Page 1

2.4 GHz 54 Mbps
802.11g Wireless Cable/DSL Router
User Manual
ENGLISH
FRANÇAIS
DEUTSCH
NEDERLANDS
ESPAÑOL
ITALIANO
F5D7230ea4-E
P74847ea-A
Page 2

Index
ENGLISH ........................................................................................................... 1
FRANÇAIS ........................................................................................................29
DEUTSCH ......................................................................................................... 59
NEDERLANDS .................................................................................................. 89
ESPAÑOL ........................................................................................................ 119
ITALIANO ......................................................................................................... 149
Page 3

2.4 GHz 54 Mbps
802.11g Wireless Cable/DSL Router
User Manual
ENGLISH
F5D7230ea4-E
P74847ea-A
Page 4

Trademarks:
Other product and company names are trademarks or registered trademarks
of their respective holders.
Page 5

Contents
About the IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2
LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
2
Features and Benefits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3
Installing the IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4
Package Contents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4
Hardware Description
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
System Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7
Connect the System
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Basic Installation Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
8
Configuring Client TCP/IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
12
Configuring Your Computer in Windows 2000 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
13
Configuring Your Computer in Windows XP
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Configuring a Macintosh Computer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
17
Manual IP Configuration (for all Windows OS) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
18
Verifying Your TCP/IP Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
20
Navigating the WEB browser Interface
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Connection Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
23
Dynamic
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Static . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24
PPPoE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
24
PPTP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
25
Page 6
2
About the IEEE 802.11G Wireless Router
Congratulations on your purchase of the IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router. The
F5D7230xx4-E is a powerful yet simple communication device for connecting
your local area network (LAN) to the Internet.
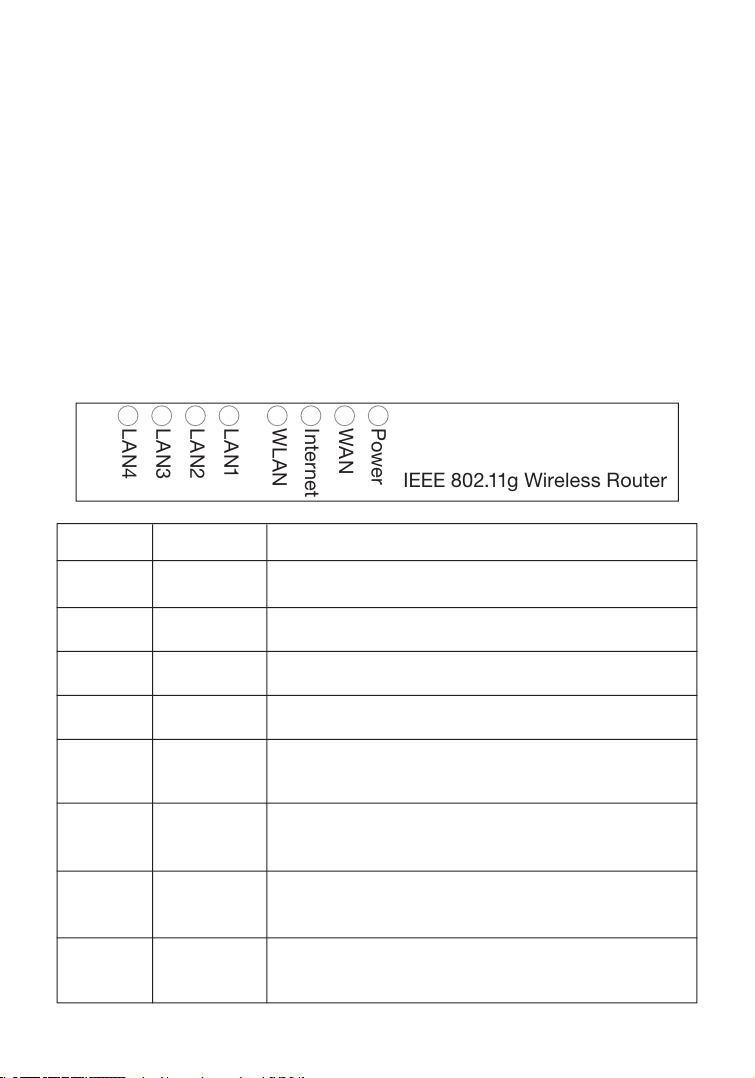
LED Indicators
The IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router includes status LED indicators, as
described in the following figure and table.
LED Status Description
Power On The Wireless Router is receiving power.
WAN On The WAN link is connected.
Online On PPP connection is on.
WLAN On The Wireless LAN is enabled.
Flashing The Wireless Router is transmitting or
receiving traffic via a wireless connection.
LAN1-4 Green On The indicated Ethernet port has established
a valid 100 Mbps network connection.
Amber On The indicated Ethernet port has established
a valid 10 Mbps network connection.
Flashing The indicated Ethernet port is transmitting
or receiving traffic.
LAN4
LAN3
LAN2
LAN1
WLAN
Internet
WAN
Power
IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router
Page 7

3
Features and Benefits
• Internet connection to DSL or cable modem via a 10/100 Mbps WAN port
• Local network connection via 10/100 Mbps Ethernet ports or 54 Mbps
wireless interface
• IEEE 802.11g Compliant – interoperable with multiple vendors
• Advanced security through 64/128-bit WEP encryption, 802.1x, SSID
broadcast disabled, and MAC address filtering features to protect your
sensitve data and authenticate only authorized users to your network
• Provides seamless roaming within 802.11g WLAN environment
• DHCP for dynamic IP configuration, and DNS for domain name mapping
• Firewall with Stateful Packet Inspection, client privileges, hacker prevention,
DoS, and NAT
• NAT also enables multi-user access with a single-user account, and virtual
server functionality such as web, mail, FTP, and Telnet
• Virtual Private Network support using PPTP, L2TP, or IPSec pass-through,
ISP permitting
• Parental controls allow the user to restrict web browsing
• Automatic email alerts when the network is being attacked
• Easy setup through a web browser on any operating system that supports
TCP/IP
• Compatible with all popular Internet applications
Page 8

4
Installing the IEEE 802.11G Wireless Router
Before installing the Wireless Router, verify that you have all the items listed
under “Package Contents.” If any of the items are missing or damaged,
contact your local distributor. Also be sure that you have all the necessary
cabling before installing the Wireless Router. After installing the Wireless
Router, refer to the web-based configuration program in “Configuring the
IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router” on page 20 for information on configuring the
Wireless Router.
Package Contents
After unpacking the Wireless Router, check the contents of the box to be sure
you have received the following components:
• IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router
• Power adapter
• One CAT-5 Ethernet cable
• User guide
Immediately inform your dealer in the event of any incorrect, missing or
damaged parts. If possible, please retain the carton and original packing
materials in case there is a need to return the product.
For complete details on this products warranty, please refer to the Micradigital
support site. www.micradigital.com
Page 9

5
Hardware Description
The Wireless Router can be connected to the Internet or to a remote site
using its WAN port. It can be connected directly to your PC or to a local area
network using any of the Fast Ethernet LAN ports.
Although access speed to the Internet is determined by your service type and
the modem type connected to the Wireless Router, data passing between the
devices connected to your local area network can run up to 100 Mbps over
the Fast Enternet ports.
The Wireless Router includes an LED display on the front panel for
system power and port indications that simplifies installation and network
troubleshooting. It also provides four RJ-45 LAN ports and one RJ-45 WAN
port on the rear panel.
• Four Ethernet ports for connection to a 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX Ethernet
Local Area Network (LAN). These ports can auto-negotiate the operating
speed to 10/100 Mbps, the mode to half/full duplex, and the pin signals to
MDI/MDI-X (i.e., allowing these ports to be connected to any network device
with straight-through cable). These ports can be connected directly to a
PC or to a server equipped with an Ethernet network interface card, or to a
networking device such as an Ethernet hub or switch.
• One RJ-45 port for connection to a DSL or cable modem (WAN). This port
also auto-negotiates operating speed to 10/100 Mbps, the mode to half/full
duplex, and the pin signals to MDI/MDI-X.
The following figure shows the components of the Wireless Router:
Page 10
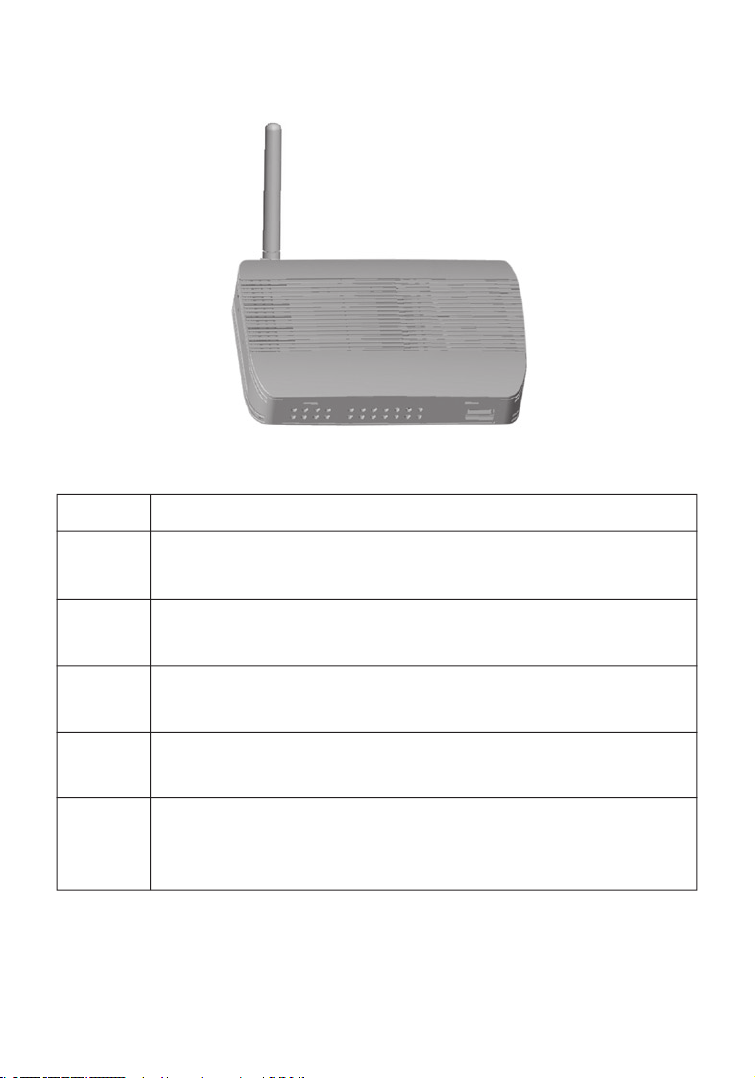
6
Figure 1. Front and Rear Panels
Item Description
LEDs Power, WLAN, WAN and LAN port status indicators.
(See “LED Indicators” on page 1.)
LAN
Fast Ethernet ports (RJ-45). Connect devices (such as a PC,
Ports hub or switch) on your local area network to these ports.
Reset
Use this button to reset the power and restore the default
Button factory settings.
WAN
WAN port (RJ-45). Connect your cable modem, DSL modem,
Port or an Ethernet router to this port.
Power Connect the included power adapter to this inlet.
Inlet Warning: Using the wrong type of power adapter may
damage your Wireless Router.
Page 11

