Page 1
BayRS Version 14.00
Part No. 308658-14.00 Rev 00
September 1999
4401 Great America Parkway
Santa Clara, CA 95054
Using Technician Interface Scripts
Page 2

Copyright © 1999 Nortel Networks
All rights reserved. Printed in the USA. September 1999.
The information in this document is subject to change without notice. The statements, configurations, technical data,
and recommendations in this document are believed to be accurate and reliable, but are presented without express or
implied warranty. Users must take full responsibility for their applications o f a ny products specifi ed in this d ocum ent.
The information in this document is proprietary to Nortel Networks NA Inc.
The software described in this document is furnished under a license agreement and may only be used in accordance
with the terms of that license. A summary of the Software License is included in this document.
Trademarks
NORTEL NETWORKS is a trademark of Nortel Networks.
Bay Networks, AN, BCN, BLN, BN, and FRE are registered trademarks and Advanced Remote Node, ANH, ARN,
ASN, BayRS, BaySecure, BayStack, BayStream, BCC, BCNX, BLNX, and System 5000 are trademarks of Nortel
Networks.
Microsoft, MS, MS-DOS, Win32, Windows, and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Cor poration.
All other trademarks and registered trademarks are t he property of their respective owners.
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the United States Government is subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c)(1)(ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Sof tware clause at DFARS 252.227-7013.
Notwithstanding any other license agreement that may pertain to, or accompany the delivery of, this computer
software, the rights of the United States Government regarding its use, reproduction, and disclosure are as set forth in
the Commercial Computer Software-Restricted Rights cl ause at FAR 52.227-19.
Statement of Conditions
In the interest of improvi ng internal design, operational fun c tion , an d/o r re lia bi lity, Nortel Networks NA Inc. reserve s
the right to make changes to the products described in this document without notice.
Nortel Networks NA Inc. does not assume any liability that may occur due to the use or application of the product(s)
or circuit layout(s) described herein.
Portions of the code in this software product may be Copyright © 1988, Regents of the University of California. All
rights reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms of such portions are permitted, provided that the
above copyright notice and this paragraph are duplicated in all such forms and that any docu mentation, advertising
materials, and other materials related to such distribution and use acknowledge that su ch portions of the software were
developed by the University of California, Berkeley. The name of the University may not be used to endorse or
promote products derived from such portions of the software without specific prior written permission.
SUCH PORTIONS OF THE SOFTWARE ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” AND WITHOUT ANY EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
In addition, the program and information containe d herein are licensed only pursuant to a license agreement that
contains restrictions on use and disclosure (that may incorporate by reference certain limitations and notices imposed
by third parties).
Nortel Networks NA Inc. Software License Agreement
NOTICE: Please carefully read this license agre ement before copying or using the accompanying software or
installing the hardware unit with pre-enabled software (each of which is referred to as “Software” in this Agreement).
BY COPYING OR USING THE SOFTWARE, YOU ACCEPT ALL OF THE TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF
THIS LICENSE AGREEMENT. THE TERMS EXPRESSED IN THIS AGREEMENT ARE THE ONLY TERMS
ii
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 3

UNDER WHICH NORTEL NETWORKS WILL PERMIT YOU TO USE THE SOFTWARE. If you do not accept
these terms and conditions, return the product, unused and in the original shipping container, within 30 days of
purchase to obtain a credit for the full purchase price.
1. License Grant. Nortel Networks NA Inc. (“Nortel Networks”) grants the end user of the Software (“Licensee”) a
personal, nonex clusive, nontransfera ble lic ense: a) to u se the Softw are eit her on a single compute r or, if applicab le, on
a single authorized device identified by host ID, for which it was originally acquired; b) to copy the Software solely
for backup purposes in support of authorized use of t he Software; and c) to use and copy the associated user manual
solely in support of authoriz ed use of th e Softwa re b y Licen see. Thi s license applies t o the So ftware o nly and d oes not
extend to Nortel Networks Agent software or other Nortel Networks software products. Nortel Networks Agent
software or other Nortel Networks software products are licensed for use under the terms of the applicable Nortel
Networks NA Inc. Software License Agreement that accompanies such software and upon payment by the end user of
the applicable license fees for such software.
2. Restrictions on use; reservation of rights. The Software and user manuals are protected und er copyright laws.
Nortel Networks and/or its licensors retain all title and ownership in both the Software and user manuals, including
any revisions made by Nortel Networks or its licensors. The copyright notice must be reproduced and included with
any copy of any portion of the Software or user manuals. Licensee may not modify, translate, decompile, disassemble,
use for any competitive analysis, reverse engineer, distribute, or create derivative works from the Software or user
manuals or any copy, in whole or in part. Except as expressly provided in this Agreement, Licensee may not copy or
transfer the Software or user manuals, in whole or in part. The Software and user manuals embody Nortel Networks’
and its licensors’ confidential and propriet ary in telle c tu al pro p erty. Licensee shall not sublicense, assign, or ot herwise
disclose to any third party the Software, or any information about the operation, design, performance, or
implementation of the Software and user manuals that is confidential to Nortel Networks and its licensors; however,
Licensee may grant permission to its consultants, subcontractors, a nd agents to use the Softw are at Licensee’s facility,
provided they have agreed to use the Software only in accordance with the terms of this license.
3. Limited warranty . Nortel Networks warrants each item of Software, as delivered by Nortel Networks and properly
installed and operated on Nortel Networks hardware or other equipment it is originally licensed for, to function
substantially as described in its accompanying user manual during its warranty period, which begins on the date
Software is first shipped to Licensee. If an y item of S oftware f ails to so function d uring its w arranty period, as the sole
remedy Nortel Networks will at its discretion provide a suitable fix, patch, or workaround for the problem that may be
included in a future Software release. Nortel Networks further warrants to Licensee that the media on which the
Software is provided will be free from defec ts in materials and wo rkman ship under no rmal use for a peri od of 90 da ys
from the date Software is first shipped to Licensee. Nortel Networks will replace defective media at no charge if it is
returned to Nortel Netw orks during the warranty period along with proof of the date of ship ment. This warranty does
not apply if the media has been damaged as a result of accident, misuse, or abuse. The Licensee assumes all
responsibility for selection of the Software to achieve Licensee’s intended results and for the installation, use, and
results obtained from the Software. Nortel Networks does not warrant a) that the functions contained in the software
will meet the Licensee’s requirements, b) that the Software will operate in the hardware or software combinations that
the Licensee may select, c) that the operation of the Software will be uninterrupted or error free, or d) that all defects
in the operation of the Softw are will be corrected . Nortel Network s is not obligate d to remedy an y Software defect that
cannot be reproduced with the latest Software release. These warranties do not apply to the Software if it has been (i)
altered, except by Nortel Networks or in accordance with i ts instructions; (ii) used in conjunction with another
vendor’s product, resulting in the de fect; or (iii) damage d by improper environment, abuse, misuse, accident, or
negligence. THE FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND LIMITATIONS ARE EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES AND ARE
IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION ANY
WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. Licensee is responsible
for the security of its own data and information and for maintaining adequate procedures apart from the Software to
reconstruct lost or altered files, data, or programs.
4. Limitation of liability. IN NO EVENT WILL NORTEL NETWORKS OR ITS LICENSORS BE LIABLE FOR
ANY COST OF SUBSTITUTE PROCUREMENT; SPECIAL, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES; OR ANY DAMAGES RESULTING FROM INACCURATE OR LOST DATA OR LOSS OF USE OR
PROFITS ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE PERFORMANCE OF THE SOFTWARE, EVEN
IF NORTEL NETWORKS HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES. IN NO EVENT
308658-14.00 Rev 00
iii
Page 4

SHALL THE LIABILITY OF NORTEL NETWORKS RELATING TO THE SOFTWARE OR THIS AGREEMENT
EXCEED THE PRICE PAID TO NORTEL NETWORKS FOR THE SOFTWARE LICENSE.
5. Government Licensees. This provision applies to a ll Softwa re and docum entation acquired d irectly or i ndirectly by
or on behalf of the United States Government. The Software and documentation are commercial products, licensed on
the open market at market prices, and were developed entirely at private expense and without th e use of any U.S.
Government funds. The license to the U.S. Government is granted only with restricted rights, and use, duplication, or
disclosure by the U.S. Government is subject to the restrictions set forth in subparagraph (c)(1) of the Commercial
Computer Software––Restricte d Rig hts cla u se o f FAR 52.227-19 and the limitations set out in thi s licen se for civilian
agencies, and subparagraph (c)(1)(ii ) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer Software clause of DFARS
252.227-7013, for agencies of t he Department of Defense or their successors, whichever is applicable.
6. Use of Software in the European Community. This provision applies to all Software acquired for use within the
European Community. If Licensee uses the Software within a country in the European Community, the Software
Directive enacted by the Council of European Communities Directive dated 14 May, 1991, will apply to the
examination of the Software to facilitate interoperability. Licensee agrees to notify Nortel Networks of any such
intended examination of the Software an d may procure support and assistance from Nortel Networks.
7. Term and termination. This license is effective until terminated; however, all of the restrictions with respect to
Nortel Networks’ copyright in the Software and user manuals will cease being effective at the date of expiration of the
Nortel Networks copyright; those restrictions relating to use and disclosure of Nortel Networks’ confidential
information shall continue in effect. Licensee may terminate this license at any time. The license will automatically
terminate if Licensee fails to comply with any of the terms and conditions of the license. Upon termination for any
reason, Licensee will immediat ely destroy or return to Nortel Networks the Software, user manuals, and all copies.
Nortel Networks is not liable to Licensee for damages in any form solely by reason of the termination of this license.
8. Export and Re-export. Licensee agrees not to export, directly or indirectly, the Software or related technical data
or information without first obtaining any required export licenses or other governmental approvals. Without limiting
the foregoing, Licensee, on behalf of itself and its subsidiaries and affiliates, agrees that it will not, without first
obtaining all export licenses and approvals required by the U.S. Government: (i) export, re-export, transfer, or divert
any such Software or technical data, or any direct product thereof, to any country to which such exports or re-exports
are restricte d or em b argoed under Un ite d Sta t e s e xport control law s an d r egulations, or to any national or resident of
such restricted or embargoed countries; or (ii) provide the Software or related technical data or information to any
military end user or for any military end use, including the design, development, or production of any chemical,
nuclear, or biological weapons.
9. General. If any provision of this Agreement is held to be invalid or unenforceable by a court of competent
jurisdiction, the remainder of the provisions of this Agreement shall remain in full force and effect. This Agreement
will be governed by the laws of the state of California.
Should you have any questions concerning this Agreement, contact Nortel Networks, 4401 Great America Par kwa y,
P.O. Box 58185, Santa Clara, Ca lifornia 95054-8185.
LICENSEE ACKNOWLEDGES THAT LICENSEE HAS READ THIS AGREEMENT, UNDERSTANDS IT, AND
AGREES TO BE BOUND BY ITS TERMS AND CONDITIONS. LICENSEE FURTHER AGREES THAT THIS
AGREEMENT IS THE ENTIRE AND EXCLUSIVE AGREEMENT BETWEEN NORTEL NETWORKS AND
LICENSEE, WHICH SUPERSEDES ALL PRIOR ORAL AND WRITTEN AGREEMENTS AND
COMMUNICATIONS BETWEEN THE PARTIES PERTAINING TO THE SUBJECT MATTER OF THIS
AGREEMENT. NO DIFFERENT OR ADDITIONAL TERMS WILL BE ENFORCEABLE AGAINST NORTEL
NETWORKS UNLESS NORTEL NETWORKS GIVES ITS EXPRESS WRITTEN CONSENT, INCLUDING AN
EXPRESS WAIVER OF THE TERMS OF THIS AGREEMENT.
iv
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 5

Contents
Preface
Before You Begin .............................................................................................................xiii
Text Conventions .............................................................................................................xiv
Acronyms ........................... .......................... .......................... ......................... .................xvi
Hard-Copy Technical Manuals ........................................................... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....x ix
How to Get Help .............................................................................................................. xx
Chapter 1
Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
What Are Technician Interface Scripts? ..........................................................................1-2
Script Types ..............................................................................................................1-2
Script Command Categories ....................................................................................1-3
Installing .bat and .mnu Files ..........................................................................................1-5
Setting Up Scripts ...........................................................................................................1-6
Using Script Commands .................................................................................................1-8
Using the show Command .......................................................................................1-8
Using the enable and disable Commands .............................................................1-15
Using the Menu Utility ...................................................................................................1-17
Displaying Menus ...................................................................................................1-17
Configuring Menus .................................................................................................1-20
Adding a Command .........................................................................................1-21
Deleting a Command .......................................................................................1-21
Clearing All Commands ...................................................................................1-21
Editing a Command ........................ ............................................. ...... ....... .......1 -2 2
Editing a Menu Title .........................................................................................1-22
Loading a New Menu .......................................................................................1-22
Toggling Menu Titles and Commands .............................................................1-23
Saving Changes Made to Menus ....................... ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... .1-2 7
308658-14.00 Rev 00
v
Page 6

Chapter 2
Using the show Command
show ahb ........................................................................................................................2-2
show appn ......................................................................................................................2-6
show at .........................................................................................................................2-50
show atm ......................................................................................................................2-66
show atmarp .................................................................................................................2-76
show atmdxi ..................................................................................................................2-84
show atmsig ..................................................................................................................2-94
show atm line ................................................................................................................2-99
show aurp ...................................................................................................................2-111
show autoneg .............................................................................................................2-120
show bgp ....................................................................................................................2-127
show bisync ................................................................................................................2-136
show bootp .................................................................................................................2-146
show bot .....................................................................................................................2-151
show bridge ................................................................................................................2-158
show circuits ...............................................................................................................2-164
show console ..............................................................................................................2-175
show csmacd ..............................................................................................................2-182
show dcm ...................................................................................................................2-195
show decnet ...............................................................................................................2-200
show dls ......................................................................................................................2-214
show ds1e1 ................................................................................................................2-226
show dsx3 ...................................................................................................................2-251
show dvmrp ................................................................................................................2-266
show e1 ......................................................................................................................2-275
show egp ....................................................................................................................2-281
show fddi ....................................................................................................................2-284
show fr ........................................................................................................................2-300
show ftp ......................................................................................................................2-318
show fwall ...................................................................................................................2-319
show hardware ...........................................................................................................2-321
show hifn ....................................................................................................................2-328
show hssi ....................................................................................................................2-331
vi
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 7

show igmp ..................................................................................................................2-339
show ip .......................................................................................................................2-343
show ip6 .....................................................................................................................2-370
show ipx ......................................................................................................................2-377
show iredund ..............................................................................................................2-411
show isdn ....................................................................................................................2-413
show isdn bri ...............................................................................................................2-424
show l2tp ....................................................................................................................2-432
show lane ...................................................................................................................2-435
show lapb ...................................................................................................................2-445
show lnm ....................................................................................................................2-451
show mospf ................................................................................................................2-462
show mpoa .................................................................................................................2-466
show nbip ...................................................................................................................2-469
show nhrp ...................................................................................................................2-471
show nml ....................................................................................................................2-478
show ntp .....................................................................................................................2-482
show osi ......................................................................................................................2-486
show ospf ...................................................................................................................2-495
show packet ................................................................................................................2-504
show ping ...................................................................................................................2-513
show ppp ....................................................................................................................2-517
show process ..............................................................................................................2-547
show protopri ..............................................................................................................2-552
show radius .................................................................................................................2-555
show rarp ....................................................................................................................2-562
show rip6 ....................................................................................................................2-565
show rptr .....................................................................................................................2-567
show rredund ..............................................................................................................2-576
show rsc .....................................................................................................................2-584
show rsvp ...................................................................................................................2-588
show sdlc ....................................................................................................................2-590
show smds ..................................................................................................................2-594
show snmp .................................................................................................................2-599
show span ..................................................................................................................2-607
308658-14.00 Rev 00
vii
Page 8

