Avycon AVK-HN41B4-2T, AVK-HN41B6-4T, AVK-HN41E4-2T, AVK-HN41E6-4T, AVK-HN41V4-2T User Manual
...Page 1

Page 2

Notes
Please read this user manual carefully to ensure that you can use the device correctly and
safely.
There may be several technically incorrect places or printing errors in this manual. The
updates will be added into the new version of this manual. The contents of this manual are
subject to change without notice.
This device should be operated only from the type of power source indicated on the
marking label. The voltage of the power must be verified before using the same. Kindly
remove the cables from the power source if the device is not to be used for a long period of
time.
Do not install this device near any heat sources such as radiators, heat registers, stoves or
other devices that produce heat.
Do not install this device near water. Clean only with a dry cloth.
Do not block any ventilation openings and ensure proper ventilation around the machine.
Do not power off the device at normal recording condition.
This machine is for indoor use only. Do not expose the machine in rain or moist
environment. In case any solid or liquid get inside the machine’s case, please turn off the
device immediately and get it checked by a qualified technician.
Do not try to repair the device by yourself without technical aid or approval.
When this product is in use, the relevant contents of Microsoft, Apple and Google will be
involved in. The pictures and screenshots in this manual are only used to explain the usage of
our product. The ownerships of trademarks, logos and other intellectual properties related to
Microsoft, Apple and Google shall belong to the above-mentioned companies.
This manual is suitable for many models. All examples and pictures used in the manual are
from one of the models for reference purpose.
Page 3

i
Contents ...................................................................................................................................... i
1 Introduction ....................................................................................................................... 1
1.1 Summary ..................................................................................................................... 1
1.2 Features ....................................................................................................................... 1
1.3 Front Panel Descriptions ............................................................................................. 4
1.4 Rear Panel Descriptions .............................................................................................. 4
1.5 Connections ................................................................................................................ 7
2 Basic Operation Guide .................................................................................................... 10
2.1 Startup & Shutdown .................................................................................................. 10
2.1.1 Startup ............................................................................................................ 10
2.1.2 Shutdown ....................................................................................................... 10
2.2 Remote Controller ..................................................................................................... 10
2.3 Mouse Control .......................................................................................................... 12
2.4 Text-input Instruction ................................................................................................ 12
2.5 Common Button Operation ....................................................................................... 13
3 Wizard & Main Interface ............................................................................................... 14
3.1 Startup Wizard........................................................................................................... 14
3.2 Main Interface ........................................................................................................... 19
3.2.1 Main Interface Introduction ........................................................................... 19
3.2.2 Setup Panel ..................................................................................................... 20
3.2.3 Main Functions .............................................................................................. 22
4 Camera Management ...................................................................................................... 24
4.1 Add/Edit Camera ...................................................................................................... 24
4.1.1 Add Camera ................................................................................................... 24
4.1.2 Edit Camera.................................................................................................... 25
4.2 Add/Edit Camera Group ........................................................................................... 26
4.2.1 Add Camera Group ........................................................................................ 26
4.2.2 Edit Camera Group ........................................................................................ 27
5 Live Preview Introduction .............................................................................................. 28
5.1 Preview Interface Introduction .................................................................................. 28
5.2 Preview Mode ........................................................................................................... 29
5.2.1 Preview By Display Mode ............................................................................. 29
5.2.2 Quick Sequence View .................................................................................... 30
5.2.3 Camera Group View In Sequence .................................................................. 31
5.2.4 Scheme View In Sequence ............................................................................. 31
5.3 Preview Image Configuration ................................................................................... 32
5.3.1 OSD Settings .................................................................................................. 32
5.3.2 Image Settings ................................................................................................ 33
5.3.3 Mask Settings ................................................................................................. 33
5.3.4 Image Adjustment .......................................................................................... 34
Page 4

ii
6 PTZ ................................................................................................................................... 37
6.1 PTZ Control Interface Introduction ........................................................................... 37
6.2 Preset Setting ............................................................................................................ 40
6.3 Cruise Setting ............................................................................................................ 41
7 Record & Disk Management .......................................................................................... 43
7.1 Record Configuration ................................................................................................ 43
7.1.1 Mode Configuration ....................................................................................... 43
7.1.2 Advanced Configuration ................................................................................ 44
7.2 Encode Parameters Setting ........................................................................................ 45
7.3 Schedule Setting ........................................................................................................ 45
7.3.1 Add Schedule ................................................................................................. 45
7.3.2 Record Schedule Configuration ..................................................................... 48
7.4 Record Mode ............................................................................................................ 48
7.4.1 Manual Recording .......................................................................................... 48
7.4.2 Timing Recording .......................................................................................... 49
7.4.3 Motion Based Recording ................................................................................ 49
7.4.4 Sensor Based Recording................................................................................. 49
7.5 Disk Management ..................................................................................................... 49
7.5.1 Storage Mode Configuration .......................................................................... 49
7.5.2 View Disk and S.M.A.R.T. Information ......................................................... 50
8 Playback & Backup ......................................................................................................... 52
8.1 Instant Playback ........................................................................................................ 52
8.2 Playback Interface Introduction ................................................................................ 52
8.3 Record Search & Playback ........................................................................................ 55
8.3.1 Search & Playback by Time-sliced Image ...................................................... 55
8.3.2 Search & Playback by Time ........................................................................... 56
8.3.3 Search & Playback by Event .......................................................................... 57
8.3.4 Search & Playback by Tag ............................................................................. 58
8.4 Backup ...................................................................................................................... 58
8.4.1 Backup by Time ............................................................................................. 58
8.4.2 Backup by Event ............................................................................................ 59
8.4.3 Image Management ........................................................................................ 60
8.4.4 View Backup Status ....................................................................................... 61
9 Alarm Management ........................................................................................................ 62
9.1 Sensor Alarm ............................................................................................................. 62
9.2 Motion Alarm ............................................................................................................ 63
9.2.1 Motion Configuration ..................................................................................... 63
9.2.2 Motion Alarm Handling Configuration .......................................................... 64
9.3 Exception Alarm ....................................................................................................... 64
9.3.1 Exception Handling Settings .......................................................................... 64
9.3.2 IPC Offline Settings ....................................................................................... 65
9.4 Alarm Event Notification .......................................................................................... 65
9.4.1 Alarm-out ....................................................................................................... 65
Page 5

iii
9.4.2 E-mail ............................................................................................................. 66
9.4.3 Display ........................................................................................................... 66
9.4.4 Buzzer ............................................................................................................ 66
9.5 Manual Alarm ........................................................................................................... 67
9.6 View Alarm Status .................................................................................................... 67
10 Account & Permission Management.............................................................................. 69
10.1 Account Management ............................................................................................. 69
10.1.1 Add User ...................................................................................................... 69
10.1.2 Edit User ...................................................................................................... 70
10.2 User Login & Logout .............................................................................................. 71
10.3 Permission Management ......................................................................................... 71
10.3.1 Add Permission Group ................................................................................. 71
10.3.2 Edit Permission Group ................................................................................. 73
10.4 Black and White List ............................................................................................... 73
11 Device Management ........................................................................................................ 74
11.1 Network Configuration ........................................................................................... 74
11.1.1 TCP/IPv4 Configuration ............................................................................... 74
11.1.2 Port Configuration ........................................................................................ 75
11.1.3 DDNS Configuration .................................................................................... 76
11.1.4 E-mail Configuration .................................................................................... 78
11.1.5 UPnP Configuration ..................................................................................... 79
11.1.6 NAT Configuration ....................................................................................... 80
11.1.7 View Network Status .................................................................................... 80
11.2 Basic Configuration ................................................................................................ 80
11.2.1 Common Configuration ................................................................................ 80
11.2.2 Date and Time Configuration ................................................................ ....... 81
11.3 Factory Default........................................................................................................ 82
11.4 Device Software Upgrade ....................................................................................... 82
11.5 Backup and Restore ................................................................................................. 82
11.6 View Log ................................................................................................................. 83
11.7 View System Information ........................................................................................ 83
12 Remote Surveillance ........................................................................................................ 84
12.1 Mobile Client Surveillance ..................................................................................... 84
12.2 Web LAN Access .................................................................................................... 84
12.3 Web WAN Access ................................................................................................... 85
12.4 Web Remote Control ............................................................................................... 86
12.4.1 Remote Preview ........................................................................................... 87
12.4.2 Remote Playback .......................................................................................... 90
12.4.3 Remote Backup ............................................................................................ 91
12.4.4 Remote Configuration .................................................................................. 91
Appendix A FAQ ................................................................................................................... 92
Appendix B Calculate Recording Capacity ........................................................................ 98
Page 6

iv
Appendix C Compatible Device List ................................................................................... 99
Page 7

1
1 Introduction
1.1 Summary
Based on the most advanced SOC technology and embedded system in the field, this series of
the NVR adopt the new designed human interface and support the smart management of the IP
camera and the record search of slice. This series of the NVR which are powerful and easy to
use are provided with excellent image quality and stable system. They are centralized
monitoring management products with high performance and high quality specially designed
for network video monitoring field.
This series of the NVR can be widely used to security system of banks at home and abroad,
schools, intelligent mansions, traffic, environmental protection, supermarkets, petrol service
stations, residential quarters and factories and so on.
1.2 Features
Basic Functions
Support network device access including IP camera/dome and the third party IP cameras
Some NVRs support the latest H.265 video coding stream and a mixture input of H.265
and H.264 IP cameras
Support standard ONVIF protocol
Support dual stream recording of each camera (max 5MP resolution)
Support IP cameras to be added quickly or manually
Support batch or single configuration of the cameras’ OSD, video parameters, mask,
motion and so on
Support a maximum of 8 user permission groups including Administrator, Advanced and
Ordinary which are the default permission groups of the system
Support a maximum of 16 users to be created, multiple web clients login by using one
username at the same time and the user’s permission control to be enabled or disabled
Support a maximum of 10 web clients login at the same time
Live Preview
Support 4K×2K/1920×1080/1280×1024 HDMI and 1920×1080/1280×1024 VGA high
definition synchronous display
Support multi-screen modes such as 1/4/6/8/9/16/25/36
Support auto adjustment of the camera’s image display proportion
Support audio monitoring of the camera to be enabled or disabled
Support manual snap of the preview camera
Support the sequence of the preview cameras to be adjusted
Support display mode to be added and saved and the saved modes can be called directly
Support quick tool bar operation of the preview window
Support camera group view and scheme view in sequence, quick sequence view and dwell
time setting
Support motion detection and video mask
Page 8

2
Support multiple popular P.T.Z. control protocol and setup of the preset and cruise
Support direct mouse control of the IP dome including rotating, zoom, focusing and so on
Support single camera image to be zoomed by sliding the scroll wheel of the mouse
Support any area of the image to be zoomed in to a maximum of 16 times of the current
size
Support image and lens adjustment (only available for some cameras)
Support quick camera adding in the camera window of the live preview interface
Disk Management
The NVRs with the 2U case can add a maximum of 8 SATA HDDs; a maximum of 4
SATA HDDs with the 1.5U case, a maximum of 2 SATA HDDs with the 1U case and a
maximum of 1 SATA HDD with the small 1U case
Each SATA interface of the NVR supports the HDDs with max 6TB storage capacity
Some of the NVRs support record to be backed up by e-SATA HDD
Support disk group configuration and management and each camera can be added into
different disk groups with different storage capacity
Support disk information and disk working status viewing
Support batch formatting of the disks
Record Configuration
Support main stream and sub stream recording at the same time and batch or single
configuration of the record stream
Support manual and auto record modes
Support schedule recording, sensor alarm recording and motion detection recording
Support schedule recording and event recording setting with different record streams
Support record schedule setting and recycle recording
Support pre recording and delay recording configuration of the event recording
Record Playback
Support time scale operation in quick playback and the playback date and time can be set
randomly by scrolling the mouse; the time interval of the time scale can be zoomed
Support record searching by time slice/time/event/tag
Support time view and camera view in searching by time slice mode
Support time slice searching by month, by day, by hour and by minute and time slice to be
displayed with camera thumbnail
Support a maximum of 16 cameras to be searched by time
Support event searching by manual/motion/sensor events
Support tag searching by the manual added tags
Support instant playback of the selected camera in the live preview interface
Support a maximum of 16 synchronous playback cameras
Support acceleration(maximum 32 times of the normal speed), deceleration (minimum
1/32 times of the normal speed) and 30s’ addition or reduction to current playing time
Record Backup
Support record to be backed up through USB (U disk, mobile HDD) or e-SATA interface
Page 9

3
Support record to be backed up by time/event/image searching
Support record cutting for backing up when playing back
Support a maximum of 10 backup tasks in background and backup status viewing
Alarm Management
Support alarm schedule setting
Support enabling or disabling of the motion detection, external sensor alarm input and
exception alarms including IP address conflict alarm, disk IO error alarm, disk full alarm, no
disk alarm, illegal access alarm, network disconnection alarm, IPC offline alarm and so on,
alarm trigger configuration supportable
Support IPC offline alarm trigger configuration of PTZ, snap, pop-up video, etc.
Support event notification modes of alarm-out, pop-up video, pop-up message box, buzzer,
e-mail and so on
The snapped images can be attached into the e-mail when alarm linkage is triggered
Support alarm status view of alarm-in, alarm-out, motion detection and exception alarm
Support alarm to be triggered and cleared manually
Support system auto reboot when exception happens
Network Functions
Support TCP/IP and PPPoE, DHCP, DNS, DDNS, UPnP, NTP, SMTP protocol and so on
Support allow and block list function and the allow and block IP address/IP segment/MAC
address can be set
Support multiple browsers including IE8/9/10/11, Firefox, Opera, Chrome (available only
for the versions lower than 45) and Safari in MAC system
Support remote achievement, configuration, import and export of the NVR parameters and
other system maintenance operations including remote upgrading and system restart
Support remote camera configuration of the NVR including video parameters, image
quality and so on
Support remote searching, playback and backup of the NVR
Support manual alarm to be triggered and cleared remotely
Support NVMS or other platform management software to access the NVR and manage it
Support NAT function and QRCode scanning by mobile phone and PAD
Support mobile surveillance by phones or PADs with iOS or Android OS
Support NVR to be accessed remotely through telnet and the telnet function can be
enabled or disabled
Other Functions
The NVR can be controlled and operated by the buttons on the front panel, the remote
controller and the mouse
Setting interfaces can be switched to one another conveniently by clicking the main menus
on the top of the setting interfaces
Support NVR information viewing including basic, camera status, alarm status, record
status, network status, disk and backup status
Support factory restoring, import and export of the system configuration, log view and
export and local upgrading by USB mobile device
Page 10

4
Support auto recognition of the displayer’s resolution
Name
Descriptions
REC
When recording, the light is blue
Net
When access to network , the light is blue
Power
Power indicator, when connection , the light is blue
Fn
No function temporarily
Name
Descriptions
Power
Power Indicator, when connected, the light is blue
HDD
The light turns blue when reading/writing HDD
Net
The light turns blue when it is able to access the network
Backup
The light turns blue when backing up files and data
Play
The light turns blue when playing video
REC
Power Indicator, when connected, the light is blue
AUDIO /+
1. Adjust audio 2. Increase the value in setup
P.T.Z / -
1. Enter PTZ mode 2. Decrease the value in setup
MENU
Enter Menu in live
INFO
Check the information of the device
BACKUP
Enter backup mode in live
SEARCH
Enter search mode in live
Exit
Exit the current interface
Manually record
Play/Pause
Speed down
Speed up
1-9
Input digital number and select camera
0/--
Input number 0, the number above 10
Direction Key
Change direction
Multi-Screen Switch
Change the screen mode
Enter
Confirm selection
USB
To connect external USB device like USB mouse or USB
flash
1.3 Front Panel Descriptions
The following descriptions are for reference only.
Type I:
Type II:
1.4 Rear Panel Descriptions
Here we only take a part of real panels for example to introduce their interfaces and
connections. The interfaces and locations of the interfaces are only for references. Please take
the real object as the standard.
Page 11

