Page 1

Product Bulletin
Bulletin Number: P-2009-0131-Global
Date: 30-Sep 2009
UNIStim Firmware Release 3.4 for IP Phones, including:
0604DCN for Phase II IP Phones (2001, 2002 & 2004),
0621C6R for IP Phone 2007,
0623C6T, 0624C6T, 0625C6T and 0627C6T for IP Phone 1110, 1120E, 1140E
and 1150E respectively and
062AC6T for IP Phone 1210, 1220, and 1230
REVISION HISTORY
Date Revision # Summary of Changes
30-Sep-09 Original bulletin This is the original publication
Introduction
Nortel* is pleased to announce the availability of UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP
Phones. UNIStim firmware release 3.4 makes available firmware version 0604DCN for the
Phase II IP Phone 2001, Phase II IP Phone 2002, and Phase II IP Phone 2004. UNIStim
firmware release 3.4 also makes available firmware version 0621C6R for the IP Phone
2007. In addition, UNIStim firmware release 3.4 makes available firmware version 0623C6T,
0624C6T, 0625C6T and 0627C6T for the IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1120E, IP Phone 1140E
and IP Phone 1150E respectively. Finally, UNIStim firmware release 3.4 makes available
firmware version 062AC6T for the IP Phone 1210, IP Phone 1220 and IP Phone 1230.
Nortel recommends an upgrade to these releases of firmware for all applicable IP Phones
and Call Servers at the earliest convenience. These releases are being provided as a no
charge update to all customers.
Nortel Page 1 of 57
Page 2

UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones is available for download from the “Software
Download” link under “Support and Training” on the Nortel website located at:
http://support.nortel.com
and Accessories”. These firmware loads have not
. The firmware is available by phone model under “Phones, Clients
been introduced as the default loads
for the IP Phones shipped from Nortel.
UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones delivers enhancements to Nortel’s IP Telephony
Solution and delivers general quality improvements. The enhancements available include:
Screen Saver support (including slideshow) on the IP Phone 2007
Support for Voice Signaling Application in LLDP-MED Network Policy TLV
Incoming calls accepted during Zone Paging
AG interface enhancement – forwarding of cookie deletion events
GXAS interface enhancement – expanded “Status Updates” commands
OS Diagnostics support on the IP Phone 1100 series
Enhancements
1. Screen Saver – including slideshow (applies to the IP Phone 2007 only)
To provide greater choice for power conservation and to extend the life of the screen on the
IP Phone 2007, as of UNIStim firmware release 3.4, the “Display Setting” Preference screen
has been enhanced to provide screen saver control.
The addition of screen saver options to the Display Setting screen also allowed the
opportunity to remove some ambiguity on the operation of the IP Phone 2007’s Dim feature.
Previously, the Dim feature did not work if the Backlight was disabled. Now the Dim control
is independent of the backlight control.
Also, with UNIStim firmware release 3.4, a new slideshow mode has been introduced.
Slideshow, Backlight and Dim are all grouped together in the new “ScreenSaver” section.
The new ScreenSaver “Display Setting” Preference screen is as depicted below:
Nortel Page 2 of 57
Page 3
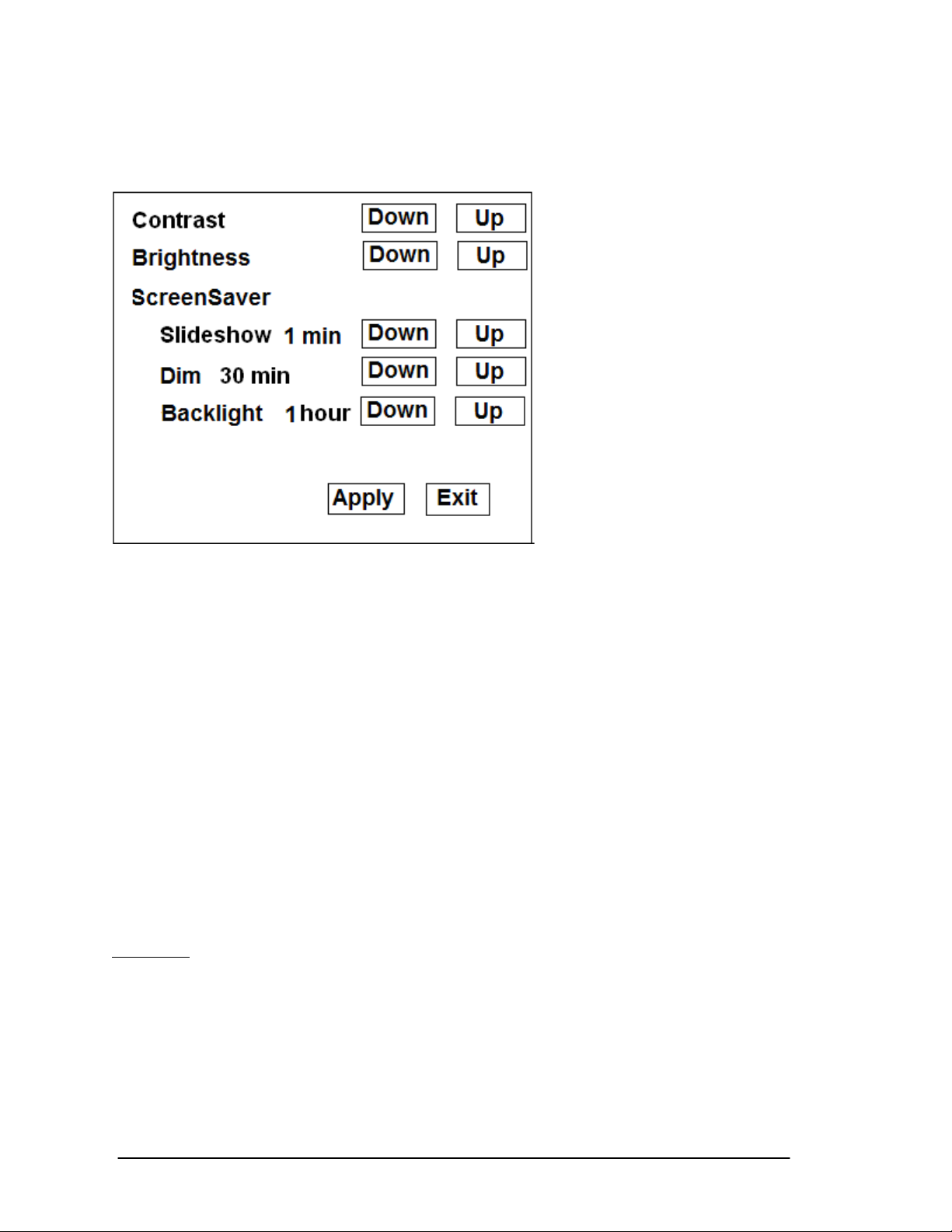
Contrast and Brightness continue to function as they did in UNIStim firmware release prior to
3.4. The new ScreenSaver sections bundles together the Slideshow, Dim, and Backlight
controls. Each timer – Slideshow, Dim, and Backlight – are now independent of each other.
But realize that once the backlight extinguishes, Dim and Slideshow become redundant.
Also note that the Slideshow can be run while the phone is in Dim mode.
The Slideshow, Dim, and Backlight timers are used to delay the start of the respective
screen saver control after the phone becomes idle.
The acceptable timer values for Slideshow are: 1 minute, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15
minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours and Off. The default timeout is Off.
The acceptable timer values for Dim are: 5 seconds, 1 minute, 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 15
minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and Off. The default timeout is 30 minutes.
The acceptable timer values for Backlight are 5 seconds, 1 minute, 5 minutes, 10 minutes,
15 minutes, 30 minutes, 1 hour, 2 hours, and “Always On”. The default timeout is 1 hour.
Slideshow
The Slideshow feature is new to the IP Phone 2007 as of UNIStim firmware release 3.4.
This feature allows users to download images onto the phone which are sequentially
displayed. A user can download up to ten images.
The Slideshow will cycle through a list of user supplied images stored in the phone’s
memory. Images can be downloaded via the IP Phone’s configuration file (i2007.cfg).
Nortel Page 3 of 57
Page 4

Once the slideshow starts, the phone sequentially displays the slide show images from the
phone’s memory. Each image is displayed for 10 seconds before the next image is loaded.
Once the last found image is displayed the phone will wrap around and start the sequence
from the beginning again. The slideshow will continue until the backlight timer turns off the
screen’s backlight. If the Dim timer is enabled, the slide show images continue to be visible,
although dimmed, after the Dim mode starts.
If the Screensaver timer is set to a value other than “Off” but no images are stored in the
phone’s memory, the Screensaver operation will be the same as if the Screensaver timer is
“Off”.
Slideshow configuration
The slideshow images are downloaded to the IP Phone 2007 via the IP Phone’s
configuration file (i2007.cfg). A new section called [IMAGES] must be added to the i2007.cfg
file. This section specifies the files to be copied. The [IMAGES] section can be in the file by
itself or with the [FW] and [FONT0N] sections.
The [IMAGES] section has six command lines:
• DOWNLOAD_MODE (required command) - The DOWNLOAD_MODE can be either
FORCED or AUTO. If FORCED, the VERSION command is ignored and the image
files are always downloaded. If AUTO, the application looks at the VERSION and
downloads the image files only if they are a newer version than what is currently
stored on the phone.
• VERSION (optional command) - if this command is not present, version 0 is
assumed. The VERSION command specifies the version of the images being
downloaded. The version applies to all files listed in the [IMAGES] section. When
images are written to the phone’s memory, the value for the .cfg file’s VERSION field
(or “0” if VERSION is not in the file) becomes the new stored version value against
which any future comparisons are made. Note that VERSION string’s values of 1,
01, and 000001 are all equivalent to decimal “1”.
• DELETE_FILES (optional command) - see “Slideshow deletion” section below for
more details.
• FILENAME (required command) - There can be up to ten FILENAME entries for the
slideshow images – one command for each image file to transfer – each containing
the filename of the image to be downloaded. The slideshow images must be 240 W
x 320 H pixel 24 bit PNG or JPG files. Files can either be in the same folder as the
i2007.cfg file or in a sub-folder. If they are in a subdirectory, the path needs to be
pre-pended to each filename. The image files must be named screensaverN.png or
screensaverN.jpg where “N” is a number from 0 to 9 inclusive. Missing files are
silently skipped. A mixture of PNG and JPG files can be loaded, but since the phone
ignores the filename extension once the file is copied to the phone, there can be only
one file with each filename.
• PROTOCOL (optional command) – The PROTOCOL command specifies the
protocol used to download the image files. The protocol can be either TFTP or
Nortel Page 4 of 57
Page 5
HTTP. If provided, the specified protocol will be used. If this command is not present
then the phone will use the same protocol that it used to obtain the i2007.cfg file.
• SERVER_IP xxx.xxx.xxx (required command) - IP Address (in decimal format) of the
TFTP server
Below is an example of an IMAGES section in an i2007.cfg file. Note that in this example
three of the image files are in a subdirectory named “2007pics” while the others are in the
same directory as the i2007.cfg file itself:
[IMAGES]
DOWNLOAD_MODE FORCED
VERSION 000001
FILENAME screensaver0.png
FILENAME screensaver1.png
FILENAME screensaver2.png
FILENAME screensaver3.png
FILENAME 2007pics/screensaver4.jpg
FILENAME 2007pics/screensaver5.jpg
FILENAME 2007pics/screensaver6.jpg
FILENAME screensaver7.png
FILENAME screensaver8.jpg
FILENAME screensaver9.png
PROTOCOL TFTP
SERVER_IP 192.168.1.101
Below is another example of an IMAGES section in an i2007.cfg file. In this example the
three images will be downloaded only if the images already stored in the phone’s memory
are version 1 or less.
[IMAGES]
DOWNLOAD_MODE AUTO
VERSION 000002
FILENAME screensaver5.png
FILENAME screensaver6.png
FILENAME screensaver8.png
PROTOCOL TFTP
SERVER_IP 192.168.1.101
Slideshow deletion
Image files are deleted from the IP Phone 2007 via the IP Phone’s configuration file
(i2007.cfg) in one of two ways: either by overwriting the existing file by transferring a new file
with the same filename, or by deleting all the image files using the DELETE_FILES
command. To overwrite an image file, simply download an image file with the identical
screensaverN name. To delete all of the images, the DELETE_FILES command must be
Nortel Page 5 of 57
Page 6
added to the configuration file. Within the [IMAGES] section, the command DELETE_FILES
is specified followed by a space and either a 'Y', 'y', or '1' character. If no character is placed
after the space following the DELETE_FILES command, or if any other character besides
'Y', 'y', or '1' is placed after the space following DELETE_FILES command, the command is
ignored and anything else in the [IMAGES] section is processed instead
1
. A valid
DELETE_FILES command deletes all image files.
The following are examples of valid delete command lines:
DELETE_FILES 1
DELETE_FILES Y
DELETE_FILES Yes
DELETE_FILES y
DELETE_FILES yES
The DOWNLOAD_MODE and VERSION fields are still processes when using the
DELETE_FILES command. If the [IMAGES] section contains both a valid DELETE_FILES
command and FILENAME parameters, the phone’s currently stored image files are first
deleted and then the new specifies images are downloaded. Thus the existing images on
the phone can be deleted and new images loaded all in one operation.
The following is an example of an [IMAGES] section that deletes all the image files of
version 2 or less which are already on the phone and then loads new images and saves
their version as value 2.
[IMAGES]
DOWNLOAD_MODE AUTO
VERSION 2
DELETE_FILES yes
FILENAME screensaver 0.png
FILENAME screensaver 1.png
FILENAME 2007pics/screensaver4.jpg
FILENAME 2007pics/screensaver5.jpg
FILENAME 2007pics/screensaver6.jpg
…
ScreenSaver Auto-provison
UNIStim firmware release 3.4 also introduces changes to the Info Block to allow the
Screensaver options to be auto-provisioned
1
It doesn’t matter what follows the 'Y', 'y', or '1'. Only the first character is read. Thus ‘Yankee’, ‘yes’
and ‘1andOnly’ would all be valid.
Nortel Page 6 of 57
Page 7
A new Info Block parameter to allow the Slideshow timer to be auto-provisioned is provided
in the table below. Please refer to Appendix B for the complete list of parameters supported
within the Info block.
sst ‘0’ Off
‘1’ 1 minute
‘2’ 5 minutes
‘3’ 10 minutes
‘4’ 15 minutes
‘5’ 30 minutes
‘6’ 1 hour
‘7’ 2 hours
The new Info Block parameter that is added to allow the Dim timer to be auto-provisioned is
provided in the table below
supported within the Info block
2
. Please refer to Appendix B for the complete list of parameters
Phone inactivity timer to initiate the slide show
dimt ‘0’ Off
‘1’ 5 seconds
‘2’ 1 minute
‘3’ 5 minutes
‘4’ 10 minutes
‘5’ 15 minutes
‘6’ 30 minutes
‘7’ 1 hour
‘8’ 2 hours
Support of the auto-provisioning parameter for backlight timer (blt) remains unchanged with
UNIStim firmware release 3.4.
Phone inactivity timer to dim the screen
2
As of UNIStim firmware release 3.4, the previously supported “dim” parameter is no longer
supported since its functionality is superseded by the dimt parameter. The phone will still accept the
dim parameter to prevent errors when reading existing provisioning files but the parameter will be
ignored in favor of the new dimt parameter.
Nortel Page 7 of 57
Page 8