7
System Requirements
• Internet access from your local telephone company or Internet Service
Provider (ISP) using a DSL modem or cable modem.
• A PC using a fixed IP address or dynamic IP address assigned via DHCP, as
well as a gateway server address and DNS server address from your service
provider.
• A computer equipped with a 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, or 10/100 Mbps Fast
Ethernet card, or a USB-to-Ethernet converter.
• TCP/IP network protocol installed on each PC that needs to access the
Internet.
• A Java-enabled web browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5
or above, Firefox 1.0 or Mozilla 1.7 installed on one PC at your site for
configuring the Wireless Router.
Connect the System
The Wireless Router can be positioned at any convenient location in your
office or home. No special wiring or cooling requirements are needed. You
should, however comply with the following guidelines:
• Keep the Wireless Router away from any heating devices.
• Do not place the Wireless Router in a dusty or wet environment.
You should also remember to turn off the power, remove the power cord from
the outlet, and keep your hands dry when you install the Wireless Router.
Page 12
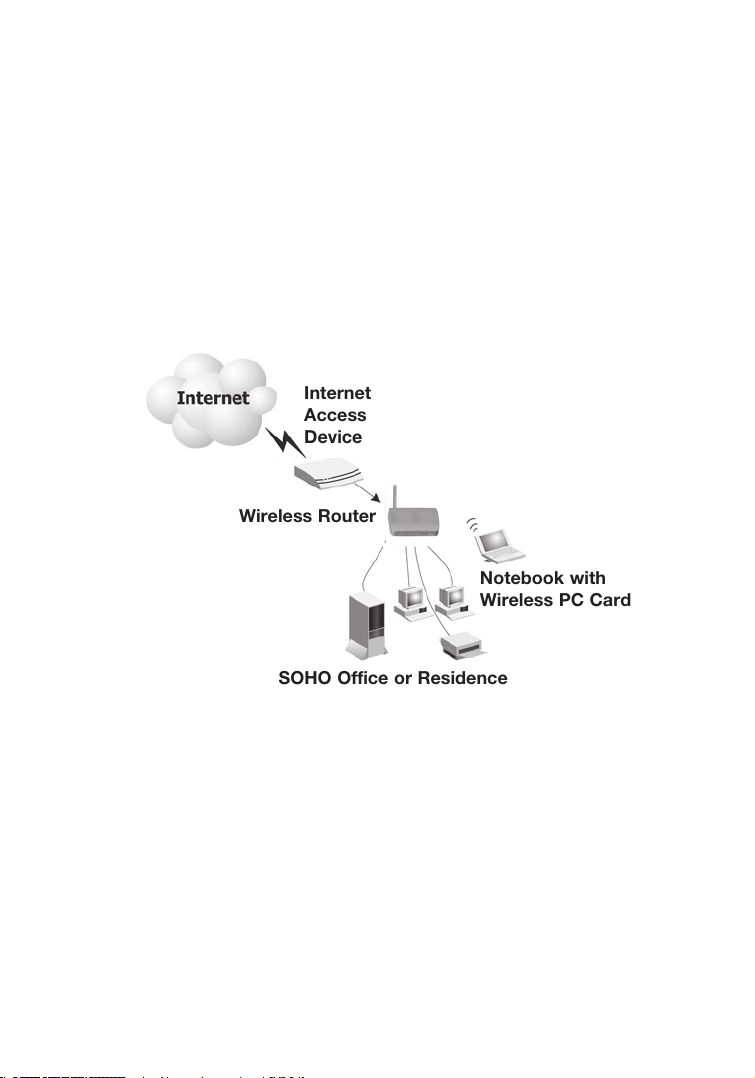
Basic Installation Procedure
1. Connect the LAN: Connect the Wireless Router to your PC, or to a hub
or switch. Run Ethernet cable from one of the LAN ports on the rear of the
Wireless Router to your computer’s network adapter or to another network
device. You may also connect the Wireless Router to your PC (using a
wireless client adapter) via radio signals.
2. Connect the WAN: Use an Ethernet cable for connecting the Wireless
Router to a cable/xDSL modem or Ethernet router.
3. Power on: Connect the power adapter to the Wireless Router.
Figure 2. Example Network Configuration
8
SOHO Office or Residence
Notebook with
Wireless PC Card
Internet
Access
Device
Wireless Router
Page 13
9
Attach to Your Network Using Ethernet Cabling
Use twisted-pair cable to connect any of the four LAN ports on the Wireless
Router to an Ethernet adapter on your PC. Otherwise, you can cascade any of
the LAN ports on the Wireless Router to an Ethernet hub or switch, and then
connect your PC or other network equipment to the hub or switch. When
inserting an RJ-45 plug, be sure the tab on the plug clicks into position to
ensure that it is properly seated.
Warning: Do not plug a phone jack connector into any RJ-45 port. This may
damage the Wireless Router. Instead, use only twisted-pair cables
with RJ-45 connectors that conform with FCC standards.
Figure 3. Making a LAN Connection
Page 14
Attach to Your Network Using Radio Signals
Install a wireless network adapter in each computer that will be connected to
the Internet or your local network via radio signals.
Try to place the Wireless Router in a position that is located in the center of
your wireless network. Normally, the higher you place the antenna, the better
the performance. Ensure that the Wireless Router’s location provides optimal
reception throughout your home or office.
A wireless infrastructure can be used for access to a central database, or for
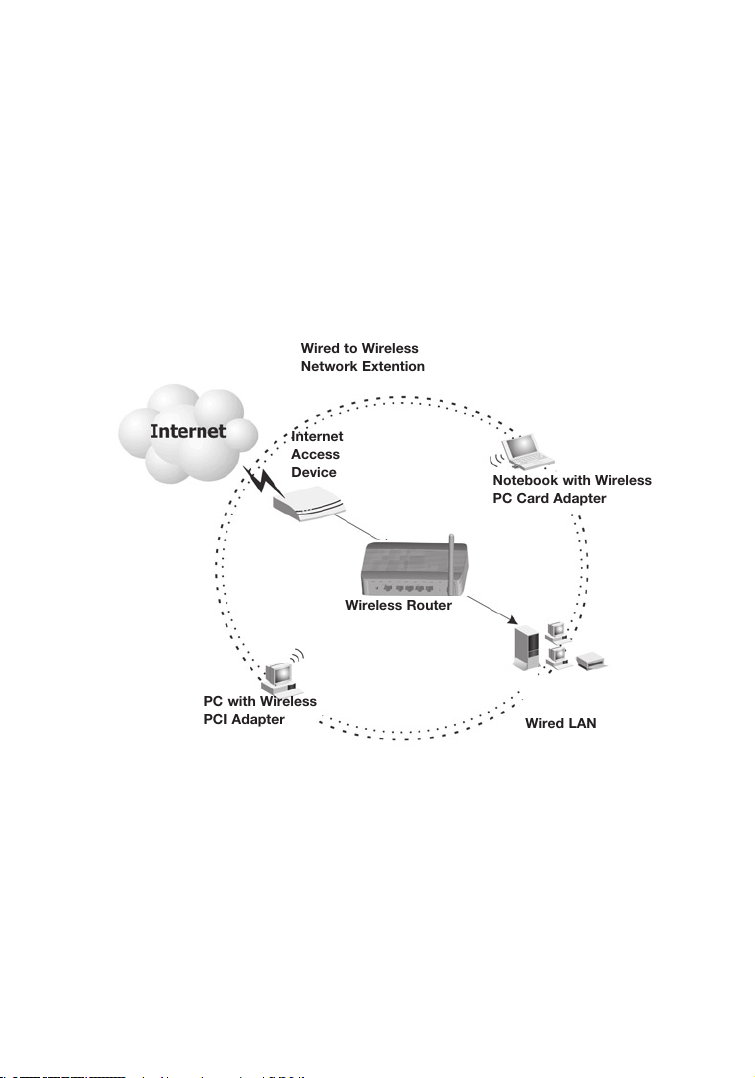
connection between mobile workers, as shown in the following figure:
Figure 4. WLAN Connection Example
1010
Wired to Wireless
Network Extention
Internet
Access
Device
Wireless Router
PC with Wireless
PCI Adapter
Notebook with Wireless
PC Card Adapter
Wired LAN
Page 15
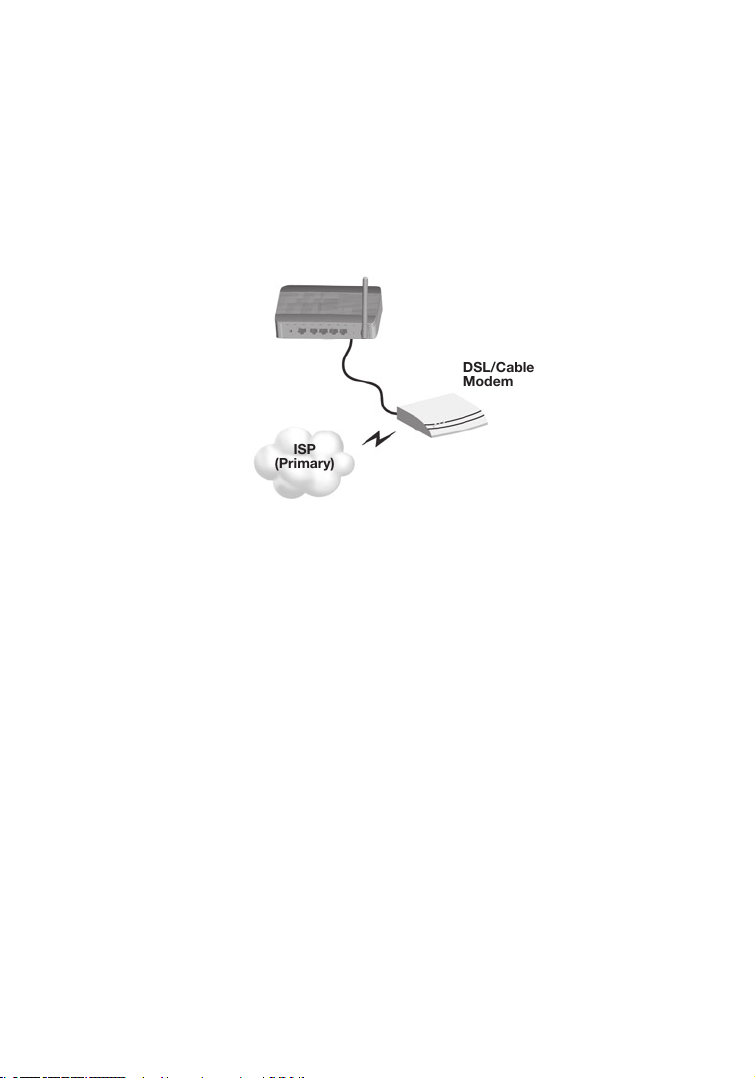
Attach the IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router to the Internet
If Internet services are provided through an xDSL or cable modem, use
unshielded or shielded twisted-pair Ethernet cable CAT 5 with RJ-45 plugs
to connect the broadband modem directly to the WAN port on the Wireless
Router.
Figure 5. WAN Connection Example
ISP
(Primary)
DSL/Cable
Modem
Page 16