show sr .......................................................................................................................2-615
show srspan ...............................................................................................................2-628
show sta .....................................................................................................................2-635
show stac ....................................................................................................................2-638
show state ..................................................................................................................2-640
show sws ....................................................................................................................2-643
show sync ...................................................................................................................2-662
show system ...............................................................................................................2-681
show t1 .......................................................................................................................2-686
show tcp .....................................................................................................................2-694
show telnet .................................................................................................................2-697
show tftp .....................................................................................................................2-699
show token ..................................................................................................................2-700
show vines ..................................................................................................................2-712
show wcp ....................................................................................................................2-723
show wep ....................................................................................................................2-731
show x25 ...................................................................................................................2-737
show xb ......................................................................................................................2-748
show xns .....................................................................................................................2-758
Chapter 3
Using enable/disable Commands
enable/disable appn ........................................................................................................3-2
enable/disable at .............................................................................................................3-5
enable/disable atm ..........................................................................................................3-6
enable/disable atmdxi .....................................................................................................3-8
enable/disable aurp ........................................................................................................3-9
enable/disable autoneg .................................................................................................3-10
enable/disable bootp .....................................................................................................3-11
enable/disable bridge ....................................................................................................3-12
enable/disable circuits ..................................................................................................3-13
enable/disable csmacd .................................................................................................3-14
enable/disable dcm .......................................................................................................3-15
enable/disable decnet ...................................................................................................3-17
enable/disable dls .........................................................................................................3-18
enable/disable ds1e1 ....................................................................................................3-19
viii
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 9

enable/disable dvmrp ...................................................................................................3-20
enable/disable e1 ..........................................................................................................3-21
enable/disable fddi ........................................................................................................3-22
enable/disable fr ...........................................................................................................3-23
enable/disable ftp ..........................................................................................................3-24
enable/disable hssi .......................................................................................................3-25
enable/disable igmp ......................................................................................................3-26
enable/disable ip ...........................................................................................................3-27
enable/disable ipx .........................................................................................................3-28
enable/disable iredund ..................................................................................................3-29
enable/disable isdn .......................................................................................................3-30
enable/disable isdn bri ..................................................................................................3-32
enable/disable lapb .......................................................................................................3-33
enable/disable lnm ........................................................................................................3-34
enable/disable nbip .......................................................................................................3-35
enable/disable nml ........................................................................................................3-36
enable/disable osi .........................................................................................................3-37
enable/disable ospf .......................................................................................................3-38
enable/disable packet ...................................................................................................3-39
enable/disable ppp ........................................................................................................3-40
enable/disable rarp .......................................................................................................3-41
enable/disable rptr ........................................................................................................3-42
enable/disable rredund .................................................................................................3-43
enable/disable sdlc .......................................................................................................3-44
disable/enable snmp .....................................................................................................3-45
enable/disable span ......................................................................................................3-46
enable/disable sr ...........................................................................................................3-47
enable/disable srspan ...................................................................................................3-48
enable/disable sta .........................................................................................................3-49
enable/disable sws .......................................................................................................3-50
enable/disable sync ......................................................................................................3-51
enable/disable t1 ...........................................................................................................3-52
enable/disable tcp .........................................................................................................3-53
enable/disable telnet .....................................................................................................3-54
enable/disable tftp .........................................................................................................3-55
308658-14.00 Rev 00
ix
Page 10

enable/disable token .....................................................................................................3-56
enable/disable vines .....................................................................................................3-57
enable/disable wcp .......................................................................................................3-58
enable/disable x25 ........................................................................................................3-59
enable/disable xb ..........................................................................................................3-60
enable/disable xns ........................................................................................................3-61
Index
x
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 11

Tables
Table 1-1. Displaying Service Information ................................................................1-9
Table 1-2. Enabling and Disabling Services ...........................................................1-15
308658-14.00 Rev 00
xi
Page 12

Page 13

Preface
This guide describe s ho w to use Technician Interface sc ripts (
display statistical and configuration information about Nortel Networks
Before You Begin
Before using this guide to issue Technician Interface
complete the following procedures:
• Install the hardware pla tform.
• Use one of the following methods to establish a connection to the platform:
-- Connect the serial port of an ASCII terminal device (for example, a DEC
VT100) directly to the console port of the platform.
-- Connect the serial port of a workstat io n or PC di rectly to the console port
of the platform. (Run ASCII terminal emulation software on the
workstation or PC.)
-- Dial in to the console port of the platform from a workstation or PC
running ASCII terminal emul at ion software. This al ternativ e requires one
modem locally attached to your workst ati on or PC, and another modem
locally attached to the console port of the platform you want to access.
-- Establish a Telnet (in-band) connection to the platform.
show
commands) to
show
commands, you must
™
routers.
Note:
platform must ha v e at lea st one assi gned IP addres s. Althou gh there is no limi t
to the number of Telnet connections that you can make to the Technician
Interface, we recommend that you establish no more than one Telnet session
per platform.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Before you can access the Technician Interface using Telnet, the
xiii
Page 14

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Text Conventions
This guide uses the following text conventions:
angle brackets (< >) Indicate that you choose the text to enter based on the
description inside the brackets. Do not type the
brackets when entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is:
ping
<
ip_address
ping 192.32.10.12
>, you enter:
bold text
Indicates command names and options and text that
you need to enter.
Example: Enter
show ip {alerts | routes
Example: Use the
dinfo
command.
}.
braces ({}) Indicate required elements in syntax descriptions
where there is more than one option. You must choose
only one of the options. Do not type the braces when
entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is:
show ip {alerts | routes
show ip alerts or show ip routes
}
, you must enter either:
, but not both.
brackets ([ ]) Indicate optional elements in syntax descriptions. Do
not type the brackets when entering the command.
Example: If the command syntax is:
show ip interfaces [-alerts
show ip interfaces
or
]
, you can enter either:
show ip interfaces -alerts
.
ellipsis points (. . . ) Indicate that you repeat the last element of the
command as needed.
xiv
Example: If the command syntax is:
ethernet/2/1
ethernet/2/1
[<
parameter> <value
>]
and as many parameter-value pairs as
needed.
. . .
, you enter
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 15

Preface
italic text Indicates file and directory names, new terms, book
titles, and variables in command syntax descriptions.
Where a variable is two or mor e words, the words are
connected by an underscore.
Example: If the command syntax is:
show at <
valid_route
valid_route
>
is one variable and you substitute one value
for it.
screen text Indicates system output, for example, prompts and
system messages.
Example:
Set Trap Monitor Filters
separator ( > ) Shows menu paths.
Example: Protocols > I P ide nti fies the I P opt ion on the
Protocols menu.
vertical line (
) Separates choices for command keywords and
|
arguments. Enter only one of the choices. Do not type
the vertical line when enteri ng the command.
Example: If the command syntax is:
show ip {alerts | routes}, you enter either:
show ip alerts or show ip routes, but not both.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
xv
Page 16

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Acronyms
AN Access Node
ANH Access Node Hub
APING APPN Ping
APPN Advanced Peer-to-Peer Routing
ARP Address Resolution Protocol
ASCII American Stand ard Code for In formation Inte rchange
ASN Access Stack Node
ASN.1 Abstract Syntax Notation
AT AppleTalk Protocol
ATM Asynchronous Transfer Mode
AURP Appletalk Update-based Routing Protocol
BCN Backbone Concentrator Node
BGP Border Gateway Protocol
xvi
BLN Backbone Link Node
BLN-2 Backbone Link Node (2 power supplies)
BOOTP Bootstrap Protocol
CLNP Connectionless Network Protocol
CPU Centr al Processing Unit
CRC Cyclic Redundancy Check
CSMA/CD Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection
DCM Data Collection Module
DLCMI Data Link Control Management Interface
DLSw Data Link Switch
DOS Disk Operating System
DRAM Dynamic RAM
DSAP Destination Service Access Point
DVMRP Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 17

Preface
EOF End of File
EGP Exterior Gateway Protocol
FAT File Allocation Table
FDDI Fiber Distributed Data Interface
FIFO First In First Out
FRSW Frame Relay Switch
FTP File Transfer Protocol
FR Frame Relay
FRE Fast Routing Engine
GAME Gate Access Management Entity
GMT Greenwich Mean Time
HDLC High-level Data Link Control
HSSI High Speed Serial Interface
ICMP Internet Con trol Message Proto col
IGMP Internet Group Membership Protocol
IN Integrated N ode
IP Internet P rotocol
IP6 Internet Protocol version 6
IPX Internet Packet Exchange
ISDN Integrated Services Digital Network
LAN Local Area Network
LAPB Link Access Procedure Balanced
LED Light Emitting Diode
LLC Logical Link Control
LMI Local Management Interface
LNM LAN Network Manager
LSP Link State Packet
MAC Media Access Control
MCT1 Multichannel T1
308658-14.00 Rev 00
xvii
Page 18

Using Technician Interface Scripts
MIB Management Information Base
MOSY Managed Object Syntax
NML Native Mode LAN
NSAP Network Service Access Point
NVFS Non-Volatile File System
OSI Open Systems Interconnection
OSPF Open Shortest Path First
PCMCIA Personal Computer Memory Card International
PPP Point-to-Point Protocol
PPX Parallel Packet Express
PROM Programmable Read-Only Memory
QENET Quad Ethernet
RAM Random Access Memory
RARP Reverse Address Resolution Protocol
Association
xviii
RIP Routing Information Protocol
RIP6 Routing Information Protocol version 6
RIF Routing Information Field
RFC Request for Comment
SAP Service Access Point
SDLC Synchronous Data Link Control
SIMM Single In-line Memory Module
SMDS S witched Multimegabit Data Serv ices
SNAP SubNetwork Access Protocol
SNMP Simple Network Management Protocol
SR Sour ce Rout ing
SRM-L System Resources Link Module
STA Statistics, Thresholds, and Alarms
SYSCON System Controller board
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 19

SWS Switched Services
TCP Transport Control Protocol
TFTP Trivial File Transfer Protocol
TIP Terminal Interface Program
TP Transaction Program
VC Virtual Circuit
VINES Virtual Networking System
WAN Wide Area Network
XB Translation Bridge
XNS Xerox Networking Systems
Hard-Copy Technical Manuals
You can print selected technical manuals and release notes free, directly from the
Internet. Go to support.baynetworks.com/library/tpubs/. Find the product for
which you need documentation. Then locate the specific category and model or
version for your hardw are or soft ware product . Usi ng Adobe Ac robat Re ader, you
can open the manuals and releas e notes, search for the sections you ne ed, and print
them on most standard printers. You can download Acrobat Reader free from the
Adobe Systems Web site, www.adobe.com.
Preface
You can purchase selected documentation sets, CDs, and technical publications
through the collateral catalog. The catalog is located on the World Wide Web at
support.baynetworks.com/catalog.html and is divided into sections arranged
alphabetically:
• The “CD ROMs” section lists available CDs.
• The “Guides/Books” section lists books on technical topics.
• The “Technical Manuals” section lists available printed documentation sets.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
xix
Page 20
Using Technician Interface Scripts
How to Get Help
If you purchased a service contract for your Nortel Networks product from a
distributor or authorized reseller, contact the technical support staff for that
distributor or reseller for assistance.
If you purchased a Nort el Net wor ks s ervice pr ogram, c ontact one of the f ollowing
Nortel Networks Technical Solutions Centers:
Technical Solutions Center Telephone Number
Billerica, MA 800-2LANWAN (800-252-6926)
Santa Clara, CA 800-2LANWAN (800-252-6926)
Valbonne, France 33-4-92-96-69-68
Sydney, Australia 61-2-9927-8800
Tokyo, Japan 81-3-5402-7041
xx
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 21

Chapter 1
Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
This chapter pro vides an o ve rvie w of the Technic ian Interf ac e scripts and explai ns
how to run them. It also describes how to:
• Load scripts.
• Set up scrip ts.
• Use script commands.
• Use the menu utility.
This guide assumes that you have a working knowledge of the Nortel Networks
Technician Interface. For complete information about this router management
tool, see Using Technician Interface Software. For information on how to write
your own Technician Interface scripts, see Writing Technician Interface Scripts.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-1
Page 22

Using Technician Interface Scripts
What Are Technician Interf ace Scripts?
Script Types
The Technicia n I nterf ac e
show/monitor
enable/disable
and
scripts are programs
that enable you to view and use information stored in the Nortel Networks
Management Information Base (MIB). You use scripts to display statistical and
configuration information about various router services, and to enable or disable
those services.
Most Technician Interface scripts run from a <protocol_name>.bat (batch) file.
The system loads a specific .bat file into active memory when you enter a scripts
command such as
show appn directory statistics
. The system software supp orts
one .bat file for each router protoc ol or service. Each .bat f ile c ontains t he routi nes
for all script subcommand options for a protoc ol or ser vi ce. The rout i ne cal led by
each subcommand genera tes and pri nts (to the router cons ole) stat istics that re v eal
a particular view of that protocol or service.
As an alternative to entering
show/enable/disable
commands at the Technician
Interface prompt, you can also access protocol-specific menus from the scripts
main menu. You enter (choose by number) a protocol/service submenu from the
scripts main menu. From a submenu, you can access all scripts options for a
protocol or service without entering commands. All scripts menus exist as *.mnu
files you install during initial configuration of each router. To save file space,
install only the .bat and .mnu files that pertain to the protocols or services you
want to support on each router.
1-2
Other Technician Interface scripts are programs embedded within the router
software image. The router software currently includes embedded scripts for the
following services:
• CSMACD • SNMP
• FR • SYNC
• FTP • TCP
• IP • TELNET
• MOSPF • TFTP
•RIP
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 23

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
These scripts run more efficiently than their batch file counterparts. You enter at
the Technician Interface prompt the command for any script, regardless of type
(batch or embedded) in the same way, as follows:
{show|enable|disable} {
Script Command Categories
The system so ftware supports scripts in the following command categories:
show
monitor
enable/disable
menu
Displays configuration, state, and statistical information
about a router service. This command helps you isolate
problems such as circuits that are not working, packets that
are not being forwarded, and so on. It uses the show.bat file.
Displays the same information as the show command but
refreshes the display periodically so you can observe trends
and changes. Since you can use
this manual does not describe syntax for the
command. This command uses the monitor.bat file.
Enables or disables system features, protocols, drivers, or
individual circuits. These commands use the enable.bat and
disable.bat files.
Provides a menu interface to the scripts. Also provides a
menu-building feature that enables you to create custom
menus. This command uses menu.bat and various .mnu files.
<protocol_name>
} {
<subcommand_option>
monitor in place of show,
}
monitor
Each
configuration information about a particular service or driver running on the
router.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
show command supports a subset of commands that display statistical and
1-3
Page 24
Using Technician Interface Scripts
Some show commands present a broad or collective view of router status and
resources. For example,
show circuits
Displays information about all drivers running on the
router. You can use this command to display information
about all circuits without needing to know the driver that
runs on each circuit.
show drivers
Displays information about the configuration of all link
modules in the router.
show hardware
Displays backplane, configuration file, image, memory,
PROM, and slot information about the router’s hardware.
show protocols
Displays information about the protocols configured on
every slot in the router.
show state
Displays information about the current state of services
running on the router.
show system
Displays information abou t router memory , b uff ers, driv ers,
and configured protocols.
Note:
You can abbreviate command names, using the first three characters of
the command name, as long as the abbreviation uniquely identifies the
command.
1-4
To establish the search path used to find the script files, use the
run setpath
command. It define s the aliases that integrate scripts in to the Technician Interface
command se t. The sectio n “Setting Up Scripts” explains the
run setpath
command, which uses the setpath.bat script.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 25

