Page 1
English
Deutsch
Français
Español
Italiano
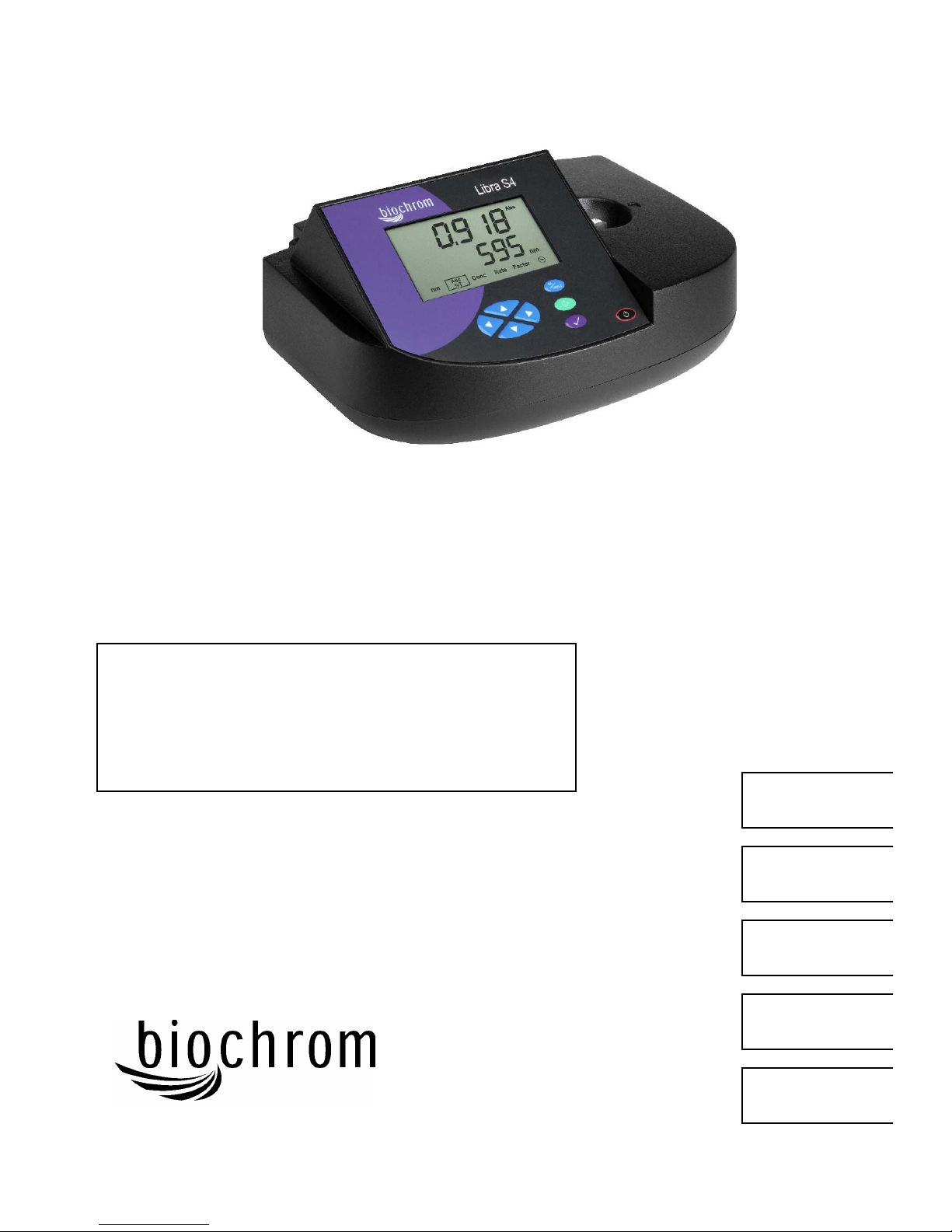
Libra S4
User Manual
Page 2

