Page 1

CARRIER COMMERCIAL REFRIGERATION, INC.
Providing BEVERAGE-AIR • FRIGIDAIRE • KELVINATOR • UNIVERSAL NOLIN Products/Services
SERVICE &
INSTALLATION
MANUAL
DIPPING
CABINETS
R-404A Refrigerant
1 / 2003
51-1298-02
Page 2
If additional information is necessary, call Carrier Refrigeraiton
Operations headquarters.
Our toll free number is 1-800-684-1199.Technical assistance engineers are
willing to assist you in any way possible. Office hours are from 8:00 a.m. to
5:30 p.m., Eastern Standard Time.
Important information is contained in this manual which should
be retained in a convenient location for future reference.
Information in this manual is subject to change without notice.
MODEL DESIGNATION INFORMATION
115V, 60HZ
PAR T # MODEL # DATA PLATE STYLE
52-1802-31 CKDC27 4HC CURVED
52-1802-32 CKDC47 8HC CURVED
52-1953-31 CKDC47 3500K LIGHTS 8HC CURVED
52-1802-33 CKDC67 12HC CURVED
52-1953-33 CKDC67 3500K LIGHTS 12HC CURVED
52-1802-34 CKDC87 16HC CURVED
52-1953-32 CKDC87 3500K LIGHTS 16HC CURVED
52-1802-35 KDC27 DL4C 4HR/4HJ STRAIGHT
52-1802-36 KDC47 DL8C 8HR/8HJ STRAIGHT
52-1963-31 KDC47F SS NO LIGHTS 8HF STRAIGHT
52-1802-37 KDC67 DL12C 12HR STRAIGHT
52-1802-38 KDC87 DL16C 16HR STRAIGHT
EXPORT 220V, 50HZ
PAR T # MODEL # DATA PLATE STYLE
52-1901-35 ECKDC27 E4HC CURVED
52-1901-36 ECKDC47 E8HC CURVED
52-1901-31 ECKDC67 ECKDC-67 CURVED
52-1901-32 ECKDC87 ECKDC-87 CURVED
52-1901-37 EKDC27 EDL4C E4HR STRAIGHT
52-1901-38 EKDC47 EDL8C E8HR STRAIGHT
52-1901-33 EKDC67 EDL12C EKDC-67 STRAIGHT
52-1901-34 EKDC87 EDL16C EKDC-87 STRAIGHT
EXPORT 220V, 60HZ
PAR T # MODEL # DATA PLATE STYLE
52-1944-35 KCKDC27 E4HC2 CURVED
52-1944-36 KCKDC47 E8HC2 CURVED
52-1944-31 KCKDC67 E12HC2 CURVED
52-1944-32 KCKDC87 E16HC2 CURVED
52-1944-37 KKDC27 E4HR2 STRAIGHT
52-1944-38 KKDC47 E8HR2 STRAIGHT
52-1944-33 KKDC67 E12HR2 STRAIGHT
52-1944-34 KKDC87 E16HR2 STRAIGHT
Manual effective for models produced January, 2003. Starting serial number 6527372.
Page 3
Introduction
Page 4

Dipping Cabinet Introduction
These Dipping Cabinets are designed to merchandise ice cream or yogurt type
products. Dipping cabinets are produced in four sizes: 4, 8, 12, and 16 facings
of ice cream containers. The cabinet systems contain R-404A refrigerant,
metered into the system by a capillary tube. The evaporator is a cold wall which
has the refrigerant lines strapped to the inner liner of the cabinet. The condenser
is a bare tube mounted on a pullout machinery compartment tray for ease of
servicing. All electrical controls are easily accessible for repair. The temperature
within the cavity is controlled thermostatically, allowing for maintenance of
correct dipping temperatures.
Mechanical equipment may require repair at times. This manual presents
information that is helpful in maintaining, diagnosing, and repairing these
cabinets.
The high level of quality built into these units will allow for many years of
trouble free operation.
2 INTRODUCTION
Page 5

TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
Introduction ........................................................................ 2
Table of Contents ................................................................3
CABINET SPECIFICATIONS/DIMENSIONAL DRAWINGS
4HR & 4 HC & EXPORT .................................................. 4
8HR & 8HC & EXPORT .................................................. 5
12HR & 12HC & EXPORT .............................................. 6
16HR & 16HC & EXPORT .............................................. 7
Handling & Installation ...................................................... 8
Product Load Line Location .............................................. 10
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
General Operations Information ........................................ 13
4HR & 4HC Electrical & Refrigeration Specs .................... 14
8HR & 8HC Electrical & Refrigeration Specs .................... 15
12HR & 12HC Electrical & Refrigeration Specs ................ 16
16HR & 16HC Electrical & Refrigeration Specs ................ 17
E4HR & E4HC Electrical & Refrigeration Specs. .............. 18
(220V / 60 Hz)
E8HR & E8HC Electrical & Refrigeration Specs. .............. 19
(220V / 60 Hz)
E12HR & E12HC Electrical & Refrigeration Specs. .......... 20
(220V / 60 Hz)
E16HR & E16HC Electrical & Refrigeration Specs. .......... 21
(220V / 60 Hz)
4HR, 4HC / 8HR, 8HC / E4HR, E4HC / E8HR, E8HC
Wiring Diagram ................................................................ 22
12HR, 12HC / 16HR, 16HC Wiring Diagram .................... 23
Condenser Fan Motor Replacement .................................. 44
Ballast Replacement ........................................................ 45
Metering Device / Heat Exchanger Replacement .............. 46
Cabinet Troubleshooting Guide ........................................ 47
Compressor Troubleshooting Guide ................................ 49
Fluorescent Lamp Troubleshooting Guide ........................ 50
Measurements - Starting Lamp Voltage .......................... 52
ILLUSTRATIONS & PARTS
Cabinet Parts - Exploded View .......................................... 54
Cabinet Parts List ............................................................ 55
Canopy Parts - Exploded View .......................................... 56
Canopy Parts List ............................................................ 57
Condensing Unit - Exploded View .................................... 58
Condensing Unit Parts List .............................................. 59
Electrical Components - Exploded View .......................... 60
Electrical Components Parts List ...................................... 61
Lid - Exploded View .......................................................... 62
Lid Parts List .................................................................... 63
ACCESSORIES
Can Skirt Accessory Parts List ........................................ 67
Can Skirt Installation ........................................................ 68
Dipperwell Installation ...................................................... 70
Sanitary Base Leg Installation .......................................... 71
Caster Installation ............................................................ 72
Lid Lock Kit Installation .................................................... 73
Can Clamp Installation ...................................................... 74
Round Can Clamp Installation .......................................... 75
Half-way Shelf Bottom Support Kit Installation ................ 76
ECKDC67, EKDC67 / ECKDC87, EKDC87
E12HC2, E12HR2 / E16HC2, E16HR2
WIRING DIAGRAM..............................................................24
8HC, 12HC, 16HC (3500K LIGHTS)
WIRING DIAGRAM..............................................................25
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Pre-Service Check List ...................................................... 29
General Maintenance Information .................................... 30
Compressor Installation / Diagnostics .............................. 32
Cleaning & Maintenance .................................................. 34
Cleaning the Lid & Touch-up Painting .............................. 35
Lid Seal Replacement ...................................................... 36
Lid Gasket Replacement .................................................. 37
Lid Pivot Bushing Assembly Replacement ...................... 38
Center & End Pivot Rod Replacement .............................. 39
Fluorescent Lamp Holder/Light Starter Socket Replac. .... 40
Fluorescent Bulb & Starter Replacement .......................... 41
Thermostat Replacement .................................................. 42
Master Power Supply Switch / Light Switch Removal ...... 43
Specifications are subject to change without notice.
TABLE OF CONTENTS 3
Page 6
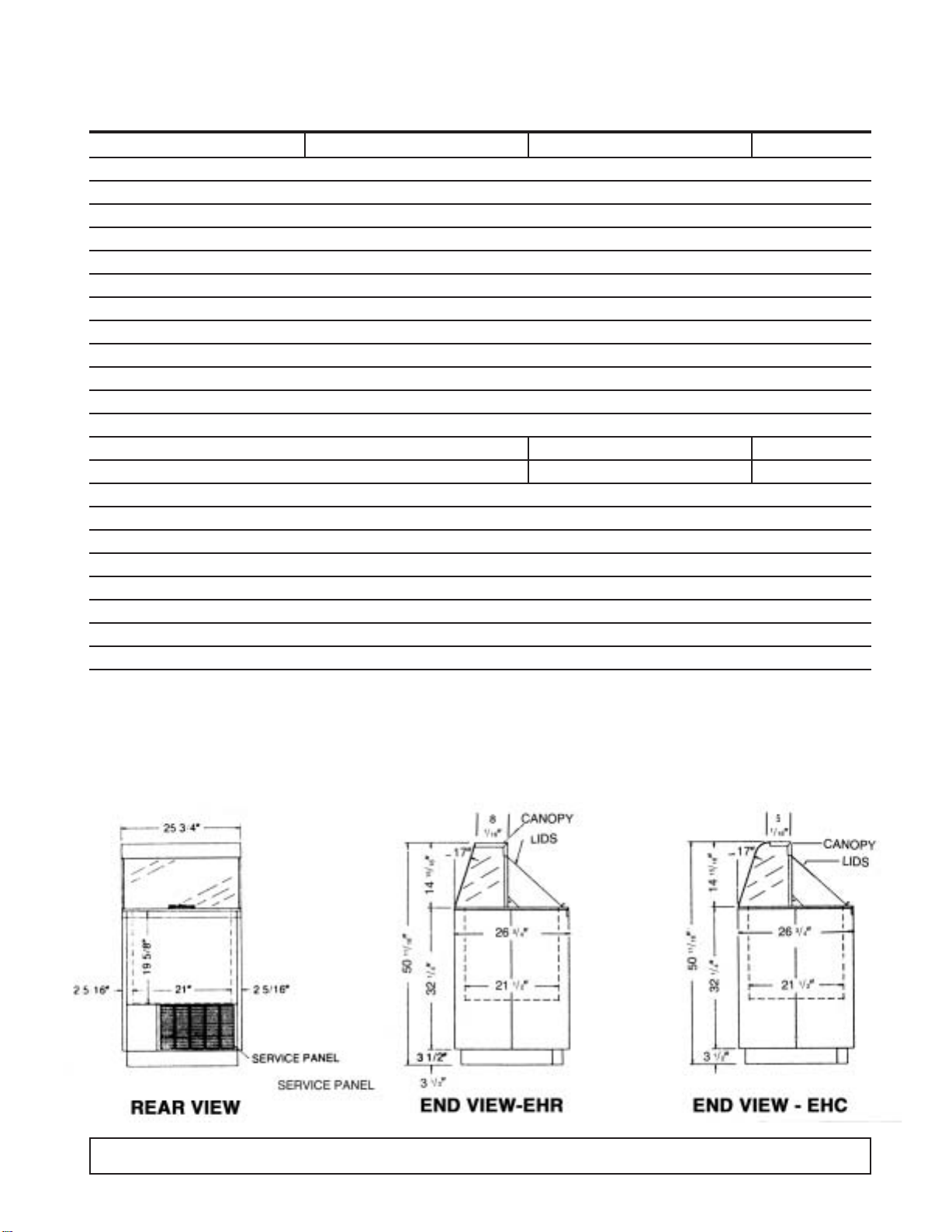
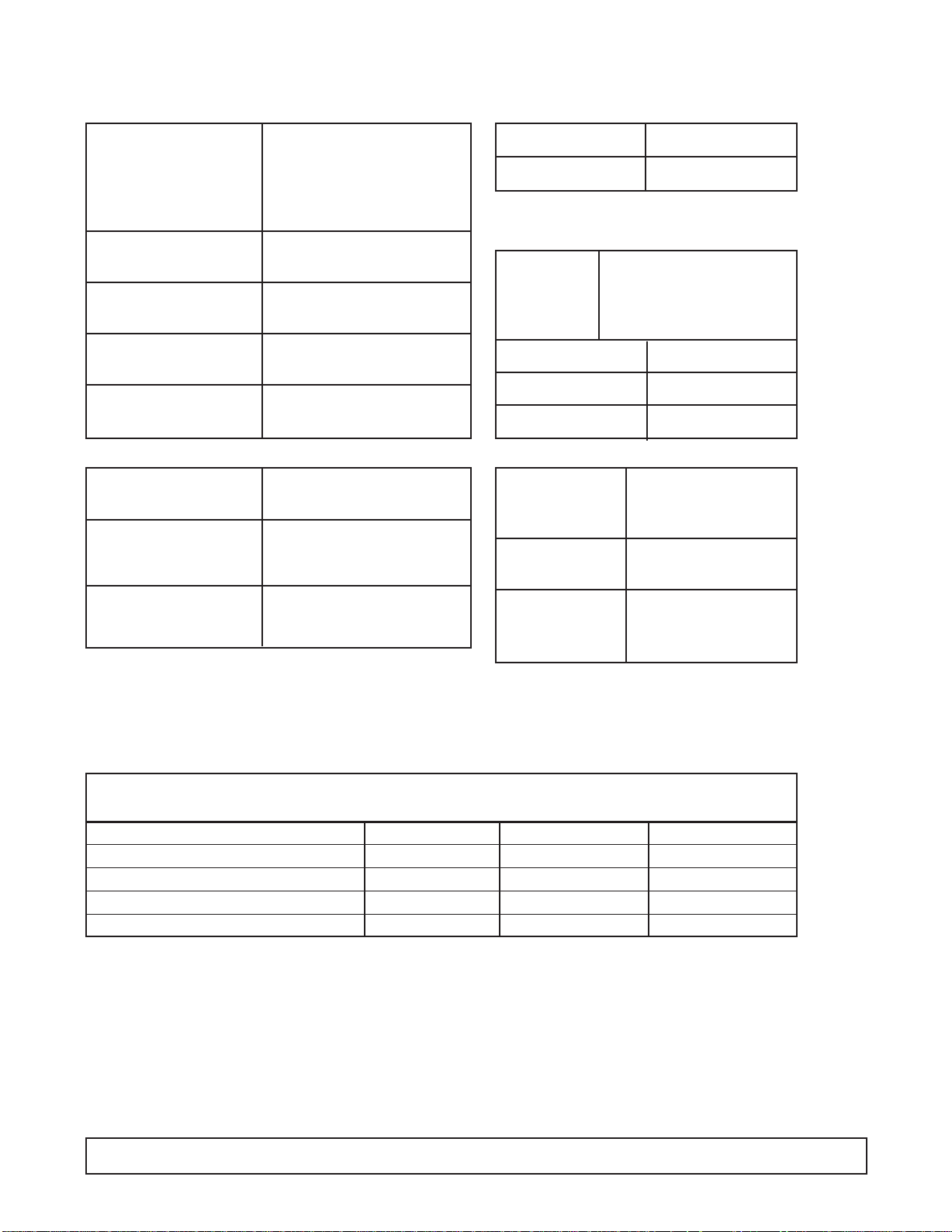
CABINET SPECIFICATIONS
4HC & 4HR/4HJ E4HC & E4HR E4HC2 & E4HR2
Temp. Range +10°F to -8°F
Capacity 4.6 Cu. Ft.
Capacity (3 Gal. Tubs) 4
Facings (3 Gal. Tubs) 4
Storage (3 Gal. Tubs) 0
Compressor Size 1/4 Hp.
Shipping Weight (App.) 235 lbs.
Condenser Type Bare Tube
Evaporator Type Cold Wall
Refrigerant R-404A
Refrigerant Control Capillary Tube
Defrost System Manual
Rated Amps 3.0 1.7 1.7
Electrical Specs. 115V, 60 Hz., 1 Ph. 220V, 50 Hz., 1Ph 220V, 60 Hz., 1 Ph.
Power Cord No. 16AWG
NSF Listing NSF7
Canopy Construction S.S. Top with Glass ends Straight or Curved Front Glass
Lids (Plexiglass) 1 Lid
Interior Finish White Baked Enamel on Galvanized Steel
Exterior Finish White Baked Enamel
Lighting One 20 Watt Bulb
Accessories Can Skirt Kit, Lid Locks, Dipperwell, Night Covers, Casters, Legs
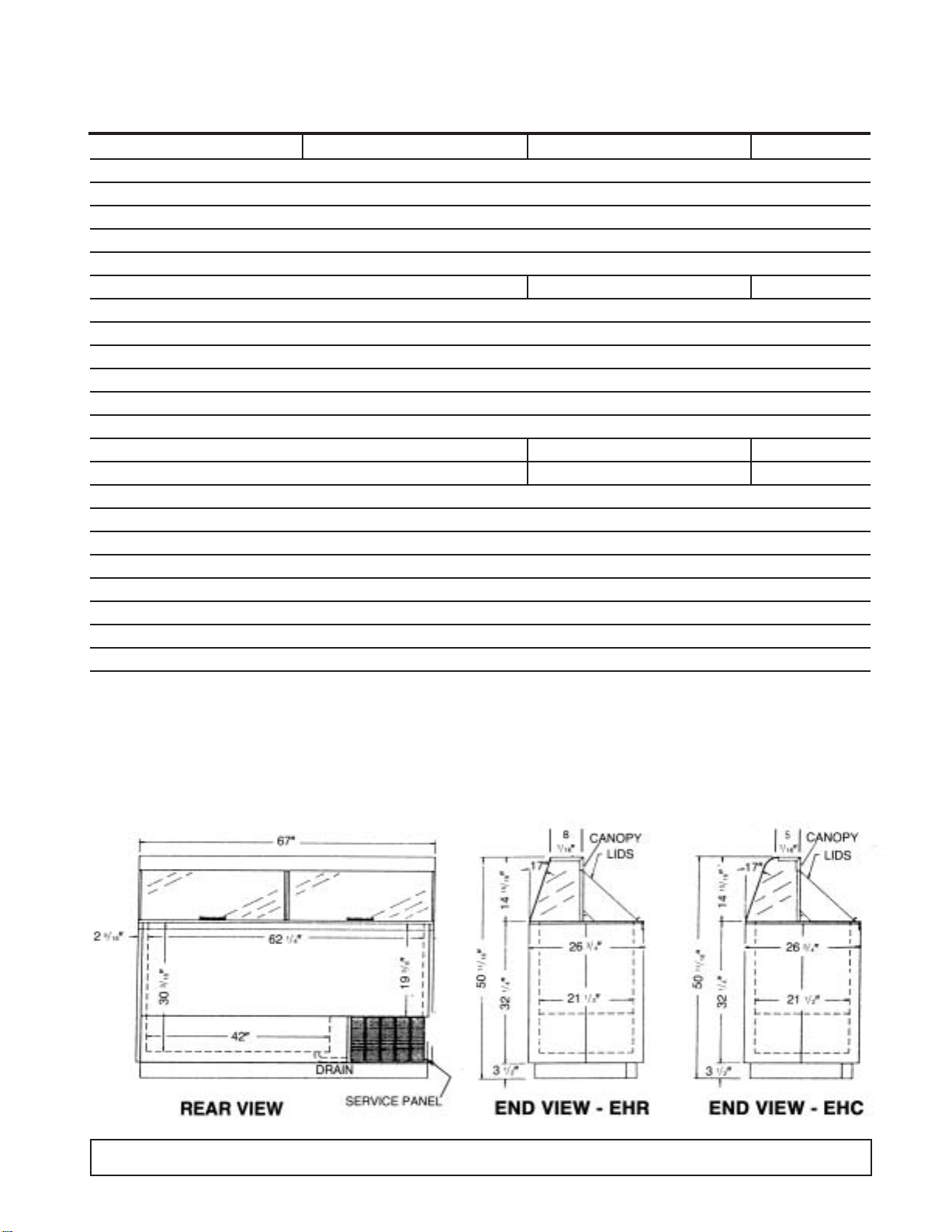
DIMENSIONAL DATA
4 INTRODUCTION
Page 7
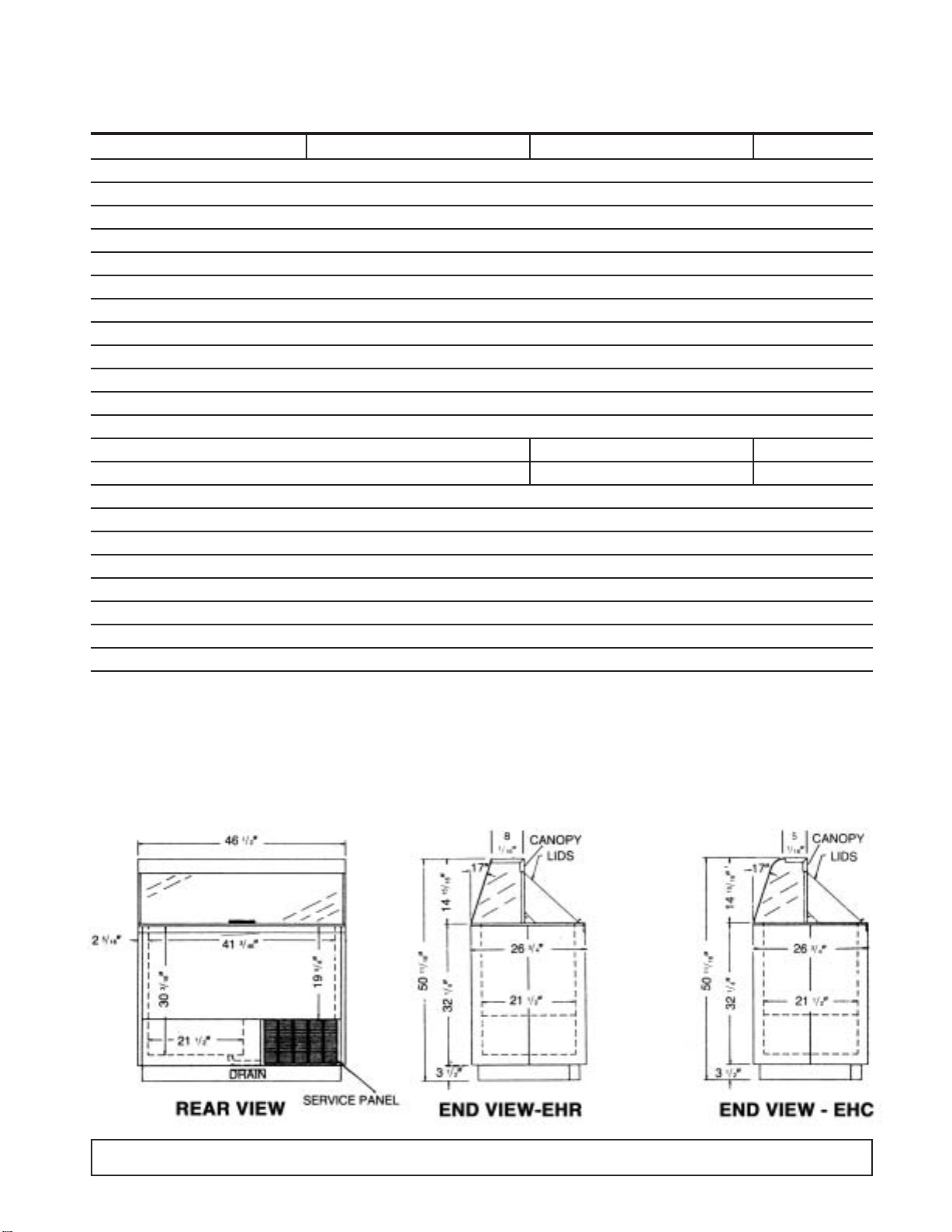
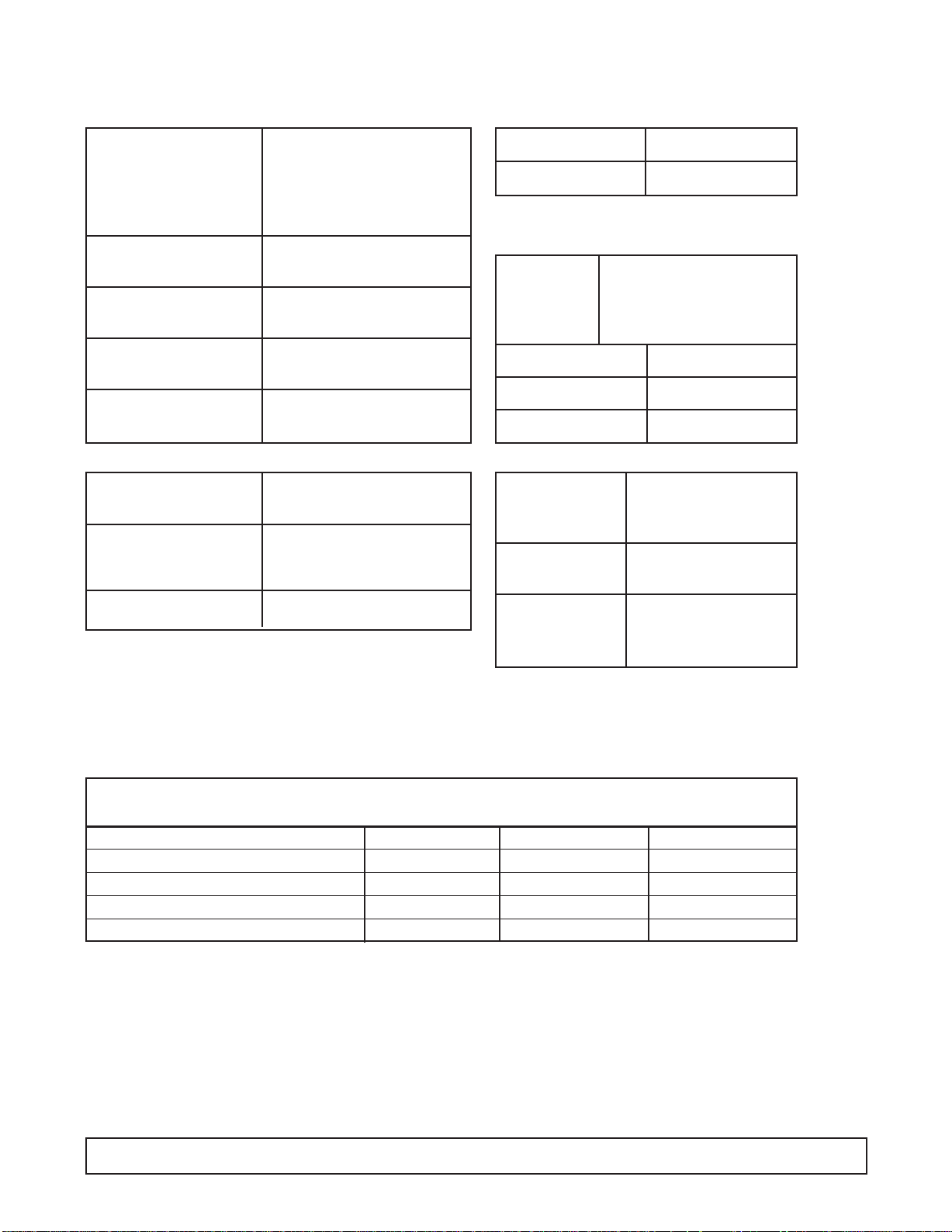
CABINET SPECIFICATIONS
8HC & 8HR/8HJ & 8HF E8HC & E8HR E8HC2 & E8HR2
Temp. Range +10°F to -8°F
Capacity 12.0 Cu. Ft.
Capacity (3 Gal. Tubs) 12
Facings (3 Gal. Tubs) 8
Storage (3 Gal. Tubs) 4
Compressor Size 1/3 Hp.
Shipping Weight (App.) 365 lbs.
Condenser Type Bare Tube
Evaporator Type Cold Wall
Refrigerant R-404A
Refrigerant Control Capillary Tube
Defrost System Manual
Rated Amps 4.0 2.1 2.1
Electrical Specs. 115V, 60 Hz., 1 Ph. 220V, 50 Hz., 1 Ph. 220V, 60 Hz., 1Ph.
Power Cord No. 16AWG
NSF Listing NSF7
Canopy Construction S.S. Top with Glass ends Straight or Curved Front Glass
Lids (Plexiglass) 1 Lid
Interior Finish White Baked Enamel on Galvanized Steel
Exterior Finish White Baked Enamel
Lighting Two 20 Watt Bulbs Standard (17 Watt Bulbs on Special Cabinets with 3500 K Lighting)
Accessories Can Skirt Kit, Lid Locks, Dipperwell, Night Covers, Casters, Legs
DIMENSIONAL DATA
INTRODUCTION 5
Page 8
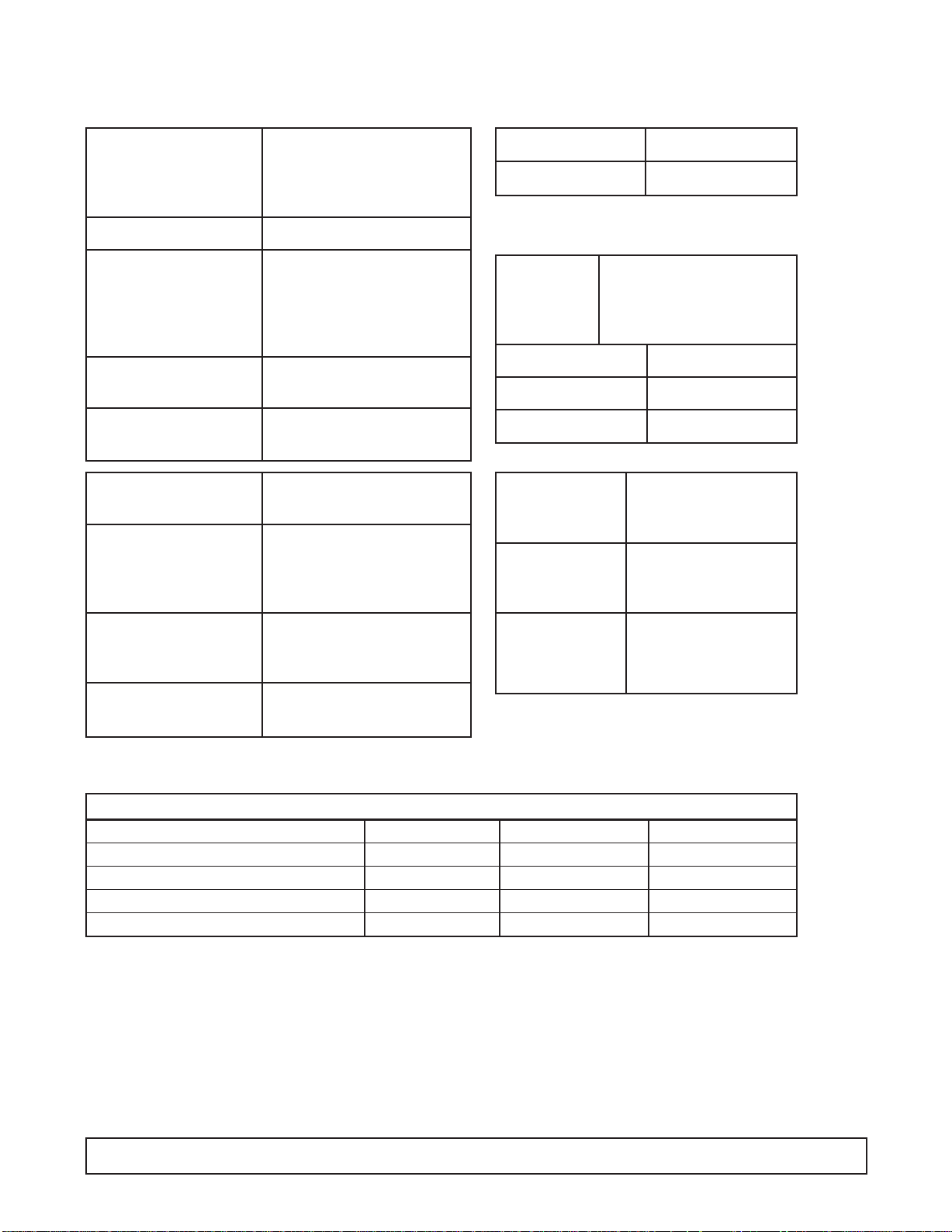
CABINET SPECIFICATIONS
12HC & 12HR ECKDC-67 & EKDC-67 E12HC2 & E12HR2
Temp. Range +10°F to -8°F
Capacity 19.1 Cu. Ft.
Capacity (3 Gal. Tubs) 20
Facings (3 Gal. Tubs) 12
Storage (3 Gal. Tubs) 8
Compressor Size 1/3 Hp. 3/4 Hp. 3/4 Hp.
Shipping Weight (App.) 525 lbs.
Condenser Type Bare Tube
Evaporator Type Cold Wall
Refrigerant R-404A
Refrigerant Control Capillary Tube
Defrost System Manual
Rated Amps 8.0 4.1 4.1
Electrical Specs. 115V., 60 Hz, 1 Ph. 220V, 50 Hz, 1 Ph. 220V, 60 Hz, 1 Ph.
Power Cord Yes
NSF Listing NSF7
Canopy Construction S.S. Top with Glass ends Straight or Curved Front Glass
Lids (Plexiglass) 2 Lid
Interior Finish White Baked Enamel on Galvanized Steel
Exterior Finish White Baked Enamel
Lighting Two 30 Watt Bulbs Standard (32 Watt Bulbs on Special Cabinets with 3500 K Lighting)
Accessories Can Skirt Kit, Lid Locks, Dipperwell, Night Covers, Casters, Legs
DIMENSIONAL DATA
6 INTRODUCTION
Page 9

