Avaya Interaction Center, Interaction Center 6.0 User Manual

Avaya™ Interaction Center
Release 6.0
Avaya Agent User’s Guide
DXX-1001-03
Issue 1.0
June 2002

2002, Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Notice
Every effort was made to ensure that the information in this book was complete
and accurate at the time of printing. However, information is subject to change.
Preventing Toll Fraud
“Toll fraud” is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications system by an
unauthorized party (for example, a person who is not a corporate employee,
agent, subcontractor, or working on your company's behalf). Be aware that
there may be a risk of toll fraud associated with your system and that, if toll
fraud occurs, it can result in substantial additional charges for your telecommunications services.
Avaya Fraud Intervention
If you suspect that you are being victimized by toll fraud and you need technical
support or assistance, call Technical Service Center Toll Fraud Intervention
Hotline at +1 800 643 2353.
Providing Telecommunications Security
Telecommunications security (of voice, data, and/or video communications) is
the prevention of any type of intrusion to (that is, either unauthorized or malicious access to or use of your company's telecommunications equipment) by
some party.
Your company's “telecommunications equipment” includes both this Avaya
product and any other voice/data/video equipment that could be accessed via
this Avaya product (that is, “networked equipment”).
An “outside party” is anyone who is not a corporate employee, agent, subcontractor, or working on your company's behalf. Whereas, a “malicious party” is
anyone (including someone who may be otherwise authorized) who accesses
your telecommunications equipment with either malicious or mischievous
intent.
Such intrusions may be either to/through synchronous (time-multiplexed and/or
circuit-based) or asynchronous (character-, message-, or packet-based) equipment or interfaces for reasons of:
• Utilization (of capabilities special to the accessed equipment)
• Theft (such as, of intellectual property, financial assets, or toll-facility
access)
• Eavesdropping (privacy invasions to humans)
• Mischief (troubling, but apparently innocuous, tampering)
• Harm (such as harmful tampering, data loss or alteration, regardless of
motive or intent)
Be aware that there may be a risk of unauthorized intrusions associated with
your system and/or its networked equipment. Also realize that, if such an intrusion should occur, it could result in a variety of losses to your company (including but not limited to, human/data privacy, intellectual property, material assets,
financial resources, labor costs, and/or legal costs).
Your Responsibility for Your Company's Telecommunications
Security
The final responsibility for securing both this system and its networked equipment rests with you - an Avaya customer's system administrator, your telecommunications peers, and your managers. Base the fulfillment of your
responsibility on acquired knowledge and resources from a variety of sources
including but not limited to:
• Installation documents
• System administration documents
• Security documents
• Hardware-/software-based security tools
• Shared information between you and your peers
• Telecommunications security experts
To prevent intrusions to your telecommunications equipment, you and your
peers should carefully program and configure your:
• Avaya-provided telecommunications systems and their interfaces
• Avaya-provided software applications, as well as their underlying
hardware/software platforms and interfaces
• Any other equipment networked to your Avaya products.
Avaya National Customer Care Center
Avaya provides a telephone number for you to use to report problems or to ask
questions about your contact center. The support telephone number
is 1-800-242-2121.
Ordering Information
Avaya Publications Center
Voice: +1 800 457 1235
International Voice: 410 568 3680
Fax: +1 800 457 1764
International Fax: 410 891 0207
Email: totalware@gwsmail.com
Write: GlobalWare Solutions
Attention: Avaya Account Manager
200 Ward Hill Avenue
Haverhill, MA 01835 USA
Order: Document No. DXX-1001-03, Issue 1.0, June 2002
To order product documentation online, go to
http://www.avayadocs.com, click on Online Services, and select the appropri-
ate product group.
Warranty
Avaya Inc. provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to the “Limited
Use Software License Agreement” or other applicable documentation provided
with your package to establish the terms of the limited warranty.
Avaya Web Page
http://www.avaya.com
Trademarks
Avaya, Conversant, CustomerQ, Definity, DefinityOne, Nabnasset, Quintus,
and WebQ are registered trademarks or trademarks of Avaya Inc. in the United
States or other countries or both.
Portions of Avaya Interaction Center include technology used under license as
listed below, and are copyright of the respective companies and/or their licensors:
ActivePerl is a trademark of ActiveState Tool Corp. This product includes
software developed by the Apache Software Foundation
(http://www.apache.org/). Cognos, Impromptu and Powerplay are registered
trademarks of Cognos Incorporated. YACC++ is a registered trademark of
Compiler Resources, Inc. APEX, ComponentOne, VideoSoft, True DBGrid,
VSVIEW, SizerOne, VS-OCX, VSFlexGrid, VSFORUM, VSREPORTS,
VSDOCX, VSSPELL, and TrueDBList are either registered trademarks or
trademarks of ComponentOne LLC. CT Connect, Dialogic, Intel, and Pentium
are trademarks or registered trademarks of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries
in the United States and other countries. Hummingbird is a registered
trademark of Hummingbird, Ltd. SearchServer is a trademark of Hummingbird,
Ltd. RISC System/6000 and DirectTalk/2 are trademarks of International
Business Machines Corporation in the United States or other countries or both.
IBM, OS/2, AS/400, CICS, WebSphere, CT, VisualAge, and DirectTalk are
registered trademarks of International Business Machines Corporation in the
United States or other countries or both. Lotus and Lotus Sametime are
trademarks or registered trademarks of Lotus Development Corporation and/or
IBM Corporation in the United States, other countries, or both. VisualX is a
registered trademark of Intergroup Technologies, Inc. ActiveX, Visio, Internet
Explorer, Windows, Windows NT, Windows 2000, Win32s, SQL Server,
Visual Basic, Visual C++, Outlook, and FrontPage are either registered
trademarks or trademarks of Microsoft Corporation in the United States and/or
other countries. TimesTen is a registered trademark of TimesTen Performance
Software. Oracle is a registered trademark, and Oracle8i and
Oracle® SQL/Services are trademarks or registered trademarks of Oracle
Corporation. Rogue Wave and .h++ are registered trademarks of Rogue Wave
Software Inc. SourcePro is a trademark of Rogue Wave Software, Inc. Siebel is
a trademark of Siebel Systems, Inc. BasicScript is a registered trademark of
Summit Software Company. Sun, iPlanet, Java, Solaris JRE, J2EE,
JavaServer Pages, and all Java-based trademarks are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Sun Microsystems, Inc. in the United States, other
countries, or both. SPARC is a registered trademark of SPARC International,
Inc. Products bearing SPARC trademarks are based on an architecture developed by Sun Microsystems, Inc. In3D is a trademark of Visual Insights, Inc.
InstallShield® is a registered trademark and service mark of InstallShield
Software Corporation in the United States and/or other countries. ORBacus is a
trademark of IONA Technologies PLC. Formula One is a licensed trademark
and Tidestone Technologies, Inc. Visual Components, First Impression, and
VisualSpeller are registered trademarks of Tidestone Technologies, Inc. JRun
is a trademark of Macromedia, Inc. in the United States and/or other countries.
Intervoice is a registered trademark of Intervoice-Brite, Inc. UNIX is a
registered trademark of The Open Group in the United States and other
countries. Acrobat is a registered trademark of Adobe Systems.
Other product and brand names are trademarks of their respective owners.
Acknowledgment
This document was written by the CRM Information Development group of
Avaya

3
BEFORE YOU BEGIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1O
VERVIEW. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Avaya Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Using Avaya Agent with Multiple Languages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Avaya Agent Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Avaya Agent Status Control Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Task Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
Softphone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .19
Outbound List Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Avaya™ Outbound Contact Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Contact History Browser and EDU Viewer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Prompter Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Web Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
The Web Agent While Handling Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
The Web Agent While Handling Chat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
The Web Agent in Supervisor Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
The Web Agent Status Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
The Web Agent Information Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Web Agent Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
The Web Agent Toolbars . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
2MANAGING AVAYA AGENT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Logging In and Logging Out . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Logging In to Avaya Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Logging In and Out of Media Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Logging Out of Avaya Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
CONTENTS

4 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
Contents
Setting Your Availability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Changing Your Agent State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Manual Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Automatic Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Setting Your Channel Loads . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Opening an Application Focus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Viewing Customer and Contact Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Viewing Active Contact Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Viewing Contact History Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Reloading Layouts in the EDU Viewer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Clearing Current Contacts in the EDU Viewer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Reloading EDU Viewer Layouts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Using the Unified Agent Directory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Looking Up Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Updating UAD Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Using Screen Pops . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Wrapping Up Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Using the WrapUp Dialog Box . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Using a WrapUp Prompter Script . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Avaya Agent Stops Responding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Avaya Agent Stops Responding with Outbound Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
3MANAGING INBOUND VOICE CONTACTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Using the Phone Task List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Handling a Basic Voice Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Handling Contacts With Auto Answer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Handling Contacts Without Auto Answer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Placing a Voice Contact on Hold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Transferring a Voice Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Using the Softphone Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Refreshing Your Softphone Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Reconnecting to Your Physical Telephone . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Initiating a Voice Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81