5
No.
Name
Descriptions
1
ALARM OUT
Relay output; connect to external alarm
2
GND
Grounding
3
AUDIO IN
Audio input; connect to audio input device, like microphone,
pickup, etc
4
DC12V
DC12V power input
5
LAN
Network port
6
VGA
Connect to monitor
7
ALARM IN
Alarm inputs for connecting sensors
8
HDMI
Connect to high definition display device
9
USB
Connect USB storage device or USB mouse
10
AUDIO OUT
Audio output; connect to sound box
11
RS485
Connect to keyboard. A is TX+; B is TX-
No.
Name
Descriptions
1
VGA
Connect to monitor
2
e-SATA
Connect to HDD with e-SATA interface
3
RS485 Y/Z interface
Unavailable right now
4
RS485 A/B interface
Connect to keyboard. A is TX+; B is TX-
5
AUDIO OUT
Audio output; connect to sound box
Page 12
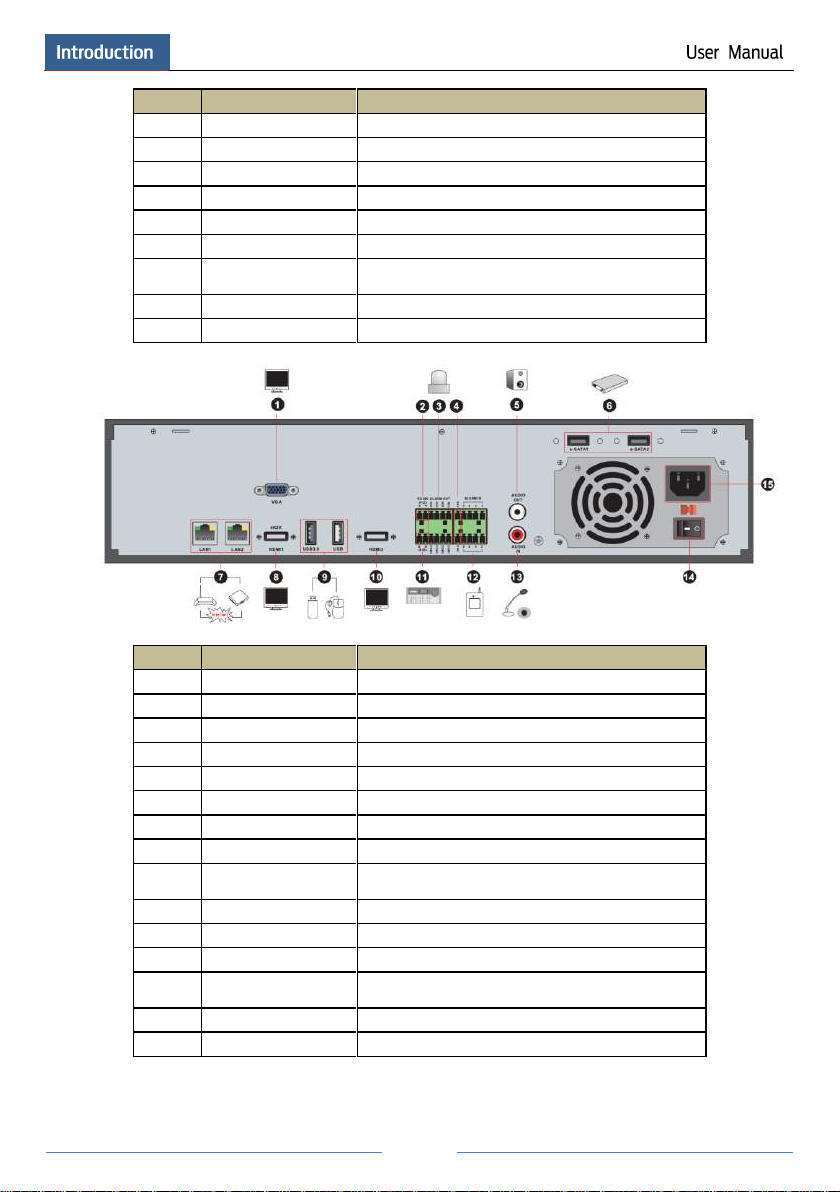
6
No.
Name
Descriptions
6
LAN
Network port
7
HDMI
Connect to high definition display device
8
USB
Connect USB storage device or USB mouse
9
GND
Grounding
10
ALARM OUT
Relay output; connect to external alarm
11
ALARM IN
Alarm inputs for connecting sensors
12
AUDIO IN
Audio input; connect to audio input device, like
microphone, pickup, etc
13
Power Switch
Press the switch to turn on/off the NVR
14
Power Supply
Power supply interface
No.
Name
Descriptions
1
VGA
Connect to monitor
2
RS485 Y/Z interface
Unavailable right now
3
ALARM OUT
Relay output; connect to external alarm
4
GND
Grounding
5
AUDIO OUT
Audio output; connect to sound box
6
e-SATA1/ e-SATA2
Connect to HDD with e-SATA interface
7
LAN1/LAN2
Network port
8
HDMI1
Connect to 4K×2K high definition display device
9
USB3.0/USB
USB3.0 and USB 2.0 interface, connect USB storage
device or USB mouse
10
HDMI2
Connect to 1920×1080 high definition display device
11
RS485 A/B interface
Connect to keyboard. A is TX+; B is TX-
12
ALARM IN
Alarm inputs for connecting sensors
13
AUDIO IN
Audio input; connect to audio input device, like
microphone, pickup, etc
14
Power Switch
Press the switch to turn on/off the NVR
15
Power Supply
Power supply interface
Page 13
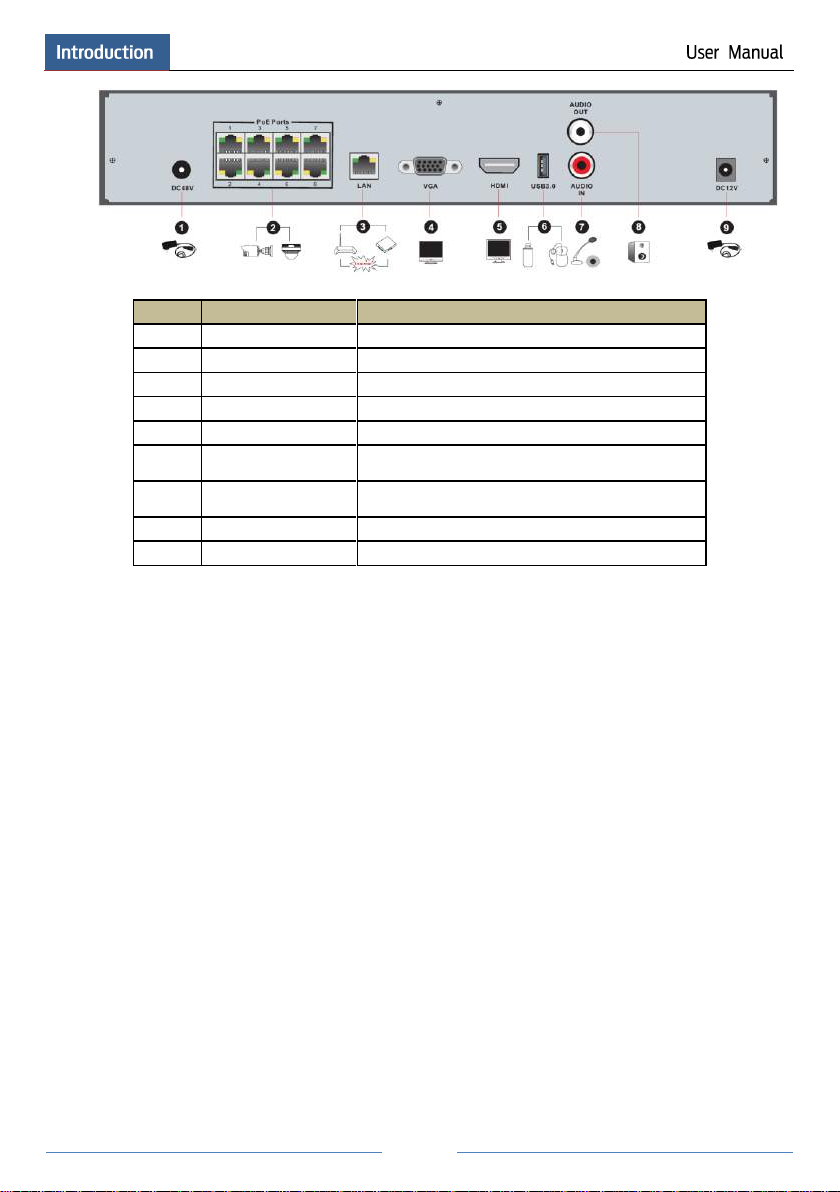
7
No.
Name
Descriptions
1
Power Supply
DC48V power supply interface
2
PoE port
8 PoE network ports; connect to 8 PoE IP cameras
3
LAN
Network port
4
VGA
Connect to monitor
5
HDMI
Connect to 1920×1080 high definition display device
6
USB3.0
USB3.0 interface, connect USB storage device or
USB mouse
7
AUDIO IN
Audio input; connect to audio input device, like
microphone, pickup, etc
8
AUDIO OUT
Audio output; connect to sound box
9
Power Supply
DC12V power supply interface
1.5 Connections
Video Connections
Video Output: Supports VGA/HDMI video output. You can connect to monitor through these
video output interfaces simultaneously or independently.
Audio Connections
Audio Input: Connect to microphone, pickup, etc.
Audio Output: Connect to headphone, sound box or other audio output devices.
Alarm Connections
Some models may support this function. Take 16 CH alarm inputs and 1 CH alarm output for
example.
Page 14
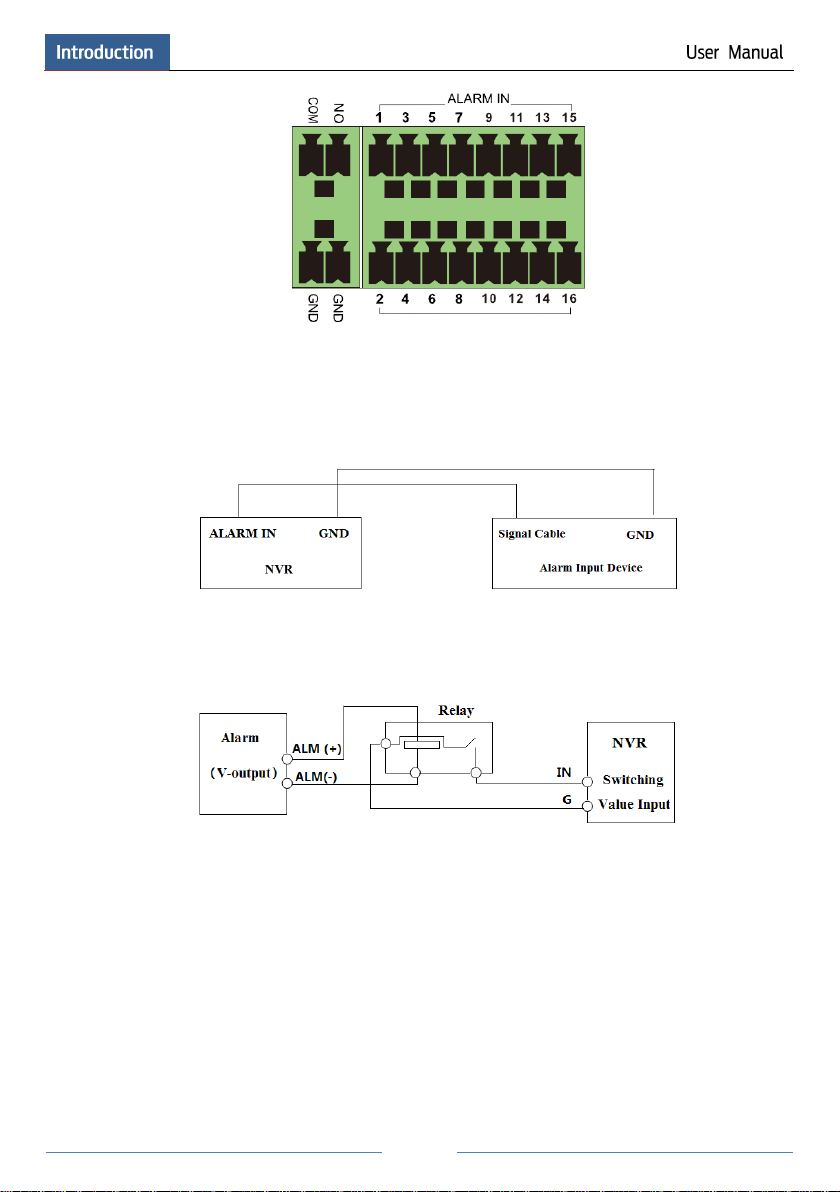
8
Alarm Input:
Alarm IN 1~16 are 16 CH alarm input interfaces. There are no type requirements for sensors.
NO type and NC type are both available.
The way to connect sensor and the device is as shown below:
The alarm input is an open/closed relay. If the input is not an open/closed relay, please refer to
the following connection diagram:
Alarm Output:
The way to connect alarm output device:
Pull out the green terminal blocks and loosen the screws in the alarm-out port. Then insert the
signal wires of the alarm output devices into the port of NO and COM separately. Finally,
tighten the screws. Provided that the external alarm output devices need power supply, you can
connect the power supply as per the following figures.
Page 15
9
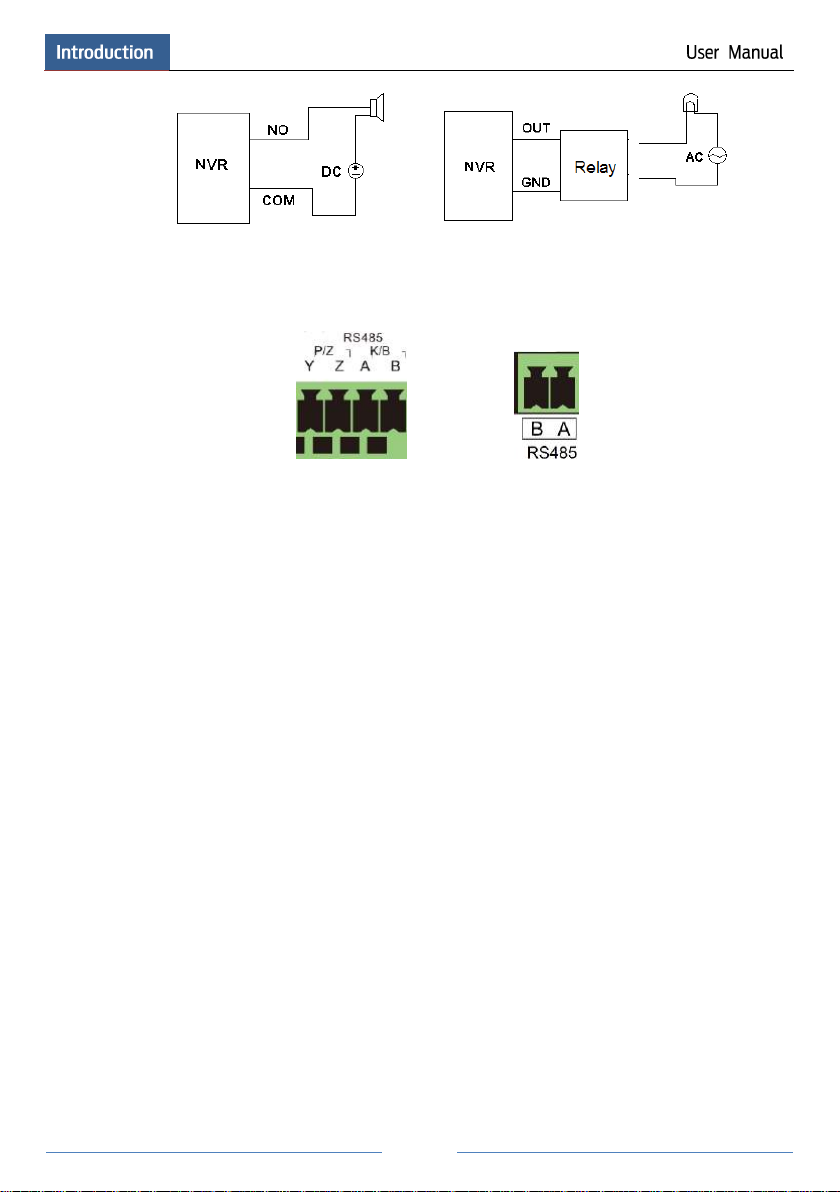
RS485 Connection
There are two types of RS485 interfaces:
(Type 1) (Type 2)
Type 1: The P/Z interfaces are unavailable temporarily. K/B interfaces are used to connect
keyboard.
Type 2: The RS485 interfaces are used to connect keyboard. A is TX+; B is TX-.
Page 16

10
2 Basic Operation Guide
2.1 Startup & Shutdown
Please make sure all the connections are done properly before you power on the unit. Proper
startup and shutdown are crucial to expending the life of your device.
2.1.1 Startup
① Connect the output display device to the VGA/HDMI interface of the NVR.
② Connect with the mouse and power. The device will boot and the power LED would turn
blue.
③ A WIZARD window will pop up (you should select the display language the first time you
use the NVR). Refer to 3.1 Startup Wizard for details.
2.1.2 Shutdown
You can power off the device by using remote controller or mouse.
By remote controller:
① Press Power button. This will take you to a shutdown window. The unit will power off
after a while by clicking “OK” button.
② Disconnect the power.
By mouse:
① Click StartShutdown to pop up the Shutdown window. Select “Shutdown” in the
window. The unit will power off after a while by clicking “OK” button.
② Disconnect the power.
2.2 Remote Controller
① It uses two AAA size batteries.
② Open the battery cover of the remote controller.
③ Place batteries. Please take care the polarity (+ and -).
④ Replace the battery cover.
Key points to check in case the remote doesn’t work.
1. Check batteries polarity.
2. Check the remaining charge in the batteries.
3. Check IR controller sensor for any masking.
If it still doesn’t work, please change a new remote controller to try, or contact your dealers.
You can just turn the IR sensor of the remote controller towards the IR receiver of the NVR to
control it when you are controlling multiple devices by remote controller.
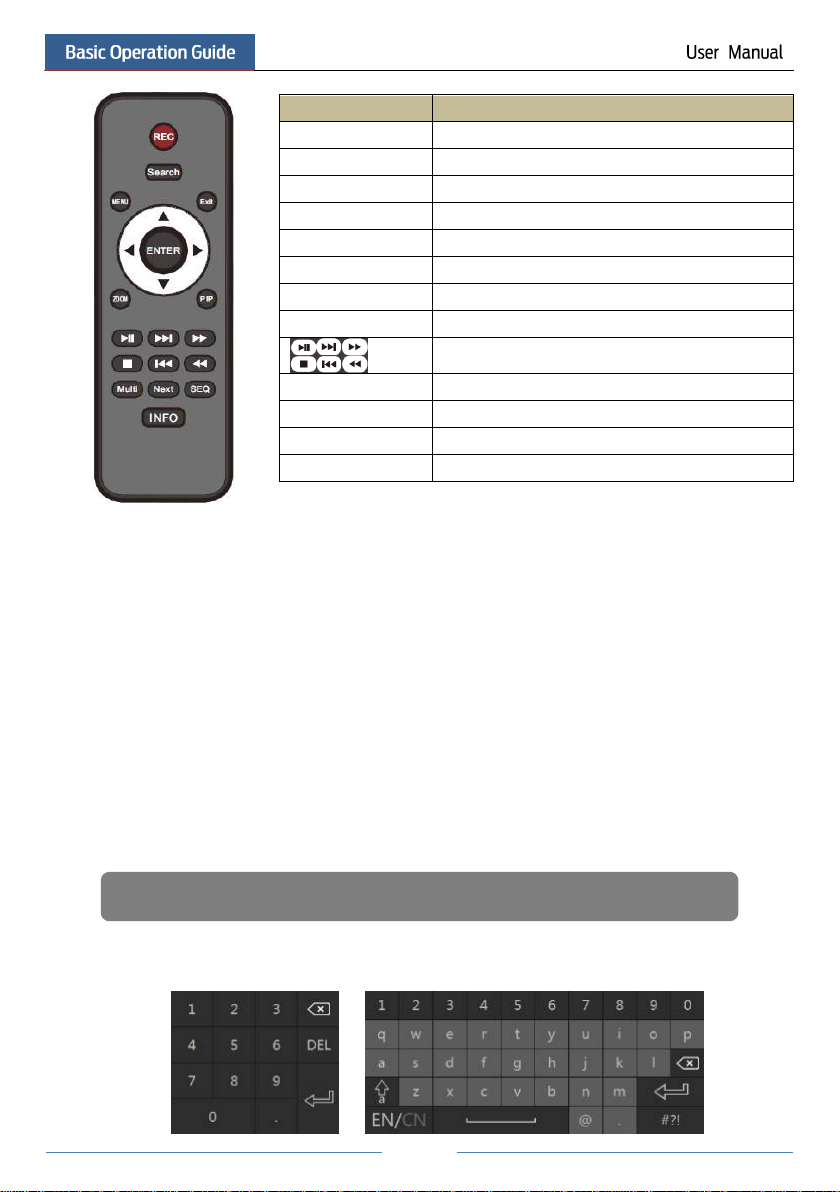
There are two kinds of remote controller. The interface of remote controller is shown as below.
Page 17

