Page 1

TwinCAT
Application Note DK9322-1109-0011
TwinCAT Supplement ‚RFID Reader Communication‘
TwinCAT RFID Library
Keywords
RFID
TwinCAT
Supplement
Reader
Middleware
Serial interface
PLC
The ‘TwinCAT PLC RFID Reader Communication’ supplement is a middleware for connecting RFID readers
by different manufacturers to TwinCAT PLC via an abstract interface. Communication between the reader
and TwinCAT PLC takes place via the serial interfaces EL60xx (Beckhoff EtherCAT Terminal system) and
KL60x1 (Beckhoff Bus Terminal system) or also via the COM port of the PC, so that automated detection of
the presence of tags can be used extending as far as write accesses to the production controller and other
applications.
Basic principles and advantages of RFID
RFID (radio frequency identification) is a contactless identification system for objects that is used in the manufacturing or
logistics controller in order to initiate further sequences and steps via presence detection. An RFID system consists of several
transponders (tags), a reader and software that evaluates the data from the tags. A tag contains an ID, which does not change
over the entire lifetime, and a memory in which data can be stored. In addition to presence detection, the memory can be
used to read or write further data. The size and writability of the memory (Write-once-Read-Only/Read-Write) of the tags are
manufacturer-specific.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
1
Page 2
Application Note DK9322-1109-0011
IPC
RFID reader
RFID tag
Areas of application
for RFID
Access systems
Payment systems
Credit chips
Immobiliser
Parts tracking
Tool identification
Product history
Process management
Security
Membership card
Time recording
Personnel
Tracking of hazardous goods
Servicing
Tracing
Waste management
Forgery-proofing
Goods marking
Goods flow
TwinCAT Supplement ‚RFID Reader Communication‘
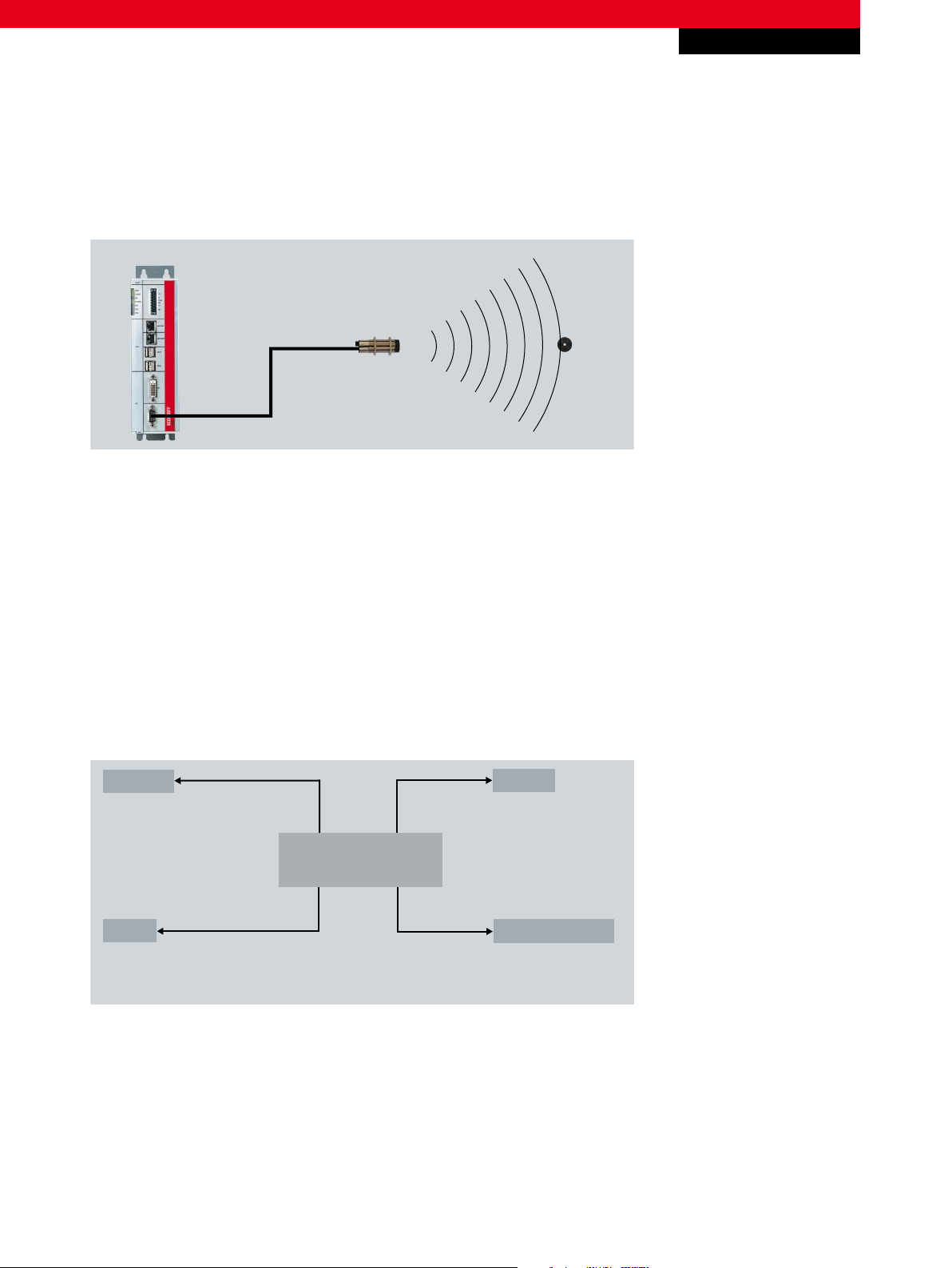
Fig. 1 Structure of an RFID connection
TwinCAT
The object to be detected is fitted with a tag that transmits its data as soon as the object is within range of the reader.
A specific alignment of the tag and the readers, such as is required with a barcode, is not necessary, since the data is
received contactlessly within the range cone of the reader. As opposed to barcodes, tag detection is also assured in poor
lighting conditions and in the case of dirty surfaces. Since RFID has short detection times and many tags can be detected
simultaneously (bulk reading ability), the individual goods on an entire pallet of different goods, for example in a goods
reception area, can be identified individually without having to take the container apart. Thus, all goods can be identified
within a very short space of time and their data made available for further processing. RFID offers many advantages over other
identification systems and is now used as an industrial standard in almost all industries.
Fig. 2 Areas of application of RFID
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
2
Page 3

