Page 1

V7N V7H
service manual
Page 2

Catalog
Chapter One About Maintenance
1.1 Safety precautions
1.1.1 Precautions for antistatic
1.1.2 About placement position
1.2 Maintenance method
1.2.1 Visualized method
1.2.2 Electric resistance method
1.2.3 Voltage method
1.2.4 Current method
1.2.5 Cutting method
1.2.6 Element substitution method
1.2.7 Comparison method
1.3 Required device for maintenance
Chapter Two Functions and Operation Instructions
2.1 QUICK OPERATION
1
1
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
2
2
3
4
4
2.1.1 BUTTONS AND JACKS ILLUSTRATION
2.1.2 POWER ON/OFF
2.1.3 PLAY MUSIC
2.1.4 VIDEO PLAYING
2.1.5 PICTURE BROWSING
2.1.6 E-BOOK BROWSING
2.1.7 RECORDING
2.1.8 TUNING
2.1.9 RESUME PLAYING
2.1.10 RESET
2.1.11 CHARGE
2.2 USAGE INTRODUCTION
2.2.1 MAIN MENU ILLUSTRATION
2.2.2 PLAYING INTERFACE
4
5
5
6
6
6
6
7
7
7
7
7
7
8
Page 3

2.2.3 RECORDING INTERFACE
8
2.2.4 TUNING INTERFACE
2.2.5 USE MOBILE STORAGE
2.2.6 DISCONNECT USB SAFELY
2.2.7 VIDEO CONVERSION TOO
2.3 OTHER INFORMATION
2.3.1 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
2.4 SPECIFICATION
Chapter Three Principle and Servicing
Section one Principle of the player
3.1.1 Block diagram of the player
3.1.2 Principle of the player
Section Two Unit circuit principle
3.2.1 Video decode circuit principle
3.2.2 Audio decode circuit principle
3.2.3 FLASH CIRCUIT PRINCIPLE
8
8
8
8
9
9
9
10
10
10
10
12
12
13
13
3.2.4 FM tuning circuit
3.2.5 Display screen boost circuit
3.2.6 Headphone output jack circuit
3.2.7 USB jack ciircuit
3.2.8 Button circuit
3.2.9 charge management circuit
3.2.10 Battery voltage detect circuit
3.2.11 Battery protection circuit
3.2.12 power management module
3.2.13 Reset circuit
3.2.14 Power on/off control circuit
3.2.15 MIC circuit
Section Three Servicing Cases
3.3.1 Troubleshooting diagram
3.3.2 servicing cases
14
14
16
17
17
18
19
20
21
21
22
23
24
24
29
Section Four Signal waveform diagram
Section Five Function Introduction to IC
3.5.1 Function introduction to HY57V641620E
3.5.2 Function introduction to Rk2608
31
35
35
36
Page 4

3.5.3 Function introduction to RT9284B
41
3.5.4 Function introduction to MCP73832
3.5.5 Function introduction to TEA5767HN
3.5.6 Function introduction to XC6206P152MR
3.5.7 Function introduction to K9G8G08U0M
Chapter Four Assembly and disassembly process
4.1 Disassembly process of the player
4.2 Assembly process of the player
Chapter CinquePCB board & Circuit diagram
Section One Circuit diagram
Section Two PCBboard
Surface layer of Main Board
Bottom layer of Main Board
Chapter six BOM List
42
43
45
46
48
48
49
50
50
54
54
55
56
Page 5

Chapter One About Maintenance
1.1 Safety precautions
1.1.1 Precautions for antistatic
Movement and friction will both bring static electricity which causes serious damages to integrated
IC. Though static charge is little, when a limited quantity of electric charge is added to large-
scaleintegrated IC, as the capacitance is very small in the meantime, now the integrated IC is very much
easy to be struck through by static electricity or the performance will decrease. Thus static electricity
prevention is of extraordinary importance. The following are several measures to prevent static
electricity:
1. Use a piece of electric conduction metal with the length of about 2 metres to insert into the earth,
and Fetch the lead wire from the top of the surplus metal and connect to the required static electricity
device. The length and depth of the metal embedded under the earth should be determined according to
the wettability of the local soil. For humid places, it may be shorter, and longer and deeper for dry places.
If possible, it can be distributed and layed in terms of “#” shape.
2. On operating table-board, the antistatic table cushion should be covered and grounded.
3. All devices and equipments should be placed on the antistatic table cushion and grounded.
4. Maintenance personnel should wear antistatic wrist ring which should be grounded.
5. Places around the operating position should also be covered with electric conduction cushion or
Painted with antistatic paint.
1.1.2 About placement position
1. Audio power amplifier cannot be installed in places with high temperature and humidity.
2. Positions for placement should be stable and secure.
1.2 Maintenance method
1.2.1 Visualized method
Directly view whether abnormalities of collision, lack of element, joint welding, shedding welding,
rosin joint, copper foil turning up, lead wire disconnection and elements burning up among pins of
- 1 -
Page 6

Elements appear. Check power supply of the machine and then use hands to touch the casing of part of
elements and check whether they are hot to judge the trouble spot. You should pay more attention when
using this method to check in high voltage parts.
1.2.2 Electric resistance method
Set the multimeter in resistance position and test whether the numerical value of resistance of each
point in the circuit has difference from the normal value to judge the trouble spot. But in the circuit the
tested numerical value of resistance is not accurate, and the tested numerical value of integrated IC's
pins can only be used for reference, so the elements should be broken down for test.
1.2.3 Voltage method
Voltage method is relatively convenient, quick and accurate. Set the multimeter in voltage position
and test power supply voltage of the player and voltage of a certain point to judge the trouble spot
according to the tested voltage variation.
1.2.4 Current method
Set the multimeter in current position and test current of the player of a certain point to judge the
trouble spot. But when testing in current method, the multimeter should be series connected in the
circuit, which makes this method too trivial and troublesome, so it is less frequently used in reality.
1.2.5 Cutting method
Cutting method should be combined with electric resistance method and voltage method to use.
This method is mainly used in phenomena of short circuit and current leakage of the circuit. When
cutting the input terminal voltage of a certain level, if voltage of the player rises again, it means that the
trouble lies in this level.
1.2.6 Element substitution method
When some elements cannot be judged good or bad, substitution method may de adopted directly.
1.2.7 Comparison method
A same good PC board is usually used to test the correct voltage and waveform. Compared these
data with those tested through fault PC board, the cause of troubles may be found.
Through the above maintenance method, theoretical knowledge and maintenance experience, all
difficulties and troubles will be readily solved.
- 2 -
Page 7

1.3 Required device for maintenance
Audio Generator
Digital oscillograph ( 100MHE)
SMD rework station
Multimeter
Soldering iron
Pointed-month pincers
Cutting nippers
Forceps
Electric screw driver
Terminals connecting cord
Headphone
Microphone
- 3 -
Page 8

Chapter Two
Functions and Operation Instructions
2.1 QUICK OPERATION
2.1.1 BUTTONS AND JACKS ILLUSTRATION
:
M
:
Press in power-off state
#
Press for long in power-on state
#
Press in playing interface
#
Press when recording
#
Press when tuning
#
#Press when in menu operation
:
#Press when recording
#Press when in music playing, tuning, e-book
browsing, picture browsing and recording
preparation interface
#Press for long when in music playing interface
#Press for long when in file browsing interface
#Press when in file browsing interface
#Press when in menu operation
:
#Press when playing or tuning
#Press when in "My sound effect setting"
#
Press when browsing e-book
#Press when in menu operation
:
#
Press when playing
#
Press for long when playing
#
Press when in tuning preset state
#
Press when in tuning search state
power on
power off
pause/play switch
pause recording
mute
enter the item or confirm the
setting
save record files
On-line menu pops up
A-B repeat
delete file
return to the previous directory
Not save the setting and then
exit from menu
adjust volume
adjust dB value
turn lines
move cursor
the previous/next track
fast backward/forward
select channel
auto search
- 4 -
Page 9

Press for long when in tuning search state
#
Press when in "My sound effect setting"
#
Press when browsing picture
#
#Press when browsing e-book
Press when in menu operation
#
USB jack
automanual search
select the frequency that you
want to set
switch pictures
turn pages
move cursor
Headphone jack
MIC: microphone
2.1.2 POWER ON/OFF
#Power on
Press button to power on, the
PUSH
power-on motion picture displays
and system enters main menu.
NOTE:
If functions of playing, tuning or recording are not used during a specified period, this player will
power off automatically.
#Power off
PUSH
FOR LONG
Push button for long to power
off.
2.1.3 PLAY MUSIC
#Play/Pause
#FF and FB
/
When playing music, pushing this
button may switch
between "Play" and "Pause".
When playing music, press this
button for long and you may enter
fast forward or backward playback.
#NEXT and PREV
When playing music, press this
/
button to skip to the previous or
next track.
# Adjust volume
When playing music, press this
button or for long and you may
adjust volume.
#Play music
In "Music playing" menu, press button to enter Interface of browsing musical files. Press
button to select songs and press button to begin playing this song. When playing music, pushing
M
M
button may pause music playing, press button to return to the previous directory and press button
to exit and enter main menu interface.
M
PRESS
CAUTION
#When the length of song's full path name is too long, this song may probably not be played.
#When playing music, use picture browsing functions and music will stop playing.
- 5 -
Page 10

2.1.4 VIDEO PLAYING
In main interface, select "Video playing" item
and press button to enter. After selecting
movie files through pressing button,
press button to play movie and press
button to pause. When playing, pressing
button may skip to the previous or next movie,
pressing button for long to enter fast
forward/backward; pressing button to
adjust volume and pressing button may return
to the previous directory.
M
M
M
PRESS
NOTE:
If some e-book format is not supportable,
please switch to TXT file with ANSI encoding
format.
#Switch of ANSI encoding format
M
PRESS
NOTE:
As for movie files with large capacity, you
need wait for several seconds to enter playing
after pressing button.
M
2.1.5 PICTURE BROWSING
After selecting picture file, press button to
M
enter picture browsing, press button to
switch pictures and press button to return to
the previous directory.
M
PRESS
When browsing picture, press button to
enter "On-line menu". In on-line menu, you may
set slide, rotate leftwards, rotate rightwards and
rotate 180 . Press button to enter "Slide";
after pressing button to select your desired
slide interval time, press button to confirm.
After pressing button to exit from on-line
menu, pictures will be played in the means of
slide.
2.1.6 E-BOOK BROWSING
After entering "E-book" item, press
button to select text file and press button to
browse e-book. Pressing button may turn
pages; pressing button may turn lines and
pressing button may enter on-line menu.
When browsing e-book, press button to
return to the previous directory.
1. Select "Save" in
"File" item.
2. After dialogue box
pops up, select "ANSI"
in the pop-up options of
encoding and then click
"Save".
2.1.7 RECORDING
In main menu, select "Record" item and
press button to enter recording preparation
stage. Press button to enter recording/
pause recording. When recording, pressing
button may generate recording files and exit to
recording preparation state. Press button
to save recording files and exit to main menu.
Recording files are saved in "RECORDER" file
folder of "Music Playing" menu.
CAUTION:
#In order to avoid sudden power-off in the
# When recording with microphone, if you press
M
M
M
PRESS
course of recording, you cannot record when
battery is low and when disc is fully written; if
recording is in process, it indicates “FULL
DISC” and exits from recording.
buttons and the sound of pressing may
probably be recorded.
- 6 -
Page 11

2.1.8 TUNING
M
PRESS
In main menu, select "Radio " item and
Press button to enter tuning mode. Now,
insert headphone and you may listen to radio
program. After entering tuning mode, pressing
button may enter "On-line menu". Press
button to exit from tuning interface and enter
main menu, but tuning still proceeds.
M
M
2.1.9 RESUME PLAYING
In main menu, after selecting "Resume
playing" item, press button to enter. In this
menu, you may select "Music resume", "Movie
resume" and "E-book resume". For instance,
select "Music resume" option, after
Pressing button, this song begins
M
playing from the position where playing
stopped last time.
M
M
PRESS
CAUTION:
When charging, the player body is slightly hot,
#
and this belongs to normal phenomenon, so
please take it easy to use it.
#
When electric charge of battery is too low, and
when USB power supply is less than 100mA, it
begins to charge, screen may probably have
no display, and even battery charge is
unavailable.
#It takes 3 hours to charge battery with computer .
#Before unplugging USB line, please stop using
USB memory function firstly. Data may be lost
or the player may be damaged if you unplug it
directly.
2.2 USAGE INTRODUCTION
2.2.1 MAIN MENU ILLUSTRATION
#Play music
Save audio files.
#Browse picture
Save picture files.
#Record
Select “Record” to enter
recording mode.
#
Setup
Select "Setup" item to set
system options.
2.1.10 RESET
When this player cannot be operated, please
reset it.
Method for reset:
press button for about 10 seconds. After
reset finishes, power on again and you may use
it normally.
2.1.11 CHARGE
This player adopts lithium-ion battery to
supply power. In any case, connect MP4 player
to computer with USB line, it will power on and
begin to charge automatically. After fully charged,
the player will stop charging automatically.
Video
#
Save video files.
#E-book
Save text files.
#FM Radio
Select to enter radio
mode.
#Resume playing
Play from the
position where the music,
movie and
e-book stopped last
time.
- 7 -
Page 12

2.2.2 PLAYING INTERFACE
ILLUSTRATION
6
1. Song name
2. Song name/singer/lyrics display
3. Volume
4. Current playback time
5. Total track time
6. Playback progress bar
7. Playback state
8. Bit rate
9.Sampling rate
10. EQ mode
11. Playback mode
12. Music file format
13. Battery capacity
14. Current track serial number
15. total track number
2.2.3 RECORDING INTERFACE
ILLUSTRATION
1.Name of recorded file
2. Time that has been recorded
As for the name of recorded file “V00001.
Wav”: 00001 is serial number of the current
recorded track and arranged according to
sequence; WAV is the file format after recording.
2.2.4 TUNING INTERFACE
3.The left recordable time
4. Battery capacity
ILLUSTRATION
1. Volume
2. Frequency of the current radio station
3. Scanning progress bar
4. Radio station serial number
5.Preset mode
6.Battery capacity
7.Scanning mode
2.2.5 USE MOBILE STORAGE
FUNCTION
This player may be used as mobile storage in
Windows ME/2000/XP operating system. Under
Windows 98SE operating system, the player
may be used as mobile storage after drive
program is being installed (please download it
from BBK official website).
Connect MP3 player and computer with USB
transmission line. After the bottom right corner of
desktop appears “ ”symbol, the mobile
storage function of MP3 player may be used
normally.
NOTES:
#To avoid abnormality of the player appears, you
are suggested to power off firstly before
connecting MP4 player with computer, and
then use USB transmission line to connect
Mp4 player, then connect computer.
#In Windows 98 system, there is no “ ”
symbol.
2.2.6 DISCONNECT USB SAFELY
After operation finishes, click “ ” symbol on
bottom right corner of Windows desktop with
right button of mouse, and disconnect USB
safely according to the computer prompt.
2.2.7 VIDEO CONVERSION TOO
1. Brief introduction
before use, please download video
conversion tool and installation program “BBK
MINIMP4 conversion tool” from BBK website and
then install to computer.
- 8 -
Page 13