CABINET SPECIFICATIONS
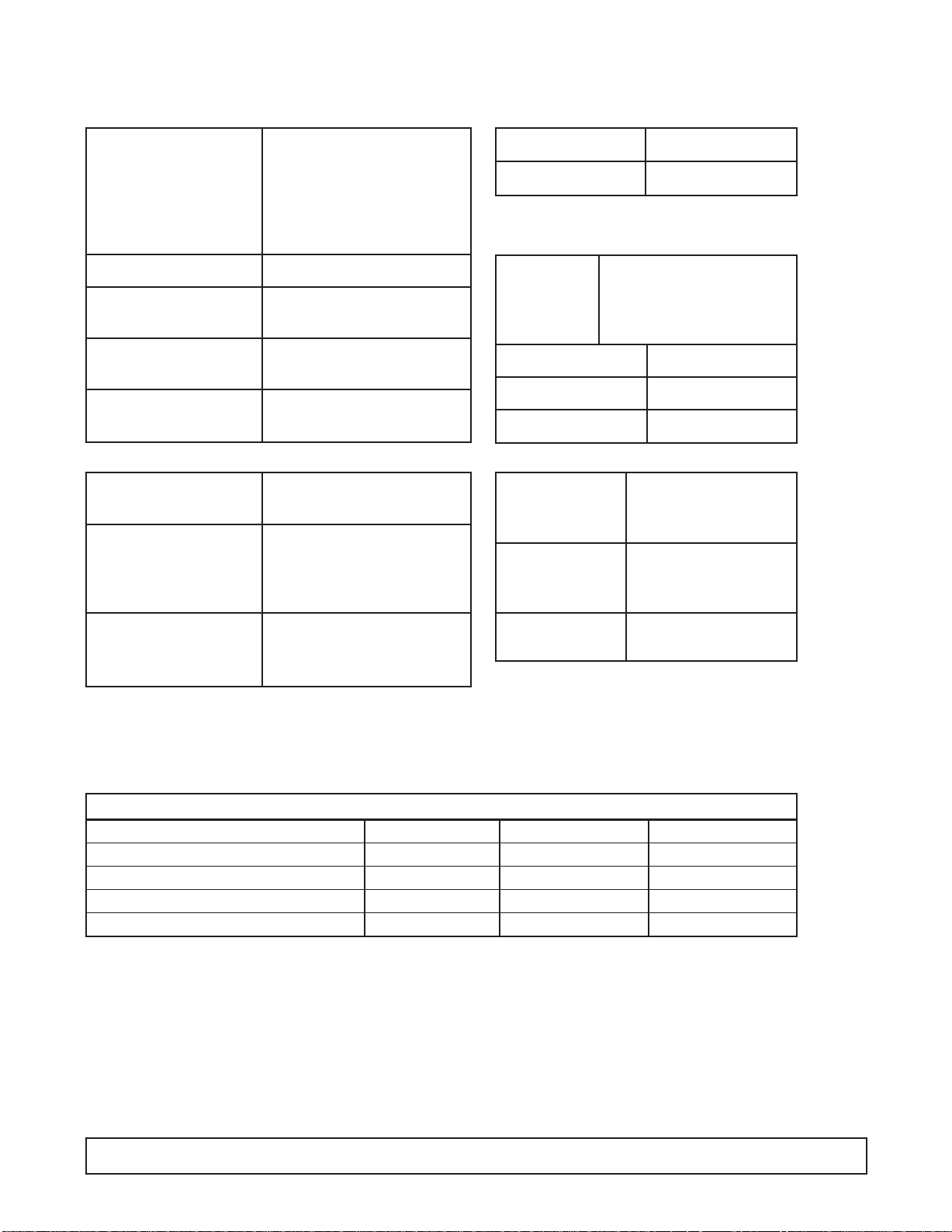
16HC & 16HR ECKDC-87 & EKDC-87 E16HC2 & E16HR2
Temp. Range +10°F to -8°F
Capacity 19.1 Cu. Ft.
Capacity (3 Gal. Tubs) 20
Facings (3 Gal. Tubs) 12
Storage (3 Gal. Tubs) 8
Compressor Size 1/3 Hp. 3/4 Hp. 3/4 Hp.
Shipping Weight (App.) 525 lbs.
Condenser Type Bare Tube
Evaporator Type Cold Wall
Refrigerant R-404A
Refrigerant Control Capillary Tube
Defrost System Manual
Rated Amps 8.0 4.1 4.1
Electrical Specs. 115V, 60 Hz., 1 Ph. 220V, 50 Hz, 1 Ph. 220V, 60 Hz, 1 Ph.
Power Cord Yes
NSF Listing NSF7
Canopy Construction S.S. Top with Glass ends Straight or Curved Front Glass
Lids (Plexiglass) 2 Lid
Interior Finish White Baked Enamel on Galvanized Steel
Exterior Finish White Baked Enamel
Lighting Two 40 Watt Bulbs Standard (32 Watt Bulbs on Special Cabinets with 3500 K Lighting)
Accessories Can Skirt Kit, Lid Locks, Dipperwell, Night Covers, Casters, Legs
DIMENSIONAL DATA
INTRODUCTION 7
Page 10
HANDLING & INSTALLATION-Illuminated Dipping Cabinets
FREIGHT DAMAGES AND SHORTAGES
IMPORTANT
The cabinet was inspected and packaged at the
factory, and should have arrived in excellent
condition. The transportation company or other
parties involved in the shipment are responsible for
loss and/or “damage.” Always make an inspection
before and after uncrating, pref erab ly at the point of
unloading by the transportation company.
INSPECTING FOR DAMAGES
Note:
Always use care when removing shipping tape,
blocks, pads, hardware or other material. Contact
your dealer or distributor if technical assistance
is required.
Check the cartons or containers. If these are damaged
in any way, open them and inspect the contents in the
driver’s presence. If damage is detected, do the
following:
1. Have the driver note the nature and extent of the
damage on the freight bill.
2. Notify the transpor tation company’s office to request
an inspection. Carrier claim policies usually require
inspections to be made within 15 days of delivery.
3. If damage is noticed, file a claim with the
transportation company.
FILING A CLAIM
File a claim for loss at once with the transportation
company for:
A. A cash adjustment B. Repairs C. Replacement
When filing your claim, retain all packaging materials
and receipts.
HANDLING THE CABINET
Note:
The refrigeration system of the cabinet is designed
to operate with the cabinet located on a flat surface.
Do not tilt the cabinet more than 30° to any side. If
the cabinet must be tilted on an angle for handling or
moving purposes, allow it to sit in an upright position
20 to 30 minutes prior to operating.
CHOOSE A LOCATION
This model cabinet should be situated to allow proper air
circulation. The cabinet must be installed on sturdy, level
floor and positioned so that it can be plugged into a
properly grounded three-prong electrical wall outlet. The
electrical outlet should not be controlled by a wall switch
which might be turned off accidentally.
UNCRATING THE CABINET
The cabinet should be moved as close as possible to
the operating location before removing the skid. Be
sure to follow the steps in the “INSPECTING FOR
DAMAGES” instructions.
INSTALLING THE CABINET
Whenever possible leave the crate skid on the cabinet
until it is moved close to the final position. When it is
necessary to move the cabinet through a doorway, it
may be necessary to remove the crate skid.
Run the cabinet down to storage temperature before
adding product.
CAUTION
A. Do not locate cabinet where sunlight or drafts from
fans, air conditioners or open doors can affect product
temperature.
B. Run cabinet before building in or attaching panels or
accessories.
C. Employee side access panel must be kept clear for
adjustments and service.
D. Cabinet must be installed on the finished floor to
assure rear raceway cover and condensing unit
(employee side) can be pulled or removed for service.
DO NOT seal in with cover molding or caulking in the
area where condensing unit pulls out.
E. Do not use extension cords to power this equipment.
Run any necessary electrical, water supply and drain
lines before setting the cabinet in position. Shim under
the cabinet as necessary to level it. N.S.F. approval
requires sealing the cabinet to the floor. This can be
done by applying a bead of mastic sealer between the
cabinet bottom flange and the floor.
Should several cabinets be set up in a row, space is
provided in the rear toe space for routing electrical and
plumbing lines.Access to this space requires removing
screws and the metal cover which runs the length of the
cabinet.
Rivnuts are provided on the operator's side for
mounting dipperwell and other accessories.
CABINET START-UP
Once the cabinet has been located in its permanent
location and the proper power and grounding have
been provided, the following items must be checked or
completed:
A. Cut and remove the compressor hold-down band (if
applicable) so the compressor “floats” freely.
8 INTRODUCTION
Page 11

B. Check for traces of oil on the compressor pan which
could mean a broken or leaking refrigeration line.
UNDER NO CIRCUMSTANCE SHOULD THE
COMPRESSOR BE STARTED WHEN OIL IS
PRESENT UNTIL INSPECTED BY A SERVICE
TECHNICIAN.
C. INSPECT THE FACTORY WIRING FOR
TERMINALS THAT MIGHT HAVE VIBRATED
LOOSE IN SHIPPING. TIGHTEN ALL SCREW
TYPE TERMINALS.
D. Check the refrigeration lines to see that they are
“free” and no damage was done during shipping.
E. Check fan blade for free operation.
F. Turn on the main power switch.Once the compressor
starts, the voltage should be checked at the
compressor terminals to determine if there is proper
voltage to the compressor. The voltage should not
exceed the 10% above or below the rated
compressor voltage.
EXAMPLE: If the voltage reads 220 volts with no load
and it drops below 210 volts when the compressor
starts, it may indicate that the supply wiring is too small
or that the wire run is too long.
G. Listen for any unusual noise such as lines vibrating,
etc. Correct the problem by tightening screws,
slightly bending tubing, etc.
H.The temperature control thermostat which is located
in the rear post is factory set for average conditions.
A customer adjustment requires a coin or
screwdriver to turn the slotted shaft.A numbered dial
makes it easy to keep track of adjustments. #1 is
warmest setting and #7 is coldest setting. An “OFF”
position is provided for your convenience in
defrosting the cabinet.
I. Allow the cabinet to pull down and cycle prior to
loading with product (Approx. 24 hours).
GROUNDING INSTRUCTIONS
This appliance is equipped with a three-prong
(grounding) plug for your protection against shock
hazards.The appliance should be plugged directly into
a properly grounded three-prong receptacle.
Where a two-prong wall receptacle is encountered, it
must be replaced with a properly grounded three-prong
receptacle in accordance with the National Electrical
Code and local codes and ordinances. The work must
be done by a licensed electrician.
IMPORTANT
Do not, under any circumstance, cut or remove the
round grounding plug from the appliance plug.
WARNING
Consult a licensed electrician if you have any doubt
about the grounding of your wall receptacle. Only a
licensed electrician can determine the polarization of
your wall receptacle. Only a properly installed threepronged wall receptacle assures the proper
polarization with the appliance plug.
IMPORTANT USAGE INSTRUCTIONS
Dipping Cabinet
The cabinet must be located in an area free from air
drafts created by open doors, air conditioning ducts,
and fans. The cabinet should not be located in the
direct sunlight.
The rear grill must be clear of any obstructions so the
intake and exhausting of air f or the condensing unit can
move freely.
Dipping cabinets are designed for use in an air
conditioned store. This cabinet is designed for
merchandising, not hardening of the product.
High humidity can cause fogging of the lid and front glass.
High temperatures, installation of warm product and
heavy usage can cause the product to soften. This
condition will be more noticeable at the top of the cans.
The corners of the cabinets are the coldest areas.
These areas should be used for product that is more
difficult to keep firm.
Frost and ice act as insulators. The need for defrosting
will depend on usage and product firmness.
If the frost is scraped daily with a plastic scraper,
intervals between complete defrosting may be
extended.
Thermostat adjustments should be made one
increment warmer or colder allowing 24 hours between
adjustments to allow the product to stabilize.
INTRODUCTION 9
Page 12
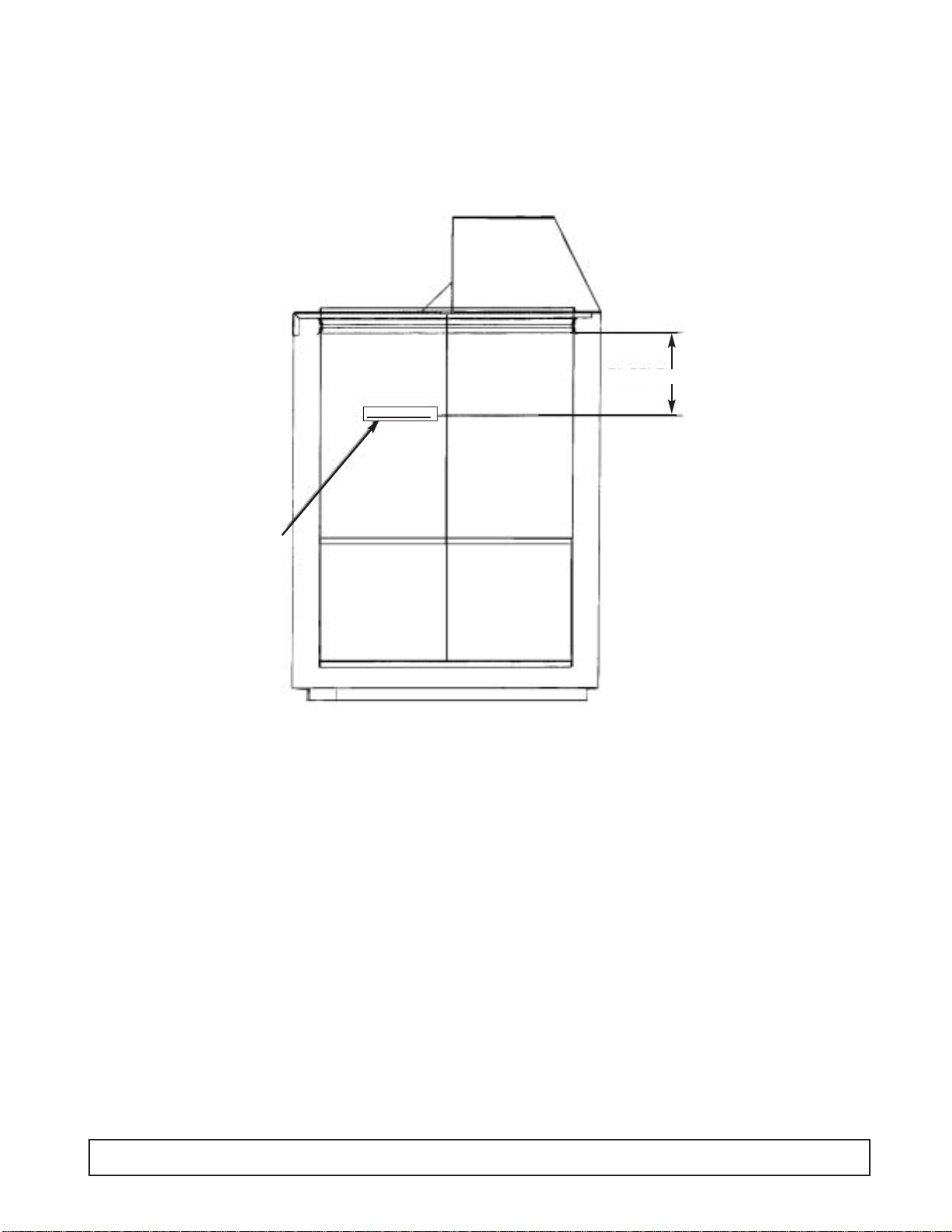
PRODUCT LOAD LINE LOCATION
KEEP PRODUCT BELOW RED LINE
7" BELOW BREAKER
NOTE:
KEEP PRODUCT
BELOW THIS LINE.
10 INTRODUCTION
Page 13
SECTION II
Principles of
Operation
Page 14