Since the Slideshow and Dim timers can be auto-provisioned, changes to the autoprovisioning menu have occurred within group #15. The “Display Dim Enabled” option is
renamed to “Screen Dim” and a new “Slideshow” checkbox has been added.
2. Support for “Voice Signaling” Application in LLDP-MED Network Policy TLV
(applies to the IP Phone 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230)
IEEE 802.1ab LLDP lets network devices transmit and receive advertisements to and from
their network neighbors. Details such as device configuration, device capabilities and device
identification can be advertised using this protocol.
LLDP devices advertise their information by sending Type-Length-Value (TLV) messages to
their neighbors. The TLVs supported in the IP phones include:
Basic Management TLV
IEEE 802.1 Organizationally Specific TLV
IEEE 802.3 Organizationally Specific TLV
TIA Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED) TLV - The Telecommunications Industry
Association (TIA) has developed an extension to LLDP for VoIP networks. VoIPrelated extensions to LLDP, known as LLDP-Media Endpoint Discovery (LLDP-MED)
enables media devices to transmit and receive media related information.
One of the LLDP-MED TLV that is supported by the IP Phone is the Network Policy
Discovery TLV. The Network Policy Discovery TLV allows both network infrastructure and
endpoints devices, such as IP Phones, to advertise VLAN identifiers and both the Layer 2
priority and DSCP value associated with a specific application type.
Support for the Network Policy Discovery TLV was first delivered in UNIStim firmware
release 1.0. Prior to UNIStim firmware release 3.4 though, the only application type
supported in the IP Phones was the application type of “Voice”. This meant that the Layer 2
priority and DSCP value associated with voice were applied to both the media and the
signaling channels.
Nortel Page 8 of 57
Page 9

With UNIStim firmware release 3.4, the IP Phones now also support the application type of
“Voice Signaling”. By supporting both “Voice” and “Voice Signaling” application types, a
separate Layer 2 priority and DSCP value can be applied to the voice media path distinct
from the voice signaling path. This is beneficial in network topologies that require a separate
policy for the voice signaling than the voice media.
Feature Limitation
The neighboring network switch must be configured to send both “Voice” and “Voice
Signaling” Network Policy TLV application types. If the network switch sends only “Voice”
application type, the same Layer 2 priority and DSCP value will be applied to both the media
and signaling packets (consistent with the behavior prior to UNIStim firmware release 3.4).
3. Incoming calls accepted during Zone Paging (applies to the IP Phone 2007, 1110,
1120E, 1140E, and 1150E)
One of the applications delivered by the Nortel Application Gateway solution is zone paging.
Prior to UNIStim firmware release 3.4, when an incoming call was received while the phone
was in paging mode, but not actually involved in a page, the screen on the IP phone did not
switch to telephony mode. By not switching, the end user could not see from where the call
was originating since the Caller Line ID (CLID) was not presented. With UNIStim firmware
release 3.4, when the phone receives an incoming call while the phone is in paging mode,
but not actually involved in a page, the phone switches to the telephony screen
automatically allowing the end user to see the calling party and decide whether to answer
the call. It should be noted, however, that the phone will still not switch to the telephony
screen if there is an incoming call while the set is actually involved in Priority Paging. This is
because Priority Paging actually has priority over regular phone calls.
4. AG interface enhancement – forwarding of cookie deletion event (applies to the IP
Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230)
Cookies are used on the IP phone to share information between the Nortel Application
Gateway (AG) and the associated call server. Prior to UNIStim firmware release 3.4, the AG
was not informed if a cookie was deleted. With UNIStim firmware release 3.4, if the call
server deletes a cookie on the phone, the phone now forwards this event to the associated
AG, so the Signaling Server and the AG remain synchronized.
Nortel Page 9 of 57
Page 10
5. GXAS interface enhancement – expanded “Status Updates” commands (applies
to the IP Phone 2007, 1120E, 1140E, and 1150E)
UNIStim firmware release 3.4 introduces additional communication command to the
interface protocol used by Nortel Developer Partners to deliver server-based applications on
the graphical IP Phone 2007, 1120E, 1140E, and 1150E.
This interface protocol provides the means for information exchange between server-based
applications and the IP Phone. The protocol and the complete list of supported commands
in documented in the “IP Clients Graphical Application Server Development Guide” This
guide is available through the Nortel Developer Program. For details on the program, please
see www.Nortel.com/developer
.
6. OS Diagnostics support (applies to the IP Phone 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210,
1220 and 1230)
3
The UNIStim firmware release 3.4 introduces Operating System (OS) diagnostic capabilities
to assist support personnel. The OS diagnostics provides support personnel the capability to
analyze the state of the OS around the time of a phone error.
This functionality is available to Nortel support personnel only.
3
Operating System (OS) diagnostic capabilities was delivered on the IP Phone 2007 in UNISt im
firmware release 3.3
Nortel Page 10 of 57
Page 11

Product Advisements
The following is a list of advisements associated with UNIStim firmware release 3.4. Some
advisements remain from previous releases of firmware, whereas other advisements reflect
new or changed behavior introduced with UNIStim firmware release 3.4. Advisements that
are new to UNIStim firmware release 3.4 or have changed since previous releases of
UNIStim firmware are prefixed with “NEW”.
NEW – A USB Hub cannot be used to simultaneously connect a mouse and a
keyboard to the USB port of the IP Phone 2007 (applies to the IP Phone 2007 only)
The USB port on the IP Phone 2007 will not support the connection of both a mouse and a
keyboard connected via a USB hub. The USB port on the IP Phone 2007 is restricted to
supported either a USB mouse or a USB keyboard, but not both simultaneously.
2-step upgrade may be required to load UNIStim Firmware release 3.4 on the IP Phone
2007 (applies to the IP Phone 2007 only)
Due to changes in the memory structure of the IP Phone 2007, a 2-step upgrade may be
required to load UNIStim firmware release 3.4 onto the IP Phone 2007 if the upgrade is
performed with TFTP. If the IP Phone 2007 is currently running UNIStim firmware release
3.2 or greater then one will be able to upgrade using TFTP directly to UNIStim firmware
release 3.4. But if the IP Phone 2007 is running any firmware prior to UNIStim firmware
release 3.2 and the upgrade is performed with TFTP, then the phone must first be upgraded
to UNIStim firmware release 3.2 before subsequently upgrading to UNIStim firmware 3.4.
The 2-step up upgrade is not required if the upgrade is performed from the call server using
UFTP.
Minimum allowable firmware on the new IP Phone 1120E and new IP Phone 1140E
with hardware changes (applies to the new IP Phone 1120E and 1140E)
Recent hardware changes in the IP Phone 1120E and IP Phone 1140E restrict the minimal
allowable firmware version on these phones. The new hardware phones will absolutely
accept an upgrade to UNIStim firmware release 3.4. But the new hardware IP Phone 1120E
and new hardware IP Phone 1140E will NOT accept a downgrade to any firmware version
previous to UNIStim firmware release 3.1 (0624C6J and 0625C6J respectively)
Nortel Page 11 of 57
Page 12
The new hardware is introduced with the following specific PEC and hardware release
numbers:
PEC Hardware
Description
Release
NTYS03ADE6 01 IP Phone 1120E Graphite with Icon Keycaps (RoHS)
NTYS03BDE6 01 IP Phone 1120E Graphite with English keycaps (RoHS)
NTYS03BDGS 01 IP Phone 1120E GSA (RoHS)
NTYS05ACE6 50 IP Phone 1140E Graphite with Icon Keycaps (RoHS)
NTYS05BCE6 50 IP Phone 1140E Graphite with English keycaps (RoHS)
NTYS05BCGS 01 IP Phone 1140E GSA (RoHS)
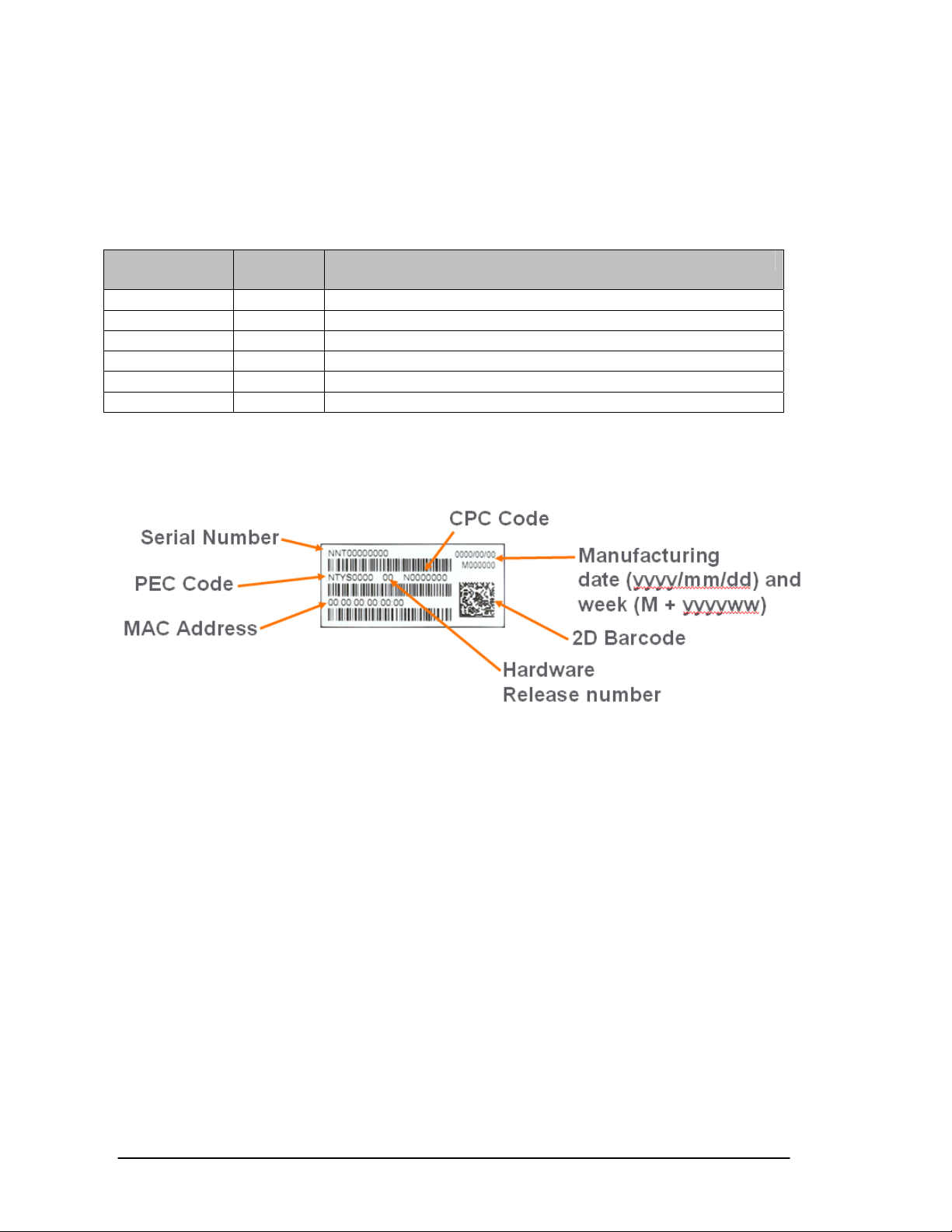
The below Figure 1 provides an explanation of where to identify the PEC and Hardware
Release Number on the white product label (located on the back of the IP Phone).
Figure 1 – IP Phone Product Label
If UFTP firmware download is used within the Communication Server 1000 environment,
Nortel recommends that the firmware image for the IP Phone 1120E and IP Phone 1140E
on the signaling server be upgraded minimally to UNIStim firmware release 3.1.
Communication Server 1000 release 5.0, and greater, will interpret denial of firmware
downgrade responses from the new hardware phones. However, Communication Server
1000 prior to release 5.0 require patch MPLR23154 to interpret correctly the phones denial
of firmware downgrade responses. Failure to install the patch introduces the risk that the call
server may continuously try and downgrade the firmware thereby denying service to the
phone.
If TFTP firmware download is used, and the TFTP server is not upgraded to UNIStim
firmware release 3.1 or greater, the TFTP server will continuously try and downgrade the
firmware in the phone. The new hardware phone will prevent the downgrade resulting in the
phone being denied service.
Nortel Page 12 of 57
Page 13

