Page 1

This manual covers the following B&B Electronics' model serial
cards:
RS-232/422/485 Serial Cards CE
3PXCC1a 3PXCC1b
3PXCC2a 3PXCC2b
Documentation Number 3PXCC1x-2x-3903
Each of these models is an RS-232 serial card and uses the same printed circuit
board. The "1" and "2" suffix designates the number of ports on the card. The model
number of the card is printed on a sticker on the board.
This product designed and manufactured in Ottawa, Illinois USA
of domestic and imported parts by
International Headquarters
707 Dayton Road -- P.O. Box 1040 -- Ottawa, IL 61350 USA
Phone (815) 433-5100 -- General Fax (815) 433-5105
Sales e-mail: orders@bb-elec.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb-elec.com
B&B Electronics Mfg. Co. Inc.
Home Page: www.bb-elec.com
-- Fax (815) 433-5109
-- Fax (815) 433-5104
European Headquarters
B&B Electronics Ltd.
Westlink Commercial Park, Oranmore, Co. Galway, Ireland
Phone +353 91-792444 -- Fax +353 91-792445
Home Page: www.bb-europe.com
Sales e-mail: orders@bb-europe.com
Technical Support e-mail: support@bb-europe.com
B&B Electronics -- Revised October 2003
Documentation No. 3PXCC1x-2x-3903 Cover Page
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 2

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Introduction and General Information........... 1
Features ................................................................................ 1
Specifications ........................................................................ 1
Chapter 2: Quick Installation Guide ................................. 3
Chapter 3: Windows Installation ...................................... 5
Checking Device Manager for Available Address/IRQ’s
(Windows 95/98) ................................................................... 5
Adding Serial Port(s) in Windows 95/98 ......................... 8
Changing COM Port Resources in Windows 95/98 ..... 12
Checking Windows NT Diagnostics for Available
Address/IRQ’s (Windows NT 4.0) ....................................... 15
Checking Windows 2000 for Available Address/IRQ’s ....... 18
Adding Serial Port(s) in Windows 2000 ........................ 22
Chapter 4: Address and IRQ Setting..............................29
Address Switch Setup ......................................................... 29
Interrupt Jumper Setup........................................................ 32
Chapter 5: Communication Jumper Settings................ 35
RS-232 Mode ...................................................................... 35
RS-422 Mode ...................................................................... 36
RS-485 Mode ...................................................................... 36
RS-485 Pinouts............................................................. 37
RS-485 Operation ......................................................... 37
RS-422 and RS-485 Termination........................................ 38
High Speed Mode................................................................ 38
Chapter 6: Physical Hook-up and Troubleshooting ..... 39
Pinouts................................................................................. 39
RS-232 Pinouts............................................................. 39
RS-422 Pinouts............................................................. 39
RS-485 Pinouts............................................................. 40
Communication Cable Data ................................................ 41
Troubleshooting................................................................... 42
Appendix A: Hardware I/O Map .................................... A-1
Appendix B: Declaration of Conformity Statement .... B-1
Documentation No. 3PXCC1x-2x-3903 Table of Contents i
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
ii Table of Contents Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 3