2. Basic operation
1) After program runs, click “Add conversion
file” button on the bottom left corner and a
dialogue box pops up, shown in the following
figure:
2) According to the position indicated by
finger, click to select the source file required to
converse and the saving target path of new file
after conversing. Click "Save" button to add this
conversion into conversion list. Multiple
conversion tasks may be added.
2.4 SPECIFICATION
Model
Lithium battery
Continuous playback time
Size/weight
Audio SNR
Headphone output
Frequency range
FM tuning range
Working temperature
Audio file
Picture file
#Design and specifications of product are
subject to change without notice.
V7
3.7V 600mAh
Longest continuous playing
time for MP3 is 11 hours
Size: 85.0mm 43.5mm 12.3mm
weight: 54g
85dB
5mW+5mW 32 ohm (10mW+10mW when headphone impedance is 16-ohm)
18Hz~20kHz
87MHz~108MHz
0 C~35 C
MPEG 1/2 Layer 3(32kbps~320kbps),
WMA(32kbps~320kbps), WAV
Support DCF standard JPEG format,
6~8 million pixel at most is supportable, BMP
3) Click "Begin to converse file" button to
start conversing, shown in the above figure:
2.3 OTHER INFORMATION
2.3.1 ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
#Longest playing time
When playing MP3 musical files with 128kbps
bit rate and 44.1kHz sampling rate in sate of
proper volume, "Normal"sound effect and screen
saver, the longest playing time of this player is
about 11 hours . Playing time in other cases will
be different.
#Accessories
1)Headphone
2)User manual
3)USB transmission line4)Warranty card
5)Hanging strip
6)Protection case
#The lowest computer configuration
Requirements
1)Above Windows98SE/2000/XP/ME,Mac8.5
2)Pentium 200MHz centre processor or above
3)CD-ROM drive
4)40MB spare hard disc space
5)32MB memory
6)USB jack
- 9 -
Page 14
Chapter Three Principle and Servicing
Section one Principle of the player
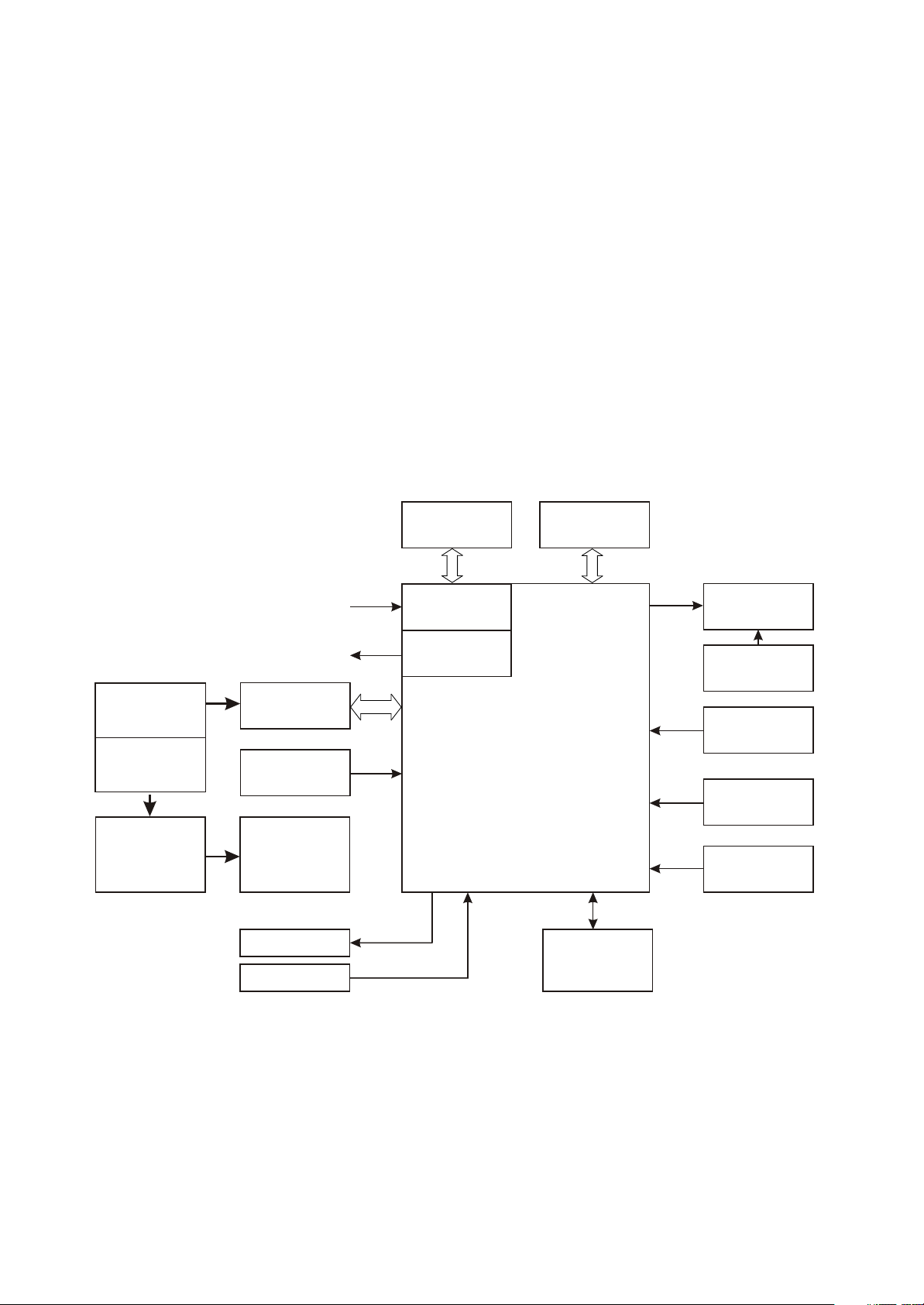
3.1.1 Block diagram of the player
Block diagram of the player is shown in the picture 3.1.1.1:
V7 Block Diagram
USB POWER
ADAPTOR POWER
CHARGE
MANAGEMENT
USB INTERFACE
24M CRYSTAL
LI-ION BETTERY
HEADPHONE
MICROPHONE
3.3V
1.8V
SDRAM
BUILT-IN LDO
CIRSUIT
BUILT-IN DC-DC
CIRCUIT
AUDIO&VEDIO CODEC
FLASH MEMORY
QVGA LCD
LDO BACKLIGHT
RT9284
SWITCH CIRCUIT
RK2606
RESET CIRCUIT
BUTTON ARRAY
FM MODULE
TEA5767
Figure 3.1.1.1 Block diagram of the player
3.1.2 Principle of the player
V7 portable MP4 player is mainly composed of following functional modules :
1. Decode parts : main decode chip adopts Rk2606 of Rockchip company with built-in ROM and
RAM, which can directly drive TFT LCD screen;
- 10 -
Page 15

2. Lithium battery part: composed of lithium battery and charge managing circuit, which supply
power for the player.
3. Periphery interface periphery interface is composed of earphone output, MIC input and USB
interface. Earphone interface is the audio output interface of the player, MIC is audio input of periphery
recording, USB jack finishes internal and external data switch of the player to realize charge function.
4. Data storage module: composed of Flash and periphery circuit to fulfill data storage of the player.
5.Display module:1.8 inch high-bright LCD screen.
6. Tuning module: FM tuning.
- 11 -
Page 16

Section Two Unit circuit principle
3.2.1 Video decode circuit principle:
Video decode circuit is mainly composed of main decode chipRK2606,SDRAM and peripheral circuit.RK2606
can realize MPEG-4 format in low frequency and power consumption with clear and smooth picture. Meanwhile,
Rk2606 integrates large amounts of I/O control jacks which may provide a max flexibility. Internal principle block
diagram of RK2606 is shown in picture3.2.1.1
Figure 3.2.1.1 Internal principle block diagram of Rk2608
Figure 3.2.1.1 Internal principle block diagram of Rk2606
1.Video decode circuit is mainly composed of main decode chipRK2606,SDRAM and peripheral
circuit.RK2606 can realize MPEG-4 format in low frequency and power consumption with clear and
smooth picture. Meanwhile, Rk2606 integrates large amounts of I/O control jacks which may provide a
max flexibility. Internal principle block diagram of RK2606 is shown in picture3.2.1.1. Low power
consumption function of Rk2606 can prolong battery usage time for portable player and its integrated
lithium battery charger supports voltage control (AVC) and its integrated power management unit
includes a DC-CD switch on high effective plate, which support ,multiple battery configuration, such as
1×AA,1×AAA, Li-ion battery. What is more, compared with traditional voltage control system, AVC
enables chip to operate with higher peak value CPU working frequency to make the highest running
- 12 -
Page 17

speed up to 100 MIPS. Rk2606 supports DRM 10 digital copyrght management technology based on
Microsoft.. Rk2606 has multi-mission dealing function, which can realize functions that listening to
music when viewing e-book or playing e-games. Rk2606 chip integrates USB 2.0 High Speed/Full
Speed PHY, which realizes a faster transmission speed. It also integrates controller that supports
TFT/CSTN/OLED colourful screen.
2.When the player power on, reset circuit keeps high level reset signal. After Rk2606 completes
reset through reset pin 115, reset signals output from pin 43 to enable end of Rt9284 to make boost
circuit work and the screen is lighten. Meanwhile, 1.8Vand3.3V circuit begin to output, 24M crystal
oscillator Y1 oscillates and decode chip begins to work and read data saved in Flash. After Rk2606
decoding, video signals are sent to LCD display screen to display.
3.2.2 Audio decode circuit principle
Audio decode chip is mainly composed of main decode chip Rk2606 internal audio decode CODEC
and periphery circuit. RK2606 internal CODEC adopts I2C bus controlling format. After the audio files
inside FLASF being processed through DSP, audio signals are sent to RK2606 internal audio decode
CODEC to decode and output from pin 75, 80 of Rk2606 and output from earphone jack at last.
When the machine is recording, external analog audio signals are sent to pin 70 of Rk2606 through
microphone. After processed by Rk2606 internal audio decode CODEC and conversed through AD
conversion unit, the digital audio signals are saved in FLASH.
When the machine is in FM mode, FM digital audio signals input from pin68,69 of Rk2606 and
directly output to earphone OUTPUT pin interface after digital filter and echo process.
3.2.3 FLASH CIRCUIT PRINCIPLE
1.FLASH circuit is shown in picture 3.2.3.1
VCC
R37
47K
VCC
R38
47K
FCE0
FCE1
C63 104
GND
R39
10K
RD/BY
FREN
FCLE/A2
FALE/RS/A1
FWEN
FWP
R49
47K
D_GND
U4
1
RES#
2
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
R/B2
7
R/B1
8
RE
9
CE1
10
CE2
11
NC
12
VCC
13
VSS
14
NC
15
NC
16
CLE
17
ALE
18
WE
19
WP
20
NC
21
NC
22
NC
23
NC
24
NC
NAND FLASH
NC
NC
NC
NC
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
NC
NC
PRE
VCC
VSS
NC
NC
NC
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
NC
NC
NC
NC
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
R43 0R
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
D7
D6
D5
D4
VCC
C64
104
D_GND
D3
D2
D1
D0
Figure 3.2.3.1 Flash circuit principle
- 13 -
Page 18

2. Working principle:Flash Memory is the storage unit of the whole player, all the AV and image files
are saved in FLASH. FLASH modules are composed of two groups FLASH chip K9G8G08U0M with the
specification2G H model is4G .Flash chip and main decode Rk2606 are connected through eight
data lines to complete the read, write and delete works. VCC provides 3.3V voltage for FLASH working.
R37,R38 is pull-up resistor of /CE and R49 is pull-down resistor of /WP. VCC is power supply pin of
FLASH. /CE is chip selection signal, effective when in high level. VCC supplies 3.3V voltage and FLASH
begins to work. /RE /WE are read-effective and write-effective signal ports to control read and write
function of FLASH.I/O1 I/O8 are eight data lines to complete external data exchange of FLASH and
realize function of write, delete and edit of Mp3.
There is firmware of the player’s working in Flash, all tasks are completed by CPU to send relevent
order after data exchange between CPU and Flash. When the player power on,3.3V voltage supplies
power for Flash through VCC. /CE inputs 3.3V high level signals and Flash begins an effective work.
When playing AV files,/RE is high level, Flash performs the operation of read out. When files are written
through USB data line or recording through microphone, /WE is in high level and Flash performs the
operation of write in. The operation of read out and writing in are performs through I/O1 I/O8 eight
data/address line.
3.2.4 FM tuning circuit
1.FM tuning circuit is shown in picture 3.2.4.1:
2. Working principle: tuning circuit is composed of mini digital tuning IC TEA5767 of Philips and
peripheral circuit. C68, C69, C70, C71 and L21 input matching circuit for antenna of FM module; Varicap
diode D3, D4 and winding inductor L22, L23 is frequency selection tuning circuit in FM module. The
control of FM adopts two-line IIC bus method and 9, 10 of TEA5767 are date and control line.
When Mp3 player switches into FM tuning state, antenna is sent to RF band-pass filter (87.6MHz
108MHz and 76MHz 87.5MHz) composed of L21, C69, C71 through C68 coupling and then to pin 35,
37 of TEA5767 for amplifying inside TEA5767. Pin 2, 3, 4 of TEA5767 is connected with internal VCO,
and connected with diode D3, D4 externally. Pin 2 is tuning voltage output pin and voltage changes in
1V when in auto search. VCO power supply is sent to pin 5 of TEA5767 by FM 3V3 through R56 limit and
C81 filter. The built-in I2C jack is controlled through pin 8, 9 of TEA5767 and CPU performs operations
of channel search and selection through I2C bus. Digital power supply is sent to pin 7 of TEA5767 by FM
3V3 throughR58 limit, C90 filter. XT1 32.768 produces basic clock of 32.768 and inputs to TEA5767
from pin 17. Analog audio signals after processed by TEA5767 output to rear stage power amplifying
from 23 (right channel), 22( left channel ) and then output through earphone jack.
3.2.5 Display screen boost circuit
1.Display screen boosts circuit is shown in picture 3.2.5.1
- 14 -
Page 19

FM_3V3
R56
22R
C81
104
FM_ANT
FM_3V3
SGND
FM_ANT
L22
33nH 2%
L23
33nH 2%
C68 101
C78 103
R58
22R
D3
BB202
D4
BB202
FM_3V3
SGND
C90
104
L21
120nH
C69 27PF
SGND
C71
47PF
R70
100K
SGND
R68
10K
C65
393
L27 601 DCR<350m
L28
C70
472
1
N.C
2
CPOP
3
VCOT1
4
VCOT2
5
VCOVCC
6
DGND
7
DVCC
8
DATA
9
CLOCK
10
N.C
SGND
601 DCR<350m
40
N.C
W/R11BUSM12BUSEN13SWP114SWP215XTAL116XTAL217PDLF18PHLF19N.C
36
37
38
39
RFI2
TCAGC
RFGND
LOOPSW
TEA5767HN
NECTAR-I
FM_3V3
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
33
34
35
RFI1
AVCC
32
AGND
R52 18K
31
N.C
IFGAI
DIFL2
DIFL1
TCIFC
VREF
MPXO
TMUTE
RAVO
LAVO
20
C72
475/X5R
N.C
N.C
R51
10R
C73 473
C74 473
C75 473
C77 333
U6
SGND
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
32.768KHz
L24
L25
XT1
C79 333
601 DCR<350m
601 DCR<350m
C85
102
SGND
C87
22PF
SGND
SGND
SGND
SGND
C80 105
C82 105
SGNDSGND
R57
33K
C88
223
SGND
SGND
FM_OUTR
FM_OUTL
C86
223
SGND
C89
102
VB
L18
601/0603
C52
106/X5R
BACK_EN
Figure 3.2.4.1 FM module circuit diagram
R30 100R
R33
10K
L19
CDRH3D16-100
6
VCC
4
EN
OVP
2
GND
U2
RT9284B
FB
D3
MBR0520/SOD123
1
LX
5
3
Figure 3.2.5.1 Display screen boost circuit
C51
102
R34
12R 1%
LED-
D_GND
L20
0R/0603
C53
106/16V/1206
LED+
LED+
- 15 -
Page 20