Declaration of Conformity
This is to certify that the Libra S4 Visible Spectrophotometer
Part number 80-5000-00
Serial number 88000 onwards
manufactured by Biochrom Ltd. conform to the requirements of the following
Directives-: 73/23/EEC & 89/336/EEC
Standards to which conformity is declared
EN 61 010-1: 2001
Safety requirements for electrical equipment for measurement, control and
laboratory use.
EN 61326: 1998
Electrical equipment for measurement, control and laboratory use – EMC
requirements
Signed: Dated: 26
th
Oct 2004
David Parr
Managi ng Direc tor
Biochrom Ltd
Postal address Telephone Telefax
Biochrom Ltd +44 1223 423723 +44 1223 420164
22 Cambridge Science Park
Milton Road e mail: enquiries@bio chr om.co.uk website: http://www.biochrom.co.uk
Cambridge CB4 0FJ
England
Registered in England No: 3526954
Registered Office: 22 Cambridge Science Park, Milton Road, Cambridge CB4 0FJ, England
.
Biochrom Ltd
Certificate No. 890333
Page 3

CONTENTS
Unpacking, Positioning and Installation 1
Essential Safety Notes 1
OPERATION 2
Introduction 2
Sample handling tips 2
Using the Instrument 3
Absorbance and % Transmission 4
Concentration 4
Rate 6
Factor 7
(time and date) 8
Use with serial printer 8
Use with chart recorder 8
USE WITH PC AND THE GRAFICO PC UTILITY
SOFTWARE 9
Installation 9
Introduction 9
Menu Descriptions 10
Practical Aspects 11
ACCESSORIES 12
ERROR MESSAGES 12
MAINTENANCE 13
After Sales Support 13
Cleaning and gen eral care of th e instru men t 13
Changing cell holder or removal for cleaning 13
Lamp Replacement 14
Changing the brightness of the display 14
STUDENT EXPERIMENTS 15
Calculation of λ max, extinction coefficient and measurement of natural
bandwidth 16
Construction of concentration plots 16
Measurement of stray light 17
SPECIFICATION AND WARRANTY 18
Page 4

Page 5
___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 1
Unpacking, Positioning and Installation
• Inspect the instru ment for any signs of damage caused in tran si t. If any damage is
discovered, inform your supp lier immediately. Check the position of the metal lamp
bracket insid e the lamp access area.
• Ensure your proposed installation site conforms to the environmental conditions for safe
operation:
Indoor use only
Temperature 5°C to 35 °C. No te that if you use the instr ument in a room sub j ect t o
extremes of temperature change du r ing the day, it may be necessary to recalibrate (b y
switching off and then on again) once thermal equilibrium has been established (2-3
hours).
Maximum relative humidity of 80 % up to 31°C decreasing linearly to 50 % at 40°C
• The instrument must be placed on a hard, flat bench or table that can take its weight (<2
kg) such that air is allowed to circulate freely around the inst rument.
• This equipment must be connected to the power supply with the power cord supplied. It
can be used on 90 - 240V supplies.
• Switch on the instrument via the display after it has been plugged in. The instrument
performs a series of self-diagnostic checks for lamp performanc e, wavelength calibration
and diode array pixels; press F2 to proceed.
If the instrument has just been unpacked or has been stored in a cold environment, it
should be allowed to come to thermal equilibrium for 2-3 hours in the laboratory
before switching on to prevent calibratio n failure as a re sult of internal co nd ensation.
• The cell holder supplied with the instrument accepts standard 10mm pathlength glass or
plastic cells (adap t er s are avai lable to convert it to accept 10, 12 and 16mm diameter test
tubes). It can be removed for cleaning if spillages occur by undoing the screws that hold
it or it can be flushed through with water in situ.
If this equipment is used in a manner not specified or in environmental conditions not
appropriate for safe operation, the protection provided by the equipment may be impaired and
instrument w a rranty withdrawn.
Essential Safety Notes
There are a number of warning labels and symbols on your instrument. These are
there to inform you where potential danger exists or particular caution is required.
Before commencing installation, please take time to familiarise yourself with these
symbols and their meaning.
Caution (refer to accompanying documents).
Background colour yellow, symbol and outline black.
Page 6

