B+B SmartWorx SEG510-2SFP-T, SEG520-4SFP-T, SEG612-4SFP-T, SEG512-4SFP-T, SEG620-4SFP-T User Manual
...
SE500 Series
CLI
USER MANUAL

ii
CLI
Advantech B+B SmartWorx - Americas
707 Dayton Road
Ottawa, IL 61350 USA
Phone (815) 433-5100
Fax (815) 433-5105
Advantech B+B SmartWorx - European Headquarters
Westlink Commercial Park
Oranmore, Co. Galway, Ireland
Phone +353 91-792444
Fax +353 91-792445
www.advantech-bb.com
support@advantech-bb.com
Document: CLI_R0_xx15m

iii
CLI
Acknowledgements
Intel and Pentium are trademarks of Intel Corporation.
Microsoft Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corp.
All other product names or trademarks are properties of their respective owners.
Supported Models
The user manual is only available for the following models:
Table 1: Supported Models
SEG510-2SFP-T SEG512-4SFP-T SEG520-4SFP-T
SEG528-4SFP-T SEG610-2SFP-T SEG612-4SFP-T
SEG620-4SFP-T SEG628-4SFP-T

iv
CLI
Technical Support and Assist ance
1. Visit the Advantech web site at www.advantech.com/support where you can find the latest information about the product.
2. Contact your distributor , sales represent ative, or Advantech's customer service center for
technical support if you need additional assistance. Please have the following information ready before you call:
– Product name and serial number
– Description of your peripheral attachments
– Description of your software (operating system, version, application software, etc.)
– A complete description of the problem
– The exact wording of any error messages
Warnings, Cautions and Notes
Document Feedback
To assist us in making improvements to this manual, we would welcome comments and constructive criticism. Please send all such - in writing to: support@advantech.com
Warning! Warnings indicate conditions, which if not observed, can cause personal injury!
Caution! Cautions are included to help you avoid damaging hardware or losing data. e.g.
There is a danger of a new battery exploding if it is incorrectly installed. Do not
attempt to recharge, force open, or heat the battery. Replace the battery only
with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer. Discard
used batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Note! Notes provide optional additional information.

v
INDUSTRIAL PROTOCOLS
Command Line Interface ............................................. 1
Using the Command-Line Interface................................................................................................. 1
Initially Configuring a Device ........................................ ... ... .......................................... ... ... ...... 1
Understanding Command Syntax............................................................................................. 1
Understanding Admin and User Accounts................................................................................ 2
Understanding Enable and Enable Secret Passwords............................................................. 2
Abbreviating Commands .......... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ............ 2
Using Aliases for CLI Commands............................................................................................. 3
L2 Features...................................................................................................................................... 3
Port Configuration..................................................................................................................... 3
MAC Address Table......................................... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... ... ...... 4
Jumbo Frame...................................... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... ...................... 5
Flow Control..............................................................................................................................5
Spanning Tree.......................................................................................................................... 6
VLAN ........................................................................................................................................ 9
Q-in-Q..................................................................................................................................... 11
Link Aggregation..................................................................................................................... 12
GARP...................................................................................................................................... 13
GVRP...................................................................................................................................... 13
Port Mirror............................................................................................................................... 14
LLDP....................................................................................................................................... 14
Multicast......................................................................................................................................... 16
IGMP Snooping ...................................................................................................................... 16
MLD Snooping........................................................................................................................ 19
Redundancy................................................................................................................................... 22
X-Ring..................................................................................................................................... 22
QoS................................................................................................................................................23
Rate Limit................................................................................................................................ 23
QoS......................................................................................................................................... 23
Security.......................................................................................................................................... 25
Loop Detection / Prevention ................................................................................................... 25
Storm Control.......................................................................................................................... 25
Port Security........................................................................................................................... 26
802.1X .................................................................................................................................... 27
Remote Authentication ...........................................................................................................27
One Time Password...............................................................................................................28
Account Manager...................................... .......................................... ... .... ... ... ....................... 28
DoS Attack Prevention..................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .................................... 29
IP Security .............................................................................................................................. 29
Management.................................................................................................................................. 30
IP Management ...................................................................................................................... 30
SNMP .....................................................................................................................................31
Configuration Management .................................................................................................... 32
Firmware Management ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... 33
DHCP Server............ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... .......................... 33
DHCP Client ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................... ... ................................................. 34
System Log (SYSLOG)........................................................................................................... 35
System Time........................................................................................................................... 35
SMTP...................................................................................................................................... 37
NTP Server............................................................................................................................. 37
RMON...........................................................................................................................
.......... 38
IP Configuration...................................................................................................................... 39
TELNET.................................................................................................................................. 40
CONTENTS

vi
INDUSTRIAL PROTOCOLS
SSH ........................................................................................................................................40
HTTP ......................................................................................................................................40
Modbus TCP........................................................................................................................... 41
IXM .........................................................................................................................................41
Diagnostic...................................................................................................................................... 42
Cable Diagnostic.............................. ... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ... ....................... 42
DMI......................................................................................................................................... 42
IP-based Diagnostic................................................................................................................ 43
PoE......................................................................................................................................... 43
LED......................................................................................................................................... 45
System.................................................................................................................................... 45

vii
INDUSTRIAL PROTOCOLS
Table 1: Supported Models ..............................................................................................................iii
Table 2: Account Management Commands ..................................................................................... 2
Table 3: Default Command Aliases.................................................................................................. 3
Table 4: Port Configuration...............................................................................................................3
Table 5: MAC Address Table ........................................................................................................... 4
Table 6: Jumbo Frame ..................................................................................................................... 5
Table 7: Flow Control .......................................................................................................................5
Table 8: Spanning Tree.................................................................................................................... 6
Table 9: VLAN.................................................................................................................................. 9
Table 10: Q-in-Q............................................................................................................................... 11
Table 11: Link Aggregation............................................................................................................... 12
Table 12: GARP ............................................................................................................................... 13
Table 13: GVRP ............................................................................................................................... 13
Table 14: GVRP ............................................................................................................................... 14
Table 15: LLDP.................................................................................................................................14
Table 16: IGMP Snooping................................................................................................................ 16
Table 17: MLD Snooping.................................................................................................................. 19
Table 18: X-Ring...............................................................................................................................22
Table 19: Rate Limit ......................................................................................................................... 23
Table 20: QoS .................................................................................................................................. 23
Table 21: Loop Detection / Prevention............................................ .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ....................... 25
Table 22: Storm Control ................................................................................................................... 25
Table 23: Port Security..................................................................................................................... 26
Table 24: 802.1X.............................................................................................................................. 27
Table 25: Remote Authentication..................................................................................................... 27
Table 26: One Time Password......................................................................................................... 28
Table 27: Account Manager ............................................................................................................. 28
Table 28: DoS Attack Prevention ..................................................................................................... 29
Table 29: IP Security........................................................................................................................ 29
Table 30: IP Management................................................................................................................ 30
Table 31: SNMP............................................................................................................................... 31
Table 32: Configuration Management.............................................................................................. 32
Table 33: Firmware Management..................................................................................................... 33
Table 34: DHCP Server.................................................................................................................... 33
Table 35: DHCP Client..................................................................................................................... 34
Table 36: System Log (SYSLOG) ....................................................................................................35
Table 37: System Time..................................................................................................................... 35
Table 38: SMTP................................................................................................................................37
Table 39: NTP Server....................................................................................................................... 37
Table 40: RMON...............................................................................................................................38
Table 41: IP Configuration................................................................................................................ 39
Table 42: TELNET............................................................................................................................ 40
Table 43: SSH.................................................................................................................................. 40
Table 44: HTTP................................................................................................................................ 40
Table 45: Modbus TCP..................................................................................................................... 41
Table 46: IXM................................................................................................................................... 41
Table 47: Cable Diagnostic .............................................................................................................. 42
Table 48: DMI................................................................................................................................... 42
Table 49: IP-based Diagnostic ...................................................................................................
......43
Table 50: PoE................................................................................................................................... 43
Table 51: LED...................................................................................................................................45
Table 52: System.............................................................................................................................. 45
LIST OF TABLES

1
CLI
Using the Command-Line Interface
The Advantech IOS command-line interface (CLI) is the primary user interface used to configure, monitor, and maintain Advantech devices. The user interface allows you to directly execute CLI commands. Note that all CLI options are also available via the web browser
interface.
This chapter describes the basic features of the Advantech IOS CLI and how to use them.
Topics covered include the following:
Layer 2 features
Multicast
IGMP Snooping
MLD Snooping
Redundancy
QoS
Security
Management
Diagnostic
The initial configuration of a device varies by device. This document provides configuration
information for the listed devices.
After initially configuring and connecting the device to the network, you can configure the
device by using the remote access method, such as Telnet or Secure Shell (SSH), to access
the CLI or by using the configuration method provided on the device, such as Security Device
Manager.
The command syntax is the format used for entering CLI commands. The commands are
derived from the use of the command, keywords, and arguments. The keywords are alphanumeric strings used literally, while arguments are used as placeholders for required values.
COMMAND LINE INTERFACE
Initially Configuring a Device
Understanding Command Syntax

2
CLI
Two levels of account privilege are available, admin (for system administrators), and user (for
general users). An admin account is required to add additional accounts and assign account
privileges. The following table displays the account management commands used to create
and edit admin and user accounts.
Some privileged EXEC commands are used for actions that impact the system, and it is recommended that you set a password for these commands to prevent unauthorized use. Two
types of passwords, enable (not encrypted) and enable secret (encrypted), can be set.
The following commands set these passwords and are issued in global configuration mode:
enable password
enable secret password
Typing a complete command name is not always required for the command to execute. The
CLI recognizes an abbreviated command when the abbreviation contains enough characters
to uniquely identify the command. For example, the show version command can be abbreviated as sh ver. It cannot be abbreviated as s ver because s could mean show, set, or systat.
The sh v abbreviation also is not valid because the show command has vrrp as a keyword in
addition to version. (Command and keyword examples are from Cisco IOS Release
12.4(13)T.)
Understanding Admin and User Accounts
Table 2: Account Management Commands
Account Manager
show username User EXEC Show all user accounts in
local database.
Switch# show username
show privilege User EXEC Show current privilege
level.
Switch# show privilege
username WORD<032> [privilege
(admin|user)] (password WORD<0-32>) | (
secret [encrypted]
WORD<0-32>) |
nopassword
Admin EXEC Use "username" command
to add a new user account
or edit an existing user
account.
switch(config)# username test
privilege admin secret 1234
no username WORD<032>
Admin EXEC Delete an existing user
account.
switch(config)# no username
test
enable (password |
(secret [encrypted]))
PASSWORD
Admin EXEC Edit password for each priv-
ilege level for enable
authentication.
switch(config)# enable secret
1234
no enable Admin EXEC Restore enable password to
default empty value.
switch(config)# no enable
Understanding Enable and Enable Secret Passwords
Abbreviating Commands

3
CLI
To save time and the repetition of entering the same command multiple times, you can use a
command alias. An alias can be configured to do anything that can be done at the command
line, but an alias cannot move between modes, type in passwords, or perform any interactive
functions.
Table 3 shows the default command aliases.
L2 Features
Using Aliases for CLI Commands
Table 3: Default Command Aliases
Command Alias Original Command
hhelp
lo logout
Pping
sshow
u or un undebug
wwhere
Port Configuration
Table 4: Port Configuration
Function Privilege Description Example
[no] shutdown Admin EXEC Use "shutdown" command
to disable port and use "no
shutdown" to enable port. If
port is error disabled for any
reason, use "no shutdown"
command to recover the
port manually.
This example shows how to
modify port duplex configuration.
switch(config)# interface fa1
switch(config-if)# shutdown"
speed (10|100) Admin EXEC Use "speed" command to
change port speed configuration. The speed is only
able to configure to the
physical maximum speed.
For example, in fast Ethernet port, speed 1000 is not
available.
This example shows how to
modify port speed configuration.
switch(config)# interface fa2
switch(config-if)# speed auto
10/100
speed (1000|) Admin EXEC
speed auto [(10|100|10/
100)]
Admin EXEC
speed auto [(1000|)] Admin EXEC
duplex (auto|full|half) Admin EXEC Use "duplex" command to
change port duplex configuration.
This example shows how to
modify port duplex configuration.
switch(config)# interface fa1
switch(config-if)# duplex full
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# interface fa2
switch(config-if)# duplex half

4
CLI
description WORD<1-"
SYS_STR_CONST(SY
S_PORTDESC_STR_L
EN) ">
Admin EXEC Use "description" com-
mand to give the port a
name to identify it easily.
If description includes
space character, please use
double quotes to wrap it.
This example shows how to
modify port descriptions.
switch(config)# interface fa2
switch(config-if)# description
"uplink port"
no description Admin EXEC Use no form to restore
description to empty string.
[no] protected Admin EXEC Use "protected" command
to protect port. Protected
port is only allowed to communicate with unprotected
port. In other words, protected port is not allowed to
communicate with another
protected port.
Use no form to make port
unprotected
This example shows how to
configure ports fa1 and fa2 as
protected ports.
switch(config)# interface range
fa1-2
switch(config-if-range)# protected
MAC Address Table
Table 5: MAC Address Table
Function Privilege Description Example
show mac address-table
aging-time
User EXEC View the aging time of the
address table.
switch# show mac addresstable aging-time
show mac address-table
A:B:C:D:E:F [vlan <14094>]
User EXEC Displays entries for a spe-
cific MAC address (for all or
VLAN).
switch# show mac addresstable 0:1:2:3:4:5 vlan 1
show mac address-table
[vlan <1-4094>] [interfaces IF_PORTS]
User EXEC View MAC entry on speci-
fied interface or VLAN or all
dynamic MAC entries in
MAC address table.
switch# show mac addresstable vlan 1 interface fa5
show mac address-table
static [vlan <1-4094>]
[interfaces IF_PORTS]
User EXEC View static MAC entry on
specified interface or VLAN
or all dynamic MAC entries
in MAC address table.
switch# show mac addresstable static vlan 1 interface fa5
show mac address-table
dynamic [vlan <1-4094>]
[interfaces IF_PORTS]
User EXEC View dynamic MACentry on
specified interface or VLAN
or all dynamic MAC entries
in MAC address table.
switch# show mac addresstable dynamic vlan 1 interface
fa5
show mac address-table
counters
User EXEC Display the number of
addresses present in MAC
address table.
switch# show mac addresstable counters
clear mac address-table
dynamic [interfaces
IF_PORTS]
Admin EXEC Delete dynamic MAC entry
on specified interface or all
dynamic MAC entries in
MAC address table.
switch(config)# clear mac
address-table dynamic interfaces fa5
clear mac address-table
dynamic vlan <1-4094>
Admin EXEC Delete dynamic MAC entry
on specified VLAN dynamic
MAC entry in MAC address
table.
switch(config)# clear mac
address-table dynamic vlan 1
Table 4: Port Configuration (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

