Page 1

Installation, Operation and
Maintenance Instructions
for AC Induction Motors
56- 6800 Frames (NEMA)
63 – 280 Frames (IEC)
MARATHON ELECTRIC
Contact Motor Customer Service at:
Phone:
www.marathonelectric.com
(715) 675-3311
Form 5554E
Page 2
INSTALLER: PLEASE LEAVE THIS MANUAL FOR THE OWNER’S USE
OWNER: READ AND SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This is the safety alert symbol. It is used to alert you to potential personal
injury hazards. Obey all safety messages that follow this symbol to avoid
possible injury or death.
WARNING
Before installing, using, or servicing this product, carefully read and fully
understand the instructions including all warnings, cautions, & safety notice
statements. To reduce risk of personal injury, death and/or property damage,
follow all instructions for proper motor installation, operation and maintenance.
These instructions are not intended as a complete listing of all details for
installation, operation, and maintenance. If you have any questions concerning
any of the procedures, STOP, and call the appropriate Regal-Beloit motor
Table of Contents
1.0 INSTALLER / OWNER / OPERATOR RESPONSIBILITY
2.0 RECEIVING & INSPECTION
3.0 INSTALLATION AND OPERATION
company.
1.1 Electrical Safety
1.2 Mechanical Safety
1.3 Environmental Safety
2.1 Initial Inspection
2.1.1 Packing List & Inspect
2.1.2 Turn Motor Shaft
2.1.3 Check Nameplate
2.2 Handling
2.2.1 Correct Lifting Angles
2.3 Storage
2.3.1 Bearing Lubrication
2.3.2 Shaft Rotation
2.3.3 Damp or Humid Storage Locations
3.1 Location
3.1.1 Selecting a Location
3.1.2 Ambient Temperature Limits
3.1.3 Construction Selection per Location
3.1.3.1 Dripproof
3.1.3.2 Totally Enclosed
3.1.3.3 Hazardous Locations Motors
3.2 Mounting Motor
3.2.1 Rigid Base (Footed)
3.2.2 Rigid Base Hole Selection -6 or 8 Hole Bases
3.2.3 Vertical
3.3 Application Assembly to Motor
3.3.1 General: Proper Alignment
3.3.2 Direct Coupling
3.3.3 Direct Connected
3.3.4 Belted
3.3.5 VFD Operation
3.3.6 Accessories
3.3.6.1 General
3.3.6.2 Brake Motors
3.3.6.3 Space Heaters
3.3.6.4 Thermal Protection General, Thermostats,
Thermisters & RTDs
3.3.6.5 RTD Alarm & Trip Settings
3.3.7 Guards
3.4 Electrical Connections
3.4.1 Power Supply / Branch Circuit
3.4.1.1 Branch Circuit Supply
3.4.1.2 Fuses, Breakers, Overload Relays
3.4.1.3 AC Power Supply Limits
3.4.2 Terminal Box
3.4.2.1 Conduit opening
3.4.2.2 Hazardous Locations
3.4.3 Lead Connections
3.4.3.1 Wire Size Requirements (Single Phase)
3.4.3.2 Extension Cords (Single Phase)
3.4.4 Ground Connections
3.4.5 Start Up
3.4.5.1 Start Up – No Load Procedure
3.4.5.2 Start Up – Load Connected Procedure
3.4.5.3 Jogging and/or repeated starts
4.0 MAINTENANCE
4.1 General Inspection
Page 3
4.1.1 Ventilation
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.1.2 Insulation
4.1.3 Electrical Connections
4.2 Lubrication and Bearings
4.2.1 Grease Type
4.2.2 Bearing Operating Temperature
4.2.3 Lubrication Interval
4.2.4 Lubrication Procedure
4.2.5 Lubrication Example
4.3 Trouble Shooting
4.3.1 General Trouble-Shooting Warnings
4.3.2 Trouble-Shooting Cause / Corrective Action
1.0
INSTALLER/OWNER/OPERATOR
1.1
ELECTRICAL SAFETY
WARNING:
Electrical connections shall be made by a qualified electrical personnel in
accordance with all applicable codes, ordinances and sound practices.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in serious personal injury,
death and/or property damage. Only qualified personnel who are familiar
with the applicable National Code (USA = NEC) and local codes should
install or repair electrical motors and their accessories.
WARNING:
Do not touch electrically live parts. Disconnect, lockout and tag input
power supply before installing or servicing motor (includes accessory
devices). Use a voltmeter to verify that power is off before contacting
conductors.
WARNING:
Failure to properly ground motors, per the National Electrical Code (NEC)
Article 430 and local codes may cause serious injury or death to
personnel. For general information on grounding refer to NEC Article
250. (Also see “Ground Connections section 3.4.4“).
WARNING:
Do not use automatic reset protectors if automatically restarting the motor
will place personnel or equipment at risk. . Failure to follow this instruction
could result in serious personal injury, death and/or property damage
WARNING:
If a tripped manual reset thermal protector is exposed to a temperature
less than –7°C (20°F) it may reset and restart the motor automatically. If
an application requires a motor with a manual reset thermal protector that
will be operated at temperatures less than –7°C (20°F) contact the
manufacturer to review the application / motor requirements. Failure to
follow this instruction could result in serious personal injury, death and/or
property damage
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
ELECTRICAL LIVE CIRCUIT HAZARD
ELECTRICAL GROUNDING HAZARD
AUTOMATIC RESET PROTECTOR HAZARD
MANUAL RESET PROTECTOR HAZARD
RESPONSIBILITY
:
1.2
MECHANICAL SAFETY
WARNING:
Before starting the motor, remove all unused shaft keys and loose
rotating parts to prevent them from flying off. Failure to follow these
instructions could result in serious personal injury, death and/or property
damage.
WARNING:
Keep extremities, hair, jewelry and clothing away from moving parts.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in serious personal injury,
death and/or property damage.
1.3
ENVIRONMENTAL SAFETY
WARNING:
(1) The NEC and the local authority having jurisdiction must be consulted
concerning the installation and suitability of motors for use in
Hazardous Locations. The local authority having jurisdiction must
make the final determination of what type of motor is required. The
application and operation is beyond the control of the motor
manufacturer.
(2) Division 1 Hazardous Locations motors can only be modified or
reworked by the manufacturer or a facility that is Listed under UL’s
category “Motors and Generators, Rebuilt for use in Hazardous
Locations”. Failure to follow these instructions could result in serious
personal injury, death and/or property damage.
(3) Do not use a Hazardous Locations motor with a Variable Frequency
Drive (VFD) unless the motor nameplate specifically states that the
LOOSE PARTS HAZARD
ROTATING PARTS HAZARD
HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS
motor is suitable for use on Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) type VFD
power. In addition, the nameplate must be marked with the inverter
rating; for example, “2:1 CT”, “2 to 1 Constant Torque”, etc.
2.0 RECEIVING AND INSPECTION
2.1
INITIAL INSPECTIONS
2.1.1
packaging to make certain no damage has occurred in shipment. If
there is visible damage to the packaging, unpack and inspect the
motor immediately. Claims for any damage done in shipment must
be made by the purchaser against the transportation company.
2.1.2
rotates freely. Note: Shaft seals and bearing seals may add drag.
CHECK PACKING LIST AND INSPECT
TURN MOTOR SHAFT
by hand to be certain that it
2.1.3
order requirements and compliance with power supply and control
equipment requirements.