2.12V high voltage is needed for lightening display screen, so the boost circuit must be matched to
fulfill. This circuit includes two parts: boost circuit and display screen jack circuit. Boost circuit is
composed of DC-DC control IC RT9284 and peripheral circuit; VIN is power input; EN is enable end of
RT9284 , effective when in high level, SW is high voltage output pin, FB is feedback pin.
After power on, voltage divide detect circuit sends detected voltage to pin 3 of RT9284. When
voltage detected by pin 3 is lower than reference voltage1.235V this IC has a1.235 V reference
voltage comparator inside ), the internal switch is saturated and internal boost circuit of L19 and
RT9284 begin to boost and store energy. When current of L19 reaches to750mA, the internal switch of
Rt9284 turns off and power is supplied to rear circuit through external diode D2 until feedback voltage is
lower than reference voltage again. As for this PFM peak current control scheme adopted by convertor
discontinuous conduction means (DCM), the frequency depands on output current and makes the
frequency of entire load very high. Pin 4 of Rt9284 is working enable pin and connect with pin43 of
Rk2606 to control level exchange through software to complete control of Rt9284 to realize screen-
save function.
When machine power on, display screen performs data communication through rear CPU, and
restores driving current signals sent by CPU onto display screen. Signals sent by CPU are different and
display screen makes different displays, so we can see different displays and also CPU controls
screen-save function through software setup.
3.2.6 Headphone output jack circuit
1.Headphone output circuit is shown in picture 3.2.6.1:
2.The left/right channel audio signals directly output from Rk2606 to earphone jack, D1 in the
circuit is TVS diode array used for ESD protection. Ground wire of headphone is also used for antenna
input of FM module.
OUTL
HP_OUTR
HP_OUTL
4
5
R2
10R
R1
10R
1
3
4
5
2SJ-A382-001(HP-DC)
CN1
OUTR
L1 601
L2 601
FM_ANT
R102 0R*
3
GND
AOM
AOMS
162
D1
RCLA MP0504F/SC-70
104
Figure 3.2.6.1 Headphone output jack circuit
- 16 -
C2
C1
104
L3 601
L4 601
FM_ANT
Page 21
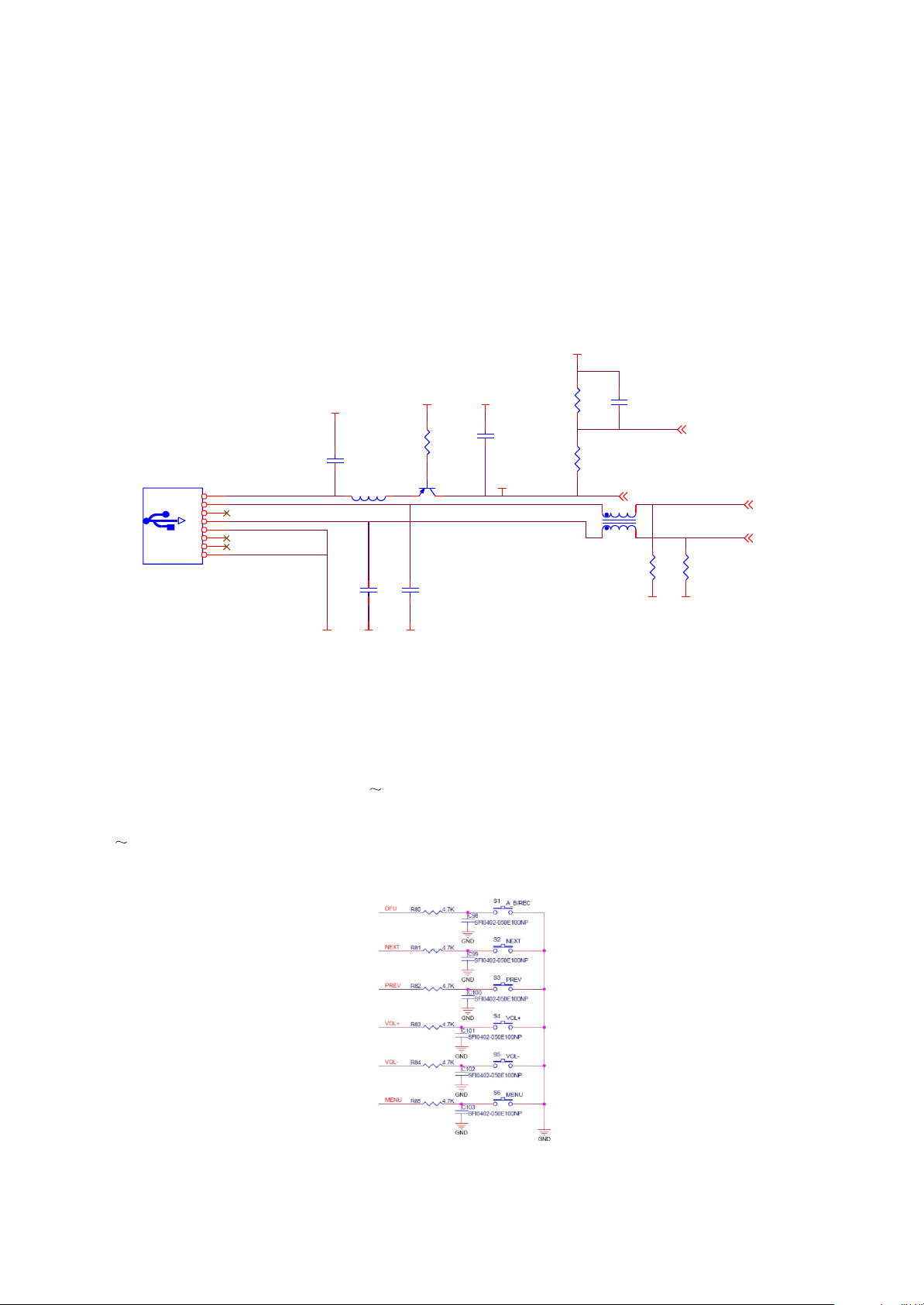
3.2.7 USB jack ciircuit
USB data jack is composed of USB_DM, USB_DP and GND (ground wire). When the player is
connected with computer or charging through USB line, USB_VBUS is power supply pin of USB jack,
and also power supply input pin of USB jack at the same time. When the player is charging through USB,
the 5V power supply inside PC charges for Li battery through USB)VBUS. USB jack circuit is shown in
picture 3.2.7.1
D_GND
R4
J1
+5V
D-
NC
D+
GND
IN_L
IN_R
GND
3DU05S-32T-10
D_GND
SFI0402-050E100NP
C5
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
L6 680
C9
SFI0402-050E100NP*
D_GND D_GND
R5
470R
SS8550LT
Q2
C10
SFI0402-050E100NP*
C4
104
+5V
12K
R6
10K
1 3
C3
104
USB_DET
USB_VBUS 2
T1
SDCW2012-2-900T
2 4
R13
1M
D_GND D_GND
USB_DET
R12
1M
USB_DM
USB_DP
D_GNDD_GNDD_GND
Figure 3.2.7.1USB jack circuit
3.2.8 Button circuit
Button circuit diagram is shown in picture 3.2.8.1. V7 button detect adopts voltage detect modul. RK2606
confirms which button works through P0.0 P0.5 scan tube pin voltage exchange. When the relevant button is
touched, the pre-determined voltage of the relevant button pull down to the ground through the relevant resistor of
R80 R85, and then make response by internal program of Rk20606 to realize function of each button.
Figure 3.2.8.1button circuitp
- 17 -
Page 22
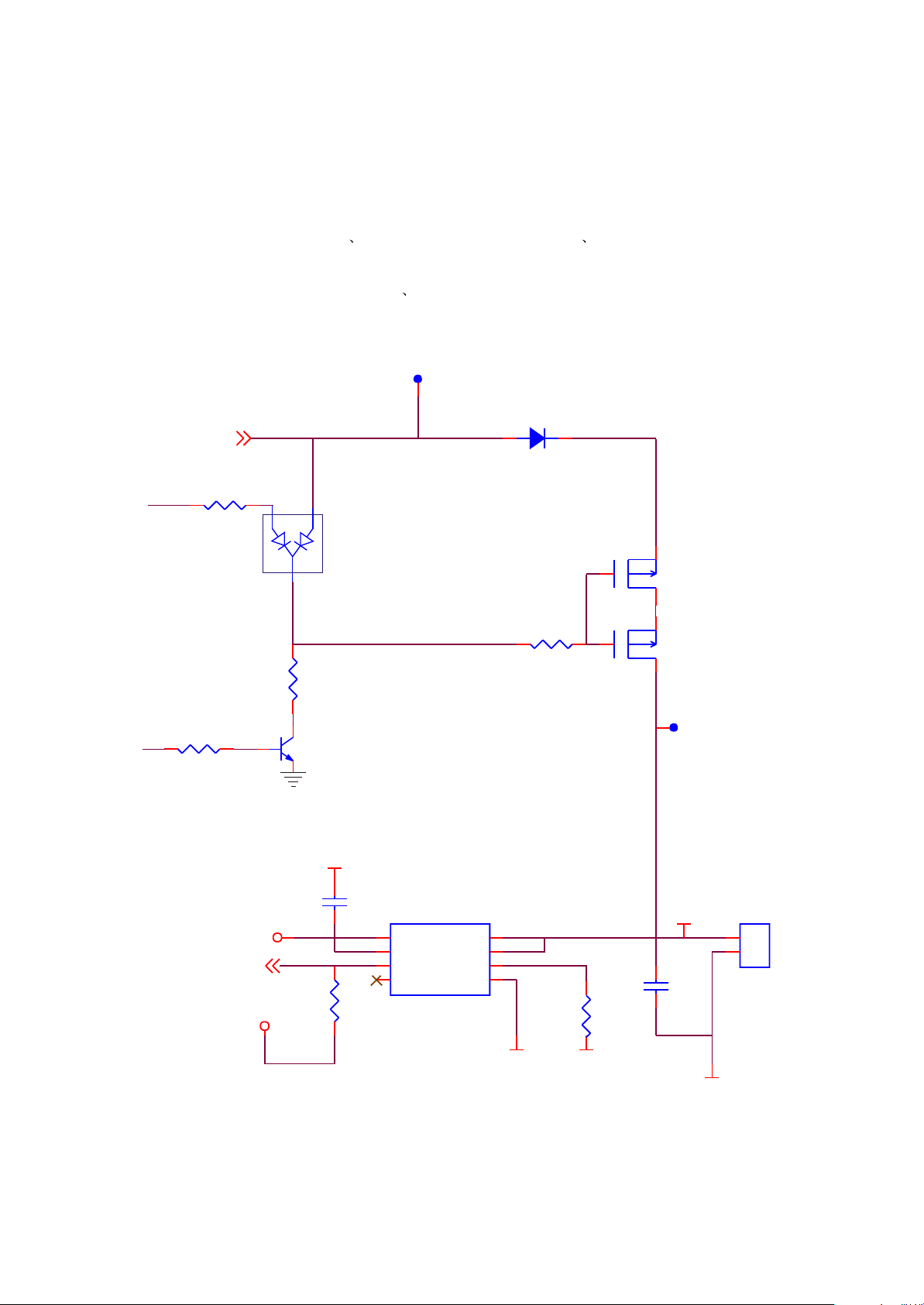
3.2.9 charge management circuit
1.Charge management circuit mainly complete charge function for Li battery including USB/battery switch
circuit and charge management. Its circuit diagram is shown in picture 3.2..9.1
2.When the player power off, EN is low level,Q8 is cutoff , the high level of battery anode passes to G electrode
of Q6, Q7 through D7. MOS tube is in cutoff state and battery has no output when the player power on, EN is high
level, Q8 is saturated, G electrode of Q6 Q7 is pulled down to low level, Q6 Q7 is saturated and battery begins to
output to supply power for the player. When connecting with USB jack of the computer, 5V voltage of USB_VBUS
passes to G electrode of Q6, Q7 through D7 , Q6 Q7 is cutoff and battery stops outputting.
5V
D5
BAT43WS
USB_VBUS
R60
BAT+
10R
D7
MMBD4148CC
EN
R63
10K
USB_VBUS
CHG_OK
R14
VCC
R14
1K
Q8
MMST3904
GND
R66
47K
P_GND
C93
475
U7
1
V_IN
2
V_IN
5
STAT E
7
NC
MCP73832
VBAT
VBAT
PROG
VSS
G
R61
100R
BAT
4
3
8
6
G
R64
3.3K
Q6
SI2305DS
D S
Q7
SI2305DS
D S
BAT+
BAT+
C95
105
CN3
1
BAT
2
P_GND
Figure 3.2.9.1 charge management circuit
- 18 -
P_GND
D_GND
Page 23

Charge management is mainly completed by charge control IC MCP73862 and peripheral circuit.
STA T1
MCP73832
Shutdow n Hi- Z
No Battery Present Hi- Z
Preconditioning L
Constant-Current Fast Charge L
Constant Voltage L
Charge Complete-Standby Hi- Z
charge c ycle s tate
Pin V_IN is power supply input pin of MCP73862 , which is input pin of USB jack 5V power supply. VBAT
is input pin of MCP73862, which is input pin of Li battery; STATE is indicator of charge state. When
STATE is low level, it indicates a charge state. On the contrary, it indicates charge is completed; PROG
is setup pin of charge circuit and MCP73862 use this reference circuit to charge for Li battery. The
relationship of charge circuit I and R64 is shown as the following:
REG
I =
REG
1000V
R
PROG
(A)
From the above, charge current is 400mA.
When adaptor or USB is connected externally, input voltage is 5V; internal oscillator begins to
oscillate; internal timer begins to time; charger begins to charge and IC fulfills a complete charge
process automatically. The indicator of STATE pin in charge is shown as the following:
3.2.10 Battery voltage detect circuit
1.The function of battery voltage detect circuit is to switch off the player when the detect input voltage of the
player is lower than a certain voltage. Low voltage detect circuit is shown in picture 3.2.10.1
RK2606
BAT_DET
LRADC0
LRADC1
LRADC2
LRADC3
REXT1 00K
Figure 3.2.10.1 Low voltage detect circuit
107
106
105
104
103
CHG_OK
LCD_SEL
- 19 -
VCC1V8
CHG_OK
R19
100K 1%
BATT
R16
100K 1%
R18
100K 1%
GND
Page 24

2.Battery voltage detect is fulfilled by RK2608 and firmware of the player. Pin 107 of is
externally connected with R16, R18 to compose divide voltage circuit. The voltage value after battery
electric charge is divided through voltage divide is processed by K displays on display screen to
indicate voltage value. When the voltage is lower than value set by internal program, switch off order is
sent out and the player switches off automatically.
3.2.11 Battery protection circuit
1.Battery protection board is installed on Li battery to protect it from being damaged by short-circuit,
over-discharge and over-charge. Li-ion battery and battery protection board are called as Li-ion battery
components. Battery protection circuit is shown in picture 3.2.11.1:
Figure 3.2.11.1 battery protection circuit
2.Battery protection circuit is mainly composed of battery protection IC S8261 and built-in dul-N
channel MOSFET ECH8601. S8261 is the protection IC of Li-ion polymer chargeable battery of built-in
and high-precision voltage detect circuit and delay circuit. DOUT and COUT are over-discharge when
Li battery voltage is lower than 2.4V protection output end and over-charge when Li battery voltage is
higher than 4.2V protection output end. When normal working, the two voltage pins are high level.
MOSFET opens and Li battery voltage output to the player through protection board; when in protection,
the two pins output low level to control MOSFET to cut off power. Over-current detect short circuit
protection is fulfilled through detecting short circuit state and controllingDOUT and COUT output.
- 20 -
Page 25

3.2.12 power management module
The function of power management module is to provide 3.3V and 1.8V voltage for the player’s
normal working. The LDO voltage management module is integrated inside RK2606, which can output
3.3V and 1.8V voltage. The output 1.8V voltage provides pure 1.8V power supply voltage for RK2606
after voltage stabilizing through XC6206, which is shown in picture 3.2.12.1
XC6206P152
VCC
U8
2
VI
VOUT
GN D
1
Figure 3.2.12.1 1.8V power supply circuit
R77
100K
3
C95
104
VCC1V8
3.2.13 Reset circuit
1.Reset circuit is to provide reset signals for the player. The reset circuit is shown in picture
3.2.13.1
VDD
C62
104
R46
100K
C58 104
R44
220K
SS8050LT
R48
1M
VCC
Q5
R45
10K
C65
104
R47
1K
RESETN
D_GND
3.2.13.1 reset circuit
- 21 -
Page 26