blank
Page 15

GENERAL OPERATIONS
All the dipping cabinet models are of the same basic
design, consisting of a bare tube condenser and a cap
tube fed tank wrap evaporator.
Ice formation on the walls over a period of time is
normal. This frost should be scraped off periodically in
order to maintain peak performance. These cabinets
are thermostatically controlled for various temperature
requirements.The thermostat is located post adjacent
to the unit compartment and can be accessed for
adjustment by the user with a screwdriver or a dime.
Thermostat position #1 being the warmest and
position #7 the coldest.
These cabinets are manual defrost and a drain is
provided for periodic cleaning. A garden hose can be
attached to the drain plug for draining away any water
that might have accumulated.This drain attachment is
located in the front base rail of the cabinet.NOTE:The
power supply cord must be disconnected when
cleaning or servicing these cabinets.
NOTE: On initial cabinet pull down the bare tube
condenser may become warm to the touch until
the normal operating temperatures are achieved.
Compressors being used in these cabinets utilize
refrigerant 404A and polyol ester oil. Because of the
hygroscopic nature of this oil, extreme care must be
taken when any component is changed within the
system. In the case of compressor replacement, work
should be completed before the caps are removed
from the compressor.
Agitation of the oil should be kept to a minimum.
Compressors should not be open to the atmosphere
for more than 15 minutes max. Should contamination
occur the oil can be removed and recharged (following
compressor manufacturer's guidelines when
performing this procedure). Because of the porous
nature of plastic, polyol ester oil should be stored in a
metal container. Moisture contained within the oil
cannot be removed even under high vacuum
conditions and must be replaced.
Refer to model serial data tag for cabinet amperage,
refrigerant charge & type.
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 13
Page 16
SYSTEM INFORMATION - 4HR & 4HC
ELECTRICAL
Compressor Manufacturer: Americold
Model: HP-110-3083
V.: 115/100 R.L.A.: 2.0
L.R.A.: 10 Phase 1
Overload Protector Americold #1456-3453
Start Relay T.I.: Americold #1456-3372
Start Capacitor V.A.C.: 165 M.F.: 88-108
Run Capacitor V.A.C.: 180 M.F.: 15
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:5KSM51GG-37845
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 7' of .031
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 120/240 L.R.A.: 100
Warm C ut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
Pow er Cord A.W.G.: 14
A.: 15 @ 125V
Light Ballast Manufacturer: G.E.
Model: 89G457
Condenser Diameter: 8" # of Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1 7/8"
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig. Charge: R-404A / 11.5 oz. / 326.02 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F20T12 CW
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CONTROL SETTINGS #4 C.S. #4 C.S. #4 C.S.
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 13 / 13 / 14 /
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 196 / 224 / 246 /
Compressor Amps 1.8 1.8 1.8
Total Cabinet Amps 2.3 2.0 2.0
Cavity Temperature C.L. 0°F / -17°C 2°F / -16°C 3°F / -16°C
14 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
Page 17
SYSTEM INFORMATION - 8HR & 8 HC
ELECTRICAL
Compressor Manufacturer: Americold
Model: HP-117-1
V.: 115/100 R.L.A.: 3.0
L.R.A.: 21.4 Ph.: 1 HP:
Overload Protector Americold #1456-3454
Start Relay T.I.: 8EA1206K1A
Start Capacitor V.A.C.: 165 M.F.: 88-108
Run Capacitor V.A.C.: 200 M.F.: 15
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: Morrill
Fan Motor Model:SPB9S1
Condenser Diameter: 8" # of Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:2 3/4"
1
⁄3
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 8' of .036
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 120/240 L.R.A.: 100
Warm C ut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
Pow er Cord A.W.G.: 14
A.: 15 V.: 125
Light Ballast Manufacturer: G.E.
Model: 89G457(STD)
B232I120RH (3500K)
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F20T12 CW (STD)
F17T8 / SP35 (3500K)
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig. Charge: R-404A / 17 oz. / 481.95 grams / No.4 Stat Position
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CONTROL SETTINGS #4 C.S. #4 C.S. #4 C.S.
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 9 / 12 / 13 /
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 187 / 228 / 251 /
Compressor Amps 2.9 2.9 2.9
Total Cabinet Amps 3.5 3.5 3.5
Cavity Temperature C.L. 5°F / -15°C 7°F / -13°C 8°F / -13°C
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 15
Page 18
SYSTEM INFORMATION - 12HR & 12HC
ELECTRICAL
Compressor Manufacturer: Americold
Model: HP-127-1
Ph.: 1 Hz.: 60
Volts: 115 Amps: 4.2
Overload Protector Manufacturer: Amer icold
Start Relay Manufacturer: Americold
Start Capacitor V.:125 M.F.: 189-227
Run Capacitor VAC: 370 M.F.: 20
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:5KSM51GG3784
Condenser Diameter: 9.5" # Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1 29/32"
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 7' of .042
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 120/250 L.R.A.: 100
Warm C ut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
Pow er Cord A.W.G.: 16
A.: 15 V.: 125
Light Ballast Manufacturer: G.E.
Model: 89G457(STD)
B232I120RH(3500K)
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F40T12CW (STD)
F32T8/SP35 (3500K)
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig. Charge: R-404A / 25 oz. / 708.75 grams / No.4 Stat Position
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CONTROL SETTINGS #4 C.S. #4 C.S. #4 C.S.
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 9 / 10 / 11 /
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 198 / 230 / 268 /
Compressor Amps 4.2 4.2 4.3
Total Cabinet Amps 6.1 6.1 6.2
Cavity Temperature 0°F / -17°C 1°F / -17°C 2°F / -16°C
16 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
Page 19
SYSTEM INFORMATION - 16HR & 16HC
ELECTRICAL
Compressor Manufacturer: Americold
Model: HP-127-1
Volts: 115 R.L.A.: 4.2
L.R.A.: — Ph.: 1 Hz.: 60
Overload Protector Americold #1456-3321
Start Relay Americold #1456-3374
Start Capacitor V.:125 M.F.: 189-227
Run Capacitor V.: 370 M.F.: 20
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:5KSM51GG3784
V.: 115 Hz.: 60 Ph.: 1
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 7' of .042
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 120/240 L.R.A.: 100
Warm C ut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
Pow er Cord A.W.G.: 16
A.: 15 V.: 125
Light Ballast Manufacturer: G.E.
Model: 8G3706 (STD)
B232I120RH (3500K)
Condenser Diameter: 9.5" # Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1 29/32"
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig. Charge: R-404A / 27 oz. / 765.45 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F40T12CW (STD)
F32T8/SP35 (3500K)
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CONTROL SETTINGS #4 C.S. #4 C.S. #4 C.S.
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 9 / 10 / 12 /
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 207 / 234 / 262 /
Compressor Amps 3.8 3.8 3.9
Total Cabinet Amps 6.3 6.3 6.3
Cavity Temperature C.L. -.5°F / -18°C -.3°F / -17.9°C -1.2°F / -18.4°C
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 17
Page 20
SYSTEM INFORMATION - E4HR & E4HC (220V / 50 Hz)
ELECTRICAL E4HR2 & E4HC2 (220V / 60 Hz)
Compressor Manufacturer: Americold
Model: HP-110-12-3084
V.: 220 R.L.A.: 2.0
L.R.A.: 12.6 Phase: 1/50Hz.
Overload Protector T.I.: Americold #1456-3444
Start Relay T.I.: Americold #1456-3374
Start Capacitor V.A.C.: 250 M.F.: 108-130
Run Capacitor V.A.C.: 370 M.F.: 7.5
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:5KSM51ECG3905
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 7' of .031
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 120/240 L.R.A.: 100
Warm C ut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
Pow er Cord A.W.G.: 14
A.: 15 @ 125V
Light Ballast Robertson #02025 (50Hz)
Robertson #02026 (60Hz)
Condenser Diameter: 8" # of Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1 7/8"
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig. Charge: R-404A / 11.5 oz. / 326.02 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F20T12/CW
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CONTROL SETTINGS #4 C.S. #4 C.S. #4 C.S.
Cavity Temperature C.L. 0°F / -17°C 2°F / -16°C 3°F / -16°C
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 12 / 82 13 / 89 14 / 96
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 206 / 1420 214 / 1475 239 / 1647
Compressor Amps 2.0 2.0 2.0
Total Cabinet Amps 2.3 2.3 2.3
18 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
Page 21
SYSTEM INFORMATION - E8HR & E8HC (220V / 50 Hz)
ELECTRICAL E8HR2 & E8HC2 (220V / 60 Hz)
Compressor Manufacturer: Americold
Model: HP-118-12
V.: 220 R.L.A.: 3.0
L.R.A.: 12.6 Phase: 1/50Hz.
Overload Protector Americold #1456-3321
Start Relay T.I.: 8EA14
Start Capacitor V.A.C.: 250 M.F.: 108-130
Run Capacitor V.A.C.: 370 M.F.: 7.5
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:5KSM51ECG3905
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 8' of .036
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 120/240 L.R.A.: 100
Warm C ut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
Pow er Cord A.W.G.: 14
A.: 15 @ 125V
Light Ballast Robertson #02026
Condenser Diameter: 8" # of Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1 7/8"
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig. Charge: R-404A / 17 oz. / 481.95 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F20T12/CW
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CONTROL SETTINGS #4 C.S. #4 C.S. #4 C.S.
Cavity Temperature Range 5°F / -15°C 7°F / -13°C 8°F / -13°C
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 13 / 89 15 / 103 16 / 110
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 213 / 1468 250 / 1723 292 / 2013
Compressor Amps 2.9 3.0 3.1
Total Cabinet Amps 3.5 3.7 3.7
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 19
Page 22
SYSTEM INFORMATION -
EKDC-67 & ECKDC-67
ELECTRICAL E12HR2 & E12HC2 (220V / 60 Hz)
Compressor Mft: Copeland (3/4 HP)
Model: KAMB-007E-CAV
Phase: 1 Hz.:50
Overload Protector Model No.: 071-0092-29
Start Relay G.E. 3ARR3CT3E5
Pick up: 340-360
Drop out: 45-115
Model No.: 040-0001-03
Start Capacitor V: 220 M.F.: 145-174
Run Capacitor 10UF - 370V
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:KSM51GG3705
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 9' of .049
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 125/250 L.R.A.: 100
Warm C ut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
Pow er Cord A.W.G.: 16
Amp: 15
Light Ballast VOSSLOH SCHWABE
Model: L36.291 (50Hz)
Robertson: 1-4026 (60 Hz)
Condenser Diameter: 9-1⁄2"# Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1-29⁄32"
Pressure Switch C.O.: 350# C.I.: 250#
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig. Charge: R-404A / 25 oz. / 708.75 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F40T12CW
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CAVITY TEMPERATURE 2°F / -17°C 4°F / -16°C 6°F / -14°C
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 8 / 55 10 / 69 12 / 82
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 188 / 1246 225 / 1551 253 / 1744
Compressor Amps 7.2 7.1 7.1
Total Cabinet Amps 9.5 9.3 9.4
20 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
Page 23
SYSTEM INFORMATION -
EKDC-87 & ECKDC-87 (220V / 50 Hz)
ELECTRICAL E16HR2 & E16HC2 (220V / 60 Hz)
Compressor Mft: Copeland (3/4 HP)
Model: KAMB-007E-CAV
R.L.A.: 5.6 L.R.A.: 36.0
Phase: 208/230V 60 Hz.
200/220V 50 Hz.
Overload Protector Model No.: 071-0092-29
Start Relay G.E. 3ARR3CT3E5
Start Capacitor V: 220 M.F.: 145-174
Run Capacitor V.: 370 M.F.:10
Condenser Manufacturer: Heatcraft
Condenser Manufacturer: G.E.
Fan Motor Model:KSM51GG3705
Evaporator Cold Wall
Capillary Tube 9' of .049
Thermostat Manufacturer: Ranco
F.L.A.: 25
V.: 125/250 L.R.A.: 100
Warm C ut-in 11° Warm Cut-out —
Mid Cut-in -12° Mid Cut-out -24°
Cold Cut-in — Cold Cut-out -34°
Pow er Cord A.W.G.: 16
Amp: 15
Light Ballast VOSSLOH SCHWABE
Model: L36.291 (50Hz)
Robertson: 1-4025 (60 Hz)
Condenser Diameter: 9-1⁄2"# Blades: 3
Fan Blade Width of Blades:1-29⁄32"
REFRIGERATION -
Refrig. Charge: R-404A / 27 oz. / 765.45 grams / No.4 Stat Position
Fluorescent Manufacturer: G.E.
Lamp F40T12CW
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE 70°F / 21.1°C 80°F / 27°C 90°F / 32.5°C
CAVITY TEMPERATURE 2°F / -17°C 4°F / -16°C 6°F / -14°C
Suction Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 8 / 55 10 / 69 12 / 82
Discharge Pressure - C.O. PSIG/Kpa 228 / 1572 257 / 1772 284 / 1958
Compressor Amps 7.4 7.5 8
Total Cabinet Amps 9.5 9.3 10
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 21
Page 24
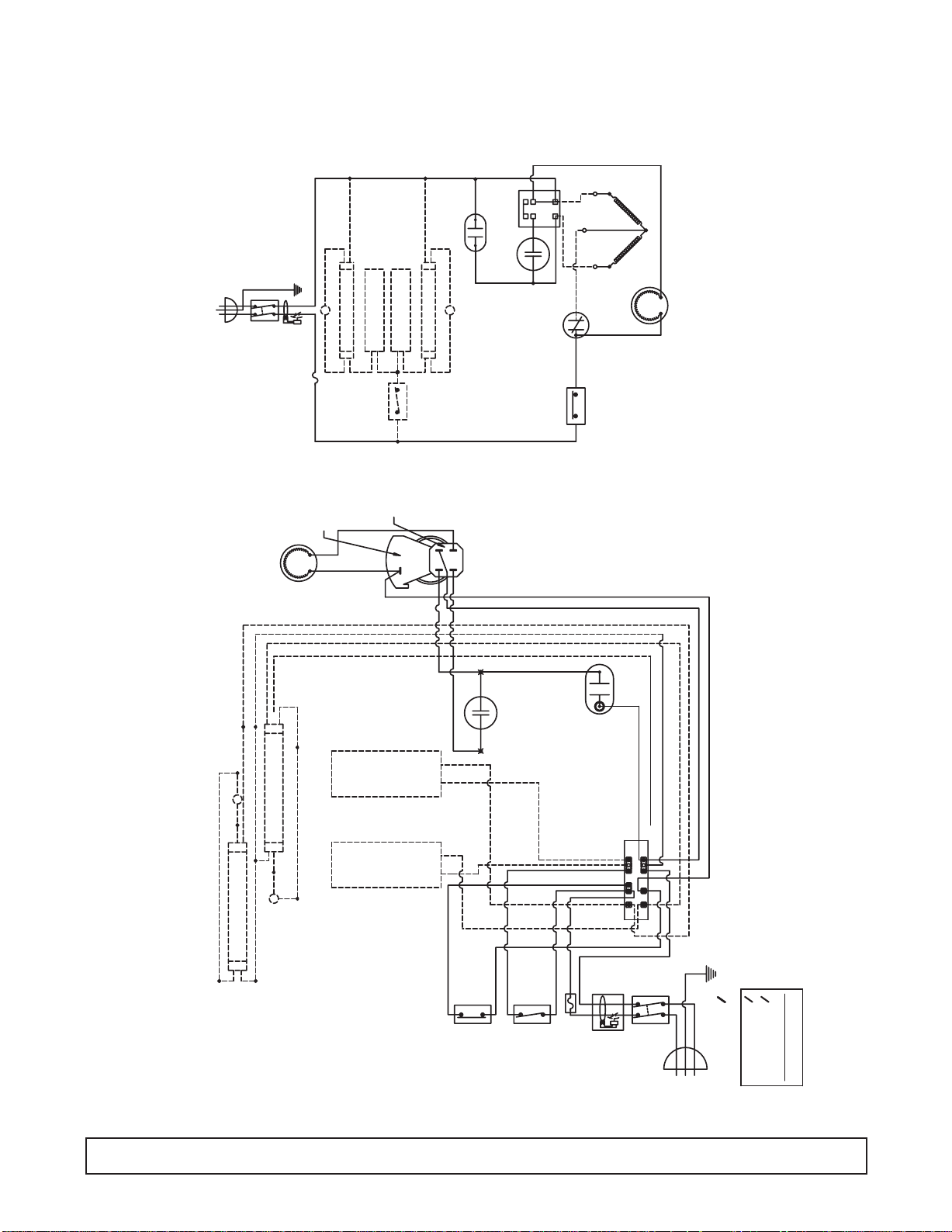
WIRING DIAGRAM - 4HR, 4HC / 8HR, 8HC
E4HR, E4HC / E8HR, E8HC
E4HR2, E4HC2 / E8HR2, E8HC2
SWITCH
SUPPLY
FAN MOTOR
S
GFCI
FUSE
BLACK WHITE
MOTOR PROTECTOR
LAMP
BALLAST
SWITCH
LIGHT
(PTCR)
BALLAST
LAMP
R
C
S
COMPRESSOR
RUN CAP.
(PTCR)
START CAP.
1
2
3
4
S
PROTECTOR
MOTOR
CONTROL
TEMP.
1
2
4
3
TERMINAL BOX
COMPRESSOR
FAN MOTOR
-THE 8HF/4HJ/8HJ HAVE NO LIGHTS.
WIRE DIAGRAM
00-C-2030-00 F
NOTES: -RED WIRE IS AN EXTRA WIRE.
-THE 4HR AND 4HC HAS ONLY ONE LIGHT.
BLUE
S
LAMP
WHITE
BLUE
LAMP
S
BALLAST
BALLAST
BLUE
BLACK
YELLOW
BLACK
BLACK
TEMP.
BLK.BLK.
BLACK
CONTROL
BLACK
BLACK
START CAP.
BLACK
BLACK
LIGHT
SWITCH
( SEE NOTES)
BLACK
BLACK
FUSE
RUN CAP.
WHITE
(SOME MODELS)
TERMINAL
ELB
(SOME MODELS)
BOARD
1
3
5
BLACK
RED (EXTRA)
2
4
6
SWITCH
SUPPLY
WHITE
BLUE
BLACK
L1
(BROWN)
BLUE
WHITE
WHITE
(L2) N
BLACK
(BLUE)
OR
220 VAC. 60 Hz.-10
POWER SUPPLY
115 VAC. 60 Hz.-10
115 VAC. 60 Hz.-10
POWER SUPPLY
220 VAC. 50 Hz.-10
POWER SUPPLY FOR
EXPORT MODELS ONLY
ELECTRICAL INFORMATION.
SEE SERIAL PLATE FOR
22 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
Page 25