Application Note DK9322-1109-0011
Wear and tear
Procurement costs
high
low
Barcode
Influence of dirt/moistrue
Influence of optical coverage failure
high
no or little influence
no or little influence
variable
depends on the technique
Manufacture by customer possible not possible
Data density low high
Bulk reading capability
Unauthorised copying
not possible
easy
possible
difficult or impossible
Complexity of the application high very easy
RFID
FB_Reader
eCommand
stAccessData
stCtrl
stCfg
bExecute
tTimeout
RxBuffer
TxBuffer
bBusy
bError
iErrorID
iErrCodeRcv
bResponseRcv
eResponse
stLowLevel
stReaderCfg
stReaderInfo
stTranspInfo
eManufacturer
TwinCAT Supplement ‚RFID Reader Communication‘
Fig. 3 Differences between barcode and RFID
TwinCAT
TwinCAT PLC RFID Reader Communication
In order to connect RFID readers to the controller, up to now the appropriate protocols had to be implemented for the various
readers on the basis of the serial interfaces. With the ‘TwinCAT PLC RFID Reader Communication’ TwinCAT library, a general,
abstract interface has been developed that can be used for any supported reader. The user sees only one block in the user
interface. The corresponding protocols have already been implemented internally for different readers; special adaptations to a
reader can be carried out simply via the configuration setting. The TwinCAT library is based on the IEC 61131-3 standard, with
which the data from the tags can be directly accessed or changed. This way, alongside the mere presence detection, the writing
of the RFID tags is also integrated into the PLC automation.
Fig. 4 TwinCAT function block for reader implementation
The system hardware, consisting of transponders and readers, can be chosen by the user according to his application and
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
3
Page 4