Installing .bat and .mnu Files
You can use the Nortel Networks implementation of File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
to install .bat version scripts and .mnu script menu files on a memory card in the
router. FTP enables you to install more than one script at a time.
Before installing any scripts on a router:
• Log in to the router. (Refer to Chapter 1 of Using Technician Interface
Software if you need more information on login procedures.)
• Enable the FTP service on the router.
dir
•Run the
on the NVFS volume reserved for scripts and their associated menu files.
(Refer to Chapter 4 of Using Technician Interface Software if you need more
information on how to run the
command to verify that you have sufficient contiguous freespace
dir
command.)
Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
•Run the
compact
command on the NVFS volume reserved for scripts and
their associated me nu files. (Refer t o Cha pter 8 of Using Technician Interfac e
Softwar e if you need more information on how to run the
compact
command.)
To install all the .bat scripts and .mnu menu files located in a direct ory on a UNIX
workstation, change to that directory using the
cd
command. Then enter the
following commands at the UNIX command line prompt:
ftp
$:
<router IP address>
Manager
Name:
Password:
ftp>
ftp>
ftp>
ftp>
ftp>
<Technician_Interface_password>
cd
<router volume>
bin
prompt
mput *.bat
mput *.mnu
:
The
each file.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
prompt
command disables t he pr ompt that asks whether you w ant to transfer
1-5
Page 26
Using Technician Interface Scripts
Note:
You must have Manager access to write to an NVFS volume using the
Nortel Networks implementation of FTP.
This procedure inst alls al l of th e . bat and .mnu files on a file system volume in the
router. To conserve space on a router’s local file system, load only scripts for the
protocols and drivers you need to run on that router.
If you want to use the Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) to install .bat and
.mnu files one at a time, refer to Chapters 4 and 5 of Using Technician Interface
Software.
Setting Up Scripts
Once you log in to a Technician Interface session on a router, you can enter any
embedded script commands at the command line prompt without any additional
preparations. Ho wever, before you run an y . bat ver sion scri pts, des ignate a def ault
file system volume, as shown in the following example:
1-6
dir 2:
Next, define the search path and alias definitions for your .bat and .mnu version
script f iles b y usin g t he
run setpath
command. The search path is a li st of v o lume
IDs you want the system to search for any script file. There are two ways to
specify a search path, as shown in the following examples.
Example 1 -- Ente ring the volume IDs on the command line
run setpath "2:;3:;4:"
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 27

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
Example 2 -- Letting the
run setpath
NVFS File System:
VOL STATE TOTAL SIZE FREE SPACE CONTIG FREE SPACE
-----------------------------------------------------------------3: FORMATTED 2097152 1218683 1017067
2: FORMATTED 2097152 431128 431128
Please enter the volume ID that contains the script files.
More than one volume may be entered; each separated by a
semi-colon.
Format: <vol>:[;<vol>: ...]
Example: 2:;3:;4:
Enter volume(s)[2:]:
setpath
3:
command prompt you for input
You can also use the Manager or User autoscript features to automatically run the
setpath.bat script (the
run setpath command). Specify a file system search path,
Manager or User script file, and logout mechanism using following
wfSerialPortEntry (router serial port) attributes:
• Login Script Search Path
• Manager’s Login Script
• User’s Login Script
• Force User Logout
You can set up separate Manager and User autoscript files for login. The User
autoscript contains a switch that enables you to lock the user into the script. With
the switch enabled, the autoscript automatically logs out a user that tries to break
out of the script. For more i nformation on the autoscript feature, see Chapter 2 of
Using Technician Interface Software.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-7
Page 28

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Using Script Commands
This section provides an overview of the
commands.
Using the show Command
After you set up scripts with the
<subcommand> <option> command to obtain a snapshot view of various data
stored in the router. For continuously updated (polled) views of system statistical
and configurat ion data, use th e
For all protocols, you can view circuit alerts, the base record, disabled or enabled
circuits, and statistics.
Table 1-1
lists the
software entity. Alternatively, obtain an active list of
subcommands directly from the router by entering at the Technician Interface
prompt
show
<entity_name>
or:
show
<entity_name>
For example, to list the AppleTalk subcommands, enter
For a detailed description of all
they generate, refer to Chapte r 2 .
show/monitor
?
help
run setpath
monitor
command in place of the
show/monitor
command, you can use the
enable/disable
and
show
subcommands for a specific service or
show/monitor
show at
show
commands and samples of the information
or
show
command.
show at ?
.
1-8
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 29
Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
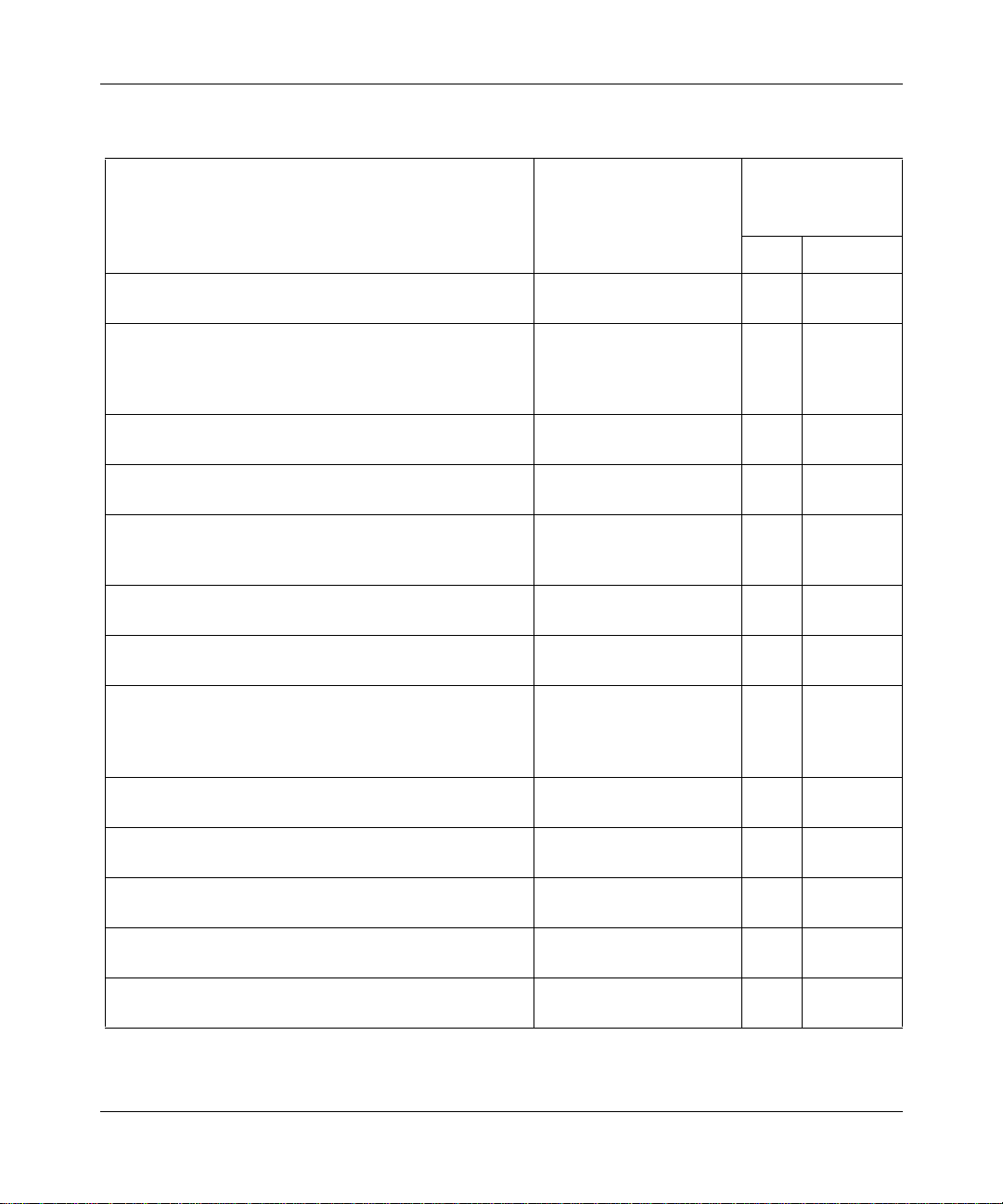
Table 1-1. Displaying Service Information
To Display Information about This Service Use This Command
Command Type
(runs from a batch
or embedded file)
batch embedded
Asynchronous Transfer Mode Half-Bridge (AHB) service
(base, circuits, hosts, routes, statistics)
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking service
(adjacencies, class of service, directories, DLC, DLUR,
endpoints, ISR, memory, mode, ports, topology, tunnels,
VRN)
AppleTalk service (AARP, circuits, configuration, routes,
statistics, zones, zone filters)
Asynchronous Transfer Mode service (interfaces, lines,
PVCs, statistics)
ATM Address Resolution Protocol service (ATMARP
client/server mode identification, ATM addresses,
interface sta tis tic s)
Asynchronous Transfer Mode DXI service (lines, PVCs,
statistics)
ATM line signaling service (ATM ILMI and SAAL
statistics)
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Adaption Layer
Controller (ALC) link module service (circuits, phy,
transmit and receive errors, transmit and receive
statistics)
AppleTalk Update-based Routing Protocol service
(connection, statistics, zone filters)
Automatic line sp eed negot iation on 100Base-T Ethernet
interfaces (alerts, circuits enabled/disabled)
Border Gateway Protocol service (errors, peers, routes,
timers, statistics, summary, weights, version)
Binary Synchronous service (errors, sample periods,
circuit statistics)
Bootstrap Protocol service (clients, relay agents,
statistics)
show ahb
show appn
show at
show atm
show atmarp
show atmdxi
show atmsig
show atm line
show aurp
show autoneg
show bgp
show bisync
show bootp
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
(continued)
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-9
Page 30
Using Technician Interface Scripts
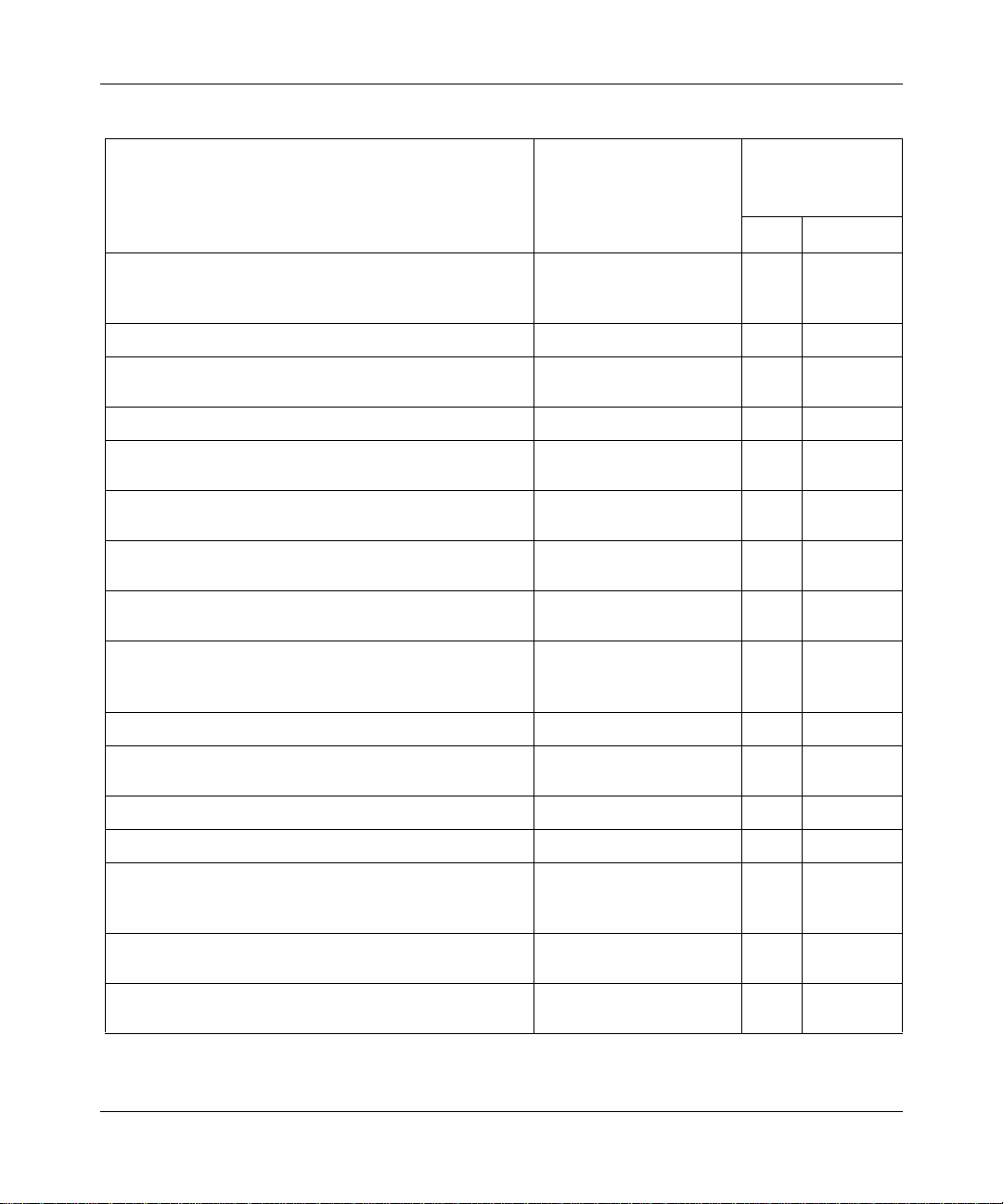
Table 1-1. Displaying Service Information
To Display Information about This Service Use This Command
Binary Synchronous Communication (BSC) over TCP
service (circuit, port, peer, and control unit connection
statistics)
Bridge service (circuits, forwarding tables, statistics)
Circuits for all drivers (configuration; hardware filters;
receive, transmit, and system errors; statistics)
Console (configuration, statistics)
CSMA/CD service (hardware filters; receive, transmit
and system errors; statistics; sample data)
N11 Data Collection Module (DCM) information for the
8-Port Access Node Hub (ANH)
DECnet service (adjacency, circuits, designated router,
routes, statistics, traffic filters)
Data Link Switching service (circuits, configuration,
connections, MAC, NETBIOS, peer, SAPs, slot numbers)
DS1/E1 lines (clock, E1 framer and E1 port, FDL;
receive, transmit, and system errors; sample data;
statistics; T1 framer and T1 port; timeslots)
DS3/E3 lines (circuit stats for ATM interfaces)
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol service
(circuits, neighbors, routes, statistics, tunnels)
E1 lines (frame and line errors)
Exterior Gateway Protocol service (neighbors, statistics)
Fiber Distributed Dat a Interf ace s ervice (hardware filters;
MAC, port, and SMT parameters; receive, transmit, and
system errors; sample data; statistics)
Frame Relay service (LAPF, lines, passthrough, PVCs,
signalling, statistics, SVCs, virtual connections)
File Transfer Protocol service (login, error, and transfer
rate statistics)
(continued)
show bot
show bridge
show circuits
show console
show csmacd
show dcm
show decnet
show dls
show ds1e1
show dsx3
show dvmrp
show e1
show egp
show fddi
show fr
show ftp
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
Command Type
(runs from a batch
or embedded file)
batch embedded
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
(continued)
1-10
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 31

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
Table 1-1. Displaying Service Information
To Display Information about This Service Use This Command
BaySecure Firewall-1 service (interface, summary)
Hi/fn LZS compression (errors, statistics)
Hardware options (backplane, configuration and router
software image files, memory, PROMs, slots)
High Speed Serial Interface service (receive, transmit,
and system errors; sample data; statistics)
Internet Gatewa y Man agement Pr otocol service (circui ts,
groups, statistics)
Internet Protocol service (ARP table, circuits, forwarding
table, route filters, RIP interfaces, routes, traffic filters)
Internet Protocol Version 6 service (adjacent hosts,
statistics, interface, circuits)
Internet Packet Exchange service (adjacent hosts,
circuits, ping, RIP, routes, service filters, server filters,
servic es, statistics, traffic filters)
Circuit and state information for all interface redundancy
ports (enabled and disabled circuits configured with
interface redu nda nc y)
Integrated Services Digital Network service
(B Channel, BRI, calls, inphone, messages, switch)
Integrated Services Digital Network BRI service (receiv e,
transmit, and system errors; sample data; statistics)
Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) (configuration,
sessions, statistics, tunnels, users)
LAN Emulation (ATM) service (clients, servers, config,
learp, mac addresses, statistics)
Link Access Procedure-Balanced service (lines,
statistics)
LAN Network Manager server agent information (for all
servers, or for servers on specific circuits)
OSPF multicast extensions (MOSPF) (base, interfaces,
neighbors, forwarding database)
(continued)
show fwall
show hifn
show hardware
show hssi
show igmp
show ip
show ip6
show ipx
show iredund
show isdn
show isdn bri
show l2tp
show lane
show lapb
show lnm
show mospf
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
Command Type
(runs from a batch
or embedded file)
batch embedded
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
(continued)
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-11
Page 32

