Page 1

F5D8001tt
N1 Wireless Desktop Card
Carte N1 sans fi l pour
ordinateur de bureau
Tarjeta inalámbrica N1 para
computadora de escritorio
User Manual
Guide d’utilisation
Manual del usuario
Page 2

Table of Contents
1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Benefits of a Home Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Advantages of a Wireless Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Placement of your Wireless Networking Hardware
for
Optimal Performance. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
2 Overview
3 Installing and Setting up the Card . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
6 Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Product Features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Applications and Advantages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Product Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 1: Install. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 2: Insert. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Step 3: Finish. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Step 4: Configure. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accessing the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
from the Windows System Tray . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Network Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Available Networks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Network Status and Solution Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Setting Wireless Network Profiles
Securing your Wi-Fi Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Configuring your Card to use Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
11
13
14
22
30
38
1
1
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
Page 3

Introduction
Thank you for purchasing the Belkin N1 Wireless Desktop Card. Now
you can take advantage of this great new technology and gain the
freedom to network your home and office computers wirelessly. This
Card allows you to connect a desktop computer to your network.
Please be sure to read through this User Manual completely, and
pay special attention to the section entitled “Placement of your
Wireless Networking Hardware for Optimal Performance”.
sectio n
1
2
3
Benefits of a Home Network
Your Belkin Home Network will allow you to:
• Share one high-speed Internet connection with all the computers
in your home
• Share resources, such as files, and hard drives among all
the connected computers in your home
• Share a single printer with the entire family
• Share documents, music, video, and digital pictures
• Store, retrieve, and copy files from one computer to another
• Simultaneously play games online, check Internet email, and chat
Advantages of a Wireless Network
Here are some of the advantages of setting up a Belkin wireless network:
• Mobility – you no longer need a dedicated “computer
room”—you can work on a networked laptop or desktop
computer anywhere within your wireless range
• Easy installation – Belkin Easy Installation Wizards
make setup simple
• Flexibility – set up and access printers, computers, and
other networking devices from anywhere in your home
• Easy expansion – the wide range of Belkin networking products
lets you expand your network to include devices such as printers
and gaming consoles
• No cabling required – you can spare the expense and hassle
of retrofitting Ethernet cabling throughout the home or office
• Widespread industry acceptance – choose from a wide range
of interoperable networking products
4
5
6
1
Page 4

Introduction
32
Placement of your Wireless Networking Hardware
for Optimal Performance
Your wireless connection will be stronger the closer your computer
is to your wireless router (or access point). Typical indoor operating
range for your wireless devices is between 100 and 200 feet. In the
same way, your wireless connection and performance will degrade
somewhat as the distance between your wireless router (or access
point) and connected devices increases. This may or may not be
noticeable to you. As you move farther from your wireless router
(or access point), connection speed may decrease. Factors that can
weaken signals simply by getting in the way of your network’s radio
waves are metal appliances or obstructions, and walls.
If you have concerns about your network’s performance that might be
related to range or obstruction factors, try moving the computer to a
position between five and 10 feet from the wireless router (or access
point) in order to see if distance is the problem. If difficulties persist
even at close range, please contact Belkin Technical Support.
Note: While some of the items listed below can affect network
performance, they will not prohibit your wireless network from
functioning; if you are concerned that your network is not operating
at its maximum effectiveness, this checklist may help.
1. Placement of your Wireless Router (or Access Point)
Place your wireless router (or access point), the central connection
point of your network, as close as possible to the center of your
wireless network devices.
To achieve the best wireless network coverage for your “wireless
clients,” (i.e. computers enabled by Belkin Wireless Notebook Cards,
Wireless Desktop Cards, and Wireless USB Adapters):
• Ensure that your wireless router’s (or access point’s) antennas
are parallel to each other, and are positioned vertically (toward
the ceiling). If your wireless router (or access point) itself is
positioned vertically, point the antennas as much as possible
in an upward direction.
• In multistory homes, place the wireless router (or access point) on a
floor that is as close to the center of the home as possible. This may
mean placing the wireless router (or access point) on an upper floor.
• Try not to place the wireless router (or access point) near a
cordless 2.4GHz phone.
Page 5
3
Introduction
2. Avoid Obstacles and Interference
Avoid placing your wireless router (or access point) near devices that
may emit radio “noise”, such as microwave ovens. Other objects that
can inhibit wireless communication can include:
• Refrigerators
• Washers and/or dryers
• Metal cabinets
• Large aquariums
• Metallic-based, UV-tinted windows
sectio n
1
2
3
4
5
If your wireless signal seems weak in some spots, make sure that
objects such as these are not blocking the signal’s path between
your computers and wireless router (or access point).
3. Cordless Phone Placement
If the performance of your wireless network is impaired after attending
to the above issues, and you have a cordless phone:
• Try moving cordless phones away from the wireless router
(or access point) and your wireless-enabled computers.
• Unplug and remove the battery from any cordless phone
that operates on the 2.4GHz band (check manufacturer’s
information). If this fixes the problem, your phone may
be interfering.
• If your phone supports channel selection, change the
channel on the phone to the farthest channel from your
wireless network as possible. For example, change the
phone to channel 1 and move your wireless router (or
access point) to channel 11. (Your channel selection will
vary depending on your region.) See your phone’s user
manual for detailed instructions.
• If necessary, consider switching to a 900MHz or
5GHz cordless phone.
6
3
Page 6

Introduction
4. Choose the “Quietest” Channel for your Wireless Network
In locations where homes or offices are close together, such as apartment
buildings or office complexes, there may be wireless networks nearby that
can conflict with yours. Use the Site Survey capabilities of your Belkin
Wireless Networking Utility to locate any other wireless networks, and
move your wireless router (or access point) and computers to a channel
as far away from other networks as possible.
Experiment with more than one of the available channels in order to
find the clearest connection and avoid interference from neighboring
cordless phones or other wireless devices.
For more Belkin wireless networking products, use the detailed Site
Survey and wireless channel information included in your User Manual.
5. Secure Connections, VPNs, and AOL
Secure connections typically require a user name and password, and
are used where security is important. Secure connections include:
• Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections, often used to connect
remotely to an office network
• The “Bring Your Own Access” program from America Online
(AOL), which lets you use AOL through broadband provided by
another cable or DSL service
• Most online banking websites
• Many commercial websites that require a user name and
password to access your account
Secure connections can be interrupted by a computer’s power
management setting, which causes it to “go to sleep.” The simplest
solution to avoid this is to simply reconnect by re-running the VPN
or AOL software, or by re-logging into the secure website.
A second alternative is to change your computer’s power management
settings so it does not go to sleep; however, this may not be appropriate
for portable computers. To change your power management setting in
Windows, see the “Power Options” item in the Control Panel.
If you continue to have difficulty with Secure Connections, VPNs, and
AOL, please review steps 1–4 in the previous pages to be sure you
have addressed these issues.
These guidelines should allow you to cover the maximum possible area
with your wireless router. Should you need to cover an even wider area,
we suggest the Belkin Wireless Range Extender/Access Point.
For more information regarding our networking products, visit
our website at www.belkin.com/networking or call Belkin
Technical Support.
Page 7

Overview
Product Features
The Card complies with the IEEE draft-802.11n specification to
communicate with other draft-802.11n-compliant wireless devices at
speeds of up to 300Mbps*. The Card is also compatible with 802.11g
devices at 54Mbps as well as 802.11b products at 11Mbps. The Card
operates on the same 2.4GHz frequency band as 802.11b/g
®
Wi-Fi
products.
• 2.4GHz ISM (Industrial, Science, and Medical) band operation
• Integrated easy-to-use Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
• PCI interface, for operation in virtually any desktop computer
• WPA, WPA2, 64-bit WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy),
or 128-bit encryption
• Wireless access to networked resources
• Data rate of up to 300Mbps* (draft 802.11n), 54Mbps
(802.11g), or 11Mbps (802.11b)
• Easy installation and use
• LED power and activity indicators
1
1
sectio n
2
3
4
5
6
5
Page 8

76
Overview
Applications and Advantages
• Connection rates of up to 300Mbps*
Provides immediate high-speed wireless connectivity at home,
work, and hotspot locations without compromising the use of
existing 802.11b/g products
• Compatibility with 802.11b/g products
The Card is backward-compatible with existing Wi-Fi
(IEEE 802.11b/g) products
• Difficult-to-wire environments
Enables networking in buildings with solid or finished walls,
or open areas where wiring is difficult to install
• Frequently changing environments
Adapts easily in offices or environments that frequently rearrange
or change locations
• SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) networking needs
Provides the easy and quick, small network installation SOHO
users need
Product Specifications
Host Interface: 32-bit PCI
Power Consumption:
802.11b: TX 920mA @ 3.3V, RX 400mA @ 3.3V
802.11g: TX 1000mA @ 3.3V, RX 400mA @ 3.3V
802.11n: 20MHz operation, TX 1000mA @ 3.3V,
40MHz operation, TX 1070mA @ 3.3V,
Operating Temperature: 32—131 degrees F (0—55 degrees C)
Storage Temperature: -4—176 degrees F (-20—80 degrees C)
Humidity: Max. 90% (non-condensing)
Typical Operating Range: Up to 1,400 ft. (426.7m)**
*
NOT E: Th e sta ndard trans mission rate– 300 Mbps–is the physic al data rate.
Act ual d ata t hro ugh put will be lower.
**Wireless perfo rmance may vary dependi ng on the netwo rki ng en vironment.
RX 400mA @ 3.3V
RX 500mA @ 3.3V
Page 9

7
7
sectio n
1
2
3
4
5
6
Overview
(a) Power/Activity LED
Lights up when the Card is powered on; flashes when wireless
activity is detected
(b) Card Connector
Part of the Card that fits into your computer’s PCI slot
(c) External Antenna Connector
Lets you connect to the cable from the exter nal antenna
System Requirements
• PC-compatible desktop computer containing:
one available 32-bit PCI slot
• 128MB RAM or greater
• 500MHz processor or greater
• Windows
®
2000 or XP
Package Contents
• N1 Wireless Desktop Card
• External Antenna with Cable
• Quick Installation Guide
• Installation Software CD
• User Manual
(b)
(a)
(c)
Page 10
Installing and Setting up the Card
98
Step 1 Install
IMPORTANT
: Install the software before inserting the Card.
1.1 Insert the Installation Software CD into your CD-ROM drive.
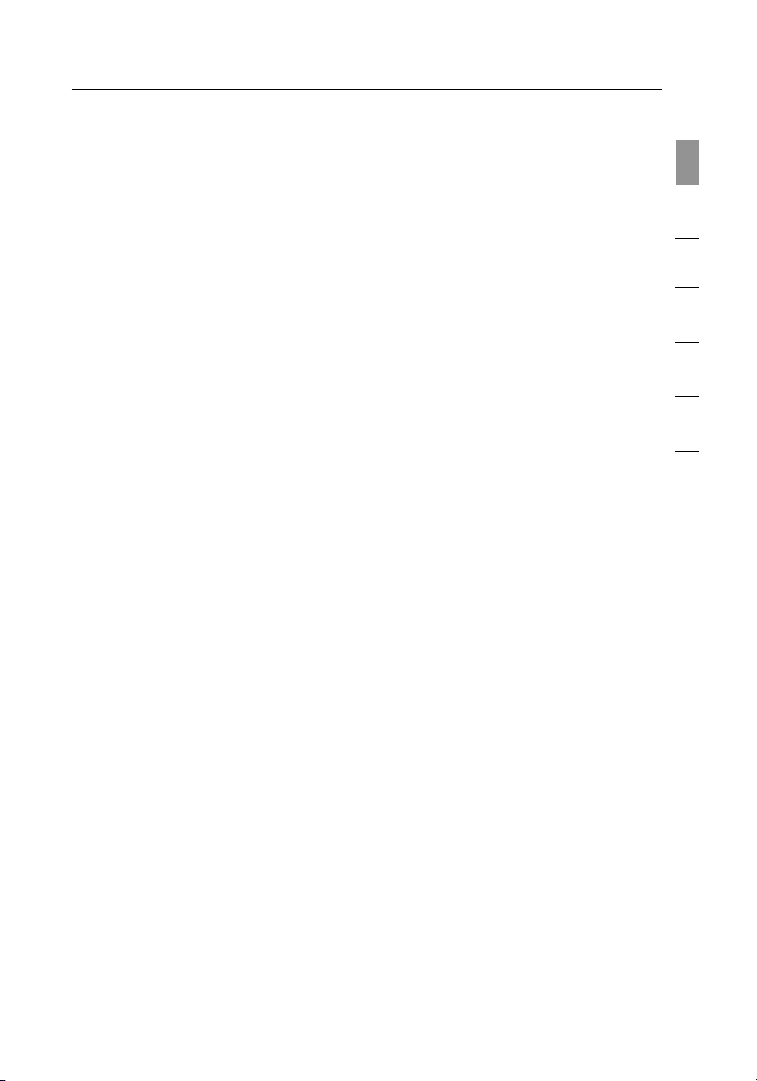
1.2 The Belkin Wireless Card Installer screen will automatically appear.
(This may take 15–20 seconds.) Click “Install Software” or “Next”
to start the installation.
Note: If the Belkin Wireless Card Installer screen does not appear within 20
seconds, access your CD-ROM by double-clicking on the “My Computer”
icon; then double-click on the CD-ROM drive into which the installation CD
has been placed. Double-click on the icon named “Setup.exe”.
1.3 The InstallShield Wizard will now
start. Click “Next” to continue.
Page 11
9
Installing and Setting up the Card
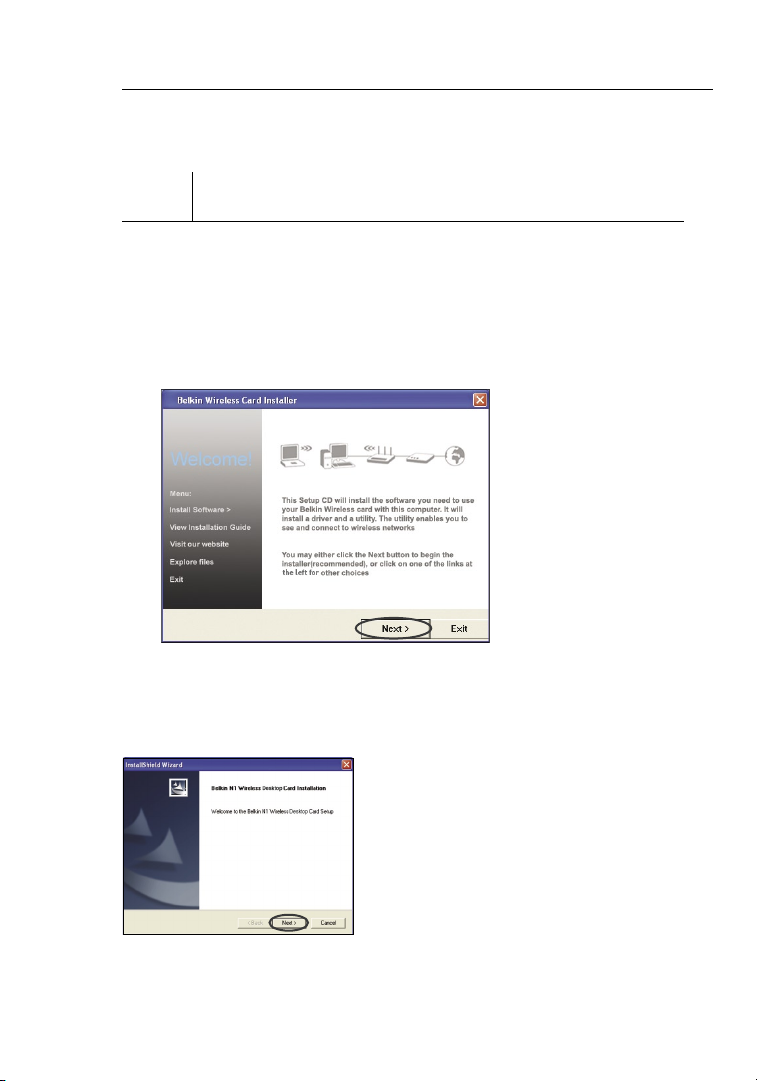
1.4 Choose a destination folder in
which to install the software,
or simply click “Next”.
1.5 The first in a series of
progress-monitoring screens
will let you know where you are
in the setup process.
1.6 You might see a screen similar to
this one. This DOES NOT mean
there is a problem. Our software has
been fully tested and is compatible
with this operating system. Select
“Continue Anyway” and follow the
on-screen instructions.
1
2
sectio n
3
4
5
6
9
Page 12

Installing and Setting up the Card
1110
Step 2 Insert
Insert the Card into your Computer
2.1 Shut down your computer and disconnect your computer’s
power cord.
2.2 Remove the screws behind your computer case that secure
the computer cover and remove the cover.
2.3 Touch any metal part of the case to discharge static electricity,
to avoid damage to your product or the computer.
2.4 Locate an empty PCI expansion
slot (usually white in color).
Confirm that the Card will fit
into the slot you have chosen.
2.5 Remove the metal PCI bracket
from the back of the computer that
corresponds to the PCI slot you
selected. If there is a screw, place
it in a safe place, as you will be
using it to attach the Card to the
computer later.
2.6 Push the Card firmly into the PCI
slot that you have chosen
.
Page 13

