Page 1

INSTRUCTION
MANUAL
Models 2530 & 2532
Digital Storage Oscilloscopes
Model 2530 25 MHz, 250 MSa/s
Model 2532 40 MHz, 500 MSa/s
Page 2

General Safety Summary
Review the following safety precautions to avoid injury and prevent damage to this product or any
products connected to it. To avoid potential hazards, use this product only as specified.
Only qualified personnel should perform service procedures.
To Avoid Fire or Personal Injury
Use Proper Power Cord. Use only the power cord specified for this product and certified for the country
of use.
Connect and Disconnect Properly. Do not connect or disconnect probes or test leads while they are
connected to a voltage source.
Ground the Product. This product is grounded through the grounding conductor of the power cord. To
avoid electric shock, the grounding conductor must be connected to earth ground. Before making
connections to the input or output terminals of the product, ensure that the product is properly grounded.
Connect the Probe Properly. The probe ground lead is at ground potential. Do not connect the ground
lead to an elevated voltage.
Observe All Terminal Ratings. To avoid fire or shock hazard, observe all ratings and marking on the
product. Consult the product manual for further ratings information before making connections to the
product.
Do Not Operate Without Covers. Do not operate this product with covers or panels removed.
Avoid Exposed Circuitry. Do not touch exposed connections and components when power is present.
Do Not Operate With Suspected Failures. If you suspect there is damage to this product, have it
inspected by qualified service personnel.
Do Not Operate in Wet/Damp Conditions.
Do Not Operate in an Explosive Atmosphere.
Keep Product Surfaces Clean and Dry.
Symbols and Terms on the Product.
Protective Ground (Earth) Terminal.
CAUTION. Refer to user manual. Caution indicates a hazard to property including this product
2
Page 3

Introduction
Description
The 2530 & 2532 Digital Storage Oscilloscope is a light-weight benchtop oscilloscope for viewing
waveforms and taking measurements. The 2530/2532 is an ideal education and training tool and also
well suited for applications in service and repair.
Key Features
40 MHz bandwidth, 500MSa/s sample rate with color display (model 2532)
25 MHz bandwidth, 250MSa/s sample rate with monochrome display (model 2530)
4000 point record length for each channel
One touch automatic setup for ease of use (Auto)
Save/Recall setup and waveform data
Capture, save and analyze waveform data and measurement results with the included EasyScope
Application Software
Cursors with readouts
Eleven automatic measurements
Waveform averaging and peak detection
Math functions: +, -, / and × operations
Fast Fourier Transformation (FFT)
Extensive Trigger capabilities: Pulse Width trigger, Video trigger capability with line-selectable
triggering, External trigger
Variable persistence display
Built in trigger frequency counter
3
Page 4

Table of Content
Chapter 1 Getting Started................................................................ 6
1.1 Installation................................................................................................................. 6
1.2 Functional check ....................................................................................................... 6
1.3 Probe handling .......................................................................................................... 8
1.3.1 Probe Safety ........................................................................................................... 8
1.3.2 Probe Compensation .............................................................................................. 8
1.3.3 Probe Attenuation Setting ...................................................................................... 9
1.4 Self Calibration ....................................................................................................... 10
Chapter 2 Main Control Sections Overview .............................. 11
2.1 Vertical System ........................................................................................................11
2.2 Horizontal System................................................................................................... 13
2.3 Trigger System........................................................................................................ 15
2.3.1 Signal Source ....................................................................................................... 16
2.3.2 Trigger Type......................................................................................................... 16
2.3.3 Coupling............................................................................................................... 19
2.3.4 Position ................................................................................................................ 19
2.3.5 Slope & Level ...................................................................................................... 19
2.4 Acquisition system .................................................................................................. 20
2.5 Display System ....................................................................................................... 23
2.5.1 X-Y Format.......................................................................................................... 25
2.6 Measurement system............................................................................................... 25
2.6.1 Graticule Measurement ........................................................................................ 26
2.6.2 Cursor Measurement ............................................................................................ 26
2.6.3 Auto Measurement ............................................................................................... 27
2.7 Utility System ......................................................................................................... 30
2.7.1 System status........................................................................................................ 31
2.7.3 Self Calibration .................................................................................................... 31
2.7.4 Self Test................................................................................................................ 31
2.8 Save/Recall System................................................................................................. 32
Chapter 3 Operating Basics........................................................36
3.1 Display Area............................................................................................................ 35
3.2 Using the Menu System .......................................................................................... 36
3.3 Using the default setup............................................................................................ 37
3.4 Using the auto setup................................................................................................ 37
3.5 Using the ADJUST knob......................................................................................... 39
3.6 Setting up the Vertical System ................................................................................ 40
3.6.1 Setting up the CH1、CH2 Channels.................................................................... 40
3.6.2 Using the Vertical Position knob and Volts/Div knob .......................................... 44
3.6.3 Using Ref ............................................................................................................. 44
3.7 Math Functions ....................................................................................................... 45
4
Page 5

3.8 Setting up the Horizontal system ............................................................................ 49
3.8.1 Horizontal control knobs...................................................................................... 49
3.8.2 Window Zone....................................................................................................... 49
3.8.3 Trigger holdoff ..................................................................................................... 50
3.9 Set trigger system.................................................................................................... 50
3.10 Menu and control button ....................................................................................... 51
3.11 Connectors ............................................................................................................ 51
Chapter 4 Application Examples...................................................53
4.1Taking Simple Measurements.................................................................................. 53
4.2 Taking Cursor Measurements ................................................................................. 54
4.2.2 Measuring Ring Amplitude.................................................................................. 55
4.3 Capturing a Single-Shot signal ............................................................................... 55
4.4 Analyzing signal details .......................................................................................... 56
4.4.1 Looking at a Noisy Signal.................................................................................... 56
4.4.2 Separating the Signal from the Noise................................................................... 56
4.5 Triggering on a Video Signal .................................................................................. 56
4.5.1 Triggering on a Video Field ................................................................................. 56
4.5.2 Triggering on Video Lines ................................................................................... 57
4.6 Application for the X-Y function............................................................................ 57
4.7 Analyzing a Differential Communication Signal.................................................... 58
Chapter 5 Prompt messages and troubleshooting hints.................60
Appendix A: Specifications........................................................... 62
Appendix B: Default setup............................................................ 65
Appendix C: Sample Rate versus Timebase Setting ..................... 66
Appendix D: Daily Maintenance and Cleaning ............. 66
Appendix E: Index ........................................................................68
Appendix F: Service and Warranty Information ...........................69
5
Page 6

Chapter 1 Getting Started
This Chapter describes the following:
◆ Installation
◆ Basic functional check
◆ Probe check and compensation
◆ Setting of probe attenuation factor
◆ Self calibration procedure
1.1 Installation
Inspection
Inspect the shipping container and the product for damage. In case of any damage, notify your authorized
B+K Precision distributor. Make sure all the accessories as described in the specification chapter are
included.
Power Source
Connect your instrument to an AC power outlet delivering 100 – 240V, 47 – 440 Hz. Use the power cord
provided or a comparable cord with an Earth ground connector.
Security Loop
The instrument provides a security loop located in the rear panel of the instrument. Use a security cable
or a security lock to secure your instrument to your location.
1.2 Functional check
Perform this check to make sure your instrument is operating correctly.
1. Power On the oscilloscope.
Press the “DEFAULT SETUP” button. Note that the probe default attenuation is 10X.
6
Page 7

ON OFF
P
/
button
Figure 1- 2
2. Set the switch to 10X on the included probe and connect it to channel 1 on the oscilloscope. To do
this, align the slot in the probe connector with the key on the CH 1 BNC, push to connect, and twist to
the right to lock the probe in place. Connect the probe tip and reference lead to the PROBE COMP
connector.
PROBE COM
CH1
Figure 1-3
3. Press the “AUTO” button. After a few seconds, you should see a square wave signal with a 1KHz
frequency and about 3V peak-peak amplitude
Figure 1- 4
4 Press the “CH1” button two times to remove the signal from CH1. Repeat steps 2) and 3) for CH2.
7
Page 8

1.3 Probe handling
1.3.1 Probe Safety
A guard around the probe body provides a finger barrier for protection from electric shock.
Figure 1-5
Connect the probe to the oscilloscope and connect the ground terminal to ground before you take any
measurements.
WARNING
● To avoid electric shock when using the probe, keep fingers behind the
● To avoid electric shock while using the probe, do not touch metallic
guard on the probe body.
portions of the probe head while it is connected to a voltage source.
1.3.2 Probe Compensation
Perform this adjustment to match your probe to the input channel. This should be done whenever you
attach a probe to any input channel for the first time.
8
Page 9

Figure 1-6
1. Set the Probe option attenuation in the channel menu to 10X. Set the switch to 10X on the probe and
connect the probe to channel 1 on the oscilloscope. If you use the probe hook-tip, ensure a proper
connection by firmly inserting the tip onto the probe.
2. Attach the probe tip to the PROBE COMP~3V connector and the reference lead to the PROBE
COMP Ground connector. Display the channel and then push the“AUTOSET” button.
3. Check the shape of the displayed waveform.
Over compensated Correctly Compensated Under compensated
Figure 1-7
4. If necessary, use a non-metallic tool to adjust the trimmer capacitor on the probe for to resemble the
Correctly Compensated wave shape as much as possible.
Repeat as necessary.
1.3.3 Probe Attenuation Setting
Probes are available with various attenuation factors which affect the vertical scale of the signal. If you
change the Attenuation switch on the probe, you also need to change the attenuation setting on the
oscilloscope accordingly.
Note. The default setting for the Probe option is 10X.
Be sure that the Attenuation switch on the probe matches the Probe option in the oscilloscope. Switch
9
Page 10

settings are 1X and 10X.
Note. When the Attenuation switch is set to 1X, the probe limits the bandwidth
of the oscilloscope to 6MHz. To use the full bandwidth of the oscilloscope, be
sure to set the switch to 10X.
1.4 Self Calibration
The self calibration routine lets you optimize the oscilloscope’s signal path for maximum measurement
accuracy. You can run the routine at any time but should always run the routine if the ambient temperature
changes by 5℃ or more.
To compensate the signal path, disconnect any probes or cables from the front-panel input connectors.
Then, push the UTILITY button, select the “Do Self Cal” option and follow the directions on the screen.
10
Page 11

Chapter 2 Main Control sections overview
The front panel is divided into easy-to-use functional areas. This chapter provides you with a quick
overview of the main controls.
Figure 1- 1 Front Panel Controls
To use your oscilloscope effectively, you need to familiarize yourself with the following control sections:
◆ Vertical System
◆ Horizontal System
◆ Trigger System
◆ Acquisition System
◆ Display System
◆ Measurement System
◆ Utility Menu
◆ Store/Recall Menu
2.1 Vertical System
Each channel has a vertical control menu which appears after pressing the CH1 or CH2 button. The
vertical controls are used to size and position the signals and to turn the waveform on or off. Below is a
figure of the vertical system controls.
11
Page 12