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Table 1-1. Displaying Service Information
To Display Information about This Service Use This Command
Multiple Protocol Over ATM (MPOA) (cache, clients,
servers, versi on)
NetBIOS over IP service (interfaces, names)
Next Hop Routing Protocol (NHRP) (cache, circuits,
clients, servers, statistics )
Native Mode LAN service (circuits, security lists, bridge
statistics)
Open Systems Interconnection service (adjacency,
circuits, routes, and TARP packets, loop detection buffer
entries, and data cache)
Open Shortest Path First Protocol service (area, AS
base, external routes, interfaces, LSDB, neighbors,
statistics)
Pac ke t Capture service (capture d pac kets , confi guratio n,
line numbers, loaded slots, status)
Ping MIB service (configuration, history, source and
trace routes)
Point-to-Point Protocol service (AppleTalk, bad packets,
Bridge, CCP, CHAP, circuits, DECnet, IP, IPX, line, LQR,
OSI, PAP, protocol, VINES, XNS)
Process statistics (buffers, cpu cycles, and memory
resources allocated to ro uter processes)
DLSw protocol prioritization queues (cc_stats, filters,
qstats)
RADIUS (ale rts, server, configuration, statistics)
Revers e Addres s Resolut ion Protocol service (circuits)
RIP Version 6 service (configuration, statistics)
Repeater service (last address , sam ple data, po rt status,
statistics)
Router redundancy (circuits, groups, resources, remote
routers in a redundancy group, member IDs)
(continued)
show mpoa
show nbip
show nhrp
show nml
show osi
show ospf
show packet
show ping
show ppp
show process
show protopri
show radius
show rarp
show rip6
show rptr
show rredund
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
Command Type
(runs from a batch
or embedded file)
batch embedded
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
(continued)
1-12
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 33

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
Table 1-1. Displaying Service Information
To Display Information about This Service Use This Command
Resources (bandwidth) reserved for lines configured with
the ST2 protocol
Resource Re servation P rotocol (RSVP) multicasting and
multimedia service (base, interfaces)
Synchronous Data Link Control service (circuits,
statistics)
Switched Mu lti-Megabit Data Service serv ice
(addresses, circuits, statistics)
Simple Network Management Protocol service
(communities, events, traps)
Spanning Tree service (configuration, circuits)
Source Routing service (bridges, circuits, configuration,
IP information, statistics, traffic filters)
Source Route Spanning Tree service (configuration,
statistics)
Statistical Threshol ds and Alarms service (configur ation,
statistics)
STAC (circuit and statistical information about Hi/fn LZS
data compression service)
State (overview of all protocols or one circuit)
Switch service (back-up dialing , on-demand- dialing)
Synchronous Interface service (receive, transmit, and
system errors; FT1/T1 DSU/CSU configuration and
statistics; sample data; statistics)
System (buffers, drivers, memory, protocols, system
information, tasks)
T1 lines (frame and line errors)
Transport Control Protocol service (configuration,
connections, statistics)
TELNET service (configuration, sessions, statistics)
(continued)
show rsc
show rsvp
show sdlc
show smds
show snmp
show span
show sr
show srspan
show sta
show stac
show state
show sws
show sync
show system
show t1
show tcp
show telnet
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
Command Type
(runs from a batch
or embedded file)
batch embedded
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
(continued)
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-13
Page 34

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Table 1-1. Displaying Service Information
To Display Information about This Service Use This Command
Trivial File Transfer Protocol service (status)
Token Ring lines (receive, transmit, and system errors;
sample data; statistics)
VINES service (circuits, config uration , neighbors , routes ,
statistics, traffic filters)
Nort el Networks Compression Protocol service (circuits,
devices, lines, statis tics, virtual circuits)
Nortel Networks WAN Encryption Protocol service
(circuits, lines, virtual circuits, statistics)
X.25 service (configurat ion , c onn ec tions, lines, services,
statistics, virtual circuits)
Translation Bridge service (configuration, RIFs, SAPs,
Source Routing interfaces and statistics, stations,
Transparent Bridge interfaces and statistics)
Xerox Networking Systems Protocol service (adjacent
hosts, configuration, RIP, routes, statistics, traffic filters,
virtual circuits)
(continued)
show tftp
show token
show vines
show wcp
show wep
show x25
show xb
show xns
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
Command Type
(runs from a batch
or embedded file)
batch embedded
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
✔
1-14
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 35

Using the enable and disable Commands
Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
After you set up sc ript s with the
specific protocols or services with the
Table 1-2
a detailed description of
lists the protocols or services you can enable or disable in this way. For
enable/disable
run setpath
enable
command options, refer to Chap ter 3 .
command, you can enab le or disa ble
disable
and
script commands.
Table 1-2. Enabling and Disabling Services
To Enable or Disable This Service Use This Command
Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking Protocol (directory, DLC, LS,
port, tunnel, VRN)
AppleTalk (base, circuit)
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (line)
Asynchronous Transfer Mode DXI (line)
AppleTalk Update-based Routing Protocol (connection)
Automatic line speed negotiation on 100Base-T Ethernet interfaces
Bootstrap protocol
Bridge (base, circuit)
Circuits for all drivers
CSMA/CD (circuit, connector)
Data Collection Module (DCM) for BayStack routers
DECnet (base, circuit)
Data Link (base, circuit)
DS1E1 lines
Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (base, circuit)
E1 line (circuit, connector)
FDDI (circuit, connector)
Frame Relay (line)
File Transfer Protocol (base)
HSSI (circuit, connector)
Internet Gateway Management Protocol (base, circuit)
Internet Protocol (base, circuit, RIP)
Internet Packet Exchange Protocol (base, circuit)
enable/disable appn
enable/disable at
enable/disable atm
enable/disable atmd xi
enable/disable aurp
enable/disable autoneg
enable/disable bootp
enable/disable bridge
enable/disable circuits
enable/disable csm acd
enable/disable dcm
enable/disable dec net
enable/disable dls
enable/disable ds1 e1
enable/disable dvmrp
enable/disable e1
enable/disable fddi
enable/disable fr
enable/disable ftp
enable/disable hss i
enable/disable igmp
enable/disable ip
enable/disable ipx
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
(continued)
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-15
Page 36

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Table 1-2. Enabling and Disabling Services
To Enable or Disable This Service Use This Command
Interface redundancy ports
Integrated Services Digital Network (B Channel, Bri, Filter)
Integrated Services Digital Network BRI (circuit, connector)
Link Access Procedure-Balanced (line.llindex)
LAN Network Manager (base, circuit)
NetBIOS over IP (base, interface)
Native Mode LAN (circuit, security list)
Open Systems Interconnect (base)
OSPF (area, base, interface)
Packet Capture (capture, line)
Point-to-Point Protocol (line)
Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (base)
Repeater (port, reset, test)
Router redundancy
Synchronous Data Link Control (base, circuit)
Simple Network Management Protocol (communities, events, traps)
Spanning Tree (base, circuit)
Source Routing (base, circuit)
Source Route Spanning Tree (base, circuit)
Statistical Thresholds and Alarm (base, object)
Switched Service
Synchronous line (circuit, connector)
T1 line (circuit, connector)
Transport Control Protocol (base)
TELNET (base)
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (base)
Token Ring line (circuit, connector)
VINES (base, circuit)
Nortel Networks Compression Protocol (circuit, line)
(continued)
enable/disable iredund
enable/disable isdn
enable/disable isdn bri
enable/disable lapb
enable/disable lnm
enable/disable nbip
enable/disable nml
enable/disable osi
enable/disable ospf
enable/disable packet
enable/disable ppp
enable/disable rarp
enable/disable rptr
enable/disable rre dund
enable/disable sdlc
disable/enable snm p
enable/disable spa n
enable/disable sr
enable/disable sr span
enable/disable sta
enable/disable s ws
enable/disable syn c
enable/disable t1
enable/disable tcp
enable/disable telnet
enable/disable tftp
enable/disable toke n
enable/disable vine s
enable/disable wcp
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
<option>
(continued)
1-16
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 37

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
Table 1-2. Enabling and Disabling Services
To Enable or Disable This Service Use This Command
X.25 (base, line, service)
Translation Bridge (base, circuit)
Xerox Networking Systems Protocol (base, circuit)
(continued)
enable/disable x25
enable/disable xb
enable/disable xns
Using the Menu Utility
You can run scripts from Technician Interface menus as an alternative to entering
commands at the Technician Interface prompt. You can also create or customize
scripts menus. Use scripts menus to access the full set of Technician Interface
scripts, including those embedded within the router software.
Displaying Menus
After you configure the
menu by entering the
main menu contains a numbered lis t of system protoc ols and serv ices, as sho wn in
the following exam ple.
run setpath
menu
command at the Technician Interface prompt. The
command, you can display the scripts main
<option>
<option>
<option>
1. APPN 24. Frame Relay Switch 47. SDLC
2. AT 25. FTP 48. SMDS
3. ATM 26. Hardware 49. SNMP
. . .
. . .
. . .
22. FDDI 45. Router Redundancy 68. X25
23. Frame Relay 46. Reservable Resources
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Main Menu
1-17
Page 38

Using Technician Interface Scripts
To display a scripts submenu for a particular protocol, enter its sequence number
from the main menu. For example, to display the IP scripts submenu, enter
the prompt under the main menu.
Enter menu number or TI command: 28
The IP menu appears:
1. Adjacent Hosts 13. IP Cache Hits Stats
2. Alerts 14. IP Datagram Stats
3. ARP Table 15. IP Fragmentation Stats
4.Base Information 16. IP RIP Filters
5. Circuits 17. IP Stats
6. Disable Circuits 18. IP .bat version
7. Enabled Circuits 19. RIP
8. ICMP Client Stats 20. Routing Table
9. ICMP In Stats 21. Security In Stats
10. ICMP Miscellaneous Stats 22. Security In Stats
11. ICMP Out Stats 23. Static Routes Table
12. ICMP Server Stats 24. Traffic Filters
28 at
IP Menu
1-18
D. Disable MORE. M. Menu control on. Q. Quit or Return
Enter menu number or TI command:
All of the choices shown in the second-level menu display information.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 39

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
Next, enter the number that corresponds to the table you want to display. For
example, to display IP statistics, enter
17. This action runs the script that displays
the IP Statistics table shown in the following example.
Enter menu number or TI command: 17
IP Statistics
-------------
In Out In Out
Circuit IP Address Receives Requests Forwards Discards Discards
------- ---------- -------- -------- -------- -------- -------E33 6.6.6.6 0 15642 0 0 0
E34 75.1.1.2 14976 15642 0 0 0
E31 192.168.130.165 46218 18459 0 0 0
3 Entries
Press Enter to continue.
When you press Enter, the menu utility returns to the submenu. In this example,
pressing Enter displays the IP menu again. Then you can perform any of the
following actions:
• Enter another option
• Return to the main menu
•Enter
• Press RETURN
You can also display a submenu by entering the name of the protocol on the
command line as an option to the menu command. For example, to display the IP
submenu directly, enter the following command at the Technician Interface
prompt:
$
308658-14.00 Rev 00
menu ip
q for Quit
1-19
Page 40

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Configuring Menus
You can change any menu that the menu utility displays. You can keep your
changes for the curr ent ses sion onl y, or you can save them pe rmanent ly. Using the
menu control feature, you can
• Change the contents of a menu (add, delete, and edit commands; edit the
menu title; show commands instead of command titles).
• Load a new menu into the menu structure.
• Enter a Technician Interface command while using the menu utility.
To use the menu control feature, enter
command:
menu, as shown in th e following example:
1. APPN 24. Frame Relay Switch 47. SDLC
2. AT 25. FTP 48. SMDS
3. ATM 26. Hardware 49. SNMP
. . .
. . .
. . .
22. FDDI 45. Router Red undancy 68. X25
23. Frame Relay 46. Reservable Resources
prompt. The menu utility displays a list of options below the main
m
at the
Main Menu
Enter menu number or TI
1-20
A. Add a command H. Change menu title Q. Quit
C. Clear all commands L. Load new menu S. Save menu commands
D. Delete command M. Menu control off T. Toggle cmd. display
E. Edit command
Enter menu number or TI command:
To turn menu control off, just enter m again at the promp t. You can add and delete
commands, edit a command, change a menu’s title, and switch the display
between menu titles and commands.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 41

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
Adding a Command
With menu control on, add a command by entering
or TI command:
prompt. Then enter the command number, name, and title, as
at the Enter menu number
a
shown in the example:
Enter menu number or TI command:
Command:
Enter new command:
Enter new title:
Setting command 69 to date
Setting title 69 to Date and Time
69
date
Date and Time
a
The main menu automatically refreshes and displays the new option (69. Date
and Time
).
Deleting a Command
With menu con trol on, delete a command b y entering
or TI command: prompt. Then enter the nu mber of the comman d to be delet ed, as
at the Enter menu number
d
shown in the example:
Enter menu number or TI command:
Enter command number (r to Return):
d
69
The main menu automaticall y refreshes and displ ays a ne w lis t of opti ons, without
command number
69
.
Clearing All Commands
With menu control on, clear all commands by entering
number or TI command: prompt . Th e me nu uti l it y r es ponds by showing only the
menu title and control options, as follows:
A. Add a command H. Change menu title Q. Quit
C. Clear all commands L. Load new menu S. Save menu commands
D. Delete command M. Menu control off T. Toggle cmd display
E. Edit Command
Enter menu number or TI command:
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Main Menu
at the Enter menu
c
1-21
Page 42

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Editing a Command
With menu control on, edit a command by entering
or TI command:
prompt. Then enter the command number, name, and title, as
at the Enter menu number
e
shown in the following example:
Enter menu number or TI command:
Enter Command number (r to Return):
2 menu at.mnu
AT
Type <return> to leave unchanged.
Enter new command:
Enter new title:
Setting command 2 to show at base
Setting title AT to AT Base
show at base
AT Base
e
2
The main menu au tomatically refr eshes and displays the new title for the
show at base
command.
Editing a Menu Title
With menu control on, edit the title for an entire menu by entering
menu number or TI command:
prompt. The follo wing e xample changes th e name
at the Enter
h
of the main menu to Protocol Statistics:
Enter menu number or TI command:
Enter new menu title:
Protocol Statistics
h
1-22
The main menu au tomatically refr eshes and displays the new menu title:
Loading a New Menu
With menu con trol on, lo ad a new menu by entering
or TI command: prompt. Then enter the name of the new menu:
Enter menu number or TI command:
Please enter menu setup file.
Type <Enter> to use default menu
[vol:filename]>
newmain.mnu
l
at the Enter menu number
l
If you do not enter a volume number or letter, the system saves the file (in this
case, newmain.mnu) to the default volume.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 43

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
Toggling Menu Titles and Commands
With menu control on, toggle between displaying menu titles and displaying
commands by entering
at the Enter menu number or TI command: prompt, as
t
shown in the example:
Enter menu number or TI command:
t
At the main menu, the screen displays the menu commands (you do not need to
enter
1. menu appn.mnu 24. menu frsw.mnu 47. menu sdlc.mnu
2. menu at.mnu 25. menu ftp.mnu 48. menu smds.mnu
3. menu atm.mnu 26. menu hardware.mnu 49. menu snmp.mnu
. . .
. . .
. . .
21. menu egp.mnu 44. menu rptr.mnu 67. menu xns.mnu
22. menu fddi.mnu 45. menu rredund.mnu 68. menu x25.mnu
23. menu fr.mnu 46. menu rsc.mnu
A. Add a command H. Change menu title Q. Quit
C. Clear all commands L. Load new menu S. Save menu commands
D. Delete command M. Menu control off T. Toggle title display
E. Edit command
when executing a
.mnu
menu
command):
Main Menu
Enter menu number or TI command:
With menu control on at the submenu level, entering t at the prompt invokes the
list of Technician Interface commands equivalent to the subcommand menu
entries.
The following example sequence of three screens shows what happens when you
enable menu control from a submenu, then toggle the submenu to display
Technician Interface commands instead of menu titles.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-23
Page 44