Chapter 1: Introduction and General Information
The B&B Electronics’ 3PXCC series serial interface cards are
designed for the IBM PC, XT, AT and compatibles. Ports are
configured as a standard DTE device, and connections are made on
9-pin D-style connectors.
The 3PXCC cards offer exceptional setup flexibility. The 3PXCC
series has the ability to use any I/O address and any hardware
interrupt. You can install as many serial ports as will physically fit in
a machine. To use one of the “non-standard” addresses or
interrupts, the serial software used must also offer that flexibility. If
you are writing your own application, be sure the communications
routines used support any address and IRQ. B&B Electronics’
SimpCom Communications Drivers support these features.
Features
• Switch selectable addresses, from 0 to hex 3F8, including
COM1 – COM4
• Jumper selectable interrupts: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 11, 12, 14, 15
• Enhanced 16 bit Address Decoding
• Baud rates up to 230.4K baud with 2X clock option enabled
• 16550A UARTs on all ports
• Supports all standard RS-232 lines: TD, RD, RTS, CTS, DSR,
DCD, DTR, and RI
Specifications
Bus: IBM PC ISA Bus
Slot: Requires 1 full length slot for complete IRQ selectability. When
installed in a short slot, IRQ’s 10-15 will not be available.
Dimensions: 6.3 x 3.3 in (16.0 X 8.4cm)
I/O connection: 9-pin male, D-sub connectors
Baud rates: 230,400 baud max with 2x clock jumper enabled
Character length: 5, 6, 7, or 8 bits
Parity: Even, odd or none
Stop bits: 1, 1.5, or 2
Interrupt: IRQ 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 10, 11, 12, 14, or 15
Address: Switch programmable, 0 to hex 3F8
RS-232 Drivers:
Device: SN75185
Transmitter output voltage: ± 10.0 V minimum
Short circuit current: ±12 mA typical
Input low level threshold voltage: 0.65 V minimum
Input high level threshold voltage: 2.5V maximum
Device will withstand ±30 V
RS-422/485 Driver/Receiver:
Device: MAX491 or equivalent
Differential driver output voltage: 1.5 - 6 V
Differential input high-threshold voltage: 0.2 V maximum
Differential input low-threshold voltage: -0.2 V minimum
Automatic RS-485 Driver Control Timing:
Driver is enabled when data is a logic “0” (start bit). Driver
remains enabled for one character transmission time (10 bits
of
data at current baud rate). Each additional logic “0” resets
the timeout.
Power Consumption (2-port model):
+5V, 180mA, 900mW
+12V, 50mA, 600mW
-12V, 65mA, 780mW
Total maximum power draw: 2.28 W
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 1
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
2 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 4
Chapter 2: Quick Installation Guide
The following steps will help you install the Model 3PXCC Serial
Card. Please follow (step-by-step) the following numbered
instructions and refer to any corresponding chapters for more
details.
Before removing the card from the anti-static protective packaging.
• Discharge any static electricity buildup on your body by touching
• Avoid touching the gold connectors or other parts on the card
• Remove AC power from the computer and unplug the power
• Retain the ESD bag for handling the card. Save the packaging
1. Make sure you have an available ISA slot for installing your B&B
2. Determine what addresses and IRQ’s are free to use on your
3. Add New Hardware – This consists of adding a port or ports to
CAUTION: Electrostatic Sensitive Device.
Use ESD precautions for safe handling.
a large grounded metal surface or the metal chassis on
equipment connected to earth ground by a 3-wire power cord.
except as necessary. After setting the jumper, ground yourself
to the computer chassis before and while inserting the card.
cord before inserting the card.
for storage or shipping.
Electronics Serial Card. You may have to remove the cover of
your PC.
PC by checking your operating system for unused addresses
and IRQ’s. Each port uses eight I/O address spaces starting at
the base address that you select. Each port I/O address and
interrupt request (IRQ) must be set as well. See “Checking
Device Manager for Available Address/IRQ’s” in Chapter 3 for
your operating system. Refer to Chapter 4 (Table 3) for
frequently unused I/O Addresses and IRQ’s. Write down the
