Belkin USB ADAPTER User manual

User Manual
F5D7050
Connect your desktop or notebook
computer to a wireless network
Wireless G USB
Network Adapter
UK
FR
DE
NL
ES
IT

Table of Contents
1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Benefits of a Home Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Advantages of a Wireless Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Placement of your Wireless Networking Hardware for
Optimal Performance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Product Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Applications and Advantages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Product Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Installing and Setting up the Adapter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 1: Install . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 2:
Step 3:
4 Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accessing the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility from the
Windows System Tray. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Setting Wireless Network Profiles
Securing your Wi-Fi Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Configuring your Belkin Wireless G USB Network Adapter
to use Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Configure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
1
1
2
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
12
20
28
36

Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Belkin Wireless G USB Network
Adapter (the Adapter). Now you can take advantage of this great
new technology and gain the freedom to network your home and
office computers wirelessly. This Adapter allows you to connect a
desktop or notebook computer to your network. The easy installation
and setup will have you networking wirelessly in minutes. Please
be sure to read through this User Manual completely, and pay
special attention to the section entitled “Placement of your Wireless
Networking Hardware for Optimal Performance” on page 2.
section
1
2
3
4
Benefits of a Home Network
Your Belkin Home Network will allow you to:
• Share one high-speed Internet connection with all the computers in
your home
• Share resources, such as files, and hard drives among all the
connected computers in your home
• Share a single printer with the entire family
• Share documents, music, video, and digital pictures
• Store, retrieve, and copy files from one computer to another
• Simultaneously play games online, check Internet email, and chat
Advantages of a Wireless Network
Here are some of the advantages of setting up a Belkin wireless network:
• Mobility – you no longer need a dedicated “computer
room”—you can work on a networked laptop or desktop
computer anywhere within your wireless range
• Easy installation – Belkin Easy Installation Wizards make
setup simple
• Flexibility – set up and access printers, computers, and other
networking devices from anywhere in your home
• Easy expansion – the wide range of Belkin networking products
lets you expand your network to include devices such as printers
and gaming consoles
• No cabling required – you can spare the expense and hassle of
retrofitting Ethernet cabling throughout the home or office
• Widespread industry acceptance – choose from a wide range
of interoperable networking products
5
6
1

Introduction
32
Placement of your Wireless Networking Hardware for Optimal
Performance
Your wireless connection will be stronger the closer your computer
is to your wireless router (or access point). Typical indoor operating
range for your wireless devices is between 100 and 200 feet. In the
same way, your wireless connection and performance will degrade
somewhat as the distance between your wireless router (or access
point) and connected devices increases. This may or may not be
noticeable to you. As you move farther from your wireless router (or
access point), connection speed may decrease. Factors that can
weaken signals simply by getting in the way of your network’s radio
waves are metal appliances or obstructions, and walls.
If you have concerns about your network’s performance that might be
related to range or obstruction factors, try moving the computer to a
position between five and 10 feet from the wireless router (or access
point) in order to see if distance is the problem. If difficulties persist
even at close range, please contact Belkin Technical Support.
Note: While some of the items listed below can affect network
performance, they will not prohibit your wireless network from
functioning; if you are concerned that your network is not operating
at its maximum effectiveness, this checklist may help.
1. Placement of your Wireless Router or (Access Point)
Place your wireless router (or access point), the central connection
point of your network, as close as possible to the center of your
wireless network devices.
To achieve the best wireless network coverage for your “wireless
clients,” (i.e. computers enabled by Belkin Wireless Notebook
Network Cards, Wireless Desktop Network Cards, and Wireless USB
Adapters):
• Ensure that your wireless router’s (or access point’s) antennas
are parallel to each other, and are positioned vertically (toward
the ceiling). If your wireless router (or access point) itself is
positioned vertically, point the antennas as much as possible in
an upward direction.
• In multistory homes, place the wireless router (or access point) on a
floor that is as close to the center of the home as possible. This may
mean placing the wireless router (or access point) on an upper floor.
• Try not to place the wireless router (or access point) near a
cordless 2.4GHz phone.
3
Introduction
2. Avoid Obstacles and Interference
Avoid placing your wireless router (or access point) near devices that
may emit radio “noise”, such as microwave ovens. Other objects that
can inhibit wireless communication can include:
• Refrigerators
• Washers and/or dryers
• Metal cabinets
• Large aquariums
• Metallic-based, UV-tinted windows
section
1
2
3
4
5
If your wireless signal seems weak in some spots, make sure that
objects such as these are not blocking the signal’s path between
your computers and wireless router (or access point).
3. Cordless Phone Placement
If the performance of your wireless network is impaired after
attending to the above issues, and you have a cordless phone:
• Try moving cordless phones away from the wireless router
(or access point) and your wireless-enabled computers.
• Unplug and remove the battery from any cordless phone
that operates on the 2.4GHz band (check the manufacturer’s
information). If this fixes the problem, the phone may
be interfering.
• If your phone supports channel selection, change the
channel on the phone to the farthest channel from your
wireless network as possible. For example, change the
phone to channel 1 and move your wireless router (or
access point) to channel 11. (Your channel selection will
vary depending on your region.) See your phone’s user
manual for detailed instructions.
• If necessary, consider switching to a 900MHz or 5GHz
cordless phone.
6
3

54
Introduction
4. Choose the “Quietest” Channel for your Wireless Network
In locations where homes or offices are close together, such as apartment
buildings or office complexes, there may be wireless networks nearby
that can conflict with yours. Use the Site Survey capabilities of your
Wireless Networking Utility to locate any other wireless networks,
and move your wireless router (or access point) and computers to a
channel as far away from other networks as possible.
Experiment with more than one of the available channels in order to
find the clearest connection and avoid interference from neighboring
cordless phones or other wireless devices.
For more Belkin wireless networking products, use the detailed site
survey and wireless channel information included in your User Manual.
5. Secure Connections, VPNs, and AOL
Secure connections typically require a user name and password, and
are used where security is important. Secure connections include:
• Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections, often used to connect
remotely to an office network
• The “Bring Your Own Access” program from America Online
(AOL), which lets you use AOL through broadband provided by
another cable or DSL service
• Most online banking websites
• Many commercial websites that require a user name and
password to access your account
Secure connections can be interrupted by a computer’s power
management setting, which causes it to “go to sleep.” The simplest
solution to avoid this is to simply reconnect by re-running the VPN or
AOL software, or by re-logging into the secure website.
A second alternative is to change your computer’s power management
settings so it does not go to sleep; however, this may not be appropriate
for portable computers. To change your power management setting in
Windows, see the “Power Options” item in the Control Panel.
If you continue to have difficulty with Secure Connections, VPNs, and
AOL, please review steps 1-4 in the previous pages to be sure you
have addressed these issues.
These guidelines should allow you to cover the maximum possible area
with your wireless router. Should you need to cover an even wider
area, we suggest the Belkin Wireless Range Extender/Access Point.
For more information regarding our networking products, visit our
website at www.belkin.com/networking or call Belkin Technical Support.