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4 , English 2
OPERATION
Introduction
Your spectrophotometer is a simple-to-use instrument that provides rapid
measurement of light absorbance and light transmission in the visible region (330 –
800 nm).
Your spectrophotometer has facilities for measurement of:
• absorbance and % transmission
• concentration, either
• absorbance multiplied by a factor or
• from a single point calibration using a known standard
• rate (absorbance against time) at one or two wavelengths simultaneously
• rate results at one wavelength can be output to chart recorder
The instrument is supplied with Grafico PC utility - on the accompanying CD - and a
serial lead. These provide the user with the means to capture, print and store data
from the instrument to a PC. Specifically it
• produces a printable graphical plot of the scan, in Abs
• logs date, time and serial number with any output from the instrument
• produces a results log in order to store, tabulate and subsequently print
output from the instrument
• enables export of the output from the instrument to Excel as a text file
A tutorial on UV/Visible spectrophotometry is included as part of the Grafico
software.
Experiments are included in this manual for the user or for students to investigate
some of the principles of UV/Visible spectrophotometry.
Sample handling tips
• Note that the light beam shines from LEFT to RIGHT through the cell chamber;
ensure the cell is inserted in the correct alignme nt.
• The optical height is 15mm, and the minimum volume that can be used is
approx. 700µl in a semi-micro cell.
• Align the indicator line on test tubes with the arrow on the cell compartment
area to ensure reproducible positioning of the tube. Note that test tubes do not
last forever, and that the surface gets scratches and blemishes through repetitive
use; if this is the case they should be replaced.
Page 7

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 3
Using the Instrument
The liquid crystal display is very easy to navigate around using the function / select
and arrow keys on the hard wearing, spill proof membrane keypad.
Keypad
To switch the ins tr u men t o n, press once
To switch the instrument off, hold the key down for 2 seconds
√
To set up or confirm an entry
0A/100%T To set reference to 0.000AU or 100%T on a reference solution at the
selected wavelength
To make a measurement or stop a rate experiment
34
To highlight the 6 measurement indicat ors in turn ( see below)
56
Depends on mode, see below
Display
Highlight your selection using 34, then:
nm
To enter wavelength; to select, press 56 then √
Abs/%T
To measure Abs or %T; to select , p r es s 56 (“Abs” or “%T”
displayed at side)
Conc To measure concentration either using a factor or relat ive to a known
standard; to select, press √ (“Conc.” displayed at side)
Rate To measure absorb an ce as a fun c tion of time; to select, p r es s √
Factor To enter a factor for use in concentration; to select, press √
To display time and change time / date if required ; to select , p r ess √
The following symbols appear and signify the following:
r r r r
Setting reference / measuring blan k
“0.123” flashing
Displaying previo usly measured value when measuring sample
Error Messages
Error messages may appear on the display and mean the following:
FAIL flashing Can carry on using; refer to error messages section
FAIL constant Cannot use; refer to error messages section and contact your supplier
Page 8

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4 , English 4
Absorbance and % Transmission
This mode is for simple absorbance measurements on samples, measuring the
amount of light that has pass ed through a sample relative to a blank (this can be air).
The pro cedure is as follows:
Action Press key Comment
Set wavelength
3 to get to nm
56 to set
√ to select
Ramps with increasing speed
Moves to Abs/%T
Select Abs/%T
5 to change between th em
Insert reference
0A/100%T to set reference
Used for subsequent samples until
changed
Insert sample to measure sampl e Value is displayed
Repeat as necessary
Concentration
This mode is for measuring the concentration of a sample using a pre-stored factor; note that
if you have a standard of known concentration, the instrument will calculate the factor for
you.
To measure sample using a stored factor, the procedure is as follows:
Action Press key Comment
Set wavelength
3 to get to nm
56 to set
√ to select
Ramps with increasing speed
Moves to Abs/%T
Select Conc
4 to get to Conc
Each wavelength can have its own
factor applied to it
Insert reference
0A/100%T to set reference
Used for subsequent samples until
changed
Entered standard value flashes
Insert standard to measure standard Measures absorbance of standard
0.000 is displayed
Insert sample to measure sample Concentration relative to st an d a rd is
displayed
Repeat as necessary
To set a factor manually for use in concentration measurements, go to Factor mode (see
later in manual).
Page 9

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 5
To measure the concentration of a sample relative to that of a known standard solution
(a one point calibration), the procedure is as follows:
Action Press key Comment
Set wav elength
3 to get to nm
56 to set
√ to select
Ramps with increasing speed
Moves to Abs/%T
Select Conc
4 to get to Conc
√ to select
Enter con cen tration
of known standard
digit by digit
56 then 4
at any time
√ at any time
56 then 4
56 then 4
56 then 4
34 then 4
√
Entry of first digit (eg 1.234)
[Escape d u r ing entry]
[Enter number, decimal points flash]
Entry of second digit (eg 1.234)
Entry of third digit (eg 1.234)
Entry of fourth dig it (eg 1.234)
Position of decimal point (eg 123.4)
Accept number, entered standard
value flashes
Insert reference
0A/100%T to set reference
Used for subsequent samples until
changed
Entered standard value flashes
Insert standard to measure standard Measures standard an d entered
concentration is displayed (factor is
calculated). Wavelength appears
when measurement finished
Insert sample to measure sample Concentration relative to standard is
displayed
Repeat as necessa r y
Page 10

