Page 1
FIP Analog Output Sensor
Ordering Information
FIP X X X
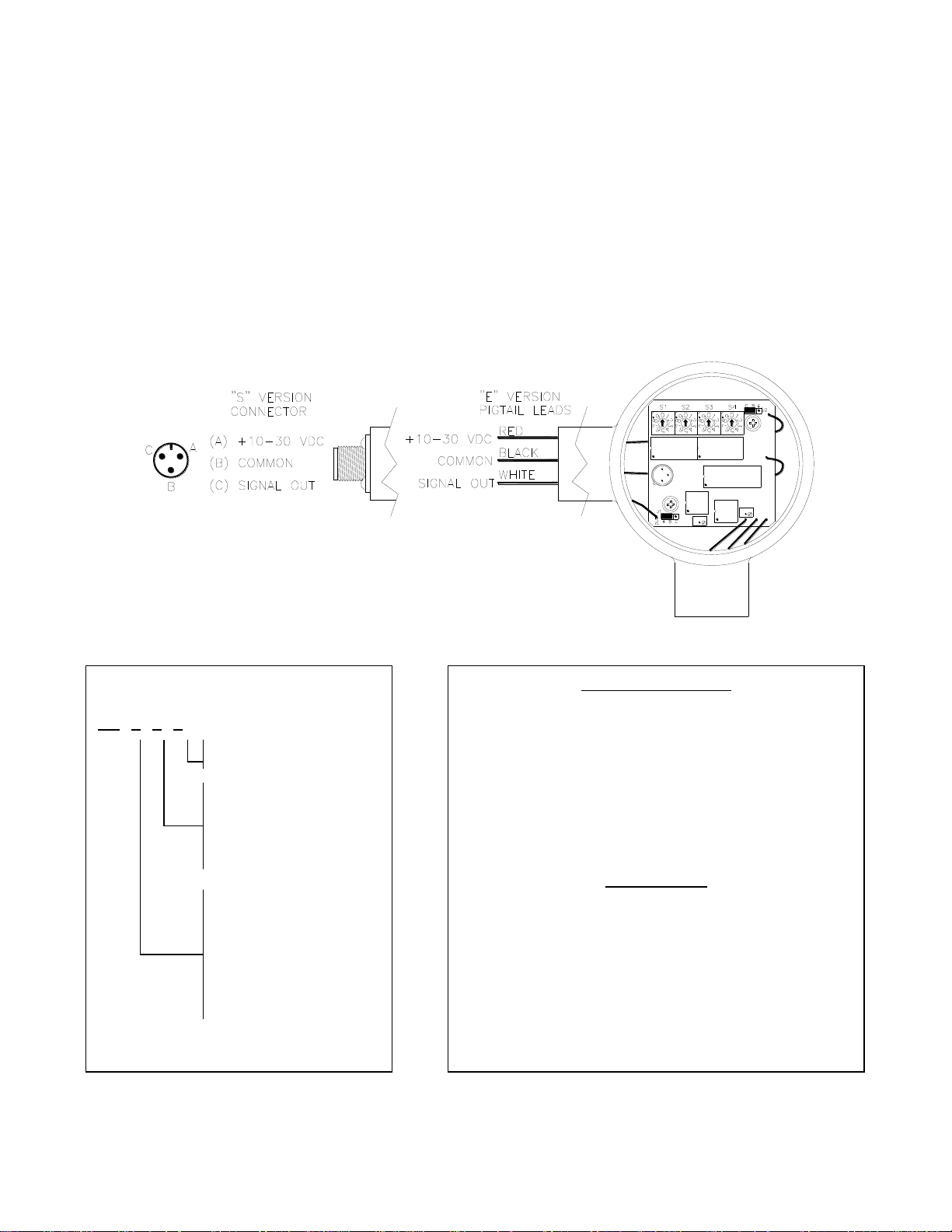
S: 3-Pin Connector
E: Conduit Connection
Meter Selection
H: JV, HPM, TRG Series
T: TR-1100 Series
IR: JVK Series
Output
1: 1-5 V
2: 2-10V
4: 4-20 mA
5: 0-5V
10: 0-10V
20: 0-20 mA
Technical Specifications
Supply Voltage: 10-30 VDC
Supply Current: 60 mA max
Signal Output: 0-20 mA, 4-20mA or
0-5V, 0-10V, 1-5V, 2-10V
Max Load Impedance (Vcc/0.02) – 275 ohm (for mA out)
Min Load Impedance: 500 ohm (for Volt out)
Driving Capacity: For Voltage output only 10 mA max
Temperature Range: 0-185° F
Jumper Settings
J1 AB: Analog Output
BC: Frequency Output
J2 AB: Housing Ground
CB: Signal ground
Response Time: 1/F + 25 msec
Frequency Input: 5 KHz max
Diagnostics: A glowing LED indicates the unit is working.