In a Communication Server 1000 environment containing SRG and SRG50 branch office
systems, the "umsUpgradeAll" Main Office system command should not to be
executed when the branch office sites has the new hardware IP Phone 1120E or the new
hardware IP Phone 1140E and the IP phone firmware at the Main Office precedes UNIStim
firmware release 3.1.
Two SRG atomic patches exist to allow the SRG and SRG50 platforms respectively to
interpret denial of firmware downgrade responses from the new hardware phones. Failure to
install the patches introduces the risk that the call server may continuously try and
downgrade the firmware thereby denying service to the phone.
For SRG 200 and SRG 400 release 1.5, the denial of firmware downgrade support is
included in atomic patch BCM.R400.294-SRG-4.8-1-0 and later.
For SRG50 release 3.0, the denial of firmware downgrade support is included in atomic
patch BCM050.R300.SRG-194-1 and later. This patch is not available for SRG50 release
2.0
For complete details on the minimal allowable firmware for the new hardware changes in the
IP Phone 1120E and IP Phone 1140E, please refer to product bulletin P-2009-0015-Global.
EAP-MD5 and Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (applies to IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004,
2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230)
If access control is enabled on the IP Phone and MD5 is chosen as the EAP mode, realize
that EAP-MD5 is not available by default in the Microsoft Windows Server 2008 NPS
4
but
can be turned on. Please refer to Microsoft support for more details on enabling EAP-MD5.
In addition, minimally, Service Pack 2 is required on the Windows Server 2008 NPS to
support the IP Phones using MD5 access control.
PC Port resets during firmware upgrade (applies to IP Phone 2002, 2004, and 2007)
The PC port on the IP Phone 2002, 2004 and 2007 temporarily resets during firmware
upgrades and phone resets due to configuration changes. As a result, traffic to and from the
network and a PC connected to the IP Phone’s PC port will be disrupted during these
periods.
Minimal firmware required on the Algo 4900 USB ATA (applies to IP Phone 1120E,
1140E, and 1150E)
The Algo 4900 USB ATA must have firmware version v1.00.32v or greater before
connecting the adapter to the IP Phone. A Windows based configuration tool to upgrade the
ATA firmware version can be found at the Algo web site:
4
In Windows Server 2008, IAS has been replaced with Network Policy Server (NPS)
Nortel Page 13 of 57
Page 14

http://www.algosolutions.com/products/usbATA/fw-download.html
Also note that the Algo 4900 USB ATA
is classified as a high power USB device and must
be connected to the phone through a powered USB hub. If it is connected to the phone
directly, it will cause the phone to shut off service to the USB port completely.
Constant humming sound may be heard in Nortel USB Adapter (applies to the IP
Phone 1120E, 1140E and 1150E)
A constant humming noise is sometime heard through the Nortel USB Adapter headset
when either the Nortel Enhanced USB Headset Adapter or the Nortel Mobile USB Headset
Adapter is connected to the IP Phone 1120E, 1140E and 1150E.
The humming noise is within the headset adapter can be corrected with upgrading the
headset adapter firmware to version 2.00.98 or greater.
Nortel USB Headset Adapter firmware version 2.00.98 is available for download from the
“Software Download” link under “Support and Training” on the Nortel website located at:
http://support.nortel.com
. The firmware is available for the IP Phone 1120E, 1140E and
1150E models under “Phones, Clients and Accessories” as file Adapter3v2.0098.zip.
To load the version 2.00.98 firmware onto the Nortel USB Headset Adapter perform the
following procedure:
1. Download the firmware file Adapter3v2.0098.zip from the Nortel Technical Support
web site
2. Load the file Adapter3v2.0098.zip onto a PC
3. Uncompress (unzip) the file to obtain Adapter3v2.0098.exe.txt.
4. Rename Adapter3v2.0098.exe.txt to Adapter3v2.0098.exe
5. Connect the Nortel USB Headset Adapter to the PC.
6. Start the Adapter3v2.0098.exe application to load the firmware onto the device.
IP Phone’s performance will be diminished during broadcast storms (applies to IP
Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230)
By default, network traffic to the IP Phone will be accepted based on the packet’s
destination MAC address. The phone will therefore accept, in addition to all unicast packets
sent to the phones MAC address, all broadcast and multicast packets as well. If the network
environment results in a high amount of broadcast or multicast traffic, the IP Phone’s
performance may be impacted.
If “Voice 802.1Q” is enabled on the phone, the phone can then be provisioned to filter some
or all of the broadcast or multicast traffic. If “VLAN Filter” is enabled, packets will be
accepted by the phone based on the packet’s destination MAC address as well as the
packet’s VLAN tag. Untagged packets and packets with a VLAN tag different from the Voice
Nortel Page 14 of 57
Page 15

VLAN ID will be prevented from reaching the phone. This will protect the voice application
from excessive traffic sent to the broadcast address or to the multicast addresses. But
please be aware, if VLAN filtering is enabled on the phone, one must ensure that voice
packets are tagged with the appropriate VLAN ID as they exit the network switch, else the
packets will be dropped by the filter.
Change in behavior of entering an asterisk (*) to manually provision the “Provision”
parameter in the network configuration menu (applies to the IP Phone 2007, 1120E,
1140E, and 1150E)
In UNIStim firmware prior to release 3.2 the asterisk (*) key could not be used to input the
dot (.) for defining an IP address in the “Provision” parameter in the network configuration
menu. Since the “Provision” parameter in the network configuration menu can accept both a
URL as well as an IP address the entry is a text based field causing the asterisk key to be
accepted as an actual asterisk. But since this is different from other parameters that accept
only
an IP address where the asterisk key is used to represent the dot the inconsistent
behavior of this field can be confusing.
Therefore with UNIStim firmware release 3.2, the typing of the asterisk key in the “Provision”
parameter in the network configuration menu has slightly changed. Now, if the asterisk key
is pressed twice
relatively quickly it will input the dot. Pressing the asterisk key once will still
input the asterisk character consistent with previous behavior.
Throughput may be slow for large file transfers on conversions from GigE to 100Mbit
(applies to the IP Phone 1120E, 1140E and 1150E)
In networks in which a PC is connected to the IP Phone’s PC port and the PC’s NIC speed
is 100Mbit but the network speed is at GigE, large file transfers to the PC can take quite a
long time. This is an issue with large file transfers only which due to the speed mismatch
between the two phone ports can overflow the buffers in the phone resulting in
retransmissions.
Although the IP Phones support Ethernet flow control (802.3x), the support is only
implemented on the phone’s PC port, not on the phone’s network port. Ethernet flow control
is a mechanism were the IP Phone can request a brief “pause” from the transmitting
Ethernet device if the IP Phone buffers are about to overflow.
Ethernet flow control cannot be implemented on the phone’s network port, since it impacts
the phone’s voice quality. As a result, in environments were the network is GigE but the PC
NIC is only 100Mbit, large file transfers from the network to the PC can take quite a long
time.
On the other hand, since Ethernet flow control is implemented on the phone’s PC port, in
environments were the PC NIC is GigE but the network is only 100Mbits, large file transfers
should be well managed by the phone’s Ethernet flow control mechanism.
Nortel Page 15 of 57
Page 16

Incompatibility between older IP Phones and the Nortel-i2004-B option string (applies
to Phase 0 IP Phone 2004, Phase 1 IP Phone 2002 and Phase 1 IP Phone 2004 only)
5
A compatibility issue was found with the new Nortel-i2004-B option type and the older Phase
0 IP Phone 2004 (NTEX00), Phase 1 IP Phone 2002 (NTDU76) and Phase 1 IP Phone
2004 (NTDU82). Even thought these older phones ignore the Nortel-i2004-B option type, the
length of the DHCP frame causes problems for the older phones. Since the list of all the
parameters that can be provisioned via the Nortel-i2004-B options is extensive, the length of
the DHCP frame can be quite large. The older phones will only accept a DHCP message to
a maximum of 590 bytes (far short of the maximum DHCP message size of 1456 bytes). In a
mixed environment of phones that support Nortel-i2004-B with Phase 0 and Phase1 phones
one must either:
Ensure any option string that are defined are small enough that the DHCP message
does not exceed 590 bytes, or
Service the Phase 0 and Phase 1 phones with a DHCP offer that excludes the
Nortel-i2004-B option.
Receiving a LLDP MED Network Policy TLV from the network infrastructure will cause
the phone to ignore DSCP from the Communication Server 1000 Element Manager
and the Info Block (applies to IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E,
1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230)
Because of the precedence order, in auto-provisioning mode (i.e. the value has not been
overridden manually) if the IP Phone receives a LLDP MED Network Policy TLV from the
network infrastructure, the phone will provision its DSCP from the LLDP MED Network
Policy TLV and not from the Call Server or Info Block. When the phone receives a Network
Policy TLV from the network infrastructure, it sets its voice VLAN, L2 Priority and DSCP to
the value specified in the VLAN ID field, L2 Priority field and DSCP Value field respectively.
Thus, if the Network Policy TLV is received, any QoS values also received from the Call
Server (i.e. Telephony Manager and/or Element Manager) or Info Block it will be ignored.
New - Special Note:
As already mentioned in this bulletin, the new feature “DSCP
provisioning precedence override” introduced in UNIStim firmware release 3.3 provides a
work-around to this advisory.
Phones default for Auto VLAN changed to “Enabled”. And Auto VLAN now supports a
No VLAN option (applies to IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E,
1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230)
In firmware loads prior to UNIStim firmware release 2.2 for IP Phone 2007, 1110, 1120E,
1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230 and in firmware loads prior to UNIStim firmware
5
The Phase 0 IP Phone 2004, Phase 1 IP Phone 2002 and Phase 1 IP Phone 2004 are now End of
Life (EOL) products
Nortel Page 16 of 57
Page 17

release 2.3 for Phase II IP Phone 2001, 2002 and 2004, one had to manually provision
whether the phone was to be installed in an 802.1Q VLAN environment or not. The default
configuration for the phone was assuming that the phone was not
being deployed into an
environment supporting a Voice VLAN. The default source for VLAN assignment was “no
VLAN”.
For the phones to be deployed into a voice VLAN environment, the phone had to be
manually provisioned with either a Voice VLAN ID, or manually provisioned to accept and
Auto VLAN assignment.
With UNIStim firmware commencing with release 2.2 (and 2.3) and continuing with UNIStim
firmware release 3.1 the default configuration for the phone now has Auto VLAN assignment
via DHCP enabled. But realizing that not all phones will be deployed in an 802.1Q VLAN
environment, the Auto VLAN assignment support has also been updated to support both an
802.1Q VLAN environment and an environment without 802.1Q VLANs.
With Auto VLAN enabled, if VLAN information is provided within the DHCP option type
VLAN-A, the phone will use the VLAN information to provision a voice VLAN. However, if no
VLAN-A option type is provided by DHCP, the phone will assume that no VLAN is to be
provisioned.
Although the default configuration for voice VLAN has changed, the new default
configuration will not be applied to field upgrades. A limitation of the new functionality is that
it could only apply to new phones being shipped from the factory with UNIStim firmware
release 2.2 or greater. The default configuration of “Auto” will not be applied to field
upgrades. Upgrading firmware does not change any pre-established values already in the
phones.
But as mentioned above, to allow phones already deployed in the field to change the source
of their VLAN information, with UNIStim firmware release 3.2 a new parameter called
“vvsource” has been added to the Info Block to allow VLAN source to be auto-provisioned.
Important Note: While these changes provide greater flexibility, the change might impact
the deployment of new phones into the network.
Manually provisioned link speed and duplex mode restored to “Auto” after firmware
upgrade (applies to IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1120E, 1140E and 1150E)
In UNIStim firmware release 1.3
for IP Phones including 0604DAX for Phase II Phones,
0621C3N for IP Phone 2007, 0623C3F, 0624C3F, 0625C3F and 0627C3F for IP Phone
1110, 1120E, 1140E and 1150E respectively, Nortel introduced greater low level network
control available through the phones configuration menus. The greater control included
allowing the link speed and the duplex mode on the IP phones to be provisioned
independently for both the network port and the PC port
Nortel Page 17 of 57
Page 18