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4 , English 6
Rate
This mode is for following a change in absorbance with time at 10 second intervals. If,
however, the instrument is connected to a chart recorder the output is linearly fitted between
data point s as the software automatically interp o l a tes th es e for the benefit of presen ta tion.
The procedure is as follows:
Action Press key Comment
Set wavelength
3 to get to nm
56 to set
√ to select
Ramps with increasing speed
Moves to Abs/%T
Select Rate
4 to get to Rate
Insert reference
0A/100%T to set
reference
Used for subsequent samples until changed
Insert sample to measure sample Absorban ce measu r ed ever y 10 seconds
Keeps measuring un til the
key is
pressed or until 1000 measurements are
made
Repeat as necessary
Note that there is no t = 0 reading; the first reading is that after 10 seconds.
You can also measure at two wavelengths simultan eously; this is useful as you can, for
example, follow th e drop in react ant absorbance and th e r is e i n product absorbance as the
reaction proceeds (the first wavel ength only is used if a chart recorder is co n nected). The
procedure is as follows:
Action Press key Comment
Set wavelength
3 to get to nm
56 to set
√ to select
Set first wavelength
Moves to Abs/%T
Select Rate
4 to get to Rate
5 to get L2
√ to select
Set second wave length
Set second
wavelength
56 to set
√ to select
Pressing √ again reverts back to sin gle
wavelength mode
Insert reference
0A/100%T to set
reference
Used for subsequent samples until changed
Insert standard to measure sample Absorban ce measu r ed ever y 10 seconds
Display alternates b et ween t h e two
absorb an ce values
Keeps measuring un til the
key is
pressed or until 1000 measurements are
made
Repeat as necessary
Note that there is no t = 0 reading; the first readings are those after 1 0 s eco nds.
Page 11

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 7
Factor
This mode is for setting a factor to be used in concentration experiments; once this
has been done, the instrument moves directly to concentration mode so that it can be
used. The procedure is as follows:
Action Press key Comment
Set wav elength
3 to get to nm
56 to set
√ to select
Ramps with increasing speed
Moves to Abs/%T
Select Facto r
4 to get to Factor
√ to select
Enter factor digit
by digit
56 then √
56 then 4
at any time
√ at any time
56 then 4
56 then 4
56 then 4
34
√
Enter if factor is positive [POS] or
negative [nEG]
Entry of first digit (eg 1.234)
[Escape d u r ing entry]
[Enter number, decimal points flash]
Entry of second digit (eg 1.234)
Entry of third digit (eg 1.234)
Entry of fourth dig it (eg 1.234)
Position of decimal point (eg 123.4)
Moves to Concentration mode
Insert reference
0A/100%T to set reference
Used for subsequent samples until
changed
Insert sample to measure sample Concentration calculated from factor
and absorb a n ce is d i splayed
Repeat as necessa r y
Page 12

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4 , English 8
(time and date)
The time is displayed (24 hour format).
To change this and the date so that they are correct, the procedure is as follows:
Action Press key Comment
Set date √ to select
56 to set day then √
56 to set month then √
56 to set year then √
Format shown on the display is
mm . yy
dd
dd flashes
mm flashes
yy flashes
Set time
56 to set hour then √
56 to set minute then √
Format shown on the display is
hh . mm
hh flashes
mm flashes
Time and date are set
Use with serial printer
Note that all results can be output to PC using the serial lead and Grafico software
supplied on the user manuals CD.
Seiko DPU-414 settings:
Dip SW-1 Serial, Auto line feed off
Dip SW-2 40 column width, International character set, USA
Dip SW-3 Baud rate 9600 bps
Note that the 80-2108-1 8 le a d that is req uire d will need two small nuts removing
before connection.
Use with chart recorder
Kinetics results can be output to a chart recorder using the appropriate cable (803003-55). Voltage setting is 1V per 1 Absorbance unit (± 10 %) with an offset of
1V = 0.000 Abs on the chart recorder; corresponding %T values are 1V per 100%T
(± 10 %) with 0V = 0%T.
To make the chart cable yourself, you require a female 9 way D type at one end with
two (1 red, 1 black) 4mm banana plugs at the other (depending on the chart recorder)
and 2 metres of coaxial cable or screened twin core, with the shield connecting the
black plug and pin 5 and the core connecting the red plug and pin 1.
Page 13