`
Figure 2-1
Table 2-1 Vertical Control menu
Menu Settings Explanation
DC
Coupling
BW limit
Volts/Div
Probe
Invert
Vertical POSITION knob :Use the VERTICAL POSITION knobs to move waveforms up or down on
AC
GND
On/Off Limits the bandwidth to 20 MHz, in order to reduce display nose and to filter out
Coarse
Fine
1X
10X
100X
1000X
on
off
Both AC and DC components of the input signal are passed on to the oscilloscope
The DC component is blocked, only the AC component of the input signal is passed
through. Signals below 10Hz are attenuated
The waveform is disconnected from the oscilloscope
unwanted high frequency components
Selects the resolution of the Volts/Div knob. Coarse defines a 1-2-5 sequence.
Fine changes the resolution to small steps between the coarse settings
Set to match the type of probe you are using to ensure correct vertical readouts
Waveform inverted
Invert function is off, original waveform is displayed.
the screen.
Vol t s /D iv kn ob :Use the VOLTS/DIV knobs to control how the oscilloscope amplifies or attenuates the
source signal. When you turn the VOLTS/DIV knob, the oscilloscope increases or decreases the vertical
size of the waveform on the screen with respect to the ground level. Press the“Volt/div” knob to toggle
between “Coarse” and“ Fine” adjustment of the Volt/Div setting.
GND Coupling. Use GND coupling to display a zero-volt waveform. Internally, the channel input is
connected to a zero-volt reference level.
Fine Resolution:The vertical scale readout displays the actual Volts/Div setting while in the fine
resolution setting. Changing the setting to coarse does not change the vertical scale until the VOLTS/DIV
control is adjusted.
12
Page 13

Remove the Waveform from the display: Push the CH1 or CH2 button to display the respective vertical
menu. Push CH1 or CH2 button again to remove the waveform.
Note:
● If DC coupling is active,you can quickly measure the DC component of the signal by
simply noting its distance from the ground symbol.
● If the channel is set to AC coupling,the DC component of the signal is blocked allowing
you to use greater sensitivity to display the AC component of the signal.
2.2 Horizontal System
The horizontal controls change the horizontal scale and position of waveforms. The horizontal center of
the screen is the time reference for waveforms. Changing the horizontal scale causes the waveform to
expand or contract around the screen center. The horizontal position knob changes the position of the
trigger point relative to the center of the screen. Below is a figure of the front panel horizontal systems
controls.
Figure 2- 2
Table 2- 2 Horizontal Control Menu:
Menu Explanation
Main Display the waveform
Win Zone Define a window (zoom window) by adjusting the cursor position using the
Horizontal control knobs
Window Expand the waveform defined in Win Zone to full screen width
Holdoff Using the Adjust knob to adjust the holdoff time
Holdoff Reset Reset the holdoff time to 100ns
The center axis of the vertical scale is GND level. The readout on the top right corner, shows the
horizontal position. “M” stands for main time base,“W” stands for window time base (Zoom function,
horizontal menu)。The arrow on the top center scale shows the vertical position.
13
Page 14

Figure 2-3
Horizontal POSITION Knob: Used to control the position of the trigger relative to the center of the
screen. When the trigger point (downward arrow) moves outside the acquired waveform, (reaches the left
or right edge of the screen) the instrument switches automatically to delayed sweep, indicated by the arrow
pointing left or right instead of downwards. In delayed sweep mode, you can use the horizontal Time/Div
knob to acquire more detail around the center of the screen.
Time/Div Knob: Used to change the horizontal time scale to magnify or compress the waveform. If
waveform acquisition is stopped (using the RUN/STOP or SINGLE button), the SEC/DIV control
expands or compresses the waveform;Pressing the Time/Div knob resets the horizontal position to
zero.
Window Zone: Define the zoom area of a waveform section. The Window time base setting cannot
be set to a value slower than the main time base setting.
Window:Press to expand the zoom area to cover the whole screen.
Holdoff:You can use Holdoff to produce a stable display of complex waveforms. During the
holdoff time the oscilloscope will not trigger until the holdoff time has expired. For a pulse train,
you can adjust the holdoff time so the oscilloscope triggers only on the first pulse in the train.
Trigger position
Figure 2-4
Holdoff time
14
Trigger level
Page 15

Note:
• When you change between the Main, Window Zone, and Window views,
the oscilloscope erases any waveform which was saved on the screen
using persistence.
• Use holdoff to help stabilize the display of aperiodic waveforms.
2.3 Trigger System
The trigger determines when the oscilloscope starts to acquire data and display a waveform. The
oscilloscope acquires data while waiting for the trigger condition to occur. After it detects a trigger, the
oscilloscope continues to acquire enough data so that it can draw the waveform on the display. Below are
the trigger section controls:
Figure 2-5
“TRIG MENU” Button:press the “TRIG MENU” Button to display the TRIG MENU
Figure 2-6
15
Page 16

LEVEL Knob:Set the trigger level
SET TO 50% Button:Use the SET TO 50% button to stabilize a waveform quickly. The
oscilloscope automatically sets the Trigger Level about halfway between the minimum and maximum
voltage levels. This is useful when you connect a signal to the EXT TRIG BNC and set the trigger
source to Ext or Ext/5.
FORCE Button:Use the FORCE TRIG button to complete the current waveform acquisition
regardless of whether or not the oscilloscope detects a trigger. This is useful for SINGLE acquisitions
and Normal trigger mode.
2.3.1 Signal Source
You can use the Trigger Source options to select the signal that the oscilloscope uses as a trigger. The
source can be any signal connected to the CH1 or CH2 connectors, the EXT TRIG connector or the AC
power line (available only with Edge trigger).
2.3.2 Trigger Type
The 2530 series supports three types of Trigger signals:Edge,Video and Pulse Trigger. Edge trigger can be
used with analog and digital circuits. An edge trigger occurs when the trigger input passes through a
specified voltage level with the specified slope. Pulse trigger is used to find pulses with certain pulse
widths. Video is used to trigger on fields or lines for standard video waveforms.
16
Page 17

Table 2-3 Edge Trigger Menu :
Menu Setting Explanation
Type Edge
CH1
CH2
EXT
Source
EXT/5
AC Line
Rising
Slope
Falling
Auto
Mode
Normal
With Edge selected, the rising or falling edge of the input signal is
used for the trigger
Triggers on CH1 or CH2 regardless of whether or not the waveform
is displayed。
Uses the signal connected to the EXT TRIG front-panel BNC as
trigger source. Trigger level range is -2.4V to +2.4V
Same as EXT but attenuates the applied trigger signal by a factor of
five. The trigger level range is extended to +12V to -12V.
Uses power line as the trigger source. Trigger coupling is set to DC
and the trigger level is 0 volts.
Trigger to the rising or falling edge
Use the Auto Mode to let acquisition free-run in the absence of a
valid trigger condition.. This mode also supports an untriggered,
scanning waveform at 100 ms/div or slower time base settings
Use this mode when you want to see only valid triggered
waveforms. When you use this mode, the oscilloscope does not
display a waveform until after the first trigger
Coupling
Single
DC Passes all components of the signal
AC Blocks DC components and attenuates signals below 10 Hz
HF Reject Attenuates the high-frequency components above 80 kHz
LF Reject
When you want the oscilloscope to acquire a single waveform,
press the “SINGLE ”button
Blocks the DC component and attenuates the low-frequency
components below 300 kHz
17
Page 18

Table 2-4 Video Trigger Menu:
Menu Setting Explanation
Type Video When you select Video Trigger mode, set coupling to AC. Now
you can trigger from a NTSC or PAL/SECAM video signal.
CH1
CH2
EXT
EXT/5
Polarity
Sync
Standard
Table 2-5 Pulse Trigger Menu:
A pulse trigger occurs when a pulse is found in a waveform that matches the pulse definition. The When
and Set Width menu buttons control the pulse definition.
Menu Setting Explanation
(Normal)
(Inverted)
Line Num
All lines
Odd field
Even Field
NTSC
Pal/Secam
Select the input source to be the trigger signal. Source
Ext and Ext/5 use the signal applied to the EXT TRIG connector as the
source.
Triggers on the negative edge of the sync pulse
Triggers on the positive edge of the sync pulse
Select on which part of the video signal you want to trigger
Select the video standard for sync and line number count
Type
Source
When
Pulse Select the pulse to trigger the
pulse match the trigger condition
CH1
CH2
EXT
EXT/5
(Positive pulse width less than pulse width setting)
(Positive pulse width larger than pulse width setting)
(Positive pulse width equal to pulse width setting)
(Negative pulse width less than pulse width setting)
(Negative pulse width larger than pulse width setting)
18
Select how to compare the trigger
pulse relative to the value
selected in the Pulse Width
option
Page 19

(Negative pulse width equal to pulse width setting)
set width
Mode
Coupling
Hint:Use Pulse Width triggering to trigger on aberrant pulses.
20.0ns~10.0s
Auto
Normal
single
DC
AC
HF Reject
LF Reject
Adjust the pulse width with the
ADJUST knob
Select the type of triggering;
Normal mode is best for most
Pulse Width trigger applications
2.3.3 Coupling
Use “Coupling” to select which component of the signal to pass on to the trigger circuit. This parameter
only applies to Edge or Pulse trigger mode, for Video trigger mode coupling is always set to AC.
2.3.4 Position
The horizontal position control establishes the time between the trigger position and the screen center. You
can adjust the HORIZONTAL POSITION control to view waveform data before the occurrence of the
trigger, after the trigger, or any point in between. When you change the horizontal position of a waveform,
you are changing the time between the trigger and the actual center of the display. (This appears to move
the waveform to the right or left on the display.). Use a pretrigger setting to acquire waveforms leading up
to a trigger event. Use a post trigger setting when you want to acquire waveforms that follow an event.
When the trigger point (downward arrow) moves outside the acquired waveform, (reaches the left or right
edge of the screen) the instrument switches automatically to delayed sweep, indicated by the arrow
pointing left or right instead of downwards. In delayed sweep mode, you can use the horizontal time/Div
knob to acquire more detail around the center of the screen.
2.3.5 Slope & Level
The Slope and Level controls help to define the trigger. The Slope option (Edge trigger type only)
determines whether the oscilloscope finds the trigger point on the rising or the falling edge of a signal. The
TRIGGER LEVEL knob controls where on the edge the trigger point occurs.
19
Page 20

T
r
i
g
g
e
r
l
e
v
e
l
c
a
n
b
e
a
d
j
u
s
t
e
d
v
e
r
t
i
c
a
l
l
y
Rising edge
Falling edge
Figure 2-7
Note:
• Press the SINGLE button when you want the oscilloscope to acquire a single waveform
• Trigger coupling affects only the signal passed to the trigger system. It does not affect the bandwidth
• Normal Polarity Sync triggers always occur on negative-going horizontal sync pulses. If the video
or coupling of the signal displayed on the screen.
waveform has positive-going horizontal sync pulses, use the Inverted Polarity selection.
2.4 Acquisition system
When you acquire a signal, the oscilloscope digitizes the signal and displays the resulting waveform on the
screen. The acquisition mode defines how the signal is digitized, and the time base setting affects the time
span and level of detail in the acquisition. The sampling rate adjusts automatically to a value suitable for
each selected Time/Div scaling factor. Refer to Appendix C for more detailed information.
Push the ACQUIRE button to access the Acquisition menu
Figure 2-8
Acquire button
20
Page 21