Using Technician Interface Scripts
PPP subcommand menu with menu control OFF/disabled:
1. Alerts 16. Line Conf
2. AppleTalk Conf. 17. Line Parameters
3. AppleTalk Neg. 18. LQR Conf.
4. Bad Packets 19. LQR Stats
5. Bridge Conf. 20. OSI
6. Bridge Neg. 21. PAP Local
7. Circuits 22. PAP Remote
8. DECnet 23. CHAP Local
9. Disabled Circuits 24. CHAP Remote
10. Enabled Circuits 25. PPP .bat version
11. IP 26. Vines
12. IPX Config. 27. XNS
13. IPX Neg. 28. Multilink Circuits
14. IPX Name Local 29. Multilink Information
15. IPX Name Remote 30. WCP
PPP Menu
1-24
D. Disable MORE M. Menu control on. Q. Quit or Return
Enter menu number or TI command: m
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 45

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
PPP subcommand menu with menu control ON/enabled:
PPP Menu
1. Alerts 16. Line Conf
2. AppleTalk Conf. 17. Line Parameters
3. AppleTalk Neg. 18. LQR Conf.
4. Bad Packets 19. LQR Stats
5. Bridge Conf. 20. OSI
6. Bridge Neg. 21. PAP Local
7. Circuits 22. PAP Remote
8. DECnet 23. CHAP Local
9. Disabled Circuits 24. CHAP Remote
10. Enabled Circuits 25. PPP .bat version
11. IP 26. Vines
12. IPX Config. 27. XNS
13. IPX Neg. 28. Multilink Circuits
14. IPX Name Local 29. Multilink Information
15. IPX Name Remote 30. WCP
A. Add a command H. Change menu title Q. Quit
C. Clear all commands L. Load new menu S. Save menu commands
D. Delete command M. Menu control off T. Toggle cmd display
E. Edit command
Enter menu number or TI command: t
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-25
Page 46

Using Technician Interface Scripts
PPP subcommand menu toggled to display only show commands:
1. show ppp alerts 16. show ppp line configuration
2. show ppp appletalk configured 17. show ppp line parameters
3. show ppp appletalk negotiated 18. show ppp lqr configured
4. show ppp bad packets 19. show ppp lqr stats
5. show ppp bridge configured 20. show ppp osi
6. show ppp bridge negotiated 21. show ppp pap local
7. show ppp circuit 22. show ppp pap remote
8. show ppp decnet 23. show ppp chap local
9. show ppp disabled 24. show ppp chap remote
10. show ppp enabled 25. show ppp version
11. show ppp ip 26. show ppp vines
12. show ppp ipx configured 27. show ppp xns
13. show ppp ipx negotiated 28. show ppp multilink circuits
14. show ppp ipx name local 29. show ppp multilink information
15. show ppp ipx name remote 30. show ppp wcp
PPP Menu
1-26
A. Add a command H. Change menu title Q. Quit
C. Clear all commands L. Load new menu S. Save menu commands
D. Delete Command M. Menu control off T. Toggle title
E. Edit command
Enter menu number or TI command:
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 47

Introducing Technician Interface Scripts
Saving Changes Made to Menus
With menu control on, save your changes for future sessions by entering
Enter menu number or TI command: prompt, add a filename, then press the
s at the
Return key. Refer to the following example:
Enter menu number or TI command: s
Enter file name [main.mnu]: testing.mnu
Saving commands to testing.mnu.
The Technician Interface saves the file to the default volume. Th e current menu
session now uses the file you specified. If you do not specify a filename at the
Enter file name [main.mnu]: prompt, the Technician Interface overwrites the
main.mnu file stored on t he router’s file system once you press t he Return key. If
you mistakenly type
Chapter 2 provide s a compl ete re feren ce fo r all
s, type q and press the Return key to quit.
show (and monitor) scripts in the
system. Refer to it for more information, sample displays, and references to other
manuals that describe each protocol in detail.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
1-27
Page 48

Page 49

Chapter 2
Using the show Command
Use the
from the Management Information Base (MIB). The type and amount of data displayed
depends on the specific protocol or network service you want to view.
In the command syntax, items in square brack e ts ([ ]) indicate optional information. Items
in curly braces ( { }) indi cate c hoices th at compl ete a co mma nd, and you must enter one of
the choices offered. Text in angle brackets (< >) indicates the type of information to enter
as an optional part of the command syntax; f or e xample <
all commands; they are case sensitive.
Note:
can display a list of available script subcommands by entering
without additional options or with a question mark as an option. For example, after
you load at.bat and associated baseline script files on a router, entering
show at ?
subcommand options.
In command syntax, <
characters. Use * to find a string of any characters and any length. Use ? to designate any
character in a specific position of the search string. For example, to locate all networks
whose addresses begin with 29, enter the search string
addresses 2901456 and 2967. Or if you have a set of names that begin and end with the
same characters but have different characters in the middle, such as xxx1.yy, xxx2.yy and
so on, you can enter the search pattern
show
command to display routing, configuration, interface, and statistical data
circuit name
For online Help -- After loading the scripts you need on a given router, you
at the Technician Interface prompt invokes the list of all
pattern
> means that you ca n use wil dcard se arching wi th the * and ?
29*
. This pattern will locate the
xxx?.yy
to locate them.
>. Use lowercase for
show
<option>
show at
show at
or
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-1
Page 50

Using Technician Interface Scripts
show ahb
base
The
show ahb
<option>
commands display configuration, state, and statistical
information about the ATM Half-Bridge (AHB) protocol. For detailed information about
the Nortel Networks impl ement at io n of AHB, s ee Configuring ATM Half-Bridge Services.
The
show ahb
base
circuits
hosts [<
routes
stats
command supports the following subcommand options:
slot> | <cctnum> | <vpi> | <vci> | <addr
>]
Displays the base record information for the AHB protocol. The base record controls the
AHB for the entire system.
2-2
Protocol Name of protocol, in this case AHB.
Forwarding Mode Indicates the state of AHB packet forwarding (enabled or
disabled).
Inbound Filtering Indicates that inbound packet filtering is enabled on the AHB
router.
Learn Method Method by which AHB automatically learns new bridge entries on
the AHB router. You can configure AHB in one of the following
learning methods:
• Secure
• Unsecure
•Both
•None
Debug Level Indicates the level of debug messaging you want the AHB router to
display in its log file.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 51

circuits
Displays circuit and state information for all AHB circuits.
Circuit Name of the circuit on which you configured AHB.
Num Number of the circuit on which you configured AHB.
Status Current state of the AHB protocol: Not Present (enabled but not
yet started), or Up.
Proxy Arp Indicates whether proxy ARP is enabled or disabled on the AHB
router. If enabled, the AHB router responds to ARP requests sent
from ATM-attached hosts with its own hardware address as the
target MAC address. If disabled, the AHB router ignores ARP
requests sent from ATM-attached hosts.
Def Subnet Mask IP subnet mask for host entries learned unsecurely.
hosts
[
<slot> | <cctnum> | <vpi> | <vci> | <addr
>]
Displays the host record information for AHB.
<slot>
<
<
<
<
> Shows only hosts on the speci fied circuit.
cctnum
> Shows only hosts on the speci fied VPI.
vpi
> Shows only hosts on the specified VCI.
vci
> Shows only hosts with th e specified IP address.
addr
Shows only hosts on the speci fied slot.
The table provides the following information:
Slt Indicates the slot on which the AHB router learned the CPE host
address.
Host Addr IP address of the CPE host that sends packets to the AHB router.
Subnet Subnet mask of the CPE host .
Cct Circuit number on which AHB is configured on the router.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-3
Page 52

Using Technician Interface Scripts
VPI Indicates the virtual path of the PVC configured on the ATM
VCI Identifies the virtual channel of the PVC configured on the ATM
F1 Indicates “Flags” field:
TxPkts Number of packets the router transmits to the CPE host at the
RxPkts Number of packets the router receives from the CPE host at the
routes
Displays information from the AHB routing table.
inteface. The VPI is part of the cell header, which can contain a
maximum of 8 VPI bits.
interface. The VCI is part of the cell header, which can contain a
maximum of 16 VCI bits.
0x2= host learned dynamically
0x10=disabling forwarding to/from host
0x20= host learned in unsecure mode
remote site.
remote site.
2-4
The fields displayed have the following meanings:
Destination Destination IP address for this route. 0.0.0.0 indicates a default
route.
Mask Subnet mask to be combined with the destination address and then
compared with the value in Destination. If the value of Destin ation
is 0.0.0.0 (a default route), then the value of Mask is also 0.0.0.0.
Proto Routing method through which the router learned t his rou te: Other,
Local, Netmgmt, ICMP, EGP, GGP, Hello, RIP, IS-IS, OSPF, or
BGP.
Age Number of seconds since this route was last updated or verified to
be correct. The meaning of “too old” depends on the routing
protocol specified under Proto.
Cost Number of hops to reach the destination.
NextHop Addr/AS IP address of the next hop and next Autonomous System of this
route. If the next hop is an unnumbered interface, the command
displays 0.0 .0.n, where n is the number of the circuit on which the
interface has been configured.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 53

stats
Displays all AHB statistics for each circuit.
The fields displayed have the following meanings:
Tot Nets The total number of networks in the AHB configuration.
Tot Hosts The total number of hosts configured on the network.
State The current state of the AHB protocol: Disabled (manually
disabled), Down, Init (Initializing), Not Present (enabled but not yet
started), or Up.
Incoming Pkts The total number of packets that the AHB router receives from the
IP routed network.
Outgoing Pkts The total number of outgoing packets that the AHB router transmits
to the IP routed network.
CCT The total number of circuits configured for AHB.
TxPkts The total number of packets transmitted by the AHB router.
TxDrop The total number of packets dropped by the AHB router.
RxPkts The total number of packets that the AHB router receives from CPE
RxDrop The total number of packets that the router drops because they are
308658-14.00 Rev 00
hosts.
not contained in the bridge table.
2-5
Page 54

Using Technician Interface Scripts
show appn
show appn
The
information about the Advanced Peer-to-Peer Networking (APPN) service. For detailed
information about the Nortel Networks implementation of APPN, refer to Configuring
APPN Services.
show appn
The
adjacencies [<node name>] ls definition [<LS name>]
base ls hpr
cos node [<COS name>] ls status [<LS name>]
cos priority [<COS name>] memory
cos tg [<COS name>] mode [<mode name>]
directory entry [<LU name>] port definition [<port name>]
<option>
command supports the followi ng subcommand options:
commands display configuration, state, and statistical
2-6
directory statistics port hpr
dlc [<DLC name>] port status [<port name> ]
dlur lu [<LU name>] rtp connection
dlur pu [<LU name>] rtp route
dlus [<DLUS name >] rtp statistics
endpoint address [<PLU name>] switch <rtp connection name>
endpoint route [<PLU name>] topology node [<CP name>]
endpoint statistics [<PLU name>] topology statistics
isr address [<FQCP name>] topology tg definition [<owner name>]
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 55

isr parameters topology tg status [<owner name>]
isr route [<FQCP name>] tunnel [<circuit>]
isr statistics [<FQCP name>] version
ls anr vrn [<VRN name>]
adjacencies
Displays the following information for all APPN nodes or for a specific APPN node:
Node Administratively assigned name for a specific node in the format
CP-CP Status Status of the Control Point to Control Point session between this
Out-of-Seq TDUs Number of out-of-sequence Topology Database Updates. In a
Last FRSN Sent Last Flow Reduction Sequence Number sent in a topology update
Last FRSN Received Last Flow Reduction Sequence Number received in a topology
<node name>
[
]
<network_ID>.<CP_name>.
node and an adjacent node. Inactive indicates that no CP-CP
sessions exist between the network node and adjacent node. Activ e
indicates that CP-CP sessions are active.
quiesced state, this value is zero. In normal operation, the value
varies depending on the network environment.
to an adjacent network node.
update from an adjacent network node.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-7
Page 56

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Sample Display - show appn adjacencies
APPN Adjacent Nodes
------------------ CP-CP Out-of-Seq Last FRSN Last FRSN
Node Status TDUs Sent Received
----------------- -------- ----------- ---------- -------- USWFLT01.AFN ACTIVE 0 3561 207
USWFLT01.SNEEZY INACTIVE 0 3554 853
USWFLT01.WF3174A ACTIVE 0 3561 687
3 Entries.
base
Displays base record in for m at ion f or APPN. The ta bl e displays the following information :
Capabilities:
Negotiated LS Support Indicates that the APPN node supports negotiable link stations.
2-8
Segment Reassembly Indicates that the APPN node supports segment reassembly.
BIND Reassembly Indicates that the APPN node supports BIND reassembly.
Parallel TG Support Indicates that the APPN node supports the ability to establish multiple
transmission groups.
Dynamic LS Support Indicates that the APPN node supports the ability to accept
connections (that have not been predefined) from adjacent nodes.
Adaptive BIND Pacing Indicates whether the APPN node supports the ability to control the
flow of BINDs.
Receive Registered Chars Indicates whether the APPN node supports resource registration.
Border Node Support Indicates whether the APPN node supports border nodes.
Central Directory Support Indicates whether the APPN node is a central directory server.
Route Tree Caching Indicates that the APPN node supports route tree caching.
Incremental Tree Updates Indicates that the APPN node supports incremental updates to the
route-selection tree cache.
Mode-to-COS Mapping Indicates that the APPN node supports mapping of mode name and
COS and transmission prior it y.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 57

Multi-Domain Support Indicates whether the APPN node supports multi-domain traffic
flows.
Endpoint RSCV Storage Indicates whether the APPN node supports Route Selection Control
Vectors (RSCVs) storage during ISR sessions.
Capacity:
Alert Queue Size Maximum number of alerts that are held while waiting for the
establishment of a link to a reporting point.
COS Cache Size Size of the COS database weight cache.
Directory Cache Size Maximum number of entries that can be stored in the directory
database at the network node.
Max Directory Entries Maximum number of cached directory entries that can be stored in the
local directory database at any one time.
Route Tree Cache Size Size of the topology and routing services tree database.
Route Tree Use Limit Maximum number of Route Selection Trees (RSTs) cached.
Max Nodes in Topology Maximum number of times an RST will be used before Route Selection
Services (RSS) calculates a new route tree for that route.
Max TGs in Topology Maximum number of transmission groups in the local topology
database.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-9
Page 58

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Sample Display - show appn base
APPN Base Information
---------------------
Node Name: USWFLT01.DURHAM
State: Active
Capabilities:
Negotiated LS Support: Yes
Segment Reassembly: Yes
BIND Reassembly: Yes
Parallel TG Support: Yes
Dynamic LS Support: Yes
Adaptive BIND Pacing: Yes
Receive Registered Chars: Yes
Border Node Support: No
Central Directory Support: No
Route Tree Caching: Yes
Incremental Tree Updates: Yes
Mode-to-COS Mapping: Yes
Multi-Domain Support: Yes
Endpoint RSCV Storage: Yes
2-10
Capacity:
Alert Queue Size: 10
COS Cache Size: 8
Directory Cache Size: 100
Max Directory Entries: Unlimited
Route Tree Cache Size: 8
Route Tree Use Limit: 8
Max Nodes in Topology: Unlimited
Max TGs in Topology: Unlimited
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 59

cos node
Displays resistance and congestion information for all COS types or for a specific COS
type.
COS COS Name: #BATCH, #INTER, #INTERSC, #BATCHSC,
Weight Size of the COS database weight cache assigned to a particular
Resist Min Minimum route addition resistance allowed. Route addition
Resist Max Maximum route addition resistance allowed.
Congest Min M inimum congestion allowed.
Congest Max Maximum congestion allowed.
<COS name>
[
]
CPSVCMG or SNASVCMG. #BATCH refers to jobs which are
batch-like in nature (i.e., where there is a lot of data is involved and
response time is not very important). #INTER refers to interactive
jobs (i.e., where there is not much data involved and response time
is very import ant). #INTERSC an d #BATCHSC are secure ver sions
of #INTER and #BATCH. CPSVCMG and SNASVCMG are used
for APPN control data.
node given its resistance and congestion characteristics.
resistance indicates the relative desirability of using this node for
intermediate session traffic. The value, which can be an integer
from 0 to 255, is used in route computatio n. The lower the value,
the more desirable the node is for intermediate routing.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-11
Page 60