address and IRQ you select to use. Do not physically install the
ISA card at this point.
your operating system. See “Adding Serial Ports” in Chapter 3
for specific instructions for your operating system.
4. Assign Address and IRQ – The address and IRQ are set in the
operating system that you are using. This is the final step of
adding new hardware. See Chapter 4 for more details.
5. Set up the address (with dipswitches) and IRQ (jumpers) on the
serial card to reflect unused addresses and IRQ’s that you want
to use. The address dipswitch setting consists of configuring
seven dipswitches that reflect a particular hex address. The IRQ
is set via a little black jumper. See Chapter 4 for an explanation
of address and IRQ settings as well as details on configuring the
card itself.
6. Set serial card hardware jumpers for the communication
parameters that you desire. See Chapter 5 for an explanation of
serial parameters and details on how to configure them.
7. Shut down the PC before installing the serial card.
8. Install ISA serial card into an available ISA slot in the PC.
9. Physical Hook-up and Troubleshooting – pinout, cable data, and
troubleshooting information. See Chapter 6 for more details.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 3
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
4 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 5
Chapter 3: Windows Installation
Checking Device Manager for Available
Address/IRQ’s (Windows 95/98)
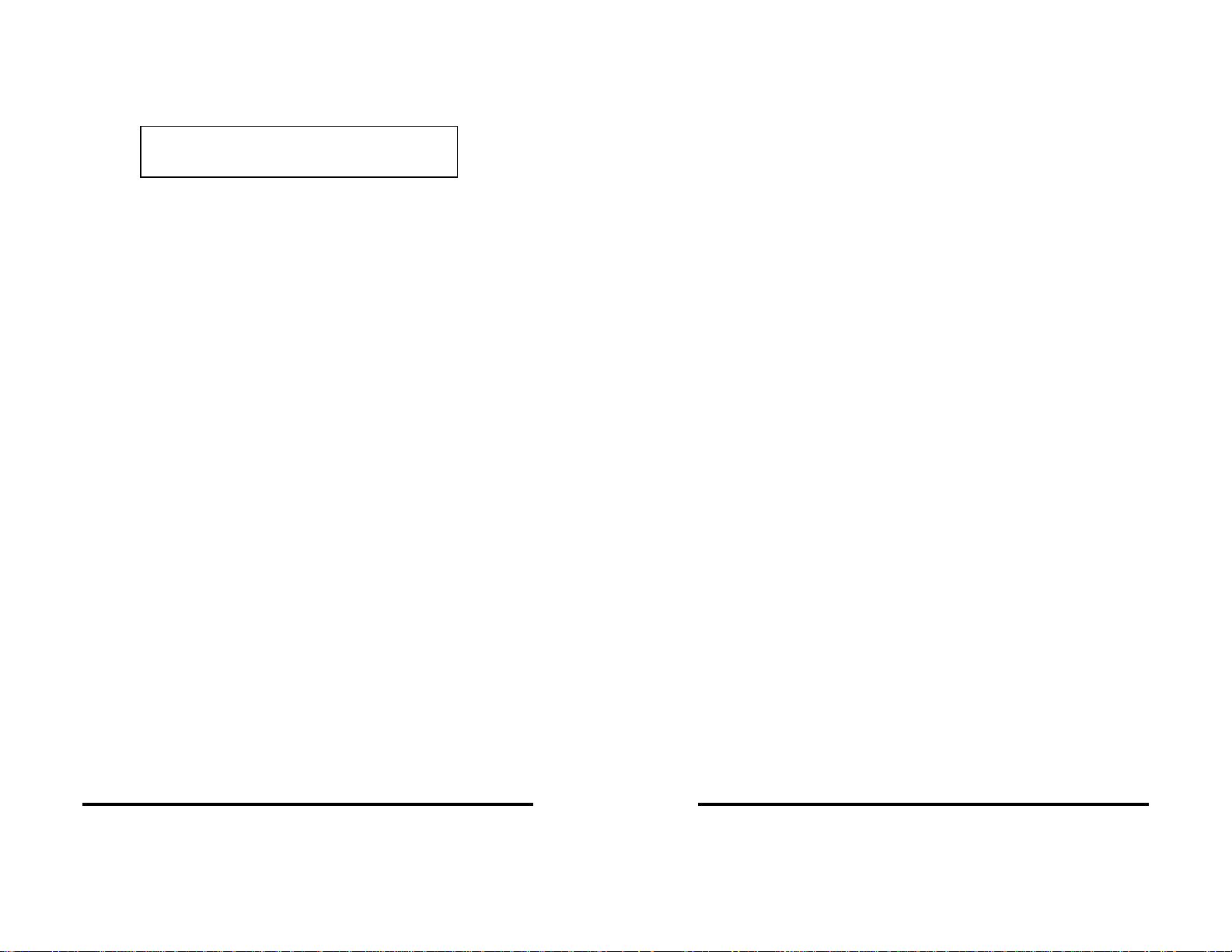
Click on Start / Settings / Control Panel and double-click on System
Properties.
Left-click on Device Manager.
Double-click on Computer.
Left-click on Interrupt Request.
Find a free IRQ in the displayed list. Any number that is seen on
the left hand side of this screen is an IRQ that is currently being
used. The object is to find a number of IRQ(s) that are not listed and
set your port(s) using those IRQ’s.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 5
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
6 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 6
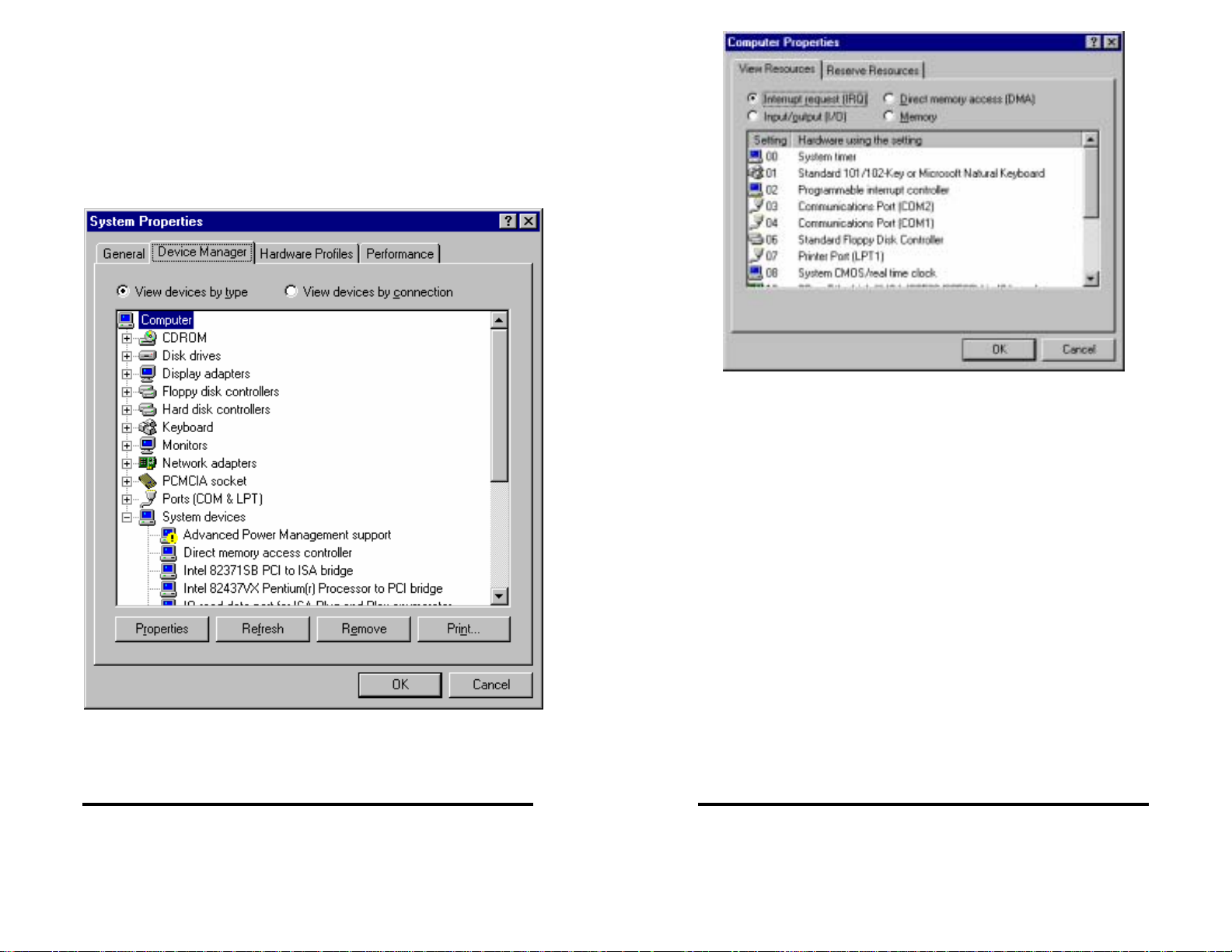
Left-click on Input/Output (I/O).
Scroll through the list, checking 03F8H, 02F8H, 03E8H, 02E8H. If
one of these is available, use it. If not, check alternates.
Find a free address in the list. Most desktop PC’s have a COM1 and
possibly a COM2 already on their system which will be seen in the
list. You might have to start at COM3 or COM4 to begin addressing
the ISA card. If these addresses are used you may have to resort to
the Frequently Unused Port Addresses (found in Chapter 4, Table 3)
of this manual. Write these open addresses and IRQ’s down for later
reference.
Adding Serial Port(s) in Windows 95/98
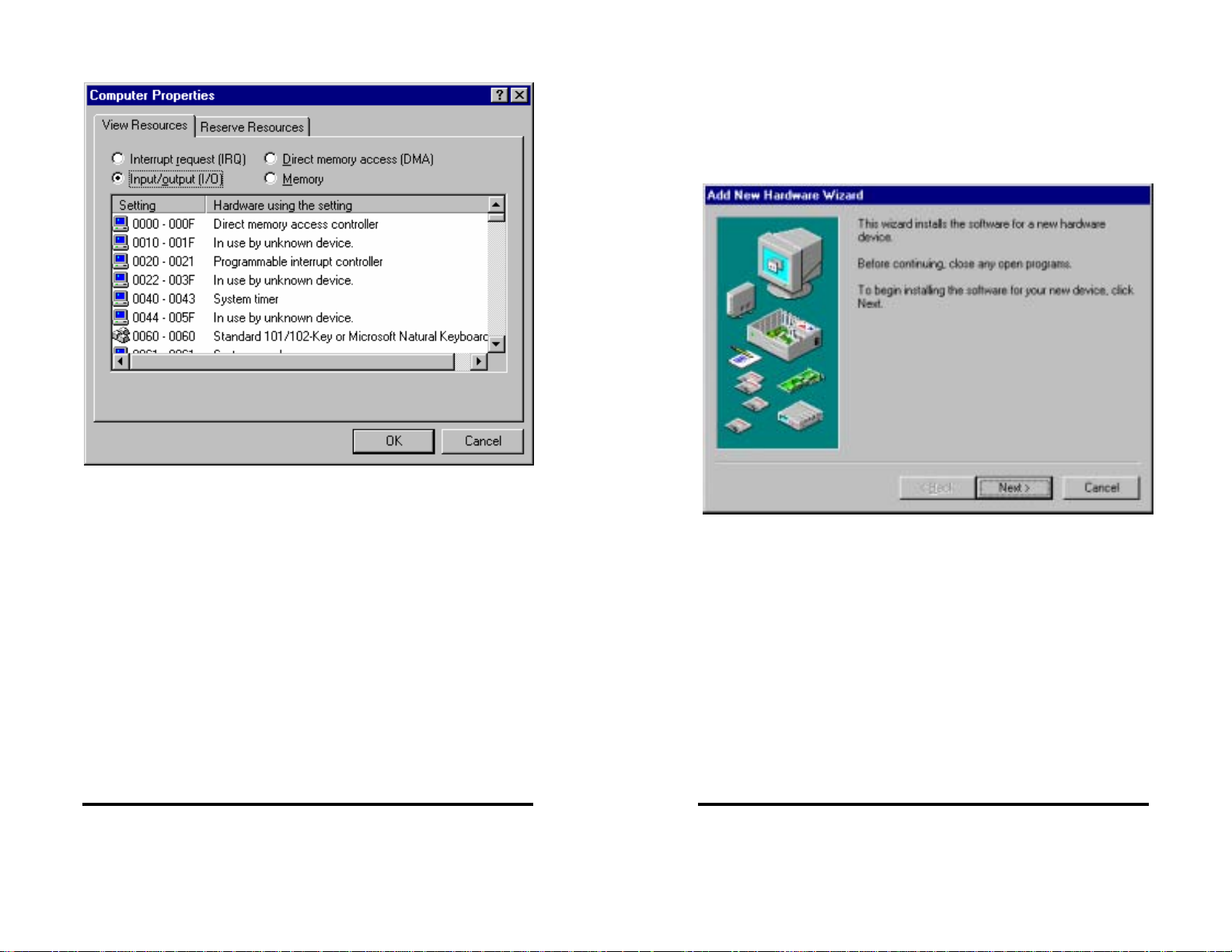
Go to Start Menu / Settings / Control Panel.
Run the Windows Add New Hardware utility found in the control
panel. Click Next.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 7
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
8 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 7
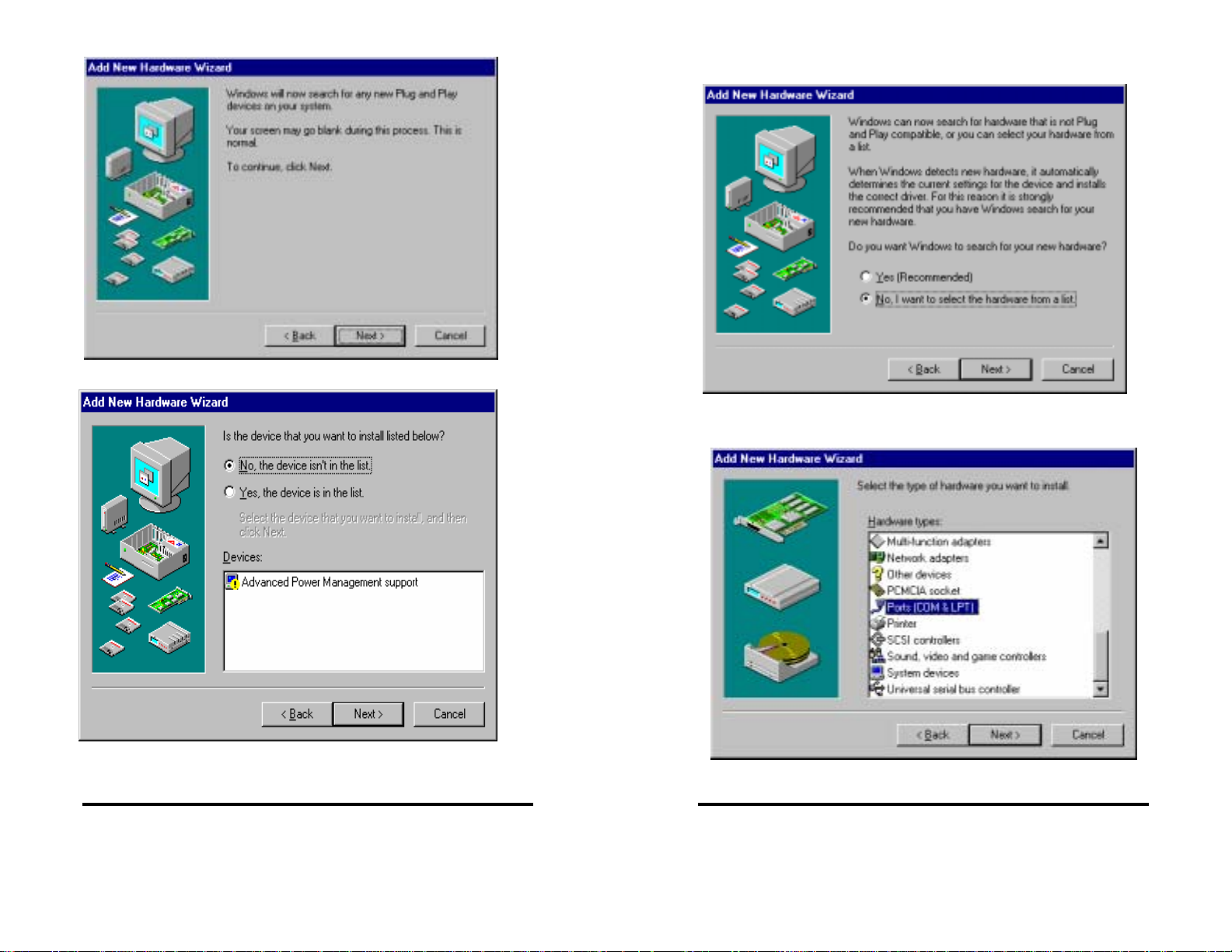
Click Next.
Select No (you do not want Windows to search for your new
hardware). Click Next.
Select Ports (COM & LPT). Click Next.
Select Yes/No for the device in the list. Click Next.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 9
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
10 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 8
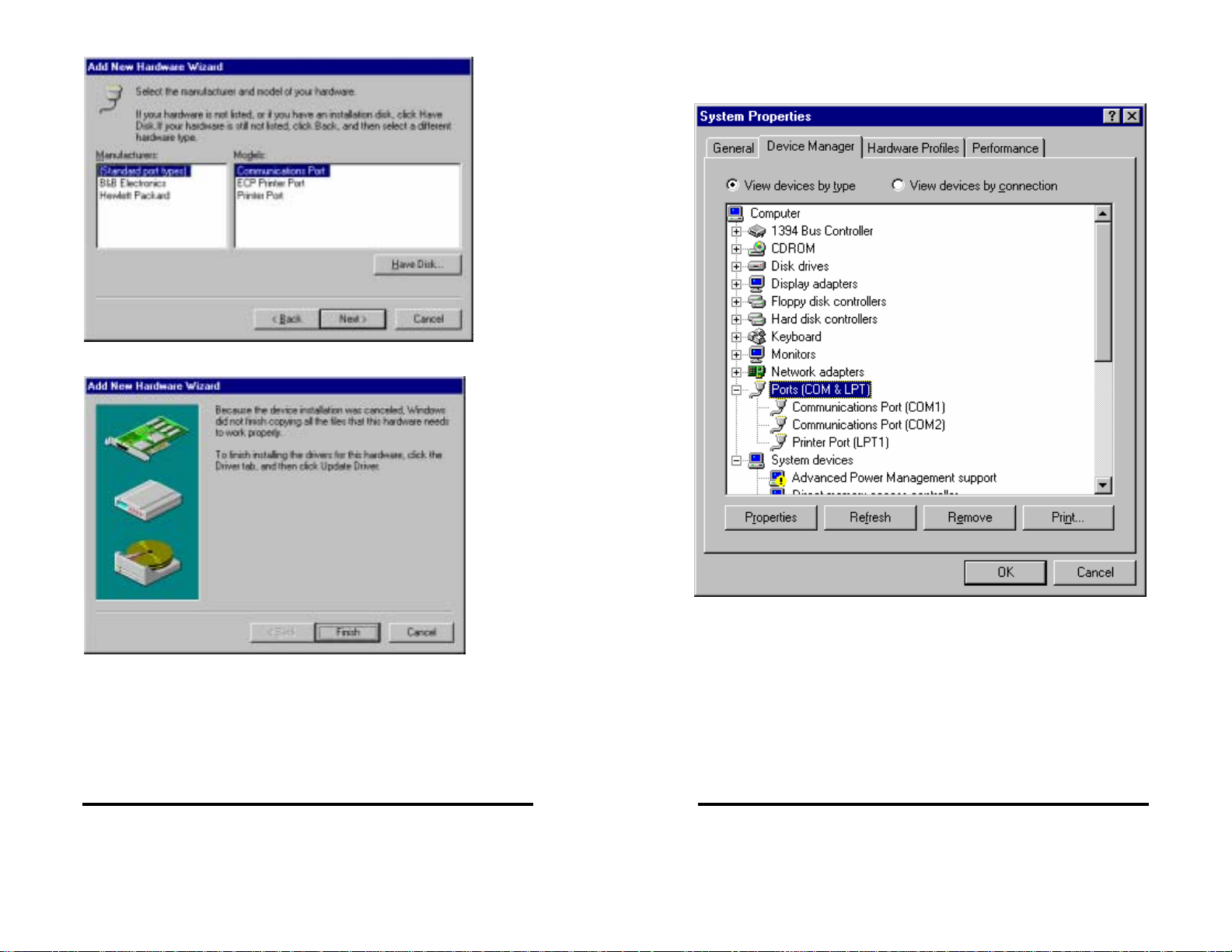
Select (Standard port types) and Communication Port. Click Next.
Changing COM Port Resources in Windows 95/98
Click Start / Settings / Control Panel and double-click on System
Properties.
The next screen will show the address and interrupt request of
the port. These may not match your configuration. For now, simply
click Next. Windows may ask for the Windows 95/98 disk/CD to be
inserted.
Finally, click Finish.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 11
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Click on Device Manager (make sure “View devices by type” is
enabled.
Double-click on Ports (COM & LPT).
Double-click on the new port that has been added.
12 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 9