5
CLI
mac address-table
aging-time <10-630>
Admin EXEC Set the aging time of the
address table.
switch(config)# mac addresstable aging-time 300
mac address-table static
A:B:C:D:E:F vlan <14094> interfaces
IF_PORTS
Admin EXEC Add static addresses to the
MAC address table.
switch(config)# mac addresstable static 0:1:2:3:4:5 vlan 1
interfaces fa5
no mac address-table
static A:B:C:D:E:F vlan
<1-4094>
Admin EXEC Delete static addresses
from the MAC address
table.
switch(config)# no mac
address-table static 0:1:2:3:4:5
vlan 1 interfaces fa5
Jumbo Frame
Table 6: Jumbo Frame
Function Privilege Description Example
jumbo-frame <15189216>
Admin EXEC Use "jumbo-frame" com-
mand to modify maximum
frame size.
The only way to show this
configuration is by using
"show running-config" command.
This example shows how to
modify maximum frame size to
9216 bytes.
switch(config)# jumbo-frame
9216
no jumbo-frame Admin EXEC Use no form to disable
jumbo-frame.
switch(config)# no jumboframe
Flow Control
Table 7: Flow Control
Function Privilege Description Example
[no] back-pressure Admin EXEC Use "back-pressure" com-
mand to change port backpressure configuration.
Use no form to restore
back-pressure to default
(off) configuration.
This example shows how to
modify port duplex configuration.
switch(config)# interface fa1
switch(config-if)# back-pressure
switch(config-if)# no backpressure
flowcontrol (off|on) Admin EXEC Use "flow-control" com-
mand to change port flow
control configuration.
Use off form to restore flow
control to default (off) configuration.
This example shows how to
modify port duplex configuration.
switch(config)# interface fa1
switch(config-if)# flow-control
on
switch(config-if)# flow-control
off
Table 5: MAC Address Table (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

6
CLI
Spanning Tree
Table 8: Spanning Tree
Function Privilege Description Example
show spanning-tree
[instance <0-15>]
User EXEC Show spanning-tree
instance information.
switch# show spanning-tree
instance 10
show spanning-tree
interfaces IF_PORTS
[instance <0-15>]
User EXEC Show spanning-tree
instance information per
port.
switch# show spanning-tree
interface gi1 instance 10
show spanning-tree User EXEC Show spanning-tree infor-
mation.
switch# show spanning-tree
show spanning-tree
interfaces IF_PORTS
User EXEC Show spanning-tree state of
one port.
switch# show spanning-tree
interface gi1
show spanning-tree
interfaces IF_PORTS
statistic
User EXEC Show spanning-tree statis-
tics of one port.
switch# show spanning-tree
interface gi1 statistic
[no] spanning-tree Admin EXEC Enable or Disable Span-
ning-Tree Protocol.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree bpdu (filtering|flooding)
Admin EXEC Specify the forwarding
action of BPDU to filtering
or flooding.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
bpdu filtering
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree bpdu Admin EXEC Restore to default BDPU
action. Default action is
flooding.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no spanningtree bpdu
switch(config)# exit"
spanning-tree mode
(stp|rstp|mstp)
Admin EXEC Specify the mode to Span-
ning Tree Protocol.
Specify the mode to Rapid
Spanni ng Tree Protocol.
Specify the mode to Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
mode stp
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree forceversion
Admin EXEC Restore to default stp ver-
sion. Default stp version is
rstp.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no spanningtree force-version
switch(config)# exit
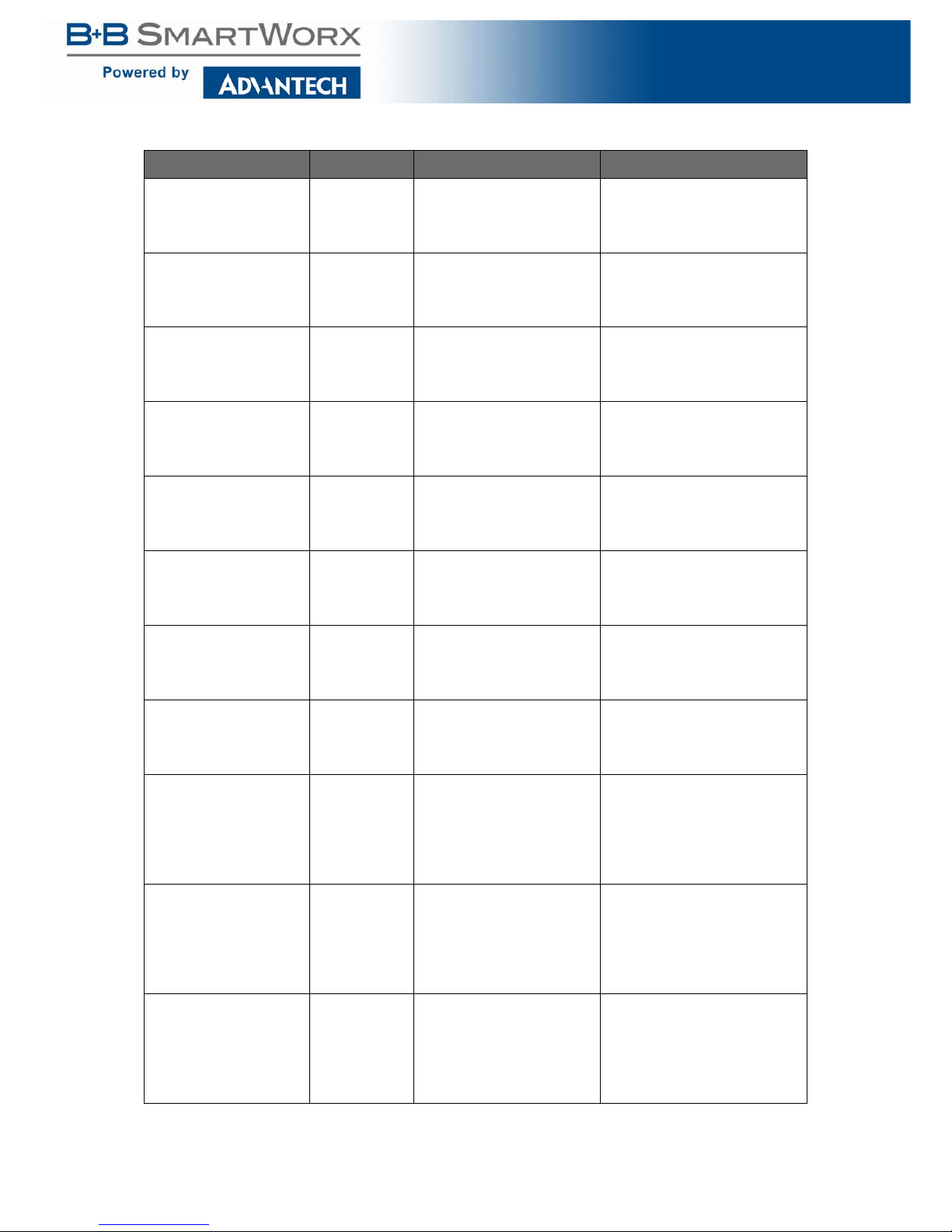
spanning-tree priority
<0-61440>
Admin EXEC Specify the bridge priority;
must use multiples of 4096.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
priority 16384
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree priority Admin EXEC Restore to default priority.
Default priority is 32768.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no spanningtree priority
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree hello-time
<1-10>
Admin EXEC Specify the hello-time inter-
val (seconds).
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
hello-time 5
switch(config)# exit
7
CLI
no spanning-tree hellotime
Admin EXEC Restore to default hello-
time. Default hello-time is 2.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no spanningtree hello-time
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree forwarddelay <4-30>
Admin EXEC Specify the forward-delay
interval (seconds).
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
forward-delay 30
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree forward-delay
Admin EXEC Restore to default forward-
delay . Default forward-delay
is 15.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no spanningtree forward-delay
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree maximum-age <6-40>
Admin EXEC Specify the maximum-age
time (seconds).
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
maximum-age 10
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree maximum-age
Admin EXEC Restore to default maxi-
mum-age. Default maximum-age is 20.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no spanningtree maximum-age
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree tx-holdcount <1-10>
Admin EXEC Specify the tx-hold-count
value.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
tx-hold-count 10
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree txhold-count
Admin EXEC Restore to default tx-hold-
count. Default tx-hold-count
is 6.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no spanningtree tx-hold-count
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree pathcost
method (long|short)
Admin EXEC Specify the type of pathcost
value as 32 bits (long).
Specify the type of p athcost
value as 16 bits (short).
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
pathcost method short
switch(config)# exit
[no] spanning-tree Admin EXEC Enable or Disable Span-
ning-Tree Protocol per port.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# spanningtree
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree port-priority <0-240>
Admin EXEC Specify the STP port prior-
ity; must use multiples of
16.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# spanningtree port-priority 64
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree portpriority
Admin EXEC Restore to default port-pri-
ority. Default port-priority is
128.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# no spanningtree port-priority
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
Table 8: Spanning Tree (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

8
CLI
spanning-tree cost long
<0-200000000>
Admin EXEC Specify the STP port cost.
In long pathcost method,
the range is from 0 to
20000000. (0 = Auto)
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# spanningtree cost long 200000
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree cost short
<0-65535>
Admin EXEC Specify the STP port cost.
In short pathcost method,
the range is from 0 to
65535. (0 = Auto).
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# spanningtree cost short 1000
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree cost Admin EXEC Restore to default cost per
port. Default cost is 0.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# no spanningtree cost
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
[no] spanning-tree edge Admin EXEC Enable or Disable Span-
ning-Tree edge.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# spanningtree edge
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree link-type
point-to-point
Admin EXEC Specify the STP port link-
type to point-to-point.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# spanningtree link-type point-to-point
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
no spanning-tree linktype point-to-point
Admin EXEC Disable the STP port link-
type from point-to-point.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# no spanningtree link-type point-to-point
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree mcheck Admin EXEC Specify the STP port to
migrate port.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# spanningtree mcheck
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree mst-config-id revision-level
LEVEL<0-65535>
Admin EXEC Specify the MSTP mst-con-
fig-id revision level.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
mst-config-id revision-level 100
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree mst-config-id name NAME<32>
Admin EXEC Specify the MSTP mst-con-
fig-id name.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
mst-config-id name MST1
switch(config)# exit
Table 8: Spanning Tree (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

9
CLI
[no] spanning-tree
instance-id INST<1-15>
Admin EXEC Create or delete MSTP
instance ID.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
instance-id 10
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree instanceid INST<1-15> vlan
(add|remove) VLANLIST
Admin EXEC Add or remove VLAN from
instance.
switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
instance-id 10 vlan add 10-20
switch(config)# exit
spanning-tree instanceid INST<1-15> priority
VALUE<0-61440>
Admin EXEC Specify the instance priority. switch# configure
switch(config)# spanning-tree
instance-id 10 priority 1000
switch(config)# exit
VLAN
Table 9: VLAN
Function Privilege Description Example
show vlan default-vlan User EXEC Display information about
default VLAN.
switch# show vlan default-vlan
show vlan VLAN-LIST
interfaces IF_PORTS
membership
User EXEC Display information about
VLAN list.
switch# show vlan 1 interfaces
GigabitEthernet 10 membership
show vlan [(VLANLIST|dynamic|static)]
User EXEC Display information about
VLAN list or dynamic or
static.
switch# show vlan 1
switch# show vlan dynamic
switch# show vlan static
show interfaces
IF_PORTS
User EXEC Use "show interface" com-
mand to show port counters, parameters and status.
show interfaces GigabitEthernet 1
show interfaces
IF_PORTS status
User EXEC Use "show interface" com-
mand to show port status.
show interfaces GigabitEthernet 1 status
show interfaces
IF_PORTS protected
User EXEC Use "show interface" com-
mand to show port protected status.
show interfaces GigabitEthernet 1 protected
show interfaces switchport IF_PORTS
User EXEC Use "show interface switch-
port" command to show port
VLAN status.
switch# show interfaces
switchport GigabitEthernet 1
[no] vlan VLAN-LIST Admin EXEC Create or remove a VLAN
entry. Using “vlan” command to enter the VLAN
configuration mode.
switch (config)# vlan 100
switch (config)# no vlan 100
name NAME Admin EXEC Configure the name of a
VLAN entry.
switch(config)# vlan 100
switch(config-vlan)# name
VLAN-one-hundred
switchport mode hybrid Admin EXEC Hybrid port: Support all
functions as defined in
IEEE 802.1Q specification.
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
show management-vlan User EXEC Display information about
management VLAN.
switch(config)# show management-vlan
Table 8: Spanning Tree (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