The LED will blink to show an active
frequency.
The FIP is a microprocessor based, meter mounted, analog output sensor. Each unit has a
sensor, amplifier and converter module built into an aluminum junction box. The FIP is designed
to handle frequencies up to 5,000 Hz. The operational frequency range is user defined via four
BCD rotary switches, where the high flow rate in frequency is set to 20 mA, 5V or 10V, and the
output signal is automatically scaled. End connection options include ½” NPT for running conduit
piping, or a 3-pin connector.
NOTE: This is a 3 wire hookup and is not suitable for a 2 wire installation.
REV. 12/12 FIP Sensor.DOC
AW-Lake Company 8809 Industrial Drive, Franksville, WI 53126 web: www.awgearmeters.com
Tel: 262-884-9800 Fax: 262-884-9810 Email: awinfo@aw-lake.com
Page 2

K Factor * Max Flow Rate
60
89,100 * 0.2
60
Scaling Analog Output:
On the front panel there are four rotary switches which are
adjustable with a small screwdriver. It is not necessary to power the
unit down to change the settings. The switches are read from left to
right in order of decreasing value as shown in the figure to the right.
If the maximum frequency is known at which the resulting
output should be 20mA, set the switches to this frequency.
The output will automatically scale itself. If the maximum frequency is not known, the correct switch settings can
be determined in 2 ways.
The following equation can be used to determine what the switch setting should be for any particular meter and flow rate.
Switch Setting =
Where: K Factor is the flow meter scaling factor in pulses / volume (found on calibration sheet)
Max. Flow Rate is the flow rate at which the analog output should be at it’s max.
Note: K-Factor and Max flow rate MUST have same units, ie: gallon/GPM, liter/LPM
60 is the scaling factor when max. flow rate is in volume/minute. Use 3600 for volume/hour
Ex: K Factor = 89,100 pulses/gallon (for a JVM-10KL), Max flow rate = 0.2 GPM
Switch Setting = = 297
If the numerical flow rate is not known, the unit can be calibrated in systems with the following:
1) Adjust system flow to the rate at which analog output should read 20 mA.
2) Set scaling switches to a value known to be above the maximum frequency (ex. 9, 49, 799, 2999) if unsure, use 4999
3) If S1 is 0, go to step 4. Decrease S1 until output shows 20 mA. Then increase its setting by one unless value is 4, in
which case value should remain 4. If the switch value is 0 and the output is below 20 mA, leave switch at 0 and go to
next switch.
4) If S2 is 0, go to step 5. Decrease S2 until output shows 20 mA. Then increase its setting by one unless value is 9, in
which case value should remain 9. If the switch value is 0 and the output is below 20 mA, leave switch at 0 and go to
next switch.
5) If S3 is 0, go to step 6. Decrease S3 until output shows 20 mA. Then increase its setting by one unless value is 9, in
which case value should remain 9. If the switch value is 0 and the output is below 20 mA, leave switch at 0 and go to
next switch.
6) Decrease S4 until output shows 20 mA and leave setting. DO NOT increase this setting by one. The switches are now
set at the frequency which will result in a 20 mA output.
When setting switches in step 1, try to use numbers ending in 9 for example: 9, 39, 299 and 2999. Any switch setting
above 5000 Hz is read as 4999 Hz.
Example: Actual maximum input frequency is 538 Hz. Switches are set to 0999 Hz, a value known to be above
actual maximum input frequency. The output shows 12.64 mA.
Starting with the switch of highest order, in this case S2 since S1 is 0, its value is decreased until the output shows
20 mA (S2 shows 4). The switch is then increased by 1 (S2 is set to 5). S3 is then decreased until the output shows
20 mA (S3 shows 2). The switch is then increased by 1 (S3 is set to 3). Finally, S4 is decreased until the output
shows 20 mA and left as such (S4 set at 8) the switches are now set to 538 Hz, the frequency which will cause
maximum output current / voltage.
Note: Wherever this procedure refers to 20 mA you may substitute either 5V or 10V depending upon the output you
have ordered.
AW-Lake Company 8809 Industrial Drive, Franksville, WI 53126 web: www.awgearmeters.com
Tel: 262-884-9800 Fax: 262-884-9810 Email: awinfo@aw-lake.com
REV. 12/12 FIP Sensor.DOC
 Loading...
Loading...