Page 1

RRSS--223322 // RRSS--442222 // RRSS--448855
Muullttii--IInntteerrffaaccee
M
EEtthheerrnneett SSeerriiaall SSeerrvveerrss
MMooddeellss:: EESSPP990011,, EESSPP990011EE,, EESSPP990022,, EESSPP990022EE
International Headquarters
B&B Electronics Mfg. Co. Inc.
707 Dayton Road
Ottawa, IL 61350 USA
Phone (815) 433-5100 -- General Fax (815) 433-5105
Website: www.bb-elec.com
Sales e-mail: orders@bb-elec.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb.elec.com
European Headquarters
B&B Electronics Ltd.
Westlink Commercial Park
Oranmore, Co. Galway, Ireland
Phone +353 91-792444 -- Fax +353 91-792445
Website: www.bb-europe.com
Sales e-mail: sales@bb-europe.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb-europe.com
© B&B Electronics – October 2005
-- Fax (815) 433-5109
-- Fax (815) 433-5104
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
Page 2

©
2004 B&B Electronics. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means,
electronic or mechanical, including photography, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system without written
consent. Information in this manual is subject to change without notice, and does not represent a commitment on the part
of B&B Electronics.
B&B Electronics shall not be liable for incidental or consequential damages resulting from the furnishing, performance, or
use of this manual.
All brand names used in this manual are the registered trademarks of their respective owners. The use of trademarks or
other designations in this publication is for reference purposes only and does not constitute an endorsement by the
trademark holder.
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
ii Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Park – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.co
Page 3

CHAPTER 4: USING ESP MANAGER........................................................ 21
TTaabbllee ooff CCoonntteennttss
TABLE OF CONTENTS ...................................................................................I
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION..................................................................... 1
FEATURES......................................................................................................... 2
COMMUNICATION MODES ................................................................................ 3
Direct IP Mode ............................................................................................ 3
Virtual COM Mode...................................................................................... 3
Paired Mode ................................................................................................ 4
Heart Beat.................................................................................................... 4
SERIAL SERVER QUICK START GUIDE .............................................................. 5
Hardware Setup........................................................................................... 5
Software Installation.................................................................................... 6
Serial Server Configuration......................................................................... 6
Install Virtual COM Ports on PC................................................................. 7
Check Communications ............................................................................... 7
CHAPTER 2: MAKING THE HARDWARE CONNECTIONS .................. 9
PACKAGE CHECKLIST ....................................................................................... 9
ESP901/ESP902 CONNECTIONS, INDICATORS AND RESET SWITCH ................. 9
Indicator Lights.......................................................................................... 10
Ethernet Connector.................................................................................... 10
Power Connector....................................................................................... 10
Reset Button............................................................................................... 10
DIP Switches.............................................................................................. 11
Serial Ports................................................................................................ 12
SERIAL SERVER/PORT OPERATIONAL MODES ................................................ 12
Default Mode ............................................................................................. 13
Console Mode............................................................................................ 13
Upgrade Mode........................................................................................... 13
RS-232 Mode.............................................................................................. 13
RS-422 Mode.............................................................................................. 14
RS-485 Mode.............................................................................................. 14
SERIAL SERVER SERIAL PORT CONNECTOR PIN-OUTS .................................... 15
CHAPTER 3: INSTALLING THE VLINX ESP SOFTWARE.................. 17
SOFTWARE INSTALLATION.............................................................................. 17
Automatic Installation................................................................................ 17
Manual Installation.................................................................................... 17
Updating an Existing Installation.............................................................. 19
Opening the ESP Manager ........................................................................ 20
SOFTWARE SETUP........................................................................................... 22
SOFTWARE OVERVIEW ................................................................................... 23
Menus......................................................................................................... 23
Server Icons Pane...................................................................................... 25
Serial Server / Virtual COM Lists.............................................................. 25
Status Bar................................................................................................... 26
SEARCH FOR SERVERS .................................................................................... 26
CONFIGURE SERVER PROPERTIES ................................................................... 27
CHAPTER 5: CONFIGURING THE SERIAL SERVER PROPERTIES. 31
DESCRIPTION OF THE SERVER PROPERTIES ..................................................... 32
Server Name............................................................................................... 32
Serial Number............................................................................................ 32
Password.................................................................................................... 32
DHCP ........................................................................................................ 32
IP Address.................................................................................................. 33
Netmask...................................................................................................... 34
Gateway..................................................................................................... 34
MAC Address............................................................................................. 34
Version & Date.......................................................................................... 34
Link Status.................................................................................................. 34
Server Serial Port ...................................................................................... 34
Baud Rate................................................................................................... 34
Data/Parity/Stop........................................................................................ 34
Flow Control.............................................................................................. 35
TCP/UDP Protocol.................................................................................... 35
Serial Timeout............................................................................................ 35
TCP Alive Timeout..................................................................................... 36
Connection Mode....................................................................................... 36
Delimiter HEX 1 and Delimiter HEX 2...................................................... 36
Force Transmit........................................................................................... 36
Port Status.................................................................................................. 37
TCP/UDP Port........................................................................................... 37
Serial Port Mode........................................................................................ 37
Connection At ............................................................................................ 38
Max Connection......................................................................................... 38
Remote IP Address..................................................................................... 38
Update/Save............................................................................................... 38
CHAPTER 6: INSTALLING VIRTUAL COM PORTS ............................. 43
VIRTUAL COM PORT INSTALLATION ............................................................. 43
MATCHING THE SERIAL SERVER AND VIRTUAL COM PORT SETTINGS .......... 46
HARDWARE SETUP ......................................................................................... 21
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Table of Contents i
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
ii Table of Contents Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 4

CHAPTER 7: REMOVING VIRTUAL COM PORTS................................ 49
REMOVING THE VIRTUAL COM PORT WITH ESP MANAGER .......................... 49
REMOVING THE VIRTUAL COM PORT USING DEVICE MANAGER ................... 50
CHAPTER 8: UPGRADING THE SERIAL SERVER FIRMWARE........ 53
DOWNLOADING THE FIRMWARE ..................................................................... 53
UPGRADING VIA ESP MANAGER .................................................................... 53
Preparing the Software.............................................................................. 53
Upgrading the Firmware........................................................................... 54
CHAPTER 9: USING CONSOLE MODE.................................................... 55
CONSOLE MODE SETUP .................................................................................. 55
Navigating the Configuration Menus......................................................... 56
Using a Password...................................................................................... 57
CHAPTER 10: USING THE WEB SERVER............................................... 59
SETTING SERVER PROPERTIES ........................................................................ 59
CHAPTER 11: USING TELNET................................................................... 63
CONFIGURATION USING TELNET .................................................................... 63
Navigating the Configuration Menu .......................................................... 64
CHAPTER 12: ESP901 AND ESP902 TECHNICAL DATA...................... 67
APPENDIX A: RS-232 CONNECTIONS...................................................... 71
SERIAL SERVER DB-9 PIN-OUTS IN RS-232 MODE ......................................... 71
RS-232 Straight-through Cable Connections............................................. 72
RS-232 Crossover (null modem) Cable Connections................................. 72
RS-232 Straight-through DB-9 to DB-25 Conversion Connections........... 73
RS-232 Crossover DB-9 to DB-25 Conversion Connections..................... 73
RS-232 DTE Loopback Connections.......................................................... 74
APPENDIX B: RS-422 CONNECTIONS...................................................... 75
SERIAL SERVER DB-9 PIN-OUTS IN RS-422 MODE ......................................... 75
APPENDIX C: RS-485 CONNECTIONS...................................................... 79
SERIAL SERVER DB-9 PIN-OUT IN RS-485 MODE........................................... 79
APPENDIX D: NETWORK CONNECTIONS............................................. 81
STANDARD ETHERNET CABLE RJ-45 PIN-OUT................................................ 81
CROSSOVER ETHERNET CABLE RJ-45 PIN-OUT .............................................. 82
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Table of Contents iii
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
iv Table of Contents Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 5

Introduction
Introduction
CChhaapptteerr 11:: IINNTTRROODDUUCCTTIIOONN
VLINX Models ESP901 and ESP902 Ethernet Serial Servers provide
Ethernet to Serial connections for RS-232, RS-422 or RS-485 devices.
The ESP901 features a single serial port and the ESP902 features two
serial ports. The serial ports can be accessed over a LAN/WAN using
Direct IP Mode, Virtual COM Port, or Paired Mode connections. The
10/100 Mbps Ethernet connection auto-selects 10BaseT or 100BaseTX
and indicates the type of connection with a bi-color link light.
Figure 1. VLINX ESP901 and ESP902 Ethernet Serial Servers
Features
• Multi-interface serial ports
o ESP901 and ESP902 Port 1 software selectable for RS-
232, RS-422, RS-485 (DIP Switch selects Console Mode)
o ESP902 Port 2 is RS-232 only
• 10/100 Mbps Ethernet with Auto Selection
• LAN and WAN Communications
• TCP or UDP Client or Server operation - configurable
• Software Support - Windows 98/ME/2000/XP or NT 4.0
• Firmware Upload for future revisions/upgrades
• Configuration of Ethernet and serial port settings can be
accomplished using any of four methods:
o VLINX ESP Manager Software for Windows allows
configuration via a network connection or directly from
the Ethernet port of a computer (using an Ethernet
crossover cable).
Web Server allows configuration via the network using
o
any web browser.
o
Telnet allows configuration via the network by accessing
the setup configuration menu.
o
Console Mode allows configuration through an RS-232
serial port in using a VT100 Terminal Emulation program
and an RS-232 crossover cable.
• Virtual COM Driver Software for Windows - installs virtual
COM ports, viewable in the Windows Device Manager under
Ports (COM & LPT). Virtual COM port provides access to any of
the ports on the ESP901 and ESP902, like any other serial port
(legacy, PCI, USB or PCMCIA) on the computer. Any program
running on the computer and using Windows-based COM ports
can access the serial devices attached to the
Serial Server. The
LAN becomes transparent to the serial device and the software
running on the PC.
• Heart Beat Connection - selectable protocol ensures reliable
communications in Virtual COM Port or Paired Connection
modes. This feature restores the connections if communications are
temporarily lost at either end due to loss of power or the Ethernet
connection.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 1 1
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
2 Chapter 1 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 6