WIRING DIAGRAM - 12HR, 12HC / 16HR, 16HC
SUPPLY
FAN MOTOR
(BLUE)
WHITE
SWITCH
(BROWN)
BLACK
(115/60 ONLY)
BALLAST
LIGHT
SWITCH
MOTOR PROTECTOR
PROTECTOR
CONTROL
R
C
FAN MOTOR
COMPRESSOR
WIRE DIAGRAM
KDC67/87-BRT68/90
00-2368-00 Rev B
S
1
2
(PTCR)
3
4
RUN CAP.
START CAP.
S
LAMP
MOTOR
TEMP.
(PTCR)
1
2
4
3
TERMINAL BOX
COMPRESSOR
BLUE
S
LAMP
WHITE
BLUE
LAMP
S
BLUE
(BLACK-220)
BLUE
(BLACK-220)
BALLASTBALLAST
NOTE: 115/60
NOTE: 115/60
SHOWN
SHOWN
220/60
220/60
WHITE LEAD.
SAME LESS
WHITE LEAD.
SAME LESS
BLUE
BLACK
YELLOW
WHITE
(115/60 ONLY)
BLK.BLK.
BLACK
TEMP.
CONTROL
BLACK
BLACK
START CAP.
BLACK
BLACK
LIGHT
SWITCH
( SEE NOTES)
(115/60 ONLY)
BLACK
RUN CAP.
BLACK (BROWN)
WHITE (BLUE)
SWITCH
SUPPLY
BOARD
TERMINAL
1
3
5
BLACK
L1
BLACK
(BROWN)
WHITE
RED (EXTRA)
2
4
6
WHITE
(BLUE)
(L2) N
BLACK
BLUE
BLUE
WHITE
220 VAC. 60 Hz.-10
POWER SUPPLY
115 VAC. 60 Hz.-10
POWER SUPPLY FOR
EXPORT MODELS ONLY
ELECTRICAL INFORMATION.
SEE SERIAL PLATE FOR
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 23
Page 26

WIRING DIAGRAM - ECKDC67, EKDC67 / ECKDC87, EKDC87
E12HC2, E12HR2 / E16HC2, E16HR2
SWITCH
SUPPLY
FAN MOTOR
(BLUE)
WHITE
GFCIFUSE
(BROWN)
LIGHT
BLACK
CONTROL (NC)
HIGH PRESSURE
(USED ON BRT-90
AND H-16 MODELS
SWITCH
ONLY.)
BALLAST
R
C
CAPACITOR. SEE COMPRESSOR
TERMINAL BOX.
S
PROTECTOR
+
+
-
P
CONTROL
HIGH PRESSURE
OPEN 350 20
CLOSE 250 20
NOTE; BLUE WIRE CONNECTS
TO #2 ON COMPRESSOR
TERMINAL BOARD WHEN
HIGH PRESSURE CONTROL
IS NOT USED.
FAN MOTOR
-
COMPRESSOR
WIRING DIAGRAM
00-C-2342-00 B
EKDC/KKDC-67/87 &
EBRT/KBRT-68/90
ONLY ON MODELS WITH RUN
CAPACITOR. SEE COMPRESSOR
TERMINAL BOX.
RELAY
1
5
S
RUN CAP.
BLEED RESISTOR
2
CONTROL
TEMP.
TERMINAL BOX
COMPRESSOR
ONLY ON MODELS WITH RUN
MOTOR
BLUE
START CAP.
POTENTIAL
S
LAMP
P
2
1
2
1
3
R
C
BLUE
LAMP
BLUE
BLACK
WHITE
LAMP
S
BLACK
BLACK
S
BALLAST
BALLAST
BLACK
YELLOW
BLACK
TEMP.
CONTROL
BLACK
POTENTIAL
BLACK
RELAY
WHITE
SWITCH
BLACK
WHITE
BLACK
RUN CAP.
WHITE
FUSE
(SOME MODELS)
WHITE
TERMINAL
ELB
(SOME MODELS)
125
BLACK
LIGHT
START CAP.
BOARD
1
3
5
WHITE
WHITE
WHITE
RED (EXTRA)
2
4
6
SUPPLY
SWITCH
BLUE
BLACK
L1
(BROWN)
BLUE
WHITE
(L2) N
(BLUE)
OR
220 VAC. 60 Hz.-10
POWER SUPPLY FOR
220 VAC. 50 Hz.-10
EXPORT MODELS ONLY
SEE SERIAL PLATE FOR
ELECTRICAL INFORMATION.
24 PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION
Page 27

WIRING DIAGRAM - 8HC, 12HC, 16HC WITH 3500K LIGHTS
FAN MOTOR
SWITCH
SUPPLY
MOTOR PROTECTOR
BLACK WHITE
LIGHT
(PTCR)
SWITCH
BALLAST
BLUE
PROTECTOR
R
C
S
FAN MOTOR
COMPRESSOR
WIRE DIAGRAM
CKDC-47. 67 & 87 (3500K LIGHTS)
00-C-3020-00A
1
2
(PTCR)
3
4
RUN CAP.
START CAP.
LAMP
LAMP
MOTOR
CONTROL
TEMP.
1
2
4
3
TERMINAL BOX
COMPRESSOR
BLUE
LAMP
BLUE
RED
LAMP
RED
BLUE
BLUE
YELLOW
BLACK
BLACK
BALLAST
START CAP.
BLACK
TEMP.
CONTROL
BLACK
BLACK
BLACK
BLACK
LIGHT
BLACK
SWITCH
BLACK
BLACK
RUN CAP.
WHITE
WHITE
TERMINAL
SUPPLY
SWITCH
BOARD
1
3
5
BLACK
L1
(BROWN)
BLACK
WHITE (EXTRA)
2
4
6
WHITE
WHITE
(BLUE)
N
(L2)
BLUE
BLUE
115 VAC. 60 Hz.-10
POWER SUPPLY
PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION 25
Page 28

BLANK 26
Page 29

SECTION III
Maintenance
& Repair
Page 30

WARNING:
To avoid the possibility of an electrical shock,
turn OFF thermostat and unplug the power cord
of the cabinet before cleaning or touching
electrical connections or parts.
Page 31

MAINTENANCE & REPAIR — PRE-SERVICE CHECK LIST
You may avoid the cost and inconvenience of an
unnecessary service call by first reviewing this check
list of the most frequently encountered situations that
are not the result of system component failure.
COMPRESSOR RUNS TOO MUCH
1. A refrigerated cabinet automatically compensates for
service loading by running longer and more often.
Before calling for service, check running time for at
least one hour the first thing in the morning (before
store traffic starts).
2. Be sure doors seal. A faulty gasket seal will cause
increased running time.
3. Check the room temperature. The warmer the room,
the more the compressor will run.
4. Check to see that condenser fans are running.
5. Be sure the condenser fan operates.
6. Check to see that condenser fans are running.
7. If product is too hard, (cold) try setting the temperature
control (thermostat) warmer.This will result in warmer
cabinet temperature and reduced running time.
CUSTOMER COMPLAINT
OR STORED PRODUCT
1. Check cleaning solutions used inside cabinet.
2. Check cleaning solutions, paint or other
contaminants used in store maintenance.
3. Sometimes the ingredients used in some products or
containers will contaminate other products.
4. Be sure to follow a weekly schedule for cleaning
cabinet interior.
SERVICE
In the event of a malfunction, damage to the cabinet, or
if the cabinet requires service beyond the items in the
“Pre-Service Check List,” contact your local
refrigeration service company or the dealer or
distributor you purchased the unit from.
POWER FAILURE
Do not open the cabinet doors unnecessarily if power is
cut off due to electrical failure.The cabinet will start up
if the power supply returns, but will require sufficient
time to reach maximum cold storage performance.
CABINET DOES NOT OPERATE
1. Be sure the cabinet is plugged in.
2. Check that the breakers or fuses are good and all
switches in the supply line are ON.
3. Be sure that cabinet Master Supply Switch is ON.
4. If you are in an area with voltage problems, try
shutting off all non-essential electric equipment.
LIGHT IS OFF
1. If the cabinet is operating, be sure the lamp is
properly seated in sockets.
2. If the cabinet is not running, check that Master Supply
Switch of cabinet is ON, fuses are okay, no switch in
the supply is off and the cabinet is plugged in.
CABINET FAILURE
1. If the cabinet has stopped operating, check that the
cabinet is securely plugged in and turned on.Contact
a licensed electrician to locate and correct any power
supply problems.
2. Do not open the cabinet lids unnecessar ily.
3. Provisions for other storage of the product may be
required to prevent spoilage.
If you call us for service, describe the problem and give
the information from the following list to the service
representative:
Cabinet Model ______________________________
Part Number ________________________________
Serial Number ______________________________
(These are located on a serial number rating plate
inside of the machinery compar tment of the cabinet.)
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 29
Page 32

SECTION III
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
TOOLS:
To provide full service diagnostics and repairs on
these cabinets the following tools are needed:
A V olt Meter
An Amp Meter
An Ohm Meter or tiplet meter to handle all three functions
An Electronic Leak Detector
An Electronic Micron Gauge
A Vacuum Pump capable of pulling to 50 microns
Four Hand Valves
A Refrigerant Reclaimer
A Compound Gauge Set
A cylinder of nitrogen with a regulator capable of 10 to
400 pounds.
Standard refrigeration hand tools like: wrenches,
tubing cutter, swage and flare tools, wire strippers,
wire crimpers, wire cutters, standard and phillips head
screwdrivers.
PRODUCT HISTORY
The first rule in accurately servicing a refrigeration
system is to determine if the problem is an electrical
or mechanical failure within the refrigeration system.
First, try to obtain the product’s history of operation
from the customer.This will help identify the source of
the problem.
Good facts from the cabinet user can help identify
whether the problem is electrical, within the
refrigeration system, or a “misapplication by the user.”
Get the history of operation and failure by asking
these questions:
1) Were there any brown-outs or power outages that
they are aware of?
2) Is the cabinet on a dedicated circuit?
8) Was the warm-up fast, as in three to six hours, or
over a prolonged time, as in three to five days?
9) If the cabinet was running for a long time, was the
temperature recovery after entering the cabinet
always within an hour, or did it appear as though
recovery time was longer as usage went on?
The refrigeration system should only be entered if it is
absolutely necessary. It is critical that a clean,
uncontaminated system be maintained.
If a system is unable to reach the proper operating
temperature, a test of the unit’s mechanical
refrigeration components is required.
COMPRESSOR EFFICIENCY TEST
If the cabinet has a semi-hermetic compressor, begin
by testing the compressor’s efficiency.
To test a semi-hermetic compressor, place compound
gauge on the compressor’s suction port.
While the compressor is running, close off the suction
line so that only the port and valve are part of the
compressor’s low side.
When the valve is closed and vacuum has started,
time how long it takes to pull the compressor’s low
side to its lowest possible vacuum.
Compressors used on these cabinets should be
capable of pulling at least 20 to 22 inches of vacuum
in less than 40 seconds.
Next, shut off the compressor and watch the gauge.A
one or two inch rise in pressure is acceptable, since a
small amount of freon may remain on the low side of the
compressor, after which the reading should stabilize.
If the pressure continues to rise, the discharge reeds
in the valve head are bad, allowing high pressure gas
to return to the compressor.
If the compressor pulls less than 20 inches, the
suction reeds are bad in the valve head.
3) Has any other equipment in this area had
operational problems?
4) When was the last time the cabinet’s operation was
confirmed as working properly?
5) When was a problem noticed?
6) How long has the equipment run without this
problem? (Years? Weeks? Days? Hours?)
7) Was anything tried prior to your arrival?
If it takes longer than 40 seconds to pull the
compressor, to its ultimate low vacuum, one or both
cylinders are not functioning as they should. Any
reading less than these will require replacement of the
compressor.
30 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 33

ENTERING THE SYSTEM
Entering the system should only be done as a last
resort. Extreme care must be used no matter what the
reason is for entering the system. Of course there are
times it cannot be avoided, such as component or
compressor replacement, or a leak within the system.
Use this time to check any joints for potential leaks.
CHARGING
You should use a charging cylinder to measure in the
the correct amount of refrigerant.The charging
methods are:
The system must also be entered any time you need
to obtain the operating pressures. Again, use extreme
caution to avoid any possible contamination.
Cabinets that use semi-hermetic compressors allow
easy access through the valve ports.
Cabinets using hermetic compressors do not have
valve ports, this product has process stubs for both
suction and discharge sides of the system.
Line taps should only be used to obtain pressure
readings, and not for reprocessing a system.The
opening of a line tap is too restrictive for pressure of
vacuum procedures.
Install hand valves at the process stub ends.Hand
valves will be less restrictive to flow because of a
larger opening.They will also be easier to use during
repair procedures.
EVACUATION
Once the system has been cleaned and components
have been replaced, you are ready to initiate the final
servicing procedures necessary to achieve proper
cabinet operation.
1) Add the refrigerant to the system until you reach a
predetermined balanced pressure.This will give you
an approximate static charge.
2) Weigh in the refrigerant using a scale calibrated in
ounces.
The cabinet’s operation is now ready to be tested. A
final check of the refrigeration lines should be made
before running the cabinet.
Be sure the refrigeration lines are not kinked or
rubbing against each other.
Also check that the door seals properly. An air leak will
affect proper operation, and the cabinet’s ability to
reach its coldest temperature.
Run the cabinet a both 100% run and also at a
cycling temperature for at least one day. If the
temperature and pressures are correct, the system
can be considered repaired.
Hermetic systems should now have their process
stubs pinched off, hand valves removed and the ends
brazed shut.
Pull an evacuation to approximately 50 microns.You
can be sure that any contaminants that can affect the
system’s operation are now removed.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 31
Page 34