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 9
USE WITH PC AND THE GRAFICO PC UTILITY
SOFTWARE
Your instrument is supplied with a serial lead and Grafico software (on the user
manuals CD) that enables it to be connected to a PC so that results can be capt ured,
stored, printed and transferred into other applications easily. In particular, a
complete wavelength scan can be visualised on the PC and copied/pasted into a word
document or powerpoint presentation. An informative tutorial on aspects of
UV/Visible Spectrophotometry is available as part of the software.
Installation
The software takes up approximately 0.5Mb of hard disk space when installed.
Proceed as foll ows to install the software:
1. Place CD into the CD drive of the PC
2. Use Windows explorer to locate the setup.exe file Grafico folder within the
appropriately named instrument folder on the user manuals CD
3. Double click on this so that the software installs, filling out the information as
requested.
4. The software can be started directly by Start > Programs > Grafico.
Introduction
• When Grafico is selected, you are prompted to enter the file details (note that
the title entered here is used as the title of the wavelength scan graph). After
pressing OK, the instrument (it should be already switched on and connected to
the PC with the serial lead) is recognised by the software.
• There are two parts to the Grafico software, data-logging and scan.
• The default mode is data-logging; this receives instrument output from
absorbance, %T, concentration and rate measurements (including time and date
stamp).
o Results can be copied from Grafico and pasted directly into Excel
for ease of data transfer. Alternativ ely results can be saved and
opened up using Excel.
• If scan mode is selected (View > Scan mode), the full 330-800nm wavelength
scan output from the instrument is shown (just press the run key as usual).
Multiple peaks can be identified using a trace routine and labelled if required
(by dragging the icon at the lef t side of the displayed graph and releasing at the
appropriate point).
o Graphs can be copied and pa sted into Word , Ex ce l o r po werp o int
o Graphs can be saved in a format that can be opened directly by
Excel
Page 14

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 10
Menu Descriptions
File
New Clears any existing data and starts a new report. Prompts for file
details (user name, organisation, title, descript ive text)
Save / Save As Saves the data file in the file format selected. The file details are
included with this data
Setup Displays a tabbed dialogue box so that automatic post process
options for saving of graph, printing of graph and the graph scaling
parameters can be defined. The default data directory can be
defined and is used for all save operations.
Print Prints the entire file, including a header if defined in File> Ne w
Print Setup Runs the Common Print Dialog function to set up the printer
Exit Closes the application
Edit
Copy Copies the data to clipboard for pasting into another application; in
data-logging and scan modes this is text and graphic, respectively
Clear Clears the data from the data set
Select All Selects data and header together
View
Scan mode Switches between scan and data logging modes. Successive scans
overwrite existing scans on the display and can be saved if the
autosave function is on
File details Shows the file details entered at the start (or after File > New) and
allows modification of these details, if required
Autoscale Automatically sets the scale of the absorbance axis to opti mise
presentation (2.5, 2.0, 1.5, 1.0, 0.5, 0.2 or 0.1A)
Set scale Sets the scale to use r pref erence (Full, Auto, Define)
Display grid Toggles on/off the grid on the graph (for presentation purposes)
Toolbar View menu bar as icons
Status bar View status bar at bottom of display
Help
Tutorial View tutorial on UV/Visible spectrophotometry
Help topics View help topics
About View version number etc
Page 15

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 11
Practical Aspects
Data logging mode
• When exporting rate mode results you can add the time in 10 second intervals to
the spreadsheet manually (note that first data point is after 1 0 sec o nd s, not ze r o
seconds) and then graph the absorbance / time data (see scan mode – export to
excel for more details).
Scan mode
• Files can be saved as *.txt, *.csv (opens directly in Excel when double clicked)
or *.wmf (picture) formats
• Label a peak by dragging and releasing the icon at the left side of the graph.
The absorbance/wavelength details are shown in the title bar. Dragging it again
moves the label; moving it the left hand side takes the label away. Multiple
peaks can be added.
• Use display grid off for clearer presentation.
• Data can be output in abs orbance only
Scan mode – export to Excel and graphing
• If saving as a *.txt file, save the results to folder of choice.
o Use Excel to open this file; with files of type set to “all files”
o Note that saving as a *.csv file and double clicking on it will open
Excel directly
• Highlight the wavelength and absorbance values and click the graph icon
• Select chart type “XY Scatter” and the curved lines (no data points) option
• Label the axes etc as required
• Double click on the x-axis, select Scale and minimum to 330 and maximum to
800
• Set colour scheme to suit your prefere nces
Page 16