11
Button
Function
Power Button
Switch off—to stop the device
Record Button
To start recording
-/-- /0-9
Input number or choose camera
Fn1 Button
Unavailable temporarily
Multi Button
To choose multi screen display mode
Next Button
To switch the live image
SEQ
To go to sequence view mode
Audio
To enable audio output in live mode
Switch
No function temporarily
Direction button
To move cursor in setup or pan/title PTZ
Enter Button
To confirm the choice or setup
Menu Button
To go to menu
Exit Button
To exit the current interface
Focus/IRIS/Zoom/PTZ
To control PTZ camera
Preset Button
To enter into preset setting in PTZ mode
Cruise Button
To go to cruise setting in PTZ mode
Track Button
No track function temporarily
Wiper Button
No function temporarily
Light Button
No function temporarily
Clear Button
No function temporarily
Fn2 Button
No function temporarily
Info Button
Get information about the device
To control playback. Play(Pause)/Stop/Previous
Frame/Next Frame/Speed Down/Speed Up
Snap Button
To take snapshots manually
Search Button
To go to search mode
Cut Button
No function temporarily
Backup Button
To go to backup mode
Zoom Button
To zoom in the images
PIP Button
No function temporarily
Note:
You shall press P.T.Z button to enter PTZ setting mode, choose a channel and press P.T.Z button again to
hide the P.T.Z control panel. Then you can press preset, cruise, track, wiper or light button to enable the
relevant function.
Page 18
12
Button
Function
REC
Record manually
Search
To enter search mode
MEUN
To enter menu
Exit
To exit the current interface
ENTER
To confirm the choice or setup
Direction button
To move cursor in setup
ZOOM
To zoom in
PIP
No function temporarily
To control playback. Play(Pause)/Next Frame/Speed
Up/Stop/Previous Frame/Speed Down
Multi
To choose multi screen display mode
Next
To switch the live image
SEQ
To go to sequence view mode
INFO
Get information about the device
Note: Mouse is the default tool for all operations unless an exception as indicated.
2.3 Mouse Control
Mouse control in Live Preview & Playback interface
In the live preview & playback interface, double click on any camera window to show the
window in single screen mode; double click the window again to restore it to the previous size.
In the live preview & playback interface, if the interfaces display in full screen, move the
mouse to the bottom of the interface to pop up a tool bar. The tool bar will disappear
automatically after you move the mouse away from it for some time; move the mouse to the
right side of the interface to pop up a panel and the panel will disappear automatically after you
move the mouse away from it.
Mouse control in text-input
Move the mouse to the text-input box and then click the box. The input keyboard will pop up
automatically.
2.4 Text-input Instruction
Page 19
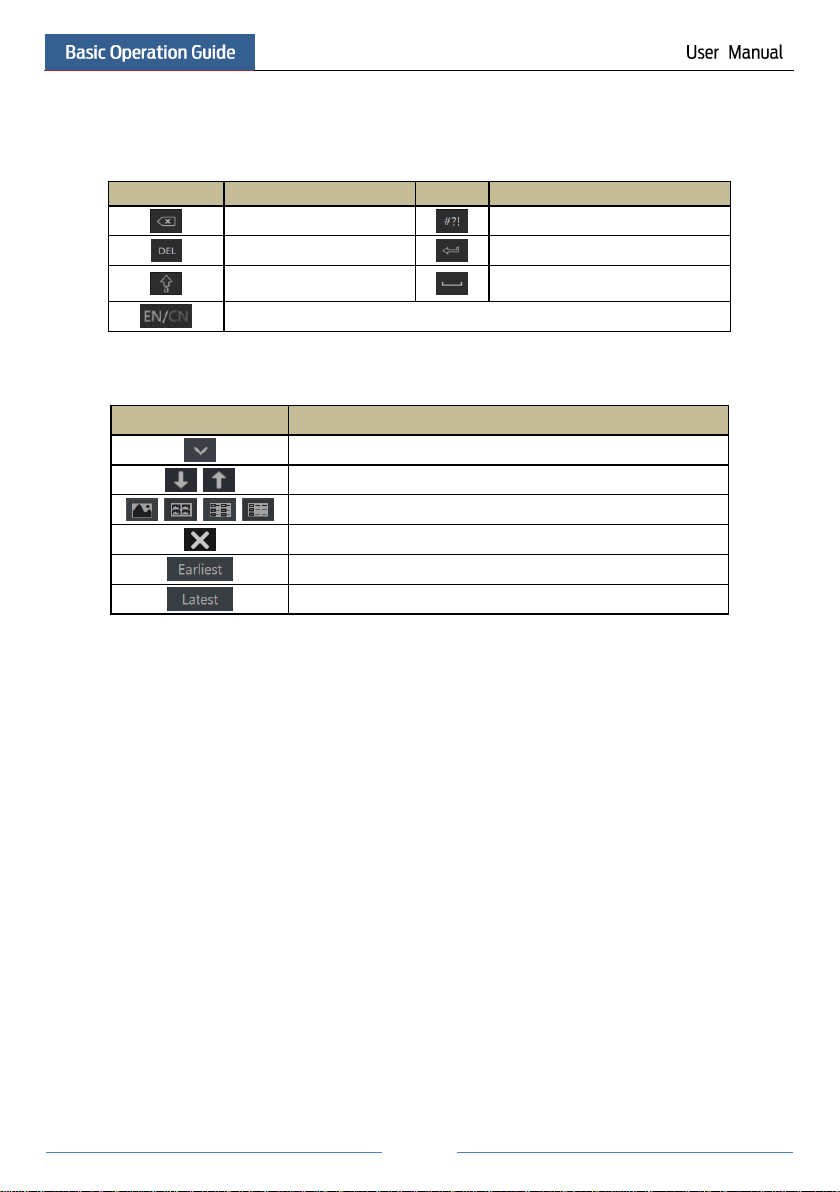
13
Button
Meaning
Button
Meaning
Backspace key
Switch key of punctuation character
Delete Key
Enter key
Switch key between upper
and lower letter
Space key
Switch key of language
Button
Meaning
Click it to show the menu list.
Click it to change the sequence of the list.
Click it to change the camera displaying mode.
Click it to close the current interface.
Click it to go to the earliest date of camera recording.
Click it to go to the latest date of camera recording.
The system includes two input boxes. Refer to the above pictures. The left box is the number
input box and the right box is the input box which provides inputs of numbers, letters and
punctuation characters. The introductions of keys on the input boxes are shown below.
2.5 Common Button Operation
Page 20
14
3 Wizard & Main Interface
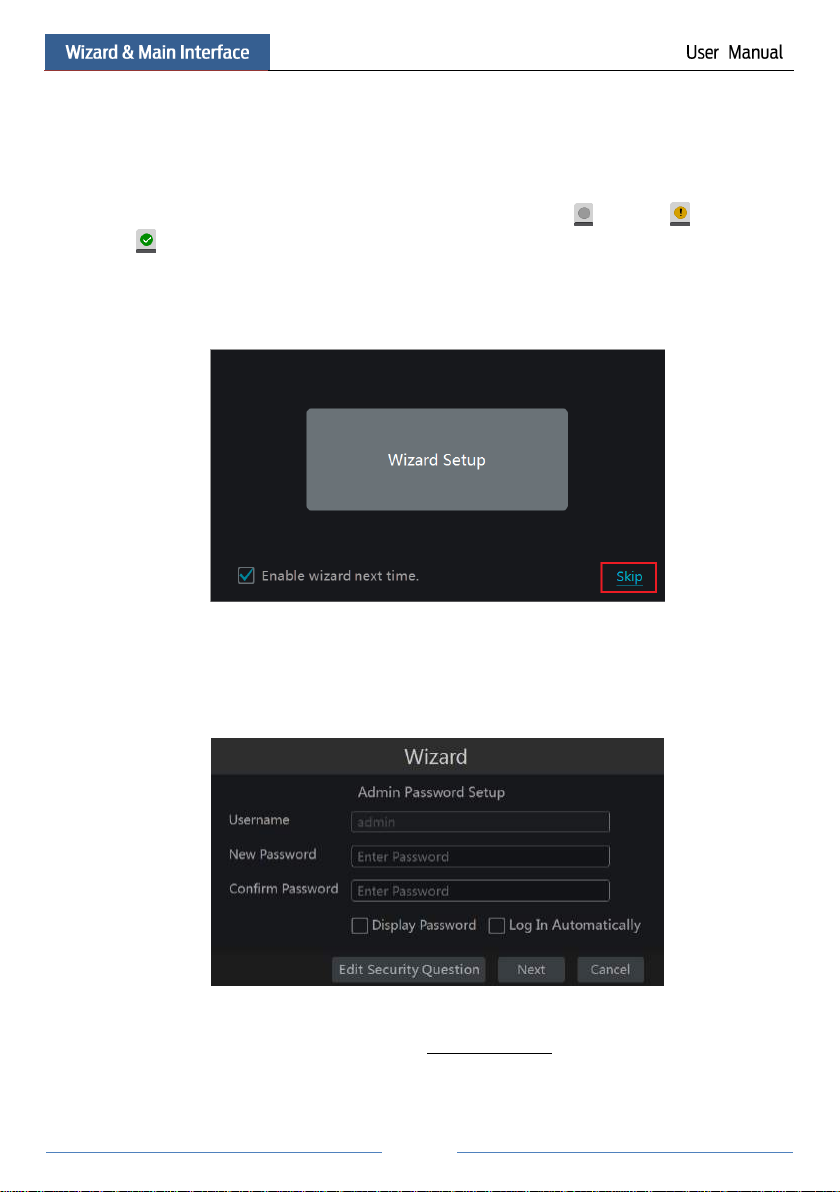
3.1 Startup Wizard
The disk icons will be shown on the top of the startup interface. You can view the number and
status of each disk quickly and conveniently through these icons ( : no disk; : unavailable
disk; : RW available disk).
You can quickly configure the NVR by wizard setup to make the NVR work normally. You
must configure the wizard if you start the NVR for the first time (or click “Skip” to cancel the
wizard next time).
Click “Wizard Setup” to start wizard. The setting steps are as follows.
① System Login. Set your own password or use the default when you use the wizard for the
first time (the default username of the system is admin and the default password of admin is
123456); select the login username and enter the corresponding password next time.
Click “Edit Security Question” to set questions and answers for password security of admin. If
you forget the password, please refer to Q4 in Appendix A FAQ for details.
Click “Next” to continue or click “Cancel” to exit the wizard.
Page 21
15
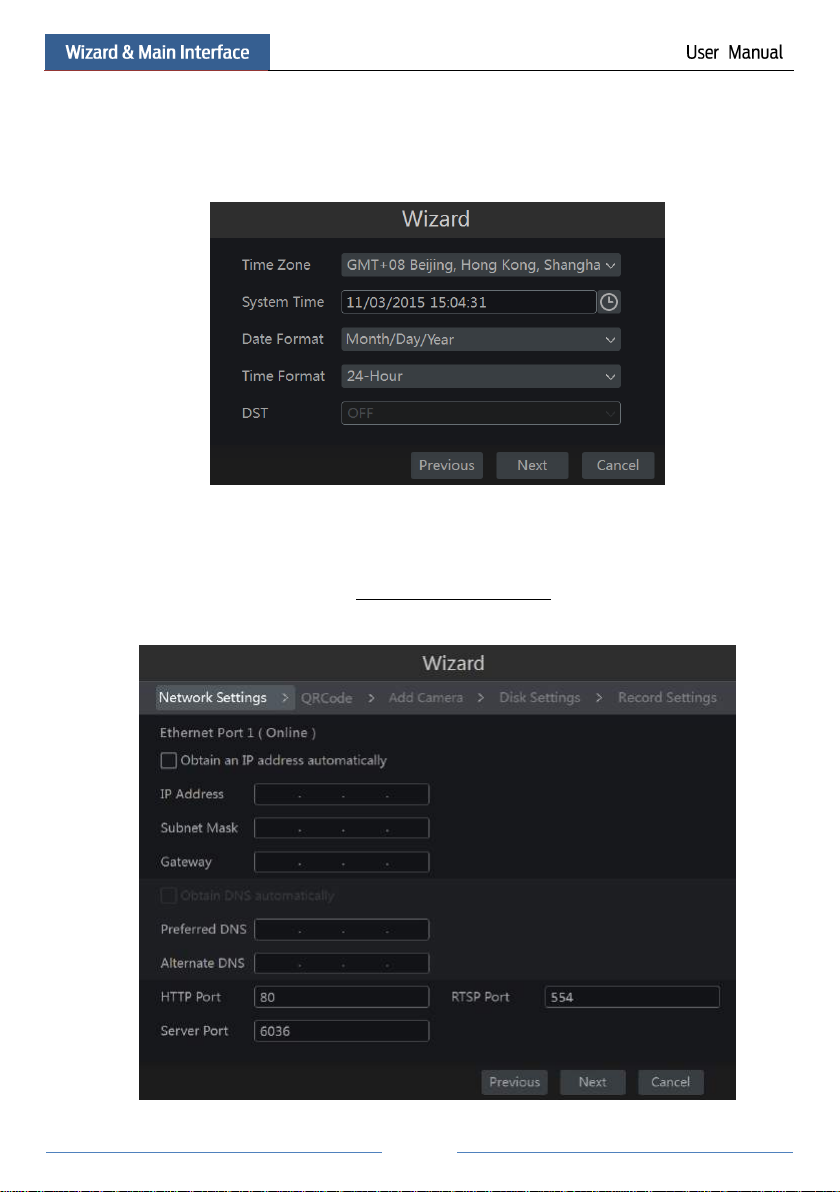
② Date and Time Configuration. The date and time of the system need to be set up if you
use the wizard for the first time. Refer to the following figure. Set the time zone, system time,
date format and time format. The DST will be enabled by default if the time zone selected
includes DST. Click “Next” to continue.
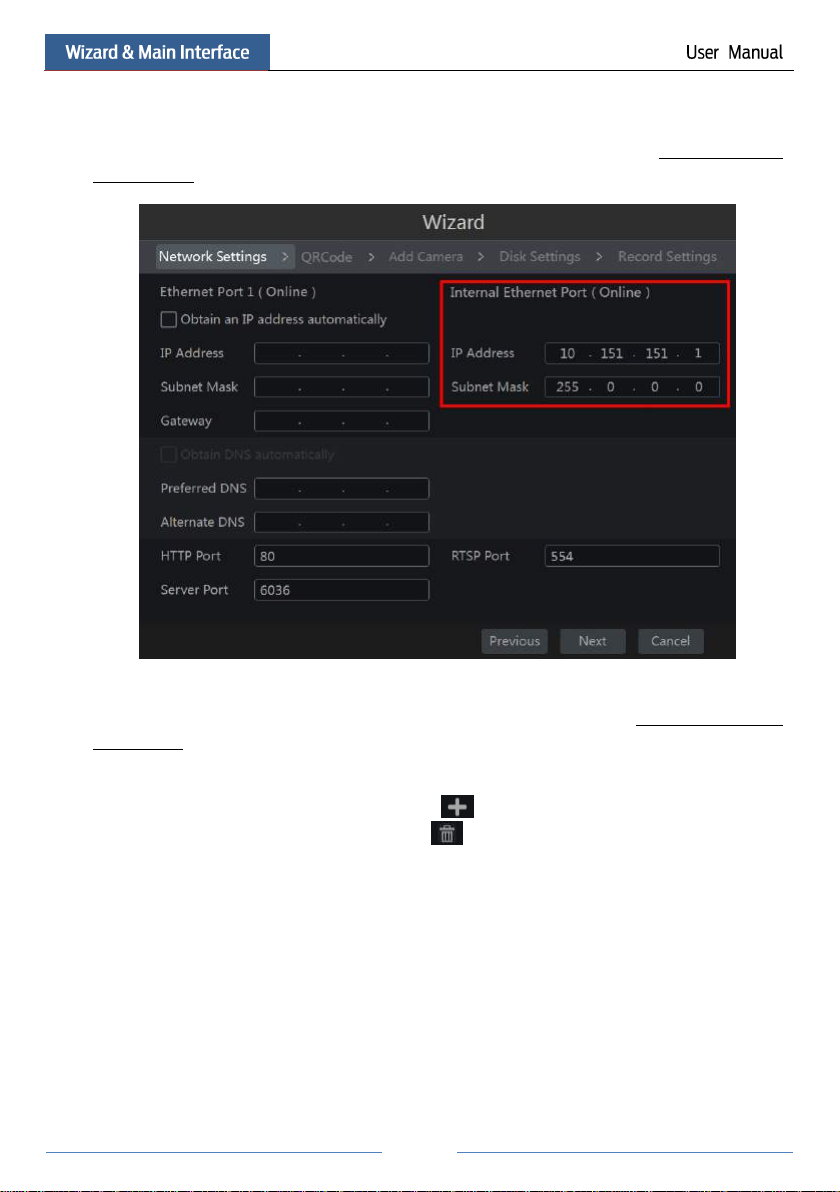
③ Network Settings. Check “Obtain an IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS
automatically” to get the IP address and DNS automatically (the DHCP function of the router
in the same LAN should also be enabled), or manually input them. Input the HTTP port, RTSP
port and Server port (please see 11.1.2 Port Configuration for details). Click “Next” to
continue.
Page 22
16
Note:
If you use the NVR with the PoE network ports, the online state of the internal ethernet port
will be shown on the interface. Refer to the picture below. Please refer to 11.1.1 TCP/IPv4
Configuration for detail introduction of the internal ethernet port.
④ QRCode. You can scan the QRCode through mobile client which is installed in the mobile
phone or PAD to log in the mobile client instantly. Please refer to 12.1 Mobile Client
Surveillance for details.
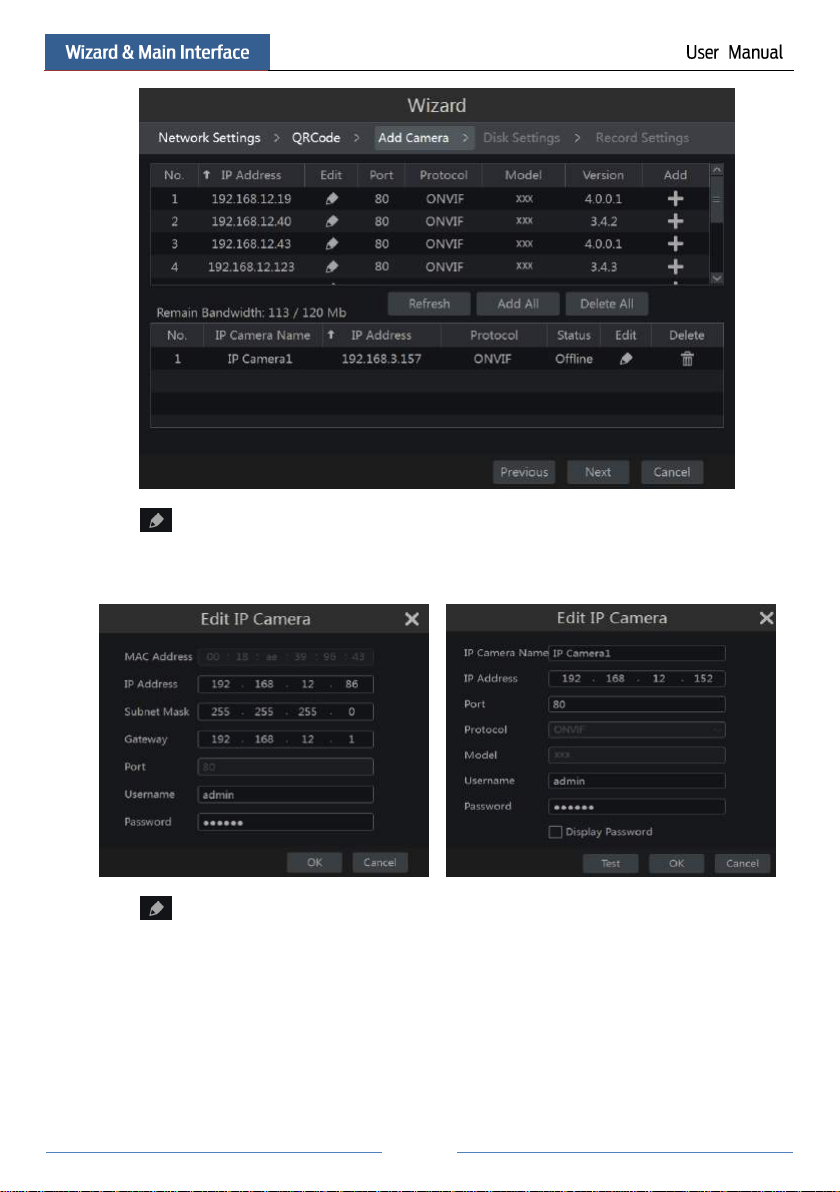
⑤ Add Camera. Click “Refresh” to refresh the list of online IP cameras which are in the
same local network with NVR and then click to add the searched camera. Click “Add
All” to add all the cameras in the list. Click to delete the added camera. Click “Delete
All” to delete all the added cameras.
Page 23
17
Click to edit the searched IP camera as shown on the below left. Input the new IP address,
subnet mask, gateway, username and the password of the camera. Click “OK” to save the
settings.
Click to edit the added camera as shown on the above right. Input the new camera name,
IP address, port, username and the password of the camera. You can click “Test” to test the
effectiveness of the input information. Click “OK” to save the settings. You can change the IP
camera name only when the added camera is online. Click “Next” to continue.
⑥ Disk Settings. You can view the disk number, disk capacity of the NVR and serial number,
R&W status of the disk. Click “Formatting” to format the disk. Click “Next” to continue.
Page 24
18
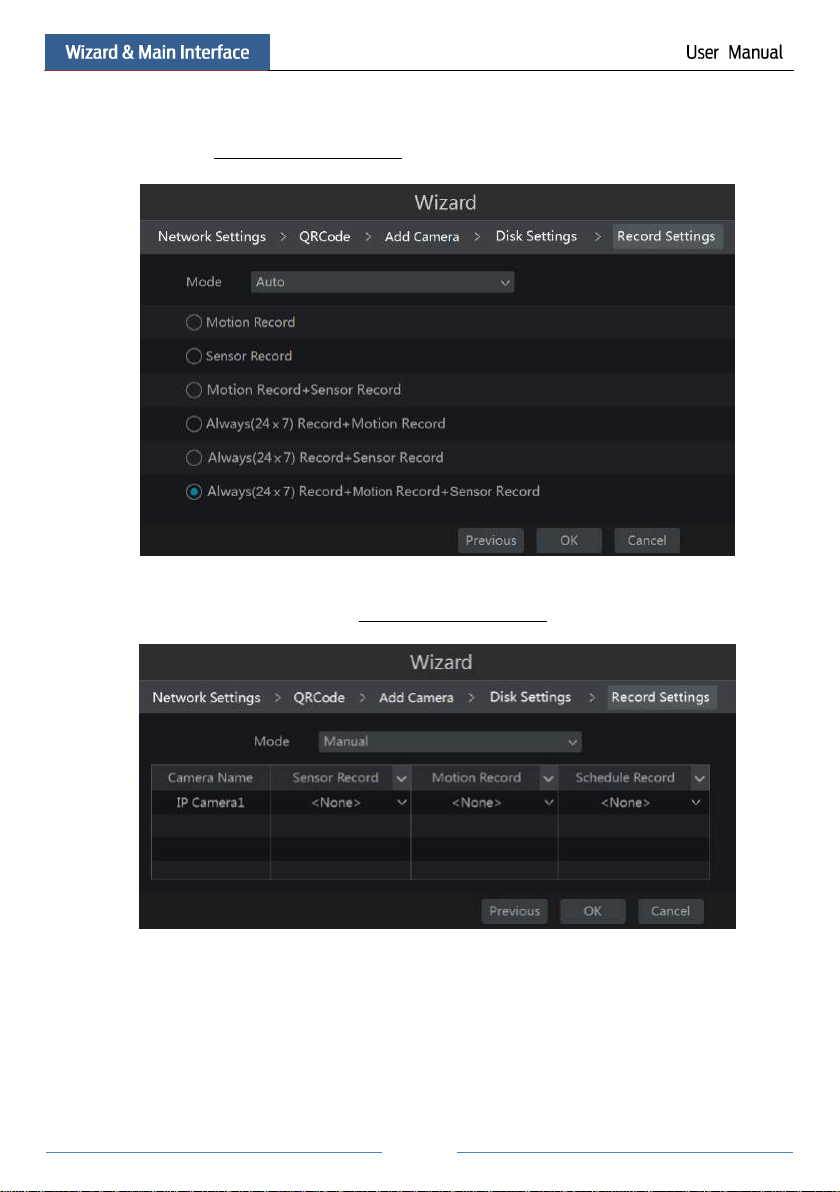
⑦ Record Settings. Two record modes are available: auto and manual.
Auto: Select one auto mode in the interface as shown below and then click “OK” button to save
the settings. See 7.1.1 Mode Configuration for details.
Manual: Set the “Sensor Record”, “Motion Record” and “Schedule Record” of each camera.
Click “OK” to save the settings. See 7.1.1 Mode Configuration for details.
Page 25
19
3.2 Main Interface
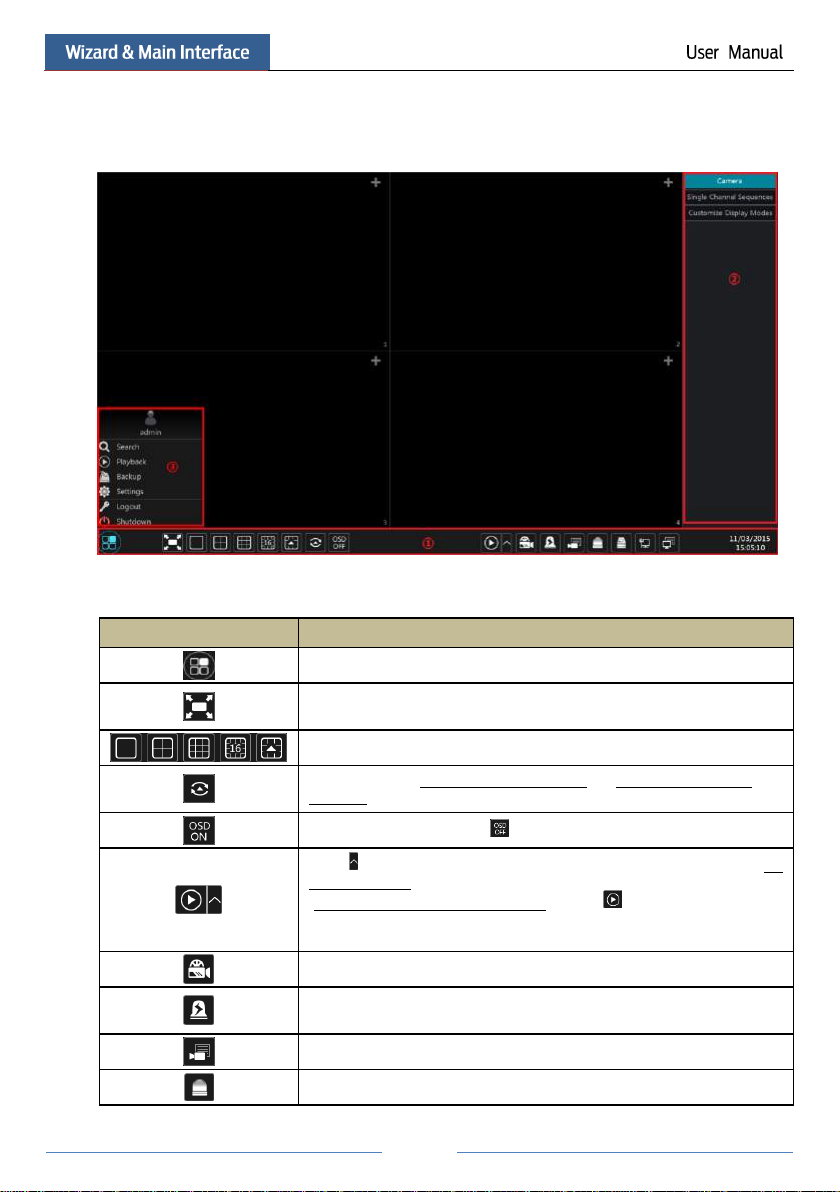
Button
Meaning
Start button. Click it to pop up area ③.
Full screen button. Click it to show full screen; click it again to exit the full
screen.
Screen mode button.
Dwell button (see 5.2.2 Quick Sequence View and 5.2.4 Scheme View In
Sequence for details).
Click it to enable OSD; click to disable OSD.
Click to set the default playback time before starting instant playback (8.1
Instant Playback) or going to the playback interface for playback operations
(8.2 Playback Interface Introduction); click to go to the playback
interface. For instance, if you choose “5 minutes ago” as the default playback
time, you can playback the record from the past five minutes.
Manual record button. Click it to enable/disable record.
Manual alarm button. Click it to trigger or clear the alarm-out manually in the
popup window.
Record status button. Click it to view the record status.
Alarm status button. Click it to view the alarm status.
3.2.1 Main Interface Introduction
The buttons in area ① are introduced in the table below.
Page 26
20
Button
Meaning
Disk status button. Click it to view the disk status and RAID status.
Network status button. Click it to view the network status.
Information button. Click it to view system information.
Icon / Button
Meaning
It shows the current login user.
Click it to go to record search interface, see 8.3 Record Search &
Playback for details.
Click it to go to playback interface (click on the tool bar at the
bottom of the live preview interface to set the default playback time),
see 8.2 Playback Interface Introduction for details.
Click it to go to backup interface, see 8.4 Backup for details.
Click it to pop up the setup panel, see 3.2.2 Setup Panel for details.
Click it to log out the system.
Click it and then select “Logout”, “Reboot” or “Shutdown” in the
popup window.
Introduction of area ②:
Click “Camera” to view all the added cameras in the camera list. Select one camera window on
the left side of the interface and then double click one camera in the list to preview the camera
image in the selected window.
Click “Single Channel Sequences” to view all the added groups in the group list; click one
group in the list to view all the added cameras in the group (refer to 4.2 Add/Edit Camera
Group for detail configuration of the camera group). Select one camera window on the left side
of the interface and then double click one group in the group list to preview the cameras’
images one by one in the selected window.
Click “Customize Display Modes” to view all the display modes in the display mode list (refer
to 5.2.1 Preview By Display Mode for detail configuration of the display mode). Double click
one display mode in the list to switch to the display mode for previewing.
Introduction of area ③:
3.2.2 Setup Panel
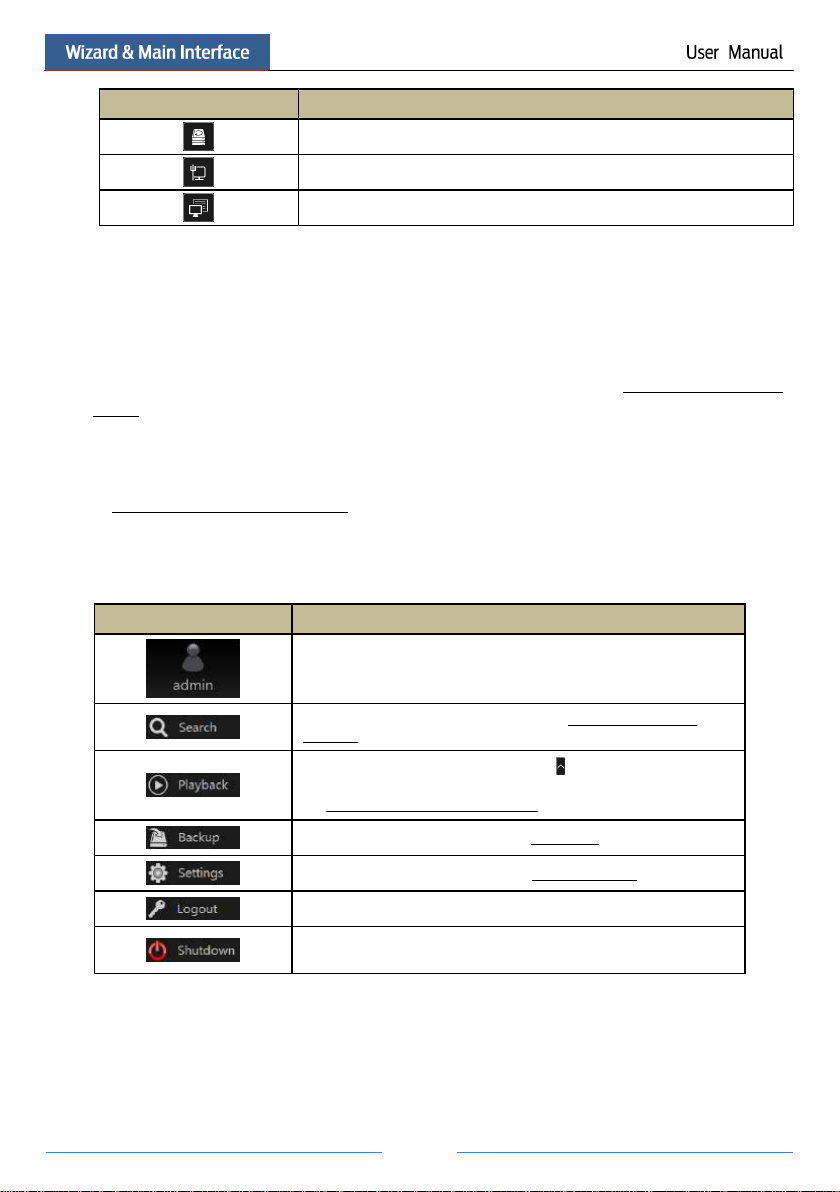
Click StartSettings to pop up the setup panel as shown below.
Page 27
21
The setup panel includes seven modules. Each module provides some function entries with
links for convenient operation.
Here we take Camera module as an example. The Camera module provides convenient links
such as “Add Camera”, “Edit Camera”, “Image Settings”, “Motion” and “PTZ”. Click Camera
to go to the camera management interface as shown below.
There are some function items on the left side of the camera management interface. Click each
item to go to corresponding interface or window. For instance, click “Add Camera” to pop up
the window as shown below.
Page 28
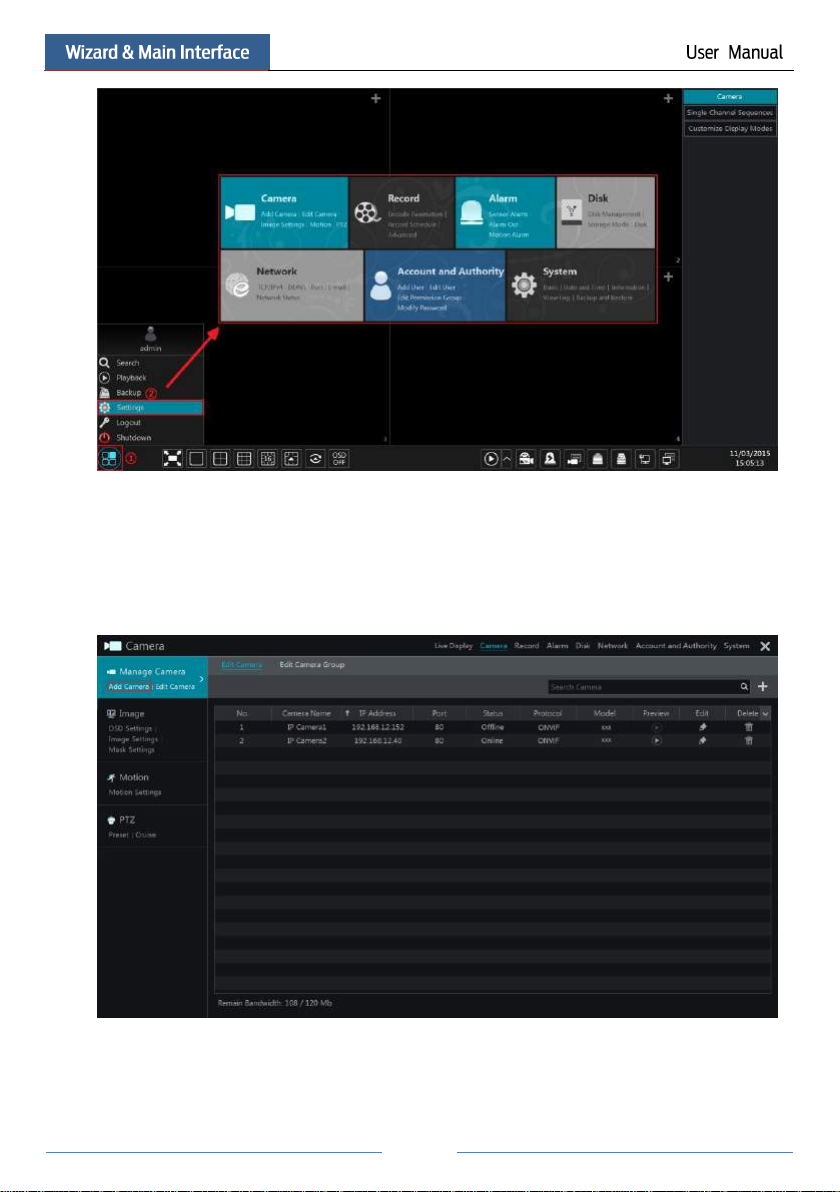
22
Click the main menus on the top of the camera management interface to go to corresponding
interfaces. Refer to the picture below. For instance, you can go to system setup interface by
clicking “System” tag.
3.2.3 Main Functions
Camera
The module covers the functions such as Camera Management (see Chapter 4 Camera
Management for details), Image Settings (see 5.3 Preview Image Configuration for details),
Motion (see 9.2.1 Motion Configuration for details) and PTZ (see Chapter 6 PTZ for details)
and so on.
Record
The module covers the functions such as Encode Parameters and Record Schedule and so on.
Please see Chapter 7 Record & Disk Management for details.
Disk
The module covers the functions such as Disk Management, Storage Mode and Disk
Information and so on. Please see Chapter 7 Record & Disk Management for details.
Alarm
The module covers the functions such as Sensor and Motion Alarm Handling and Alarm Out
Settings. Please see Chapter 9 Alarm Management for details.
Network
The module covers the functions such as TCP/IPv4, DDNS, Port, E-mail and Network Status
Page 29