By delivering this greater network control, the firmware unfortunately has to reset link speed
and duplex mode back to “Auto” after an upgrade. Regrettably, preservation of the forced
manual override could not be maintained during the upgrade.
What this means, is that if the IP Phone is running firmware prior to UNIStim firmware
release 1.3 and if the link speed was manually provisioned to force the link to 10Mbit Full
Duplex or 100MBit Full Duplex, after upgrading the firmware to UNIStim firmware release
1.3 or greater (including the current UNIStim firmware release 3.0), the link speed and
duplex mode is reset to “Auto” representing Auto-negotiation. With the phone now
configured for Auto-negotiation a duplex mode mis-match will occur if the other end of the
link is still provisioned to force the link to 10Mbit Full Duplex or 100MBit Full Duplex.
But, with UNIStim firmware release 3.1 for IP Phones, the means to provision the network
port speed and the network port duplex mode has been added to the Info-Block (see feature
#3 “Auto-Provisioning Support for Network Port Speed and Network Port Duplex Mode”
detailed earlier in this bulletin. If a duplex mis-match occurs as a result of the firmware
upgrade, the speed and duplex mode can forced, by provisioning them via the Info Block.
This is possible because the auto-negotiation will pick the correct speed but the wrong
duplex mode. Since the speed is correct, but the duplex mode is wrong, transmission can
occur, albeit of poor quality. The duplex mismatch will impact the time taken for the phone to
receive the Info Block, but re-transmission mechanisms built into the transmission protocols
should allow the Info Block to eventually be received by the phone thus correcting the
resetting of link speed and duplex mode to “Auto”.
Proportional spacing may not be optimal (applies to IP Phone 2007, IP Phone 1110,
1120E, 1140E, 1150E and 1210)
The IP Phone 2007, IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1120E, IP Phone 1140E, IP Phone 1150E
and IP Phone 1210 support graphical fonts. The supported fonts include hinting – or
‘intelligence’ – to the font outline, making the font more readable by preventing the letters in
the font from becoming distorted and difficult to identify. But in some rare instances, the
hinting may impact the proportional spacing resulting in characters appearing too close or
too far apart.
Some models of Plantronics Bluetooth headset may unexpectedly become unpaired.
(applies to IP Phone 1140E and 1150E)
An issue was uncovered with certain Plantronics Bluetooth headsets (including the formerly
validated Plantronics Voyager 510/510S) in which the headset may unexpectedly become
unpaired. If the unpair occurs during an active call, all audio will be lost to and from the
headset. In such a situation the call will remain active and the user is recommended to
switch to handset or handsfree.
Due to the severity of this issue, Nortel does not recommend the use of the Plantronics
Voyager 510/510S headset. For a complete list of wired and wireless headsets that Nortel
has confirmed provide acceptable audio quality when used in conjunction with Nortel IP
Nortel Page 18 of 57
Page 19

Phones please refer to the product bulletin Headsets for Nortel IP Phones, P-2006-0084Global-Rev7
2-step upgrade may be required (applies to IP Phone 1120E and 1140E)
One important note when upgrading the IP Phone 1120E and IP Phone 1140E to UNIStim
firmware release 3.4 from any load previous to 0624C1B or 0625C1B respectively is that a
2-step upgrade will be required. The IP Phone 1120E and 1140E cannot be upgraded
directly to the newly released firmware if they are currently running firmware previous to
0624C1B and 0625C1B respectively. Instead, the phones must first be upgraded to
0624C1B and 0625C1B or newer (recommend 0624C3G and 0625C3G). Once the phones
are running at least 0624C1B and 0625C1B firmware, they will accept being upgraded to
UNIStim firmware release 3.4 respectively.
2-step upgrade may be required to load Asian fonts (applies to IP Phone 2007)
Adding Asian languages to an IP Phone 2007 that has firmware version 0621C3N (UNIStim
firmware release 1.3) or earlier requires a 2 step process since the configuration file format
has changed to support the new font downloads.
1. One must first upgrade the IP Phone 2007 firmware to using TFPT with the former
configuration files (“BasicConfig” folder) – or upgrade the firmware from the call server.
2. Once the IP Phone 2007 is running the new firmware one must update the TFTP server
to the new configuration files (“AsianConfig” folder) to download the Asian font files.
Running SRTP PSK with Communication Server 1000 release 5.0 requires a patch
(applies to IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E and 1150E)
In association with Communication Server 1000 release 5.0, UNIStim firmware since release
2.0 delivered media stream protection using SRTP UNIStim Keys (USK). However, running
SRTP using PreShared Keys (PSK) is still a valid option in the IP Phones. But, if one wishes
to run SRTP PSK with Communication Server Release 5.0, patch MPLR24632 is required
on the Communication Server 1000
the Meridian PEP library at the www.nortel.com/support
6
. The Communication Server 1000 patch is located in
web site.
Current release of SRTP PSK is not backward compatible with older version of SRTP
PSK (applies to IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E and 1150E)
As stated above, running SRTP using PreShared Keys (PSK) is still a valid option in the IP
Phones. But one important note when upgrading the IP Phones to the current releases of
firmware is to realize that the current releases of SRTP PSK is not compatible with older
versions of SRTP PSK. The minimum firmware releases for which the current release of
SRTP PSK is backward compatible is UNIStim firmware release 1.3 for IP Phones (including
firmware version 0604DAX for the Phase II IP Phone 2001, Phase II IP Phone 2002, and
Phase II IP Phone 2004, firmware version 0621C3N for the IP Phone 2007 and firmware
6
The patch is not required on Communication Server 1000 Release 5.5
Nortel Page 19 of 57
Page 20

0623C3G, 0624C3G, 0625C3G and 0627C3G for the IP Phone 1110, 1120E, 1140E and IP
Phone 1150E respectively).
One way speech path behind NAT routers (applies to IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007,
1120E, 1140E and 1150E)
A problem exists with some NAT routers that cause one way speech path. This problem is
addressed by the application of patch MPLR21030 on the Communication Server 1000
Release 4.5 and 4.0
PEP library at the www.nortel.com/support
7
. The Communication Server 1000 patch is located in the Meridian
web site.
Backlight Interaction with USB devices (applies to IP Phone 2007, 1120E, 1140E and
1150E)
Some USB devices (i.e. Mice or Keyboards) send regular coordinate update messages to
the phone even when the device is not being used. This can cause the sleep mode for the
backlight to not be properly invoked.
Certain USB mice do not work with IP Phone 2007 (applies to IP Phone 2007 only)
It has been discovered that certain USB Mice do not work with the IP Phone 2007. If the
mouse does not transit information in the “Production”, “Vendor” and “Manufacturing” fields
of the USB communication exchange, the mouse will not be recognized by the IP Phone
2007. Note that failure to send the above mentioned information is in violation of the USB
communication exchange standard. Most leading brands of mice do send the required
information.
Contrast adjustments: Local & TPS contrast adjustments are not synchronized
(applies to IP Phone 1110, 1120E, 1140E and 1150E)
The IP Phone 1110, 1120E, 1140E and 1150E graphical display contrast control can be
adjusted either locally (on the phone) or through the call server (TPS) control. The
Communication Server 1000 TPS does not yet synchronize its contrast setting with the local
control. This means if the local control is used exclusively, then whenever the phone has a
power cycle, the TPS contrast setting is restored and the user may need to adjust contrast
again.
The local contrast control on the IP Phone 1110, 1120E, 1140E and 1150E is accessed by a
“double press”
in the menu. The TPS contrast control is accessed with a “single press
of the Services key and selecting “1. Preferences”, then “1. Display Settings”
” of the Services key,
then selecting “Telephone Options”, then “Contrast Adjustment”.
7
The patch is not required on Communication Server 1000 Release 5.0 and greater
Nortel Page 20 of 57
Page 21

Volume adjustments are not persistent across phone resets (applies to IP Phone
2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230)
Even though the speech volume and ringer volume is controlled by the IP phone, the user
selected preferences are stored by the Communication Server 1000. Prior to release 5.0 of
the Communication Server 1000, the server did not save the user selected preferences
across a phone reboot. Thus, if the phone rebooted, for whatever reason, the speech
volume and ringer volume would be reset to their default values. Upgrading to release 5.0 or
greater of the Communication Server 1000 corrects this issue.
Power disruption during firmware upgrade will corrupt the upgrade (applies to IP
Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230)
During a firmware upgrade, if a power disruption is experienced by the phone, the firmware
upgrade will fail. In some instances a power disruption during an upgrade may also corrupt
the existing firmware on the phone. If this corruption should occur, the phone will fail over
into its boot code known as “BootC”. BootC will automatically try to restore the phone’s
firmware from the image on a call server. But for the IP Phone 2007, the IP Phone 1100
series and the IP Phone 1200 series, if the phone’s firmware was obtained from a TFTP
server instead, in order to restore, or upgrade, the firmware from BootC a manual TFTP
download from BootC must be performed. The Manual TFTP Download from BootC
Procedure is documented in the IP Phones Fundamentals
caution should be exercised to avoid power disruptions during firmware upgrades.
NTP NN43001-368. Regardless,
Nortel Page 21 of 57
Page 22

Quality Improvements
In addition to delivering the enhancements listed above, the UNIStim firmware release 3.4
for IP Phones also continues to improve the overall quality of the IP Phone firmware through
the delivery of ongoing resolution of CRs and closed cases. Numerous quality
improvements have been delivered, and 6 customer cases have been closed in UNIStim
3.4.
UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones close the following cases:
Case # Title
Slight chance that the IP Phone 2004 may freeze when ending an IP Call
090708-75234
090824-03336
090805-92397 Issue with Mouse Cursor on the IP Phone 2007 when backlight turns off
090713-78022
090519-43214
090728-87526 Concern with lowest ring tone setting on the IP Phone 1120E
Recording (IPCR) call
Problem with the IP Phone 2004 obtaining an IP address when 802.1Q is
enabled
Issue with menu access when Lock Menu is enabled
SSH challenge prompt causes issue on IP Phone 1100 series
Nortel Page 22 of 57
Page 23

IP Phone Compatibility
UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones is compatible with the following IP Phones:
PEC Description Firmware file
NTDU90xxxxxx IP Phone 2001 0604DCN.bin
NTDU91xxxxxx IP Phone 2002
NTDU92xxxxxx IP Phone 2004
NTDU96xxxxxx IP Phone 2007
NTYS02xxxxxx IP Phone 1110
NTYS03xxxxxx IP Phone 1120E
0604DCN.bin
0604DCN.bin
0621C6R.bin
0623C6T.bin
0624C6T.bin
NTYS05xxxxxx IP Phone 1140E 0625C6T.bin
NTYS06xxxxxx IP Phone 1150E 0627C6T.bin
NTYS18xxxxxx IP Phone 1210 062AC6T.bin
NTYS19xxxxxx IP Phone 1220 062AC6T.bin
NTYS20xxxxxx IP Phone 1230 062AC6T.bin
IP Phone 2004 (NTEX00), Phase 1 IP Phone 2002 (NTDU76), and Phase 1 IP Phone 2004
(NTDU82) cannot load these releases.
Nortel Page 23 of 57
Page 24

Call Server Compatibility and Requirements
These firmware releases are compatible with the below Nortel Call Servers. Note that the IP
Phone 1200 series is only supported on Communication Server 1000 release 5.5 and
greater, SRG 50 release 3.0, BCM 50 release 3.0, BCM 450 release 1.0, and
Communication Server 2100 CICM 10.1 MR2.
Communications Server 1000
Call Server Release Notes / Advisements
CS 1000 6.0R
- IP Line 6.00.18
- SS (Linux App) 6.00.018
CS 1000 5.5J
- IP Line 5.5.12
- SS 5.5.12
CS 1000 5.00W
- IP Line 5.00.31
- SS 5.00.31
CS 1000 4.5
- X21 4.50W
- IP Line 4.50.88 or later
- SS 4.50.88 or later
CS 1000 4.0
- X21 4.00T
- IP Line 4.00.55 or later
- SS 4.00.55 or later
Nortel recommends an upgrade to these firmware releases at the earliest
opportunity.
Nortel recommends an upgrade to these firmware releases at the earliest
opportunity.
Nortel recommends an upgrade to these firmware releases at the earliest
opportunity.
The IP Phone 1200 series is not supported on this platform.
Nortel recommends an upgrade to these firmware releases at the earliest
opportunity.
The IP Phone 1200 series is not supported on this platform.
Nortel recommends an upgrade to these firmware releases at the earliest
opportunity.
For Phase II IP Phones, the UFTP process direct from the CS 1000 is
required to distribute firmware to the IP Phones.
For IP Phone 2007, 1110, 1120E and 1140E a TFTP Server is required to
distribute firmware to the IP Phones.
The IP Phone 1150E and IP Phone 1200 series are not supported on this
platform.
Nortel Page 24 of 57
Page 25