2.When the player power on, stabilizing voltage starts to work and output 3.3V voltage VCC. The two ends
voltage of capacitor C58 can not change suddenly, B electrode of triode Q5 is low voltage, Q5 is in cutoff state and
RESETN is high level to reset Rk2606 and display screen. Meanwhile, VCC charges for capacitor C19. When B
electrode voltage of Q5 reaches to saturated voltage, Q5 is saturated on, VCC is grounded andRESETN is low level
to fulfill the player’s reset. The reset time depends on C58 and parameter of voltage divide resistorR44, R48.
3.2.14 Power on/off control circuit
1.Power on/ off control circuit is shown in picture 3.2.14.1:
VCC
R65
100K
D7
EN
R71
470K
GND
MMBD4148CC
Q7
SS8050LT
R74
100K
Q11
MMST3904
Q9
MMST3906
R69
100K
C94
475/X5R
BAT+
R70
10M
GND
R76 1M
R67
47K R68
10K
10K
R75
2M
START
VCC
R59
START
PLAY/PAUSE
D9
1N4148WSR72
R73
10K
OFF
GND
SFI0402-050E100NP
PLAY
C91
GND
100k
D6
1N4148WS
L29
601
S7
PLAY
GND
Figure 3.2.14.1 power on/off control circuit
2.START/PLAY/PAUSE is a group of combination button and functions are different in different
times, which is decided by software. When the player is in power-off state without connecting with USB,
Q9 is cutoff. When press S7 to power on, START is pulled down to ground to output low level, Q9 is on,
diode D8 is also on, BAT+ pulls up EN through Q9, D8. Rk2606 begins to work and its internal DC-DC
output1.8V and 3.3V voltage to supply power for the whole system. System voltage VCC, VDD, OLED
voltage 13V begin to output, crystal oscillator Y1 oscillates, reset circuit works, main chip and
display screen initialize, OSD appears and machine begins to work.
When in power on state, press START/PLAY/PAUSE, Q9 is on andBAT+ produces a voltage drop
through CE of Q9. As VCC voltage is normal, the circuit composed through R69, R70 makes N electrode
of D9 keep 3.3V voltage. D9 cannot be on and it is in cutoff state, the player does not make response to
power off. After pressing button, voltage of PLAY/PAUSE pin changes and inputs to pin 57 of Rk2606 to
realize different functions in different operation interfaces.
When the time of pressing PLAY button is more than 1 second but less than 4 seconds pin 57 of
Rk2606 detects the change of voltage; software decides this signal is power- off signal and saves
contents of machine; pin 58 output OFF high level, D9 is on to make Q10 on, VCC is grounded through
CE electrode of Q10, enable end EN is low level, Rk2606 stops working to realize the player’s software
power-off.
- 22 -
Page 27

When machine down because of software problem, press START/PLAY/PAUSE button more than 4
seconds to realize firmware power-off. The process is : press the button, B electrode of Q9 is low level,
Q9 is on, BAT+ charges C94 through CE electrode of Q9 and R70. Voltage on capacitor increases
gradually to make Q10 on, VCC is grounded through CE electrode of Q10, enable end EN is low level,
Rk2606 stops working and the player is power-off. When loosening button, BAT+ keeps START pin a
high level through R67, R68; Q11 is on; electric charge saved in C94 discharges quickly through CE
electrode of R75 and R74, Q11 to ensure an normal power on when press START/PLAY/PAUSE button
next time.
3.2.15 MIC circuit
1.MIC circuit is shown in picture 3.2.15.1:
2.MIC circuit is mainly composed of MIC and microphone power bias circuit. MIC1 switches the
recorded external audio signals into electric signals and input to ADC circuit of RK2606 audio
processing after C7 coupling and switches analog signals into digital signals to form WAV file through
software encoding to save inside FLASH. R7, R11,Q1 and C6 are triode voltage stabilizing system in
circuit to supply stable voltage bias.R8 is bias resistor of MIC.
R7
100K
R11
470K
Q1
MMST3904
C6
106
MIC1
1
2
MICROPHONE
VCC
C96
104
L30
601
R14
47K
R8
2.2K
C8
221
C7
104
MIC
3.2.15.1 MIC circuit
- 23 -
Page 28

Section Three Servicing Cases
3.3.1 Troubleshooting diagram
1.Troubleshooting flow chart for "no OSD"
No OSD
Whether
D2 anode 12V voltage
is normal
Y
Whether there is 12V
voltage on display
screensocket
Y
Whether 3.3V
power supply is normal
Y
Whether it is
normal after changing
display screen
components
Y
N
Check DC-DC boost circuit
and peripheral elements
N
Check whether display screen
flat cable holderhas false welding
N
Display screen flat cable
holder has false welding
N
Display screen flat cable
holder has trouble
Whether 8-digit number
of screen is normal
Y
Change display screen
components
N
Replace decode chip
Figure 3.3.1.1 Troubleshooting diagram for “No OSD”
- 24 -
Page 29

2. Troubleshooting flow chart for"USB is not connected”
USB is not connected
Check whether 5V
of Q2 is grounded
normally
Y
Check whether 3.3V
and 1.8V are normal
whether oscillation
of 12M crystal oscillator
D+, D- resistance
software upgrading is
Y
Check
is normal
Y
Check
to ground
Y
Whether
available
N
Q2 has trouble or USB
socket has rosin joint
N
Check each LDO output circuit
and peripheral elements
N
Replace crystal oscillator or
capacitors on two sides
N
Check wether USB socket
pin has rosin joint
N
Replace main decode
chip
Y
Upgrade software
Figure 3.3.1.2 Troubleshooting diagram for “USB is not
- 25 -
Page 30

3.Troubleshooting for"Do not charge"
Do not charge
Whether
battery is fully
charge with voltage
4.2V-4.3V
Y
Battery
is fully charged,
then protection
Y
Normal after discharge
Figure 3.3.1.3 Troubleshooting diagram for “Do not charge”
N
Change battery or battery
holder if battery compone
nts have trouble
Check
whether USB_VBUS
has 5V voltage
Y
Whether
BAT voltage has
change
Y
N
Check power supply circuit
N
ReplaceMCP73862
- 26 -
Page 31

4.Troubleshooting flow chart for "power not on"
Power not on
Check charge circuit
Check U1 and
peripheral circuit
Check U1 and
peripheral circuit
Whether battery
voltage is lower than
3.4V
Y
N
Whether battery
voltageis up to 3.6V
after charge
Y
N
N
Refer to troubleshooting
diagram for "machine not
power on"
Check
wetheRK2606 outputs
3.3V normally
Y
Check
wether Rk2606 outputs
1.8V normally
Y
N
Whether there is OSD
after connecting with
RK2606 P99 input pin
voltage is normal
BGA has trouble
computer
Y
Wether
Y
N
Replace battery components
N
Check battery toBGA circuit
Figure 3.3.1.4 Troubleshooting diagram for “Power not on”
- 27 -
Page 32
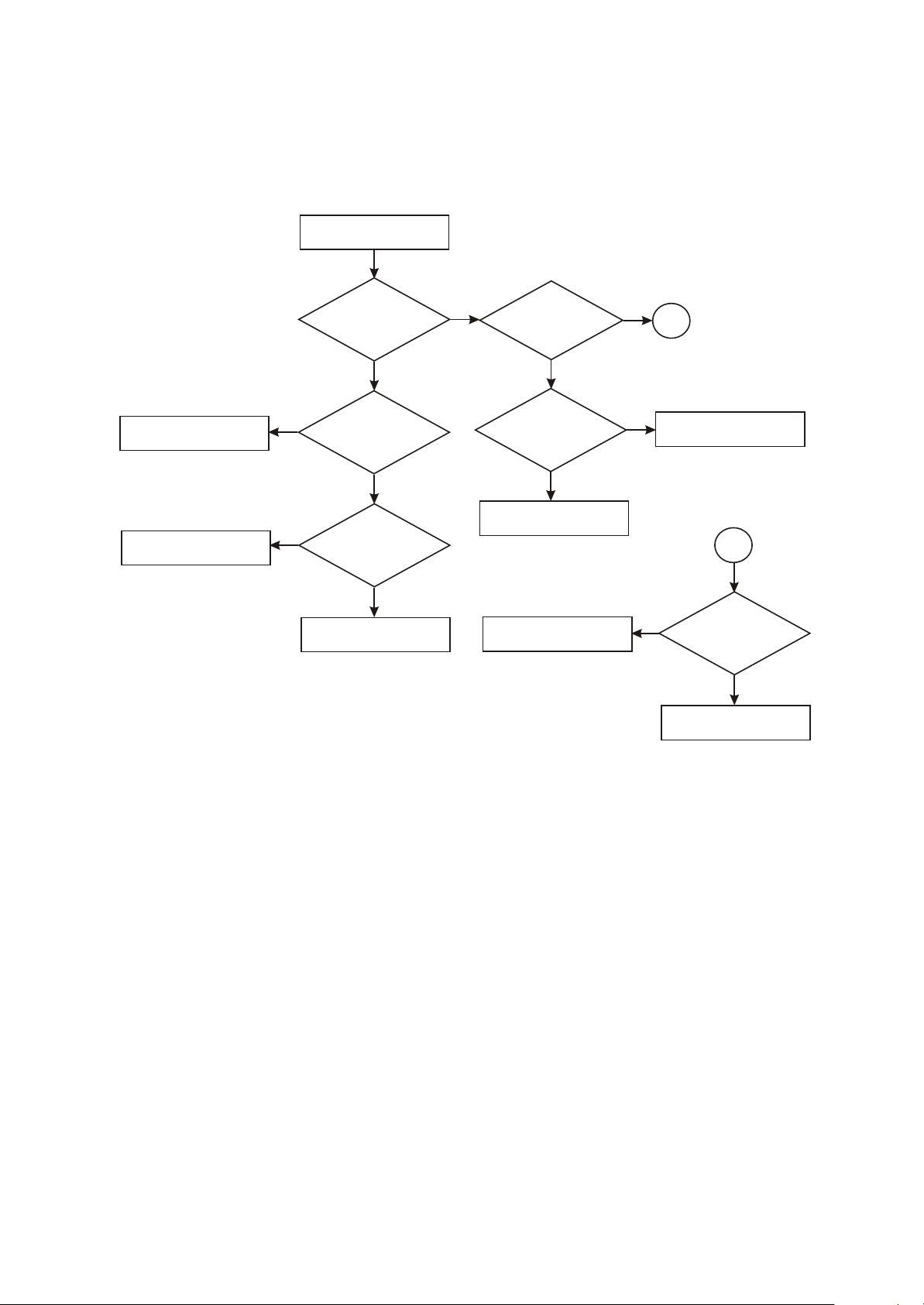
5.Troubleshooting flow chart for" Machine not power on"
Machine not power on
Replace crystal oscillator
Check reset circuit
Whether
3.3V, 1.8V voltage output
is normal
Y
N
N
Whether
crystal oscillator Y1
has normal
oscillation
Y
Whether
reset circuit is normal
Y
Replace main decode chip
Whether
N
software upgrading
is available after connecting
with computer
Whether
it is normal
after upgrading
software
Y
Trouble is removed
Check USB terminal welding
N
A
Y
N
Replace maindecode chip
A
Test
N
whether DM,
DP resistance to
ground is
normal
Y
Replace main decode chip
Figure 3.3.1.5 Troubleshooting diagram for “Machine not
- 28 -
Page 33

3.3.2 servicing cases
[ Example 1 ] Symptom: power not on.
Description: no OSD and no output.
Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly confirm whether it is caused by battery or power circuit. Connect with
computer and check whether display screen has display. Power on, connect and there is no display. Take the player
apart and check. Firstly test power supply voltage and it cannot be lower than 3.2V.Use multimeter to test between
anode and cathode of battery and then check VCC3.3V and 1.8V that output through BGA. During the checking, we
find that 3.3V is normal and 1.8V is normal.When pressing ON button in normal working, after testing actually,
VCC1.8V should be pulled down to about 1.7V, which is normal. When working normally, VCC3.3V should be
slightly lower to 3.1--3.2V, which is normal. Then test crystal oscillator X1 and oscillation is normal. The frequency
is 12MHZ and it is 11.999MHZ after testing actually. Reset is also normal, so we finally judge that main decode chip
has trouble. Change chip RK2608 and upgrade software again. Power on and trouble is removed.
[ Example 2 ] Symptom: power not on.
Description: no OSD and no output.
Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly confirm whether it is caused by battery or power circuit. Connect with
power adapter and check whether charge is available and whether screen has display. After taking machine apart,
firstly test power supply 3.3V and 1.8V and we find 3.3V is normal. Then test 1.8V and find that voltage only has
0.7V, replace Rk2606 and trouble is removed.
[ Example 3 ] Symptom: noise when tuning.
Description: radio station has noise when tuning.
Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly judge whether the tuning components or common part has trouble. Listen
to radio station by using headphone and check whether only one side of headphone has sound and the result is
normal. Then switch in tuning state to search radio station automatically and the result is normal, which means
power supply, data and clock are normal. To remove interferences from outside, we receiver the nearest radio
station to listen and check whether it is clear, and it has noise in result. The circuit that causes noise is mainly high
frequency tuning and mixed frequency part. Check carefully and find that pin 37 of U6 (TEA5767HN) has false
welding. After welding again, trouble is removed.
[ Example 4 ] Symptom: no OSD.
Description: screen has no display.
Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly confirm whether power or display screen itself has trouble. Power on,
listen to playing sound and it is normal, so we preliminarily decide power supply 3.3V and 1.8V are normally
basically. Test voltage on two ends of L19 and it is about 4.3V, which is normal. Then test voltage on two ends of D2
and find the anode does not form 13V. Take out display screen and there is still no 13V, Check input end voltage
and EN enable end is normal. Then check feedback pin FB end voltage and it is low obviously and EN enable end
has false welding. After welding again, trouble is removed.
[ Example 5 ] Symptom: machien down when power on.
Description: after power on, machine down before entering menu operation.
Analysis and troubleshooting: when power on, machine down before entering main menu. Press PLAY button
to power on, when screen appears BBK picture justly, image of the player halts and button has no function. Firstly
test power supply 3.3V, 3.8V and it normal. Then test crystal oscillator oscillation frequency and it is normal, so we
judge that data has abnormality. Because machine down, data cannot be tested normally. Change main chip and
trouble still exists. After changing Flash U4, trouble is removed.
- 29 -
Page 34

[ Example 6 ] Symptom: machine down when tuning.
Description: machine is normal when playing Mp3, Mp4. Machine down when entering tuning state.
Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly check tuning IC power supply 3.3V, and SCL, SDA are normal.
Test whether 32.768 crystal oscillator oscillates normally and whether it has false welding. This crystal
oscillator has direction when changing it, so it cannot be stuck reversely, otherwise machine down will
happen. Test crystal oscillator and we find it has false welding. After welding again, trouble is removed.
[ Example 7 ] Symptom: computer cannot be connected.
Description: after connecting with computer, no display and disk cannot be found.
Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly confirm whether charge is available and it is normal after
power on. Use diode level of multimeter to test the resistance value to ground of D+, D- data signals in
USB terminal position and it should be close to several hundred ohm. Then test between D+ and D- and
it should not have short-circuit.Test DP and DM and they are normal. est power supply 3.3V, 1.8V and it
is normal. Crystal oscillator oscillates normally. Change chip RK2608, upgrade software again, connect
with computer and trouble is removed.
[ Example 8 ] Symptom: machine down when playing MP4.
Description: machine down when playing video files.
Analysis and troubleshooting: firstly confirm whether machine is normal when playing Mp3. If it is
normal, we can decide power supply, reset and oscillation are normal. Check data and image
processing IC and we preliminarily judge that it is not related to image processing but related to data
and address. Picture information buffers and it is mainly processed through U3. Test power supply 3.3V
voltage of U1 and it is normal. Change SDRAM directly and trouble is removed.
- 30 -
Page 35