2.2
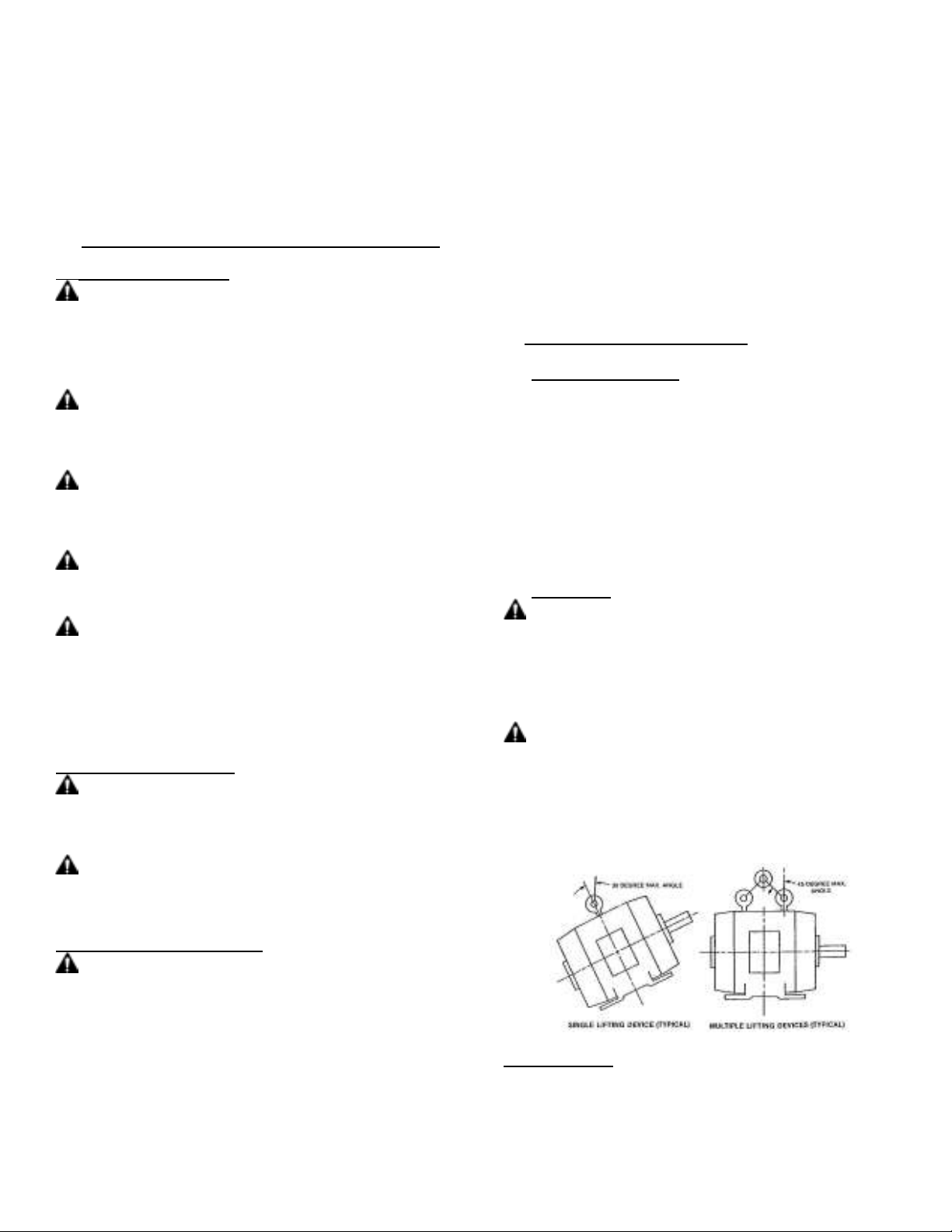
Eyebolts or lifting lugs, where provided, are intended for lifting
only the motor and accessories mounted by the motor
manufacturer (unless specifically stated otherwise on the motor).
Utilizing the motor lifting provision to lift other components such as
pumps and gear boxes could result in serious personal injury, death
and/or property damage.
Before using the lifting provision, check the eyebolts and/or other lifting
means to assure they are not bent or damaged and are completely
threaded, seated & secured to the motor. Equipment to lift motor must
have adequate lifting capacity. While lifting the motor DO NOT stand
under or in the vicinity of the motor. Failure to follow these instructions
could result in serious personal injury, death and/or property damage.
2.2.1
CHECK NAMEPLATE
HANDLING
WARNING:
WARNING:
:
FALLING OBJECT HAZARD
FALLING OBJECT HAZARD
LIFTING ANGLE LIMITATIONS
for conformance with purchase
2.3 STORAGE:
stored indoors in a clean, dry location. Avoid locations with large
temperature swings that will result in condensation. Motors must be
covered to eliminate airborne dust and dirt. If the storage location
exhibits high vibration, place isolation pads under motor to minimize
damage to motor bearings.
Motors, not put into service immediately, must be
the
Page 4
2.3.1
BEARING LUBRICATION:
at the factory; relubrication upon receipt of motor or while in storage
is not necessary. If stored more than one year, add grease per
lubrication instructions (Table 4-4) before start-up.
2.3.2
SHAFT ROTATION:
shaft be rotated 5 to 10 rotations every three months to distribute the
grease in the bearings. This will reduce the chance for corrosion to
form on the bearing rolling elements and raceways. Note: Shaft
seals and bearing seals may add drag.
2.3.3
DAMP OR HUMID STORAGE LOCATIONS:
unpainted flanges, shafts, and fittings with a rust inhibitor. Apply
appropriate power to the motor’s space heaters (if so equipped)
Bearings are grease packed
It is recommended that the motor
Treat
3.0 INSTALLATION AND OPERATION
WARNING:
appropriate national code, local codes and sound practices should install
or repair electrical motors and their accessories. Installation should
conform to the appropriate national code as well as local codes and
sound practices. Failure to follow these instructions could result in serious
personal injury, death and/or property damage.
WARNING:
Do not touch electrically live parts. Disconnect, Lockout and Tag input
power supply before installing or servicing motor (includes accessory
devices). Use a voltmeter to verify that power is off before contacting
conductors.
3.1
LOCATION
Only qualified personnel who are familiar with the
ELECTRICAL LIVE CIRCUIT HAZARD
3.1.1
SELECTING A LOCATION:
given to environment and ventilation. Motors should be installed in
an area that is protected from direct sunlight, corrosives, harmful
gases or liquids, dust, metallic particles, and vibration. A motor with
the proper enclosure for the expected operating condition should be
selected. Provide accessible clearance for cleaning, repair, service,
and inspections (See section 3.1.3 for construction clearances).
The location should be considered for possible future motor removal
/ handling. The free flow of air around the motor should not be
obstructed.
3.1.2
temperatures of the air inlet to the motor should not exceed 40°C
(104°F) or be less than -30°C (-22°F) unless the motor nameplate
specifically states an ambient temperature outside of these limits.
The ambient inside an enclosure built around the motor shall not
exceed the nameplate ambient. For ambient temperatures outside of
these limits consult the motor manufacturer.
Insulation at high temperatures ages at an accelerated rate. Each
10°C increase in temperature reduces the insulation life by one half.
Division 1 Hazardous Locations motors shall NOT be operated
below –25°C (-13°F) ambient. (Low temperatures reduce the
component mechanical properties.)
3.1.3
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE LIMITS:
CAUTION:
WARNING:
INSULATION DEGRADATION WARNING
HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS AMBIENT LIMIT:
CONSTRUCTION SELECTION per LOCATION:
3.1.3.1
3.1.3.2
indoor or outdoor standard service applications.
DRIPPROOF (OPEN) MOTORS are intended for use
indoors where the atmosphere is relatively clean, dry,
and non-corrosive. Recommended a minimum
clearance of ½ the shaft height between vent openings
and the nearest obstruction.
TOTALLY ENCLOSED MOTORS are suitable for
TEAO or AOM (Totally Enclosed Air Over) motors must be
mounted in the air stream. When the motor nameplate states a
minimum airflow the motor must be mounted in an air stream
meeting this minimum value.
Consideration should be
The ambient
TEFC (Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled) motors must meet a
minimum distance of ½ the shaft height between the fan guard
grill openings and the nearest obstruction.
3.1.3.3
Locations motors are intended for installations in accordance with
NEC Article 500. For all installations involving Hazardous
Locations motors, consult the applicable national codes, local
codes, and the authority having jurisdiction.
A motor should never be placed in an area with a hazardous
process or where flammable gases or combustible materials may
be present unless it is specifically designed and nameplated for
this type of service. Hazardous Locations motors are intended for
installations in accordance with NEC Article 500. For all
installations involving Hazardous Locations motors, consult the
NEC, local codes, and the authority having jurisdiction. Failure to
follow these instructions could result in serious personal injury,
death and/or property damage. (For other limitations see section
1.3)
3.2
HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS MOTORS: Hazardous
Division 1 Installations – includes Class I & II: Use only
motors that are UL Listed and CSA Certified or UL Listed and
UL Certified for Canada. These motors bear a separate
nameplate that includes the UL Listing Mark and CSA
Certification Mark or includes the UL Listing Mark and the UL
Mark for Canada. This plate also bears the phrase: “ Electric
motor for Hazardous Locations” and is marked with the Class,
Group and Operating Temperature Code.