Configuring Client TCP/IP
To access the Internet through the Wireless Router, you must configure the
network settings of the computers on your LAN to use the same IP subnet as
the Wireless Router. The default network settings for the Wireless Router are:
Gateway IP Address: 192.168.2.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Note: These settings may be changed to suit your network requirements,
but you must first configure at least one computer as described in this
chapter to access the Wireless Router’s web configuration interface.
See “Configuring the IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router” on page 20 for
information on configuring the Wireless Router.
The IP address of the connected client PC should be 192.168.2.x (where
x means 2–254). You can set the IP address for client PCs either by
automatically obtaining an IP address from the Wireless Router’s DHCP
service or by manual configuration.
12
Page 17
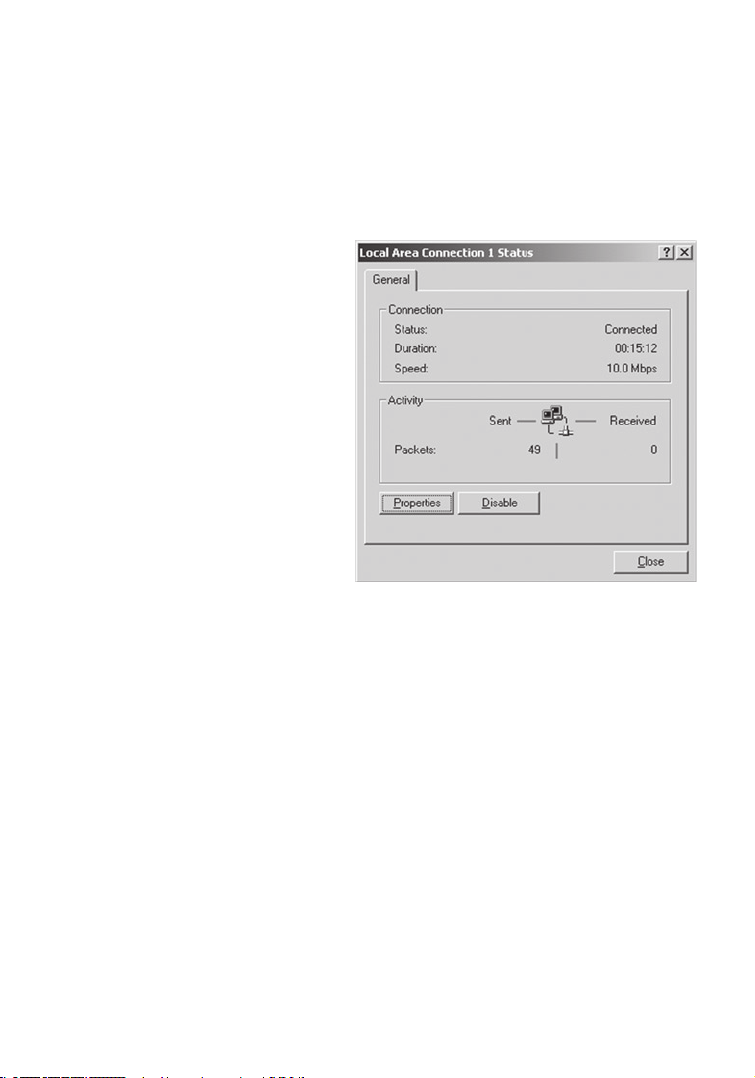
13
Configuring Your Computer in Windows 2000
1. Access your network settings by clicking Start, then choose Settings and
then select Control Panel.
2. In the Control Panel, locate and double-click the Network and Dial-up
Connections icon.
3. Locate and double-click the
Local Area Connection icon
for the Ethernet adapter that
is connected to the Wireless
Router. When the Status dialog
box window opens, click the
Properties button.
4. In the Local Area Connection
Properties box, verify the box
next to Internet Protocol (TCP/
IP) is checked. Then highlight the
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), and
click the
Properties button.
5. Select Obtain an IP address
automatically to configure your
computer for DHCP. Click the
OK button to save this change and close the
Properties window.
6. Click the
OK button again to save these new changes.
7. Reboot your PC.
8. To obtain new network settings see See “Obtain IP Settings from Your IEEE
802.11g Wireless Router” on the next page.
Page 18
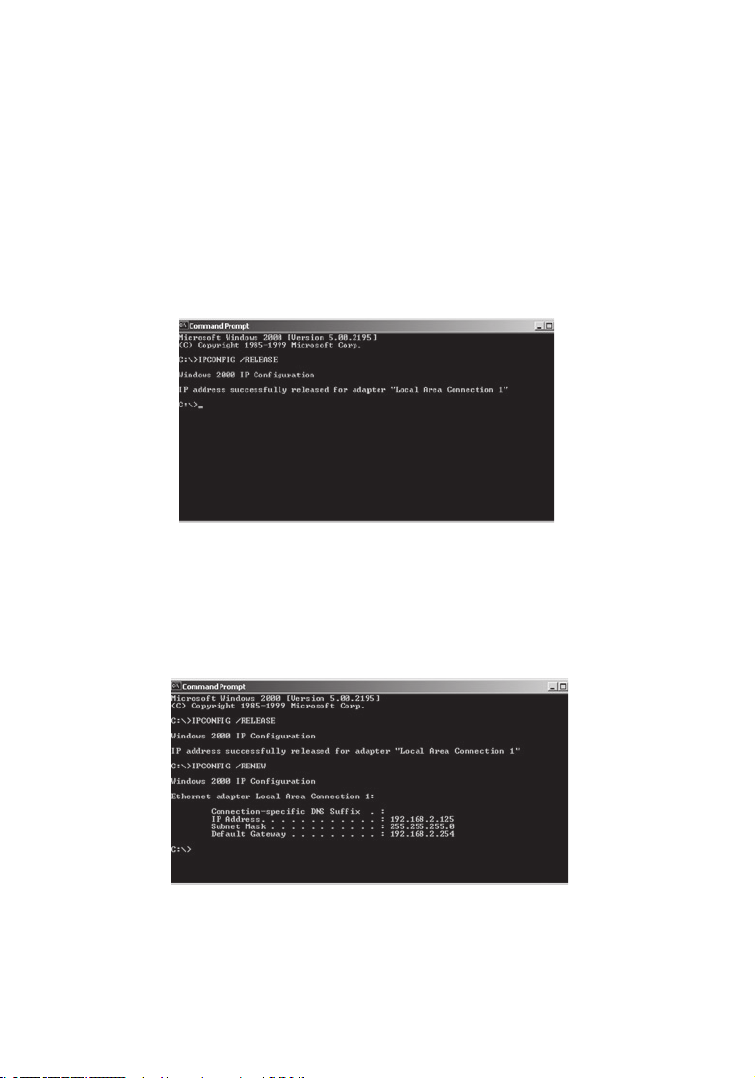
Obtain IP Settings from Your IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router
Now that you have configured your computer to connect to the Wireless
Router, it needs to obtain new network settings. By releasing old IP settings
and renewing them with settings from the Wireless Router, you will also verify
that you have configured your computer correctly.
1. On the Windows desktop, click Start/Programs/Command Prompt.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type ipconfig /release and press the Enter
key.
3. Type ipconfig /renew and press the Enter key. Verify that your IP Address
is now 192.168.2.xxx, your Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0 and your Default
Gateway is 192.168.2.1. These values confirm that the Wireless Router is
functioning.
4. Type exit and press Enter to close the Command Prompt window.
14
Page 19
15
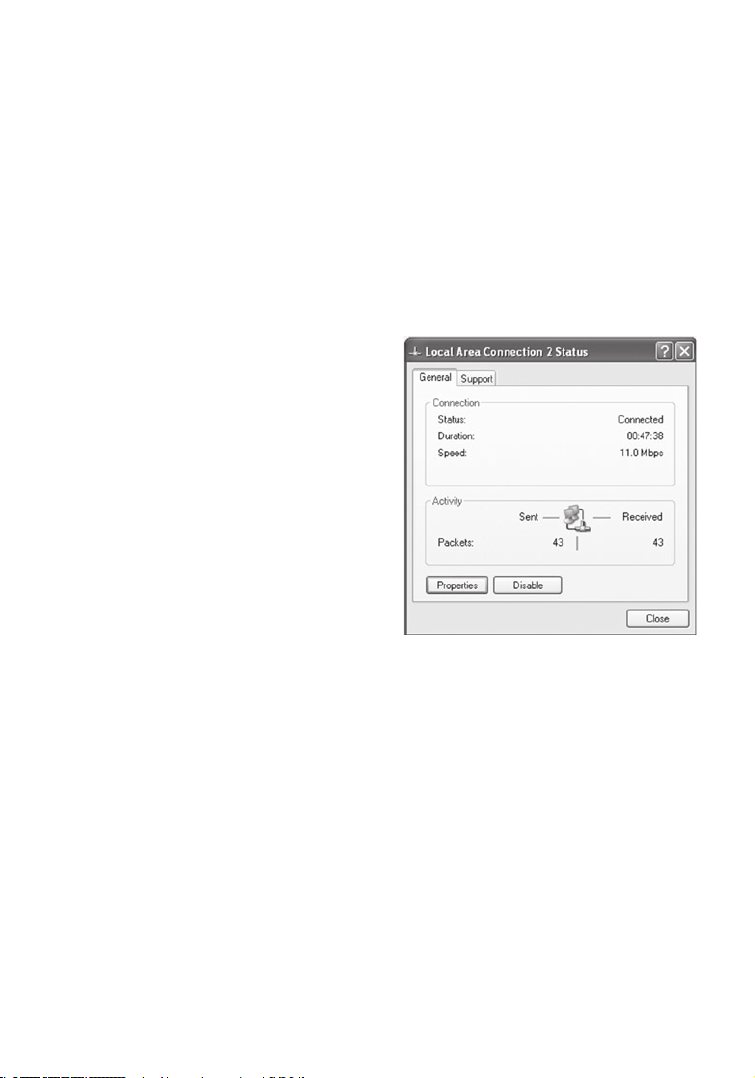
Configuring Your Computer in Windows XP
The following instructions assume you are running Windows XP with the
default interface. If you are using the Classic interface (where the icons and
menus look like previous Windows versions), please follow the instructions for
Windows 2000 outlined above.
1. Access your Network settings by clicking Start, choose Control Panel,
select Network and Internet Connections and then click on the Network
Connections icon.
2. Locate and double-click the Local
Area Connection icon for the
Ethernet adapter that is connected to
the Wireless Router. Next, click the
Properties button.
3. In the Local Area Connection Properties box, verify the box next to
Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) is checked. Then highlight the Internet
Protocol (TCP/IP), and click the Properties
button.
4. Select Obtain an IP address automatically to configure your computer for
DHCP. Click the
OK button to save this change and close the Properties
window.
5. Click the
OK button again to save these new changes.
6. Reboot your PC.
Page 20
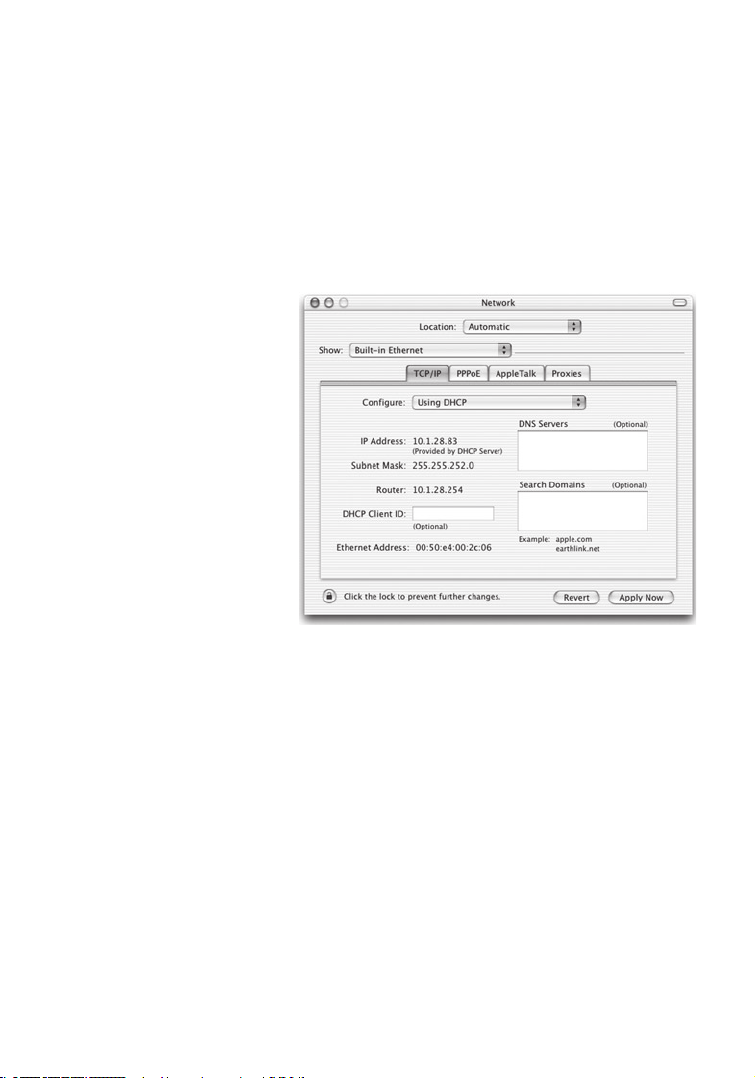
Configuring a Macintosh Computer
You may find that the instructions here do not exactly match your screen.
This is because these steps and screen shots were created using Mac OS
10.2. Mac OS 7.x and above are all very similar, but may not be identical to
Mac OS 10.2.
1. Pull down the Apple Menu. Click System Preferences and select Network
.
2. Make sure that
Built-in
Ethernet is selected in the
Show field.
3. On the
TCP/IP tab, select
Using DHCP in the
Configure field.
4. Close the
TCP/IP
dialog box.
16
Page 21
17
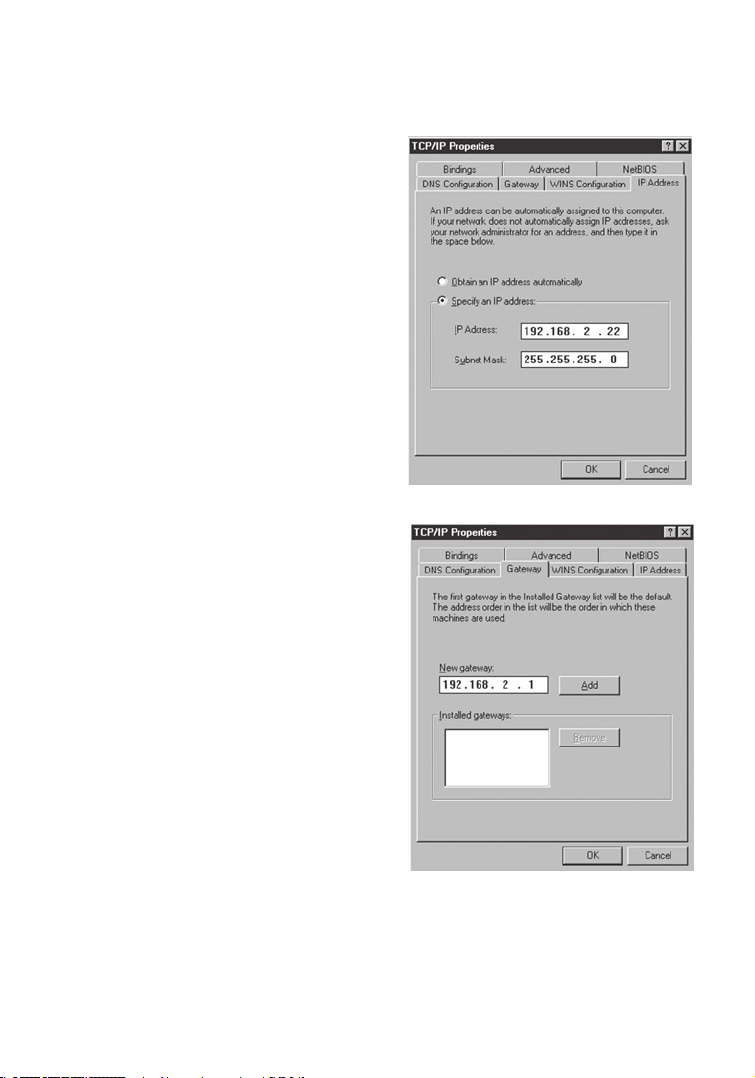
Manual IP Configuration (for all Windows OS)
1. Check Specify an IP address on the IP
Address tab. Enter an IP address based
on the default network 192.168.2.x
(where x is between 2 and 254), and
use 255.255.255.0 for the subnet mask.
2. In the
Gateway tab, add the IP
address of the Wireless Router (default:
192.168.2.1) in the New gateway field
and click
Add.
Page 22
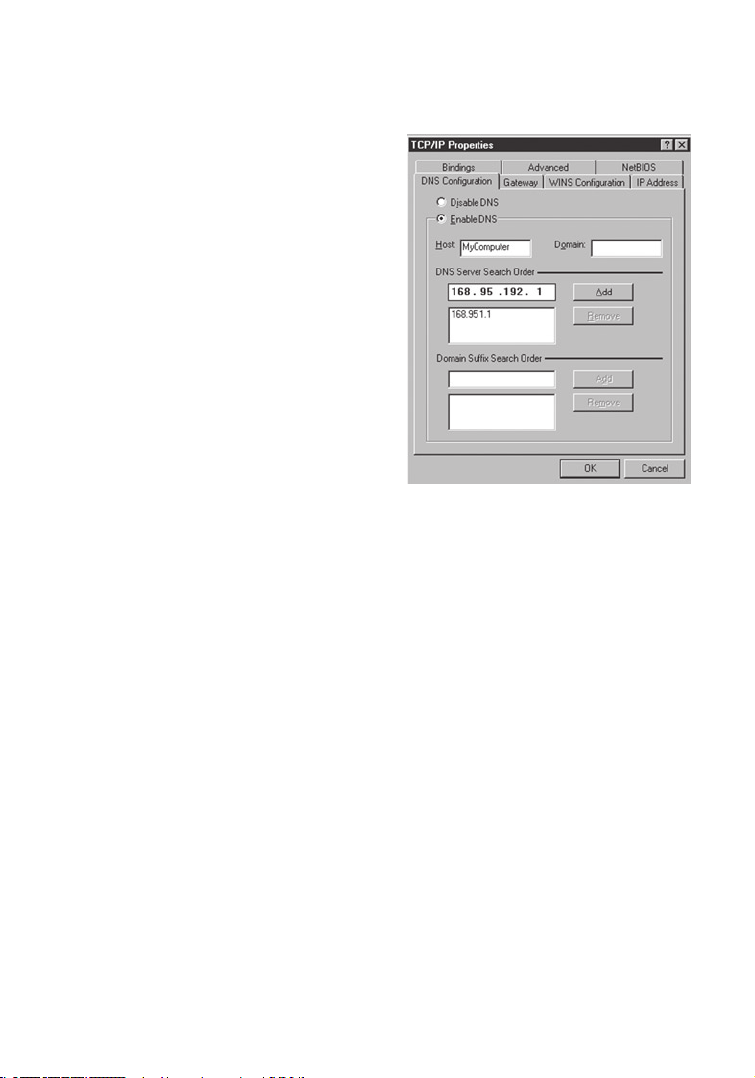
3. On the DNS Configuration tab, add the
IP address for the Wireless Router and
click Add. This automatically relays DNS
requests to the DNS server(s) provided
by your ISP. Otherwise, add specific
DNS servers into the DNS Server
Search Order field and click Add.
4. After finishing TCP/IP setup, click OK,
and then reboot the computer. After
that, set up other PCs on the LAN
according to the procedures described
above.
18
Page 23

19
Verifying Your TCP/IP Connection
After installing the TCP/IP communication protocols and configuring an IP
address in the same network as the Wireless Router, use the ping command
to check if your computer has successfully connected to the Wireless Router.
The following example shows how the ping procedure can be executed in an
MS-DOS window. First, execute the ping command:
ping 192.168.2.1
If a message similar to the following appears:
Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=64
a communication link between your computer and the Wireless
Router has been successfully established.
If you get the following message,
Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
there may be something wrong in your installation procedure.
Check the following items in sequence:
1. Is the Ethernet cable correctly connected between the Wireless Router
and the computer?
The LAN LED on the Wireless Router and the Link LED of the network card
on your computer must be on.
2. Is TCP/IP properly configured on your computer?
If the IP address of the Wireless Router is 192.168.2.1, the IP address of
your PC must be from 192.168.2.2-254 and the default gateway must be
192.168.2.1.
If you can successfully ping the Wireless Router you are now ready to
connect to the Internet!
Page 24