Introduction
Communication Modes
Introduction
The ESP901 and ESP902 Serial Servers enable communication with
serial devices over a LAN or WAN. Serial devices no longer are
limited to a physical connection to the PC COM port. They can be
installed anywhere on the LAN using TCP/IP or UDP/IP
communications. This allows traditional Windows PC software access
to serial devices anywhere on the LAN/WAN network.
Direct IP Mode
Direct IP connections allow applications using TCP/IP or UDP/IP
socket programs to communicate with the asynchronous serial ports on
the
Serial Server. In this type of application the Serial Server is
configured as a TCP or UDP server. The socket program running on the
PC establishes a communication connection with the
The data is sent directly to and from the serial port on the server. When
using UDP protocol the server can be configured to broadcast data to
and receive data from multiple IP addresses.
Virtual COM Mode
Install Virtual COM Mode allows the user to add a driver, to provide a
virtual COM port on the computer. The new COM port shows up in the
Device Manager. Windows programs using standard Windows API
calls are able to interface to virtual COM ports. When a program on the
PC opens the new COM port, it communicates with the remote serial
device connected to one of the ports on the
After connection, the LAN is transparent to the program and serial
device. Applications are able to work just as if the serial device is
connected directly to a physical COM port on the computer. The virtual
COM port software converts the application’s data into IP packets,
sends it across the network to the
packet back to serial data and sends the data out a serial port located on
the
Serial Server.
Serial Server.
Serial Server.
Serial Server, which converts the IP
Paired Mode
Paired Mode is also called serial tunneling. In this mode any two serial
devices that can communicate with a serial link will be able to
communicate using two
Two
Serial Servers are connected to a network, one configured as a
TCP or UDP client and the other as a TCP/UDP server. When setting
up the server the remote IP address section must contain the address of
the client. This will allow the client’s IP address to pass the IP addressfiltering feature of the server. Conversely, the Remote IP address of the
client must contain the server’s IP address. Both communication port
numbers must be the same.
Heart Beat
The Heart Beat protocol connection provides a reliable
communications connection in
Connection Mode. This feature restores the connection if
communications are temporarily lost at either end due to loss of power
or Ethernet connection.
Without this feature a device that loses a connection and stops
communicating would not be able to reconnect without human
intervention. A TCP data connection can be lost when there is a power
failure or temporary loss of an Ethernet connection on either the client
or server. If a loss occurs the Heart Beat feature will try to reconnect
the TCP data connection every five seconds until communications is
established again. The Heart Beat feature is available for use in
COM Port Mode and Paired Connection Mode. This is not available
when using a UDP application.
Serial Servers and the LAN.
Virtual COM Port Mode or with Paired
Virtual
To use this mode, the
Serial Server must be set to either TCP/server or
UDP/server with a designated communication port number. The virtual
COM driver is the TCP or UDP client.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 1 3
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
4 Chapter 1 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 7
Introduction
Introduction
Serial Server Quick Start Guide
For descriptive purposes this Quick Start Guide considers a typical
configuration consisting of a PC connected via an Ethernet LAN to an
ESP901 or ESP902 Serial Server connected to the RS-232 port of a
serial device.
Hardware Setup
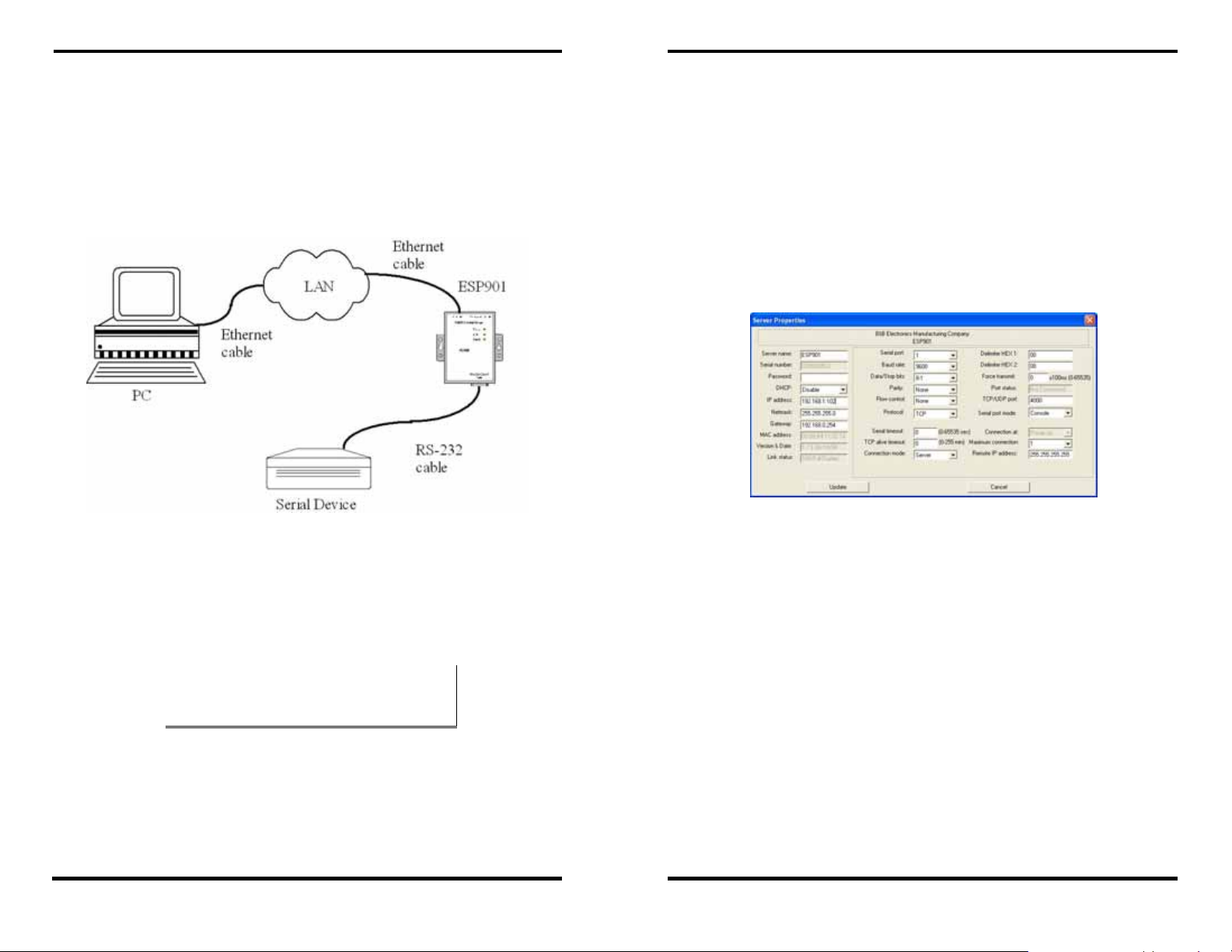
Figure 2. Typical Hardware Setup
Step 1: Connect the Serial Server to the network using a standard
network cable.
Step 2: Connect the
device.
NNoottee::
If the serial device is configured as a DCE use a straight-through serial
cable. If the serial device is configured as a DTE use a crossover (null
modem) cable.
Step 3: Set all the DIP switches to the OFF position.
Step 4: Apply power to the
Serial Server to the RS-232 port on the serial
Serial Server.
Software Installation
Using the CD included with the Serial Server, install the VLINX ESP
Manager
software on the configuring computer.
Serial Server Configuration
Step 1: Open the ESP Manager software. It will automatically search
for any reachable (ESP90x) Serial Servers. A list of all Serial
Servers
Server List window.
Step 2: Double click the desired
up the
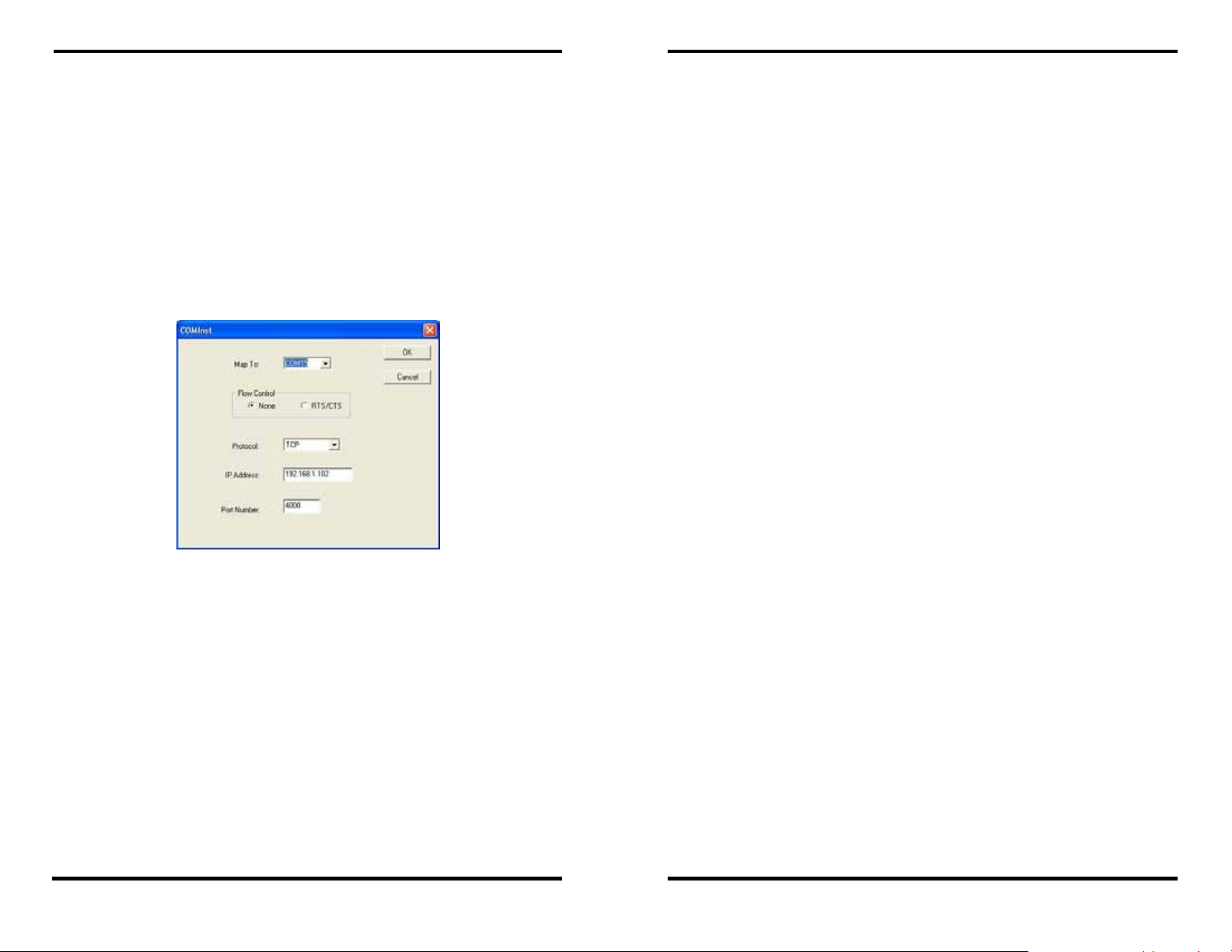
Figure 3. The Server Properties Window
Step 3: Change the Server Properties as required.
• Enable
• Obtain appropriate static
• Set the
• Set
connected to the LAN will appear in the Serial
Serial Server port on the list to bring
Server Properties configuration screen.
DHCP to allow the Serial Server to generate its
own IP address
OR
IP, Netmask and Gateway
addresses from your Network Administrator
(recommended)
Serial Port Mode property to RS-232 to match the
serial device connected to the Serial Server.
Baud Rate, Data/Parity/Stop, and Flow Control to
match the configuration of the serial device connected to
the
Serial Server port
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 1 5
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Step 4: When the parameters have been set, click
the prompts in the dialogue boxes,
Update. Following
Restart the Serial Server
and Search all reachable servers again.
6 Chapter 1 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 8
Introduction
Step 5: Re-enter Server Properties to verify the changes have taken
Introduction
effect, or to view/change the configuration of other ports. Each
port must be configured separately.
Install Virtual COM Ports on PC
Step 1: From the Windows Start menu, run the Install Virtual COM
Ports
utility included with the VLINX software,
Step 2: Search for all servers on the network
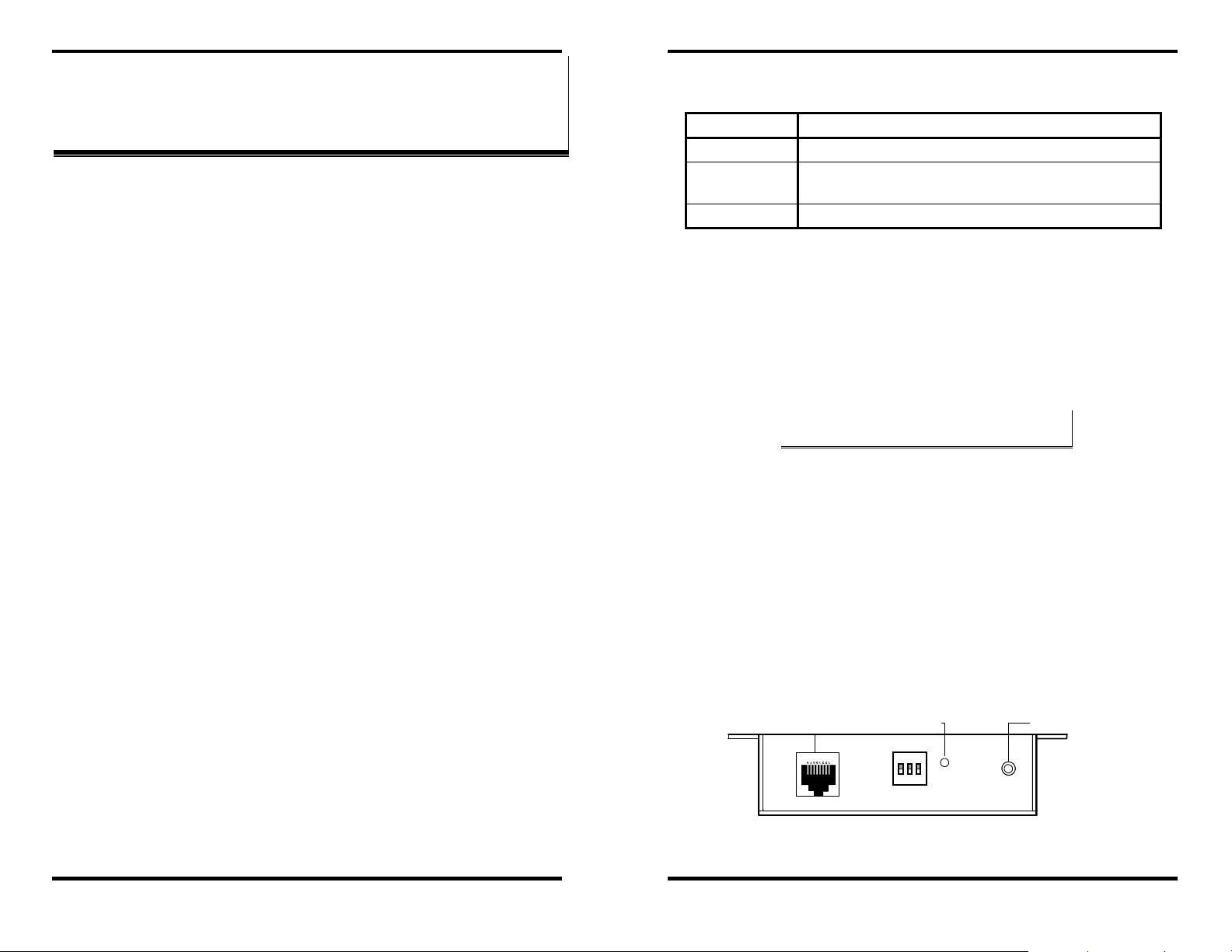
Step 3: Select a port and map it to an unused COM port (e.g. Port 15).
Configure it for TCP protocol and the appropriate IP address
(determined in the last section).
Figure 4. Configuring the Virtual COM Port
Check Communications
Step 1: From the Windows Start menu, run HyperTerminal
Step 2: Configure
configured in the last section (e.g. Port 15).
Step 3: Set
Baud Rate, Data/Parity/Stop, and Flow Control to match
the configuration of the serial device connected to the Serial
Server serial port.
Step 4: Communications with the serial device should now be
operational.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 1 7
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
HyperTerminal to connect using the COM port
8 Chapter 1 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 9
Making Hardware Connections
Making Hardware Connections
CChhaapptteerr 22:: MMAAKKIINNGG TTHHEE HHAARRDDWWAARREE
CCOONNNNEECCTTIIOONNSS
Package Checklist
ESP901 and ESP902 Serial Servers are shipped with the following
items included:
9 ESP901 or ESP902 Serial Server Module
9 Power supply
9 This Operation Manual
9 CD-ROM disc with manual, VLINX ESP Manager and Virtual
COM Driver software for Windows 98/ME/2000/XP/NT 4.0
ESP901/ESP902 Connections, Indicators and
Reset Switch
Connectors, Indicators and Switches:
• Three indicator LEDs
• One Ethernet connector (RJ-45 female)
• A power connector
• A recessed reset switch
• Triple DIP switch
• ESP901: One serial port connector (DB-9M)
• ESP902: Two serial port connectors (DB-9M)
Indicator Lights
Light Indication
Power
Link
Ready
Red - power is applied
Yellow – 10BaseT Ethernet connection established
Green – 100BaseTX Ethernet connection established
Flashing Green – system is ready
Figure 5. Indicator Lights
Ethernet Connector
The Serial Server has a standard RJ-45 receptacle mounted in the top
edge of the chassis. The Serial Server can be connected to an Ethernet
hub, switch, or wall plate using a standard straight-through RJ-45
(male) Ethernet cable. To connect directly to an RJ45 Ethernet port on
a PC or laptop a crossover Ethernet cable must be used.
NNoottee::
Refer to Appendix D for details on Network Cables
Power Connector
Plug the ultra-miniature phone plug from the included power supply
into the power jack and then plug the supply in. When power is applied
the Red power light will illuminate. The tip of the power plug is
positive; the sleeve is negative.
Reset Button
This switch resets the unit, similar to the effect of removing/applying
power. The Reset switch is recessed to avoid accidental operation. To
reset the unit, insert a small plastic tool, press lightly and hold for three
seconds. The Link and Ready lights will go out and then come back on.
RJ-45
female
Reset
Off
Power jack
2.5 mm Tip (+)
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 2 9
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 6. Top View of ESP901 and ESP902 (when mounted vertically)
10 Chapter 2 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 10
Making Hardware Connections
DIP Switches
A triple DIP (dual inline package) switch allows the Serial Server to
be placed into
the ON position the Serial Server enters Console Mode, allowing
configuration of the Serial Server (using an RS-232 connection
through the serial port on the ESP901 or Serial Port 1 on the ESP902)
from a PC running a terminal program such as
the Serial Server enters Console Mode the Console Mode screen will
appear in the HyperTerminal program window. The serial port settings
must be 8-N-1 at 9600 baud.
Console Mode. When all three switches are moved into
HyperTerminal. When
Making Hardware Connections
Serial Ports
The ESP901 has one serial port. The port can be configured as a
Console Mode connection or as an RS-232, RS-422 or RS-485
interface to the Serial Server (if any of the DIP switches are in the
OFF position) using the ESP Manager software, via Telnet, or using
the
Web Server.
The
ESP902 has two serial ports. Port 1 operates the same as the
ESP901 serial port. Port 2 on the ESP902 is an RS-232 only interface.
The RS-232 interfaces are configured as DTEs. The connectors for all
ports are DB-9M.
Serial Port
DB-9 Male
Figure 8. The ESP901 Serial Port Connector
Figure 7. The Console Mode (Server) Screen in the
HyperTerminal Window
When any of the DIP switches are switched back to the OFF position,
the Serial Server will revert to the mode it was in before Console
Mode.
NNoottee::
The Serial Server can be put into Console mode using either of two
methods:
1. Switching all the DIP switches to the ON position
2. With any DIP switch in the OFF position set the Server
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 2 11
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Properties Console Mode field to Console and Update/Save the
configuration
Serial Port 1
DB-9 Male
Serial Port 2
DB-9 Male
Figure 9. The ESP902 Serial Port Connectors
Serial Server/Port Operational Modes
Using the ESP Manager the Serial Server can be put into Console
Mode, Default Mode
configured for RS-232, RS-422 or RS-485 operation. The server also
can be put into
ON position.
12 Chapter 2 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
or Upgrade Mode. The serial ports can be
Console Mode by placing all the DIP switches into the
Page 11
Making Hardware Connections
Default Mode
Making Hardware Connections
RS-422 Mode
When
Default Mode is selected and the server properties are Updated
(
Saved) all the configuration settings return to their default values.
Console Mode
In Console Mode the Configuration Menu can be accessed from a PC
by connecting its RS-232 serial port to the ESP901 serial port or
ESP902 Serial Port 1. Since the computer is a DTE device, and the
serial ports are configured as DTEs (with DB-9M connectors), a null
modem crossover cable must be used.
In
Console Mode the default serial port settings are: 9600 baud, 8 data
bits, No parity, and 1 stop bit. From Windows, HyperTerminal with
VT100 terminal emulation can be used for Console Mode
configuration.
Upgrade Mode
In Upgrade Mode firmware can be uploaded from a PC via its serial
port to the ESP901 serial port or ESP902 Serial Port 1. Upgrading also
can be accomplished via the network connection, using the ESP
Manager software and a virtual COM port.
NNoottee::
Refer to Chapter 5 for details on Serial Server Configuration settings.
See Chapter 12 for Serial Server default parameters.
NNoottee::
Refer to Chapter 9 for details on Console Mode
In RS-422 Mode the currently selected serial port is configured as an
RS-422 interface supporting four RS-422 signal channels with full
duplex operation for
CTS (Clear To Send). The data lines are differential pairs (A & B) in
which the B line is positive relative to the A line in the idle (mark)
state. Ground provides a common mode reference. To use handshaking,
Flow Control must be set to RTS/CTS during configuration.
NNoottee::
Refer to Appendix B RS-422 connection pin-outs.
RS-485 Mode
In RS-485 Mode the currently selected port is configured as an RS-485
interface supporting transmit (TX) and receive (RX) signal channels
using 2-wire, half-duplex operation. The data lines are differential with
the Data B line positive relative to Data A in the idle (mark) state.
Ground provides a common mode reference.
NNoottee::
Refer to Appendix C for RS-485 connection pin-outs.
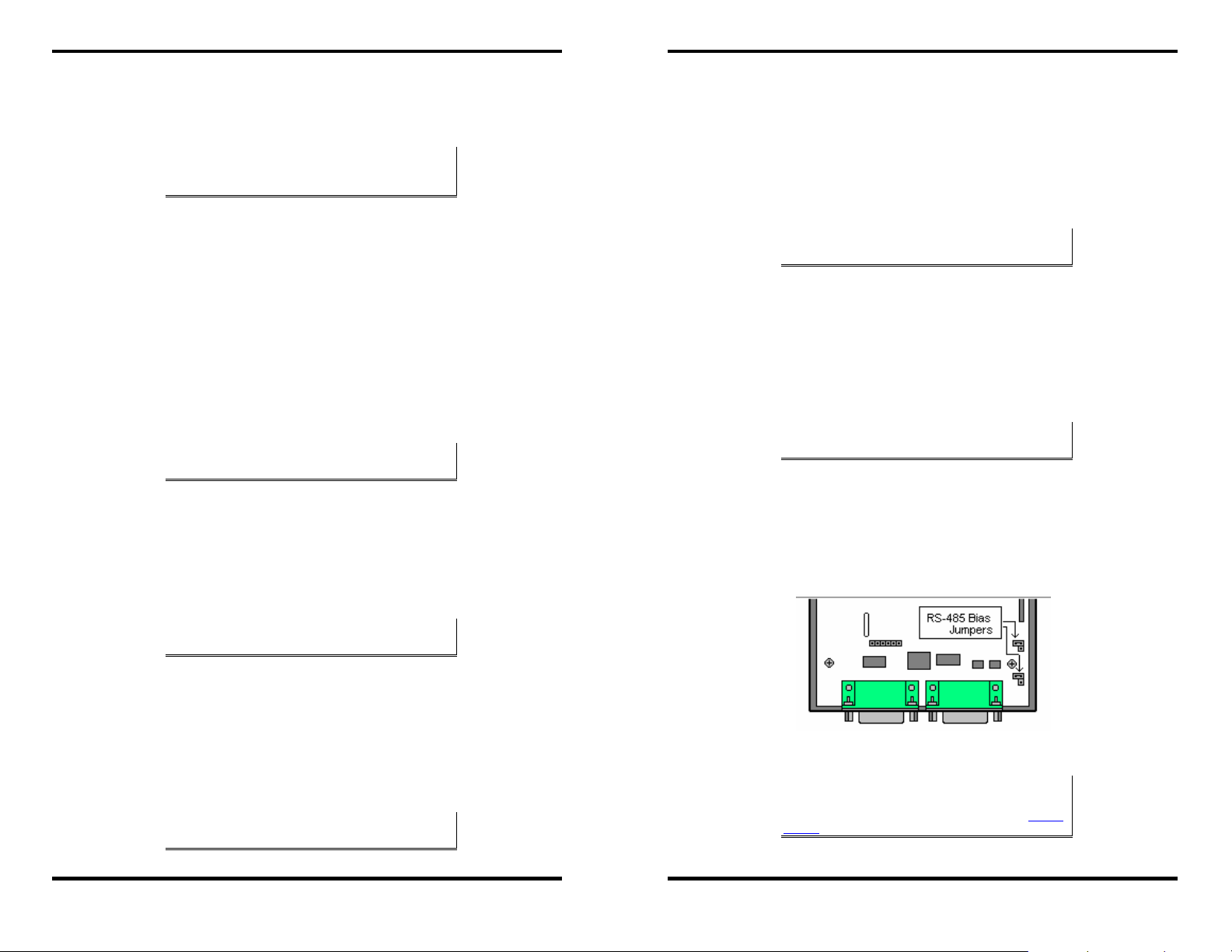
RS-485 Receiver Biasing
RS-485 Receiver Biasing
if the network does not supply it. Remove the two side-cover screws of
the
Serial Server, slide the cover off and re-position the bias jumpers
(shown open in the figure below) to enable biasing (shorting).
Receive, Transmit, RTS (Request To Send) and
can be implemented from the Serial Server
NNoottee::
Refer to Chapter 8 for details on Upgrade Mode
RS-232 Mode
In RS-232 Mode the currently selected serial port is configured as an
RS-232 interface supporting eight RS-232 signal lines plus Signal
Ground and is configured as a DTE, like a computer. Signals are single
ended and referenced to Ground. To use handshaking, Flow Control
must be set to RTS/CTS during Configuration.
NNoottee::
Refer to Appendix A for RS-232 connection pin-outs.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 2 13
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 10. Internal Setting to Select RS-485 Bias
NNoottee::
(For more information on RS-485 Receiver Biasing, see B&B
Electronics RS-422/485 Application Note available at www.bb-
elec.com)
14 Chapter 2 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 12
Making Hardware Connections
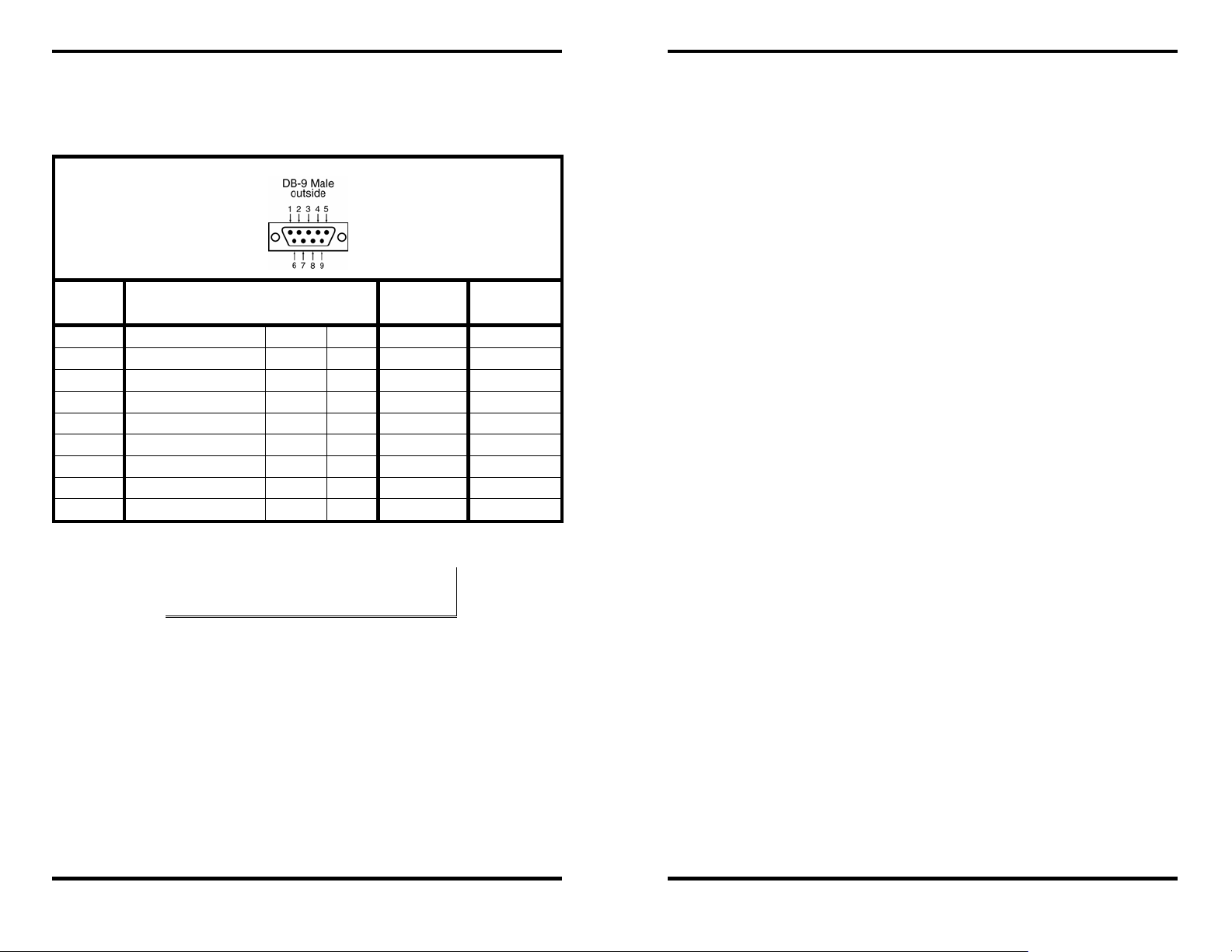
Serial Server Serial Port Connector Pin-outs
Pin-outs for RS-232, RS-422 and RS-485 operation are shown below.
Making Hardware Connections
DB-9M
Pin
1 Carrier Detect DCD In RXDA (−) -2 Receive Data RXD In RXDB (+) --
3 Transmit Data TXD Out TXDB (+) Data B (+)
4 Data Terminal Ready DTR Out TXDA (−) Data A (−)
5 Signal Ground GND --- GND GND
6 Data Set Ready DSR In CTSA (−) --
7 Request To Send RTS Out CTSB (+) --
8 Clear To Send CTS In RTSB (+) --
9 Ring Indicator RI In RTSA (−)
Figure 11. Serial Connection Pin-outs for RS-232/RS-422/RS-485
RS-232
Signal Name
NNoottee::
For more information on RS-232, RS-422 and RS-485 pin-outs, cable
connections and loopback connections refer to Appendices A, B and C
DTE RS-422 RS-485
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 2 15
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
16 Chapter 2 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 13
Installing the VLINX ESP Software
Installing the VLINX ESP Software
CChhaapptteerr 33:: IINNSSTTAALLLLIINNGG TTHHEE VVLLIINNXX
EESSPP SSOOFFTTWWAARREE
The Windows-based ESP Manager and Virtual COM Port software
makes configuration fast and easy. If using Windows, installing the
ESP Manager software and setting up virtual COM ports to configure
the
Serial Server is recommended.
Software Installation
The VLINX ESP software includes:
• ESP Manager
• Install Virtual COM Ports
• Uninstall Virtual COM Ports
Automatic Installation
Step 1a: Inserting the VLINX CD in the CD-ROM should
automatically launch the Install Shield Wizard.
Manual Installation
Figure 13. The Install Shield Wizard Window
Step 2: When the VLINX ESP Setup window appears, click Next.
Figure 14. VLINX ESP Setup Window
Step 1b: To manually start the software installation, from the
Windows Desktop, click Start button. At the Run command
line type
the CD ROM.)
Figure 12. The Run Dialogue Box
The Install Shield Wizard window will be displayed.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 3 17
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
D:start.exe then click OK. (D: is the drive letter for
Figure 15. The Choose Destination Window
Step 3: When Choose Destination Location appears, click Next.
The installation progress will be shown until complete.
18 Chapter 3 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 14
Installing the VLINX ESP Software
Installing the VLINX ESP Software
The recommended procedure is to Remove all installed components
first. Once the software has been removed, Install the new software.
Opening the ESP Manager
Step 5: If the Serial Server is not already connected to the network or
to the Ethernet port on the computer, connect it. Set all the
DIP switches to the OFF position. Apply power.
The
Power indicator should light red, the Link light should
indicate which type of Ethernet connection has been made and
the
Ready LED will flash indicating configuration can begin.
Figure 16. The Install Shield Wizard Complete Window
Step 4: Click Finish when the Install Shield Wizard Complete
dialogue appears. When finished, dialogue box will close.
Updating an Existing Installation
If an older version of the ESP Manager software is already installed,
the
Modify, repair or remove the program window will appear when
the installation process is initiated:
Step 6: Start the
Start → Programs → B&B Electronics → VLINX → ESP
Servers → VLINX ESP Manager
As soon as the
Server and after a few seconds the Serial Server List will
display all (ESP90x)
ESP Manager software. In Windows Desktop, click:
.
ESP Manager opens it will initiate Searching
Serial Servers on the network.
Figure 18. ESP Manager Displaying all ESP90x Serial Servers
Figure 17. The InstallShield Wizard Modify, Repair or Remove Screen
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 3 19
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
20 Chapter 3 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 15