5
Overview
Product Features
The Adapter complies with the IEEE 802.11g standard in order to
communicate with other 802.11g-compliant wireless devices at
54Mbps. The Adapter is compatible with all 802.11g devices as well
as other 802.11b products at 11Mbps. 802.11g products operate on
the same 2.4GHz frequency band as 802.11b Wi-Fi
• 2.4GHz ISM (Industrial, Science, and Medical) band operation
• Integrated easy-to-use Wireless Networking Utility
• USB 2.0 interface, for operation in virtually any desktop or
notebook computer
• WPA, WPA2, 64-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy), or
128-bit encryption
• Wireless access to networked resources
• Support for both Infrastructure and Ad-Hoc (peer-to-peer)
networking modes
• Easy installation and use
• External antenna
• LED power and
network link
®
products.
1
section
2
3
4
5
6
5

76
Overview
Applications and Advantages
• Wireless roaming with a laptop around the home or office
Offers the freedom of networking—without cables
• Connection rates of up to 54Mbps
Provides immediate wireless connectivity at home, work, and
hotspot locations without compromising the use of existing
802.11b and 802.11g products
• Compatibility with 802.11b products
802.11g wireless LAN solutions are backward-compatible with
existing Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11b) products and with other products
that display the 54g logo
• Difficult-to-wire environments
Enables networking in buildings with solid or finished walls, or
open areas where wiring is difficult to install
• Frequently changing environments
Adapts easily in offices or environments that frequently rearrange
or change locations
• Temporary LANs for special projects or peak time
Sets up temporary networks such as at trade shows, exhibitions,
and construction sites, which need networks on a short-term
basis; also companies who need additional workstations for a
peak activity period
• SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) networking needs
Provides the easy and quick, small network installation SOHO
users need
Product Specifications
Host Interface: USB 2.0 interface
Power Consumption: Tx/Rx peak 510/250mA @ 3.3VDC (max.)
Operating Temperature: 32—140 degrees F (0—60 degrees C)
Storage Temperature: -4—176 degrees F (-20—80 degrees C)
Humidity: Max. 90% (non-condensing)
Typical Operating Range: 100–200 ft.* (30—60m) indoors
*Wireless p erf orm anc e may va ry

7
7
section
1
2
3
4
5
6
(a) Protective Cap
(b) Activity LED
(d) Desktop Adapter Base
(Optional
Use)
(c) USB Adapter
(a) Protective Cap
(b) Activity LED
Lights up and flashes when the Adapter is active
Blinking Green: Active
Off: Not connected to network
On: Connected to network
(c) USB Adapter
Fits securely into your computer’s USB slot or into the Desktop Adapter
Base (included).
(d) Desktop Adapter Base
Lets you extend the USB Adapter away from interfering objects around
your computer.
The cap can be stored on the
opposite end of the USB connector.
Overview
The cap snaps over the USB
connector for protection.
System Requirements
• PC-compatible desktop computer
with one available USB slot and
CD-ROM drive
• Windows
®
98SE, 2000, Me, or XP
Package Contents
• Wireless G USB Network Adapter
• Desktop Adapter Base
• Quick Installation Guide
• Installation Software CD
• User Manual

Installing and Setting up the Adapter
98
Step 1 Install
Important Note:
Install the software before inserting the Card.
1.1 Insert the Installation Software CD into your CD-ROM drive.
1.2 The Belkin Wireless Networking Utility screen will automatically
appear (may take 15–20 seconds to appear).
Note: If the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility screen does not appear
within 20 seconds, access your CD-ROM by double-clicking on the “My
Computer” icon; then, double-click on the CD-ROM drive into which the
installation CD has been placed. Double-click on the folder named “Files”,
then double-click on the icon named “setup.exe”.
1.4 Choose an installation location,
and click “Next” to accept the
default location or click “Browse”
to select a different location before
clicking “Next”.
1.3 Click “install” from the menu.
9
Installing and Setting up the Adapter
Step 2 Connect
Plug the Adapter into an Available USB Slot on your Notebook Computer
During the install process,
2.1
you will be prompted to insert
your Adapter. Plug the Adapter
into an available USB port on
your computer and follow the
on-screen instructions.
Note: If your system did not
prompt you to insert your Adapter
after the installation is completed,
please do so now.
2.2 Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
installation is now complete. Click
“Finish” to close the Wizard.
1
2
section
3
4
5
6
9

Installing and Setting up the Adapter
1110
Step 3 Configure
Use the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
After successfully installing the
3.1
Adapter, double-click the Belkin
Wireless Networking Utility icon
located on the desktop screen.
3.2 The Wireless Networking Utility
screen will appear. Select a
network to connect to by selecting
a network from the “Available
Networks” list. Then, click
“Connect”.
Note: In order to see your available
networks, you must be near a working
wireless router or access point.
11
Installing and Setting up the Adapter
3.3 The Belkin Wireless Networking
Utility icon can also be found on
the system tray.
Note: Double-clicking on the
Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
icon on the system tray will bring
up the “Utility” screen.
Installation is now complete.
1
2
section
3
4
5
6
11
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1312
After successfully installing the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
(WNU), configurations for wireless connection and security are just a
few easy clicks away.
Accessing the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
from the Windows System Tray
To access the WNU, simply place your mouse pointer and right-click
over the WNU icon on the Windows system tray on the lower right-hand
corner of your computer’s desktop.
If the icon is not present, click on “Start > Programs > Belkin >
Wireless Networking Utility”.
13
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
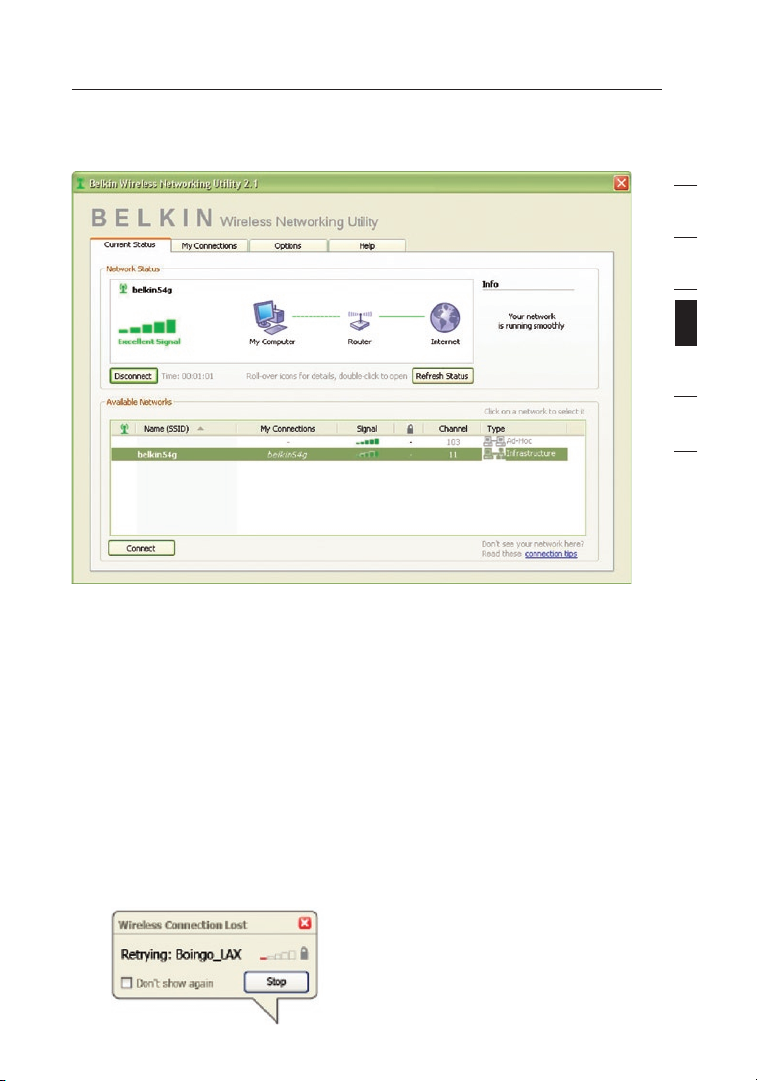
The WNU’s default screen is the “Current Status” tab. The “Current
Status” tab displays the current network status and available networks.