Issue 1.0 June 2002 5
Contents
Using Softphone with DEFINITY Switches . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Sending Numerical Information with DTMF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Entering Reasons for Becoming Unavailable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Using the Auto-In Work Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Handling Two Voice Contacts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
4MANAGING EMAIL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Being Alerted to a New Email Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Using the Email Task List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Icons in the Email Task List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Text in the Email Task List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Viewing Email History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Composing a Normal Email Reply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 94
Addressing Emails with the UAD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Using Resources in Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Using Global, Agent, or Email Template Resources in an Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Using Suggested Responses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Sending an Email to an External Agent . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Transferring an Email Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Deferring an Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Saving a Draft . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Forwarding an Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 107
Spell Checking Your Emails . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Requesting More Information from Customer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Responding to an Email Alert . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Resolving an Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Originating an Outbound Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Approving or Rejecting an Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Handling a Rejected Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Using Multiple Languages with Email . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 119
Wrapping Up and Completing an Email Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120

6 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
Contents
5MANAGING CHAT SESSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Being Alerted to a New Chat Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
Using the Chat Task List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Handling a Basic Chat Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
Sharing Browsers with a Customer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 128
Technical Issues with Shared Browsing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Using Auto-Sync . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Pushing a Web Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Helping Your Customer Enter Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Using Resources in a Chat Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Spell Checking Your Messages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Using the Phone in a Chat Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Handling a Chat & Phone Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 137
Handling a Chat & VoIP Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Transferring a Chat Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Handling a Join Us Conference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
Handling Simultaneous Chat Sessions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Monitoring a Chat Session (Supervisors Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Starting a Lotus Sametime Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Viewing the Customer’s DataWake Record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Escalation Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Browse Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Using Multiple Languages in Chat Sessions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Wrapping Up and Completing a Chat Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
6PERFORMING CHAT & EMAIL TASKS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Managing Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Resource Types and Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Creating New Agent Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Creating New Global Resources (Supervisors Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Editing Your Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Deleting a Resource . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161

Issue 1.0 June 2002 7
Contents
Viewing Your Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 161
Organizing Your Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Importing Migrated Resources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 164
Setting Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
User Interface Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Contact Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Email Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Chat Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Other Preferences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Using Web Self-Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Finding Documents in Web Self-Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Submitting Documents to Web Self-Service . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Viewing, Editing, or Deleting Your Proposed Documents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
Approving or Rejecting Documents (Supervisors Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Viewing Your Own DataWake Record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
7MANAGING OUTBOUND CONTACT CALLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Using Avaya Agent with Outbound Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Getting Started with Outbound Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Logging In to Outbound Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Making Yourself Available for Outbound Contact Calls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Joining Outbound Jobs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Previewing a Customer’s Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Proceeding Through Agent Tasks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
Identifying an Unsuccessful Call . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Managing the Conversation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Leaving Outbound Jobs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Logging Out of Outbound Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Agent Blending . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Releasing You from Outbound Contact . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
“Acquiring” You from Media Channels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Task Summary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Performing an Outbound Contact Job . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 196

8 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
Contents
8MANAGING OUTBOUND LISTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Overview of Outbound List Processing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 199
Making Calls with Outbound Lists . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 201
9USING AVAYA AGENT WITH SIEBEL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 203
Comparing Avaya IC and Siebel Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Logging In to Siebel Call Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 205
Logging Out of Siebel Call Center with Pop-Up Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Logging In to Siebel Call Center with Pop-Up Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 206
Answering Contacts with Siebel Call Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Handling Screen Pops . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 207
Updating a Siebel Contact Record . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 208
Answering a Chat Contact from a New Customer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 209
Viewing Contact Information with Siebel Call Center . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 211
INDEX . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 213
9
BEFORE YOU BEGIN
Typographical Conventions
This guide uses the following font conventions:
Notes, Tips, and Cautions
Note: A note calls attention to important information.
Tip: A tip offers additional how-to advice.
Caution: A caution points out actions that may lead to data loss or other serious problems.
Contacting Technical Support
If you are having trouble using Avaya software, you should:
1 Retry the action. Carefully follow the instructions in written or online documentation.
2 Check the documentation that came with your hardware for maintenance or hardware-related
issues.
Font Type Meaning
code This font signifies commands, information that you enter into the computer, or
information contained in a file on your computer.
italics This font is used to add emphasis to important words and for references to other chapter
names and manual titles.
It also indicates variables in a command string.
jump Blue text in online documents indicates a hypertext jump to related information. To view
the related material, click on the blue text.
!

10 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
3 Note the sequence of events that led to the problem and the exact messages displayed. Have the
Avaya documentation available.
4 If you continue to have a problem, contact Avaya Technical Support by:
w
Logging in to the Avaya Technical Support Web site http://www.avaya.com/support/qq
w
Calling or faxing one of the following numbers from 8:30 a.m. to 8:30 p.m. (Eastern
Standard Time), Monday through Friday (excluding holidays):
w
Toll free in the U.S. only: 1-888-TECH-SPT (1-888-832-4778)
w
Direct line for international and domestic calls: 512-425-2201
w
Direct line for faxes: 512-997-4330
w
Sending email with your question or problem to crmsupport@avaya.com. You may be asked
to email one or more files to Technical Support for analysis of your application and its
environment.
Note: If you have difficulty reaching Avaya Technical Support through the above URL or email
address, please go to http://www.avaya.com for further information.
Product Documentation
Most Avaya product documentation is available in both printed and online form. However, some
reference material is available only online, and certain information is available only in printed
form. A PDF document with detailed information about all of the documentation for the Avaya
Interaction Center is included in the
Doc directory on the product CD-ROM. This PDF document is
also included on the separate documentation CD-ROM.
Readme File
The Readme file is an HTML file included on the Avaya Interaction Center software CD-ROM.
This file contains important information that was collected too late for inclusion in the printed
documentation. The Readme file can include installation instructions, system requirements,
information on new product features and enhancements, suggested work-arounds to known
problems, and other information critical to successfully installing and using your Avaya software.
You may also receive a printed Addendum to the Readme, containing similar information
uncovered after the manufacture of the product CD-ROM. You should review the Readme file and
the Readme Addendum before you install your new Avaya software.
Electronic Documentation
The electronic documentation (in PDF or HTML format) for each Avaya Interaction Center
product is installed automatically with the program. Electronic documentation for the entire Avaya
product suite is included on the product CD-ROM and the documentation CD-ROM.
You can also view the documentation set online at http://www.avayadocs.com.

Educational Services
Issue 1.0 June 2002 11
Printed Documentation
You can purchase printed copies of these manuals separately. For details, see “Ordering
Information” on the back of this manual’s title page.
License to Print the Electronic Documentation
Online copies of documentation are included on the CD-ROM that accompanies every software
release. An Avaya customer who has licensed software (a “Licensee”) is entitled to make this
online documentation available on an internal network or “intranet” solely for the Licensee's use
for internal business purposes. Licensees are granted the right to print the documentation
corresponding to the software they have purchased solely for such purposes.
Right-To-Print License Terms
Documents must be printed “as-is” from the provided online versions. Making changes to
documents is not permitted. Documents may be printed only by any employee or contractor of
Licensee that has been given access to the online documentation versions solely for Licensee's
internal business purposes and subject to all applicable license agreements with Avaya. Both
online and printed versions of the documents may not be distributed outside of Licensee enterprise
or used as part of commercial time-sharing, rental, outsourcing, or service bureau use, or to train
persons other than Licensee's employees and contractors for Licensee's internal business purposes,
unless previously agreed to in writing by Avaya. If Licensee reproduces copies of printed
documents for Licensee's internal business purposes, then these copies should be marked “For
internal use only within <Licensee> only.” on the first page or cover (where <Licensee> is the
name of Licensee). Licensee must fully and faithfully reproduce any proprietary notices contained
in the documentation. The copyrights to all documentation provided by Avaya are owned by
Avaya and its licensors. By printing any copy of online documentation Licensee indicates its
acceptance of these terms and conditions. This license only governs terms and conditions of
printing online documentation. Please reference the appropriate license agreement for terms and
conditions applicable to any other use, reproduction, modification, distribution or display of Avaya
software and documentation.
Educational Services
Avaya University provides excellent training courses on a variety of topics. For the latest course
descriptions, schedules, and online registration, you can get in touch with us:
n
Through the web at http://www.avaya-learning.com/logon_form.asp
n
Over the telephone at 800-288-5327 (within the U.S.) +001 303-406-6089 (outside of the U.S.)
n
Through email at Avaya.U.Helpdesk@accenture.com

12 Avaya Agent User’s Guide

13
CHAPTER 1
OVERVIEW
The Avaya Agent, and its integrated component the Web Agent, are installed on your computer
desktop, as part of the Avaya™ Interaction Center (Avaya IC) software suite. The Avaya Agent
and Web Agent make it possible for you to interact with your contact center’s customers. You may
use one or more of the following media or features of the Avaya Agent and the Web Agent:
Telephony, Email Management, Web Management, Outbound List Processing, and Avaya™
Outbound Contact Management.
This chapter briefly describes how the Avaya Agent and the Web Agent display customer contacts
to you for these media. Subsequent chapters present instructions on how to use the two software
components to handle your customer contacts.
With the Avaya Agent and the Web Agent, you can interact with customers in the following ways:
n
Speak with customers whose inbound telephone calls are assigned to you (Telephony).
n
Speak with customers who are called on the telephone by the software (Outbound Contact
Management).
n
Speak with customers whom you call on the telephone (Outbound List Processing).
n
Reply to customer emails (Email Management).
n
Chat with customers over the Web. If desired, speak to these customers on the phone while in a
chat session with them, or share Internet browsers with them (Web Management).
Note: In this manual, the illustrations show the Avaya Agent framework displayed on the right
side and across the bottom of the desktop. The frames, panes, and dialog boxes that you see on
your desktop may look different from the illustrations. Contact your system administrator if you
need help understanding the setup of Avaya Agent that you see on your desktop.