23
and so on. Please see 11.1 Network Configuration for details.
Account and Authority
The module covers the functions such as Account Management (see 10.1 Account
Management for details) and Permission Management (see 10.3 Permission Management for
details) and so on.
System
The module covers the functions such as Basic Configuration (see 11.2 Basic Configuration
for details), Device Information (see 11.7 View System Information for details), Log
Information (see 11.6 View Log for details) and Configuration File Import&Export (see 11.5
Backup and Restore for details) and so on.
Page 30
24
4 Camera Management
4.1 Add/Edit Camera
4.1.1 Add Camera
The network of the NVR should be set before adding IP camera (see 11.1.1 TCP/IPv4
Configuration for details).
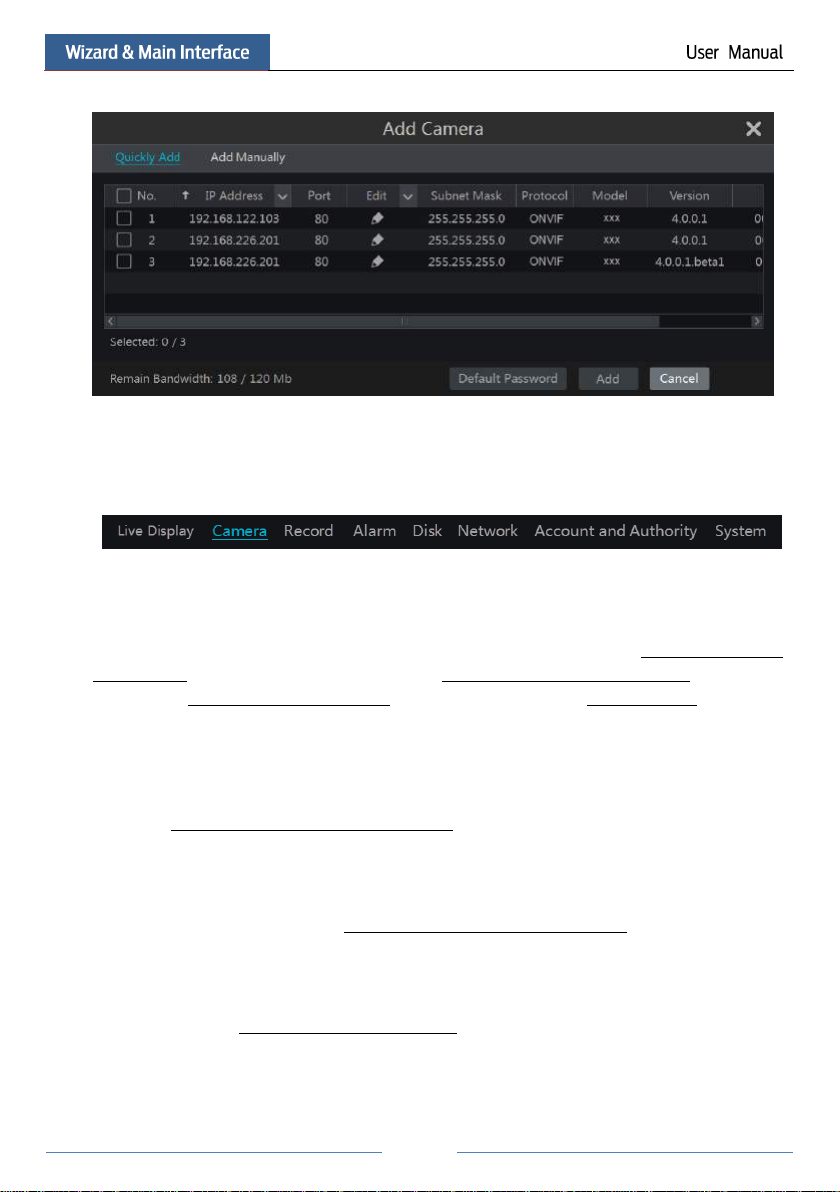
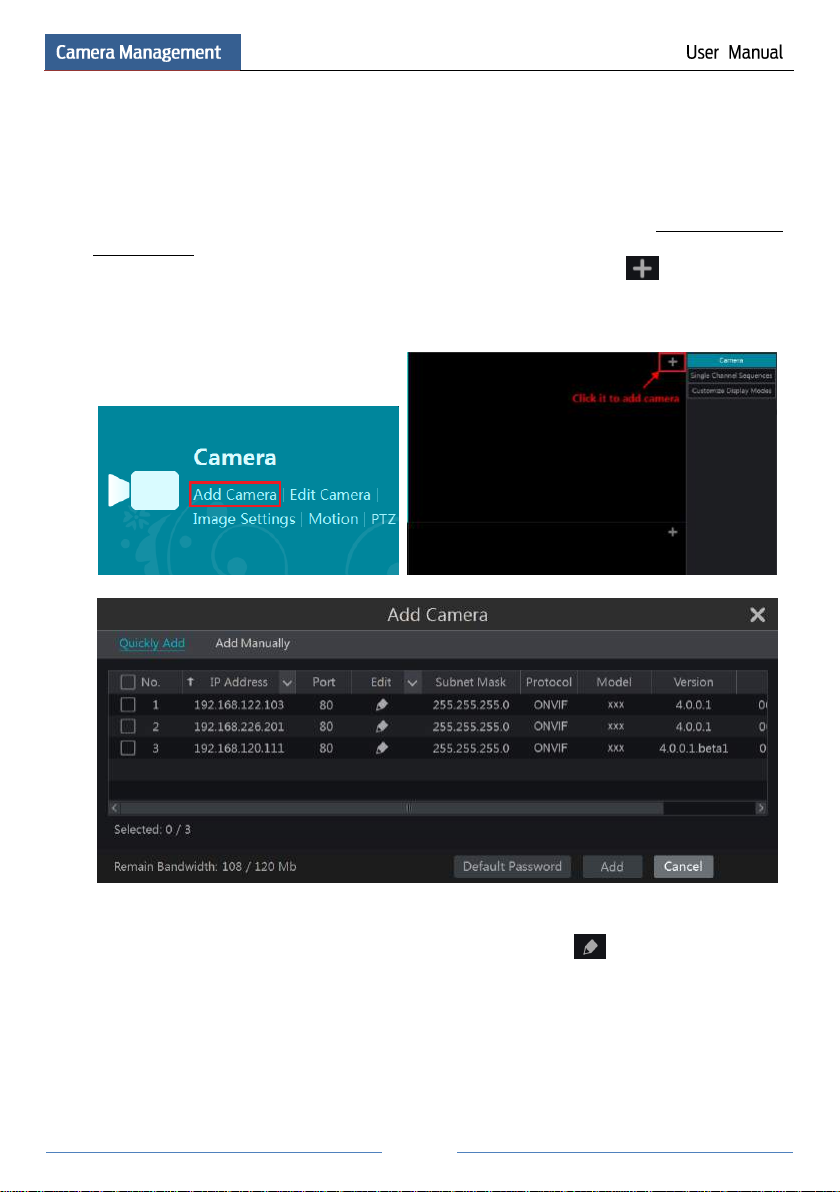
Refer to the pictures below. Click Add Camera in the setup panel or in the top right
corner of the preview window to pop up the “Add Camera” window as shown below. You can
quickly add or add the IP camera manually.
Quickly Add
Check the cameras and then click “Add” to add cameras. Click to edit the camera’s IP
address, username and password and so on. Click “Default Password” to set the default
username and password of each camera.
Page 31

