates the type of delay measure.
COMMAND SYNTAX MEASURE_DELY
SOURCE,<mode>,TYPE,<type>
<mode>:= {C1-C2, C1-C3, C1-C4, C2-C3,
C2-C4, C3-C4}
<type>:=
{PHA,FRR,FRF,FFR,FFF,LRR,LRF,LFR,
LFF},
The PHA is phase, the others are the same as
the specified type of the instrument’s delay
measure
QUERY SYNTAX MEASURE_DELY?
RESPONSE FORMAT MEASURE_DELY
SOURCE,<mode>,TYPE,<type>
EXAMPLE The following instruction sets the type of
delay measure to phase between C1 and C2.
Command message:
MEAD SOURCE,C1-C2,TYPE,PHA
71
Page 72

ACQUISITION
OFFSET, OFST
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The OFFSET command allows adjustment of
the vertical offset of the specified input
channel. The maximum ranges depend on the
fixed sensitivity setting.
If an out-of-range value is entered, the
oscilloscope is set to the closest possible
value and the VAB bit (bit 2) in the STB
register is set.
The OFFSET? query returns the offset value
of the specified channel.
COMMAND SYNTAX <channel>: OFfSeT <offset>
<channel> : = {C1, C2, C3,C4}
<offset> : = See specifications.
QUERY SYNTAX <channel>: OFfSeT?
RESPONSE FORMAT <channel>: OFfSeT <offset>
EXAMPLE The following command sets the offset of
Channel 2 to -3 V:
Command message:
C2: OFST -3V
72
Page 73

STATUS
*OPC
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The *OPC (OPeration Complete) command
sets to true the OPC bit (bit 0) in the standard
Event Status Register (ESR). This command
has no other effect on the operation of the
oscilloscope because the instrument starts
parsing a command or query only after it has
completely processed the previous command
or query.
The *OPC? query always responds with the
ASCII character “1” because the oscilloscope
only responds to the query when the previous
command has been entirely executed.
COMMAND SYNTAX *OPC
QUERY SYNTAX *OPC?
RESPONSE FORMAT *OPC 1
73
Page 74

MISCELLANEOUS
*OPT
Query
DESCRIPTION The *OPT? query identifies oscilloscope options:
installed software or hardware that is additional
to the standard instrument configuration. The
response consists of a series of response fields
listing all the installed options.
QUERY SYNTAX *OPT?
RESPONSE FORMAT *OPT <option>
NOTE: If no option is present, the character 0
will be returned.
EXAMPLE :The following instruction queries
the installed options:
*OPT?
Return: *OPT RS232,NET,USBTMC
74
Page 75

CURSOR
PARAMETER_CLR, PACL
Command
DESCRIPTION The PARAMETER_CLR command clears the P/F
test counter and starts it again at 0.
COMMAND SYNTAX PArameter_CLr
RELATED COMMANDS PARAMETER_VALUE PFDD
75
Page 76

CURSOR
PARAMETER_CUSTOM, PACU
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The PARAMETER_CUSTOM command
controls the parameters that have customizable
qualifiers.
Note: The measured value of a parameter setup
with PACU may be read using PAVA?
COMMAND SYNTAX PArameter_CUstom <line>,
<parameter>,<qualifier><line> : = 1 to 5
<parameter> : ={PKPK, MAX, MIN, AMPL,
TOP, BASE, CMEAN, MEAN, RMS, CRMS,
OVSN, FPRE, OVSP, RPRE, PER, FREQ,
PWID, NWID, RISE, FALL, WID, DUTY,
NDUTY }
<qualifier> : = Measurement qualifier specific
to each(source option)
QUERY SYNTAX PArameter_CUstom? <line>
RESPONSE FORMAT PArameter_Custom <line>, <parameter>,
<qualifier>
EXAMPLE
Command Example PACU 2, PKPK, C1
Query/Response Examples PACU? 2 returns:
PACU 2, PKPK, C1
PAVA? CUST2 returns:
C2: PAVA CUST2, 160.00mV
RELATED COMMANDS PARAMETER_CLR,
PARAMETER_VALUE
76
Page 77