COMPRESSOR INSTALLATION & MAINTENANCE / DIAGNOSTICS
HOLD DOWN BOLTS
All models with Copeland compressors have hold
down bolts.The compressor has a metal hold down
band strapping it tightly to the cabinet body.This band
should be removed and discarded upon installation.If
compressor does not float freely, keep backing off all of
the retaining nuts until it does.
CHECKING COMPRESSOR THAT WON’T
START ON CORD CONNECTED CABINETS
1. Check that the supply plug is in wall outlet and that
outlet has the proper voltage.
2. Check that the cabinet thermostat is on a numer ical
setting.
If items 1 & 2 are OK:
3. Pull condensing unit out of the cabinet and remove
compressor terminal cover.Check proper voltage at
terminals.
TO CHANGE THE COMPRESSOR:
1. Disconnect the power supply to the cabinet.
2. Disconnect power supply leads at the compressor.
3. Disconnect the wires to the relay and capacitors.
4. Remove the relay and starting capacitor and install
on the new compressor.
5. Remove the defective compressor from the
condensing unit base.
6. Set the new compressor in place.
7. Reconnect the relay and capacitor wires.
8. Reconnect the power supply lead.
9. Leak test, evacuate, and weigh in charge.
CAUTION
This type valve should be tightly capped except when
making the gauge connection.
TO CHECK FOR OPEN WINDINGS
Use a multimeter.Measure ohms between “C” and “R”
and between “C” and “S”.
If windings are OK, multimeter will show a resistance
reading between terminals.
If there is no reading, the compressor, winding or
windings are open and the compressor should be
replaced.
TO CHECK FOR GROUNDED COMPRESSOR
Use multimeter.Touch probe from each terminal to an
unpainted surface of compressor body. If there is no
ground, there will be no change of the meter.
WARNING: Be Careful Not to Touch
Uninsulated Parts of the Meter Probes.
A reading indicates a ground and the compressor
should be replaced.
If there is voltage at the compressor terminals and the
compressor tries, but does not run, check voltage at the
compressor terminals while attempting to start the
compressor.If the voltage at the compressor terminal is
below 90% of the nameplate voltage, it is possible the
motor may not have developed sufficient torque to start.
Check to determine if:
A.Wire sizes are adequate.
B. Electrical connections are loose.
C. The circuit is overloaded.
D. The power supply is adequate.
CHANGING DRIER
If flare connected, make sure flares and faces of
fittings on new drier are clean and in good condition
before installing new drier.
Cut tubing only with tube cutters, not hacksaw’s, to
avoid metal filings from entering the system. Driers
must be replaced any time you enter the system,
except when you are obtaining operating pressures.
SERVICE VALVES
The compressors on some cabinets have service
valves for measuring suction and discharge pressures.
Two types are used.The first type is connected directly
to the compressor body or shell and back seats to
connect gauges to the access port. The second
(Schrader type) is on the end of a process tube and
requires a gauge or charging line with a depressing pin
to open valve when the connection is made.
A defective relay or capacitor may prevent the
compressor starting.
TO CHECK OUT THE RELAY
1. Disconnect the cabinet from the power supply.
2. Remove the wires from the relay.
3. Touch probes to the terminals. Meter should show
infinity if closed.
4.Touch probes to the terminals of coil. The meter
should show a resistance reading.
If items 3 & 4 are OK, the relay is good. If items 3 & 4
are not as indicated, change the relay.
32 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 35

COMPRESSOR INSTALLATION & MAINTENANCE / DIAGNOSTICS
TO CHECK CAPACITORS
1. Disconnect the cabinet from the power supply.
2. Make sure the capacitors are discharged before
checking. (Shunt across the ter minal of capacitor
with a heavy insulated wire.)
3. Remove the wires from the capacitors.
4. Any capacitor found to be bulging, leading, or
damaged should be replaced.
5. Use a multimeter to check the run and start
capacitors for shorts or open circuits.
With a good capacitor, the indicator should first move
to a reading and then gradually increase to infinity.
If there is no reading change, an open circuit is
indicated.
If the multimeter remains on a low resistance reading,
a short circuit is indicated.
On run capacitor, touch probes to metal case and
each terminal. If meter shows any reading, a ground is
indicated. All defective capacitors should be replaced.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 33
Page 36

CLEANING & MAINTENANCE
CLEANING THE CABINET EXTERIOR
Wipe the exterior occasionally with a cloth dampened
in mild detergent water; rinse, and wipe dry with a
soft, dry cloth. Do not use abrasive or caustic
cleaners or scouring pads.
CLEANING THE CONDENSER - FIG. 1A
Periodic cleaning of the condenser can be easily
accomplished by brushing the coils with a soft brush
and/or using a vacuum cleaner with a brush
attachment.
Be sure that dirt, dust and collection of other debris
do not build up to a point air circulation through the
condenser is restricted.
CLEANING THE STORAGE COMPARTMENT
1. Remove product and store it in another suitable
cabinet, if possible.Be sure to prevent spoilage of
the product which may occur if it is left at room
temperature.
2.Turn OFF the thermostat and unplug the cabinet.
3. Remove the can skirts.
5.Wash the can skirts and the entire interior storage
area with warm water and baking soda solution —
about a tablespoon of baking soda per quart of
water.Rinse thoroughly with clean water and wipe
dry.
This procedure can also be used for cleaning door
gaskets.
6. A drain hose (FIG. 1B) is provided in the
compressor compartment. Connection is made to fit
a standard garden hose for ease of draining water
from inside of the tank area.
IMPORTANT: Do not use any objects or cleaner which
may leave residues, odors, or particles. Avoid the use
of strong chemicals or abrasive cleaners which may
damage the interior surfaces and contaminate product
within the storage area.
6.Wash, rinse, and dry the can skirts while they are
outside of the cabinet, using the same procedure as
described for the storage area.
7. Be sure to correctly reinstall the can skirts, plug in
the cabinet, set the temperature control and allow time
for cooling of the storage area before storing product.
4. Defrost completely pr ior to cleaning.
A
B
34 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 37

CLEANING THE LID
If the lid has been removed from the cabinet, wash
with plenty of non-abrasive soap or detergent and
water.Use the bare hand to feel and dislodge any
caked soil. Rinse thoroughly with clean water. Do not
use hard, rough cloths that will scratch the surface of
the plastic lid. Dr y with a clean, damp chamois.
If the lid is on the cabinet where water cannot be used
freely, it should first be lightly dusted (not wiped) with
a soft, clean cloth.Then the surface can be wiped
carefully with a wet cloth or chamois.The cloth or
chamois should be kept free of grit by frequent rinsing
in clean water.
Do not use solvents such as acetone, alcohol,
benzene, carbon tetrachloride, fire extinguisher fluid,
dry-cleaning fluid, and lacquer thinners, since they
attack the plastic part of the lid. Do not use window
sprays or kitchen scouring compounds.
TOUCH-UP PAINTING INSTRUCTIONS
-SPRAY PAINT
White 9 oz.Touch-up Paint:
Part No.26-0899-01
1. Sand the entire bare metal or affected area and its
edges until the edges are smooth or feathered.This
insures that you are spraying on to a painted area
that has adhesion.
2.Use an automotive primer (lacquer) ov er the bare area.
3. Scuff sand the pr imered area lightly.
4.Test spray can before using on cabinet surface.
Apply in short, even strokes holding can 10" to 12"
from surface, and moving rapidly during use. Apply
top coat of paint in thin layers (4-5 layers minimum)
with air drying time in between coats. Scuff sand
very lightly between coats.This will remove uneven
spots or roughness and will create a high gloss,
smooth finish.
5. Use rubbing compound (preferred) or wax over the
finished area after a few days of hardening/drying
time.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 35
Page 38

LID SEAL REPLACEMENT
from epics
The lid seal is located on the server side of the cabinet,
attached to the underside of the stainless steel top.
1. Remove lids from the cabinet.
2. Remove screws on the underside of the stainless
top on the server side of the cabinet.
3. Remove the stainless top from the cabinet.
4. Slide the lid seal off of the top channel.
5. Replace the lid seal with new correct ar t number.
Seal needs to be cut to fit the cabinet width.
6. Replace the stainless steel top with the lid seal
attached.
7. Replace screws along the stainless steel top server
side.
8. Replace lids on the cabinet.
36 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 39

LID GASKET REPLACEMENT
1. Remove the lid from the cabinet.
2. Set the lid on a flat, protected surface.
3. Rotate lid upside down.
4. Slide old gasket from the aluminum lid
frame.
5. Install new gasket in the groove
provided. See end detail.
6. Reinstall lid in cabinet.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 37
Page 40

LID PIVOT BUSHING ASSEMBLY REPLACEMENT
New Style
Old Style
The pivot pin bushing is located on the outside edge of
each lid.
1. Remove the lid from the cabinet. Lay the lid on a
smooth, non-scratch surface.
2. Remove the two acorn nuts from the outside edge
of the lid assembly.
3. Remove the shake-proof washer, flat washer, pivot
bushing retainer, and pivot pin bushing.
4. Replace assembly with the correct new part number.
5. Replace the shake-proof washer, flat washer, pivot
bushing retainer, and pivot pin bushing.
6. Replace the two acorn nuts attaching the assembly
to the lid.Tighten nuts to 20" lbs. torque.
7. Replace the lid onto the cabinet.
Remove lid from cabinet. Lay the lid on a
smooth, non-scratch surface. Simply
unsnap lid pivot assembly and replace with
a new part.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 38
Page 41

CENTER/END PIVOT ROD REPLACEMENT
Remove lids from the cabinet.
Remove 2 mounting screws from the mounting bracket.
Replace the pivot bracket with correct new part number.
Reinstall lid assembly.
The 4-hole and 8-hole dipping cabinets have end pivot pins only. The 12- and 16-hole
dipping cabinets have end and center pivot brackets.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 39
Page 42

FLUORESCENT LAMP HOLDER/LIGHT STARTER
SOCKET REPLACEMENT
The lamp holder and the light starter socket are located on the lamp channel assembly.
1. Disconnect the power to the cabinet.
2. Remove the lids from the cabinet.
3. Remove the fluorescent bulbs.
4. Remove the screws holding the stainless steel
countertop in place. The screws are located
under the inside length of the top of the server
side of the cabinet.
5. Lift the stainless steel top off of the cabinet. Set
it aside. (FIG. 1)
6. For both the lamp holder and the starter socket,
remove the screws holding the part in place.
(FIG. 4-D) Remove the tape holding the wires to
the channel frame. (FIG. 2)
7. Disconnect the lead wires at the butt splice
connector. (FIG. 2-C)
8. Replace part with correct new part number.
9. Replace screws removed in Step 4. (FIG. 4-D)
10. Connect white and blue lead wires to main wire
with butt connectors. Replace the tape holding
the wires to the lamp channel.
11. Replace the stainless steel top (FIG. 1) using
screws removed in Step 4.
12. Replace the starter.
13. Replace the bulbs (fluorescent).
14. Reconnect the power to the cabinet.
40 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 43

FLUORESCENT BULB & STARTER REPLACEMENT
BULB STARTER REPLACEMENT (The
fluorescent bulb starter is located on the lamp
BULB REPLACEMENT
channel assembly. One star ter is necessar y per
bulb.)
1. Turn light switch off on the cabinet.
2. Pull down on the socket (A).
3. Remove the plastic outer lamp shield (B) and
bulb (C).
4. Raise the bulb up. Pull out of the socket.
5. Remove lamp shields and end caps (D).
6. Place the new bulb in the shield. Attach
end caps.
7. Inser t the bulb into the cabinet, push up an
snap into place.
8. Turn light switch back on.
1. Turn light switch off on the cabinet.
2. Remove the lid from the cabinet.
3. Grasp the star ter (E), push in.
Turn counterclockwise. Pull the star ter out of the
lamp channel assembly (F).
4. Replace the starter with the correct new part
number.
5. Grasp the starter, push into contact holes.Turn
the starter clockwise to seat properly.
6. Turn light switch back on.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 41
Page 44

THERMOSTAT REPLACEMENT
1. Disconnect the power to the cabinet.
2. Remove the grill.
3. Remove screws from the thermostat mount.
The thermostat is located on the server side of the
cabinet, directly behind the service grill. It functions
to control the temperature inside the cabinet.The
range on the thermostat dial is adjustable from 1 to
7 (7 being the coldest setting).The OFF position is
provided for defrosting the cabinet.
4. Pull the thermal bulb out of the cabinet.
5. Replace the thermostat with the correct new
part number.
6. Slide the capillary tube up the control well which
extends into the machinery compartment. (Be very
careful. Do not kink the thermal bulb capillary tube.)
7. Reattach the thermostat screws to mounting holes.
8. Replace the grill assembly.
9. Reconnect the power to the cabinet.
42 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 45

MASTER POWER SUPPLY SWITCH / LIGHT SWITCH REPLACEMENT
The master supply switch (A) and the light
switch (B) are located behind the grill panel, on
the righthand server side of the unit.
1. Disconnect the power to the cabinet.
2. Remove the grill.
3. Remove screws holding the switch in place.
4. Detach the switch leads.
5. Remove the lock nut on exterior of switch.
6. Replace with new switch.
7. Reattach the electrical leads.
8. Replace the front grill.
9. Reconnect the power to the cabinet.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 43
Page 46

CONDENSER FAN MOTOR REPLACEMENT
The condenser fan motor is located in the
machinery compar tment, directly behind the
condenser coil.
Motor Specifications:
220 V olts
60 Hz.
1 Phase
9 Watt
1. Disconnect the power to the cabinet.
2. Remove the grill panel.
3. Remove the condensing tray hold
down bolts.
4. Pull the condenser tray out of the
cabinet. Disconnect the wire at the
compressor.
5. Remove the motor from the fan motor
mounting bracket.
6. Replace with correct motor.
7. Reconnect wires at the compressor.
8. Slide the tray back into the cabinet.
Replace hold down bolts.
9. Replace the front grill.
10. Reconnect the power to the cabinet.
44 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 47

BALLAST REPLACEMENT
The ballast is located in the machinery
compartment inside the electrical box.
1. Disconnect the power to the cabinet.
2. Remove the front grill.
3. Remove the electrical wiring box.
4. Disconnect the leads to the ballast.
5. Replace the ballast with correct par t.
6. Reconnect the leads to the ballast.
7. Replace the electrical box assembly.
8. Replace the front grill.
9. Reconnect the power to the cabinet.
BALLAST REPLACEMENT 45
Page 48

METERING DEVICE/HEAT EXCHANGER REPLACEMENT
1. Disconnect power to the cabinet.
2. Pull out the condensing unit.
3. Disconnect the liquid line.
4. Disconnect the suction line at the compressor.
5. Cut off the evaporator inlet tube about five
inches down below the point where it comes out
of the cabinet.
6. Remove the capillary tube from the inside of the
evaporator inlet tube.
7. Connect the end of the capillary on the new heat
exchanger to the evaporator inlet tube.
8. Connect the suction line to the compressor valve
and the capillary line to the bottom of the drier.
Replace the drier.
9. Evacuate and recharge.
10. Secure shor t lengths of insulating tubing provided
around exposed tubing in place with tape and
seal to bottom of the cabinet with permagum
which is provided.
11. Reconnect power to the cabinet.
46 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 49