10
CLI
switchport hybrid pvid
<1-4094>
Admin EXEC This command configures
the hybrid port’s PVID. Use
"show interface switchport"
command to show configuration.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
switch(config-if)# switchport
hybrid pvid 100
[no] switchport hybrid
ingress-filtering
Admin EXEC This command per port
configures the ingress-filtering status. This filtering is
used to filter the frames
come from the non-member
ingress port. Use "show
interface switchport" command to show configuration.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
switch(config-if)# switchport
hybrid ingress-filtering
switchport hybrid
acceptable-frame-type
(all|taggedonly|untagged-only)
Admin EXEC This command per port
configures the acceptableframe-type. Use "show
interface switchport" command to show configuration.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
switch(config-if)# switchport
hybrid acceptable-frame-type
tagged-only
switchport hybrid
allowed vlan add VLANLIST
[(tagged|untagged)]
Admin EXEC This command per hybrid
port configures adds the
allowed VLAN list. Use
"show interface switchport"
command to show configuration.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
switch(config-if)# switchport
hybrid allowed vlan add 1
tagged
switchport hybrid
allowed vlan remove
VLAN-LIST
Admin EXEC This command per hybrid
port configures removes the
allowed VLAN list. Use
"show interface switchport"
command to show configuration.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
switch(config-if)# switchport
hybrid allowed vlan remove
100
[no] switchport defaultvlan tagged
Admin EXEC This command perport con-
figures the membership of
the default VLAN to tagged.
Use "show interface switchport" command to show
configuration.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
switch(config-if)# switchport
default-vlan tagged
[no] switchport forbidden
default-vlan
Admin EXEC This command perport con-
figures the membership of
the default VLAN to forbidden. Use "show interface
switchport" command to
show configuration.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
switch(config-if)# switchport
forbidden default-vlan
Table 9: VLAN (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

11
CLI
switchport forbidden
vlan (add|remove)
VLAN-LIST
Admin EXEC This command perport con-
figures the membership of
the specfied VLANs to forbidden. Use "show interface
switchport" command to
show configuration.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
mode hybrid
switch(config-if)# switchport
forbidden vlan 100
management-vlan vlan
<1-4094>
no management-vlan
Admin EXEC (1) Set <1-4094> as man-
agement VLAN ID; it is recommended to first create
the VLAN and then assign
the port to it.
(2) When using no command, restore management VLAN to default
VLAN.
(3) To view the created
management VLAN, use
"show management-vlan".
(1) The following example
specifies that management
VLAN 2 is created.
switch(config)# managementvlan vlan 2
(2) The following example
specifies that managementVLAN is restored to be default
VLAN.
switch(config)# no management-vlan
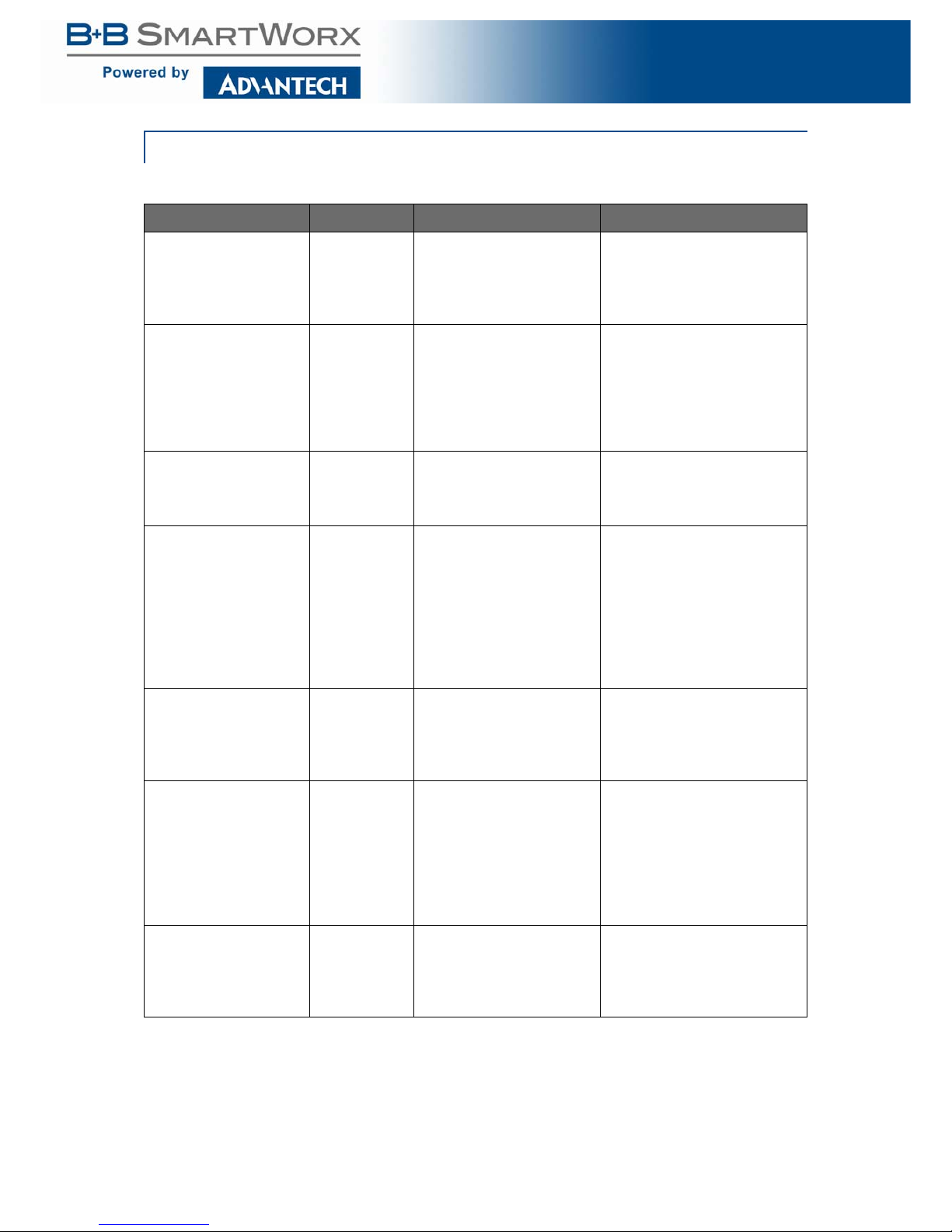
Q-in-Q
Table 10: Q-in-Q
Function Privilege Description Example
switchport outerpvid <14094>
Admin EXEC This command configures
the hybrid port’s Outer
PVID. Use "show interface
switchport" command to
show configuration.
This example sets gi2's Outer
PVID to 1024.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 2
switch(config-if)# switchport
outerpvid 1024
switchport qinqmode
(nni|uni)
Admin EXEC The qinqmode is used to
configure the hybrid port for
different port roles.
Nni: transfer frame will be
add outer tag Vlan-Identifier
Uni: transfer frame will not
be add outer tag Vlan-Identifier.
This example shows how to
change gi1 to nni mode and
gi2 to uni mode.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# switchport
qinqmode nni
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 2
switch(config-if)# switchport
qinqmode uni
vlan outertpid <0x00000xFFFF>
Admin EXEC Use "vlan outertpid" com-
mand to change outer
VLAN's Tag Protocol Identifier(tpid) configuration.
This example shows how to
modify Tag Protocol Identifier
configuration.
switch(config)# vlan outertpid
0x9100
Table 9: VLAN (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example
12
CLI
Link Aggregation
Table 11: Link Aggregation
Function Privilege Description Example
show lag User EXEC Use "show lag" command
to show current LAG load
balance algorithm and
members active/inactive
status.
This example shows how to
show current LAG status.
switch# show lag
lag load-balance (srcdst-mac|src-dst-macip|src-port)
Admin EXEC Link aggregation group port
should transmit packets
spread to all ports to balance traffic loading. Two
algorithms are supported;
use this command to select
the required algorithm.
This example shows how to
change load balance algorithm to src-dst-mac-ip.
switch(config)# lag load-balance src-dst-mac-ip
no lag load-balance Admin EXEC Use no form to disable
load-blance.
This example shows how to
disable load balance algorithm.
switch(config)# no lag load-balance
lag <1-8> mode (static |
active | passive)
Admin EXEC Link aggregation group
function aggregates multiple physical ports into one
logic port to increase bandwidth. This command
makes normal port joins a
normal port to a specific
LAG logic port in static or
dynamic mode.
This example shows how to
create a dynamic LAG and join
fa1-fa3 to this LAG.
switch(config)# interface range
fa1-3
switch(config-if)# lag 1 mode
active
no lag Admin EXEC Use "no lag" to leave the
LAG logic port.
This example shows how to
remove gi1 from LAG.
switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet 1
switch(config-if)# no lag
lacp system-priority <165535>
Admin EXEC LACP system priority is
used for two connected
DUT to select master
switch. Lower system priority value has higher priority.
The DUT with higher priority
can decide which ports are
able to join the LAG.
This example shows how to
configure lacp system priority
to 1000.
switch(config)# lacp systempriority 1000
no lacp system-priority Admin EXEC Use "no lacp system-prior-
ity" to restore to the default
priority value. Use "show
running-config" command
to show configuration.
This example shows how to
restore lacp system priority to
default value.
switch(config)# no lacp system-priority

13
CLI
lacp port-priority <165535>
Admin EXEC LACP port priority is used
for two connected DUT to
select aggregation ports.
Lower port priority value
has higher priority. The port
with higher priority will be
selected into LAG first.
Use "show running-config"
command to show configuration.
This example shows how to
configure interface fa1 lacp
port priority to 100.
switch(config)# interface fa1
switch(config-if)# lacp port-priority 100
no lacp port-priority Admin EXEC Use no form to restore port-
priority to default value.
lacp timeout (long|short) Admin EXEC LACP must send LACP
packet to partner switch to
check the link status. This
command configures the
LACP packet sending interval.
This example shows how to
configure interface fa1 lacp
timeout to short.
switch(config)# interface fa1
switch(config-if)# lacp timeout
short
no lacp timeout Admin EXEC
GARP
Table 12: GARP
Function Privilege Description Example
show garp User EXEC Display GARP status. switch# show garp
garp join-time <6-600> Admin EXEC Set interval of join timer. switch(config)# garp join-time
10
garp leave-time <123000>
Admin EXEC Set interval of leave timer. switch(config)# garp leave-
time 30
garp leaveall-time <1212000>
Admin EXEC Set interval of leave all
timer.
switch(config)# garp leavealltime 240
garp timer join <6-600>
leave <12-3000> leaveall <12-12000>
Admin EXEC Set interval of all timers. switch(config)# garp timer join
10 leave 30 leaveall 240
GVRP
Table 13: GVRP
Function Privilege Description Example
show gvrp User EXEC Display GVRP status. switch# show gvrp
[no] gvrp Admin EXEC Enable or disable GVRP
function.
switch(config)# gvrp
Table 11: Link Aggregation (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

14
CLI
Port Mirror
Table 14: GVRP
Function Privilege Description Example
show mirror User EXEC Display all mirror sessions. switch# show mirror
show mirror session <1-4>User EXEC Specify the mirror session
to display.
switch# show mirror session 1
mirror session <1-4>
source interfaces
IF_PORTS (both|rx|tx)
Admin EXEC Specify the mirror session
to configure.
Specify the source interface, include physical ports
and LA port.
Specify the traffic direction
to mirror.
switch# configure
switch(config)# mirror session
1 source interface fa2-5 both
switch(config)# exit
mirror session <1-4>
destination interface
IF_NMLPORT [allowingress]
Admin EXEC Specify the mirror session
to configure.
Specify the SPAN destination. A destination must be
a physical port.
Enable ingress traffic forwarding.
switch# configure
switch(config)# mirror session
1 destination interface fa1
switch(config)# exit
no mirror session (<14>|all)
Admin EXEC Clear the configuration of
specified mirror session.
Clear the configuration of all
of the mirror sessions.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no mirror session 1
switch(config)# exit
no mirror session <1-4>
destination interface
IF_NMLPORT
Admin EXEC Delete the destination inter-
face of the mirror session.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no mirror session 1 destination interface fa1
switch(config)# exit
no mirror session <1-4>
source interfaces
IF_PORTS (both|rx|tx)
Admin EXEC Delete the source interface
of the mirror session.
Delete the traffic direction of
the mirror port.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no mirror session 1 source interface fa2-5
both
switch(config)# exit
LLDP
Table 15: LLDP
Function Privilege Description Example
show lldp User EXEC Display LLDP information. switch# show lldp
show lldp interfaces
IF_NMLPORTS
User EXEC Display LLDP information in
specified ports.
switch# show lldp interfaces
fa5
show lldp local-device User EXEC Display the local configura-
tion.
switch# show lldp local-device
show lldp interfaces
IF_NMLPORTS localdevice
User EXEC Display the local configura-
tion in specified ports.
switch# show lldp interfaces
fa5,fa6 local-device
show lldp neighbor User EXEC Display the neighbor's
LLDP information.
switch# show lldp neighbor