Table 2- 6 Acquire Menu:
Menu Set up Explanation
Sampling Use to acquire and accurately display most waveforms
Peak Detect Use to detect glitches and decrease the possibility of aliasing.
Average Select this mode to reduce the displayed random noise.
Averages 4
16
32
64
128
256
Mode Equ time
Real time
The 3 acquisition modes Sample, Peak Detect and Average:
Specify number of averages
Select realtime or equivalent sampling
Sampling: In this acquisition mode, the oscilloscope samples the signal in evenly spaced intervals to
reconstruct the waveform. This mode accurately represents the signal most of the time.
Advantage
Disadvantage
samples. This can result in aliasing and may cause narrow pulses to be missed. In these cases, you
should use the Peak Detect mode to acquire data.
: You can use this mode to reduce random noise.
: This mode does not capture rapid variations in the signal that may occur between
Figure 2-9 Sampling mode
Peak Detect: Peak Detect finds the maximum and minimum values of a signal.
Advantage
otherwise been missed in Sample mode.
Disadvantage
: In this way, the oscilloscope can acquire and display narrow pulses, which may have
: Noise will appear to be higher in this mode.
21
Page 22

Figure 2-10 Peak Detect mode
Average: The oscilloscope acquires several waveforms, averages them, and displays the resulting
waveform.
Advantage
Figure 2-11 Average mode
: You can use this mode to reduce random noise.
Equivalent Time Sampling: The equivalent time sampling mode can achieve up to 20 ps of
horizontal resolution (equivalent to 50 GSa/s). This mode is good for observing repetitive
waveforms.
Real Time Sampling: The maximum sampling rate for the 2530 is 250 MSa/s and 500MSa/s for
the 2532.
RUN/STOP Button: Press the RUN/STOP button when you want the oscilloscope to acquire
waveforms continuously (Run/Stop button is green). Press the button again to stop the
acquisition.( Run/Stop button is red)
22
Page 23

SINGLE Button:Push the SINGLE button when you want the oscilloscope to acquire a single
waveform and then stop. (Make sure the Run Stop button is green and the display annunciator is in
the Ready state). After the oscilloscope detects a trigger, it completes the acquisition then stops.
Each time you push the SINGLE button, the oscilloscope begins to acquire another waveform.
Base time: The oscilloscope digitizes waveforms by acquiring the value of an input signal at discrete
points. The time base allows you to control how often the values are digitized. Appendix C details the
corresponding sampling rate for each time base setting. To adjust the time base to a horizontal scale
that suits your purpose, use the Time/DIV knob.
Time Domain Aliasing:Aliasing occurs when the oscilloscope does not sample the signal fast
enough to construct an accurate waveform record. When this happens, the oscilloscope displays a
waveform with a frequency lower than the actual input waveform, or triggers and displays an unstable
waveform.
Actual high-frequency waveform
Apparent low-frequency
waveform due to aliasing
Sampled points
Figure 2-12
2.5 Display System
Push the display button to choose how waveforms are presented and to change the appearance of the entire
display.
Display System
Figure 2-13
23
Page 24

Table 2-7
Options Set up Explanation
Type
Persist
Contrast
Format
Screen
Ve c to r s
Dots
Off
1 sec
2 sec
5 sec
Infinite
+
-
YT
XY
Normal
Inverted
Vectors fills the space between adjacent sample
points in the display
Display sample points
Sets the length of time each sampling point
remains visible.
Increase the display contrast
Decrease the display contrast
YT format displays the vertical voltage in
relation to time (horizontal scale)
XY format displays a dot each time a sample is
acquired on channel 1 and channel 2
set to normal mode
set to invert color display mode
Figure 2-14
Grid
Display grids and axes on the screen
Turn off the grids
Turn off the grids and axes
Figure 2-15
24
Page 25

2.5.1 X-Y Format
play typ
Use the XY format to analyze phase differences, such as those represented by Lissajous patterns. The
format plots the voltage on channel 1 against the voltage on channel 2, where channel 1 is the horizontal
axis and channel 2 is the vertical axis. The oscilloscope uses the untriggered sample acquisition mode and
displays data as dots. In this mode, the sampling default sampling rate is 1 MSa/s and is adjustable from
5kSA/s – 200 MSa/s..
Note:The oscilloscope can capture a waveform in normal YT mode at any
sampling rate. You can view the same waveform in XY mode. To do so, stop
the acquisition and change the display format to XY.
In this mode, the controls operate as followed:
• The Channel 1“Volts/div”and vertical “POSITION” controls set the horizontal scale and position.
• The Channel 2“Volts/div”and vertical “POSITION” controls continue to set vertical scale and
position.
The following functions do not work in XY mode:
• Reference or math waveform
• Cursors
• Autoset(resets display format to YT)
• Trigger Controls
• Horizontal Position Knob
• Vector Display Type
• Scan Display
Note: When the display Type is set to Vectors, the oscilloscope connects the sample points by using digital
interpolation. Interpolation mode contain linearity interpolation and sin(x)/x interpolation. Sin(x)/x interpolation
is suitable for real time mode and is most effective at 250ns/div or faster time. The oscilloscope automatically
switches to the most suitable dis
e based on the timebase setting.
2.6 Measurement system
There are several ways to take measurements. You can use the graticule, the cursors, or make an
automated measurement.
25
Page 26

2.6.1 Graticule Measurement
This method allows you to make a quick, visual estimate. For example, you might look at a waveform
amplitude and determine that it is a little more than 100 mV. You can take simple measurements by
counting the major and minor graticule divisions involved and multiplying by the scale factor. For example,
if you counted five major vertical graticule divisions between the minimum and maximum values of a
waveform and knew you had a scale factor of 100 mV/division, then you could easily calculate your
peak-to-peak voltage as follows:
5 divisions x 100 mV/division = 500 mV.
2.6.2 Cursor Measurement
This method allows you to take measurements by moving the cursors, which always appear in pairs, and
reading their numeric values from the display readouts. Access the Cursor menu by pressing the Cursor
button.
Cursors Button
Table 2-7 Functional Menu of the Cursor
Menu Setting Comment
Type Voltage
Time
Off
Source CH1
CH2
MATH
REFA
REFB
Cur1
Cur2
Activate Cursor 1. Use the ADJUST knob to adjust the cursor position
Activate Cursor 2. Use the ADJUST knob to adjust the cursor position.
Figure 2-16
Select and display the measurement cursors. The horizontal cursor measures
amplitude and the vertical cursor measures time and frequency.
Select the wave form source to be measured by the cursors
26
Page 27

Figure 2-17
Voltage Cursor: Voltage cursors appear as horizontal lines on the display and measure the
vertical parameters.
Time Cursor: Time cursors appear as vertical lines on the display and measure the horizontal
parameters.
Moving Cursors:Use the ADJUST knob to move cursor1 and cursor2. Cursors can be moved
when the cursor menu is displayed.
2.6.3 Auto Measurement “MEASURE”:
When you take automatic measurements, the oscilloscope does all the calculating for you. Because this
method relies on the digital samples of the waveform, this method is more accurate than graticule or cursor
measurements.
Auto Measurement button
Figure 2-18
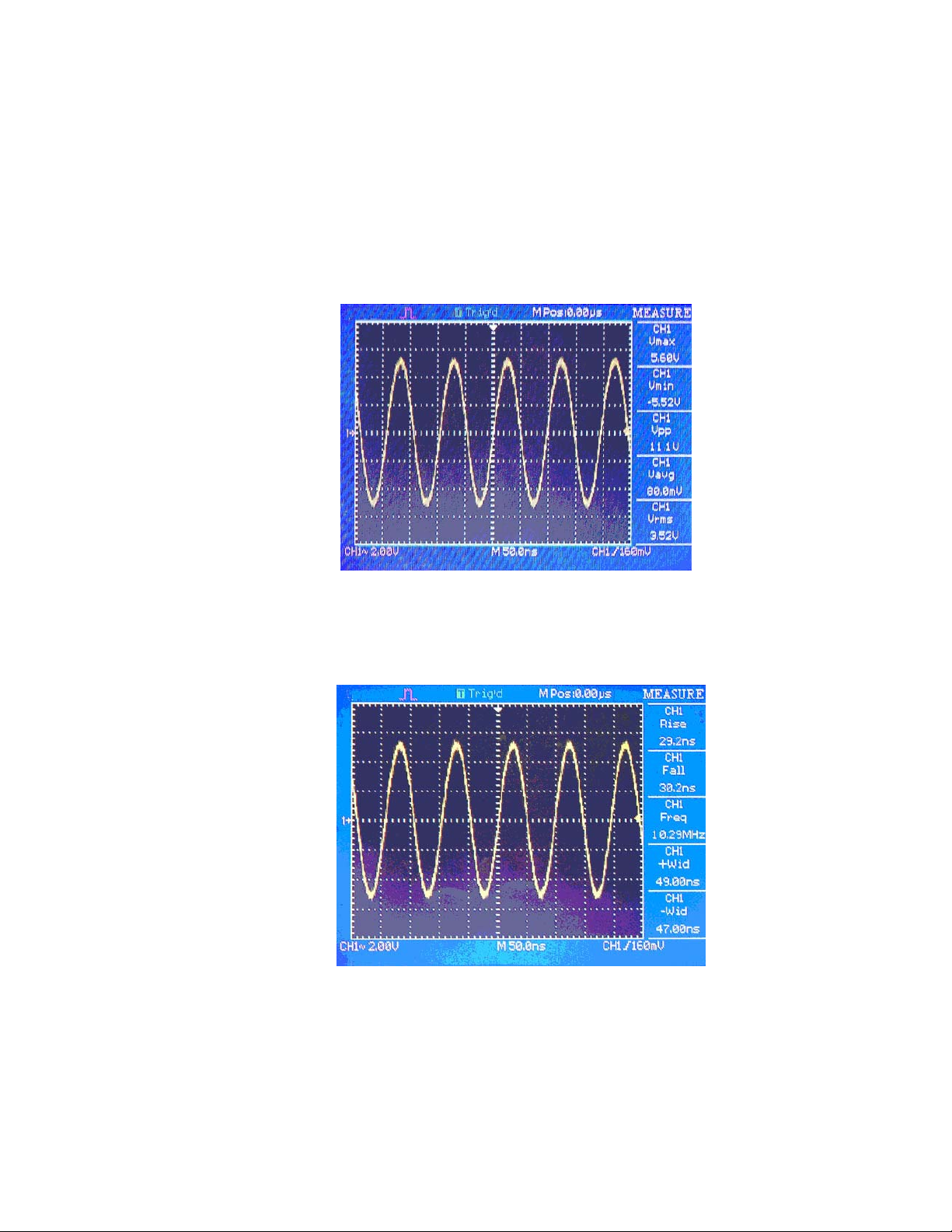
Press the ‘MEASURE’ button. There are 11 types of measurements available. You can display up to five
measurements at a time. To define each of the 5 measurements, do the following:
27
Page 28
1. Press one of the five option buttons corresponding to measurement 1 – 5 . This will open a sub
menu.
2. Enter the Source of the measurement and the measurement type
3. Press the bottom option button to turn the measurement on
If you want to display all eleven measurements at once, select “All Mea” from the sub menu (step 2)
Voltage Measurements:Max, Min, Peak-Peak, Average, Vrms。
Figure 2-19
Time Measurements:Rise time, Fall time, Frequency, Period, positive pulse width, negative pulse width.
Figure 2-20
28
Page 29