Parameters Available on All Models
ALL
all parameters
NDUTY
negative duty cycle
AMPL
amplitude
NWID
negative width
BASE
base
OVSN
negative overshoot
CMEAN
mean for cyclic
waveform
OVSP
positive overshoot
CRMS
root mean square for
cyclic part of waveform
PKPK
peak-to-peak
DUTY
duty cycle
PER
period
FALL
falltime
RPRE
(Vmin-Vbase)/ Vamp
before the waveform
rising transition
FREQ
frequency
PWID
positive width
FPRE
(Vmin-Vbase)/ Vamp
before the waveform
falling transition
RMS
root mean square
MAX
maximum
RISE
risetime
MIN
minimum
TOP
top
MEAN
mean
WID
width
CURSOR
PARAMETER_VALUE?, PAVA?
Query
DESCRIPTION The PARAMETER_VALUE query returns the
measurement values.
QUERY SYNTAX <trace>: PArameter_VAlue? [<parameter>, ... ,
<parameter>]
<trace>: = { C1, C2, C3, C4}
<parameter> : = See table of parameter names
on previous table.
RESPONSE FORMAT <trace>: PArameter_VAlue <parameter>,
<value> [, ... , <parameter>,<value>]
EXAMPLE The following query reads the risetime of
Channel 2
Command message:
C2: PAVA? RISE
Response message:
C2: PAVA RISE, 3.6E-9S
77
Page 78

RELATED COMMANDS CURSOR_MEASURE, CURSOR_SET,
PARAMETER_CUSTOM
78
Page 79

ACQUISITION
PEAK_DETECT, PDET
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The PEAK_DETECT command switches ON
or OFF the peak detector built into the
acquisition system.
The PEAK_DETECT? query returns the
current status of the peak detector.
COMMAND SYNTAX Peak_DETect <state>
<state> : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX Peak_DETect?
RESPONSE FORMAT PDET <state>
EXAMPLE The following instruction turns on the peak
detector:
Command message:
PDET ON
79
Page 80

DISPLAY
PERSIST, PERS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The PERSIST command enables or disables the
persistence display mode.
COMMAND SYNTAX PERSist <mode>
<mode> : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX PERSist?
RESPONSE FORMAT PERSist <mode>
EXAMPLE The following code turns the persistence
display ON:
Command message:
PERS ON
RELATED COMMANDS PERSIST_SETUP
80
Page 81

DISPLAY
PERSIST_SETUP, PESU
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The PERSIST_SETUP command selects the
persistence duration of the display, in
seconds,in persistence mode.
The PERSIST_SETUP? query indicates the
current status of the persistence.
COMMAND SYNTAX PErsist_SetUp <time>
<time>:={1,2,5,Infinite}
QUERY SYNTAX PErsist_SetUp?
RESPONSE FORMAT PErsist_SetUp <time>
EXAMPLE The following instruction sets the variable
persistence at 5 Seconds:
Command message:
PESU 5
RELATED COMMANDS PERSIST
81
Page 82

SAVE/RECALL SETUP
PANEL_SETUP, PNSU
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The PANEL_SETUP command complements
the *SAV or *RST commands.
PANEL_SETUP allows you to archive panel
setups in encoded form on external storage
media.Only setup data read by the PNSU?
query can be recalled into the oscilloscope.
COMMAND SYNTAX PaNel_SetUp <setup>
<setup> : = A setup previously read by PNSU?
QUERY SYNTAX PaNel_SetUp?
RESPONSE FORMAT PaNel_SetUp <setup>
EXAMPLE The following instruction saves the scilloscope’s
current panel setupin the file PANEL.SET:
Command message:
PNSU?
RELATED COMMANDS *RCL, *SAV
82
Page 83

FUNCTION
PF_DISPLAY, PFDS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The PF_DISPLAY command enables or
disables to turn the test and display the message
in the pass/fail option.
The response to the PF_DISPLAY? query
indicates whether the test is enabled and the
message of pass/fail is displayed
COMMAND SYNTAX PF_DISPLAY TEST,<state>,DISPLAY,<state>
<state> : = {ON, OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX PF_DISPLAY TEST?
RESPONSE FORMAT PF_DISPLAY TEST <state>,DISPLAY,<state>
EXAMPLE The following instruction enables to turn on the
test and display the message of pass/fail:
Command message:
PFDS TEST,ON,DISPLAY,ON
83
Page 84