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Sample Display - show appn cos node
APPN COS Nodes
--------------
Resist Resist Congest Congest
COS Weight Min Max Min Max
-------- ------ ------ ------ ------- ------ #BATCH 5 0 31 0 0
#BATCH 10 0 63 0 0
#BATCH 20 0 95 0 0
#BATCH 40 0 127 0 0
#BATCH 60 0 159 0 0
#BATCH 80 0 191 0 0
#BATCH 120 0 223 0 1
#BATCH 160 0 255 0 1
#INTER 5 0 31 0 0
#INTER 10 0 63 0 0
#INTER 20 0 95 0 0
#INTER 40 0 127 0 0
#INTER 60 0 159 0 0
#INTER 80 0 191 0 0
#INTER 120 0 223 0 1
#INTER 160 0 255 0 1
CPSVCMG 5 0 31 0 0
2-12
17 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 61

cos priority
Displays the transmission priority for all COS types or for a specific COS type. For more
information about COS types, see the
Medium, High, or Network.
Sample Display - show appn cos priority
APPN COS Priorities
-------------------
COS Priority
-------- ------- #BATCH Low
#INTER High
CPSVCMG Network
#BATCHSC Low
#CONNECT Medium
#INTERSC High
SNASVCMG Network
7 Entries.
<COS name>
[
]
cos node
command. The priority can be Low,
cos tg
<COS name>
[
Displays Transmission Group (TG) information for all COS types or for a specific COS
type.
Eff-Cap Min Minimum effective capacity. Effective capacity is the bit-transmission
Eff-Cap Max Maximum effective capacity.
Connect Min Minimum cost per connection time. This value represents the relative
Connect Max Maximum cost per connection time.
Byte Cst Min Minimum cost of transmitting a byte over this connection. Range is
308658-14.00 Rev 00
]
rate of the transmission gro up. It is deri ve d from the link bandwid th and
maximum load factor with the range of 0 through 255.
cost per unit of time to use the transmission group. Range is from 0,
which means no cost, to 255, which indicates maximum cost.
from 0 (lowest cost) to 255.
2-13
Page 62

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Byte Cst Max Maximum cost of transmitting a byte over this connection. Range is
Security Min Minimum security, with security represented as an inte ger with a ran ge
Security Max Maximum security, with security represented as an integ er with a range
Delay Min Minimum amount of time that it takes for a signal to travel the length of
Delay Max Maximum amount of time that it takes for a signal to travel the length
User-1 Min First minimum user-defined transmission group characteristic for this
User-1 Max First maximum user-defined transmission group characteristic for this
User-2 Min Second minimum user-defined transmission group characteristic for
from 0 (lowest cost) to 255.
of 1 through 255: 1 (nonsecure), 32 (public switched), 64
(underground), 128 (conduit), 160 (encrypted), 192 (guarded
radiation), 255 (maximum).
of 1 through 255: 1 (nonsecure), 32 (public switched), 64
(underground), 128 (conduit), 160 (encrypted), 192 (guarded
radiation), 255 (maximum).
the logical link, with a range of from 0 to 255: 76 (negligible), 113
(terrestrial), 145 (packet), 153 (long), 255 (maximum).
of the logical link, with a range of from 0 to 255: 76 (negligible), 113
(terrestrial), 145 (packet), 153 (long), 255 (maximum).
transmission group with a range of from 0 to 255.
transmission group with a range of from 0 to 255.
this transmission group with a range of from 0 to 255 .
2-14
User-2 Max Second maximum user-defined transmission group characteristic for
this transmission group with a range of from 0 to 255 .
User-3 Min Third minimum user-defined transmission group characteristic for this
transmission group with a range of from 0 to 255.
User-3 Max Third maximum user-defined transmission group characteristic for this
transmission group with a range of from 0 to 255.
For more information about COS types and weight, see the cos node command.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 63

Sample Display - show appn cos tg
APPN COS TGs
------------
Eff-Cap Connect ByteCst Securty Delay User-1 User-2 User-3
COS
------
Wgt
------
Min
-----
Max
-----
Min
-----
Max
-----
Min
-----
Max
-----
Min
-----
Max
-----
Min
-----
Max
-----
Min
-----
Max
-----
Min
-----
Max
-----
Min
-----
Max
----#BATCH 3068255000012550255025502550255
#BATCH 6056255000012550255025502550255
#BATCH 90 56 255 0 128 0 128 1 255 0 255 0 255 0 255 0 255
#BATCH 12048255000012550255025502550255
#BATCH 150 48255 0128 0128 1255 0255 0255 0255 0255
#BATCH 180 48255 0196 0196 1255 0255 0255 0255 0255
#BATCH 210 40255 0196 0196 1255 0255 0255 0255 0255
#BATCH 240 0 255 0 255 0 255 1 255 0 255 0 255 0 255 0 255
#INTER 3011825500001255076025502550255
#INTER 6068255000012550113025502550255
#INTER 90 68 255 0 128 0 128 1 255 0 113 0 255 0 255 0 255
#INTER 12056255000012550113025502550255
#INTER 150 56255 0128 0128 1255 0145 0255 0255 0255
#INTER 18048255000012550145025502550255
#INTER 210 48255 0196 0196 1255 0255 0255 0255 0255
#INTER 240 0 255 0 255 0 255 1 255 0 255 0 255 0 255 0 255
CPSVCMG3011825500001255076025502550255
17 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-15
Page 64

Using Technician Interface Scripts
directory entry
Displays directory information fo r all Logical Units (LUs) or for a speci fic LU.
LU Logical Unit name.
NN Server Network Node server name.
LU Owner Logical Unit owner name.
Location Location of the Logical Unit: Local, Dom ain, or XDomain (cross-domain).
Type Directory type: Home, Cache, or Registered. Home means that the LU is in
Wildcard Type of wildcard: Explicit, Partial, or Full. Explicit means the full LU name
[
<LU name>
the domain of the local network node and that the LU information has been
configured at the local node. Cache means that the LU has previously been
located by a broadcast search and that the location information has been
saved. Register means that the LU is at an end node that is in the domain of
the local network node. Registered entries are registered by the served end
node.
has been specified. Partial means the entry is a partial wildcard. Full means
the entry is a full wildcard, and all searches for unknown LUs will be
directed to this node.
]
Sample Display - show appn directory entry
APPN Directory Entries
----------------------
LU
----------------USWFLT01.TESTEN USWFLT01.RALEIGH USWFLT01.TESTEN Domain Registr Explicit
USWFLT01.RALEIGH USWFLT01.RALEIGH USWFLT01.RALEIGH Local Home Explicit
USWFLT01.TESTENLU USWFLT01.RALEIGH USWFLT01.TESTEN Domain Registr Explicit
3 Entries.
2-16
NN Server
----------------
LU Owner
----------------
Location
--------
Type
-------
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Wildcard
--------
Page 65

directory statistics
Displays information concerning the performance of the directory services function.
Maximum Cached Entries Maximum number of cache entries allowed.
Current Cached Entries Current number of cache entries.
Current Home Entries Current number of home entries.
Current Registered Entries Current number of registered entries.
Directed Locates Received Number of directed locates received.
Broadcast Locates Received Number of broadcast locates received.
Directed Locates Sent Number of directed locates sent.
Broadcast Locates Sent Number of broadcast locates sent.
Directed Locates Not Found Number of directed locates returned with a “not found.”
Broadcast Locates Not Found Number of broadcast locates returned with a “not found.”
Outstanding Locates Current number of outstanding locates, both directed and
broadcast. This value varies. A value of zero indicates that no
locates are unanswered.
Sample Display - show appn stats directory
APPN Directory Statistics
---------------------- Maximum Cached Entries: 100
Current Cached Entries: 0
Current Home Entries: 2
Current Registered Entries: 3
Directed Locates Received: 0
Broadcast Locates Received: 0
Directed Locates Sent: 0
Broadcast Locates Sent: 0
Directed Locates Not Found: 0
Broadcast Locates Not Found: 0
Outstanding Locates: 0
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-17
Page 66

Using Technician Interface Scripts
[
dlc
<DLC name>
Displays information for all Data Link Controls (DLCs) or for a specific DLC.
DLC Eight-character name given to this DLC.
Circuit Name Name of the circuit used by this DLC.
State Current state of this DLC: Inactive, Pending Active, Active, or
CCT Circuit number.
DLC Type Type of DLC: SDLC, LLC SRB, LLC TB, or DLS.
Negotiated LS Support Indicates whether Link Station roles can be negotiated on this
Sample Display - show appn dlc
APPN DLCs
---------
DLC Negotiated
DLC Circuit Name State CCT Type LS Support
-------- ------------ ---------------- ---- ------- --------- DLC00001 S51 Active 1 SDLC Yes
DLC00002 S52 Active 2 SDLC Yes
DLC00003 S53 Active 3 SDLC Yes
DLC00004 S54 Active 4 SDLC Yes
DLC00006 E23.llc2 Active 6 LLC-TB Yes
DLC00008 E24.llc2 Active 8 LLC-TB Yes
DLC00010 O31.llc2 Active 10 LLC-SRB Yes
]
Pending Inactive.
DLC.
2-18
7 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 67

dlur lu
<LU name>
[
]
Displays the status of all the DLUR LUs or a specific DLUR LU.
LU Logical Unit name.
PU Physical Unit name with up to 8 characters.
DLUS Fully qualified Dependent LU Server name c ontaining 3 to 17
characters.
NAU Address Network Addressable Unit address.
PLU Primary LU name.
Sample Display - show appn dlur lu
APPN DLUR LUs
-------------
NAU
LU PU DLUS Address PLU
-------- -------- ----------------- ------- ----------------L0000C22 PU188004 USWFLT01.S156CDRM 2
L0000C23 PU188004 USWFLT01.S156CDRM 3
2 Entries.
dlur pu
<LU name>
[
Displays the status of all the DLUR PUs or a specific DLUR PU.
PU Physical Unit name with up to 8 characters.
Active DLUS Displays the fully qualified name of the active DLUS. The name
Primary DLUS Displays the fully qualified primary Dependent Logical Unit
Backup DLUS Displays the fully qualified backup Dependent Logical Unit Serv er
308658-14.00 Rev 00
]
can contain from 3 to 17 characters.
Server name. The name can contain from 3 to 17 characters.
name. The name can contain from 3 to 17 characters.
2-19
Page 68

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Sample Display - show appn dlur pu
APPN DLUR PUs
-------------
PU Active DLUS Primary DLUS Backup DLUS
-------- ----------------- ----------------- ---------------- PU188004 USWFLT01.S156CDRM USWFLT01.S156CDRM USWFLT01.S157CDRM
1 Entry.
dlus
[
<DLUS name>
]
Displays the status of all the DLUSs or a specific DLUS.
DLUS Displays the fully qualified name of the active DLUS. The name
can contain from 3 to 17 characters.
Pipe State State of the CP-SVR pipe between the DLUR and DLUS:
Active, Inactive, PendingActive, PendingInact.
Active PUs Number of active PUs to the DLUS.
SSCP-PU MU Rcvd Number of Message Units Received on the SSCP-PU session.
SSCP-PU MU Sent Number of Message Units Sent on the SSCP-PU session.
SSCP-LU MU Rcvd Number of Message Units Received on the SSCP-LU session.
SSCP-LU MU Sent Number of Message Units Sent on the SSCP-LU session.
Sample Display - show appn dlus
APPN DLUS Nodes
---------------
Active SSCP-PU SSCP-PU SSCP-LU SSCP-LU
DLUS Pipe State PUs MU Sent MU Rcvd MU Sent MU Rcvd
----------------- ---------------- ------ ------- ------- ------- ------ USWFLT01.S156CDRM Active 1 0 0 5 4
2-20
1 Entry.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 69

endpoint address
<PLU name>
[
]
Displays address information for all endpoint sessions or for sessions to a specific LU.
Partner LU Name of the Partner Logical Unit being used by this session.
PCID Procedure Correlation Identifier of this session.
Priority Transmission priority being used by this session: Low, Medium,
High, or Network level priority.
COS Class-of-Service being used by this session.
LS Adjacen t Link Station used by this session.
SIDH Session Identifier High value used by this session.
SIDL Session Identifier Low value used by this session.
ODAI OAF-DAF Assignor Indicator value used by this session.
Sample Display - show appn endpoint address
APPN Endpoint Session Addressing Info
-------------------------------------
Partner LU
----------------USWFLT01.WF3174A dbf36f442150b151 Network CPSVCMG @I000004 2 0 1
USWFLT01.WF3174A fbbf52e94a9b96c9 Network CPSVCMG @I000004 2 0 0
USWFLT01.AFN ccebbc6be89f3909 Network CPSVCMG @I000003 2 0 0
USWFLT01.AFN fbbf52e94a9b96c8 Network CPSVCMG @I000003 2 0 1
USWFLT01.TESTEN fbbf52e94a9b96c7 Network CPSVCMG @I000002 2 0 0
USWFLT01.TESTEN eebbbebc4474cd92 Network CPSVCMG @I000002 2 1 1
PCID
-----------------
Priority
--------
COS
---------LS---------
SIDH
----
SIDL
----
ODAI
----
6 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-21
Page 70

Using Technician Interface Scripts
endpoint route [
<PLU name>
]
Displays routing inf ormation for a ll endpoi nt sessi ons or for sessions to a speci fi c LU. The
Route column indicates the route used by the endpoint sessions. CP sessions (between
adjacent nodes) do not show routes. For more information about column definitions, see
endpoint address
the
Note:
Routing information is only available if the endpoint session RSCV storage
command.
option is enabled.
Sample Display - show appn endpoint route
APPN Endpoint Session Routing Info
----------------------------------
Partner LU
------------------USWFLT01.WFAS400 fbbf52e94a9b96cc USWFLT01.RALEIGH->TG:1->
USWFLT01.WFAS400 fbbf52e94a9b96cb USWFLT01.RALEIGH->TG:1->USWFLT01.AFN->
USWFLT01.WF3174A dbf36f442150b151
USWFLT01.WF3174A fbbf52e94a9b96c9
USWFLT01.AFN ccebbc6be89f3909
USWFLT01.AFN fbbf52e94a9b96c8
USWFLT01.TESTEN fbbf52e94a9b96c7
USWFLT01.TESTEN eebbbebc4474cd92
PCID
-------------------
Route
---------------------------------------
USWFLT01.AFN>TG:21->USWFLT01.WFAS400
TG:21->USWFLT01.WFAS400
8 Entries.
2-22
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 71

endpoint statistics
Displays statistics for all endpoint sessions or for sessions to a specific LU.
Dir Indicates the direction: Rx (receive) or Tx (transmit).
BTU Size Maximum send Basic Transmission Unit size on each hop of this
Pacing Max Maximum send pacing on each hop of this session.
Pacing Cur Current send pacing on each hop of this session.
Frames Number of normal-flow frames sent on each hop of this session.
Bytes Number of bytes sent on each hop of this session.
Sample Display - show appn stats endpoint
APPN Endpoint Session Statistics
------------------------------- BTU Pacing
Partner LU PCID Dir Size Max Cur Frames Bytes
----------------- ---------------- --- ----- --- --- ------ ----- USWFLT01.WFAS400 fbbf52e94a9b96cc Rx 2048 3 3 1 40
Tx 2048 1 1 1 62
USWFLT01.WFAS400 fbbf52e94a9b96cb Rx 2048 3 3 1 28
Tx 2048 1 1 1 76
USWFLT01.WF3174A dbf36f442150b151 Rx 2048 11 7 11 4K
Tx 2048 1 1 1 15
USWFLT01.WF3174A fbbf52e94a9b96c9 Rx 2048 1 1 1 15
Tx 2048 4 3 14 351K
USWFLT01.AFN ccebbc6be89f3909 Rx 2048 11 7 11 4K
Tx 2048 1 1 1 15
USWFLT01.AFN fbbf52e94a9b96c8 Rx 2048 1 1 1 15
Tx 2048 13 13 19 136K
USWFLT01.TESTEN fbbf52e94a9b96c7 Rx 1929 1 1 1 15
Tx 1929 1 1 194 23K
USWFLT01.TESTEN eebbbebc4474cd92 Rx 1929 1 1 195 53K
Tx 1929 1 1 1 15
<PLU name>
[
session.
]
8 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-23
Page 72