Click Resources.
Click off (check mark out of box) Use automatic settings.
Select Basic Configuration 0007 (or last one).
Select Input / Output Range.
Click Change Setting.
Change Address to match the free address settings you found
earlier.
Click OK.
Select Interrupt Request.
Click Change Settings.
Change IRQ to match the free IRQ settings you found earlier.
At this point you can shut down the system and physically install
your B&B Electronics Serial Card into an available ISA Slot. Double
check to make sure the addresses and IRQ’s on the Serial Card are
set to the correct settings.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 13
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
14 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 10

Checking Windows NT Diagnostics for Available
Address/IRQ’s (Windows NT 4.0)
Click on Start / Programs / Administrative Tools / Windows NT
Diagnostics.
Left-click on Resources.
Left-click on I/O Port in Resources. Tab to view currently used
addresses.
Find a free IRQ in the following list. Any number that is seen on
the left hand side of this screen is an IRQ that is currently being
used. The object is to find a number of IRQ(s) not listed and set
your port(s) using those IRQ’s.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 15
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Scroll through the list, checking 03F8H, 02F8H, 03E8H, 02E8H. If
one of these is available, use it. If not, check alternates.
Find a free address in the list. Most desktop PC’s have a COM1
and possibly a COM2 already on their system, which will be seen in
the list. You may have to start at COM3 or COM4 to start your
addressing of the ISA card you have. If these addresses are used
you may have to resort to the Frequently Unused Port Addresses
(found in Chapter 4, Table 3) of this manual. Write these open
addresses and IRQ’s down for later reference.
16 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 11