Chapter 1 Overview
14 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
Avaya Agent
The Avaya Agent is the application that enables you to handle incoming and outgoing contacts
with customers. The Avaya Agent is displayed as a framework that surrounds the desktop on your
computer monitor. You may see one or all of the following components on the Avaya Agent on
your desktop:
n
Media tab, which contains:
w
Task lists where you receive telephone calls, emails, and chat requests assigned to you
w
Softphone for speaking with customers who have called (inbound calls)
n
Outbound Lists tab for manual outbound calling
n
Outbound Contact tab for automated outbound calling
n
Contact History Browser for information about previous contacts your customers have had
with your company
n
Prompter tab (located on the Contact History Browser) for scripts telling you what to say to
customers
n
EDU (electronic data unit) Viewer for information about your current contacts
The Web Agent opens within the Avaya Agent framework when you handle emails and chat
sessions. For overview information about the Web Agent, see “Web Agent,” on page 24.
You may also work with other Avaya applications, such as CallCenterQ, HRQ, and Siebel Call
Center, which open within the Avaya Agent framework. Similarly, other applications that you
work with, such as Microsoft Word, may be set to open within the Avaya Agent framework.
Tip: Press Alt+Tab to proceed through these applications while looking at the contact information
displayed in the Avaya Agent. You can move the Avaya Agent behind the other applications by
clicking to remove the check mark beside Always on Top in the Avaya Agent menu (see “Avaya
Agent Menu,” on page 16).
Avaya Agent
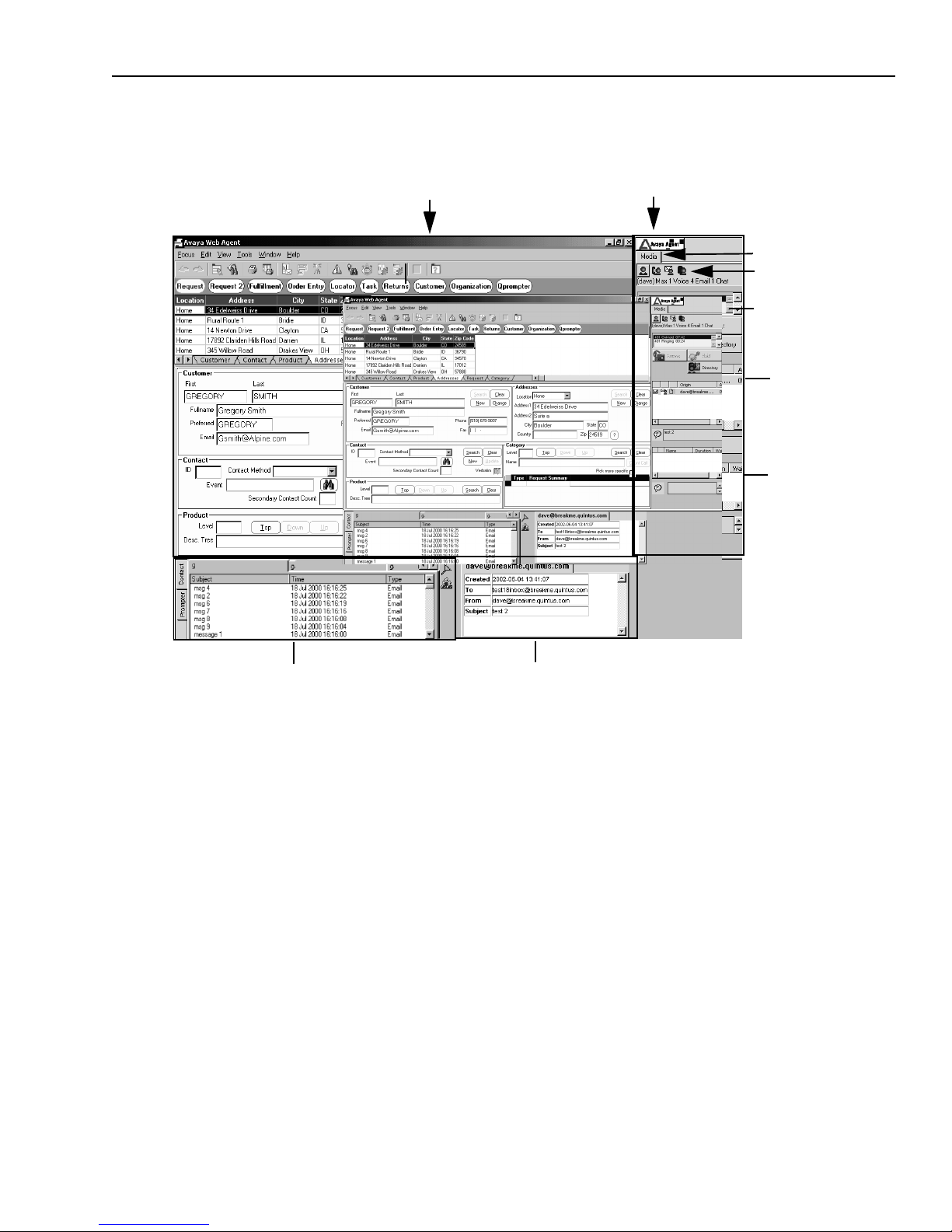
Issue 1.0 June 2002 15
The Avaya Agent with CallCenterQ in the desktop and the Email task list in the Media pane may
look like this:
CallCenterQ application running in
the desktop area
Contact History Browser
Avaya Agent menu
button
Status Control bar in
Media pane
EDU Viewer
Media tab
Email task list
Phone task list
Chat task list
Chapter 1 Overview
16 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
Using Avaya Agent with Multiple Languages
You may be able to communicate with customers in more than one language. The main features of
the Avaya Agent and the Web Agent in which you may be able to use more than one language are
as follows:
n
CallCenterQ application
n
Unified Agent Directory
n
Email
n
Chat
n
Spell checking of email and chat contents
n
Auto-Sync and Page Push
n
Global Resources and Agent Resources
n
Email Templates
n
Suggested Responses
n
Web Self-Service database
n
DataWake
n
Chat transcripts that are emailed to customers
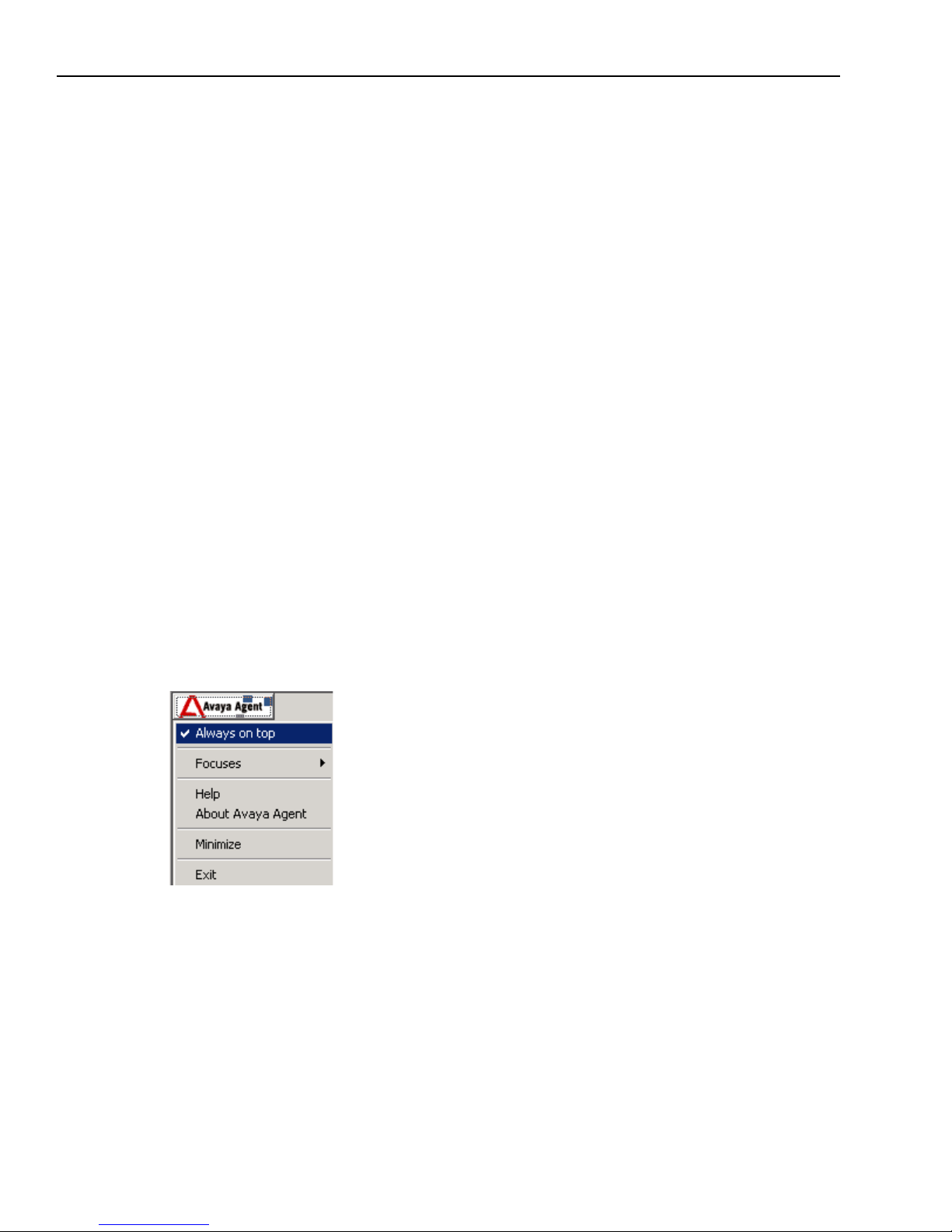
Avaya Agent Menu
You access the Avaya Agent menu by clicking the Avaya Agent button at the top of the right
frame. The Avaya Agent menu includes the options shown in the following illustration and
described in the following table:

Avaya Agent
Issue 1.0 June 2002 17
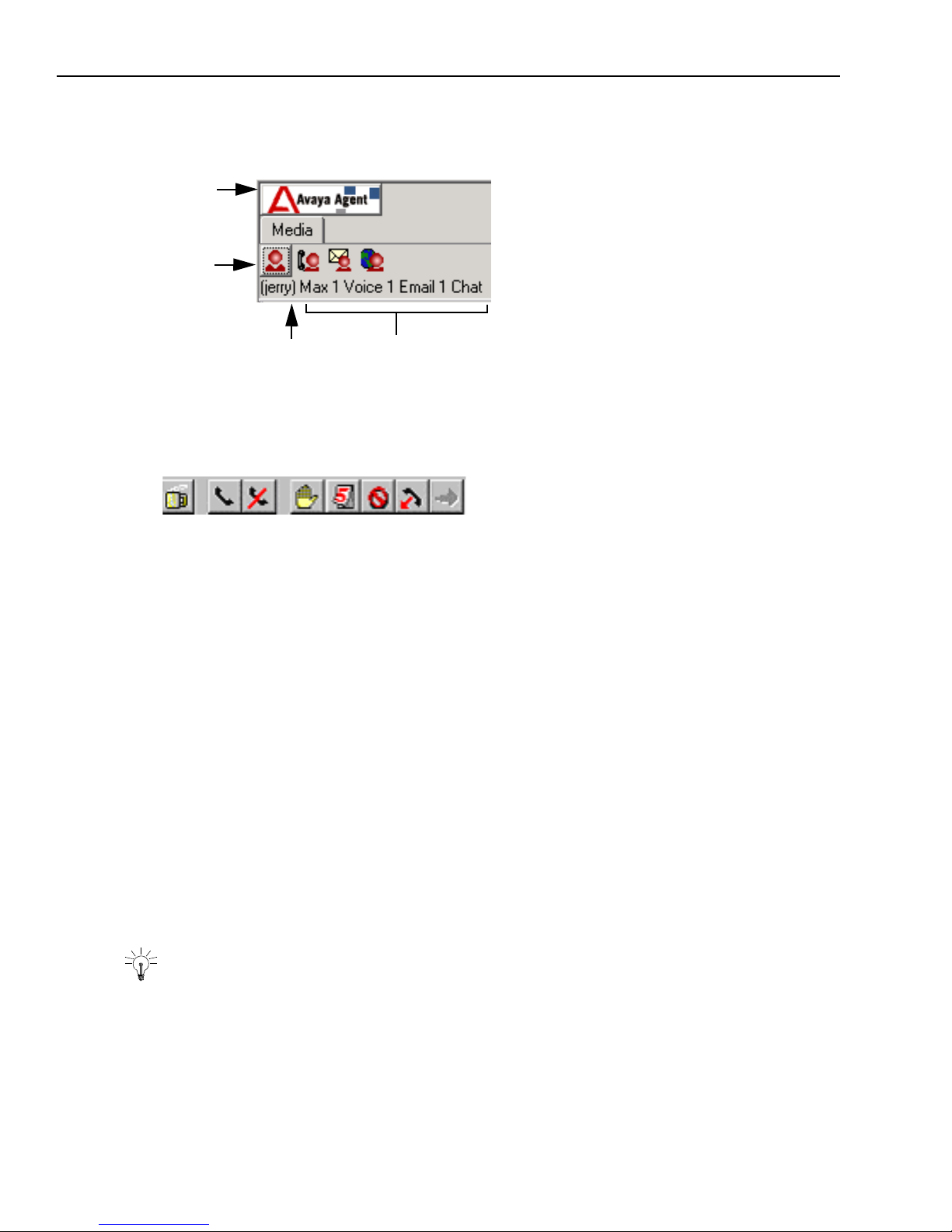
Avaya Agent Status Control Bar
When either the Media tab or the Outbound Contact tab of the Avaya Agent is selected, you see a
Status Control bar with icons or buttons that display or control your current state and the work you
can do.
The Status Control bar displays different icons and buttons, depending on whether the Media tab
or the Outbound Contact tab is selected.
Media Tab
When the Media tab is selected, the Status Control bar displays an Agent button and a button (or
icon) for each inbound media channel (Voice, Email, and Web Chat). (A button is different from an
icon. You can press a button, which has a frame around it, to control your status. An icon does not
have a frame around it and you cannot press it.)
The text below the Status Bar displays the following information:
n
Your login ID
n
Your channel load in the media channels (the maximum number of customer contacts of each
media channel that you can handle at a time)
Menu Item Action
Always on top When this item has a check mark, it ensures that the Avaya Agent always
remains on top of other applications on your desktop. If you want the Avaya
Agent to go behind other applications, click this menu item to remove the check
mark.
Focuses Lets you select a new Business Application focus to display on your desktop. A
focus is a window containing information that you use to complete a particular
job. For example, CallCenterQ is a focus containing information you use when
you respond to a request from a customer. It includes Request, Fulfillment,
Order Entry, Locator, Task, Returns, Customer, and Prompter information.
Help Displays the Avaya Agent online help.
About Avaya Agent Displays information about this Avaya Agent application release.
Minimize Minimizes the Avaya Agent. To restore the Avaya Agent, click the Avaya Agent
icon on the Windows task bar.
Exit Closes Avaya Agent, the Web Agent, and all open Avaya focuses.
Chapter 1 Overview
18 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
In the example below, Agent01 is currently available for Voice, Email, and Chat. This agent can
handle up to one voice contact, one email contact, and three chat contacts at the same time.
Outbound Contact Tab
Click the Outbound Contact tab to see a Status Control bar with buttons related to outbound jobs.
The Status Control bar buttons indicate whether you are available to handle outbound calls and
identify the activities that you can complete during the call. The buttons guide you through the
process of handling calls to customers that Outbound Contact Management initiates.
For more information on agent states, see “Changing Your Agent State,” on page 46. For more
information on channel loads, see “Setting Your Channel Loads,” on page 49.
Task Lists
Depending on your company and your responsibilities, you may see any or all of the following
task lists in the Media pane of your Avaya Agent:
n
“Using the Phone Task List,” on page 73
n
“Using the Email Task List,” on page 88
n
“Using the Chat Task List,” on page 123
When incoming contacts are assigned to you, they are displayed in the appropriate task list. The
task list also displays relevant information, such as the time the contact was assigned to you and
the state of the contact. Some of the information is indicated by the icons that represent the
contacts.
Tip: If you select a contact and hold your mouse over it for a moment, you will see a “tool tip”
with some of the same information about the contact. This tool tip may be easier to read than the
information within the task list and it may contain additional information.
Agent
button
Channel loads
Login ID
A
vaya
A
gent
button

Avaya Agent
Issue 1.0 June 2002 19
To begin responding to an incoming contact, you must select the contact in the task list and
double-click.
Softphone
Softphone makes it possible for you to perform standard telephone operations using your computer
instead of a physical telephone. Your Softphone interface is in the Media pane of Avaya Agent.
This interface contains the Phone task list and the telephony buttons that you use to manage your
incoming and outgoing voice contacts.
The out-of-the-box Softphone interface in the Media pane is shown in the following illustration.
Your Softphone may resemble the following illustration, or it may have a different set of buttons.
With the telephony buttons, you can perform various Softphone functions. These buttons can
include:
n
Answer
n
Hang Up
n
Hold
n
Reconnect
n
Ready
n
Busy
n
Directory
Telephony buttons may be available or unavailable to you, depending on the current state of the
active voice contact and on your agent state. For example, the Hold and Hang Up buttons are
available only if the active voice contact is in an InCall state. If it is not in an InCall state, the Hang
Up button is disabled (greyed out), and the Hold button is either disabled or replaced by the
Reconnect button.
Hang up voice contact and
enter WrapUp state
Phone task list with
information about current
voice contacts
Put voice contact on hold
Display Unified Agent Directory (UAD)