11
Installing and Setting up the Card
2.7 Now secure the Card with the screw that you previously placed
in a safe place.
2.8 Replace the computer’s cover. Plug in the external antenna cable
to the connector on the back of the Card.
2.9 Now that the Card is installed, you can reconnect the power cord
and turn the computer back on.
Step 3 Finish
Finish Installation of the Card
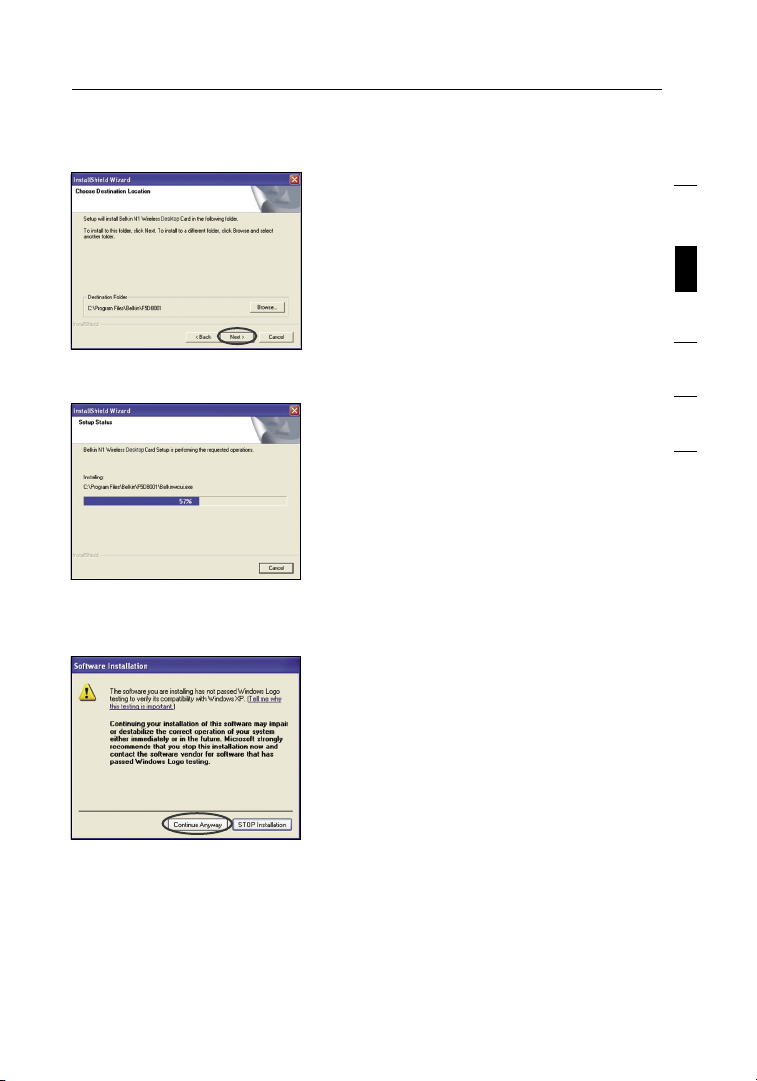
3.1 The Found New Hardware Wizard
will appear. (This may take 3–15
seconds.) Select “Yes, this time
only” and click “Next” to install
the hardware.
3.2 Select “Install the software
automatically” and “Next” to
install the hardware.
1
2
sectio n
3
4
5
6
11
Page 14
Installing and Setting up the Card
1312
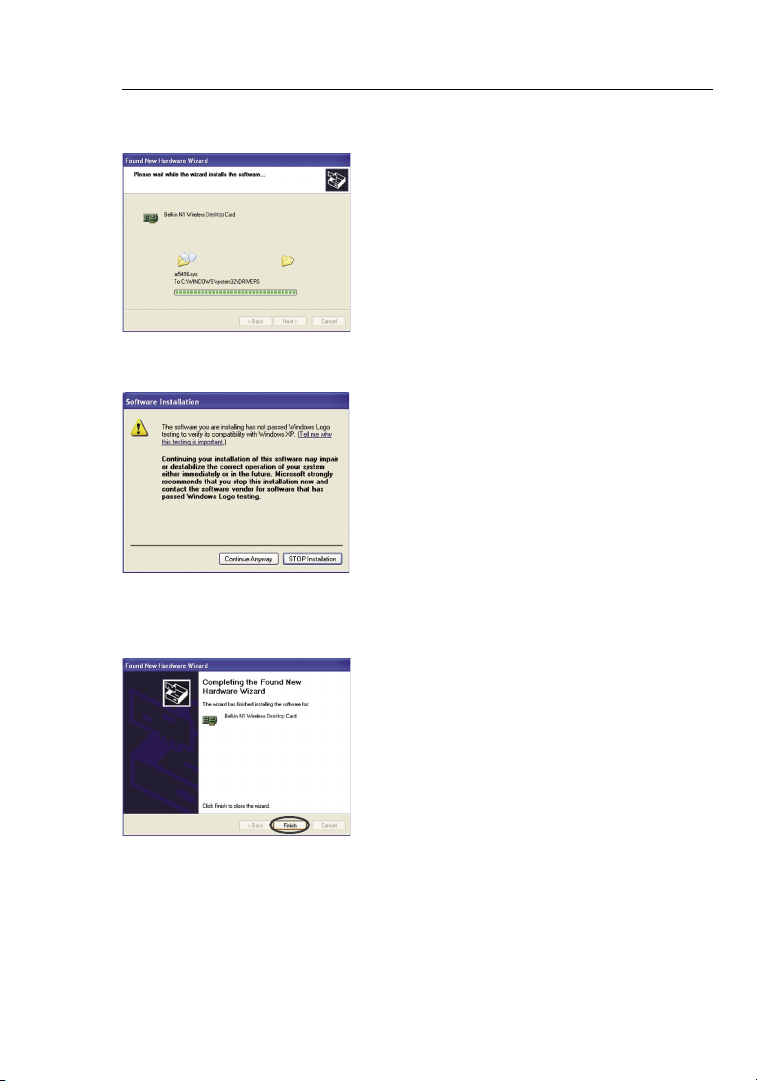
3.3 The Wizard will now install
your software.
3.4 You might see a screen similar
to this one. This DOES NOT
mean there is a problem. Our
software has been fully tested
and is compatible with this
operating system. Select “Continue
Anyway” and follow the on-screen
instructions
.
3.5 The installation is now complete.
Click “Finish” to exit.
Page 15
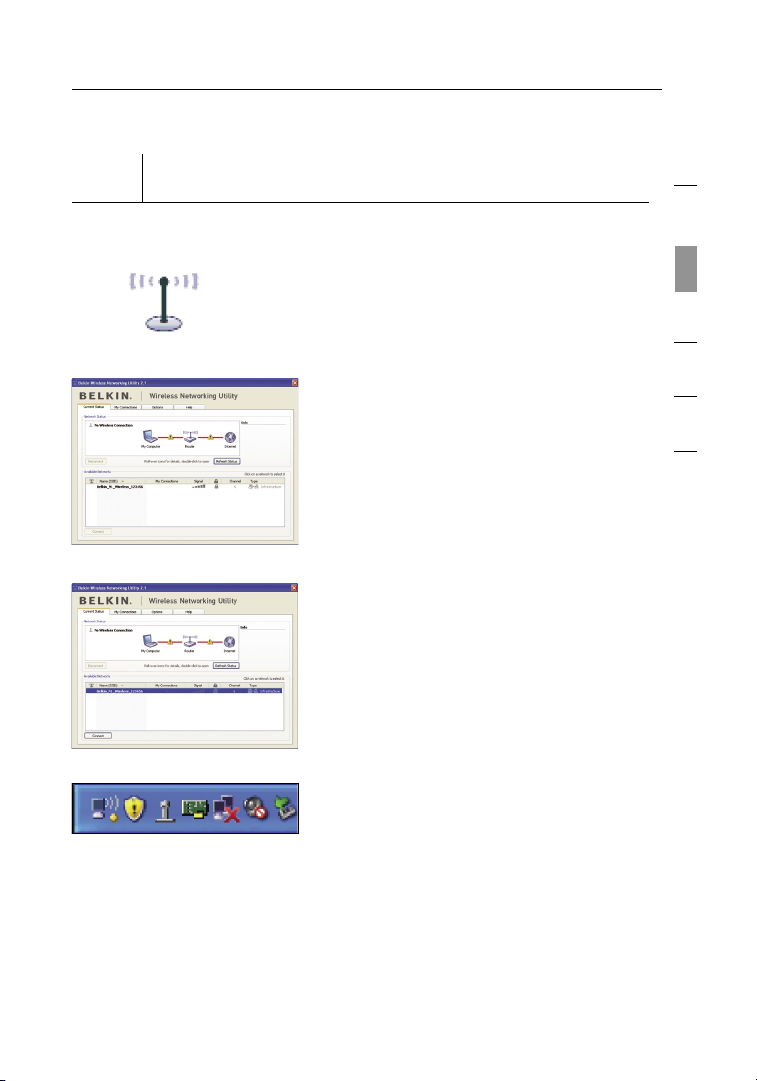
13
Installing and Setting up the Card
Step 4 Configure
Use the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
4.1 After restarting your computer,
double-click the Belkin Wireless
Networking Utility icon on the
desktop screen.
4.2 The Belkin Wireless Networking
Utility screen will appear.
4.3 Select a network to connect to from
the “Available Networks” list and
click “Connect”.
In order to see your available
Note:
networks, you must be near a working
wireless router or access point.
1
2
sectio n
3
4
5
6
4.4 The Belkin Wireless Networking
Utility icon can also be found on
the system tray
Double-clicking on the Belkin
Note:
Wireless Networking Utility icon on
the system tray will bring up the
“Utility” screen
Installation is now complete.
13
.
.
Page 16
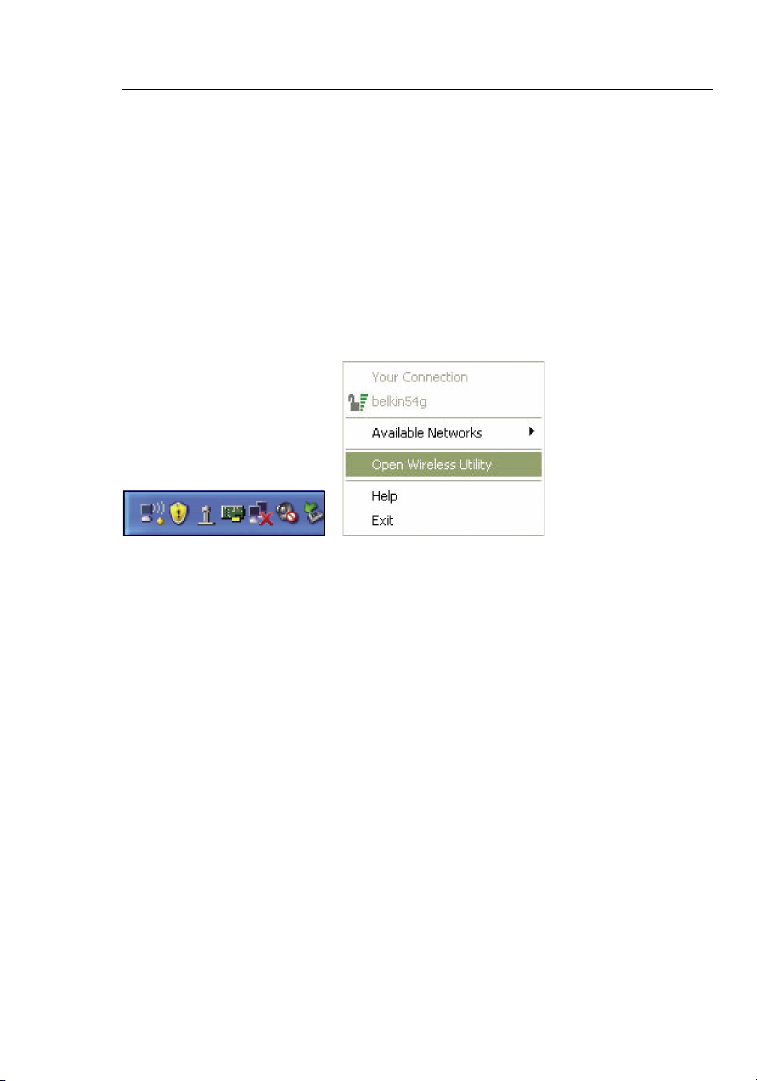
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1514
After successfully installing the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
(WNU), configurations for wireless connection and security are just
a few easy clicks away.
Accessing the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
from the Windows System Tray
To access the WNU, simply place your mouse pointer and right-click
over the WNU icon on the Windows task tray.
If the icon is not present, click on “Start > Programs > Belkin >
Belkin Wireless Utility”.
Page 17
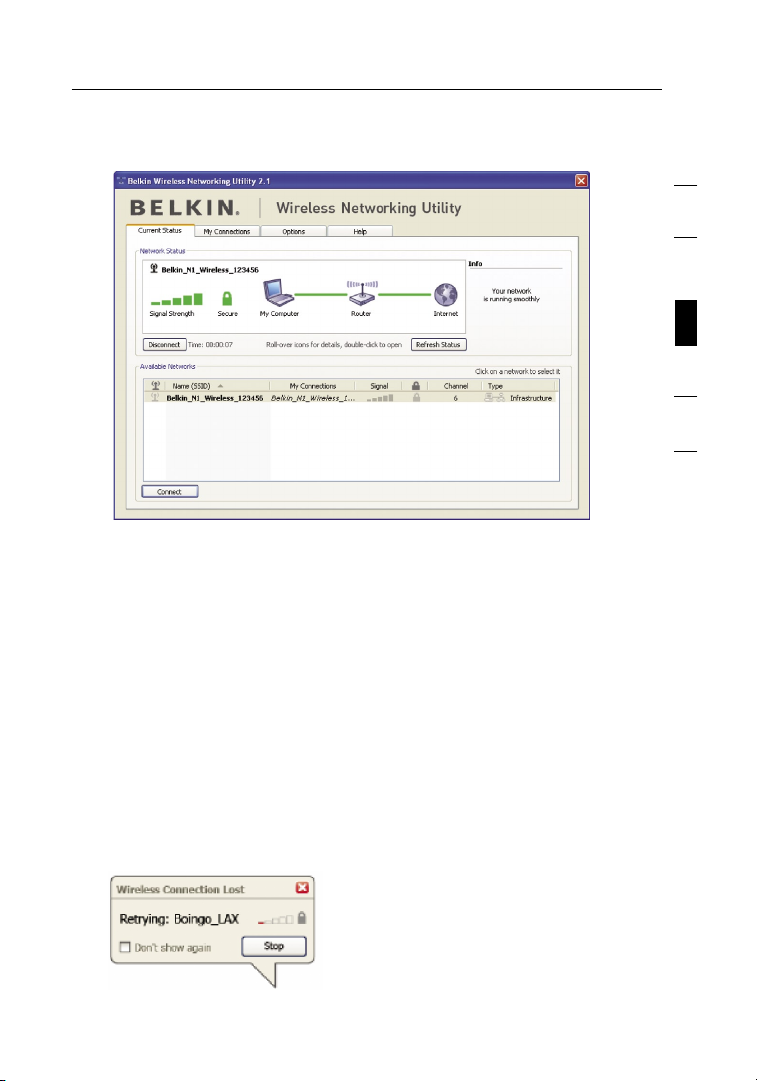
15
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
The WNU’s default screen is the “Current Status” tab. The “Current
Status” tab displays the current Network Status and Available Networks.
Network Status
This window displays the connectivity status of the current network.
It even displays connectivity between the computer and router,
and router and Internet. In the event of a connectivity problem,
this window can be used to determine the problem’s source
(e.g. computer, router, or Internet/modem).
Available Networks
This window displays the available networks at the current
location as well as their SSID, Signal Strength, Security Type,
Channel, and Network Type
.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
Lost Wireless Connection
If the current wireless connection is lost, a window will pop up
and the WNU will attempt to reconnect.
15
Page 18
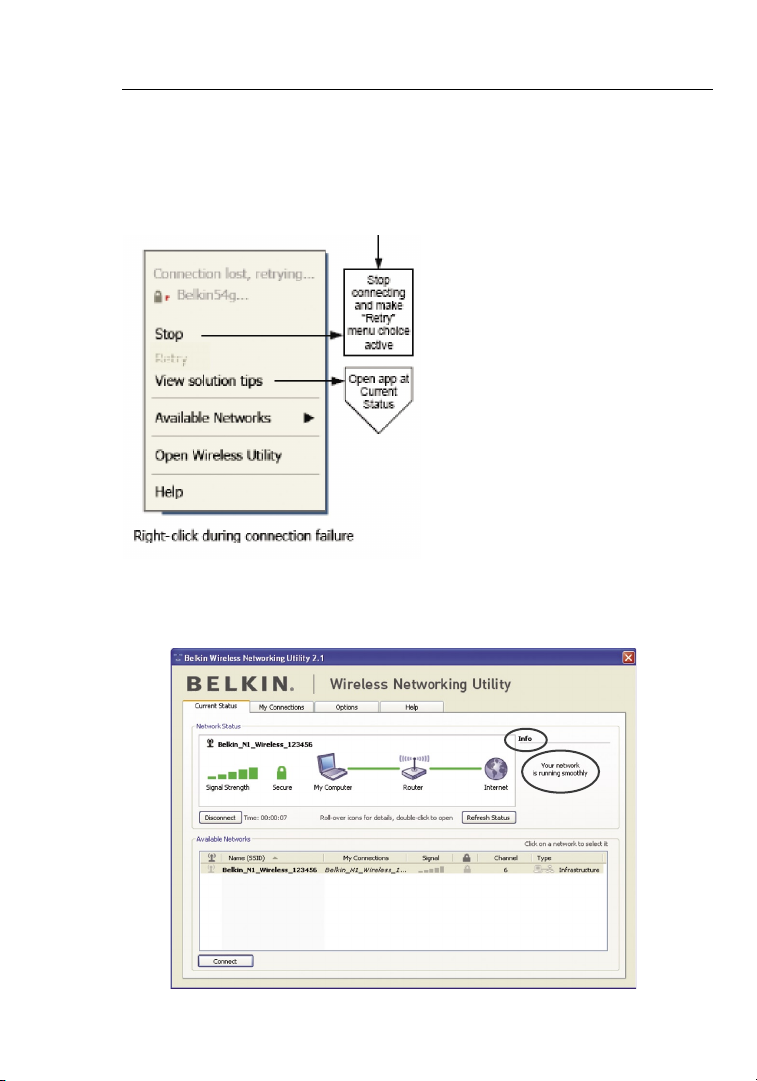
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1716
Connection Failure
Other options will appear during attempts to reconnect. To stop
connecting, click “Stop” and to reattempt connection, click “Retry”.
Network Status and Solution Tips
To further understand the current Network Status, click “Open Wireless
Utility”. The default screen will be the “Current Status” tab and the “Network
Status” section determines which connections are good and/or faulty.
The WNU also features a “Solution Tips” section that provides
troubleshooting guidelines.
Page 19
17
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
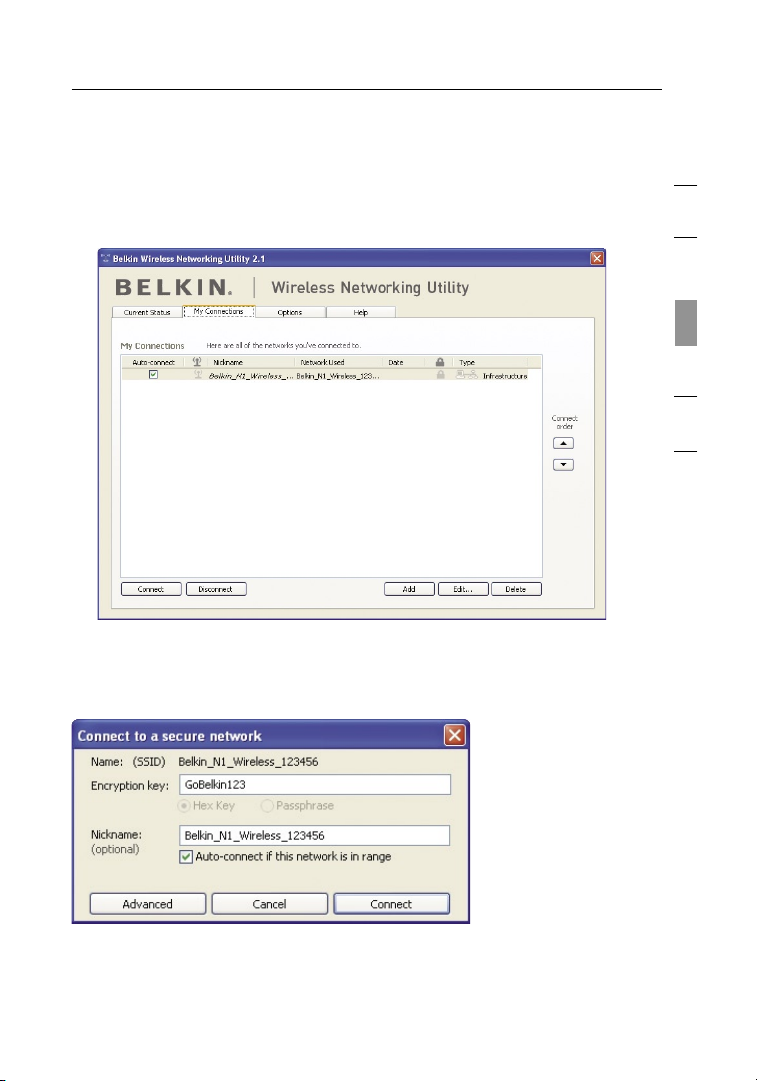
Setting Wireless Network Profiles
The “My Connections” tab on the WNU allows you to add, edit, and delete
connection profiles. It also displays signal strength, security, and network type.
Securing your Wi-Fi® Network
If you choose to connect to a secure network, determine the type of
security (WPA or WEP*) and use the appropriate field in the dialog box.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
*Note: Types of security
17
Page 20
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1918
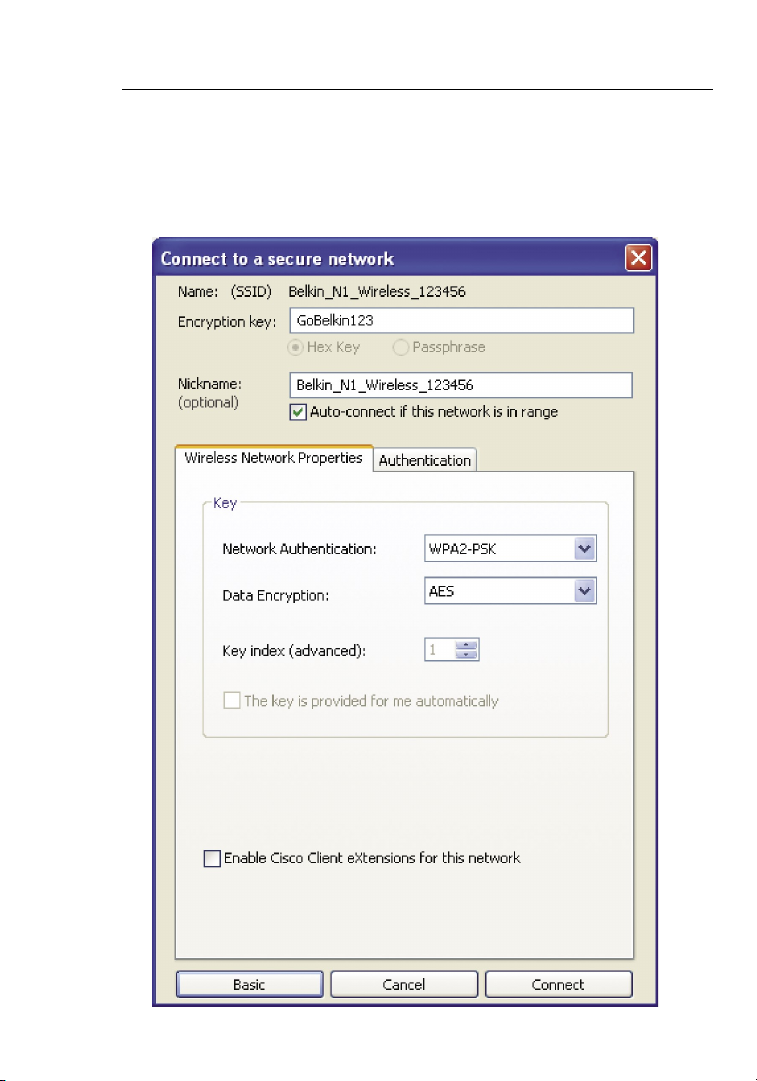
Note: When you select a network using encryption, you will first see
the simple security screen. Click the “Advanced” button to see other
security options (below).
Page 21
19
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
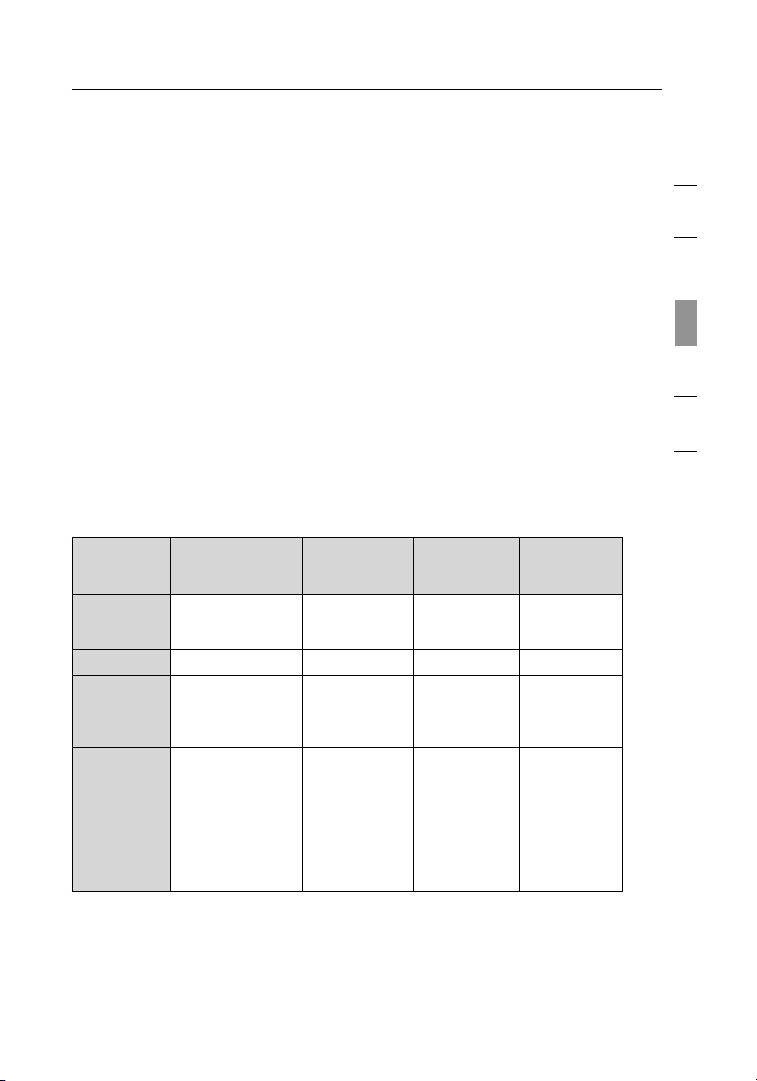
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) is a less secure, but more
widely adopted wireless security protocol. Depending on the security
level (64- or 128-bit), the user will be asked to input a 10- or 26character hex key. A hex key is a combination of letters, a–f, and
numbers, 0–9.
Wireless Protected Access (WPA) is the new standard in
the wireless security. However, not all wireless cards and adapters
support this technology. Please check your wireless adapter’s user
manual to check if it supports WPA. Instead of a hex key, WPA uses
only passphrases, which are much easier to remember.
The following section, intended for the home, home-office, and
small-office user, presents a few different ways to maximize the
security of your wireless network.
At the time of publication, four encryption methods are available:
Encryption Methods:
Nam e 64- bit W ire d
Acrony m 64- bit W EP 128 -bit WEP WPA-TKIP/
Sec urity Goo d Bet ter Bes t Bes t
Fea tures Sta tic k eys Stat ic ke ys Dyn amic key
Equ ivalent Privacy
Enc ryption keys
bas ed on R C4
alg orithm ( typicall y
40- bit k eys)
128 -Bit Wired
Equ ivalent
Pri vacy
More secure
tha n 64- bit
WEP u sin g a
key l eng th of
104 b its p lus
24 addit ional
bit s of syste mgen erated data
Wi- Fi
Protec ted
Acc ess-TKIP
AES ( or just
WPA)
enc ryption
and m utu al
aut hentication
TKI P
(Tempora l
Key I nte grity
Protoc ol)
add ed so
tha t key s are
rotate d and
enc ryption is
streng the ned
Wi- Fi
Protec ted
Acc ess 2
WPA2-AES ( or
jus t WPA2)
Dyn amic key
enc ryption
and m utu al
aut hentication
AES
(Ad vanced
Enc ryption
Sta ndard)
doe s not
cau se an y
throug hpu t
los s
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
19
Page 22

Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2120
WEP
WEP is a common protocol that adds security to all Wi-Fi-compliant
wireless products. WEP gives wireless networks the equivalent level
of privacy protection as a comparable wired network.
64-Bit WEP
64-bit WEP was first introduced with 64-bit encryption, which includes
a key length of 40 bits plus 24 additional bits of system-generated data
(64 bits total). Some hardware manufacturers refer to 64-bit as 40-bit
encryption. Shortly after the technology was introduced, researchers
found that 64-bit encryption was too easy to decode.
128-Bit Encryption
As a result of 64-bit WEP’s potential security weaknesses, a more
secure method of 128-bit encryption was developed. 128-bit
encryption includes a key length of 104 bits plus 24 additional
bits of system-generated data (128 bits total). Some hardware
manufacturers refer to 128-bit as 104-bit encryption. Most of
the new wireless equipment in the market today supports both
64-bit WEP and 128-bit WEP encryption, but you might have
older equipment that only supports 64-bit WEP. All Belkin
wireless products will support both 64-bit WEP and
128-bit encryption.
Encryption Keys
After selecting either the 64-bit WEP or 128-bit encryption mode, it is
critical that you generate an encryption key. If the encryption key is
not consistent throughout the entire wireless network, your wireless
networking devices will be unable to communicate with one another.
You can enter your key by typing in the hex key. A hex (hexadecimal)
key is a combination of numbers and letters from A–F and 0–9. For
64-bit WEP, you need to enter 10 hex keys. For 128-bit WEP, you
need to enter 26 hex keys.
For instance:
AF
0F 4B C3 D4 = 64-bit WEP key
C3
03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = 128-bit WEP key
Write down the hex WEP key from your wireless router (or access
point) and enter it manually into the hex WEP key table in your Card’s
configuration screen.
Page 23

21
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
WPA
WPA is a new Wi-Fi standard that improves upon the security features
of WEP. To use WPA security, the drivers and software of your wireless
equipment must be upgraded to support it. These updates will be found
on your wireless vendor’s website. There are three types of WPA security:
WPA-PSK (no server),WPA (with radius server), and WPA2.
WPA-PSK (no server) uses what is known as a pre-shared key as the
network key. A network key is a password that is between eight and
63 characters long. It can be a combination of letters, numbers, or
characters. Each client uses the same network key to access the network.
Typically, this is the mode that will be used in a home environment.
WPA (with radius server) works best in a business environment,
in which a radius server automatically distributes the network
key to clients.
WPA2 requires Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for
encryption of data, which offers much greater security than
WPA. WPA uses both Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
and AES for encryption.
Setting up your Belkin Wireless Router (or Access Point)
to use Security
To start using security, you need to first enable WEP or WPA for
your wireless router (or access point). For Belkin Wireless Routers
(or Access Points), these security features can be configured by using
the web-based interface. See your wireless router’s (or access point’s)
manual for directions on how to access the management interface.
IMPORTANT: You must now set all wireless network cards/adapters
to match these settings.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
21
Page 24
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2322
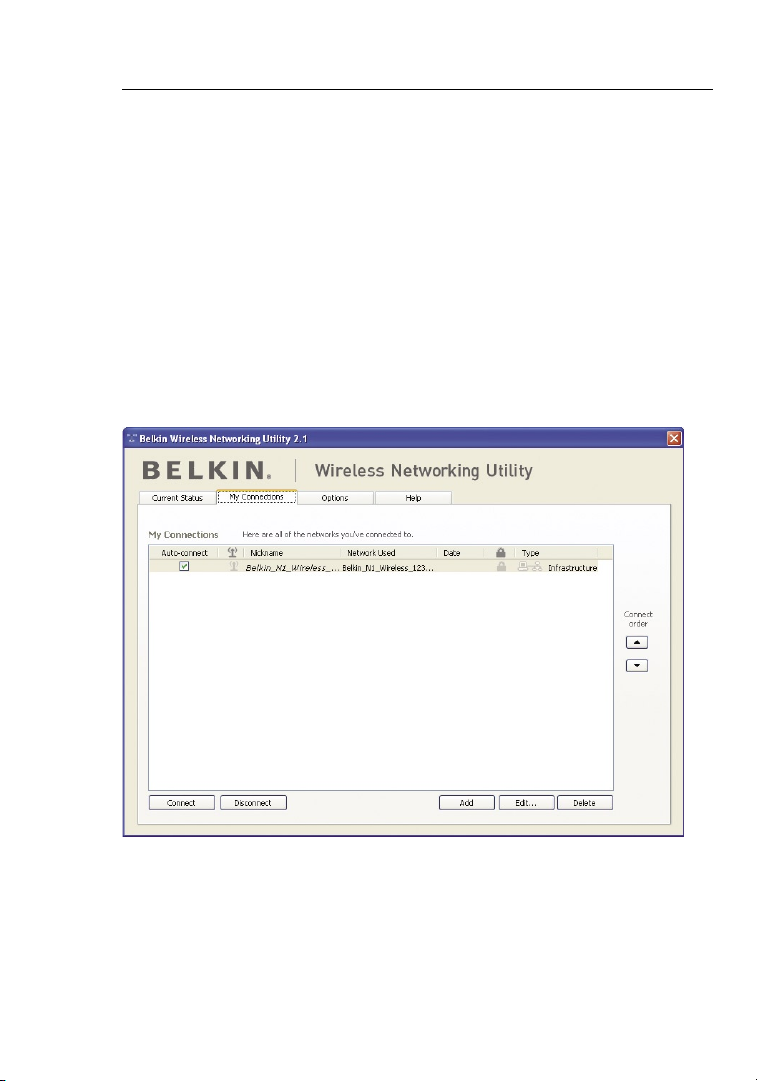
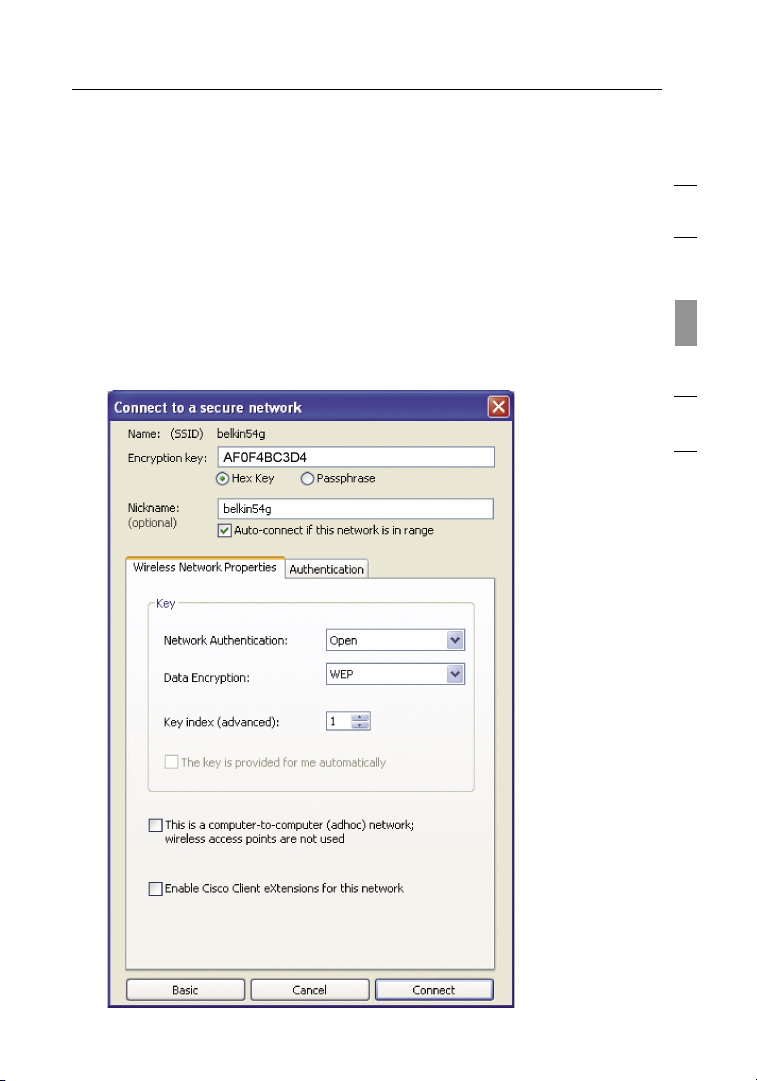
Configuring your Card to use Security
At this point, you should already have your wireless router (or access
point) set to use WPA or WEP. In order for you to gain wireless
connection, you will need to set your N1 Wireless Desktop Card to
use the same security settings.
Changing the Wireless Security Settings
The Belkin N1 Wireless Desktop Card supports the latest WPA security
feature as well as the legacy WEP security standard. By default, wireless
security is disabled.
To enable security, you will first need to determine which standard is
used by the router (or access point). (See your wireless router’s or access
point’s manual for directions on how to access the security settings.)
To access the security settings on your Card, click the “My
Connections” tab and point to the connection for which you want
to change security settings. Click “Edit” to change settings.
Page 25
23
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
WEP Setup
64-Bit WEP Encryption
1. Select “WEP” from the “Data Encryption” drop-down menu.
2. After selecting your WEP encryption mode, you can enter your key
by typing in the hex key manually.
A hex (hexadecimal) key is a combination of numbers and letters
from A–F and 0–9. For 64-bit WEP, you need to enter 10 hex keys.
For instance:
0F 4B C3 D4 = 64-bit WEP key
AF
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
23
Page 26

Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2524
3. Click “Save” to finish. Encryption in the wireless router
(or access point) is now set. Each of your computers on your
wireless network will now need to be configured with the same
security settings.
WARNING: If you are using a wireless client to turn on the security
settings in your wireless router (or access point), you will temporarily
lose your wireless connection until you activate security on your
wireless client. Please record the key prior to applying changes in the
wireless router (or access point). If you don’t remember the hex key,
your client will be locked out of the wireless router (or access point).
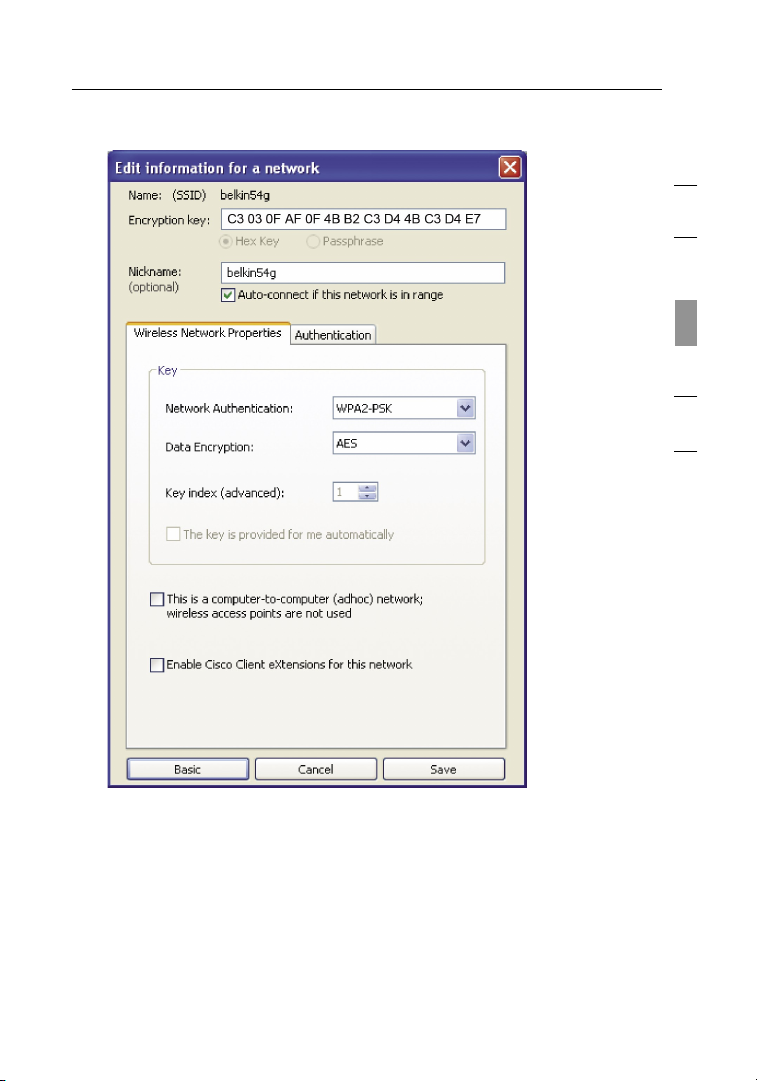
128-Bit WEP Encryption
Select “WEP” from the drop-down menu.
1.
2. After selecting your WEP encryption mode, you can enter your
key by typing in the hex key manually. A hex (hexadecimal) key
is a combination of numbers and letters from A–F and 0–9. For
128-bit WEP, you need to enter 26 hex keys
For instance:
C3
03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = 128-bit WEP key
.
Page 27
25
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
3. Click “Save” to finish. Encryption in the wireless router (or access
point) is now set. Each of the computers on your wireless network
will now need to be configured with the same security settings.
WARNING: If you are using a wireless client to turn on the security
settings in your wireless router (or access point), you will temporarily
lose your wireless connection until you activate security on your
wireless client. Please record the key prior to applying changes in the
wireless router (or access point). If you don’t remember the hex key,
your client will be locked out of the wireless router (or access point).
25
Page 28
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2726
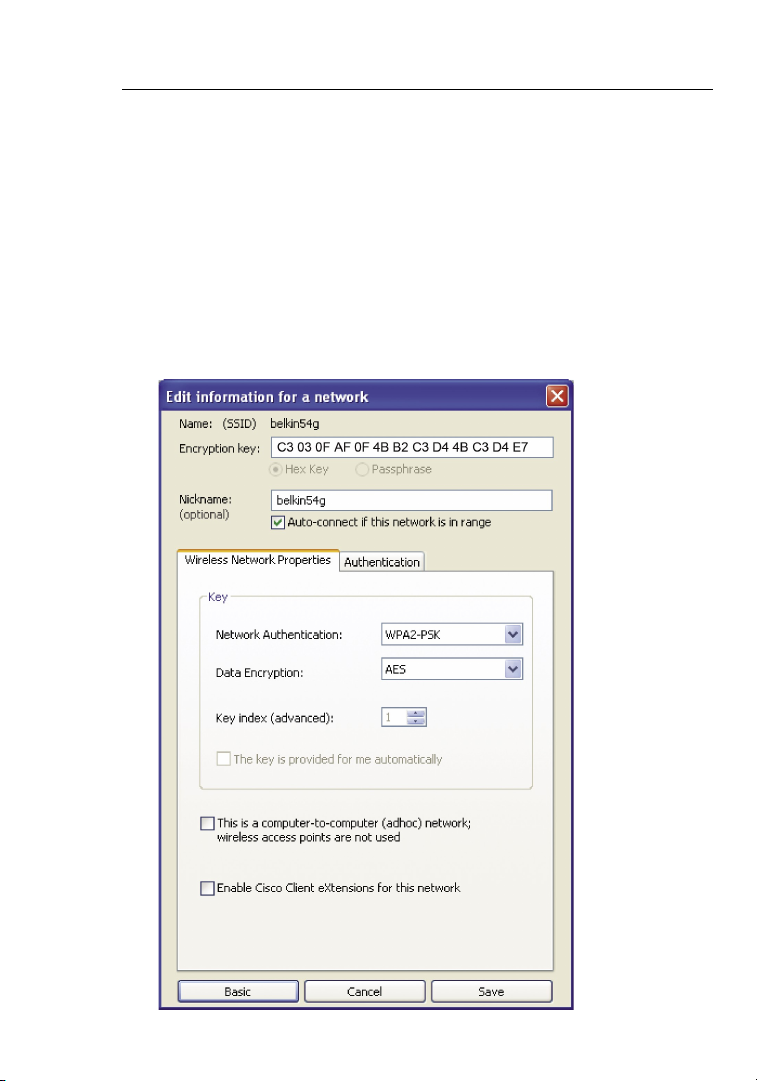
WPA-PSK (no server)
Choose this setting if your network does not use a radius server. WPA-PSK
(no server) is typically used in home and small office networking.
1. From the “Network Authentication” drop-down menu, select
“WPA-PSK (no server)”.
2. Enter your network key. This can be from eight to 63 characters
and can be letters, numbers, or symbols. This same key must be
used on all of the clients (network cards) that you want to include
in your wireless network.
Page 29
27
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
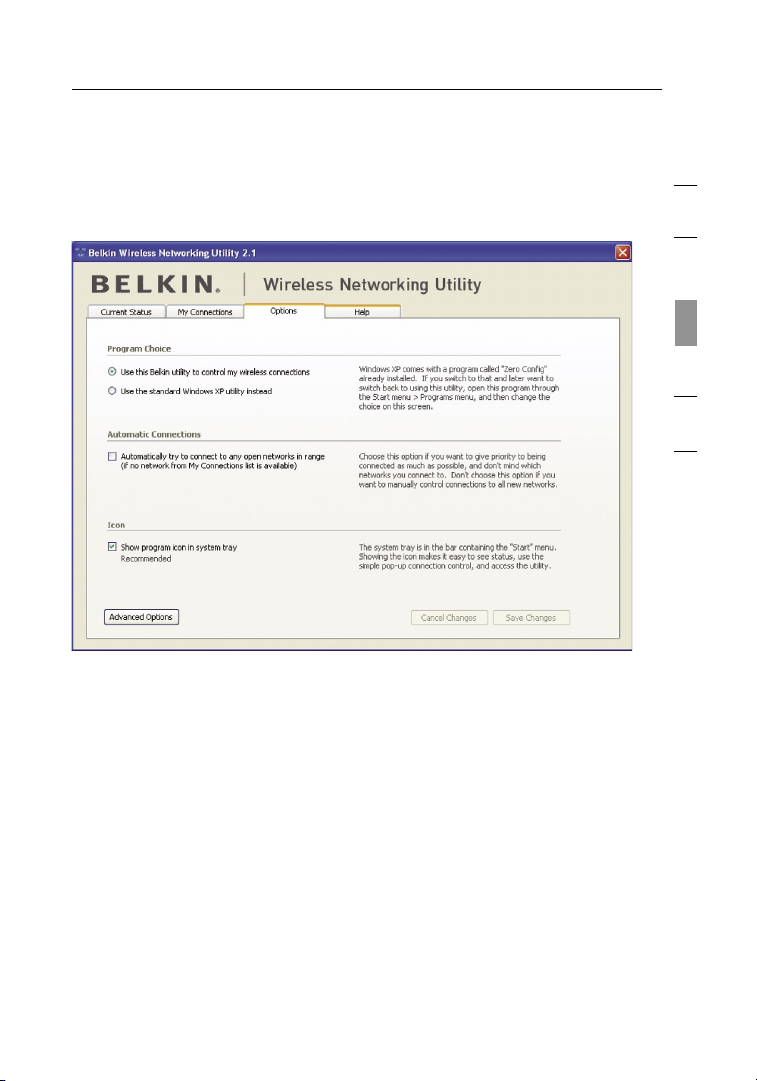
3. Click “Save” to finish. You must now set all clients (network
cards) to match these settings.
Wireless Networking Utility Options
The “Options” tab on the WNU provides the user the ability
to customize his or her WNU settings
.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
27
Page 30
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
2928
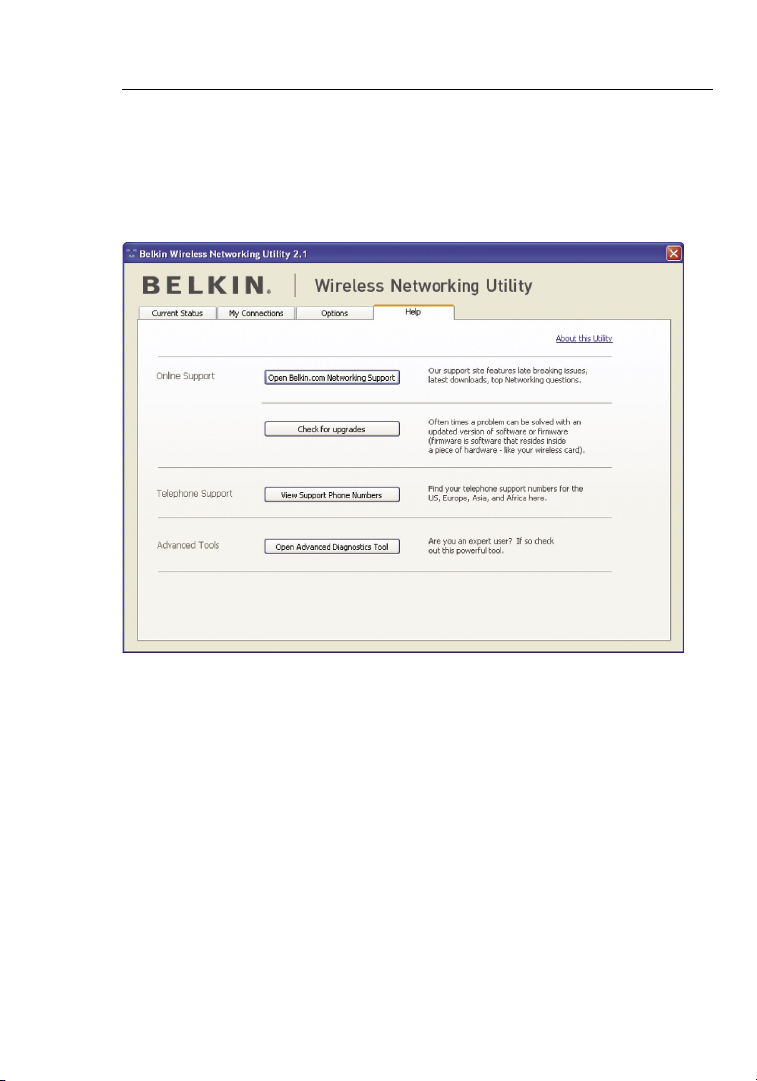
Wireless Networking Utility Help
The WNU “Help” tab provides users with access to online and
telephone support, a one-click check for software updates, and
advanced diagnostic tools.
Page 31

29
Using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
The “Advanced Diagnostic Tools” section is the central control panel
for all the settings of the hardware and software components of
the wireless network. It provides an array of tests and connectivity
services to ensure optimal network performance.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
29
Page 32

Troubleshooting
3130
I can’t connect to the Internet wirelessly.
If you are unable to connect to the Internet from a wireless computer,
please check the following items:
1. Look at the lights on your wireless router. If you’re using a Belkin
Wireless Router, the lights should be as follows:
• The “Power” light should be on.
• The “Connected” light should be on, and not blinking.
• The “WAN” light should be either on or blinking.
If your Belkin Wireless Router’s lights have the above characteristics,
go to number
If this is
• The router’s power cord is plugged in.
• All cables are connected between the router and the modem.
• All the modem’s LEDs are functioning correctly. If not,
see your modem’s user manual.
• Reboot the router.
• Reboot the modem.
If you continue to have issues, please contact Belkin Technical Support.
If you are not using a Belkin Wireless Router, consult that router
manufacturer’s user guide.
2. Open your wireless utility software by clicking on the icon in the
system tray at the bottom right-hand corner of the screen. If you’re
using a Belkin Wireless Card, the tray icon should look like this
(the icon may be red or green):
2 below.
NOT the case, make sure:
3. The exact window that opens will vary depending on the model of
wireless card you have; however, any of the utilities should have a list
of “Available Networks”.
Available networks are wireless networks to which you can connect.
If you are using a Belkin 802.11g (G Plus) Router, or Belkin 802.11g
(54g) Router, “Belkin54g” is the default name.
If you are using a Belkin 802.11b Router, the default name should
be “WLAN”.
If you are NOT using a Belkin Router, please consult your router
manufacturer’s user manual for the default name.
Page 33

31
Troubleshooting
The name of your wireless network appears in
“Available Networks”.
If the correct network name is listed in the “Available Networks”
list, please follow the steps below to connect wirelessly:
1. Click on the correct network name in the “Available Networks” list.
2. If the network has security (encryption) enabled, you will
need to enter the network key. Click “Connect”. For more
information regarding security, see the page entitled: “Securing
your Wi-Fi Network” on page 17 of this User Manual.
3. Within a few seconds, the tray icon in the lower right-hand
corner of your screen should turn green, indicating a successful
connection to the network.
If you are still unable to access the Internet after connecting to
the wireless network, please contact Belkin Technical Support.
The name of your wireless network DOES NOT appear
in the list of “Available Networks”.
If the correct network name is not listed, check the SSID settings
to see if they match. The SSID is case-sensitive and the spelling
on each computer must be exactly the same in order for the Card
to connect to the wireless router (or access point).
Note: To check the SSID settings or look for an available
network, double-click the Signal Indicator icon to bring up the
“Wireless Networks” screen. Click “Add” if you do not see the
network you are trying to connect to and type in the SSID. For
more information about setting up an SSID, please reference
your router manufacturer’s user manual.
If issues persist even at close range, please contact Belkin
Technical Support.
1
2
3
4
sectio n
5
6
31
Page 34

3332
Troubleshooting
Installation CD-ROM does not start
Belkin Wireless Networking Utility.
If the CD-ROM does not start the Belkin Wireless Networking
Utility automatically, it could be that the computer is running
other applications that are interfering with the CD drive. If the
Belkin Wireless Networking Utility screen does not appear within
15-20 seconds, open up your CD-ROM drive by double-clicking
on the “My Computer” icon. Next, double-click on the CD-ROM
drive that the Installation CD has been placed in to start the
installation. Then double-click on the folder named “Files”.
Next, double-click on the icon named “setup.exe”.
Power LED does not come ON; Card is not working.
If the LED indicators are not ON, the problem may be that the
Card is not connected or installed properly. Verify that the Card is
plugged firmly into the CardBus slot of your computer. Check to
see that the drivers for the Card have been installed. Right-click
on the “My Computer” icon on your desktop. Choose “Properties”
and navigate to the “Device Manager” and see if your CardBus
Card is listed without any errors. If an error is indicated, contact
Belkin Technical Support.
Link LED is blinking slowly; I cannot connect
to a wireless network or the Internet.
If your Card appears to be functioning properly, but you cannot
connect to a network or you have a red wireless icon at the
bottom of your screen, the problem may be that there is a
mismatch between the network name (SSID) settings in your
wireless network properties.
Check the SSID settings to see if they match. The SSID is
case-sensitive and the spelling on each computer must be
exactly the same in order for the Card to connect to the
wireless router (or access point).
Note:
To check the SSID settings or look for an available
network, double-click the Signal Indicator icon to bring up the
“Wireless Networks” screen. Click “Add” if you do not see the
network you are trying to connect to and type in the SSID.
For more information about setting up an SSID, please
reference your router manufacturer’s user manual.
If issues persist even at close range, please contact Belkin
Technical Support.
Page 35

33
Troubleshooting
Link LED is solid but I cannot connect to the Internet.
If you have a signal but can’t get online or obtain an IP address,
the problem may be that there is a mismatch between the
encryption key settings in your computer and wireless router (or
access point). Check the WEP, WPA, or WPA2 key settings to see
if they match. The key is case-sensitive and the spelling on each
computer and wireless router (or access point) must be exactly
the same in order for the Card to connect to the router. For more
information about encryption, please see “Securing your Wi-Fi
Network” on page 17 of this User Manual.
If issues persist even at close range, please contact Belkin
Technical Support.
Data transfer is sometimes slow.
Wireless technology is radio-based, which means connectivity
and the throughput performance between devices decreases
when the distance between devices increases. Other factors that
will cause signal degradation (metal is generally the worst culprit)
are obstructions such as walls and metal appliances. As a result,
the typical indoor range of your wireless devices will be between
100 to 200 feet. Note also that connection speed may decrease
as you move farther from the wireless router (or access point).
In order to determine if wireless issues are related to range, we
suggest temporarily moving the computer, if possible, to five to
10 feet away from the wireless router (or access point). Please
see the section titled “Placement of your Wireless Networking
Hardware for Optimal Performance” on page 2 of this User
Manual. If issues persist even at close range, please contact
Belkin Technical Support.
1
2
3
4
sectio n
5
6
Signal strength is poor.
Wireless technology is radio-based, which means connectivity
and the throughput performance between devices decreases
when the distance between devices increases. Other factors that
will cause signal degradation (metal is generally the worst culprit)
are obstructions such as walls and metal appliances. As a result,
the typical indoor range of your wireless devices will be between
100 to 200 feet. Note also that connection speed may decrease
as you move farther from the wireless router (or access point).
In order to determine if wireless issues are related to range, we
suggest temporarily moving the computer, if possible, to five to
10 feet away from wireless router (or access point).
33
Page 36

3534
Troubleshooting
Changing the wireless channel – Depending on local wireless
traffic and interference, switching the wireless channel of your
network can improve performance and reliability. The default
channel the router is shipped with is channel 6. You may choose
from several other channels depending on your region; see your
router’s (or access point’s) user manual for instructions on how
to choose other channels.
Limiting the wireless transmit rate – Limiting the wireless
transmit rate can help improve the maximum wireless range, and
connection stability. Most wireless cards have the ability to limit
the transmission rate. To change this property, go to the Windows
Control Panel, open “Network Connections” and double-click
on your Card’s connection. In the “Properties” dialog, select the
“Configure” button on the “General” tab (Windows 98 users will
have to select the Wireless Card in the list box and then click
“Properties”), then choose the “Advanced” tab and select the rate
property. Wireless client cards are usually set to automatically
adjust the wireless transmit rate for you, but doing so can cause
periodic disconnects when the wireless signal is too weak; as a
rule, slower transmission rates are more stable. Experiment with
different connection rates until you find the best one for your
environment; note that all available transmission rates should
be acceptable for browsing the Internet. For more assistance,
see your wireless card’s literature. If issues persist even at close
range, please contact Belkin Technical Support.
Why are there two wireless utilities in my system tray?
Which one do I use?
There are several features and advantages from using the Belkin
Wireless Networking Utility over the Windows XP Wireless
Zero Configuration utility. We offer a site survey, detailed link
information, and adapter diagnosis, to name a few.
It’s essential to know which utility is managing your Card. We
recommend using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility. To use
the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility, follow the steps below:
Step 1 Right-click on the network status icon in the system tray
and select the “Status” tab.
Step 2 From the “Status” tab, uncheck the “Use Windows to
configure my wireless network settings” box. Once the box
is unchecked, click the “Close” button to close the window.
You are now using the Belkin Wireless Networking Utility
to configure the Card.
Page 37

35
Troubleshooting
Card does not perform or connection is unstable when
computer has a second built-in wireless network card
®
(such as a mini PCI or Intel
This condition occurs if your computer has a built-in wireless
card while your Belkin Wireless Card is also active. This
happens because Windows must now handle two active
wireless connections.
You need to disable the built-in wireless card from your computer
under “Network Adapters” in the Device Manager.
Centrino™).
Card does not perform or connection is slow when
computer has a built-in wired Ethernet card.
This condition occurs if your computer has an active Ethernet
card while your Wireless Card is also active. This happens
because Windows must now handle two active network
connections. You need to disable the Ethernet card from your
computer under “Network Adapters” in the Device Manager.
What’s the difference between 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11a,
and draft 802.11n?
Currently there are four levels of wireless networking standards,
which transmit data at very different maximum speeds. Each is
based on the designation for certifying network standards. The
most common wireless networking standard, 802.11b, transmits
information at 11Mbps; 802.11a and 802.11g work at 54Mbps;
and draft 802.11n works at 108Mbps. See the chart on the next
page for more detailed information.
1
2
3
4
sectio n
5
6
35
Page 38

3736
Troubleshooting
Wireless Comparison Chart
Wireless
Technology
802.11b
G
(draft 802.11n
(802.11g with
(802.11g)
G Plus
(802.11g with
HSM)
MIMO MRC)
G Plus MIMO
with MIMO)
N1 MIMO
11Mbps link
rate/baseline
Speed*
Common
household
devices such
as cordless
phones and
microwave
ovens may
Frequency
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2.4GHz
Compatible
with 802.11g
Compatibility
Typically
100–200 ft.
indoors
Coverage*
Mature—legacy
technology
Advantage
*Di stance and connect ion s pee ds wi ll va ry de pending on your network ing e nviron ment.
**T his C ard is compat ible with pro duc ts based on the s ame v ersion of the draft
802 .11n specificati ons a nd ma y require a software upgrade for best results.
5x faster than
802.11b*
Common
household
devices such
as cordless
phones and
microwave
ovens may
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2.4GHz
Compatible
with 802.11b/g
Up to 400 ft.* Up to 700 ft.* Up to 1,000 ft.* Up to 1,400 ft.*
Common—
widespread
use for Inter net
sharing
10x faster
than 802.11b*
Common
household
devices such
as cordless
phones and
microwave
ovens may
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2.4GHz
Compatible
with 802.11b/g
Enhanced
speed and
coverage
10x faster than
802.11b*
Common
household
devices such
as cordless
phones and
microwave
ovens may
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2.4GHz
Compatible
with 802.11b/g
Better coverage
and consistent
speed at range
Wired speed
over the air*
Common
household
devices such
as cordless
phones and
microwave
ovens may
interfere with
the unlicensed
band 2.4GHz
Compatible
with draft
802.11n** and
802.11b/g
Leading
edge— best
coverage and
throughput
Page 39

37
Troubleshooting
Technical Support
You can find technical support information at
www.belkin.com/networking. If you want to contact
technical support by phone, please call:
US: 877-736-5771
Europe: 00 800 223 55 460
Australia: 1800 235 546
New Zealand: 0800 235 546
Singapore: 800 616 1790
1
2
3
4
sectio n
5
6
37
Page 40

Information
3938
Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class
B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions,
may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is
no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged
to try to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the distance between the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject
to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful
interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the
party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate
this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an
uncontrolled environment. This equipment should be installed and operated
with a minimum distance of 20cm between the radiator and your body.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction
with any other antenna or transmitter.
Belkin declares that F5D8001 (FCC ID: K7SF5D8001) is limited in
CH1~CH11 for 2.4GHz by specified firmware controlled in the U.S.A.
Page 41

39
Information
Belkin Corporation Limited Lifetime Product Warranty
What this warranty covers.
Belkin Corporation warrants to the original purchaser of this Belkin product
that the product shall be free of defects in design, assembly, material,
or workmanship.
What the period of coverage is.
Belkin Corporation warrants the Belkin product for the lifetime of the product.
What will we do to correct problems?
Product Warranty.
Belkin will repair or replace, at its option, any defective product free of charge
(except for shipping charges for the product).
What is not covered by this warranty?
All above warranties are null and void if the Belkin product is not provided to
Belkin Corporation for inspection upon Belkin’s request at the sole expense
of the purchaser, or if Belkin Corporation determines that the Belkin product
has been improperly installed, altered in any way, or tampered with. The
Belkin Product Warranty does not protect against acts of God (other than
lightning) such as flood, earthquake, war, vandalism, theft, normal-use wear
and tear, erosion, depletion, obsolescence, abuse, damage due to low
voltage disturbances (i.e. brownouts or sags), non-authorized program,
or system equipment modification or alteration.
How to get service.
To get service for your Belkin product you must take the following steps:
1. Contact Belkin Corporation at 501 W. Walnut St., Compton CA 90220,
Attn: Customer Service, or call (800)-223-5546, within 15 days of the
Occurrence. Be prepared to provide the following information:
a. The part number of the Belkin product.
b. Where you purchased the product.
c. When you purchased the product.
d. Copy of original receipt.
2. Your Belkin Customer Service Representative will then instruct you on
how to forward your receipt and Belkin product and how to proceed
with your claim.
1
2
3
4
5
sectio n
6
39
Page 42