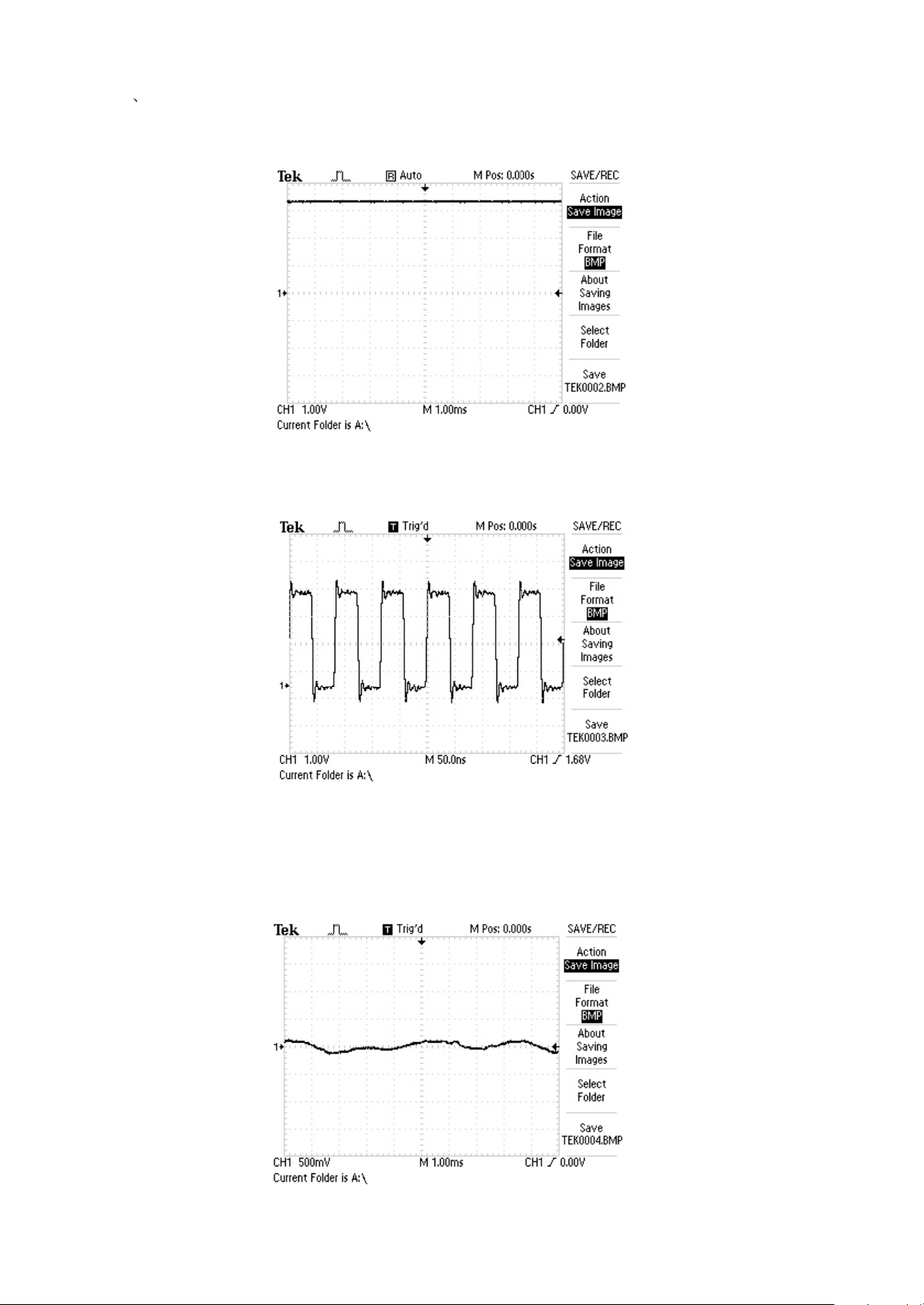
Section Four Signal waveform diagram
This section collects signal waveform diagram of audio, video and each unit circuit with the purpose
To help servicing personnel to judge where trouble lies in accurately and quickly to improve servicing
skills. For the difference of oscillograph's type, model and tuner, a certain difference may exist, so the
servicing personnel are expected to pay more attention to check in daily operation.
1.Battery voltage BAT1 waveform diagram
µÚËÄ½Ú Î¬ÐÞ²ÎÊý
2.VDD waveform diagram
- 31 -
Page 36
3 VCC waveform diagram
4.Display screen background light BCLK waveform diagram
5.PLAY1 waveform diagram when playing
- 32 -
Page 37
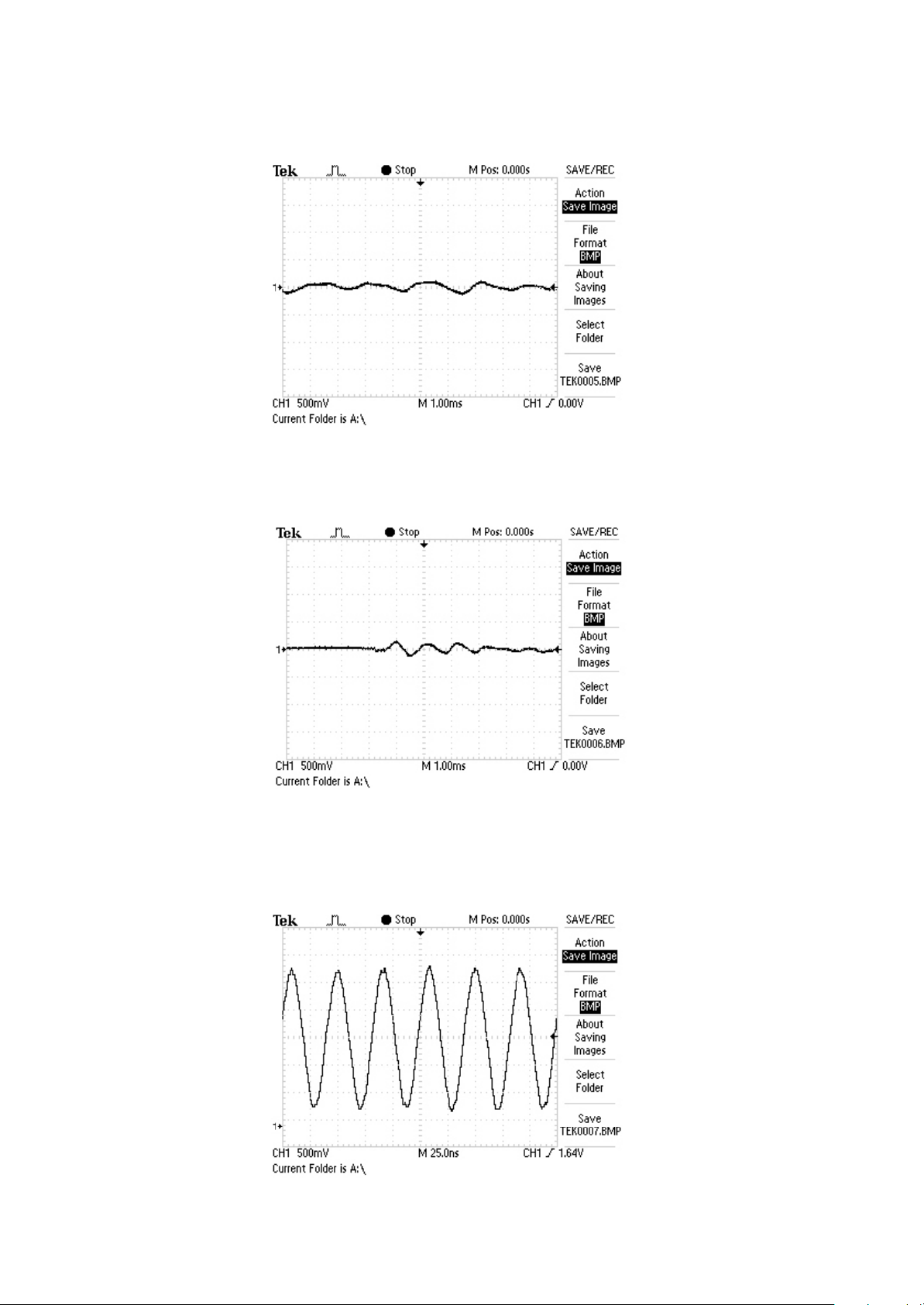
6.OUT_R waveform diagram when playing music files
7.OUT_L waveform diagram when playing music files
8. Crystal oscillator Y1 waveform diagram
- 33 -
Page 38

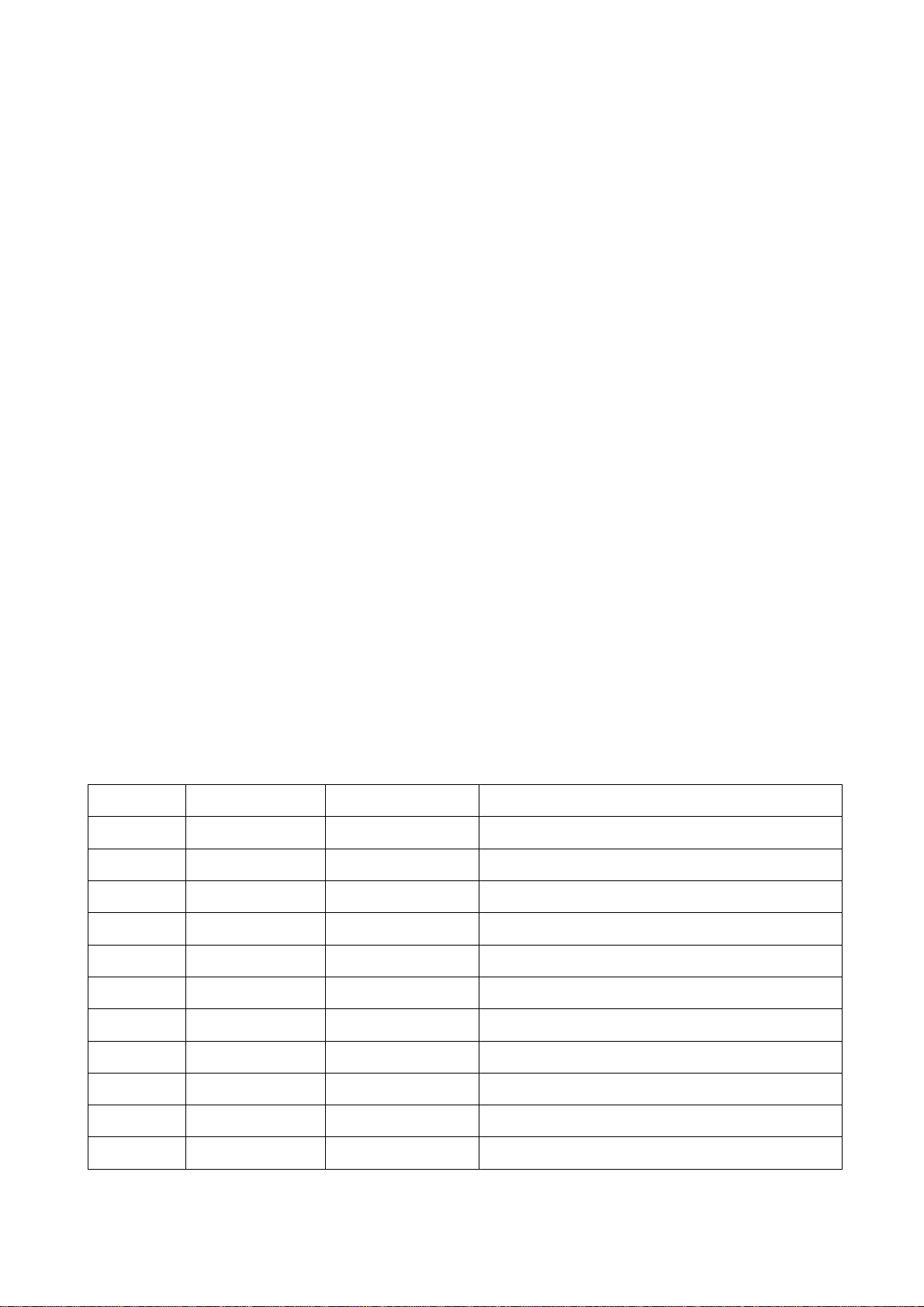
9.U2 DC-DC switch waveform diagram
10.Power-on reset RESETN waveform diagram
11.Crystal oscillator Xt1 waveform diagram
- 34 -
Page 39

Section Five Function Introduction to IC
3.5.1 Function introduction to HY57V641620E
1. Description
The Hynix HY57V641620E(L/S)T(P) series is a 67,108,864bit CMOS Synchronous DRAM, ideally suited
for the memory applications which require wide data I/O and high bandwidth. HY57V641620E(L/S)T(P) is
organized as 4banks of 1,048,576x16.
HY57V641620E(L/S)T(P) is offering fully synchronous operation referenced to a positive edge of the
clock. All inputs and outputs are synchronized with the rising edge of the clock input. The data paths are
internally pipelined to achieve very high bandwidth. All input and output voltage levels are compatible with
LVTTL.
Programmable options include the length of pipeline (Read latency of 2 or 3), the number of consecutive
read or write cycles initiated by a single control command (Burst length of 1,2,4,8 or full page), and the burst
count sequence(sequential or interleave). A burst of read or write cycles in progress can be terminated by a
burst terminate command or can be interrupted and replaced by a new burst read or write command on any
cycle. (This pipelined design is not restricted by a '2N' rule).
2. Features
◆ Voltage : VDD, VDDQ 3.3V supply voltage
◆ All device pins are compatible with LVTTL interface
◆ 54 Pin TSOPII (Lead or Lead Free Package)
◆ All inputs and outputs referenced to positive edge of system clock
◆ Data mask function by UDQM, LDQM
◆ Internal four banks operation
◆ Auto refresh and self refresh
◆ 4096 Refresh cycles / 64ms
◆ Programmable Burst Length and Burst Type
- 1, 2, 4, 8 or full page for Sequential Burst
- 1, 2, 4 or 8 for Interleave Burst
◆ Programmable /CAS Latency ; 2, 3 Clocks
◆ Burst Read Single Write operation
3. PIN Description
SYMBOL TYPE DESCRIPTION
CLK Clock
The system clock input. All other inputs are registered to the SDRAM on
the rising edge of CLK
- 35 -
Page 40

CKE Clock Enable
CS Chip Select Enables or disables all inputs except CLK, CKE, UDQM and LDQM
Controls internal clock signal and when deactivated, the SDRAM will be
one of the states among power down, suspend or self refresh
BA0, BA1 Bank Address
A0 ~ A11 Address
RAS, CAS, WE
UDQM, LDQM
DQ0 ~ DQ15 Data Input/Output Multiplexed data input / output pin
VDD/VSS Power Supply/Ground Power supply for internal circuits and input buffers
VDDQ/VSSQ Data Output Power/Ground Power supply for output buffers
NC No Connection No connection
Row Address Strobe, Column
Address Strobe, Write Enable
Data Input/Output Mask Controls output buffers in read mode and masks input data in write mode
Selects bank to be activated during RAS activity Selects bank to be
read/written during CAS activity
Row Address : RA0 ~ RA11, Column Address : CA0 ~ CA7
Auto-precharge flag : A10
RAS, CAS and WE define the operation Refer function truth table for
details
3.5.2 Function introduction to RK2608
1. Features
◆ 128 pins LQFP package
◆ Typical power voltage 3.3V(IO), 1.8V(Core)
◆ Use one 24MHz crystal oscillator
◆ 38 GPIO (8bits P0,P1,P3,14bits P2)
◆ 10-bit low resolution ADC with 4-channel Analog Input
◆ Build in Stereo 24-bit Delta-Sigma DAC with on-chip headphone amplifier
◆ Build in Stereo 16-bit Sigma-Delta ADC (Line-in /FM Input/ Microphone with analog mixer)
◆ 40 levels digital volume control
◆ Support external CODEC through I2DSP interface
◆ Support I2C interface
◆ Support USB 2.0 high speed and full speed
◆ Integrated 3 Channel DMA
◆ Embedded DSP Core:
· 4K words Boot Sync ROM
· 56K words Program Sync SRAM
· 48K words Data Sync SRAM
- 36 -
Page 41
· 2K words Register Space for Peripherals
· Upgradable firmware through USB/Flash interface
◆ Memory interface:
· External up to 4(cs) x 64M-4G bytes Nand type Flash accessed by DMA
· Support both 8-bit (X8 device) and 16-bit (X16 device) IO bus
· support Toshiba/ Hynix/ Infineon/ Micron/ ST Nand flash memory
· Support 2048+64 / 512+16 bytes per page
· Support various Samsung SmartMedia Cards and their listed commands
· Support SDRAM
· Support SD/MMC
◆ Video Driver: Support TFT LCD/ OLED Interface
◆ Pulse Width Modulators for EL backlights
◆ Support watchdog timer
◆ DSP-based Software:
· MPEG1/2/2.5 Audio Layer 1, 2, 3 decoding, Layer3 encoding
· WMA 9 decoding (RK2608A only)
· G.729 based voice recording and playback
· Equalizer (RK2608A only)
· MPEG-4 @QVGA decoding
· Digital photo frame application software (RK2609A only)
◆ Headphone driver output 2x9mW @32 Ohm(TYP) ; SNR: 90dB (DAC TYP)
· Low Power Consumption, <100mW at typical MP3 decoder solution
2. PIN Description
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 VDDA P
2 RREF I
3 AGND P
4 DM A I/O
5 DP A I/O
6 VCCA P
7 D0 I/O Pull up Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 0
Analog 1.8V power output, Connect one external 10uF CAP
Reference Resistor input
Analog GND
USB data minus
USB data plus
Analog 3.3V power input
8 D1 I/O Pull up
9 D2 I/O Pull up
10 D3 I/O Pull up
11 D4 I/O Pull up
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 1
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 2
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 3
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 4
- 37 -
Page 42