Using ESP Manager
Using ESP Manager
CChhaapptteerr 44:: UUSSIINNGG EESSPP MMAANNAAGGEERR
The ESP Manager software allows:
• Searching for servers connected to the network
• Displaying and changing the configuration of those servers
• Installing virtual COM ports on a computer
• Displaying and configuring virtual COM ports
• Uninstalling virtual COM ports on a computer
• Upgrading the
• Monitoring Port Status
• Saving and Loading Configuration Files
Hardware Setup
Step 1: Connect the Serial Server to the LAN or to a computer
Ethernet port. Set all the DIP switches on the
the OFF position
Serial Server firmware
Serial Server to
Figure 20. Direct Ethernet Connection using a Crossover Cable
NNoottee::
Use an Ethernet Crossover Cable if connecting directly to a computer
LAN card.
Step 2: Apply power. The red Power indicator will light, the Link
indicator lights when an Ethernet connection is made, and the
Ready indicator will flash.
Figure 19. Ethernet Connection via a LAN
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 4 21
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Software Setup
Step 3. To run the ESP Manager, from the Windows Desktop click:
Start → Programs → B&B Electronics → VLINX → ESP
Servers → VLINX ESP Manager
As soon as the
Server and after a few seconds the Serial Server List will
display all (ESP90x)
22 Chapter 4 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
ESP Manager opens it will initiate Searching
Serial Servers on the network.
Page 16