Information
4140
Belkin Corporation reserves the right to review the damaged Belkin product.
All costs of shipping the Belkin product to Belkin Corporation for inspection
shall be borne solely by the purchaser. If Belkin determines, in its sole
discretion, that it is impractical to ship the damaged equipment to Belkin
Corporation, Belkin may designate, in its sole discretion, an equipment repair
facility to inspect and estimate the cost to repair such equipment. The cost,
if any, of shipping the equipment to and from such repair facility and of such
estimate shall be borne solely by the purchaser. Damaged equipment must
remain available for inspection until the claim is finalized. Whenever claims
are settled, Belkin Corporation reserves the right to be subrogated under
any existing insurance policies the purchaser may have.
How state law relates to the warranty.
THIS WARRANTY CONTAINS THE SOLE WARRANTY OF BELKIN
CORPORATION, THERE ARE NO OTHER WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED
OR, EXCEPT AS REQUIRED BY LAW, IMPLIED, INCLUDING THE IMPLIED
WARRANTY OR CONDITION OF QUALITY, MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS
FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE, AND SUCH IMPLIED WARRANTIES, IF ANY,
ARE LIMITED IN DURATION TO THE TERM OF THIS WARRANTY.
Some states do not allow limitations on how long an implied warranty lasts,
so the above limitations may not apply to you.
IN NO EVENT SHALL BELKIN CORPORATION BE LIABLE FOR INCIDENTAL,
SPECIAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL OR MULTIPLE DAMAGES
SUCH AS, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, LOST BUSINESS OR PROFITS ARISING
OUT OF THE SALE OR USE OF ANY BELKIN PRODUCT, EVEN IF ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
This warranty gives you specific legal rights, and you may also have other
rights, which may vary from state to state. Some states do not allow the
exclusion or limitation of incidental, consequential, or other damages,
so the above limitations may not apply to you.
Page 43

41
Information
1
2
3
4
5
sectio n
6
41
Page 44

Table des matières
1 Introduction. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Avantages d’un réseau domestique . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Avantages d’un réseau sans fil. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Choix d’un emplacement permettant d’obtenir
un rendement optimal de votre matériel réseau sans fil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Vue d’ensemble . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Caractéristiques du produit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Applications et avantages. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Caractéristiques du produit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Configuration requise. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contenu de l’emballage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Installation et configuration de la carte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Étape 1 : Installez. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Étape 2 : Insérez . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Étape 3 : Terminez . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Étape 4 : Configurez . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Accès à l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil (WNU)
à partir de la barre d’état système Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
« Network Status » (État du réseau) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
« Available Networks » (Réseaux disponibles) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
État du réseau et pistes de solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Définition de profils de réseau sans fil . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Sécurisation de votre réseau Wi-Fi. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Configuration de votre carte avec fonctions de sécurité . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Dépannage
6 Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
11
13
17
22
38
1
1
2
5
6
6
7
7
8
Page 45

Introduction
Merci d’avoir choisi la carte N1 sans fil pour ordinateur de bureau de
Belkin. Vous pouvez maintenant profiter de cette nouvelle technologie
exceptionnelle et avoir toute la liberté voulue pour raccorder en réseau
sans fil vos ordinateurs au bureau ou à la maison. Cette carte vous
permet de raccorder un ordinateur de bureau à votre réseau. Veuillez lire
au complet le présent guide d’utilisation, en insistant particulièrement
sur la section intitulée « Choix d’un emplacement permettant d’obtenir
un rendement optimal de votre matériel réseau sans fil ».
Avantages d’un réseau domestique
Votre réseau domestique Belkin vous permettra de faire ce qui suit :
• Partager une connexion Internet haute vitesse avec tous vos
ordinateurs à la maison
• Partager des ressources telles que fichiers et disques durs avec
tous les ordinateurs raccordés à votre réseau domestique
• Partager une même imprimante avec tous les membres de la famille
• Partager des documents, des fichiers musicaux et vidéo et des
photos numériques
• Stocker, récupérer et copier des fichiers d’un ordinateur à l’autre
• Jouer simultanément à des jeux en ligne, vérifier votre courrier
électronique et bavarder
Avantages d’un réseau sans fil
Voici quelques-uns des avantages que procure l’établissement
d’un réseau sans fil Belkin :
• Mobilité – Vous n’aurez plus besoin d’une « salle d’ordinateur
dédiée »—Vous pourrez utiliser un ordinateur portatif ou de
bureau raccordé en réseau n’importe où à l’intérieur de la zone
de couverture sans fil
• Installation facile – L’Assistant d’installation Belkin simplifie
la configuration
• Souplesse – Configurez et utilisez vos imprimantes, ordinateurs
et autres périphériques réseau n’importe où à la maison
• Expansion facile – Le vaste choix de produits réseau Belkin vous
permet d’étendre votre réseau pour y ajouter des périphériques
tels que consoles de jeu et imprimantes
• Aucun câble nécessaire – Vous pouvez vous éviter
l’embêtement et les dépenses qu’entraîne la mise à niveau
du câblage Ether net au bureau ou à la maison
• Largement accepté dans l’industrie – Choisissez parmi
une vaste gamme de produits réseau compatibles
1
sectio n
1
2
3
4
5
6
Page 46

Introduction
32
Choix d’un emplacement permettant d’obtenir un rendement
optimal de votre matériel réseau sans fil
Plus votre ordinateur sera situé près du routeur ou du point d’accès
sans fil, plus votre connexion sera puissante. Le rayon d’action
de vos périphériques sans fil dans un environnement intérieur
varie habituellement entre 100 et 200 pieds. De la même façon, la
performance de votre connexion sans fil diminuera quelque peu à
mesure que la distance entre le routeur (ou le point d’accès) sans
fil augmentera. Il se pourrait cependant que vous ne remarquiez
aucune différence. Plus vous vous éloignerez du routeur (ou du point
d’accès) sans fil, plus la vitesse de connexion diminuera. Les facteurs
qui peuvent contribuer à affaiblir les signaux simplement en gênant
la circulation des ondes radioélectriques sur votre réseau sont la
présence de murs, d’obstacles ou d’appareils métalliques.
Si vous croyez que la performance de votre réseau peut être atténuée
par des facteurs ayant trait à la portée ou à des obstacles, placez
l’ordinateur à une distance de cinq à dix pieds du routeur ou du point
d’accès sans fil pour voir si la distance est la cause du problème. Si
le problème persiste même à distance rapprochée, veuillez contacter
le Soutien technique Belkin.
Remarque : Bien que certains des facteurs indiqués ci-dessous
puissent atténuer la performance de votre réseau sans fil, cela ne
devrait pas l’empêcher de fonctionner. Si le fait que votre réseau ne
fonctionne pas de façon optimale vous préoccupe, reportez-vous à la
liste de contrôle ci-dessous pour essayer de trouver une solution.
1. Choix d’un emplacement pour votre routeur (ou point
d’accès) sans fil
Placez votre routeur ou votre point d’accès (qui constitue le point
de connexion central de votre réseau) le plus près possible de vos
périphériques réseau sans fil.
Pour obtenir la meilleure portée de réseau possible pour vos « clients
sans fil » (c.-à-d. ordinateurs avec carte sans fil pour ordinateur de
bureau ou portatif, et adaptateurs USB Belkin), faites ce qui suit :
• Assurez-vous que les antennes de votre routeur ou de votre point
d’accès sans fil sont parallèles l’une à l’autre, et qu’elles sont en
position verticale (pointant vers le plafond). Si votre périphérique
sans fil est installé à la verticale, orientez les antennes le plus
possible vers le haut.
• Dans les maisons à plusieurs étages, installez-le sur celui situé le plus
près possible du centre de la maison, c’est-à-dire l’étage supérieur.
• Évitez de placer le routeur ou le point d’accès sans fil près
d’un téléphone sans fil 2,4 GHz.
Page 47

3
Introduction
2. Évitez les obstacles et les interférences
Évitez de placer le routeur ou le point d’accès sans fil près de
périphériques pouvant émettre des bruits radioélectriques, comme les
fours à micro-ondes. Voici une liste de quelques objets qui peuvent
gêner les communications sans fil :
• Réfrigérateurs
• Laveuses et/ou sécheuses
• Armoires métalliques
• Gros aquariums
• Fenêtres teintées à filtre UV et cadrage métallique
Si le signal semble faible à certains endroits, assurez-vous que de
tels objets ne se trouvent pas sur son parcours, c’est-à-dire entre vos
ordinateurs et votre routeur ou point d’accès sans fil.
3. Choix d’un emplacement pour votre téléphone sans fil
Si la performance de votre réseau sans fil continue d’être affaiblie
même après avoir suivi les conseils ci-dessus, et que vous avez un
téléphone sans fil :
• Éloignez le téléphone sans fil du routeur (ou point d’accès)
et de vos ordinateurs avec fonctionnalité sans fil.
• Débranchez le téléphone fonctionnant dans la bande 2,4
GHz et enlevez la pile (voir le manuel du fabricant). Si le
problème est résolu, c’est que votre téléphone provoquait
probablement des interférences.
• Si votre téléphone permet la sélection de canal, réglez-le
sur le canal le plus loin possible de votre réseau sans fil.
Par exemple, réglez le téléphone sur le canal 1 et le routeur
ou le point d’accès sans fil sur le canal 11. (Votre choix de
canal variera selon votre région.) Pour des instructions plus
détaillées, consultez le guide d’utilisation de votre téléphone.
• Si nécessaire, envisagez l’achat d’un téléphone sans fil
de 900 MHz ou 5 GHz.
4. Sélectionnez le canal le moins « achalandé »
pour votre réseau sans fil
Dans les quartiers où les maisons ou les bureaux sont rapprochés les
uns des autres, comme dans les immeubles d’appartements ou les
grands ensembles à usage de bureaux, il se pourrait qu’il y ait des
réseaux sans fil à proximité qui entrent en conflit avec le vôtre.
Utilisez la fonction « surveillance de site » de votre utilitaire pour
réseau sans fil Belkin pour détecter la présence d’autres réseaux sans
sectio n
1
2
3
4
5
6
3
Page 48

Introduction
fil, et réglez votre routeur (ou point d’accès) et vos ordinateurs sur le
canal le plus éloigné possible des autres réseaux.
Faites l’essai des différents canaux disponibles de façon à trouver
la connexion la plus nette et éviter les interférences attribuables aux
téléphones ou autres périphériques sans fil situés à proximité.
Pour de plus amples renseignements sur les autres produits réseau sans
fil Belkin, consultez la section de votre guide d’utilisation portant sur la
surveillance de site et les canaux sans fil.
5. Connexions sécurisées, RPV et AOL
Les connexions sécurisées nécessitent généralement l’entrée d’un
code d’utilisateur et d’un mot de passe, et elles sont utilisées pour les
applications où la sécurité revêt une importance particulière. Parmi les
connexions sécurisées, notons :
• Connexions de réseau privé virtuel (RPV), souvent utilisées pour
se connecter à distance au réseau d’une entreprise
• Programme « Bring Your Own Access » d’America Online (AOL) qui
vous permet d’utiliser son service au moyen d’une connexion large
bande d’un autre fournisseur (câble ou DSL)
• La plupart des sites Web permettant les transactions bancaires en ligne
• Nombreux sites Web commerciaux exigeant de l’utilisateur l’entrée d’un
code et d’un mot de passe pour accéder à son compte personnel
Les connexions sécurisées peuvent être interrompues au moyen d’un
réglage de gestion de l’alimentation de l’ordinateur, ce qui entraîne son
passage au « mode sommeil ». La solution la plus simple pour éviter ce
genre de situation consiste à se reconnecter en exécutant à nouveau le
logiciel RPV ou AOL, ou à se reconnecter au site Web sécurisé.
Une deuxième solution consiste à modifier les réglages de gestion
d’alimentation de votre ordinateur pour qu’il ne passe plus au mode
sommeil. Cependant, il se pourrait que cette solution ne convienne
pas aux ordinateurs portatifs. Pour modifier votre paramètre de gestion
d’alimentation dans Windows, reportez-vous aux « options d’alimentation »
du panneau de configuration.
Si vous continuez d’éprouver des difficultés avec les connexions
sécurisées, les RVP et AOL, revoyez les étapes 1 à 4 des pages
précédentes pour vous assurer que vous avez suivi toutes les consignes.
En respectant ces consignes, vous devriez être en mesure d’obtenir une zone
de couverture optimale de votre routeur sans fil. Toutefois, si vous désirez
obtenir une zone encore plus étendue, nous vous suggérons de vous procurer
un module prolongateur de portée de réseau sans fil/point d’accès Belkin.
Pour de plus amples renseignements sur les produits réseau Belkin, visitez
notre site Web à l’adresse www.belkin.com/networking, ou appelez le
Soutien technique Belkin.
Page 49

Vue d’ensemble
Caractéristiques du produit
La carte est conforme à la norme IEEE 802.11n préliminaire qui
permet de communiquer avec d’autres périphériques sans fil
répondant aussi à la norme 802.11n préliminaire à un débit pouvant
atteindre jusqu’à 300 Mbit/s*. Elle est aussi compatible avec les
périphériques 802.11g fonctionnant à un débit de 54 Mbit/s, ainsi
qu’avec les produits 802.11b fonctionnant à 11 Mbit/s. La carte
fonctionne dans la même bande de fréquences de 2,4 GHz que les
produits Wi-Fi® répondant aux normes 802.11b/g.
• Fonctionnement sur la bande ISM (industrielle, scientifique
et médicale) 2,4 GHz
• Utilitaire pour réseau sans fil convivial intégré Belkin
• Interface PCI permettant le fonctionnement sur pratiquement
n’importe quel ordinateur de bureau
• WPA, WPA2, cryptage WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
64 ou 128 bits
• Accès sans fil aux ressources réseau
• Transmission de données jusqu’à 300 Mbit/s* (norme 802.11n
préliminaire), 54 Mbit/s (802.11g) ou 11 Mbit/s (802.11b)
• Facile à installer et à utiliser
• Indicateurs d’alimentation et d’activité
1
1
sectio n
2
3
4
5
6
5
Page 50

76
Vue d’ensemble
Applications et avantages
• Connexions à des débits pouvant atteindre jusqu’à 300 Mbit/s*
Assure une connectivité sans fil immédiate à haut débit au
bureau, à la maison et dans tout autre point d’accès public,
sans empêcher l’utilisation des produits 802.11b/g existants.
• Compatibilité avec les produits 802.11b/g
Le carte est rétrocompatible avec les produits Wi-Fi
(IEEE 802.11b/g) existants
• Environnements difficiles à câbler
Permet le raccordement en réseau dans les immeubles dont les murs
sont finis ou solides, ou dans les aires ouvertes difficiles à câbler
• Environnements évolutifs
S’adapte facilement aux bureaux ou aux environnements
qui changent fréquemment
• Réseaux pour travailleurs à domicile
Mise en place facile et rapide de petits réseaux domestiques
Caractéristiques du produit
Interface hôte : PCI 32 bits
Consommation de courant :
802.11b: TX 920mA @ 3.3V, RX 400mA @ 3.3V
802.11g: TX 1000mA @ 3.3V, RX 400mA @ 3.3V
802.11n: fonctionnement 20 MHz, TX 1000 mA
fonctionnement 40 MHz, TX 1070 mA
Température de fonctionnement:
Température d’entreposage:
Humidité: Max. 90 %, sans condensation
Rayon d’action habituel: Jusqu’à 1 400 pi (426,7 m)**
*REMARQUE
phy sique des données. Le débit réel sera moind re.
**L a per formance peut vari er selon l ’en vironnement réseau.
: Le débit de transm iss ion s tandard (300 Mbit/s) est le taux de transfert
@ 3,3 V, RX 400 mA @ 3,3 V
@ 3,3 V, RX 500 mA @ 3,3 V
32—131 degrees F (0—55 degrees C)
-4—176 degrees F (-20—80 degrees C)
Page 51

7
7
sectio n
1
2
3
4
5
6
Vue d’ensemble
(a) Voyant « Power/Activity » (Alimentation/Activité)
S’allume lorsque la carte est sous tension; clignote lorsqu’une
activité est détectée sur le réseau sans fil
(b) Connecteur de la carte
Côté de la carte qui s’imbrique dans l’emplacement PCI de votre ordinateur
(c) Connecteur d’antenne externe
Permet le raccordement au câble à partir de l’antenne externe
Configuration requise
• Ordinateur de bureau compatible PC avec
un emplacement PCI 32 bits libre
• 128 Mo ou plus de mémoire vive (RAM)
• Processeur 500 MHz ou plus puissant
• Windows
®
2000 ou XP
Contenu de l’emballage
• Carte N1 sans fil pour ordinateur de bureau
• Antenne externe avec câble
• Guide d’installation rapide
• CD contenant le programme d’installation
• Guide d’utilisation
(b)
(a)
(c)
Page 52

Étape 1 Installez
IMPORTANT
: Installez le logiciel avant d’insérer la carte.
1.1 Insérez le CD contenant le programme d’installation dans votre lecteur
de CD-ROM.
1.2 L’écran de l’utilitaire d’installation de carte sans fil Belkin apparaît
automatiquement. (Cela peut prendre de 15 à 20 secondes.) Cliquez
sur « Install Software » (Installer le logiciel) ou sur « Next » (Suivant)
pour commencer l’installation.
Remarque: S’il n’apparaît pas dans les 20 secondes qui suivent, double-
cliquez sur l’icône « My Computer » (Poste de travail) pour accéder à
votre lecteur de CD-ROM, puis double-cliquez sur le lecteur pour lancer
l’installation. Double-cliquez sur l’icône « Setup.exe ».exe”.
1.3 Le programme InstallShield Wizard
démarrera. Cliquez sur « Next »
(Suivant) pour continuer.
Installation et configuration de la carte
Page 53

Installation et configuration de la carte
1.4 Sélectionnez un dossier de
destination pour l’installation du
logiciel, ou cliquez simplement sur
« Next » (Suivant).
1.5 Vous verrez maintenant le premier
d’une série d’écrans indicateurs
d’état qui vous permettront de
savoir où en est rendu le processus
de configuration.
1.6 Il se pourrait qu’un écran semblable
à celui-ci apparaisse. Cela ne
signifie PAS qu’il y a un problème.
Notre logiciel a été testé à fond et
il est compatible avec ce système
d’exploitation. Cliquez sur «
Continue Anyway » (Continuer
quand même) et suivez les
instructions à l’écran.
1
2
sectio n
3
4
5
6
9
Page 54

Installation et configuration de la carte
Étape 2 Insérez
Insérez la carte dans votre ordinateur
2.1 Éteignez votre ordinateur et débranchez le cordon d’alimentation.
2.2 Enlevez les vis à l’arrière du boîtier qui maintiennent le couvercle
en place, puis retirez-le.
2.3 Touchez à n’importe quelle partie métallique du boîtier pour vous
décharger de toute électricité statique et éviter d’endommager
votre carte ou l’ordinateur.
2.4 Repérez un emplacement
d’extension PCI libre
(habituellement de couleur
blanche). Vérifiez que la carte
s’insérera facilement dans
l’emplacement choisi.
2.5 Retirez la languette à l’arrière
de l’ordinateur correspondant à
l’emplacement PCI que vous avez
choisi. S’il y a une vis, gardez-la
dans un endroit sûr car vous en
aurez besoin plus tard pour fixer
la carte à l’ordinateur.
2.6 Insérez la carte fermement dans
l’emplacement PCI voulu.
Page 55