12 D5 I/O Pull up
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 5
13 D6 I/O Pull up
14 D7 I/O Pull up
15 RD/BY I, Pull up
16 FREN O
17 FWEN O
18 FWP O
19 VDD P
20 VSSD P
21 VCC P
22 P2.4/A0 I/O
23 P2.5/A1 I/O
24 P2.6/A2 I/O
25 P2.7/A3 I/O
26 A4 O
27 A5 O
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 6
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 7
Flash ready/busy signal
Flash read enable
Flash write enable
Flash write protect
Digital Core power(1.8V)
Digital Core Ground
I/O POWER(3.3V)
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 0 GPIO
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 1 GPIO; FALE/LCDRS
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 2 GPIO; FCLE
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 3 GPIO
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 4
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 5
28 A6 O
29 A7 O
30 A8 O
31 A9 O
32 A10 O
33 A11 O
34 A12 O SDRAM Address Bit 12 SRAM Address Bit 11
35 BA0 O SDRAM Bank Address 0 SRAM Address Bit 12
36 BA1 O SDRAM Bank Address 1 SRAM Address Bit 13
37 CKE O SDRAM clock enable to SDRAM
38 CLK O system clock to SDRAM
39 P2.8/WEN I/O
40 P2.9/CASN I/O
41 P2.10/RASN I/O
42 P2.11/CSN I/O
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 6
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 7
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 8
SDRAM/ SRAM Address Bit 9
SDRAM Address Bit 10
SDRAM Address Bit 11 SRAM Address Bit 10
SDRAM write enable GPIO
SDRAM column address strobe GPIO
SDRAM row address strobe GPIO
SDRAM chip strobe GPIO
43 P2.13/PWM0 I/O GPIO/ PWM output0
44 P2.0/SDDO I/O
- 38 -
SD/MMC Data output, Rock2 as input Connect to SD/MMC
SDDO
Page 43

45 P2.1/SDDI I/O
46 P2.2/SDCLK I/O SD/MMC Clock output
47 P2.3/SDCS I/O SD/MMC chip select output
SD/MMC Data input, Rock2 as output Connect to SD/MMC
SDDI
48 VCC P
49 VSSD P
50 VDD P
51 P0.0 I/O Pull up
52 P0.1 I/O Pull up
53 P0.2 I/O Pull up GPIO, External int2
54 P0.3 I/O Pull up GPIO, External int3
55 P0.4
56 P0.5
57 P0.6
58 P0.7
59
60
61
62
P1.1/ I2C_SDA I/O Pull up & EN
P1.2/ I2C_SCL I/O Pull up & EN
P1.3/ I2SMCLK I/O Pull up & EN
P1.4 DAC_LRCK I/O Pull up & EN
I/O Pull up & EN
I/O Pull up & EN
I/O Pull up & EN
I/O Pull up & EN
GPIO, I2SMCLK of External CODEC
GPIO, DAC LRCK of External CODEC
I/O POWER(3.3V)
Digital Ground
Digital Core power(1.8V)
GPIO, External int0
GPIO, External int1
GPIO
GPIO
GPIO
GPIO
GPIO, External SDA of I2C
GPIO, External SCL of I2C
63
64
65
66 AIL1 I L-channel single-end input 1
67 AIR1 I R-channel single-end input 1
68 AIL2 I L-channel single-end input 2
69
70
71 IREF O Bias current reference of CODEC
72 VCOM O Internal biasing voltage for CODEC
73 VSSA P Negative power supply for CODEC
74 VDDA P Positive power supply for CODEC
75 AOL O L-channel single ended analog output
76 VSSAO P
77 AOM O Common mode analog output
P1.5/ ADC_LRCK I/O Pull up & EN
P1.6/ SDI I/O Pull up & EN GPIO, SDI Data input Connect to SDO of External CODEC
P1.7/ SDO
AIR2 I R-channel single-end input 2
MIC
I/O Pull up & EN GPIO, SDO Data output Connect to SDI of External CODEC
I Mic single-end analog input
GPIO, ADC LRCK of External CODEC
Negative power supply to output amplifiers
- 39 -
Page 44
78 AOMS I Common mode sense input
79 VDDAO P Positive power supply to output amplifiers
80 AOR O R-channel single ended analog output
81 HP_SENSE I Sense of jack insertion
82 VDD P
83 VCC P
84 VSSD P
85 IBOOT I, Pull up Boot select,
86 DQM0 O SDRAM DQM0
87 DQM1 O SDRAM DQM1
88 VSSD G LDO37 ground
89 VBAT42 P LDO37 Power input
90 VDD37 P LDO37 voltage output
91 SENSE I DCDC voltage sense input
92 PVSS G DCDC power ground
93 LX O DCDC switch output
94 PVDD P DCDC power supply
95 VDDD P DCDC power
96 VSS G DCDC ground
Digital Core power(1.8V)
I/O POWER(3.3V)
Digital Ground
97 CP O DCDC frequency compensation
98 FB I DCDC feedback input
99 VBAT42 P LDO33 Power input
100 VCC33 P LDO33 Voltage output
101 VSSD G LDO33 ground
102 VCCA P ADC 3.3V power input
103 REXT100K I
104 LRADC3 I Low resolution ADC input3
105 LRADC2 I Low resolution ADC input2
106 LRADC1 I Low resolution ADC input1
107 LRADC0 I Low resolution ADC input0
108 VDDPLL P Analog power of PLL
109 VSSPLL P Analog GND of PLL
110 XIN I, OSC
ADC reference Resistor input
Crystal 24MHz OSC input PAD
- 40 -
Page 45
111 XOUT O, OSC Crystal 24MHz OSC output PAD
112 VDD P
113 VSSD G
114 VCC P
115 RESET I, Pull up System reset pin, low enable
116 TEST I, Pull down Test mode
117 D8/P3.0 I/O
118 D9/P3.1 I/O
119 D10/P3.2 I/O
120 D11/P3.3 I/O
121 D12/P3.4 I/O
122 D13/P3.5 I/O
123 D14/P3.6 I/O
124 D15/P3.7 I/O
125 LCDRDN O LCD Read execution pin
126 LCDWRN O LCD Write execution pin
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 10 GPIO
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 11 GPIO
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 12 GPIO
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 13 GPIO
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 14 GPIO
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 15 GPIO
Digital Core power(1.8V)
Digital Ground
I/O POWER(3.3V)
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 8 GPIO
Flash/ LCD/ SDRAM data bus bit 9 GPIO
127 LCDCSN O LCD driver chip select
128 FCE0 O Flash chip select 0
3.5.3 Function introduction to RT9284B
1. Description
The RT9284A/B is a compact, high efficient and high integration LED driver. Internal 22V MOSFET can
support 2 to 5 White LEDs for backlighting and camera flashing.
Highly integration and internal compensation network minimizes as 5 external component counts.
Optimized operation frequency can meet the requirement of small LC filters value and low operation current
with high efficiency. Internal soft start function can reduce the inrush current. Tiny package type of TSOT-23-5
and TSOT-23-6 packages provide the best solution for PCB space saving and total BOM cost.
2. Features
◆ VIN Operating Range : 2.7V to 5.5V
◆ Maximum Output Voltage up to 20V
◆ Dimming with Zero-inrush and Wide Frequency Range of 100 to 100kHz
◆ Over Voltage Protection
◆ Output Current up to 100mA at VOUT = 12V.
◆ Zero Shutdown Supply Current
◆ Minimize the External Component
- 41 -
Page 46

◆ Small LC Filter
◆ Internal Soft Start
◆ RoHS Compliant and 100% Lead (Pb)-Free
3. PIN Description
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 LX O
2 GND
3
4
5
6
FB
EN
OVP
VDD
I
I
I
I Supply Input Voltage Pin
Feedback Reference Voltage Pin
Switch Pin
Ground Pin
Chip Enable (Active High)
over voltage protection
3.5.4 Function introduction to MCP73832
1. Description
The MCP73831/2 devices are highly advanced linear charge management controllers for use in
space-limited, cost-sensitive applications. The MCP73831/2 are available in an 8-Lead, 2 mm x 3 mm DFN
package or a 5-Lead, SOT23 package. Along with their small physical size, the low number of external
components required make the MCP73831/2 ideally suited for portable applications. For applications
charging from a USB port, the MCP73831/2 adhere to all the specifications governing the USB power bus.
The MCP73831/2 employ a constant-current/constantvoltage charge algorithm with selectable
preconditioning and charge termination. The constant voltage regulation is fixed with four available options:
4.20V, 4.35V, 4.40V or 4.50V, to accommodate new, emerging battery charging requirements. The constant
current value is set with one external resistor. The MCP73831/2 devices limit the charge current based on die
temperature during high power or high ambient conditions. This thermal regulation optimizes the charge cycle
time while maintaining device reliability.
2. Features
◆ Linear Charge Management Controller:
· Integrated Pass Transistor
· Integrated Current Sense
· Reverse Discharge Protection
◆ High Accuracy Preset Voltage Regulation: + 0.75%
◆ Four Voltage Regulation Options:
· 4.20V, 4.35V, 4.40V, 4.50V
◆ Programmable Charge Current
◆ Selectable Preconditioning
◆ Selectable End-of-Charge Control
- 42 -
Page 47

◆ Charge Status Output
· Tri-State Output - MCP73831
· Open-Drain Output - MCP73832
◆ Automatic Power-Down
◆ Thermal Regulation
◆ Temperature Range: -40°C to +85°C
◆ Packaging:
· 8-Lead, 2 mm x 3 mm DFN
· 5-Lead, SOT23
3.5.5 Function introduction to TEA5767HN
1. Description
The TEA5767HN is a single-chip electronically tuned FM stereo radio for low-voltage application with fully
integrated IF selectivity and demodulation. The radio is completely adjustment-free and only requires a
minimum of small and low cost external components. The radio can be tuned to the European, US and
Japanese FM bands.
2. Features
◆ High sensitivity due to integrated low-noise RF input amplifier
◆ FM mixer for conversion to IF of the US/Europe (87.5 to 108 MHz) and Japanese (76 to 91MHz) FM
band
◆ Preset tuning to receive Japanese TV audio up to 108 MHz
◆ RF Automatic Gain Control (AGC) circuit
◆ LC tuner oscillator operating with low cost fixed chip inductors
◆ FM IF selectivity performed internally
◆ No external discriminator needed due to fully integrated FM demodulator
◆ Crystal reference frequency oscillator; the oscillator operates with a 32.768 kHz clock crystal or with a
13 MHz crystal and with an externally applied 6.5 MHz reference frequency
◆ PLL synthesizer tuning system
◆ I2C-bus and 3-wire bus, selectable via pin BUSMODE
◆ 7-bit IF counter output via the bus
◆ 4-bit level information output via the bus
◆ Soft mute
◆ Signal dependent mono to stereo blend [Stereo Noise Cancelling (SNC)]
◆ Signal dependent High Cut Control (HCC)
◆ Soft mute, SNC and HCC can be switched off via the bus
◆ Adjustment-free stereo decoder
◆ Autonomous search tuning function
- 43 -
Page 48

◆ Standby mode
◆ Two software programmable ports
◆ Bus enable line to switch the bus input and output lines into 3-state mode
◆ Automotive temperature range (at VCCA, VCC(VCO) and VCCD = 5 V).
3. PIN Description
PIN No. Symbol I/O Description
1 n.c. not connected
2 CPOUT O charge pump output of synthesizer PLL
3 VCOTANK1 O voltage controlled oscillator tuned circuit output 1
4 VCOTANK2 O voltage controlled oscillator tuned circuit output 2
5 VCC(VCO) P voltage controlled oscillator supply voltage
6 DGND digital ground
7 VCCD P digital supply voltage
8 DATA I/O bus data line input/output
9 CLOCK I bus clock line input
10 n.c. not connected
11 WRITE/READ I write/read control input for the 3-wire bus
12 BUSMODE I bus mode select input
13 BUSENABLE I bus enable input
14 SWPORT1 software programmable port 1
15 SWPORT2 software programmable port 2
16 XTAL1 I crystal oscillator input 1
17 XTAL2 I crystal oscillator input 2
18 PHASEFIL phase detector loop filter
19 PILFIL pilot detector low-pass filter
20 n.c. not connected
21 n.c. not connected
22 VAFL O left audio frequency output voltage
23 VAFR O right audio frequency output voltage
24 TMUTE I time constant for soft mute
25 MPXO O FM demodulator MPX signal output
26 Vref P reference voltage
27 TIFC I time constant for IF centre adjust
28 LIMDEC1 I decoupling IF limiter 1
- 44 -
Page 49

29 LIMDEC2 I decoupling IF limiter 2
30 n.c. not connected
31 n.c. not connected
32 Igain I gain control current for IF filter
33 AGND analog ground
34 VCCA P analog supply voltage
35 RFI1 I RF input 1
36 RFGND RF ground
37 RFI2 I RF input 2
38 TAGC time constant RF AGC
39 LOOPSW switch output of synthesizer PLL loop filter
40 n.c.
not connected
3.5.6 Function introduction to XC6206P152MR
1. Description
The XC6206 series are highly precise, low power consumption, high voltage, positive voltage regulators
manufactured using CMOS and laser trimming technologies. The series provides large currents with a
significantly small dropout voltage.
The XC6206 consists of a current limiter circuit, a driver transistor, a precision reference voltage and an
error correction circuit.
The series is compatible with low ESR ceramic capacitors. The current limiter's foldback circuit also
operates as a short protect for the output current limiter and the output pin.
Output voltage can be set internally by laser trimming technologies. It is selectable in 0.1V increments
within a range of 1.2V to 5.0V.
SOT-23 (250mW) and SOT-89 (500mW) packages are available.
2. Features
◆ Maximum Output Current : 250mA (5.0V type)
◆ Dropout Voltage : 160mV @ 100mA (5.0V type)
◆ Maximum Operating Voltage : 6.0V
◆ Output Voltage Range : 1.2V ~ 5.0V (selectable in 0.1V steps)
◆ Highly Accurate : ± 2%
◆ Low Power Consumption : Typ. 1.0µA
◆ Operational Temperature Range : -40OC ~ 85OC
◆ Ultra Small Packages : SOT-23 (250mW), SOT-89 (500mW)
◆ Low ESR Capacitor : Ceramic compatible
- 45 -
Page 50