2-8 Measurement Types:
Measure Type Introduction
Vmax
Vmin
Vpp
Vavg
Vrm s
Rise
Fall
+ Width
- Width
Prd Measure the Period
Freq Measure the Frequency
* The instrument displays 2500 points. The full record length of 4000 points can be retrieved from internal memory with
the included EasyScope application Software
Vmax examines the entire 2500 point waveform record and displays the
maximum value
Vmin examines the entire 2500 point waveform record and displays the
minimum value
Vpp calculates the absolute difference between the maximum and minimum
peaks of the entire waveform
Count the arithmetic average value in the record
Calculates a RMS measurement of the first complete cycle of the waveform
Rise Time measures the time between 10% and 90% of the first rising edge
of the waveform.
Fall Time measures the time between 90% and 10% of the first falling edge
of the waveform.
+ Width measures the time between the first rising edge and the next falling
edge at the waveform 50% level.
-Width Measures the time between the first falling edge and the next rising
edge at the waveform 50% level.
Select “All measurements”to display all eleven measurements at once.
Fig. 2.21
29
Page 30
2.7 Utility System
”: The Utility System Button。
Utility Setup button
Figure 2-22
Table 2- 9 Utility Menu options
Option Setting Comment
System Status Displays information about the hardware and software
configuration
Sound This option turns the button beep on or off
Counter On
Off
Language English
DO self cal Run the Self Calibration routine
Do Self Test Screen Test
Keyboard Test
LED Test
Press the UTILITY button to see the “Utility menu”
Turn the Trigger frequency counter On/Off*
Run a screen test
Run a keyboard test
Run the LED test
Figure 2-23
30
Figure 2-24
Page 31

2.7.1 System status
Selecting “System Status” from the Utility Menu to display information about a particular unit
Tabl e 2- 1 0
Display Explanation
Startup Times Counts the times the unit was turned on/off.
Software version Gives the software version
Hardware Version Gives the hardware version
Product type Lists the model number
Serial No. List the unit’s serial number
2.7.3 Self Calibration
Before executing the Self Calibration routine, disconnect all probes and leads from the input connector.
Then press the “Utility” button and select “Do self cal” to show the self Calibration Menu.
Figure 2-25
2.7.4 Self Test
Tab le 2- 12 Press“UTILITY”→“Do Self Test”
Option Introduction
Screen Test Run Screen Test Program
Keyboard Test Run Keyboard Test Program
LED Test Run LED Test Program
31
Page 32

(1) Screen Test:
Select “Screen Test” to enter the screen mode. Press the SINGLE key to continue,press RUN/STOP to
exit.
(2) Keyboard Test
Select “Keyboard Test” to enter the key test mode. The shapes with two arrows beside them represent the
front panel knobs. The squares represent the knob presses for scale knobs. Test all keys and knobs and
verify that all the backlit buttons illuminate correctly. Press RUN/STOP 3 times to exit.
(3) LED test
Select “LED Test” to run the LED test procedure. Continually press the SINGLE key to step through all
the buttons. Press RUN/STOP to exit.
2.8 Save/Recall System
Use this menu to save and recall waveforms and setups. The instrument can store/recall 10 setups and 10
waveforms.
Save/Recall control button
Figure 2-26
SAVE/RECALL SETUP
SAVE/RECALL Setup: The complete setup is stored in nonvolatile memory. When you recall the
setup, the oscilloscope will be in the mode from which the setup was saved. The oscilloscope will
automatically save the current setup if you wait three seconds after the last change before you power
off the oscilloscope. The oscilloscope recalls this setup the next time you apply power. Up to 10
setups can be recalled/stored.
32
Page 33

Table 2-13
Menu Setting Explanation
Type Setups Menu for the Storage/Recall setting in the
oscilloscope
Setup NO.1 to NO.10 Select the memory location to/from which you want
to save/recall a setup
Save Save a setup to the memory location selected
Recall Recall a setup from the memory location selected
Figure 2-27
RECALL FACTORY: You can use this option to recall the factory setup. Select type Factory then
press LOAD.
Figure 2-28
33
Page 34

SAVE/RECALL WAVEFORM
SAVE/RECALL CAPTURED WAVEFORM: The oscilloscope must display any waveform that
you want to save. The oscilloscopes can store ten captured waveforms in nonvolatile memory.
Table 2-15
Option Setup Introduction
Type waveforms Menu for the Storage/Recall waveforms in the oscilloscope
waveform NO.1 to NO.10 Save/Recall the waveforms in the currently position
Save
Recall Recall the storage in the “waveform” operation
Accomplish the storage
Figure 2-29
■ SAVE/RECALL REFERENCE WAVEFORM:The oscilloscopes can store two reference
waveforms in nonvolatile memory. The oscilloscope can display 2 reference waveforms at a time.
Reference waveforms are not adjustable, but the oscilloscope does display the horizontal and vertical
scales at the bottom of the screen. (more details see Chapter 3)
34
Page 35

Chapter 3 Operating Basics
The previous chapter introduced the main functional blocks of the instrument. This chapter explains in
more detail how to set up the oscilloscope to view signals and to make measurements.
Explanation of Display area
Using the Menu System
Using the Default Setup
Using the Auto Setup
Using the Universal knob
Setting up the Vertical System
Setting up the Horizontal System
Setting up the Trigger System
Using Math and FFT Functions
Menu and Control Buttons
Connectors
3.1 Display Area
Figure 3-1A Figure 3-2B
1 Acquisition mode
Sampling mode
Peak detect mode
35
Page 36

Average mode
2 Trigger status
□ Armed. The oscilloscope is acquiring pretrigger data. All triggers are ignored in this state.
Ready. All pretrigger data has been acquired and the oscilloscope is ready to accept a
trigger
T
Trig’d. The oscilloscope has received a trigger signal and is acquiring the post trigger data.
Stop. The oscilloscope has stopped acquiring waveform data. Single Trigger mode: The
oscilloscope has completed a Single acquisition.
Auto. The oscilloscope is in auto mode and is acquiring waveforms in the absence of a
trigger signal.
□ Scan. The oscilloscope is acquiring and displaying waveform data continuously in scan
mode.
3 Marker shows horizontal trigger position. Turn the HORIZONTAL POSITION knob to adjust
the position of the marker.
4 Read out of the time at the center graticule.
5 The marker indicates the edge and pulse width trigger level.
6 The on-screen markers show the ground reference points of the displayed waveforms. If there is
no marker, the channel is not displayed.
7 Readout shows the vertical factor of the channels
8 Readout of the main time base setting
9 Readout of the window time base setting, when window mode (zoom) is activated
10 Trigger source for trigger section
11 Icon indicates selected trigger types
12 Readout of edge and pulse width trigger level. Indicates the line number when in Video trigger
mode
13 Displays Reference A Voltage and time base setting if REFA is activated
14 Displays Reference B Voltage and time base setting if REFB is activated
15 Displays reading of Trigger reference counter if activated
3.2 Using the Menu System
When you press a front-panel button, the oscilloscope displays the corresponding menu on the right side of
the screen.
directly to the right of the screen.
The menu shows the options that are available when you press the unlabeled option buttons
36
Page 37
The oscilloscope uses three methods to display menu options:
■ Circular List: The oscilloscope sets the parameter to a different value each time you press the option
button.
■ Action: The oscilloscope displays the type of action that will immediately occur when you push an
Action option button. For example, when you push the DISPLAY Menu button and then push the
Contrast Increase option button, the oscilloscope changes the contrast immediately.
■ Radio: The oscilloscope uses a different button for each option. The currently-selected option is
highlighted.
Circular list Action Radio
Figure 3-3
3.3 Using the default setup
The oscilloscope is set up for normal operation when it is shipped from the factory. This is the default
setup. To recall this setup, press the DEFAULT SETUP button. The options, buttons and controls that
change settings when you press the DEFAULT SETUP button, refer to appendix B. The DEFAULT
SETUP button does not reset the following settings:
● Saved reference waveform files
● Saved setup files
● Display contrast
● Calibration data
3.4 Using the auto setup
The 2530 & 2532 Digital Storage Oscilloscope has an auto setup function which can identify the type of
waveform and automatically adjust controls to produce a usable display of the input signal. Press the Auto
button to activate this mode
37
Page 38

Table 3-1 Auto set the function Menu :
Option Set Up Comment
(Undo Setup)
(
Auto set the screen and display multiple cycles
Auto set the screen and display a single cycle
Auto set and show the rise time
Auto set and show the fall time
Causes the oscilloscope to recall the previous setup
Figure 3-3
When you press the AUTOSET button, the oscilloscope identifies the type of waveform and adjusts
controls to produce a usable display of the input signal. Autoset determines the trigger source based on the
following conditions:
● If a signal is applied to both channels, the instrument displays the channel with the lowest frequency
● If no signals are found, the oscilloscope displays Channel 1.
Table 3-2 Oscilloscope settings for Auto mode
Function Setting
Acquire Mode Set to Sampling
Acquire Type Equ time (Equivalent Sampling)
Display Format Y-T
Display Type Set to Dots for a video signal, set to Vectors for an FFT spectrum;
otherwise, unchanged
Vertical Coupling Set to DC or AC according to the input signal
38
Page 39

Volts/DIV Adjusted
VOLTS/DIV
adjustability
Signal inverted off
Horizontal position Adjusted
Time/div Adjusted
Trigger type Edge
Trigger source Auto detect the channel which has the input signal
Trigger slope Rising
Trigger mode Auto
Trigger coupling DC
Trigger holdoff Minimum
Trigger level Set to 50%
Coarse
3.5 Using the ADJUST knob
ADJUST knob
Figure 3-4
The 2530 Series Digital Storage Oscilloscope comes with an ADJUST knob. Use this knob to set up the
holdoff time, cursor positions for measurements, pulse width
Adjust holdoff time
1. Press the HORI MENU button to show the “Hori Menu”.
2. Press the holdoff option button
3. Turn the ADJUST knob to adjust the holdoff time。
and the Video Line number
Cursor Measure
1. Press the CURSORS button to display the cursor Menu.
2. Press the “Source” option button to select the source.
39
Page 40

3. Press the Cur1 option button, turn the ADJUST knob to adjust Cur1.
4. Press the Cur2option button, turn the ADJUST knob to adjust Cur2.
5. The value of Cursor1 and Cursor2 is incremented and displayed on the top right of the screen.
Pulse Setup
1. Press the “TRIG MENU” button to display the Trigger Menu.
2. Press the “Type” Option and choose “Pulse”.
3. Press the “ Set Width” button.
4. Turn the ADJUST knob to adjust the pulse width.
Set the Video Line Number
1. Press “TRIG MENU” to show the Trigger Menu
2. Press the “Type” button and select Video trigger.
3. Press the “Sync” operation button, select the line number.
4. Turn the ADJUST knob to adjust Line Num.
3.6 Setting up the Vertical System
3.6.1 Setting up the CH1, CH2 Channels
Each channel has its own separate Menu. The items are set up separately according to each channel.
1. Set up the coupling mode
Apply a sine wave signal with a DC offset to CH1
• Press“CH1”→“Coupling”→“AC”. Set AC coupling mode. Now the DC component of the signal
is blocked.
Figure 3-5
•
Press“CH1”→“Coupling”→“DC”. Set DC coupling mode. Both the DC and AC component of the
signal will be passed on and displayed on the screen.
40
Page 41