Installation et configuration de la carte
2.7 Ensuite, fixez la carte à l’aide de la vis que vous avez mise de côté.
2.8 Remettez le couvercle. Branchez le câble d’antenne externe
sur le connecteur situé à l’arrière de la carte.
2.9 Maintenant que la carte est installée, vous pouvez rebrancher
le cordon d’alimentation et rallumer l’ordinateur.
Étape 3 Terminez
Terminez l’installation de la carte
3.1 L’assistant « Found New Hardware
Wizard » (Nouveau matériel
détecté) » apparaîtra. (Cela peut
prendre de 3 à 15 secondes.)
Sélectionnez « Yes, this time only
» (Oui, cette fois-ci seulement) et
cliquez sur « Next » (Suivant) pour
commencer l’installation.
3.2 Sélectionnez « Install the software
automatically » (Installez le logiciel
automatiquement) et cliquez
sur « Next » (Suivant) pour
commencer l’installation.
1
2
sectio n
3
4
5
6
11
Page 56

Installation et configuration de la carte
3.3 L’Assistant installera maintenant
le logiciel.
3.4 Il se pourrait qu’un écran
semblable à celui-ci apparaisse.
Cela ne signifie PAS qu’il y a un
problème. Notre logiciel a été
testé à fond et il est compatible
avec ce système d’exploitation.
Cliquez sur « Continue Anyway »
(Continuer quand même) et suivez
les instructions à l’écran.
3.5 L’installation est maintenant
terminée. Cliquez sur « Finish »
(Terminer) pour quitter.
Page 57

Installation et configuration de la carte
Étape 4 Configurez
Exécutez l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
4.1 Après avoir redémarré votre
ordinateur, double-cliquez sur l’icône
WNU (utilitaire réseau sans fil) Belkin
à l’écran.
4.2 L’écran de l’utilitaire apparaît.
4.3 Sélectionnez un réseau dans la liste
des réseaux disponibles et cliquez
sur « Connect » (Connecter) pour
vous y connecter.
Remarque
les réseaux disponibles, vous devez
être près d’un routeur ou d’un point
d’accès sans fil qui fonctionne.
: Pour pouvoir afficher
1
2
sectio n
3
4
5
6
4.4 L’icône de l’utilitaire pour réseau
sans fil Belkin apparaît également
dans la barre d’état système.
Remarque:
WNU dans la barre d’état système pour
afficher l’écran « Utility » (Utilitaire).
Ceci termine l’installation.
13
Double-cliquez sur l’icône
Page 58

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
Une fois que l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil (WNU) Belkin a été
installé, quelques clics suffiront pour effectuer la configuration
de la connexion sans fil et de la fonction de sécurité.
Accès à l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil (WNU)
à partir de la barre d’état système Windows
Pour accéder à l’utilitaire WNU, cliquez simplement sur l’icône
WNU dans de la barre d’état système Windows.
Si l’icône n’apparaît pas, cliquez successivement sur
« Start > Programs > Belkin > Belkin Wireless Utility »
(Démarrer > Programmes > Belkin > Utilitaire sans fil Belkin).
Page 59

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
L’écran WNU par défaut est l’onglet « Current Status » (État actuel). Cet
onglet affiche l’état actuel du réseau ainsi que les réseaux disponibles.
« Network Status » (État du réseau)
Cette fenêtre affiche l’état de la connexion du réseau actuel. Elle
indique même l’état de la connexion entre l’ordinateur et le routeur,
et entre le routeur et Internet. En cas de problème de connexion,
cette fenêtre peut même servir à déterminer l’origine du problème
(c.-à-d. ordinateur, routeur ou Internet/modem).
« Available Networks » (Réseaux disponibles)
Cette fenêtre affiche les réseaux disponibles à l’emplacement
actuel ainsi que des renseignements tels que SSID, puissance
du signal, type de sécurité, canal, et type de réseau.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
Perte de connexion sans fil
Advenant que vous perdiez votre connexion sans fil, une fenêtre
apparaîtra et l’utilitaire WNU essaiera de la rétablir.
15
Page 60

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
1716
Échec de connexion
D’autres options seront proposées pendant les tentatives de reconnexion.
Pour mettre fin à la connexion, cliquez sur « Stop » (Arrêter); pour essayer
de rétablir la connexion, cliquez sur « Retry » (Réessayer).
État du réseau et pistes de solution
Pour comprendre davantage l’état actuel du réseau, cliquez sur « Open
Wireless Utility » (Ouvrir utilitaire sans fil). L’écran par défaut sera l’onglet «
Current Status » (État actuel); la section « Network Status » (État du réseau)
indique les connexions qui sont bonnes et/ou qui fonctionnent mal.
L’utilitaire WNU comprend également une section intitulée « Pistes
de solution » qui vous propose des solutions de dépannage.
Page 61

17
Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
Définition de profils de réseau sans fil
L’onglet « My Connections » (Mes connexions) de l’utilitaire WNU
vous permet d’ajouter, de modifier et de supprimer des profils de
connexion. Il indique également la puissance du signal, le type de
sécurité et le type de réseau.
Sécurisation de votre réseau Wi-Fi®
Si vous choisissez de vous connecter à un réseau sécurisé, déterminez
le type de sécurité souhaité (WPA ou WEP*) et remplissez le champ
approprié dans la boîte de dialogue.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
*Remarque: Types de sécurité
17
Page 62

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
1918
Remarque: Lorsque vous sélectionnez un réseau qui utilise la
fonction de cryptage, vous verrez d’abord apparaître l’écran de
sécurité standard. Cliquez sur le bouton « Advanced » (Avancé)
pour afficher d’autres options de sécurité (voir ci-dessous).
Page 63

19
Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
Le protocole de sécurité WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
pour réseau sans fil est moins perfectionné mais plus largement
répandu. Selon le niveau de sécurité voulu (64 ou 128 bits),
l’utilisateur sera invité à entrer une clé hexadécimale de 10 ou 26
caractères. Une clé hexadécimale est une combinaison de lettres
(A à F) et de chiffres (0 à 9).
Le protocole WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) est la
nouvelle norme en matière de sécurité sans fil. Cependant, tous les
adaptateurs et les cartes sans fil ne prennent pas en charge cette
technologie. Pour savoir si votre adaptateur sans fil prend en charge
la technologie WPA, consultez votre guide d’utilisation. Au lieu d’une
clé hexadécimale, le protocole WPA n’utilise que des expressions de
passe qui sont beaucoup plus facile à retenir.
La section suivante, qui s’adresse aux utilisateurs et travailleurs à
domicile et à ceux dans les petites entreprises, explique différentes
façons de maximiser la sécurité de votre réseau sans fil.
Au moment de mettre sous presse, quatre méthodes de cryptage
étaient disponibles
Méthodes de cryptage
Nom W ired
Acrony me WEP 6 4 bit s WEP 128 bits WPA-TKIP/AES
Séc urité Bon Mei lleur Excell ent Excellent
Caractéristiques Clé s sta tiques Clé s sta tiques Cryp tag e
:
:
Equ ivalent
Pri vacy 64 bi ts
Clé s de
cry ptage
bas ées s ur
l’a lgorithme
RC4
(gé néralement
des c lés d e 40
bit s)
Wired
Equivalent
Privacy 128 bits
Plu s séc uritaire
que l e
cry ptage WEP
64 bits – utili se
une c lé de
104 b its ,
plu s 24 bits
Wi- Fi Prote cte d
Acc ess-TKIP
(ou simplement
WPA)
par c lé
dyn amique et
aut hentificati on
mut uelle
Ajo ut du
protoc ole T KIP
(Tempora l
Key I nte grity
Protoc ol) p our
fai re la ro tation
ent re les clés
et renforcer le
cry ptage
Wi- Fi
Protec ted
Acc ess 2
WPA2-AES
(ou simplement
WPA2)
Cryptage
par clé
dynamique et
authentification
mutuelle
La norme A ES
(Ad vanced
Enc ryption
Sta ndard)
n’o ccasionne
auc une p erte
de débit
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
19
Page 64

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
2120
WEP
Le cryptage WEP est un protocole commun qui permet d’ajouter un
composant de sécurité à tous les produits sans fil Wi-Fi. Il procure
aux réseaux sans fil un niveau de protection comparable à celui
d’un réseau câblé.
WEP 64 bits
La sécurité WEP 64 bits a d’abord été introduite avec le cryptage 64
bits, lequel comprend une clé d’une longueur de 40 bits, plus 24 bits
supplémentaires de données générés par le système (pour un total
de 64 bits). Certains fabricants de composants matériels parlent de
cryptage 40 bits pour désigner le 64 bits. Peu de temps après que
cette technologie ait fait son apparition, des chercheurs ont constaté
que le cryptage 64 bits était trop facile à décoder.
Cryptage 128 bits
Suite à la découverte de cette faiblesse, une méthode de cryptage
128 bits plus sécuritaire a été mise au point. Le cryptage 128
bits comprend une clé d’une longueur de 104 bits, plus 24 bits
supplémentaires de données générés par le système (pour un total
de 128 bits). Certains fabricants de composants matériels parlent de
cryptage 104 bits pour désigner le 128 bits. La plupart des nouveaux
équipements sans fil sur le marché aujourd’hui prennent en charge
les cryptages WEP 64 et 128 bits, mais il se pourrait que votre
ancien équipement ne permette que le 64 bits. Tous les produits
sans fil Belkin prennent en charge les deux (WEP 64 et 128 bits).
ClÉs de cryptage
Après avoir sélectionné le mode de cryptage WEP 64 ou 128 bits, il
est extrêmement important que vous génériez une clé de cryptage.
Si la clé utilisée n’est pas la même sur l’ensemble de votre réseau
sans fil, vos périphériques sans fil seront incapables de communiquer
les uns avec les autres. Vous pouvez entrer votre clé en tapant la clé
hexadécimale. Une clé hexadécimale est une combinaison de lettres
(A à F) et de chiffres (0 à 9). Pour le cryptage WEP 64 bits, vous
devez entrer 10 clés hexadécimales. Pour le cryptage WEP 128 bits,
vous devez entrer 26 clés hexadécimales.
Par exemple
AF
0F 4B C3 D4 = clé WEP 64 bits
C3
03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = clé WEP 128 bits
Prenez note de la clé WEP hexadécimale de votre routeur ou de votre
point d’accès sans fil et entrez-la manuellement dans la table des clés
WEP hexadécimales à l’écran de configuration de votre carte.
:
Page 65

21
Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
WPA
WPA est une nouvelle norme Wi-Fi qui améliore les fonctions de
sécurité WEP. Pour utiliser la sécurité WPA, vous devez mettre
à niveau les pilotes et le logiciel de votre équipement sans fil.
Vous pouvez obtenir ces mises à niveau sur le site Web de votre
fournisseur d’équipement sans fil. Il y a trois types de sécurité WPA:
WPA-PSK (sans serveur), WPA (avec serveur Radius) et WPA2.
Le mode WPA-PSK (sans serveur) utilise une clé dite « pré-partagée
» comme clé réseau. Il s’agit d’un mot de passe pouvant compter
entre 8 et 63 caractères (lettres, chiffres et symboles). Chaque client
utilise la même clé pour accéder au réseau. Habituellement, ce mode
s’utilise dans un environnement domestique.
Le mode WPA (avec serveur Radius) donne un meilleur
rendement dans un environnement d’affaires où un serveur
Radius distribue automatiquement les clés réseau aux clients.
Le mode WPA2 nécessite la norme AES (Advanced Encryption
Standard) pour le cryptage des données et offre une niveau de
sécurité plus élevé que le WPA. Le mode WPA utilise à la fois le
protocole TKIP (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) et la norme AES
pour le cryptage des données.
Définition des paramètres de sécurité sur votre routeur
ou point d’accès sans fil Belkin
Pour commencer à utiliser les fonctions de sécurité, vous devez
d’abord activer le cryptage WEP ou WPA sur votre routeur ou votre
point d’accès sans fil. Dans le cas des produits Belkin, ces fonctions
peuvent être configurées à partir de l’interface Web. Consultez le
manuel de votre routeur ou de votre point d’accès sans fil pour savoir
comment accéder à l’interface de gestion.
IMPORTANT: Vous devez maintenant définir ces paramètres sur tous
les adaptateurs et/ou cartes réseau sans fil.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
21
Page 66

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
2322
Configuration de votre carte avec fonctions de sécurité
À ce stade-ci, votre routeur ou votre point d’accès sans fil devrait
déjà avoir été configuré pour utiliser le cryptage WPA ou WEP. Pour
être en mesure d’établir la connexion sans fil, vous devrez configurer
votre carte N1 sans fil pour ordinateur de bureau de façon à ce qu’elle
utilise les mêmes paramètres de sécurité.
Modification des paramètres de sécurité sans fil
La carte N1 sans fil pour ordinateur de bureau Belkin prend en charge les
plus récentes fonctions de sécurité WPA ainsi que l’ancienne norme de
sécurité WEP. Par défaut, la fonction de sécurité sans fil est désactivée.
Pour l’activer, vous devez d’abord déterminer la norme qu’utilise votre
routeur ou votre point d’accès. (Consultez le manuel de votre routeur
ou de votre point d’accès sans fil pour savoir comment accéder aux
paramètres de sécurité.)
Pour accéder aux paramètres de sécurité de votre carte, cliquez
sur l’onglet « My Connections » (Mes connexions) et sélectionnez
la connexion dont vous voulez modifier les paramètres. Cliquez sur
« Edit » (Éditer) pour modifier les paramètres.
Page 67

23
Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
Configuration WEP
Cryptage WEP 64 bits
1. Sélectionnez « WEP » au menu déroulant « Data Encryption »
(Cryptage des données).
2. Vous pouvez entrer votre clé en tapant la clé hexadécimale.
Une clé hexadécimale est une combinaison de lettres (A à F)
et de chiffres (0 à 9). Pour le cryptage WEP 64 bits, vous devez
entrer 10 clés hexadécimales.
Par exemple
0F 4B C3 D4 = clé WEP 64 bits
AF
:
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
23
Page 68

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
2524
3. Cliquez sur « Save » (Enregistrer) pour terminer. Le mode de
cryptage du routeur ou du point d’accès sans fil est maintenant
défini. Chaque ordinateur dans votre réseau sans fil devra être
configuré avec les mêmes paramètres de sécurité.
MISE EN GARDE : Si vous utilisez un client sans fil pour activer les
paramètres de sécurité sur votre point d’accès ou votre routeur sans
fil, vous perdrez temporairement votre connexion jusqu’à ce que vous
les ayez activés. Il est donc important de prendre note de votre clé
avant d’appliquer les modifications au routeur ou au point d’accès
sans fil. Si vous oubliez votre clé hexadécimale, votre client ne pourra
plus y avoir accès.
Cryptage WEP 128 bits
Sélectionnez « WEP » au menu déroulant.
1.
2. Vous pouvez entrer votre clé en tapant la clé hexadécimale. Une
clé hexadécimale est une combinaison de lettres (A à F) et de
chiffres (0 à 9). Pour le cryptage WEP 128 bits, vous devez entrer
26 clés hexadécimales.
Par exemple
C3
03 0F AF 0F 4B B2 C3 D4 4B C3 D4 E7 = clé WEP 128 bits
:
Page 69

25
Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
3. Cliquez sur « Save » (Enregistrer) pour terminer. Le mode de
cryptage du routeur ou du point d’accès sans fil est maintenant
défini. Chaque ordinateur dans votre réseau sans fil devra être
configuré avec les mêmes paramètres de sécurité.
MISE EN GARDE : Si vous utilisez un client sans fil pour activer les
paramètres de sécurité sur votre point d’accès ou votre routeur sans
fil, vous perdrez temporairement votre connexion jusqu’à ce que vous
les ayez activés. Il est donc important de prendre note de votre clé
avant d’appliquer les modifications au routeur ou au point d’accès
sans fil. Si vous oubliez votre clé hexadécimale, votre client ne pourra
plus y avoir accès.
25
Page 70

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
2726
WPA-PSK (sans serveur)
Sélectionnez ce paramètre si votre réseau n’utilise pas de serveur Radius.
WPA-PSK (sans serveur) s’utilise habituellement pour les petits réseaux
domestiques ou de bureau.
1. Au menu déroulant « Network Authentication » (Authentification
du réseau), sélectionnez « WPA-PSK (no server) » (WPA-PSK
– sans serveur).
2. Entrez votre clé réseau, laquelle peut compter entre 8 et 63
caractères (lettres, chiffres ou symboles). Vous devez entrer la
même clé sur tous les clients (cartes réseau) que vous voulez
ajouter à votre réseau sans fil.
Page 71

27
Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
3. Cliquez sur « Save » (Enregistrer) pour terminer. Vous devez
maintenant définir ces paramètres sur tous les clients (cartes réseau).
Options de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil
L’onglet « Options » de l’utilitaire WNU permet à l’utilisateur
de personnaliser ses paramètres WNU.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
27
Page 72

Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
2928
Aide concernant l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil
L’onglet « Help » (Aide) de l’utilitaire WNU permet à l’utilisateur
d’avoir accès au soutien téléphonique et en ligne, à des outils de
diagnostic avancés et de vérifier les mises à niveau logicielles au
moyen d’un seul clic.
Page 73

29
Exécution de l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin
Outils de diagnostic évolués
La section « Advanced Diagnostic Tools » (Outils de diagnostic
évolués) est le panneau de configuration central de tous les éléments
matériels et logiciels du réseau sans fil. Il offre un éventail de tests
et de services de connectivité qui vous permettront d’obtenir un
rendement optimal de votre réseau.
1
2
3
sectio n
4
5
6
29
Page 74

Dépannage
Je ne parviens pas à me connecter sans fil à Internet.
Si vous êtes incapable de vous connecter à Internet à partir
d’un ordinateur sans fil, faites les vérifications suivantes :
1. Vérifiez les voyants sur le routeur sans fil. Si vous utilisez un routeur
Belkin, les voyants devraient apparaître comme suit :
• Le voyant d’alimentation devrait être allumé.
• Le voyant de connexion devrait être allumé, sans clignoter.
•
Le voyant de réseau longue distance (WAN) devrait être allumé ou clignoter.
Si les voyants présentent les caractéristiques ci-dessus, passez
au numéro 2 ci-dessous.
Cependant, si ce n’est PAS le cas, assurez-vous que :
• Le cordon d’alimentation de votre routeur est branché.
• Tous les câbles entre le routeur et le modem sont branchés.
• Tous les voyants sur le modem fonctionnent correctement. Dans
la négative, reportez-vous au guide d’utilisation de votre modem.
• Redémarrez le routeur.
• Redémarrez le modem.
Si le problème persiste, veuillez communiquer avec le Soutien technique Belkin.
Si vous n’utilisez pas un routeur sans fil Belkin, consultez le guide
d’utilisation du fabricant.
2. Lancez l’utilitaire sans fil en cliquant sur l’icône dans la barre d’état
système située dans le coin inférieur droit de l’écran. Si vous
utilisez une carte sans fil Belkin, l’icône dans la barre d’état devrait
ressembler à ceci (elle peut être rouge ou verte) :
3. La fenêtre qui apparaît varie selon le modèle de carte sans fil que
vous utilisez. Cependant, tous les utilitaires devraient avoir une liste
de « réseaux disponibles ».
Les réseaux disponibles sont ceux auxquels vous pouvez vous
connecter sans fil. Si vous utilisez un routeur 802.11g (G Plus)
ou 802.11g (54g) Belkin, « Belkin54g » sera le nom par défaut.
Si vous utilisez un routeur 802.11b Belkin, le nom par défaut
devrait être « WLAN ».
Si vous n’utilisez PAS de routeur sans fil Belkin, reportez-vous au
guide d’utilisation du fabricant pour connaître le nom par défaut.
Page 75

Dépannage
Le nom de votre réseau sans fil apparaît dans la liste
des réseaux disponibles.
Si le nom du réseau voulu figure dans la liste, suivez les étapes
ci-dessous pour vous y connecter sans fil :
1. Cliquez sur le nom du réseau voulu dans la liste
« Available Networks » (Réseaux disponibles).
2. Si la fonction de sécurité (cryptage) est activée, vous devrez
entrer la clé réseau. Cliquez sur « Connect » (Se connecter). Pour
de plus amples renseignements sur la sécurité, reportez-vous à la
section intitulée « Sécurisation de votre réseau Wi-Fi » à la page
17 du présent guide.
3. Quelques secondes plus tard, l’icône dans le coin inférieur droit
de l’écran devrait passer au vert, indiquant qu’une connexion a
été établie avec le réseau.
Si vous êtes toujours incapable d’accéder à Internet après vous
être connecté au réseau sans fil, veuillez contacter le Soutien
technique Belkin.
Le nom de votre réseau sans fil n’apparaît PAS dans la liste
des réseaux disponibles.
Si le nom du réseau voulu n’apparaît pas, vérifiez que les
paramètres SSID concordent. Le nom du réseau (SSID) est sensible
à la casse (c.-à-d. qu’il faut obligatoirement faire la distinction entre
lettres majuscules et minuscules) et il doit être entré exactement de
la même façon sur chaque ordinateur pour que la carte puisse se
connecter au point d’accès ou au routeur sans fil.
Remarque: Pour vérifier les paramètres SSID ou chercher
un réseau disponible, double-cliquez sur l’icône indicateur de
signal pour afficher l’écran « Wireless Networks » (Réseaux
sans fil). Cliquez sur « Add » (Ajouter) si vous ne voyez pas le
réseau auquel vous essayez de vous connecter et tapez le SSID.
Pour de plus amples renseignements sur la définition d’un SSID,
veuillez consulter le guide d’utilisation de votre routeur fourni
par le fabricant.
Si le problème persiste même à distance rapprochée, contactez
le Soutien technique Belkin.
1
2
3
4
sectio n
5
6
31
Page 76