Network Status
This window displays the connectivity status of the current network,
between the computer and router, and between the router and the
Internet. In the event of a problem, use the “Network Status” window
to determine the source (e.g., computer, router, or Internet/modem).
Available Networks
This window displays the available networks at the current
location as well as their SSID, Signal Strength, Security Type,
Channel, and Network Type.
1
2
3
section
4
5
6
Lost Wireless Connection
If the current wireless connection is lost, a window will pop up and the
WNU will attempt to reconnect.
13
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1514
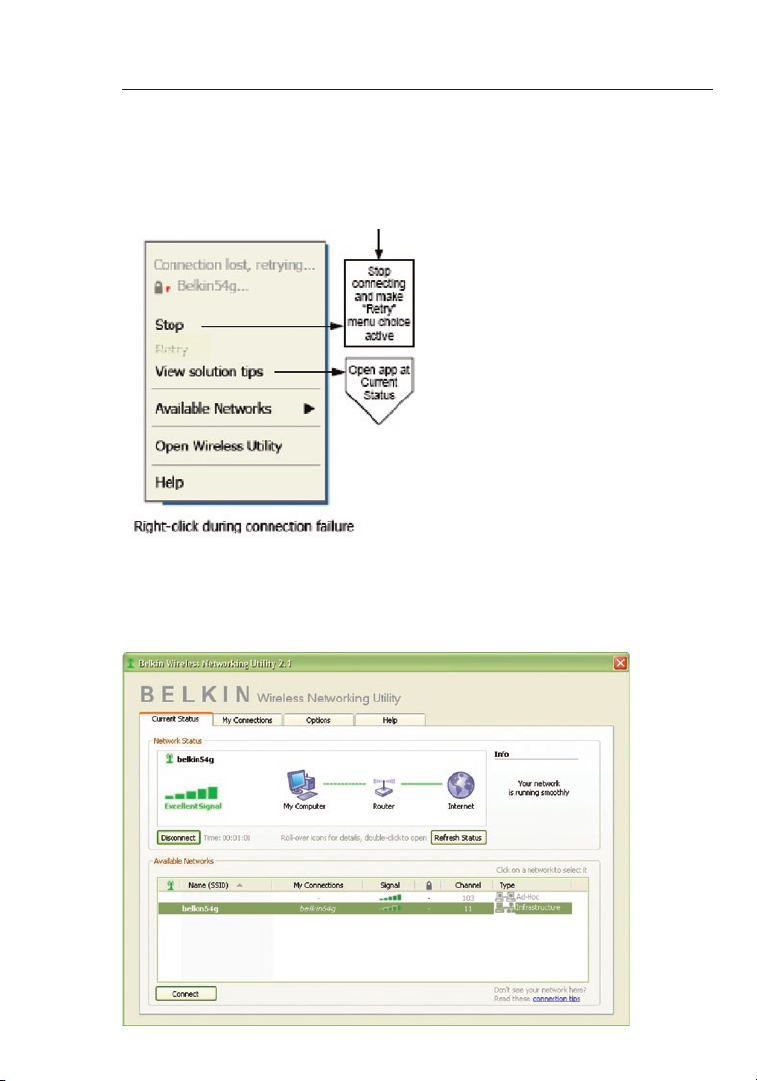
Connection Failure
Other options will appear during attempts to reconnect. To stop
connecting, click “Stop” and to reattempt connection, click “Retry”.
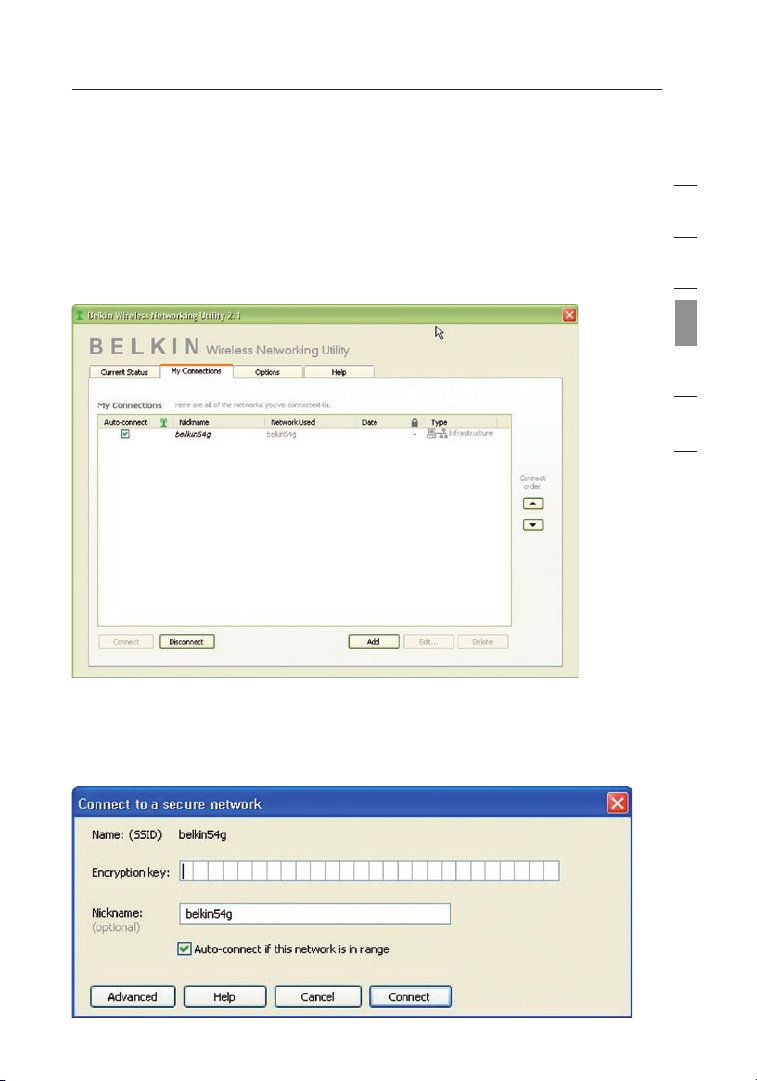
Network Status and Solution Tips
To further understand the current Network Status, click “Open Wireless
Utility”. The default screen will be the “Current Status” tab and the
“Network Status” section determines which connections are good and/or
faulty.