Division 2 Installations – Class I only: Use only motors that
are CSA Certified and bear the CSA Certification Mark.
These motors include a phrase on the main motor nameplate
that indicates the motor is CSA Certified for Class I, Division 2
/ Zone 2 locations.
Division 2 Installation – Class II only: Use only Class II
motors as described above under “Division I Installations”.
WARNING:
EXPLOSION HAZARD
MOUNTING MOTOR:
3.2.1
installed to a rigid foundation or a mounting surface to minimize
RIGID BASE (FOOTED):
vibration and maintain alignment between the motor shaft and the
load’s shaft. The mounting surfaces of the four mounting pads must
be flat within 0.01 inches for 210 frame & smaller; 0.015 inches for
250 frame & larger. [IEC 0.25 mm for 130 frame & smaller, 0.38 mm
for 160 frame & larger]. This may be accomplished by shims under
the motor feet. For special isolation mounting, contact manufacturer
for assistance
The motor must be securely
3.2.2
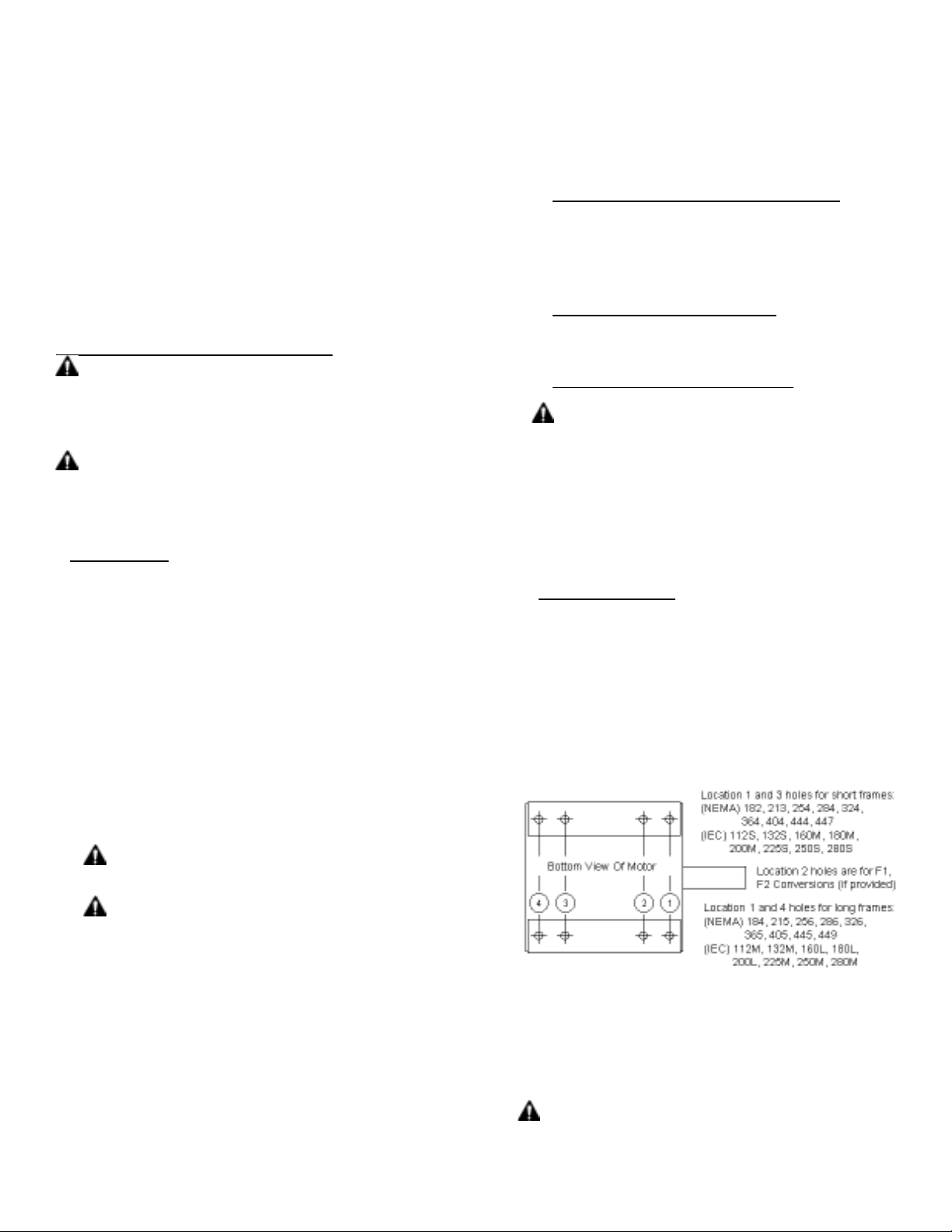
RIGID BASE HOLE SELECTION -6 OR 8 HOLES
3.2.3
VERTICAL MOUNTING:
CAUTION:
Dripproof rigid base (footed) motors do NOT meet “Dripproof”
requirements when mounted vertically. If the motor is located in
unprotected environments, the addition of a drip cover may be
available. Drip covers not available for cast iron rigid base motors.
WARNING:
The lifting provision on standard horizontal footed motors is not
designed for lifting the motor in a vertical shaft up or shaft down
position. (see 2.2.1 lifting angles). Lifting method / provisions for
ENCLOSURE PROTECTION CAUTION: Most
FALLING OBJECT HAZARD
Page 5
mounting a rigid base (footed) motor vertically is the responsibility of
the installer.
VERTICAL SHAFT DOWN: Most standard horizontal motors thru
449 Fr. (excluding brake motors) can be mounted in a vertical shaft
down orientation. For vertical brake motors see section 3.3.6.2.
VERTICAL SHAFT UP:
WARNING:
MOUNT: Hazardous locations motors must NOT be mounted
vertically shaft up without approval by the motor manufacturer.
Without proper retaining provisions the rotor may move axially and
contact components, creating a spark hazard.
HAZARDOUS LOCATIONS VERTICAL
Belted or Radial Load when mounted vertically
following frame sizes / constructions with applied (axial) down
loads within the limit stated are acceptable when mounted vertical
shaft up.
Table 3-1 Belted or Radial Load Applications (All speeds)
Frame
280-320
360 &
Notes:
1
2 The max applied down load is any applied load external to the
3 ”Build-up only”, refers to motors that are specifically ordered
3.3
CAUTION:
Do not connect or couple motor to load until correct rotational direction
is established.
Enclosure Construction
Size
TEFC &
56
140
180
210
250
Up
For TEFC model numbers beginning with 324TTFC or 326TTFC
consult the motor manufacturer to determine if a build up motor
is required.
motor, including such things as sheave weight, fan loads, axial
belt force, pump load, etc. If the application is direct drive with
no applied radial load, consult the motor manufacturer.
and built for shaft up applications. It does not imply that all buildup motors are suitable for shaft up applications.
ODP
TEFC
ODP Steel Yes 25 lbs
TEFC All Yes 35 lbs
ODP Steel Yes 35 lbs
TEFC All Yes 40 lbs
ODP Steel Yes 40 lbs
TEFC All Yes 40 lbs
ODP
320 TTFC
models
All Other
TEFC
ODP Cast Iron
TEFC &
ODP
TEFC Cast Iron
ODP Cast Iron No2 N/A
TEFC &
ODP
Steel Yes 25 lbs
Steel & Cast
Iron
Steel Yes 40 lbs
Cast Iron
Cast Iron
Cast Iron &
Aluminum
Steel
Steel
APPLICATION ASSEMBLY TO MOTOR:
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE:
Shaft Up
OK
Yes 25 lbs
No2
Eng1
Yes 30 lbs
No2
Build Up
Only4
Build Up
Only4
Build Up
Only4
Max
Applied
Down
Load3
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
3.3.1
driven equipment minimizes vibration levels, maximizes bearing life,
and extends the overall life of the machinery. Consult the drive or
equipment manufacturer for more information.
During assembly do NOT force components onto the shaft. Striking
or hammering the component may result in bearing damage.
GENERAL: PROPER ALIGNMENT
CAUTION:
BEARING FAILURE
of the motor and
: The
3.3.2
For applications that apply radial, axial or moment loading on the
motor shaft see section 3.3.3.
Unless approved by the motor manufacturer do NOT direct couple a
vertical shaft up or roller bearing motor. Direct coupling a vertical
shaft up motor or a motor with a roller bearing may result in bearing
damage.