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 12
ACCESSORIES
PC serial cable (spare) 80-3001-00
S1000P ser ial printer (includes serial pr inter cab le ) 80-30 02 -5 3
Seiko DPU-414 printer 80-2108-80
Serial cable for Seiko printer 80-2118-18
Chart recorder interface cable 80-3003-55
Test tube adapters (10, 12, 16mm) 80-2117-47
ERROR MESSAGES
After switch on, the instrument undergoes self-diagnostic tests for the tungsten lamp,
wavelength calibration and diode array as part of its calibration procedure. In the
unlikely event of an internal instrument error, the word FAIL will appear on the
display together with a symbol and a number; if FAIL is fl ashing the instrument can
still be used, but if FAIL is constant the instrument cannot be used. The error
messages that are displayed as follows:
Error code Symbol FAIL Comment and action
009
!
Flashing Lamp agei n g (t oo much UV), n o is y resu lt s -
change lamp when possible
003
Flashing Lamp ageing (too little UV), noisy results -
change lamp when possible
010
!
Flashing Lamp ageing (too much IR), noisy results -
change lamp when possible
004
Flashing Lamp ageing (to little IR), noisy results - change
lamp when possible
N (the
number of nm
that it is out)
nm
Flashing Wavel en gth calibratio n er r o r ; can compensate by
addition or subtraction of the number displayed,
as appropriate, to the wavelength that is
required, but contact your local distributor.
Press 5 to proceed
011
!
Constant LED failure, contact your local distributor
001
Constant Lamp failur e, change the lamp
005 Constant LED lamp failure, contact your local distributor
006
Constant Pixel clock too high, contact your local
distributor
002
!
Constant Pixel clock too low, contact your local
distributor
007
!
Constant Pi xel clock unstable, contact your local
distributor
008
!
Constant P DA failure, contact your local distributor
Page 17

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 13
MAINTENANCE
After Sales Support
Support agreements that help you to fulfil the demands of regulatory guidelines
concerning GLP/GMP are available.
• Calibration, cert ific at io n using filters tracea b le to international standards
• Certificated engineers and calibrated test equipment
• Approved to ISO 9001 standard
Choice of agreement apart from break down coverage can include
• Preventative maintenance
• Certification
When using calibration standard filters, insert such that the flat surface is facing
away from the spring end of the cell holder
Observe all necessary precautions if dealing with hazardous samples or solvents.
Cleaning and general care of the instrument
External cleaning
Switch off the instrument and disconnect the power cord.
Use a soft damp cloth.
Clean all external surfaces.
A mild liquid detergent may be used to remove stubborn marks.
Changing cell holder or removal for cleaning
• Undo the screws that are visible on the top of the cell holder using a small flat
headed screwdriver and lift the holder out by holding onto the projection; this may
require pushing to the right as you do so in order to prevent fouling against the left
side of the instrument cover. If necessary, the cell holder can be helped out by
pushing from the bottom of the instrument.
• Insert the test tube holder and secure in place using the same screws.
• Note that as well removal for cleaning, spillages in the cell holder ca n be flushed
through using water from a squeeze bottle in order to prevent crystallisation /
fermentation of residues.
Page 18

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 14
Lamp Replacement
A replacement lamp is available from your supplier using the following part
numbers:
Tungsten Lamp, S1000L 80-2115-33
(use only this tungsten lamp as it is supplied with the connection wires; others will
not operate correctly in this spectrophotometer)
• The design of the lamp area is such that users are able to change their own
lamps. No lamp alignment is necessary as the lamp is pre-aligned.
• The lamp becomes hot in use. Ensure it is cool before changing it.
• Do not touch the optical surfaces of the lamp with your fingers (use tissue); if
touched, the area should be cleaned with iso-propanol.
• Instructions for lamp change are provided with the lamp and overleaf.
To change the lamp, proceed as follows:
1. Switch off the instrument, remove the sample from the cell holder and
disconnect the power supply cord
2. Remove the pr ot ective layers at the lamp access and plug in points on the
underneath of the instrument
3. Remove the lamp wires from the groove by gently unclipping it
4. Remove the lamp by twisting the lamp assembly anti-clockwise
5. Remove the lamp connection end by gently pulling with your fingers
6. Replace with new lamp usin g the reverse of these actions
Changing the brightness of the display
To change display brightness, proceed as follows:
1. Ensure the instrument is on and that there is no sample in the cell holder
2. Remove the protective layer at the lamp plug in point (underneath and at the rear
of instrument)
3. Place the instrument on its back, insert a sm all flat headed screwdriver into the
potentiometer slot and turn it right or left until a suitable level of brightness is
obtained.
Page 19