Adding Serial Port(s) in Windows NT 4.0
Go to Start Menu / Settings / Control Panel.
Double-click on Ports.
Click Add.
Checking Windows 2000 for Available Address/IRQ’s
Click on Start / Settings / Control Panel.
Double-click on System.
Choose COM Port Number, Base I/O Address, and IRQ that you
want to use for the new Serial Port(s) being added.
After clicking OK, you will see a screen – System Setting
Change. Click the button Restart Now to restart Windows NT 4.0.
At this point you can shut down the system and physically install
your B&B Electronics Serial Card into an available ISA slot. Double
check to make sure the addresses and IRQ’s on the Serial Card are
set to the correct settings.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 17
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Click on Hardware.
18 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 12

Click on Device Manager.
Click on View (top of screen).
Click on Resources by type.
Double-click on Input/Output. Find an unused address to set your
B&B Electronics serial card to.
Scroll through the list, checking 03F8H, 02F8H, 03E8H, 02E8H. If
one of these is available, use it. If not, check alternates.
Find a free address in the list. Most desktop PC’s have a COM1
and possibly a COM2 already on their system, which will be seen in
the list. You may have to start at COM3 or COM4 to start your
addressing of the ISA card you have. If these addresses are used
you may have to resort to the Frequently Unused Port Addresses
(found in Chapter 4, Table 3) of this manual. Write these open
addresses and IRQ’s down for later reference.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 19
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
20 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 13