15
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
The WNU also features a “Solution Tips” section that provides
troubleshooting guidelines.
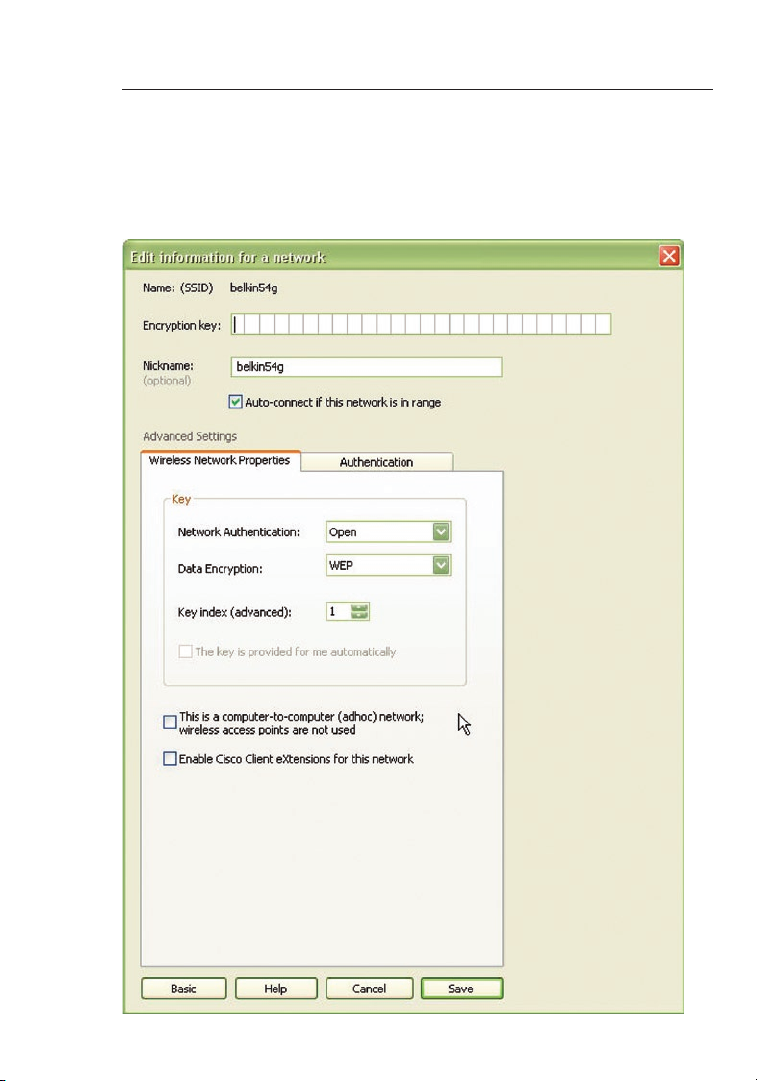
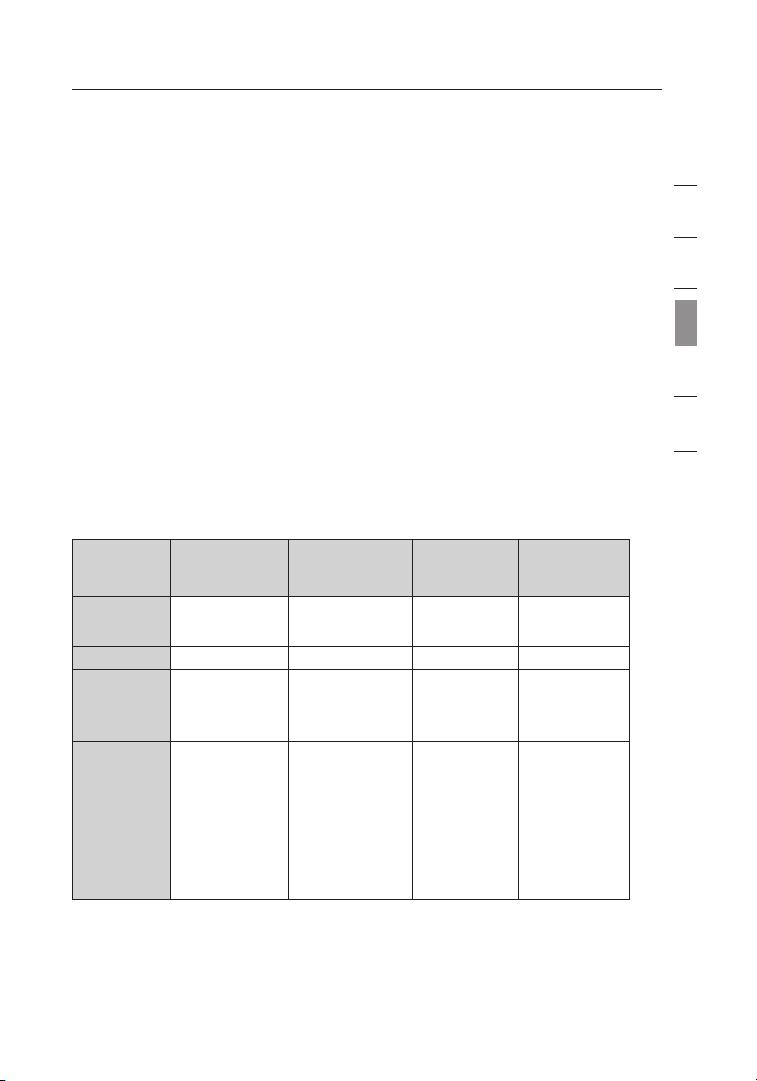
Setting Wireless Network Profiles
The “My Connections” tab on the WNU allows you to add, edit, and delete
connection profiles. It also displays signal strength, security, and network type.
Securing your Wi-Fi® Network
If you choose to connect to a secure network, determine the type of
security (WPA or WEP*) and use the appropriate field in the dialog box.
1
2
3
section
4
5
6
*Note: Types of security
15
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1716
Note: When you select a network using encryption, you will first see
the simple security screen. Click the “Advanced” button to see other
security options (below).
17
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a less secure, but more
widely adopted wireless security protocol. Depending on the security
level (64- or 128-bit), the user will be asked to input a 10- or 26character hex key. A hex key is a combination of letters, a–f, and
numbers, 0–9.
Wireless Protected Access (WPA) is the new standard in
the wireless security. However, not all wireless cards and adapters
support this technology. Please check your wireless adapter’s user
manual to check if it supports WPA. Instead of a hex key, WPA uses
only passphrases, which are much easier to remember.
The following section, intended for the home, home office, and small
office user, presents a few different ways to maximize the security of
your wireless network.