25
Add Manually
Input the IP address, port, username and password of the camera and then select the protocol.
Click “Test” to test the effectiveness of the input information and then click “Add” button (you
can input one camera’s information or above such as IP address, username and password before
clicking “Add” button). Click to delete the camera. Click “Default Password” to set the
default username and password of each camera.
4.1.2 Edit Camera
Click “Edit Camera” in the setup panel to go to the interface as shown below. Click to
view the live image of the camera in the popup window. Click to edit the camera (see
Add camera in 3.1Startup Wizard for details). Click to delete the camera.
Note:
If you use the NVR with the PoE network ports, the IP cameras (with PoE function) which
directly connect to the PoE port of the NVR will be displayed automatically in the camera list.
Refer to the picture below. The IP camera which occupies the PoE resource has a prefix shown
before its camera name. The prefix consists of PoE plus PoE port number. The IP camera which
connects to the PoE port cannot be deleted from the camera list manually.
Page 32

26
The IP camera which directly connects to the PoE port of the NVR through private
protocol will be shown automatically in the camera list.
One of the two conditions must be met if the IP camera which directly connects to the PoE
port of the NVR through ONVIF protocol should be shown automatically in the camera list.
The IP camera which directly connects to the PoE port is in the same network segment
with the internal ethernet port.
The DHCP (obtain an IP address automatically) of the IP camera which directly
connects to the PoE port is enabled.
If the IP camera which connects to the PoE port cannot be displayed automatically in the
camera list, please refer to Q6 in Appendix A FAQ for details.
4.2 Add/Edit Camera Group
4.2.1 Add Camera Group
Click “Edit Camera Group” in the above interface to go to the interface as shown below.
Page 33

27
Click to pop up the window as shown below. Set the group name and dwell time (the
dwell time of the camera group sequence view) in the window. Check the cameras and then
click “Add” to add group. Click to view the cameras in the group after adding group.
4.2.2 Edit Camera Group
Click to modify the group information such as group name and dwell time. Click
to delete the group.
Page 34

28
Button
Menu List
Meaning
--
Move tool. Click it to move the tool bar anywhere.
Manually Record On
Click it to start recording.
Instant Playback
Click to playback the record; click “Instant Playback” to select
or self-define the instant playback time. See 8.1 Instant Playback for
details.
Enable Audio
Click it to enable audio. You can listen to the camera audio by
enabling audio.
Snap
Click it to pop up the snap window. Click “Save” in the window to
save the image. Click “Export” to export the image.
PTZ Control
Click it to go to PTZ control interface. See Chapter 6 PTZ for details.
Zoom In
Click it to go to single channel amplification interface.
--
Click it to go to image adjustment interface. Refer to 5.3.4 Image
Adjustment for details.
--
Camera Info
Click it to view the camera information.
5 Live Preview Introduction
5.1 Preview Interface Introduction
You should add camera first after logging on to the system (see 4.1.1 Add Camera for details).
Refer to the interface as shown below, drag one camera in the preview window to another
window for camera window exchanging.
Click the preview window to show the tool bar as shown in area ①; right click the preview
window to show the menu list. The tool bar and menu list are introduced in the table below.
Page 35

29
The single channel amplification interface is as shown below. Press and drag the blue box to
select the zoom in area. Click / to zoom the image. Click the camera selection box
to select other cameras for amplification. Click “Back” to return to the live preview interface.
5.2 Preview Mode
5.2.1 Preview By Display Mode
Set different screen modes and cameras’ display sequences as required and then save the
display modes classified by surveillance areas, priorities and so on. Refer to the picture below.
Double click one display mode in the display mode list to view the live images in this mode.
Page 36

30
Add Display Mode
Method One:
① Click “Customize Display Modes” in the above interface and then set the screen mode.
② Add the cameras and adjust the cameras’ display sequence as required.
③ Click “Save” button under the display mode list and then enter the display mode name in
the popup window, click “OK” button to save the current display mode.
Method Two:
① Click StartSettingsSystemBasicOutput Settings to go to the interface and then
set the screen mode.
② Double click the camera or camera group in the list to add them to the selected window.
③ Click to save the current display mode (refer to 5.2.4 Scheme View In Sequence for
detail configurations). The display mode will be saved and displayed in the display mode list in
the live preview interface.
Edit Display Mode
Click “Customize Display Modes” tab in the live preview interface and then select one display
mode in the list. Click “Rename” to edit the display mode name; click “Delete” to delete the
display mode.
5.2.2 Quick Sequence View
You can start quick sequence view if the scheme has not been created. If the scheme has been
created, please refer to 5.2.4 Scheme View in Sequence for details.
Go to the live preview interface and then click to pop up a little window. Set the dwell
time in the window and then click to view the live group by group according to the
Page 37

31
camera number of the current screen mode. Double click the sequence view interface to pause
the view; double click again to restore the view. Click to stop the view.
5.2.3 Camera Group View In Sequence
You can start camera group view in sequence if camera group has been created (see 4.2.1 Add
Camera Group for details).
① Go to the live preview interface and then select a camera window.
② Double click one camera group on the right side of the interface. The cameras in the group
will start camera group view one by one in the selected camera window.
You can also drag the group directly to any preview window. Right click on the group view
window and then click “Close Dwell” button to stop the view.
5.2.4 Scheme View In Sequence
Click StartSettingsSystemBasicOutput Settings to go to the interface as shown below.
Area ① displays all the dwell schemes; area ② shows the detailed information of the scheme;
area ③ displays all the cameras and groups; area ④ is the tool bar ( : clear button; :
favourite button, click it to pop up a window, enter the display mode name in the window and
then click “OK” to save the current display mode; other buttons are screen mode buttons).
Page 38

32
Add Scheme
Click in area ① to create a new scheme. Click on the top right corner of the
scheme to delete it.
Configure Scheme
a) Select a scheme in area ① and then click the screen mode button on the tool bar to set the
screen mode of the scheme.
b) Select a camera window in area ② and then double click the camera or group in area ③.
The camera or group will be added into the selected window. One camera in the same scheme
cannot repeat. You can click the right-click menu “Clear” in area ② to remove a single camera
or click to remove all the cameras.
c) Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Start Sequence View
Go to live preview interface and then click to pop up a window. Set the dwell time in the
window and then click to start scheme view in sequence. Double click the sequence view
interface to pause the view; double click again to restore the view. Click to stop the view.
5.3 Preview Image Configuration
5.3.1 OSD Settings
Click StartSettingsCameraImageOSD Settings to go to the interface as shown below.
Select the camera, input the camera name (or double click the camera name in the camera list
to change the camera name), enable or disable the name and time OSDs (if enabled, drag the
red name and time OSDs directly in the image view area to change the OSDs’ display position)
and select the date and time formats. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Page 39

33
5.3.2 Image Settings
Click StartSettingsCameraImageImage Settings to go to the following interface.
Select the camera and then set the brightness, contrast, saturation and hue of the camera. You
can click “Default” button to restore the image settings to the default factory settings.
5.3.3 Mask Settings
Some areas of the image can be masked for privacy. Up to four mask areas can be set for each
camera. Click StartSettingsCameraImageMask Settings to go to the interface as
shown below. Select the camera and enable the mask. Click “Draw” button and then drag the
mouse on the image area to set the mask area; click “Delete” button to delete the mask areas;
click “Apply” to save the settings.
Page 40

34
5.3.4 Image Adjustment
Go to live preview interface and then click button on the tool bar under the camera
window to go to the image adjustment interface.
Image Adjustment
Select the camera and then click “Image Adjustment” to go to image adjustment tab. Refer to
the above picture. Drag the slider to set the camera’s brightness, contrast, saturation and hue
value. Check sharpen, wide dynamic and denoise and then drag the slider to set the value. Click
“Default” button to set these parameters to default values.
Page 41

35
Parameter
Meaning
Brightness
It is the brightness level of the camera’s image.
Contrast
It is the color difference between the brightest and darkest parts.
Saturation
It is the degree of color purity. The color is purer, the image is brighter.
Hue
It relates to the total color degree of the image.
Sharpen
It relates to the resolution level of the image plane and the sharpness level of the
image edge.
Wide Dynamic
The wide dynamic range (WDR) function helps the camera provide clear images
even under back light circumstances. When there are both very bright and very
dark areas simultaneously in the field of view, WDR balances the brightness level
of the whole image and provide clear images with details.
Denoise
Adopt the noise reduction technology to decrease the noise and make the image
more thorough. Increasing the value will make the noise reduction effect better but
it will reduce the image resolution.
White Balance
White balance is the white rendition function of the camera to adjust the color
temperature according to the environment automatically.
Image Mirror
Reverse the current video image right and left.
Image Flip
Turn the current video image upside down.
The introductions of these parameters are as follows:
Lens Control
Select the camera and then click “Lens Control” to go to lens control tab. Click or
to adjust the zoom and focus parameters of the camera’s lens. Click “Save” to save the settings.
Page 42

36
Button/Parameter
Meaning
Click / to zoom in/out the image.
Focus Mode
If manual mode is selected, focus button & “One Key Focus” & “Day/night
mode switch autofocus” will be available; if auto mode is selected, the time
interval setup will be available.
Click / to increase/decrease the focal length.
Click it to focus instantly.
Day/night mode
switch autofocus
If checked, the lens will focus automatically when the camera is switching
day/night mode.
Time Interval
It is the time interval when camera lens is auto-focusing. The interval can
be set in the drop-down list.
Note: This function is only available for the models with auto varifocal lens, or the settings here
are ineffective.
The introductions of these parameters and buttons are as follows:
Page 43

37
Button
Meaning
Click / / / / / / /
to rotate the dome. Click to stop rotating the dome.
Click / to zoom in / out the camera image.
Click / to increase / decrease the focal length.
Click / to increase / decrease the iris of the dome.
Drag the slider to adjust the rotating speed of the dome.
/
Click / to start / stop recording.
/
Click / to hide / show the analog joystick.
Click it to return to the live preview interface.
6 PTZ
6.1 PTZ Control Interface Introduction
You can control the IP dome or PTZ which connects to the IP camera for PTZ control.
Click on the tool bar at the bottom of the live preview window to go to the PTZ control
interface as shown below. You can select another IP dome or PTZ which connects to the IP
camera on the top right of the interface for PTZ control.
Introductions of the buttons on the bottom right of the interface:
Page 44

38
Analog Joystick Control
The analog joystick on the left side of the interface provides quick PTZ control. The dome or
PTZ will rotate when you drag the analog joystick. The farther you drag the analog joystick
from the middle of the image, the faster the dome or PTZ rotates. The dome or PTZ will stop
rotating when you stop dragging the analog joystick.
3D Control
Click the camera image on any area and then the image will be centered on the clicked point.
Refer to the picture as shown below. Drag the mouse from A to B to get a green rectangle and
the rectangle area will be zoomed in.
Refer to the picture as shown below. Drag the mouse from C to D to get a green rectangle and
the rectangle area will be zoomed out.
Page 45

39
Advanced 3D Control
Double click the left button of the mouse on any area of the camera image and then the image
size will be doubled and centered on the clicked point.
Press and hold the left button of the mouse on any area of the camera image to zoom in the
image; press and hold the right button to zoom out the image.
Move the cursor of the mouse to the camera image and then slide the scroll wheel of the mouse
forward to zoom in the image, slide the scroll wheel of the mouse backward to zoom out the
image.
Preset Setting
Click “Preset” to go to preset operation tab and then click “Add” button to pop up a window as
shown below. Select the preset and then input the preset name in the window; finally click
“OK” button to save the settings. You can add 255 presets for each dome at most.
Adjust the dome’s direction and then click “Save Position” to save the current preset position
(you can also click another preset in the preset list and then save the preset position after
Page 46

40
adjusting the dome’s direction); click in the preset list to call the preset; click “Delete”
button to delete the selected preset.
You can also go to preset setting interface for preset setting, see 6.2 Preset Setting for details.
Cruise Setting
Click “Cruise” to go to cruise operation tab and then click “Add” button to pop up a window as
shown below left. You can add 8 cruises for each dome at most.
① Input the cruise name in the “Add Cruise” window and then click “Add preset” to pop up
the “Add Preset” window (Before adding preset to the cruise, please add preset of the dome
first).
② In the “Add Preset” window, select the preset name, preset time and preset speed and then
click “OK” button.
③ In the “Add Cruise” window, you can click to reselect the preset, then change the
preset time and speed. Click to delete the preset. Click “Add” button to save the cruise.
Click to start the cruise and click to stop the cruise in the cruise list of the cruise
operation tab; click “Delete” button to delete the selected cruise.
You can also go to cruise setting interface for cruise setting, see 6.3 Cruise Setting for details.
6.2 Preset Setting
Click StartSettingsCameraPTZPreset to go to the interface as shown below.
Page 47

41
Add preset
Select camera and then click “Add” button to add preset; or click in the camera list on
the right side of the interface to display the preset information of the dome and then click
to add preset. The operations of the “Add Preset” window are similar to that of the
PTZ control interface; please see 6.1 PTZ Control Interface Introduction for details.
Edit preset
Select camera and preset. You can input the new name of the preset and then click to
save the new preset name. Adjust the rotating speed, position, zoom, focus and iris of the preset
and then click “Save Position” to save the preset.
Delete Preset
Select camera and preset and then click “Delete” to delete the preset.
6.3 Cruise Setting
Click StartSettingsCameraPTZCruise to go to the interface as shown below.
Page 48

42
Add Cruise
Click in the camera list on the right side of the interface to display the cruise information
of the dome and then click to add cruise. The operations of the “Add Cruise”
window are similar to that of the PTZ control interface; please see 6.1 PTZ Control Interface
Introduction for details.
Edit Cruise
Select the camera and cruise in the “Cruise” interface. Input the new cruise name and then click
to save the cruise name. Click “Add Preset” to add preset to the cruise. Click to
delete the preset from the cruise. Click one preset in the preset list and then click to move
down the preset and click to move up the preset. Click to start the cruise and click
to stop it.
Delete Cruise
Click in the camera list on the right side of the interface to display the cruise information
of the dome and then click on the top right corner of the cruise to delete the cruise.
Page 49

43
7 Record & Disk Management
7.1 Record Configuration
7.1.1 Mode Configuration
Please format the HDDs before recording (refer to 7.5 Disk Management for details). Click
StartSettingsRecordMode Settings to go to the mode settings interface. You can set the
record time under the “Manual Record Settings” and then click “Apply” button to save the
settings. There are two record modes: auto mode and manual mode.
Auto Mode
Motion Record: Motion alarm record will be enabled when motion alarm happens.
Sensor Record: Sensor alarm record will be enabled when sensor alarm happens.
Motion Record+Sensor Record: Motion/sensor alarm record will be enabled when
motion/sensor alarm happens.
Always(24ⅹ7) Record+Motion Record: Normal record is enabled all the time; motion alarm
record will be started when motion alarm happens.
Always(24ⅹ7) Record+Sensor Record: Normal record is enabled all the time; sensor alarm
record will be started when sensor alarm happens.
Always(24ⅹ7) Record+Motion Record+Sensor Record: Normal record is enabled all the time;
motion/sensor alarm record will be enabled when motion/sensor alarm happens.
Select one auto mode to pop up the corresponding window. Set the video encode, resolution,
FPS, bitrate and audio of each camera and then click “OK” to save the settings.
Page 50

44
Video Encode: the available options will be H.265 and H.264 if the connected IP camera
supports H.265, or the option will be H.264 only.
Resolution: the higher the resolution is, the clearer the image is.
FPS: the higher the frame rate is, the more fluency the video is. However, more storage room
will be taken up.
Bitrate: the higher the image quality you choose, the more bit rate will be required.
Manual Mode
If the manual mode is selected, you need to set the encode parameters and record schedules of
each camera. See 7.2 Encode Parameters Setting and 7.3 Schedule Setting for details.
7.1.2 Advanced Configuration
Click StartSettingsRecordAdvanced to go to the following interface. Enable or disable
cycle record (cycle record: the earliest record data will be replaced by the latest when the disks
are full). Set the pre-alarm record time, post-alarm record time and expiration time of each
camera and then click “Apply” to save the settings.
Pre-alarm Record Time: set the time to record before the actual recording begins.
Post-alarm Record Time: set the time to record after the actual recording is finished.
Expiration Time: set the expiration time for recorded video. If the set date is overdue, the
recorded data will be deleted automatically.
Page 51