Figure 3-6
• Press“CH1”→“Coupling”→“GND”. Select GROUND mode to disconnect the input signal.
Figure 3-7
2.Volts/Div settings
Vertical scaling can be adjusted in 2 modes, Coarse and Fine. The vertical sensitivity range is 2mV/div~
5V/div scale。
Take CH1 for example
• Press“CH1”→“Vo l t s / D i v ”→“Coarse”. This is the default setting of Volts/Div,and it allows
adjustment of the vertical scale in a 1-2-5-step sequence starting from 2mV/Div,5mV/Div,10mv/div
up to 5V/Div.
41
Page 42

Figure 3-10
●
Press“CH1”→“Volts/Div”→“Fine”. This setting changes the vertical scale to small steps between the
coarse settings. It is useful when you need to adjust the vertical scale in small steps to set a specific value.
Figure 3-11
4. Probe Attenuation
The setting of the attenuation coefficient in the menu must match the setting of the probe., If the
attenuation coefficient is 10 :1, the input coefficient should be set to 10X in order to obtain correct
readings.
Example: Probe connected to CH1 has factor of 100:1
● Press“CH1”→“Probe”-“100X.
42
Page 43

Figure 3-12
5. To invert a waveform
● Press“CH1”→“Invert”→“off”
Figure 3-13
●Press“CH1”→“Invert”→“on”
Figure 3-14
43
Page 44

3.6.2 Using the Vertical Position knob and Volts/Div knob
1. The vertical“POSITION”knob is used to adjust the vertical position of each channel (including
MATH and REF wave). This knob’s resolution varies according to the currently set scale factor (set
by Volts/Div knob).
2. The Volts/Div knob adjusts the vertical resolution of each channel, (including the MATH and REF
waves). In Coarse mode, the scale factor steps are adjustable in a 1-2-5 step sequence. To magnify the
display signal turn the knob clockwise, to decrease the waveform turn counter clockwise. Pressing the
Volts/Div knob toggles between Coarse and Fine mode. In the Fine mode, the knob adjusts the
Volts/Div factor in small increments between the coarse settings.
3. When you adjust the vertical position of a channel waveform, the vertical position information will be
displayed on the bottom left of the screen.
3.6.3 Using Ref
The reference control saves waveforms to nonvolatile waveform memory. The reference function
becomes available after a waveform has been saved. Press the Ref button to display the reference
waveform menu
Table 3-7
Option Setup Comment
Source
REF A B Choose the store/recall location
Save Store the current waveform to the selected location
REFA/REFB On
How to Save and Recall waveforms:
1. Press the “REF” menu button to display the reference waveform menu.
2. Select channel1 or channel2
3. Turn the
appropriately.
4. Press Save to save waveforms on the current screen as ref waveforms.
5. Recall reference waveform by setting REF A or REB to On
CH1
CH2
Off
Choose the waveform display you want to store. This option is turned OFF
if the corresponding channel is turned off
Determines which reference wave from is visible on the screen
vertical “POSITION” knob and “Volt/div” knob to adjust the vertical position and scale
Note:
The Ref function is not available in XY mode
You cannot adjust the horizontal position and scale of the reference waveform.
44
Page 45
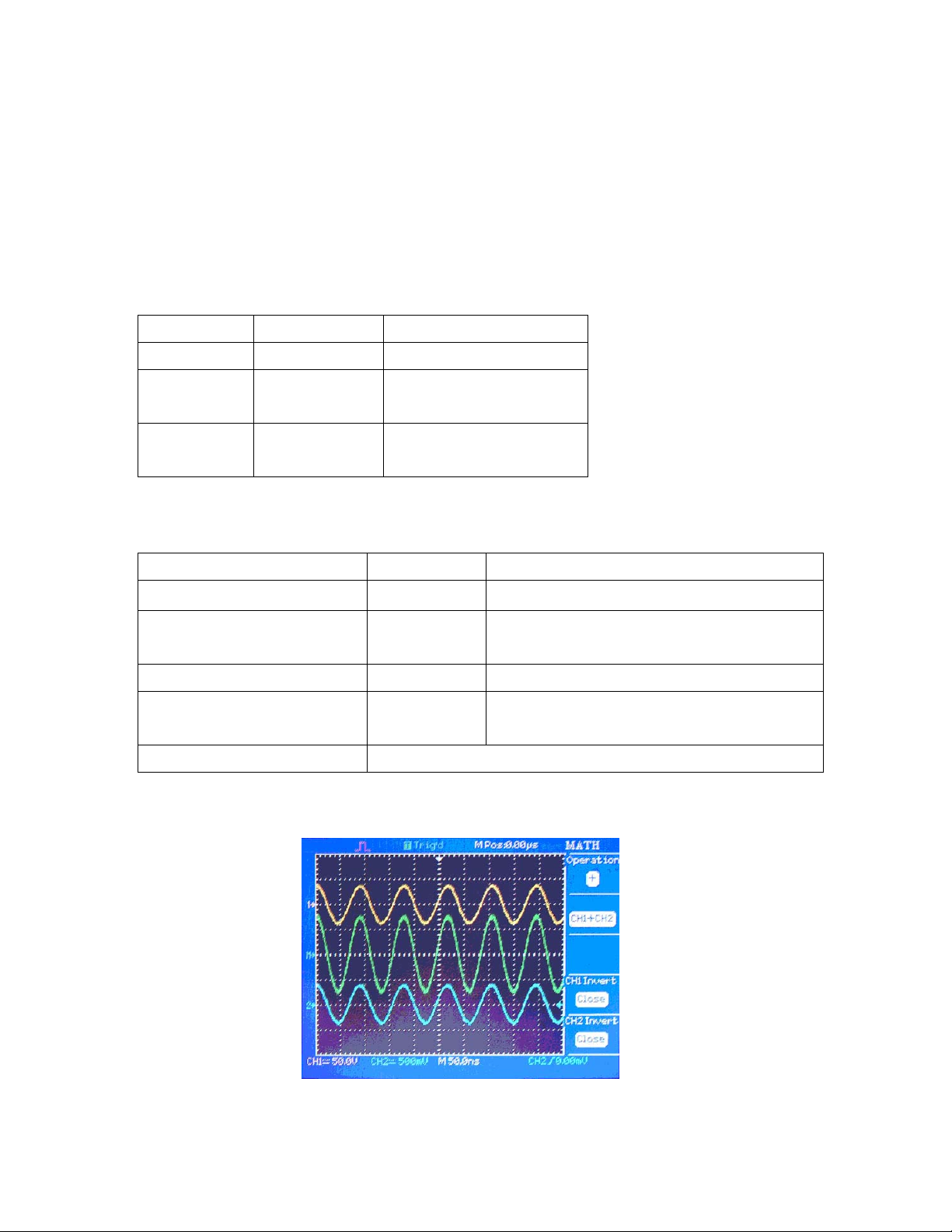
3.7 Math Functions
This oscilloscope supports arithmetic math functions +,-,*, and FFT operations which depending on the
operation, can be applied to either channel or both channels. Press the MATH MENU button to display the
waveform math operations.
Table 3-3 MATH Menu
Function Set up Comment
Operation +, -, *, /, FFT Source 1 plus Source 2
CH1 Invert on
off
CH2 Invert on
off
Table 3-4
Operation Set up Introduction
+
-
* CH1*CH2 Multiply CH1 with CH2 waveform
/
FFT Fast Fourier Transform
Invert the CH1 waveform
Invert the CH2 waveform
CH1+CH2 Add CH1 and CH2 waveforms
CH1-CH2
CH2-CH1
CH1/CH2
CH2/CH1
Subtract channel 2 from channel 1 waveform
Subtract channel 1 from channel 2 waveform
CH1 divided by CH2 waveform
CH2 divided by CH1 waveform
Figure 3-15
45
Page 46
1. FFT Spectrum Analyzer
The FFT process mathematically converts a time-domain signal into its frequency components. You can
use the Math FFT to analyze the following type of signals:
• Characterize noise in DC Power supplies
• Test the impulse response of filters and systems
• Analyze vibration
• Analyze harmonics in power lines
• Measure harmonic content and distortion in a system
Table 3-5
FFT Option Set Introduction
Source
Window
FFT ZOOM
Scale
CH1
CH2
Hanning
Hamming
Rectangular
Blackman
1X
2X
5X
10X
Vrm s
dBVrms
Select the channel to which you want to apply the FFT
operation
Select the FFT window type
Changes the horizontal magnification of the FFT display
Set Vrms to be the Vertical Scale unit
Set dBVrms to be the vertical Scale unit
Figure 3-16
46
Page 47