Using ESP Manager
Figure 21. The VLINX ESP Manager Window
Software Overview
The VLINX ESP Manager window provides the following information:
Menus (Server, View, Exit, Help)
•
Server Icons (Firmware Upgrade, Virtual COM Configuration,
•
Searching Server, Uninstall Virtual COM, Monitor Port Status)
Serial Server / Virtual COM Lists
•
•
Software Status (Ready, Updating, Searching, etc)
Menus
Using ESP Manager
• Searching Server - Searches for Serial Servers on the network
and brings back configuration information that will be displayed in
the
Server Properties window.
Uninstall Virtual COM - Allows virtual COM ports to be
•
uninstalled from the ESP Manager window.
Monitor Port Status - Brings up a screen that displays the
•
following information associated with the selected serial port:
o Serial TX: Displays the number of bytes of data sent to
the
serial device since the IP connection was established.
o Serial RX: Displays the number of bytes of data received
from the connected
serial device since the IP connection
was established.
o DTR/RTS: The
DTR/RTS Port Status indicator displays
the current logic state of the DTR and RTS hardware
handshake (output) lines for the selected
Serial Server
port (1 = asserted, 0 = not asserted).
o DCD/DSR/CTS: The
DCD/DSR/CTS Port Status
indicator displays the current logic state being received on
the DCD, DSR and CTS hardware handshake (input) lines
for the selected
Serial Server port (1 = asserted, 0 = not
asserted)
o Status: Indicates whether the client software has made a
connection with the
Serial Server.
o IP Address: Displays the IP address of the connected
client when there is a client connection
Save Configuration File - Allows the user to save the current
•
configuration information to a file with a .vcom extension.
Load Configuration File - Allows the user to load a configuration
•
file.
Server
• Firmware Upgrade - Used when downloading new firmware to
the Serial Server.
NNoottee::
See Chapter 8 for more information on upgrading firmware.
• Virtual COM Configuration - Selects the Virtual COM List.
Double clicking on any COM port in the
Virtual COM List brings
up a window that allows changing the virtual COM settings such
as
Flow Control, Protocol, IP address, and Port Number. Virtual
COM settings must match
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 4 23
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Serial Server port settings.
View
Provides three viewing options for the ESP Manager screen:
Toolbar – allows the toolbar (directly under the menu bar) to be
•
viewable or hidden
Status Bar – allows the Status Bar (at the bottom of the screen to
•
be viewable or hidden
Split – allows the position of the split between the Icons pane and
•
the Virtual COM List / Serial Server List panes to be dragged
horizontally using the mouse
24 Chapter 4 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 17