15
CLI
show lldp interfaces
IF_NMLPORTS neighbor
User EXEC Display the neighbor's
LLDP information in specified ports.
switch# show lldp interfaces
fa5,fa6 neighbor
show lldp statistics User EXEC Display the LLDP RX/TX
statistics.
switch# show lldp statistics
show lldp interfaces
IF_NMLPORTS statistics
User EXEC Display the LLDP RX/TX
statistics in specified ports.
switch# show lldp interfaces
fa5,fa6 statistics
show lldp interfaces
IF_NMLPORTS tlvsoverloading
User EXEC Display the length of LLDP
TLVs and if the TLVs overload the PDU length in
specified ports.
switch# show lldp interfaces
fa5,fa6 tlvs-overloading
clear lldp statistics Admin EXEC Clear statistics of LLDP. switch# clear lldp statistics
[no] lldp Admin EXEC Disable or enable LLDP. switch(config)# lldp
[no] lldp tx Admin EXEC Per port disable or enable
LLDP TX.
switch(config-if)# lldp rx
[no] lldp rx Admin EXEC Per port disable or enable
LLDP RX.
switch(config-if)# lldp tx
lldp holdtime-multiplier
<2-10>
Admin EXEC Set the LLDP PDU hold
multiplier that decides timeto-live (TTL) value sent in
LLDP advertisements: TTL
= (tx-interval * holdtimemultiplier).
switch(config)# lldp holdtimemultiplier 4
no lldp holdtime-multiplier
Admin EXEC switch(config)# no lldp hold-
time-multiplier
lldp tx-interval <532767>
Admin EXEC Set the LLDP TX interval. switch(config)# lldp tx-interval
30
no lldp tx-interval Admin EXEC switch(config)# no lldp tx-inter-
val
lldp reinit-delay <1-10> Admin EXEC Set the LLDP re-initial
delay. This delay avoids
LLDP generating too many
PDUs if the port is up and
down frequently.
switch(config)# lldp reinit-delay
2
no lldp reinit-delay Admin EXEC switch(config)# no lldp reinit-
delay
lldp tx-delay <1-8191> Admin EXEC Set the delay in seconds
between successive LLDP
frame transmissions. The
delay starts to count any
time that LLDP PDU is sent,
such as by LLDP PDU
advertise routine, LLDP
PDU content change, port
link up, etc.
switch(config)# lldp tx-delay 2
no lldp tx-delay Admin EXEC switch(config)# no lldp tx-delay
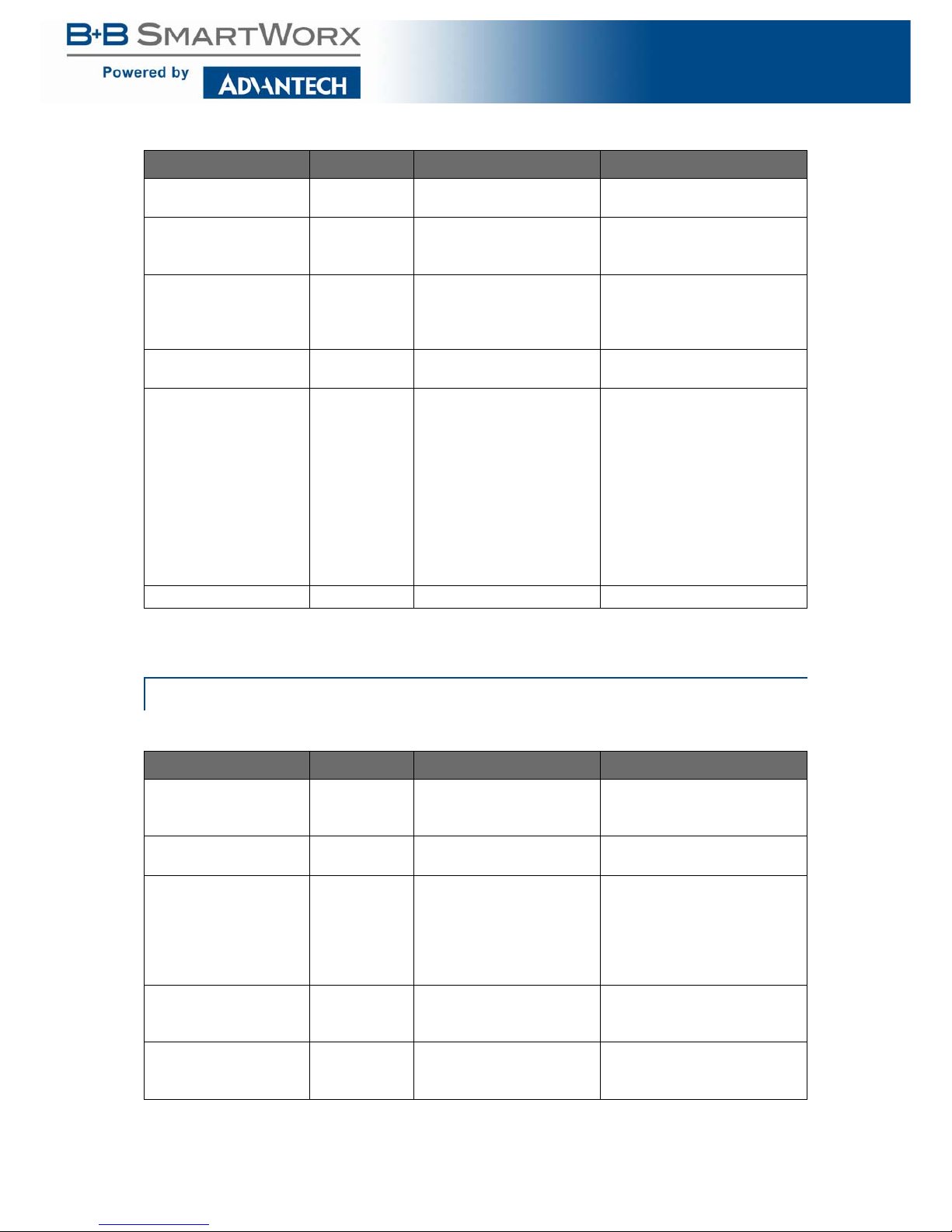
lldp tlv-select pvid
(enable|disable)
Admin EXEC This command per port
configures the 802.1 PVID
TLV attach enable status.
switch(config-if)# lldp tlv-select
pvid enable
Table 15: LLDP (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example
16
CLI
Multicast
no lldp tlv-select pvid Admin EXEC switch(config-if)# no lldp tlv-
select pvid
lldp tlv-select vlan-name
(add|remove) VLANLIST
Admin EXEC The commands per port
add or remove VLAN list for
802.1 VLAN-NAME TLV.
switch(config-if)# lldp tlv-select
vlan-name add 1,2,3,4
lldp tlv-select TLV [TLV]
[TLV] [TLV] [TLV] [TLV]
[TLV] [TLV]
Admin EXEC This command per port
configures the selected TL V
attaching in PDU.
switch(config-if)# lldp tlv-select
port-desc sys-name sys-desc
sys-cap mac-phy lag maxframe-size management-addr
no lldp tlv-select Admin EXEC switch(config-if)# no lldp tlv-
select
lldp lldpdu (filtering|bridging|flooding)
Admin EXEC This command globally
configures the LLDP PDU
handling behavior when
LLDP is globally disabled. It
should be noted that if
LLDP is globally enabled
and per port LLDP RX status is configured to disable,
the received LLDP PDU is
dropped instead of taking
the global disable behavior.
switch(config)# lldp lldpdu filtering
no lldp lldpdu Admin EXEC switch(config)# no lldp lldpdu
IGMP Snooping
Table 16: IGMP Snooping
Function Privilege Description Example
show ip igmp snooping User EXEC This command will display
IP IGMP snooping global
info.
switch# show ip igmp snooping
show ip igmp snooping
router
User EXEC This command will display
the IP IGMP router info.
switch# show ip igmp snooping
router
show ip igmp snooping
groups [(dynamic |
static)]
User EXEC This command will display
the IP IGMP groups for
dynamic or static or all
types.
switch# show ip igmp snooping
groups
switch# show ip igmp snooping
groups dynamic
switch# show ip igmp snooping
groups static
show ip igmp snooping
vlan [VLAN-LIST]
User EXEC This command will display
IP IGMP snooping VLAN
info.
switch# show ip igmp snooping
vlan
show ip igmp snooping
groups counters
User EXEC This command will display
the IP IGMP group counter
include static group.
switch# show ip igmp snooping
counters
Table 15: LLDP (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

17
CLI
show ip igmp snooping
querier
User EXEC This command will display
all of the static VLAN IP
IGMP querier info.
switch# show ip igmp snooping
querier
clear ip igmp snooping
groups [(dynamic
|static)]
Admin EXEC This command will clear the
IP IGMP groups for
dynamic or static or all
types.
switch# clear ip igmp snooping
groups static
clear ip igmp snooping
statistics
Admin EXEC This command will clear the
IGMP statistics.
switch# clear ip igmp snooping
statistics
[no] ip igmp snooping Admin EXEC "No IP IGMP snooping" will
clear all ip igmp snooping
dynamic groups and
dynamic router ports, and
make the static IP IGMP
group invalid. Subsequently , dynamic group and
router port will not be
learned via IGMP message.
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping
switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping
[no] ip igmp snooping
report-suppression
Admin EXEC "No IP IGMP snooping
report-suppression" will disable IGMP v1/v2 IGMP
report suppression function.
When received, report will
be forwarded to the VLAN
router ports.
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping report-suppression
switch(config)# no ip igmp
snooping report-suppression
no ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST group
A.B.C.D
Admin EXEC "IP IGMP snooping vlan 1
static-group 224.1.1.1 interfaces gi1" will add static
group.
The static group will not
learn other dynamic ports. If
the dynamic group exists,
the static group will overlap
the dynamic group. If the
last member of the static
group is removed, the static
group will be deleted.
To validate the static group,
IGMP snooping VLAN and
IP IGMP snooping must be
enabled.
Use "Show IP IGMP snooping group [(dynamic |
static)]" command to display configuration. Use "No
IP IGMP snooping vlan 1
group 224.1.1.1" command
to delete the static group.
The "clear ip igmp snooping
groups" command can also
be used to delete the static
group.
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1 static-group
224.1.1.1 interfaces gi1-2
Table 16: IGMP Snooping (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

18
CLI
no ip unknown-multicast
action
Admin EXEC When IGMP snooping and
MLD snooping are disabled, router port actions
cannot be set.
Disabling IGMP snooping &
MLD snooping will flood
multicast traffic to all members of the VLAN.
When the action is a router
port flood or drop, it will
delete the unknown multicast group entry.
switch(config)# ip unknownmulticast action router-port
switch(config)# no ip unknownmulticast action
[no] ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST
fastleave
[no] ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST router
learn pim-dvmrp
ip igmp snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST robustnessvariable <1-7>
no ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST robustness-variable
ip igmp snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST responsetime <5-20>
no ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST
response-time
ip igmp snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST query-interval <30-18000>
no ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST queryinterval
ip igmp snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST last-member-query-interval <125>
no ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST lastmember-query-interval
ip igmp snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST last-member-query-count <1-7>
no ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST lastmember-query-count
Admin EXEC "No IP IGMP snooping vlan
1 (last-member-query-count
| last-member-query-interval | query-interval |
response-time | robustnessvariable)" will set the VLAN
parameters to default.
The CLI setting will change
the IP IGMP VLAN parameters admin settings.
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1 fastleave
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1 last-member-querycount 5
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1 last-member-queryinterval 3
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1 query-interval 100
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1 response-time 12
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1 robustness-variable
4
Table 16: IGMP Snooping (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

19
CLI
[no] ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST
Admin EXEC "No IP IGMP snooping vlan
1" will clear all VLAN IP
IGMP snooping dynamic
groups and dynamic router
ports, and invalidate any
static IP IGMP groups with
a VLAN ID of 1. Subsequently , the dynamic groups
and router ports will not be
learned via IGMP message
for VLAN 1.
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 1
ip igmp snooping version (2|3)
Admin EXEC "IP IGMP snooping version
3" supports v3 basic mode.
When the version changes
from v3 to v2, all querier
versions will update to version 2.
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping version 3
no ip igmp snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST querier
[version (2|3)]
ip igmp snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST querier
Admin EXEC When IP IGMP vlan querier
is enabled, a router selection process will be triggered. The selected router
will send a general and specific query.
switch(config)# ip igmp snooping vlan 2 querier
MLD Snooping
Table 17: MLD Snooping
Function Privilege Description Example
show ip mld snooping User EXEC This command will display
IP MLD snooping global
info.
switch# show ip mld snooping
show ip mld snooping
router
User EXEC This command will display
the IP MLD router info.
switch# show ip mld snooping
router
show ip mld snooping
groups [(dynamic |
static)]
User EXEC This command will display
the IP MLD groups for
dynamic or static ports, or
for all types.
switch# show ip mld snooping
groups
switch# show ip mld snooping
groups dynamic
Switch# show ip mld snooping
groups static
show ip mld snooping
vlan [VLAN-LIST]
User EXEC This command will display
IP MLD snooping VLAN
info.
switch# show ip mld snooping
vlan
show ip mld snooping
groups counters
User EXEC This command will display
the IP MLD group counter
include static group.
switch# show ip mld snooping
counters
show ip mld snooping
querier
User EXEC This command will display
all of the static VLAN IP
MLD querier info.
switch# show ip mld snooping
querier
Table 16: IGMP Snooping (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

20
CLI
clear ip mld snooping
groups [(dynamic
|static)]
Admin EXEC This command will clear the
IP MLD groups for dynamic
or static ports, or for all
types.
switch# clear ip mld snooping
groups static
clear ip mld snooping
statistics
Admin EXEC This command will clear the
MLD statistics.
switch# clear ip mld snooping
statistics
[no] ip mld snooping Admin EXEC "No IP MLD snooping" will
clear all IP MLD snooping
dynamic groups and
dynamic router ports, and
make the static IP MLD
group invalid. Subsequently, the dynamic group
and router ports will not be
learned via MLD message.
switch(config)# ip mld snooping
switch(config)# no ip mld
snooping
[no] ip mld snooping
report-suppression
Admin EXEC "No IP MLD snooping
report-suppression" will disable MLD v1/v2 MLD report
suppression function.
Reports received will be forwarded to the VLAN router
ports.
switch(config)# ip mld snooping report-suppression
switch(config)# no ip mld
snooping report-suppression
[no] ip mld snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST staticgroup X:X::X:X interfaces IF_PORTS
no ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST group
X:X::X:X
Admin EXEC "IP MLD snooping vlan 1
static-group ff0e:dd::00:dd
interfaces gi1" will add
static group.
The static group willl not
learn other dynamic ports. If
the dynamic group exists,
the static group will overlap
the dynamic group. If the
last member of the static
group is removed, the static
group will be deleted.
For the static group to be
valid, IGMP snooping VLAN
and IP IGMP snooping
must both be enabled.
Use "Show IP IGMP snooping group [(dynamic |
static)]" to display the configuration. Use "No IP MLD
snooping vlan 1 group
ff0e:dd::00:dd" or "Clear IP
MLD snooping groups" to
delete the static group.
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 1 static-group
ff0e:dd::00:dd interfaces gi1-2
Table 17: MLD Snooping (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