45
7.2 Encode Parameters Setting
Click StartSettingsRecordEncode Parameters to go to the interface as shown below. Set
the video encode, resolution, FPS, bitrate and audio of main stream for each camera in “Event
Record Stream” and “Timing Record Stream” interfaces. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
You can set the record stream of each camera one by one or batch set them for all cameras.
Click StartSettingsRecordStream Settings to go to “Sub-stream” interface. Set the video
encode, resolution, FPS and bitrate of sub-stream for each camera in the interface and then
click “Apply” to save the settings.
7.3 Schedule Setting
7.3.1 Add Schedule
Click StartSettingsRecordRecord ScheduleEdit Schedules to go to the interface as
shown below. “24ⅹ7”, “24ⅹ5” and “24ⅹ2” are the default schedules; you cannot edit or
delete “24ⅹ7” while “24ⅹ5” and “24ⅹ2” can be edited and deleted. Click the schedule name
to display the detailed schedule information on the left side of the interface. The seven rows
stand for the seven days in a week and each row stands for 24 hours in a day. Blue stands for
the selected time and gray stands for unselected time.
Page 52

46
Click to add a new schedule. Refer to the picture below.
Page 53

47
Set the schedule name and schedule time and then click “Add” to save the schedule. You can
set day schedule or week schedule. : add button; : delete button.
Set Day Schedule
Click and then drag the cursor on the time scale to set record time; click and then
drag the cursor on the time scale to delete the selected area.
You can manually set the record start time and end time. Click or and then click
“Manual” on each day to pop up a window as shown below. Set the start and end time in the
window and then click “OK” to save the settings.
Click “All” to set all day recording; click “Reverse” to swap the selected and unselected time
in a day; click “Clear All” to clear all the selected area in a day.
Click “Copy To” to copy the schedule of the day to other days. Refer to the picture below.
Check the days in the window and then click “OK” to save the settings.
Set Week Schedule
Click or and then click “Manual” beside to set the week schedule. Refer to
the picture below. Set the start and end time, check the days in the window and then click “OK”
to save the settings.
Page 54

48
Note: Click StartSettingsRecordMode Settings and then set the manual record time in the
interface. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Click “All” to set all week recording; click “Reverse” to swap the selected and unselected time
in a week; click “Clear All” to clear all the selected area in a week.
7.3.2 Record Schedule Configuration
Click StartSettingsRecordRecord ScheduleSchedule Configuration to go to the
interface as shown below. Set the schedule of sensor record, motion record and timed record.
Click “None” in the drop-down menu to clear the schedule. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Go to “Edit Schedules” interface and then click to edit the schedule. The settings of “Edit
Schedule” are similar to that of the “Add Schedule”. Click to delete the schedule.
7.4 Record Mode
7.4.1 Manual Recording
Method One: Click on the tool bar at the bottom of the live preview interface to enable
recording of the camera.
Method Two: Go to live preview interface and then click the right-click menu “Manually
Record On” in the camera window or click on the tool bar under the camera window to
start recording.
Page 55

49
Note: 1. The new HDD should be formatted for normal use.
2. For normal use of the HDD which has been used in other NVR, if the NVR is of the same
model with the new NVR, please import the configuration file of the NVR to the new NVR or
format the HDD; if the models of the two NVRs are different, please format the HDD.
7.4.2 Timing Recording
Timing Recording: the system will record automatically according to the schedule.
Set the timing record schedule of each camera. See 7.3 Schedule Setting for details.
7.4.3 Motion Based Recording
Motion Based Recording: the system will start motion based recording when the motion
object appears in the setup schedule. The setup steps are as follows:
① Set the motion based recording schedule of each camera. See 7.3 Schedule Setting for
details.
② Enable the motion and set the motion area of each camera. See 9.2.1 Motion
Configuration for details.
The camera will start motion based recording once you finish the above settings.
7.4.4 Sensor Based Recording
① Set the sensor based recording schedule of each camera. See 7.3 Schedule Setting for
details.
② Set the NO/NC type of the sensor, enable the sensor alarm and then check and configure
the “Record”. See 9.1 Sensor Alarm for details.
7.5 Disk Management
Click StartSettingsDiskDisk Management to go to disk management interface. You can
view the NVR’s disk number and disk status and so on in the interface. Click “Formatting”
button to format the HDD.
7.5.1 Storage Mode Configuration
Click StartSettingsDiskStorage Mode to go to the interface as shown below.
Page 56

50
There are all four disk groups. By using disk group, you can correspond the camera to disk (the
record data of the camera in the group will be stored into the disks in the same group).
The added disks and cameras will be added into group one automatically. The disks and
cameras in the groups can be deleted except group one (select a disk group and then click
on the top right corner of the added disk or camera to delete it from the group). The deleted
disks and cameras will be moved into group one automatically.
Each group can add the disks and cameras from other groups. Each disk and camera can only
be added into one group. Select a disk group and then click in the disk or camera
row to pop up a window. Check the disks or cameras in the window and then click “Add”.
7.5.2 View Disk and S.M.A.R.T. Information
Click StartSettingsDiskView Disk Information to view the HDD information; click
“S.M.A.R.T. Information” to view the working status of the HDD. Refer to the picture below.
Page 57
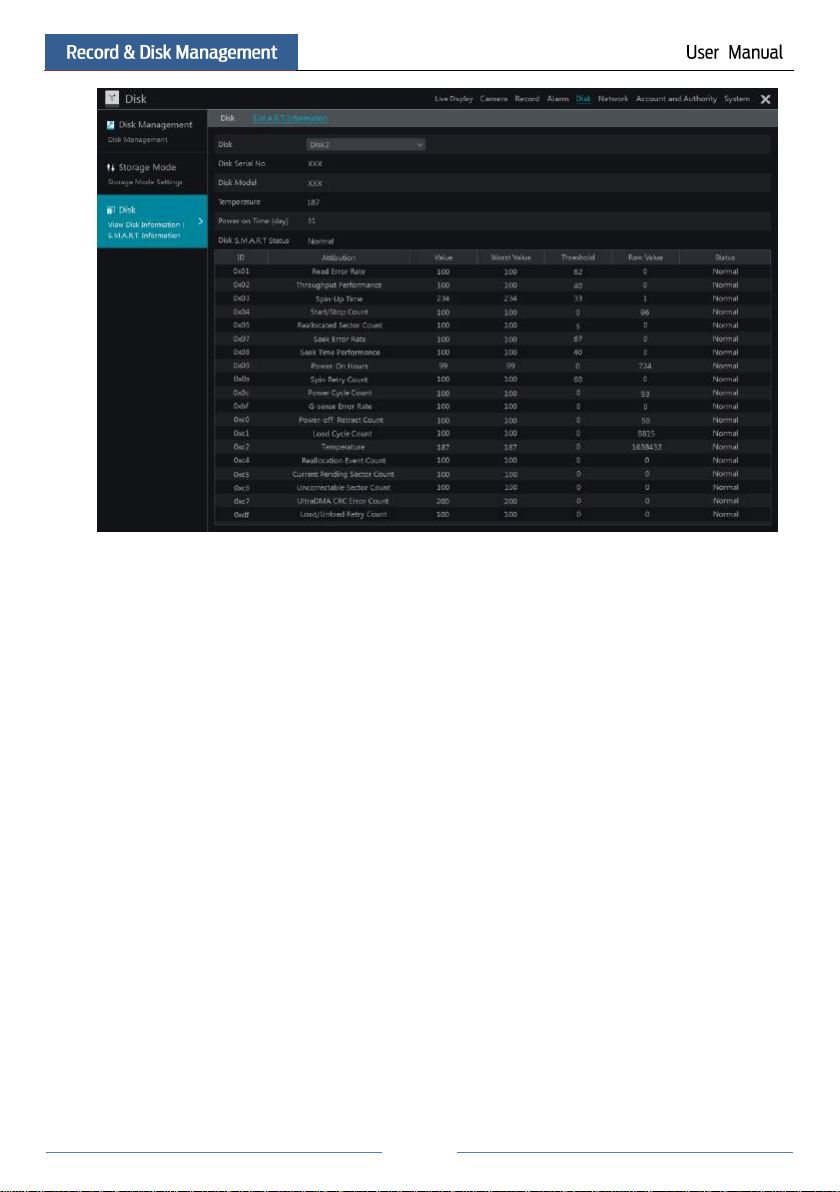
51
Page 58

52
8 Playback & Backup
8.1 Instant Playback
Click on the tool bar at the bottom of the preview camera window to play back the record
(click on the tool bar at the bottom of the live preview interface to set the default playback
time). Refer to the picture below. Drag the playback progress bar to change the playback time.
You can also click the right-click menu “Instant Playback” in the camera window and then set
the instant playback time to play back the record.
8.2 Playback Interface Introduction
Click on the tool bar at the bottom of the live preview interface or click StartPlayback
to go to the playback interface as shown below (click on the tool bar at the bottom of the
live preview interface to set the default playback time).
Page 59

53
Button
Meaning
Start button. Click it to pop up area ②.
Full screen button. Click it to show full screen; click it again to exit the full
screen.
Screen mode button.
OSD ON button. Click it to enable OSD; click to disable OSD.
Stop button.
Rewind button. Click it to play video backward.
Play button. Click it to play video forward.
Pause button.
Deceleration button. Click it to decrease the playing speed.
Acceleration button. Click it to increase the playing speed.
Previous frame button. It works only when the forward playing is paused in
single screen mode.
Next frame button. It works only when the forward playing is paused in single
screen mode.
Click to step backward 30s and click to step forward 30s.
Event list/tag button. Click it to view the event record of
manual/schedule/sensor/ motion and the tag information.
Backup button. Drag the mouse on the time scale to select the time periods and
cameras, and then click the button to back up the record.
Backup status button. Click it to view the backup status.
Back button. Click it to return.
Button
Meaning
Click it to go to record search interface; see 8.3 Record Search & Playback for
details.
Click it to go to backup interface; see 8.4 Backup for details.
Click it to go to live preview interface; see Chapter 5 Live Preview Introduction
for details.
The added cameras will playback their records in the playback interface automatically. You can
also add the playback camera manually. Click in the playback window to pop up the
“Add Camera” window. Check the cameras in the window and then click “Add” to add
playback camera. The system supports a maximum of 16 synchronous playback cameras.
The buttons on the tool bar (area ①) at the bottom of the playback interface are introduced in
the table below.
Introduction of area ②:
Page 60

54
Click on the playback window to show the tool bar as shown in area ③; right click on the
Button
Menu List
Meaning
--
Move tool. Click it to move the tool bar anywhere.
Enable Audio
Click it to enable audio. You can listen to the camera audio by
enabling audio.
Snap
Click it to snap.
Zoom In
Click it to go to the zoom in interface. The zoom in interface is
similar to that of the camera window in the live preview interface.
Click to pause the record playing; click to play the
record. When the record is paused in forward playing mode, you
can click to view the previous frame and click to
view the next frame.
Add Tag
Click it to add tag. You can play back the record by searching the
added tag. Click it and then input the tag name in the popup
window. Click “Add” to add tag.
Switch Camera
Click it to switch the playback camera. Click it and then check the
camera in the popup window. Click “OK” to change the camera.
Close Camera
Click it to close the playback camera.
window to show the menu list. The tool bar and menu list are introduced in the table below.
Introduction of area ④:
Click to set the date; click to set the time and then the playback camera will play the
record from the time you set. You can check the record type as required for record playback;
first you should click on the tool bar at the bottom of the interface to clear all the playback
camera, then check the record type ( : manual record; : sensor based record; : motion
based record; : schedule record) and finally click in the playback window to add
camera for playback (the record time scale will show the record data of the checked record type
only after the above operations).
Introduction of the record time scale (area ⑤):
A tool bar will appear after moving the mouse to the record time scale. Click / to
zoom the timeline; click to recover the timeline to 24 hours’ ratio. Drag the timeline or
slide the scroll wheel of the mouse on the time scale to show the hidden time on the top or
bottom of the timeline. You can also click to show the hidden time on the top of the
timeline or click to show the hidden time on the bottom of the timeline. Drag the slider at
the bottom of the time scale to show the hidden playback cameras.
The record time scale shows different record types with different colors. The green block
stands for manual record, red block stands for sensor based record, yellow block stands for
motion based record and blue block stands for schedule record. Click the record block to set the
time and then the playback camera will play the record from the time you set.
Drag the color block on the time scale to select the backup area and then right click the area or
click to pop up a backup information window. Click “Backup” button in the window to
Page 61
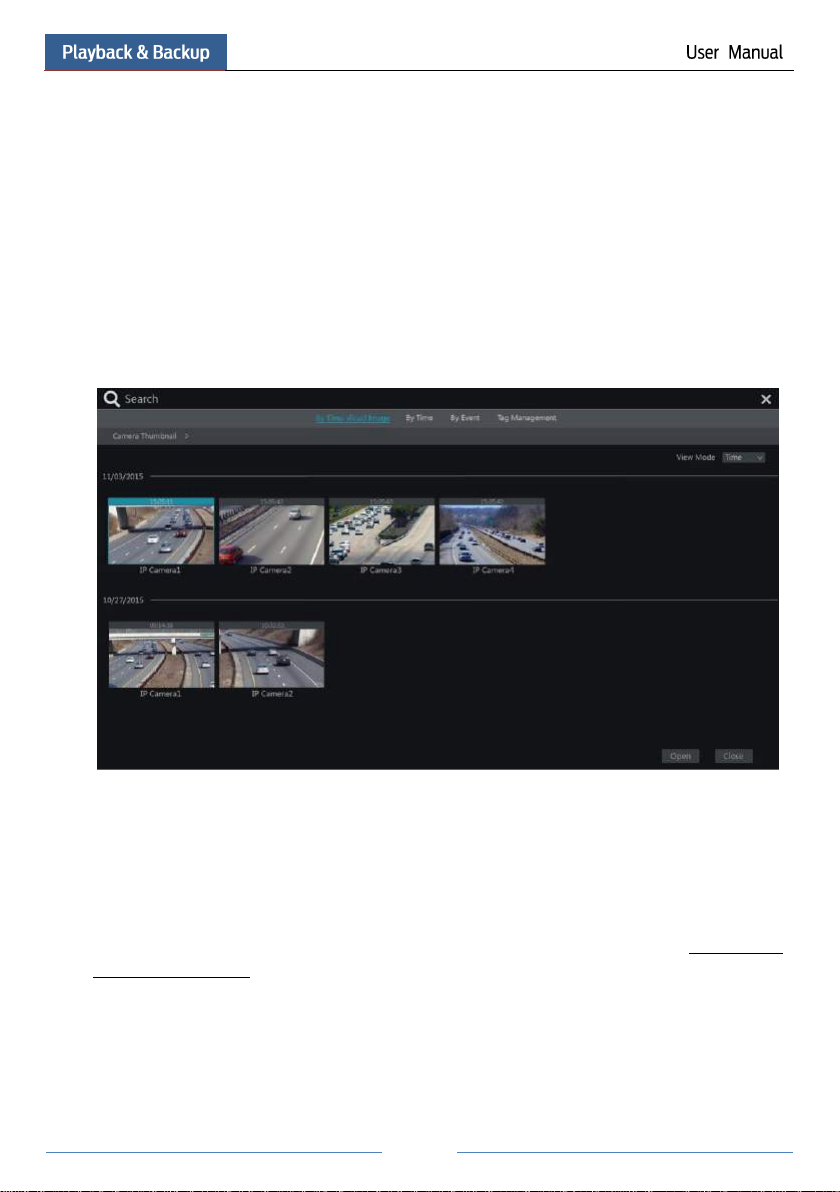
55
pop up the backup window. Select the device, backup path and backup format and then click
“Backup” button to start the backup.
8.3 Record Search & Playback
8.3.1 Search & Playback by Time-sliced Image
① Click StartSearchBy Time-sliced Image to go to “By Time-sliced Image” tab. There
are two view modes: by time and by camera. In the time view mode, a maximum of 64 camera
thumbnails can be showed. If the camera thumbnail number is more than 64, the cameras will
be listed directly by their camera name, not the thumbnail. A maximum of 196 camera names
can be listed. If the camera name number is more than 196, the time view mode will be
disabled and the camera view mode will be available only.
② Select one camera in the interface and then click “Open” button.
③ Click the image box to play the record in the small playback box on the left side of the
interface (the box which has image inside indicates that the record data exist).
④ Refer to the picture below. Drag the color blocks on the time scale to select the record data
and then click “Backup” button to pop up a window; select the device, backup path and backup
format in the window and then click “Backup” button to start the backup.
⑤ Click “Playback” button to play the record in the playback interface (refer to 8.2 Playback
Interface Introduction for details). Click “Close” to close the interface.
Page 62

56
Time Slice Mode Selecting:
Method One: Click “Year”, “Month” or “Day” button under the record time scale to select the
time slice mode. In “Day” mode, click / on the left/right side of the time scale to
view the record of the last/next day; click “Minute” in the “Picture” option under the time scale
to select “Minute” mode (in “Minute” mode, click the time scale to change the time of the 60
display windows) and click “Hour” to select “Hour” mode.
Method Two: Click beside “Camera Thumbnail” on the left top corner of the interface to
select the time slice mode.
Method Three: Right-click the mouse on any area of the time-sliced interface to go back to the
upper interface.
8.3.2 Search & Playback by Time
① Click StartSearchBy Time to go to “By Time” tab as shown below.
② Click on the bottom of the interface to add playback camera. A maximum of 16
cameras can be added for playback. Click “Modify” on the top right corner of the camera
window to change the camera and click “Clear” to remove the camera.
③ Click the camera window to play the record in the small playback box on the left side of
the interface. You can set the date on the top left of the interface, check the event type as
required and click the time scale or click under the time scale to set the time. The camera
window will play the record according to the time and event type you set.
④ Drag the color blocks on the time scale to select the record data and then click “Backup”
button for record backup. Click “Playback” button to play the record in the playback interface.
Page 63

57
8.3.3 Search & Playback by Event
① Click StartSearchBy Event to go to “By Event” tab as shown below.
② Check the event type in the interface as required.
③ Click to set the start time and end time on the top left of the interface.
④ Check cameras on the left side of the interface and then click to search the record.
The searched record will be displayed in the list.
Page 64

58
⑤ Click in the list to play back the record in the popup window. Select one record data
in the list and then click “Backup” button for record backup.
⑥ Select one record data in the list and then click “Playback” button to play the record in the
playback interface.
8.3.4 Search & Playback by Tag
Only if you add the tags can you play the record by tag search. Click StartPlayback to go to
the playback interface and then click on the bottom of the camera window to add tag
when you want to mark the playback time point of the selected camera.
Click StartSearchTag Management to go to “Tag Management” tab.
Click in the interface to play the record. Click to edit the tag name. Click to
delete the tag.
8.4 Backup
The record data and the snapped pictures can be backed up through network, USB (U disk or
USB mobile HDD) or e-SATA (only available for some models). The file system of the backup
devices should be FAT32 format.
8.4.1 Backup by Time
① Click StartBackupBy Time to go to the “By Time” tab.
② Click in the tab to pop up the add camera window. Check the cameras in the window
and then click “Add” button. Click “Modify” on the top right corner of the camera window to
change the camera and click “Clear” to remove the camera.
③ Set the date on the top left of the interface. Drag the time scale to set the backup time
period or click under the time scale to set the backup start time and end time.
Page 65

59
Note: If you back up the record in private format, the system will back up a RPAS player to USB
device automatically. The private format record can be played by RPAS player only.
④ Click “Backup” button to pop up the “Record Backup” window as shown below. Select
the device name, backup format and path and then click “Backup” button to start the backup.
8.4.2 Backup by Event
① Click StartBackupBy Event to go to “By Event” tab.
Page 66