Using ESP Manager
Exit
• Allows you to Exit the ESP Manager program
Help
• Accesses the About vcomui dialogue box, which indicates the
software version number
Using ESP Manager
• Port - Displays the port number for each Serial Server port.
Flow Control - Indicates what type of flow control is configured
•
for each port.
Status - Indicates whether each port is currently In Use or Not
•
Used.
Server Icons Pane
Firmware Upgrade, Virtual COM Configuration, Searching Server,
Uninstall Virtual COM and Monitor Port Status can also be selected
using icons located in the left window.
Serial Server / Virtual COM Lists
To make management of lists of serial server easier, lists can be sorted
by clicking on any tab heading. Scrolling bars facilitate scrolling
through long lists.
Serial Server List
• Server Name - Displays the name of the Serial Server. The name
is listed once for each port.
IP Address - Displays the IP Address for the Serial Server. All
•
ports in a Serial Server have the same the same IP address.
Protocol - Displays the currently selected TCP or UDP mode for
•
the Serial Server.
Port - Displays the port number for each Serial Server port.
•
COM Name - Displays the name of the computer COM port
•
mapped to each Serial Server port. If no computer port has been
mapped it displays Not mapped.
Status - The Status indicates the mapped virtual COM port
•
condition.
o
Not Connected is shown when a program does not have the
port Open.
o
Connected is shown when that mapped port is Open for use.
Status Bar
Displays the current status of the software in the bottom, left corner of the
screen
• Ready
• Updating
• Searching reachable servers…
Search for Servers
Upon opening the ESP Manager software it will automatically
execute Searching Server and search for all reachable ESP90x
serial servers.
Step 4: To manually initiate a search for servers, click Searching
Servers (under the Servers menu or the icon on the left side
of the screen). The
It provides two options for searching for servers on the
network:
Specify the IP Address of the Serial Server
Search all reachable servers
Search Setup box will appear.
Virtual COM List
• COM Name - Displays the number of the COM port mapped to
each
Serial Server port.
IP Address - Displays the IP Address for the Serial Server. All
•
ports in a
Protocol - Displays the currently selected TCP or UDP mode for
•
the
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 4 25
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Serial Server have the same IP address.
Serial Server.
Figure 22. The Search Setup W indow
26 Chapter 4 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 18

Using ESP Manager
Step 5: Enter the IP Address assigned to the desired Serial Server or
click Search all reachable servers, then OK. IP Address is
used to find Serial Server units that are not on the same
subnet. (Routers on the network will block the standard
broadcast used to find servers if
Search all reachable servers
is selected.) The user must set an IP address that conforms to
the LAN addressing scheme.
Using ESP Manager
The Searching window is shown until all active
Servers on the LAN are listed in the Serial Server List
window.
Figure 23. The Search VLINX ESP Dialogue Box
Configure Server Properties
The Server Properties window displays the current
configuration properties for the currently selected server.
Step 6: To open the Server Properties window, highlight the Serial
Server in the Serial Server List window, double-click to
open.
The
Server Properties window is used to configure and store
the Server configuration settings. Details for setting Properties
are described in the next chapter.
Serial
Figure 24. The Server Properties Window
NNoottee::
ESP Manager Navigation:
Step 7: After configuring as needed, click Update to store the
- Use the mouse to select the property and parameters or
- Tab to move to the next property
- Tab+Shift to move back to previous property
- Arrows to move between properties or change values or
- Enter to select update or cancel
contents of the current property
configuration in the server. The following window will
appear:
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 4 27
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 25. The Restart Dialogue Box
Step 8:
Click Yes to restart. The following dialogue box will appear:
28 Chapter 4 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 19

Using ESP Manager
Figure 26. The Restarting Dialogue Box
After eight seconds a dialogue box will ask whether you want to search
for all reachable servers again.
Figure 27. The Server Search Dialogue Box
While the Serial Server is searching for all reachable servers the
following dialogue box appears:
Using ESP Manager
Figure 28. The Search VLINX ESP Dialogue Box
After that port has been updated you may want to re-enter Server
Properties
to verify the changes have taken effect, or to
view/change the configuration of other ports. Each port must
be configured separately.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 4 29
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
30 Chapter 4 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 20

Server Properties Configuration
Server Properties Configuration
Description of the Server Properties
CChhaapptteerr 55:: CCOONNFFIIGGUURRIINNGG TTHHEE
SSEERRIIAALL SSEERRVVEERR PPRROOPPEERRTTIIEESS
The VLINX Serial Server can be configured using any of four different
user interfaces: the
the Web Server. The Server Properties described in this chapter can
be changed from any of these user interfaces.
ESP Manager software, Console Mode, Telnet or
Figure 30. ESP Manager Server Properties Window
Server Name
This field displays the name that has been assigned to the Serial
Server
. A new Server Name of up to 16 characters can be entered. If
more than one Serial Server is connected on the LAN it is
recommended that a new name be assigned to each. When the ESP
Manager
and IP Address allowing the user to distinguish between Serial
Servers.
finds a Serial Server on the LAN it displays the server name
Figure 29. The Four Methods of Configuring Server Properties
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 5 31
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Serial Number
Each Serial Server has a unique serial number. This is fixed and
cannot be changed.
Password
Entering a password activates a security feature on the Serial Server.
Once a password is entered it will be required to access the menu and
make changes.
DHCP
DHCP servers are a part of numerous LAN management systems. The
DHCP field provides two choices:
normal, or default, setting. When enabled, the
DHCP request to the DHCP server, which will assign a dynamic IP
32 Chapter 5 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Disable and Enable. Disable is the
Serial Server will send a
Page 21

Server Properties Configuration
address, net mask, and gateway to the Serial Server. If a DHCP server
is not available on the network the Serial Server will time out after 10
seconds and the default values will remain. When DHCP is enabled, the
IP Address, Netmask and Gateway fields become inaccessible and
cannot be changed by the user.
NNoottee::
A dynamic address assigned by the DHCP server may change if the
server loses the Ethernet connection or power is removed. The host
(client) communication software requests a connection to the specific
IP address of the serial server. If the DHCP reassigns a different IP
address the software will not be able to communicate with the
hardware. Therefore, using a static IP address is recommended.
IP Address
Software or hardware attempting to access the Serial Server via the
network must know the IP Address of the server. A static IP address is
retained and remains the same each time the server is powered up or
starts/restarts. The default IP address of the
a label on its bottom cover. Entering an appropriate address in the IP
Address field and updating the server will change the server’s IP
address. The network administrator can assign/establish the static
address or group of addresses to be used.
The IP Address of the
Serial Server can be confirmed using the DOS
Ping command.
Serial Server is printed on
Server Properties Configuration
Netmask
The default LAN netmask is configured for a Class C address. The user
may change this. Default is 255.255.255.0
Gateway
The Gateway IP address allows users to access the Serial Server from
outside the LAN.
MAC Address
The MAC address is fixed and cannot be changed. It is assigned in the
factory. Every Ethernet device manufactured has it own unique MAC
address.
Version & Date
The currently loaded version of the firmware, and when it was released,
is shown here.
Link Status
Link status automatically displays the type of Ethernet connection. It
will either display 10BaseT or 100BaseTX in full duplex or half
duplex. This will depend on the LAN, switches, hubs used in the LAN
topology.
NNoottee::
To use Ping to check for communications:
- Access a DOS window (in XP click Start, then Run)
- At run prompt enter: CMD
- In the DOS window enter: Ping xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx (IP address for the
server to be confirmed)
- The command will return the Ping results indicating 4 replies
Figure 31. Pinging using the DOS command window
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 5 33
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Server Serial Port
This field indicates the number of the port for with Serial Server
properties are currently being displayed. Changing the number in this
field will cause all the other fields to display the properties for the
specified port. Note, however, that before changing ports, any changes
to properties must be
Updated (Saved) or the Serial Server will not
retain them.
Baud Rate
The serial port baud rate on the Serial Server must match the serial
baud rate of the connected device unless using Virtual COM Mode. In
Virtual COM Mode the software program will establish serial settings.
Data/Parity/Stop
Set this to match the data format used by the serial device connected
when Virtual COM Mode is not being used.
34 Chapter 5 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 22

