Page 1

Avaya Integrated Management
Release 2.2
Network Management
Console
User Guide
14-300169
Issue 2
January 2005
Page 2
Copyright 2004, Avaya Inc.
All Rights Reserved
Notice
Every effort was made to ensure that the information in this document
was complete and accurate at the time of printing. However, information
is subject to change.
Warranty
Avaya Inc. provides a limited warranty on this product. Refer to your
sales agreement to establish the terms of the limited warranty. In
addition, Avaya’s standard warranty language as well as information
regarding support for this product, while under warranty, is available
through the following Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support
.
Preventing Toll Fraud
"Toll fraud" is the unauthorized use of your telecommunications system
by an unauthorized party (for example, a person who is not a corporate
employee, agent, subcontractor, or is not working on your company's
behalf). Be aware that there may be a risk of toll fraud associated with
your system and that, if toll fraud occurs, it can result in substantial
additional charges for your telecommunications services.
Avaya Fraud Intervention
If you suspect that you are being victimized by toll fraud and you need
technical assistance or support, in the United States and Canada, call the
Technical Service Center's Toll Fraud Intervention Hotline at
1-800-643-2353.
Disclaimer
Avaya is not responsible for any modifications, additions or deletions to
the original published version of this documentation unless such
modifications, additions or deletions were performed by Avaya.
Customer and/or End User agree to indemnify and hold harmless Avaya,
Avaya's agents, servants and employees against all claims, lawsuits,
demands and judgments arising out of, or in connection with,
subsequent modifications, additions or deletions to this documentation
to the extent made by the Customer or End User.
How to Get Help
For additional support telephone numbers, go to the Avaya support Web
site: http://www.avaya.com/support
• Within the United States, click the Escalation Management
link. Then click the appropriate link for the type of support
you need.
• Outside the United States, click the Escalation Management
link. Then click the International Services link that includes
telephone numbers for the international Centers of
Excellence.
. If you are:
Providing Telecommunications Security
Telecommunications security (of voice, data, and/or video
communications) is the prevention of any type of intrusion to (that is,
either unauthorized or malicious access to or use of) your company's
telecommunications equipment by some party.
Your company's "telecommunications equipment" includes both this
Avaya product and any other voice/data/video equipment that could be
accessed via this Avaya product (that is, "networked equipment").
An "outside party" is anyone who is not a corporate employee, agent,
subcontractor, or is not working on your company's behalf. Whereas, a
"malicious party" is anyone (including someone who may be otherwise
authorized) who accesses your telecommunications equipment with
either malicious or mischievous intent.
Such intrusions may be either to/through synchronous
(time-multiplexed and/or circuit-based), or asynchronous (character-,
message-, or packet-based) equipment, or interfaces for reasons of:
• Utilization (of capabilities special to the accessed equipment)
• Theft (such as, of intellectual property, financial assets, or toll
facility access)
• Eavesdropping (privacy invasions to humans)
• Mischief (troubling, but apparently innocuous, tampering)
• Harm (such as harmful tampering, data loss or alteration,
regardless of motive or intent)
Be aware that there may be a risk of unauthorized intrusions associated
with your system and/or its networked equipment. Also realize that, if
such an intrusion should occur, it could result in a variety of losses to
your company (including but not limited to, human/data privacy,
intellectual property, material assets, financial resources, labor costs,
and/or legal costs).
Responsibility for Your Company’s Telecommunications Security
The final responsibility for securing both this system and its networked
equipment rests with you - Avaya’s customer system administrator, your
telecommunications peers, and your managers. Base the fulfillment of
your responsibility on acquired knowledge and resources from a variety
of sources including but not limited to:
• Installation documents
• System administration documents
• Security documents
• Hardware-/software-based security tools
• Shared information between you and your peers
• Telecommunications security experts
To prevent intrusions to your telecommunications equipment, you and
your peers should carefully program and configure:
• Your Avaya-provided telecommunications systems and their
interfaces
• Your Avaya-provided software applications, as well as their
underlying hardware/software platforms and interfaces
• Any other equipment networked to your Avaya products
TCP/IP Facilities
Customers may experience differences in product performance,
reliability and security depending upon network configurations/design
and topologies, even when the product performs as warranted.
