Page 1

Installation,
Configuration
and Operation
FRITZ!Box
3270
Page 2

Table of Contents
Symbols and Highlighting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1 Getting to Know Your FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.1 The FRITZ!Box at a Glance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.2 Ports and Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.3 Buttons. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.4 LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2 Before You Connect the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.1 Contents of the FRITZ!Box Package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.2 Requirements for Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.3 Security and Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3 Connecting the FRITZ!Box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.1 Connecting to Electrical Power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
3.2 Connecting to the Internet. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
4 Connecting the Computer to the FRITZ!Box. . . . . . . . . . 17
4.1 Connecting Computers to the LAN Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
4.2 Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
5 The FRITZ!Box User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.1 Opening the User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.2 Protecting the User Interface with a Password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
5.3 Saving the FRITZ!Box Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6 Configuring an Internet Connection in the FRITZ!Box . . 28
6.1 Configuring an Internet Connection for DSL. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.2 Changing the Annex Setting of the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.3 Configuring the Internet Connection for Cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.4 Configuring the Internet Connection for
the Mobile Telephone Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.5 Surfing the Net. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2
Page 3

7 Firmware Update: Updating the FRITZ!Box Software . . 32
8 The FRITZ!Box as an Internet Router . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.1 Child Protection: Restricting Internet Access. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
8.2 Port Forwarding: Making Computers Accessible from the Internet. 34
8.3 Dynamic DNS: Name Instead of IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
8.4 Remote Access over HTTPS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.5 Prioritization: Right of Way for Internet Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
8.6 VPN: Remote Access to the Home Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
8.7 DNSSEC: Security for DNS Queries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
8.8 IPv6: The New Internet Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
9 The FRITZ!Box as a WLAN Base Station . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.1 Security. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.2 Guest Access: WLAN Connection for Guests . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
9.3 Setting Up Night Service for WLAN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
9.4 Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
9.5 WLAN Standards . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
9.6 Frequency Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
10 The FRITZ!Box Home Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
11 Network Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network . . . . 60
11.1 Network Settings in the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
11.2 Obtaining an IP Address Automatically . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
12 USB Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network . . . . . . . . 71
12.1 Power Supply for USB Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12.2 USB Devices on the FRITZ!Box. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
12.3 Using USB Devices Safely . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
12.4 Accessing USB Memory. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
12.5 Sharing a USB Printer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
3
Page 4

13 Saving Energy with the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
13.1 Saving Energy with the WLAN Radio Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
13.2 Enabling Energy-saving Mode for USB Hard Drives. . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
13.3 Saving Energy at the LAN Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
14 Help in Case of Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
14.1 Cannot Establish a DSL Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
14.2 The User Interface Does Not Open . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
14.3 Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
15 Taking the FRITZ!Box out of Operation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
15.1 Restoring the FRITZ!Box Factory Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
15.2 Uninstalling Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
16 Technical Specifications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
16.1 Ports and Interfaces. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
16.2 Router Functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
16.3 User Interface and Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
16.4 Physical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
16.5 Cable. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
17 Customer Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
17.1 Documentation on the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
17.2 Information in the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
17.3 Support from the Support Team . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
17.4 Manufacturer’s Warranty. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
18 AVM Products for the FRITZ!Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Legal Notice. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Legal Notice . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Declaration of CE Conformity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Disposal Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
4
Page 5

Drilling Template. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Glossary. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
5
Page 6
Symbols and Highlighting
Symbols and emphasized text are used to mark certain information in
this manual.
Symbols
This symbol designates hints and tips that are useful in operating your product.
This symbol indicates important instructions that must be
observed to avoid malfunctions.
Highlighting
Highlighting Function Examples
Quotation marks Keys
Pointed brackets Joker <Telephone number>
Blue and underlined text
Blue text Links and references
Bold text Emphasis Do not click the
Buttons
Menus
File paths
Folder and file
names
Address to be entered in the web
browser
within this manual
“F1” key
“Help”
“Home Network”
“C:\My Documents”
“Info”
fritz.box
For more information on
customer service, see
the section from
page 98.
button ...
6
Page 7

Getting to Know Your FRITZ!Box
1 Getting to Know Your FRITZ!Box
This chapter gives you an overview of the features and functions of
your FRITZ!Box 3270 and describes ports, buttons and LEDs.
1.1 The FRITZ!Box at a Glance
Access to the Internet
The FRITZ!Box connects multiple computers fast and safely
with the Internet. Other network-compatible devices like
smartphones and game consoles can use the FRITZ!Box for
their Internet connection.
For fast Internet connections an ADSL modem is integrated into the FRITZ!Box. A preconfigured firewall protects your network from attacks from the Internet.
The FRITZ!Box also offers a variety of functions to control access to the Internet as well as access from the Internet. The
“Internet filter” feature allows you to restrict access to the
Internet for individual Windows users or computers, for instance for your children’s computers. With the integrated VPN
server you can link remote computers securely with the home
network of the FRITZ!Box over the Internet.
WLAN Base Station for Wireless Connections
Computers and other network devices that support WLAN can
be connected wirelessly with the FRITZ!Box. If no WLAN device is integrated in your computer, you can install an external
WLAN adapter like a FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick by AVM (see also
AVM Products for the FRITZ!Box from page 102).
The FRITZ!Box supports the fast WLAN N standard, which provides for data throughput of up to 300 Mbit/s (gross).
You can use the FRITZ!Box in either the 2.4-GHz frequency
band or the 5-GHz frequency band (dual band). Because the
5-GHz frequency band is used less frequently, connections in
this band are subject to less interference.
With the “guest access” feature you can grant friends and
visitors fast, secure access to the Internet over your wireless
network.
7
Page 8

The FRITZ!Box at a Glance
Switchboard in the Home Network
The FRITZ!Box connects your computers and other network
devices not only with the Internet, but also with each other.
The connected network devices constitute the home network
of the FRITZ!Box and can exchange data among each other.
You connect computers and other network devices with the
FRITZ!Box either wirelessly via WLAN or using a network cable.
The FRITZ!Box can manage various storage media and make
them available to all participants in the home network. These
include connected USB flash drives, USB hard drives and online storage.
USB 2.0 Port
The FRITZ!Box has a USB port which can be used to integrate
USB devices into your home network, for instance a printer or
a storage medium. The connected USB devices can then be
used simultaneously by all network devices in the home network of the FRITZ!Box.
If you connect a USB modem for mobile broadband Internet
(UMTS/HSPA), the FRITZ!Box can establish Internet connections via the mobile communications network.
Media Server for Music, Images, and Video in the Home
Network
As a media server the FRITZ!Box makes music, video and image files available throughout the entire home network. With
suitable playback devices in the home network of the
FRITZ!Box you can even play back the media files when the
computer is turned off.
Your music, video and image files can be stored on a USB
storage medium connected to the FRITZ!Box.
The playback devices or programs, for instance computers or
television sets, must support the UPnP AV or DLNA standard.
8
Page 9

Ports and Interfaces
1.2 Ports and Interfaces
DSL
For DSL without
a telephone line
Possibilities for connecting the FRITZ!Box
USB 2.0 4 x LAN
storage media
• DSL
Socket for connecting to ADSL2+ (see glossary) and
ADSL (see glossary)
• LAN 1 – LAN 4
4 Ethernet ports (10/100 Base-T) for connecting computers and other network devices like game consoles and
network hubs
• USB
USB 2.0 port for connecting USB devices like printers or
storage media
• WLAN base station
Integrated WLAN base station for connecting to WLAN
devices that use the radio standard IEEE 802.11a,
IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g or IEEE 802.11n (in the 2.4or 5-GHz frequency band)
Printer,
Computer, game console,
network
WLAN
2.4 GHz/5 GHz
Notebook, computer, smartphone,
video/TV streaming
9
Page 10

Buttons
1.3 Buttons
The FRITZ!Box has two buttons on the upper side of the housing.
FRITZ!Box buttons
WLAN Button
With the “WLAN” button you can turn the WLAN function on
and off and connect wireless devices with the FRITZ!Box by
WPS. WPS is an easy way to establish secure wireless connections (see page 20).
STANDBY Button
The “STANDBY” button was originally included for the energysaving mode. However, this function was never allocated to
the button.
With the latest firmware the energy-saving mode is switched
on and off automatically by the FRITZ!Box.
10
Page 11
LEDs
1.4 LEDs
Five LEDs are built into the top of the FRITZ!Box 3270, which
flash or light up to display various connection statuses and
events.
LED Condition Meaning
Power on
flashing
LAN on Network connection is active to at least one connected de-
WLAN on WLAN function is enabled
flashing
DSL on Internet connection active
Info flashing
flashing red Error: Open the FRITZ!Box user interface and follow the in-
• Device has electrical power and the DSL line is ready
for operation
• Device has electrical power and the connection to DSL
is being established or has been interrupted
vice (network adapter or hub/switch)
• Switching the WLAN function on or off
• Adopting the WLAN settings
• Performing WPS
• WPS procedure aborted: More than two WLAN devices
are performing WPS at the same time. Repeat the WPS
procedure.
• Updating the firmware
• Online meter reached the defined value, or another
event defined in the user interface under “System /
“Info” Display” is signaled
structions on the “Overview” page
11
Page 12

Before You Connect the FRITZ!Box
2 Before You Connect the FRITZ!Box
• Check the contents of your FRITZ!Box package. See the section
Contents of the FRITZ!Box Package on page 12 for more informa-
tion.
• Make sure that the requirements for connecting and operating
the FRITZ!Box have been met. See the section Requirements for
Operation on page 12 for more information.
• Please see the security and handling instructions in the section
Security and Handling on page 13.
2.1 Contents of the FRITZ!Box Package
• FRITZ!Box 3270
• one power supply unit
• one network cable
• one DSL cable
• printed product information
2.2 Requirements for Operation
In order to operate the FRITZ!Box, you must have the following:
• a web browser that supports Java script (for instance, In-
ternet Explorer version 8.0 or higher, or Firefox version 7
or higher)
• a connection to the Internet
– a DSL line, standard ITU G.992.1 Annex A and B
(G.dmt), ITU G.992.3 Annex A and B (ADSL2),
ITU G.992.5 Annex A and B (ADSL2+), ITU G.992.3/5
Annex M, ITU G.992.3/5 Annex J, ITU G.994.1 (G.hs)
– or an Internet cable access with cable modem
– or a USB modem for mobile Internet access (UMTS
/HSPA)
– or another Internet connection
12
Page 13

Security and Handling
• for connecting computers via WLAN:
computer with WLAN support (compliant with
IEEE 802.11n, IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11a or
IEEE 802.11b). Computers that do not have integrated
WLAN can be equipped with WLAN support by installing
a WLAN device like a FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick N, for instance.
• for connecting computers using network cable:
computer with a network port (network adapter standard
Ethernet 10/100 Base-T)
2.3 Security and Handling
Before installing and using the FRITZ!Box, please read the following security and handling instructions.
Safety Instructions
When working with the FRITZ!Box 3270, be sure to observe
the following security instructions in order to protect yourself
and the FRITZ!Box from harm.
• Before mounting the FRITZ!Box on the wall, make sure
that there are no electrical lines, gas or water pipes located where you need to drill the holes.
If necessary, check the site with a pipe detector or consult with qualified experts.
• Do not place FRITZ!Box on excessively heat-sensitive sur-
faces, as the base of the device can heat up during normal operation.
• Make sure that the ventilation slits on the FRITZ!Box
housing are always unobstructed. The ventilation slits
provide for air cooling.
– The FRITZ!Box should not be placed on a carpet or on
upholstered furniture.
– Do not cover the FRITZ!Box.
• Do not install the FRITZ!Box during an electrical storm.
13
Page 14

Security and Handling
• Disconnect the FRITZ!Box from the power supply and
• Never let liquids get inside the FRITZ!Box. Otherwise,
• The FRITZ!Box is intended for indoor use only.
• Do not open the FRITZ!Box housing. The device contains
Handling the FRITZ!Box
• You can either place FRITZ!Box on a horizontal surface or
• Place or hang the FRITZ!Box in a dry location that is free
• For ideal operating conditions, mount the FRITZ!Box on a
• When connecting FRITZ!Box to your computer using a
from the DSL or VDSL line during electrical storms.
electric shocks or short circuits may result.
hazardous components and should only be opened by
authorized repair technicians.
mount it on a wall. For a drilling template to mount the
FRITZ!Box on a wall, see page 110.
of dust and protected from direct sunlight.
wall with the cables connected on the bottom.
network cable, keep in mind that the cable can be no
longer than 100 m.
• If you would like to establish wireless connections be-
tween the FRITZ!Box and the computer, position the
FRITZ!Box at a central location.
• Make sure to keep sufficient distance from potential
sources of interference like microwave devices or electric devices with large metal housings.
14
Page 15

Connecting the FRITZ!Box
3 Connecting the FRITZ!Box
• Connect the FRITZ!Box to the power supply.
• Connect the FRITZ!Box to your Internet connection.
This chapter tells you how.
Before you connect the FRITZ!Box, note the additional instructions in the section Security and Handling on page 13.
3.1 Connecting to Electrical Power
Connecting to the power supply
1. Pick up the power supply unit included in the FRITZ!Box
package.
Use only this power supply unit for connecting to electrical power.
2. Connect the power supply unit to the socket on the
FRITZ!Box labeled “Power”.
3. Plug the other end into an AC power outlet.
The “Power” LED begins flashing after a few seconds to indicate that the FRITZ!Box is ready for operation.
15
Page 16