21
CLI
[no] ip mld snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST
fastleave
[no] ip mld snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST router
learn pim-dvmrp
ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST robustnessvariable <1-7>
no ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST robustnessvariable
ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST responsetime <5-20>
no ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST responsetime
ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST query-interval <30-18000>
no ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST query-interval
ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST last-member-query-interval <125>
no ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST last-member-query-interval
ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST last-member-query-count <1-7>
no ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST last-member-query-count
Admin EXEC "No IP MLD snooping vlan
1 (last-member-query-count
| last-member-query-interval | query-interval |
response-time | robustnessvariable)" will set the VLAN
parameters to default.
The CLI setting will change
the IP MLD vlan parameters
admin settings.
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 1 fastleave
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 1 last-member-querycount 5
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 1 last-member-queryinterval 3
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 1 query-interval 100
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 1 response-time 12
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 1 robustness-variable
4
[no] ip mld snooping
vlan VLAN-LIST
Admin EXEC "No IP MLD snooping vlan
1" will clear vlan all IP MLD
snooping dynamic group
and dynamic router ports,
and invalidate any static IP
MLD group invalid with a
VLAN ID of 1. Subsequently, the dynamic group
and router ports will not be
learned via MLD message
for VLAN 1.
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 1
Table 17: MLD Snooping (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

22
CLI
Redundancy
ip mld snooping version
(1|2)
Admin EXEC "IP MLD snooping version
2", supports v2 basic mode.
When the version changes
from v2 to v1, all querier
versions will update to version 2.
switch(config)# ip mld snooping version 2
ip mld snooping vlan
VLAN-LIST querier [version (1|2)]
no ip mld snooping [vlan
VLAN-LIST] querier
Admin EXEC When enable IP MLD vlan
querier is enabled, a router
selection process will be
triggered. The selected
router will send a general
and specific query.
switch(config)# ip mld snooping vlan 2 querier
X-Ring
Table 18: X-Ring
Function Privilege Description Example
show xring-elite User EXEC Display xring-elite status. switch# show xring-elite
[no] xring-elite Admin EXEC Disable or enable xring-elite
function.
switch(config)# no xring-elite
switch(config)# xring-elite
xring-elite ring-id <1255> ports IF_PORTS
Admin EXEC Create a normal ring. switch(config)# xring-elite ring-
id 1 ports GigabitEthernet 1,2
xring-elite legacy ring-id
<1-255> ports
IF_PORTS
Admin EXEC Create a legacy ring. switch(config)# xring-elite leg-
acy ring-id 2 ports GigabitEthernet 3,4
no xring-elite ring-id <1255>
Admin EXEC Delete a normal ring or leg-
acy ring.
switch(config)# no xring-elite
ring-id 1
show xring-plus User EXEC Display xring-plus status. switch# show xring-plus
[no] xring-plus Admin EXEC Disable or enable xring-plus
function.
switch(config)# no xring-plus
switch(config)# xring-plus
xring-plus create ring-id
<1-255> interface
IF_PORT interface
IF_PORT
Admin EXEC Create a ring. switch(config)# xring-plus cre-
ate ring-id 5 interface Giga-
bitEthernet 1 interface
GigabitEthernet 2
xring-plus create ring-id
<1-255> coupling interfaces IF_PORTS master-ring ring-id <1-255>
Admin EXEC Create a coupling. switch(config)# xring-plus cre-
ate ring-id 6 coupling inter-
faces 3 master-ring ring-id 5
switch(config)# xring-plus cre-
ate ring-id 6 coupling inter-
faces 3,4 master-ring ring-id 5
xring-plus delete ring-id
<1-255>
Admin EXEC Delete a ring or coupling. switch(config)# xring-plus
delete ring-id 5
Table 17: MLD Snooping (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

23
CLI
QoS
Rate Limit
Table 19: Rate Limit
Function Privilege Description Example
show rate-limit User EXEC Display rate-limit infor-
mation.
switch# show rate-limit
show rate-limit interfaces IF_NMLPORTS
User EXEC Display rate-limit infor-
mation in specified interface.
switch# show rate-limit
interfaces fa 5
rate-limit ingress <161000000>
Admin EXEC Set ingress rate-limit. switch(config-if)# rate-
limit ingress 10000
no rate-limit ingress Admin EXEC No ingress rate-limit. switch(config-if)# no
rate-limit ingress
rate-limit egress <161000000>
Admin EXEC Set egress rate-limit. switch(config-if)# rate-
limit egress 10000
no rate-limit egress Admin EXEC No egress rate-limit. switch(config-if)# no
rate-limit egress
rate-limit egress queue
<1-8> <16-1000000>
Admin EXEC Set egress rate-limit in
queue.
switch(config-if)# ratelimit egress queue 3
10000
no rate-limit egress
queue <1-8>
Admin EXEC No egress rate-limit in
queue.
switch(config-if)# no
rate-limit egress queue 3
QoS
Table 20: QoS
Function Privilege Description Example
show qos User EXEC Display qos state. switch# show qos
show qos queueing User EXEC Display qos queueing state. switch# show qos queueing
show qos interfaces
IF_PORTS
User EXEC Display qos state by inter-
face.
switch# show qos interface gi1
show qos map [(cosqueue|dscp-queue|precedence-queue|queuecos|queue-dscp|queueprecedence)]
User EXEC Display qos map detail. switch# show qos map
[no] qos Admin EXEC Enabled or disabled the
device to qos mode.
switch# configure
switch(config)# qos
switch(config)# exit
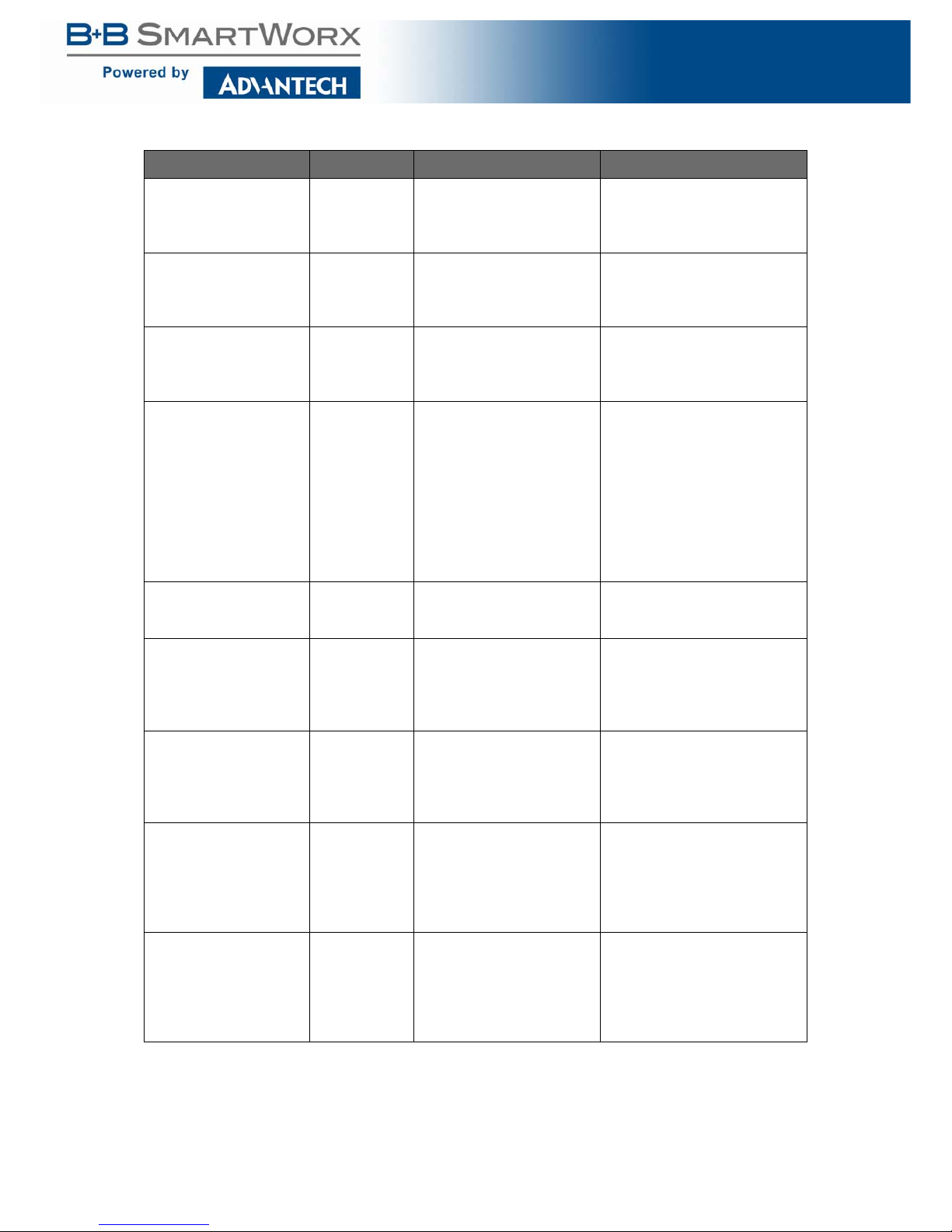
qos queue strict-priority-
num <0-8>
Admin EXEC Specify the strict priority
queue number.
switch# configure
switch(config)# qos queue
strict-priority-num 1
switch(config)# exit
qos queue weight
SEQUENCE
Admin EXEC Specify the non-strict prior-
ity queue weight value. The
valid queue weight value is
from 1 to 127.
switch# configure
switch(config)# qos queue
weight 3
switch(config)# exit
24
CLI
qos map cos-queue
SEQUENCE to <1-8>
Admin EXEC Configure or show CoS to
queue map
switch# configure
switch(config)# qos map cos-
queue 6 7 to 1
switch(config)# exit
qos map dscp-queue
SEQUENCE to <1-8>
Admin EXEC Configure or show DSCP to
queue map.
switch# configure
switch(config)# qos map dscp-
queue 6 7 to 1
switch(config)# exit
qos map precedence-
queue SEQUENCE to
<1-8>
Admin EXEC Configure or show IP Pre-
cedence to queue map.
switch# configure
switch(config)# qos map pre-
cedence-queue 6 7 to 1
switch(config)# exit
qos trust (cos|cos-
dscp|dscp|precedence)
Admin EXEC Specify the device to trust
CoS.
Specify the device to trust
DSCP for IP packets, and
trust CoS for non-IP packets.
Specify the device to trust
DSCP.
Specify the device to trust
IP Precedence
switch# configure
switch(config)# qos trust cos
switch(config)# qos trust dscp
switch(config)# exit
no qos trust Admin EXEC Clear qos trust configure. switch# configure
switch(config)# no qos trust
switch(config)# exit
qos cos <0-7> Admin EXEC Specify the CoS value for
the interface.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# qos cos 1
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
[no] qos trust Admin EXEC Enabled or disabled the qos
mode per port.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# qos
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
qos map queue-cos
SEQUENCE to <0-7>
Admin EXEC Configure or show CoS to
queue map.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# qos map cos-
queue 6 7 to 1
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
qos map queue-dscp
SEQUENCE to <0-63>
Admin EXEC Configure or show DSCP to
queue map.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# qos map
dscp-queue 6 7 to 1
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
Table 20: QoS (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example
25
CLI
Security
qos map queue-precedence SEQUENCE to
<0-7>
Admin EXEC Configure or show IP Pre-
cedence to queue map.
switch# configure
switch(config)# interface gi1
switch(config-if)# qos map pre-
cedence-queue 6 7 to 1
switch(config-if)# exit
switch(config)# exit
[no] qos remark
(cos|dscp|precedence)
Admin EXEC
Loop Detection / Prevention
Table 21: Loop Detection / Prevention
Function Privilege Description Example
show loopback-detection
User EXEC Display loopback-detection
global status.
switch# show loopback-detec-
tion
show loopback-detec-
tion interfaces
IF_PORTS state
User EXEC Display loopback-detection
status of specified ports.
show loopback-detection inter-
faces GigabitEthernet 1,2 state
[no] loopback-detection Admin EXEC Enable or disable loopback-
detection.
switch(config)# loopback-
detection
switch(config)# no loopback-
detection
loopback-detection inter-
val <1-32767>
Admin EXEC Set loopback detection
interval.
switch(config)# loopback-
detection interval 1
loopback-detection
recover-time <601000000>
Admin EXEC Set block port recover time. switch(config)# loopback-
detection recover-time 60
[no] loopback-detection Admin EXEC Enable or disable loopback-
detection of a specified
port.
switch(config-if)# loopback-
detection
switch(config-if)# no loopback-
detection
Storm Control
Table 22: Storm Control
Function Privilege Description Example
show storm-control User EXEC Display storm-control infor-
mation.
switch# show storm-control
show storm-control
interfaces
IF_NMLPORTS
User EXEC Display storm-control infor-
mation in specified interface.
switch# show storm-control
interfaces fa5
storm-control ifg
(include|exclude)
Admin EXEC Decide whether to include/
exclude the preamble and
inter frame gap into the calculation or not.
switch(config)# storm-control
ifg include
Table 20: QoS (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