At the time of publication, four encryption methods are available:
Encryption Methods:
Nam e 64- bit W ired
Equ ivalent
Pri vacy
Acr onym 64- bit W EP 128 -bit WEP WPA-TKIP/
Sec urity Good Bet ter Best Bes t
Fea tures Sta tic k eys St atic keys Dyn amic key
Enc ryption
key s bas ed on
RC4 algo rithm
(ty pically 40-bit
key s)
128 -Bit Wired
Equ ivalent
Pri vacy
Mor e sec ure t han
64- bit W EP us ing
a key length of
104 bits plus
24 addit ional
bit s of syste mgen erated data
Wi- Fi
Pro tected
Acc ess-TKIP
AES (or just
WPA )
enc ryption
and mutu al
aut hentication
TKI P
(Te mporal
Key Inte grity
Pro tocol)
add ed so
tha t key s are
rot ated and
enc ryption is
str engthened
Wi- Fi Pr otected
Acc ess 2
WPA 2-AES (or
jus t WPA 2)
Dyn amic key
enc ryption
and mutu al
aut hentication
AES (Adv anced
Enc ryption
Sta ndard) does
not caus e any
thr oughput loss
1
2
3
section
4
5
6
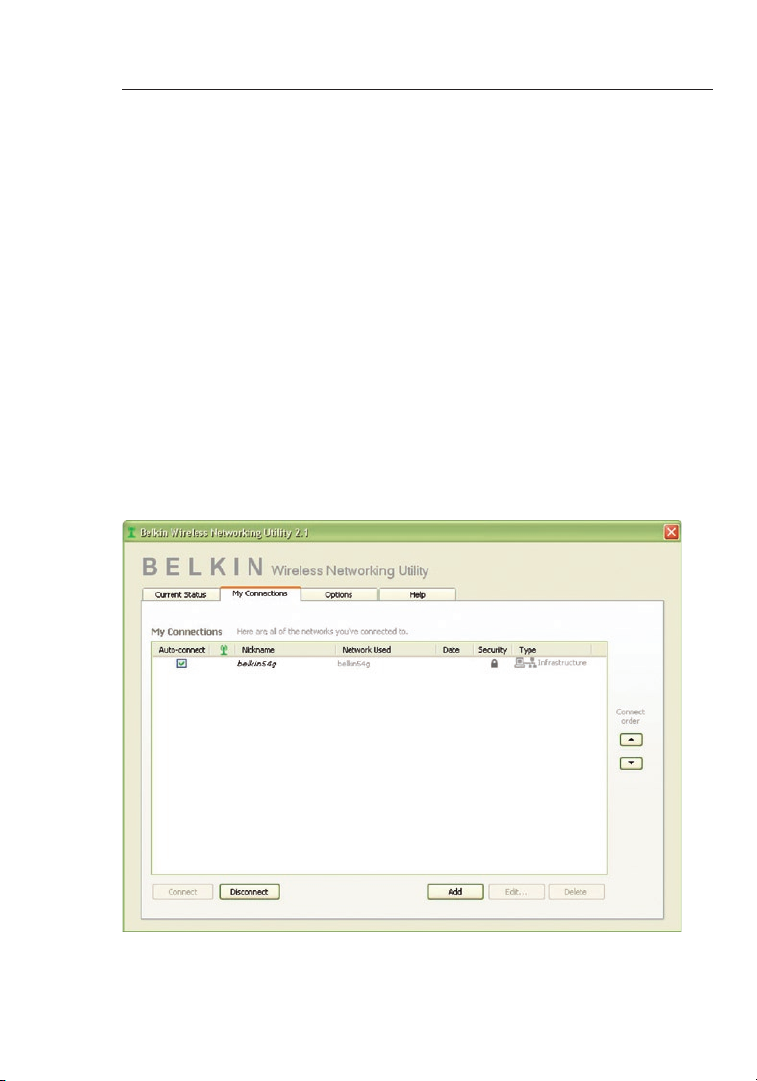
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
WEP is a common protocol that adds security to all Wi-Fi-compliant
wireless products. WEP gives wireless networks the equivalent level
of privacy protection as a comparable wired network.
17

Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1918
64-Bit WEP
64-bit WEP was first introduced with 64-bit encryption, which includes
a key length of 40 bits plus 24 additional bits of system-generated
data (64 bits total). Some hardware manufacturers refer to 64-bit
as 40-bit encryption. Shortly after the technology was introduced,
researchers found that 64-bit encryption was too easy to decode.
128-Bit Encryption
As a result of 64-bit WEP’s potential security weaknesses, a more
secure method of 128-bit encryption was developed. 128-bit
encryption includes a key length of 104 bits plus 24 additional
bits of system-generated data (128 bits total). Some hardware
manufacturers refer to 128-bit as 104-bit encryption.
Most of the new wireless equipment in the market today supports
both 64-bit and 128-bit WEP encryption, but you might have
older equipment that only supports 64-bit WEP. All Belkin
wireless products will support both 64-bit and 128-bit WEP.
Encryption Keys
After selecting either the 64-bit or 128-bit WEP encryption mode, it is
critical that you generate an encryption key. If the encryption key is
not consistent throughout the entire wireless network, your wireless
networking devices will be unable to communicate with one another.
You can enter your key by typing in the hex key manually, or you can
type a passphrase into the “Passphrase” field and click “Generate”
to create a key. A hex (hexadecimal) key is a combination of numbers
and letters from A–F and 0–9. For 64-bit WEP, you need to enter 10
hex keys. For 128-bit WEP, you need to enter 26 hex keys.

19
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
Wireless G Router
Wirele
ss G
Notebook Card
Wireless G
Desktop Car
d
Wireless G
Desktop Car
d
For instance:
AF
0F 4B C3 D4 = 64-bit WEP key
C3
03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = 128-bit WEP key
The WEP passphrase is NOT the same as a WEP key. Your Adapter
uses this passphrase to generate your WEP keys, but different
hardware manufacturers might have different methods on generating
the keys. If you have multiple vendors’ equipment in your network,
the easiest thing to do is to use the hex WEP key from your wireless
router (or access point) and enter it manually into the hex WEP key
table in your Adapter’s configuration screen.