FUNCTION
PF_SET, PFST
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The PF_SET command sets the X mask and the
Y mask of the mask setting in the pass/fail
option.
The response to the PF_ SET? query indicates
the value of the X mask and the Y mask.
COMMAND SYNTAX PF_ SET XMASK, <div>,YMASK, <div>
<div> : = 0.04div~4.0div
QUERY SYNTAX PF_ SET?
RESPONSE FORMAT PF_ SET XMASK, <div>,YMASK, <div>
EXAMPLE The following instruction sets the X mask to
0.4div and the Y mask to 0.5div of the mask
setting in the pass/fail option:
Command message:
PFST XMASK,0.4,YMASK,0.5
RELATED COMMANDS PFSL PFST
84
Page 85

SAVE/RECALL
PF_SAVELOAD, PFSL
Command
DESCRIPTION The PF_SAVELOAD command saves or recalls
the created mask setting.
COMMAND SYNTAX PF_ SAVELOAD LOCATION,
<location>,ACTION, <action>
The <location> means to save the created mask
setting to the internal memories or the
external memories.
<location> : = {IN,EX}
IN means to save the mask setting to the
internal memories while EX means the external
memories.
<action> := {SAVE,LOAD}
SAVE means to save the mask setting while
LOAD means recall the stored mask setting.
EXAMPLE The following instruction saves the mask
setting to the internal memories:
Command message:
PFSL LOCATION,IN,ACTION,SAVE
RELATED COMMANDS PFCM
85
Page 86

FUNCTION
PF_CONTROL, PFCT
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The PF_CONTROL command controls the
pass/fail controlling options: “operate”, “output”
and the “stop on output”.
See instrument’s Operator Manual for these
options
The response to the PF_ CONTROL? query
indicates the controlling options of the pass/fail.
COMMAND SYNTAX PF_ CONTROL
TRACE,<trace>,CONTROL,<control>,OUTP
UT,<output>,OUTPUTSTOP,<state>
<trace> : = {C1,C2,C3,C4}
<control> : = {START,STOP}
<output> : = {FAIL,PASS}
<state> : = {ON,OFF}
QUERY SYNTAX PF_ CONTROL?
RESPONSE FORMAT PF_ CONTROL
TRACE,<trace>,CONTROL,<control>,
OUTPUT,<output>,OUTPUTSTOP,<state>
EXAMPLE The following instruction sets source to channel
1, “operate” to “start”, “output” to “pass” and
“stop on output” to “off”:
Command message:
PFCT TRACE,C1,CONTROL,START,
OUTPUT,PASS,OUTPUTSTOP,OFF
86
Page 87

FUNCTION
PF_CREATEM, PFCM
Command
DESCRIPTION The PF_CREATEM command creates the mask
of the pass/fail.
COMMAND SYNTAX PF_ CREATEM
EXAMPLE The following instruction creates the mask of
the pass/fail.:
Command message:
PFCM
RELATED COMMANDS PFSL PFST
87
Page 88

FUNCTION
PF_DATADIS, PFDD
Query
DESCRIPTION The PF_DATADIS? query returns the number
of the fail ,pass and total number that the screen
showing.
QUERY SYNTAX PF_ DATADIS?
RESPONSE FORMAT PF_ DATADIS
FAIL,<num>,PASS,<num>,total,<num>
EXAMPLE The following instruction returns the number of
the message display of the pass/fail:
Command message:
PFDD FAIL,0,PASS,0,TOTAL,0
RELATED COMMANDS PACL
88
Page 89

SAVE/RECALL SETUP
*RCL
Command
DESCRIPTION The *RCL command sets the state of the
instrument, using one of the ten non-volatile
panel setups, by recalling the complete frontpanel setup of the instrument. Panel setup 0
corresponds to the default panel setup.
The *RCL command produces the opposite
effect of the *SAV command.
If the desired panel setup is not acceptable, the
EXecution error status Register (EXR) is set and
the EXE bit of the standard Event Status
Register (ESR) is set.
COMMAND SYNTAX *RCL <panel_setup>
<panel_setup>:= 0 to 20
EXAMPLE The following recalls the instrument setup
previously stored in panel setup 3:
Command message:
*RCL 3
RELATED COMMANDS PANEL_SETUP, *SAV, EXR
89
Page 90