Connecting to the Internet
3.2 Connecting to the Internet
Connect the FRITZ!Box to your Internet connection.
The FRITZ!Box can be connected using various types of Internet connections:
• DSL line
• Internet cable access using a cable modem
• Internet via mobile telephone network using a
UMTS/HSPA modem
Connecting with a Cable Connection
With an additional cable modem you can also use your
FRITZ!Box 3270 on a cable connection. Use a network cable.
1. Connect one end of the network cable to the LAN (Ether-
net) port on the cable modem.
2. Connect the other end of the network cable to the socket
on FRITZ!Box labeled “LAN 1”.
3. Connect a computer with the FRITZ!Box either wirelessly
via WLAN or using a network cable (see page 17).
4. Set up the Internet connection for connections via cable
in the FRITZ!Box (see page 30).
Connecting with the Internet via the Mobile Telephone
Network
If no other kind of Internet connection is available, you can
use your FRITZ!Box to connect to the Internet via the mobile
telephone network. A USB modem for mobile Internet access
(UMTS/HSPA) is required for this.
The FRITZ!Box supports UMTS/HSPA modems from various
manufacturers.
1. Insert the USB modem into the USB port on the
FRITZ!Box.
2. Set up the Internet connection via the mobile telephone
network (see page 30).
16
Page 17
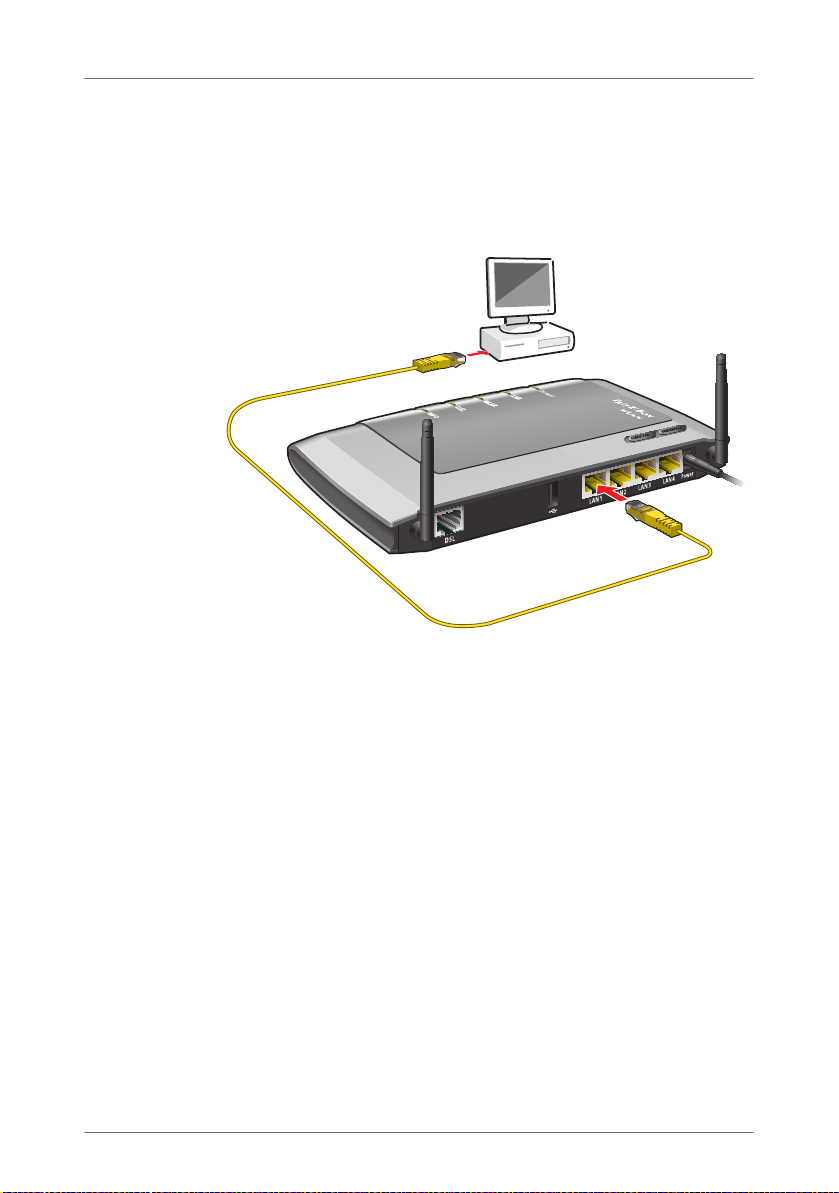
Connecting the Computer to the FRITZ!Box
4 Connecting the Computer to the FRITZ!Box
Connect one or several computers to the FRITZ!Box.
4.1 Connecting Computers to the LAN Port
Connecting a computer to a LAN port on the FRITZ!Box
1. Set aside the network cable (yellow) from the FRITZ!Box
package.
2. If you work with a Linux operating system: Configure the
network adapter of the computer with the setting
“DHCP”.
3. Connect one end of the network cable to the network
port (network card) of the computer.
4. Connect the other end to the “LAN 1”, “LAN 2”, “LAN 3”
or “LAN 4” socket on the FRITZ!Box.
Now the FRITZ!Box and the computer are connected to each
other.
17
Page 18
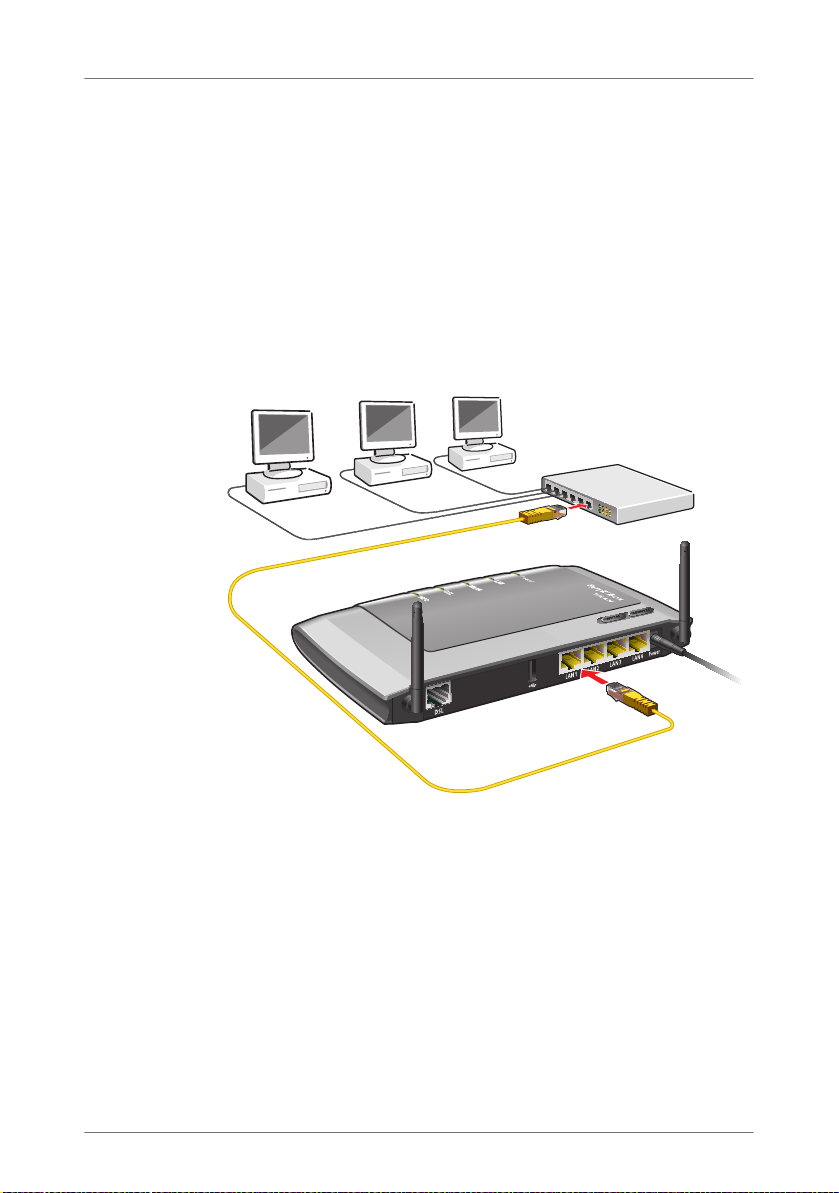
Connecting Computers to the LAN Port
Connecting More Computers to the LAN Ports
Additional cables are required to connect further computers.
In purchasing a LAN cable, note the instructions in the section Network Cable on page 97.
One computer can be connected to each network port of the
FRITZ!Box.
Connecting a Network Hub or Switch
You can also connect a network hub or switch to the LAN
ports on the FRITZ!Box.
Connecting FRITZ!Box to a network hub
1. Set aside the network cable (yellow) from the FRITZ!Box
package.
2. Connect one end of the LAN cable to the uplink port (see
glossary) of the network hub or network switch.
3. Connect the other end of the cable to one of the LAN
ports on the FRITZ!Box.
The FRITZ!Box and the network hub are now connected with
each other.
18
Page 19

Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
4.2 Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
Using WLAN radio technology you can connect multiple computers with the FRITZ!Box wirelessly.
Please note the following before establishing a wireless connection between the computer and the FRITZ!Box:
• WLAN device
A computer to be connected to the FRITZ!Box via WLAN
must be equipped with a WLAN device for it to support
WLAN. A WLAN device can be an external WLAN adapter—like a USB stick, for example—or a device integrated
in the computer. Many modern computers and notebooks come with a WLAN device integrated.
• WLAN security settings
In the FRITZ!Box, WLAN security settings are enabled upon delivery. Before a computer can establish a wireless
connection to the FRITZ!Box, the WLAN security settings
of the FRITZ!Box must be transferred to the WLAN device.
For this procedure the FRITZ!Box supports the two automatic methods AVM Stick & Surf and WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup). The security settings can also be transferred
manually.
For more information on WLAN, see the section The FRITZ!Box
as a WLAN Base Station from page 44.
Establishing a WLAN Connection with AVM Stick & Surf
If you use a FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick from AVM as the WLAN device, you can use AVM Stick & Surf to establish a secure
WLAN connection quickly and conveniently.
1. Switch on your computer.
19
Page 20

Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
2. Insert the your FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick into the USB port
on the FRITZ!Box.
The WLAN security settings are transmitted to the
FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick. The “Info” LED on the FRITZ!Box
begins flashing quickly.
As soon as the “Info” LED stops flashing, transmission
of the settings has been concluded.
3. Remove the FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick.
4. Now insert the FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick into the USB port
of the computer.
The security settings will be adopted and the WLAN connection between the FRITZ!Box and the FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick
will be established. As soon as the WLAN connection has
been established the computer is connected to the FRITZ!Box.
See the AVM FRITZ!WLAN USB Stick manual for details.
Establishing a WLAN Connection Using WPS
The FRITZ!Box supports WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup). WLAN
devices that also support WPS can be connected with your
FRITZ!Box securely using this method. All of the necessary
WLAN security settings are transferred in the process. There
are two kinds of WPS: the push-button method and the PIN
method.
WPS with the Push-button Method
The push-button method (WPS PBC) can be used if your WLAN
device is also equipped with a WPS button, or if WPS can be
enabled via the control software of the WLAN device.
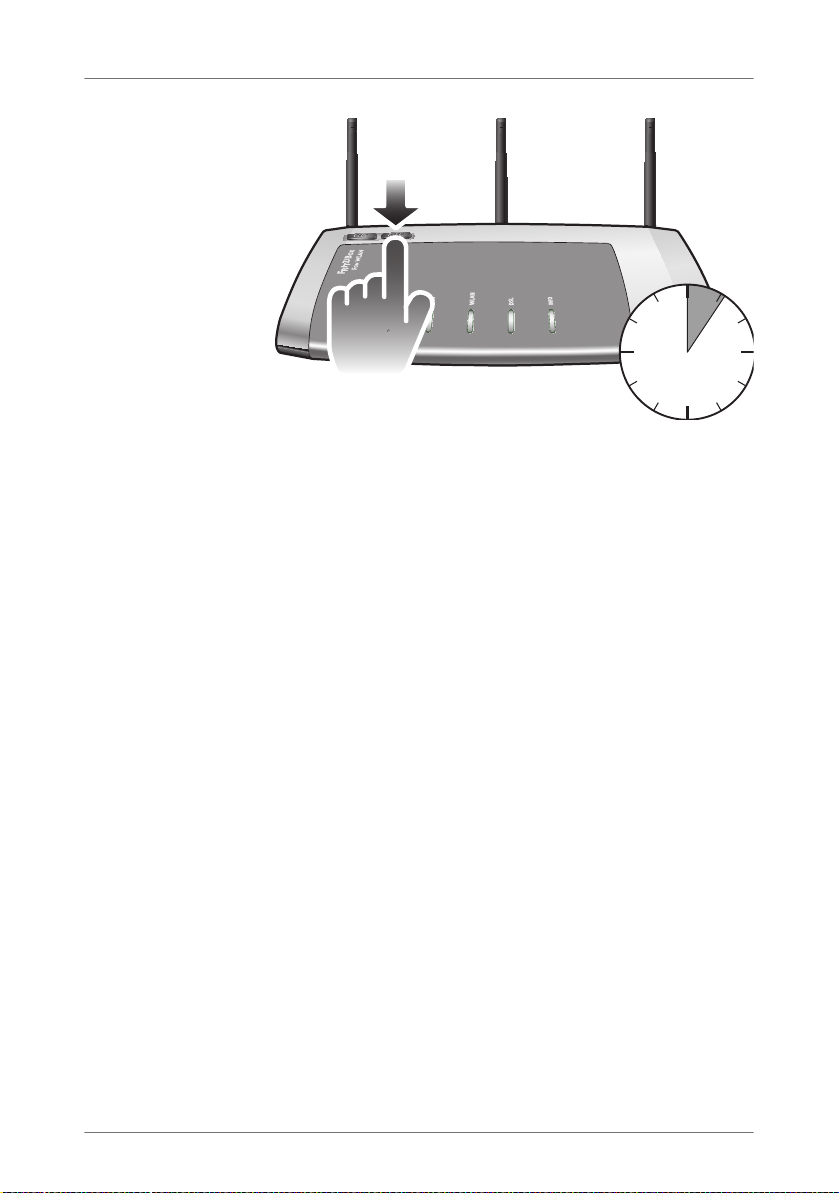
1. Press the “WLAN” button on the FRITZ!Box and hold it
down for at least six seconds.
20
Page 21
Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
2. As soon as the “WLAN” LED begins flashing, enable the
WPS function on the other WLAN device, either by pressing a button or in the device’s user interface (depending
on the device). Activation must be started within
two minutes.
The FRITZ!Box and the WLAN device now connect with each
other automatically. The WLAN device adopts the security settings of the FRITZ!Box.
Push for approx.
6 seconds
As soon as the WLAN connection has been established the
computer is connected to the FRITZ!Box.
WPS with the PIN Method
If your WLAN device supports WPS, but does not have a button to start the push method nor any possibility to enable it in
its control software, use the PIN method to establish the
WLAN connection.
You can choose between two methods:
• the FRITZ!Box specifies the PIN
• the WLAN device specifies the PIN.
21
Page 22

Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
The FRITZ!Box Specifies the PIN
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Select the “WLAN / Security” menu.
3. Go to the “WPS Quick Connection”page.
4. Enable the setting “WPS enabled”.
5. Select the option “PIN method (WPS-PIN), the FRITZ!Box
specifies the PIN”.
6. The PIN will be displayed. Enter this PIN in the control
software of the WLAN device.
7. Click “Start WPS”.
The “WLAN” LED on the FRITZ!Box flashes slowly, indicating
that the WPS procedure has begun. Now a secure WLAN connection is being established between the FRITZ!Box and the
WLAN device.
The WLAN Device Specifies the PIN
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Select the “WLAN / Security” menu.
3. Go to the “WPS Quick Connection”page.
4. Enable the setting “WPS enabled”.
5. Select the option “PIN method (WPS-PIN), the WLAN de-
vice specifies the PIN”.
6. Now start the control software of the WLAN device. The
program outputs a PIN for establishing a connection.
7. Enter this PIN in the FRITZ!Box user interface.
8. Click “Start WPS”.
The “WLAN” LED on the FRITZ!Box flashes slowly, indicating
that the WPS procedure has begun. Now a secure WLAN connection is being established between the FRITZ!Box and the
WLAN device.
22
Page 23

Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
Transferring the WLAN Security Settings Manually
The WLAN security settings for WLAN devices can also be
transferred manually. Manual transfer is unavoidable if a
WLAN device does not support any methods for transferring
the security settings automatically.
For manual transfer the WLAN security settings have to be entered in the WLAN software.
WLAN devices are generally delivered with their own WLAN
software, which is installed in the computer along with the
WLAN device. By now many operating systems have WLAN
software included. Integrated WLAN devices sometimes use
the operating system’s WLAN software.
Installing a WLAN Device
If you need to use a separate WLAN device because you do
not have one integrated, then install the WLAN device in the
computer along with the corresponding WLAN software.
Please take note of the instructions in the documentation of
the device.
Transferring WLAN Security Settings
The values for WLAN security preconfigured in the FRITZ!Box
have to be transferred to the WLAN device.
If you would like to establish a WLAN connection using the
values preset in the FRITZ!Box, then your WLAN device must
support the WPA encryption procedure.
1. Start the WLAN software.
23
Page 24
Connecting Computers Wirelessly over WLAN
2. Enter the following values for the connection between
the FRITZ!Box and the WLAN device:
SSID (name of the
WLAN radio network)
Encryption method WPA (TKIP) or WPA2 (AES-CCMP)
Encryption WPA PSK or WPA2 PSK (AES)
WLAN key The key is printed on the sticker at-
Network mode Infrastructure
FRITZ!Box 3270
tached to the bottom of the housing.
3. Confirm your entries using the relevant button in the us-
er interface (for instance, “OK” or “Connect”).
Now your WLAN device and the FRITZ!Box are connected with
each other wirelessly.
24
Page 25
The FRITZ!Box User Interface
5The FRITZ!Box User Interface
The FRITZ!Box has a user interface you can open in a web browser on
your computer.
In the user interface you can set up the FRITZ!Box, enable or disable
functions and receive information on the FRITZ!Box and on your connections.
5.1 Opening the User Interface
The FRITZ!Box user interface can be opened on every computer connected with the FRITZ!Box.
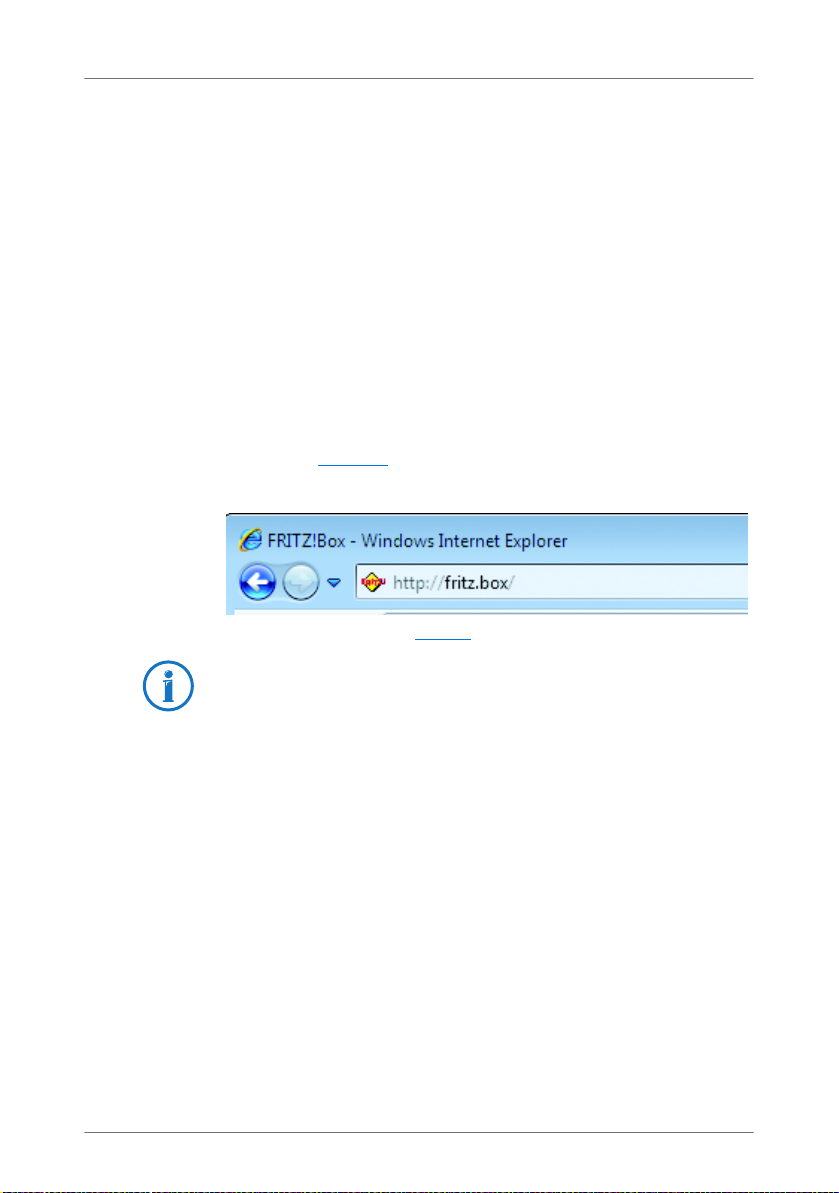
1. Start a web browser on your computer.
2. Enter fritz.box
in the address line of the browser.
The FRITZ!Box user interface opens.
Entering the address fritz.box in the browser
If the user interface does not open, see the instructions on
resolving errors in the section from page 82.
The Wizard: Opening the User Interface for the First Time
When you open the user interface for the first time, a wizard
starts to assist you in configuring the FRITZ!Box.
If you cancel the wizard, you can configure your FRITZ!Box
without this wizard. You can change the settings configured
with this wizard at any time.
For comprehensive information on configuring the many diverse functions of your FRITZ!Box, see the following chapters
in this manual.
25
Page 26