Using Technician Interface Scripts
isr address
Displays address information for all Intermediate Session Routing (ISR) sessions or for
sessions from a particular node.
FQ CP Name Fully Qualified Control Point name of the node assigning the PCID
PCID Procedure Correlation Identifier of this session.
Priority Transmission priority used by this session: Low , Medium, High, or
COS Class-of-Service being used by this session.
Hop Indicates whether the local LU was the BIND sender (Primary) or
LS Adjacen t Link Station used by this session.
SIDH Session Identifier High value used by this session.
SIDL Session Identifier Low value used by this session.
ODAI OAF-DAF Assignor Indicator value used by this session.
Sample Display - show appn isr address
[
<FQCP name>
]
for this session.
Network.
the BIND receiver (Secondary).
APPN ISR Session Addressing Info
--------------------------------
FQ CP Name PCID Priority COS Hop LS SIDH SIDL ODAI
----------------- ---------------- ------- -------- --- -------- ---- ---- --- USWFLT01.TESTEN eebbbebc4774cd92 Network SNASVCMG Pri @I000002 2 2 1
Sec @I000003 2 1 1
1 Entry.
2-24
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 73

isr parameters
Displays pa rameter information about the Intermediate Session Rout ing (ISR) function.
ISR State Indicates whether ISR is enabled. The default is enabled.
Maximum RU Size Maximum Request Unit size for intermediate sessions.
Receive Pacing Window Maximum number of messages that the network node can receive
Maximum ISR Sessions Maximum number of ISR sessions that the local network node will
Congestion Upper Threshold Maximum number of ISR sessions that can take place before new
Congestion Lower Threshold Number of active ISR sessions that the local network node must
ISR RSCV Storage Indicates whether Route Selection Control Vectors are stored
in one pacing window during an ISR session.
process concurrently.
sessions are directed away from the network node.
drop to before it is no longer considered congested.
during ISR sessions (see
isr route
command).
Sample Display - show appn isr parameters
APPN ISR Parameters
-------------------
ISR State: Enabled
Maximum RU Size: 1024
Receive Pacing Window: 7
Maximum ISR Sessions: 1000
Congestion Upper Threshold: 900
Congestion Lower Threshold: 800
ISR RSCV Storage: Yes
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-25
Page 74

Using Technician Interface Scripts
isr route
Displays routing i nforma ti on for a ll IS R ses sions o r for ISR s ession s from a spe cif ic nod e.
For more information about column definitions, see the
Note:
Sample Display - show appn isr route
APPN ISR Session Routing Info
---------------------------- FQ CP Name PCID Route
----------------- ---------------- ---- USWFLT01.TESTEN eebbbebc4774cd92 USWFLT01.TESTEN->TG:21-
>
USWFLT01.RALEIGH->TG:1->USWFLT01.AFN->TG:21->USWFLT01.WFAS400
1 Entry.
[
<FQCP name>
]
isr address
ISR RSCV storage must be enabled in order to display the route.
command.
isr statistics
Displays session statistics for all ISR sessions or for ISR sessions from a specific node.
For more information about column definitions, see the
address
Sample Display - show appn stats isr
APPN ISR Session Statistics
-------------------------- BTU Pacing
FQ CP Name PCID Hop Size Max Cur Frames Bytes
----------------- ---------------- ---- ----- --- --- ------ ----- USWFLT01.TESTEN eebbbebc4774cd92 P-Rx 1929 1 1 388 29K
P-Tx 1929 3 3 388 10K
S-Rx 2048 5 3 388 10K
S-Tx 2048 5 3 388 29K
1 Entry.
2-26
[
<FQCP name>
commands.
]
endpoint statistics
308658-14.00 Rev 00
and
isr
Page 75

ls anr
Displays automatic network routing labels for a single link station or multiple link
stations.
LS Administratively assigned name for the link station. The name can
be from one to eight characters.
CP Name Fully qualified name of the adjacent node for this link station. The
name can be from three to 17 characters. Format is
<network_ID>.<CP_name>.
State The current state of the link station, active or inactive.
ANR Label The Automatic Network R ou ting label assigned during RTP route
setup.
Sample Display - show appn ls anr
APPN Link Station ANR Info
---------------------------
ANR
LS CP Name State Label
-------- ----------------- ----------- -----
RALEIGH USBNET01.RALEIGH Active 91
VEGAS USBNET01.VEGAS Active 90
2 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-27
Page 76

Using Technician Interface Scripts
ls definition
Displays Link Station (LS) information for all defined link stations or for a specific link
station.
LS Administratively assigned name for the link station. The name can
CP Name Fully qualified name of the adjacent node for this link station. The
Port Administratively assigned name for the port. The name can be from
TG Num Number associated with the transmission group for this link
CP-CP Sessn Indicates whether CP-CP sessions are supported by this link
Max BTU Numeric value between 256 and 4105 inclusive, indicating the
Link Address Link address using MAC address and SAP, or SDLC address.
[
<LS name>
]
be from one to eight characters.
name can be from three to 17 characters. Format is
<network_ID>.<CP_name>.
one to eight characters.
station.
station.
maximum number of bytes in a Basic Transmission Unit (BTU)
that can be sent on this transmission group. This is an
administratively assigned value.
2-28
Sample Display - show appn ls definition
APPN Link Station Definition
----------------------------
TG CP-CP Max
LS CP Name Port Num Sessn BTU Link Address
-------- ----------------- -------- --- ----- ----- -------------- DURHAM USWFLT01.DURHAM PORT22 0 Yes 1417 00004500e476:04
WFAS400 USWFLT01.WFAS400 PORT22 0 Yes 1476 40000104877a:04
2 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 77

ls hpr
Displays High Performance Routing capabilities for a single link station or multiple link
stations.
LS Administratively assigned name for the link station. The name can
be from one to eight characters.
CP Name Fully qualified name of the adjacent node for this link station. The
name can be from three to 17 characters. Format is
<network_ID>.<CP_name>.
HPR Enabled Specifies whether HPR support has been enabled for this link
station.
Link Level Error Recovery Specifies whether link level error recovery support has been
selected for this link station.
Sample Display - show appn ls hpr
APPN Link Station HPR info
------------------------------
HPR Link Level
LS CP Name Enabled Error Recovery
-------- ----------------- ------- ------------- RALEIGH USWFLT01.RALEIGH Yes No
VEGAS USWFLT01.VEGAS Yes Yes
2 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-29
Page 78

Using Technician Interface Scripts
ls status
Displays the status of all link stations or a specific link station.
LS Administratively assigned name for the link station. The name can
CP Name Fully qualified name of the adjacent node for this link station. The
State State of this link station: Inactive, Pending Active, Active,
TG Num Number of the transmission group for this link station.
Cur Sessn Number of active sessions on this link.
Frames Rcvd Number of message frames received.
Bytes Rcvd Number of message bytes received.
Frames Sent Number of message frames sent.
Bytes Sent Number of messag e bytes sent.
[
<LS name>
]
be from one to eight characters. Names that begin with an “@”
symbol indicate dynamic link stations.
name can be from three to 17 characters. Format is
<network_ID>.<CP_name>.
PendingInactive.
Sample Display - show appn ls status
APPN Link Station Status
------------------------
TG
LS
--------PLUTO USWFLT01.PLUTO Active 21 4 56 10K 57 9K
ANAHEIM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM Pend Active 3 0 0 0 0 0
WF3174A USWFLT01.WF3174A Active 21 2 51 10K 41 5K
ANAHEIM2 USWFLT01.ANAHEIM Active 2 6 81 4K 68 3K
4 Entries.
CP Name
------------------
State
----------
Num
----
2-30
Cur
Sessn
-----
Frames
Rcvd
-----
Bytes
Rcvd
-----
Frames
Sent
-----
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Bytes
Sent
----
Page 79

memory
Displays information about CP memory usage.
Available Memory Total memory available to the APPN service (0 means unlimited).
Memory in Use Memory in use by the APPN service.
Warning Threshold Warning memory threshold (0 means no threshold).
Critical Threshold Critical memory threshold (0 means no threshold).
Sample Display - show appn memory
APPN Memory Utilization
-----------------------
Available Memory: 0
Memory in Use: 147915
Warning Threshold: 0
Critical Threshold: 0
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-31
Page 80

Using Technician Interface Scripts
mode
[
<mode name>
Displays mode-to-COS mappi ngs fo r a ll modes or for a spec ific mode. Fo r inf ormati on on
the columns, see the
Sample Display - show appn mode
APPN Mode to COS Mappings
-------------------------
Mode COS
-------- ------- #BATCH #BATCH
#INTER #INTER
CPSVCMG CPSVCMG
#BATCHSC #BATCHSC
#INTERSC #INTERSC
SNASVCMG SNASVCMG
6 Entries.
port definition
]
cos node
[
<port name>
cos priority
and
commands .
]
2-32
Displays port definition information for all ports or for a specific port.
Port Administratively assigned name for this APPN port. The name can
be from one to eight characters.
Number Port number associated with the port name.
DLC Indicates the name of the DLC supporting this port.
Receive BTU Size Maximum Basic Transmission Unit (BTU) size that a link station
on this port can receive.
Send BTU Size Maximum BTU size that a link station on this port can send.
Max Window Maximum number of I-frames that can be received by the
Exchange Identification (XID) sender before an acknowledgement
is received.
Port Type Identifies the type of line used by this port: Leased, Switched, or
Shared Access Transport Facility (SATF).
Link Address Link address using MAC address and SAP.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 81

Sample Display - show appn port definition
APPN Port Definitions
---------------------
Receive
Port
---------PORT0001 0 DLC00001 2048 2048 7 Leased :01
PORT0002 0 DLC00002 2048 2048 7 Leased :03
PORT0003 0 DLC00003 2048 2048 7 Leased :05
PORT0004 0 DLC00004 2048 2048 7 Leased :07
PORT0008 0 DLC00008 2057 2057 7 SATF 000045222224:04
PORT0010 0 DLC00010 2057 2057 7 SATF 000045C0E4B6:04
6 Entries.
Number
--------
DLC
------
BTU Size
---------
Send
BTU Size
--------
Max
Window
-----
Port
Type
----
Link Address
---------------
port hpr
Displays High Performance Routing capabilities for a single port or multiple ports.
Port Administratively assigned name for this APPN port. The name can
be from one to eight characters.
Implicit HPR Enabled Specifies whether HPR support has been enabled for dynamic link
stations on this port.
Implicit Link Level Error
Recovery
Specifies whether link level error recovery support has been
selected for dynamic link stations on this port.
Implicit Link Deactivation
Time
HPR SAP Defines the chosen SAP for HPR traffic on this port.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Specifies the link deactivation time (in seconds) for dynamic link
stations on this port.
2-33
Page 82

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Sample Display - show appn port hpr
APPN Port Defined HPR info
-----------------------------
Implicit Implicit Implicit
HPR Link Level Link Deact HPR
Port Enabled Error Recovery Time sap
-------- -------- -------------- ---------- --- PORT0003 Yes No 120 C8
PORT0005 No No 5 none
2 Entries.
port status
Displays port status information regarding the Exchange Identification (XID) and link role
for all ports or for a specific port.
Port Administratively assigned name for this APPN port. The name can
Number Port number associated with the port name.
State State of this port: Inactive, Pending Active, Active,
Link Role Initial role for the link stations activated through this port: Primary,
Good XIDs Number of successful XID sequences that have occurred on all
Bad XIDs Number of unsuccessful XID sequences that have occurred on all
[
<port name>
]
be from one to eight characters.
PendingInactive.
Secondary, Negotiable, or ABM (Asynchronous Balance Mode).
defined link stations on this port since the last time this port was
started.
defined link stations on this port since the last time this port was
started.
2-34
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 83

Sample Display - show appn port status
APPN Port Status
----------------
Port Number State Link Role Good XIDs Bad XIDs
-------- ------ ---------------- ---------- --------- ------- PORT0001 0 Active Negotiable 1 0
PORT0002 0 Active Negotiable 0 0
PORT0003 0 Active Primary 1 0
PORT0004 0 Active Primary 1 0
4 Entries.
rtp connection
Displays information about all RTP connections or a specific RTP connection.
RTP Conn Name Name of the RTP connection.
Destination CP Name Fully qualified name of the destination network node . The name
can be from three to 17 characters. Format is
<network_ID>.<CP_name>.
1st Hop Ls Name Name of the link station which suppo rts the RTP connection.
COS Class of service for the RTP connection.
Local TCID Local Transport Connection Identifier of the RTP connection.
Remote TCID Remote Transport Connection Identifier of the RTP connection.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-35
Page 84

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Sample Display - show appn rtp connection
APPN RTP Connections
--------------------
RTP
Conn
Name
------@R000001 USWFLT01.DURHAM RALEIGH SNASVCMG 0000000001000000 0000000005000000
@R000002 USWFLT01.DURHAM RALEIGH #CONNECT 0000000002000000 0000000006000000
@R000003 USWFLT01.DURHAM RALEIGH #INTER 0000000003000000 0000000007000000
@R000004 USWFLT01.DURHAM RALEIGH #BATCH 0000000004000000 0000000008000000
@R000005 USWFLT01.VEGAS BOSTON SNASVCMG 0000000005000000 0000000009000000
@R000006 USWFLT01.VEGAS BOSTON #CONNECT 0000000006000000 000000000A000000
6 Entries.
rtp route
Destination
CP Name
------------
1st Hop
Ls
Name
------
COS
------
Local
TCID
---------------
Remote
TCID
---------------
Displays the RTP route selection control vector for all RTP connections or a specific RTP
connection.
RTP Conn Name Name of the RTP connection.
Route Route selection control vector (RSCV) of the RTP connection.
2-36
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 85

Sample Display - show appn rtp route
APPN RTP Connection Routing Info
----------------------------------
RTP
Conn
Name Route
-------- ---- @R000001 USWFLT01.VEGAS->TG:21->USWFLT01.RALEIGH
@R000002 USWFLT01.VEGAS->TG:21->USWFLT01.RALEIGH
@R000003 USWFLT01.VEGAS->TG:21->USWFLT01.RALEIGH
@R000004 USWFLT01.VEGAS->TG:21->USWFLT01.RALEIGH
4 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-37
Page 86