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 15
STUDENT EXPERIMENTS
The simple experiments that follow are designed to illustrate some of the principles
of UV/Visible spectrophotometry, and can be carried out using commonly available
chemicals and this instrument (although any instrument could be used).
Potassium Dichromate stock solution
Potassium dichromate is used in the majority of the experiments. Make a stock
solution as follows:
1. Weigh out approx. 0.93g of potassium dichromate (K
2Cr2O7
) and record the
weight accurately.
2. Put the weighed dichromate into a 1 litre volumetric flask and add 100 ml of
0.1 N sulphuric acid. Make up to 1 litr e with distilled water, shaking the flask
all the time.
3. Calculate the precise concentration by dividing the exact weight of dichromate
used (recorded in 1 above) by 294.2 (the relative molecular mass of potassium
dichromate).
Use the precise weight recorded - in this example assumed to be 0.93g.
0.93
= 0.0031611
294.2
The concentratio n of the stock solution would in this case be 3.16 x 10
-3
mol
1itre
-1
.
4. Make a series of dilutions of the stock solution as follows:
1 part of stock solution to 9 parts of distilled wate r,
3 parts of stock solution to 7 parts of distilled water,
5 parts of stock solution to 5 parts of distilled water,
7 parts of stock solution to 3 parts of distilled water,
9 parts of stock solution to 1 part of distilled water.
Calculate the concentrations of all dilutio ns and rec o rd them.
Apparatus required
For weighing
A balance accurate to at least ± 0.001 g, spatulas, weighing boats, etc.
For measuring volumes ('B' grade equipment is adequate)
1 litre volumetric flask
either (a) a range of volumetric flasks and pipettes
or (b) two 25 ml burettes or 10 ml graduated pipettes together with glass
sample containers (preferably sealed).
Other equipment
Beakers or conica l flasks for d istill ed water, wash bottle and supp ly of distilled
water, pipette filler bulb, graph paper.
Chemicals required (general purpose reagent grade)
Potassi u m dic hromat e K
2Cr2O7
Page 20

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 16
Sodium nitrite NaNO
2
,
Dilute sulphuric acid (0.1 N) H
2SO4
As with all chemicals, care must be taken when handling the above.
Any other chemicals that have a visible colour in aqueous solution, e.g. copper
sulphate, cobalt chloride, indicator dyes or food colourings.
Calculation of λ max, extinction coefficient and measurement of
natural bandwidth
1. P ut ap p r o ximately 3 ml of the 1 : 9 dilution in a10 mm cuvette. The
concentration will be appro ximately 3.16 x 10
-4
mol
-1
2. Set the spectrophotometer wavelength to 330 nm and with nothing in the
spectrophotometer light path (or with a cuvette containing distilled water) set
reference.
3. Place the cuvette containing the prepared dilution in the sample compartment.
Record the absorbance.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 at wavelength increments of 10 nm up to 405 nm and
record absorbance at each wavelength setting.
5. P lot the results as absorbance against wavelength.
6. To determine more precisely the wavelength of maximum absorbance (λ max)
repeat the measurements from 340 to 360 nm at increments of 5 nm.
7. From the graph note the wavelength of maximum absorbance for this solution.
NOTE: The PC utility could be used to export a complete wavelength scan if
preferred so that steps 4-6 are not required
8. Calculate the molar absorptivity (extinction coefficient) of potassium
dichromate, at the wavelength of maximum absorption, using the equation
E = A
c b
The result should be approximately 3150 1 mol
-l
cm-1 at λ max 350 nm.
9. Project the slopes of the peak at λ max to the base line to give a triangular figure.
Estimate the natural bandwidth of this peak by measuring the width of the
triangle (in nm from the wavelength axis) at half its height.
Construction of concentration plots
1. Set the wavelength of the spectrophotometer to λ max as determined in
Experiment 1, and record both absorption and transmission of all the dilutions
of the stock solution of potassium dichromate prepared earlier.
2. On the same graph paper prepare two plots, one of absorbance at λ max against
concentration and one of transmission against concentration.
Note that the absorbance p lo t is linear to about 1.5A and that the transmission
plot is exponential. The flattening of the absorbance plot at higher values is
Page 21