Protecting the User Interface with a Password
5.2 Protecting the User Interface with a Password
You can protect the user interface of the FRITZ!Box with a
password. The password will be requested every time the
user interface is opened. This protects the settings of your
FRITZ!Box from unauthorized access.
We strongly recommend setting up and using password protection for the user interface.
Setting Up Password Protection
As long as no password protection has been set up, every
time you open the user interface you will be prompted to enter a password. If you disabled this message, here is how to
set password protection:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Go to the “System / FRITZ!Box Password” menu.
3. Enter a password and save the password by clicking
“Apply”.
Password protection is now enabled.
Be sure to remember the password! If you forget the password, the factory settings will have to be restored to your
FRITZ!Box (see page 94). All of the settings you configured
will be discarded.
Logging Off the User Interface
When password protection is enabled, you can log off the
user interface at any time. To do so, click .
If you do not click on the user interface for a period of longer
than ten minutes, you will be logged off automatically. The
only pages excepted from this are those which are constantly
updated, like the “Overview” page. No automatic logout will
take place on these pages.
26
Page 27

Saving the FRITZ!Box Settings
5.3 Saving the FRITZ!Box Settings
All of the settings you configure in your FRITZ!Box can be
saved in a backup file on your computer. With this backup file
you can restore your settings to the FRITZ!Box at any time or
load your settings to another FRITZ!Box.
Saving and Restoring Settings
To save and restore your FRITZ!Box settings, use the “System
/ Save Settings” menu in the user interface. Here you can
• save your FRITZ!Box settings on the “Save” tab.
• restore all of your saved settings to the same FRITZ!Box
on the “Restore” tab.
• load all of your saved settings to another FRITZ!Box of
the same model on the “Restore” tab.
• load your saved settings to another FRITZ!Box model on
the “Apply” tab. In this case you can select which settings are to be applied to the FRITZ!Box.
To load your saved settings to another FRITZ!Box of the same
model, or to apply your FRITZ!Box settings to another
FRITZ!Box model, the backup file must always be password-
protected.
Instructions for saving, restoring and applying FRITZ!Box files
are presented in the user interface’s Online Help.
27
Page 28

Configuring an Internet Connection in the FRITZ!Box
6 Configuring an Internet Connection in the FRITZ!Box
Once you have connected the FRITZ!Box to your Internet connection,
you must configure the Internet connection in the FRITZ!Box user interface so that the FRITZ!Box can establish the connection to your
Internet Service Provider and connect to the Internet.
The sequence and number of steps required to configure your Internet
connection depend on the kind of connection, the desired operating
mode, and the Internet Service Provider.
6.1 Configuring an Internet Connection for DSL
If you have a DSL line, you received Internet account information from your DSL or Internet Service Provider. The Internet
account information is required to configure the Internet connection.
Your Internet Service Provider also supplied information
about the configuration of your Internet connection. Always
perform the Internet connection setup as described by your
provider.
Configuring an Internet Connection Automatically
If your Internet Service Provider arranges for the service of automatically configuring your Internet connection, the automatic configuration will be performed right after the
FRITZ!Box is connected. No additional settings for the Internet connection have to be configured in the FRITZ!Box. To
start automatic configuration, some providers require that
you enter a start code.
Configuring the Internet Connection Using the Wizard
With the Wizard it is simple to configure the Internet connection.
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Select “Wizards” in the menu.
3. Click the “Check Internet Connection” Wizard and follow
the instructions.
When the Wizard is finished, your Internet connection has
been configured.
28
Page 29

Changing the Annex Setting of the FRITZ!Box
Configuring the Internet Connection Without the Wizard
You can also set up the Internet connection without the Wizard.
Choose this method if the FRITZ!Box is connected to a DSL
modem or a DSL router, or integrated into an existing network.
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Enable the expert settings in the “System / Expert
Mode” menu.
3. Select the “Internet / Account Information” menu and
enter your account information.
Also take advantage of the Help available in the FRITZ!Box
user interface.
6.2 Changing the Annex Setting of the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box cannot establish a connection to the DSL
network. This is signaled by the continued flashing of the
“Power” LED.
Cause
The kind of DSL (Annex A, B, M or J) set in the FRITZ!Box is not
the same as the annex used on your DSL line.
Help
1. Contact your Internet Service Provider to find out which
annex is used on your DSL line.
2. Connect a computer with the FRITZ!Box either wirelessly
via WLAN or using a network cable.
3. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
4. Open the “Internet / DSL Information” and select the
“Line Settings” page.
5. In the “Annex Settings” area, make sure that the annex
working on your DSL line is set. Save your settings by
clicking “Apply”.
29
Page 30
Configuring the Internet Connection for Cable
After the annex setting has been changed, the FRITZ!Box restarts automatically. The connection to the DSL network has
been established as soon as the “Power” LED stops flashing
and remains lit up.
6.3 Configuring the Internet Connection for Cable
With an additional cable modem you can also use your
FRITZ!Box 3270 on a cable connection. Then the Internet connection is established and controlled by the FRITZ!Box itself,
so that in this operating mode, too, all FRITZ!Box functions
(like Internet telephony, firewall) are available without restriction.
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Select “Wizards” in the menu.
3. Click the “Check Internet Connection” Wizard and follow
the instructions.
6.4 Configuring the Internet Connection for the Mobile Telephone
Network
With a USB modem you can also establish the Internet connection with your FRITZ!Box 3270 via the mobile telephone
network. A USB modem for mobile Internet access
(UMTS/HSPA) is required for this. The FRITZ!Box supports
UMTS/HSPA modems from various manufacturers.
The USB modem is already installed on the USB port of the
FRITZ!Box.
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. In the “Internet” menu, the sub-menu “Mobile Tele-
phone Network” is displayed.
The “Mobile Telephone Network” menu is not available
until the UMTS/HSPA modem has been connected to the
FRITZ!Box. From this point on the menu is always available, even when the USB modem has been disconnected.
30
Page 31

Surfing the Net
3. Configure the settings for your Internet connection over
the mobile telephone network. For more information,
see the Online Help of the FRITZ!Box.
When the mobile telephone network function is used, the
FRITZ!Box user interface presents information about network
availability, connection status and throughput.
Due to technical limitations on the part of the mobile telephone network providers, some limitations may arise for
Internet telephone calls and for applications requiring an incoming connection. The same is true for using port forwarding, sharing USB storage memory, remote access via HTTPS,
dynamic DNS and VPN. Contact your network provider for details on any restrictions that may apply.
6.5 Surfing the Net
Once you have set up the Internet connection in your
FRITZ!Box, you can surf the Internet with any computer connected to the FRITZ!Box.
1. Start a web browser on your computer.
2. Enter in the address field the URL of the web page you
would like to visit, for instance www.avm.de/en
.
The requested Internet page is opened and displayed.
31
Page 32

Firmware Update: Updating the FRITZ!Box Software
7 Firmware Update: Updating the FRITZ!Box Software
AVM provides free updates of the firmware for the FRITZ!Box. The firmware is the software stored in the FRITZ!Box that controls all of the
FRITZ!Box functions.
Firmware updates contain further developments of existing FRITZ!Box
functions and often also introduce new functions for your FRITZ!Box.
Finding New Firmware and Transferring It to the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Click “Wizards” in the menu and start the “Update Firm-
ware” Wizard.
The Wizard checks whether new firmware is available for
your FRITZ!Box.
If the Wizard finds new firmware, it displays the version
number of the firmware. Click the link under the firmware version to view information about further developments and new functions contained in the firmware update. Read this information before starting the firmware
update.
3. To transfer new firmware to the FRITZ!Box, click “Start
Firmware Update Now”.
The firmware update begins and the “Info” LED on the
FRITZ!Box starts flashing.
Do not interrupt the power supply to the FRITZ!Box during the firmware update!
The firmware update is complete when the “Info” LED stops
flashing.
32
Page 33

The FRITZ!Box as an Internet Router
8 The FRITZ!Box as an Internet Router
The FRITZ!Box connects computers in your home network with the Internet. This chapter explains the possibilities offered by using the
FRITZ!Box as an Internet router and how to take advantage of them.
8.1 Child Protection: Restricting Internet Access
The child protection feature allows you to define access rules
to the Internet for individual computers or Windows users.
These access rules may include restrictions of Internet access
time, filter lists and a list with blocked network applications.
• Restrict Internet access time: Using the time restriction
you can restrict the amount of time the user can surf the
web. You can define on which days of the week, at what
times of day, and for how long a computer or Windows
user is allowed to use the Internet connection.
• Block or permit web sites: you can use filter lists to de-
fine which Internet pages are allowed to be accessed
and to which access is blocked. For instance, you can
block all Internet pages the government has defined as
offensive or harmful to minors.
You can create both filter lists, the whitelist and the
blacklist. A whitelist contains all Internet pages to which
access is allowed. A blacklist contains all Internet pages
to which access is blocked.
• Block network applications: You can list network appli-
cations for which Internet access should be blocked. For
instance, you can block Internet access for file-sharing
software.
Child protection can be enabled for each computer individually, regardless of the computer’s operating system.
You can also enable child protection individually in all Windows operating systems (Windows 7, Windows Vista and
Windows XP). This option is very beneficial if a computer is
used by multiple users.
33
Page 34

Port Forwarding: Making Computers Accessible from the Internet
Setting Up Child Protection in the FRITZ!Box
The child protection feature is available only if you have set
up the Internet connection in the FRITZ!Box and established
an Internet connection. Child protection is not available if you
have configured the FRITZ!Box as a DSL modem or IP client.
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Select the “Internet / Filters” menu.
3. Set up the child protection feature, making use of the
Online Help in the FRITZ!Box user interface.
8.2 Port Forwarding: Making Computers Accessible from the
Internet
With default settings in the FRITZ!Box, programs on your computer and LAN cannot be accessed from the Internet. For a
number of applications like online games and file sharing
software, you have to make your computer accessible for other Internet users. In order to grant controlled access to your
computer to other Internet users, you release certain ports for
incoming connections. The ports serve to distinguish between running applications on a computer that has only one
IP address.
Setting Up Port Forwarding in the FRITZ!Box
• Port Forwarding is set up in the “Internet / Permit Ac-
cess” menu.
• Port Forwarding for IPv6 is also set up in the “Internet /
Permit Access” menu, on the “IPv6” page. To see this
page, make sure you enabled the expert mode in the
“System / Expert Mode” menu.
34
Page 35

Dynamic DNS: Name Instead of IP Address
Address for Accessing the FRITZ!Box
If you have enabled the ports for forwarding in the FRITZ!Box,
other users can access your computer at the IP address assigned to your FRITZ!Box by the Internet Service Provider. This
is a public IP address.
Here is how to determine the public IP address of the
FRITZ!Box:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Enable the expert settings in the “System / Expert
Mode” menu.
3. Open any Internet page in order to establish an Internet
connection.
4. The FRITZ!Box’s public IP address is displayed on the
“Overview” page in the “Connections” area.
Every time the Internet connection is interrupted the Internet
Service Provider re-assigns the IP address. The IP address
may change in the process. Therefore it is a good idea to use
dynamic DNS so that the IP address can always be reached
under the same name. For more information, see the section
Dynamic DNS: Name Instead of IP Address on page 35.
8.3 Dynamic DNS: Name Instead of IP Address
Dynamic DNS is an Internet service that makes it possible for
the FRITZ!Box to remain accessible from the Internet at all
times under a fixed name, even though the public IP address
changes.
You must register with a dynamic DNS provider to use this
service. When you register, you agree on the fixed name (domain name) at which your FRITZ!Box should be accessible
from the Internet. You also define a user name and password.
Every time the IP address changes, the FRITZ!Box transmits
the new IP address to the dynamic DNS provider in the form of
an update request. Then the domain name is assigned to the
current IP address by the dynamic DNS provider.
35
Page 36

Remote Access over HTTPS
Setting Up Dynamic DNS in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Select the “Internet / Permit Access” menu.
4. Select the “Dynamic DNS” page and set up dynamic
DNS. Consult the Online Help available in the FRITZ!Box
user interface for more information.
8.4 Remote Access over HTTPS
With this function it is possible to access the user interface of
the FRITZ!Box from another location. With this feature you can
configure settings in the FRITZ!Box or perform a firmware update using a computer that is not in your own network (LAN or
WLAN).
Setting Up Remote Access over HTTPS in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Select the “Internet / Permit Access” menu.
4. Select the “Remote Access” page and set up dynamic
DNS. For more information, see the Online Help.
8.5 Prioritization: Right of Way for Internet Access
Prioritization is a function you can use to specify that network
applications and network devices be treated with higher or
lower priority when they access the Internet connection. For
example, you may wish to ensure that applications like IPTV
and video on demand are always treated with higher priority
than other applications. You can also specify that file-sharing
applications like eMule and BitTorrent always have to wait behind online games.
36
Page 37

Prioritization: Right of Way for Internet Access
Categories for Prioritization
There are three categories for prioritization: “Real-time applications”, “Prioritized applications” and “Background applications”. The categories are explained below.
Network applications and network devices are assigned to
the categories using rules.
Real-time Applications
This category is suitable for applications with high demands
on transmission speed and reaction times (for example, IPTV
or video on demand).
• Network applications of this category always have priori-
ty over other applications accessing the Internet at the
same time.
• When the Internet connection is working at full capacity,
the network packets of the applications of this category
will always be sent first. In this case data from network
applications assigned to other categories, like “Prioritized applications”, will be transmitted later.
• If multiple network applications are assigned to this cat-
egory, then they must share the available capacity.
• Whenever Internet telephony is included in this catego-
ry, this application always has the highest priority, even
over other real-time applications.
Prioritized Applications
This category is suitable for applications that require a fast
reaction time (for example, company access, terminal applications, games).
• For network applications prioritized in this category,
90% of the FRITZ!Box’s upload bandwidth is available,
as long as no application from the “Real-time applications” category requires bandwidth. The remaining 10%
of the upload bandwidth is available for applications
that are prioritized in lower categories or not prioritized
at all.
37
Page 38