Chapter 1 Overview
20 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
By clicking the Directory button, you can access the Unified Agent Directory (UAD). From the
UAD, you can do such things as transfer a voice, email, or chat contact; set up a conference call;
initiate a telephone call to a colleague; look up agent information; address an email to a colleague.
For information about the UAD, see “Using the Unified Agent Directory,” on page 56. For
information about using the Softphone, see “Handling a Basic Voice Contact,” on page 75.
Outbound List Processing
The Outbound List Processing component is available through the Outbound Lists tab, which is
beside the Media tab. Outbound List Processing gives you access to customer lists that you use
with customer contact campaigns, such as outbound calling campaigns to notify customers about
upcoming sales and marketing events.
Your system administrator creates the outbound lists in CallCenterQ, which then passes the lists to
the Outbound Lists pane. Each outbound list contains a group of customers that are related in some
way, such as customers located in the same area, or customers who have purchased the same
product. The lists provide you with information like the following, which you can use during your
interaction with the customer:
n
Campaign name
n
Marketing event
n
List name
n
Customer information
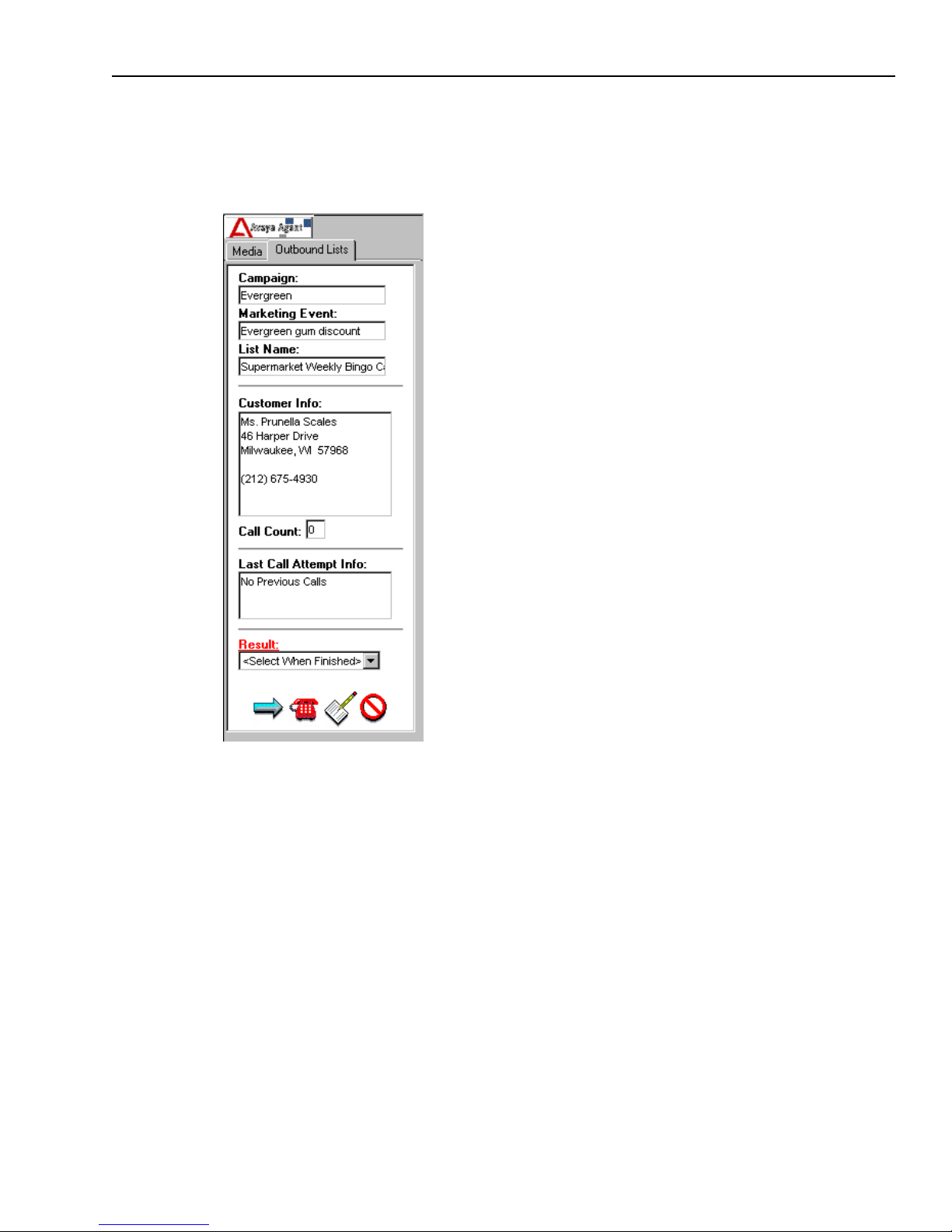
Avaya Agent
Issue 1.0 June 2002 21
The out-of-the-box Outbound List Processing component is in the Outbound Lists pane of Avaya
Agent. When you click the Outbound Lists tab, the default Outbound Lists tab looks like this:
For information about using the Outbound List Processing component, see Chapter 8, “Managing
Outbound Lists”.
Avaya™ Outbound Contact Management
Avaya™ Outbound Contact Management (Outbound Contact) automates outbound calling
activities. The software runs outbound jobs that dial customer telephone numbers and display
customer information for you. A job is a list of customers to be called. When you join a job, you
manage automated outbound calls. With Outbound Contact, you can spend more time helping
customers and less time trying to call them.
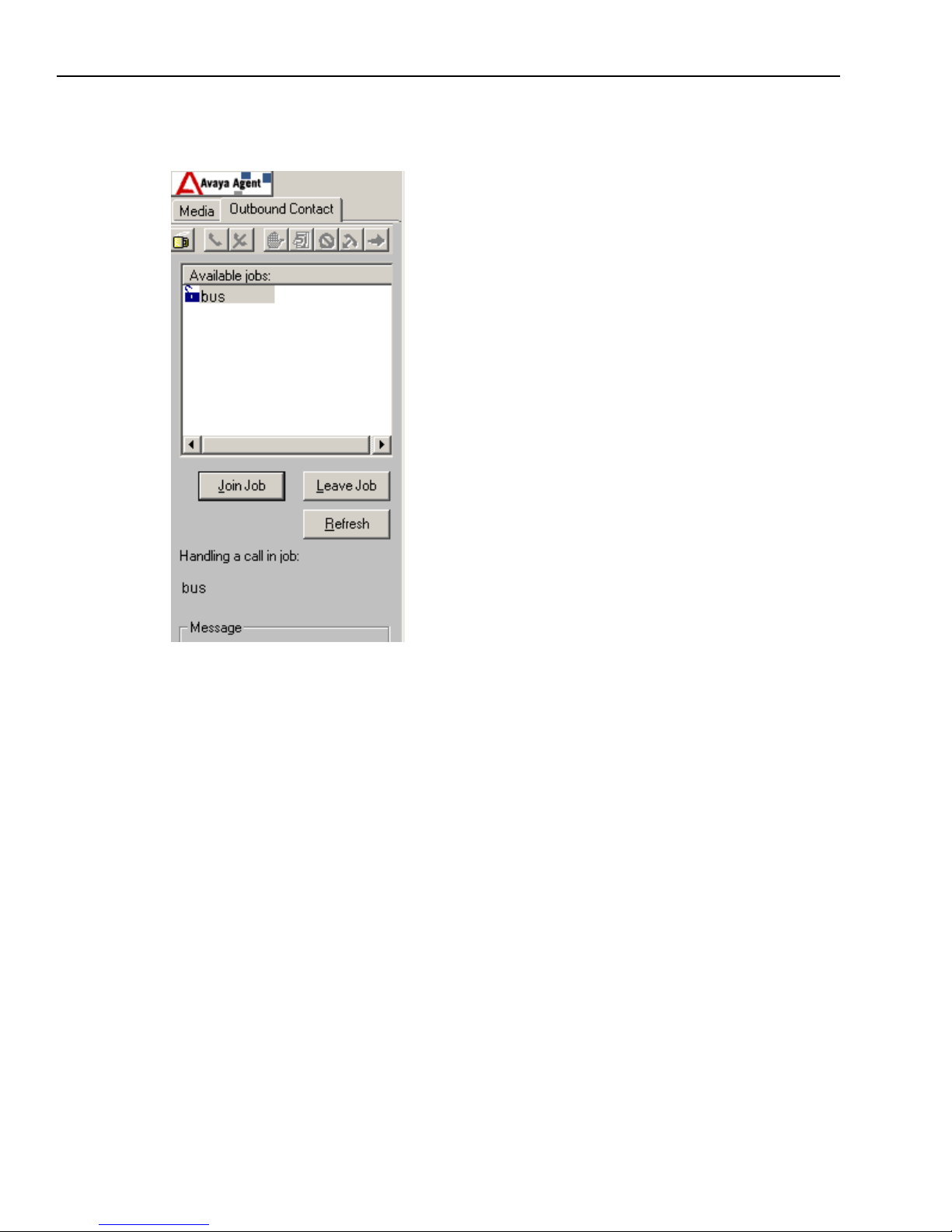
Chapter 1 Overview
22 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
The Outbound Contact Management component is available through the Outbound Contact tab.
The Outbound Contact tab display looks like this:
Outbound Contact Management enables and disables Status Control Bar buttons to guide you
through the tasks as you handle calls. The coffee cup icon identifies your current agent state and
indicates whether you are available to speak with customer. Your agent state can be one of the
following three positions:
n
Off Break (Available) – The coffee cup toolbar button is raised, indicating that you are
available to handle outbound calls and speak with customers.
n
On Break (Unavailable) – The coffee cup toolbar button is depressed, indicating that you are
unavailable to handle outbound calls or speak with customers.
n
Disabled – The coffee cup toolbar button is greyed out, indicating that you have not joined a
job.
The Outbound Contact tab displays the following information:
n
Customer information in the CallCenterQ
n
Other contacts with this customer in the Contact History Browser
n
Agent script on the Prompter tab