3.5.7 Function introduction to K9G8G08U0M
1. Description
Offered in 2Gx8bit, the K9LAG08U0M is a 16G-bit NAND Flash Memory with spare 512M-bit. Its NAND
cell provides the most costeffective solution for the solid state mass storage market. A program operation can
be performed in typical 800μs on the 2,112-byte page and an erase operation can be performed in typical
1.5ms on a (256K+8K)byte block. Data in the data register can be read out at 30ns(K9MCG08U5M:50ns)
cycle time per byte. The I/O pins serve as the ports for address and data input/output as well as command
input. The on-chip write controller automates all program and erase functions including pulse repetition,
where required, and internal verification and margining of data. Even the write-intensive systems can take
advantage of the K9LAG08U0M′s extended reliability of 5K program/erase cycles by providing ECC(Error
Correcting Code) with real time mapping-out algorithm. The K9LAG08U0M is an optimum solution for large
nonvolatile storage applications such as solid state file storage and other portable applications requiring
non-volatility.
2. Features
◆ Voltage Supply : 2.7 V ~ 3.6 V Organization
- Memory Cell Array : (2G + 64M)bit x 8bit
- Data Register : (2K + 64)bit x8bit
◆ Automatic Program and Erase
- Page Program : (2K + 64)Byte
- Block Erase : (256K + 8K)Byte
◆ Page Read Operation
- Page Size : (2K + 64)Byte
- Random Read : 60μs(Max.)
- Serial Access : 30ns(Min.)
*K9MCG08U5M : 50ns(Min.)
◆ Memory Cell : 2bit / Memory Cell
◆ Fast Write Cycle Time
- Program time : 800μs(Typ.)
- Block Erase Time : 1.5ms(Typ.)
◆ Command/Address/Data Multiplexed I/O Port
◆ Hardware Data Protection
- Program/Erase Lockout During Power Transitions Reliable CMOS Floating-Gate Technology
- Endurance : 5K Program/Erase Cycles(with 4bit/512byte ECC)
- Data Retention : 10 Years
◆ Command Register Operation
◆ Unique ID for Copyright Protection
3. PIN Description
- 46 -
Page 51

Pin Name Pin Function
I/O0 ~ I/O7
CLE
ALE
CE / CE1
CE2
RE
DATA INPUTS/OUTPUTS
The I/O pins are used to input command, address and data, and to output data during read operations. The I/
O pins float to high-z when the chip is deselected or when the outputs are disabled.
COMMAND LATCH ENABLE
The CLE input controls the activating path for commands sent to the command register. When active high,
commands are latched into the command register through the I/O ports on the rising edge of the WE signal.
ADDRESS LATCH ENABLE
The ALE input controls the activating path for address to the internal address registers. Addresses are
latched on the rising edge of WE with ALE high.
CHIP ENABLE
The CE / CE 1 input is the device selection control. When the device is in the Busy state, CE / CE1 high is
ignored, and the device does not return to standby mode in program or erase operation.
Regarding CE / CE1 control during read operation , refer to ’Page Read’ section of Device operation
CHIP ENABLE
The CE2 input enables the second K9LAG08U0M
READ ENABLE
WE
WP
R/B / R/B1
Vcc
Vss
N.C
The RE input is the serial data-out control, and when active drives the data onto the I/O bus. Data is valid
tREA after the falling edge of RE which also increments the internal column address counter by one.
WRITE ENABLE
The WE input controls writes to the I/O port. Commands, address and data are latched on the rising edge of
the WE pulse.
WRITE PROTECT
The WP pin provides inadvertent program/erase protection during power transitions. The internal high voltage generator is reset when the WP pin is active low.
READY/BUSY OUTPUT
The R/B / R/B1 output indicates the status of the device operation. When low, it indicates that a program,
erase or random read operation is in process and returns to high state upon completion. It is an open drain
output and does not float to high-z condition when the chip is deselected or when outputs are disabled.
POWER VCC is the power supply for device.
GROUND
NO CONNECTION Lead is not internally connected.
- 47 -
Page 52

Chapter Four
Assembly and disassembly process
In order to get to know the structure of V7 more easily and directly, now we use pictures to present
each key point of assembly and disassembly process to all users to prevent users from operating blindly
and damaging elements. So, we hope you can operate according to the instructions strictly.
Note All operations must be with strict anti-static measures, operators must wear anti-static
gloves or wrist ring, electric screwdriver must be grounded effectively and articles, such as nippers must
remove static before using !
4.1 Disassembly process of the player
1. Use electric screwdriver or "+” shaped
screwdriver to take out two stainless steel
screws of two sides of USB interface;
3.Take out bottom cover;
2. Use nail to force from gap of middle and bottom
casing, disassemble bottom casing and the player;
4. Take out battery from main board, pay attention to
glue of rear side of battery;
- 48 -
Page 53

5. Use electric screwdriver or"+” shaped
screwdriver to take out four screws of
main board.
6. Separate middle cover and surface cover, do not
damage the six clamps shown in the figure.
7.Use electric screwdriver or "+” shaped
screwdriver to take out two screws of main
board;
8. Take out main board from surface board,
do not damage each terminal;
4.2 Assembly process of the player
Assembly process of the player is similar with disassembly process, and only the sequence is reverse.
- 49 -
Page 54

Chapter Cinque
PCB board & Circuit diagram
Section One Circuit diagram
FM_3V3
R56
22R
C81
104
FM_3V3
SGND
FM_ANT1
FM_ANT
O603CS
L22
33nH±2%
MURATA
COILCRAFT OR
TOKO SMD
LLQ1608-A33NG
C78 103
L23
33nH±2%
MURATA
COILCRAFT OR
TOKO SMD
LLQ1608-A33NG
C68 101
O603CS
MURATA
COILCRAFT
TOKO SMD
LLQ1608-AR10G
D3
BB202
D4
BB202
FM_3V3
R58
22R
SGND
C90
104
L21
120nH
SGND
C69 27PF
C71
47PF
R54
100K
SGND
R53
10K
C76
393
L28
1
N.C
2
CPOP
3
VCOT1
4
VCOT2
5
VCOVCC
6
DGND
7
DVCC
8
DATA
9
CLOCK
10
N.C
L27 601/0402
601/0402
C70
472
40
N.C
RFI1
RFI2
TCAGC
RFGND
LOOPSW
TEA5767HN
NECTAR-IO603CS
W/R
BUSM
BUSEN
SWP1
SWP2
XTAL1
111213141516171819
SGND
FM_3V3
I2C_SCL 2
I2C_SDA 2
AVCC
XTAL2
AGND
PDLF
R52 18K
313233343536373839
N.C
IFGAI
DIFL2
DIFL1
TCIFC
VREF
MPXO
TMUTE
RAVO
LAVO
PHLF
N.C
20
R51
10R
C72
475/X5R
N.C
N.C
C73 473
C74 473
U6
SGND
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
XT1
32.768KHz
OR 13MHz
CRYSTAL
SGND SGND
C77 333
C85
102
C75 473
C79 333
L24
L25
C87
22PF
SGND
R57
33K
C88
223
SGND
SGND
SGND
SGND
SGND
601/0402
601/0402
SGND
C86
223
SGND
C80 105/X5R
C82 105/X5R
C89
102
FM_OUTR 1
FM_OUTL 1
VCC33A
D_GND
L26 10UH/2012
R55
0R
C83
106/X5R
SGND
SGND
FM_3V3
C84
104
- 50 -
Page 55

VCC
USB_VBUS3
BAT+
EN
USB_VBUS
P_GND
VBUS
R60 10K
R63
C93
475/X5R
+5V VB
R62
10K/47K
BAT+
1K
Q8
MMST3904
GND
U7 MCP73832 DFN8
1
V_IN
2
3
4 5
PROG
V_IN
BAT
BAT STATE
D5 BAT43WS
D7
MMBD4148CC
R61 100R
8
7
NC
6
VSS
G
G
P_GND
VCC
R64 3.3K
P_GND
DS
Q6
SI2305DS SOT23
Q7
SI2305DS SOT23
D S
BAT+
C92
105/X5R
GND
R66
47K
BAT+
CHG_OK 2
R59
100K
D6
D10
PLAY/PAUSE2
1N4148WS
SFI0402-050E100NP
CN3
1
BAT
2
R67
START
R68 10K
47K
PLAY
C91
GND
BAT+
Q9
MMST3906
START
1N4148WS
L29
601/0402
S7
PLAY
GND
VCC
R65
100K
R69 100K
D8 MMBD4148CC
EN
VCC
U8 XC6206P152
2
VI
GND
1
D_GND
VOUT
R77 100K
3
VCC1V8 2
C95
104
P_GND
R70
5.6M
OFF2
D9 1N4148WS R72 10K
R73
10K
START
GND
D_GNDP_GND
GND
R76 1M
R74
100K
Q11
MMST3904
GND
R75
2M
GNDGND
C94
475/X5R
Q10
SS8050LT
R71
470K
GNDGND
- 51 -
Page 56

CN1
2
5
6
3
7
4
1
2SJ-0890-A02 USB/HPOUT
FM_ANT
L1 601
L2 601
FM_ANT
R3 0R
OUTL
5
OUTR
HP_OUTR
R1
10R
C1
104
HP_OUTL
HP_OUTR
R2
10R
C2
104
HP_OUTL
J1
+5V
NC
D+
GND
IN_L
IN_R
GND
3DU05S-32T-10
R12
1M
D_GND
L3 601
L4 601
USB_DM
USB_DP
2
2
104
C96
VCC
FM_ANT
L30
601/0402
R7
100K
R11
470K
Q1
MMST3904
C6
106/X5R
MIC1
MICROPHONE
1
2
R14
47K
R8
2.2K
C8
221
C7 104
MIC
MIC
1 6
RCLAMP0504F/SC-70 6L
GND
D_GND
SFI0402-050E100NP
C5
1
2
D-
3
4
5
6
7
8
L5 680
C9
SFI0402-050E100NP*
D_GND
R5
470R
SS8550LT
Q2
C10
SFI0402-050E100NP*
D_GND
D1
2
3 4
C4
104
+5V
AOM
AOMS
D_GND
R4
12K
R6
10K
USB_VBUS2
C3
104
USB_DET
R9
R10 0R
USB_DET 2
0R
R13
1M
D_GND
D_GNDD_GND
D_GND
- 52 -
Page 57