Prioritization: Right of Way for Internet Access
• If multiple network applications are assigned to the “Pri-
oritized applications” category, then they must share
the available capacity.
Background Applications
This category is suitable for applications that do not require
any high transmission speed and which are not time-critical
(for example, peer-to-peer services or automatic updates).
• Network applications assigned to this category are al-
ways treated with the lowest priority when the Internet
connection is working at full capacity. So whenever an
application from a different category or a non-prioritized
application requires the entire bandwidth, all background applications must wait until bandwidth capacity
becomes available again.
• If no other network applications are active, then the
background applications receive the entire bandwidth.
Prioritization Method in the FRITZ!Box
The following algorithm is used in the FRITZ!Box to send data
packets according to their prioritization:
• Change in the order in which packets are sent to the
Internet (upstream direction)
The order of the packets the FRITZ!Box receives from the
Internet (downstream direction) cannot be changed.
• Discard low-priority packets in order to ensure the trans-
mission of higher-priority packets. This algorithm is
used whenever more packets are supposed to be sent to
the Internet than the upstream transmission rate of the
Internet connection allows.
• As long as no packets are being sent from higher-priority
applications, the full transmission rate of the Internet
connection is available for low-priority packets.
38
Page 39

VPN: Remote Access to the Home Network
Setting Up Prioritization in the FRITZ!Box
In order to use prioritization, the expert mode must be enabled in the user interface of the FRITZ!Box.
1. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
2. Prioritization is set up in the “Internet / Filters / Prioriti-
zation” menu.
8.6 VPN: Remote Access to the Home Network
Via VPN (see glossary) a secure remote access to the network
of the FRITZ!Box can be established. The VPN solution for the
FRITZ!Box features the following:
• The VPN solution for the FRITZ!Box is based on the IPSec
standard.
• Computer-LAN coupling and LAN-LAN coupling: VPN con-
nections can be set up for individual remote computers
or even for remote networks.
• A maximum of eight simultaneous active VPN connec-
tions is supported.
• The configuration files for the VPN connections are creat-
ed using a separate program. The program is provided
free of charge and can be downloaded from the AVM web
site.
• A free VPN client for individual computers can also be
downloaded from the AVM web site.
The AVM web site offers a Service Portal which presents comprehensive information on VPN in general and in connection
with the FRITZ!Box. Visit this portal to obtain more detailed information.
www.avm.de/en/vpn
39
Page 40

VPN: Remote Access to the Home Network
Setting Up VPN in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Enable the expert settings in the “System / Expert
Mode” menu.
3. Select the “Internet / Permit Access” menu.
4. Select the “VPN” page.
See the Online Help of the FRITZ!Box to set up VPN.
Supplementary Software for VPN
All of the information required for a VPN is saved in a configuration file. The terminals involved in any VPN must receive
this file.
If an individual computer is integrated into a network via a
VPN, the computer must have a VPN client installed.
• “Configure FRITZ!Box VPN Connection” Wizard
AVM provides the “Configure FRITZ!Box VPN” software
for creating configuration files. This program is a Wizard
that takes you step by step through the VPN configuration. All of the necessary VPN settings, like the encryption method and access rules, are set automatically. The
resulting configuration files must be imported to the respective terminals of the VPN tunnel. At the terminal
with the FRITZ!Box the configuration file is then imported
to the FRITZ!Box. The VPN parameters in these files can
be adjusted manually to connect to products by other
manufacturers.
• The “FRITZ!VPN” VPN Client
AVM offers the “FRITZ!VPN” software as a VPN client.
Both the Wizard and the client can be downloaded free of
charge from the VPN Service Portal on the AVM web site:
www.avm.de/en/vpn
40
Page 41

DNSSEC: Security for DNS Queries
8.7 DNSSEC: Security for DNS Queries
DNSSEC is short for Domain Name System Security Extensions. As the name says, this is an extension of DNS, the domain name system.
DNSSEC ensures that both the DNS server and the information returned by the DNS server are authentic, or genuine.
Support with the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box supports DNSSEC queries over UDP.
The FRITZ!Box has a DNS proxy. The computers in the home
network use the FRITZ!Box as a DNS server. The FRITZ!Box forwards DNSSEC queries from the home network to the Internet. The FRITZ!Box forwards DNSSEC responses from the
Internet to the home network.The DNSSEC information must
be validated on the computer in the home network. For this
DNSSEC must be supported in the operating system.
Security with DNSSEC
When a home user surfs the web, she or he sends queries to
the Internet by entering URLs in the address line of his browser. A URL is the name of a web site that is easy to remember,
such as avm.de/en
first. The DNS server resolves the URL into the corresponding
IP address. There is one unambiguous IP address for every
URL.
. Every query is sent to the DNS server
The home user relies on the authenticity of the IP address returned by the DNS server. Authentic means that the response
is the IP address of the desired web site, and not a faked IP
address that leads to a fake web site. DNSSEC can ensure that
the returned addresses are authentic.
41
Page 42

IPv6: The New Internet Protocol
8.8 IPv6: The New Internet Protocol
IPv6 stands for Internet protocol version 6 and is the successor to IPv4.
The FRITZ!Box supports the new IPv6 web protocol and can already establish IPv6 connections today:
• IPv6 support can be switched on in the FRITZ!Box user
interface, in the “Internet / Account Information” menu.
• For simultaneous use of IPv6 and IPv4, the FRITZ!Box
supports dual-stack and dual-stack lite. This means that
the FRITZ!Box can communicate with both IPv4 and IPv6
domains in the Internet.
• The FRITZ!Box supports native IPv6 and IPv6 with a tun-
nel protocol. Native IPv6 means that your Internet Service Provider supports IPv6 directly on your line.
IPv6-capable Services in the Home Network
• FRITZ!NAS access via SMB or FTP/FTPS
• access to the user interface with http or https over IPv6
• The DNS resolver of the FRITZ!Box supports queries for
IPv6 addresses (AAAA records) and can query the upstream DNS resolver of the Internet Service Provider over
IPv6.
• The globally valid prefix is distributed via router adver-
tisement.
• For guest access to the WLAN, the home network and
WLAN guests are separated by IPv6 subnetworks.
• UPnP, UPnP AV media server
IPv6-capable Services in the Internet
• FRITZ!NAS access via FTPS
• completely closed firewall to protect against unwanted
data from the Internet (Stateful Inspection Firewall)
• automatic provisioning (TR-069)
• time synchronization over NTP (Network Time Protocol)
• remote access via https
42
Page 43

IPv6: The New Internet Protocol
Setting Up IPv6 in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Enable the expert settings in the “System / Expert
Mode” menu.
3. Then select the “Internet / Account Information” menu.
4. Select the “IPv6” page and set up IPv6 in the FRITZ!Box.
Consult the Online Help of the FRITZ!Box user interface
for more information.
Setting Up IPv6 on the Computer
You can establish connections in the IPv6 range of the Internet only if IPv6 is installed and enabled on the computers in
your home network.
• IPv6 is already installed and enabled in the Windows 7
and Windows Vista operating systems.
• IPv6 is not installed and enabled in standard
Windows XP. You must install and enable IPv6 in order to
use it. The IPv6 installation requires Service Pack 2 for
Windows XP.
• IPv6 has been available in the Mac OS X operating sys-
tems since Mac OS 10.
43
Page 44

The FRITZ!Box as a WLAN Base Station
9 The FRITZ!Box as a WLAN Base Station
The FRITZ!Box supports WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) technology. In this chapter you will learn how you can use WLAN with the
FRITZ!Box.
9.1 Security
Security is of utmost importance within radio networks.
Radio signals can also be received outside of office or residential spaces and abused for criminal purposes.
Therefore it is important that no unauthorized users can register in a WLAN to use its Internet access or shared network
resources.
FRITZ!Box includes settings on various levels that contribute
to the security of your WLAN and thus to the security of your
computers.
Wireless Network Name (SSID)
In the factory settings of the FRITZ!Box, the name of the wireless network (SSID) is set to “FRITZ!Box 3270”.
It may occur that an additional device with the same
FRITZ!Box network name is located in the vicinity of your
FRITZ!Box. Therefore we recommend changing the preset radio network name.
9.2 Guest Access: WLAN Connection for Guests
You can connect computers with the FRITZ!Box via WLAN so
that they can access the Internet without being integrated in
the home network of the FRITZ!Box. This function is called
“guest access”.
Your guests can use the guest access, for instance, to surf the
web with a notebook and to receive e-mail.
Prerequisites for Guest Access
The FRITZ!Box must be connected directly to the DSL line.
44
Page 45

Setting Up Night Service for WLAN
Guest Access Properties
• The guest radio network is a separate radio network with
its own name (SSID). It is independent of the wireless
network of the FRITZ!Box that integrates computers in
the home network.
• Computers connected via guest access are not part of
the home network.
• The guest network is secured with its own network key.
This network key can be changed as desired without affecting the computers in your home network.
Setting Up Guest Access in the FRITZ!Box
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Make sure that the wireless radio network (WLAN) is en-
abled in the “WLAN / Radio Network” menu.
4. Select the menu “WLAN / Guest Access” and configure
the guest radio network. For more information, see the
Online Help of the FRITZ!Box.
9.3 Setting Up Night Service for WLAN
In the FRITZ!Box you can set up night service for the WLAN radio network. Then the FRITZ!Box switches to hibernation at
specified times and turns off the radio network. This has the
following advantages:
• reduced power consumption when idle
• time-controlled Internet access: with night service you
can ensure that your children are only allowed to surf the
web until a certain time of day
45
Page 46

Setting Up Night Service for WLAN
Switching Night Service for WLAN On and Off
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Select the “System / Night Service” menu.
3. Enable the “Use schedule for WLAN radio network” op-
tion.
4. Enable or disable the option “The radio network cannot
be switched off until no more WLAN devices are active”.
Option enabled: The radio network remains switched on
until all wireless connections between the FRITZ!Box and
other WLAN devices have been ended.
Option is disabled: The radio network is switched off immediately at the start of the specified period.
5. Define the days and times at which the FRITZ!Box WLAN
radio network should be switched off.
6. Save your settings by clicking “Apply”.
Night service for WLAN is now enabled. To disable night service, remove the checkmark in front of “Use schedule for
WLAN radio network” and click “Apply”.
Switching On WLAN during Night Service
The WLAN radio network of the FRITZ!Box can be switched
back on at any time during night service:
Press the “WLAN” button on the FRITZ!Box. The WLAN radio
network will be switched on.
46
Page 47

Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection
9.4 Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection
The range of a WLAN radio network is influenced by various
external circumstances. The following factors have an especially strong influence on the distance over which your
FRITZ!Box can establish a stable, high-throughput wireless
connection:
• the WLAN device used
• structural conditions
• the number of devices operating near the access point in
the same frequency range.
If needed, you can extend the range of your WLAN radio network with a WLAN repeater, for instance with the FRITZ!WLAN
Repeater N/G or FRITZ!WLAN Repeater 300E from AVM. A
WLAN repeater is a supplementary device that is not included
in the FRITZ!Box package.
Instead of using a WLAN repeater, you can set up a Wireless
Distribution System. For this you need, in addition to the
FRITZ!Box, another WLAN access point that is configured as a
WDS repeater (see page 48).
Using the FRITZ!WLAN Repeater
With the FRITZ!WLAN Repeater N/G from AVM you can extend
the range of your WLAN radio network quickly and easily, for
instance to overcome structural conditions that are characterized by thick materials and heavy shielding. The FRITZ!WLAN
Repeater N/G supports all common WLAN standards, is especially easy to install and can be operated at any 230-V power
outlet. For more information on the FRITZ!WLAN
Repeater N/G, see the web site at:
www.avm.de/en/Produkte/FRITZ_WLAN/FRITZ_WLAN_
Repeater_N_G
47
Page 48
Increasing the Range of the WLAN Connection
Power
Setting Up a WDS
To use WDS (Wireless Distribution System) to increase the
range of your WLAN radio network, you need another WLAN
base station in addition to the FRITZ!Box. This can be a second FRITZ!Box or any other WLAN base station that supports
WDS. The first WLAN base station then works as a WDS base
station and the second as a WDS repeater.
The WDS base station and WDS repeater are connected to
each other via WLAN. The WDS base station then can use the
WDS repeater to reach even computers that are outside its
own range, but within the range of the WDS repeater.
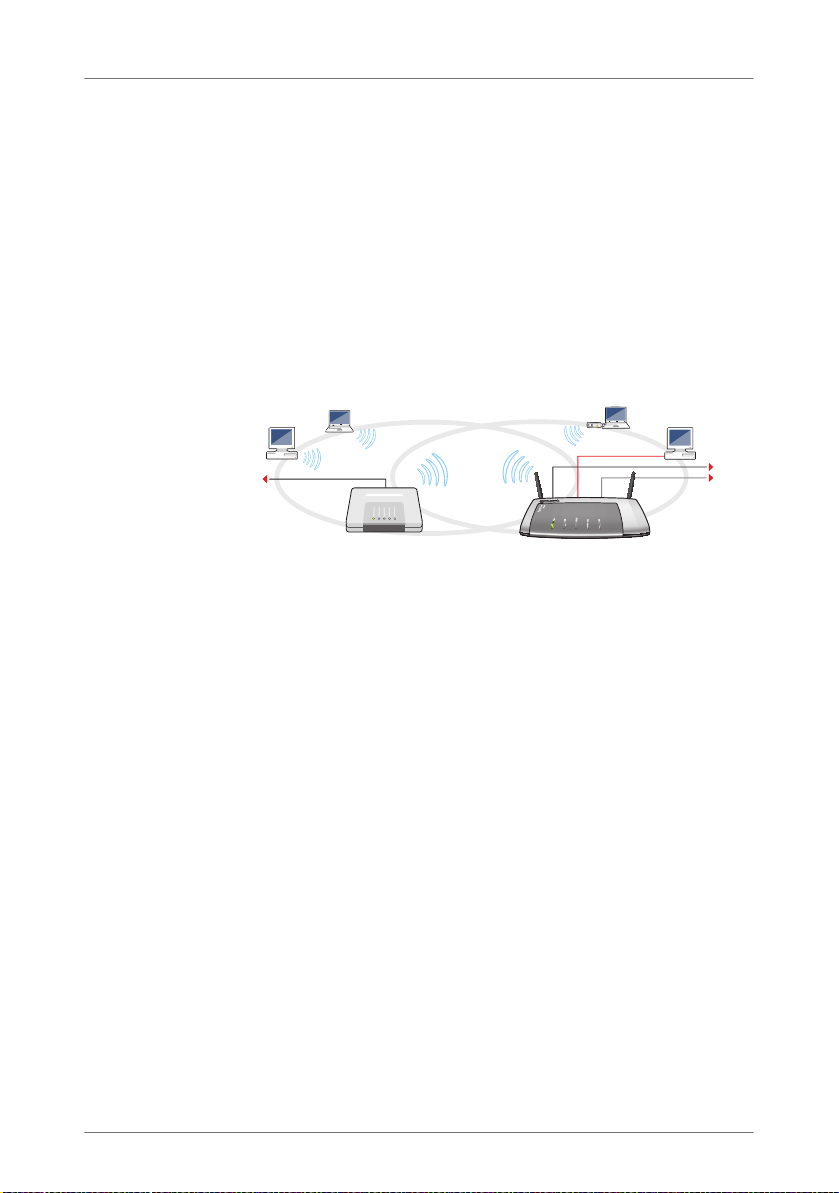
WDS: Expanding the WLAN range using a WDS repeater
Note the following for WDS configuration:
Power
DSL
FRITZ!Box (Base station)WDS repeater
• To expand the range of your wireless network, you need
at least one additional WLAN base station. The wireless
network of your FRITZ!Box can be expanded to a WDS
(Wireless Distribution System) with up to three WLAN
base stations.
• All WLAN base stations implemented in the WDS must
support WDS and be configured for this technology.
• All WLAN base stations implemented as repeaters in the
WDS must be located within the radio range of the WDS
base station.
• The FRITZ!Box can function as a WDS base station to es-
tablish the Internet connection for other WDS repeaters,
or as a WDS repeater to expand the range of a WDS base
station.
48
Page 49

WLAN Standards
• All WDS connections between the WDS base station and
the WDS repeaters must be secured using the same
encryption (e.g. WPA/WPA2). Note that the WPA2 en-
cryption method is available only when your network
consists of AVM devices, since in the WLAN standard
only WEP encryption has been specified for WDS connections.
• All WLAN base stations in the WDS must use the same
radio channel.
• Every WLAN base station participating in the WDS fulfills
the tasks of a WLAN access point for its WLAN clients.
This means that the WLAN clients see each WLAN base
station with an individual name (SSID) and individual
encryption settings.
If you use the WLAN control software provided in
Windows 7, Windows Vista or by the Windows XP Service Pack 2 on your WLAN clients, you can assign the
same SSID and the same encryption settings to different
WLAN base stations. Each client can then automatically
register at the WLAN base station with the best availability.
• Each IP address may be assigned only once in the wire-
less network.
9.5 WLAN Standards
The WLAN standards IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b,
IEEE 802.11g, IEEE 802.11n and IEEE 802.11i were developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronic Engineers
(IEEE).
The IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g and
IEEE 802.11n standards define the throughput within a wireless radio network. IEEE 802.11i is a security standard.
49
Page 50