3.3.3
connected equipment (gears, fans etc.) must be approved by the
motor manufacturer unless within the maximum overhung load limits
(Table 3-2). Combined loading (axial, radial and/or moments) must
be approved by motor manufacturer. For belted loads see section
3.3.4.
Values based on 26,280 hrs B-10 Life
For “End of Shaft” Load multiply value by 0.88
To convert from lbf to N multiply value by 4.4482.
DIRECT COUPLING:
CAUTION:
BEARING FAILURE
DIRECT CONNECTED:
Table 3-2 Maximum Radial Load (lbf) @ Middle of the Shaft
Extension Length
Frame
Number
143T 106 166 193 210
145T 109 170 199 218
182T 187 230 261 287
184T 193 237 273 301
213T 319 317 470 510
215T 327 320 480 533
254T 500 631 729 793
256T 510 631 736 820
284T - 866 990 1100
286T - 871 1005 1107
324T - 950 1100 1215
326T - 950 1113 1230
364T - 1078 1365 1515
365T - 1078 1380 1540
404T - 1388 1590 1762
405T - 1400 1610 1780
444T - 1580 1795 2005
445T - 1520 1795 1985
447T - 1455 1765 1985
449T - 1640 1885 2130
3600 1800 1200 900
Use flexible couplings if possible.
Radial loading for direct
Motor Rated RPM
3.3.4
BELTED:
The goal of any belted system is to efficiently transmit the required
torque while minimizing the loads on the bearings and shafts of the
motor and driven equipment. This can be accomplished by following
four basic guidelines:
1. Use the largest practical sheave diameter.
2. Use the fewest number of belts possible.
3. Keep sheaves as close as possible to support bearings.
4. Tension the belts to the lowest tension that will still transmit the
required torque without slipping. It is normal for V-belts to
squeal initially when line starting a motor
3.3.4.1
In general, smaller sheaves produce greater shaft stress and shaft
deflection due to increased belt tension. See Table 3-3 for
recommended minimum sheave diameters. Using larger sheaves
increases the contact with belts which reduces the number of belts
required. It also increases the belt speed, resulting in higher system
efficiencies. When selecting sheaves, do not exceed the
manufacturer's recommended maximum belt speed, typically 6,500
feet per minute for cast iron sheaves. Determine belt speed by the
following formula:
Sheave Diameter Guidelines:
Page 6

BELT SPEED (Ft/min) =
Figure 1
inches Dia Sheavex 3.14 x RPM Shaft )(
12
3.3.4.2
In general, use the fewest number of belts that will transmit the
required torque without slipping. See Table 3-3 for recommended
maximum number of belts. Each belt adds to the tension in the
system, which increases load on the shafts and bearings. Belts are
most efficient when operated at or near their rated horsepower.
If the sheaves have more grooves than the number of belts required,
use the grooves closest to the motor.
Number of Belts
3.3.4.3 Sheave Location
Install sheaves as close to the housing as possible to increase the
bearing life of the motor and driven equipment
Figure 2
3.3.4.4
Belt tensioning by feel is NOT acceptable. Tensioning by "feel" can
be very misleading, and can damage motor and equipment.
It is normal for V-belts to squeal initially when line starting a motor.
In general, belt tensions should be kept as loose as possible while
still transmitting the required torque without slipping. Belt tensions
must be measured with a belt tension gage. These inexpensive
gages may be obtained through belt manufacturers, or distributors.
Proper belt tension is determined by measuring the force required to
deflect the center of the belt a given distance. The proper deflection
(in inches) is determined by dividing the belt span in inches by 64.
Calculate the proper deflection and then see Table 3-3 for the
required “Deflected Force” to achieve that deflection.
After tensioning the belt, rotate the sheaves for several rotations or
operate the system for a few minutes to seat belts into the grooves,
then re-tension the belts. New belts will stretch during use, and
should be retensioned after the first eight hours of use.
Belt Tension
CAUTION:
Equipment Failure Caution
Page 7

100 10.0 5VX 6 16.0 8.6 5VX 6 13
5V
/8V 11 / 7
5V/8V
12 / 7
5V/8V
13 / 8
5V/8V
14 / 9
5V/8V
15 / 9
when Belting
Table 3-3 Recommended Minimum Sheave Diameters, Belt Type, Number of Belts and Deflected Force
1200 rpm 1800 rpm 3600 rpm
Motor Hp
Min
Sheave
Dia (in)
Belt
Type
Max
#
of
Belts
Avg.
Deflected
Force
(lbs)
Min
Sheave
Dia (in)
Belt
Type
Max
#
of
Belts
Avg.
Deflected
Force
(lbs)
Min
Sheave
Dia (in)
Belt
Type
Max
#
of
Belts
Avg.
Deflected
Force
(lbs)
Contact Motor
Manufacturer
3600 rpm Motors
Greater than 25 HP
Notes:
1. Horsepower is the nameplate motor horsepower, and RPM is the motor (driver) speed.
2. Minimum sheave diameters are from NEMA standards where applicable.
3. For variable speed applications or values outside these recommendations, consult motor manufacturer.
4. Selections are based on a 1.4 service factor, 5 to 1 speed ratio and various Power Transmission Manufacturers’ catalogs.
5. These selections are for Narrow V-belt sections only. Consult manufacturer for details on conventional V-belt sections (A, B, C, D and E), or other
belt types.
6. “Average Deflected Force is per section 3.3.4.4 of this document and is the force required to deflect the center of a belt 1/64 of the belt span
distance. Tolerance on this force is ±1 lbf for forces ≤10 lbs, and ±2 lbs for forces >10 lbs as measured utilizing a belt tension gage.
7. When more than one belt is required the belts must be a matched set (matched for length).
8. If possible, the lower side of the belt should be the driving side to increase the length of wrap on the sheave).
9. For belted loads do not exceed 125% of 60 Hz operating RPM.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
3.3.5 VFD (Variable Frequency Drives) OPERATION:
WARNING:
UL Recognition, UL Listing, or CSA certification does not apply to
motors that are equipped with a manual or automatic reset thermal
protector when the motor is operated on VFD power.
WARNING:
Power factor correction capacitors should never be installed
between the drive and the motor.
CAUTION: VFD / Motor Setup:
It is the responsibility of the startup personnel during set up of the
VFD / motor system to properly tune the drive to the motor for the
specific application per the VFD user manual. The correct voltage
boost and volts per hertz settings are application dependent and
unique to each motor design. Failure to connect over temperature
devices (when provided) will void the warranty.
VFD Motors with Reset Thermal Protectors
Power Factor Correction Capacitors:
3.3.5.1 Overspeed Capability:
Belted loads: Do not exceed 125% of 60 Hz operating RPM.
Table 3-4 Maximum Safe Continuous Speed (RPM)
For Coupled and Direct Connected Loads
NEMA / [IEC]
Frame Size
56-180 [80-110] 7200 * 5400 *
210-250 [130-160] 5400 * 4200*
280 [180] 5400 * 3600
320 [200] 4500 * 3600
360 [225] 4500 * 2700
400-440 [250-280] 3600 2700
>440 [>280] 3600 1800
* = Fan cooled motors (Totally Enclosed & Hazardous
Locations Motors) are limited to a maximum safe
continuous speed of 4000 RPM For higher speeds or
shortened duty cycle contact motor manufacturer
3.3.5.2 Cable Lengths:
limit VFD to motor cable lengths of general purpose motors
2-Pole
For optimum insulation life,
4, 6, or 8
Pole
Page 8

to Table 3-5 values. Definite purpose VFD motors may
accommodate longer cable lengths. For additional
information contact motor manufacturer.
Table 3-5 Max Cable Lengths General Purpose Motors
These values are based on 3 kHz carrier frequency. Add
suitable VFD output-side filters when exceeding the listed
values.
Frame Size
NEMA 56-320
NEMA 360-5011
IEC 80-200
IEC 225-280.
230V
600 ft. 125 ft. 40 ft.
1000 ft. 225 ft. 60 ft.
180 m. 40 m. 12 m.
300 m. 70 m. 18 m.
460 V
575 V
3.3.5.3
may be run in the same conduit as the AC motor power leads.
This wire must be used as the equipment ground for the motor and
not as the fourth current carrying wire of a “WYE” motor circuit.