Dépannage
3332
L’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin ne démarre
pas à partir du CD-ROM d’installation.
Si l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin ne démarre pas
automatiquement à partir du CD-ROM d’installation, il se pourrait
que d’autres applications actuellement en cours d’exécution
interfèrent avec le lecteur de CD. S’il n’apparaît pas dans les 15 à
20 secondes qui suivent, double-cliquez sur l’icône « My Computer
» (Poste de travail) pour ouvrir votre lecteur de CD-ROM. Doublecliquez sur le lecteur dans lequel le CD d’installation a été placé
pour lancer l’installation. Ensuite, double-cliquez sur le dossier «
Files » (Fichiers). Enfin, double-cliquez sur l’icône « setup.exe ».
Le voyant d’alimentation reste éteint; la carte
ne fonctionne pas.
Si les voyants ne sont pas allumés, le problème peut être que
la carte n’est pas connectée ou installée correctement. Vérifiez
que la carte est bien branchée sur le port CardBus de votre
ordinateur. Vérifiez que les pilotes de la carte ont été installés.
À l’aide du bouton de droite, cliquez sur l’icône « My Computer
» (Poste de travail) sur votre bureau. Sélectionnez « Properties
» (Propriétés), puis dans le gestionnaire de périphériques, voyez
si votre carte CardBus apparaît sans erreur. Si une erreur est
indiquée, contactez le Soutien technique Belkin.
Le voyant de liaison clignote lentement; je suis incapable
de me connecter à un réseau sans fil ou à Internet.
Si votre carte semble fonctionner correctement mais que vous
êtes incapable de vous connecter à un réseau ou qu’une icône
rouge sans fil apparaît au bas de l’écran, le problème pourrait être
attribuable à une incompatibilité entre les paramètres de nom de
réseau (SSID) dans les propriétés de votre réseau sans fil.
Vérifiez si les paramètres SSID concordent. Le nom du réseau
(SSID) est sensible à la casse (c.-à-d. qu’il faut obligatoirement
faire la distinction entre lettres majuscules et minuscules) et
il doit être entré exactement de la même façon sur chaque
ordinateur pour que la carte puisse se connecter au point
d’accès ou au routeur sans fil.
Remarque
réseau disponible, double-cliquez sur l’icône indicateur de signal
pour afficher l’écran « Wireless Networks » (Réseaux sans fil).
Cliquez sur « Add » (Ajouter) si vous ne voyez pas le réseau
auquel vous essayez de vous connecter et tapez le SSID.
Pour de plus amples renseignements sur la définition d’un SSID,
veuillez consulter le guide d’utilisation de votre routeur four ni par
le fabricant.
: Pour vérifier les paramètres SSID ou chercher un
Page 77

33
Dépannage
Si le problème persiste même à distance rapprochée, contactez
le Soutien technique Belkin.
Le voyant de liaison est allumé (fixe) mais je ne peux
toujours pas me connecter à Internet.
Si vous recevez un signal mais que vous ne pouvez pas établir de
connexion Internet ou obtenir une adresse IP, le problème pourrait
être attribuable à une incompatibilité entre les paramètres de clé
de cryptage sur votre ordinateur et ceux du point d’accès ou du
routeur sans fil. Vérifiez si les paramètres de clé WEP, WPA ou
WPA2 concordent. La clé WEP est sensible à la casse (c.-à-d. qu’il
faut obligatoirement faire la distinction entre les lettres majuscules
et minuscules) et elle doit entrée exactement de la même façon
sur chaque ordinateur et sur le point d’accès ou le routeur sans fil
pour que la carte puisse établir la connexion. Pour de plus amples
renseignements sur le cryptage, reportez-vous à la section intitulée
« Sécurisation de votre réseau Wi-Fi » à la page 17 du présent guide.
Si le problème persiste même à distance rapprochée, contactez
le Soutien technique Belkin.
Le transfert de données est parfois lent.
Comme la technologie sans fil est basée sur les ondes
radioélectriques, cela signifie que la connectivité et le débit entre
les périphériques ont tendance à diminuer à mesure que la distance
entre eux augmente. Les autres facteurs qui peuvent entraîner une
dégradation du signal sont les obstacles tels que murs et appareils
électriques (le métal étant généralement le pire). En conséquence, la
portée de vos périphériques sans fil dans un environnement intérieur
sera habituellement de 100 à 200 pieds. Remarquez également que
la vitesse de votre connexion diminuera probablement à mesure que
vous vous éloignerez du point d’accès ou du routeur sans fil.
Pour vérifier si le problème est lié à un facteur de distance,
nous vous suggérons d’éloigner temporairement (si possible)
l’ordinateur d’une distance de cinq à 10 pieds du routeur ou du
point d’accès sans fil. Veuillez vous reporter à la section intitulée
« Choix d’un emplacement permettant d’obtenir un rendement
optimal de votre matériel réseau sans fil » à la page 2 du présent
guide. Si le problème persiste même à distance rapprochée,
contactez le Soutien technique Belkin.
Le signal est faible.
Comme la technologie sans fil est basée sur les ondes
radioélectriques, cela signifie que la connectivité et le débit
entre les périphériques ont tendance à diminuer à mesure que
la distance entre eux augmente. Les autres facteurs qui peuvent
entraîner une dégradation du signal sont les obstacles tels que
33
1
2
3
4
sectio n
5
6
Page 78

Dépannage
3534
murs et appareils électriques (le métal étant généralement le
pire). En conséquence, la portée de vos périphériques sans fil
dans un environnement intérieur sera habituellement de 100 à 200
pieds. Remarquez également que la vitesse de votre connexion
diminuera probablement à mesure que vous vous éloignerez du
point d’accès ou du routeur sans fil. Pour vérifier si le problème
est lié à un facteur de distance, nous vous suggérons d’éloigner
temporairement (si possible) l’ordinateur d’une distance de cinq à
10 pieds du routeur ou du point d’accès sans fil.
Changement de canal sans fil – Selon les interférences et le
trafic local sans fil, il se pourrait que vous puissiez améliorer la
performance et la fiabilité de votre réseau en changeant de canal.
Par défaut, votre routeur est réglé sur le canal 6; vous avez le
choix de plusieurs autres canaux, selon la région où vous habitez.
Pour de plus amples renseignements à ce sujet, consultez le
guide d’utilisation de votre routeur ou de votre point d’accès.
Limitation de la vitesse de transmission sans fil – Limiter la
vitesse de transmission de votre réseau sans fil peut contribuer à
améliorer la portée du réseau et la stabilité de la connexion. Sur la
plupart des cartes sans fil, vous pouvez modifier ce paramètre. Pour
ce faire, ouvrez le « Control Panel » (Panneau de configuration) de
Windows, sélectionnez « Network Connections » (Connexions réseau)
et double-cliquez sur la connexion de votre carte. Dans la boîte de
dialogue « Properties » (Propriétés), cliquez sur le bouton « Configure
» (Configurer) sous l’onglet « General » (Général) (les utilisateurs de
Windows 98 devront sélectionner la carte sans fil dans la boîte de
liste et cliquer sur Propriétés), puis cliquez sur l’onglet « Advanced
» (Avancé) et sélectionnez la vitesse (débit). Les cartes de clients
sans fil sont habituellement configurées pour régler automatiquement
la vitesse de transmission sans fil pour vous, ce qui peut entraîner
des déconnexions périodiques lorsque le signal est trop faible. En
règle générale, les transmissions plus lentes sont plus stables. Faites
différents essais jusqu’à ce que vous trouviez la vitesse qui convient
le mieux à votre environnement. Il est à noter que toutes les vitesses
disponibles devraient être acceptables pour naviguer sur Internet.
Pour toute assistance, reportez-vous à la documentation fournie
avec votre carte sans fil. Si le problème persiste même à distance
rapprochée, contactez le Soutien technique Belkin.
Pourquoi y a-t-il deux utilitaires sans fil dans ma barre
d’état système ? Lequel dois-je utiliser ?
L’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin comporte plusieurs fonctions et
avantages par rapport à l’utilitaire WZC (Configuration automatique
sans fil) de Windows XP. En effet, nous offrons une fonction d’inspection
Page 79

35
Dépannage
de site et de diagnostic de l’adaptateur, sans compter les données
détaillées concernant la liaison, pour ne donner que quelques exemples.
Il est essentiel de savoir quel utilitaire gère votre carte. Nous
recommandons d’utiliser celui fourni par Belkin. Pour sélectionner
l’utilitaire pour réseau sans fil Belkin, suivez les étapes ci-dessous:
Étape 1 Avec le bouton droit de la souris, cliquez sur l’icône
d’état du réseau située dans la barre d’état système, puis
sélectionnez l’onglet « Status » (État).
Étape 2 Sur l’onglet « Status » (État), décochez la boîte « Use
Windows to Configure my Wireless Network » (Utiliser Windows
pour configurer mon réseau sans fil). Ensuite, cliquez sur le
bouton « Close » (Fermer) pour fermer la fenêtre.
Vous utilisez maintenant l’utilitaire réseau sans fil Belkin pour
configurer la carte.
.
La carte ne fonctionne pas ou la connexion est instable
lorsque l’ordinateur a une deuxième carte réseau sans
fil intégrée (p. ex. mini PCI ou Intel® Centrino™).
Cette condition se produit si votre ordinateur a une carte sans fil
intégrée et que votre carte sans fil Belkin est également active.
Windows doit alors gérer deux connexions sans fil actives.
Vous devez désactiver la carte sans fil intégrée à partir de la
rubrique « Network Adapters » (Adaptateur réseau) dans le
gestionnaire de périphériques.
La carte ne fonctionne pas ou la connexion est lente
lorsque l’ordinateur a une carte Ethernet intégrée.
Cette condition se produit si votre ordinateur a une carte
Ethernet active et que votre carte sans fil est également active.
Windows doit alors gérer deux connexions réseau actives. Vous
devez désactiver la carte Ethernet sur votre ordinateur à partir
de la rubrique « Network Adapters » (Adaptateurs réseau) dans le
gestionnaire de périphériques.
Quelle différence y a-t-il entre les normes 802.11b,
802.11g, 802.11a et 802.11n préliminaire?
À l’heure actuelle, il existe quatre normes réseau sans fil qui
permettent chacune de transmettre des données à des débits
maximum très différents. Chaque norme est basée sur la
désignation appropriée. La norme réseau sans fil la plus courante
(802.11b) transmet les données à un débit de 11 Mbit/s, les
normes 802.11a et 802.11g fonctionnent à 54 Mbit/s alors que la
norme 802.11n préliminaire fonctionne à 108 Mbit/s. Pour plus de
détails, voir le tableau de la page suivante.
35
1
2
3
4
sectio n
5
6
Page 80

Dépannage
3736
Tableau comparatif des normes sans fil
Technologie
sans fil
Débit*
Fréquence
802.11b
Vitesse de
base 11Mbit/s
Les petits
appareils
courants tels
que téléphones
sans fil et
fours microondes peuvent
interférer avec
la bande sans
licence 2,4 GHz
G
(802.11g)
5 fois plus
rapide que la
norme 802.11b*
Les petits
appareils
courants tels
que téléphones
sans fil et
fours microondes peuvent
interférer avec
la bande sans
licence 2,4 GHz
G Plus
10 fois plus
rapide que la
norme 802.11b*
Les petits
appareils
courants tels
que téléphones
sans fil et
fours microondes peuvent
interférer avec
la bande sans
licence 2,4 GHz
(802.11g avec
HSM)
(802.11g avec
MIMO MRC)
G Plus MIMO
10 fois plus
rapide que
la norme
802.11b*
Les petits
appareils
courants tels
que téléphones
sans fil et
fours microondes peuvent
interférer avec
la bande sans
licence 2,4 GHz
(802.11n
préliminaire
avec MIMO)
N1 MIMO
Vitesse câblée
en liaison
radio*
Les petits
appareils
courants tels
que téléphones
sans fil et
fours microondes peuvent
interférer avec
la bande sans
licence 2,4 GHz
Compatible
avec la norme
802.11g
Compatibilité
Habituellement
100 à 200 pi à
l’intérieur
Portée*
Mature—
ancienne
technologie
Avantage
*La d ist ance et le s vit esses de connexion vari ent s elon votre envir onn ement réseau.
**Cette carte es t compatible avec les produits basé s sur la même vers ion de la norme 80 2.11n
prélimi naire et pour rait n écessit er une mi se à nive au log icielle pour des résultats optimaux.
Compatible
avec la norme
802.11g
Jusqu’à 400 pi* Jusqu’à 700 pi*
Courante—
largement
utilisée pour
les applications
Inter net
Compatible
avec la norme
802.11g
Rapidité
et portée
améliorées
Compatible
avec la norme
802.11g
Jusqu’à 1,000 pi* Jusqu’à 1,400 pi*
Meilleure
couverture
et rapidité
constante
Compatible
avec les normes
802.11n**
préliminaire et
802.11b/g
D’avantgarde—
meilleurs débit
et portée
Page 81

37
Dépannage
Soutien technique
Pour obtenir de plus amples données techniques,
veuillez visiter notre site Web à l’adresse www.belkin.
com/networking. Pour toute assistance téléphonique,
composez le :
États-Unis : 877-736-5771
Europe: 00 800 223 55 460
Australie: 1800 235 546
Nouvelle-Zélande: 0800 235 546
Singapour: 800 616 1790
1
2
3
4
sectio n
5
6
37
Page 82

Information
3938
Attestation de la Federal Communication Commission (FCC)
relative aux interférences Cet appareil a été testé et jugé conforme aux
limites imposées pour les unités numériques de classe B, en vertu de l’alinéa 15
de la réglementation FCC. Ces limites visent à assurer une protection raisonnable
contre les interférences en milieu résidentiel. Cet appareil génère, utilise et peut
émettre de l’énergie radioélectrique et, s’il n’est pas installé et utilisé selon les
instructions fournies, il peut causer des interférences dans les communications
radio. Néanmoins, aucune installation n’est par définition exempte de ce
phénomène. Si cet appareil cause effectivement des interférences nuisibles
lors de la réception d’émissions radio ou télévisées (et il suffit, pour s’en rendre
compte, d’allumer et d’éteindre l’appareil), l’utilisateur devra tenter de corriger
ces interférences en prenant l’une des mesures suivantes :
• Réorienter ou changer la position de l’antenne réceptrice.
• Augmenter la distance entre l’équipement et le récepteur.
• Brancher l’équipement sur une prise de courant appartenant à
un circuit différent de celui sur lequel est branché le récepteur.
• Demander l’assistance du fournisseur ou d’un technicien de télé
ou de radio expérimenté.
Cet appareil répond aux exigences de l’alinéa 15 de la réglementation FCC.
Le fonctionnement est assujetti aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) cet
appareil ne peut pas provoquer d’interférence nuisible, et (2) cet appareil
doit accepter toute interférence reçue, y compris des interférences pouvant
entraîner un fonctionnement non désiré.
Mise en garde de la FCC : Toute modification qui n’a pas été expressément
approuvée par la partie responsable des questions de conformité pourrait
annuler le droit de l’utilisateur de se servir de cet équipement.
NOTE IMPORTANTE :
Attestation de la FCC relative à l’exposition aux rayonnements:
Cet équipement respecte les limites imposées par la FCC en matière d’exposition
aux rayonnements dans un environnement non contrôlé. Il doit être installé et
utilisé en laissant une distance minimale de 20 cm entre le radiateur et vous.
Cet émetteur ne doit pas être installé ou utilisé de pair avec tout autre
émetteur ou antenne.
Belkin déclare que le produit F5D8001 (code d’identification de
la FCC : K7SF5D8001) est limité à 2,4 GHz (CH1~CH11) par le
micrologiciel spécifié contrôlé aux États-Unis.
Page 83

39
Information
Garantie à vie limitée de Belkin Corporation sur le produit
Portée de la garantie.
Belkin Corporation garantit à l’acheteur initial que ce produit Belkin sera exempt
de tout défaut de conception, d’assemblage, de matériau et de fabrication.
Durée de la garantie.
Belkin Corporation garantit ce produit pendant toute la durée de vie du produit.
Que ferons-nous en cas de problème ?
Garantie sur le produit.
Belkin réparera ou remplacera, à son gré et sans frais, tout produit
défectueux (les frais d’expédition ne sont cependant pas compris).
Qu’est-ce que la présente garantie ne couvre pas ?
Toutes les garanties ci-dessus sont nulles et non avenues si le produit Belkin
n’est pas expédié à Belkin Corporation pour inspection, à sa demande mais
aux frais de l’acheteur, ou si Belkin Corporation s’aperçoit que le produit a
été mal installé, modifié ou altéré de quelque façon. La garantie Belkin sur
le produit ne s’applique pas aux cas de force majeure (autres que la foudre)
tels que tremblement de terre, inondation, guerre, vandalisme, vol, usure
normale, érosion, épuisement, obsolescence, abus, dommages causés par
des perturbations de tension, programme non autorisé ou modification de
système ou d’équipement.
Pour obtenir de l’assistance.
Voici la marche à suivre pour obtenir de l’assistance concernant
votre produit Belkin :
1. Communiquez avec Belkin Corporation, au 501 W. Walnut St.,
Compton CA 90220, à l’attention de : Service à la clientèle,
ou appelez au (800) 223-5546, dans les 15 jours suivant
l’événement. Soyez prêt à fournir les renseignements suivants :
a. Numéro de produit Belkin.
b. Endroit où vous avez acheté le produit.
c. Date d’achat du produit.
d. Copie du reçu d’origine.
2. Le représentant du Service à la clientèle Belkin vous indiquera alors
la marche à suivre pour retourner le produit Belkin, avec le reçu,
et comment faire votre réclamation.
1
2
3
4
5
sectio n
6
39
Page 84

Information
4140
Belkin Corporation se réserve le droit d’examiner le produit endommagé. Tous
les coûts d’expédition du produit Belkin pour inspection seront entièrement
assumés par l’acheteur. Si Belkin détermine, à son entière discrétion, qu’il
est peu pratique d’expédier l’équipement endommagé à Belkin Corporation,
Belkin peut désigner, à son entière discrétion, un atelier de réparation pour
inspecter l’équipement et évaluer les coûts de réparation. Les coûts, s’il
en est, pour l’expédition de l’équipement jusqu’à l’atelier de réparation et
le retour, et pour l’estimation, seront entièrement assumés par l’acheteur.
L’équipement endommagé doit être disponible pour inspection jusqu’à ce
que la demande de réclamation soit réglée. Lorsqu’un règlement intervient,
Belkin Corporation se réserve le droit d’être subrogé en vertu de quelque
police d’assurance que l’acheteur pourrait avoir.
Rapport entre la loi des états et la présente garantie.
CETTE GARANTIE CONTIENT LA GARANTIE EXCLUSIVE DE BELKIN
CORPORATION. IL N’Y A PAS D’AUTRE GARANTIE EXPRESSE OU, SAUF
DANS LES CAS EXIGÉS PAR LA LOI, IMPLICITE, Y COMPRIS DE GARANTIE
IMPLICITE OU CONDITION DE QUALITÉ OU DE CONFORMITÉ À UN USAGE
PARTICULIER. DE TELLES GARANTIES IMPLICITES, S’IL EN EST, SONT
LIMITÉES À LA DURÉE DE LA PRÉSENTE GARANTIE.
Certains états n’autorisent pas de limite quant à la durée d’une garantie
implicite; il se pourrait donc que les limites indiquées ci-dessus ne
s’appliquent pas dans votre cas.
EN AUCUN CAS BELKIN CORPORATION NE SERA RESPONSABLE
DE QUELQUES DOMMAGES-INTÉRÊTS POUR CAUSE DIRECTE,
INDIRECTE, SPÉCIALE, FORTUITE OU MULTIPLE, NOTAMMENT MAIS NON
EXCLUSIVEMENT, PERTE D’OCCASIONS D’AFFAIRES OU DE PROFITS
DÉCOULANT DE LA VENTE OU DE L’UTILISATION DE TOUT PRODUIT BELKIN,
MÊME SI ELLE ÉTAIT INFORMÉE DE LA POSSIBILITÉ DE TELS DOMMAGES.
Cette garantie vous confère des droits légaux spécifiques, et vous pouvez
aussi avoir d’autres droits pouvant varier d’un état à l’autre. Certains états ne
permettent pas l’exclusion ou la limitation des dommages-intérêts pour une
cause indirecte, fortuite ou autre; il se pourrait donc que les limites indiquées
ci-dessus ne s’appliquent pas dans votre cas.
Page 85