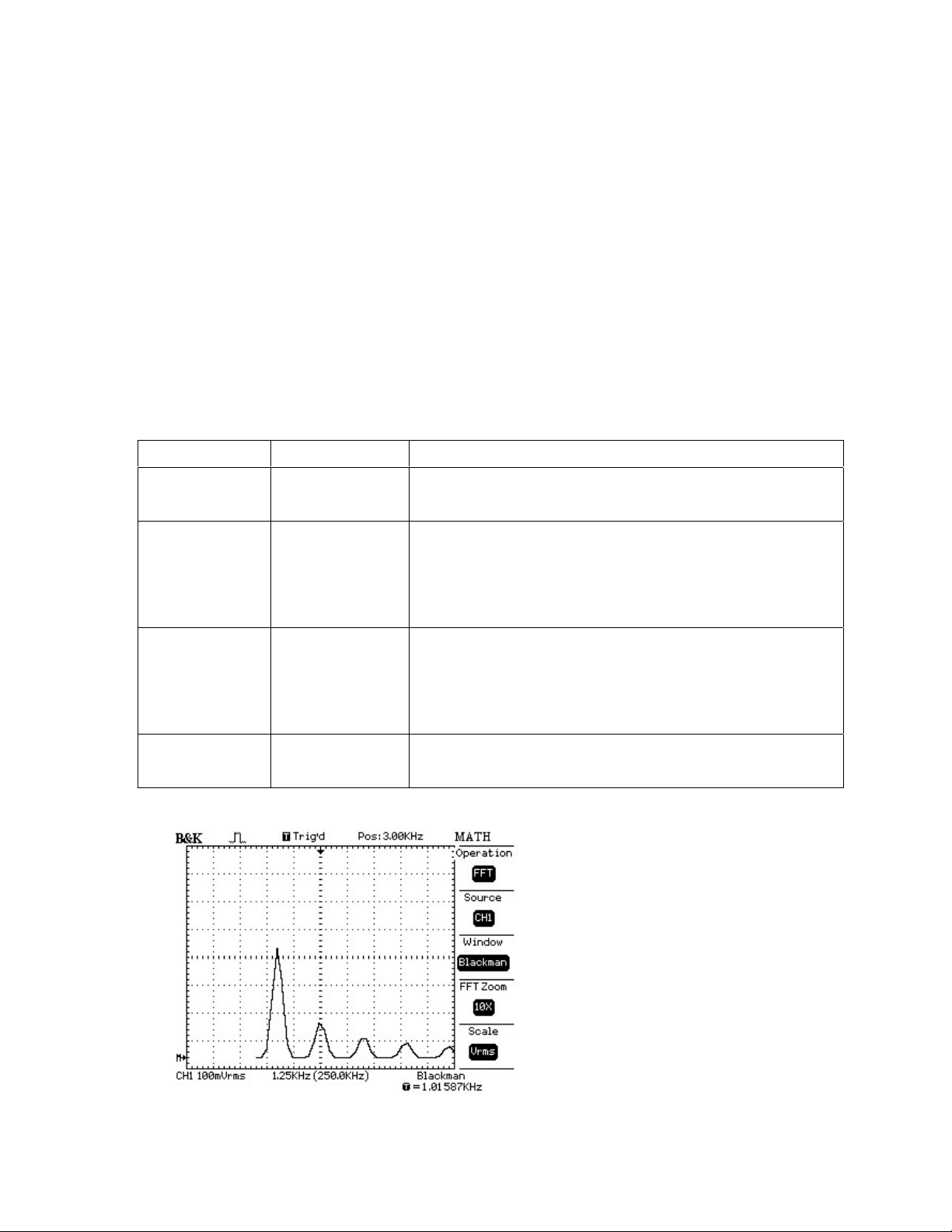
Explanation of Figure 3-16:
In this example the position at the center graticule is 3kHz (Pos: 3.00 kHz), the frequency of the second
harmonic. The vertical scale is set to 100mVrms/Div and the horizontal scale is set to 12.5kHz (1.25kHz x
10 zoom factor). The window type is Blackman
To use the Math FFT mode, you need to perform the following tasks:
1. Set up the source YT (time-domain) waveform.
● Press AUTOSET to display a YT waveform.
● Turn the VERTICAL POSITION knob to move the YT waveform to the center vertically (zero
divisions).
● Turn the HORIZONTAL POSITION knob to position the part of the YT waveform that you want to
analyze in the center eight divisions of the screen. The oscilloscope calculates the FFT spectrum
using the center 1024 points of the time-domain waveform.
● Turn the VOLTS/DIV knob to ensure that the entire waveform remains on the screen.
● Turn the Time/DIV knob to provide the resolution you want in the FFT spectrum.
● If possible, set the oscilloscope to display many signal cycles.
To set up the FFT display, follow these steps:
- Push the MATH MENU button.
- Set the Operation option to FFT.
- Select the Math FFT Source channel.
2. Displaying the FFT Spectrum
Press the MATH MENU button to display the Math Menu. Use the options to select the Source channel,
Window algorithm, and FFT Zoom factor. You can display only one FFT spectrum at a time
3. Select an FFT window
Windows reduce spectral leakage in the FFT spectrum. The FFT assumes that the YT waveform repeats
forever. With an integral number of cycles, the YT waveform starts and ends at the same amplitude and
there are no discontinuities in the signal shape A non-integral number of cycles in the YT waveform causes
the signal start and end points to be at different amplitudes. The transitions between the start and end
points cause discontinuities in the signal that introduce high-frequency transients.
There are 4 FFT windows. Each window has trade-offs between frequency resolution and amplitude
accuracy. Your source waveform characteristics along with your measurement priorities help determine
which window to use. Use the following guidelines to select the best window.
47
Page 48

Table 3-6
Window Characteristics Application/ Measurement
Rectangular
Hanning/
Hamming
Blackman
Best frequency resolution, worst
magnitude resolution. This is
essentially the same as no window.
Better frequency, poorer magnitude
accuracy than Rectangular.
Hamming has slightly better
frequency resolution than Hanning.
Best magnitude, worst frequency
resolution.
Symmetric transients or bursts.
Equal-amplitude sine waves with
fixed frequencies. Broadband
random noise with a relatively
slowly varying spectrum.
Sine, periodic, and narrow-band
random noise. Asymmetric
transients or bursts.
Single frequency waveforms, to
find higher order harmonics.
4. Magnifying and Positioning an FFT Spectrum
You can magnify and use cursors to take measurements on the FFT spectrum. The oscilloscope includes an
FFT Zoom option to magnify horizontally. To magnify vertically, you can use the vertical controls.
5. Measuring an FFT Spectrum Using Cursors
You can take two types of measurements on FFT spectrums: magnitude (in dB) and frequency (in Hz).
Magnitude is referenced to 0 dB, where 0 dB equals 1 Vrms. You can use the cursors to take
measurements at any zoom factor.
Use horizontal cursors to measure magnitude and vertical cursors to measure frequency. Make sure to
select the “MATH” as source in the cursor menu.. The options display the delta between the two cursors,
the value at cursor 1 position, and the value at cursor position. Delta is the absolute value of cursor 1 minus
cursor 2.
NOTE:
● The FFT of a waveform that has a DC component or offset can cause incorrect FFT waveform
magnitude values. To minimize the DC component, choose AC Coupling on the source waveform.
● To display FFT waveforms with a large dynamic range, use the dBVrms scale. The dBVrms scale
displays component magnitudes using a log scale.
● The Nyquist frequency is the highest frequency that any real-time digitizing oscilloscope can acquire
without aliasing. This frequency is half that of the sample rate, provided it is within the analog
bandwidth of the oscilloscope. Frequencies above the Nyquist frequency will be under sampled,
which causes aliasing.
48
Page 49

3.8 Set up the Horizontal system
3.8.1 Horizontal control knobs
The oscilloscope shows the time per division in the center of the bottom status bar. The horizontal controls
change the horizontal scale and position of waveforms. The horizontal center of the screen is the time
reference for waveforms. Changing the horizontal scale causes the waveform to expand or contract around
the screen center. The horizontal position knob changes the position of the trigger point relative to the
center of the screen.
The oscilloscope digitizes waveforms by acquiring the value of an input waveform at discrete points. The
time base also controls the sampling rate of this digitizing process. The sampling rate adjusts
automatically to a value suitable for each selected Time/Div scaling factor. Refer to Appendix C for more
detailed information.
■ Horizontal POSITION knob:Adjusts the horizontal position of both channels and math waveforms.
The resolution of this control varies according to the horizontal scale factor.
■ Time/Div knob:Selects the horizontal scale factor for the main or the window time base. When
Window Zone is enabled, it changes the width of the window zone by changing the window time base.
■ Display scan mode:
When the Time/DIV control is set to 100 ms/div or slower and the trigger mode is set to Auto, the
oscilloscope enters the scan acquisition mode. In this mode, the waveform display updates from left to
right. In this mode, trigger or horizontal position control of waveforms is disabled.
Figure 3-18 scan mode display
3.8.2 Window Zone
Use the Window Zone option to define a segment of a waveform you want to see in greater detail. The
Window time base setting cannot be set slower than the Main time base setting. Adjust the Horizontal
49
Page 50

Position and Time//Div controls to enlarge or minimize waveforms in the Window Zone
Figure 3-19 Window setup
Figure 3-20 Window zone
3.8.3 Trigger holdoff
If you want to change the holdoff time, do the following:
1. Press the HORI MENU button to show the Horizontal Menu
2. Press Holdoff。
3. Adjust the ADJUST knob to change the holdoff time until the waveforms triggers reliably.
3.9 Set trigger system
The trigger determines when the oscilloscope starts to acquire data and display a waveform. When a
trigger is set up properly, the oscilloscope converts unstable displays or blank screens into meaningful
waveforms.
The trigger Control area includes the Level knob, TRIG MENU button, SET TO 50% button and FORCE
50
Page 51

button.
.
■ “LEVEL”knob:The LEVEL knob sets the amplitude level the signal must cross to cause an
acquisition.
■ “SET TO 50%”: The trigger level is set to the vertical midpoint between the peak values of the
trigger signal.
■ “FORCE”button: Completes an acquisition regardless of an adequate trigger signal. This button is
usually used in normal mode and single mode
3.10 Menu and control button
Figure 3-23
■ CURSORS:Display the Cursor Menu
■ MEASURE:Display the automated measurements menu.
■ ACQUIRE:Display the Acquire Menu.
■ DISPLAY:Display the Display Menu.
■ UTILITY:Display the Utility Menu.
■ SAVE/RECALL: Display the Save/Recall Menu for setups and waveforms.
■ DEFAULT SETUP:Recall the factory setup.
■ AUTO:Automatically sets the oscilloscope controls to produce a usable display of the input signals.
■ RUN/STOP:Continuously acquires waveforms or stops the acquisition.
Note:If waveform acquisition is stopped (using the RUN/STOP or SINGLE button), the TIME/DIV
control expands or compresses the waveform.
■ SINGLE:Acquire a single waveform and then stop.
3.11 Connectors
51
Page 52

Figure 3-24
■ Probe component: Voltage probe compensation output and ground. Use to electrically match the
probe to the oscilloscope input circuit.
■ CH1、CH2 :Input connectors for waveform display.
■ EXT TRIG: Input connector for an external trigger source. Use the Trigger Menu to select the Ext or
Ext/5 trigger source.
Note: If you connect a voltage source to a ground terminal, you may damage the
oscilloscope or the circuit under test. To avoid this, do not connect a voltage source to
any ground terminals.
52
Page 53

Chapter 4 Application Examples
This section presents a series of application examples. These basic examples highlight the features of the
oscilloscope and provide you with ideas how you can solve your testing problems using the 2530/2532
oscilloscope.
◆ Taking simple measurements
◆ Taking cursor measurements
◆ Capturing a single-shot signal
◆ Analyzing signal details
◆ Triggering on a video signal
◆ Application of X-Y function
◆ Analyzing a differential communication signal using math functions
4.1 Taking Simple Measurements
Example: Observe a unknown signal, display the signal quickly and measure the frequency and
peak-to-peak amplitude.
1. Using Auto set
To quickly display a signal, follow these steps:
1 Press the CH 1 button , set the Probe option attenuation to 10X and set the switch to 10X on the
probe.
2. Connect the channel 1 probe to the signal.
3. Press the AUTO button.
The oscilloscope sets vertical, horizontal, and trigger controls automatically. If you want to optimize the
display of the waveform, you can manually adjust these controls.
NOTE. The oscilloscope displays relevant automatic measurements in the
waveform area of the screen based on the signal type detected.
2. Taking Automatic Measurements
The oscilloscope can take automatic measurements of most displayed signals. To measure signal frequency
and peak-to-peak amplitude, follow these steps:
(1) Measure signal frequency
● Input the signal to channel 1.
● Press the “AUTO” button.
● Press the “MEASURE ”button to see the Measure Menu.
53
Page 54

● Press the top option button, Measure value#1 Menu appears.
● Press the “Type” option button and select “Freq”.
● Press the “off” option button.
The value below “freq” is the result of the measurement.
(2) Measure signal peak-to-peak amplitude
● Press the second option button from the top, the Measure value#2 menu appears.
●Press the Type option button and select “Vpp”.
● Press the “off” option button.
The value below “Vpp”is the result of measurement
4.2 Taking Cursor Measurements
You can use the cursors to quickly take time and voltage measurements on a waveform.
4.2.1 Measuring Ring Frequency
To measure the ring frequency at the rising edge of a signal, follow these steps:
1 Press the “CURSORS” button to see the “Cursor Menu”.
2. Press the “ Type” option button and select “Time”.
3. Press the “Source” option button and select“ CH1”.
4. Press the “Cur1 ” button and turn the ADJUST knob to place the cursor 1 on the first peak of the ring.
5. Press the “Cur 2” button and turn the ADJUST knob to place the cursor 2 on the second peak of the
ring.
You can see the delta time and frequency (the measured ring frequency) on the top right of the screen.
Figure 4-1
54
Page 55