The grounded metal conduit carrying the output power conductors
can provide EMI shielding, but the conduit does not provide an
adequate ground for the motor; a separate grounding conductor
must be used. Grounding the motor neutral (WYE) of a VFD
powered motor may result in a VFD ground fault trip. Improper
grounding of an inverter fed motor may result in frame voltages in
excess of 500 Volts. Refer to Grounding section 3.4.4
VFD Grounding:
Equipment grounding conductors
3.3.5.4
CAUTION
Single Phase motors are NOT suitable for use on VFD power.
Connecting a Single Phase Motor to a VFD voids the warranty.
VFD – Single Phase:
: SINGLE PHASE MOTOR FAILURE:
3.3.5.5
VFD’s will couple stray (common-mode) voltage to motormounted RTDs, thermistors, thermostats and space
heaters. The leads of these elements must be properly
insulated and control input circuits must be designed to
withstand this common-mode voltage.
Stray Voltage on Accessory Leads:
3.3.6
ACCESSORIES / PROVISIONS:
3.3.6.1
manufacturer’s instructions, supplied with motor. Contact the
manufacturer for additional information.
3.3.6.2
Motors with brakes that are designed for vertical applications are
equipped with springs to support the brake pressure plate.
Mounting a horizontal brake motor vertically shaft up or down may
require a pressure plate spring modification. Failure to modify the
brake for the vertical application may result in premature brake
failure. If in question, consult brake literature or brake
manufacturer.
3.3.6.3
Motors provided with space heaters have two leads that are
brought into the conduit box or into an auxiliary box. These leads
are marked ”H1”, “H2” (”H3”, “H4” if a second space heater is
supplied). See the space heater nameplate on motor for heater
rating.
The space heater temperature rating when used in Class I,
Division 2 motors shall NOT exceed 80% of the auto ignition
temperature of the hazardous gas or vapor. See the space heater
nameplate on motor for heater Temperature Code and heater
rating. Failure to follow this instruction could result in serious
personal injury, death and/or property damage
3.3.6.4
General:
Brake Motors
CAUTION
Brake Solenoid Wiring:
solenoid to the output of a VFD. The brake solenoids must be
wired to 50/60 Hz line power
Carefully read and understand the accessory
:
: Vertical
Motor
Premature Brake Failure
Do NOT connect the brake
Space Heaters:
WARNING:
Thermal Protection:
DIVISION 2 EXPLOSION HAZARD
General Information: When thermal protection is provided, one of
the following will be stamped on the nameplate:
1. “THERMALLY PROTECTED” This motor has built in thermal
protection. Thermal protectors open the motor circuit
electrically when the motor overheats or is overloaded. The
protector cannot be reset until the motor cools. If the
protector is automatic, it will reset itself. If the protector is
manual, disconnect motor from power supply. After protector
cools (five minutes or more) press the reset button and
reapply power to the motor. In some cases a motor is marked
“Auto” and the connection diagram on the motor will identify
T’Stat leads – see “2 ” below. (See warnings on Manual and
Automatic reset protectors - section 1.1)
2.
“WITH OVERHEAT PROTECTIVE DEVICE”: This motor is
provided with an overheat protective device that does not
directly open the motor circuit. Motors nameplated with this
phrase have either thermostats, thermisters or RTD’s. The
leads to these devices are routed into the motor conduit box
or into an auxiliary box. The lead markings are defined on the
nameplate (normally “P1”, “P2”) . The circuit controlled by the
overheat protection device must be limited to a maximum of
600 volts and 360 volt-amps. See connection decal provided
inside the terminal box cover. Failure to connect these over
temperature devices (when provided) will void the warranty.
WARNING:
For Hazardous Locations motors provided with thermostats
UL and the NEC require connection of thermostat leads into
the control portion of a manual reset start circuit. Failure to
follow this instruction could result in serious personal injury,
death and/or property damage
Resistance Temperature Detectors (RTD):
and/or bearing RTDs are provided the RTD lead markings are
defined on the nameplate. (Normally “R1”, “R2”, “R3” etc.)
EXPLOSION HAZARD
When winding
3.3.6.5
Tables 3-6 & 3-7 are suggested initial RTD alarm and trip settings.
For motors found to operate significantly below these values the
settings may be reduced accordingly.
Motor Load
>1.0 to 1.15 SF 140 150 160 165
RTD Alarm & Trip Settings:
Table 3-6 Winding RTD – Temperature Limit (C)
40 C Max Ambient
Class B Temp
Rise≤≤≤≤ 80C
Up to 1.0 SF 130 140 155 165
Alarm Trip Alarm Trip
Class F Temp
Rise≤≤≤≤ 105C
Table 3-7 Bearing RTD – Temperature Limit (C)
40 C Max Ambient
Alarm Trip
95 100
110 115
130 135
Ambient
Up to 40
Bearings that are
Heat Stabilized to
> 40
C
150 C
C
3.3.7
GUARDS:
WARNING:
When devices are assembled to the motor shaft, be sure to install
protective devices such as belt guards, chain guards, and shaft
covers. These devices must protect against accidental contact with
extremities, hair, and clothing. Consider the application and provide
guarding to protect personnel. Remove all unused shaft keys and
loose rotating parts to prevent them from flying off and causing
bodily injury. Failure to follow this warning could result in serious
personal injury, death and/or property damage.
ROTATING PARTS HAZARD
Page 9

3.4 ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS:
WARNING:
Before proceeding read Section 1-1 on Electrical Safety. Failure to
follow the instructions in Section 1-1 could result in serious personal
injury, death and/or property damage
3.4.1
POWER SUPPLY / BRANCH CIRCUIT
WARNING:
Check power supply to make certain that voltage, frequency and
current carrying capacity are in accordance with the motor
nameplate. Failure to match motor nameplate values could result in
serious personal injury, death and/or property damage
WARNING:
Motor and control wiring, fusing, overload protection, disconnects,
accessories and grounding must always conform to the applicable
electrical codes as well as local codes and sound practices.
3.4.1.1
disconnect switch, short circuit current fuse or breaker protection,
motor starter (controller) and correctly sized thermal elements or
overload relay protection.
3.4.1.2
Short Circuit Current Fuses or Breakers are for the protection of the
branch circuit. Starter or motor controller overload relays are for the
protection of the motor. Each of these should be properly sized and
installed per the applicable electrical codes as well as local codes
and practices.
WARNING:
DO NOT bypass or disable protective devices. Protection removal
could result in serious personal injury, death and/or property
damage
ELECTRICAL HAZARDS
POWER SUPPLY INCOMPATIBILITY HAZARD
BRANCH CIRCUIT SUPPLY HAZARD
Branch Circuit Supply
Fuses, Breakers, Overload Relays
PROTECTIVE DEVICE DISABLED HAZARD
to a motor should include a
3.4.1.3
Motors are designed to operate within the following limits at the
motor terminals:
1- AC power is within +/- 10 % of rated voltage with rated
frequency applied. (Verify with nameplate ratings) OR
2- AC power is within +/- 5% of rated frequency with rated voltage
OR
3- A combined variation in voltage and frequency of +/- 10% (sum
of absolute values) of rated values, provided the frequency variation
does not exceed +/-5% of rated frequency.
4- For 3 phase motors the line to line full load voltage must be
5- If the motor is rated 208-230V, the voltage deviations must be
CAUTION:
Operation outside of these limits will degrade motor performance
and increase operating temperature.
3.4.2
3.4.2.1
motors are typically provided with large terminal boxes. Most motors
have conduit access in 90 degree increments, the terminal box
conduit opening is typically provided via knockouts, holes with
covers, or the terminal box is rotate-able. Fabricated conduit boxes
may have a removable plate for the installer to provide correctly
sized hole(s).
3.4.2.2
(1) Terminal Boxes mounted to motor with a pipe nipple: If a
pipe nipple mounted terminal box is removed or rotated it must be
reassembled with a minimum of five full threads of engagement.
(2) Component Removal: Do not set a terminal box component on
its machined surfaces. Prior to component reassembly wipe clean
all machined surfaces.
AC Power Supply Limits
balanced within 1%.
calculated from 230V.