Survivable Remote Gateway (SRG)
Call Server Release Notes / Advisements
SRG 50 3.0 Nortel recommends an upgrade to these firmware releases at the earliest
opportunity.
No SRG50 patches are required to support the Enhanced Firmware
Download feature that allows the IP Phone firmware supported on the
SRG50 to remain in synch with the Communication Server 1000 Main office.
In addition, if the “Main” Communication Server 1000 is on release 4.5, or
later, no patch is necessary on the Communication Server 1000 to upgrade
the IP Phone. But if the “Main” Communication Server 1000 is on release 4.0
a Communication Server 1000 patch is required on the “Main” to allow the
SRG50 to upgrade the IP Phone firmware. The patch is MPLR21148 and is
available from the Meridian PEP library at the www.nortel.com/support
site.
The IP Phone 1150E is not supported on the SRG50 3.0.
web
SRG 50 2.0 Nortel recommends an upgrade to these firmware releases at the earliest
opportunity.
No SRG 50 patches are required to support the Enhanced Firmware
Download feature that allows the IP Phone firmware supported on the SRG
50 to remain in synch with the Communication Server 1000 Main office.
In addition, if the “Main” is Communication Server 1000 release 4.5, or later,
no patch is necessary on the Communication Server 1000 to upgrade the IP
Phone. But if the “Main” is Communication Server 1000 release 4.0, a
Communication Server 1000 patch is required on the “Main” to allow the
SRG 50 to upgrade the IP Phone firmware. The patch is MPLR21148 and is
available from the Meridian PEP library at the
site.
The IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1150E and IP Phone 1200 series are not
supported on SRG 50 2.0.
www.nortel.com/support web
Nortel Page 25 of 57
Page 26

SRG 200/400 1.5
Nortel recommends an upgrade to these firmware releases at the earliest
opportunity.
No SRG patches are required to support the Enhanced Firmware Download
feature that allows the IP Phone firmware supported on the SRG 200/400
1.5 to remain in synch with the Communication Server 1000 Main office.
In addition, if the “Main” is Communication Server 1000 release 4.5, or later,
no patch is necessary on the Communication Server 1000 to upgrade the IP
Phone. But if the “Main” is Communication Server 1000 release 4.0, a
CS1000 patch is required on the “Main” to allow the SRG 200/400 to
upgrade the IP Phone firmware. The patch is MPLR21148 and is available
from the Meridian PEP library at the
The IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1150E and IP Phone 1200 series are not
supported on SRG200/400 Rls1.5
www.nortel.com/support web site.
Nortel Page 26 of 57
Page 27

Business Communications Manager (BCM)
Call Server Release Notes / Advisements
BCM 200/400 4.0 Upgrading of the set firmware is dependent upon a BCM system patch that
includes the set firmware.
Although UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones is GA quality, at the
time of this writing, the extent of BCM support is being confirmed.
The IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1150E and IP Phone 1200 series are not
supported on BCM 200/400.
BCM 50 3.0 Upgrading of the set firmware is dependent upon a BCM system patch that
includes the set firmware.
Although UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones is GA quality, at the
time of this writing, the extent of BCM support is being confirmed.
The IP Phone 1150E is not supported on BCM 50 3.0.
BCM450 1.0 Upgrading of the set firmware is dependent upon a BCM system patch that
includes the set firmware.
Although UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones is GA quality, at the
time of this writing, the extent of BCM support is being confirmed.
The IP Phone 1150E is not supported on BCM 450 1.0.
Nortel Page 27 of 57
Page 28

Communication Server 2100 Centrex IP Client Manager (CICM)
Call Server Release
CICM 10.1 MR2
(Succession)
CICM 10.0
(Succession)
CICM 9.0
(Succession)
Notes / Advisements
Upgrading of the set firmware is dependent upon CICM performing
regression test activities on UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones to
verify their performance on this CICM product.
Although UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones is GA quality, at the
time of this writing, the extent of CICM support is being confirmed.
The IP Phone 1210 is not supported on CICM 10.1
Upgrading of the set firmware is dependent upon CICM performing
regression test activities on UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones to
verify their performance on this CICM product.
Although UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones is GA quality, at the
time of this writing, the extent of CICM support is being confirmed.
The IP Phone 1200 series are not supported on CICM 10.0
Upgrading of the set firmware is dependent upon CICM performing
regression test activities on UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones to
verify their performance on this CICM product.
Although UNIStim firmware release 3.4 for IP Phones is GA quality, at the
time of this writing, the extent of CICM support is being confirmed.
The IP Phone 1200 series are not supported on CICM 9.0
Nortel Page 28 of 57
Page 29

System Compatibility and Requirements
System Notes / Advisements
Nortel Application
Gateway 2000 6.3
and higher
Nortel Secure
Multimedia
Controller (SMC) 1.0
These firmware releases provide support to interwork with Nortel
Application Gateway 2000 (AG2000) release 6.3
The Nortel Application Gateway solution continues to deliver on IP
Telephony's promise of convergence with important enhancements to the
powerful packaged applications on the IP Phone's desktop, applications
that are simply not possible to deliver with the traditional digital telephone.
With the Nortel Application Gateway, IP Phone communication is truly
transformed into a new feature-rich communications experience.
For more information on the capabilities introduced with AG2000 please
refer to the Product Bulletin P-2008-0005-Global.
The AG2000 does not support the IP Phone 1150E.
These firmware releases continue to provide support to interwork with
Nortel Secure Multimedia Controller (SMC) 2450.
The SMC 2450 is a purpose-built application firewall, delivering an
integrated inside threat security solution to protect Nortel’s IP phones and
multimedia communication servers. The SMC 2450 creates a “Secure
Multimedia Zone” around the converged infrastructure to protect against
Denial of Service attacks and other security threats, while pre-configured
policy settings simplify deployment and ensure the integrity and availability
of the business critical converged, multimedia infrastructure.
For more information on the capabilities introduced with Nortel SMC 2450
please refer to the SMC 2450 Product bulletin P-2006-0131-Global and the
SMC 2450 Sales and Marketing bulletin SM-2006-0132-Global.
Nortel Page 29 of 57
Page 30

IP Phone Firmware Upgrade Methods (Communication Server Dependent)
Upgrading the firmware in a Communication Server 1000 environment
The Phase II IP Phones (2001, 2002 and 2004) only support the UFTP firmware upgrade
process for the Communication Server 1000.
The IP Phone 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230 supports remote
firmware upgrades through both a TFTP process and the more automated UFTP process
direct from the Communication Server 1000. The method to upgrade the IP Phone 2007,
1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220 and 1230 firmware depends on the call server
software release.
• Communication Server 1000 Release 4.0 must use TFTP
• Communication Server 1000 Release 4.5 or later systems can use UFTP or TFTP
Note that the IP Phone 1150E is only supported on Communication Server 1000 Release
4.5 or later. Therefore the firmware can be upgraded by either UFTP or TFTP.
Also, note that the IP Phone 1200 series is only supported on Communication Server 1000
Release 5.5 or later. Therefore the firmware can be upgraded by either UFTP or TFTP.
For information on the TFTP firmware upgrade process for the Communication Server 1000,
please refer to the IP Phones Fundamentals
NTP NN43001-368.
For information on the UFTP firmware upgrade process for the Communication Server 1000,
please refer to the IP Line Fundamentals
NTP NN43100-500.
Upgrading the firmware in a Survivable Remote Gateway (SRG) 200/400 and SRG50
environment
For information on the firmware upgrade process for the SRG200/400, please refer to the
Main Office Configuration Guide for SRG200/400 Rls1.5, NTP 553-3001-207
For information on the firmware upgrade process for the SRG50, please refer to the Main
Office Configuration Guide for SRG50 Rls 2.0, NTP 553-3001-207.
Upgrading the firmware in a Business Communications Manager (BCM) environment
Upgrading of the firmware is dependent upon a BCM system patch that includes the set
firmware. This is applicable to all BCM platforms. BCM system patches will be delivered
initially as atomic patches that are individually installable. These patches will be rolled up
into a monthly Smart Update which includes all atomic patch content since the previous
Smart Update.
Nortel Page 30 of 57
Page 31

Patches and Smart Updates are posted for partner access on the www.nortel.com/support
web site under “Voice, Multimedia & Unified Communications” then under the respective
BCM platform.
Upgrading the firmware in a Communication Server 2100 CICM environment
Depending on the MR level, the IP Phone firmware will either be included in the installation
files or will need to be transfer to the CICM Element Manager.
If the firmware is included in the installation files some manual administrator configuration
will still be required. If the firmware is not included in the installation file the administrator can
transfer these firmware loads to the CICM Element Manager, configure the terminal’s
Recommended and Minimum firmware levels and the Element Manager will propagate the
firmware to the CICM. The user will be prompted to upgrade their firmware at their own
convenience.
For details on using the CICM Element Manager to configure the recommended firmware
and how to upgrade the IP Phones, refer to the CICM Administration and Security NTP
(NTP NN10252-611.06.03) in the section titled “Downloading firmware to the CICM Element
Manager”.
*Nortel, the Nortel logo and the Globemark are trademarks of Nortel.
Nortel is a recognized leader in delivering communications capabilities that enhance the
human experience, ignite and power global commerce, and secure and protect the world’s
most critical information. Serving both service provider and enterprise customers, Nortel
delivers innovative technology solutions encompassing end-to-end broadband, Voice over
IP, multimedia services and applications, and wireless broadband designed to help people
solve the world’s greatest challenges. Nortel does business in more than 150 countries. For
more information, visit Nortel on the Web at www.nortel.com
.
Nortel Page 31 of 57
Page 32

Appendix A: Certificate Installation (applies to the IP Phone 2007, 1110, 1120E,
1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220, 1230)
CA Root Certificate Installation
The recommended means to install the CA root certificate on the phone is to use the
configuration file (e.g. 1140e.cfg). An example of the modified configuration file is shown
below where cacert.pem contains the PEM format CA root certificate
[USER_KEYS]
DOWNLOAD_MODE AUTO
PROTOCOL TFTP
VERSION 1
FILENAME cacert.pem
When the phone boots and connects to the TFTP server, the phone will download the
certificate. The installer will then be prompted to accept the fingerprint of the certificate file.
Once accepted, the certificate is saved and the phone will be ready to use the CA root
certificate.
Device Certificate Installation
Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) is used to request both the CA root certificate
and then the Device certificate.
To successfully install the certificates, the following phone parameters must be configured
(either manually or using auto-provisioning):
CA Server: Enter the URL of the SCEP interface of the CA Server. As an example,
for a Microsoft CA server this would be:
http://www.<<ca_url.com>>/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll
Domain Name: The domain to which the phone will belong. (e.g. acme.com)
Hostname: The name assigned to the phone. For some authentication servers (i.e.
Microsoft IAS), this must match a username that can be authenticated in the server.
If left blank, the hostname will be automatically filled with NTIPP012345 where the
final 6 characters are the last 6 hex characters from the phone’s MAC address.
When the phone boots with the above configuration, a CA root certificate will be requested
from the CA Server. Once the CA root certificate is received, the prompt “CA Fingerprint” will
be displayed on the phone’s screen. The installer must press the “Accept” softkey to install
the CA root certificate. Once accepted, the certificate will be saved on the phone and the
prompt will never appear again.
Nortel Page 32 of 57
Page 33

After the CA root certificate is installed, a Device certificate must be installed. Depending on
the CA Server configuration, the user may be prompted to enter a challenge password.
8
If
no challenge password is required, the installer must simply select the OK softkey.
Once the challenge password is entered (or the OK softkey is pressed), the phone will then
request a device certificate and “Waiting for Approval…” will be displayed on the phone’s
screen. Depending on the CA Server configuration, it may be necessary for the installer to
manually approve the certificate request using the CA Server.
After the certificate is approved (automatically or manually), the “Waiting for Approval…”
prompt will be removed. If for any reason the approval fails (and while the phone is actually
waiting for approval), an “Abort” key will appear to allow the installer a chance to abort the
process.
Once approved, phone will be ready to use the device certificate.
For additional information on installing certificates into the IP phone, please refer to the IP
Phones Fundamentals document (NTP NN43001-368).
8
For the Microsoft CA Server, MSCEP installation allows the option of configuring a challenge
password. If configured, the user must access http://www.<<ca_url>>/certsrv/mscep/mscep.dll with a
web browser to obtain a temporary password. For the EJBCA CA Server, the password (if any)
defined for the End Entity for each phone must be entered.
Nortel Page 33 of 57
Page 34