4.2.2 Measuring Ring Amplitude
To measure the amplitude, follow these steps:
1. Press the “CURSORS” button to see the Cursor Menu.
2. Press the “Type” option button and select “Voltage”.
3. Press the “Source” option button and select“ CH1”.
4. Press the“ cur1 ”option button and turn the universal knob to place the cursor 1 on the highest peak
of the ring.
5. Press the “cur2” option button and turn the universal knob to place the cursor 2 on the lowest peak of
the ring.
You can see the following measurements on the top right of the screen.
-The delta voltage (peak-to-peak voltage of the ringing)
- The voltage at Cursor 1.
- The voltage at Cursor 2.
Figure 4-2
4.3 Capturing a Single-Shot signal
To capture a single event, you need to gain a basic understanding of the signal characteristics to correctly
set up the trigger level and slope . You can use auto or normal trigger mode to obtain the proper trigger
level and slope. The following steps demonstrate how to use the oscilloscope to capture a single event.
Set the Probe option attenuation to 10X and set the switch to 10X on the probe.
Trigger set up :
1. Press “TRIG MENU” button to show the “ Trigger Menu”
2. Under this menu , set the trigger type to Edge, Edge type is “rising”, source is “CH1”, trigger mode is
“Single”, couple is “DC”
3. Adjust the horizontal time base and vertical scale appropriately
55
Page 56

4. Turn the “LEVEL” knob to adjust the trigger level
5. Press the “SINGLE” button to start capturing. (Make sure Run/Stop button is green) When the trigger
conditions are met, data appears on the display representing the data points that the oscilloscope obtained
with one acquisition. Pressing the RUN/STOP button again rearms the trigger circuit and erases the
display.
4.4 Analyzing signal details
Scenario: You have a noisy signal displayed on the oscilloscope and you need to learn more about it. You
suspect that the signal contains more details than you can now see on the display.
4.4.1 Looking at a Noisy Signal
The signal appears noisy and you suspect that noise is causing problems in your circuit. To better analyze
the noise, follow these steps:
1. Press the “ACQUIRE button to see the acquire menu.
2. Press the “Peak Detect” option button.
3. If necessary, press the “DISPLAY” button to see the display menu。Adjust the contrast for better
visibility of the noisy signal.
Note: Peak detect emphasizes noise spikes and glitches in your signal, especially when the time base is set
to a slow setting.
4.4.2 Separating the Signal from the Noise
To reduce random noise in the oscilloscope display, follow these steps:
1. Press the “ACQUIRE”button to display the acquire menu.
2. Press the Average button。
3. Press the Averages button and vary the number and monitor the effect on the waveform.
Averaging reduces random noise and makes it easier to see detail in a signal.
4.5 Triggering on a Video Signal
Scenario: Observe the video circuit in an analog TV set. Use the video trigger to obtain a stable display.
4.5. 1Triggering on a Video Field
To trigger on the video field, follow these steps:
56
Page 57

1 Press the “TRIGMENU” button to see the “trig menu”
2. Press the top option button and select “Video”.
3 Press the “source” option button and select “CH1”.
4. Press the “Sync” option button and select “Odd Field” or “Even Field”.
5 Press the “Standard” option button and select “NTSC”.
6 Adjust the horizontal “Time/Div” knob to see a complete field across the screen.
7 Turn the vertical “Volts/Div” knob to ensure that the entire video signal is visible on the screen.
4.5.2 Triggering on Video Lines
To trigger on the video lines, follow these steps:
1 Press the “TRIGMENU” button to see the trig menu
2 Press the top “option” button and select “Video”.
3 Press the “Sync ” option button and select “Line Num” and turn the universal knob to set a specific
line number.
4 Press the “ Standard” option button and select “NTSC”.
5 Turn the “Time/Div ”knob to see a complete video line across the screen.
6 Turn the “Volts/Div” knob to ensure that the entire video signal is visible on the screen.
4.6 Application for the X-Y function
Viewing Impedance Changes in a Network
Scenario: You want to evaluate the impedance changes in your circuit as the ambient temperature is
changing. Connect the oscilloscope to monitor the input and output of your circuit. To view the input and
output of the circuit in an XY display, follow these steps:
1. Press the “CH 1” MENU button and set the Probe option attenuation to 10X.
2. .Press the “CH 2” MENU button and set the Probe option attenuation to 10X.
3. Set the switches to 10X on the probes.
4. Connect the channel 1 probe to the input of the network, and connect the channel 2 probe to the
output.
5. Press the “AUTO” button.
6. Turn the “VOLTS/DIV ”knobs to display approximately the same amplitude signals on each channel.
7 Press the DISPLAY button.
8 Press the Format option button and select “XY”.
The oscilloscope displays a Lissajous pattern representing the input and output characteristics of the
circuit.
57
Page 58

9 Turn the VOLTS/DIV and VERTICAL POSITION knobs to optimize the display.
10 Press the “Persist” option button and select “Infinite”.
11 Press the “Contrast -” or “Contrast + ”option buttons to adjust the contrast of the screen.
12 Apply the Ellipse method to observe the phase difference between the two channels
D
A B
C
Figure 4-3
sinθ=A/B or C/D where θ=phase shift (in degrees )between the two signals. From the formula above ,you
could get: θ= ± arcsine (A/B) or ±arcsine (C/D)
4.7 Analyzing a Differential Communication Signal
You are having intermittent problems with a serial data communication link, and you suspect poor signal
quality. Set up the oscilloscope to show you a snapshot of the serial data stream so you can verify the
signal levels and transition times.
Because this is a differential signal, you can use the math function of the oscilloscope to view a better
representation of the waveform.
To activate the differential signals connected to channel 1 and channel 2, follow these steps:
1 Press the CH 1 button and set the Probe option attenuation to 10X.
2 Press the CH 2 button and set the Probe option attenuation to 10X.
3 Set the switches to 10X on the probes.
4 Press the AUTO button.
5 Press the “MATH” button to see the Math Menu.
6 Press the “Operation” option button and select “-”.
7 Press the “CH1-CH2” option button to display a new waveform that is the difference between the
displayed waveforms.
8 You can adjust the vertical scale and position of the Math waveform. To do so, follow these steps:
- Remove the channel 1 and channel 2 waveforms from the display.
58
Page 59

- Turn the CH 1 and CH 2 VOLTS/DIV and VERTICAL POSITION knobs to adjust the vertical scale
and position.
NOTE. Be sure to first compensate both probes. Differences in probe
compensation appear as errors in the differential signal.
59
Page 60

Chapter 5 Prompt messages and troubleshooting hints
5.1 Prompt messages:
■ Trig volt level at limit :When turning the trigger knob, Alerts the user that the trigger level reached
its limit
■ Horizon position at limit:When turning the horizontal position knob , alerts user that the horizontal
position reached its limit
■ Volts/Div at limit:Alerts the user that the vertical volt/Div knob was adjusted to the min (2mV/div)
or maximum ( 5V/div ) value
■ Volts position at limit:When turning the vertical position knob , alerts user that the vertical knob
reached its limit.
■ Sec/Div at limit:Prompts the user that the Volts/Div is at full range while turning the vertical scale
knob.
■ Functions isn’t useable:Function not supported in this mode. (Example: Reference mode is not
available in YX format)
■ No signal!:The system could not detect a suitable signal ( used in the auto set )
■ Adjust at limit: You could adjust the pulse width with the ADJUST knob until the pulse width has
reached the min of 20.0ns or max 10.0s limit.
5.2 Troubleshooting
1. If the screen remains dark after the oscilloscope is powered on, try the following:
a) Check if the power cable is connected properly
b) Ensure the power switch is turned on.
c) After verifying a) and b) restart the oscilloscope.
d) If the oscilloscope is still not working, contact your authorized B+K Precision distributor.
2. If there is no signal displayed on the screen, do the following :
a) Verify that the probe or BNC cable is properly connected to CH1 or CH2.
b) Make sure your BNC cable or probe is connected to a life signal
3. If the signal amplitude is 10 times higher/lower than the actual signal, try the following:
Check the attenuation factor and make sure it matches the probe attenuation setting
4. If the waveform is displayed, but not stable, do the following:
a) Make sure signal source and trigger setup match.
b) Check the trigger mode: Common signals should use Edge trigger. Video signals should the Video
60
Page 61

Trigger mode. The signal will be stable only if the appropriate trigger mode is used.
c) Try changing coupling to “HF Reject” or “LF Reject” to filter out High/low frequency noise
5. No display after pressing the RUN/STOP button
a) Check the trigger mode is set to Normal or Single
b) Check the trigger level exceeds the maximum waveform amplitude. If so, please put the trigger level
to the middle position or set the trigger mode to Auto. Or you could press the Auto button to do the
set up automatically.
6. After Acquisition is set to Averages or Display Persistence is set ON, the refresh rate is slow.
This is normal
61
Page 62

Appendix A: Specifications
All specification apply to a 10X probe setting. To verify that the oscilloscope meets specifications, the
oscilloscope must first meet the following conditions:
The oscilloscope must have been operating continuously for twenty minutes within the specified
operating temperature.
You must perform the Do Self Cal operation, accessible through the Utility menu, if the operating
I) Specifications
temperature changes by more than 5° C.
The oscilloscope must be within the factory calibration interval
Inputs
Input Coupling AC, DC,GND
Input Impedance 1MΩ || 13Pf
Probe Attenuation
Supported probe attenuation factor 1X, 10X, 100X, 1000X
Max. Voltage between signal and reference BNC connector: 300 Vrms, CAT II
1X、10X
Vertical System
Vertical Range 2mV - 5V/div (1-2-5 sequence)
Position range 2mV – 100mV range ±2V
Vertical Resolution 8 bit
Channels 2
Gain accuracy ±3.0%
Analog Bandwidth 40 MHz (2532) / 25MHz (2530)
Single-shot Bandwidth Full bandwidth
Lower frequency limit (AC -3dB) ≤5Hz (at input BNC)
Rise time < 8.8ns < 14 ns
Band width limit Model 2532 only: 20 MHz (-3dB)
Horizontal System
Timebase accuracy ± 0.01%
10 ns/DIV – 50 s/DIV 25 ns/DIV – 50 s/DIV Horizontal Scan Range
Roll mode: 100ms/DIV ~50s/DIV (1-2-5 sequence)
Measure Display Modes MAIN, WINDOW, WINDOW ZOOM, ROLL, X-Y
Acquisition System
Real Time Sample Rate 500MSa/s ** 250 MSa/s
Equivalent Sample Rate 50GSa/s
Acquisition modes Real time , Equivalent
Record Length * 4000 samples for each channel
Sampling modes
* The instrument displays 2500 points. 4000 points can be retrieved from internal memory with the included EasyScope
application Software. This mode is supported for time base settings ranging from 2.5µs/Div-50ms/Div. (This option is not
supported in scan mode which is automatically activated when selecting a time base setting in the 100ms/div-50s/div range)
Sample, Peak Detect, Average: N selectable from 4, 16, 32, 64, 128, 256
2532 2530
200mV - 5V range: ±40V
2532 2530
2532 2530
62
Page 63

