BARIX IPAM400 Users Manual

IPAM 400
Preliminary Development Specification
Advanced, multi format IP audio module with network, USB and serial
interfaces plus Wi-Fi, adding IP based streaming and controlling
capabilities to OEM products
Document version 02.20
Release date 9th April 2018
Hardware Rev. HW 12
© 2017 Barix AG, all rights reserved. All information is subject to change without notice.
All mentioned trademarks belong to their respective owners and are used for reference only

Preliminary Development – BARIX IP AUDIO MODULE 400 – V 02.20 – 9.April.2018
Table of contents 2
Table of Con tents
TABLE OF CONTENTS 2
INTRODUCTION 4
About this document 4
Additional documents 4
About the IP AUDIO MODULE 400 4
Hardware features 4
Evaluation of the Barix IP Audio Module 4
Basic Support Package (BSP) Yocto layer 5
HARDWARE 6
Mechanical drawing 6
Block diagram 7
Network interfaces 7
Serial interfaces 7
Digital audio 7
Analog audio 8
Power supply 8
Peripheral I/O 8
CONNECTORS 9
Connector placement 9
Connector pin out 9
J1 pin out (analog audio input and output) 9
J2 pin out (GPIO, UART, USB, I2C) 9
J4 pin out (network, USB) 10
J5 pin out (I2S output) 10
LAYOUT GUIDELINES 11
General rules 11
Carrier PCB Power and Signal Domains 12
TECHNICAL DATA 13
Power supply input 13
CPUs / Boot / Memory 13
Network interfaces 13

Preliminary Development – BARIX IP AUDIO MODULE 400 – V 02.20 – 9.April.2018
Table of contents 3
Serial interfaces 13
Peripheral I/O interfaces 13
Audio interfaces 13
Audio Processor (Codec) Decoding features 13
Line Input and A/D Conversion typical values 14
Microphone input and A/D conversion typical values 14
Line output and D/A conversion typical values 14
Mechanical 14
Dimensions 14
Weight 14
MTBF calculations 15
Environmental 15
Core frequency versus Temperature variation 15
Certifications / Compliances 16
ORDERING INFORMATION 17

Preliminary Development – BARIX IP AUDIO MODULE 400 – V 02.20 – 9.April.2018
Introduction 4
In trodu c tion
About this
document
This Development Specification aims at giving insight to detailed
technical aspects of the Barix IP AUDIO MODULE 400 (IPAM400) and
complements the information given in the product sheet.
Additional
documents
As several different Linux OS based images and packages can be used
with the Barix IP AUDIO MODULE 400, the process of loading or
updating software is covered in individual documents.
For information about the loading and configuration of the loaded
firmware please refer to the corresponding software user manual and
firmware technical documentation.
About the IP
AUDIO MODULE
400
The IP AUDIO MODULE 400 enables manufacturers of traditional audio
devices to add network capabilities to their products as well as develop
IP streaming devices.
Hardware
features
The Barix IP AUDIO MODULE 400 features:
• Stereo line input and output, 0dBuStereo Line in and outputs
• Microphone input (coil, powered or passive capacitive,
balanced or unbalanced)
• I2S input and output (192k capable)
• Integrated SoC with ARM Cortex quad core CPU
• 10/100/100Mbit Ethernet port (with PHY)
• SD/TF card slot
• 16MB SPI Flash
• TTL level UART
• USB2.0 OTG interface, two USB2.0 Host
• Dallas 1-wire interface (e.g. for Real Time Clock)
• 7 GPIOs
• Small form factor
• Low Power consumption, runs off a single +3.3Volt DC
power source
• 2 mounting holes (0.106”/2.7mm) for fixation of IP Audio
Module
Evaluation of the
Barix IP Audio
Module
Barix recommends the IPAM evaluation board based on Annucicom 60
for evaluation purposes prior to development of an own carrier board.