Appendix B: IP Phone Info Block (applies to the IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004,
2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220, 1230)
The list of all the parameters that can be provisioned via the Info-Block is provided in the
table below. Note that not all parameters need be specified in the Info-Block. If the option is
included, the parameter will be provisioned with the value specified. If the option is not
included, the parameter will retain its default value, or the value that was previously
provisioned for the parameter if the “stickiness” parameter is also set.
Parameter Value Description
s1ip Value from 0.0.0.0 to
255.255.255.255
p1 Value from 1 to 65535 Primary server port number
a1 Value from 0 to 255 Primary server action code
r1 Value from 0 to 255 Primary server retry count
s2ip Value from 0.0.0.0 to
255.255.255.255
p2 Value from 1 to 65535 Secondary server port number
a2 Value from 0 to 255 Secondary server action code
r2 Value from 0 to 255 Secondary server retry count
dhcp ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
xip Value from 0.0.0.0 to
255.255.255.255
xp Value from 0 to 65535 XAS server port number
xa Character string up of the
following character
‘g’ graphical XAS mode
‘f’ full screen XAS mode
‘s’ secure XAS mode
‘h’ hidden Phone mode
‘r’ reduced Phone mode
unid Character string up to 32
characters
Primary server IP address
Secondary server IP address
Enable DHCP
XAS server IP address
XAS server action code (XAS Mode and Phone Mode)
Note that there is no explicit character to select text-mode.
Instead, the lack of specifying graphical ‘g’ implies the XAS
mode is text.
Also note that there is no explicit character to select Full
phone mode. Instead, the lack of specifying either hidden
‘h’ or reduced ‘r” implies the phone is to be provisioned for
Full phone mode. Please be careful not to confuse Full
Screen XAS mode ‘f’ with Full phone mode.
Unique network identification
Nortel Page 34 of 57
Page 35

menulock ‘f’ full lock
‘p’ partial lock
‘u’ unlock
vq ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
vcp Value from 0 to 15 802.1Q control p bit for voice stream
vmp Value from 0 to 15 802.1Q media p bit for voice stream
vlanf ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
nis ‘a’ auto negotiation
‘10’ 10 Mbps
‘100’ 100 Mbps
nid ‘a’ auto negotia tion
‘f’ full duplex
‘h’ half duplex
pc ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
pcs ‘a’ auto negotiation
‘10’ 10 Mbps
‘100’ 100 Mbps
pcd ‘a’ auto negotiation
‘f’ full duplex
‘h’ half duplex
dq ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
dv ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
dvid Value from 1 to 4094 VLAN ID for data VLAN
dp Value from 0 to 15 802.1Q p bit for data stream
pcuntag ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
lldp ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
pk1 Character string of16
character representing 16
hexadecimal digits
pk2 Character string of 16
character representing 16
hexadecimal digits
Menu lock mode
Enable 802.1Q for voice [1]
Enable VLAN filter on voice stream
Network port speed [1]
Network port duplex [1]
Enable PC port
PC port speed
PC port duplex
Enable 802.1Q for PC port
Enable VLAN for data
Enable stripping of tags on packets forwarded to PC port
Enable 802.1ab LLDP [1]
S1 PK [2]
S2 PK [2]
Nortel Page 35 of 57
Page 36

stickiness ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
cachedip ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
igarp ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
srtp ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
eap ‘dis’ disable
‘md5’ EAP-MD5
‘peap’ PEAP/MD5
‘tls’ EAP-TLS
eapid1 Character string up to 32
characters
eapid2 Character string up to 32
characters
eappwd Character string up to 32
characters
ca Character string up to 80
characters
cahost Character string up to 32
characters
cadomain Character string up to 50
characters
cdiff Value from 0 to 255 Diffserv code points for control messages
mdiff Value from 0 to 255 Diffserv code points for media messages
prov Character string up to 50
characters
dns Character string up to 50
characters
dns2 Character string up to 50
characters
ct Value from 0 to 15 for IP
Phone 1100 series
Value from 7 to 39 for IP
Phone 2007
br Value from 2 to 32 Brightness value
Enable stickiness (provisioning is persistent in the event a
new info block is not received)
Enable cached IP
Ignore GARP
Enable SRTP-PSK
Disable or choose an EAP authentication method [1] [2]
802.1x (EAP) device ID1 [1] [2]
802.1x (EAP) device ID2 [1] [2]
802.1x (EAP) password [1] [2]
Certificate Authority (CA) server
Certificate Authority (CA) host name
Certificate Authority (CA) domain name
Provisioning server address or URL (if the string is prefixed
with “http://” the phone will connect to a HTTP server,
otherwise the phone will connect to a TFTP server)
Primary DNS server URL
Secondary DNS server URL
Contrast value
Nortel Page 36 of 57
Page 37

blt ‘0’ 5 seconds
‘1’ 1 minute
‘2’ 5 minutes
‘3’ 10 minutes
‘4’ 15 minutes
‘5’ 30 minutes
‘6’ 1 hour
‘7’ 2 hours
‘8’ always on
dim ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
dimt ‘0’ Off
‘1’ 5 seconds
‘2’ 1 minute
‘3’ 5 minutes
‘4’ 10 minutes
‘5’ 15 minutes
‘6’ 30 minutes
‘7’ 1 hour
‘8’ 2 hours
sst ‘0’ Off
‘1’ 1 minute
‘2’ 5 minutes
‘3’ 10 minutes
‘4’ 15 minutes
‘5’ 30 minutes
‘6’ 1 hour
‘7’ 2 hours
bt ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
zone Character string up to 8
characters
file Character string up of the
following character
‘z’ read zone file
‘t’ read type file
‘d’ read device file
Backlight timer
As of UNIStim firmware release 3.4, the previously
supported “dim” parameter is no longer supported since its
functionality is superseded by the dimt parameter. The
phone will still accept the dim parameter to prevent errors
when reading existing provisioning files but the parameter
will be ignored in favor of the new dimt parameter.
Phone inactivity timer to dim the screen (IP Phone 2007
only)
Phone inactivity timer to initiate the slide show (IP Phone
2007 only)
Enable Bluetooth (IP Phone 1140E and 1150E only)
Zone ID
For system specific provisioning file specifies what other
provisioning files to read
Nortel Page 37 of 57
Page 38

hd Character string up of the
following character
‘w’ wired
‘b’ Bluetooth
‘n’ none
ar ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
arl ‘cr’ critical
‘ma’ major
‘mi’ minor
ll ‘cr’ critical
‘ma’ major
‘mi’ minor
ssh ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
sshid Character string between 4
and 12 characters
sshpwd Character string between 4
and 12 characters
bold ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
menupwd String between and 21
characters containing only
numeric digits, asterisk (*) and
hash (#) – i.e. only the dialpad
symbols
vvsource ‘n’ no VLAN
‘a’ auto VLAN via DHCP
‘lv’ auto VLAN via VLAN Name
TLV
‘lm’ auto VLAN via Network
Policy TLV
srtpid 96
115
120
ntqos ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
dscpovr ‘y’ yes
‘n’ no
[1]: Warning - changing this parameter could impact the network connectivity and may require manual correction
[2]: Warning – provisioning this parameter via TFTP, HTTP, or DHCP means that secure information is
transferred in clear text
Headset type
Enable Auto-recovery
Auto-recovery level
Log level
Enable SSH
SSH user ID [2]
SSH password [2]
Enable bold on font display
Administrator password [2]
Source of VLAN information
Payload type ID
Enable Nortel Automatic QoS
DSCP Precedence Override
Nortel Page 38 of 57
Page 39

Appendix C: Provisioning the IP Phone with an Info Block via TFTP or HTTP
(applies to the IP Phone 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220, 1230)
The IP Phones can receive the Info-Block inside one or more provisioning files that can be
retrieved from a TFTP or HTTP server. Multiple provisioning files are supported by the
phone:
SYSTEM provisioning file – provides provisioning information to all IP Phones that
support the auto-provisioning feature (e.g. system.prv)
ZONE provisioning file – provides provisioning information to IP Phones that belong
to a unique defined zone or group (e.g. headqrtr.prv)
TYPE provisioning file – provides provisioning information to all the IP Phones of a
particular model types (i.e. 1140E.prv)
DEVICE provisioning file – provides provisioning information to a specific single
device based on the device’s MAC address (i.e. 001365FEF4D4.prv)
The provisioning files contain the provisioning Info Block only. The IP Phone continues to
use the configuration file(s) for obtaining firmware and font file updates. The provisioning
files are text-based file, which contains parameters that require provisioning.
An example of using hierarchal provisioning files (using system, zone and type provisioning
files) is as per the following:
system.prv
# System level provisioning file
# Applies to all phones
file=zt; # read <zone>.prv and <type>.prv
zone=headqrtr; # Zone id
unid=Main-tower; # Unique network identification
menulock=p; # Menu lock mode
vq=y; # Enable 802.1Q for voice
vcp=3; # 802.1Q control p bit for voice
vmp=4; # 802.1Q media p bit for voice
vlanf=y; # Enable VLAN filter
pc=y; # Enable PC port
pcs=a; # PC port speed
pcd=a; # PC port duplex
dq=y; # Enable 802.1Q for PC port
lldp=y; # Enable 802.1ab (LLDP)
pk1= ffffffffffffffff; # force pk1 to ff SMC will update
pk2= ffffffffffffffff; # force pk1 to ff SMC will update
stickiness=y; # Enable stickiness
cachedip=n; # Enable cached IP
igarp=n; # Ignore GARP
srtp=n; # Enable PSK SRTP
eap=peap; # Enable 802.1x (EAP)
eapid1=DEV1024; # 802.1x (EAP) device ID 1
eapid2=TOW2234; # 802.1X (EAP) device ID 2
eappwd=D3c6v5; # 802.1x (EAP) password
cdiff=13; # DiffServ code point for control
Nortel Page 39 of 57
Page 40

mdiff=12; # DiffServ code point for media
prov=47.11.232.115; # Provisioning server IP address
dns=47.11.20.20; # Primary DNS server IP address
dns2=47.11.20.21; # Secondary DNS server IP address
ct=20; # Contrast value
br=18; # Brightness value
blt=1; # Backlight timer
dimt=3; # Set dim timer to 5 minutes
hd=w; # Headset type
bold=y # Enable font display in bold
headqrtr.prv
# Zone level provisioning file
# Applies to all phones within the headquarters zone
s1ip=47.11.62.20; # Primary server IP address
p1=4100; # Primary server port number
a1=1; # Primary server action code
r1=10; # Primary server retry count
s2ip=47.11.62.21; # Secondary server IP address
p2=4100; # Secondary server port number
a2=1; # Secondary server action code
r2=10; # Secondary server retry count
xip=47.11.62.147; # XAS server IP address
xp=5000; # XAS server port number
xa=g; # XAS server action code
1140E.prv
# Type level provisioning file specific to IP Phone 1140E
# Applies to all IP Phone 1140E within the network
bt=y; # Enable Bluetooth
For additional information on configuring the IP phone with the Info Block and on autoprovisioning in general, please refer to the IP Phones Fundamentals
NN43001-368).
document (NTP
Info Block Feature Restriction
Please note that support for provisioning the IP Phone via an Info Block in provisioning files
was not extended to the Phase II IP Phone 2001, Phase II IP Phone 2002 and Phase II IP
Phone 2004. For these phones, provisioning the IP Phone with an Info Block can be
accomplished via DHCP only. UNIStim firmware release 2.3 for IP Phones introduced
provisioning with an Info Block via DHCP for the Phase II IP Phones. Firmware 0604DBP, or
greater, for the Phase II IP Phone
2001, 2002, and 2004 supports the new Nortel specific
option type (“Nortel-i2004-B”) which allows the Info Block to be sent via DHCP. For more
details on provisioning the IP Phone with an Info Block via DHCP please refer to “Appendix
E”.
Nortel Page 40 of 57
Page 41