WAVEFORM TRANSFER
RECALL, REC
Command
DESCRIPTION The RECALL command recalls a waveform file
from the current directory on mass storage into
any or all of the internal memories M1 to
M10(or M20 in the CFL series).
COMMAND SYNTAX <memory>: RECall DISK, <device>, FILE,
‘<filename>’
<memory> : = {M1~M10}(or M1~M20 in the
CFL series)
<device> : = {UDSK}
<filename>:= A waveform file under a legal
DOS path . A filename-string of up to eight
characters, with the extension “.DAV”. (This
can include the ‘/’ character to define the root
directory.)
EXAMPLE The following recalls a waveform file called
“C1WF.DAV” from the memory card into
Memory M1:
Command message:
M1: REC DISK, UDSK FILE, ‘C1WF.DAV’
RELATED COMMANDS STORE, INR?
90
Page 91

SAVE/RECALL SETUP
RECALL_PANEL, RCPN
Command
DESCRIPTION The RECALL_PANEL command recalls a
front-panel setup from the current directory on
mass storage.
COMMAND SYNTAX ReCall_PaNel DISK, <device>, FILE,
‘<filename>’
<device> : = {UDSK}
<filename>:= A waveform file under a legal
DOS path . A filename-string of up to eight
characters, with the extension “.SET”. (This
can include the ‘/’ character to define the root
directory.)
EXAMPLE The following recalls the front-panel setup from
file SEAN. SET in a USB memory device:
Command message:
RCPN DISK, UDSK, FILE,‘SEAN. SET’
RELATED COMMANDS PANEL_SETUP, *SAV, STORE_PANEL,
*RCL
91
Page 92

SAVE/RECALL SETUP
*RST
Command
DESCRIPTION The *RST command initiates a device reset.
The *RST sets recalls the default setup.
COMMAND SYNTAX *RST
EXAMPLE This example resets the oscilloscope:
Command message:
*RST
RELATED COMMANDS *CAL, *RCL
92
Page 93

FUNCTION
REF_SET, REFS
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The REF_SET command sets the reference
waveform and its options.
The response to the REF_ SET? query indicates
whether the specified reference waveform is
turned on.
COMMAND SYNTAX REF _ SET TRACE,<trace>REF,<ref>,state,
<state>,SAVE,DO
<trace> : =
{C1,C2,C3,C4,C1OFF,C2OFF,C3OFF,C4OFF}
If the trace is closed , the specified trace will be
CxOFF,(x is 1,2,3,4), the closed trace couldn’t
be saved or set
<ref> : = {RA,RB,RC,RD}
The Rx(x is A,B,C,D) is that which one can be
stored or displayed
<state> := {ON,OFF}
The state enables or disables to display the
specified reference waveform.
If the command syntax have the option that
SAVE,DO, means that the specified trace will
be saved to the specified reference waveform.
QUERY SYNTAX REF _ SET? REF,<ref>
RESPONSE FORMAT REF _ SET REF,<ref>,STATE,<state>
EXAMPLE The following instruction saves the channel 1
waveform to the REFA, and turns on REFA:
Command message:
REFS TRACE,C1,REF,RA,
STATE,ON,SAVE,DO
93
Page 94

SAVE/RECALL SETUP
*SAV
Command
DESCRIPTION The *SAV command stores the current state of
the instrument in internal memory. The *SAV
command stores the complete front-panel
setup of the instrument at the time the
command is issued.
COMMAND SYNTAX *SAV <panel_setup>
<panel_setup>: = 1 to 20
EXAMPLE The following saves the current instrument
setup in Panel Setup 3:
Command message:
*SAV 3
RELATED COMMANDS PANEL_SETUP, *RCL
94
Page 95

SCREEN_DUMP, SCDP
Command
DESCRIPTION The SCREEN_DUMP command is used to
obtain the screen information of image format .
COMMAND SYNTAX SCreen_DumP
EXAMPLE The following command transfers the screen
information of image format to the controller
Command message:
SCDP
95
Page 96

DISPLAY
SCREEN_SAVE, SCSV
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The SCREEN_SAVE command controls the
automatic Screen Saver, which automatically
shuts down the internal color monitor after a
preset time.
The response to the SCREEN_SAVE? query
indicates whether the automatic screen saver
feature is on or off.
Note: When the screen save is in effect, the
oscilloscope is still fully functional.
COMMAND SYNTAX SCreen_SaVe <enabled>
<enabled> : = {YES, NO}
QUERY SYNTAX SCreen_SaVe?
RESPONSE FORMAT SCreen_SaVe <enabled>
EXAMPLE The following enables the automatic screen saver:
Command message:
SCSV YES
96
Page 97