WLAN Standards
Standards for the Throughput Rate
Data Throughput
The throughputs listed differentiate between gross and net
transmission rates. The net speed describes the transmission
rate of the user data.
The FRITZ!Box supports your choice of the standards
IEEE 802.11a, IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g and IEEE 802.11n.
WLAN devices based on one or more of the standards listed
can be used for WLAN connections with the FRITZ!Box.
Standard Frequency Band Gross Data Throughput up to Net Data Throughput up to
802.11b 2.4 GHz 11 Mbit/s 5 Mbit/s
802.11g 2.4 GHz 54 Mbit/s 25 Mbit/s
802.11a 5 GHz 54 Mbit/s 25 Mbit/s
802.11n 2.4 / 5 GHz 300 Mbit/s 150 Mbit/s
The standards are intended for different frequency bands.
IEEE 802.11a
Because this standard works exclusively in the seldom used
5-GHz range, it offers the opportunity to transmit data relatively free of interference from external influences. WLAN devices that support 802.11a are much less common than devices that work in accordance with the 802.11b/g standard.
IEEE 802.11b
With a maximum throughput rate of 11 Mbit/s, this is the oldest WLAN standard. Older WLAN devices of the first generation can communicate with the FRITZ!Box using 802.11b.
However, if the WLAN device supports newer standards such
as 802.11g, the latest standard should be used.
IEEE 802.11g
This is currently the most common WLAN standard. It communicates with a maximum of 54 Mbit/s gross in the 2.4-GHz
frequency range (ISM) and guarantees broad compatibility
with many WLAN devices.
However, due to heavy use of the 2.4-GHz range, interference
is more common than in the less-used 5-GHz range.
50
Page 51

WLAN Standards
IEEE 802.11n
This standard allows for high throughput rates and ranges.
The FRITZ!Box supports 802.11n in the 2.4-GHz frequency
band, or, if desired, also in the 5-GHz frequency band. Modulation processes and antenna techniques like MIMO (Multiple
Input, Multiple Output) use whichever frequency band is
available more effectively than the older standards.
The use of the 802.11n standard—and thus the availability
of higher throughput rates—is possible only if the WLAN connection is secured using the WPA2 security mechanism (AESCCMP).
Thanks to compatibility with the 802.11g standard, you can
also continue to use older WLAN devices.
Setting the Right Standard in the FRITZ!Box
The throughput rate that can be achieved in your WLAN radio
network depends on the WLAN standards used by the integrated WLAN devices. These WLAN standards must also be
set in the FRITZ!Box. Proceed as follows to check which WLAN
standards are set and change them if needed:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Open the “WLAN / Radio Channel” menu and select “Ad-
just radio channel settings” to make the desired changes.
Note the following for the configuration of this setting:
• In order to communicate with each other, the FRITZ!Box
and all WLAN devices must work in the same frequency
band.
• The standard you configure in the FRITZ!Box must be
compatible with the standards of all WLAN devices used
in the WLAN.
51
Page 52

WLAN Standards
Make a note of which standards the WLAN devices in your
network are compatible with and then adjust the FRITZ!Box
settings according to the following information:
• Your radio network integrates only WLAN devices that
are compatible with one or both of the following standards:
802.11n
802.11g
Set the following mode in the FRITZ!Box:
Mode: 802.11n+g
The 2.4-GHz frequency band will be used.
• Your radio network integrates only WLAN devices that
are compatible with one or both of the following standards:
802.11b
802.11g
Set the following mode in the FRITZ!Box:
Mode: 802.11b+g
The 2.4-GHz frequency band will be used.
• Your radio network integrates only WLAN devices that
are compatible with one or several of the following standards:
802.11n
802.11g
802.11b
Set the following mode in the FRITZ!Box:
Mode: 802.11n+g+b
The 2.4-GHz frequency band will be used.
52
Page 53
WLAN Standards
• Your radio network integrates only WLAN devices that
are compatible with one or both of the following standards:
802.11n
802.11a
Set the following mode in the FRITZ!Box:
Mode: 802.11n+a
The 5-GHz frequency band will be used.
The Standard for Security
IEEE 802.11i
The WPA2 security mechanism is defined in the IEEE 802.11i
standard. WPA2 is an extension of the familiar security mechanism WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access).
The main feature of the extension of WPA to WPA2 is the AESCCMP encryption process.
Mechanism Encryption
WPA TKIP (Temporary Key Integrity Protocol)
WPA2 TKIP
AES-CCMP
based on the extremely secure AES (Advanced
Encryption Standard) procedure. CCMP (Counter Mode with CBC-MAC Protocol) defines how
the AES procedure is applied to WLAN packets.
FRITZ!Box supports the AES encryption procedure as part of
the WPA2 mechanism, and the TKIP encryption procedure as
part of the WPA mechanism. This means that the FRITZ!Box
can be used in combination with any WLAN devices that also
support WPA2 with AES or WPA with TKIP.
53
Page 54

Frequency Ranges
9.6 Frequency Ranges
WLAN uses the frequency ranges at 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz as its
transmission range.
With the FRITZ!Box you can establish WLAN connections in either the 2.4-GHz or the 5-GHz frequency range.
2.4-GHz Frequency Band
In the 2.4-GHz frequency band WLAN works in the same range
as Bluetooth, microwave devices and various other devices
like radio-controlled toys, garage-door openers and video
bridges. This means that interference may occur within
WLANs operated in the vicinity of such devices. Generally this
has adverse effects on the transmission rate, including aborted connections.
In the 2.4-GHz frequency range the European regulation authorities have designated 13 channels for WLAN. A channel
can have a bandwidth of 20 MHz (throughput up to
130 Mbit/s) or 40 MHz (throughput of up to 300 Mbit/s).
Channels located directly next to each other in the 2.4-GHz
band may overlap and result in mutual interference. For instance, if several WLANs are operated close to each other in
the 2.4-GHz frequency range with a bandwidth of 20 MHz, a
distance of at least five channels should be left empty between each two channels used. This means that if channel 1
is selected for one WLAN, the channels 6 through 13 can be
selected for a second WLAN. This maintains the minimum distance between channels.
Should interference in a WLAN persist, the first step should
be to select a different channel.
WLAN Autochannel
With the WLAN autochannel function, the FRITZ!Box automatically searches for the channel subject to the least interference. This process takes into consideration interference from
radio networks in the vicinity (WLAN base stations) and potential sources of interference (for instance video bridges,
54
Page 55

Frequency Ranges
baby monitors, microwave ovens). Should problems with interference persist despite this function, try to identify the
source of interference and switch it off manually.
Additional tips on interference in the WLAN radio network are
presented in the section Ruling Out Interference Caused by
Other Wireless Networks from page 92.
5-GHz Frequency Band
The FRITZ!Box can operate in the 5-GHz frequency band as an
alternative. This frequency range is used much less often
than the most common 2.4-GHz frequency range.
In the 5-GHz frequency band the FRITZ!Box supports automatic channel switching by DFS (Dynamic Frequency Selection).
DFS ensures that the channels from 52 to 140 are kept free
for higher-priority users, like weather radar systems. If you
are operating your FRITZ!Box in one of these channels, it monitors the selected channel periodically for higher-priority users, and, if necessary, switches to a different channel. Note
that the FRITZ!Box waits up to ten minutes, as legally required, before occupying a free channel. During this period
you cannot register any WLAN devices. The WLAN connection
is then established automatically. For more information, see
the section Avoiding WLAN Channels with DFS on page 91.
A prerequisite for use of the 5-GHz frequency band is that all
WLAN devices in the network support this frequency range in
accordance with the IEEE 802.11a or IEEE 8002.11n standard.
2.4GHz or 5GHz
The FRITZ!Box works in the wireless network either in the 2.4GHz range or in the 5-GHz range, but not parallel in both frequency ranges at the same time.
Bandwidth
In both frequency ranges you can select between channel
bandwidths of 20 MHz or 40 MHz (exception: channel 140 in
the 5-GHz frequency band). The FRITZ!Box initially attempts
to select a channel with 40 MHz bandwidth (throughput up to
300 Mbit/s). If this is not possible due to interference or
55
Page 56
Frequency Ranges
channels already being used by other WLANs in the vicinity,
the FRITZ!Box automatically switches temporarily to a channel with 20 MHz bandwidth. Greater bandwidth provides for
higher data throughput:
Bandwidth (MHz) Maximum Data Throughput (Mbit/s)
20 130
40 300
Increasing bandwidths also increases the probability of interference by wireless networks in the vicinity. Large bandwidths
reduce the frequency range available to other wireless networks in the vicinity.
Allocation of the WLAN Channels in the 2.4-GHz Range
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
12.412 82.447
22.417 92.452
3 2.422 10 2.457
4 2.427 11 2.462
5 2.432 12 2.467
6 2.437 13 2.472
72.442
56
Page 57
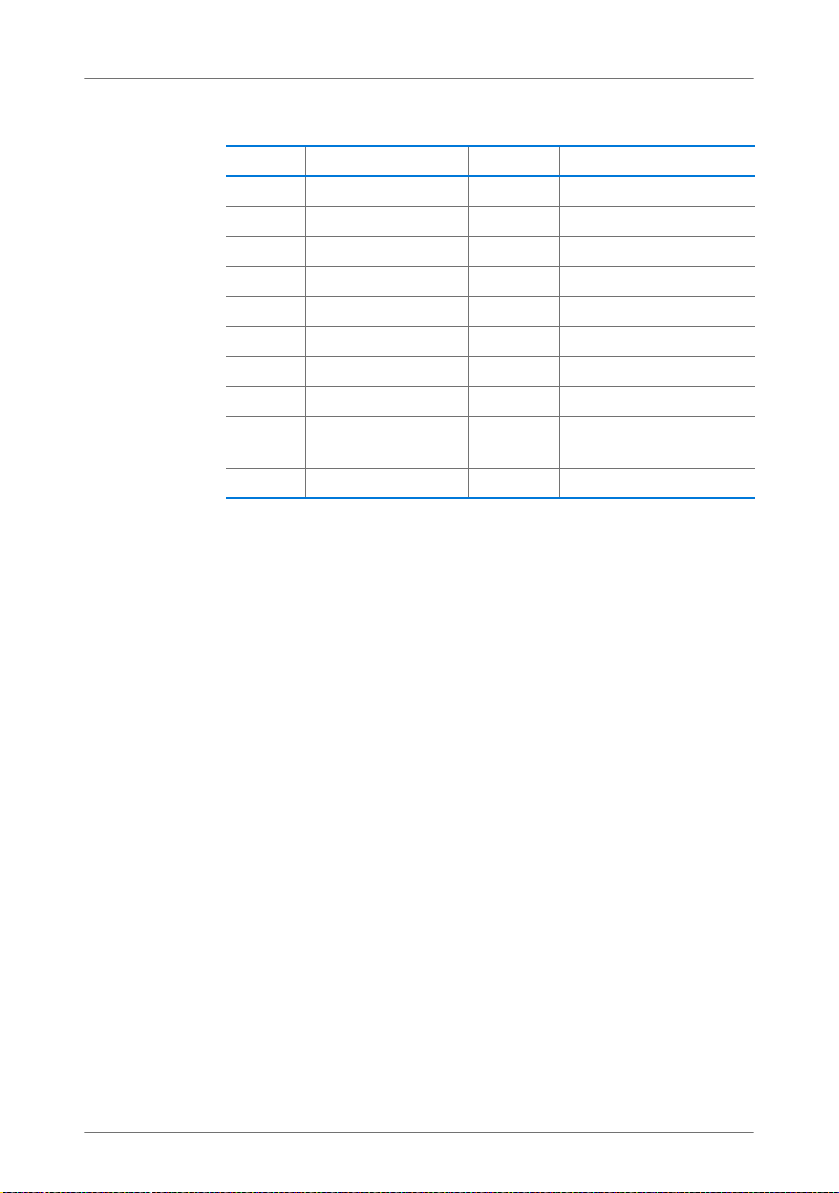
Frequency Ranges
Allocation of the WLAN Channels in the 5-GHz Range
Channel Frequency (GHz) Channel Frequency (GHz)
36 5.18 108 5.54
40 5.20 112 5.56
44 5.22 116 5.58
48 5.24 120 5.60
52 5.26 124 5.62
56 5.28 128 5.64
60 5.30 132 5.66
64 5.32 136 5.68
100 5.50 140 5.70 (20 MHz band-
width only)
104 5.52
57
Page 58

The FRITZ!Box Home Network
10 The FRITZ!Box Home Network
The FRITZ!Box connects your network devices, USB devices and storage devices in what we call a FRITZ!Box home network. In the home
network the FRITZ!Box makes data like images, music and videos
available to all connected users and allows them to share a printer.
Network Devices
Network devices include, for instance, computers, game consoles and smartphones that are connected with the FRITZ!Box
via a network cable connection or via WLAN.
All network devices can access each other’s folders released
for sharing, and share connected USB devices and available
memory.
If you would like to learn more about the possibilities of network devices in your FRITZ!Box home network, continue reading in the chapter Network Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home
Network from page 60.
USB Devices
USB devices include, for instance, printers, multi-function devices, and flash memory on the USB ports of the FRITZ!Box.
Connected USB devices can be used jointly and simultaneously by all network devices of your FRITZ!Box home network.
For more information about how to best configure USB devices in your home network and how to use them securely, see
the chapter USB Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network from
page 71.
Storage (NAS)
The memory of the FRITZ!Box includes storage media like
flash memory or hard drives connected to the USB ports of
the FRITZ!Box.
What is more, the FRITZ!Box can manage online storage configured on the server of your telecommunications provider.
58
Page 59

The FRITZ!Box Home Network
For more information about how to access the memory in your
FRITZ!Box home network safely and conveniently, see the
chapter Accessing USB Memory from page 72.
59
Page 60

Network Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network
11 Network Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network
All network devices connected with the FRITZ!Box comprise a network.
Network devices include, for instance, computers, game consoles and
smartphones. The devices can be connected with the FRITZ!Box by cable or wirelessly. This chapter describes the network settings in the
FRITZ!Box and how you can change them. You will also learn how you
can change the IP settings for the computer in the most common operating systems.
11.1 Network Settings in the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box is delivered with preconfigured network settings. According to these settings, all network devices connected with the FRITZ!Box are located in a single network.
The network settings can be changed and adapted to your
conditions and needs. But you should do so only if you are
well versed in networking technology.
The Glossary (from page 112) explains concepts and terminology having to do with IP networks.
Network Overview
The FRITZ!Box user interface shows an overview with all of the
devices and users connected with the FRITZ!Box.
The network overview “Devices and Users” is found in the
menu “Home Network / Network”.
60
Page 61

Network Settings in the FRITZ!Box
For each user and each network device, you find an entry in
the network overview. The columns have the following meanings:
Icon Each name is preceded by a green LED if the de-
Name This column displays the name under which the
IP Address For network devices, also displayed is the IP ad-
Connection The WLAN icon is displayed for wireless connec-
Properties This column indicates whether port forwarding or
vice is actively connected with the FRITZ!Box, but
currently not using the Internet connection. Any
device using the Internet connection appears with
a green-blue globe icon in front of its name.
user or the network device is known to the
FRITZ!Box. The names of network devices can be
changed by clicking the button to edit the entry.
dress with which the device is integrated into the
FRITZ!Box network.
tions.
child protection is enabled for the respective user
or network device.
Button for editing the entry
The button opens the entry in editing mode. This
view displays information about the network device, for instance on child protection or port forwarding settings. The name of the device in the
FRITZ!Box can be changed here.
Button for deleting the entry
Users or network devices that do not have an active connection to the FRITZ!Box can be deleted
from the network overview by clicking this button.
Always Assigning the Same IP Address
The editing mode for network devices includes the setting
“Always assign this network device the same IP address”.
When this setting is enabled for a network device, the DHCP
server of the FRITZ!Box will always assign the same IP address
to this device each time the connection is established.
61
Page 62

Network Settings in the FRITZ!Box
Starting the Computer – Wake on LAN
The editing mode for network devices that are connected with
the FRITZ!Box via a network (LAN) port includes the “Start
Computer” button. Use this button to start computers that
support wake on LAN.
With the wake on LAN function you can start computers in
your FRITZ!Box via the Internet. For instance, you can access a
computer at any time using remote maintenance software,
without wasting electricity by keeping the computer switched
on permanently.
IP Settings in the FRITZ!Box
The IP settings of the FRITZ!Box are preset upon delivery with
the following values:
FRITZ!Box Factory Settings
IP address 192.168.178.1
Subnet mask 255.255.255.0
DHCP server enabled
The IP address and the corresponding subnet mask yield the
following values:
Network address of the subnet 192.168.178.0
Entire IP address range for the computers
192.168.178.2 -
192.168.178.254
The following addresses cannot be assigned because they
are reserved for certain purposes:
This IP address is used by the
FRITZ!Box itself
This IP address is the broadcast address used to send messages into the
network
62
192.168.178.1
192.168.178.255
Page 63