CABINET TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
TROUBLE COMMON CAUSE REMEDY
UNIT WILL NOT RUN.
Blown Fuse.
Broken temperature control.
Broken relay.
Broken overload.
Broken compressor.
Defective service cord.
Broken lead to compressors or cold control.
Replace fuse. Check outlet with voltmeter,
should check 115V plus or minus 10%. If
circuit overloaded, either reduce load or
have electrician install separate circuit. If
unable to remedy any other way, install
autotransformer.
Jumper across terminals of control. If unit
runs and connections are all tight, replace
control.
Check relay, replace if necessary.
Check overload. Replace if necessary.
Check compressor. Replace if necessary.
Check with test light at unit. If no circuit
and current is indicated at outlet, replace
or repair.
Repair or replace broken leads.
CABINET TOO WARM.
CABINET TOO COLD.
Broken timer
Fan motor not running.
Cold control set too warm or broken.
Shortage of refrigerant.
Not enough air circulation around cabinet.
Dirty condenser or obstructed condenser
ducts.
Poor lid seal.
Cold control knob improperly set.
Check with test light and replace
if necessary.
Check and replace fan motor if necessary.
Check and replace if necessary.
Check for leaks. Repair, evacuate and
recharge system.
Relocate cabinet or provide clearance to
allow sufficient circulation.
Clean the condenser.
Level cabinet, replace lid seal.
Turn knob to warmer position
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 47
Page 50

CABINET TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
TROUBLE COMMON CAUSE REMEDY
UNIT RUNS ALL THE TIME.
NOISY OPERATION.
UNIT CYCLES ON OVERLOAD.
Not enough air circulation around cabinet or
air circulation is restricted.
Poor lid seal.
Refrigerant charge.
Room temperature too warm.
Cold Control.
Loose flooring or floor not firm.
Tubing contacting cabinet or other tubing.
Cabinet not level.
Fan hitting shroud.
Compressor mechanically grounded.
Broken relay.
Relocate cabinet or provide proper
clearances around cabinet.
Check and make necessary adjustments.
Undercharge or overcharge--check,
evacuate and recharge with proper charge.
Ventilate room as much as possible.
Check control; if it allows unit to operate
all the time, replace control.
Tighten flooring or brace floor.
Move tubing.
Level cabinet.
Move fan blade.
Replace compressor mounts.
Replace relay.
STUCK MOTOR COMPRESSOR
CABINET RUNS ALL THE
ITEM. TEMP TOO COLD.
RAPID ICE BUILDUP
ON EVAP.
FREEZER WORKS, THEN
WARMS UP.
Weak overload protector.
Low voltage.
Broken valve.
Faulty thermostat.
Leaky door gasket; lid left open.
Moisture in system.
Replace overload protector.
Check outlet with voltmeter. Underload
voltage should be 115V plus or minus
10%. Check for several appliances on
same circuit or extremely long or
undersized extension cord being used.
Replace motor compressor.
Check thermostat—test and replace if
necessary.
Replace gasket; close lids when not serving.
Evacuate and recharge.
48 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 51

COMPRESSOR TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
PROBLEMS & CAUSE REMEDY
Compressor won’t start—no hum.
1. Open line circuit. 1. Check wiring, fuses, receptacle.
2. Protector open. 2. Wait for reset - check current.
3. Control contacts open. 3. Check control; check pressures.
Compressor won’t start—hums intermittently (cycling on protector).
1. Improperly wired. 1. Check wiring against diagram.
2. Low line voltage. 2. Check main line voltage, determine location of voltage drop.
3. Open starting capacitor. 3. Replace starting capacitor.
4. Relay contacts not closing. 4. Check by operating manually. Replace relay if defective.
5. Open circuit in starting winding. 5. Check stator leads. If leads are all right, replace compressor.
6. High discharge pressure. 6. Eliminate cause of excessive pressure.
7. Tight compressor. 7. Check oil level-correct binding condition, if possible. If not, replace compressor.
8. Weak starting capacitor or one weak capacitor of a set. 8. Check oil level. Check binding. Replace compressor if necessary.
Compressor starts; motor will not get off starting winding.
1. Low line voltage. 1. Bring up voltage.
2. Improperly wired. 2. Check wiring against diagram.
3. Defective relay. 3. Check operation - replace relay if defective.
4. Discharge pressure too high. 4. Check ventilation, restrictions and overcharge.
5. Starting and running windings shorted. 5. Check resistances. Replace compressor if defective.
6. Starting capacitor weak or one of a set open. 6. Check capacitance - replace if defective.
7. High discharge pressure. 7. Condenser dirty.
8. Tight compressor. 8. Check oil level. Check binding. Replace compressor if necessary.
Compressor starts and runs, but cycles on protector.
1. Short cycling. 1. Reduce number of starts to 20 or less per hour.
2. Additional current passing through protector. 2. Check for added fan motors and pumps connected to wrong side of protector.
3. Suction pressure too high. 3. Check compressor for proper application.
4. Discharge pressure too high. 4. Check ventilation, restrictions and overcharge.
5. Starting and running windings shorted. 5. Check resistances. Replace compressor if defective.
6. Starting capacitor weak or one of a set open. 6. Check capacitance - replace if defective.
7. Inadequate motor cooling. 7. Correct cooling system.
8. Compressor tight. 8. Check oil level. Check for binding condition.
9. Unbalanced line (three-phase) 9. Check voltage of each phase. If not equal, correct condition of unbalance.
10. Discharge valve leaking or broken. 10. Replace valve plate.
Starting capacitors burn out.
1. Short cycling. 1. Reduce number of starts to 20 or less per hour.
2. Prolonged operation on starting winding. 2. Reduce starting load.
3. Relay contact sticking. 3. Clean contacts or replace relay.
4. Improper relay or incorrect relay setting. 4. Replace relay.
5. Improper capacitor. 5. Check parts list for proper capacitor rating—mfd. and voltage.
6. Capacitor voltage rating too low. 6. Check capacitors with recommended voltage rating.
7. Capacitor terminals shorted by water. 7. Install capacitors so terminals will not be wet.
Running capacitors burn out.
1. Excessive line voltage. 1. Reduce line voltage to not over 10% above rating of motor.
2. High line voltage and light load. 2. Reduce voltage if over 10% excessive.
3. Capacitor voltage rating too low. 3. Install capacitors with recommended voltage rating.
Relays burn out.
1. Low line voltage. 1. Increase voltage to not less than 10% under compressor motor rating.
2. Excessive line voltage. 2. Reduce voltage to maximum of 10% above motor rating.
3. Incorrect running capacitor. 3. Replace running capacitor with correct mfd. capacitance.
4. Short cycling. 4. Reduce number of starts per hour.
5. Relay vibrating. 5. Mount relay rigidly.
6. Incorrect relay. 6. Use relay recommended for specific motor compressor.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 49
Page 52

FLUORESCENT LAMPS - TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
Carrier Refrigeration uses standard fluorescent lamps in all of its applications. Standard one- and two- lamp ballast circuits are used.
Replacement lamps should be purchased over the counter from a local electrical wholesaler. The table below indicates general problems that
may be encountered with fluorescent lighting applications, possible causes, and corrective maintenance suggestions.
TROUBLE COMMON CAUSE REMEDY
NORMAL END OF LIFE.
Lamp won’t operate. Flashes
momentarily and goes out or blinks
on and off.
Ends probably blackened.
SHORT LIFE.
Normal failure. Active material on
cathodes exhausted.
Wrong lamp type used.
Wrong type of starter.
Ballast not supplying the specified electrical
values.
Wrong type of ballast used.
Too low or too high voltage.
Poor circuit contact. (likely at lampholders)
Ballast improperly or incompletely connected.
Too many lamp starts.
Replace lamp properly.
Replace with lamp type marked in owner’s
manual.
Replace with correct starter.
Replace with correct ballast for rating for
lamp size.
Replace ballast with proper type.
Check primary voltage with range specified
on ballast name plate.
Lamholder should be rigidly mounted and
lamp securely seated.
Study ballast label wiring diagrm and check
connections.
Average life for most lamps is dependant on
number of starts and hours of operation.
END BLACKENING.
Dense blackening at one end or
both, extending 2" to 3" from base.
Normal end of life.
Mercury deposit - generally within 1" of
lamp end.
Poor circuit contact likely at the lampholder.
Ballast improperly or incompletely connected.
Wrong type lamp used.
Wrong type of starter or defective starter
causing on /off blinking or prolonged flashing
at each start.
Ballast intalled not supplying the specified
electrical values.
Line voltage too low or too high.
Ballast improperly or incompletely connected.
Replace lamp promptly.
Should evaporate as lamp is operated.
Lampholders should be rigidly mounted and
lamp securely seated.
Study ballast wiring instructions and check
connections.
Replace with correct lamp type.
Replace with proper starter.
Replace with ballast of correct rating for
lamp size.
Check line voltage with range specified on
ballast plate.
Study ballast label wiring instuctions and
check connections.
50 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 53

TROUBLE COMMON CAUSE REMEDY
NO STARTING EFFORT OR
SLOW STARTING.
DECREASED LIGHT
OUTPUT. Full illumination of
bulbs requires correct
assembly of all components
of lighting system.
Open lamp cathode circuit due to broken
cathode, air leak, or open weld.
Wrong lamp type used.
Starter at end of life.
Starter sluggish.
Ballast installed not supplying the specified
electrical values.
Temperature cold air contact to bulb.
Circuit voltage.
Temperature operation, cold air affects lamp
performance.
Circuit voltage.
Ballast improperly or incompletely
connected.
If open, circuit is shown by continuity test
or by viewing end of bulb against a
pinhole of light. Replace lamp.
Replace with lamp type indicated in
owner’s manual.
Replace starter.
Replace starter.
Replace with certified ballast of correct
rating for lamp size.
Correct installation of lamp protection
tubes, or shields to prevent cold air
effects.
Check voltage and correct if possible.
Properly install jacketed lamps where
applicable.
Check voltage and correct if possible.
Study ballast label wiring instructions and
check connections.
BLINKING ON/OFF.
Accompanied by shimmering
effect during “lighted” period.
OVERHEATED BALLAST.
Dust or dirt on lamp or fixture.
Normal failure. Active material on cathodes
exhausted.
Possible lamp fault.
Wrong type of starter or defective starter.
Ballast installed not supplying the specified
electrical circuit.
Circuit voltage.
Loose circuit contact.
Wrong lamp type used.
Wrong ballast used. Wrong voltage rating.
Circuit voltage.
Clean.
Replace lamp promptly.
Replace lamp. Investigate further if
successive lamps blink or flicker in same
lampholders.
Replace with proper starter.
Replace with correct ballast with correct
rating for lamp size.
Check voltage and correct if possible.
Lampholders should be rigidly mounted
and lamp securely seated.
Replace with correct lamp number located
in owner’s manual.
Replace ballast.
Check voltage and correct to design
specification.
Ballast improperly or incompletely connected.
Study ballast label. Correct if installed
wrong.
MAINTENANCE & REPAIR 51
Page 54

MEASUREMENTS - Starting Lamp Voltage
WHITE
BLACK
BALLAST
Y-1
Y-2
R
B
TYPICAL TWO-LAMP RS BALLAST
Starting Voltage
TYPICAL TWO-LAMP RS BALLAST
The largest percentage of light ballast used today are of the two-lamp rapid start type. In order
to read starting or open circuit voltage, as it is often called, remove both lamps from their
sockets.The high voltage (OVC) which starts and operated the lamp is always between the
“R” and “B” sockets.The two lamps are in series between these sockets.The Y-1 and Y-2
connections provide cathode heat, and serve to connect the lamp ends together. Because the
leads between Y-1 and Y-2 are connected together by jumper leads, they are always wired to
sockets at one end of the fixture.Therefore, the “R” and “B” sockets are always at the other
end of the fixture.This means that in order to measure the voltage which starts the lamps
(OVC), the meter probes must be placed in the sockets at one end of the fixture.The Y-1 and
Y-2 end of the fixture will read zero while the “R” and “B” end of the indoor ballast should read
as follows:
Min. RMS
Voltage
250
350
470
Lamp T ype
F40
F30
Min. RMS
Voltage
256
215
Min. RMS
HO
48"
72"
96"
Voltage
256
395
465
1500 MA.
48"
72"
96"
52 MAINTENANCE & REPAIR
Page 55

PARTS LISTING
With Illustration
Identification
Page 56

CABINET PARTS - EXPLODED VIEW
5
1
2
3
6
7
9
10
8
4
11
54 CABINET PARTS - EXPLODED VIEW
Page 57

CABINET PARTS
Dipping Cabinets
Curved & Flat & Export
DESCRIPTION U/M QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.#
05-1199-* Canopy Top EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -02 1 -03 1 -03 1 -04 1 -04
05-1187-* Canopy Top EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
2 44-0862 Upper Lid Seal IN 24.3 - 44 - 44 - 64.5 - 64.5 - 86.8 - 86.8 - 24.3 - 44 - 64.5 - 86.8 -
51-1506-* Canopy Assembly EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -04 1 -03 1 -05 1 -04 1 -06
51-1505-* Canopy Assembly EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
4 05-1029-* Lower Front Trim EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -02 1 -03 1 -03 1 -04 1 -04 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
5 05-1198-01 Outside Post, RH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
6 05-1198-02 Outside Post, LH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
7 10-1158-01 Pivot Bracket, RH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
8 10-1158-02 Pivot Bracket, LH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
9 10-1157-00 Pivot Bracket, Center EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
10 51-1507-* Lid Assembly EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -02 2 -03 2 -03 2 -04 2 -04 1 -01 1 -02 2 -03 2 -04
11 50-4192-01 Grill Panel Assembly EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
3
(3500K)
MODEL NO.
4HC 8HC 12HC
MODEL NO.
16HC
MODEL NO.
12HC
MODEL NO.
4HR
MODEL NO.
8HR
MODEL NO.
12HR
MODEL NO.
16HR
MODEL NO.
16HC
(3500K)
1
PART NUMBER
MODEL NO. MODEL NO.
8HC
MODEL NO.
(3500K)
CABINET PARTS - EXPLODED VIEW 55
CABINET PARTS LIST
Page 58

CANOPY PARTS - EXPLODED VIEW
17
25
16
11
10
12
22
9
8
15
1
5
2
20
21
18
23
19
24
6
14
6
13
6
4
7
6
3
56 CANOPY PARTS - EXPLODED VIEW
Page 59