Appendix D: Auto-Provisioning the IP Phone’s Node and TN in a
Communication Server 1000 Environment (applies to the IP Phone 2007, 1110,
1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220, 1230)
The introduction of auto-provisioning on the IP Phone 2007, the IP Phone 1100 series, and
the IP Phone 1200 series also provides a centralized method of provisioning the Node and
TN fields for these IP Phones when they are connected on a Communication Server 1000
system.
Prior to the availability of UNIStim firmware release 3.0 for IP Phones, if the Node and TN
values in the phone were un-initialized, the only means to provision the Node and TN value
was for the phone installer to manually enter these values at the phone when prompted to
do so on the phone’s display.
With the delivery of UNIStim firmware release 3.0 for IP Phones the phones will now accept
a list of Node and TN values associated to particular MAC addresses. The Node and TN
value is assigned to an appropriate phone by the phone recognizing its own MAC address
within the list of Node and TN values.
The phone will accept the Node and TN information when contained in any of the existing
.PRV files including:
• Device file (XXXXXXXXXXXX.PRV)
• Zone file (ZZZZZZZZ.PRV)
• Type file (TTTTT.PRV)
• System file (SYSTEM.PRV)
If the phone’s MAC address is found in more than one valid association across the different
.PRV files, the association that the phone ultimately accepts will be the one in the highest
priority file. The precedence order of the .PRV files from highest priority to lowest is device,
zone, type then system as shown above.
A format has been defined, which is similar to the existing auto-provisioning info block items,
to provision the Node and TN values. The new Node and TN provision string has the
following format:
reg =MACaddr, CallServerType, ConnectServer, NodeID, TN
Nortel Page 41 of 57
Page 42

The items can be separated by spaces or commas or any combination of them. The string
is case insensitive, so uppercase, lowercase or mixed case is all acceptable.
MACaddr
combination thereof. The following are examples of valid MAC address formats:
00-13-65-FE-F4-D4
00:13:65:FE:F4:D4
00 13 65 FE F4 D4
001365FEF4D4
CallServerType
1000, thus the only supported CallServerType is CS1K.
ConnectServer
NodeID
TN
- The same format is used for the Terminal Number as would be entered via the TN
prompt on the phone's display during registration. So two formats exist:
Large system TN: "LLL-SS-CC-UU" or “LLL SS CC UU”
Small system TN: “CC-UU” or “CC UU”
The TN must be in one of the formats shown above. The numbers in the TN can be
separated by spaces, dashes or any combination thereof. The numbers can either have
leading zeros to fill the field size, or not – e.g. LLL can be 096 or just 96.
Format errors resulting in no processing of the reg provisioning are silently discarded (no
error message is provided).
The “reg” item(s) must be at the end of the file’s provisioning info data items. No other
provisioning info items should come after it (them). This is required to optimize the speed of
the parsing.
The following is an example of a valid Node and TN provision string that could be included
in any of the .PRV files.
# Set Auto Node and TN
reg=00:1B:BA:F8:82:0D,CS1K,S1,123,096-1-22-01;
reg=00:1B:BA:F8:82:0E,CS1K,S1,123,096-1-22-02;
: Delimiters in the MAC address can be dashes, colons, spaces or any
: Currently the implementation only supports the Communication Server
: Only values S1 and S1S2 are supported at this time.
– The Node ID can be any number from 0 - 9999.
Nortel Page 42 of 57
Page 43

Appendix E: Provisioning the IP Phone with an Info Block via DHCP (applies to
the IP Phone 2001, 2002, 2004, 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220,
1230)
The new Nortel specific option type (“Nortel-i2004-B”) that was introduced in UNIStim
firmware release 2.2 and release 2.3 for IP Phones. The Nortel-i2004-B specific option type
expands the number of parameters that can be provisioned to include all those previously
provisioned in the existing option type of Nortel-i2004-A, plus more.
In firmware loads prior to UNIStim firmware release 2.2 for the IP Phone 2007, IP Phone
1110, IP Phone 1120E, IP Phone 1140E and IP Phone 1150E and prior to UNIStim firmware
release 2.3 for the Phase II IP Phone 2001, 2002 and 2004 the IP Phones could obtain only
limited provisioning parameters via Nortel specific DHCP options. The Nortel specific DHCP
option types supported included:
• Nortel-i2004-A is a unique identifier for provisioning Nortel call server
information into the IP Phone
• VLAN-A is a unique identifier for provisioning 802.1Q VLAN information into the
IP Phone
With the introduction of the UNIStim firmware release 2.2 and greater for the IP Phone
2007, IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1120E, IP Phone 1140E and IP Phone 1150E
UNIStim firmware release 2.3 and greater for the Phase II IP Phone 2001, 2002 and 2004,
9
, and
a
new Nortel specific option type is introduced (“Nortel-i2004-B”). The new Nortel-i2004-B
specific option type expands the number of parameters that can be provisioned to include all
those previously provisioned in the existing option type of Nortel-i2004-A, plus more. The
existing option type of Nortel-i2004-A will continue to be supported for backward
compatibility. In fact, the new firmware will accept both option types, although it is
recommended to either remain with the existing option type or move to the new option type,
but not both. In the event that the IP Phone receives both option types, values provisioned
with the new option type of Nortel-i2004-B will have a higher priority than values provisioned
with the old option type Nortel-i2004-A.
DHCP option type VLAN-A continues to be supported.
DHCP support for provisioning the IP Phones requires DHCP to send a class identifier
option with the valid option type in each DHCP Offer and DHCP Acknowledgement.
9
IP Phone 1210, 1220 and 1230 were introduced with UNIStim firmware release 2.2 for IP Phones
and support Nortel-i2004-B from initial release.
Nortel Page 43 of 57
Page 44

The IP Phone supports both vendor specific sub-ops and site specific options. The new
firmware now supports 42 Nortel specific DHCP options as listed below. Newly claimed
options are in bold where as the reclassified
10
options are in italics.
• 21 DHCP vender specific options: 128, 131, 144, 157, 188, 191, 205, 219, 223, 224,
227, 230, 232, 235, 238, 241, 244, 247, 249, 251, and 254
• 21 DHCP site specific options: 128, 131, 144, 157, 188, 191, 205, 219, 223, 224,
227, 230, 232, 235, 238, 241, 244, 247, 249, 251, and 254
The vendor specific field of the DHCP response is parsed to extract the provisioning
information.
The format of the “Nortel-i2004-B” DHCP option type is:
Nortel-i2004-B,param1=value1;param2=value2;param3=value3; …
An example DHCP provisioning string is as per the following
11
:
Nortel-i2004-B,s1ip=47.11.62.20;p1=4100;a1=1;r1=255;s2ip=47.11.62.21;
p2=4100;a2=1;r2=2;xip=47.11.62.147;xp=5000;xa=g;
menulock=p;vq=y;vcp=3;vmp=4;vlanf=y;pc=y;pcs=a;pcd=a;
dq=y;dv=y;dvid=60;dp=5;pcuntag=y;
The list of all the parameters that can be provisioned via the Nortel-i2004-B options is
provided in the following table. Note that not all parameters need be specified in the option
string. If the option is included, the parameter will be provisioned with the value specified. If
the option is not included, the parameter will retain its default value, or the value that was
previously provisioned for said parameter.
Feature Advisements
A compatibility issue was found with the new Nortel-i2004-B option type and the older Phase
0 IP Phone 2004, Phase 1 IP Phone 2002 and Phase 1 IP Phone 2004. Even thought these
older phones ignore the Nortel-i2004-B option type, the length of the DHCP frame causes
problems for the older phones. Since the list of all the parameters that can be provisioned
via the Nortel-i2004-B options is extensive, the length of the DHCP frame can be quite large.
The older phones will only accept a DHCP message to a maximum of 590 bytes (far short of
10
RFC 3942 states that DHCP site-specific options 128 to 223 are hereby reclassified as publicly
defined options. The IP Phone supports 9 vender specific options in this range and will continue to
do so for backward compatibility. However, as suggested in RFC3942, the use of these options
should be discouraged to avoid potential future collisions.
11
Carriage returns have been added to the DHCP configuration string for readability only. A true
DHCP configuration string would contain no such carriage returns
Nortel Page 44 of 57
Page 45

the maximum DHCP message size of 1456 bytes). In a mixed environment of phones that
support Nortel-i2004-B with Phase 0 and Phase1 phones one must either:
Ensure any option string that are defined are small enough that the DHCP message
does not exceed 590 bytes, or
Service the Phase 0 and Phase 1 phones with a DHCP offer that excludes the
Nortel-i2004-B option.
Nortel Page 45 of 57
Page 46

Appendix F: IP Phone Provisioning Precedence Rule and Stickiness Control
(applies to the IP Phone 2007, 1110, 1120E, 1140E, 1150E, 1210, 1220, 1230)
The IP Phone 2007, IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1120E, IP Phone 1140E, IP Phone 1150E, IP
Phone 1210, IP Phone 1220 and IP Phone 1230 can obtain provisioning information from
multiple sources when the parameter source is defined as AUTO from the Auto Provisioning
page. The sources of automatic provisioning information include:
LLDP when the phone is connected to an 802.1ab enabled network switch
DHCP
Provisioning file transferred via TFTP or HTTP
Call server (and/or associated telephony manager) using UNIStim
It is assumed that each network provisioning parameter will be supplied by one and only one
source. However, if the phone receives network configuration information from multiple
sources a precedence rule is applied to determine the one source the phone selects for its
provisioning information.
The precedence rule from highest priority to lowest priority for IP Phone provisioning is as
follows:
• Manual provisioning
• Automatic provisioning using Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) from an 802.1ab
enabled network switch
• Automatic provisioning using Info Block contained within provisioning files (and transferred
via TFTP or HTTP). Provisioning files contain their own precedence order based on the file
type:
— Info Block carried by the Device-specific provisioning file
— Info Block carried by the Zone-specific provisioning file
— Info Block carried by the Type-specific provisioning file
— Info Block carried by the System-specific provisioning file
• Automatic provisioning using Info Block contained within DHCP option strings (and
transferred via DHCP Acknowledge message). DHCP provision contain its own precedence
order based on the DHCP option
— Info Block carried by the Nortel-i2004-B DHCP option
— Former provisionable parameters carried by the Nortel-i2004-A DHCP option
(Note that VLAN-A option is still supported with both Nortel-i2004-B DHCP and
Nortel-i2004-A DHCP options)
• Automatic provisioning from the call server (and/or associated telephony manager) using
UNIStim
• Last automatic provisioned value
• Factory default
Automatic provisioning defines provisioning control for each parameter. One can either
manually or automatically provision each parameter. Each provisioning parameter provides
an attribute that specifies if the parameter was previously provisioned manually or
automatically.
Nortel Page 46 of 57
Page 47

If the provisioning parameter is AUTO, the IP Phone can receive the value from automatic
provisioning sources based on the precedence rule. If one manually changes the parameter,
the attribute value is MANUAL. If the attribute is MANUAL, the provisioning information from
automatic provisioning sources is ignored except for the standard DHCP parameters. If one
enables DHCP, then the phone’s IP address, the subnet mask, and the default gateway
address, which the IP Phone obtains from the DHCP server, overwrites any manually
configured value.
Provisioning information from a provisioning source with high priority will overwrite the
provisioning information from a provisioning source with low priority. Manual provisioning
always has the highest priority.
If one configure stickiness and the current provisioning source does not provide the
provisioning information for the particular parameter, the last received provisioning value is
used. The default value of the stickiness attribute is AUTO.
The Phase II IP Phones (IP Phone 2001, IP Phone 2002, and IP Phone 2004) do not
support the precedence rule, therefore the phones use the last value received.
Nortel Page 47 of 57
Page 48

Appendix G: IP Phone Configuration Menu on the IP Phone 1120E, IP Phone
1140E and IP Phone 1150E
The full-screen based configuration menu structure below presents the complete
configuration menu now available on the IP Phone 1120E, IP Phone 1140E and IP Phone
1150E:
EAP Mode: [Disable, MD5, PEAP, TLS]
ID 1:
ID 2:
Password:
Enable 802.1ab (LLDP): []
DHCP: [No, Yes]
Set IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Net Mask: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Gateway: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
DNS1 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
DNS2 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
CA Server:
Domain Name:
Hostname:
S1 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Port:
S1 Action:
Retry:
S1 PK: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
S2 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Port:
S2 Action:
Retry:
S2 PK: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Ntwk Port Speed: [Auto, 10BT, 100BT]
Ntwk Port Duplex: [Auto, Force Full, Force Half]
XAS Mode: [Text Mode, Graphical, Secure Graphical]
XAS IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
XAS Port:
Enable Voice 802.1Q: []
VoiceVLAN: [No VLAN, Auto, Enter VLAN ID]
The Auto option in the VoiceVLAN menu is only available if DHCP is provisioned to “Yes”
above or if LLDP is enabled above
VLAN Filter : []
Ctrl Priority Bits: [Auto, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Media Priority Bits: [Auto, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Nortel Page 48 of 57
Page 49