Configuring the IEEE 802.11G Wireless Router
The IEEE 802.11g Wireless Router can be configured by Internet Explorer
5.5 or above. Using the web management interface, you can configure the
Wireless Router and view statistics to monitor network activity.
Before you attempt to log into the web-based administration, please verify the
following.
1. Your browser is configured properly (see below).
2. Disable any firewall or security software that may be running.
3. Confirm that you have a good link LED where your computer is plugged into
the Wireless Router. If you don’t have a link light, then try another cable until
you get a good link.
Browser Configuration
Confirm your browser is configured for a direct connection to the Internet
using the Ethernet cable that is installed in the computer.
Disable Proxy Connection
You will also need to verify that the HTTP Proxy feature of your web browser
is disabled. This is so that your web browser will be able to view the Wireless
Router configuration pages. The following steps are for Internet Explorer.
Internet Explorer 5.5 or above (For Windows)
1. Open Internet Explorer. Click Tools, and then select Internet Options.
2. In the Internet Options window, click the Connections tab. Navigating the
Web Browser Interface
3. Click the LAN Settings button.
4. Clear all the check boxes and click OK to save these LAN settings changes.
5. Click OK again to close the Internet Options window.
20
Page 25
21
Internet Explorer (For Macintosh)
1. Open Internet Explorer. Click Explorer/Preferences
.
2. In the Internet Explorer Preferences window, under Network, select
Proxies.
3. Uncheck all check boxes and click OK.
Navigating the Web Browser Interface
1. To access the Wireless routers management interface, enter the
address or the wireless router in the address bar of your web browser:
http://192.168.2.1
2. You are required to Log in before you can proceed any further. Click on
the Login button on the top right hand side of the screen. By default the
password is blank so you can just click the ‘Submit’ button
Page 26

3. To set-up the Internet connection, In Menu list on the left hand side of the
screen, locate the option ‘Connection Type’ which can be found under the
‘Internet WAN’ category
4. WAN > Connection type screen allows you to select the connection type
needed to make a connection to your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Please
consult the information provided by you ISP to make sure you make the
correct selection. Once you have selected the correct Connection type, click
on ‘Next’
22
Page 27

23
Connection Type
a. Dynamic:
Your Internet Service
Provider may have
given you a host
name. If so enter it
into the field.
If your ISP used the Mac Address of an Ethernet card as an Identifier when
first setting up your broadband account click on the button ‘Change WAN
MAC address’ It is important to note that you should only connect the
computer with the registered MAC address to the router during configuration.
Click on the button marked ‘
Clone‘ to replace the Wireles router MAC address
with the one from your computers Ethernet card, which is registered with your
ISP.
Page 28

b. Static:
If your Internet
Service provider has
given you your own
IP address choose
this option and fill
in the details in the
relevant fields
c. PPPoE:
Enter the PPPoE User Name and Password assigned by your Service Provider.
The Service Name is normally optional, but may be required by some service
providers.
Leave the Maximum
Transmission Unit
(MTU) at the default
value (1454) unless
you have a particular
reason to change it.
Enter a Maximum
Idle Time
(in minutes)
to define a maximum
period of time for
which the Internet
connection is
maintained during
inactivity. If the
connection is inactive
for longer than the Maximum Idle Time, it will be dropped. (Default: 3 minutes)
2424
Page 29
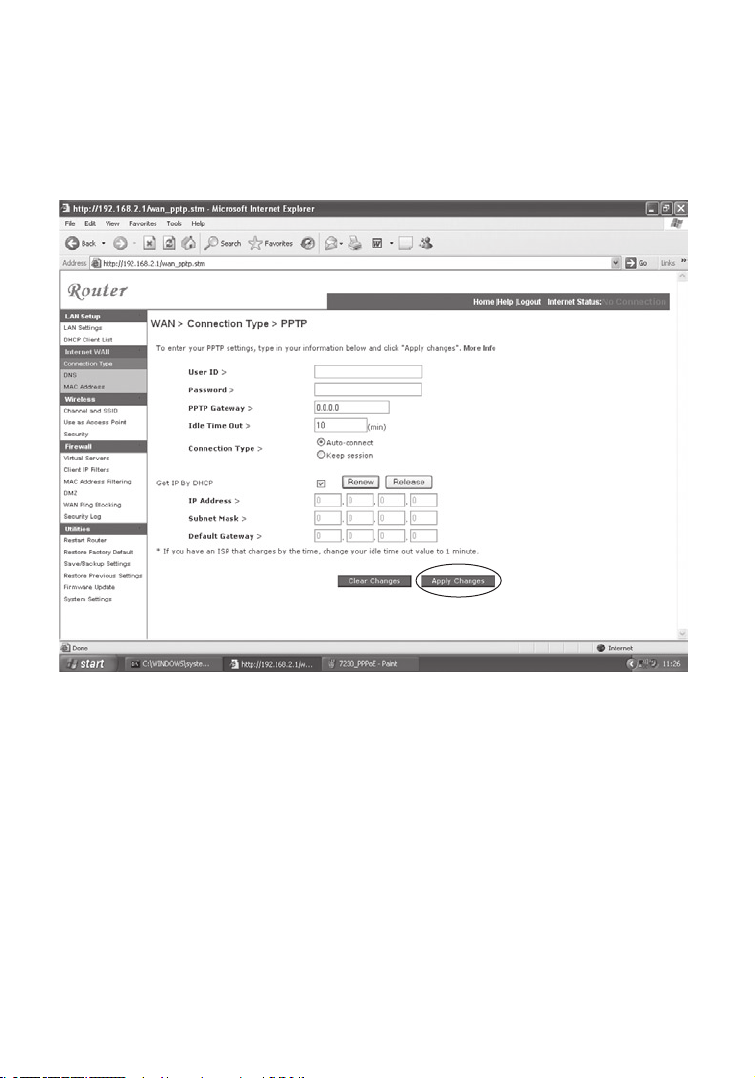
d. PPTP:
If your ISP has specified this connection type for making the connection to the
internet. Enter the details in the relevant fileds and click on the Apply Changes
button
Page 30

If you have been provided with the information as shown on the screen, enter
the PPTP Account name and password, Host Name, Service IP Address, the
assigned IP Address, and Subnet Mask.
Leave the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) at the default value (1460) unless
you have a particular reason to change it.
Enter a Maximum Idle Time (in minutes) to define a maximum period of time for
which the Internet connection is maintained during inactivity. If the connection
is inactive for longer than the Maximum Idle Time, it will be dropped. (Default:
3 minutes)
Note: If you are on a leased line or pay-per min. connection, please set
your maximum idle time to 3 minutes. This will cause your Internet
connection to drop after 3 minutes of idle time so you won’t be charged
for extra online time from your ISP.
Click FINISH to complete the setup.
26
Page 31

27
Page 32

Page 33

2.4 GHz 54 Mbps
Routeur Câble/DSL Sans Fil 802.11g 2,4 GHz
54 Mbps
Manuel de l’utilisateur
FRANÇAIS
F5D7230ea4-E
P74847ea-A
Page 34

Marques de commerce :
Les autres noms de produits et de sociétés sont des marques de commerce
ou des marques déposés de leurs propriétaires respectifs.
Page 35

Table des matières
Présentation du Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g ........................................ 32
Témoins ......................................................................................................
32
Caractéristiques et avantages ....................................................................
33
Installation du Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g ...........................................
34
Contenu de l’emballage .............................................................................
34
Description du matériel ..............................................................................
35
Configuration requise .................................................................................
37
Branchement du système ..........................................................................
37
Procédure d’installation de base .........................................................
38
Configuration TCP/IP côté client ................................................................
42
Configuration de votre ordinateur sous Windows 2000 ......................
43
Configuration de votre ordinateur sous Windows XP .........................
45
Configuration d’un ordinateur Macintosh ............................................
46
Configuration IP manuelle (tous systèmes Windows) .........................
47
Vérification de votre connexion TCP/IP ...............................................
49
Présentation de l’interface du navigateur Web
.......................................... 51
Type de Connexion ....................................................................................
53
Dinamique ............................................................................................
53
Fixe ......................................................................................................
54
PPPoE ..................................................................................................
54
PPTP ....................................................................................................
55
Page 36

32
Présentation du Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g
Merci d’avoir choisi le Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g. Le F5D7230xx4-E est
un appareil de communication simple mais puissant permettant de connecter
votre réseau local (LAN) à Internet.
Témoins
Le Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g comporte plusieurs témoins indicateurs,
présentés dans le tableau suivant.
TÉMOINS État Description
Power Activé Le Routeur Sans Fil est sous tension.
WAN Activé La liaison WAN est établie.
Online Activé La connexion PPP est établie.
WLAN Activé Le réseau sans fil est activé.
Clignotant Le Routeur Sans Fil émet ou reçoit
du trafic par la connexion sans fil.
LAN1-4 Allumé Le port Ethernet indiqué a établi une
(vert) connexion réseau à 100 Mbps.
Allumé Le port Ethernet indiqué a établi une
(ambre) connexion réseau à 10 Mbps.
Clignotant Le port Ethernet indiqué émet
ou reçoit du trafic.
LAN4
LAN3
LAN2
LAN1
WLAN
Internet
WAN
Power
Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g
Page 37

33
Caractéristiques et avantages
• Connexion Internet à un modem câble ou DSL via un port WAN
à 10/100 Mbps
• Connexion à un réseau local via des ports Ethernet 10/100 Mbps ou une
interface sans fil à 54 Mbps
• Compatible IEEE 802.11g pour assurer l’interopérabilité avec les matériels de
multiples constructeurs
• Fonctions de sécurité évoluées par chiffrement WEP 64/128 bits, 802.1x,
diffusion SSID désactivée et filtrage des adresses MAC pour protéger vos
données sensibles et autoriser l’accès à votre réseau uniquement aux
utilisateurs authentifiés
• Autorise une itinérance transparente au sein d’un environnement WLAN
802.11g
• DHCP pour configuration IP dynamique et DNS pour affectation des noms
de domaine
• Pare-feu avec Stateful Packet Inspection, privilèges clients, blocage des
attaques, DoS et NAT
• Le NAT permet aussi un accès multi-utilisateur avec un compte d’utilisateur
unique et offre une fonctionnalité de serveur virtuel de type web, courriel,
FTP et Telnet
• Prise en charge des réseaux privés virtuels (VPN) avec protocoles PPTP,
L2TP ou IPSec pass-through, si le FAI l’autorise
• Contrôle parental permettant à l’utilisateur de restreindre la navigation
sur le Web
• Alertes automatiques par courriel quand le réseau est attaqué
• Configuration facile par un navigateur web ou n’importe quel système
d’exploitation prenant en charge TCP/IP
• Compatible avec toutes les applications Internet courantes
Page 38

34
Installation du Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11G
Avant d’installer le Routeur Sans Fil, vérifiez que vous disposez bien de tous
les éléments énumérés sous “Contenu de l’Emballage.” Si un quelconque
élément est manquant ou endommagé, contactez votre revendeur local.
Assurez-vous également d’avoir tous les câbles nécessaires sous la main
avant d’installer le Routeur Sans Fil. Après l’installation du Routeur Sans Fil,
reportez-vous au programme de configuration basé sur le web expliqué sous
“Configuration du Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g” à la page 20 pour obtenir
des précisions sur la configuration du Routeur Sans Fil.
Contenu de l’emballage
Après avoir déballé le Routeur Sans Fil, vérifiez le contenu de la boîte pour
vous assurer d’avoir bien reçu tous les éléments énumérés ci-après :
• Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g
• Bloc d’alimentation
• Câble Ethernet CAT-5
• Guide de l’utilisateur
Contactez immédiatement votre revendeur si des pièces sont manquantes,
inexactes ou endommagées. Si possible, conservez le carton et les emballages
originaux pour le cas où il faudrait ramener le produit au revendeur.
Pour de plus amples informations sur la garantie de ce produit, veuillez visiter
le site d’assistance Micradifital au www.micradigital.com
Page 39

35
Description du matériel
Le Routeur Sans Fil peut être connecté à Internet ou à un site distant grâce à
son port WAN. Il peut être relié directement à votre PC ou à un réseau local au
moyen de l’un des ports LAN Fast Ethernet.
Bien que la vitesse d’accès à Internet soit déterminée par votre formule
d’abonnement et par le type de modem connecté au Routeur Sans Fil, les
données échangées entre les périphériques connectés à votre réseau local
peuvent circuler jusqu’à 100 Mbps par les ports Fast Ethernet.
Le Routeur Sans Fil comporte en face avant une série de témoins à DEL
permettant de surveiller l’alimentation du système et l’état des ports afin de
faciliter l’installation et la résolution des problèmes de connexion réseau. Il
comprend également sur la face arrière quatre ports LAN RJ-45 et un port
WAN RJ-45.
• Quatre ports Ethernet permettant la connexion à un réseau local (LAN)
de type Ethernet 10BASE-T/100BASE-TX. Ces ports peuvent négocier
automatiquement la vitesse de transfert en 10 ou 100 Mbps, le mode en
semi-duplex ou duplex intégral, et les signaux de broches en MDI ou MDIX (ce qui permet de connecter ces ports à n’importe quel périphérique de
réseau avec un câble droit). Ces ports peuvent être connectés directement
à un PC ou à un serveur équipé d’une interface réseau Ethernet, ou
à un périphérique de mise en réseau comme un concentrateur ou un
commutateur Ethernet.
• Un port RJ-45 permettant la connexion à un modem câble ou DSL (WAN).
Ce port peut lui aussi négocier automatiquement la vitesse de transfert en 10
ou 100 Mbps, le mode en semi-duplex ou duplex intégral et les signaux de
broches en MDI ou MDI-X.
L’illustration suivante montre les composants du Routeur Sans Fil :
Page 40

36
Figure 1. Faces avant et arrière
Elément Description
Témoins Témoins d’alimentation et d’état des ports WLAN, WAN
et LAN. (Voir le tableau “Témoins” en page 1.)
Ports LAN Ports Fast Ethernet (RJ-45). Connectez les appareils
(tels que PC, concentrateur ou commutateur) de votre
réseau local à ces ports.
Bouton de Utilisez ce bouton pour réinitialiser l’alimentation et rétablir
réinitialisation les paramètres par défaut du constructeur.
Port WAN Port WAN (RJ-45). Connectez votre modem câble,
votre modem DSL ou un routeur Ethernet à ce port.
Prise Branchez le bloc d’alimentation fourni sur cette prise.
d’alimentation
Avertissement : L’emploi d’un bloc d’alimentation inadapté
peut endommager votre Routeur Sans Fil.
Page 41

37
Configuration requise
• Accès à Internet par votre opérateur téléphonique ou votre Fournisseur
d’Accès à Internet (FAI) avec un modem câble ou un modem DSL.
• PC utilisant une adresse IP fixe ou une adresse IP dynamique attribuée via
DHCP, ainsi qu’une adresse de serveur de passerelle et une adresse de
serveur DNS de votre fournisseur d’accès.
• Ordinateur équipé d’une carte Fast Ethernet 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps ou 10/100
Mbps ou bien d’un adaptateur USB-Ethernet.
• Protocole de réseau TCP/IP installé sur chaque PC nécessitant un accès à
Internet.
• Navigateur web compatible Java, tel que Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5
ou au-delà, Firefox 1.0 ou Mozilla 1.7, installé sur un PC de votre site pour
configurer le Routeur Sans Fil.
Branchement du système
Le Routeur Sans Fil peut être placé à n’importe quel endroit pratique dans
votre bureau ou votre domicile. Il ne requiert aucun câblage spécial et aucune
exigence particulière pour son refroidissement. Respectez néanmoins les
recommandations suivantes :
• Maintenez le Routeur Sans Fil à l’écart de tout appareil de chauffage.
• Ne placez pas le Routeur Sans Fil dans un environnement poussiéreux ou
humide.
N’oubliez pas non plus, lorsque vous installez le Routeur Sans Fil, de le mettre
hors tension, de débrancher le cordon d’alimentation de la prise de courant et
de garder les mains sèches.
Page 42