Avaya Agent
Issue 1.0 June 2002 23
For more information about using Outbound Contact Management, see Chapter 7, “Managing
Outbound Contact Calls”. For information about setting your agent state, see “Changing Your
Agent State,” on page 46.
Contact History Browser and EDU Viewer
You use the Contact History Browser and the EDU (electronic data unit) Viewer to locate
information about the contacts in your task lists. Each tab in the Contact History Browser contains
the history of a current contact in your task lists. Each tab in the EDU Viewer contains information
about a different current contact in your task lists. The EDU Viewer identifies each contact by the
EDU assigned to the contact by the Business Application.
The bottom frame of the Avaya Agent also contains buttons that you use to access the following:
Contact History Filter – Filters the records in the Contact History Browser to access only
the historical information you need for the current customer contact.
Active Contact Viewer – Displays information about an active email contact from the same
customer that was assigned to another agent.
Prompter Scripts
Your system administrator develops Prompter scripts to assist you while you handle contacts. Each
script is designed to provide a consistent method for you and other agents to communicate with
customers. It ensures that you obtain information from customers and give them other information,
as your company requires. Prompter scripts may contain statements for you to say to customers.
They may also contain radio buttons and text fields you use to indicate a customer’s answers, and
a selection of reasons that explain the customer’s question and how you handled the contact.
You may use Prompter scripts to do the following:
n
Collect information about customers
n
Provide answers and information to customers
n
Enter wrap-up information about a contact with a customer
n
Contact a customer for a marketing or sales campaign
Each answer that a customer gives determines the next step in a Prompter script. For example, if a
customer calls with a problem about a product they purchased from your company, the script is
different for a customer who has a valid product warranty than for a customer who does not.
A Prompter script may be displayed automatically at certain times, for example when you answer
a customer contact or when you press the Next Call button in the Outbound Lists pane.
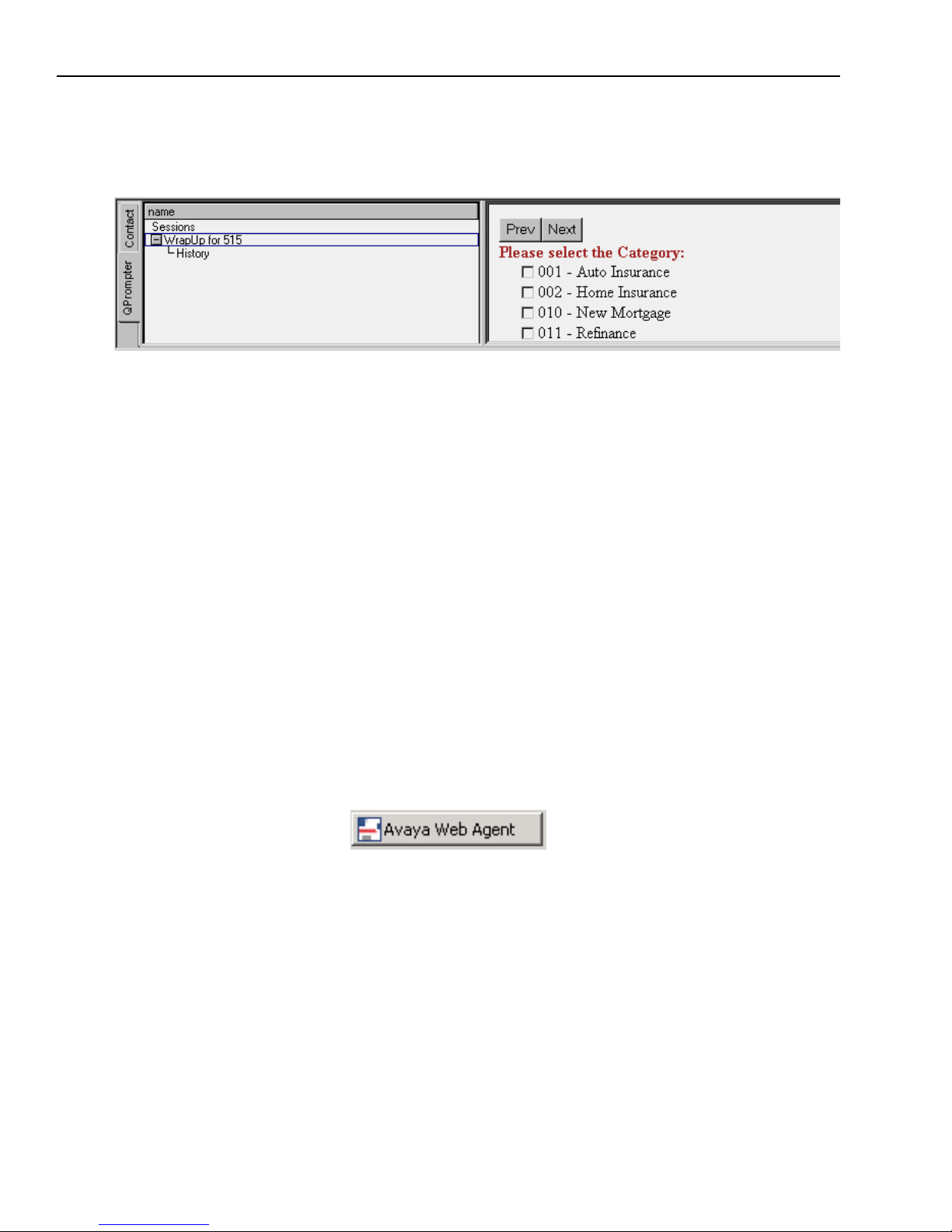
Chapter 1 Overview
24 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
As shown in the following example from a Prompter wrap-up script,
Prompter scripts are displayed in the Prompter pane. In the out-of-the-box Avaya Agent, the
Prompter pane is displayed in the frame that runs across the bottom of your desktop.
Web Agent
The Web Agent is the component of Avaya IC that makes it possible for you to interact with
customers using Email Management or Web Management. With Web Management, you conduct a
chat session with customers. While in a chat session, you can use the following features:
n
Text Chat (exchanging typed messages with your customer in real-time)
n
Voice Chat (talking to your customer, using either Chat & Phone or Chat & VoIP)
n
Shared Browsing (viewing the same Web pages with your customer, using the Auto-Sync, Page
Push, and Collaborative Form Filling features)
Customers send an email or initiate a chat session by clicking an appropriate button on your
company’s Web site. According to your availability for email or chat, some of these emails and
chat requests are assigned to you as email contacts or chat contacts. When you double-click a
contact in your Email task list or your Chat task list, the Web Agent is displayed. The Web Agent
is where you compose your email responses and conduct your chat sessions.
When you log in to Avaya Agent, you log in to the Web Agent automatically. The Web Agent is
minimized when you log in and appears as an icon in the Windows task bar, as shown in the
following illustration.
You can click the Web Agent icon to restore the Web Agent to its normal size at any time. The Web
Agent also opens whenever you click an email contact or a chat contact in the task lists in Avaya
Agent.
Web Agent
Issue 1.0 June 2002 25
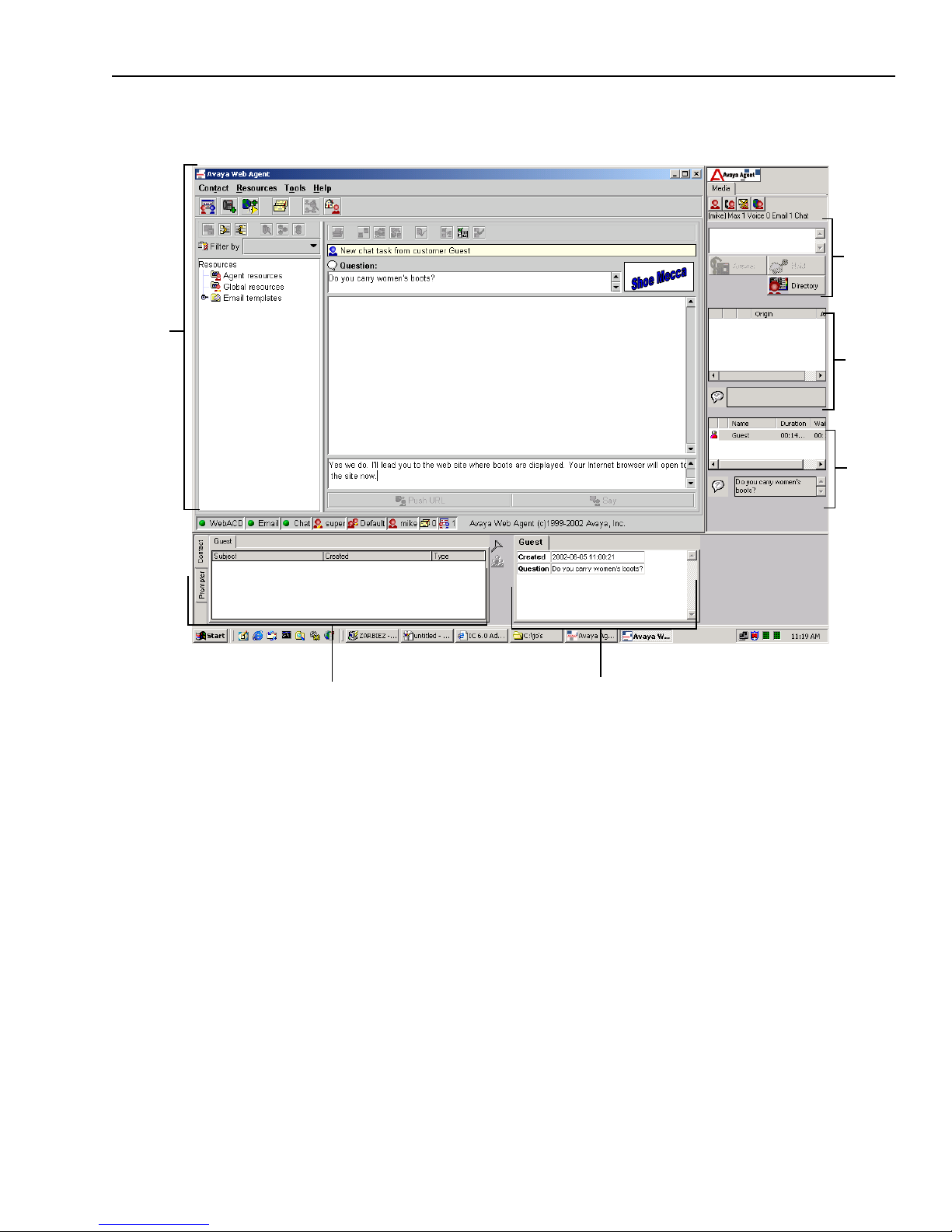
Avaya Agent with the Web Agent and an active chat contact in the desktop looks like this:
The appearance of the Web Agent changes, according to what you are doing. This section explains
the features of the Web Agent window while you are handling email or chat contacts. The section
contains the following topics:
n
The Web Agent While Handling Email
n
The Web Agent While Handling Chat
n
The Web Agent in Supervisor Mode
n
The Web Agent Status Bar
n
The Web Agent Information Bar
n
Web Age n t M en us
n
The Web Agent Toolbars
Contact History Browser and Prompter
EDU Viewer
Web Agent
Softphone
Email
task
list
Chat
task
list
and
Phone
task
list
Chapter 1 Overview
26 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
The Web Agent While Handling Email
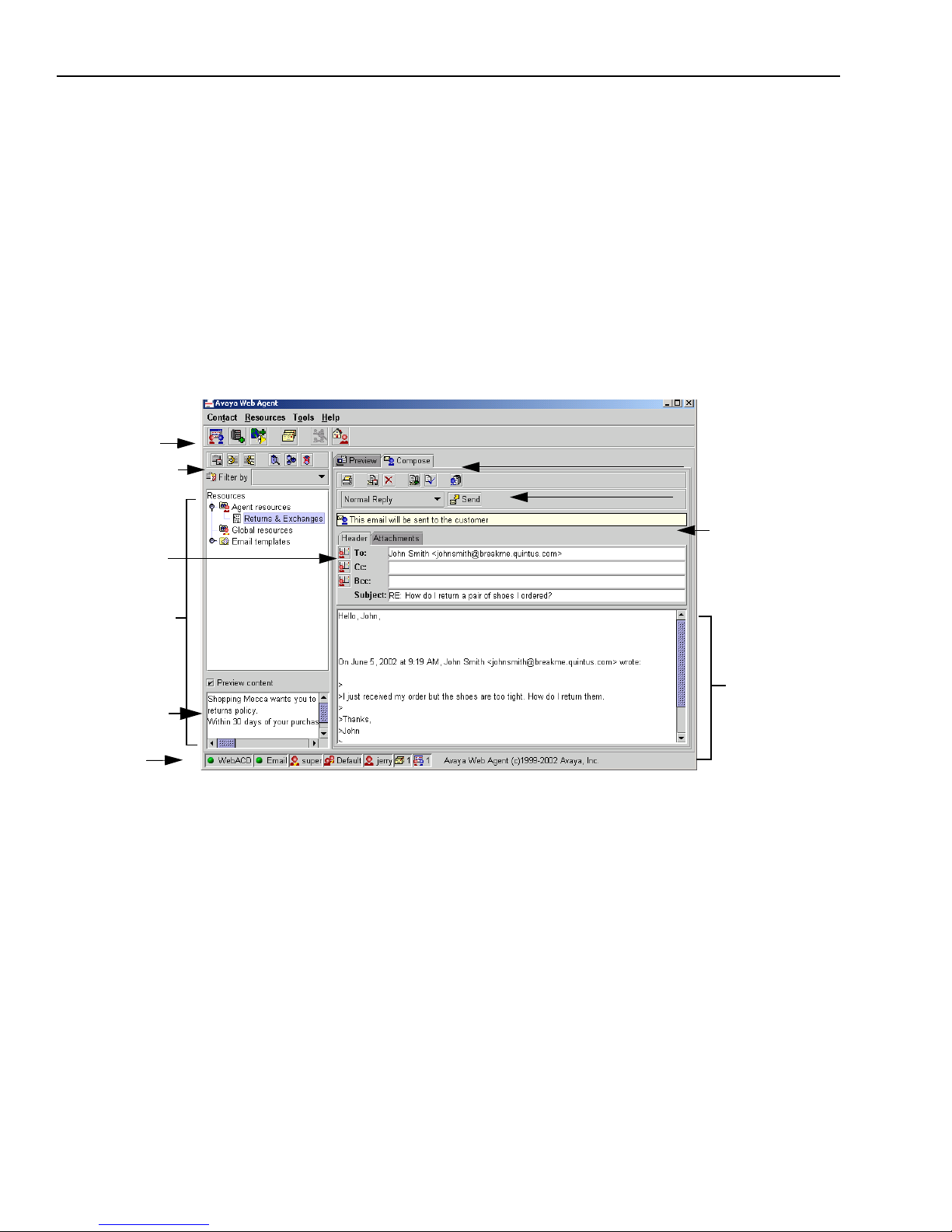
If you are enabled for email, you will use the Web Agent together with the Avaya Agent to handle
email contacts from customers. You will use two email views in the Web Agent:
n
Email Preview – This is a read-only view of the customer’s email. If you click the Reply, Reply
to All, or Forward buttons in the email toolbar, the view changes to the Email Compose mode.
n
Email Compose – This is where you write a reply to an email, forward an email you have
received, or originate an email.
You can switch between the two views by clicking the Preview tab or the Compose tab. If you are
handling multiple emails simultaneously, each email will have its own Compose tab for your reply.
The following illustration shows an email reply that an agent is composing in the Web Agent.
The features of the Web Agent window that are common to the Preview and Compose views are as
follows:
n
Menu Bar – The names of three menus containing commands: Contact, Resources, and Tools.
Click the name of a menu to open it and display the commands.
n
Main Toolbar – Buttons below the menu bar for quick access to frequently used commands.
The toolbar remains the same, whether you are currently in Email mode or a Chat mode. See
“The Main Toolbar,” on page 34.
n
Resource Toolbar and Filters – Buttons for resource-related commands and a Filter menu for
displaying only the type of resources you want to see. See “Resource Toolbar,” on page 39.
Message
Composition
area
Information Bar
Tabs for active email
Status Bar
Main toolbar
Resource toolbar
and filters
Resource area
Email Compose toolbar
and menu
UAD buttons
Resource preview
scroll box