Network Settings in the FRITZ!Box
IP Address in the FRITZ!Box
Upon delivery the FRITZ!Box is assigned the following IP address:
192.168.178.1
If you would like to change the IP address, please read
through the following sections.
When Does It Make Sense to Change the IP Address?
You should change the IP address of the FRITZ!Box if the following apply to your network:
• You have an existing local IP network, one subnet with
several computers.
• Fixed IP addresses are registered in the network settings
of the computer, and you do not want to or are not permitted to change these addresses.
• You want to connect the FRITZ!Box to the local IP network
in order to make the FRITZ!Box features available to all of
the computers in the IP network.
Reserved IP Addresses
The entire IP network 192.168.180.0 in the FRITZ!Box is reserved for internal purposes.
IP addresses from this network may not be assigned to the
FRITZ!Box.
DHCP Server of the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box is equipped with its own DHCP server. The
DHCP server is enabled by default in the factory settings. The
following range of IP addresses is reserved for the DHCP server in the factory settings:
192.168.178.20 - 192.168.178.200
This IP address can be changed as needed.
63
Page 64

Network Settings in the FRITZ!Box
Every time the operating system on a computer connected
with FRITZ!Box is started, the DHCP server assigns it an IP address from the IP address range of the DHCP server.
Only one DHCP server may be active within any network.
Assigning the IP addresses via the DHCP server ensures that
all of the computers connected with the FRITZ!Box are located
in the same IP network.
The computers can receive their IP addresses from the DHCP
server only if the setting “Obtain an IP address automatically” is enabled in the their IP settings. For more information,
see the section Obtaining an IP Address Automatically from
page 66.
Fixed IP Addresses when the DHCP Server Is Enabled
If you would like to configure fixed IP addresses on individual
computers connected with the FRITZ!Box despite the enabled
DHCP server, please note the following:
• The IP addresses must be from the IP network of the
FRITZ!Box.
• The IP addresses may not come from the address range
of the DHCP server.
• Each IP address can be assigned only once.
Disabling the DHCP Server
You can disable the DHCP server.
To make sure that all computers remain in the same IP network when the DHCP server is disabled, you must enter the IP
addresses manually in the computers’ network settings. First
disable the option “Obtain an IP address automatically” and
then enter the IP address manually in the appropriate field.
64
Page 65

Network Settings in the FRITZ!Box
In the case of the preset IP address of the FRITZ!Box, the following IP addresses are available for assignment to the computers:
192.168.178.2 - 192.168.178.254
Here too: each IP address can be assigned only once.
Changing Network Settings
In order to change the network settings of the FRITZ!Box, the
Expert Mode must be enabled in the user interface:
1. Select the “System / Expert Mode” menu and enable
“Show expert settings”.
2. Select the “Home Network / Network” menu.
3. Select the “Network Settings” page.
4. Click the “IP Addresses” button.
The “IP Settings” page is opened.
5. Make the desired changes and then confirm with “OK”
so that all changes will be applied.
Please note that changes to the network settings in the
FRITZ!Box may make it necessary to adjust the network settings of your computers so that you can continue to access
the FRITZ!Box user interface.
UPnP Settings
The Universal Plug-and-Play (UPnP) service included in your
FRITZ!Box provides status information about the FRITZ!Box to
all connected computers. Programs with UPnP support on
these computers can receive this information and use them
to display the status of the FRITZ!Box (e.g., connection status,
data transmission). UPnP service thus allows you to monitor
your FRITZ!Box from a connected computer.
65
Page 66

Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
Here is how to change the UPnP settings:
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface (see page 25).
2. Make sure that the expert mode is enabled in the “Sys-
tem / Expert Mode” menu.
3. Configure the UPnP settings in the “Home Network / Net-
work” menu on the “Programs” page.
11.2 Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
The FRITZ!Box has its own DHCP server, which assigns IP addresses to the connected computers. The connected computers must be configured such that they can receive their IP
addresses automatically. The steps for checking and adjusting this option differ among the operating systems. See the
relevant section for your operating system.
If FRITZ!Box is operated in a network, no other DHCP server
may be activated in this network.
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Windows 7
1. Click the “Start” button in the task bar and select the
“Control Panel / Network and Internet”.
2. Under “Network and Sharing Center”, click “View net-
work status and tasks”.
3. From the left column, select the “Change adapter set-
tings” command.
4. Select the LAN connection between your computer and
the FRITZ!Box. Click the right mouse button and select
“Properties”.
5. Under “This connection uses the following items”, select
the “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” entry and
click “Properties”.
6. On the “General” tab, enable the options “Obtain an IP
address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address
automatically”.
66
Page 67
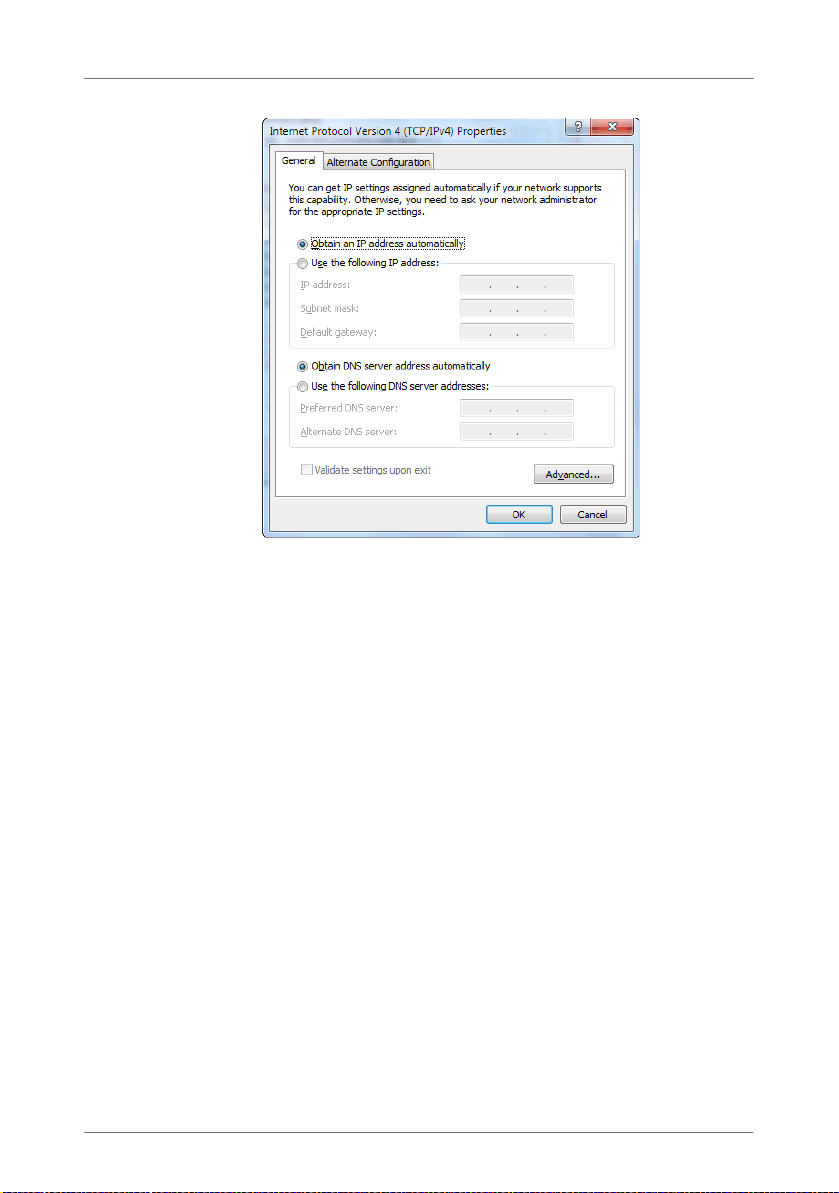
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
Properties of the Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
7. Confirm your selection by clicking “OK”.
Repeat steps 5 through 7 for the “Internet Protocol
Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)” as well.
The computer now receives an IP address from the FRITZ!Box.
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Windows Vista
1. Click the “Start” button in the task bar and select the
“Control Panel / Network and Sharing Center”.
2. From the “Tasks”, select “Manage network connec-
tions”.
3. In the “LAN or High-Speed Internet” area, select the LAN
connection between your computer and the FRITZ!Box.
Click the right mouse button and select “Properties”.
4. If the “User Account Control” window is displayed, click
“Continue” in this window.
5. Under “This connection uses the following items”, select
the “Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)” entry and
click “Properties”.
67
Page 68
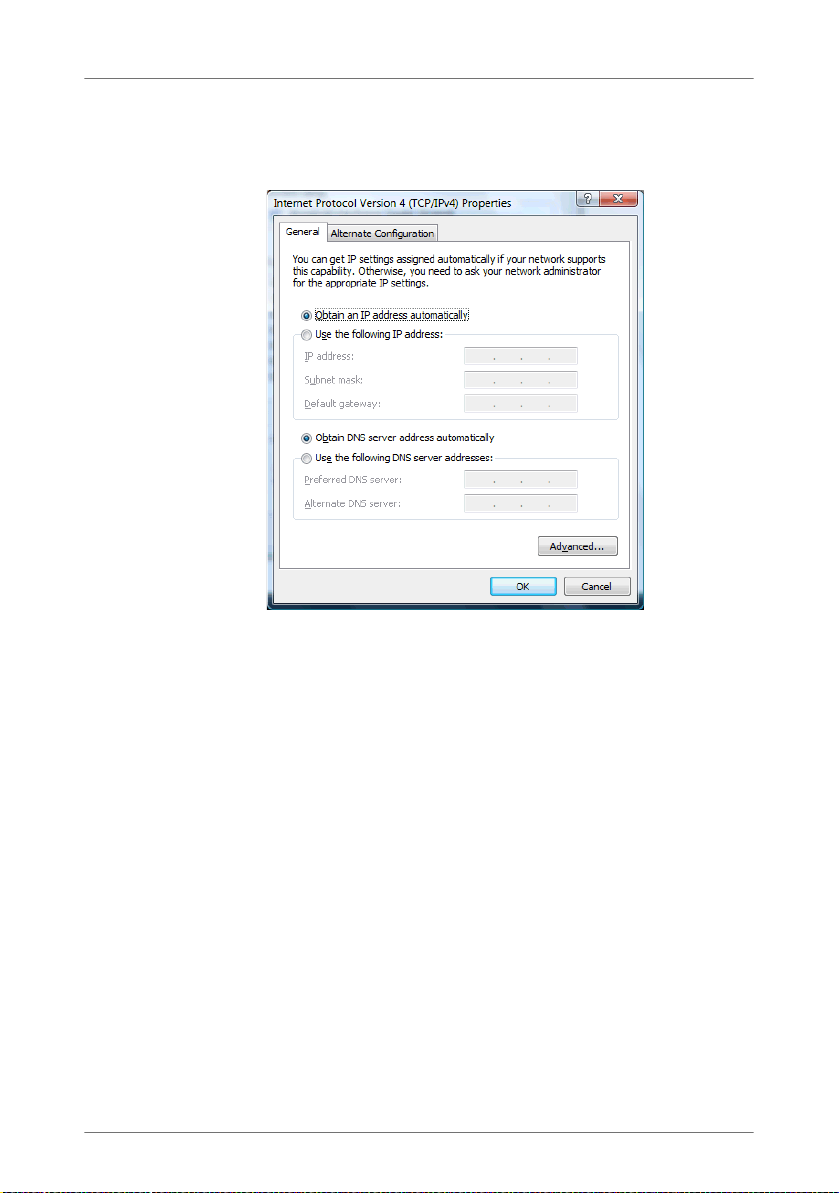
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
6. On the “General” tab, enable the options “Obtain an IP
address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address
automatically”.
Properties of the Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
7. Confirm your selection by clicking “OK”.
If necessary, repeat steps 5 through 7 for the “Internet
Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6)” as well.
The computer now receives an IP address from the FRITZ!Box.
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Windows XP
1. Go to “start / Control Panel / Network and Internet Con-
nections / Network Connections” and double-click the
LAN connection icon of the network adapter connected
to the FRITZ!Box.
2. Click the “Properties” button.
3. Select “Internet Protocol (TCP/IP)” in the list of items
used in this network connection and click “Properties”.
4. On the “General” tab, enable the options “Obtain an IP
address automatically” and “Obtain DNS server address
automatically”.
68
Page 69
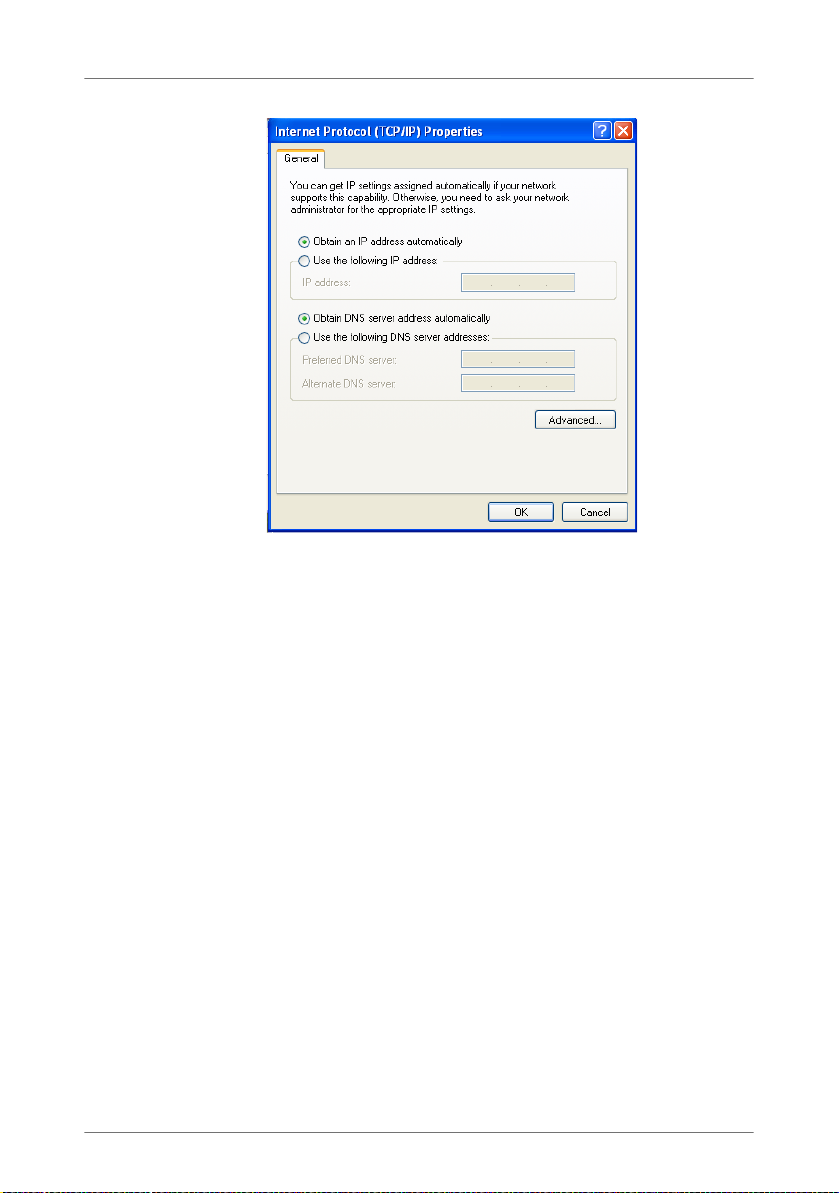
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
Properties of the Internet protocol (TCP/IP)
5. Confirm your selection by clicking “OK”.
The computer now receives an IP address from the FRITZ!Box.
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Mac OS X
1. Select the “System Preferences” in the Apple menu.
2. In the “System Preferences” window, click the “Net-
work” icon.
3. In the “Network” window, select the “Built-in Ethernet”
entry from the “Show:” drop-down list.
4. Switch to the “TCP/IP” settings page and select the “Us-
ing DHCP:” option from the “Configure IPv4” drop-down
menu.
5. Click “Apply Now”.
The computer now receives an IP address from the FRITZ!Box.
69
Page 70

Obtaining an IP Address Automatically
Obtaining an IP Address Automatically in Linux
For comprehensive information and tips on the topic of network settings in Linux, see, for example:
http://www.tldp.org/HOWTO/NET3-4-HOWTO-5.html
70
Page 71