** sample rate 2532: The maximum sample rate is 500MSa/s for single channel operation. With both channels active, the
sample rate for each channel is half or 250MSa/s
X-Y Mode
X-pole Input / Y-Pole Input Channel 1 (CH1) / Channel 2 (CH2)
Phase Error ±3 degrees
Trigger System
Trigger Types Edge, Pulse (Width), Video
Trigger Modes Auto, Normal, Single
Trigger Coupling AC, DC, LF reject, HF reject
Trigger Source CH1, CH2, AC line, Ext, Ext/5
Trigger Level Range
CH1, CH2:±12 divisions from center of screen
EXT: ±2.4V
EXT/5: ±12V
Holdoff range 100ns – 1.5s
Pulse Trigger,
Trigger conditions
(>、<、=) positive Pulse
(>、<、=) negative Pulse
Pulse Width Range :20ns – 10s
Support formats PAL/SECAM, NTSC Video Trigger
Trigger conditions:odd field, even field, all lines, line Num
Trigger Frequency Counter
Readout resolution 6 digits
Range DC Coupling, 10Hz to max Bandwidth
Supported signal types Works with all trigger modes except pulse width trigger and Video
Trigger
Control Panel Function
Auto Set Auto adjusting the Vertical, Horizontal system and Trigger
Position
Settings Save/Recall 10 setups
Waveforms Save/Recall 10 captured waveforms
2 reference waveforms
Display System
2532 2530
Display Mode 5.7 inch (145mm) diagonal Liquid Crystal Display
Resolution 320 horizontal x 240 vertical pixels
Color color monochrome
Display Contrast Adjustable
Waveform display range 8 x 10 DIV
Wave Display Mode Point, Vector
Persist None, 1 sec, 2 sec, 5 sec, infinity
Waveform interpolation
Sin(x)/x、Linear
Measurement System
Voltage: MAX, MIN, Peak-Peak, Average, Vrms Automatic measurements
Time: Rise time, Fall Time, Cycle Frequency, Period,
Positive Pulse width, Negative Pulse width
Cursor Measurement Voltage Differences between the Cursors (∆V)
Time/Frequency Differences between the Cursors (∆T)
Frequency/Time Differences between the Cursors (1/∆T)
63
Page 64

Math operation +, -, * , /, FFT
FFT Windows Hanning, Hamming, Blackman, Rectangular
Environmental
Temperature
Humidity
Altitude
Pollution Degree
Power Supply
Input Voltage 100-240 VAC, CAT II, Auto selection
Frequency 45Hz to 440Hz
Power 50VA Max
Mechanical
Dimensions 300mm (Depth) x 290 mm (Width) x 150mm (Height)
11.8in x 11.4in x 5.9in
Weight 4.6 kg (10 lbs)
NOTE: Specifications and information are subject to change without notice. Please visit www.bkprecision.com for the
most current product information.
Operating:0℃ to +55℃
Nonoperating :-40℃ to +70℃
Operating:95%RH,40℃
Nonoperating:90%RH,65℃s
Operating:4000m
Pollution degree 2 for indoor use only.
II) Accessories:
User Manual
1:1/10:1 passive probe set (2 pieces)
Power cord
USB interface cable
Installation disk with EasyScope Software
III) EMC and Safety Compliances
Declaration of Conformity - EMC
This oscilloscope is in compliance with council EMC directive 2004/108/EC
EN 61326. EN61326: 1998, +A1 2002 +A2:2003
EMC requirements for Class A electrical equipment for measurement, control, and laboratory use.
Safety
This oscilloscope meet intent of Directive LVD 72/23/EEC amended 93/68/EEC
EN61010-1:2001:
Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use
64
Page 65

Appendix B: Default setup
MEASURE
ACQUIRE
DISPLAY
REF
TRIGGER (edge)
source CH1
type Average
mode Sample
Averages
Sample mode Equ time
type
Persist
grid
type waveform
source CH1
REFA off
type Edge
source CH1
slope Rising
Mode
Coupling DC
16
Vectors
off
Auto
TRIGGER (pulse)
TRIGGER (Video)
LEVEL
type Pulse
source CH1
when =
Set Pulse Width
Mode Auto
Coupling DC
Type Video
Source CH1
Polarity Normal
Sync All Lines
Standard
0.00V
1.00ms
NTSC
65
Page 66

Appendix C: Sample rate versus time base setting
Time base
(/div)
2.5ns 50G 250M 500M / 250M
5ns 50G 250M 500M / 250M
10ns 25G 250M 500M / 250M
25ns 10G 250M 500M / 250M
50ns 5G 250M 500M / 250M
0.1µs 2.5G 250M 500M / 250M
0.25µs 1G 250M 500M / 250M
Equivalent
time sampling
Real time, 2530 Real time, 2532
Time base (/div) Sample rate(S/s)
0.5µs 200M
1µs 200M
2.5µs 100M
5µs 50M
10µs 25M
25µs 10M
50µs 5M
0.1ms 2.5M
0.25ms 1M
0.5ms 500K
1ms 250K
2.5ms 100K
5ms 50k
10ms 25k
25ms 10k
50ms 5k
Time base (/div) Sample rate(S/s)
Scan Normal & Single
0.1s 25k 2.5K
0.25s 10k 1k
0.5s 5k 0.5K
1s 2.5k 0.25K
2.5s 1k 0.1K
5s 0.5k 50HZ
10s 250Hz 25HZ
25s 100Hz 10HZ
50s 50Hz 5HZ
Sample rate(S/s)
Single / dual channel operation
66
Page 67

Appendix D: Daily Maintenance and Cleaning
General Care
DO not store or leave the instrument where the LCD display will be exposed to direct sunlight for long
periods of time.
CAUTION
solvents
Cleaning
If this instrument requires cleaning, disconnect it from all power sources and clean it with a mild detergent
and water. Make sure the instrument is completely dry before reconnecting it to a power source.
To clean the exterior surface, perform the following steps:
1 Remove loose dust on the outside of the instrument and probes with a lint-free cloth. Use care to
2. Use a soft cloth dampened with water to clean the instrument.
Note
cleaning agents.
: To avoid damage to the instrument or probes, do not expose them to sprays, liquids, or
avoid scratching the clear plastic display filter.
:To avoid damage to the surface of the instrument or probes, do not use any abrasive or chemical
67
Page 68

Appendix E: Index
- Width ............................................................. 29
+ Width ............................................................ 29
AC Line ........................................................... 17
Acquiring Signals system ................................ 20
Aliasing ........................................................... 23
Application of X-Y function ............................ 58
Auto ........................................................... 17, 38
auto setup ......................................................... 38
Averag e ........................................................... 22
Base time......................................................... 23
Coarse .............................................................. 12
Connector ....................................................... 53
Coupling .................................................... 12, 19
Cursor Measurement........................................ 26
Cursor Moving ............................................... 27
Cymometer ...................................................... 30
default setup............................................... 38, 52
Display Area ................................................... 36
Display sweep mode ....................................... 50
Display System ................................................ 24
DO self cal ....................................................... 30
Do Self Test ..................................................... 31
Equivalent Time Sampling:........................ 23
EXT.................................................................. 17
EXT TRIG ...................................................... 53
EXT/5 .............................................................. 17
Fall ................................................................... 29
FFT.................................................................. 46
Fine Resolution:............................................ 12
FORCE ..................................................... 16, 52
Functional check ................................................ 6
Grid .................................................................. 25
Holdoff............................................................. 14
Horizontal System............................................ 13
Invert................................................................ 12
Language.......................................................... 30
LEVEL...................................................... 16, 52
MEASURE ...................................................... 27
Measure system ............................................. 26
Menu and control button............................ 52
Model............................................................... 17
Normal ............................................................. 17
Operation Basics
Peak Detect..................................................... 22
Persist............................................................... 24
Polarity............................................................. 18
............................................ 36
Position.............................................................19
Probe.............................................................8, 12
Probe Attenuation Setting...................................9
Probe Compensation...........................................8
Probe component ............................................53
Probe Safety........................................................8
Real Time Sampling .......................................23
Ref ....................................................................45
Rise...................................................................29
RUN/STOP ................................................23, 52
Sampling..........................................................21
SAVE/RECALL ..............................................33
SAVE/RECALL WAVEFORM ................34, 35
Scale Measurement...........................................26
Screen ...............................................................25
Self Calibration.................................................10
Self Test ............................................................32
SET TO 50%...................................................16
Set trigger system .............................................51
Set up the Horizontal system .........................50
Setting up the Vertical System..........................41
Signal Source....................................................16
Single....................................................17, 23, 52
Sound................................................................30
Storage System................................................32
Sync ..................................................................18
Time Cursor ....................................................27
Time/Div...........................................................14
TRIG MENU...................................................15
Troubleshooting................................................60
Universal knob..................................................40
UTILITY ..........................................................30
Utility System...................................................30
Vavg..................................................................29
Vertical System.................................................11
Vmax ................................................................29
Vmin.................................................................29
Volt/div .............................................................12
Voltage Cursor ................................................27
Vpp ...................................................................29
Vrms .................................................................29
Wave Cancel .....................................................13
Window ............................................................14
Window Zone ...................................................50
X-Y Format.....................................................25
YT.....................................................................25
68
Page 69

Appendix F: Service and Warranty Information
Service Information
Warranty Service: Please return the product in the original packaging with proof of purchase to the
address below. Clearly state in writing the performance problem and return any leads, probes, connectors
and accessories that you are using with the device.
Non-Warranty Service: Return the product in the original packaging to the address below. Clearly state in
writing the performance problem and return any leads, probes, connectors and accessories that you are
using with the device. Customers not on open account must include payment in the form of a money order
or credit card. For the most current repair charges please visit www.bkprecision.com
“service/repair”.
Return all merchandise to B&K Precision Corp. with pre-paid shipping. The flat-rate repair charge for
Non-Warranty Service does not include return shipping. Return shipping to locations in North American is
included for Warranty Service. For overnight shipments and non-North American shipping fees please
contact B&K Precision Corp.
B&K Precision Corp.
22820 Savi Ranch Parkway
Yorba Linda, CA 92887
www.bkprecision.com
714-921-9095
Include with the returned instrument your complete return shipping address, contact name, phone
number and description of problem.
Limited One-Year Warranty
B&K Precision Corp. warrants to the original purchaser that its products and the component parts thereof,
will be free from defects in workmanship and materials for a period of one year from date of purchase.
B&K Precision Corp. will, without charge, repair or replace, at its option, defective product or component
parts. Returned product must be accompanied by proof of the purchase date in the form of a sales receipt.
To obtain warranty coverage in the U.S.A., this product must be registered by completing a warranty
registration form on www.bkprecision.com
Exclusions: This warranty does not apply in the event of misuse or abuse of the product or as a
result of unauthorized alterations or repairs. The warranty is void if the serial number is altered,
defaced or removed.
B&K Precision Corp. shall not be liable for any consequential damages, including without limitation
damages resulting from loss of use. Some states do not allow limitations of incidental or consequential
damages. So the above limitation or exclusion may not apply to you.
This warranty gives you specific rights and you may have other rights, which vary from state-to-state.
B&K Precision Corp.
22820 Savi Ranch Parkway
Yorba Linda, CA 92887
www.bkprecision.com
714-921-9095
within fifteen (15) days of purchase.
and click on
69
Page 70

Edition 1.2
22820 Savi Ranch Parkway
Yorba Linda, CA 92887
www.bkprecision.com
© 2007 B&K Precision Corp.
Printed in China
70
 Loading...
Loading...