Standards Compliance
Avaya Inc. is not responsible for any radio or television interference
caused by unauthorized modifications of this equipment or the
substitution or attachment of connecting cables and equipment other
than those specified by Avaya Inc. The correction of interference caused
by such unauthorized modifications, substitution or attachment will be
the responsibility of the user. Pursuant to Part 15 of the Federal
Communications Commission (FCC) Rules, the user is cautioned that
changes or modifications not expressly approved by Avaya Inc. could
void the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
Product Safety Standards
This product complies with and conforms to the following international
Product Safety standards as applicable:
Safety of Information Technology Equipment, IEC 60950, 3rd Edition, or
IEC 60950-1, 1st Edition, including all relevant national deviations as
listed in Compliance with IEC for Electrical Equipment (IECEE) CB-96A.
Safety of Information Technology Equipment, CAN/CSA-C22.2
No. 60950-00 / UL 60950, 3rd Edition, or CAN/CSA-C22.2 No.
60950-1-03 / UL 60950-1.
Safety Requirements for Information Technology Equipment, AS/NZS
60950:2000.
One or more of the following Mexican national standards, as applicable:
NOM 001 SCFI 1993, NOM SCFI 016 1993, NOM 019 SCFI 1998.
The equipment described in this document may contain Class 1 LASER
Device(s). These devices comply with the following standards:
• EN 60825-1, Edition 1.1, 1998-01
• 21 CFR 1040.10 and CFR 1040.11.
The LASER devices used in Avaya equipment typically operate within
the following parameters:
Typical Center W avelength Maximum Output Power
830 nm - 860 nm -1.5 dBm
1270 nm - 1360 nm -3.0 dBm
1540 nm - 1570 nm 5.0 dBm
Luokan 1 Laserlaite
Klass 1 Laser Apparat
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than
those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposures.
Contact your Avaya representative for more laser product information.
Page 3
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Standards
This product complies with and conforms to the following international
EMC standards and all relevant national deviations:
Limits and Methods of Measurement of Radio Interference of
Information Technology Equipment, CISPR 22:1997, EN55022:1998,
and AS/NZS 3548.
Information Technology Equipment - Immunity Characteristics - Limits
and Methods of Measurement, CISPR 24:1997 and EN55024:1998,
including:
• Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) IEC 61000-4-2
• Radiated Immunity IEC 61000-4-3
• Electrical Fast Transient IEC 61000-4-4
• Lightning Effects IEC 61000-4-5
• Conducted Immunity IEC 61000-4-6
• Mains Frequency Magnetic Field IEC 61000-4-8
• Voltage Dips and Variations IEC 61000-4-11
Power Line Emissions, IEC 61000-3-2: Electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC) - Part 3-2: Limits - Limits for harmonic current emissions.
Power Line Emissions, IEC 61000-3-3: Electromagnetic compatibility
(EMC) - Part 3-3: Limits - Limitation of voltage changes, voltage
fluctuations and flicker in public low-voltage supply systems.
Federal Communications Commission Statement
Part 15:
REN is not required for some types of analog or digital facilities. Means
of Connection
Connection of this equipment to the telephone network is shown in the
following tables.
For MCC1, SCC1, CMC1, G600, and G650 Media Gateways:
Manufac t urer’s Port
Identifier
Off premises station OL13C 9.0F RJ2GX,
DID trunk 02RV2-T 0.0B RJ2GX,
CO trunk 02GS2 0.3A RJ21X
Tie trunk TL31M 9.0F RJ2GX
Basic Rate Interface 02IS5 6.0F, 6.0Y RJ49C
FIC Code SOC/
REN/
A.S. Code
02LS2 0.3A RJ21X
Network
Jacks
RJ21X,
RJ11C
RJ21X
* Note: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with
the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC
Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a
commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful
interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment
in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which
case the user will be required to correct the interference at his own
expense.
Part 68: Answer-Supervision Signaling
Allowing this equipment to be operated in a manner that does not
provide proper answer-supervision signaling is in violation of Part 68
rules. This equipment returns answer-supervision signals to the public
switched network when:
• answered by the called station,
• answered by the attendant, or
• routed to a recorded announcement that can be
administered by the customer premises equipment (CPE)
user.
This equipment returns answer-supervision signals on all direct inward
dialed (DID) calls forwarded back to the public switched telephone
network. Permissible exceptions are:
• A call is unanswered.
• A busy tone is received.
• A reorder tone is received.
Avaya attests that this registered equipment is capable of providing users
access to interstate providers of operator services through the use of
access codes. Modification of this equipment by call aggregators to block
access dialing codes is a violation of the Telephone Operator Consumers
Act of 1990.