Server Properties Configuration
Flow Control
The Flow Control setting must match the requirements of the serial
device connected.
Server Properties Configuration
communications are ideal for 5 seconds the Serial Server will reset and
make itself available for another client connection.
TCP Alive Timeout
NNoottee::
Select None when setting the port as RS-485 or 4-wire RS-422.
TCP/UDP Protocol
Select TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) or UDP (User Datagram
Protocol) protocol. If the application does not require a UDP
connection, select TCP. TCP guarantees reliable communication with
error checking whereas UDP provides faster transmission.
UDP Mode
When UDP mode is chosen the Serial timeout, TCP alive timeout,
Connection mode, Connection at, Max connection and
Remote IP address fields are replaced with the following
four fields:
Source IP address range. In this mode the server can be
configured to broadcast data to and receive data from multiple
IP addresses. Four IP address range fields are provided.
Figure 32. The Server UDP Configuration Screen
Destination IP address range, Port number and
The Serial Server monitors TCP activity. If TCP activity stops for the
length of time specified in this field the connection will be closed. This
field can be set to any value between 0 and 255 minutes. If zero, or no
value, is entered into this field the server will not disconnect.
Connection Mode
The Connection Mode field has three options: Server, Client and
Client (no heartbeat). When Client or Client (no heartbeat) is
selected the Connection at field automatically becomes active
(allowing the user to select
• When using the
• When using a
• When using
TCP or UDP Socket program, select Server.
Paired Mode communication between two serial
Power up or Data Arrival).
Virtual COM Port feature, select Server.
servers set up one as a Client and the other as a Server.
• When connecting to a server that does not support
select
Client (no Heartbeat).
Heartbeat,
Delimiter HEX 1 and Delimiter HEX 2
These fields allow the user to enter two ASCII characters (in hex
format) that delimit the beginning and end of a message. When a
message with both these delimiters is received at the serial port, the
data contained in the serial buffer is placed in an Ethernet packet and
sent out the Ethernet port. If only Delimiter 1 is set (Delimiter 2 is zero
or blank), upon receiving Delimiter 1 the ESP901/902 will put all the
data in the serial buffer in an Ethernet packet and send it out the
Ethernet port. If serial data greater than 1 kilobyte is received it will
automatically be placed in an Ethernet packet and sent out the Ethernet
port .
Force Transmit
Serial Timeout
Default for the Timeout property is 0, or no timeout. Setting Timeout
to any value between 1 and 65535 seconds activates it. If
set to 5 seconds and the Serial Server is configured as a Server, the
Client makes a connection and communications starts. If
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 5 35
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Timeout is
This field allows the user to set a maximum time limit between
transmissions of data. The value set in this field multiplied by 100 ms
determines the Force Transmit time. When the elapsed time reaches the
time configured in this field, the TCP/IP protocol will pack the data
currently in the serial buffer into a packet and send it out the Ethernet
port.
36 Chapter 5 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 23

Server Properties Configuration
Port Status
This field indicates whether a serial port is connected via the Serial
Server
to a virtual COM port of a device on the network.
Server Properties Configuration
• RS-485 – When this mode is selected and the server updated, the
selected serial port will become an RS-485 serial port on the
server.
TCP/UDP Port
This sets the port number for connection. The default port number for
the ESP901 is 4000. The default port numbers for the ESP902 are 4000
and
4001 for serial ports 1 and 2 respectively.
In all modes of operation,
set in the Server Properties menu must match the Virtual COM or
socket software port settings.
NNoottee::
Example: The Virtual COM default setting is TCP/UDP Port 4000. If
the port # property is changed to 4001, the virtual COM port will have
to be changed to 4001. The hardware settings can be changed from
the ESP Manager or Console Configuration Menu. The Virtual COM
port setting also can be changed within the Device Manager of the
computer on which it is installed.
Serial Port Mode
Serial Port Mode allows configuration of the serial server for the
following modes of operation:
Console – When this mode is selected and the server is updated, a
•
PC running a communications program such as HyperTerminal can
communicate with the
port (the serial Port on ESP901 or Port 1 on ESP902), displaying
the
Server Properties screen and allowing configuration of the
server and its ports.
Upgrade – When this mode is selected and the server is updated,
•
firmware can be uploaded into the
Mode serial port or a virtual COM port mapped to the number of
the Console Mode serial port.
Default – When this mode is selected and the server is updated, it
•
will revert the server to its default configuration.
RS-232 – When this mode is selected and the server updated, the
•
selected serial port will become an RS-232 serial port on the
server.
RS-422 – When this mode is selected and the server updated, the
•
selected serial port will become an RS-422 serial port on the
server.
Connection At
When the Connection Mode field is set to Client or Client (no
heartbeat)
, this field becomes active, allowing the ESP901/902 (acting
as a client) to connect to the server either on Power up or on Data
Arrival (first character arriving).
Direct IP or Virtual COM, the port number
Max Connection
This field allows the user to configure the Serial Server to have up to
eight TCP connections.
Remote IP Address
This is a security feature activated by entering the IP address of the
desired client. The Serial Server will only communicate with the listed
IP address and all other requests for connection will be filtered out. The
Serial Server must be set up as a TCP or UDP Server to use this
feature. The default setting is 255.255.255.255.
If
Paired Mode is not being used, do not change this setting until the
application has been tested and is communicating properly. Then
activate the address filtering feature.
Serial Server via the Console Mode serial
Serial Server via the Console
Update/Save
Server properties must be updated separately for each serial port.
Updating varies slightly depending on which of the four configuration
user interfaces are used.
Updating the Server Properties in ESP Manager
From the Server Properties screen, click the Update button to store
the configuration settings for the currently selected port. The vcomui
dialogue box will appear indicating you must restart the device before
the new settings will take effect. Click
NNoottee::
Refer to Chapter 1 Paired Mode
Yes.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 5 37
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
38 Chapter 5 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 24

Server Properties Configuration
Server Properties Configuration
After that port has been updated you may want to re-enter Server
Properties to verify the changes have taken effect, or to view/change
the configuration of other ports. Each port must be configured
separately.
Figure 33. The Restart Dialogue Box
The following dialogue box will appear:
Figure 34. The Restarting Dialogue Box
After eight seconds a dialogue box will ask whether you want to search
for all reachable servers again.
Figure 35. The Server Search Dialogue Box
While the Serial Server is searching for all reachable servers the
following dialogue box appears:
Figure 36. The Search VLINX ESP Dialogue Box
Saving Configuration Data in Console Mode or Telnet
Saving (updating) server properties is done from the Configuration
screen. Access the Configuration screen by tabbing through the list of
screens on the left side of the window and highlighting
There are four options shown on the right side of the
Configuration.
Configuration
screen: Save, Default, Running and Reset. Use Tab, Backspace, or
arrow keys to move the cursor to the option position, then press Enter.
Console Mode and Telnet Configuration Screens
•
• Save stores the configuration data to the
Serial Server flash
memory and resets it.
• Default restores the configuration data to factory default settings.
• Running restores the configuration data to the last values stored in
the flash memory.
• Reset re-boots the
Serial Server, making it available for a client
connection.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 5 39
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
40 Chapter 5 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 25

Server Properties Configuration
Web Server Interface
• The Web Server interface provides the same updating options as
Console Mode and Telnet. These are located at the bottom of all
three Web Server pages. If a field is changed, you must click Save
before leaving that page or the changes will be ignored.
Server Properties Configuration
Figure 37. The Web Server Page
NNoottee::
If you leave any Web Server page without saving, any changes you
have made will be ignored.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 5 41
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
42 Chapter 5 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 26

Installing Virtual COM Port
CChhaapptteerr 66:: IINNSSTTAALLLLIINNGG VVIIRRTTUUAALL
Installing Virtual COM Port
The program searches the LAN for all available Serial Servers. When
complete, the Found Server window appears and displays a list of the
servers that were found.
CCOOMM PPOORRTTSS
The Virtual COM Port feature allows Windows platform software, using
standard API calls, to be used in an Ethernet application.
The
Install Virtual COM Port software adds a Serial Server (COM#) port to the
computer. This shows up in the Device Manager. The COM number can be
selected from a list of available numbers. For example, in a computer already
having a COM1 and COM2, COM3 to COM 254 are available for the
Server. It is recommended that COM Port 5 or higher be selected. The virtual
COM port looks like a standard COM port to most Windows based applications
which allows the software to open a connection with the serial port located
anywhere on the LAN/WAN. When using the virtual COM port the
Server is configured as a TCP or UDP Server.
Virtual COM Port Installation
Step 1: From the Windows Desktop, click:
Start → Programs → B&B Electronics → VLINX → ESP
Servers → Install Virtual COM
Search Setup window will appear.
The
Serial
Serial
Figure 39. The Found Server Window
Step 3: Select the Serial Server at the IP Address to be mapped to a
virtual COM port, then click
OK.
Step 2: Select the
OK.
Search all reachable servers check box, then click
Figure 38. The Search Setup Window
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 6 43
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 40. The COMInst Window
Windows XP provides a notice concerning Windows Logo testing for
XP.
44 Chapter 6 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 27

Installing Virtual COM Port
Installing Virtual COM Port
Matching the Serial Server and Virtual COM Port
Settings
The settings of the virtual COM ports in the Device Manager and the
Serial Server Configuration Menu must match. If the settings do not
match, the virtual COM ports will not work. If these settings are
changed in the
virtual COM port. It will not change the settings stored in the
Server. Use the ESP Manager to change the Serial Server settings.
Device Manager, it will only affect the operation of the
Serial
Figure 41. The Windows Logo Testing Window
This XP feature simply indicates that these drivers have not yet
undergone the Microsoft testing procedures required to use the
Windows XP Logo on the packaging. Driver compatibility is not
affected.
Step 4: Click
Continue Anyway to proceed with the installation.
The Protocol TCP/UDP, IP Address, and Port Number will mirror the
settings of the selected serial server.
Step 5: After setting all
ports, click
NNoottee::
PCs may have hardware COM ports and devices such as Modems, IR
ports or USB based COM ports that are not currently connected Try
selecting a COM number above COM4 if problems occur.
Serial Server serial ports as virtual COM
Cancel on the Found Server form.
The default Flow Control setting is None. RTS/CTS can be selected if
used by the application program and serial hardware. The Serial Server
must be set to match.
Step 1: Use Device Manager to
View New Ports
Confirm the virtual COM ports in the Device Manager.
Step 2: Double-click
Ports to view the list of COM port numbers.
The installed Virtual COM port will be displayed as
#).
Figure 42. The Device Manager Window
VLINX ESP (COM
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 6 45
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Step 3: In the Device Manager select a VLINX ESP COM#. Double-
click it to bring up the
46 Chapter 6 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Properties window.
Page 28

Installing Virtual COM Port
.
Figure 43. The VLINX ESP (COM3) Properties Window
Step 4: Click the Configuration or Port Settings tab. This screen
allows the settings to be changed if necessary. Click Cancel to
keep the existing settings.
Installing Virtual COM Port
Step 5: Click
OK to change the settings. Use Refresh in the Device
Manager if Windows does not auto refresh.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 6 47
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
48 Chapter 6 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 29