Network key=
MyPassword
1
2
3
section
4
5
6
Network key=
MyPassword
Network key=
MyPassword
Network key=
WRONG Password
19
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2120
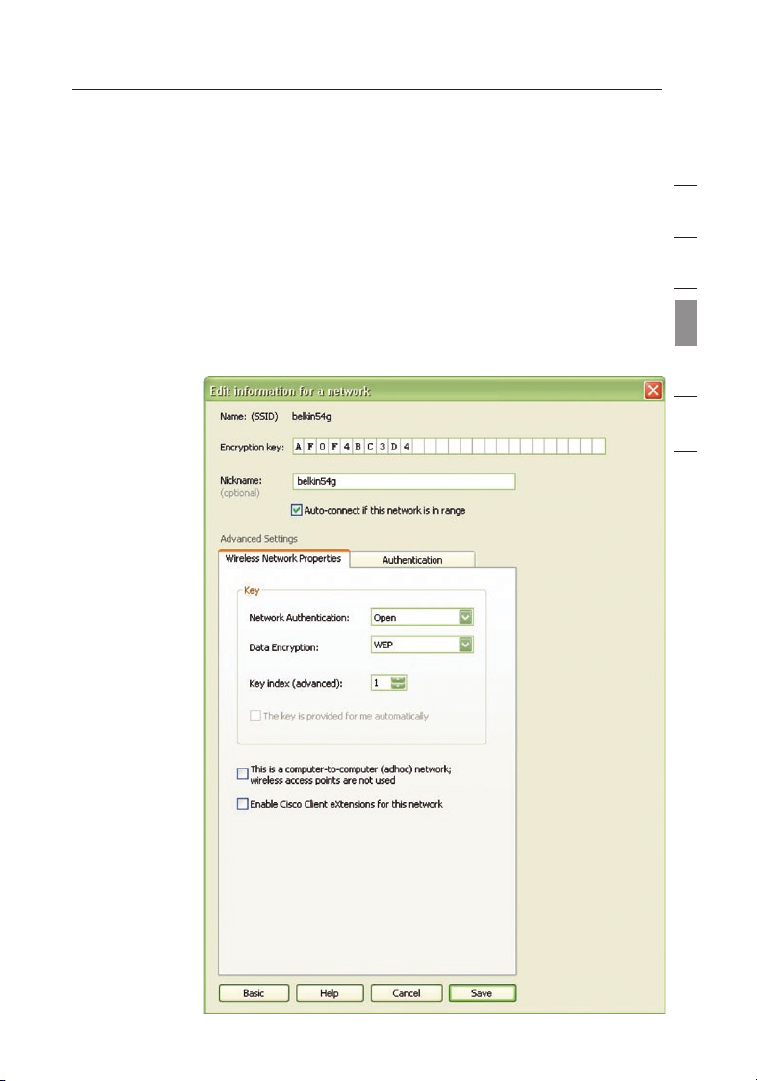
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
WPA is a new Wi-Fi standard that improves upon the security features
of WEP. To use WPA security, the drivers and software of your wireless
equipment must be upgraded to support it. These updates will be found on
your wireless vendor’s website. There are three types of WPA security: WPAPSK (no server), WPA (with radius server), and WPA2.
WPA-PSK (no server) uses what is known as a pre-shared key as the
network key. A network key is a password that is between eight and 63
characters long. It can be a combination of letters, numbers, or characters.
Each client uses the same network key to access the network. Typically, this
is the mode that will be used in a home environment.
WPA (with radius server) is a system where a radius server
distributes the network key to the clients automatically. This is
typically found in a business environment.
requires Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for encryption
WPA2
of data, which offers much greater security than WPA. WPA uses both
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and (AES) for encryption.
For a list of Belkin wireless products that support WPA, please visit
our website at www.belkin.com/networking.
Most Wi-Fi products ship with security turned off. So once you have
your network working, you need to activate WEP or WPA and make
sure all your wireless devices are sharing the same network key.
21
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
The following diagram shows the effect of not having the correct
network key throughout your network.
The Card cannot access the network because it uses a different network key than the one
configured on the wireless router.
IMPORTANT: You must now set all wireless network cards/adapters
to match these settings.
Configuring your Belkin Wireless G USB Network
Adapter to use Security
At this point, you should already have your wireless router (or access
point) set to use WPA or WEP. In order for you to gain a wireless
connection, you
will need to set
your Wireless
G USB Network
Adapter to
use the same
security
settings.
Changing
the Wireless
Security
Settings
The Belkin
Wireless G
USB Network
Adapter
supports the
latest WPA
security feature
as well as
the legacy
WEP security
standard. By
default, wireless
security is
disabled.
To enable
security, you
will first need to
determine which
standard is
used by the
21
1
2
3
section
4
5
6

Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2322
WEP Setup
64-Bit WEP Encryption
1. Select “WEP” from the drop-down menu.
2. After selecting your WEP encryption mode, you can enter your key
by typing in the hex key manually, or you can type in a passphrase
in the “Passphrase” field and click “Generate” to create a key.