60
② Click to set the start time and end time on the left top of the interface.
③ Check the event types and cameras.
④ Click to search the record. The searched record data will be displayed in the list.
Click in the list to play the record in the small popup playback window. Click to
back up the record. Check one record data or above in the list and then click “Backup” button
to back up the record data.
8.4.3 Image Management
Click StartBackupImage Management to go to “Image Management” tab. The system will
display all the snapped images automatically in the list.
Click to delete the image. Click to pop up the “Export” window. Select the device
name and save path in the window and then click “Save” button.
Click to pop up the “View Image” window. Click to export the image. Click
to view the previous image; click to view the next image; click to delete the image;
click to play all the images.
Page 67

61
8.4.4 View Backup Status
Click StartBackupBackup Status or click on the tool bar at the bottom of the
playback interface to view the backup status.
Page 68

62
9 Alarm Management
9.1 Sensor Alarm
To complete the entire sensor alarm settings, you should enable the sensor alarm of each
camera and then set up the alarm handling of each camera.
① Click StartSettingsAlarmSensor Alarm to go to the following interface.
② Select the alarm type (NO or NC) according to trigger type of the sensor.
③ Enable the sensor alarm of each camera.
④ Check the “Record”, “Snap”, “Alarm-out” and “Preset” and enable or disable the
“Buzzer”, “Pop-up Video”, “Pop-up Message Box” and “E-mail” as required.
⑤ Click “Apply” to save the settings.
The configuration steps of the above mentioned alarm linkages are as follows.
Record: check it and then the “Trigger Record” window will pop up automatically (you can
also click “Configure” button to pop up the window). Select camera on the left side and then
click to set the camera as the trigger camera. Select trigger camera on the right side and
then click to cancel the trigger camera. Click “OK” button to save the settings. The
trigger cameras will record automatically when the sensor alarm is triggered.
Snap: check it and then the “Trigger Snapshot” window will pop up automatically. Configure
the trigger camera in the window. The trigger cameras will snap automatically when the sensor
alarm is triggered.
Alarm-out: check it and then the “Trigger Alarm-out” window will pop up automatically.
Configure the trigger alarm-out in the window. The system will trigger the alarm-out
automatically when the sensor alarm is triggered. You need to set the delay time and the
schedule of the alarm outputs. See 9.4.1 Alarm-out for details.
Preset: check it and then the “Trigger Preset” window will pop up automatically. Configure the
trigger preset of each camera. To add presets, please see 6.2 Preset Setting for details.
Buzzer: if enabled, the system will begin to buzz when the sensor alarm is triggered. To set the
delay time of the buzzer, please see 9.4.4 Buzzer for details.
Pop-up Video: After camera setting, the system will pop up the corresponding video
automatically when the sensor alarm is triggered. To set the duration time of the video, please
see 9.4.3 Display for details.
Page 69

63
Pop-up Message Box: if enabled, the system will pop up the corresponding alarm message box
automatically when the sensor alarm is triggered. To set the duration time of the message box,
please see 9.4.3 Display for details.
E-mail: if enabled, the system will send an e-mail when the sensor alarm is triggered. Before
you enable the email, please configure the recipient’s e-mail address first (see 11.1.4 E-mail
Configuration for details).
9.2 Motion Alarm
Motion Alarm: when the motion object appears in the specified area, it will trigger the alarm.
You should enable the motion of each camera first and then set the alarm handling of the
camera to complete the whole configuration of the motion alarm.
9.2.1 Motion Configuration
① Click StartSettingsCameraMotion to go to the following interface.
② Select the camera, enable the motion and set the sensitivity and duration of the camera.
Sensitivity: the higher the value is, the more sensitive it is to motion. You should adjust the
value according to the practical conditions since the sensitivity is influenced by color and time
(day or night).
Duration: it refers to the interval time between the adjacent motion detections. For instance, if
the duration time is set to 10 seconds, once the system detects a motion, it will go to alarm and
would not detect any other motion (specific to camera) in 10 seconds. If there is another motion
detected during this period, it will be considered as continuous movement; otherwise it will be
considered as a single motion.
Page 70

64
③ Drag the camera image to set the motion area. You can set more than one motion area.
Click “All” to set the whole camera image as the motion area. Click “Reverse” to swap the
motion area and the non-motion area. Click “Clear” to clear all the motion areas.
④ Click “Apply” to save the settings. Click “Processing Mode” to go to the alarm handling
configuration interface of the motion alarm.
9.2.2 Motion Alarm Handling Configuration
① Click StartSettingsAlarmMotion Alarm to go to the following interface.
② Enable or disable “Snap”, “Alarm-out”, “Preset”, “Buzzer”, “Pop-up Video” and “E-mail”.
The alarm handling setting of motion alarm is similar to that of the sensor alarm (see 9.1
Sensor Alarm for details).
③ Click “Apply” to save the settings. You can click “Motion Settings” to go to the motion
configuration interface.
9.3 Exception Alarm
9.3.1 Exception Handling Settings
① Click StartSettingsAlarmExceptionException Handling Settings to go to the
interface as shown below.
② Enable or disable “Alarm-out”, “Buzzer”, “Pop-up Message Box” and “E-mail”. The
exception handling settings are similar to that of the sensor alarm (see 9.1 Sensor Alarm for
details).
③ Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Page 71

65
9.3.2 IPC Offline Settings
① Click StartSettingsAlarmExceptionIPC Offline Settings to go to the interface as
shown below.
② Enable or disable “Snap”, “Alarm-out”, “Preset”, “Buzzer”, “Pop-up Video”, “Pop-up
Message Box” and “E-mail”. The IPC Offline Settings are similar to that of the sensor alarm
(see 9.1 Sensor Alarm for details).
③ Click “Apply” to save the settings.
9.4 Alarm Event Notification
9.4.1 Alarm-out
① Click StartSettingsAlarmEvent Notification to go to the following interface.
Page 72

66
② Set the delay time and the schedule of each alarm-out. You can click “Edit Schedules” to
edit the schedules (see 7.3.1 Add Schedule for details).
③ Click “Apply” to save the settings. You can click “Test” to test the alarm output.
9.4.2 E-mail
Click StartSettingsAlarmEvent NotificationE-mail to go to the e-mail configuration
interface. Set the e-mail address of the recipients. See 11.1.4 E-mail Configuration for details.
9.4.3 Display
Click StartSettingsAlarmEvent NotificationDisplay to go to the display configuration
interface. Set the duration time of the pop-up video and the pop-up message box. Click
“Apply” to save the settings.
9.4.4 Buzzer
Click StartSettingsAlarmEvent NotificationBuzzer to go to the buzzer configuration
interface. Set the delay time of the buzzer and then click “Apply” to save the setting. You can
click “Test” to test the buzzer.
Page 73

67
9.5 Manual Alarm
Click on the tool bar at the bottom of the live preview interface to pop up a window. Click
“Trigger” to start alarm. Click “Clear” to stop alarm.
9.6 View Alarm Status
Click StartSettingsAlarmAlarm Status or click on the tool bar at the bottom of the
live preview interface to view the alarm status.
Click “Clear” button to stop the buzzer when the buzzer alarm happens. Click to view
the detail information as shown below.
Page 74

68
If the exception information is more than one page, you can input the number in the box and
then click to jump to the specified page. Click / to view the exception alarm
information in the previous/next page. Click to play the alarm record.
Page 75

69
10 Account & Permission Management
10.1 Account Management
Click StartSettingsAccount and AuthorityAccountEdit User to go to the interface as
shown below.
Area ① displays the user permissions. Area ② displays the user list. Click the user in the list
to display its user permissions in area ①.
There are three default permission groups (“Administrator”, “Advanced” and “Ordinary”)
available when adding accounts. You can manually add new permission group (see 10.3.1 Add
Permission Group for details).
The user admin owns all the permissions and it can manage the system’s accounts. Group
“Administrator” owns all the permissions displayed in area ① and its permissions cannot be
changed while the permissions of “Advanced” and “Ordinary” can be changed.
10.1.1 Add User
① Click StartSettingsAccount and AuthorityAccountAdd User or click
beside the search box to pop up the window as shown below.
Page 76
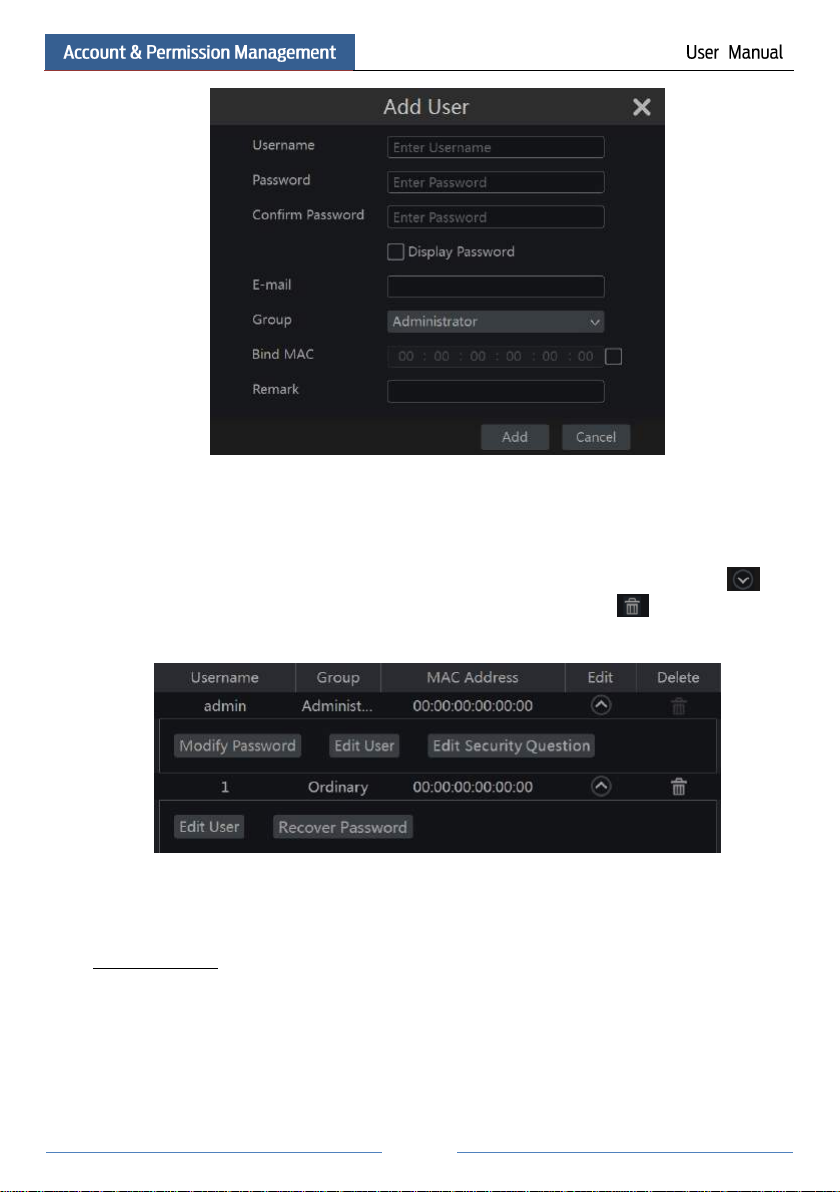
70
② Set the username, password and group. The e-mail address, MAC address and the remark
are optional (input the MAC address after you check it). Click “Add” to add the user.
10.1.2 Edit User
Click StartSettingsAccount and AuthorityAccountEdit User and then click in
the user list or double click the user to edit the user information. Click to delete the user
(the user admin cannot be deleted).
Edit Security Question
You can set password security only for admin. Click “Edit Security Question” and then set
questions and answers in the popup window. If you forget the password, please refer to Q4 in
Appendix A FAQ for details.
Modify Password
Only the password of admin can be modified. Click “Modify Password” to pop up a window.
Input the current password and then set new password. Click “OK” to save the settings.
Recover Password
Click “Recover Password” to reset the password to 123456.
Page 77

71
Edit User
Click “Edit User” to pop up the window as shown below. The admin is enabled, its permission
control is closed and permission group cannot be changed by default. You can enable or disable
other users (if disabled, the user will be invalid), open or close their permission control (if
closed, the user will get all the permissions which the administrator permission group has) and
set their permission groups. Click “OK” to save the settings.
10.2 User Login & Logout
Login: Click StartLogin or directly click the preview interface and then select username and
enter the password in the popup window. Click “Login” button to log in the system.
Logout: Click StartLogout or click StartShutdown to pop up the “Shutdown” window.
Select “Logout” in the window and then click “OK” button to log out the system.
10.3 Permission Management
10.3.1 Add Permission Group
Click StartSettingsAccount and AuthorityAccountEdit Permission Group to go to the
interface as shown below.
Page 78

72
Click to add permission group. Set the group name, check the permissions as required
and then set the “Local” and “Remote” permissions. Click “Add” to save the settings.
Page 79

73
10.3.2 Edit Permission Group
Go to “Edit Permission Group” interface and then click in the group list to edit the
permission group (the operations of the “Edit Permission Group” are similar to that of the “Add
Permission Group”, please see 10.3.1 Add Permission Group for details). Click to save
the group as another group. Click to delete the permission group. The three default
permission groups (“Administrator”, “Advanced” and “Ordinary”) cannot be deleted.
10.4 Black and White List
① Click StartSettingsAccount and AuthoritySecurity to go to the following interface.
② Check “Enable” and then choose “Enable Allow List” or “Enable Block List” (the PC
client of which the IP address is in the allow list can access NVR remotely while the PC client
in the block list cannot).
③ Add IP/IP segment/MAC. Click “Add IP” or “Add MAC” button and then check “Enable”
in the popup window (only if you check it can the IP/IP segment/MAC you add be effective).
Enter the IP/IP segment/MAC and then click “OK” button. In the above interface, click
to edit IP/IP segment/MAC, click to delete it. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Page 80

74
11 Device Management
11.1 Network Configuration
11.1.1 TCP/IPv4 Configuration
IP Address Settings
Click StartSettingsNetworkTCP/IPv4 to go to the following interface. Check “Obtain an
IP address automatically” and “Obtain DNS automatically” to get the IP address and DNS
automatically, or manually input IP address, subnet mask, gateway, preferred DNS and
alternate DNS. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Internal Ethernet Port Introduction:
If you use the NVR with the PoE network ports, the online state of the internal ethernet port
will be shown on the interface. Refer to the picture below.
The internal ethernet port is the port which connects all the PoE ports with the NVR system.
The PoE ports are available if the internal ethernet port is online; if it is offline, all the PoE
ports will be unavailable, may be the internal ethernet port is broken. The IP address and subnet
mask of the internal ethernet port can be changed to make the port in the same network
Page 81

75
segment with the IP cameras which directly connect to the PoE ports of the NVR (it is not
recommended to change the IP address and subnet mask of the internal ethernet port).
PPPoE Settings
In the above interface, check “Enable” in “PPPoE Settings” and then input the username and
password obtained from the dealer. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
11.1.2 Port Configuration
Click StartSettingsNetworkPort to go to the interface as shown below. Input the HTTP
port, server port and RTSP port of the NVR and then click “Apply” to save the ports.
HTTP Port: the default HTTP port of the NVR is 80. The port number can be changed to
others like 81. The port is mainly used to IE remote access. If you want to access the NVR
Page 82

76
Note: The HTTP port and server port of the NVR should be mapped to the router before you access
the NVR via WAN.
through IE, you should input IP address plus HTTP port in the IE address bar like
http://192.168.11.61:81.
Server Port: the default server port of the NVR is 6036. The server port number can be
changed as required. The port is mainly used in network video management system.
RTSP Port: RTSP real-time stream protocol can be used to control the sending of real-time data.
By media player which supports the RTSP real-time stream protocol, you can view the live
images synchronously. The default RTSP port is 554 and it can be changed as required.
11.1.3 DDNS Configuration
The DDNS is used to control the dynamic IP address through domain name. You can access to
the NVR easily if the DDNS is enabled and configured.
Click StartSettingsNetworkDDNS to go to the interface as shown below.
Check “Enable” and then select the DDNS type. Input the server address, domain name,
username and password according to the selected DDNS type. Click “Test” to test
the effectiveness of the input information. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
You will have to input the server address and domain name if some DDNS types are selected.
Go to the relative DNS website to register domain name and then input the registered domain
information here). Now we take www.dvrdydns.com for example.
① Input www.dvrdydns.com in the IE address bar to visit its DNS website.
Page 83

77
② Click Registration button to go to the interface as shown below. Set the DDNS account
information (username, password and so on) and then click Submit button to save the account.
③ Create domain name and then click Request Domain.
Page 84

78
④ After you successfully request your domain name, you will see your domain name
information in the list.
⑤ Click StartSettingsNetworkDDNS to go to DDNS setting interface. Enable DDNS
and then select the www.dvrdydns.com DDNS type. Input the registered username, password
and domain name and then click “Apply”.
⑥ Map the IP address and HTTP port in the router (you can skip this step if UPnP function is
enabled).
⑦ Input the registered domain name plus HTTP port like http://www.xxx.dvrdydns.com:81
in the IE address bar and then press Enter key to go to the IE client.
11.1.4 E-mail Configuration
Click StartSettingsNetworkE-mail to go to the following interface. Input the sender’s
e-mail address, name, password, SMTP server and SMTP port (you can click “Default” to reset
the SMTP port to the default value) and then enable or disable the SSL and attaching image.
Click “Test” to pop up a window. Input the e-mail address of the recipient in the window and
then click “OK” button. The e-mail address of the sender will send an e-mail to the recipient. If
the e-mail is sent successfully, it indicates that the e-mail address of the sender is configured
correctly. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Page 85

79
Click “Edit Recipient” to go to the following interface.
Click “Add” and then input the recipient’s e-mail address in the popup window. Click “Add” in
the window to add the recipient. Click to delete the recipient in the list. Click “Apply” to
save the settings. Click “Edit Sender” to go to the e-mail configuration interface of the sender.
11.1.5 UPnP Configuration
By UPnP you can access the NVR through IE client which is in WAN via router without port
mapping.
① Click StartSettingsNetworkUPnP to go to the following interface.
② Make sure the router supports UPnP function and the UPnP is enabled in the router.
Page 86