Reduced Motor Performance
TERMINAL BOX
:
Conduit Opening:
Hazardous Locations Motors:
WARNING:
EXPLOSION HAZARDS
For ease of connections,
(3) Machined Surface Gap (Hazardous Locations Terminal
Boxes): The gap between mating surfaces with the machined
terminal box MUST BE LESS THAN 0.002 inches. This gap must
be checked with a feeler gage along the entire perimeter. If there is
visible damage to the mating surfaces, or if the gap between these
surfaces exceeds 0.002 inches, DO NOT complete the installation
and contact the motor manufacturer. Failure to follow these
instructions could result in serious personal injury, death and/or
property damage
3.4.3
LEAD CONNECTIONS
Electrical connections to be made per nameplate connection diagram
or separate connection plate. In making connections follow the
applicable electrical code as well as local codes and practices.
WARNING:
Failure to correctly connect the motor leads and grounding
conductor can result in injury or death. Motor lead connections can
short and cause damage or injury if not well secured and insulated.
ELECTRICAL CONNECTION HAZARD
3.4.3.1 Wire Size (Single Phase) Requirements
The minimum wire size for Single Phase, 115 & 230 Volt Circuits
must meet table 3-8 for a given distance between motor and
either Fuse or Meter Box.
Table 3-8 Minimum Wire Gage Size Single Phase
115 & 230 Volt Circuits
Distance (Feet) - Motor to Fuse or Meter Box
Motor
HP
1/4
1/3
1/2
3/4
1 1/2
100 Ft. 200 Ft. 300 Ft. 500 Ft.
115 230 115 230 115 230 115 230
14 14 10 12 8 10 6 8
12 14 10 12 6 10 4 8
10 12 8 10 6 8 4 6
10 12 6 10 4 8 2 6
1
8 10 6 8 4 6 4
4 10 0 8 6 4
2
8 6 4 2
3
8 6 4 2
5
6 4 2 0
3.4.3.2 Extension Cords (Single Phase Motors):
Where an extension cord(s) is utilized to provide power to the
motor the extension cord(s) must be…(1) the proper gauge size
per table 3-8, (2) in good working condition (3) properly
grounded.
3.4.4
GROUND CONNECTION(S):
WARNING:
For general information on grounding (USA) refer to NEC Article 250.
Improper grounding of an inverter fed motor may result in frame
voltages in excess of 500 Volts. In making the ground connection,
the installer must make certain that a good electrical connection is
obtained between motor and grounding lead. Failure to properly
ground motors, per the applicable national code (such as NEC Article
430) and local codes may cause serious injury or death to personnel.
Primary “Internal” Ground: A grounding conductor must be
connected to the grounding terminal provided in the terminal housing.
This grounding terminal is either a ground screw, ground lug, or a
tapped hole to be used with a separately provided ground screw. The
internal grounding feature is accessible inside the terminal housing
and must be used as the primary grounding connection.
Secondary “External” Ground: Some motors are provided with a
supplemental grounding terminal located on the external surface of
the motor frame or feet. This external terminal is for supplemental
bonding connections where local codes permit or require such
connection
3.4.5
START UP:
WARNING:
Be certain that all connections are secure and the conduit box cover
is fastened in place before electrical power is connected. Failure to
follow these instructions could result in serious personal injury, death,
and/or property damage.
ELECTRICAL GROUNDING HAZARD
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD:
Page 10

WARNING:
Before proceeding read Section 1-2 on Mechanical Safety. Failure to
follow the instructions in Section 1-2 could result in serious personal
injury, death and/or property damage
WARNING:
HAZARD
Motors with the temperature code stated on the nameplate are
designed to operate within this limit. Improper application or
operation can cause the maximum surface temperature to be
exceeded. A motor operated in a Hazardous Location that exceeds
this surface temperature limit increases the potential of igniting
hazardous materials. Therefore, motor selection, installation,
operation, and maintenance must be carefully considered to ensure
against the following conditions: (1) Motor load exceeds service
factor value, (2) Ambient temperature above nameplate value, (3)
Voltages outside of limits (3.4.1.3), (4) Loss of proper ventilation, (5)
VFD operation exceeding motor nameplate rating, (6) Altitude above
3300 feet / 1000 meters, (7) Severe duty cycles, (8) Repeated starts,
(9) Motor stall, (10) Motor reversing, and (10) Single phase
operation. Failure to follow these instructions could result in serious
personal injury, death and/or property damage.
CAUTION:
Normal motor surface temperatures may exceed 90 ° C (194° F).
Touching the motor frame may cause discomfort or injury. Surface
temperatures should only be measured with suitable instruments and
not estimated by hand touch.
3.4.5.1
1. Check Instructions:
understand these instructions including all warnings, cautions,
and safety notice statements.
2. Motor out of storage after more than three months:
C
heck winding insulation integrity with a Megger. If winding
resistance to ground is less than 1.5 Meg-ohms consult the local
authorized service shop before energizing the motor.
3. Check Installation:
bolts and nuts. Manually rotate the motor shaft to ensure motor
shaft rotates freely. Note: Shaft & bearing seals will add drag.
Electrical - Inspect all electrical connections for proper
terminations, clearance, mechanical tightness and electrical
continuity. Be sure to verify connections are made per the
nameplate connection diagram or separate connection plate.
Replace all panels and covers that were removed during
installation before energizing the motor.
4. Energize Motor:
If practical check motor rotation before coupling to the load.
Unlock the electrical system. Momentarily provide power to
motor to verify direction of rotation. If opposite rotation is
required, lock out power before reconnecting motor. If motor has
a rotational arrow only operate the motor in the rotation
identified. Reapply power to ensure proper operation.
5. Record No Load Amps, Watts & Voltage:
Recommend - To establish a baseline value check and record
the no load amps, watts, and voltage.
3.4.5.2
1. Check Instructions:
understand these instructions including all warnings, cautions, &
safety notice statements.
2. Coupling Installation:
is properly aligned and not binding. Check that all guards and
protective devices are properly installed.
3. Energize Motor:
machine, apply power and verify that the load is not transmitting
excessive vibration back to the motor though the shaft or the
foundation. Verify that motor amps are within nameplate rating.
For repeated starts see 3.4.5.3. The equipment can now be
fully loaded and operated within specified limits as stated on the
nameplate.
3.4.5.3
LOOSE & ROTATING PARTS HAZARD
EXCESSIVE SURFACE TEMPERATURE
HOT SURFACE
Start Up - No Load Procedure
Before startup carefully read and fully
Mechanical - Check tightness of all
Check Rotation
Start Up – Load Connected Procedure
Before startup carefully read and fully
Check that the connected equipment
When all personnel are clear of the
Jogging and/or Repeated Starts
Do not start more than twice in succession under full load.
Repeated starts and/or jogs of induction motors can cause
overheating and immediate failure. Contact the motor manufacturer
if it is necessary to repeatedly start or jog the motor.
4.0 MAINTENANCE:
WARNING: Hazardous Locations
Division 1 Hazardous Locations motors can only be modified or repaired
by the manufacturer or a facility that is Listed under UL’s category
“Motors and Generators, Rebuilt for use in Hazardous Locations”. Failure
to follow these instructions could result in serious personal injury, death
and/or property damage.
WARNING:
Electrical connections are to be made by qualified electrical personnel in
accordance with all applicable codes, ordinances and sound practices.
Failure to follow these instructions could result in serious personal injury,
death and/or property damage. Only qualified personnel who are familiar
with the applicable national codes, local codes and sound practices
should install or repair electric motors and their accessories.
WARNING:
Do not touch electrically live parts. Disconnect, lockout and tag input
power supply before installing or servicing motor (includes accessory
devices).
4.1
GENERAL INSPECTION
Inspect the motor approximately every 500 hours of operation or every
three months, whichever occurs first. Keep the motor clean and the
ventilation and fin openings clear. The following steps should be
performed at each inspection:
4.1.1
exterior of the motor is free of dirt, oil, grease, water, etc, which can
accumulate and block motor ventilation. If the motor is not properly
ventilated, overheating can occur and cause early motor failure.
ELECTRICAL SHOCK HAZARD
ELECTRICAL LIVE CIRCUIT HAZARD
VENTILATION
: Check that the ventilation openings and/or
Motor Repair HAZARD:
4.1.2
INSULATION
the integrity of the winding insulation has been maintained. Record
the Megger readings. If winding resistance to ground is less than 1.5
Meg-ohms consult the local authorized service shop before reenergizing the motor.
: Use a “Megger” periodically to ensure that
4.1.3
ELECTRICAL CONNECTIONS:
connectors to be sure that they are tight.