Web Agent
Issue 1.0 June 2002 27
n
Resource Area – Frame of window that contains resources, previously prepared text responses,
emails, and URLs (Internet addresses), which you can send to customers. It may contain folders
for each of the following: Agent Resources, Global Resources, Email Templates, and
Suggested Responses.
n
Resource Preview Scroll Box – When you select a resource from a folder and then click the
Preview Contents check box, a scroll box displays the contents of the resource.
n
Information Bar – An area that displays important information about the current email. If you
switch to a chat contact, it displays information about your active chat. See “The Web Agent
Information Bar,” on page 32.
n
Status Bar – Icons that indicate certain aspects of your current Web Agent status. See “The Web
Agent Status Bar,” on page 30.
The following areas are displayed only in Email Preview mode:
n
Company Logo – Area that displays a logo that represents a company. If your contact center
supports different companies or tenants, the logo may change, according to the Web site from
which the customer sent the active email.
n
Email Preview Toolbar – Toolbar with buttons that let you perform various actions to the email,
such as reply to, forward, defer, resolve, or transfer the email, or view previous emails this
customer sent to the contact center. See “Email Toolbars,” on page 35.
n
Customer Email Header Area – Information about the customer’s email, consisting of the email
address of the customer, any other addresses to which the email was sent, the date and time the
email was sent, and the subject that the customer entered for the email. UAD buttons display
the Unified Agent Directory to let you find and add addresses of people in your company. For
detailed technical information on how the email was routed, click the Headers button.
n
Customer Message Area – Box where you can read the customer’s email. You cannot edit the
text in the message in Email Preview mode.
The following areas are displayed only in Email Compose mode:
n
Email Compose Toolbar – The Email Compose toolbar contains buttons that let you perform
various actions to the email, such as reply to, forward, defer, resolve, or transfer the email, or
view previous emails this customer sent to the contact center. See “Email Toolbars,” on
page 35.
n
Drop-down Menu and Send Button – The menu lets you choose whether this is a normal reply,
a message to an external agent, or a request to the customer for additional information. (An
external agent is a person outside the company who has been designated as a subject matter
expert who can help customers when agents request their assistance.) The Send button sends
the email that is currently in the Message Composition area to the addresses in the header
fields.
n
Outbound Email Header Area – Tab that displays information about the email you are
composing, with the addresses to which the email will be sent and the subject of the message.
n
Attachments Area – Tab that lets you attach files to the email and displays information about
any files you have attached.
Chapter 1 Overview
28 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
n
Message Composition Area – Area where you compose an email. It may contain the message
that you are replying to in addition to the message that you compose.
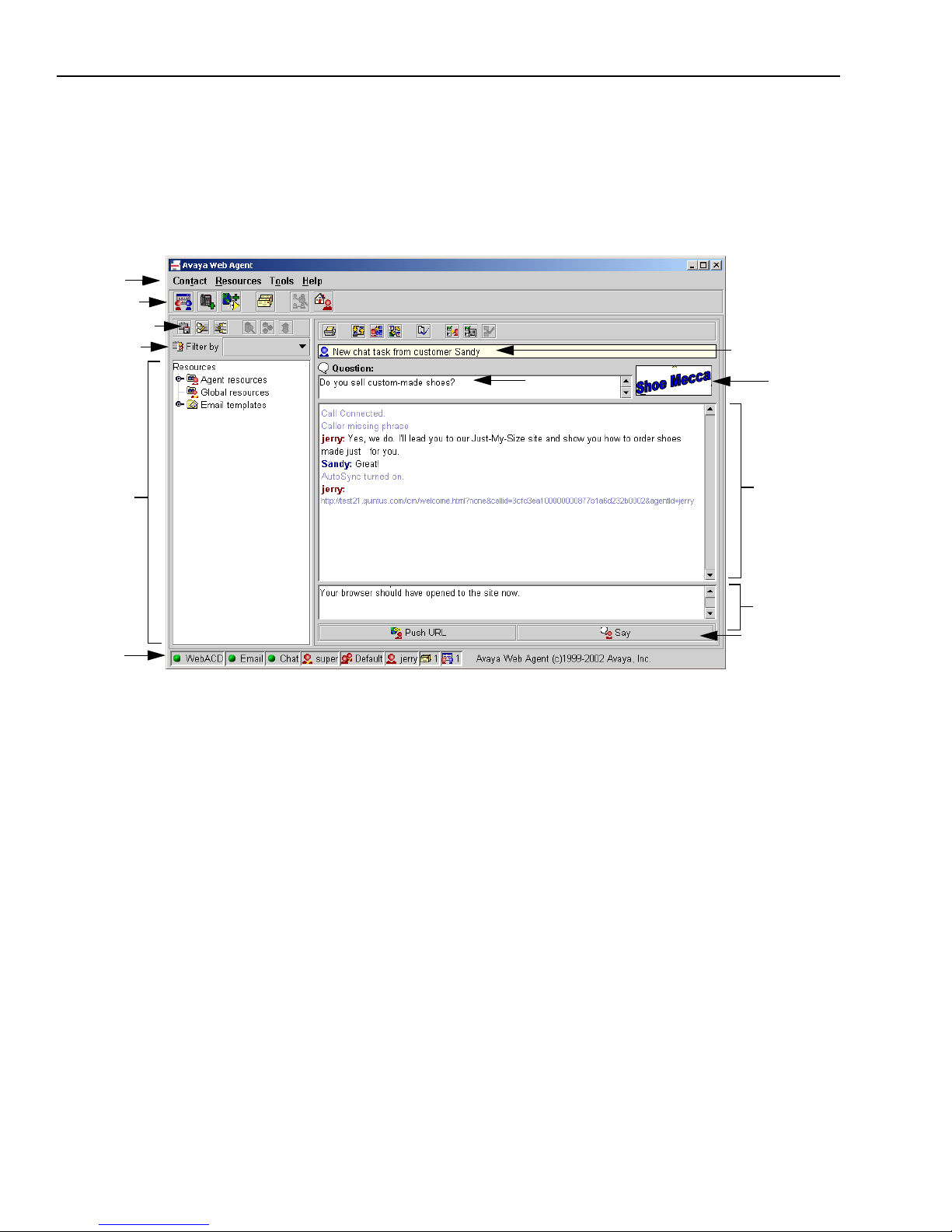
The Web Agent While Handling Chat
The following illustration shows the Web Agent window during a chat session.
The features of the Web Agent window in Chat mode are as follows:
n
Menus – The names of menus that contain commands. Click the name of a menu to open it and
display the commands.
n
Main Toolbar – Buttons below the menu bar for quick access to frequently used commands for
email or chat. See “The Main Toolbar,” on page 34.
n
Resource Toolbar and Filters – Buttons for resource-related commands and a Filter menu for
displaying only the type of resources you want to see. See “Resource Toolbar,” on page 39.
n
Resource Area – Pane that contains resources, which are previously prepared text responses,
emails, and URLs (Internet addresses) that you can send to customers. The resource area may
contain folders for each of the following: Agent Resources, Global Resources, Email
Templates, and Suggested Responses.
n
Resource Preview Scroll Box (not shown) – When you select a resource from a folder and then
click the Preview Contents check box, a scroll box displays the contents of the resource.
n
Company Logo – Area that displays a logo that represents a company. If your contact center
supports different companies or tenants, the logo may change, according to the Web site from
which the customer requested the current chat session.
Company
Resource
Text Entry area
Main Toolbar
Menu Bar
Send bar
Status Bar
Transcript area
Customer
Question
logo
Area
Resource Toolbar
Information bar
Resource filters