41
Information
1
2
3
4
5
sectio n
6
41
Page 86

Tabla de contenido
1 Introducción . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Beneficios de una red doméstica. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ventajas de una red inalámbrica . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Colocación del hardware de su red
inalámbrica para un rendimiento óptimo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2 Descripción general . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Características del producto. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Aplicaciones y ventajas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Especificaciones del producto . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Requisitos del sistema . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Contenido del paquete . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3 Cómo instalar y configurar la tarjeta. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Paso 1: Instale . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Paso 2: Inserte . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Paso 3: Termine . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Paso 4: Configuración . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4 Cómo usar la utilidad de red inalámbrica de Belkin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Cómo acceder la Utilidad de red inalámbrica
de Belkin en la bandeja del sistema de Windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Estatus de la red . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Redes disponibles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Estatus de la red y consejos de resolución . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuración de perfiles de red inalámbrica. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cómo asegurar su red Wi-Fi. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Cómo configurar su tarjeta para usar la seguridad. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5 Resolución de problemas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6 Información . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
11
13
17
22
1
1
2
5
6
6
7
7
8
Page 87

Introducción
Gracias por comprar la tarjeta inalámbrica N1 para computadora
de escritorio de Belkin. Ahora puede aprovechar las ventajas que
ofrece esta tecnología nueva y lograr la libertad de conectar sus
computadoras de casa u oficina a la red de manera inalámbrica.
Esta tarjeta le permite conectar una computadora de escritorio a
su red. No deje de leer este manual del usuario en su totalidad,
prestando particular atención a la sección titulada “Colocación
de su hardware de red inalámbrica para rendimiento óptimo”.
Beneficios de una red doméstica
Su red doméstica Belkin le permitirá:
• Compartir una conexión a Inter net de alta velocidad con todas
las computadoras de su hogar
• Compartir recursos como archivos y discos duros entre todas
las computadoras conectadas en su hogar
• Compartir una impresora con toda la familia
• Compartir documentos, música, video y fotos digitales
• Almacenar, recuperar y copiar archivos de una computadora a otra
• Jugar juegos en línea, verificar el correo electrónico en el Internet
y hacer chats simultáneamente
Ventajas de una red inalámbrica
Éstas son algunas ventajas de establecer una red inalámbrica Belkin:
• Movilidad – no necesita usar un cuarto dedicado exclusivamente
como “sala de computación”– puede trabajar en red con una
computadora laptop o de escritorio en cualquier lugar dentro
del alcance de su red inalámbrica
• Fácil de instalar – el Asistente de instalación fácil Belkin
simplifica la instalación
• Flexibilidad – configure y acceda a impresoras, computadoras
y demás dispositivos en red desde cualquier lugar de su hogar
• Fácil de expandir – el alcance amplio de los productos de red
Belkin le permite expandir su red e incluir dispositivos como
impresoras y consolas de juego
• No se necesita cableado – usted se evita los gastos
y problemas vinculados a la instalación del cableado
de Ethernet en su casa u oficina
• Aceptación generalizada en la industria – elija de una amplia
gama de productos de trabajo en red interoperables
1
sección
1
2
3
4
5
6
Page 88

Introducción
Colocación del hardware de su red inalámbrica
para un rendimiento óptimo
Su conexión inalámbrica será más potente cuanto más cerca esté
su computadora del enrutador inalámbrico (o punto de acceso). El
alcance operativo en interiores típico de sus dispositivos inalámbricos
es de entre 100 y 200 pies (30–60 m). De la misma forma, la conexión
y el rendimiento de su red inalámbrica bajarán ligeramente cuando
aumente la distancia entre su enrutador inalámbrico (o punto de
acceso) y los dispositivos conectados. Esta diferencia pudiera o no
notarse. En medida que se aleja de su enrutador inalámbrico (o punto
de acceso), la velocidad de la conexión pudiera bajar. Los factores
que pueden debilitar las señales simplemente entorpeciendo el camino
de las ondas radiales de su red son los aparatos electrodomésticos
o las obstrucciones de metal, al igual que las paredes.
Si tiene alguna inquietud sobre el redimiendo de su red que pudiera
relacionarse al alcance o a factores de obstrucción, intente cambiar
la computadora de sitio, desplazándola a un lugar que esté entre
cinco y diez pies (1.5 a 3 metros) del enrutador inalámbrico (o punto
de acceso) para ver si la distancia es el problema. Si las dificultades
persisten, aún en una distancia corta, sírvase poner en contacto con
la asistencia técnica Belkin.
Nota: Si bien algunos puntos enumerados más abajo pueden afectar
el rendimiento de la red, no impiden que su red inalámbrica funcione.
Pero si le preocupa la posibilidad de que su red no esté operando al
máximo de eficiencia, esta lista de verificación le puede ser útil.
1. Ubicación de su enrutador inalámbrico (o punto de acceso)
Coloque su enrutador inalámbrico (o punto de acceso), el punto de
conexión central de su red, lo más cerca posible del centro de los
dispositivos de su red inalámbrica.
Para obtener la mejor cobertura de la red inalámbrica para sus
“clientes inalámbricos” (o sea, computadoras habilitadas con tarjetas
de red inalámbrica para laptop, tarjetas para computadoras de
escritorio y adaptadores USB inalámbricos Belkin):
• Asegúrese de que las antenas de su enrutador inalámbrico
(o punto de acceso) estén paralelas entre sí y colocadas
verticalmente (hacia el techo). Si su enrutador inalámbrico
(o punto de acceso) está en posición vertical, apunte las
antenas lo máximo posible hacia arriba.
Page 89

• En casas de varios pisos, coloque el enrutador inalámbrico (o punto
de acceso) en un piso tan cercano al centro de la casa como sea
posible. Esto puede significar que el enrutador inalámbrico (o punto
de acceso) debe colocarse en un piso superior.
• Trate de no colocar el enrutador inalámbrico (o punto de acceso)
cerca de un teléfono inalámbrico de 2.4 GHz.
2. Evite los obstáculos y la interferencia
Evite colocar su enrutador inalámbrico (o punto de acceso) cerca
de dispositivos que pudieran emitir “ruido”, tales como hornos
de microondas. Otros objetos que también pueden inhibir las
comunicaciones inalámbricas pueden ser:
• Refrigeradores
• Lavarropas y/o secadores
• Armarios de metal
• Acuarios grandes
• Ventanas con tinte ultravioleta con base metálica
Si su señal inalámbrica parece débil en algunos puntos, asegúrese de
que no hay objetos como los anteriores que bloqueen la ruta de la señal
(entre sus computadores y el enrutador inalámbrico o punto de acceso).
3. Ubicación del teléfono inalámbrico
Si el rendimiento de su red inalámbrica se ve afectado una vez
resueltos los posibles inconvenientes mencionados anteriormente,
y usted tiene un teléfono inalámbrico:
• Trate de alejar los teléfonos inalámbricos del enrutador
inalámbrico (o punto de acceso) y de sus computadoras
habilitadas con conexión en red inalámbrica
• Desconecte y retire las baterías de cualquier teléfono
inalámbrico que opere en la banda de 2.4 GHz (consulte
la información del fabricante). Si esto resuelve el problema,
es posible que la interferencia provenga de su teléfono.
• Si su teléfono soporta la selección de canales, cambie el
canal en el teléfono al canal más lejano posible de su red
inalámbrica. Por ejemplo, cambie el teléfono al canal 1
y mueva su enrutador inalámbrico (o punto de acceso) al
canal 11. (Su selección de canal variará dependiendo de
su región.) Consulte el manual del usuario de su teléfono
para instrucciones detalladas.
• Si fuera necesario, contemple la posibilidad de cambiar
su teléfono por uno de 900 MHz ó 5 GHz
3
.
.
sección
1
2
3
4
5
6
Page 90

Introducción
4. Elija el canal “más silencioso” para su red inalámbrica.
En lugares donde los hogares u oficinas están próximos entre sí, como
edificios de apartamentos o complejos de oficinas, es posible que haya
redes inalámbricas próximas que pudieran entrar en conflicto con la suya.
Use la función de “Site Survey” (Reconocimiento de sitio) de su utilidad
de red inalámbrica Belkin para ubicar otras redes inalámbricas y mueva
su enrutador inalámbrico (o punto de acceso) y computadoras a un canal
lo más lejano posible de las demás redes.
Experimente con más de un canal de los que hay disponibles para
encontrar la conexión más clara y evitar la interferencia de teléfonos
inalámbricos u otros dispositivos inalámbricos cercanos.
Para más productos inalámbricos de trabajo en red de Belkin, use
la información detallada sobre reconocimiento de sitios y canales
inalámbricos que se incluye en su Manual del Usuario.
5. Conexiones seguras, VPNs y AOL
Secure connections typically require a user name and password, and
are used where security is important. Secure connections include:
• Virtual Private Network (VPN) connections, often used to connect
remotely to an office network
• The “Bring Your Own Access” program from America Online (AOL),
which lets you use AOL through broadband provided by another
cable or DSL service
• Most online banking websites
• Many commercial websites that require a user name
and password to access your account
Secure connections can be interrupted by a computer’s power
management setting, which causes it to “go to sleep.” The simplest
solution to avoid this is to simply reconnect by re-running the VPN
or AOL software, or by re-logging into the secure website.
A second alternative is to change your computer’s power management
settings so it does not go to sleep; however, this may not be appropriate
for portable computers. To change your power management setting in
Windows, see the “Power Options” item in the Control Panel.
If you continue to have difficulty with Secure Connections, VPNs, and
AOL, please review steps 1–4 in the previous pages to be sure you
have addressed these issues.
These guidelines should allow you to cover the maximum possible area
with your wireless router. Should you need to cover an even wider area,
we suggest the Belkin Wireless Range Extender/Access Point.
For more information regarding our networking products, visit our website
at www.belkin.com/networking or call Belkin Technical Support.
Page 91

Descripción general
Características del producto
La tarjeta cumple con la especificación IEEE 802.11n preliminar
para comunicarse con otros dispositivos inalámbricos que cumplen
con 802.11n preliminar a velocidades de hasta 300 Mbps*. La tarjeta
también es compatible con todos los dispositivos 802.11g a 54 Mps al
igual que productos 802.11b a 11 Mbps. La tarjeta opera en la misma
banda de frecuencia de 2.4 GHz que los productos 802.11b/g Wi-Fi®.
• Operación en banda de 2.4 GHz ISM (Industrial, Científica y Médica)
• Utilidad de red inalámbrica de Belkin integrada y fácil de usar
• Interfaz PCI, para operación prácticamente en cualquier
computadora de escritorio
• WPA, WPA2, encriptación WEP (Privacidad equivalente
a la cableada) de 64 bits ó 128 bits
• Acceso inalámbrico a recursos en red
• Velocidad de datos de hasta 300 Mbps* (802.11n preliminar),
54 Mbps (802.11g) ó 11 Mbps (802.11b)
• Instalación y uso fáciles
• Luces LED de encendido y de actividad
1
1
sección
2
3
4
5
6
5
Page 92

Descripción general
Aplicaciones y ventajas
• Velocidades de conexión hasta de 300 Mbps*
Proporciona conectividad inalámbrica de alta velocidad inmediata
en la casa, el trabajo y en otros lugares de acceso público sin
afectar el rendimiento de otros productos 802.11b/g existentes
• Compatibilidad con productos 802.11b/g
La tarjeta es compatible con productos anteriores
y existentes Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11b/g preliminar)
• Entornosdifíciles de cablear
Permite instalar redes en edificios con paredes sólidas,
terminadas o áreas abiertas donde es difícil instalar cables.
• Ambientes con cambios frecuentes
Se adapta fácilmente en oficinas o entornos con cambios
frecuentes en la disposición o ubicación
• Necesidades de conexión en red para oficinas
pequeñas y oficinas domésticas
Proporciona la instalación fácil y rápida de redes pequeñas
que necesitan los usuarios
Especificaciones del producto
Interfaz host: PCI de 32 bits
Consumo de energía eléctrica:
802.11b: TX 920mA @ 3.3V, RX 400mA @ 3.3V
802.11g: TX 1000mA @ 3.3V, RX 400mA @ 3.3V
802.11n: Operación en 20 MHz, TX 1000 mA a 3.3 V,
Operación en 40 MHz, TX 1070 mA a 3.3 V,
Temperatura de operación: 32–131 grados F (0–55 grados C)
Temperatura de almacenaje:
Humedad: Máx. 90% (sin condensación)
Rango de operación típico: Hasta 1,400 pies. (426.7m)**
*
NOTA: La velocida d de trans mis ión e stándar de 300 Mbps es la v elocidad físi ca de
la trans misión de datos. La capacida d real de tranferencia de datos será meno r.
RX 400 mA a 3.3 V
RX 500 mA a 3.3 V
-4–176 grados F (-20–80 grados C)
**El desem peñ o ina lámbrico podr ía varia r dependiendo del ambie nte d e la red.
Page 93

Descripción general
(a) Luz LED de encendido/actividad
Se enciende cuando la tarjeta está encendida; parpadea cuando
se detecta actividad inalámbrica
(b) Conector de la tarjeta
Parte de la tarjeta que entra en la ranura PCI de su computadora
(c) Conector de la antena externa
Le permite conectarse al cable de la antena externa
Requisitos del sistema
• Computadora de escritorio compatible con PC que contiene:
una ranura PCI de 32 bits disponible
• 128 MB de RAM o superior
• Procesador de 500 MHz o superior
• Windows
®
2000 ó XP
Contenido del paquete
• Tarjeta inalámbrica N1 para computadora de escritorio
• Antena externa con cable
• Guía de instalación rápida
• CD con el software de instalación
• Manual del usuario
(b)
(a)
(c)
7
sección
1
2
3
4
5
6
Page 94

Paso 1 Instale
IMPORTANTE
: Instale el software antes de insertar la tarjeta.
1.1 Inserte el CD de instalación en la unidad de CD-ROM.
1.2 La pantalla del instalador de la tarjeta inalámbrica Belkin
aparecerá automáticamente. (Esto podría tomar de 15 a 20
segundos.) Pulse en “Install Software” (Instalar el software)
o en “Next” (Siguiente) para iniciar la instalación.
Nota: Si el instalador de la tarjeta inalámbrica Belkin no aparece en
20 segundos, acceda su unidad de CD-ROM pulsando dos veces en
el icono “My Computer” (Mi PC); luego pulse dos veces en la unidad
de CD-ROM en la que se ha colocado el disco CD de Instalación.
Después, pulse dos veces en el icono “Setup.exe”.
1.3 Ahora iniciará el “InstallShield Wizard”
(Asistente InstallShield). Pulse en
“Next” (Siguiente) para continuar.
Cómo instalar y configurar la tarjeta
Page 95

Cómo instalar y configurar la tarjeta
1.4 Seleccione una carpeta de destino
diferente para la instalación del
software o simplemente pulse
en “Next” (Siguiente).
1.5 La primera de una serie de pantallas
de monitoreo de progreso le
permitirá saber dónde está en
el proceso de configuración.
1.6 Podría ver una pantalla similar a
ésta. Esto NO SIGNIFICA que haya
un problema. Nuestro software
ha sido probado por completo y
es compatible con este sistema
operativo. Seleccione “Continue
Anyway” (Continuar de cualquier
manera) y siga las instrucciones
en la pantalla.
1
2
sección
3
4
5
6
9
Page 96

Cómo instalar y configurar la tarjeta
Paso 2 Inserte
Inserte la tarjeta a su computadora
2.1 Apague su computadora y desconecte el cable de energía
de su computadora.
2.2 Retire los tornillos que se encuentran en la parte trasera de la
caja de su computadora y que sujetan la tapa; retire la tapa.
2.3 Toque cualquier parte de metal de la caja para descargar electricidad
estática y así evitar daños a su producto o a la computadora.
2.4 Localice una ranura PCI de
expansión vacía (usualmente es
de color blanco). Asegúrese de
que la tarjeta cabe en la ranura
que haya elegido.
2.5 Quite el herraje de metal de la
ranura PCI en la parte trasera de
la computadora que corresponda a
la ranura PCI que ha seleccionado.
Si hay un tornillo, colóquelo en un
lugar seguro ya que lo necesitará
usar para colocar la tarjeta en la
computadora posteriormente.
2.6 Inserte la tarjeta firmemente en la
ranura PCI que usted eligió usar.
Page 97

Cómo instalar y configurar la tarjeta
2.7 Ahora asegure la tarjeta con el tornillo que colocó en un lugar seguro.
2.8 Reemplazca la cubierta de la computadora. Conecte el cable de
la antena externa en el conector de la parte de atrás de la tarjeta.
2.9 Ahora que la tarjeta está instalada, puede volver a conectar
el cable de corriente a la computadora y volver a encenderla.
Paso 3 Terminar
Termine la instalación de la tarjeta
3.1 Aparecerá la pantalla de “Found
New Hardware Wizard” (Asistente
para añadir el nuevo hardware
detectado). (Esto podría tomar de
3 a 15 segundos.) Seleccione “Yes,
this time only” (Sí, por esta única
vez) y pulse en “Next” (Siguiente)
para instalar el hardware.
3.2 Seleccione “Install the software
automatically” (Instalar el software
automáticamente) y pulse “Next”
(Siguiente) para instalar el hardware.
1
2
sección
3
4
5
6
11
Page 98

Cómo instalar y configurar la tarjeta
3.3 The Asistente ahora instalará
su software.
3.4 Podría ver una pantalla similar a
ésta. Esto NO SIGNIFICA que haya
un problema. Nuestro software
ha sido probado por completo y
es compatible con este sistema
operativo. Seleccione “Continue
Anyway” (Continuar de cualquier
manera) y siga las instrucciones
en la pantalla.
3.5 La instalación ya está terminada.
Pulse en “Finish” (Terminar)
para salir.
Page 99

Cómo instalar y configurar la tarjeta
Paso 4 Configuración
Use la Utilidad de red inalámbrica Belkin
4.1 Después de reiniciar su computadora,
pulse dos veces el icono de Utilidad
de red inalámbrica de Belkin en la
pantalla del escritorio.
4.2 La pantalla de la utilidad de la
red inalámbrica Belkin aparecerá
automáticamente.
4.3 Seleccione una red a la cual
conectarse en la lista “Available
networks” (Redes disponibles) y
pulse en “Connect” (Conectar).
Nota:
debe estar cerca de un enrutador
inalámbrico o punto de acceso
inalámbrico que funcione.
1
2
sección
3
4
5
6
Para ver sus redes disponibles,
4.4 El icono de la Utilidad de red
inalámbrica de Belkin también
se puede encontrar en la bandeja
del sistema.
El pulsar dos veces en
Nota:
el icono de la Utilidad de red
inalámbrica de Belkin en la bandeja
del sistema hará que aparezca la
pantalla de “Utility” (Utilidad).
La instalación ya está terminada.
13
Page 100

Cómo usar la utilidad de red inalámbrica Belkin
Después de instalar con éxito la Utilidad de red inalámbrica de Belkin,
las configuraciones para la conexión y la seguridad inalámbricas
están a unos cuantos pulsos.
Cómo acceder la Utilidad de red inalámbrica de
Belkin en la bandeja del sistema de Windows
Para tener acceso a la Utilidad de red inalámbrica, sólo coloque
el puntero del ratón y pulse el botón derecho sobre el icono de la
Utilidad de red inalámbrica en la bandeja de tareas de Windows.
Si el icono no está presente, pulse en “Start > Programs >
Belkin Wireless Utility” (Inicio > Programas > Utilidad de red
inalámbrica de Belkin).
 Loading...
Loading...