26
CLI
storm-control unit
(bps|pps)
Admin EXEC Set the unit of calculation
method.
switch(config)# storm-control
unit bps
[no] storm-control Admin EXEC Disable or enable storm-
control.
switch(config)# storm-control
[no] storm-control
(broadcast|unknownunicast|unknown-multicast)
Admin EXEC Disable or enable storm-
control type.
switch(config-if)# storm-con-
trol broadcast
storm-control (broadcast|unknown-unicast|unknown-multicast)
level <1-1000000>
Admin EXEC Set control rate of storm-
control type.
switch(config-if)# storm-con-
trol broadcast level 1000
no storm-control (broadcast|unknown-unicast|unknown-multicast)
level
Admin EXEC No control rate of storm-
control type.
switch(config-if)# no storm-
control broadcast level
storm-control action
(drop|shutdown)
Admin EXEC The storm control mecha-
nism drops packets which
exceed storm control rate or
just shuts down the port.
switch(config-if)# storm-con-
trol action shutdown
no storm-control action Admin EXEC Set action to drop. switch(config-if)# no storm-
control action
Port Security
Table 23: Port Security
Function Privilege Description Example
show port-security User EXEC Display port-security status. switch# show port-security
[no] port-security [learn-
ing-limit <0-64>]
Admin EXEC Enable port security of a
port and specify a maximum FDB learning number
of that port.
Disable port security.
switch(config-if)# port-security
learning-limit 5
switch(config-if)# port-security
switch(config-if)# no port-secu-
rity
[no] mac-violation-notify Admin EXEC When a port reaches its
maximum FDB learning
number, the system will
send to SNMP trap for a
new MAC.
switch(config-if)# mac-viola-
tion-notify
switch(config-if)# no mac-viola-
tion-notify
Table 22: Storm Control (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

27
CLI
802.1X
Table 24: 802.1X
Function Privilege Description Example
show dot1x status User EXEC Show Dot1x configuration. switch# show dot1x
[no] dot1x Admin EXEC Configure radius server
enable/disable.
The “dot1x” command globally enables 802.1x ability.
The “no dot1x run" command disables the 802.1x
ability.
switch#show dot1x
switch(config)# no dot1x
dot1x authenticationbased (port | mac)
Admin EXEC Configure radius server
authentication mode.
switch(config)# dot1x authenti-
cation-based port
switch(config)# dot1x authenti-
cation-based mac
dot1x authentication-
port IF_PORTS sectype
(authorize | disable)
Admin EXEC Configure radius server
authentication port.
switch(config)# dot1x authenti-
cation-port FastEthernet 1 sec-
type authorize
switch(config)# dot1x authenti-
cation-port FastEthernet 1 sec-
type disable
dot1x sys-configuration
ip X.X.X.X radius-port
<1-65535> accountingport <1-65535> secret
WORD<0-128>
Admin EXEC Configure radius server IP
& port and secret key.
switch(config)# dot1x sys-con-
figuration ip 192.168.1.100
radius-port 1812 accounting-
port 1813 secret 12345678
dot1x misc-configuration reauth-period <165535>
Admin EXEC Configure radius server
reauth period.
switch(config)# dot1x misc-
configuration reauth-period
3600
Remote Authentication
Table 25: Remote Authentication
Function Privilege Description Example
show security-login User EXEC Show security login config-
uration.
switch# show security-login
[no] security-login Admin EXEC Use "security-login" com-
mand to enable securitylogin services.
Use no form to disable service.
switch(config)# security-login
switch(config)# no security-
login
security-login radiusconfig ip X.X.X.X port
<1-65535> secret
WORD<0-128>
Admin EXEC Configure radius login
access control.
switch(config)# security-login
radius-config ip 192.168.1.100
port 1812 secret 12345678
security-login tacacsconfig ip X.X.X.X port
<1-65535> secret
WORD<0-128>
Admin EXEC Configure security login
access control.
switch(config)# security-login
rtacacs-config ip
192.168.1.100 port 1812
secret 12345678

28
CLI
security-login accesscontrl (http | telnet | ssh |
all)
Admin EXEC Configure security login
access control.
switch(config)# security-login
access-contrl http
no security-login
access-contrl (http | telnet | ssh | all)
Admin EXEC Reset security login access
control.
switch(config)# no security-
login access-contrl
security-login login-type
(radius | tacacs | both |
all)
Admin EXEC Configure security login
type.
switch(config)# security-login
login-type radius
no security-login logintype
Admin EXEC Reset security login type. switch(config)# no security-
login login-type
One Time Password
Table 26: One Time Password
Function Privilege Description Example
show otp User EXEC Show otp configuration. switch# show otp
[no] otp Admin EXEC Use "otp" command to
enable otp services.
Use no form to disable service.
switch(config)# otp
switch(config)# no otp
otp secure-key-mode
(one-time-used | timerestricted)
Admin EXEC Configure otp secure key
mode.
switch(config)# otp secure-
key-mode one-time-used
switch(config)# otp secure-
key-mode time-restricted
otp interval <3600-
86400>
Admin EXEC Configure otp survival time. switch(config)# otp interval
otp display-mode
(attempt-failed | fixeddisplay)
Admin EXEC Configure otp display
mode.
switch(config)# otp display-
mode attempt-failed
switch(config)# otp display-
mode fixed-display
otp ssh-first-phase-auth
username WORD<132> password
WORD<1-32>
Admin EXEC Configure otp ssh login
information.
switch(config)# otp ssh-first-
phase-auth username admin
password 12345678
Account Manager
Table 27: Account Manager
Function Privilege Description Example
show username User EXEC Show all user accounts in
local database.
switch# show username
show privilege User EXEC Show current privilege
level.
switch# show privilege
Table 25: Remote Authentication (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

29
CLI
username WORD<032> [privilege
(admin|user)] (password WORD<0-32>) | (
secret [encrypted]
WORD<0-32>) |
nopassword
Admin EXEC Use "username" command
to add a new user account
or edit an existing user
account.
switch(config)# username test
privilege admin secret 1234
no username WORD<032>
Admin EXEC Delete an existing user
account.
switch(config)# no username
test
enable (password |
(secret [encrypted]))
PASSWORD
Admin EXEC Edit password for each priv-
ilege level to enable
authentication.
switch(config)# enable secret
1234
no enable Admin EXEC Restore enable password to
default empty value.
switch(config)# no enable
DoS Attack Prevention
Table 28: DoS Attack Prevention
Function Privilege Description Example
show dos User EXEC Show current dos global
state.
switch# show dos
show dos interfaces
IF_PORTS
User EXEC Show dos configuration
on selected ports.
switch# show dos interfaces GigabitEthernet 1
[no] dos (tcp-frag-offmin-check|synrstdeny|synfin-deny|xmadeny|nullscan-deny|synsportl1024-deny|tcphdrmin-check|smurfdeny|icmpv6-ping-maxcheck|icmpv4-ping-maxcheck|icmp-frag-pktsdeny|ipv6-min-frag-sizecheck|pod-deny|tcpblatdeny|udpblat-deny|landdeny|daeqsa-deny)
Admin EXEC Configure DUT to
enable/disable support
types of attacks.
switch(config)# no dos
land-deny
switch(config)# dos
land-deny
IP Security
Table 29: IP Security
Function Privilege Description Example
show ip-security User EXEC Display IP security informa-
tion.
switch# show ip-security
[no] ip-security Admin EXEC Disable or enable IP secu-
rity.
switch(config)# ip-security
Table 27: Account Manager (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

30
CLI
Management
ip-security ip A.B.C.D
mask A.B.C.D [service (
ping | http | https | telnet
| ssh | snmp ) state
(enable | disable)]
Admin EXEC Add a specified IP (and ser-
vice) entry for IP security
usage.
switch(config)# ip-security ip
192.168.1.1 mask 255.255.0.0
service ping state enable
no ip-security ip A.B.C.D
mask A.B.C.D
Admin EXEC Remove specified IP secu-
rity entry.
switch(config)# no ip-security
ip 192.168.1.1 mask
255.255.0.0
IP Management
Table 30: IP Management
Function Privilege Description Example
show ip User EXEC Show system IPv4 address,
subnet mask and default
gateway.
switch# show ip
show ip dhcp User EXEC Show IPv4 DHCP client
enable state.
switch# show ip dhcp
show auto-ip User EXEC
[no] ip dhcp Admin EXEC Use "IP DHCP" command
to enable DHCP client to
get IP address from remote
DHCP server.
Use "No IP DHCP" command to disable DHCP client and use static IP
address.
switch(config)# ip dhcp
switch(config)# no ip dhcp
ip address A.B.C.D
[mask A.B.C.D]
Admin EXEC Modify administration IPv4
address.
switch(config)# ip address
192.168.1.200 mask
255.255.255.0
default-gateway A.B.C.D Admin EXEC Modify default gateway
address.
switch(config)# ip default-gate-
way 192.168.1.100
show ipv6 dhcp User EXEC Show system IPv6 DHCP
client enable state.
switch# show ipv6 dhcp
show ipv6 User EXEC Show system IPv6 address,
net mask, default gateway
and auto config state.
switch# show ipv6
[no] ipv6 dhcp Admin EXEC Use "IPv6 DHCP" com-
mand enable DHCPv6 client to get IP address from
remote DHCPv6 server.
Use "No IPv6 DHCP" command to disable DHCPv6
client and use static IPv6
address or IPv6 auto config
address.
switch(config)# ipv6 dhcp
Table 29: IP Security (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

31
CLI
[no] ipv6 autoconfig Admin EXEC Use "IPv6 autoconfig" com-
mand to enable IPv6 auto
configuration feature.
Use "No IPv6 autoconfig"
command to disable IPv6
auto configuration feature.
switch(config)# no ipv6 auto-
config
ipv6 address X:X::X:X
prefix <0-128>
Admin EXEC Use "IPv6 address" com-
mand to specify static IPv6
address.
switch(config)# ipv6 address
fe80::20e:2eff:fef1:4b3c prefix
128
ipv6 default-gateway
X:X::X:X
Admin EXEC Use "IPv6 default-gateway"
command to modify default
gateway IPv6 address.
switch(config)# ipv6 default-
gateway
fe80::dcad:beff:feef:103
SNMP
Table 31: SNMP
Function Privilege Description Example
show snmp User EXEC Display SNMP state. switch# show snmp
show snmpv3 User EXEC Display SNMPv3 configure
state.
switch# show snmpv3
show snmp trap User EXEC Display SNMP trap setting. switch# show snmp trap
[no] snmp Admin EXEC Enable or disabled SNMP
engine.
switch# configure
switch(config)# snmp
switch(config)# exit
[no] snmp trap
(auth|linkUpDown|warmstart|cold-start|portsecurity)
Admin EXEC Specify SNMP trap setting. switch# configure
switch(config)# snmp trap auth
switch(config)# exit
snmp community NAME
(ro|rw)
Admin EXEC SNMP v1/v2 community
name.
SNMP community read or
readwrite attribute for basic
mode.
switch# configure
switch(config)# snmp commu-
nity user rw
switch(config)# exit
no snmp community
NAME
Admin EXEC Delete SNMP community
name.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no snmp com-
munity user
switch(config)# exit
snmp host
(A.B.C.D|X:X::X:X|HOS
TNAME) [version (1|2c)]
NAME
Admin EXEC SNMP trap host IPv4/IPv6
address or host name.
v1/v2c/v3 traps.
SNMP community name or
user name.
switch# configure
switch(config)# snmp host
192.168.1.100 version 2c pri-
vate
switch(config)# exit
no snmp host
(A.B.C.D|X:X::X:X|HOS
TNAME) [version (1|2c)]
Admin EXEC Delete SNMP host. switch# configure
switch(config)# no snmp host
192.168.1.100 version 2c
switch(config)# exit
Table 30: IP Management (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

32
CLI
snmpv3 user NAME
(ro|rw) auth (md5|sha)
password WORD<8-32>
priv password
WORD<8-32>
Admin EXEC SNMPv3 user name.
SNMPv3 user read or readwrite attribute for basic
mode.
SNMPv3 user security
level, auth-protocol, prviprotocol.
switch# configure
switch(config)# snmpv3 user
root rw auth md5 password
12345678
switch(config)# exit
no snmpv3 user NAME Admin EXEC Delete SNMPv3 user name. switch# configure
switch(config)# no snmp user
root
switch(config)# exit
Configuration Management
Table 32: Configuration Management
Function Privilege Description Example
show (startup-config|running-config)
Admin EXEC Show startup/running con-
figuration.
switch# show startup-config
switch# show running-config
show running-config
interfaces IF_PORTS
Admin EXEC Show running configuration
on selected ports.
switch# show running-config
interfaces GigabitEthernet 1
copy running-config
(startup-config|)
Admin EXEC Copy running configuration
to startup configuration.
switch# copy running-config
startupst-config
copy (running-con-
fig|startup-config) tftp://
Admin EXEC Copy running/startup con-
figuration to remote tftp
server.
switch# copy running-config
startupst-config tftp://
192.168.1.111/test1.cfg
copy tftp:// (running-config|startup-config)
Admin EXEC Upgrade running/startup
configuration from remote
tftp server.
switch# copy tftp://
192.168.1.111/test2.cfg
startup-config
copy (startup-config)
running-config
Admin EXEC Copy startup configuration
to running configuration.
switch# copy startupst-config
running-config
delete (startup-con-
fig|flash://)
Admin EXEC Restore factory default,
equal to command "restoredefaults".
switch# delete backup-config
reset Admin EXEC Restore system to all fac-
tory defaults.
switch# reset
reset except for [ipaddress] [vlan] [useraccount]
Admin EXEC Restore system to all fac-
tory defaults except for
specified settings.
switch# reset except for ip-
address
save Admin EXEC
Table 31: SNMP (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