Double-click on Interrupt Request (IRQ). Here you need to find an
unused IRQ to set your B&B Electronics serial card to.
Adding Serial Port(s) in Windows 2000
Go to Start Menu / Settings / Control Panel.
Double-click on Add/Remove Hardware.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 21
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
22 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 14

Click Next.
Click on Add/Troubleshoot a device.
The following screen will appear after a few seconds.
Click Add a new device.
Click Next.
Click Next.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 23
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
24 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 15

Click No, I want to select the hardware from a list.
Click Ports (COM & LPT).
Click Next.
Select Standard port types and Communication Ports and Click
Next. You will see the following screen, go ahead and Click OK.
The Resources area will allow you to set the IRQ and address of
your new ports.
Click on the down arrow to the middle right of the screen after
“Setting based on”:
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 25
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
26 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 16

Click on the highest Basic configuration number in the list on the
“Setting based on” category.
Double-click on the Input/Output Range to set the Address.
Double-click on the Interrupt Request to set the IRQ.
Select IRQ and Address that you want your port(s) configured at.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 27
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
At this point you can shut down the system and physically install
your B&B Electronics Serial Card into an available ISA slot. Double
check to make sure the addresses and IRQ’s on the Serial Card are
set to the correct settings.
28 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 17

Chapter 4: Address and IRQ Setting
Address Switch Setup
A Windows PC has I/O port addresses and memory addresses.
Some devices use both types of addresses. I/O port addresses have
a 64K address space. Devices may decode all 16 address bits or
only some of the lower bits. Traditionally, serial cards have only
decoded 10 bits of the address bus. Recently this has begun to
cause address conflicts with full 16 bit decoded devices, most
notably between video cards and COM 4. B&B has solved these
conflicts by decoding all 16 bits of the ISA address bus. Address
settings in our ISA bus serial cards is set by DIP switches (selecting
bits 11-4) or jumpers.
CAUTION: Electrostatic Sensitive Device.
Use ESD precautions for safe handling.
B&B Electronics 3PXCC cards are factory configured for COM1
IRQ4, and COM2 IRQ3 (2-port models). If you plan on installing the
3PXCC as standard COM1 and COM2, you may leave the address
and IRQ set to the factory defaults.
The 3PXCC cards use a 7-position DIP switch to program the
binary I/O address of each port on the card. Figure 1 is a drawing of
the printed circuit board that shows the locations of the setup
switches and jumpers on the 3PXCC cards.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 29
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Figure 1. Silk Screen Plot of 3PXCC PCB
30 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 18

When setting the address (via the dipswitch) use the silkscreen
on the printed circuit board. This silkscreen shows a “1” and a “0” to
refer to the “on and “off” states that each switch is set to. Switch S1
configures port one (labeled J1) and, on two port cards, switch S2
configures port two (labeled J2). Least significant bit (LSB) and most
significant bit (MSB) are labeled on the card. Table 1 shows the
numerical weight and electrical connection of each switch position.
Refer to Table 2 for COM port addresses. Table 3 shows frequently
unused port addresses for applications when COM port addresses
1-4 are already used.
Table 1. Address Switches
Switch Position 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Bus Connection
Decimal Weight
Hex Weight
SA9 SA8 SA7 SA6 SA5 SA4 SA3
512 256 128 64 32 16 8
200 100 80 40 20 10 8
To install the 3PXCC card as COM1, 2, 3, or 4, follow the switch
settings shown in Table 2. To install at another address, follow the
switch settings shown in Table 3.
Table 2. Standard Port Addresses
Base Hex
Address
Binary
Equivalent
Switch Settings
MSB LSB
7654321
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4
3F8 1111111000 1111111
2F8 1011111000 1011111
3E8 1111101000 1111101
2E8 1011101000 1011101
Table 3. Frequently Unused Port Addresses
Base
Hex
Address
Binary
Equivalent
Switch
Settings
MSB LSB
I/O Space
Description
7654321
200
208
300
308
310
318
380
388
3A0
3A8
1000000000 1000000 game port
1000001000 1000001 game port
1100000000 1100000 prototype
1100001000 1100001 prototype
1100010000 1100010 prototype
1100011000 1100011 prototype
1110000000 1110000 SDLC
1110001000 1110001 SDLC
1110100000 1110100 bisync com
1110101000 1110101 bisync com
Interrupt Jumper Setup
The IRQ is a hardware Interrupt Request line in an ISA Bus
expansion slot on a PC or AT compatible computer. The 8 bit PC
ISA slot has 8 interrupts, the 16 bit slot has another 7 since one of
the first 8 is used to link in the remaining 8. The IRQ is used by
devices to request immediate service by the main microprocessor.
When the IRQ line is set, the microprocessor stops whatever it’s
doing, saves status, checks which line was set, then jumps to code
to handle the interrupt. The processor then clears the interrupt and
returns to what it was doing before. IRQ lines are set by the internal
timer, keyboard, hard drive controller, PCI, USB controller, sound
card, serial ports, printer and more. The 3PXCC2 serial cards
include special circuitry which allows one IRQ to be shared between
the cards two ports even during simultaneous use. The software
driver must support shared IRQs for this feature to work. Both
Windows 9x and NT support shared IRQs. To configure both ports
of the card to share one IRQ, set both jumpers of JP4 to the “Share”
position. The Port 1 IRQ Select jumper should then be set to the
desired IRQ. The Port 2 IRQ Select jumper is ignored when in
shared mode.
The 3PXCC cards allow the use of interrupts (IRQ) 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 10, 11, 12, 14, and 15. Table 4 shows the standard serial port IRQ
settings. NOTE: If two ports use the same IRQ setting, both ports
cannot use the serial port at once. Only one port at a time may
communicate.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 31
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
32 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 19

Table 4. Standard IRQ Settings
COM1 IRQ4
COM2 IRQ3
COM3 IRQ4
COM4 IRQ3
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 33
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
34 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 20