Web Agent
Issue 1.0 June 2002 29
n
Chat Toolbars – The main chat toolbar contains buttons for controlling the current chat session.
Additional toolbars are added when you conduct a Chat & Phone or a Chat & VoIP session. See
“Chat Toolbars,” on page 37.
n
Send Bar – Buttons for sending a URL that opens in your customer’s browser and for sending
the text you entered in the Text Entry area to your customer.
n
Information Bar – An area that displays important information about your active chat session.
If you switch to an email contact, it displays information about your active email. See “The
Web Agent Information Bar,” on page 32.
n
Customer Question – Area that displays the original question typed by the customer on the Web
site. This area also displays other information about the customer and the site from which the
customer requested the chat. This information can also help you identify guest users (people
who log on to the company Web site without a user account).
n
Transcript Area – Area that displays the chat conversation that has occurred so far between you
and the customer.
n
Text Entry – Area where you enter text or URLs to send to the customer.
n
Status Bar – Icons that indicate certain aspects of your current Web Agent status.

Chapter 1 Overview
30 Avaya Agent User’s Guide
The Web Agent in Supervisor Mode
If you are a supervisor, you can click the Supervisor Mode button whenever you want to monitor a
chat session. The Web Agent displays a Supervisor Mode panel, as shown in the following
illustration, showing all the chat sessions that agents in your workgroup are currently conducting.
When you select the session you want to monitor, the Transcript and Text Entry areas display the
chat session. See “Monitoring a Chat Session (Supervisors Only),” on page 147 for more
information.
The Web Agent Status Bar
The bottom of the Web Agent, as shown in the above illustration, contains a Status Bar with icons
that show aspects of your current Web Agent status. The Status Bar remains the same, whether you
are currently in Email mode or Chat mode.
Current chat sessions
Agent
Workgroup
Customer
Your workgroup
Your login ID and status
Your current chat contact load
Connection to Email Server
Your supervisor’s login ID and status
Your current email contact load
Connection to WebACD Server
 Loading...
Loading...