33
CLI
Firmware Management
Table 33: Firmware Management
Function Privilege Description Example
boot system
(image0|image1)
Admin EXEC Dual image stores a backup
image in the flash partition.
Use "boot system" command to select the active
firmware image.
The other firmware image
will become a backup.
switch(config)# boot system
image1
delete system
(image0|image1)
Admin EXEC Delete firmware image
stored in flash.
switch# delete system image1
copy (flash://|tftp://)
(flash://|tftp://)
Admin EXEC Upgrade/backup firmware
image from/to remote tftp
server.
switch# copy tftp://
192.168.1.100/vmlinux.bix
flash://image0
DHCP Server
Table 34: DHCP Server
Function Privilege Description Example
show dhcp-server
[lease]
User EXEC Show DHCP server infor-
mation.
Show leased client information.
switch# show dhcp-server
switch# show dhcp-server
lease
[no] dhcp-server Admin EXEC Enable or disable DHCP
server.
switch(config)# dhcp-server
dhcp-server lease-time
<60-86400>
Admin EXEC Set the lease-time of DHCP
server.
switch(config)# dhcp-server
lease-time 16888
dhcp-server global low-
ip-address A.B.C.D
high-ip-address A.B.C.D
subnet-mask A.B.C.D
gateway A.B.C.D dns
A.B.C.D
Admin EXEC Set allocate IP range, sub-
net mask, gateway, DNS in
global settings of DHCP
server.
switch(config)# dhcp-server
global low-ip-address 10.1.1.1
high-ip-address 10.1.2.1 sub-
net-mask 255.255.0.0 gate-
way 10.1.1.254 dns 10.1.1.100
no dhcp-server global Admin EXEC Remove global settings of
DHCP server
switch(config)# no dhcp-server
global
dhcp-server interface
IF_NMLPORT low-ipaddress A.B.C.D highip-address A.B.C.D subnet-mask A.B.C.D gateway A.B.C.D dns
A.B.C.D
Admin EXEC Set allocate IP range, sub-
net mask, gateway, DNS in
specified port settings of
DHCP server.
switch(config)# dhcp-server
interface GigabitEthernet1 low-
ip-address 1 1.1.1.1 high-ip-
address 11.1.2.1 subnet-mask
255.255.0.0 gateway
11.1.1.254 dns 11.1.1.100
no dhcp-server interfaces IF_NMLPORT
Admin EXEC Remove specific port set-
tings of DHCP server.
switch(config)# no dhcp-server
interfaces GigabitEthernet1

34
CLI
dhcp-server vlan entry
<1-8> vlan <1-4094>
low-ip-address A.B.C.D
high-ip-address A.B.C.D
subnet-mask A.B.C.D
gateway A.B.C.D dns
A.B.C.D
Admin EXEC Set allocate IP range, sub-
net mask, gateway, DNS in
specified VLAN settings of
DHCP server.
switch(config)# dhcp-server
vlan entry 2 vlan 12 low-ip-
address 12.1.1.1 high-ip-
address 12.1.2.1 subnet-mask
255.255.0.0 gateway
12.1.1.254 dns 12.1.1.100
no dhcp-server vlan
entry <1-8>
Admin EXEC Remove specific VLAN set-
tings of DHCP server.
switch(config)# no dhcp-server
vlan entry 2
dhcp-server option82
entry <1-2> low-ipaddress A.B.C.D highip-address A.B.C.D subnet-mask A.B.C.D gateway A.B.C.D dns
A.B.C.D
Admin EXEC Set allocate IP range, sub-
net mask, gateway, DNS in
specified option 82 settings
of DHCP server.
switch(config)# dhcp-server
option82 entry 1 low-ip-
address 13.1.1.1 high-ip-
address 13.1.2.1 subnet-mask
255.255.0.0 gateway
13.1.1.254 dns 13.1.1.100
dhcp-server option82
entry <1-2> circuit-id format ( string | hex ) content WORD<0-120>
Admin EXEC Set circuit ID in specified
option 82 settings of DHCP
server.
switch(config)# dhcp-server
option82 entry 1 circuit-id for-
mat string content Hello
dhcp-server option82
entry <1-2> remote-id
format ( string | hex )
content WORD<0-120>
Admin EXEC Set remote ID in specified
option 82 settings of DHCP
server.
switch(config)# dhcp-server
option82 entry 1 remote-id for-
mat string content World
no dhcp-server option82
entry <1-2>
Admin EXEC Remove specific option 82
settings of DHCP server.
switch(config)# no dhcp-server
option82 entry 1
DHCP Client
Table 35: DHCP Client
Function Privilege Description Example
show dhcp-auto-provision
User EXEC View DHCP-auto-provision
status.
switch# show dhcp-auto-provi-
sion
[no] dhcp-auto-provision Admin EXEC Enable of disable DHCP-
auto-provision.
switch(config)# dhcp-auto-pro-
vision
[no] ip dhcp option82 Admin EXEC Enable or disable DHCP
option 82 for DHCP client.
switch(config)# ip dhcp
option82
ip dhcp option82 circuit-
id format ( string | hex |
user-define ) [content
WORD<0-120>]
Admin EXEC Set circuid-id in DHCP
option 82 for DHCP client.
switch(config)# ip dhcp
option82 circuit-id format string
Hello
ip dhcp option82
remote-id format ( string
| hex | user-define ) [content WORD<0-120>]
Admin EXEC Set remote-id in DHCP
option 82 for DHCP client.
switch(config)# ip dhcp
option82 remote-id format
string World
Table 34: DHCP Server (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

35
CLI
System Log (SYSLOG)
Table 36: System Log (SYSLOG)
Function Privilege Description Example
show logging User EXEC Display the global logging
status.
switch# show logging
show logging (buffered|file)
User EXEC Display log of buffer or file. switch# show logging buffered
clear logging (buffered|file)
Admin EXEC Clear logging information. switch# clear logging buffered
[no] logging Admin EXEC Disable or enable logging
service.
switch(config)# logging
logging host
(A.B.C.D|HOSTNAME)
[port <0-65535>] [severity <0-7>] [facility
(local0|local1|local2|loca
l3|local4|local5|local6|loc
al7)]
Admin EXEC Set remote log server infor-
mation and specify the minimum severity mask and
facility of logging message.
switch(config)# logging host
192.168.1.100 severity 6 facil-
ity local0
logging (buffered|console|file) [severity <0-7>]
Admin EXEC Enable logging into buffer
or console of file and specify the minimum severity
mask of logging message.
switch(config)# logging buff-
ered severity 6
no logging (buffered|console|file)
Admin EXEC Disable logging into buffer
or console or file.
switch(config)# no logging buff-
ered
no logging host
(A.B.C.D|HOSTNAME)
Admin EXEC Remove remote log server. switch(config)# no logging host
192.168.1.100
System Time
Table 37: System Time
Function Privilege Description Example
clock source (local|sntp) Admin EXEC Set the source of time.
Use the no form of this
command to select the
default setting.
switch(config)# clock source
sntp
switch(config)# show clock
detail
08:32:12 test(UTC+5) Sep 21
2012
No time source
Time zone:
Acronym is DFL
Offset is UTC+8
clock timezone ACRO-
NYM HOUR-OFFSET
[minutes <0-59>]
Admin EXEC Use the clock timezone
command to set timezone
setting.
switch(config)# clock timezone
test +5
switch(config)# show clock
detail
10:13:27 test(UTC+5) Sep 21
2012
No time source
Time zone:
Acronym is test
Offset is UTC+5

36
CLI
no clock timezone Admin EXEC Use the no form of this
command to timezone
default setting.
switch(config)# no clock time-
zone
sntp host HOSTNAME
[port <1-65535>]
Admin EXEC Use the clock set command
to set static time.
The static time won’t save
to configuration file.
switch# clock set 11:03:00 sep
21 2012
11:03:00 DFL(UTC+8) Sep 21
2012
no sntp Ad m in E XEC Use the no form of this
command to restore sntp
default setting.
switch(config)# no sntp
clock set HH:MM:SS
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
<1-31> <2000-2035>
Admin EXEC Use the clock set command
to set static time.
The static time won’t save
to configuration file.
switch# clock set 11:03:00 sep
21 2012
11:03:00 DFL(UTC+8) Sep 21
2012
clock summer-time
ACRONYM date
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
<1-31> <2000-2037>
HH:MM
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
<1-31> <2000-2037>
HH:MM [<1-1440>]
Admin EXEC Use the clock summer-time
command to set daylight
saving time for system time.
switch(config)# clock summer-
time ACRONYM date jan 1
2017 00:00 apr 30 2017 23:59
60
clock summer-time
ACRONYM recurring
(usa|eu) [<1-1440>]
Admin EXEC Use the global daylight sav-
ing policy defined by an
international organization.
switch(config)# clock summer-
time DLS recurring usa 60
clock summer-time
ACRONYM recurring
(<1-5>|first|last)
(sun|mon|tue|wed|thu|fri|
sat)
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
HH:MM (<1-5>|first|last)
(sun|mon|tue|wed|thu|fri|
sat)
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
HH:MM [<1-1440>]
Admin EXEC Use the clock summer-time
recurring daylight saving
time duration. The first part
of the command specifies
when summer time begins,
and the second part specifies when it ends.
clock summer-time ACRONYM
recurring 1 sun jan 20:00 last
sun jan 22:00 60
no clock summer-time Admin EXEC Use the no form of this
command to clock summertime default setting.
switch(config)# no clock sum-
mer-time
Table 37: System Time
Function Privilege Description Example

37
CLI
SMTP
Table 38: SMTP
Function Privilege Description Example
show smtp User EXEC View SMTP client informa-
tion.
smtpc profile-id <1-2>
server-ip A.B.C.D
server-port <25-25>
Admin EXEC Set SMTP server's IP and
udp port in profile 1 or 2.
switch(config)# smtpc profile-id
1 server-ip 192.168.1.100
server-port 25
smtpc profile-id <1-2>
sender-mail WORD<164>
Admin EXEC Set sender's mail address
in profile 1 or 2.
switch(config)# smtpc profile-id
1 sender-mail sender@advan-
tech.com.tw
no smtpc profile-id <1-
2> sender-mail
Admin EXEC Remove sender's mail
address in profile 1 or 2.
switch(config)# no smtpc pro-
file-id 1 sender-mail
sender@advantech.com.tw
smtpc profile-id <1-2>
target-mail WORD<164>
Admin EXEC Set target's mail address in
profile 1 or 2.
switch(config)# smtpc profile-id
1 sender-mail target@advan-
tech.com.tw
no smtpc profile-id <1-
2> target-mail ( all |
WORD<1-64>)
Admin EXEC Remove target's mail
address in profile 1 or 2.
switch(config)# no smtpc pro-
file-id 1 sender-mail tar-
get@advantech.com.tw
smtpc active profile-id
<1-2>
Admin EXEC Select an enabled profile for
SMTP client used.
switch(config)# smtpc active
profile-id 1
no smtpc active profile Admin EXEC SMTP client will not use
any profile. It means disabled.
switch(config)# no smtpc
active profile
smtpc sendmsg title
WORD<1-20> content
WORD<1-64>
Admin EXEC Send a mail for testing
SMTP client.
switch(config)# smtpc send-
msg title hello content world
NTP Server
Table 39: NTP Server
Function Privilege Description Example
show ntp-server User EXEC Show NTP server configu-
ration.
switch# show ntp-server
[no] ntp-server Admin EXEC Use "ntp-server" command
to enable NTP server services.
Use no form to disable service.
switch(config)# ntp-server
switch(config)# no ntp-server
ntp-server server-num
<1-10> address
WORD<0-64>
Admin EXEC NTP server address config-
uration.
switch(config)# ntp-server
server-num 1 address
192.168.1.100
[no] ntp-server servernum <1-10>
Admin EXEC Use the command to delete
specific NTP server.
switch(config)# ntp-server
server-num 1
ntp-server server-time
HH:MM:SS
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
<1-31> <2000-2035>
Admin EXEC Use the command to set
static time. The static time
won’t save to configuration
file.
switch(config)# ntp-server
server-time 11:03:00 sep 21
2012

38
CLI
ntp-server timezone
ACRONYM HOUROFFSET [minutes <059>]
Admin EXEC Use the command to set
timezone setting. Use the
no form of this command to
default setting.
switch(config)# ntp-server
timezone test +5
no ntp-server timezone Admin EXEC Disable timezone setting.
ntp-server summer-time
ACRONYM date
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
<1-31> <2000-2037>
HH:MM
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
<1-31> <2000-2037>
HH:MM [<1-1440>]
Admin EXEC Use the command to set
daylight saving time for system time.
Reference clock summer-time
setting.
ntp-server summer-time
ACRONYM recurring
(usa|eu) [<1-1440>]
Admin EXEC Use the command to set
daylight saving time for system time.
Reference clock summer-time
setting.
ntp-server summer-time
ACRONYM recurring
(<1-5>|first|last)
(sun|mon|tue|wed|thu|fri|
sat)
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
HH:MM (<1-5>|first|last)
(sun|mon|tue|wed|thu|fri|
sat)
(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun
|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)
HH:MM [<1-1440>]
Admin EXEC Use the command to set
daylight saving time for system time.
Reference clock summer-time
setting.
ntp-server manual-time
(enable | disable)
Admin EXEC Manually set the system
clock.
switch(config)# ntp-server
manual-time enable
switch(config)# ntp-server
manual-time disable
RMON
Table 40: RMON
Function Privilege Description Example
show rmon (statistics |
history | alarms | events)
User EXEC Display RMON setting con-
figuration.
switch# show rmon history
rmon statistics index <165535> interface
IF_NMLPORT [owner
OWNER<1-32>]
Admin EXEC Specify RMON statistics
index.
Specify statistics interface.
Specify owner.
switch# configure
switch(config)# rmon statistics
index 10 interface gi1 owner
ADV
switch(config)# exit
no rmon statistics index
<1-65535>
Admin EXEC Delete snmp statistics
index.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no rmon statis-
tics index 10
switch(config)# exit
Table 39: NTP Server (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