Chapter 5: Communication Jumper Settings
This chapter will cover all of the jumper settings to set your B&B
Serial Card for the proper communications that you desire.
CAUTION: Electrostatic Sensitive Device.
Use ESD precautions for safe handling.
RS-232 Mode
To configure a port for RS-232 mode, 5 jumpers must be
checked. The following settings will configure Port 1 as RS-232.
1. JP1A - must be set in the "232" (left) position.
2. JP1F - all four jumpers must be set in the "232" (left) position.
Jumpers JP1B - JP1E have no meaning in RS-232 mode
and may be in either position. Figure 2 shows the jumper
configuration to set both ports for RS-232 mode.
RS-422 Mode
To configure a port for RS-422 mode, 7 jumpers must be
checked. The following settings configure Port 1 as RS-422.
1. JP1A, JP1B, JP1C - must be set in the "422" (right) position.
2. JP1F - all four jumpers must be in the "422" (right) position.
Figure 3 shows the jumper configuration to set both ports for
RS-422 mode.
Figure 3. RS-422 Mode Jumper Settings
Note that the EIA RS-422 Specification labels data lines with
an "A" and "B" designator. Some RS-422 equipment uses a "+" and
"-" designator. In almost all cases, the "A" line is the equivalent of
the "-" line and the "B" line is the equivalent of the "+" line. More
information on RS-422 communications can be found in B&B
Electronics’ free RS-422/RS-485 Application Note.
Figure 2. RS-232 Mode Jumper Settings
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 35
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
RS-485 Mode
To configure a port for RS-485 mode, 9 jumpers must be
checked. The following settings configure Port 1 as RS-485.
1. JP1A - must be set in the "422" (right) position.
2. JP1B, JP1C - must be set in the "485" (left) position.
3. JP1D, JP1E - set to match software and installation
requirements.
4. JP1F - all four jumpers must be in the "422" (right) position.
36 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 21

Figure 4 shows the jumper settings for RS-485 mode.
Figure 4. RS-485 Mode Jumper Settings
RS-485 Pinouts
The pinouts in RS-485 mode are the same as those listed in
Table 7 for RS-422 mode.
RS-485 Operation
RS-485 mode requires that the driver be enabled and
disabled as needed, allowing two or four-wire communications. To
set up the 3PXCC1A Serial Card up for two wire mode you can
simply jumper TD(A) to RD(A) (for your Data “-“) and TD(B) to RD(B)
(for your Data “+”). Use the Signal Ground for your return path as
the third wire in this configuration. For four wire mode, simply use all
four data lines and signal ground for a return path.
The 3PXCC card provides two methods of
enabling/disabling the driver: automatic send data (SD) control and
request to send (RTS) control. With automatic SD control, the driver
is enabled when data is transmitted. It remains enabled for the
transmission time of one character after data transfer is complete.
The SD circuit automatically adjusts its timing to the baud rate of the
data. With RTS control, software must set the RTS bit to a logic 1 to
enable the driver and logic 0 to disable the driver. To select SD
control, place jumpers JP1D and JP2D in the SD position (left).
Place these jumpers in the RTS position (right) for RTS control.
The receiver can also be enabled and disabled, a useful
feature in two-wire communications to prevent the transmitted data
from "echoing back" on its own receiver. Jumpers JP1C and JP2C
control this feature for Port 1 and Port 2. If these jumpers are placed
in the RS-485 position, the "echo" is turned off. This is achieved by
disabling the receiver when the driver is enabled. Placing these
jumpers in the RS-422 position will hold the receiver enabled at all
times. More information on RS-485 communications can be found in
B&B Electronics’ free RS-422/RS-485 Application Note.
RS-422 and RS-485 Termination
A 120Ω termination resistor has been provided for the RS-
422/485 receivers. To enable the termination provided, place JP1E
for Port 1 or JP2E for Port 2 in the Rt IN position (right). If you do not
need to use termination, place the jumpers in the Rt OUT position
(left). Termination should only be used when very long wiring runs
are used with high baud rates. For example, with most cables which
are 4000 feet or shorter and have baud rates at 19.2K baud or
lower, termination is not required. Note that if the termination is
enabled (IN), the biasing of the RS-485 network is altered and the
value of the bias resistors will likely need to be changed somewhere
on the network. More information on termination and biasing can be
found in B&B Electronics’ free RS-422/RS-485 Application Note.
High Speed Mode
High data rates can be obtained with the 3PXCC cards by
adjusting JP1G and JP2G. This multiplies the clock speed supplied
to the UARTs by 4 times to 7.328MHz for ports 1 and 2 respectively,
allowing data rates up to 460.8K baud in RS-422 and RS-485
modes. Note: RS-232 does not support these extended baud rates.
To use the higher clock rate, place the jumper for the
appropriate port in the *4 (left) position. The jumpers are shipped
from the factory in the standard clock (right) position.
Note that serial software is not aware of the change in
oscillator frequency. For example, in the ×4 position, setting the
baud rate to 57.6K baud in software will result in a actual baud rate
of 230.4K baud. It is important to note that increasing the baud rate
may not increase actual throughput. In heavy multitasking cases or
with a slow computer, the computer’s inability to respond to
interrupts quickly enough will cause large idle spaces between
characters. Increasing the baud rate to this point will not increase
actual throughput.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 37
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
38 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 22

Chapter 6: Physical Hook-up and Troubleshooting
c
This chapter will cover 3PXCC pinout, communication cable
data, and troubleshooting information.
Pinouts
RS-232 Pinouts
The 3PXCC Serial Cards are wired as DTE (Data Terminal
Equipment) devices. The 3PXCC Serial Cards can be connected
directly to DCE (Data Communication Equipment) devices with a
straight through cable. If you need to connect two DTE devices, you
will need a null modem cable or cross-over cable.
Table 5. RS-232 Pinout Description
Pin Name Description Direction
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
DCD Data Carrier Detect input
RD Receive Data input
TD Transmit Data output
DTR Data Terminal Ready output
GND Signal Ground -----DSR Data Set Ready input
RTS Request to Send output
CTS Clear to Send input
RI Ring Indicator input
Pin Name Description
1 RD(A) Receive Data A
2 TD(B) Transmit Data B
3 TD(A) Transmit Data A
5 GND Signal Ground
9 RD(B) Receive Data B
Table 6. RS-422/RS-485 Pinout Description
RS-485 Pinouts
RS-485 mode supports both full and half duplex
communications (transmit and receive data signals). The pinouts of
the DB-9 connector are given in Table 6 (if full duplex
communication is used). Figure 5 shows how to connect a typical
RS-422/RS-485 full duplex communication link. Figure 6 shows how
to connect a typical RS-485 half duplex communication link.
3PXCCXX Serial Card
TD(A-) Pin 3
TD(B+) Pin 2
RD(A-) Pin 1
RD(B+) Pin 9
GND Pin 5
RS-422 Four Wire Devi
RD(-)
RD(+)
TD(-)
TD(+)
GND
RS-422 Pinouts
RS-422 mode supports transmit and receive data signals.
The pinouts of the DB-9 connector are given in Table 6. Figure 5
shows how to connect a typical RS-422/RS-485 full duplex
communication link.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 39
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Figure 5. RS-422/RS-485 (Four Wire) Pinout Description
40 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 23