Using Technician Interface Scripts
rtp statistics
Displays statistics for all RTP connections or a specific RTP connection.
RTP Connection Name Name of the RTP connection.
Cur Session Number of currently active sessions on this RTP connection.
Dir Direction (Rx/Tx) of the specified statistic.
Bytes Number of bytes received/transmitted on the RTP connection.
Pkts Number of packets received/transmitted on the RTP connection.
SessCtl Frames Number of session control frames sent on the RTP connection.
Rate Current receive/transmit rate (in Kbits/sec) of the RTP connection.
Discarded Bytes Total number of bytes sent by the remote node that were discarded
Discarded Pkts Total number of packets sent by the remote node that were
Resent Bytes Total number of bytes resent by the local node that were lost in
Resent Pkts Total number of packets resent by the local node that were lost in
as duplicates.
discarded as duplicates.
transit.
transit.
Sample Display - show appn rtp statistics
APPN RTP Connection Statistics
------------------------------
RTP
Conn
Name
@R000001 1 RxTx196
@R000002 1 RxTx344
@R000003 1 RxTx352
@R000004 1 RxTx352
4 Entries.
Cur
Sessn Dir Bytes Pkts
2-38
285
354
420
420
SessCtl
Frames Rate
7
7
14
15
218
215
195
199
111K
1K
111K
1K
111K
1K
111K
1K
Discarded
Bytes Pkts
0
0
0
0
-
Resent
Bytes Pkts
0
0
0
0
-
308658-14.00 Rev 00
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Page 87

switch
<rtp connection name>
Requests the APPN node to perf orm a path s witch with a cur rentl y act i ve RTP connection.
If a better path is not found, the connection remains unchanged. The
<rtp_connection_name> is the name of the RTP connection that displays with the
appn rtp connection
Sample Display - show appn switch
path switching RTP connection @R000001
topology node
Displays node informati on on the topology database for al l control points or for a specific
control point.
Node Administratively assigned name for a specific node in the format
Type Type of APPN node: NN (network node) or VRN (virtual node).
FRSN Flow Reduction Sequence Numbers are associated with Topology
command.
<CP name>
[
<network_ID>.<CP_name>
Database Updates (TDUs) and are unique only within each APPN network
node. A TDU can be associated with multiple APPN resources. This FRSN
indicates the last time this resource was updated at this node.
show
]
.
RSN Resource Sequence Number that is assigned and contro lled b y the n etwo rk
RAR Rou te Addition Resistance indicates the relative desirability of using this
Congested Indicates whether this node is congested. This is set or reset by a node
308658-14.00 Rev 00
node that owns this resource. This is always an even 32-bit number unless
an error has occurred.
node for intermediate session traffic. The value, which can be any integer
from 0 to 255, is used in route computation. The lower the value, the more
desirable the node is for intermediate routing.
based upon one or both of the following congestion measures: cycle
utilization of the hardware and total buffer utilization. When this
congestion exists this node is not included in route selection by other
nodes.
2-39
Page 88

Using Technician Interface Scripts
Depleted Indicates whether Intermediate Session Routing resources are depleted.
This node is not included in intermediate route selection by other nodes
when resources are depleted.
Quiescing Ind icates whether the node is quiescing. This node is not included in route
selection by other nodes when the node is quiescing.
GW Indicates whether the node provide gateway functions.
CDS Indicates whether the node provides Central Directory Support.
Sample Display - show appn topology node
APPN Topology Nodes
-------------------
Node
----------------USWFLT01.AN NN 3547 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.AFN NN 3547 4 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.ASN NN 3547 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.BCN NN 3547 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.BUD NN 3547 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.CN1 VRN 0 0 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.PCX NN 3547 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.PLUTO NN 3547 6 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.VEGAS NN 3548 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.DURHAM NN 3548 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.SNEEZY NN 3548 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM NN 3548 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.MERCURY NN 3549 14 0 No No No No No
USWFLT01.RALEIGH NN 3549 2 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.WF3174A NN 3551 64 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.WFAS400 NN 3550 88 128 No No No No No
USWFLT01.BROOKLYN NN 3550 2 128 No No No No No
17 Entries.
Type
----
FRSN
----
RSN
---
RAR
---
Congested
---------
Depleted
--------
Quiescing
---------GW--
CDS
---
2-40
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 89

topology statistics
Displays APPN topology statistics.
Node Record Statistics:
Max Nodes Maximum number of nodes allowed in the APPN topology
Current Nodes Current number of nodes in this node's topology database. If this
Received TDUs Number of TDUs received from all adjacent network nodes since
Sent TDUs Number of TDUs built by this node to be sent to all adjacent
Received Low RSNs Number of topology node updates received by this node with a
database. This administratively assigned value must be equal to or
greater than the maximum total number of end nodes and network
nodes. If the number of nodes exceeds this value, APPN will issue
an alert and the node can no longer participate as a network node.
value exceeds the maximum number of nodes allowed, an APPN
alert is issued.
last initialization.
network nodes since last initialization.
RSN less than the current RSN. Both even and odd RSNs are
included in this count.
Received Equal RSNs Number of topology node updates received by this node with a
Received High RSNs Number of topology node updates received by this node with an
Received Bad RSNs Number of topology node updates received by this node with an
State Updates Number of topology no de records built as a result of in ternally
Errors Number of topology node record inconsistencies detected by this
Timer Updates Number of topology node r ecords b u ilt fo r thi s node's reso urce due
Records Purged Number of topology node records purged from this nod e's topology
308658-14.00 Rev 00
RSN equal to the current RSN. Both even and odd RSNs are
included in this count.
RSN greater than the current RSN.
odd RSN greater than the current RSN.
detected node state changes that af fect APPN topology and routing.
node.
to timer updates.
database.
2-41
Page 90

Using Technician Interface Scripts
TG Record Statistics:
Received Low RSNs Number of topology transmission group updates received by this
Received Equal RSNs Number of topology transmission group updates received by this
Received High RSNs Number of topology transmission group updates received by this
Received Bad RSNs Number of topology transmission group updates received by this
State Updates Number of topology trans mi ssi on gro up reco rds built as a result of
Errors Number of topology transmission group records inconsistencies
Timer Updates Number of topology transmission group records built for this
Records Purged Number of topology transmission group records purged from this
node with an RSN less than the current RSN. Both even and odd
RSNs are included in this count.
node with an RSN equal to the current RSN. Both even and odd
RSNs are included in this count.
node with an RSN greater than the current RSN.
node with an odd RSN greater than the current RSN.
internally detected node state changes that affect APPN topology
and routing.
detected by this node.
node's resource due to timer updates.
node's topology database.
2-42
Routes Calculated Number of routes calculated for all class of services since the last
initialization.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 91

Sample Display - show appn topology statistics
APPN Topology Statistics
----------------------Node Record Statistics
--------------------- Max Nodes: 0
Current Nodes: 38
Received TDUs: 45
Sent TDUs: 50
Received Low RSNs: 3
Received Equal RSNs: 39
Received High RSNs: 19
Received Bad RSNs: 10
State Updates: 0
Errors: 0
Timer Updates: 0
Records Purged: 0
TG record Statistics
------------------- Received Low RSNs: 18
Received Equal RSNs: 210
Received High RSNs: 125
Received Bad RSNs: 43
State Updates: 5
Errors: 1
Timer Updates: 0
Records Purged: 0
Routes Calculated: 0
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-43
Page 92

Using Technician Interface Scripts
topology tg definition
Displays transmission group information for all transmission group owners or for a
specific transmission group owner.
TG Owner Fully qualified name for the originating node for this transmission group. The
format is
TG Destination Fully qualified network name for the destination node for this transmiss ion
group.
TG Num Number associated with this transmission group. Range is 0 to 255.
Eff Cap Indicates the effective capacity of this transmission group. I t is derived from the
link bandwidth and maxi mu m l oad f act or wit h th e range of 0 through 255. This
is an administratively assigned value for this transmission group.
Conn Cost Cost per connection time. This value represents the relativ e cost per unit of time
to use the transmission group. Range is from 0, which means no cost, to 255,
which indicates maximum cost. This is an administratively assigned value
associated with this transmission group.
Byte Cost Relative cost of transmitting a byte over this link. Range is from 0 (lowest cost)
to 255. This is an administratively assigned value associated with this
transmission group.
Security Security is represented as an integer with a range of 1 to 255. This is an
administratively assigned value associated with this transmission group. The
most common values are 1 (nonsecure), 32 (public-switched), 64
(underground), 128 (conduit), 160 (encrypted), 192 (guarded radiation), and
255 (maximum).
[
<owner name>
<network_ID>.<CP_name>
]
.
2-44
Delay Relative amount of time that it takes for a signal to travel the length of the
logical link, with a range of 0 through 255 . Thi s is an admini s trat ively assigned
value associated with this transmission group. The most common values are 76
(negligible), 113 (terrestrial), 145 (packet), 153 (long), and 255 (maximum).
User 1 First user-defined transmission group characteristic for this transmission group,
with a range of 0 to 255. This is an administratively assigned value associated
with this transmission group.
User 2 Second user-defined transmission group characteristic for this transmission
group, with a range of 0 to 255. This is an adm inistratively assigned value
associated with this transmission group.
User 3 Third user-defined transmission group characteristic for this transmission
group, with a range of 0 to 255. This is an adm inistratively assigned value
associated with this transmission group.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 93

Sample Display - show appn tg definition
APPN Topology TG Definition
--------------------------TG
Err
Conn
Byte
Secu
TG Owner
---------------USWFLT01.PLUTO USWFLT01.DURHAM 21 48001113128128128
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.PLUTO 21 133 128 128 1 0 128 128 128
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM 1 133 128 128 1 0 128 128 128
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM 2 133 128 128 1 0 128 128 128
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM 3 00010000
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM 4 00010000
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.WF3174A 21 133 128 128 1 0 128 128 128
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM USWFLT01.DURHAM 1 133 128 128 1 0 128 128 128
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM USWFLT01.DURHAM 2 133 128 128 1 0 128 128 128
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM USWFLT01.DURHAM 3 00010000
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM USWFLT01.WFAS400 21 00010000
USWFLT01.WF3174A USWFLT01.DURHAM 21 68 0 0 32 113 0 0 0
12 Entries.
TG Destination
---------------
Num
---
Cap
---
Cost
----
Cost
----
rity
----
Delay
---
User
1
---
User
2
---
User
3
---
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-45
Page 94

Using Technician Interface Scripts
topology tg status
Displays transmission group topology information for all transmission group owners or
for a specific transmission group owner.
TG Owner Fully qualified name for the originating node for this transmission
TG Destination Fully qualified network name for the destination node for this
TG Num Number associated with this transmission group. Range is 0 to 255.
FRSN Flow Reduction Sequence Numbers are associated with Topology
RSN Current owning node's Resource Sequence Number for this
Up? Indicates whether the transmission group is operational.
Quiescing Indicates whether the transmission group is quiescing.
CP-CP Sessn Indicates whether CP-CP sessions are supported on this
[
<owner name>
group. The format is
transmission gr oup.
Database Updates (TDUs) and are unique only within each APPN
network node. This FRSN indicates the last time this resource was
updated at this node.
resource.
transmission gr oup.
]
<network_ID>.<CP_name>.
2-46
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 95

Sample Display - show appn tg status
APPN Topology TG Status
-----------------------
TG Quie- CP-CP
TG Owner TG Destination Num FRSN RSN Up? scing Sessn
----------------- ----------------- --- -------- -------- --- ----- ---- USWFLT01.PLUTO USWFLT01.DURHAM 21 2512 522 Yes No Yes
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.PLUTO 21 2538 272 Yes No Yes
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM 1 2551 264 No No Yes
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM 2 2546 170 Yes No Yes
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM 3 2504 142 No No Yes
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.ANAHEIM 4 2504 22 No No Yes
USWFLT01.DURHAM USWFLT01.WF3174A 21 2538 166 Yes No Yes
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM USWFLT01.DURHAM 1 2553 86 No No Yes
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM USWFLT01.DURHAM 2 2532 82 Yes No Yes
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM USWFLT01.DURHAM 3 2532 60 No No Yes
USWFLT01.ANAHEIM USWFLT01.WFAS400 21 2532 38 No No Yes
USWFLT01.WF3174A USWFLT01.DURHAM 21 2537 168 Yes No Yes
12 Entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
2-47
Page 96

Using Technician Interface Scripts
tunnel
[
<circuit>
]
Displays APPN tunnel information for all circuits or for a specific circuit.
CCT Circuit number of the circuit running over this APPN tunnel.
Partner Node Partner LU for this APPN tunnel.
State Current state of the tunnel: Up, Down, Init (initializing), or Not
Present.
Frames Rcvd Number of frames received over this APPN tunnel.
Frames Sent Number of frames transmitted over this APPN tunnel.
Frames Dropped Number of frames dropped by this APPN tunnel due to congestion.
Sample Display - show appn tunnel
APPN Tunnels
------------
Frames Frames Frames
CCT Partner Node State Rcvd Sent Dropped
---- ----------------- ------------ ------ ------ ------ 100 USWFLT01.ANAHEIM Active 26 7 0
2-48
1 Entry.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 97

version
Displays the current version and modification date of the appn.bat script.
Sample Display - show appn version
APPN.bat Version: #.## Date: mm/dd/yy.
vrn
<VRN name>
[
Displays state information for all Virtual Routing Nodes (VRNs) or for a specific VRN.
VRN Fully qualified network name that is locally defined at each
State Current state of this VRN: Inactive, Pending Active, Active,
]
network node in the format
Pending Inactive.
<network_ID>.<CP_name>
.
Port Administratively assigned name for this APPN port. The name can
Port State Current state of this port: Inactive, Pending Active, Active,
Sample Display - show appn vrn
APPN Virtual Routing Nodes
--------------------------
VRN State Port Port State
----------------- ---------------- -------- --------------- USWFLT01.CN1 Pending Active PORT31 Inactive
308658-14.00 Rev 00
be from one to eight characters.
Pending Inactive.
2-49
Page 98

Using Technician Interface Scripts
show at
show at
The
services. For detailed information on the Nortel Networks implementation of AppleTalk
services, refer to Configuring AppleTalk Services.
show at
The
aarp [<net>.<node> | find <net>] filters zone [circuit <circuit name>]
alerts routes | nets [find <netlow>-<nethigh>]
base stats [aarp | ddp | rtmp | zipquery | zipgni |
circuit [<circuit name>] total [routes | nets | zones | aarp]
<option>
commands display information about the AppleTalk protocol and
command supports the following subcommand options:
[zones]
zipes | nbp | echo] [<circuit name>]
2-50
configuration [circuit <circuit name>] version
disabled zones | zip [find <pattern>]
enabled
308658-14.00 Rev 00
Page 99

aarp
<net>.<node>
[
| find
<net>
]
Displays all entries in th e Apple Talk Address Resolution Protocol (AARP) tab le, only the
AARP entry for a specific node, or all entries that have a network address that matches a
specified pattern.
<net>.<node>
find
<network_pattern>
Displays the AARP entry for the specified network node in the
<network_ID>.<node_ID>
format
Displays the AARP entries that have a network address that
matches the given pattern.
.
The table inc ludes the following information:
Address AppleTalk network address of the node.
Physical Address Hardware address of the node (for example, the Ethernet address).
Circuit Name of the circuit on which the address resolution is in effect.
Sample Display - show at aarp
AppleTalk AARP Table
--------------------
Address Physical Address Circuit
--------- ----------------------- --------
60020.19 00-00-A2-01-51-AD S32
60060.193 00-2B S31
60100.213 00-00-A2-00-F9-B0 E24
60120.2
60130.179 00-00-89-01-A3-8A E23
60130.226 00-80-D3-A0-0A-62 E23
6 total entries.
308658-14.00 Rev 00
<
null-PPP> S34
2-51
Page 100

Using Technician Interface Scripts
alerts
Displays all AppleTalk circuits that are enabled but not up. Mode is always Enabled but
the state will be down. Use this di splay to identify the interfaces that are not wo r kin g. The
table includes the following information:
Circuit Name of the circuit the port is on.
Mode Mode will be Enabled, in this case.
Network Network start and end numbers that constitute the range of the
Address Network address of the port, which is Dynamic, meaning that the
Zone List List containing all the zones configured for the network range.
Sample Display - show at alerts
network numbers. These numbers are in the range of 1 through
65,279.
seed router assigns it, or a manually configured network address
and identifier.
2-52
AppleTalk Circuit Alerts: Enabled but state is down
-----------------------------------------------------
Circuit
-------S31 Enabled 60060-60060 Dynamic ’WAN’
1 entries found.
1 total entries.
Mode
--------
Network
----------
Address
---------------
----------------------
Zone List
308658-14.00 Rev 00
 Loading...
Loading...