USB Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network
12 USB Devices in the FRITZ!Box Home Network
The FRITZ!Box has a USB port to which you can connect various USB
devices. All network devices in the FRITZ!Box home network can use
these USB devices jointly and simultaneously.
This chapter describes how to share a printer in the network, which
USB devices can be used in your FRITZ!Box home network, and how to
use these devices safely.
12.1 Power Supply for USB Devices
You can connect USB devices with the following properties to
the FRITZ!Box:
• Some USB devices require more than one USB port for
operation, for instance, hard drives with a USB Y cable.
Connect this type of USB devices to the FRITZ!Box using
a USB hub with its own power supply.
• The total current consumption of connected USB devices
without their own power supply may not exceed 500 mA.
Check the rating plates of the connected USB devices.
USB devices that exceed the total current consumption
of 500 mA can be connected to the FRITZ!Box using a
USB hub with its own power supply.
12.2 USB Devices on the FRITZ!Box
These USB devices can be connected to the FRITZ!Box:
• You can connect up to four USB storage media like hard
disks, USB flash drives or card readers.
• USB storage media must use the file systems EXT2, FAT,
FAT32 or NTFS. On storage media with the FAT and FAT32
file systems you can use files up to a size of 4 GB. In the
NTFS file system there is no limit to the size of files that
can be used.
• You can connect one standard USB printer or one all-in-
one device with scanner and fax function. The complete
range of functions available in a all-in-one printers
71
Page 72

Using USB Devices Safely
device is guaranteed only with the USB remote connection of the FRITZ!Box (see also: Sharing a USB Printer on
page 73).
• You can connect a USB stick from the FRITZ!WLAN USB
Stick series by AVM to conveniently establish secure
WLAN connections using AVM Stick & Surf (see:
Establishing a WLAN Connection with AVM Stick & Surf
on page 19).
12.3 Using USB Devices Safely
Follow the instructions below about how to use USB devices
on your FRITZ!Box.
• The FRITZ!Box can not defend the USB memory from ex-
ternal influences. This means that voltage spikes or
drops, like those that occur during electrical storms, may
lead to data losses on connected USB memory media.
We recommend making regular backups of the USB
memory contents to avoid any losses.
• Whenever you want to remove USB devices from the
FRITZ!Box, go to the “Home Network / USB Devices” area
in the FRITZ!Box user interface to remove them safely
and avoid any loss of data.
12.4 Accessing USB Memory
The participants in the home network have various possibilities for accessing the various storage media of the FRITZ!Box.
• Participants in the home network can use FTP software
like FireFTP to exchange files among the FRITZ!Box storage media and workplaces.
Alternatively, you can enter ftp://fritz.box
line of your Internet browser to access the memory of the
FRITZ!Box.
If you would like to use FTP software, see the documentation of the software as well as the instructions in the
Online Help of the FRITZ!Box user interface.
in the address
72
Page 73

Sharing a USB Printer
• For access to media data like music, images and videos
available on the memory or on storage media of the
FRITZ!Box you can enable the FRITZ!Box media server.
Suitable playback devices like TV sets, web radios,
smartphones and the Windows Media Player can then
call up the data for streaming from the media server.
Playback devices to be used in connection with the media server must support the UPnP AV standard.
Enable the “media server” function in the FRITZ!Box user
interface under “Home Network / Storage (NAS) / Options Enabled”.
12.5 Sharing a USB Printer
You can connect a USB printer to the USB port of the
FRITZ!Box to make it available to all participants in your home
network. You can either release the printer for sharing as a
network printer or use the FRITZ!Box USB remote connection
software to connect it with a computer. Which option is preferable depends on how you intend to use the printer.
Using a USB Printer as a Network Printer
Configure the USB printer as a network printer on the
FRITZ!Box if
• the participants in the home network are to be able to
use the printer jointly and simultaneously.
• the printer is to be used by computers that use an oper-
ating system other than Windows (e.g. Mac OS X or
Linux).
For information about how to configure a USB printer as a network printer, see the section Setting Up a USB Printer as a
Network Printer on page 74.
73
Page 74

Sharing a USB Printer
Using a USB Printer with FRITZ!Box USB Remote Connection
Configure the USB printer on the FRITZ!Box with the FRITZ!Box
USB remote connection if
• the USB printer is an all-in-one device (fax/printer/scan-
• the USB printer is equipped with convenient features
• the USB printer uses bidirectional data exchange. In oth-
For information about how to configure a USB printer with the
USB Remote Connection, continue reading from the section
Configuring a USB Printer with FRITZ!Box USB Remote Connection on page 77.
Setting Up a USB Printer as a Network Printer
ner) and the entire range of functions is to be used.
like ink level display and you would like to use these.
er words: Not only does the computer send data to the
printer, the printer also sends status messages to the
computer. This communication in both directions is typical of the “Windows printers” or “GDI printers” that work
only with special Windows device drivers.
Work through the following steps to connect a USB printer to
the FRITZ!Box and configure it for use as a network printer.
Preparing Configuration
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Enable the Expert Mode.
3. Click “Home Network / USB Devices / USB Remote Con-
nection”.
4. Make sure that the option “printers (including all-in-one
printers)” is disabled.
5. Click “Apply”.
6. Connect the USB printer to the FRITZ!Box.
This concludes the preparations. Continue reading in the section for your operating system.
74
Page 75

Sharing a USB Printer
Setting Up a USB Printer in Windows 7, Vista and XP
1. Click “Start / Control Panel” and select the printer cate-
2. Click the printer icon with the right mouse button and se-
3. Switch to the “Ports” tab.
4. Click “Add” or “Add Port...”.
5. Double-click the “Standard TCP/IP Port” entry and click
6.
gory of your operating system:
– “Devices and Printers” (Windows 7)
– “Printers” (Windows Vista)
– “Printers and Faxes” (Window XP)
lect “Properties” or “Printer properties”.
If the printer is not displayed, you must first install the
printer drivers for this device. Consult the documentation of your printer for instructions.
“New Port”, then “Next”.
Enter “fritz.box” in the “Printer Name or IP Address” field.
If the FRITZ!Box is configured as a WDS repeater or as an
IP client, enter here the IP address at which the
FRITZ!Box can be reached within the network.
7. Enter any name you wish in the “Port Name” field and
click “Next”.
8. Select the “Custom” option and click “Settings...”.
9. Enable the “Raw” option.
10. Enter “9100” in the “Port Number” field and click “OK”.
11. Click “Next” and confirm with “Finish” and “Close”.
12. In the “[Printer name] Properties” window, switch to the
“Ports” tab.
13. Disable the “Enable bidirectional support” option and
click “Apply”.
The USB printer has been configured and can be used as a
network printer.
75
Page 76

Sharing a USB Printer
Setting Up a USB Printer in Mac OS 10.5
1. Click in the dock on “System settings”.
2. Click “Print & Fax”.
3. Click the “+” sign.
4. Click “IP Printer”.
5. In the “Protocol” drop-down list, select the entry “HP Jet
6. Enter “fritz.box” in the “Address:” input field.
7. In the “Print Using:” drop-down list, select the printer
8. Click “Add”.
Direct – Socket”.
If the FRITZ!Box is configured as a WDS repeater or as an
IP client, enter here the IP address at which the
FRITZ!Box can be reached within the network.
that is connected to the USB port of your FRITZ!Box.
If the printer is not displayed, you must first install the
printer drivers for this device. Consult the documentation of your printer for instructions.
The USB printer has been configured and can be used as a
network printer.
Setting Up a USB Printer in Other Operating Systems
The names of entries or menus in other operating systems
not described above may be slightly different than the terms
we use here.
• As the port type, select “Raw TCP”.
• Enter “9100” as the port.
• As the printer name, enter “fritz.box”.
If the FRITZ!Box is configured as a WDS repeater or as an IP
client, enter here the IP address at which the FRITZ!Box can
be reached within the network.
76
Page 77

Sharing a USB Printer
Configuring a USB Printer with FRITZ!Box USB Remote
Connection
If you are using an all-in-one device or would like to use the
convenience features of a USB printer connected to the
FRITZ!Box, we recommend installing the FRITZ!Box USB remote connection software. The FRITZ!Box USB remote connection program can be installed on computers with
Windows 7, Vista or XP (32- and 64-bit).
Installing FRITZ!Box USB Remote Connection
Install the program for FRITZ!Box USB remote connection on
all of the computers with which you want to use the connected USB device.
1. Connect the USB printer to the USB port of the
2. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
3. Click “Expert Mode” and enable the expert settings.
4. Click “Home Network / USB Devices / USB Remote Con-
FRITZ!Box.
nection”.
5. Enable “USB remote connection enbled”, then click the
“USB remote connection software” link.
6. In the window “USB Remote Connection” click “Down-
load”.
7. Download the file “fritzbox-usb-fernanschluss.exe”.
8. Double-click the file and follow the instructions on your
screen.
The FRITZ!Box USB remote connection software is now installed on your computer. Repeat the steps in these instructions for all further Windows users who wish to use the USB
remote connection on this computer.
77
Page 78

Sharing a USB Printer
Enabling the FRITZ!Box USB Remote Connection
1. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface.
2. Click “Expert Mode” and enable the expert settings.
3. Click “Home Network / USB Devices / USB Remote Con-
4. Enable the USB remote connection for printers and se-
5. Click “Apply”.
The FRITZ!Box USB remote connection is enabled.
Using a USB Printer with FRITZ!Box USB Remote Connection
1. Open the FRITZ!Box USB remote connection by clicking
2. Enter in the “My FRITZ!Box” area the FRITZ!Box pass-
nection”.
lect the option “printers (including all-in-one printers)”.
For an all-in-one printer with a memory function, also enable the “USB storage media” option.
For an all-in-one printer with a scanner function, also enable the “Others (e.g. scanner)” option.
the icon in the Windows task bar.
word.
3. Click “Refresh”.
4. Click the USB printer in the “Devices” area.
The USB printer is being connected to the computer.
Do not conduct any firmware updates for USB devices that
are connected with the computer via the FRITZ!Box USB remote connection.
78
Page 79

Saving Energy with the FRITZ!Box
13 Saving Energy with the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box combines a variety of devices in one device: VDSL and
ADSL modem, WLAN router and media server. This means that you
generally use much less power with the FRITZ!Box than you would
with several separate devices.
What is more, the FRITZ!Box saves energy by reducing processing
power on standby and lowering the power consumption of idle functions. The FRITZ!Box also offers various settings for energy-saving operation.
13.1 Saving Energy with the WLAN Radio Network
You can reduce the power consumption of the WLAN radio
network by
• setting up night service for the WLAN radio network (see
page 45).
• turning off the WLAN radio network with the “WLAN” but-
ton whenever no more WLAN devices are registered on
the FRITZ!Box.
• enabling the setting “Automatically reduce transmitter
power to the level actually needed”. This setting is configured in the “WLAN / Radio Channel” menu on the
FRITZ!Box user interface.
13.2 Enabling Energy-saving Mode for USB Hard Drives
In the FRITZ!Box you can enable an energy-saving function for
USB hard drives connected to the FRITZ!Box.
When the energy-saving function is enabled, connected USB
hard drives will be switched off when they are idle—as long
as the hard drives support the energy-saving function.
Enable the energy-saving function in the “Home Network /
USB Devices” menu in the FRITZ!Box user interface. You can
also test here, wether your USB hard disk supports the energy-saving function.
79
Page 80
Saving Energy at the LAN Ports
13.3 Saving Energy at the LAN Ports
For the individual LAN ports of your FRITZ!Box you can configure various operation modes. The power consumption of
some modes is higher than others. Select the operation
mode that is best suited to your needs in order to minimize
the power consumption of the LAN ports.
The LAN ports can be configured in the FRITZ!Box user interface. In the “System / Energy Monitor” menu, the following
operating modes are available on the “Settings” page:
Operating Mode Functionality and Power Consumption
Always Enabled The LAN port is always enabled.
Highest power consumption.
Identify Automatically
Disabled The LAN port is disabled and consumes no
The FRITZ!Box establishes LAN connections as
needed.
Lower power consumption than for the “Always Enabled” setting.
power.
The first LAN port cannot be disabled.
80
Page 81

Help in Case of Errors
14 Help in Case of Errors
This chapter provides assistance if you are not able to open
the user interface of your FRITZ!Box or are having problems
with the DSL or WLAN connection.
For more comprehensive help, see the AVM knowledge database in the Internet, which can be accessed at the following
address:
www.avm.de/en/service/FAQs
14.1 Cannot Establish a DSL Connection
The FRITZ!Box automatically establishes a connection to the
DSL network as soon as it is connected with the DSL line. If
the DSL connection is not established, check which kind (annex) of DSL is set in your FRITZ!Box and attempt to resolve the
error.
Changing the Annex Setting of the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box cannot establish a connection to the DSL
network. This is signaled by the continued flashing of the
“Power” LED.
Cause
The kind of DSL (Annex A, B, J odr M) set in the FRITZ!Box is
not the same as the annex used on your DSL line.
Help
1. Contact your Internet Service Provider to find out which
annex is used on your DSL line.
2. Connect a computer with the FRITZ!Box either wirelessly
via WLAN or using a network cable.
3. Open the FRITZ!Box user interface as described on
page 25.
4. Click the toolbar entry “Expert Mode” or in the “System /
Expert Mode” menu to enable the expert settings of the
FRITZ!Box and confirm your setting by clicking “Apply”.
81
Page 82

The User Interface Does Not Open
5. Click “Internet / DSL Information” in the menu and se-
lect the “Line Settings” tab. In the “Annex Settings” section, make sure that the annex working on your DSL line
is set. Save your settings by clicking “Apply”.
After the annex setting has been changed, the FRITZ!Box restarts automatically. The connection to the DSL network has
been established as soon as the “Power” LED stops flashing
and remains lit up.
14.2 The User Interface Does Not Open
If an error message is returned when you open the FRITZ!Box
user interface, this can have various causes. Check the
causes listed below and attempt to resolve the error.
Restarting the FRITZ!Box
The user interface cannot be opened or does not react.
Cause
Inconsistencies within the FRITZ!Box.
Help
1. Restart the FRITZ!Box.
Remove the power cable from the outlet.
2. Wait about five seconds before reconnecting to the pow-
er supply.
3. To make sure that the FRITZ!Box has finished restarting,
wait until the “Power” LED lights up and stops flashing
and, if you have switched on WLAN, the “WLAN” LED remains lit up as well. This ensures that the FRITZ!Box restart has been completed.
4. Try again to open the FRITZ!Box user interface by enter-
ing fritz.box
in the address field.
82
Page 83

The User Interface Does Not Open
Checking the Cable Connections
The FRITZ!Box user interface is not displayed in your web
browser.
Cause
The cable connections are not secure.
Help
Make sure that all cables are plugged in securely.
Checking Name Resolution
The user interface of the FRITZ!Box cannot be opened by
entering fritz.box.
Cause
The name resolution of the FRITZ!Box is not working.
Help
1. In the web browser, enter the following IP address in
place of fritz.box
192.168.178.1
:
2. If the user interface opens in response to this address,
set the network adapters used to “Obtain the IP address
automatically” (see Obtaining an IP Address Automati-
cally from page 66).
Checking the IP Address
The user interface of the FRITZ!Box cannot be opened by a
fritz.box nor by entering 192.168.178.1.
Cause
Incorrect IP address on the connected computer.
Help
Set the network adapter to DHCP so that the network address
can obtain its IP address from the DHCP server of the
FRITZ!Box. See the section Obtaining an IP Address
Automatically from page 66 for instructions.
83
Page 84

The User Interface Does Not Open
If you still cannot open the user interface by entering fritz.box
or by 192.168.178.1
FRITZ!Box as described on page 87.
Disabling Dial-up Connections
The user interface is not opened; a window for a dial-up
connection appears instead.
Cause
The browser must use the network connection between the
computer and FRITZ!Box when the user interface is opened.
For this the automatic establishment of a Dial-up Networking
connection must be disabled.
Help
You can disable the automatic attempt to establish a Dial-up
Networking connection. The following example explains how
to check the settings of Internet Explorer 8:
1. Select the “Connections” settings page under “Tools /
Internet Options”.
, use the fixed IP address of the
2. In the “Dial-up and Virtual Private Network settings” sec-
tion, enable the option “Never dial a connection”.
3. As a final step, click “OK”.
Disabling Online Operation
The user interface does not appear in the window of your web
browser.
Cause
The web browser is set for offline operation.
Help
Configure the web browser for online operation. Using the example of Internet Explorer 8:
1. Open the “Tools” menu.
2. If a checkmark is displayed in front of “Work Offline”,
click this line.
84
Page 85