3PXCCXX Serial Card
TD(A-) Pin 3
TD(B+) Pin 2
RD(A-) Pin 1
RD(B+) Pin 9
GND Pin 5
RS-485 Two Wire Device
DATA (-)
DATA(+)
GND
Figure 6. RS-485 (Two-Wire) Pinout Description
Communication Cable Data
The 3PXCC Serial Card communicates using RS-232, RS-422,
and RS-485 communications. The communication cable
specifications are 24AWG (wire gauge) and 30pF/ft. (capacitance
rating). Twisted pairs are ideal for the RS-422/RS-485 Cable in
order to suppress noise on the data line. B&B Electronics can
provide this communication cable for RS-232 or RS-422/RS-485
Applications. The Model ETC8195 is a cable style that can be used
for RS-232 Applications, and Model ETC8506 can be used for RS422/RS-485 Applications.
Troubleshooting
If you are unable to communicate with the card from your software:
1. Consult your software manual to make sure it supports the
address and interrupt that you have configured.
2. Double check that the address and interrupt are properly set.
3. Try another software package for troubleshooting. Download
SimpTerm (DOS Terminal Emulator) or Comtest (Windows
Terminal Emulator) from B&B Electronics’ web site. SimpTerm
and Comtest are shareware Simple Terminal Emulators that can
be used to vary the setup of any serial card. Both can be
downloaded from the following site location.
http://www.bb-elec.com/support.asp
4. Troubleshooting with a Loopback Test
Load Simpterm or Comtest on the test PC. When loading
Simpterm you must set up the port address and IRQ you have set
on the B&B Electronics serial card.
Jumper TD to RD on the DB9 male connector located on the
serial card. You may have to make a “loopback connector” in order
to do this. This is done by jumping pin 2 and pin 3 of a DB9 female
connector and plugging it into the DB9 male port on the serial card.
To test the RS-232 handshake lines you can also jumper RTS to
CTS and DTR to DSR. When you raise the RTS line you should see
CTS also go high. When you raise the DTR line you should see
DSR also go high.
Send data from the Serial Port (B&B Electronics serial card) and
see if the data is echoed back to the port. When a character is typed
on the keyboard you must see a duplicate character after the first
character to verify that the same character was received. Perform
this test on all ports of your serial card to verify the ports can (or
cannot) transmit and receive data.
5. Call B&B Electronics' Technical Support at the number/s shown
below:
International/USA Office:
(815) 433-5100, 8a.m. - 5:00 p.m. weekdays (Central USA Time).
European Office:
+353 91-792444, 8a.m. – 4:30 p.m. weekdays (UK).
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 41
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
42 Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 24

Appendix A: Hardware I/O Map
I/O Map of XT Class Machines
Hex Address Address Function in XT Class Machines
000-00F
020-021
040-043
060-063
080-083
0A0-0AF
200-20F
210-217
2E8-2EF
2F8-2FF
300-31F
320-32F
378-37F
380-38F
3B0-3BF
3D0-3D7
3E8-3EF
3F0-3F7
3F8-3FF
DMA controller (8237A)
interrupt controller (8259A)
timer (8253)
PPI(8255A)
DMA page register (74LS612)
NMI - non maskable interrupt
game port joystick controller
expansion unit
COM4 serial port
COM2 serial port
prototype card
hard disk
parallel print
SDLC
MDA - monochrome adapter and printer
CGA - color graphics adapter
COM3 serial port
floppy diskette controller
COM1 serial port
I/O Map of AT Class Machines
Hex Address Address Function in AT Class Machines
000-01F
020-03F
040-05F
060-06F
070-07F
080-09F
0A0-0BF
0C0-0DF
0F0-0FF
1F0-1F8
200-20F
258-25F
278-27F
2E8-2EF
2F8-2FF
300-31F
378-37F
380-38F
3A0-3AF
3B0-3BF
3BC-3BE
3C0-3CF
3D0-3D7
3E8-3EF
3F0-3F7
3F8-3FF
DMA controller #1 (8237A-5)
interrupt controller #1 (8259A)
timer (8254)
keyboard (8042)
NMI - non maskable interrupt & CMOS RAM
DMA page register (74LS612)
interrupt controller #2 (8259A)
DMA controller #2 (8237A)
80287 math coprocessor
hard disk
game port joystick controller
Intel Above Board
parallel printer port 2
COM4 serial port
COM2 serial port
prototype card
parallel printer 1
SDLC or bisync com 2
bisync com 1
MDA - monochrome adapter
parallel printer on monochrome adapter
EGA - reserved
CGA - color graphics adapter
COM 3 serial port
floppy diskette controller
COM1 serial port
Any eight-byte space not used by one of the devices listed in the
table and not used by any other equipment in your system may be
used for the serial port.
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 Appendix A: Hardware I/O A-1
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
A-2 Appendix A: Hardware I/O Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
Page 25

Appendix B: Declaration of Conformity Statement
Manufacturer’s Name: B&B Electronics Manufacturing Company
Manufacturer’s Address: P.O. Box 1040
707 Dayton Road
Ottawa, IL 61350 USA
Model Numbers: 3PXCC1A, 3PXCC1B, 3PXCC2A, 3PXCC2B
Description: RS-232 Serial Card
Type: Light industrial ITE equipment
Application of Council Directive: 89/336/EEC
Standards: EN 55022
EN 61000-6-1
EN 61000 (-4-2, -4-3, -4-4, -4-5, -4-6, -4-8, -4-11)
DECLARATION OF CONFORMITY
William H. Franklin III, Director of Engineering
Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903 Declaration of Conformity B-1
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
B-2 Declaration of Conformity Documentation No.3PXCC1x-2x-3903
B&B Electronics Mfg Co – 707 Dayton Rd - PO Box 1040 - Ottawa IL 61350 - Ph 815-433-5100 - Fax 815-433-5104
B&B Electronics Ltd – Westlink Comm. Pk – Oranmore, Galway, Ireland – Ph +353 91-792444 – Fax +353 91-792445
 Loading...
Loading...