*SRE
Command /Query
DESCRIPTION The *SRE command sets the Service Request
Enable register (SRE). This command allows
the user to specify which summary message
bit(s) in the STB register will generate a service
request.
A summary message bit is enabled by writing a
‘1’ into the corresponding bit location.
Conversely, writing a ‘0’ into a given bit
location prevents the associated event from
generating a service request (SRQ). Clearing
the SRE register disables SRQ interrupts.
The *SRE? query returns a value that, when
converted to a binary number, represents the
bit settings of the SRE register.
Note: that bit 6 (MSS) cannot be set and its
returned value is always zero.
COMMAND SYNTAX *SRE <value>
<value> : = 0 to 255
QUERY SYNTAX *SRE?
RESPONSE FORMAT *SRE <value>
EXAMPLE The following instruction allows an SRQ to be
generated as soon as the MAV summary bit (bit
4, i.e. decimal 16) or the INB summary bit (bit
0, i.e. decimal 1) in the STB register, or both,
are set. Summing these two values yields the
SRE mask 16+1 = 17.
Command message:
*SRE 17
97
Page 98

STATUS
*STB?
Query
DESCRIPTION The *STB? query reads the contents of the
488.1 defined status register (STB), and the
Master Summary Status (MSS). The response
represents the values of bits 0 to 5 and 7 of the
Status Byte register and the MSS summary
message.
The response to a *STB? Query is identical to
the response of a serial poll except that the MSS
summary message appears in bit 6 in place of
the RQS message.
QUERY SYNTAX *STB?
RESPONSE FORMAT *STB <value>
<value> : = 0 to 255
EXAMPLE The following reads the status byte register:
Command message:
*STB?
Response message:
*STB 0
RELATED COMMANDS ALL_STATUS, *CLS, *SRE
98
Page 99

Status Byte Register (STB)
Bit
Bit Value
Bit Name
Description
Note 7 128
DIO7
0 reserved for future use
6
64
MSS/RQS
MSS=1
RQS=1
at least 1 bit in STB masked by SRE is 1
service is
requested
(1)
(2)
5
32
ESB
1 an ESR enabled event has occurred
(3) 4 16
MAV
1 output queue is not empty
(4) 3 8
DIO3
0 reserved
2 4
VAB
1 a command data value has been adapted
(5) 1 2
DIO1
0 reserved
0 1 INB
1 an enabled INternal state change has
occurred
(6)
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
Notes
(1) The Master Summary Status (MSS) indicates that the instrument requests service, whilst the
Service Request status — when set — specifies that the oscilloscope issued a service request.
Bit position 6 depends on the polling method:
Bit 6 = MSS if an *STB? Query is received
= RQS if serial polling is conducted
(2) Example: If SRE=10 and STB=10 then MSS=1. If SRE=010 and STB=100 then MSS=0.
(3) The Event Status Bit (ESB) indicates whether or not one or more of the enabled IEEE 488.2
events have occurred since the last reading or clearing of the Standard Event Status Register
(ESR). ESB is set if an enabled event becomes true (1).
(4) The Message AVailable bit (MAV) indicates whether or not the Output queue is empty. The
MAV summary bit is set true (1) whenever a data byte resides in the Output queue.
(5) The Value Adapted Bit (VAB) is set true (1) whenever a data value in a command has been
adapted to the nearest legal value. For instance, the VAB bit would be set if the timebase is
redefined as 2 μs/div since the adapted value is 2.5 μs/div.
(6) The INternal state Bit (INB) is set true (1) whenever certain enabled internal states are
entered. For further information, refer to the INR query.
99
Page 100

ACQUISITION
STOP
Command
DESCRIPTION The STOP command immediately stops the
COMMAND SYNTAX STOP
EXAMPLE The following stops the acquisition process:
Command message:
RELATED COMMANDS ARM_ACQUISITION, TRIG_MODE, WAIT
acquisition of a signal. If the trigger mode is
AUTO or NORM.
STOP
100
 Loading...
Loading...