GND
VDD
D_GND
VCC
GND
C62
104
R46
100K
C56
GND
+
C35
106/X5R
R44
220K
R48
1M
VCC_SDRAM
104
GND
GND
C67
D_GND
104
GND
C36
103
C42
104
C46 104
C58 104
FALE/RS/A1
FCLE/A2
104
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
DQM0
WEN
CASN
RASN
CSN
BA0
BA1
A10
A0
A3
20PF/NPO
C24
+
106/X5R
C26
USB_DM
USB_DP
VDDD
VCC
XOUT
C13
R22 10K
2
2
VCC
SS8050LT
D_GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
D_GND
FALE/RS/A1
FCLE/A2
R45
10K
Q5
U3
VDD
DQ0
VDDQ
DQ1
DQ2
VSSQ
DQ3
DQ4
VDDQ
DQ5
DQ6
VSSQ
DQ7
VDD
DQM0
WEN
CASN
RASN
CS
BA0
BA1
A10AP
A0
A1
A2
A3
VDD
SDRAM
R15 1M
Y1
24MHz
DM
DP
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
RD/BY
FREN
FWEN
FWP
A0
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
R47 1K
C65
104
HY57V641620ETP
VSS
DQ15
VSSQ
DQ14
DQ13
VDDQ
DQ12
DQ11
VSSQ
DQ10
DQ9
VDDQ
DQ8
VSS
NC
DQM1
CLK
CKE
A12
A11
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
VSS
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
RESETN
20PF/NPO
D_GND
U1
VDDA
RREF
AGND
DM
DP
VCCA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
RD/BY
FREN
FWEN
FWP
VDD
VSSD
VCC
P2.4/A0
FALE/RS/A1
FCLE/A2
P2.7/A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
33
A11
R50 33R
54
53
52
51
50
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
XIN
C14
LCDWRN
FCE0
LCDCSN
127
126
128
FCE0
LCDCSN
BA0
BA1
CKE
A12
34
353637
38
CLK
A12
BA0
CKE
BA1
C66
6P
D_GND
D15
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9
D8
DQM1
CLK#
CKE
A12
A11
A9
A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
LCDRDN
D9
D8
D11
D10
D14
D13
D12
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
P3.1/D9
LCDRDN
P3.2/D10
P3.3/D11
P3.4/D12
P3.5/D13
P3.6/D14
P3.7/D15
LCDWRN
P2.8/WEN
P2.9/CASN
P2.10/RASN
P2.11/CSN
P2.13/PWM0
P2.0/SDDO
P2.1/SDDI
CLK
P2.2/SDCLK
3940414243444546474849
WEN
RASN
CASN D15
CSN
FCE1
LCD_REST
BACK_EN
VCC
C54
104
CLK#CLK
D_GND
C11
104
GND
VDDD
C18
105/X5R
GND
XOUT
XIN
111
112
113
114
VDD
VCC
VSSD
XOUT
RESETN
RK2606
VSSD
VDD
50
DFU
C55
104
C57
104
C61
104
VDD_PLL
BATT
C12
104
2
2
VCC1V8
BAT_DET
CHG_OK
106
105
107
109
110
108
XIN
VSSPLL
VDDPLL
LRADC1
LRADC0
P0.0
P0.1
P0.2
51
52
5355565758
PREV
NEXT
VDDD
R16
100K±1%
R18 100K±1%
100K±1%
CHG_OK
GND
VCC
LCD_SEL
104
101
103
102
VSSD
VCCA
LRADC2
LRADC3
REXT100K
P0.4
P0.3
54
VOL+
VOL-
R19
P0.5
MENU
GND
VCC
GND
100
P0.6
PLAY/PAUSE
2
DFU
NEXT
PREV
VOL+
VOL-
MENU
106/X5R
VCC33
OFF
2
2
C20
+
P0.7
59
I2C_SDA
VB
C21
+
106/X5R
GND
99
VBAT42
P1.1/I2C_SDA
P1.2/I2C_SCL
P1.3/I2SMCLK
P1.4/DAC_LRCLK
6061626364
I2C_SCL
2
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
2
R80 4.7K
R81 4.7K
R82 4.7K
R83 4.7K
R84 4.7K
R85 4.7K
98
HP_SENSE
P1.5/ADC_LRCLK
P1.6/SDI
USB_DET
USB_DET
1K
FB
SENSE
VCC37
VBAT42
IBOOT
VDDAO
AOMS
VSSAO
VCOM
P1.7/SDO
R32
C22 47P
C23 101
97
CP
VSS
VDDD
PVDD
LX
PVSS
VSSD
DQM1
DQM0
VSSD
VCC
VDD
AOR
AOM
AOL
VDDA
VSSA
IREF
MIC
AIR2
AIL2
AIR1
AIL1
VDDO
C98
GND
C99
GND
C100
GND
C101
SFI0402-050E100NP
GND
C102
SFI0402-050E100NP
GND
C103
SFI0402-050E100NP
GND
R21 330K
96
GND
95
94
93
92
GND
91
VCC37
90
89
88
DQM1
87
DQM0
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
AOMS
78
AOM
77
76
75
74
73
72
71
MIC
70
69
68
67
66
65
Q4
SI2305DS SOT23
R29
100K
S1
A_B/REC
SFI0402-050E100NP
S2
NEXT
SFI0402-050E100NP
S3
PREV
SFI0402-050E100NP
S4
VOL+
S5
VOL-
S6
MENU
VDDO
C19
0R
C33
C34
104
106/X5R
GND
GND
L14 CDRH2D11-470
R23 1K
R24 10K
R25 2R2
C41
106/X5R
C43
GND
104
VCC
HP_OUTR 2
AOMS 2
AOM 2
HP_OUTL 2
MIC 2
R27
FM_OUTR 2
56K±1%
FM_OUTL 2
VDDAO
I2C_SCL
2
I2C_SDA
2
GND
L13 601
C37
106/X5R
GND
C44
104
VDDD
GND
C50
C49
+
106/X5R
GND
104
I2C_SCL
I2C_SDA
VCC
RESETN
115
116
TEST
P3.0/D8
128-Pin TQFP
P2.3FCE1/SDCS
VCC
GND
D_GND
D_GND
VCC37
10K
L15 601
C38
104
GND
VB
C47
106/X5R
R35
I2C_SDA
I2C_SCL
R26
2.2K
C48
+
VCC
R36
10K
VCC_FLASH
- 53 -
C39
47uF/6.3v
GND
C45
+
106/X5R
GND
L17
601/0402
104
R40 0R
R41 0R
C59 104
VDDVDDO
D_GND
C40
104
GND
L16
601/0402
VDDO
RD/BY
FALE/RS/A1
FREN
FCLE/A2
FWEN
FWP
VDDAO
VB
L18
106/X5R
U5
1
RES#
2
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
R/B2
7
R/B1
8
RE
9
CE1
10
CE2
11
NC
12
VCC
13
VSS
14
NC
15
NC
16
CLE
17
ALE
18
WE
19
WP
20
NC
21
NC
22
NC
23
NC
24 25
NC NC
NAND FLASH
VDD
VDD
L6 601/0402*
L7 601/0402
L8 601
C15
C16
104*
GND
VCC
VCC
L9 601/0402
L10 601/0402
L11 601
L12 601/0402
C25
47uF/6.3v
GND
CN2
VCC1V8
R86
10K*
LCD_SEL
R87 4.7K*
R88
47K*
D_GND
32pin
601
BACK_EN
C52
48
NC
47
NC
46
NC
45
NC
D7
44
I/O7
D6
43
I/O6
D5
42
I/O5
D4
41
I/O4
40
NC
39
NC
R42 0R
38
PRE
37
VCC
36
VSS
35
NC
34
NC
33
NC
D3
32
I/O3
D2
31
I/O2
D1
30
I/O1
D0
29
I/O0
28
NC
27
NC
26
NC
GND
L19 CDRH2D11-100
L31
C60
104
4
2
GNDENFB
U2
RT9284/RT9271
R37
47K
LXVCC
OVP
C63 104
R30 100R
R33
10K
VCC
601/0402
VCC_FLASH1
D_GND D_GND
D_GND
C17
104
104
D_GND
GND
C27
C28
104
104
GND
GND
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
176*220(RGB)
28
29
30
31
32
R28 0R
D2
MBR0520/SOD123
16
5
R31 0R
3
VCC_FLASH
R39
10K
R38
47K
RD/BY
FREN
FCE0
FCE1
GND
FCLE/A2
FALE/RS/A1
FWEN
FWP
R49
47K
D_GND
VCC1V8
C30
C29
104
106/X5R
GND
LED+
LED-
D_GND
LCD_3V3
LCDCSN
FALE/RS/A1
LCDWRN
LCDRDN
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
D_GND
LCD_3V3
D_GND
C51
102/25V
R34
12R±1%
D_GND
U4
1
RES#
2
NC
3
NC
4
NC
5
NC
6
R/B2
7
R/B1
8
RE
9
CE1
10
CE2
11
NC
12
VCC
13
VSS
14
NC
15
NC
16
CLE
17
ALE
18
WE
19
WP
20
NC
21
NC
22
NC
23
NC
24 25
NC NC
NAND FLASH
C31
106/X5R
GND
L20 0R/0603
C53
106/25V/1206
NC
NC
NC
NC
I/O7
I/O6
I/O5
I/O4
NC
NC
PRE
VCC
VSS
NC
NC
NC
I/O3
I/O2
I/O1
I/O0
NC
NC
NC
VCC1V8
VDD_PLL
VDDD
VCC_FLASH
LCD_3V3
VCC33A
VCC_SDRAM
C32
104
GNDGND
R78 0R
R79 0R*
NAND FlashNAND Flash
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
R43 0R
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
LED+
D7
D6
D5
D4
VCC_FLASH2
D3
D2
D1
D0
RESETN
LCD_REST
LED-
LED+
VCC
L32
601/0402
C64
C97
104
104
Page 58
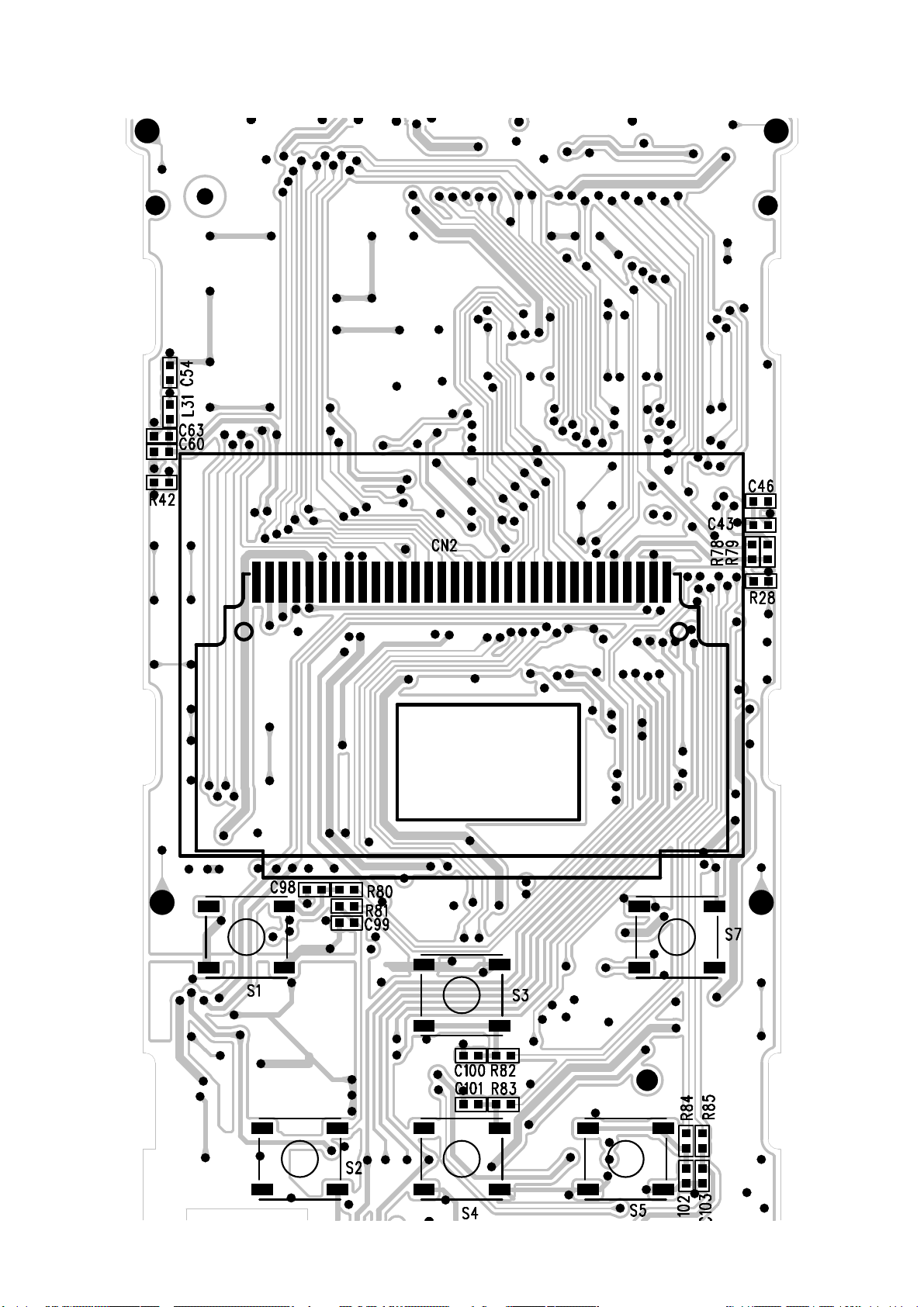
Section Two PCBboard
Surface layer of Main Board
- 54 -
Page 59

Bottom layer of Main Board
- 55 -
Page 60
Chapter six BOM List
BATTERY PROTECT BOARD 5448893
MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION
0090354 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 470O±5% 0402 R1
0090368 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2K±5% 0402 R2
0310480 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 104±10% 5R 0402 C1,C2,C3
0790065 SMD FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR ECH8601 TSSOP
0790090 SMD FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR ECH8601R TSSOP
0882570 IC S-8261AANMG22 SO23-6 U1
1633305 PCB E29-0
U2 ①
U2 ①
V7H(RU) BLACK[2606]
MAINBOARD 2V7-1 4940266
MATERIAL CODE MATERIAL NAME SPECIFICATIONS LOCATION
0090324 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0402 R3,R9,R10,R28,R31,R40,R41,R42,R43,R55,R78,C19
0090046 SMD RESISTOR 1/10W 470O±5% 0805 R5
0090037 SMD RESISTOR 1/10W 2.2O±5% 0805 R25
0090326 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10O±5% 0402 R1,R2,R51
0090830 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 1/1612O±1% 0402 R34
0090447 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 22O±5% 0402 R56,R58
0090330 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 33O±5% 0402 R50
0090339 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100O±5% 0402 R30,R61
0090362 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1K±5% 0402 R23,R32,R47,R62
0090369 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2.2K±5% 0402 R8,R26
0090373 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 3.3K±5% 0402 R64
- 56 -
Page 61

0090377 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 4.7K±5% 0402 R80,R81,R82,R83,R84,R85,R87
SMD PRESS SENSITIVITY RESISTOR
SMD PRESS SENSITIVITY RESISTOR
0090385 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 10K±5% 0402 R6,R22,R24,R33,R39,R45,R53,R60,R63,R68,R72,R73,R35,R36
0090387 SMD RESISTOR 1/1612K±5% 0402 R4
0090390 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 18K±5% 0402 R52
0090396 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 33K±5% 0402 R57
0090400 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 47K±5% 0402 R14,R37,R38,R49,R66,R67,R88
0090402 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 56K±5% 0402 R27
0090408 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100K±5% 0402 R7,R29,R46,R54,R59,R65,R69,R74,R77
0090417 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 220K±5% 0402 R44
0090421 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 330K±5% 0402 R21
0090001 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 0O±5% 0603 L20
0090425 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 470K±5% 0402 R11,R71
0090433 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 1MO±5% 0402 R12,R13,R15,R48,R76
0090436 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 2MO±5% 0402 R75
0090443 SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 5.6MO±5% 0402 R70
0090509 PRECISION SMD RESISTOR 1/16W 100K±1% 0402 R16,R18,R19
1030029
1030033
0310503 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 6P±0.25P NPO 0402 C66
0310415 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 20P±5% NPO 0402 C13,C14
0310416 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 22P±5% NPO 0402 C87
0310418 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 27P±5% NPO 0402 C69
0310424 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 47P±5% NPO 0402 C71,C22
0310432 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 101±5% NPO 0402 C23,C68
0310435 SMD CAPACITOR 50V 221±5% NPO 0402 C8
SFI0402-050E100NP
S1005H180C100GPT 0402
C5,C91,C98,C99,C100,C101, C102, C103 ②
C5,C91,C98,C99,C100,C101, C102, C103 ②
- 57 -
Page 62
0310704 SMD CAPACITOR 25V 102±10% 7R 0402 C51,C85,C89
0310706 SMD CAPACITOR 25V 472±10% 7R 0402 C70
0310453 SMD CAPACITOR 25V 103±10% 7R 0402 C36,C78
0310455 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 223±10% 7R 0402 C86,C88
0310710 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 333±10% 5R 0402 C77,C79
0310711 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 393±10% 5R 0402 C76
0310712 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 473±10% 5R 0402 C73,C74,C75
C1,C2,C3,C4,C7,C11,C12,C16,C17,C26,C27,C28,C30,C32,C33,C
0310480 SMD CAPACITOR 10V 104±10% 5R 0402
0310790 SMD CAPACITOR
10V 104±20% 5R 0402
38,C40,C42,C43,C44,C46,C48,C50,C54,C55,C56,C57,C58,C59,C
60,C61,C62,C63,C64,C65,C67,C81,C84,C90,C95,C96,C97
③
C1,C2,C3,C4,C7,C11,C12,C16,C17,C26,C27,C28,C30,C32,C33,C
38,C40,C42,C43,C44,C46,C48,C50,C54,C55,C56,C57,C58,C59,C
60,C61,C62,C63,C64,C65,C67,C81,C84,C90,C95,C96,C97
③
0310776 SMD CAPACITOR 6.3V 105±20% 5R 0402 ? ?
0310662 SMD CAPACITOR 6.3V 105±10% 5R 0402
0310717 SMD CAPACITOR 6.3V 475±20% 5R 0603 C72,C93,C94
0310486 SMD CAPACITOR 6.3V 106±20% 5R 0805
0310831 SMD CAPACITOR
0310834 SMD CAPACITOR 16V 106±20% 5R 1206 C53
0310866 SMD CAPACITOR
0390142 SMD MAGNETIC BEADS FC1608-60102 L1,L2,L3,L4,L8,L11,L13,L15,L18
0390354 SMD MAGNETIC BEADS 68O/100MHz±25% 1608 L5
6.3V106±10%5R 0805 T≤0.85
6.3V 476 M X5R 1206 T≤1.6
- 58 -
C18,C80,C82,C92 ④
C18,C80,C82,C92 ④
C6,C20,C21,C24,C29,C31,C34,C35,C37,C41,C45,C47,C49,C52,
C83,C25 ⑤
C6,C20,C21,C24,C29,C31,C34,C35,C37,C41,C45,C47,C49,C52,
C83,C25 ⑤
C39
Page 63

0390388 SMD MAGNETIC BEADS 600O/100MHZ±25% 1005 L7,L9,L10,L12,L16,L17,L24,L25,L27,L28, L29,L30,L31,L32
0390221 SMD COIL THREAD INDUCTOR 33nH±2% 1608 L22,L23
0390398 SMD COIL THREAD INDUCTOR 120nH±2% 1608 L21
0390044 SMD INDUCTOR 10UH±10% 2012 L26
0390541 SMD CORES INDUCTOR 10uH ±20% 0.49A 7E03LAM L19
0390540 SMD CORES INDUCTOR 33uH ±20% 0.27A 7E03LAM L14
0700154 SMD TRIODE 14148WS SO323 D6,D9,D10
0700057 SMD DUAL DIODE MMBD4148CC SO23 D7,D8
0680077 SMD SCHOTTKY DIODE MBR0520 SOD123 D2
0700115 SMD TRANSFIGURATION DIODE BB202 D4,D3
0680074 SMD SCHOTTKY DIODE B43WS SO323 D5
0780300 SMD TRIODE SS8550LT SO323 Q2
0780298 SMD TRIODE MMS3904 SO323 Q1,Q8,Q11
0780299 SMD TRIODE SS8050LT SO323 Q5,Q10
0780293 SMD TRIODE MMS3906 SO323 Q9
0790041 SMD FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR SI2305DS SO23 Q4,Q6,Q7
1090080 ESD ELEMENT RCL0504 SC70-6L
1090084 ESD ELEMENT PLR0504P SC70-6L
0883370 IC MCP73832 DFN U7
0883477 IC R2606A LQFP U1
08825598 IC HY57V641620ETP-7 TSOP$ U3
0883456 IC K9LAG08U0M-PCBO TSOP U4
0883384 IC XC6206P152MR SOT-23 U8
- 59 -
D1 ⑥
D1 ⑥
Page 64
0882388 IC TE5767HN HVQFN U6
0883217 IC RT9284B-20PJ6E SOT23-6 U2
0960279 SMD CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 32.768KHz±20ppm SS6 12.5P XT1
1340174 LIGHT TOUCH SWITCH TS-1186-2(180 GRAM PUISSANCE) S1,S2,S3,S4,S5,S6,S7
1860140 USB SOCKET 3DG08S-30G-P J1
1980104 SMD EARPHONE SOCKET 2SJ-0890-03 CN1
1140082 MICROPHONE 44dB±3dB 4×1.2 WITH NEEDLE
1140105 MICROPHONE
0960278 SMD CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR 24MHz±30ppm 5032/4 20P Y1
1634135 PCB 2 7-1 FR4 D0.8×4 OSP
42dB±2dB 4×1.5 WITH NEEDLE MIC1 ⑦
MIC1 ⑦
- 60 -
 Loading...
Loading...