TwinCAT
Application Note DK9322-1109-0011
TwinCAT Supplement ‚RFID Reader Communication‘
procured externally. The RFID reader is connected to the industrial PC either via a serial interface (KL60x1 Bus Terminal | EL60xx
EtherCAT Terminal) or via the COM port. If the range is not sufficient for serial transmission, the connection point of the RFID
reader can be distributed anywhere in the I/O field using the corresponding coupler. The selected system can be integrated into
the automation environment via TwinCAT and the RFID reader supplement.
Advantages
In conjunction with the serial interfaces in terminal form, the RFID reader can be used in any fieldbus. Several readers can also
be integrated in the simplest way in the TwinCAT-encompassing automation world; all that is required for integrating several
readers is to create multiple instances of a function block. This way, even extensive applications that use different functions
of the RFID reader can easily be implemented. The implementation expenditure is very low, because the manufacturer-specific
interface protocol does not need to be researched in detail and implemented.
The handling and the interface of the PLC library are the same for all the supported RFID reader models. The frame structure,
the composition of the telegrams, the command name and other protocol specifications are performed automatically by the
library. This saves the user valuable development and implementation time and he can concentrate fully on his application.
Access to the RFID reader with tools from the Windows environment is similarly not a problem with the ‘Virtual Serial COM
Driver’ supplement for virtual interfaces.
If networking takes place at process control level, then detection of the RFID tags can take place at each station in order to
implement the traceability of components within the production process.
Practical application: detection of the presence of components
RFID is used to detect the presence of individual components within a production line for wooden products. The RFID tag is
attached to each component and is read by readers at different stations.
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
4
Page 5

Application Note DK9322-1109-0011
Windows XP or
Windows CE
TwinCAT
Industrial PC
Hardware
management
KL/EL60xx
Fieldbus adapter
RS232
Tags
Option 2
RFID reader
Option 1
COM
port
TwinCAT PLC
RFID Reader Communication
TwinCAT Supplement ‚RFID Reader Communication‘
TwinCAT
Fig. 5 Two options for connecting the reader to the PLC
Various components are created from the blanks in order to minimise cutting waste. For this reason, the boards are fitted with
a tag after being cut to size and the ID is assigned to an order or an assembly within a database. Once the tags have been
written, the components are transported by conveyor belts and parts trolleys to the individual machining centres. Due to the
fully automated manufacturing, the boards reach speeds of 60 metres per minute on the conveyor belts. Since RFID, as opposed
to barcodes, allows detection without stopping and speed reduction, the selection of the branching points can be executed in
real-time. If the component passes a reader attached to the conveyor belt, the tag is read, the destination is recognised and the
points are set accordingly.
– TwinCAT PLC RFID Reader Communication www.beckhoff.com/TwinCAT-RFID-Reader
– Optional TwinCAT software packages www.beckhoff.com/supplements
– EtherCAT Terminal, RS232 interface www.beckhoff.com/EL6001
– EtherCAT Terminal, RS422/485 interface www.beckhoff.com/EL6021
– EtherCAT Terminal, 2-channel RS232 interface www.beckhoff.com/EL6002
– EtherCAT Terminal, 2-channel RS422/485 interface www.beckhoff.com/EL6022
– Busterminal, RS232 interface www.beckhoff.com/KL6001
– Busterminal, RS422/485 interface www.beckhoff.com/KL6021
– Busterminals www.beckhoff.com/Busterminal
– EtherCAT Terminals www.beckhoff.com/EtherCAT-Terminals
For application notes see disclaimer on the last page
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
5
Page 6

Application Note DK9322-1109-0011
TwinCAT Supplement ‚RFID Reader Communication‘
TwinCAT
This publication contains statements about the suitability of our products for certain areas of application. These statements are based on typical features of our products. The examples shown in this publication are for demonstration purposes only. The information provided herein should not be regarded as specific operation characteristics. It is incumbent on the
customer to check and decide whether a product is suit-able for use in a particular application. We do not give any warranty that the source code which is made available with this
publication is complete or accurate. This publication may be changed at any time with-out prior notice. No liability is assumed for errors and/or omissions. Our products are described
in detail in our data sheets and documentations. Product-specific warnings and cautions must be observed. For the latest version of our data sheets and documentations please visit
our website (www.beckhoff.com).
© Beckhoff Automation GmbH, November 2009
The reproduction, distribution and utilisation of this document as well as the communication of its contents to others without express authorisation is prohibited. Offenders will be
held liable for the payment of damages. All rights reserved in the event of the grant of a patent, utility model or design.
Beckhoff
New Automation Technology
6
 Loading...
Loading...