38
Procédure d’installation de base
1. Connexion au réseau local (LAN) : Connectez le Routeur Sans Fil à votre
PC ou bien à un concentrateur ou un commutateur. Branchez un câble
Ethernet entre l’un des ports LAN à l’arrière du Routeur Sans Fil et la carte
réseau de votre ordinateur ou un autre périphérique de réseau. Vous pouvez
aussi connecter le Routeur Sans Fil à votre PC (avec un adaptateur client
sans fil) par signaux radio.
2. Connexion au réseau distant (WAN) : Utilisez un câble Ethernet pour
connecter le Routeur Sans Fil à un modem câble/xDSL ou à un routeur
Ethernet.
3. Mise sous tension : Branchez le bloc d’alimentation au Routeur Sans Fil.
Figure 2. Exemple de configuration du réseau
3838
Bureau SOHO ou domicile privé
Portable avec
carte PC sans fil
Périphérique
d’accès à Internet
Routeur Sans Fil
Page 43

39
Branchement à votre réseau par un câblage Ethernet
Utilisez un câble à paire torsadée pour connecter l’un des quatre ports LAN
du Routeur Sans Fil à une carte Ethernet installée dans votre PC. En variante,
vous pouvez brancher en cascade l’un des ports LAN du Routeur Sans Fil à un
concentrateur ou commutateur Ethernet, puis connecter votre PC ou un autre
équipement de réseau à ce concentrateur ou commutateur.
Lorsque vous insérez une fiche RJ-45, assurez-vous que l’onglet de la fiche
s’enclenche pour garantir une bonne fixation.
Avertissement : Ne tentez pas de brancher une fiche téléphonique RJ-11
dans un port RJ-45. Ceci pourrait endommager le Routeur
Sans Fil. Utilisez uniquement des câbles à paire torsadée
dotés de connecteurs RJ-45 conformes aux normes FCC.
Figure 3. Agencement d’une connexion LAN
Page 44

40
Branchement à votre réseau par signaux radio
Installez une carte réseau sans fil dans chaque ordinateur qui sera connecté à
Internet ou à votre réseau local par signaux radio.
Essayez de placer le Routeur Sans Fil à un emplacement situé au centre de
votre réseau sans fil. Normalement, plus l’antenne sera placée en hauteur,
meilleures seront les performances. Assurez-vous que l’emplacement du
Routeur Sans Fil permet une réception optimale partout dans votre domicile
ou votre bureau.
Une infrastructure sans fil peut être utilisée pour accéder à une base de
données centralisée ou pour établir une connexion entre des collaborateurs
mobiles, comme représenté sur l’illustration suivante :
Figure 4. Exemple de connexion WLAN
40
Liaison vers une extension
de réseau sans fil
Périphérique
d’accès à
Internet
Routeur Sans Fil
PC avec adaptateur PCI
sans fil
Portable avec adaptateur
PC Card sans fil
Réseau câblé
Page 45

4141
Connexion du Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g à Internet
Si l’accès aux services Internet est assuré par l’intermédiaire d’un modem
câble ou xDSL, utilisez un câble Ethernet CAT 5 à paire torsadée blindé ou non
blindé avec fiches RJ-45 pour connecter le modem à large bande directement
au port WAN du Routeur Sans Fil.
Figure 5. Exemple de connexion WAN
FAI
(Principal)
ADSL/Câble
Modem
Page 46

42
Configuration TCP/IP côté client
Pour accéder à Internet par l’intermédiaire du Routeur Sans Fil, vous devez
configurer les paramètres réseau des ordinateurs de votre réseau local
pour qu’ils utilisent le même sous-réseau IP que le Routeur Sans Fil. Les
paramètres réseau par défaut pour le Routeur Sans Fil sont les suivants :
Adresse IP de passerelle : 192.168.2.1
Masque de sous-réseau : 255.255.255.0
Remarque : Vous pouvez modifier ces paramètres en fonction de vos
exigences pour votre réseau mais vous devez
préalablement configurer au moins un ordinateur selon les
instructions de ce chapitre pour accéder à l’interface de
configuration web du Routeur Sans Fil. Voir “Configuration du
Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g” à la page 20 pour obtenir des
précisions sur la configuration du Routeur Sans Fil.
L’adresse IP du PC client connecté doit être 192.168.2.x (où x a une valeur
comprise entre 2 et 254). Vous pouvez régler l’adresse IP des PC clients
en obtenant automatiquement une adresse IP auprès du service DHCP du
Routeur Sans Fil ou en procédant à une configuration manuelle.
42
Page 47

4343
Configuration de votre ordinateur sous Windows 2000
1. Accédez à vos paramètres réseau en cliquant sur Démarrer, puis pointez sur
Paramètres, puis sélectionnez Panneau de configuration.
2. Dans le Panneau de configuration, repérez et double-cliquez sur l’icône
Réseau et Connexions d’accès à distance.
3. Repérez et double-cliquez
sur l’icône Connexion locale
correspondant à l’adaptateur
Ethernet qui est connecté au
Routeur Sans Fil. Quand la
fenêtre de dialogue État s’ouvre,
cliquez sur le bouton
Propriétés.
4. Dans la fenêtre Propriétés de
Connexion locale, assurezvous que la case à côté de
Protocole Internet (TCP/IP) est
cochée. Puis sélectionnez la ligne
Protocole Internet (TCP/IP) et
cliquez sur le bouton
Propriétés.
5. Sélectionnez Obtenir une
adresse IP automatiquement pour configurer votre ordinateur pour le
DHCP. Cliquez sur le bouton
OK pour enregistrer cette modification et
fermer la fenêtre Propriétés.
6. Cliquez une nouvelle fois sur le bouton OK pour enregistrer ces nouveaux
paramètres.
7. Redémarrez votre PC.
8. Pour obtenir de nouveaux paramètres de réseau, voir “Obtenir des
paramètres IP auprès de votre Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g” à la page
suivante.
Page 48

44
Obtenir des paramètres IP auprès de votre Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g
Maintenant que vous avez configuré votre ordinateur pour qu’il se connecte
au Routeur Sans Fil, il doit obtenir de nouveaux paramètres réseau. En libérant
les anciens paramètres IP et en les renouvelant avec des paramètres obtenus
auprès du Routeur Sans Fil, vous pourrez aussi vérifier si votre ordinateur a été
correctement configuré.
1. A partir du bureau Windows, cliquez sur Démarrer/Programmes/Invite de
commandes.
2. Dans la fenêtre Invite de commandes, tapez ipconfig /release et appuyez
sur la touche Entrée.
3. Tapez ipconfig /renew et appuyez sur la touche Entrée. Assurez-vous que
votre adresse IP est à présent 192.168.2.xxx, que votre masque de sousréseau est 255.255.255.0 et que votre passerelle par défaut est 192.168.2.1.
Ces valeurs confirment que le Routeur Sans Fil fonctionne.
4. Tapez exit et appuyez sur Entrée pour fermer la fenêtre Invite de
commandes.
44
Page 49

4545
Configuration de votre ordinateur sous
Windows XP
Les instructions suivantes supposent que vous utilisez Windows XP avec
l’interface par défaut. Si vous utilisez l’interface Classique (où les icônes et
menus adoptent le style des précédentes versions de Windows), veuillez suivre
les instructions pour Windows 2000 exposées ci-avant.
1. Accédez à vos paramètres réseau en cliquant sur Démarrer, puis sur
Panneau de configuration, sélectionnez Connexions réseau et cliquez sur
l’icône Connexions réseau.
2. Repérez et double-cliquez sur l’icône
Connexion locale correspondant à
l’adaptateur Ethernet qui est connecté
au Routeur Sans Fil. Ensuite, cliquez
sur le bouton
Propriétés.
3. Dans la fenêtre Propriétés de Connexion locale, assurez-vous que la case
à côté de Protocole Internet (TCP/IP) est cochée. Puis sélectionnez la
ligne Protocole Internet (TCP/IP) et cliquez sur le bouton Propriétés.
4. Sélectionnez Obtenir une adresse IP automatiquement pour configurer
votre ordinateur pour le DHCP. Cliquez sur le bouton OK pour enregistrer
cette modification et fermer la fenêtre Propriétés
.
5. Cliquez une nouvelle fois sur le bouton OK pour enregistrer ces nouveaux
paramètres.
6. Redémarrez votre PC.
Page 50

46
Configuration d’un ordinateur Macintosh
Il se peut que les instructions suivantes ne soient pas tout à fait identiques
à celles de votre écran. Ceci est dû au fait que ces étapes et copies d’écran
ont été réalisées à partir de Mac OS 10.2. Les versions Mac OS 7.x et au-delà
sont toutes très similaires mais pas toujours identiques à Mac OS 10.2.
1. Déroulez le menu
Pomme. Cliquez sur
System Preferences
[Préférences du
système] et sélectionnez
Network [Réseau]
.
2. Assurez-vous que
Builtin Ethernet [Ethernet
intégré] est sélectionné
dans le champ
Show
[Montrer].
3. Sous l’onglet
TCP/IP,
sélectionnez Using DHCP
dans le champ
Configure
[Configurer].
4. Fermez la boîte de dialogue TCP/IP
.
46
Page 51

4747
Configuration IP manuelle (tous systèmes
Windows)
1. Vérifiez la zone Spécifier une adresse
IP sous l’onglet Adresse IP. Saisissez
une adresse IP basée sur le réseau par
défaut 192.168.2.x (où x est compris
entre 2 et 254) et utilisez 255.255.255.0
pour le masque de sous-réseau.
2. Sous l’onglet
Passerelle, ajoutez
l’adresse IP du Routeur Sans Fil (par
défaut :
192.168.2.1) dans le champ
Nouvelle passerelle et cliquez sur
Ajouter.
Page 52

48
3. Sous l’onglet Configuration DNS,
ajoutez l’adresse IP correspondant
au Routeur Sans Fil et cliquez sur
Ajouter. Ceci permet de relayer
automatiquement les requêtes DNS
vers le ou les serveurs DNS fournis par
votre FAI. Sinon, ajoutez des serveurs
DNS spécifiques dans le champ Ordre
de recherche DNS et cliquez sur
Ajouter.
4. Une fois la configuration TCP/IP
terminée, cliquez sur
OK et redémarrez
l’ordinateur. Configurez ensuite les
autres PC du réseau local en répétant
les procédures décrites ci-avant.
48
Page 53

4949
Vérification de votre connexion TCP/IP
Après avoir installé les protocoles de communication TCP/IP et configuré une
adresse IP dans le même réseau que le Routeur Sans Fil, utilisez la commande
ping pour vérifier si votre ordinateur a réussi à se connecter au Routeur Sans
Fil. L’exemple suivant montre comment exécuter la procédure ping dans une
fenêtre MS-DOS. Pour commencer, exécutez la commande ping (dans une
fenêtre Invite de commandes) :
ping 192.168.2.1
Si vous obtenez un message similaire à ceci :
Envoi d’une requête ‘ping’ sur 192.168.2.1 avec 32 octets de données :
Réponse de 192.168.2.1 : octets=32 temps=2ms TTL=64
cela signifie qu’une liaison de communication s’est bien établie
entre votre ordinateur et le Routeur Sans Fil.
Si vous obtenez le message suivant,
Envoi d’une requête ‘ping’ sur 192.168.2.1 avec 32 octets de données :
Délai d’attente de la demande dépassé.
il y a sans doute une anomalie dans votre procédure d’installation.
Vérifiez les points suivants dans l’ordre :
1. Le câble Ethernet est-il correctement branché entre le Routeur Sans Fil
et l’ordinateur ?
Le témoin LAN sur le Routeur Sans Fil et la diode Link sur la carte réseau de
votre ordinateur doivent être allumés.
2. Le protocole TCP/IP est-il correctement configuré sur votre ordinateur?
Si l’adresse IP du Routeur Sans Fil est 192.168.2.1, l’adresse IP de votre PC
doit être dans la plage 192.168.2.2-254 et la passerelle par défaut doit être
192.168.2.1.
Si vous parvenez à envoyer une requête ping au Routeur Sans Fil, vous êtes
prêt à vous connecter à Internet !
Page 54

50
Configuration du Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g
Le Routeur Sans Fil IEEE 802.11g peut être configuré avec Internet Explorer
5.5 ou au-delà. L’interface d’administration web vous permet de configurer le
Routeur Sans Fil et de consulter des statistiques pour surveiller l’activité du
réseau.
Avant d’essayer de vous connecter à l’interface d’administration basée sur le
Web, vérifiez les points suivants.
1. Votre navigateur est correctement configuré (voir ci-après).
2. Désactivez tout logiciel de pare-feu ou de sécurité pouvant être en service.
3. Assurez-vous que la diode Link est allumée quand votre ordinateur est
connecté au Routeur Sans Fil. Si le témoin Link n’est pas allumé, essayez
un autre câble jusqu’à l’obtention d’une liaison confirmée par ce témoin.
Configuration du navigateur
Assurez-vous que votre navigateur est configuré pour permettre une
connexion directe à Internet avec la carte Ethernet qui est installée dans
l’ordinateur.
Désactivation de la connexion par serveur proxy
Vous devez aussi vérifier que la fonction Serveur Proxy HTTP de votre
navigateur web est désactivée. Ceci est nécessaire afin que votre navigateur
web puisse voir les pages de configuration du Routeur Sans Fil. Les étapes
décrites ci-après s’appliquent à Internet Explorer.
Internet Explorer 5.5 ou au-delà (pour Windows)
1. Ouvrez Internet Explorer. Cliquez sur Outils, puis sélectionnez Options
Internet.
2. Dans la fenêtre Options Internet, cliquez sur l’onglet Connexions.
Présentation de l’interface du navigateur Web
3. Cliquez sur le bouton Paramètres réseau.
4. Décochez toutes les cases et cliquez sur OK pour enregistrer ces
modifications des paramètres du réseau local.
50
Page 55