A hex (hexadecimal) key is a combination of numbers and letters from
A–F and 0–9. For 64-bit WEP, you need to enter 10 hex keys.
For instance:
AF
0F 4B C3 D4 = 64-bit WEP key
23
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1
2
3
section
4
5
6
3. Click “Save” to finish. Encryption in the wireless router (or
access point) is now set. Each of your computers on your
wireless network will now need to be configured with the same
security settings.
WARNING: If you are using a wireless client to turn on the security
settings in your wireless router (or access point), you will temporarily
lose your wireless connection until you activate security on your
wireless client. Please record the key prior to applying changes in the
wireless router (or access point). If you don’t remember the hex key,
your client will be locked out of the wireless router (or access point).
23
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2524
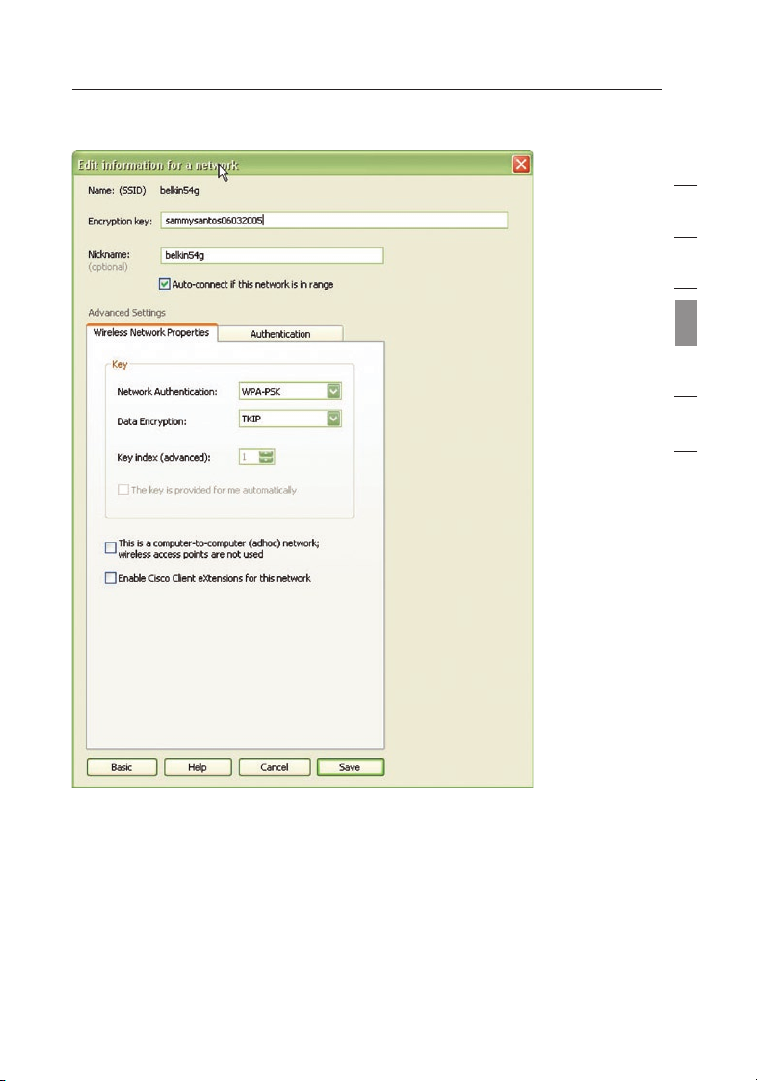
128-Bit WEP Encryption
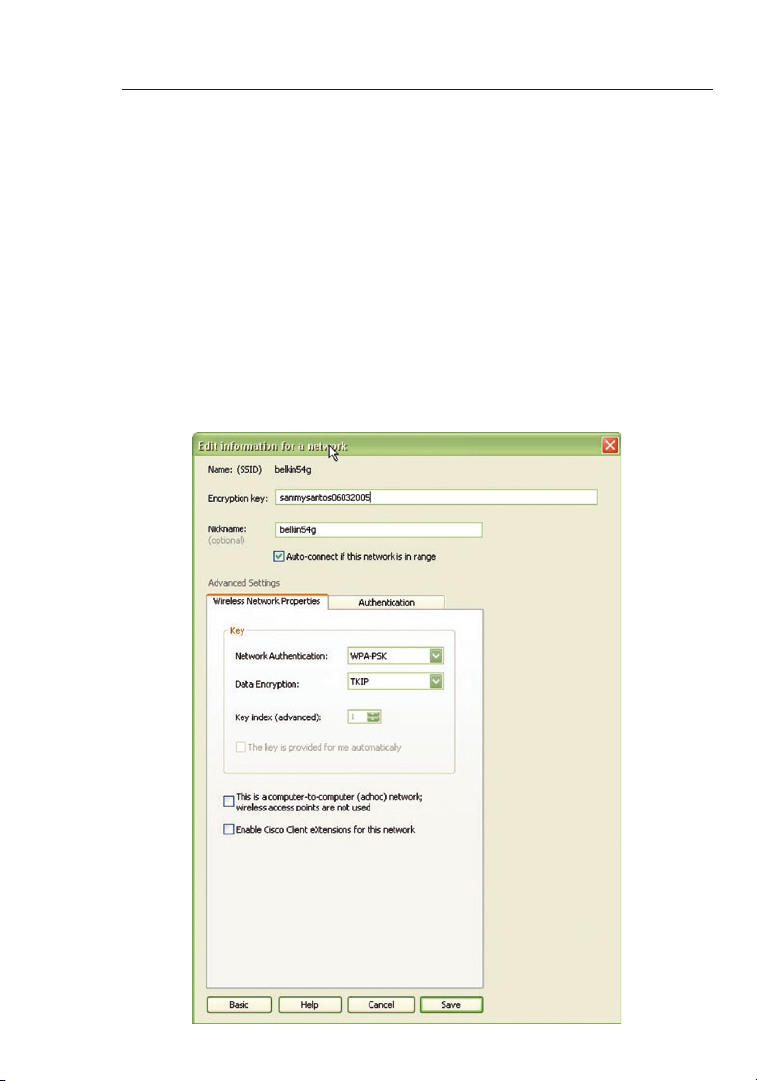
Select “WEP” from the drop-down menu.
1.
2. After selecting your WEP encryption mode, you can enter your
key manually by typing in the hex key manually, or you can type
in a passphrase in the “Passphrase” field and click “Generate” to
create a key.
A hex (hexadecimal) key is a combination of numbers and letters from
A–F and 0–9. For 128-bit WEP, you need to enter 26 hex keys
For instance:
C3
03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = 128-bit WEP key
.
25
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
3. Click “Save” to finish. Encryption in the wireless router (or
access point) is now set. Each of the computers on your
wireless network will now need to be configured with the
same security settings.
WARNING: If you are using a wireless client to turn on the security
settings in your wireless router (or access point), you will temporarily
lose your wireless connection until you activate security on your
wireless client. Please record the key prior to applying changes in the
wireless router (or access point). If you don’t remember the hex key,
your client will be locked out of the wireless router (or access point).
1
2
3
section
4
5
6
25
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2726
WPA-PSK (no server)
Choose this setting if your network does not use a radius server. WPA-PSK
(no server) is typically used in home and small office networking.
1. From the “Network Authentication” drop-down menu, select “WPA-
PSK (no server)”.
2. Enter your network key. This can be from eight to 63 characters
and can be letters, numbers, or symbols. This same key must be
used on all of the clients (network cards) that you want to include
in your network.
3. Click “Save” to finish. You must now set all clients (network cards)
to match these settings.
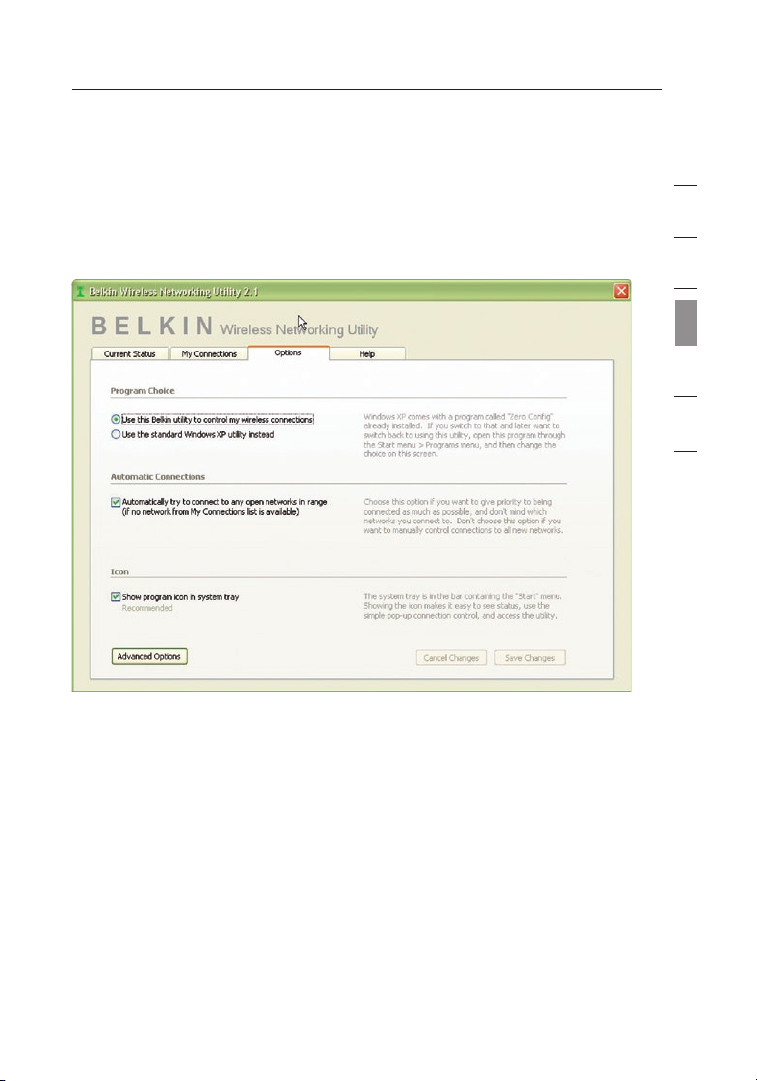
Wireless Networking Utility Options
The “Options” tab on the WNU provides the user the ability to
customize his or her WNU settings.