Enable Nortel Auto Qos: []
DSCP Override: [] This DSCP Override menu item is only presented if “Enable 802.1ab
(LLDP)” is enabled above and “Control DSCP” or “Media DSCP” are not manually set
below
Control DSCP: xxx
Media DSCP: xxx
Enable PC Port: []
PC Port Speed: [Auto, 10BT, 100BT]
PC Port Duplex: [Auto, Force Full, Force Half]
Enable Data 802.1Q: []
DataVLAN: [No VLAN, Enter VLAN ID]
Data Priority Bits: [Auto, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
PC-Port Untag All: []
Enable Stickiness []
Cached IP: [] This Cached IP menu item is only presented if DHCP is provisioned to “Yes”.
Ignore GARP: []
Enable SRTP PSK: []
SRTP PSK Payload ID: [96, 115, 120]
Provision: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Provision Zone ID:
Enable Bluetooth: [Yes, No] This menu item is on the IP Phone 1140E and 1150E only.
The IP Phone 1120E, IP Phone 1140E, and IP Phone 1150E contain a password protection
mechanism to lock out access to the Local Tools menu including the Network Configuration
menu. If enabled, access to the Local Tools menu is password protected and the password
is prompted by a pop up window. One must type the password 26567*738 (color*set) from
the dial pad and press the center of the navigation cluster (enter key) to enter the Network
Configuration menu.
When an incorrect password is entered, the Local Tools menu is not opened.
To thwart password guessing, only 3 incorrect password entries in a row are allowed. After
rd
the 3
incorrect entry, the password entry is ignored for 5 minutes. During this period of
time, the password prompt is displayed and the entered digits accepted; however, the phone
will not process the incoming digits. The password prompt window simply closes and the
behavior is identical to that of an incorrect password entry. The user will assume the
incorrect password has been entered and try again. Thus even if the correct password is
guessed during the 5 minute period, it will be ignored. This effectively reduces the guess
entry rate to 3 guesses every 5 minutes.
Once the password has been entered, access to the Local Tools menu remains active for 5
minutes. During the 5 minutes, the menu can be freely navigated, exited and entered
without being prompted again for the password. When the 5 minutes expires, the menu is
closed. The password must be reentered to access the Local Tools menu.
Nortel Page 49 of 57
Page 50

Appendix H: IP Phone Configuration Menu on the IP Phone 2007
The full-screen based configuration menu structure below presents the complete
configuration menu now available on the IP Phone 2007:
EAP Mode: [Disable, MD5, PEAP, TLS]
ID 1:
ID 2:
Password:
Enable 802.1ab (LLDP): []
DHCP: [No, Yes]
Set IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Net Mask: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Gateway: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
DNS1 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
DNS2 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
CA Server:
Domain Name:
Hostname:
S1 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Port:
S1 Action:
Retry:
S1 PK: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
S2 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Port:
S2 Action:
Retry:
S2 PK: FFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
Ntwk Port Speed: [Auto, 10BT, 100BT]
Ntwk Port Duplex: [Auto, Force Full, Force Half]
Phone Mode [Hidden, Full, Reduced]
XAS Mode [Text Mode, Graphical, Full Screen, Secure Graphical, Secure Full Screen]
XAS IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Port:
Enable Voice 802.1Q: []
VoiceVLAN: [No VLAN, Auto, Enter VLAN ID]
The Auto option in the VoiceVLAN menu is only available if DHCP is provisioned to “Yes”
above or if LLDP is enabled above, respectively.
VLAN Filter : []
Ctrl Priority Bits: [Auto, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Media Priority Bits: [Auto, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
Enable Nortel Auto QoS: []
Nortel Page 50 of 57
Page 51

DSCP Override: [] This DSCP Override menu item is only presen t ed if “Enable 802.1ab
(LLDP)” is enabled above and “Control DSCP” or “Media DSCP” are not manually set
below
Control DSCP: xxx
Media DSCP: xxx
Enable PC Port: []
PC Port Speed: [Auto, 10BT, 100BT]
PC Port Duplex: [Auto, Force Full, Force Half]
Enable Data 802.1Q: []
DataVLAN: [No VLAN, Enter VLAN ID]
Data Priority Bits: [Auto, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
PC-Port Untag All: []
Enable Stickiness []
Cached IP: [] This Cached IP menu item is only presented if DHCP is provisioned to “Yes” above.
Ignore GARP: []
Enable SRTP PSK: []
SRTP PSK Payload ID: [96, 115, 120]
Provision: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Provision Zone ID:
The IP Phone 2007 contains a password protection mechanism to lock out access to the
Local Tools menu including the Network Configuration menu. If enabled, access to the
Local Tools menu is password protected and the password is prompted by a pop up
window. One must type the password 26567*738 (color*set) from the dial pad and press
the “OK” softkey to enter the Local Tools menu.
When an incorrect password is entered, the Local Tools menu is not opened.
To thwart password guessing, only 3 incorrect password entries in a row are allowed. After
rd
the 3
incorrect entry, the password entry is ignored for 5 minutes. During this period of
time, the password prompt is displayed and the entered digits accepted; however, the phone
will not process the incoming digits. The password prompt window simply closes and the
behavior is identical to that of an incorrect password entry. The user will assume the
incorrect password has been entered and try again. Thus even if the correct password is
guessed during the 5 minute period, it will be ignored. This effectively reduces the guess
entry rate to 3 guesses every 5 minutes.
Once the password has been entered, access to the Local Tools menu remains active for 5
minutes. During the 5 minutes, the menu can be freely navigated, exited and entered
without being prompted again for the password. When the 5 minutes expires, the menu is
closed. The password must be reentered to access the Local Tools menu.
Nortel Page 51 of 57
Page 52

Appendix I: IP Phone Configuration Menu on IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1210, IP
Phone 1220 and IP Phone 1230
The single-line based configuration menu structure below presents the complete
configuration menu now available on the IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1210, IP Phone 1220
and IP Phone 1230:
EAP[0-N,1-M, 2-P, 3-T]:0
if “1” or “2” or “3”
ID 1: [ ]
also if “1” or “2”
ID 2: [ ]
Password: [*******]
LLDP Enable?[0-N,1-Y]:0
DHCP? [0-N,1-Y]:1
if “0”
Set IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Netmsk: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Def GW: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
DNS1 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
DNS2 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
CA Server:
Domain Name:
Hostname:
S1 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
S1 Port:
S1 Action:
S1 Retry Count:
S2 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
S2 Port:
S2 Action:
S2 Retry Count:
Speed[0-A,1-10,2-100]:0
if “1” or “2”
Duplex[0-A,1-F,2-H]:0
Cfg XAS? [0-N, 1-Y]:1
if “1”
XAS IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Nortel Page 52 of 57
Page 53

Voice 802.1Q[0-N,1-Y]:1
if “1”
Voice VLAN?[0-N,1-Y]:0
if “1”
VLAN Cfg ?0-Auto,1-Man :1
This VLAN Cfg menu is only presented if DHCP is provisioned to “Y” above or if
LLDP Enabled is provisioned to “Y” above.
if “1”
VLAN ID :
VLAN Filter?[0-N,1-Y] :0
Ctrl pBits[0-7,8-Au] :8
Media pBits[0-7,8-Au] :8
NT AutoQOS? [0-N,1-Y]:0
DSCP Ovride [0-N,1-Y]:0 This DSCP Override menu item is only presented if “LLDP
Enable?” is enabled above and neither the “Control DSCP” or “Media DSCP” are not
manually set below
CTRL DSCP [0-63]: xxx
Media DSCP [0-63]: xxx
PC Port ? [0-Off,1-On] :1
if “1”
Speed[0-A,1-10,2-100]:0
if “1” or “2”
Duplex[0-A,1-F,2-H]:0
Data 802.1Q[0-N,1-Y]:1
if “1”
VLAN ID :
Data pBits[0-7,8-Au] :8
PCUntagAll? [0-N,1-Y]:1
Stickiness? [0-N,1-Y]:1
Cached IP? [0-N, 1-Y]:0 This Cached IP menu item is only presented if DHCP is pro vi sioned to “Y”
above
GARP Ignore?[0-N,1-Y]:0
SRTP PSK? [0-N, 1-Y]:0
PayID[0-96,1-115,2-120]0
Prov: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Prov Zone ID:
End of Menu
The IP Phone 1110, IP Phone 1210, IP Phone 1220 and IP Phone 1230 contain a password
protection mechanism to lock out access to the Local Tools menu including the Network
Configuration menu. If enabled, access to the Local Tools menu is password protected and
the password is prompted by a pop up window. One must type the password 26567*738
Nortel Page 53 of 57
Page 54

(color*set) from the dial pad and press the center of the navigation cluster (enter key) to
enter the Local Tools menu.
When an incorrect password is entered, the Local Tools menu is not opened.
To thwart password guessing, only 3 incorrect password entries in a row are allowed. After
rd
the 3
incorrect entry, the password entry is ignored for 5 minutes. During this period of
time, the password prompt is displayed and the entered digits accepted; however, the phone
will not process the incoming digits. The password prompt window simply closes and the
behavior is identical to that of an incorrect password entry. The user will assume the
incorrect password has been entered and try again. Thus even if the correct password is
guessed during the 5 minute period, it will be ignored. This effectively reduces the guess
entry rate to 3 guesses every 5 minutes.
Once the password has been entered, access to the Local Tools menu remains active for 5
minutes. During the 5 minutes, the menu can be freely navigated, exited and entered
without being prompted again for the password. When the 5 minutes expires, the menu is
closed. The password must be reentered to access the Local Tools menu.
Nortel Page 54 of 57
Page 55

Appendix J: IP Phone Configuration Menu on Phase II IP Phone 2001, Phase II
IP Phone 2002 and Phase II IP Phone 2004
The single-line based configuration menu structure below presents the complete
configuration menu now available on the Phase II IP Phone 2001, Phase II IP Phone 2002
and Phase II IP Phone 2004:
EAP Enable?[0-N,1-Y]:0
if “1”
DeviceID:[ ]
Password:
LLDP Enable?[0-N,1-Y]:0
DHCP? [0-N, 1-Y]:1
if “0”
SET IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
NETMSK: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
DEF GW: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
S1 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
S1 PORT:
S1 ACTION:
S1 RETRY COUNT:
S2 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
S2 PORT:
S2 ACTION:
S2 RETRY COUNT:
else if “1”
DHCP:0-Full,1-Partial:1
if “1”
S1 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
S1 PORT:
S1 ACTION:
S1 RETRY COUNT:
S2 IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
S2 PORT:
S2 ACTION:
S2 RETRY COUNT:
Speed[0-A,1-10,2-100]:0
if “1” or “2”
Duplex[0-A,1-F,2-H]:0
Cfg XAS?[0-N, 1-Y]:1
if “1”
XAS IP: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
Nortel Page 55 of 57
Page 56

Voice 802.1Q[0-N,1-Y]:1
if “1”
VOICE VLAN?[0-N,1-Y]:0
if “1”
VLAN Cfg?0-Auto,1-Man :1
The VLAN Cfg menu is only presented if DHCP is provisioned to “Partial” or “Full”
above or if LLDP is enabled above.
if “0”
LLDP MED? [0-N, 1-Y] :0
The LLDP MED menu is only presented if LLDP is enabled above.
if “0”
LLDP VLAN? [0-N,1-Y] :0
The LLDP VLAN menu is only presented if LLDP is enabled above.
if “0”
DHCP? [0-N, 1-Y] :0
The DHCP menu is only presented if DHCP is provisioned
to “Partial” or “Full” above.
else if “1”
VOICE VLAN ID :
VLANFILTER?[0-N, 1-Y] :0
Ctrl pBits[0-7,8-Au] :8
Media pBits[0-7,8-Au] :8
PC Port? [0-OFF,1-ON] :1 This menu item, and submenus, are not available on the IP Phone 2001.
if “1”
Speed[0-A,1-10,2-100]:0
if “1” or “2”
Duplex[0-A,1-F,2-H]:0
Data 802.1Q[0-N,1-Y]:1
if “1”
DATA VLAN? [0-N, 1-Y]:0
if “1”
DATA VLAN Cfg?0-A,1-M:0
This DATA VLAN Cfg menu item is only presented if LLDP is enabled above.
if “1”
DATA VLAN ID:
Data pBits[0-7,8-Au] :8
PCUntagAll?[0-N,1-Y]:0
Cached IP? [0-N, 1-Y]:0
This Cached IP menu item is only presented if DHCP is provisioned to “Yes” above and Voice
VLAN is not provisioned as “Auto”.
GARP Ignore?[0-N,1-Y]:0
PSK SRTP?[0-N, 1-Y]:0
PayID[0-96,1-115,2-120]0
Nortel Page 56 of 57
Page 57

Appendix K: Restore to Factory Defaults
The UNIStim firmware release 3.0 for IP Phones introduced the ability to restore an IP
Phone to a “factory default” configuration. This can be useful when redeploying an IP Phone
from one location to another, when starting to use an IP Phone with unknown history, or to
reset to a known baseline configuration.
With UNIStim firmware release 3.0, and greater, the following keypad sequence is used to
reset all provisioning parameters to a “factory default”:
[*][*][7][3][6][3][9][MAC][#][#]
Where MAC corresponds to the MAC address of the IP Phone which can be found
on a label on the back of the IP Phone.
Since a MAC address can contain the letters A through F, the letters A, B and C can
be entered via the [2] key on the dialpad, and letters D, E and F can be entered via
the [3] key.
For example, an IP Phone with MAC address 00:19:E1:E2:17:12 would be reset to
“factory default” when the sequence **73639001931321712## is entered on the
keypad.
Please note that the keypad sequence will only be accepted by the phone after the IP
Phone has finished its boot-up procedure.
Nortel Page 57 of 57
 Loading...
Loading...