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 17
due to stray light. It is good laboratory practise to measure between 0.1 and 1.0
Abs on any spectrophotometer.
Concentration plots similar to that just co nstructe d ar e used to find the concentration
of an unknown sample of the same solution (it is customary to plot only the
absorbance values against concentration, not transmission.), the so-called standard
curve.
If the measured absorbance of the unknown lies outside the linear section of the plot,
the reading may be brought within the linear section either by using a cuvette of
shorter pathlength or by diluting the sample by a known factor. If a shorter
pathlength is chosen the observed absorbance must be multiplied by a factor related
to the ratio of the two pathlengths, e.g. if the curve is based on 10 mm cells and a 5
mm cell is used, multiply by 2. If the dilution method is selected, calculate the
concentration by multiplying the absorbance by the same factor as the dilution and
then read the value from the plot prepared as described above.
Measurement of stray light
1. Make up a solution of sodium nitrite (NaNO
2
) in distilled water at a
concentration of 50 g l
-l
(e.g. 5g in 100 ml) and fill a l0 mm cuvette.
2. Set the wavelength of the spectrophotometer to 340 nm and set the reference
(100%T) with nothing in the sample compartment (or with a cuvette filled with
distilled water).
3. Put the cuvette containing the sodium nitrite solution in the sample
compartment of the spectrophotometer.
Sodium nitrite acts as a blocking filter, absorbing all incident radiation at the
wavelength selected, but transmitting virtually all of the radiation at longer
wavelengths. Therefore any transmission recorded at 340 nm will be a direct
measurement of the stray light of the instrument.
The value should be in accordance with the manufacturer’s specification.
Page 22

___________________________________________________________________
Issue 02 - 03/2005 Libra S4, English 18
SPECIFICATION AND WARRANTY
Wavelength range 330 - 800 nm
Monochromator Flat grating
Wavelength ca l ibration Automatic upon switch on
Spectral bandwidth 7 nm
Wavelength a cc u racy
± 2nm
Wavelength reproducibility
± 1nm
Light sources Pulsed Tungsten halogen
Detector Diode array
Photometric range - 0.300 to 2.500A, 0 to 200%T
Photometric linearity
± 2.0 % or ± 0.010A to 1.000A at 546nm, whichever is
the greater
Photometric reproducibility < 0.002 A at 0A and 500nm
Stray Light < 1%T 340nm according to ANSI/ASTM E387-72
Stability
± 0.005A/h at 0A and 546nm after warm-up
Noise
± 0.002A near 0A and ± 0.020A near 2A at 600nm
Analogue output
1V per 1 Abs (±10%), 1V = 0A offset
1V per 100%T (±10%), 0V = 0%T offs et
Digital outp u t 9 pin serial
Dimensions 180 x 270 x 390 mm
Weight 1.75 kg
Power input 90-265 V, 50/60 Hz, 15 VA
Safety standard EN61010-1
EMC emissions EN 61326-2.3 Generic emissions
EMC immunity EN 61000-4-6 Generic immunity part 1
Mains harmonics EN 61000-3-2
Susceptibility standard IEC 801
Quality System Designed and manufactured in accor d an ce with an ISO
9001 approved quality system
Specifications are measured after the instrument has warmed up at a constant
ambient temperature and are typical of a production unit. As part of our policy of
continuous development, we reserve the right to alter specifications without notice.
Warranty
Your supplier guarantees that the product supplied has been thoroughly tested to ensure that it
meets its published specification. The warranty inc luded in the conditions of supply is va lid
for 12 months only if the product has been used according to the instructions supplied. They
can accept no lia b i lity for loss or damage, however cau sed, arising from the faulty or i n co r r ect
use of this product.
This product has been designed and manufactured by Biochrom Ltd, 22 Cambridge Science
Park, Milton Ro ad, Cambridge CB4 0F J, UK.
 Loading...
Loading...