Removing Virtual COM Ports
Removing Virtual COM Ports
CChhaapptteerr 77:: RREEMMOOVVIINNGG VVIIRRTTUUAALL CCOOMM
PPOORRTTSS
The ESP Manager software Uninstall Virtual COM Port feature will
remove a mapped COM port in the Device Manager of Windows 2000 and
XP operating systems. It may also be removed in the Device Manager of
Windows 98, ME, NT, 2000, and XP. Windows 98 users also will find a
Remove Virtual COM feature in the Programs file.
Removing the Virtual COM port with ESP
Manager
Step1: From the Windows Desktop, click:
Start → Programs → B&B Electronics → VLINX → ESP Servers →
VLINX ESP Manager
Step 2: In the
Highlight the mapped COM port number to be removed.
ESP Manager window click the Virtual COM List tab.
Step 3: Click the
for conformation. Click
procedure.
Figure 45. The vcomui Dialogue Box
Uninstall Virtual COM icon. The Manager will ask
OK to complete the uninstall
Removing the Virtual COM Port using Device
Manager
Figure 44. The ESP Manager Window
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 7 49
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
NNoottee::
The screen shots were taken from a Windows XP operating system
Step 1: From the Windows Desktop click:
Start → Settings → Control Panel.
Step 2: Click the
50 Chapter 7 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
System icon when the manager window opens.
Page 30

Removing Virtual COM Ports
Removing Virtual COM Ports
Figure 46. The Control Panel Window
Step 3: Click Device Manager in the Systems Properties window. In
the Device Manager dialogue click the + next to Ports (COM
LPT) to expand.
Figure 47. The Device Ma nager Window
Figure 48. Confirm Dev ice Removal
Step 5: click OK to proceed.
The
ESP COM # will be removed and the Device Manager window will
refresh and display the remaining COM ports
Step 4: Highlight ESP (COM #) to be removed and click the Action tab
at the top of window, then click
Removal
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 7 51
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
window will appear.
Uninstall. A confirm Device
52 Chapter 7 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 31

Upgrade Mode
Upgrade Mode
Step 4: Click Yes on the vcomui dialogue to restart the Serial Server.
CChhaapptteerr 88:: UUPPGGRRAADDIINNGG TTHHEE SSEERRIIAALL
SSEERRVVEERR FFIIRRMMWWAARREE
New Serial Server firmware updates may become available through
the B&B Electronics website for installation into the server. The
firmware can be uploaded using either a virtual COM port connection
or hardware COM port connection.
Downloading the Firmware
Make a folder to receive the firmware file. Download the compressed
software file from the B&B Electronics website. Unzip or expand the
file into the (.hex) format so it will be ready to upload to the
Server
.
Upgrading Via ESP Manager
The ESP Manager software can upload new firmware to the server
using a direct PC connection via the ESP901 serial port, ESP902 Port
1, or using a virtual COM port.
NNoottee::
If connecting directly to a computer serial port, use a null modem
cable between the Computer RS-232 port and the ESP901 serial port
or ESP902 Port 1.
Serial
Upgrading the Firmware
Step 5: Double-click the Firmware Upgrade icon (or click the Server
menu and Firmware Upgrade)
Step 6: In the
Upgrade window, click Browse. The Open dialogue
box will appear. Locate the folder on your PC that contains the
firmware .hex file.
Select the file and click Open. The Open
dialogue box will disappear.
Step 7: In the
Upgrade window select the serial port to be used in
transferring the firmware.
a. If connected directly from the PC to a
Serial Server
port it will typically be COM1 or COM2
b. If using a virtual COM port to upgrade via the
network, identify the virtual COM number and
Step 8: Click
Step 9: In the
bits
, Parity and Stop bits to the same values as set up in the
Server Properties window. Click OK.
address mapped to Port 1 on the
Upgrade
Port Settings window set the Bits per second, Data
Serial Server.
Preparing the Software
Step 1: In the ESP Manager Serial Server List window, double click
the server to be upgraded. The Server Properties window will
appear.
Step 2: If using a direct connection to upload the firmware to the
Server, set the baud rate to 115200 for the fastest possible
upload.
Step 3: Set the
Serial Port field to upgrade and click the Update
button. (Ensure that the DIP switches on the ESP901 or
ESP902 are all in the OFF position.)
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 8 53
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Serial
Figure 49. The Port Settings Window
Step 10: Upgrade progress will be shown until the Upgrade finished!
message is shown. Click OK.
54 Chapter 8 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 32

Using Console Mode
Using Console Mode
Navigating the Configuration Menus
CChhaapptteerr 99:: UUSSIINNGG CCOONNSSOOLLEE MMOODDEE
Before the Serial Server is installed on a LAN the Console Mode can
be used to change the settings from the defaults. The
shipped in the RS-232 Mode. Connect a crossover (null modem) cable
between the COM port on the computer and the appropriate serial port
on the
Serial Server.
NNoottee::
See Chapter 5 for details of each Server Property Settings.
Console Mode Setup
Step 1: Apply power to the Serial Server. The power and ready LED
will light.
Step 2: Using a VT100 Terminal emulation program (typically
HyperTerminal in Windows) open the computer COM port
connected to the
cable).
Step 3: In the HyperTerminal
Serial Server (via an RS-232 crossover
Port Settings window set:
Serial Server is
There are six Console Mode screens: Server, Network, Serial Mode,
Operation, Monitor and Configuration. Tab, Back Space and arrow
keys can be used to highlight the desired function on the screen list.
Pressing
screen. The configuration fields can be changed by pressing
Enter moves the cursor to the first field with the current
Enter and
selecting from the list that appears. The Escape key moves the cursor
back to the screen list. Pressing the Space Bar refreshes the page.
o Baud rate: 9600
o Data bits: 8
o Parity: None
o Stop bits: 1
o Flow control: None
Click
OK
Step 4: Ensure all the DIP switches are in the ON position.
Step 5: To view the
Configuration Menu, press the space bar. The
menu will appear within a few seconds.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 9 55
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 50. Console Mode Configuration Screens
56 Chapter 9 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 33

Using Console Mode
Step 5: Once all the changes have been made move to the
Configuration screen, select Save and press Enter.
Figure 51. Saving and Re starting the Configuration
The restart message will appear.
Using Console Mode
Step 6: Select
Yes to save changes. This is necessary to write the
settings to the server.
Using a Password
If a password is used it must be entered before the Configuration screen
can be seen. If the server is accessed with a password but no changes
are made,
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 9 57
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Reset to end before disconnecting.
58 Chapter 9 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 34

Using the Web Server
CChhaapptteerr 1100:: UUSSIINNGG TTHHEE WWEEBB
SSEERRVVEERR
The Web Server can be used to configure the Serial Server from any
web browser software (such as Internet Explorer). Server properties can
be set up using three browser pages.
NNoottee::
See Chapter 5 for details on Server Properties.
Setting Server Properties
In Internet Explorer type the IP Address of the Serial Server into the
address field near the top of the window and press the Enter key. The
following window will appear:
Using the Web Server
Navigate and change properties as required using the mouse and
keyboard.
To change serial port properties, click
browser window. The following page will appear:
Serial Port on the left side of the
Figure 52. The Web Server Page
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 10 59
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 53. The Web Server Serial Port Properties Page
To change other operational properties, click Operation on the left side
of the browser window. The following page will appear:
60 Chapter 10 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 35

Using the Web Server
Using the Web Server
Figure 54. The Web Server Operation Page
Click Save to store changes to the Serial Server. Settings for each Port
must be saved separately.
NNoottee::
If new property settings are not saved before leaving this page they
will not take effect.
Return to the main Server page by clicking on Server on the left side of
the browser window.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 10 61
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
62 Chapter 10 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 36

Using Telnet
Using Telnet
Step 6. The Telnet window will open (unless the server is still in
Console mode) and the Server screen will appear.
CCHHAAPPTTEERR 1111:: UUssiinngg TTeellnneett
Telnet can be used to configure the Serial Server from any PC on the
LAN. The
Telnet window displays the same configuration information
shown in Console Mode and allows server properties to be configured.
NNoottee::
See Chapter 5 for details on Server Properties.
Configuration Using Telnet
Step 1: Ensure the PC and Serial Server are connected to the LAN.
Step 2: Apply power to the
will light.
Step 3: If the DIP switches on the
position (Console mode), switch them to the OFF position.
The Serial Server will revert to the operational mode it was in
before the switches were all set to ON.
Step 4: From the
Desktop, click Start, then Run. The Run dialogue
box will open.
Step 5: Type in
Telnet and the IP address of the Serial Server to be
configured, then click OK.
Serial Server. The power and ready LED
Serial Server all are in the ON
Navigating the Configuration Menu
There are six Telnet screens: Server, Network, Serial Mode,
Operation, Monitor and Configuration. Tab, Back Space and arrow
keys can be used to highlight the desired function on the screen list.
Pressing
screen. The configuration fields can be changed by pressing Enter and
selecting from the list that appears. The
back to the screen list. Pressing the Space Bar refreshes the page.
Enter moves the cursor to the first field with the current
Escape key moves the cursor
Figure 55. The Run dialogue box
NNoottee::
The Serial Server must be in RS-232, RS-422 or RS-485 mode before you can
Telnet to it and access the configuration screens. If it was last configured in
Console mode you may not be able to access it using Telnet. In this case use
ESP Manager, Console Mode or Web Server for configuration.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 11 63
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
64 Chapter 11 Manual Documentation Number: ESP904-0504
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 37

Using Telnet
Using Telnet
Step 7: Once all the changes have been made move to the
and select
Enter. The restart message will appear.
Save field
Figure 57. Saving and Restarting the Configuration
Step 8: Select Yes to save changes. This is necessary to write the
settings to the server. The Telnet window will disappear.
Step 9: To view the changes re-enter
Telnet and re-establish
communications. The configuration menu will appear and
display the current settings.
Figure 56. Telnet Configuration Screens
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 11 65
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
66 Chapter 11 Manual Documentation Number: ESP904-0504
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 38

ESP901 and ESP902 Technical Data
ESP901 and ESP902 Technical Data
CChhaapptteerr 1122:: EESSPP990011 aanndd EESSPP990022
Hardware and
Included
Accessories
Dimensions
Power &
Environment
Indicators
Connectors
TTEECCHHNNIICCAALL DDAATTAA
ESP901 and ESP902 Serial Server modules
Power Supply: 12 VDC/500mA (tip positive/sleeve
negative)
Power Plug: (Area Dependent: North America
120VAC/60Hz, Europe/United Kingdom
220/240VAC/50Hz)
Manual: Paper copy of this manual, PDF available
CD-ROM disc: VLINX ESP Manager and Virtual COM
Driver software for Windows
98/ME/2000/XP/NT 4.0
ESP901/ESP902: 3.35 x 4.5 x 0.90 in (8.5 x 11.5 x 2.3 cm)
Power
Requirements: 12 VDC @ 200 mA (ESP901), 300mA
(ESP902)
Operating
Temperature: -10 to +80 °C
Storage
Temperature: −20 to 85 °C
Humidity: 0 – 90% non-condensing
Approvals: CE, FCC
Power: Red LED
Link: Yellow or green LED (10BaseT or 100
BaseTX)
Ready: Flashing green LED
Ethernet: Single RJ-45 female
Serial: ESP901: one 9 pin D-type male (DB-9M)
DTE (software selectable as RS-232, 422, or
485)
ESP902: Two 9 pin D-type male (DB-9M)
DTE, Port 1 - software selectable as RS-232,
422 or 485, Port 2 – RS232 only
DC Power: Ultra-miniature phone jack (2.5mm), Tip (+),
Sleeve (−)
Serial Interfaces
Memory
Network
Communications
Protocols
Configuration
Options
Optional
Accessories
RS-232(DTE): TXD, RXD, RTS, CTS, DTR, DSR, DCD,
GND
RS-422: TXDB(+), TXDA(−), RXDB(+), RXDA(−),
RTS(+), RTS(−), CTS(+), CTS(−) and GND
RS-485: Data B (+), Data A (–) and GND
Baud Rate: 110 bps to 230.4 k bps
Parity: None, Even, Odd, Mark, Space
Data Bits: 5, 6, 7 or 8
Stop Bits: 1, 1.5 or 2
Serial Memory: 8K bytes per port
LAN: 10/100 Mbps Auto-detecting 10 BaseT or
100 BaseTX
TCP, IP, ARP, DHCP, Telnet, HTTP, UDP,
ICMP
Console Mode: Using RS-232 with VT100 emulation (All
DIP Switches ON
Telnet Mode: Using HyperTerminal with VT100 emulation
ESP Manager: Using Windows 98/ME/2000/XP or NT
software
Web Server: Using a standard web browser such as
Internet Explorer
232NM9 Null Modem Crossover Cable for DTE to DTE
connection
DRAD35 DIN Rail mounting clips for 35mm DIN Rail
ERS35 one-meter length of steel 35mm DIN Rail
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 12 67
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
68 Chapter 12 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 39