Check all electrical
4.2
LUBRICATION & BEARINGS:
The lubricating ability of grease (over time) depends primarily on the
type of grease, the size of the bearing, the speed at which the bearing
operates and the severity of the operating conditions. Longer bearing
life can be obtained if the listed recommendations are followed:
NOTE: If lubrication instructions are provided on the motor nameplate,
the nameplate instructions will supersede these instructions. Motors
marked “Permanently Lubricated” do not require additional service.
CAUTION:
Lubricant should be added at a steady moderate pressure. If added
under heavy pressure bearing shield(s) may collapse. Over greasing
bearings greatly increases bearing friction and can cause premature
bearing and/or motor failure.
4.2.1
GREASE TYPE
Nameplate Ambient Temperature between -30°C (-22°F) to 65°C
(150°F) inclusive: Recommended grease for standard service
conditions is Mobil Polyrex ® EM. Equivalent and compatible greases
include: Texaco Polystar RB, Rykon Premium #2, Pennzoil Pen 2
Lube, Chevron SRI & Mobil SHC 100.
Nameplate Ambient Temperature below -30°C (-22°F): Special low
temperature grease is recommended, such as Aeroshell 7 or Beacon
325 for ball bearings and Mobil SHC 100 for roller bearings.
BEARING / MOTOR DAMAGE WARNING
(unless nameplate states otherwise):
Page 11

Nameplate Ambient Temperature above 65°C (150°F): Dow
Corning DC44 or equivalent, a special high temperature grease is
required. Note that Dow Corning DC44 grease does not mix with
other grease types.
4.2.2
BEARING OPERATING TEMPERATURE:
CAUTION:
The external surface temperature of the end shield (bracket) bearing
hub may reach 100° C (212° F) during normal operation. Touching
this surface may cause discomfort or injury. Surface temperatures
should only be measured with suitable instruments and not estimated
by hand touch.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
4.2.3
LUBRICATION INTERVALS: (For motors with regreasing provisions)
HOT SURFACE
For RTD settings see Table 3-7.
Eq. 4.2 Lubrication Interval = [(Table 4-1) hrs] x [Interval Multiplier (Table 4-2)] x [Construction Multiplier (Table 4-3)]
Table 4-1 Lubrication Intervals (Hours) These values are based on average use.
Operating Speed – RPM (See Table 3.4 for Maximum Operating Speed)
NEMA / [IEC] Frame Size
56-180 [80-110] 2500 Hrs. 4000 Hrs 5000 Hrs 6000 Hrs. 17000 Hrs. 20000 Hrs.
210-250 [130-160] 2500 Hrs 4000 Hrs 5000 Hrs. 12000 Hrs. 16000 Hrs.
280 [180] 2000 Hrs 3000 Hrs 4000 Hrs. 10000 Hrs. 14000 Hrs.
320 [200] 2000 Hrs 3000 Hrs. 9000 Hrs. 12000 Hrs.
360 [225] 1500 Hrs 2000 Hrs. 8000 Hrs. 10000 Hrs.
400-440 [250 – 280] 1500 Hrs. 4000 Hrs. 7000 Hrs.
>440 [>280] 1000 Hrs. 3000 Hrs. 5000 Hrs.
Seasonal Service: If motor remains idle for more than six months, Lubricate at the beginning of the season, then follow lubrication interval.
Do not exceed maximum safe operating speed Table 3-4 without manufacturer’s approval
<7200 <5400 <4500 <3600 <1800 <1200
Table 4-2 Service Conditions
Use highest level Multiplier
Severity of
Service
Standard Less than 40° C (104° F) Clean, Slight Corrosion, indoors, less than 16 hrs per day
Severe
Extreme
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Table 4-3 Construction Multiplier
Construction Multiplier
Angular Contact or Roller Bearing 0.5
Vertical Motor 0.5
All others 1.0
: Maximum Ambient Temperature and Contamination are independent factors
Maximum Ambient
Temperature
Above 40° C (104° F) to 50° C Moderate dirt or Corrosion or outdoors or more than 16 hrs
Greater than 50° C or
Class H Insulation
Atmospheric Contamination Multiplier
per day
Severe dirt or Abrasive dust or Corrosion
Table 4-4 Relubrication Amounts
Frame Size
NEMA IEC Cu. In. Fluid oz ml
48-56 80 0.25 0.14 4.0
143-145 90 0.25 0.14 4.0
182-184 110 0.50 0.28 8.0
213-215 130 0.75 0.42 12.5
254-256 160 1.00 0.55 16.0
284-286 180 1.50 0.83 25.0
324-326 200 2.00 1.11 33.0
364-365 225 3.00 1.66 50.0
404-405 250 3.80 2.11 62.0
444-449 280 4.10 2.27 67.0
>449 >280 4.50 2.50 74.0
For regreasing while operating multiply volume by 125%.
Volume
1.0
0.5
0.2
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 12

4.2.4
LUBRICATION PROCEDURE:
(For Motors with Regreasing Provisions)
CAUTION:
Added grease must be compatible with the original equipment’s
grease. If a grease other than those stated in 4.2.1 is to be utilized
contact the motor manufacturer. Nameplate information
supersedes section 4.2.1 (GREASE TYPE). New grease must be
free of dirt. Failure to follow these instructions and procedure
below may result in bearing and/or motor damage.
For an extremely dirty environment, contact the motor
manufacturer for additional information.
LUBRICATION PROCEDURE:
1.
Clean the grease inlet plug or zerk fittings prior to regreasing.
2.
(If present) Remove grease drain plug and clear outlet hole
CAUTION:
Old grease may completely block the drain opening and must be
mechanically removed prior to regreasing. Forcing a blocked
drain open by increased greasing pressure may collapse bearing
shields and / or force excess grease through the bearings and
into the motor.
3.
4.
Re-install grease inlet and drain plugs (if removed).
Do NOT energize a Hazardous Locations motor without all grease
fittings properly installed.
BEARING DAMAGE WARNING
blockage.
GREASE DRAIN PLUGGED:
Add grease per Table 4-4
WARNING:
EXPLOSION HAZARD
4.2.5
EXAMPLE: LUBRICATION
Assume - NEMA 286T (IEC 180), 1750 RPM Vertical motor driving
an exhaust fan in an ambient temperature of 43° C and the
atmosphere is moderately corrosive.
1. Table 4-1 list 10,000 hours for standard conditions.
2. Table 4-2 classifies severity of service as “Severe” with a
multiplier of 0.5.
3.
Table 4-3 lists a multiplier value of 0.5 for “Vertical”
4.
(Eq. 4.2) Interval = 10,000 hrs x 0.5 x 0.5 = 2500 hrs
Table 4-4 shows that 1.5 in3 of grease is to be added.
Relubricate every 2,500 hrs of service with 1.5 in3 of
recommended grease.
4.3 TROUBLE-SHOOTING
WARNING:
Before trouble-shooting a motor, carefully read and fully understand
the warnings, cautions, & safety notice statements in this manual.
WARNING: Hazardous Locations
Motors nameplated for use in Division 1 Hazardous Locations can
only be disassembled, modified or repaired by the plant of
manufacturer or a facility that is Listed under UL’s category “Motors
and Generators, Rebuilt for use in Hazardous Locations”. Failure to
follow these instructions could result in serious personal injury,
death and/or property damage
CAUTION:
Motor disassembly must be performed by a party approved by the
motor manufacturer. To disassemble the motor without approval
voids the warranty.
4.3.1
GENERAL TROUBLE-SHOOTING WARNINGS
1. DISCONNECT POWER TO THE MOTOR BEFORE
PERFORMING SERVICE OR MAINTENANCE.
2. Discharge all capacitors before servicing motor.
3. Always keep hands and clothing away from moving
parts.
4. Be sure required safety guards are in place before
starting equipment.