80
③ Set the NVR’s IP address, subnet mask and gateway and so on corresponding to the router.
④ Check “Enable” in the interface as shown below and then click “Apply” button.
Click “Refresh” button to refresh the UPnP status. If the UPnP status were still “Invalid UPnP”
after refreshing it for many times, the port number would be wrong. Please change the mapping
type to “Manual” and then click to modify the port until the UPnP status turns to “Valid
UPnP”. Refer to the following picture. You can view the external IP address of the NVR. Input
the external IP address plus port in the IE address bar to access the NVR such as
http://183.17.254.19:81.
11.1.6 NAT Configuration
Click StartSettingsNetworkNAT to go to the interface for NAT configuration. Check
“Enable” and then select the NAT server address (nat.autonat.com by default). Click “Apply”
to save the settings.
11.1.7 View Network Status
Click StartSettingsNetworkNetwork Status to view the network status or click on
the tool bar at the bottom of the live preview interface to view network status conveniently.
11.2 Basic Configuration
11.2.1 Common Configuration
Click StartSettingsSystemBasicGeneral Settings to go to the following interface. Set
the device name, device No., language, video format and resolution. Enable or disable wizard,
“Log In Automatically” and “Log Out Automatically” (if checked, you can set the wait time).
Click “Apply” to save the settings.
Page 87
81
Device Name: The name of the device. It may display on the client end or CMS that help user
to recognize the device remotely.
Video Format: Two modes: PAL and NTSC. Select the video format according to the camera.
11.2.2 Date and Time Configuration
Click StartSettingsSystemBasicDate and Time to go to the interface as shown below.
Set the system time, date format, time format and time zone of the NVR. The default time zone
is GMT+08 Beijing, Hong Kong, Shanghai, Taipei. If the selected time zone includes DST, the
DST of the time zone will be checked by default. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
You can manually set the system time or synchronize system time with network through NTP.
Manual: select “Manual” in the “Synchronous” option and then click after the “System
Time” option to set the system time.
NTP: select “NTP” in the “Synchronous” option and then input the NTP server.
Page 88
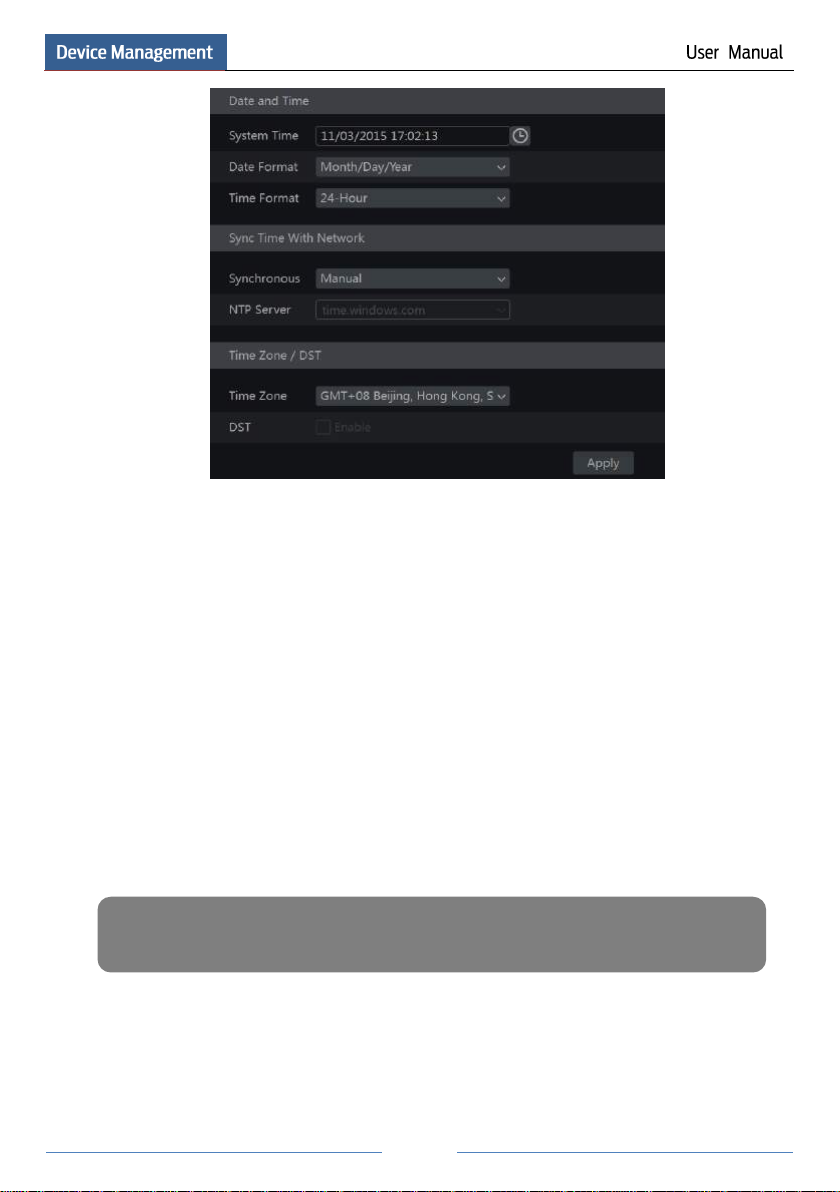
82
Note: The file system of the USB mobile device which is used for upgrading, backing up and restoring
should be FAT32 format.
11.3 Factory Default
Click StartSettingsSystemMaintenanceFactory Default and then click “Reset to
factory default” button in the interface to reset to the factory default settings.
11.4 Device Software Upgrade
You can click StartSettingsSystemInformationBasic to view MCU, kernel version and
firmware version and so on. Before upgrade, please get the upgrade file from your dealer.
The upgrade steps are as follows:
① Copy the upgrade software into the USB storage device.
② Insert the USB storage device into the USB interface of the NVR.
③ Click StartSettingsSystemMaintenanceUpgrade to go to “Upgrade” interface.
Select the USB device in “Device Name” option and go to the path where the upgrade software
exists. Select the upgrade software and then click “Upgrade”. The system may automatically
restart during upgrading. Please wait for a while and do not power off the NVR during
upgrading.
11.5 Backup and Restore
You can back up the configuration file of the NVR by exporting the file to other storage
devices; you can recover the configuration to other NVRs which are of the same model with
the NVR by importing the configuration file to other NVRs for time saving.
Page 89

83
Insert the USB storage device into the USB interface of the NVR and then click
StartSettingsSystemMaintenanceBackup and Restore to go to the interface.
Backup
Select the USB device in “Device Name” option; go to the path where you want to store the
configuration backup file and then click “Backup” button; finally click “OK” button in the
popup window.
Recover
Select the USB device in “Device Name” option; find the configuration backup file and then
click “Recover” button; finally click “OK” button in the popup window.
11.6 View Log
Click StartSettingsSystemMaintenanceView Log to go to the log view interface.
Select the log main type, click to set start time and end time and then click “Search”
button. The searched log files will be displayed in the list.
Choose the log file in the list and then click “Export” button to export the log file. Click
on the “Content” title bar to pop up a menu list. Check contents in the menu list and then the
log list will show the checked log contents only. Click to play the video log.
11.7 View System Information
Click StartSettingsSystemInformation and then click the corresponding menu to view
the “Basic”, “Camera Status”, “Alarm Status”, “Record Status”, “Network Status” and “Disk”
information of the system.
Page 90

84
12 Remote Surveillance
12.1 Mobile Client Surveillance
① Enable NAT in the NVR. Refer to 11.1.6 NAT Configuration for details.
② Download and install the mobile client “SuperLive Plus” into the mobile device with the
Android or iOS system.
③ Run the mobile client, go to the “Add Device” interface and then click to scan the
QRCode of the NVR (Go to StartSettingsSystemInformationBasic to view the
QRCode of the NVR).
④ After scanning the QRCode successfully, input the login password to log in mobile client.
12.2 Web LAN Access
① Click StartSettingsNetworkTCP/IPv4 to go to the “TCP/IPv4” interface. Set the IP
address, subnet mask, gateway, preferred DNS and alternate DNS of the NVR.
② Open IE browser on a computer, input the IP address of the NVR in the IE address bar and
then press enter to go to the login interface as shown below. You can change the display
language on the top right corner of the login interface. Input the username and password of the
NVR in the interface and then click “Login” to go to the live preview interface.
Page 91

85
Notes: 1. Please make sure that the IP address of the NVR and the computer are both in the same
local network segment. For example, supposing that the IP address of the computer is
192.168.1.41, the IP address of the NVR shall be set to 192.168.1.XXX.
2. If the HTTP port of the NVR is not 80, but other number instead, you need to input the IP
address plus port number in the IE address bar when accessing the NVR over network. For
example, the HTTP port is 81. You should enter http://192.168.1.42:81 in the IE address bar.
12.3 Web WAN Access
NAT Access
① Set the network of the NVR. Please refer to 11.1.1 TCP/IPv4 Configuration for details.
② Enable NAT and then set the NAT server address. Please refer to 11.1.6 NAT
Configuration for details.
③ Open IE browser on a computer, input the NAT server address
http://www.autonat.com/n9000 in the IE address bar and then press enter to go to the interface
as shown below (download and install the relative plugin according to the popup tip if you
access the NVR through NAT for the first time).
Page 92

86
Note: If the WAN IP address is a dynamic IP address, it is necessary for you to use the domain name to
access the NVR. Click StartSettingsNetworkDDNS to set DDNS (see 11.1.3 DDNS Configuration
for details). By using DDNS function you can use the domain name plus HTTP port like
http://sunshine.dvrdydns.com:100 to access the NVR via internet.
Input the serial number (click on the tool bar at the bottom of the live preview interface to
see the serial number of the NVR), user name (the user name of the NVR, admin by default)
and password (the password of the NVR, 123456 by default) of the NVR, select the display
language on the top right corner of the interface and then click “Login” button to go to the web
client interface.
PPPoE Access
① Click StartSettingsNetworkTCP/IPv4 to go to the “TCP/IPv4” interface. Check
“Enable” in the “PPPoE settings” and then input the username and password you get from your
ISP. Click “Apply” to save the settings.
② Click StartSettingsNetworkNetwork Status to view the IP address of the NVR.
③ Open IE browser on a computer, input the IP address of the NVR like
http://210.21.229.138 in the IE address bar and then press enter to go to the login interface.
Input the username and password of the NVR in the interface and then click “Login” to go to
the live preview interface.
Router Access
① Click StartSettingsNetworkTCP/IPv4 to go to the “TCP/IPv4” interface. Set the IP
address, subnet mask, gateway, preferred DNS and alternate DNS of the NVR.
② Set the HTTP port (it is suggested to modify the HTTP port because the default HTTP port
80 might be taken up) and enable UPnP function in both the NVR and the router. If the UPnP
function is not available in the router, you need to forward the LAN IP address, HTTP port and
server port of the NVR to the router. Port mapping settings may be different in different routers,
so please refer to the user manual of the router for details.
③ Get the WAN IP address of the NVR from the router. Open IE browser on a computer,
input the WAN IP address plus HTTP port like http://116.30.18.215:100 in the IE address bar
and then press enter to go to the login interface. Input the username and password of the NVR
in the interface and then click “Login” to go to the live preview interface.
12.4 Web Remote Control
The supported browsers of the remote surveillance are IE8/9/10/11, Firefox, Opera and Chrome
(available only for the versions lower than 45) in Windows system and Safari in MAC system.
When you access the NVR through IE for the first time, you need to download and install the
relative components for normal preview and playback. Please refer to the tips in the remote
interfaces for details. The buttons and icons on the top right corner of the remote interface are
introduced as follows.
Page 93

87
admin: the current login username.
Logout: click it to log out and return to the login interface.
Modify Password: click it to change the password of the current login user. Input current
password and then set a new password in the popup window. Click “OK” button to save the
new password.
Local Settings: click it to change the local settings. Set the snapshot number and click
“Browse” to set the snapshot path and record path as shown below. Click “Apply” button to
save the settings.
12.4.1 Remote Preview
Click “Live Display” in the remote interface to go to the preview interface. The preview
interface consists of the four areas marked in the following picture.
Start Preview
Select a window in the preview area and then click one online camera on the left panel to
preview the camera in the window. You can click in the tool bar to preview all the
cameras.
Page 94

88
Button
Meaning
Screen mode button.
Click it to disable OSD. Click to enable OSD.
Click it to show full screen. Right click on the full screen to exit full
screen.
Click “All Main Stream” or “All Sub Stream” to set the stream of all the
cameras.
Manual alarm button. Click it to pop up a window and then trigger and
clear the alarm-out in the window manually.
Click it to preview all the cameras.
Click it to close all the preview cameras.
Click it to start recording. Click to stop recording.
Click it to enable talk with the NVR.
Left Panel Introduction
Click on the left panel to hide the panel and click to show the panel. You can view
all the added cameras and groups on the left panel.
View Camera
Click to view the cameras. You can view the number of all the added cameras
and the online cameras. For instance, the left number 3 in on the left panel
stands for the number of online cameras; the right number 4 stands for the number of all the
added cameras. Input the camera name in the search box and then click to search the
camera. Click to refresh the camera list.
View Group
Click to view the groups. The up side of the left panel displays all
the groups and the down side displays all the cameras in the group.
Tool Bar Introduction
Right Panel Introduction
Click on the right panel to show the panel and click to hide the panel. Click
at the bottom of the panel to go to “PTZ” panel. Click to go to
“Operation” panel.
Page 95

89
Button
Meaning
Click it to snap.
Click it to start recording; click it again to stop recording.
Click it to zoom in the image of the camera and then drag the mouse on the
camera image to view the hidden area.
Click it to zoom out the image of the camera.
The 3D zoom in function is designed for P.T.Z. Click the button and then
drag the image to zoom in or zoom out the image; click the image on
different areas to view the image of the dome omni-directionally.
Click it to close the preview camera.
Click it to enable audio and then drag the slider bar to adjust the volume. You
can listen to the camera audio by enabling audio.
Click one camera window in the preview area and then click to set the camera’s live
preview stream and record stream to main stream in manual record mode; click to
set the camera’s live preview stream and record stream to sub stream. In sub stream tab, set the
resolution, FPS and bitrate and then click “Apply” to save the settings.
Operation panel introduction:
Page 96

90
Button
Meaning
Click / / / / / / /
to rotate the dome; click to stop rotating the dome.
Drag the slider to adjust the rotating speed of dome.
Click / to zoom in/out camera image.
Click / to increase/ decrease the focal length.
Click / to increase/decrease the iris of the dome.
Click it to view the preset list and then click the button in the list to call
the preset.
Click it to view the cruise list and then click the corresponding buttons
in the list to start or stop the cruise.
Button
Meaning
Stop button.
Rewind button. Click it to play video backward.
Play button. Click it to play video forward.
Pause button.
Deceleration button. Click it to decrease the playing speed.
Acceleration button. Click it to increase the playing speed.
Previous frame button. It works only when the forward playing is paused in single screen
mode.
Next frame button. It works only when the forward playing is paused in single screen mode.
Click to step backward 30s and click to step forward 30s.
Backup start time button. Click the time scale and then click it to set the backup start time.
Backup end time button. Click the time scale and then click it to set the backup end time.
Backup button.
PTZ panel introduction:
12.4.2 Remote Playback
Click “Playback” in the remote interface to go to the playback interface.
① Check the record event types and cameras on the left panel. Set the record date on the
calendar beside the time scale.
② Click to search the record data and then click or directly click the
time scale to play the record.
The operation of the playback time scale is similar to that of the time scale in the main program
of the NVR. Please refer to 8.2 Playback Interface Introduction for details.
Introduction of playback control buttons:
Page 97

91
Button
Meaning
Backup tasks button. Click it to view the backup status.
Event list button. Click it to view the event record of manual/schedule/sensor/motion.
12.4.3 Remote Backup
Click “Backup” in the remote interface to go to the backup interface. You can back up the
record by event or by time.
By Event
Check the record type on the left side of the interface and then click to set the start time
and end time; check the cameras and then click on the right side to search the record (the
searched record data will be displayed in the list); check the record data in the list and then
click “Backup” button to backup the record.
By Time
Click to set the start time and end time on the left side of the interface; check the cameras
and then click on the right side to backup the record.
View Backup Status: Click “Backup Status” to view the backup status. Click “Pause” to pause
the backup; click “Resume” to continue the backup; click “Delete” to delete the task.
12.4.4 Remote Configuration
Click “Function Panel” in the remote interface and then configure the camera, record, alarm,
disk, network, account and authority and system of the NVR remotely. All of these settings are
similar to that of the NVR. See the configurations of the NVR for details.
Page 98

92
Appendix A FAQ
Q1. Why can’t I find the HDD?
a. Please check the power and SATA data cables of the HDD to make sure they are well
connected.
b. For some NVRs with the 1U or small 1U case, the power of the adapter may be not
enough for operating them. Please use the power adaptor supplied along with the NVR.
c. Please make sure the HDDs are compatible with the NVR. See Appendix C Compatible
Device List for details.
d. The HDD could have gone bad. Change a new one.
Q2. Why are there no images output in some or all of the camera windows?
a. Please make sure the resolutions of the cameras are supported by the NVR.
b. Please make sure the network cables of the IP camera and NVR are both connected
properly and the network parameters are set correctly.
c. Please make sure the network and the switch both work normally.
Q3. The screen has no output after booting the NVR normally.
a. Please make sure the screen, HDMI or VGA cables are good and well connected.
b. Please make sure the screen supports the resolution of 1280*1024, 1920*1080 or
3840*2160 (4K*2K). The NVR cannot self adapt to the screen of which the resolution is lower
than 1280*1024, and then the screen will remind you that the screen resolution is not supported
by the NVR or just have no display. Please change a screen at 1280*1024, 1920*1080 or
3840*2160 resolution before booting the NVR.
Q4. Forget the passwords?
a. The password of the super administrator admin can be reset through “Edit Security
Question” function.
Click “Edit Security Question” button in the login window and then enter the corresponding
answer of the selected question in the popup window, the password of admin will be reset to
123456 by default. If you forget the answer of the question, this way will be invalid, please
contact your dealer for help.
b. The passwords of other users can be reset by the super administrator admin, please refer to
10.1.2 Edit User for details.
Q5. The NVR cannot add up to the maximum number of IP cameras?
Take the 16 CH NVR as an example. Some 16 CH NVR support a maximum of 120Mbps
bandwidth input (please take the real device for standard). Refer to the picture below. The
remaining bandwidth should be larger than the bandwidth of the IP camera you want to add, or
you would fail to add the IP camera. You should lower the added cameras’ bitrate to release the
bandwidth. It is recommended to add cameras by “Quickly Add” for batch adding.
Page 99

93
Q6. The IP camera which connects to the PoE port of the NVR cannot be displayed
automatically in the camera list, why?
a. Please check whether the resource of the PoE port is occupied by another IP camera that is
added through network.
Take the 16 CH NVR with 8 PoE ports as an example. The resource distribution of the 16
CH IP cameras is shown in the picture below.
When you add IP cameras through network, the IP cameras will occupy the resource from CH1,
CH2, CH3, CH4… by the adding sequence; if you directly connect the IP cameras to the PoE
ports of the NVR, the IP cameras will occupy the resource from CH9 to CH16 according to the
number of the PoE port each IP camera is connecting to.
Supposing that 12 CH IP cameras have been added to the NVR through network and no IP
camera has been directly connected to the PoE port. The 12 CH IP cameras occupy the 8
network resources from CH1 to CH8 and 4 PoE resources from CH9 to CH12 which are
supposed to be occupied by connecting the IP cameras directly. In this situation, if you directly
connect one IP camera to PoE5, PoE6, PoE7 or PoE8, the IP camera will be displayed in the
camera list automatically; if you connect it to PoE1, PoE2, PoE3 or PoE4, it won’t be displayed
in the camera list by showing resource conflict; if you just need to connect it to PoE1, PoE2,
PoE3 or PoE4, you should first delete the IP camera which occupies the PoE port resource and
then reconnect it to the PoE port.
Take the 8 CH NVR with 8 PoE ports as another example. The resource distribution of the
8 CH IP cameras is shown in the picture below and the adding rules of the IP cameras are
similar to the rules mentioned in the above. Please refer to the above for details.
Page 100

94
b. Please make sure that the internal ethernet port and the IP camera which directly connects
to the PoE port through ONVIF protocol are in the same network segment.
The internal ethernet port and the IP camera which directly connects to the PoE port through
ONVIF protocol should be in the same network segment, or you will fail to add the IP camera.
Log in the IP camera’s web client and then enable DHCP (obtain an IP address automatically);
or manually change the IP address of the IP camera to make it in the same network segment
with the internal ethernet port.
c. Check whether the number of the added IP camera is the maximum.
If the number of the added IP camera is the maximum, the system will show you the message
that the IP camera number is beyond the maximum when you directly connect another IP
camera to the available PoE port and thus you will fail to add the IP camera.
Q7. The IP camera which directly connects to the PoE port of the NVR through ONVIF
protocol is shown in the camera list, but there is no image output, why?
Please make sure the username and password of the IP camera are correct. The IP camera’s
username and password can be modified through the two ways mentioned as below.
① Click “Edit Camera” in the Camera module of the setup panel to go to the interface as
shown below. Click to modify the username and password of the IP camera (input the
correct username and password of the IP camera in the popup window and then click “OK”
button).
② Go to the live preview interface and then click in the preview window of the IP
camera to edit the IP camera’s username and password.
 Loading...
Loading...