The User Interface Does Not Open
The checkmark will be removed and Internet Explorer will
switch to online operation.
Checking the Proxy Settings
The user interface does not appear in the window of your web
browser.
Cause
The proxy settings of the web browser prevent the user interface from being opened.
Help
Enter the DNS name and the IP address of the FRITZ!Box as an
exception in the proxy settings of the web browser, as
described here for the example of the Internet Explorer 8.
1. Select the “Connections” settings page under “Tools /
Internet Options”.
2. Click the “LAN settings” button in the “Local Area Net-
work (LAN) settings” area.
3. In the “Proxy server” area of the next window, check the
“Use a proxy server for your LAN” option and then click
“Advanced”.
4. Enter as “Exceptions”:
fritz.box
; 192.168.178.1; 169.254.1.1
and click “OK”.
Checking the CGI Settings
The user interface does not appear in the window of your web
browser.
Cause
The execution of CGI scripts is disabled in the web browser.
85
Page 86

The User Interface Does Not Open
Help
Configure the web browser so that the execution of scripts is
allowed in the user interface. Using the example of the
Internet Explorer 8:
1. Select the “Security” settings page under “Tools / Inter-
net Options”.
2. If the “Default level” button is not available for selec-
tion, the “Medium-high” security level is already configured, which means that CGI scripts can be executed in
the Internet browser.
3. Proceed as follows if the “Default level” button is avail-
able for selection:
4. Select the “Local intranet” icon and click the “Sites” but-
ton.
5. In the next window, click the “Advanced” button and en-
ter in the “Add this website to the zone:” field:
fritz.box
Click “Add”.
6. Disable the “Require server verification (https:) for all
sites in this zone” option and click “Close”.
Checking Security Software
The user interface cannot be displayed in the web browser.
Cause
Security software is blocking access to the user interface.
Help
Security software like firewalls can prevent access to the user
interface of the FRITZ!Box. Configure exceptions for the
FRITZ!Box in all of the enabled security software.
86
Page 87

The User Interface Does Not Open
If you would like to exit security software to test access to the
FRITZ!Box, remove the DSL cable first. After testing, first start
the security software before reinserting the DSL cable and
connecting to the Internet!
Opening the User Interface of the FRITZ!Box
The FRITZ!Box is equipped with a fixed IP address that cannot
be changed. The FRITZ!Box always can be reached at this IP
address. This fixed IP address is:
Fixed IP address 169.254.1.1
Proceed as follows to open the FRITZ!Box user interface using
this IP address:
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to the computer using the net-
work cable (yellow). For more information, see the
section Connecting Computers to the LAN Port from
page 17.
2. Make sure that the computer obtains its IP address auto-
matically. You can check this setting in the computer’s IP
settings (see section Obtaining an IP Address Automati-
cally from page 66).
3. Restart your computer.
4. Start your Internet browser and enter the FRITZ!Box’s
fixed IP address:
169.254.1.1
The FRITZ!Box user interface opens.
Once you have reached the FRITZ!Box user interface again,
you should check the FRITZ!Box settings and correct them if
necessary.
87
Page 88

Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection
14.3 Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection
If you are not able to establish a WLAN connection between
your computer and the FRITZ!Box, then please undertake the
following measures to seek the source of the error and resolve it.
Enabling the WLAN Device
The WLAN device cannot find a wireless network.
Cause
The WLAN device is not ready for operation.
Help
Make sure that the WLAN device is ready for operation. Some
of the WLAN devices installed in notebooks must be activated
by flipping a switch on the notebook.
For questions on the WLAN device of your computer, please
contact the manufacturer.
Enabling WLAN
The wireless network of the FRITZ!Box is not found by the
WLAN device.
Cause
WLAN is not enabled in the FRITZ!Box. If the “WLAN” LED on
the FRITZ!Box is not lit up or is flashing, this means that WLAN
is not enabled.
Help
Press the WLAN button on the FRITZ!Box. The “WLAN” LED
begins flashing and then lights constantly. This means that
the WLAN function is enabled.
88
Page 89

Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection
Announcing the Name of the Radio Network
The WLAN device cannot find the wireless network of the
FRITZ!Box.
Cause
The name of the wireless network of the FRITZ!Box is concealed.
Help
In the WLAN settings of the FRITZ!Box, enable the “Name of
the radio network visible” option.
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to a computer using a network ca-
ble, as described in the section Connecting Computers
to the LAN Port on page 17.
2. Start a web browser.
3. Enter fritz.box
in the address field.
4. In the “Interfaces” area on the “Overview” page, select
“WLAN”, or open the “WLAN” menu in the navigation bar
on the left.
5. In the “Radio Network” page, enable the option “Name
of the radio network visible”.
6. Click the “Apply” button at the bottom of the page.
7. Remove the network cable and try again to establish a
connection via WLAN.
Comparing the Security Settings for WLAN
Make sure that the WLAN security settings registered in the
FRITZ!Box agree with the security settings of the WLAN adapter.
Here is how to view the WLAN security settings of the
FRITZ!Box and print them out.
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to a computer using a network ca-
ble. Proceed as described in the section Connecting
Computers to the LAN Port from page 17.
2. Start a web browser.
89
Page 90

Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection
3. Enter fritz.box in the address field.
4. In the “Interfaces” area on the “Overview” page, select
“WLAN”, or select the “WLAN” menu in the navigation
bar on the left.
5. Open the “WLAN / Security” menu.
6. Click the “Apply” button.
A window with the WLAN security settings will be displayed. Print out the page by clicking the “Print Page”
button.
7. Remove the network cable and check the configuration
of the WLAN adapter in the printout. Try again to establish a connection.
Testing the WLAN Connection Without Security Settings
Disable the WLAN security settings to test whether a WLAN
connection between the FRITZ!Box and the WLAN device is
possible at all.
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to a computer using a network ca-
ble. Proceed as described in the section Connecting
Computers to the LAN Port from page 17.
2. Open the user interface of the FRITZ!Box in a web brows-
er. Proceed as described in the section Opening the User
Interface on page 25.
3. In the “Interfaces” area on the “Overview” page, select
“WLAN”, or open the “WLAN” menu in the navigation bar
on the left.
4. Click the “WLAN / Security” menu and enable the option
“non-encrypted”.
5. Then click the “Apply” button.
6. Remove the network cable and try again to establish a
connection.
This non-secured condition should be used only for testing, to find out whether a WLAN connection is possible
at all.
90
Page 91

Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection
If the attempt to connect to the WLAN using the non-encrypted connection is not successful either, check the installation
of the WLAN device and contact the manufacturer of the
WLAN device if necessary.
Enable WLAN encryption again after completing the tests.
Follow the steps listed above and then enable the kind of encryption that was previously configured.
Installing the Current Service Pack
The WLAN connection to the FRITZ!Box cannot be established
using the Microsoft WLAN Service (WZC: Windows Zero
Configuration) in Windows XP with Service Pack 2.
Cause
The required Microsoft patch for WPA2 (IEEE 802.11i) may not
be not installed.
Help
Install Service Pack 3 (SP3) for Windows XP, available as a
free download from Microsoft. Then Microsoft WLAN Service
will support WPA2, so that a WLAN connection can be
established to the FRITZ!Box.
Avoiding WLAN Channels with DFS
The FRITZ!Box loses the WLAN connection in the 5-GHz
frequency band for no apparent reason.
Cause
A forced channel change is taking place. In the 5-GHz frequency band the WLAN base station is programmed to
change the channel whenever a radar source transmits on the
same channel (Dynamic Frequency Selection, DFS).
Help
You can prevent forced channel changes by selecting in the
FRITZ!Box a channel for the 5-GHz frequency band that does
not use DFS (channels 36, 40, 44, 48).
91
Page 92

Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection
Ruling Out Interference Caused by Other Wireless
Networks
If there are other devices in the immediate vicinity of your
FRITZ!Box that use the same frequency band, simultaneous
use of frequencies can result in mutual interference (for example, fluctuations or interrupted connections). Disruptions
can be caused by other WLAN base stations, but also by devices like baby monitors, game consoles, garage door openers, Bluetooth devices, or wireless AV bridges, which also use
the 2.4-GHz frequency band. In this case, please test a different radio channel for your FRITZ!Box.
Alternatively, you can set the radio channel to “Autochannel”.
This enables the autochannel function, so that the FRITZ!Box
searches for the best WLAN channel itself.
For applications that rely on a steady, high throughput rate
(“streaming”), you should use the 5-GHz frequency band.
This radio band provides more channels and is subject to significantly less external interference.
To set the radio channel in the user interface, your computer
must be connected with the FRITZ!Box by network cable or
wirelessly. If your computer is connected via WLAN, continue
with Step 2 of the instructions below. In this case, note that
the existing WLAN connection is interrupted as soon as you
apply the changed settings. Afterward you have to reconnect
your computer with the FRITZ!Box.
1. Connect the FRITZ!Box to a computer using a network ca-
ble. Proceed as described in the section Connecting
Computers to the LAN Port from page 17.
2. Start a web browser.
3. Enter fritz.box
4. Open the “WLAN / Radio Channel” menu in the naviga-
tion bar on the left.
5. You may have to enable the “Adjust radio channel set-
tings” option.
6. Select a different radio channel from the “Radio chan-
nel” list.
in the address field.
92
Page 93

Cannot Establish a WLAN Connection
7. Click the “Apply” button.
8. Remove the network cable and check whether interfer-
ence continues to occur.
93
Page 94

Taking the FRITZ!Box out of Operation
15 Taking the FRITZ!Box out of Operation
In this chapter you receive tips and recommendations for taking the
FRITZ!Box out of operation.
Please also follow our instructions for the correct disposal of
waste equipment on page 109.
15.1 Restoring the FRITZ!Box Factory Settings
Restore the factory settings of the FRITZ!Box. This is strongly
recommended if you are planning to pass the FRITZ!Box on to
another user.
Resetting the FRITZ!Box has the following effects:
• All settings you made in the FRITZ!Box are then deleted.
• The factory settings’ WLAN key will be activated again.
• The IP configuration of the factory settings will be re-
stored.
Restoring Factory Settings
1. In the FRITZ!Box user interface, select the “System / Re-
set” menu.
2. On the “Factory Settings” page, click the “Load Factory
Settings” button.
The FRITZ!Box is reset to its factory settings.
94
Page 95

Uninstalling Software
15.2 Uninstalling Software
Additional software for the FRITZ!Box is available on the web
pages of AVM at www.avm.de/en/download
If you have installed supplementary programs on one or more
computers, uninstall the software using the control panel of
your Windows operating system.
Uninstalling Software in Windows 7
1. Open “Start / Control Panel / Programs”.
2. Under “Programs and Features”, click “Uninstall a pro-
gram”.
3. Select in the list the AVM software to be uninstalled.
4. Click the “Uninstall/Change” button.
The software will be uninstalled.
Uninstalling Software in Windows Vista
1. Open “Start / Settings / Control Panel / Programs and
Functions”.
.
2. Select in the list the AVM software to be uninstalled.
3. Click the “Uninstall/Change” button and confirm with
“Continue”.
The software will be uninstalled.
Uninstalling Software in Windows XP
1. Open “start / Control Panel / Add or Remove Programs”.
Make sure that the “Change or Remove Programs” button is selected in the column at left.
2. Select the AVM software to be uninstalled from the list of
“Currently installed programs”.
3. Click the “Change/Remove” button.
The software will be uninstalled.
95
Page 96

Technical Specifications
16 Technical Specifications
16.1 Ports and Interfaces
• DSL modem in accordance with standard ITU G.992.1
Annex A and B (G.dmt), ITU G.992.3 Annex A and B
(ADSL2), ITU G.992.5 Annex A and B (ADSL2+),
ITU G.992.3/5 Annex M, ITU G.992.3/5 Annex J,
ITU G.994.1 (G.hs)
• Four LAN ports via RJ45 sockets (standard Ethernet,
10/100 base-T)
• One USB host controller (USB version 2.0)
• WLAN base station with support for wireless networks
– IEEE 802.11a – 54 Mbit/s
– IEEE 802.11b – 11 Mbit/s
– IEEE 802.11g – 54 Mbit/s
– IEEE 802.11n – 300 Mbit/s
16.2 Router Functions
• Router
• DHCP server
• Firewall with IP masquerading/NAT
• IPv4 and IPv6
• Child protection and filter lists
• Port forwarding
• Dynamic DNS
• VPN
96
Page 97

User Interface and Display
16.3 User Interface and Display
• Settings and status messages via a web browser on a
connected computer
• Five LEDs indicate the condition of the device
16.4 Physical Specifications
• Dimensions (W x D x H): approx. 210 x 155 x 25 mm
• Supply voltage: 230 V / 50 Hz
• Maximum power consumption: 12 W
• Firmware can be updated
• Conform to CE standards
• Ambient conditions
– operating temperature: 0°C – +40°C
– storage temperature: -20°C – +70°C
– relative humidity (operation): 10% – 90%
– relative humidity (idle): 5% – 95%
16.5 Cable
Network Cable
The network cable (yellow) of the FRITZ!Box 3270 is a standard category 5 (Cat 5) Ethernet cable. Please use a standard
STP-type (Shielded Twisted Pair) Ethernet cable of category 5
(Cat 5) to replace or extend the Ethernet cable. To extend the
cable you will need a shielded RJ45 double coupling (Cat 5)
with a 1:1 pin assignment. You can use both straight cables
and crosslink cables. All components are available from specialized vendors.
When components of a category smaller than Cat 5 are used,
reduced transmission rates may result.
AVM recommends using a network cable no more than
100 meters long.
97
Page 98
Customer Service
17 Customer Service
Be it product documentation, frequently asked questions (FAQs) or
support: this chapter presents information on all important service
topics.
17.1 Documentation on the FRITZ!Box
To take advantage of all commands and features of your
FRITZ!Box, consult the following documentation:
Help
In the FRITZ!Box user interface you can open the comprehensive Help by clicking the “Help” icon and the “Help” buttons.
Manual
The PDF file of the manual can be opened and downloaded
from the Internet at the following address:
www.avm.de/en/service/manuals
Choose the “FRITZ!Box” product group and then your
“FRITZ!Box 3270”. The PDF is opened.
The current Adobe Acrobat Reader for reading PDF documents can be downloaded from the Internet free of charge at
www.adobe.com
.
17.2 Information in the Internet
On its web site AVM presents comprehensive information on
your AVM product.
Videos on the FRITZ!Box
Videos on many of the FRITZ!Box functions are available,
showing animated demonstrations of how to set up the individual functions.
The videos can be viewed at the following address:
www.avm.de/en/service/FRITZ_Clips
98
Page 99
Support from the Support Team
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
We would like to make our products as easy to use as possible. If you still have problems, sometimes you need just a tip
to resolve them.
In our FAQs you will find answers to the questions users ask
about our products most often. The FAQs can be viewed at
the following address:
www.avm.de/en/service/FAQs
17.3 Support from the Support Team
Should problems with your FRITZ!Box arise, we recommend
taking the following steps:
1. If you have questions about starting operation of your
FRITZ!Box, please consult the following chapters again:
– Before You Connect the FRITZ!Box from page 12
– Connecting the FRITZ!Box from page 15
– Connecting the Computer to the FRITZ!Box from
page 17
2. If you have any problems, seek first aid by consulting the
chapter Help in Case of Errors from page 81.
This chapter also presents tips on problems with establishing connections.
3. Read our FAQs in the Internet.
www.avm.de/en/service/FAQs
This site contains answers to questions our customers
have frequently asked our Support team.
Please take advantage of the information sources described
above before contacting AVM support.
99
Page 100

Manufacturer’s Warranty
Support by E-mail
You can send us an English-language e-mail request at any
time using the “Service” area of our web site. The “Service”
area can be reached at:
www.avm.de/en/service
1. Select the product for which you need support from the
“Support” area.
2. Click the “Mail Form” link to open the e-mail form.
3. Fill out the form in English.
4. Send it to AVM by clicking the “Send” button.
Our Support team will respond by e-mail as quickly as possible.
17.4 Manufacturer’s Warranty
We offer a manufacturer’s warranty of 5 years on the hardware of this original product. The warranty period begins with
the purchase date from the first end user. Compliance with
the warranty period can be proven by submission of the original invoice or comparable documents. This warranty does not
restrict your warranty rights based on the contract of sale or
other statutory rights.
We will remove defects to the product which are demonstrably due to faults in materials or manufacturing. Our warranty
does not cover defects which occur due to incorrect installation, improper use, non-observance of instructions in the user manual, normal wear and tear or defects in the environment of the system (third-party hardware or software). We
may, at our discretion, repair or replace the defective product.
Claims other than the right to the removal of defects which is
mentioned in these terms of warranty are not constituted.
We guarantee that the software conforms with general specifications, not, however, that the software meets your individual requirements. Delivery costs will not be reimbursed.
Products which have been replaced revert to our ownership.
Claims recognized under warranty entail neither an extension
100
 Loading...
Loading...