5151
5. Cliquez encore sur OK pour fermer la fenêtre Options Internet.
Internet Explorer (pour Macintosh)
1. Ouvrez Internet Explorer. Cliquez sur Explorer/Préférences
.
2. Dans la fenêtre Préférences d’Internet Explorer, sous Network [Réseau],
sélectionnez Proxies.
3. Décochez toutes les cases et cliquez sur OK.
Présentation de l’interface du navigateur Web
1. Pour accéder à l’interface de gestion du Routeur sans fil, tapez l’adresse
du Routeur sans fil dans la barre d’adresse de votre navigateur :
http://192.168.2.1
2. Vous devez ouvrir une session avant de poursuivre. Cliquez sur le bouton
Connexion à l’angle supérieur droit de l’écran. Par défaut, le champ du mot
de passe est vide. Cliquez simplement sur le bouton « Envoyer ».
Page 56

52
3. Pour établir une connexion Internet, dans la liste Menu à la gauche de
l’écran, recherchez l’option « Type de Connexion », dans la catégorie «
Internet WAN ».
4. L’écran WAN > Type de Connexion vous permet de sélectionner le type
de connexion nécessaire pour établir une connexion avec votre Fournisseur
d’accès à Internet. Consultez la documentation fournie par votre FAI afin
de choisir la connexion appropriée. Après avoir sélectionné le Type de
connexion, cliquez sur «
Suivant ».
52
Page 57

5353
Type de connexion
a. Dynamique
Votre Fournisseur
d’Accès à Internet
peut vous avoir
donné un nom
d’hôte. Si tel est
le cas, saisissez-le
dans le champ.
Si votre FAI se sert de l’adresse MAC d’une carte Ethernet comme identifiant
lors de mise en œuvre de votre compte à haut débit, cliquez sur le bouton
« Modifier l’adresse MAC WAN ». Assurez-vous de ne brancher que
l’ordinateur avec l’adresse MAC enregistrée à votre Routeur pendant la
configuration.
Cliquez sur le bouton «
Cloner » pour remplacer l’adresse MAC du Routeur
sans fil avec celle de l’une de vos cartes Ethernet, enregistrée auprès de
votre FAI.
Page 58

54
b. Fixe
Si votre Fournisseur
d’accès à Intenet
vous a attribué votre
propre adresse IP,
choisissez cette
option et remplissez
les champs.
c. PPPoE
Saisissez le Nom
d’utilisateur PPPoE et le Mot de passe que votre FAI vous a attribués. Le Nom
de service est normalement facultatif mais il peut être demandé par certains
fournisseurs.
Laissez le champ
Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) à
la valeur par défaut
(1454) sauf si vous
avez une raison
particulière de la
modifier.
Saisissez un
temps d’inactivité
maximum (Maximum
Idle Time) en minutes
pour définir une durée
maximale pendant
laquelle la connexion à Internet peut être maintenue en cas d’inactivité. Si la
connexion est inactive pendant une durée supérieure au temps d’inactivité
maximum, elle sera interrompue. (Défaut : 3 minutes).
5454
Page 59

55
c. PPTP
Si votre FAI a spécifié ce type de connexion pour la connexion à Internet.
Entrez les informations dans les champs et cliquez sur le bouton « Enregistrer
les modifications ».
Page 60

56
Si votre FAI vous a fourni les informations visibles sur la copie d’écran,
saisissez un Nom de compte PPTP et le mot de passe, un Nom d’hôte,
l’Adresse IP du service, l’Adresse IP attribuée et le Masque de sous-réseau.
Laissez le champ Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) à la valeur par défaut
(1460) sauf si vous avez une raison particulière de la modifier.
Saisissez un temps d’inactivité maximum (Maximum Idle Time) en minutes
pour définir une durée maximale pendant laquelle la connexion à Internet
peut être maintenue en cas d’inactivité. Si la connexion est inactive pendant
une durée supérieure au temps d’inactivité maximum, elle sera interrompue.
(Défaut : 3 minutes).
Remarque : Si vous utilisez une ligne louée ou une connexion facturée à la
minute, veillez à régler votre temps d’inactivité maximum à 3
minutes. Ceci forcera l’interruption de votre connexion à Internet
au bout de 3 minutes d’inactivité et votre FAI ne vous facturera
pas de temps de connexion supplémentaire.
Cliquez sur FINISH [Terminer] pour achever la configuration.
56
Page 61

5757
Page 62

Page 63

2.4 GHz 54 Mbit/s
Kabelloser 802.11g DSL/Kabel-Router
Benutzerhandbuch
DEUTSCH
F5D7230ea4-E
P74847ea-A
Page 64

Handelsmarken:
Andere Produkt- und Firmennamen sind (registrierte) Handelsmarken der
entsprechenden Rechteinhaber.
Page 65

Inhalt
Über den kabellosen IEEE 802.11g-Router ................................................ 62
LED-Anzeigen .............................................................................................
62
Funktionen und Vorzüge ............................................................................
63
Installieren des kabellosen IEEE 802.11g-Routers ....................................
64
Verpackungsinhalt ......................................................................................
64
Beschreibung der Hardware ....................................................................... 65
Systemanforderungen ................................................................................
67
Anschließen des Systems ..........................................................................
67
Basis-Installationsvorgang ...................................................................
68
Client-TCP/IP einstellen ..............................................................................
72
Ihren Computer mit Windows 2000 einstellen ....................................
73
Ihren Computer mit Windows XP einstellen ........................................
75
Einstellungen für Macintosh-Computer ...............................................
76
Manuelle IP-Einstellung (für alle Windows-Betriebssysteme) .............
77
Ihre TCP/IP-Verbindung bestimmen ....................................................
79
Bedienung der Webgestützten Benutzeroberfläche
................................. 81
Verbindungstyp ...........................................................................................
83
Dynamisch ...........................................................................................
83
Statisch ................................................................................................
84
PPPoE ..................................................................................................
84
PPTP ....................................................................................................
85
Page 66

62
Über den kabellosen IEEE 802.11g-Router
Wir beglückwünschen Sie zum Kauf des kabellosen Kabellosen IEEE 802.11gRouters. Das F5D7230xx4-E ist ein leistungsstarkes und doch einfaches
Kommunikationsgerät für Ihr lokales Netzwerk (LAN - Local Area Network).
LED-Anzeigen
Der kabellose IEEE 802.11g-Router verfügt über LED-Statusanzeigen, wie in
der folgenden Tabelle beschrieben und abgebildet.
LED Status Beschreibung
Betrieb An Der kabellose Router ist an die Stromversorgung
angeschlossen.
WAN An Der WAN-Verknüpfung ist verbunden.
Online An PPP-Verbindung ist an.
WLAN An Das kabellose Netzwerk ist aktiviert.
Blinkt Der kabellose Router überträgt oder
empfängt Daten über eine kabellose Verbindung.
LAN1-4 Grün Ein Über den Ethernet-Port ist eine gültige
100 Mbit/s-Netzwerkverbindung eingerichtet.
Orange Ein Über den Ethernet-Port ist eine gültige
10 Mbit/s-Netzwerkverbindung eingerichtet.
Blinkt Über den Ethernet-Port werden Daten übertragen
oder empfangen.
LAN4
LAN3
LAN2
LAN1
WLAN
Internet
WAN
Leistung
Kabelloser IEEE 802.11g-Router
Page 67

63
Funktionen und Vorzüge
• Internet-Verbindungen zu DSL- oder Kabelmodem über einen 10/100 Mbit/s
WAN-Port
• Lokale Netzwerkverbindung über 10/100 Mbit/s-Ethernetports oder kabellose
54 Mbit/s-Schnittstellen.
• IEEE 802.11g-kompatibel - funktioniert mit Geräten vieler unterschiedlicher
Hersteller
• Erweiterte Sicherheitsfunktionen wie 64/128-Bit WEP-Verschlüsselung,
802.1x, SSID-Schutz und MAC-Adressenfilter bieten den Schutz, den Ihre
wichtigen Daten benötigen und erlauben nur befugten Nutzern den Zugang
zu Ihrem Netzwerk.
• Bietet völlige Bewegungsfreiheit innerhalb der 802.11g WLAN-Umgebung
• DHCP für dynamische IP-Konfiguration und DNS für die Belegung von
Domänennamen
• Firewall mit SPI (Stateful Packet Inspection - zustandsabhängige
Paketanalyse), Client Privileges (Client-Berechtigungen), Hackerschutz, DoS
und NAT (Network Address Translation - Netzwerk-Adressübersetzung)
• NAT aktiviert auch den Mehrfachzugriff auf ein Einzelkonto und virtuelle
Server-Funktionalitäten, wie Web, Mail, FTP und Telnet
• Das Virtuelle Private Netzwerk (VPN) unterstützt den Einsatz von PPTP, L2TP
oder IPSec Pass-through, sofern vom Provider erlaubt
• Kindersicherungen ermöglichen die Einschränkung der Internetnutzung
• Automatische E-Mail-Benachrichtigungen, wenn das Netzwerk angegriffen
wurde
• Einfache Einrichtung mit Hilfe eines Web-Browsers auf jedem beliebigen
Betriebssystem mit TCP/IP-Unterstützung
• Mit allen gängigen Browsern kompatibel
Page 68

64
Installation des kabellosen IEEE 802.11gRouters
Vor der Installation des kabellosen Routers müssen Sie prüfen, ob alle Teile,
die in der Auflistung des Verpackungsinhalts aufgeführt sind, vorhanden
sind. Wenn eines dieser Teile fehlt oder beschädigt ist, wenden Sie sich an
Ihren Händler. Vergewissern Sie sich auch, dass Sie alle notwendigen Kabel
haben, bevor Sie den Router installieren. Nach der Installation des Routers
beachten Sie bitte in der Webgestützten Benutzeroberfläche den Abschnitt
“Den kabellosen IEEE 802.11g-Router einstellen” auf Seite 20 für weitere
Informationen über die Einstellungen.
Verpackungsinhalt
Nachdem Sie den Router ausgepackt haben, prüfen Sie den Inhalt der
Verpackung auf Vollständigkeit.
• Kabelloser IEEE 802.11g-Router
• Netzteil
• Ein CAT-5 Ethernet-Kabel
• Benutzerhandbuch
Informieren Sie bitte umgehend Ihren Händler, wenn einige Teile falsch, nicht
vorhanden oder beschädigt sind. Sofern möglich, heben Sie den Karton und
die Verpackungsmaterialien für den Fall auf, dass Sie das Produkt einsenden
müssen.
Genauere Informationen zur Garantie dieses Produkts finden Sie auf der
Website von Micradigital: www.micradigital.com
Page 69

65
Beschreibung der Hardware
Der kabellose Router kann mit dem Internet oder über den WAN-Port mit
einem entfernten Zugang verbunden werden. Er kann direkt mit Ihrem PC
oder mit einem lokalen Netzwerk (LAN) über einen der Fast Ethernet LAN-Ports
verbunden werden.
Obwohl die Übertragungsgeschwindigkeit im Internet von Ihrem Servicetyp
und dem Modem, mit dem der Router verbunden ist, abhängig ist, beträgt
die Übertragungsgeschwindigkeit innerhalb des lokalen Netzwerks bis zu
100 Mbit/s über die Fast Ethernet-Ports.
Der kabellose Router verfügt über eine LED-Leuchtanzeige an der Vorderseite,
die die Betriebsbereitschaft und die Portaktivität zeigt. Installation und
Problemlösungen werden dadurch sehr vereinfacht. An der Rückseite befinden
sich vier RJ-45 LAN-Ports und ein RJ-45 WAN-Port.
• Vier Ethernet-Ports für Verbindungen mit einem lokalen 10BASE-T/100BASE-
TX Ethernet-Netzwerk (LAN). Diese Ports können die Verbindungsgeschw
indigkeit automatisch auf 10/100 Mbit/s, den Modus auf Half Duplex oder
Full Duplex und die Pin-Signale zu MDI/MDI-X (z. B. ermöglichen es diese
Ports, mit jedem Netzwerkgerät über ein 1:1 verdrahtetes Kabel verbunden
zu werden) einstellen. Diese Ports können direkt mit einem PC oder einem
Server verbunden werden, der über eine Ethernet-Netzwerkkarte oder ein
anderes Netzwerkgerät wie einen Ethernet-Hub oder -Switch verfügt.
• Ein RJ-45-Port für Verbindungen mit einem DSL- oder Kabelmodem (WAN).
Dieser Port stellt die Betriebsgeschwindigkeit automatisch auf 10/100 Mbit/s,
den Modus auf Half Duplex oder Full Duplex und die Pin-Signale zu MDI/
MDI-X ein.
Auf der folgenden Abbildung werden die Komponenten des kabellosen
Routers wiedergegeben.
Page 70

66
Abbildung 1. Vorder- und Rückseite
Element Beschreibung
Leucht- Statusanzeigen für die Betriebsbereitschaft, WLAN, WAN- und
anzeigen LAN-Ports (Beachten Sie den Abschnitt “LED-Anzeigen” auf
Seite 1).
LAN- Fast Ethernet-Ports (RJ-45). Verbindet Geräte ( wie PC,
Ports Hub oder Switch) in Ihrem lokalen Netzwerk mit diesen Ports.
Rücksetz- Verwenden Sie diesen Schalter, um den Router neu zu starten
taste und auf die Werkseinstellungen zurückzusetzen.
WAN- WAN-Port (RJ-45). Verbindet ihr Kabel-, DSL-Modem
Port oder einen Ethernet-Router mit diesem Port.
Netz- Zum Anschließen des enthaltenen Netzteils.
eingang Warnung: Die Verwendung eines falschen Netzadapters
kann zu Schäden an Ihrem Router führen.
Page 71

67
Systemanforderungen
• Internetzugang von Ihrer örtlichen Telefongesellschaft oder Ihrem Internet-
Anbieter (Internet Service Provider - ISP) über ein DSL- oder Kabelmodem.
• Einen PC mit fester oder dynamischer IP-Adresse über DHCP sowie eine
Gateway-Serveradresse und eine DNS-Serveradresse vom Internetanbieter.
• Ein Computer mit einer 10 Mbit/s, 100 Mbit/s oder 10/100 Mbit/s Fast
Ethernet-Karte oder einem USB/Ethernet-Konverter.
• TCP/IP Netzwerk-Protokolle auf jedem PC installiert, der Verbindung mit dem
Internet hat.
• Ein installierter Browser mit aktiviertem Java, wie Microsoft Internet Explorer
5.5 oder höher, Firefox 1.0 oder Mozilla 1.7 für die Konfiguration des
kabellosen Routers.
Anschließen des Systems
Der kabellose Router kann an jedem beliebigen Ort in Ihrem Büro oder zu
Hause aufgestellt werden. Es sind keine besonderen Kabel und keine Kühlung
erforderlich. Sie sollten aber die folgenden Hinweise beachten:
• Stellen Sie den Router nicht in die Nähe von Heizkörpern oder -geräten.
• Setzen die den Router keiner staubigen oder feuchten Umgebung aus.
Vergessen Sie nicht, den Router auszuschalten, den Netzstecker zu ziehen
und auf trockene Hände zu achten, wenn Sie den Kabellosen ADSL-Router
installieren.
Page 72