39
CLI
rmon history index <165535> interface
IF_NMLPORT [buckets
<1-50>] [interval <13600>] [owner
OWNER<1-32>]
Admin EXEC Specify RMON history
index.
Specify history interface.
Specify history bucket time.
Specify history record interval time.
Specify owner.
switch# configure
switch(config)# rmon history
index 10 interface gi1 buckets
20 interval 1000 owner ADV
switch(config)# exit
no rmon history index
<1-65535>
Admin EXEC Delete SNMP history index. switch# configure
switch(config)# no rmon history
index 10
switch(config)# exit
rmon alarm index <1-
65535> oid-variable
OID<255> interval <12147483647> (absolute|delta) rising-threshold <0-2147483647>
rising-event-index <165535> falling-threshold
<0-2147483647> fallingevent-index <1-65535>
[owner OWNER<1-32>]
Admin EXEC Specify RMON alarm index.
Specify alarm OID.
Specify alarm check value
frequency.
How to compare values
Specify rasing-threshold.
Specify rasing-event-index.
Specify falling-threshold.
Specify falling-event-index.
Specify owner.
switch# configure
switch(config)# rmon statistics
index 10 interface gi1 owner
ADV
switch(config)# exit
no rmon alarm index <165535>
Admin EXEC Delete SNMP statistics
index.
switch# configure
switch(config)# no rmon alarm
index 10
switch(config)# exit
rmon event index <1-
65535> description
DESC<128> [log] [trap
community-name
OWNER<1-32>] [owner
OWNER<1-32>]
Admin EXEC Specify RMON event index.
Specify event description.
Specify log flag for recording.
Specify trap name to send
SNMP trap message.
Specify owner.
switch# configure
switch(config)# rmon event
index 10 description Good for
us. log trap public owner ADV
switch(config)# exit
no rmon event index <165535>
Admin EXEC Delete SNMP event index. switch# configure
switch(config)# no rmon event
index 10
switch(config)# exit
IP Configuration
Table 41: IP Configuration
Function Privilege Description Example
ip address A.B.C.D
[mask A.B.C.D]
Admin EXEC Use "IP address" com-
mand to modify administration IPv4 address.
switch(config)# ip address
192.168.1.200 mask
255.255.255.0
ip default-gateway
A.B.C.D
Admin EXEC Use "IP default-gateway"
command to modify default
gateway address.
switch(config)# ip default-gate-
way 192.168.1.100
Table 40: RMON (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

40
CLI
no ip default-gateway Admin EXEC Use "No IP default-gate-
way" to restore default gateway address to factory
default.
switch(config)# no ip default-
gateway
ip dns A.B.C.D [A.B.C.D] Admin EXEC Use "IP DNS" command to
modify DNS server
address.
switch(config)# ip dns
111.111.111.111
no ip dns A.B.C.D Admin EXEC Use "No IP DNS" to delete
existing DNS server.
switch(config)# no ip dns
111.111.111.111
TELNET
Table 42: TELNET
Function Privilege Description Example
ip telnet Admin EXEC Use "IP service" command
to enable telnet services.
switch(config)# ip telnet
[no] ip telnet Admin EXEC Use no form to disable ser-
vice.
switch(config)# no ip telnet
SSH
Table 43: SSH
Function Privilege Description Example
ip ssh Admin EXEC Us e "IP servic e" command
to enable ssh services.
switch(config)# ip ssh
[no] ip ssh Admin EXEC Use no form to disable ser-
vice.
switch(config)# no ip ssh
show ip ssh User EXEC Show current ssh service
status.
switch# show ip ssh
HTTP
Table 44: HTTP
Function Privilege Description Example
ip http Admin EXEC Use "IP service" command
to enable http services.
switch(config)# ip http
ip https Admin EXEC Us e "IP servic e" command
to enable https services.
switch(config)# ip https
[no] ip https Admin EXEC Use no form to disable ser-
vice.
switch(config)# no ip http
[no] ip http Admin EXEC Use no form to disable ser-
vice.
switch(config)# no ip http
switch(config)# no ip https
Table 41: IP Configuration (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

41
CLI
show ip (http|https) User EXEC Show current https or http
service status.
switch# show ip https
ip (http|https) sessiontimeout <0-86400>
Admin EXEC Use "IP session-timeout"
command to specify the
session timeout value for
http or https service.
switch(config)# ip http session-
timeout 15
switch(config)# ip https ses-
sion-timeout 20
Modbus TCP
Table 45: Modbus TCP
Function Privilege Description Example
show tcp-modbus status User EXEC Show current TCP-modbus
status.
switch# show tcp-modbus sta-
tus
show tcp-modbus time-
out
User EXEC Show current TCP-modbus
timeouts value.
switch# show tcp-modbus
timeout
[no] tcp-modbus Admin EXEC Use "TCP-modbus" com-
mand to enable TCP modbus services.
Use no form to disable service.
switch(config)# tcp-modbus
switch(config)# no tcp-modbus
IXM
Table 46: IXM
Function Privilege Description Example
[no] ixm Admin EXEC Use "IXM" command to
enable IXM services.
Use no form to disable service.
switch(config)# ixm
switch(config)# no ixm
Table 44: HTTP (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

42
CLI
Diagnostic
Cable Diagnostic
Table 47: Cable Diagnostic
Function Privilege Description Example
show cable-diag interfaces IF_NMLPORTS
User EXEC Display the estimated
length of copper cable
attached to the ports.
Show cable-diag interface
all.
Display the estimated
length of copper cables
attached to all ports.
show cable-diag interface
Display the estimated
length of copper cable
attached to port gi1.
This example show the cable's
information which link in gi1.
switch(config)# show cable-
diag interfaces gi1
Port | Speed | Local pair | Pair
length | Pair status
------ + ------- + ------------+ -------
------ + --------------
gi1 | auto | Pair A | 0.88
| Open
Pair B | 0.87
| Open
Pair C | 0.82
| Open
Pair D | 0.82
| Open
DMI
Table 48: DMI
Function Privilege Description Example
show dmi IF_PORTS
information
Admin EXEC Use this command to dis-
play the information of
EEPROM and Digital Diagnostic Monitoring Interface
in SFP Optical Transceivers.
This example show SFP Opti-
cal Transceivers information
whicn plug-in fa10.
switch# show dmi FastEthernet
10 information
[no] dmi (alarm|warning) (temperature|voltag|txbasis|txpow
er|rxpower) (high|low)
state
Admin EXEC Use this command to
enable/disable the mechanism that monitors SFP
Optical Transceiver's Digital
Diagnostic Monitoring interface information.
Use no form to disable
warning/alarm mechanism.
This example shows how to
enable temperature's high
threshold monitor mechanism
with alarm level. (Current sfp
plug-in in fa10).
switch(config)# interface
FastEthernet 10
switch(config-if)# dmi alarm
temperature high state

43
CLI
dmi (alarm|warning)
(temperature|voltag|txbasis|txpower|rxpower)
(high|low) value
INPUT_VALUE
Admin EXEC Use this command to con-
figure high/low threshold
value used to compare with
SFP Optical Transceiver's
Digital Diagnostic Monitoring interface's value (temperature, voltage, etc).
This example shows how to
configure the temperature high
threshold value is 30.5 with
alarm level.
switch(config-if)# dmi alarm
temperature high value 30.5
[no] dmi alarm-warning
message
(log|snmp|mail)
Admin EXEC Use this command to deter-
mine which method to use
when notifying of user
alarm/warning events.
This example shows how to
configure alarm-warning mes-
sage is system log.
switch(config)# dmi alarm-
warning message log
IP-based Diagnostic
Table 49: IP-based Diagnostic
Function Privilege Description Example
ping HOSTNAME [count
<1-5>] [interval <1-5>]
[size <8-5120>]
User EXEC Use "ping" command to do
network ping diagnostic.
switch# ping 192.168.1.100
count 4 interval 4 size 128
ping6 HOSTNAME
[count <1-5>] [interval
<1-5>] [size <8-5120>]
User EXEC Use "ping6" command to
carry out network ping diagnostic.
switch# ping6 192.168.1.100
count 4 interval 4 size 128
show arp User EXEC Use "show arp" command
to show all arp entries.
Switch# show arp
clear arp [A.B.C.D] Admin EXEC Use "clear arp" command to
clear all arp entries or one
specific arp entry.
Switch# clear arp
PoE
Table 50: PoE
Function Privilege Description Example
show poe (system|port) User EXEC Use "show PoE (sys-
tem|port)" command to
show current PoE setting
value and status.
This example shows current
PoE status per port.
switch# show poe port
poe Admin EXEC Use PoE command to enter
PoE's control level.
This example shows how to
enter PoE control level.
switch# configure
switch(config)# poe
switch(config-poe)#
system powerlimit <0-
800>
Admin EXEC Us e "sys tem powerlimit"
command to configure how
much power can be used in
entire system.
This example shows how to
configure whole system avail-
able power to 720W.
switch(config-poe)# system
power-limit 120
Table 48: DMI (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

44
CLI
system ac-disconnect
(enable|disable)
Admin EXEC Use ac-disconnect com-
mand to determine which
disconnect type will be
selected.
This example shows how to
configure disconnect type to
DC typeswitch(config-poe)#.
system ac-disconnect disable
system overload-discon-
nect (port-priority|overload-port-first)
Admin EXEC Use system overload-dis-
connect command to determine which PoE port will
supply power when the total
power is at full load.
There are two algorithms
supported, and this command allows selection of
the algorithm.
This example shows how to
select overload-port-first to be
the overload-disconnect's algo-
rithm.
switch(config-poe)# system
overload-disconnect overload-
port-first
interfaces IF_NMLPORT
legacy-mode
(enable|disable)
Admin EXEC Use "legacy-mode
(enable|disable)" command
to configure supply power
mechanism to legacy mode
in PoE port.
This example shows how to
configure fa1's PoE power to
legacy mode.
switch(config-poe)# interfaces
FastEthernet 1 legacy-mode
enable
interfaces IF_NMLPORT
state (enable|disable)
Admin EXEC Use "state (enable|dis-
able)" command to configure whether PoE port will
supply power or not.
This example shows how to
stop PoE port supply power via
fa1.
switch(config-poe)# interfaces
FastEthernet 1 state disable
interfaces IF_NMLPORT
plfc (enable|disable)
Admin EXEC Use "plfc (enable|disable)"
command to configure how
much power PoE port will
supply based on PD's class
level.
This example shows how to
configure fa1's PoE supply
power mode to plfc(power-limit
from class).
switch(config-poe)# interfaces
FastEthernet 1 plfc enable
interfaces IF_NMLPORT
priority
(low|medium|high|critical)
Admin EXEC Use "priority
(low|medium|high|critical)"
command to configure PoE
port's priority of power supply sequence.
This example shows how to
configure fa1 as the most high
priority level in power supply
sequence.
switch(config-poe)# interfaces
FastEthernet 1 priority critical
interfaces IF_NMLPORT
power-limit <0-30000>
Admin EXEC Use "power-limit <0-
30000>" command to configure how much power can
be used via PoE port.
This example shows how PoE
configure fa1's power of POE
to 15W.
switch(config-poe)# interfaces
FastEthernet 1 power-limit
15000
Table 50: PoE (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example

45
CLI
LED
Table 51: LED
Function Privilege Description Example
show led User EXEC Use "show LED" command
to show current LED event
status and error times.
This example shows current
LED event and its own error
times.
switch# show led
( ALARM LED ) EVENTS |
STATUS | ERROR TIMES
------------------------ + ----------- +
-------------
Power Failure |
ERROR | 1
------------------------ + ----------- +
-------------
[no] led (alarm | system) Admin EXEC Use "LED (alarm | system)"
command to configure LED
indication mechanism.
Use no form to disable LED
indication mechanism configuration.
This example shows how to
configure enable alarm LED
indication mechanism.
switch(config)# led alarm
[no] led (alarm | system)
(power-failure | fiberdown | always)
Admin EXEC Use "(power-failure | fiber-
down | always)" command
to configure which event will
be binding with which LED
indication mechanism.
Use no form to remove
event from LED indication
mechanism.
This example shows how to
add the event fiber-down to
alarm LED indication mecha-
nism.
switch(config)# led alarm fiber-
down
led system blink interval
<0-3>
Admin EXEC Use "LED system blink
interval" command to configure how long system LED
will blink for.
This example shows how to
configure system LED blink
interval.
switch(config)# led system
blink interval 3
System
Table 52: System
Function Privilege Description Example
show version User EXEC Use "show version" com-
mand to show loader and
firmware version and build
date.
switch# show version
show info User EXEC Use "show info" command
to show system summary
information.
switch# show info
reboot Admin EXEC Use "reboot" command to
make system hot restart.
switch# reboot
show language User EXEC

46
CLI
show flash User EXEC Use "show flash" command
to show all files" status
which stored in flash.
switch# show flash
clear line telnet Admin EXEC
terminal length <0-24> User EXEC
show network-port User EXEC Show network port informa-
tion.
switch(config)# no network-
port type http
[no] network-port type
(http|https|telnet|ssh)
Admin EXEC Use no form to restore
default value.
network-port type
(http|https|telnet|ssh)
port-num <1-65535>
Admin EXEC Use the command to
change network port.
switch(config)# network-port
type http port-num 8080
system name NAME Admin EXEC Use "sys tem name" com-
mand to modify system
name information of the
switch.
switch(config)# system name
myname
system location LOCATION
Admin EXEC Us e "sys tem contact" com-
mand to modify contact
information of the switch.
switch(config)# system con-
tact callme
system contact CONTACT
Admin EXEC Use "system location" com-
mand to modify location
information of the switch.
switch(config)# system loca-
tion home
Table 52: System (Continued)
Function Privilege Description Example
 Loading...
Loading...