5. If the problem persists contact the manufacturer.
READ INSTRUCTIONS:
Motor Repair:
DISASSEMBLY APPROVAL REQUIRED:
Page 13

4.3.2 Motor Trouble-shooting Cause / Corrective Action - Table 4-5
ply voltage is too low or is severely unbalanced (one
(1) Check power supply fuses (2) Match motor lead wiring to nameplate connection
diagram and supply voltage (3) Ensure that steady state supply voltage at motor
within limits (see section 3.4.1.3). Correct as needed (4) Obtain correct
onnect motor from load & ensure
motor turns freely. Note: Roller bearings make noise when motor is uncoupled and
shaft is rotated (3) Verify that motor starts when disconnected from load (4)
(1) Repeat checks listed above (2) Verify that VFD current limit and starting boost
check motor and feedback parameter settings and
peat autotune (for vector drives) procedure (7) Consult
Supply voltage has drooped or has become severely
motor to cool down before resetting
See section 1.1 for automatic and manual
reset protector warnings (2) Verify that rated and balanced supply voltage has
restart. Ensure that
(1) Verify that motor & load turn freely. Repair binding components as needed (2)
ity or increase motor size to match load
(1) Check fault codes on VFD and follow VFD troubleshooting procedures (2)
voltage is balanced and within limits (3) Remove excessive
Supply voltage has drooped or become severely
(1) Ensure that steady state supply voltage at motor terminals is within limits (see
4.1.3). Correct as needed (2) Obtain correct motor to match actual supply
Determine correct motor size and contact motor representative to obtain
Motor may be too small for load. Record acceleration time. Start capacitors may
(1) Check to make sure motor & load turn freely (2) Disconnect motor from load &
[Single Phase] Reconnect motor according to wiring schematic provided. Note:
(1) If motor current exceeds nameplate value, ensure that driven load has not
rating is the same as the old motor. If previous motor was a special design, a
2
clear vent openings, fan guard air inlets and frame
irflow next to motor surface
Issue: Likely Cause: Corrective Action:
Motor fails to start upon initial installation:
Sup
A.)
phase is low or missing).
Motor leads are miswired at conduit box.
B.)
Driven load exceeds motor capacity
C.)
Load is jammed.
D.)
Fan guard is bent and making contact with fan Replace fan guard & fan (if blades are damaged)
E.)
VFD with power factor capacitors installed Remove power factor correction capacitors if equipped
F.)
VFD with motor neutral lead grounded Ensure that motor neutral lead is ungrounded
G.)
VFD programmed incorrectly
H.)
terminals is
motor to match actual supply voltage.
(1) Verify that motor & load turn freely (2) Disc
Remove excessive / binding load if present.
are set correctly (5) DoubleVFD permissives (6) Re
VFD supplier.
Motor has been running, then slow down, stalls, or fails to restart:
A.)
unbalanced
Motor is overloaded
B.)
Motor bearings are seized
C.)
Load Is jammed.
D.)
VFD will not restart motor after tripping
E.)
Capacitor failure on single phase motor (if equipped)
F.)
Motor takes too long to accelerate:
Motor leads are not connected correctly Match motor lead wiring to nameplate diagram.
A.)
B.)
unbalanced.
Load exceeds motor capability
C.)
Faulty start capacitor (Single Phase)
D.)
(1) Replace fuse or reset circuit breaker. Allow
manual protector on motor. Warnings -
been restored before restarting motor. Measure voltage during
steady state supply voltage at motor terminals is within limits (see section 3.4.1.3).
Reduce driven load to match motor capac
requirements.
Verify that VFD input
mechanical load if present.
Warning: Potential Shock Hazard: Contact service shop to check capacitor.
section 3.
voltage.
replacement motor.
fail if acceleration time exceeds 3 seconds.
Mechanical Failure
E.)
ensure motor turns freely
Motor rotates in the wrong direction:
Incorrect wiring connection at motor
A.)
Some motors are non-reversible
[Three Phase] Interchange any two power supply (phase) leads.
Motor overheats or overload protector repeatedly trips
Driven Load is excessive
A.)
Ambient temperature too high
B.)
Motor cooling fins and/or vent openings blocked
C.)
Insufficient Air Flow
D.)
increased. Correct as needed. (2) If new motor is a replacement, verify that the
general purpose motor may not have the correct performance.
Most motors are designed to operate in an ambient up to 40 C. (See section 4.2.
Hot Surface Caution)
Remove foreign materials –
fins (TEFC motors)
TEAO (Totally Enclosed Air Over) motors: Measure a
and obtain minimum requirements from motor manufacturer.
Page 14

Motor is started too frequently See section 3.4.5.3
minals is within limits (see
section 3.4.1.3) Correct as needed (2) Reconnect motor per input voltage (3)
(1) Ensure that load is dynamically balanced: (2) Remove motor from load and
inspect motor by itself. Verify that motor shaft is not bent. Rule of thumb is 0.002”
runout for shafts extension lengths up to 3.00”. Add 0.0005” per every additional
Mixing new with used belts. Replace multiple belt applications with a complete set
Driven load operating at resonant point / natural
gize motor and record vibration as load coasts from 100% speed to 0
RPM. If vibration drops immediately, vibration source is electrical. If levels do not
drop immediately, source is mechanical (2) Redesign system to operate below the
driven loads, program skip frequencies to bypass
resonant points (4) Increase carrier frequency to obtain <3% THD current (5) On
current @ rated motor current (2) Adjust VFD
Test motor by itself. If bearings are bad, you will hear noise or feel roughness.
Roller bearings are normally noisy when operated without load. If sleeve bearing,
per nameplate instructions. For motors with regreasing provisions, add
grease per relubricating instructions (see section 4.2.3). If noise persists contact
olid floor. Secure a ½ height
key in shaft keyway and energize from balanced power supply @ rated voltage.
Record vibration levels and compare with appropriate standards. If excessive
(1) If belt drive check system per section 3.3.4. (2) Other than belting, check
loading on motor shaft. An unbalanced load will also cause the bearings to fail. (3)
Motor enclosure not suitable for environment. Replace with correct enclosure
Ground brush, common mode filter, or insulated bearings must be added. Contact
oss the line starting is normal: (1) Verify that supply voltage
is within limits (see section 3.4.1.3). (2) Ensure that motor lead wiring matches
nameplate connection diagram: (3) Isolate motor from load. (4) To locate point of
hand. (5) If point of contact is not located contact
Motor may be too small for load. Record acceleration time. Start capacitors may
Excessive starting will damage motor capacitors. Contact motor manufacturer if
motor is started more than 20 times/hour or if acceleration time exceeds 3
Motor internal switch failure overheats start capacitor. Contact service shop or
E.)
Supply voltage too low, too high, or unbalanced
F.)
Motor Vibrates
Motor misaligned to load. Realign load
A.)
Load out of balance (Direct drive application)
B.)
Uneven tension on multiple belts
C.)
D.)
frequency.
(1) Ensure that steady state supply voltage at motor ter
Obtain correct motor to match power supply.
inch of shaft length beyond 3.00”.
of matched belts.
(1) De-ener
resonant point (3) On VFD-
variable torque loads reduce volts/hertz below base speed.
VFD torque pulsations
E.)
Motor miswired at terminal box Match motor lead wiring to nameplate connection diagram.
F.)
Uneven, weak or loose mounting support. Shim, strengthen or tighten where required.
G.)
Motor bearings defective
H.)
Motor out of balance
I.)
(1) Adjust VFD to obtain <3% THD
stability for smooth operation. Vector drives may be unstable at light load.
add oil
warranty service.
Disconnect from load. Set motor on rubber pads on s
vibration persists contact motor manufacturer.
Bearings repeatedly fail.
Bearings contaminated.
B.)
Incorrect grease or bearings for ambient extremes. See section 4.2.1
C.)
VFD bearing damage
D.)
Check runouts of mating components, such as a C-face and pump flange.
construction
motor manufacturer.
Load to motor may be excessive or unbalanced
A.)
Motor, at start up, makes a loud rubbing, grinding, or squealing noise.
Belt squeal during acr
contact turn motor shaft by
motor service shop.
Contact between rotating and stationary components
A.)
Start capacitors repeatedly fail.
Motor is being started too frequently
B.)
Motor voltage low Verify that voltage at the motor terminals is within limits (see section 3.4.1.3).
C.)
Defective start switch inside motor
D.)
fail if acceleration time exceeds 3 seconds.
seconds.
motor manufacturer.
The motor acceleration time is too long
A.)
Run capacitor fails.
High ambient temperature Verify that the ambient does not exceed motor’s nameplate value
A.)
Page 15

Input voltage exceeds limit Verify that voltage to the motor terminals is within limits (see section 3.4.1.3).
g strike or other
B.)
high transient voltage).
Power surge to motor (caused by lightnin
C.)
If a common problem, install surge protector.
 Loading...
Loading...