68
Basis-Installationsvorgang
1. Einrichten des LAN: Verbinden Sie den kabellosen Router mit Ihrem PC
oder einem Hub oder Switch. Verbinden Sie ein Ethernetkabel mit einem der
LAN-Ports an der Rückseite des Routers und dem Netzwerkadapter Ihres
Computers oder einem anderen Netzwerkgerät. Sie können den Router
auch über Funksignale mit dem PC verbinden (mit einem kabellosen ClientAdapter).
2. Einrichten des WAN: Verbinden Sie mit einem Ethernetkabel den Router
mit einem Kabel/DSL-Modem oder einem Ethernet-Router.
3. Anschalten: Schließen Sie das Netzteil an den Router an.
Abbildung 2. Beispielhafte Netzwerkeinstellung
68
SOHO Büro oder zu Hause
Notebook mit kabellosem
PC Card-Adapter
Internet
Zugang
Gerät
Kabelloser
DSL/Kabel-Router
Page 73

6969
Ethernet-Kabelanschluss an das Netzwerk
Verwenden Sie Kabel mit verdrilltem Leitungspaar, um einen der vier LANPorts des Routers mit einen Ethernetadapter am PC zu verbinden. Kaskadieren
Sie andernfalls einen der LAN-Ports des Routers mit einem Ethernet-Hub oder
-Switch und verbinden Sie dann den PC oder ein Netzwerkgerät mit dem Hub
oder Switch. Wenn
Sie einen RJ-45-Stecker verwenden, achten Sie darauf, dass der Stecker in
der Wandsteckdose fest einrastet.
Achtung: Stecken Sie keinen Telefonstecker in einen RJ-45-Port. Dadurch
könnte der kabellose Router beschädigt werden. Verwenden Sie
daher auch nur Kabel mit verdrilltem Leitungspaar und RJ-45Steckern, die den FCC-Standards entsprechen.
Abbildung 3. Herstellen einer LAN-Verbindung
Page 74

70
Funkverbindung mit dem Netzwerk
Installieren Sie in jedem Computer, der über das lokale Funknetzwerk mit dem
Internet verbunden werden soll, einen kabellosen Netzwerkadapter.
Stellen Sie den kabellosen Router möglichst in das Zentrum des
Funknetzwerks. Je höher die Antenne reicht, desto besser ist in der Regel die
Netzwerkleistung. Vergewissern Sie sich, dass der Standpunkt des Routers
einen optimalen Empfang überall im Büro oder zu Hause gewährleistet.
Eine kabellose Infrastruktur kann dazu genutzt werden, auf eine zentrale
Datenbank zuzugreifen oder eine Verbindung zwischen mobilen Geräte zu
erstellen, wie die folgende Abbildung zeigt.
Abbildung 4. WLAN-Beispielverbindung
70
Kabel zu Funk
Netzwerk-Erweiterung
Internet-
Zugangsgerät
Kabelloser
DSL/Kabel-Router
PC mit kabellosem PCI-
Netzwerkadapter
Notebook mit kabellosem
PC Card-Adapter
Verkabeltes LAN
Page 75

7171
Verbindung des kabellosen IEEE 802.11g-Routers mit dem Internet
Für eine Internetverbindung über ein DSL- oder Kabelmodem verwenden
Sie nicht abgeschirmte oder abgeschirmte Ethernetkabel CAT mit verdrilltem
Leitungspaar und RJ-45-Steckern, um das Breitbandmodem direkt mit dem
WAN-Port des Routers zu verbinden.
Abbildung 5. WAN-Beispielverbindung
Internetanbieter
(Hauptanbieter)
DSL/Kabel
Modem
Page 76

72
Client-TCP/IP einstellen
Um über den Router auf das Internet zugreifen zu können, müssen die
Netzwerkeinstellungen des Computers im Netzwerk dasselbe IP-Subnet wie
der Router aufweisen. Die Standard-Netzwerkeinstellungen für den kabellosen
Router lauten:
Gateway IP-Adresse: 192.168.2.1
Subnet-Mask: 255.255.255.0
Hinweis: Diese Einstellungen können für Ihre Netzwerkanforderungen
verändert werden, Sie müssen aber erst mindestens einen
Computer wie beschrieben einstellen, um auf die webgestützte
Benutzeroberfläche zugreifen zu können. Beachten Sie den Abschnitt
“Einstellen des kabellosen IEEE 802.11g-Routers” auf Seite 20 für
Informationen über die Einstellung des kabellosen Routers.
Die IP-Adresse des angeschlossenen Client-PCs sollte 192.168.2.x (wobei x
für 2–254 steht) lauten. Sie können die IP-Adresse für Client-PCs entweder
automatisch über den DHCP-Dienst des Routers erhalten oder manuell
einstellen.
72
Page 77

7373
Ihren Computer mit Windows 2000 einstellen
1. Sie können auf das Netzwerk zugreifen, in dem Sie auf Start klicken und
Einstellungen und Systemsteuerung wählen.
2. In der
Systemsteuerung, suchen Sie das Symbol für die Netzwerk-
Verbindungen und klicken doppelt darauf.
3. Suchen Sie das
LAN-
Verbindungssymbol für den
Ethernet-Adapter, der mit dem
kabellosen Router verbunden
ist und klicken Sie doppelt
darauf. Wenn die Statusanzeige
geöffnet wird, klicken Sie auf die
Schaltfläche Eigenschaften.
4. In dem Fenster
Eigenschaften
der LAN-Verbindung, prüfen
Sie, ob das Feld neben dem
EintragInternet Protocol (TCP/IP)
aktiviert ist. Markieren Sie dann
den Eintrag Internet Protocol
(TCP/IP) und klicken Sie auf die
Schaltfläche Eigenschaften.
5. Wählen Sie IP-Adresse automatisch beziehen, um Ihren Computer für
DHCP einzustellen. Klicken Sie auf OK, um die Einstellungen zu speichern
und schließen Sie das Eigenschafts-Fenster.
6. Klicken Sie nochmals auf
OK, um diese neuen Änderungen zu speichern.
7. Starten Sie Ihren PC neu.
8. Um die neuen Netzwerkeinstellungen zu beziehen, beachten Sie den
Abschnitt “IP-Einstellungen vom Router beziehen” auf der nächsten Seite.
Page 78

74
IP-Einstellungen vom Router beziehen
Jetzt, nachdem Sie Ihren Computer auf die Verbindung mit dem Router
eingestellt haben, muss dieser neue Netzwerkeinstellungen beziehen. Über
die Ersetzung der alten IP-Einstellungen durch die des Routers können Sie
feststellen, ob Sie ihren Computer richtig eingestellt haben.
1. Klicken Sie auf dem Windows-Desktop auf Start>Alle Programme>Zubehör>
Eingabeaufforderung.
2. Geben Sie in dem geöffneten Fenster “ipconfig /release” ein und drücken
Sie die Eingabetaste.
3. Geben Sie “ipconfig /renew” ein und drücken Sie die Eingabetaste. Ihre
IP-Adresse sollte nun 192.168.2.xxx, Ihre Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 und
Ihr Default Gateway 192.168.2.1 lauten. Diese Werte geben an, dass Ihr
kabelloser Router funktioniert.
4. Geben Sie “exit” ein und drücken Sie die Eingabetaste, um das Fenster
wieder zu schließen.
74
Page 79

7575
Ihren Computer mit Windows XP einstellen
Die folgende Anleitung beschreibt Windows XP mit Standardeinstellungen.
Wenn Sie die klassische Anzeige (Symbole und Menüs wie in vorheriger
Windows-Version) verwenden, beachten Sie bitte die Anleitung für Windows
2000 im Abschnitt zuvor.
1. Sie greifen auf Ihre Netzwerk zu, indem Sie auf Start klicken,
Systemsteuerung, Netzwerk- und Internetverbindungen wählen und
anschließend auf das Symbol Netzwerkverbindungen klicken.
2. Suchen Sie das
LAN-
Verbindungssymbol für den Ethernet-
Adapter, der mit dem kabellosen Router
verbunden ist und klicken Sie doppelt
darauf. Klicken Sie anschließend auf die
Schaltfläche Eigenschaften.
3. In dem FensterEigenschaften der LAN-Verbindung, prüfen Sie, ob das
Feld neben dem EintragInternet Protocol (TCP/IP) aktiviert ist. Markieren
Sie dann den Eintrag Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) und klicken Sie auf die
Schaltfläche Eigenschaften.
4. Wählen Sie IP-Adresse automatisch beziehen, um Ihren Computer für
DHCP einzustellen. Klicken Sie auf OK, um die Einstellungen zu speichern
und schließen Sie das Eigenschafts-Fenster.
5. Klicken Sie nochmals auf
OK, um diese neuen Änderungen zu speichern.
6. Starten Sie Ihren PC neu.
Page 80

76
Einstellungen für Macintosh-Computer
Die hier beschriebenen Schritte können leicht von denen für Ihr Betriebssystem
abweichen. Dies kann vorkommen, weil die Schritte und Abbildungen in Mac
OS 10.2 erstellt wurden. Die Schritte in Mac OS 7.x und höher sind ähnlich
aber nicht identisch mit denen aus Mac OS 10.2.
1. Öffnen Sie das Applemenü.
Klicken Sie auf
System-
einstellungen und wählen
Sie Netzwerk.
2. Stellen Sie sicher, dass
Built-in Ethernet im
Fenster Anzeigen
ausgewählt ist.
3. Auf dem Registerblatt
TCP/IP, wählen Sie im
Abschnitt Einstellen
DHCP verwenden
.
4. Schließen Sie das
Dialogfeld TCP/IP.
76
Page 81

7777
Manuelle IP-Einstellung (für alle WindowsBetriebssysteme)
1. Aktivieren Sie im Registerblatt IPAdresse IP-Adresse bestimmen.
Geben Sie eine IP-Adresse für das
Standardnetzwerk ein: 192.168.2.x
(wobei x für eine Zahl zwischen 2 und
254 steht) und 255.255.255.0 für die
Subnet-Mask.
2. Im Registerblatt
Gateway, fügen Sie
die IP-Adresse des kabellosen Routers
(Standard: 192.168.2.1) in das Neue
Gateway-Feld New ein und klicken Sie
aufHinzufügen.
Page 82

78
3. Im RegisterblattDNS-Konfiguration
geben Sie die IP-Adresse für den
kabellosen Router ein und klicken auf
Hinzufügen. Damit ist die automatische
DNS-Nachfrage an den DNS-Server
Ihres Internetanbieters eingestellt.
Geben Sie andernfalls spezifische DNSServer im Feld DNS-Serversuche an
und klicken Sie auf
Hinzufügen.
4. Nachdem sie TCP/IP-Einstellungen
abgeschlossen haben, klicken Sie auf
OK und starten den Computer neu.
Danach können Sie andere PCs im LAN
wie oben beschrieben einrichten.
78
Page 83

7979
Ihre TCP/IP-Verbindung bestimmen
Nach der Installierung der TCP/IP-Verbindungsprotokolle und der Einrichtung
der IP-Adresse in demselben Netzwerk wie der Router, können Sie den PingBefehl verwenden, um zu überprüfen, ob Ihre Computer eine Verbindung mit
dem Router erfolgreich aufgebaut hat. Im folgenden Beispiel wird gezeigt, wie
dieser Vorgang in einem MS-DOS-Fenster ausgeführt werden kann. Führen Sie
erst den Ping-Befehl aus:
ping 192.168.2.1
Wenn eine folgende oder ähnliche Mitteilung angezeigt wird:
Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.2.1: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=64
besteht eine Kommunikationsverbindung zwischen Ihrem Computer und dem
kabellosen
Router.
Wenn die folgende Meldung angezeigt wird,
Pinging 192.168.2.1 with 32 bytes of data:
Request timed out.
deutet dies auf einen Fehler während des Installationsvorgangs hin.
Überprüfen Sie die folgenden Dinge in der angegebenen Reihenfolge:
1. Ist das Ethernetkabel richtig mit dem kabellosen Router und dem
Computer verbunden?
Die LAN-Anzeige am Router und die Link-Anzeige der Netzwerkkarte Ihres
Computers müssen aufleuchten.
2. Ist TCP/IP auf Ihren Computer richtig eingerichtet
Wenn die IP-Adresse des kabellosen Routers 192.168.2.1 lautet, muss die
IP-Adresse auf Ihren PC auf 192.168.2.2-254 und der Default-Gateway auf
192.168.2.1 eingestellt sein.
Wenn Sie den Router erfolgreich “gepingt” haben, können Sie nun eine
Verbindung mit dem Internet herstellen!
Page 84

80
Einrichten des kabellosen IEEE 802.11g-Routers
Der kabellose IEEE 802.11g-Router kann mit dem Internet Explorer 5.5 oder
höher eingerichtet werden. Mit der webgestützten Benutzeroberfläche können
Sie den Router einrichten und Statistiken zur Netzwerkaktivität einsehen.
Bevor Sie versuchen, sich auf der Benutzeroberfläche anzumelden, prüfen Sie
bitte Folgendes:
1. Ihr Browser ist richtig eingestellt (siehe unten).
2. Deaktivieren Sie Firewalls und andere Sicherheitssoftware, die ausgeführt
wird.
3. Prüfen Sie, ob die Link-Anzeige leuchtet, wenn Ihre Computer mit dem
Router verbunden ist. Wenn diese LED-Anzeige nicht leuchtet, versuchen
Sie, ein anderes Kabel zu verwenden.
Browser-Einstellung
Prüfen Sie, ob Ihr Browser für eine direkte Verbindung mit dem Internet über
ein Ethernetkabel eingestellt ist.
Proxy-Verbindung deaktivieren
Sie müssen auch überprüfen, ob die Funktion “HTTP Proxy” Ihres
Webbrowsers deaktiviert ist. Nur dann lässt sich mit dem Browser eine
informative Verbindung mit den Einstellungsseiten des Routers herstellen. Die
folgenden Schritte beziehen sich auf den Internet Explorer.
Internet Explorer 5.5 oder höher (Für Windows)
1. Öffnen Sie den Internet Explorer. Klicken Sie auf “Extras” und wählen Sie
die “Internetoptionen” aus.
2. Im Fenster “Internetoptionen” klicken Sie auf das Registerblatt
“Verbindungen”. Bedienung der Webgestützten Benutzeroberfläche
3. Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche “Einstellungen” im Abschnitt “LANEinstellungen”.
4. Deaktivieren Sie alle Felder und klicken Sie auf OK, um die Änderungen in
den LAN-Einstellungen zu speichern.
5. Klicken Sie auf OK, um das Fenster “Internetoptionen” zu schließen.
80
Page 85