CANOPY PARTS 57
CANOPY PARTS
MODEL NO.
Dipping Cabinets
Curved & Flat & Export
PART NUMBER
01-0902-01 Glass Bracket, Top EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 3 - 3 - 3 - 3 -
1
02-0942-00 Glass Bracket, Top EA 2-2-3-3-
51-1502-* Lamp Channel Assembly EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04 1 -05 1 -06 1 -07 1 -08
51-1503-* Lamp Channel Assembly EA 1 -01 1 -03 1 .02
2
01-1129-* Lamp Channel EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -02 1 -03 1 -03 1 -04 1 -04
01-1128-* Lamp Channel EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
3 02-0936-00 Clamp Top End EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
05-1034-02 Corner Trim, RH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
4
05-1035-02 Corner Trim, RH EA 1-1-1-1-
05-1034-01 Corner Trim, LH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
5
05-1035-01 Corner Trim, LH EA 1-1-1-1-
626-6504-00 Tape, Double Sided FT 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 - 1.8 -
7 10-1061-02 Glass Channel, Vert. EA 2-2-2-2-
10-1042-00 Gasket, Glass (Curved) EA 3 - 3 - 3 - 3 - 3 - 3 - 3 -
19-1975-00 Lampholder EA 1 - 2 - 4 - 2 - 4 - 2 - 4 - 1 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
8
19-0088-00 Lampholder, W/Starter Soc. EA 1 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 1 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
10-0445-00 Lamp Shield &Cap, 40 Watt EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
9
10-0551-00 Lamp Shield &Cap, 20 Watt EA 1 - 2 - 2 - 1 - 2 -
19-0151-00 Lamp, 40 Watt EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
19-0149-00 Lamp, 20 Watt EA 1 - 2 - 1 - 2 -
10
19-1277-00 Lamp, 34 Watt (3500K) EA 2 - 2 -
19-1312-00 Lamp, 17 Watt (3500K) EA 2 -
11 26-1006-00 Tape, Cush. FT 2.25 - 4 - 4 - 5.5 - 5.5 - 7.25 - 7.25 - 2.25 - 4 - 5.5 - 7.25 -
19-0145-00 Starter, FS4 EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
12
19-0144-00 Starter, FS2 EA 1 - 2 - 1 - 2 -
05-1036-* Light Shield EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
13
05-0935-* Light Shield EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -02 1 -03 1 -03 1 -04 1 -04
14 05-1197-02 Inside Post RH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
15 05-1197-01 Inside Post LH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
16 05-1192-01 Inside Post, Center EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
17 05-1031-* Frame, Lower Front EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -02 1 -03 1 -03 1 -04 1 -04 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
20-0073-00 Glass, End EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
18
20-0076-00 Glass, End EA 2-2-2-2-
19 10-1061-01 Glass Channel, Horz. EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
20 02-0937-00 Clamp Bottom End EA 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 - 2 -
21 05-1015-02 Frame, Canopy End RH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
22 05-1015-01 Frame, Canopy End LH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
23 05-1030-* Glass Retainer, Lower Front EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -02 1 -03 1 -03 1 -04 1 -04 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
20-0072-* Glass, Front EA 1 -02 1 -02 1 -03 1 -03 1 -04 1 -04
24
20-0075-* Glass, Front EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
25 05-1193-01 Outside Post, Center EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
DESCRIPTION U/M QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.#
MODEL NO. MODEL NO.
4HC 8HC 12HC
MODEL NO.
8HC
(3500K)
MODEL NO.
12HC
(3500K)
MODEL NO. MODEL NO.
16HC
MODEL NO.
16HC
(3500K)
MODEL NO.
4HR
MODEL NO.
8HR
12HR
MODEL NO.
16HR
CANOPY PARTS LIST
Page 60

CONDENSING UNIT EXPLODED VIEW
58 CONDENSING UNIT EXPLODED VIEW
Page 61

CONDENSING UNIT PARTS
Dipping Cabinets
Curved & Flat & Export
DESCRIPTION U/M QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.#
1 310A0010 Flavor Strip holder EA 2 - 4 - 6 - 8 - 2 - 4 - 6 - 8 -
2 90-0125 Insert Bottom Pad EA 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 - 1 - 2 - 3 - 4 -
3 315256 Nameplate Frame EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
31-5257 Nameplate Insert (Kelv) EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
26-959-00 Nameplate Insert (U/N) EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
5 92-0242 Tape, Double Sided IN 7.5 - 7.5 - 7.5 - 7.5 - 7.5 - 7.5 - 7.5 - 7.5 -
51-1509-* Condensing Unit As'y EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -05 1 -06 1 -03 1 -04
51-1510-00 Condensing Unit As'y EA 1-1-
02-0255-00 Condenser Shroud EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
02-1007-00 Condenser Shroud EA 1-1-
24-0396 Condenser Fan Motor EA 1 - 1 -
19-0933-00 Condenser Fan Motor EA 1 - 1-
24-0397 Condenser Fan Motor EA 1-1-
19-0934-00 Condenser Fan Motor EA 1-1-
19-0410-00 Condenser Fan Blade EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
19-0101-00 Condenser Fan Blade EA 1 - 1- 1 - 1-
9 19-0925-00 Condenser Fan Bracket EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1- 1 - 1-1-1-
10 50-0165-02 Unit Base Plate Weld As'y EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1- 1 - 1-1-1-
51-0709-* Condenser Coil EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -02 1 -03 1 -01 1 -02
18-0543-00 Condenser Coil EA 1-1-
02-0274-00 Baffle, RH EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
02-0275-00 Baffle, RH EA 1-1-
13 02-0851-00 Baffle, LH EA 1-1-
12-3024 Filter Drier EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
18-1122-00 Filter Drier EA 1-1-
16-0308-00 Compressor EA 1 -
16-0309-00 Compressor EA 1 -
16-0313-00 Compressor EA 1 - 1 -
16-0311-00 Compressor EA 1 -
16-0312-00 Compressor EA 1 -
16-0301-00 Compressor EA 1-1-
17-0314-00 Motor Protector EA 1 -
17-0315-00 Motor Protector EA 1 -
17-0316-00 Motor Protector EA 1 - 1 -
17-0317-00 Motor Protector EA 1 -
17-0290-00 Motor Protector EA 1 -
17-0286-00 Start Relay EA 1 - 1 -
17-0300-00 Start Relay EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
15-0325 Cover, Comp Terminals EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
15-0326 Strap, Cover EA 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 - 1 -
50-3488-* Heat Exchange, Coil EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -01 1 -02
50-4035-00 Heat Exchange, Coil EA 1 - 1 -
50-3475-02 Heat Exchange, Coil EA 1-1-
E8HR
E8HR2
ECKDC-67
E12HC2
EKDC-67
E12HR2
4HR 8HR 16HR
E4HC
E4HC2
E4HR
E4HR2
16
15
14
12
11
8
7
6
4
EKDC-87
E16HR2
ECKDC-87
E16HC2
PART NUMBER
12HR
4HC 8HC 12HC 16HC
E8HC
E8HC2
CONDENSING UNIT PARTS 59
MODEL NO. MODEL NO.
CONDENSING UNIT PARTS
Page 62

ELECTRICAL PARTS - EXPLODED VIEW
60 ELECTRICAL PARTS EXPLODED VIEW
Page 63

ELECTRICAL PARTS 61
ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
ELECTRICAL PARTS
MODEL NO.
Dipping Cabinets
Curved & Flat & Export
PART NUMBER
19-1148-00 Wire Harness, Compr EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1- 1-1-
1
19-1149-00 Wire Harness, Compr EA 1-1- 1-1-
202-0835-01 Electrical Box EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1- 1-1-1-1-1-1-
3 19-1414-00 Terminal Board EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1- 1-1-1-1-1-1-
19-0146-00 Ballast, 20w EA 1 - 2 -
19-0912-00 Ballast, EA 1-
19-0916-00 Ballast, EA 2- 1-2-
19-0458-00 Ballast, EA 2 - 2 -
4
19-1329-00 Ballast, EA 2-2-
19-0539-00 Ballast, EA 2-2-
19-1276-00 Ballast, 3500k EA 1 - 1 - 1 -
17-0288-00 Capacitor, Run EA 1-1-1-
17-0302-00 Capacitor, Run EA 1-1- 1-1-
5
17-0320-00 Capacitor, Run EA 1-1-1-1-
17-0283-00 Capacitor, Run EA 1-1- 1-1-
17-0291-00 Capacitor, Start EA 1-1-1-
17-0301-00 Capacitor, Start EA 1-1- 1-1-
17-0319-00 Capacitor, Start EA 1-1-1-1-
6
19-1327-00 Capacitor, Start EA 1-1-
17-0168-00 Capacitor, Start EA 1-1-
717-0306-00 Start Relay EA 1-1- 1-1-
843-0182 Grommet, Temp Control EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-
982-0141 Dial Plate, Temp Control EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-
10 19-1222-00 Temperature Control EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1- 1-1-1-1-1-1-
11 19-0659-00 Switch, Light EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1- 1-1-1-1-1-1-
12 01-1136-00 Bracket, Power Switch EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1- 1-1-1-1-1-1-
13 19-0103-00 Switch, Power Supply EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1- 1-1-1-1-1-1-
14 19-0813-00 Strain Relief EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-
19-0620 Power Supply Cord EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-
15
19-1349-00 Power Supply Cord EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-
16 19-0915-00 Wire Harness, Cabinet EA 1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1- 1-1-1-1-1-1-
DESCRIPTION U/M QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.#
MODEL NO.
4HC 8HC 12HC
(3500K)4HR
8HR
MODEL NO.
8HC
12HR
MODEL NO.
12HC
(3500K)
MODEL NO.
16HC
16HR
MODEL NO.
16HC
(3500K)
MODEL NO. MODEL NO.
E4HC E8HC
E4HR E8HR
MODEL NO.
ECKDC-67
EKDC-67
MODEL NO.
ECHKD-87
ECKDC-87 E16HR2
MODEL NO.
E4HC2 E8HC2
E4HR2 E8HR2
MODEL NO.
E12HC2 E16HC2
E12HR2
Page 64

LID - EXPLODED VIEW
2
3
1
6
7
4
5
62 LID - EXPLODED VIEW
Page 65

LID PARTS
Dipping Cabinets
Curved & Flat & Export
DESCRIPTION U/M QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.# QTY GR.#
1 10-1141-* Lid, Plexiglas EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
208-0517-* Lid Frame, Top EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 1 -04
323-0164-00 U-Clip EA 6 - 10 - 10 - 10 -
408-0520-* Lid Frame, Handle EA 1 -01 1 -02 1 -03 2 -04
509-0219-00 Bumper, Lid Front FT 1.73 - 3.46 - 2.49 - 3.66 -
6 10-1156-00 Pivot Bushing, Male EA 2 - 2 -2-2-
7 10-1135-02 Pivot Fushing,Female EA 2 - 2 -2-2-
PART NUMBER
MODEL NO. MODEL NO.
4HR 8HR 12HR
MODEL NO.
16HC
16HR
MODEL NO.
4HC 8HC 12HC
LID PARTS LIST
LID PARTS LIST 63
Page 66

BLANK
Page 67

ACCESSORIES
Page 68

Page 69

CAN SKIRT ACCESSORY PARTS LIST
Can Skirt Assembly w/ Gripper ................50-3326-02
A
Gripper ......................................................09-0202-00
Can Skirt Only ........................................ 10-0952-02
B Thumbscrew ............................................ 22-1729-00
C Can Rack .............................................. 15-0296-00
D Support Bracket (Short) .......................... 01-0930-00
Support Bracket (Long) .......................... 01-0931-00
E Thumbscrew ............................................ 22-1729-00
F Product Spacer ........................................ 05-1011-00
G Product Spacer Angle .............................. 05-1010-00
ACCESSORIES 67
Page 70

CAN SKIRT INSTALLATION INFORMATION
ACCESSORY PART NUMBER CABINET MODEL NUMBER
52-1804-01 4-Hole CKDC27, CKDC27C, DL4C 4HC & 4HR
52-1804-02 8-Hole CKDC47, CKDC47C, DL8C 8HC & 8HR
(1) 52-1804-01 plus (1) 52-1804-2
(2) 52-1804-01 plus (1) 52-1804-2
Each accessory assembly contains a complete set of can skirts & brackets for the size cabinet as indicated in the chart above.
12-Hole CKDC67, CKDC67C, DL12C 12HC & 12 HR
16-Hole CKDC87, CKDC87C, DL16C 16HC & 16HR
1. Set cabinet into its ser ving location.
2. Remove all packaging material, clean interior.
3. Locate can skirt assembly cartons.
4. Open can skirt assembly cartons.
5. Sort parts by style.
ACan Skirt Ass’y w/Gripper ............50-3326-02
B Thumbscrew..................................22-1729-00
CCan Rack ......................................15-0296-00
D Support Bracket (Short) ................01-0930-00
Support Bracket (Long) ................01-0931-00
EProduct Spacer..............................05-1011-00
FProduct Spacer Angle....................05-1010-00
6. Clean all parts.
7. Remove plastic hole
covers in rivnut holes
inside cabinet tank.
Discard plastic hole
covers.
8. Attach can rack
support bracket D
to the inside wall
of the tank using
thumbscrews B
provided. One
thumbscrew is
necessary per
mount hole series.
Adjust height of
can rack support
bracket to desired dipping height.Can rack support
brackets attach to front and rear wall of inner tank.
9. Place can
racks C into
support
bracket.
Place ball of
can rack into
slot on the
support
bracket.
10. Place can skirt A
over the product
container.Slide
the product
container with can
skirt attached into
the can rack.Fill
the complete
cabinet with
product
containers.
68 ACCESSORIES
Page 71

CAN SKIRT INSTALLATION INFORMATION
11. Place product spacer E into the cabinet at center of
tank. Eight-hole and 12-hole assemblies have one
spacer bar; 16-hole has 2 spacer bars.
12. Can skirt is now installed.
ACCESSORIES 69
Page 72

DIPPERWELL INSTALLATION INFORMATION - 7300000
NOTE: There are provisions for either
righthand or lefthand dipperwell positioning.
To install dipperwell:
1. Remove plastic hole tabs.
2. Mount dipperwell to cabinet using (2) 1/4-20 x 1/2 M.S.
3. Mounting plate must be under flange of stainless
steel cap.
4. Slide flange of dipperwell under stainless steel cap and
line up hole in dipperwell to hole provided in cabinet.
5. Secure dipperwell to cabinet with (2) 1/4-20 x 1/2 M.S.
70 ACCESSORIES
Page 73

ADJUSTABLE LEG KIT - 52-1831-01
ACCESSORIES 71
Page 74

CASTER KIT- 52-1830-01
72 ACCESSORIES
Page 75

INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS FOR LID LOCK KIT-52-2081-00
(DIPPING CABINETS)
1. Locate and dr ill a 5/16" (.313) dia. hole 3/8" (.375) from the edge
of the handle.
2. Slip the hooked end of the lock bracket under the stainless steel top
(see end view above), pull out to allow lid handle to pass and place the
padlock through the handle and the bracket.
ACCESSORIES 73
Page 76

CAN CLAMP INSTALLATION
74 ACCESSORIES
Page 77

INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS - ACCESSORY PART NO. 52-1874-01
ROUND CAN CLAMP - 9 1Ú4" to 9 5Ú8" Dia. - PLASTIC CANS
Each accessory contains parts to clamp one 4-can
cluster of ice cream containers.
1. Install 4 mounting angles, using 2 thumbscrews
each. Select a hole location which will meet your
height requirements. Other cans or other means to
obtain proper height of the four cans in relation to
the can clamps may be used.
NOTE: Cans cannot extend above clamps more
than 1-1/2" in order for the cam handle to clear the
top of the cans. Can clamp mounting angles offer
approximately 4" of adjustment.
2. Slide rear clamp body (without cam) on mounting
angles on operator’s side.
3. Slide front clamp body (with cam) on mounting
angles on customer’s side. Position 4 cans against
front and rear clamp bodies.
4. Drop in the center clamp section and turn cam about
90 degrees to lock in cans.
5. If it is necessary to increase clamping pressure,
install plastic shim or shims. Rest the notchedout corners on the mounting angles (operator’s
side) between the rear of the rear clamp body and
the liner wall. Shims drop in place without
removing parts.
PARTS LIST
Center Clamp Section .................................. 764183P
Front Clamp Body ...................................... 764181 P
Rear Clamp Body ........................................ 764182P
R-12 Mounting Angle, LH ............................ 764185P
R-12 Mounting Angle, RH ............................ 764184P
R-22 Metal Mounting Bracket, Flat .......... 01-0917-00
R-22 Metal Mounting Bracket, Curved .... 01-0918-00
Thumbscrews .............................................. 530536P
Thumbnuts .................................................. 548905P
Handle .......................................................... 371057P
Cam ................................................................ 371059
Cap .............................................................. 430243P
ACCESSORIES 75
Page 78

HALF-WAY SELF BOTTOM SUPPORT KIT
1. Assemble vertical supports to cabinet with thumbscrews through
top hole of support onto rivnuts in liner. The dimple formed in
each support should be towards the wall. The four (4) short
supports go over the unit compartment.
2. Engage the shouldered rivets in each bottom angle in the
keyhole slots of two vertical supports as illustrated, note that in
the deep section you have a choice of two locations. For cans
one row deep, use top keyhole slot. For cans two deep, use
lower keyhole slot.
3. Hook bottom support channels over bottom angle between
verticle supports.
4. Set bottom pads on angles and load product.
5. To raise product - move supports up to position on 2nd through
6th hole.
76 ACCESSORIES
Page 79

IBC
Page 80

CARRIER COMMERCIAL REFRIGERATION, INC.
Providing BEVERAGE-AIR • FRIGIDAIRE • KELVINATOR • UNIVERSAL NOLIN Products/Services
P.O. Box 5932
Spartanburg, S.C. 29304-5932 • (800) 684-1199
 Loading...
Loading...