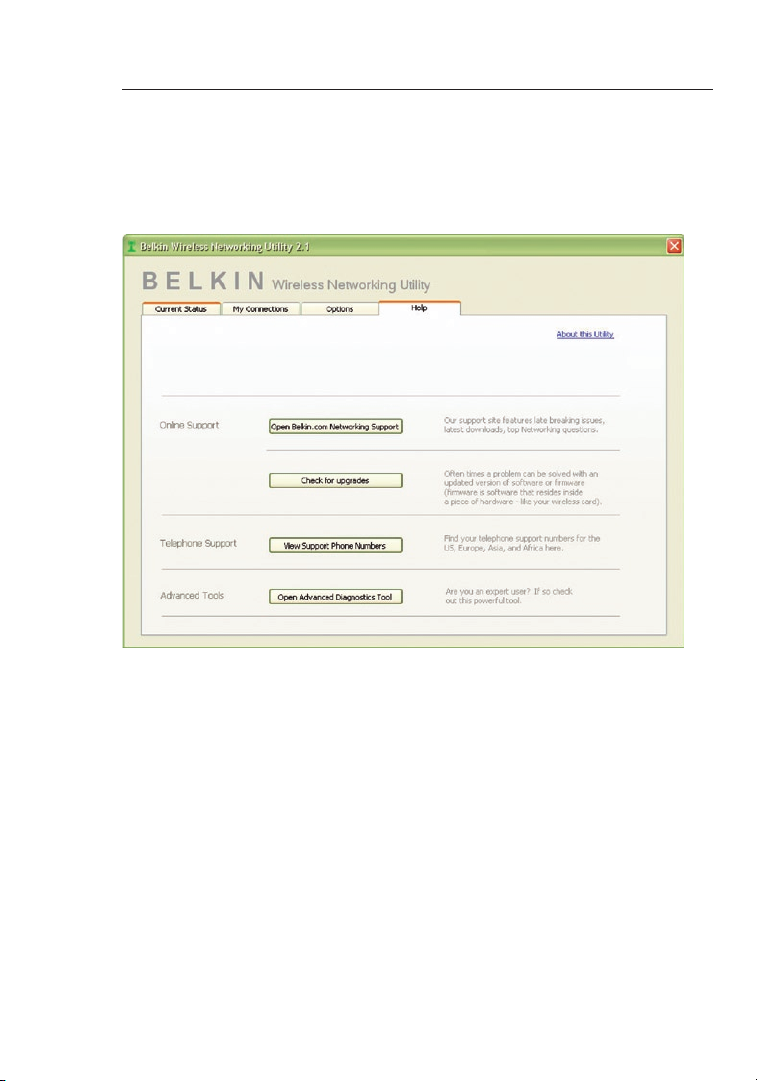
Wireless Networking Utility Help
The WNU “Help” tab provides users with access to online and telephone
support, as well as advanced diagnostic tools.
27
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
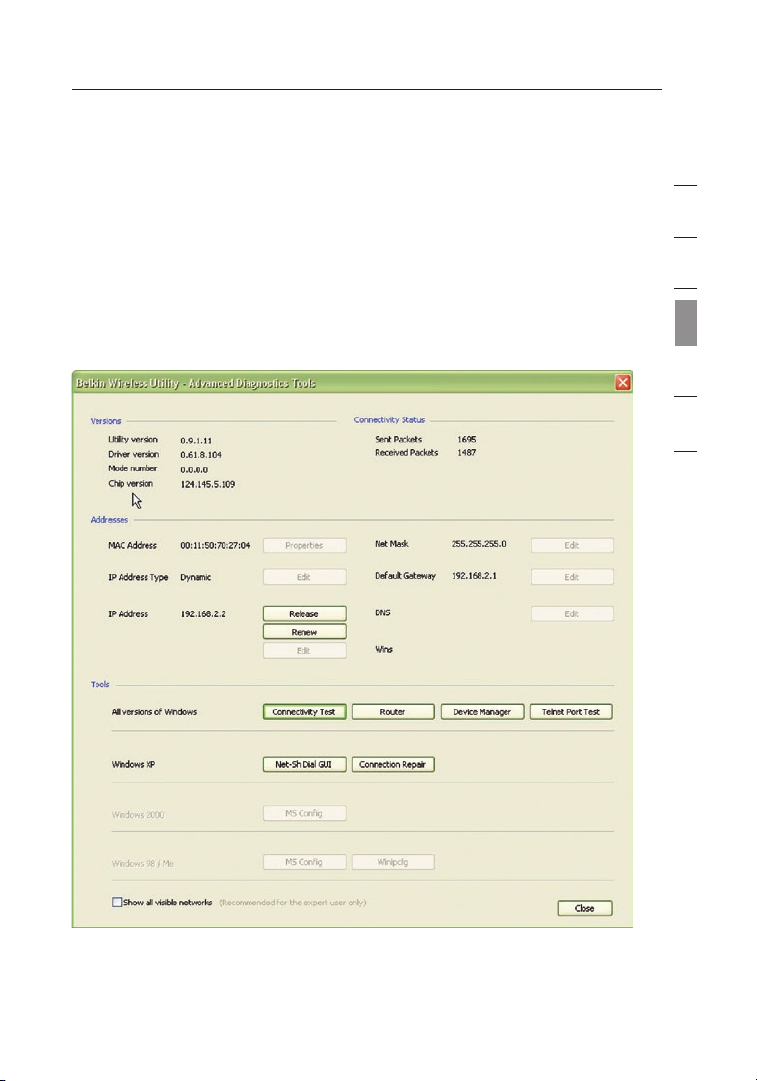
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
The “Advanced Diagnostic Tools” section is the central control panel
for all the settings of the hardware and software components of
the wireless network. It provides an array of tests and connectivity
services to ensure optimal network performance.
1
2
3
section
4
5
6
27

Troubleshooting
2928
I can’t connect to the Internet wirelessly.
If you are unable to connect to the Internet from a wireless computer,
please check the following items:
1. Look at the lights on your wireless router. If you’re using a Belkin
Wireless Router, the lights should be as follows:
• The “Power” light should be on.
• The “Connected” light should be on, and not blinking.
• The “WAN” light should be either on or blinking.
If your Belkin Wireless Router’s lights match these descriptions, go to
number 2, below.
If this is
I f you are not using a Belkin Wireless Router, consult that router
NOT the case, please contact Belkin technical support.
manufacturer’s user guide.
2. Open your Wireless Networking Utility software by clicking on the
icon in the system tray at the bottom right-hand corner of the screen:
the tray icon should look like this (the icon may be red or green):
3. The window that opens will show a list of “Available Networks”.
Available networks are wireless networks you can connect to.
If you are using a Belkin 802.11g (54g) Router, “Belkin54g” is the
default name.
If you are using a Belkin 802.11b Router, the default name should be
“WLAN”.
If you are NOT using a Belkin Router, please consult your router
manufacturer’s user manual for the default name.
 Loading...
Loading...