8181
Internet Explorer (Für Macintosh)
1. Öffnen Sie den Internet Explorer. Klicken Sie auf Explorer /Einstellungen
.
2. Im Fenster “Einstellungen für Internet Explorer” wählen Sie unter Netzwerk
Proxiesaus.
3. Deaktivieren Sie alle Felder und klicken Sie auf “OK”
Bedienung der Webgestützten Benutzeroberfläche
1. Um auf die Webgestützte Benutzeroberfläche des Browsers zugreifen zu
können, geben Sie die Adresse Ihres kabellosen Routers in die Adressleiste
Ihres Browsers ein: http://192.168.2.1
2. Um fortzufahren, müssen Sie sich anmelden. Klicken oben rechts auf dem
Bildschirm auf die Schaltfläche „
Login” (Anmelden). Standardmäßig ist kein
Kennwort eingegeben. Klicken Sie einfach auf die Schaltfläche „Submit
”
(Absenden)
Page 86

82
3. Um die Internetverbindung einzustellen, gehen Sie links auf dem Bildschirm
zur Menüliste. Dort finden Sie unter der Kategorie „Internet WAN” die Option
„Connection Type” (Verbindungstyp)
4. Das Fenster WAN > Connection type (WAN > Verbindungstyp) gibt Ihnen
die Möglichkeit, den Verbindungstyp zu wählen, den Sie zur Herstellung
einer Verbindung mit Ihrem Internetprovider benötigen. In den Unterlagen,
die Sie von Ihrem Internetprovider erhalten haben, finden Sie die nötigen
Informationen hierzu. Wenn Sie den richtigen Verbindungstyp gewählt
haben, klicken Sie auf „
Next” (Weiter)
82
Page 87

8383
Verbindungstyp
a. Dynamisch
Falls Ihr Internetprovider Ihnen einen
Host-Namen zugeteilt
hat, geben Sie diesen
in das entsprechende
Feld ein.
Wenn Ihr Internetprovider die Mac-Adresse einer Ethernetkarte als Kennung
verwendet hat, als er Ihr Breitbandkonto eingerichtet hat, klicken Sie auf die
Schaltfläche „Change WAN MAC address” (WAN MAC-Adresse ändern).
Bitte verbinden Sie während der Konfiguration nur den Computer mit der
eingetragenen MAC-Adresse mit dem Router.
Klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche „Clone” (Klonen), um die MAC-Adresse des
kabellosen Routers durch die der Ethernetkarte Ihres Computers zu ersetzen,
die bei Ihrem Internetprovider eingetragen ist.
Page 88

84
b. Statisch
Wählen Sie diese Option,
wenn Sie eine eigene
IP-Adresse von Ihrem
Internetprovider erhalten
haben und geben Sie
die nötigen Daten in die
entsprechenden Felder
ein
c. PPPoE
Geben Sie den PPPoE-Benutzernamen und das Kennwort ein, dass Sie von
Ihrem Dienst-Anbieter (Service Provider) erhalten haben. Die Angabe des
Dienstnamens (Service
Name) ist in der Regel
freigestellt, aber einige
Anbieter verlangen die
Angabe dennoch.
Belassen Sie
die maximale
Übertragungseinheit
(MTU - Maximum
Transmission Unit) auf
dem Standardwert
(1454), wenn Sie keinen
besonderen Grund zu
Änderung des Werts
haben.
Geben Sie das maximale Zeitlimit (Idle Time) in Minuten an, um die Zeit zu
festzulegen, nach der die Internetverbindung bei Inaktivität unterbrochen wird.
Wenn die Verbindung länger als im Zeitlimit festgelegt inaktiv ist, wird sie
unterbrochen. (Standard: 3 Minuten)
84
Page 89

8585
d. PPTP
Wenn Ihr Internetprovider diesen Verbindungstyp zur Herstellung einer
Internetverbindung festgelegt hat, geben Sie die Daten in die entsprechenden
Felder ein und klicken Sie auf die Schaltfläche „Apply Changes“ (Änderungen
übernehmen)
Page 90

86
Wenn Sie die abgebildeten Informationen erhalten haben, geben Sie den
Namen für das PPTP-Konto und das Kennwort, den Host-Namen, die ServerIP-Adresse, die zugewiesene IP-Adresse und die Subnet-Mask an.
Belassen Sie die maximale Übertragungseinheit (MTU - Maximum
Transmission Unit) auf dem Standardwert (1460), wenn Sie keinen besonderen
Grund zu Änderung des Werts haben.
Geben Sie das maximale Zeitlimit (Idle Time) in Minuten an, um die Zeit zu
festzulegen, nach der die Internetverbindung bei Inaktivität unterbrochen wird.
Wenn die Verbindung länger als im Zeitlimit festgelegt inaktiv ist, wird sie
unterbrochen. (Standard: 3 Minuten)
Hinweis: Wenn Sie über eine kostenpflichtige oder zeitbegrenzte Leitung
verbunden sind, setzen Sie das Zeitlimit bitte auf 3 Minuten. Die
Internetverbindung wird dann nach 3 Minuten unterbrochen, sodass
Sie die Zeit, in der Sie die Verbindung nicht benötigen auch nicht
bezahlen müssen.
Klicken Sie auf FERTIGSTELLEN, um die Installation abzuschließen.
86
Page 91

8787
Page 92

Page 93

2,4 GHz 54 Mbps
draadloze 802.11g kabel/DSL-router
Handleiding
NEDERLANDS
F5D7230ea4-E
P74847ea-A
Page 94

Handelsmerken:
Andere product- en bedrijfsnamen zijn handelsmerken of geregistreerde
handelsmerken van de betreffende rechthebbenden.
Page 95

Inhoud
Over de draadloze IEEE 802.11g router ...................................................... 92
LED-signaallampjes ....................................................................................
92
Productkenmerken en voordelen ...............................................................
93
De draadloze IEEE 802.11g router installeren ............................................
94
Inhoud van de verpakking ..........................................................................
94
Hardware-beschrijving ................................................................................
95
Systeemvereisten .......................................................................................
97
Plaatsing en aansluiting van uw router ......................................................
97
Basis-installatieprocedure ...................................................................
99
Configuratie van het TCP/IP van de cliënt ...............................................
102
Configuratie van uw computer in Windows 2000 .............................
103
Configuratie van uw computer in Windows XP .................................
105
Configuratie van een Macintosh-computer .......................................
106
Handmatige IP-configuratie
(voor alle Windows-besturingssystemen) ..........................................
107
Verificatie van uw TCP/IP-verbinding ................................................
109
Gebruik maken van de web-browserinterface
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Verbindingstype . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Dynamic (Dinamisch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Static (Statisch) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
PPPoE
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
PPTP
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Page 96

Over de draadloze IEEE 802.11g router
Gefeliciteerd met de aankoop van deze draadloze IEEE 802.11g router.
Deze router, met artikelnummer F5D7230xx4-E, is een krachtig en
toch gebruikersvriendelijk communicatiemiddel dat u in staat stelt een
internetverbinding voor uw lokale netwerk tot stand te brengen.
LED-signaallampjes
De draadloze IEEE 802.11g router is voorzien van status-LED’s die hieronder
beschreven zijn.
LED Status Beschrijving
Voeding Brandt De draadloze router wordt gevoed.
WAN Brandt De WAN-verbinding is tot stand gebracht.
Online Brandt PPP-verbinding is tot stand gebracht.
WLAN Brandt Het draadloze LAN is gedeactiveerd.
Knippert De draadloze router is gegevens aan het
verzenden of ontvangen via een draadloze
verbinding.
LAN1-4 Groen - brandt De betrokken Ethernet-poort heeft
een
correcte 100Mbps-netwerkverbinding tot
stand gebracht.
Ambergeel - brandt De betrokken Ethernet-poort heeft
een
correcte 10Mbps-netwerkverbinding tot stand
gebracht.
Knippert De betrokken Ethernet-poort is gegevens aan
het verzenden
of ontvangen.
LAN4
LAN3
LAN2
LAN1
WLAN
Online
WAN
Voeding
Draadloze IEEE 802.11g router
Page 97

93
Productkenmerken en voordelen
• Internet-verbinding met DSL- of kabelmodem via een 10/100Mbps WANpoort
• Lokaal-netwerkverbinding via 10/100Mbps Ethernet-poorten of 54Mbps
draadloze interface
• Voldoet aan IEEE 802.11g – kan gebruikt worden in combinatie met
producten van verschillende leveranciers
• Geavanceerde beveiliging via 64/128-bits WEP-encryptie, 802.1x, SSIDuitzending gedeactiveerd en MAC-adresfilter ter bescherming van uw
gevoelige gegevens en toegangverlening tot het netwerk van uitsluitend
bevoegde gebruikers.
• Maakt draadloos roamen mogelijk binnen een 802.11g WLAN-omgeving
• DHCP voor dynamische IP-configuratie en DNS voor domeinnaamtoewijzing
• Firewall met Stateful Packet Inspection, cliënt-privileges, beveiliging tegen
hackers, DoS en NAT
• NAT maakt toegang van meerdere gebruikers met een enkel
gebruikersaccount mogelijk evenals virtuele serverfunctionaliteit, beschermde
toegang tot Internetdiensten als webtoegang, e-mail, FTP en Telnet
• Virtual Private Network ondersteuning bij gebruik van PPTP, L2TP of IPSec
pass-through, ISP permitting
• Parental control webfilter stelt de gebruiker in staat de toegang tot bepaalde
websites te verbieden
• Automatische e-mailwaarschuwing als onbevoegden proberen het netwerk
binnen te dringen
• Eenvoudige setup via een web-browser of een willekeurig besturingssysteem
dat TCP/IP ondersteunt
• Is compatibel met alle populaire internetapplicaties
Page 98

94
De draadloze IEEE 802.11g router installeren
Voordat u de draadloze router installeert, dient u te controleren of u alle
onderdelen die genoemd staan onder “Inhoud van de verpakking” bij de hand
hebt. Als een van de onderdelen uit de verpakking ontbreekt of is beschadigd,
neem dan contact op met uw leverancier. Zorg er ook voor dat u over alle
benodigde kabels beschikt voordat u de installatie van de draadloze router
begint. Nadat u de draadloze router hebt geïnstalleerd, raden wij u aan het
hoofdstuk “Configuratie van de draadloze IEEE 802.11g router” op pagina 20
te raadplegen voor meer informatie over de configuratie van de router.
Inhoud van de verpakking
Controleer, nadat u de draadloze router uit de verpakking heeft gehaald,
de inhoud van de doos om er zeker van te zijn dat u alle onderdelen hebt
ontvangen:
• Draadloze IEEE 802.11g router
• Voedingsadapter
• Een CAT-5 Ethernet-kabel
• Handleiding
Neem direct contact op met uw leverancier indien de inhoud van de
verpakking afwijkt van bovenstaand overzicht of wanneer de inhoud
beschadigd is. Wij raden u aan de doos en het originele verpakkingsmateriaal
dat u ontvangen hebt te bewaren, voor het geval u het product wilt
retourneren.
Voor meer informatie over deze producten kunt u terecht op de website van
Micradigital: www.micradigital.com.
Page 99

95
Hardware-beschrijving
De draadloze router kan worden verbonden met het Internet of met een locatie
op afstand met behulp van een WAN-poort. U kunt hem direct aansluiten op
een pc of op een lokaal netwerk met behulp van snelle Ethernet LAN-poorten.
Gegevensoverdracht tussen de apparaten die op uw lokale netwerk zijn
aangesloten kan plaatsvinden met snelheden tot 100 Mbps via de Fast
Ethernet-poorten. De toegangssnelheid tot het Internet is echter ook
afhankelijk van uw servicetype en het type modem dat is aangesloten op de
draadloze router.
Op het frontpaneel van de draadloze router bevindt zich een LED-display voor
weergave van de status van de voeding en de poorten waardoor de installatie
en het oplossen van problemen een stuk eenvoudiger is. Op het achterpaneel
van de router bevinden zich tevens vier RJ-45 LAN-poorten en een RJ-45
WAN-poort.
• Vier Ethernet-poorten voor verbinding met een 10BASE-T/100BASETX Ethernet Local Area Network (LAN). Via auto-negotiation kunnen de
poorten zelf de van toepassing zijnde snelheid (10/100 Mbps), de modus
(half/full duplex) en de pinsignalen (MDI/MDI-X) bepalen (wat betekent dat
deze poorten kunnen worden verbonden met alle netwerkapparaten die
zijn aangesloten met een straight-through-kabel. Deze poorten kunnen
rechtstreeks met een pc of server worden verbonden die is uitgerust met
een Ethernet-netwerkinterfacekaart of met een netwerkapparaat zoals een
Ethernet-hub of switch.
• Een RJ-45-poort voor aansluiting van een DSL- of kabelmodem (WAN). Deze
poort maakt ook gebruik van de auto-negotiation-functionaliteit voor het
bepalen van de overdrachtssnelheid (10 of 100 Mbps), de modus (half of full
duplex) en de pinsignalen (MDI of MDI-X).
De volgende afbeelding toont de componenten van de draadloze router.
Page 100

96
Afbeelding 1. Voor- en achterpanelen
Onderdeel Beschrijving
LED’s Voeding-, WLAN-, WAN- en LAN-poortstatusindicatoren.
(Zie “LED-signaallampjes” op pagina 1.)
LAN-
poorten Fast Ethernet-poorten (RJ-45). Sluit apparaten (zoals een
PC,hub of switch) die onderdeel uitmaken van uw lokale
netwerk (LAN) aan op deze poorten.
Reset-
knop Gebruik deze knop om de voeding te resetten en de
fabriekswaarden
te herstellen.
WLAN-
poorten WAN-poort (RJ-45). Sluit uw kabelmodem, DSL-modem
of een Ethernet-router op deze poort aan.
Voedingsingang Sluit de meegeleverde voedingsadapter op deze
aansluiting aan.
Waarschuwing: Als u het verkeerde type voedingsadapter
gebruikt, kan uw router beschadigd raken.
 Loading...
Loading...