ESP901 and ESP902 Technical Data
ESP901 and ESP902 Technical Data
Default Server
Settings
Server Name ESP901 or ESP902
Serial Number: xxxxxxxxx (printed on bottom of
unit)
Password: Blank
DHCP: Disable
IP Address: 192.168.0.1
Net Mask: 255.255.255.0
Gateway: 192.168.0.254
MAC Address: Fixed – see bottom label
Version&Date: current firmware version number &
date
Serial server port: 1
Baud Rate: 9600
Data//Stop: 8-1
Parity: None
Flow Control: None
TCP/UDP Protocol: ESP901 serial port: TCP
ESP902 Ports 1 & 2: TCP
Serial timeout: 0 seconds
TCP alive timeout: 0 minutes
Connection Mode: Server
Delimiter HEX 1: 00
Delimiter HEX 2: 00
Force transmit: 0 ms
TCP/UDP port: ESP901 serial port: 4000
ESP902 Port 1: 4000
ESP902 Port 2: 4001
Serial port mode: Console
Max connection: 1
Remote IP Address: 255.255.255.255
Figure 58. Dimensional Diagram of the ESP901
Figure 59. Dimens ional Diagram of the ESP902
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Chapter 12 69
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
70 Chapter 12 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 40

RS-232 Connections
RS-232 Connections
RS-232 Straight-through Cable Connections
AAPPPPEENNDDIIXX AA:: RRSS--223322 CCOONNNNEECCTTIIOONNSS
Serial Server DB-9 Pin-outs in RS-232 Mode
RS-232
Signal Name
Carrier Detect In DCD 1
Receive Data In RXD 2
Transmit Data Out TXD 3
Data Terminal Ready Out DTR 4
Signal Ground --- GND 5
Data Set Ready In DSR 6
Request To Send Out RTS 7
Clear To Send In CTS 8
Ring Indicator In RI 9
Figure 60. RS-232 Connections in a DB-9 Connector
DTE RS-232 DB-9M
Pin
In the RS-232 mode, the Serial Server’s ports are configured as DTEs
like a computer. If the device connected to the
Serial Server is
configured as a DCE use a straight through cable wired as shown
below:
RS-232 Signal Names DB-9
Carrier Detect CD 1 1 CD
Receive Data RD 2 2 RD
Transmit Data TD 3 3 TD
Data Terminal Ready DTR 4 4 DTR
Signal Ground/Common GND 5 5 GND
Data Set Ready DSR 6 6 DSR
Request to Send RTS 7 7 RTS
Clear to Send CTS 8 8 CTS
Ring Indicator RI 9 9 RI
Figure 61. Straight-through DB-9 to DB-9 RS-232 Ser ial Cable
Connections DB-9
Pin#
Signal
Pin#
RS-232 Crossover (null modem) Cable Connections
When connecting to a PC or another DTE device, use a crossover cable
(also called a null modem cable).
RS-232 Signal Names DB-9
Pin#
Carrier Detect CD 1 1 CD
Receive Data RD 2 2 RD
Transmit Data TD 3 3 TD
Data Terminal Ready DTR 4 4 DTR
Signal Ground/Common GND 5 5 GND
Data Set Ready DSR 6 6 DSR
Request to Send RTS 7 7 RTS
Clear to Send CTS 8 8 CTS
Ring Indicator RI 9 9 RI
Connections DB-9
Pin#
Signal
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Appendix A 71
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Figure 62. Crossover DB-9 to DB-9 RS-232 Serial Cable
72 Appendix A Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 41

RS-232 Connections
RS-232 Connections
RS-232 Straight-through DB-9 to DB-25 Conversion
Connections
Figure 63. DB-9 to DB-25 Straight-through Cable Connections
RS-232 Crossover DB-9 to DB-25 Conversion Connections
RS-232 DTE Loopback Connections
Figure 65. Loopback Connections for RS-232
For Transmit and Receive loopback, connect only those lines.
When Flow Control setting on the
Serial Server is set for RTS/CTS,
those lines must be looped. Usually DTR and DSR must also be
looped. The Flow Control setting for the program must match the
Server settings. The CD connection is needed by some terminal
programs to simulate Carrier.
Figure 64. DB-9 to DB-25 Crossover (null modem) Cable Connections
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Appendix A 73
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
74 Appendix A Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 42

RS-422 Connections
AAPPPPEENNDDIIXX BB:: RRSS--442222 CCOONNNNEECCTTIIOONNSS
Serial Server DB-9 Pin-outs in RS-422 Mode
RS-422
Signal Name
Receive Data A (−) In RXDA (−) 1
Receive Data B (+) In RXDB (+) 2
Transmit Data B (+) Out TXDB (+) 3
Transmit Data A (−) Out TXDA (−) 4
Signal Ground --- GND 5
Clear to Send A (−) In CTSA (−) 6
Clear to Send B (+) In CTSB (+) 7
Request to Send B (+) Out RTSB (+) 8
Request to Send A (−) Out RTSA (−) 9
Figure 66. RS-422 Connections in a DB-9 Connector
Direction
RS-422
DB9M
Pin
RS-422 Connections
Serial Server pin-out
RS-422 Signal Names DB-9
Receive A (-) RXDA(-) 1 TDA(-)
Receive B (+) RXDB(+) 2 TDB(+)
Transmit B (+) TXDB(+) 3 RDB(+)
Transmit A (-) TXDA(-) 4 RDA(-)
Ground GND 5 GND
Clear to Send A (-) CTSA(-) 6 RTSA(-)
Clear to Send B (+) CTSB(+) 7 RTSB(+)
Ready to Send B (+) RTSB(+) 8 CTSB(+)
Ready to Send A (-) RTSA(-) 9 CTSA(-)
Figure 67. RS-422 Connections with Flow Control
In the RS-422 mode, TXD lines are outputs and RXD lines are inputs.
Connect the
serial device, and the Serial Server TXDA(-) to the RXDA(-) of the
serial device.
If Flow Control is set for RTS/CTS, connect the
RTSB(+) to CTSB(+) of the serial device and the Serial Server
RTSA(-) line to the CTSA(-) of the serial device. Connect from the
Serial Server CTSB(+) line to the RTSB(+) of the serial device and
from the Serial Server CTSA(-) line to the RTSB(+) line of the serial
device.
in RS-422 mode
Serial Server TXDB(+) line to the RXDB(+) line of the
RS-422
Device
Connections Signal
Pin#
Serial Server
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Appendix B 75
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
If connecting to Receive Only RS-422 devices, connect from the
Serial Server TXDB(+) and TXDA(-) lines to the receive pairs on all
serial devices.
Ground is signal ground and provides a common mode reference for
the RS-422 Receiver and Transmitters.
NNoottee::
The RS-422 mode can be used for full duplex 4-wire RS-485 operation
provided that the serial server is acting as a sole master connecting to
all the slave devices, and all slave devices share the Receive signal
lines to the master. Set Flow Control for none, and omit connections to
RTS/CTS line pairs.
76 Appendix B Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 43

RS-422 Connections
RS-422 Connections
Figure 68. Loopback Connections for RS-422
The RS-485 Connections are half duplex, either Receive or Transmit,
so another half duplex device must be used to check operation.
Figure 69. RS-422 Connection w ith No F low Control
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Appendix B 77
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
78 Appendix B Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 44

RS-485 Connections
RS-485 Connections
AAPPPPEENNDDIIXX CC:: RRSS--448855 CCOONNNNEECCTTIIOONNSS
Serial Server DB-9 Pin-out in RS-485 Mode
RS-485
Signal Name
Data B (+) In/Out DATA B (+) 3
Data A (−) In/Out DATA A (−) 4
Signal Ground --- GND 5
Figure 70. DB-9 Pin-out in RS-485 Mode
NNoottee::
Some RS-485 devices are marked opposite the RS-485 standard,
which defines the Data B line as positive relative to Data A during a
Mark state before enabling the transmitter, and after transmitting
before tri-stating. If an RS-485 device does not respond, try swappi ng
the Data B and Data A lines.
Direction RS-485 DB9M
Pin
Figure 71. 2-wire RS-485 Connection
To connect 4-Wire RS-485 devices, the RS-422 Mode can be used
provided the
Serial Server will be connected as a master in a single
master system. If using multiple masters, the Serial Server cannot be
used, as it does not tri-state the transmitter in RS-422 mode.
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Appendix C 79
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
80 Appendix D Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 45

Network Connections
AAPPPPEENNDDIIXX DD:: NNEETTWWOORRKK
CCOONNNNEECCTTIIOONNSS
Network Connections
Crossover Ethernet Cable RJ-45 Pin-out
Standard Ethernet Cable RJ-45 Pin-out
RJ-45 Pin Signal Wire Color RJ-45 Pin
1 TX+ White-Green 3
2 TX+ Green 6
RJ-45 Pin Signal Wire Color RJ-45 Pin
1 TX+ White-Green 1
2 TX+ Green 2
3 RX+ White-Orange 3
4 Not used Blue 4
5 Not used White-Blue 5
6 RX- Orange 6
7 Not used White-Brown 7
8 Not used Brown 8
Figure 73. Pin-out for a Crossover Ethernet Cabl e
3 RX+ White-Orange 1
4 Not used Blue 4
5 Not used White-Blue 5
6 RX- Orange 2
7 Not used White-Brown 7
8 Not used Brown 8
Figure 72. Pin-out for a Standard Ethernet Cable
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m Appendix D 81
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
82 Appendix D Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
Page 46

International Headquarters
B&B Electronics Mfg. Co. Inc.
707 Dayton Road
Ottawa, IL 61350 USA
Phone (815) 433-5100 -- General Fax (815) 433-5105
Website: www.bb-elec.com
Sales e-mail: orders@bb-elec.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb.elec.com
European Headquarters
B&B Electronics Ltd.
Westlink Commercial Park
Oranmore, Co. Galway, Ireland
Phone +353 91-792444 -- Fax +353 91-792445
Website: www.bb-europe.com
Sales e-mail: sales@bb-europe.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb-europe.com
© B&B Electronics – October 2005
-- Fax (815) 433-5109
-- Fax (815) 433-5104
Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m 83
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
84 Manual Documentation Number: ESP901-902_4105m
B&B Electronics Mfg Co Inc – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104 – www.bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Commercial Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445 – www.bb-europe.com
 Loading...
Loading...