Preliminary Development – BARIX IP AUDIO MODULE 400 – V 02.20 – 9.April.2018
Introduction 5
Basic Support
Package (BSP)
Yocto layer
The BARIX IPAM400 can be used for developing multiple applications
related to networked audio distribution, playback and control.
BARIX provides an embedded Linux system based on the Yocto
framework and the associated Yocto layer that contains the board's
Basic Support Package (BSP) for the IPAM400.
This Yocto layer can be used as a base platform to develop all kind of
applications on top of it.
The provided BSP Yocto layer includes:
· Definitions for the "barix-ipam400" machine
· U-Boot boot loader
· Linux Kernel 4.x
· A default Linux Kernel device tree and Kernel configuration
· Secure Firmware update mechanism featuring a dual root file
system strategy and a recovery mechanism
· Definition for a base SW image
· Scripts to create and install SW images and SW updates
All these functionalities are configurable and adaptable to the
developer's needs.
Developers can use the BSP to generate the toolchain that enables the
development of any application.
The BSP package is a starting point and can be easily extended by
creating or adding Yocto layers that allow developers to quickly add
more applications and libraries to completely customize the software
and to create new SW images.
The common feature set includes:
• Embedded and robust operating system with IPv4/IPv6 IP stack
• IP standard based protocols (TCP/IP, UDP, HTTP, ICMP, SNMP)
• OEM Software development by BARIX on request
• High quality, multi standard audio encoding and decoding can be
implemented in software:
• G.711, G.722, PCM linear, Ogg Vorbis, MP3, AAC+, FLAC
• Acoustic echo cancellation (AEC)
Preliminary Development – BARIX IP AUDIO MODULE 400 – V 02.20 – 9.April.2018
Hardware 6
Hardwa re
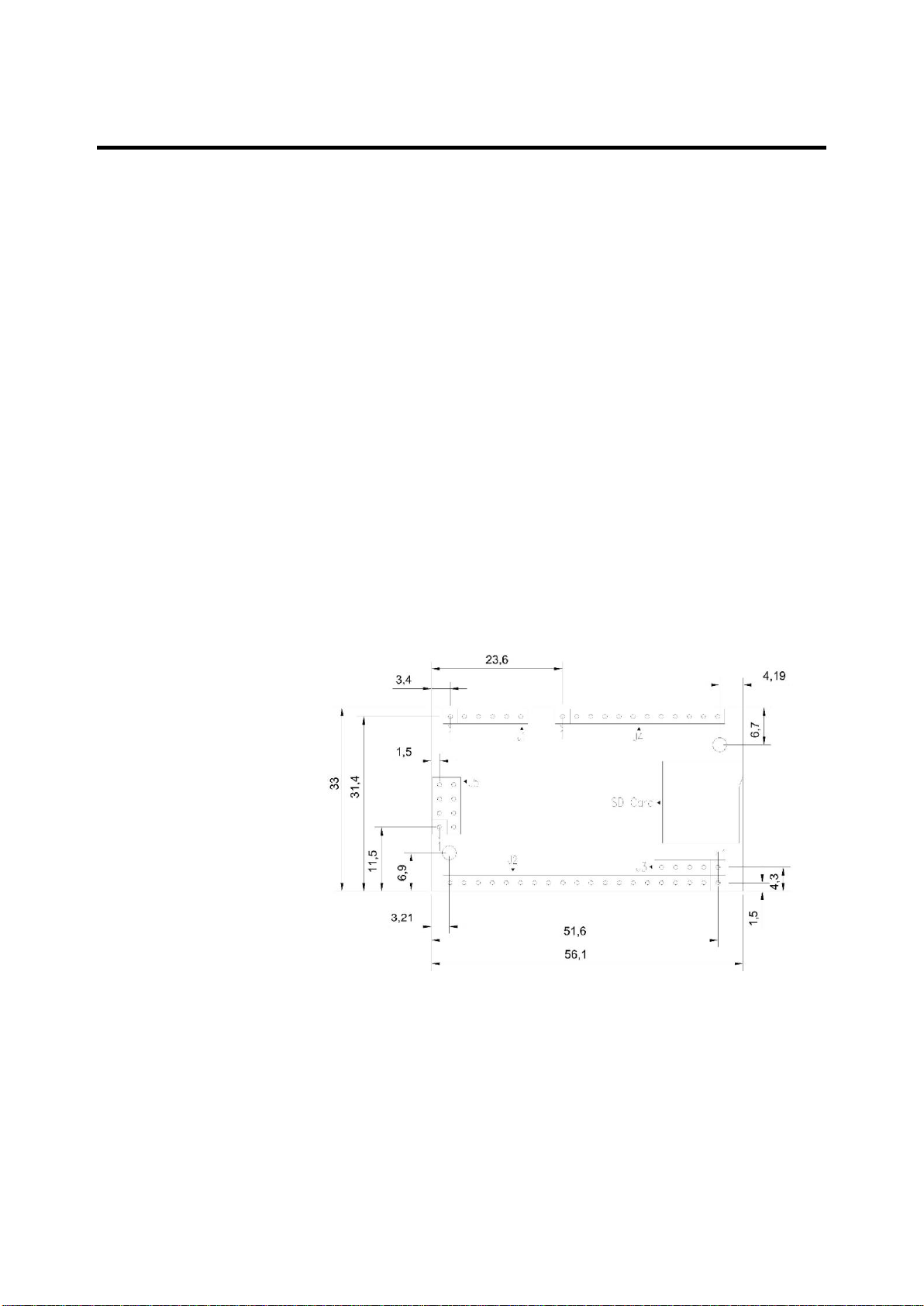
Mechanical drawing
The Barix IP AUDIO MODULE 400 provides five, standard 2,54mm
spacing, single row pin headers, intended to match target connector or
motherboard, also suitable to soldering.
For mechanical fixation, the board provides two 2.7mm mounting holes
for 2.5mm screws.
The total size is 56.1mm +/-0.2 by 33.0mm +/-0.2.
Maximum component height is 5.6mm. Using standard distance bolts of
6mm a total height of 9mm above the carrier board can be achieved
when mounted on a carrier board by means of soldering the pin headers
into holes of the carrier board directly.
Using single row female headers (counterpart to pin headers) the height
will increase and must be measured by the integrator (our experience in
production shows a minimal height of 11.5mm above the carrier board
without using distance bolts and 12mm using 9mm distance bolts).
Although the total height is increased, the advantage of being able to
replace a module should be considered.
The above drawing shows the component side which faces down onto
the carrier PCB.
Dimensions are metric (mm)
Drawing is not to scale
Tolerance of PCB dimension is +-0.2mm, others 0.1mm
 Loading...
Loading...