REN Number
For MCC1, SCC1, CMC1, G600, and G650 Media Gateways:
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC rules. On either the
rear or inside the front cover of this equipment is a label that contains,
among other information, the FCC registration number, and ringer
equivalence number (REN) for this equipment. If requested, this
information must be provided to the telephone company.
For G350 and G700 Media Gateways:
This equipment complies with Part 68 of the FCC rules and the
requirements adopted by the ACTA. On the rear of this equipment is a
label that contains, among other information, a product identifier in the
format US:AAAEQ##TXXXX. The digits represented by ## are the ringer
equivalence number (REN) without a decimal point (for example, 03 is a
REN of 0.3). If requested, this number must be provided to the
telephone company.
For all media gateways:
The REN is used to determine the quantity of devices that may be
connected to the telephone line. Excessive RENs on the telephone line
may result in devices not ringing in response to an incoming call. In
most, but not all areas, the sum of RENs should not exceed 5.0. To be
certain of the number of devices that may be connected to a line, as
determined by the total RENs, contact the local telephone company.
1.544 digital interface 04DU9-BN6.0F RJ48C,
04DU9-IKN6.0F RJ48C,
04DU9-ISN6.0F RJ48C,
120A4 channel service
unit
04DU9-DN6.0Y RJ48C
RJ48M
RJ48M
RJ48M
For G350 and G700 Media Gateways:
Manufacturer’s Port
Identifier
FIC Code SOC/
REN/
Network
Jacks
A.S. Code
Ground Start CO trunk 02GS2 1.0A RJ11C
DID trunk 02RV2-T AS.0 RJ11C
Loop Start CO trunk 02LS2 0.5A RJ11C
1.544 digital interface 04DU9-BN 6.0Y RJ48C
04DU9-DN 6.0Y RJ48C
04DU9-IKN 6.0Y RJ48C
04DU9-ISN 6.0Y RJ48C
Basic Rate Interface 02IS5 6.0F RJ49C
For all media gateways:
If the terminal equipment (for example, the media server or media
gateway) causes harm to the telephone network, the telephone
company will notify you in advance that temporary discontinuance of
service may be required. But if advance notice is not practical, the
telephone company will notify the customer as soon as possible. Also,
you will be advised of your right to file a complaint with the FCC if you
believe it is necessary.
The telephone company may make changes in its facilities, equipment,
operations or procedures that could affect the operation of the
equipment. If this happens, the telephone company will provide
advance notice in order for you to make necessary modifications to
maintain uninterrupted service.
If trouble is experienced with this equipment, for repair or warranty
information, please contact the Technical Service Center at
1-800-242- 2121 or contact your local Avaya representative. If the
equipment is causing harm to the telephone network, the telephone
company may request that you disconnect the equipment until the
problem is resolved.
Page 4
A plug and jack used to connect this equipment to the premises wiring
and telephone network must comply with the applicable FCC Part 68
rules and requirements adopted by the ACTA. A compliant telephone
cord and modular plug is provided with this product. It is designed to be
connected to a compatible modular jack that is also compliant. It is
recommended that repairs be performed by Avaya certified technicians.
The equipment cannot be used on public coin phone service provided by
the telephone company. Connection to party line service is subject to
state tariffs. Contact the state public utility commission, public service
commission or corporation commission for information.
This equipment, if it uses a telephone receiver, is hearing aid compatible.
Canadian Department of Communications (DOC) Interference Information
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme
NMB-003 du Canada.
This equipment meets the applicable Industry Canada Terminal
Equipment Technical Specifications. This is confirmed by the registration
number. The abbreviation, IC, before the registration number signifies
that registration was performed based on a Declaration of Conformity
indicating that Industry Canada technical specifications were met. It
does not imply that Industry Canada approved the equipment.
Installation and Repairs
Before installing this equipment, users should ensure that it is
permissible to be connected to the facilities of the local
telecommunications company. The equipment must also be installed
using an acceptable method of connection. The customer should be
aware that compliance with the above conditions may not prevent
degradation of service in some situations.
Repairs to certified equipment should be coordinated by a representative
designated by the supplier. Any repairs or alterations made by the user
to this equipment, or equipment malfunctions, may give the
telecommunications company cause to request the user to disconnect
the equipment.
Declarations of Conformity
United States FCC Part 68 Supplier’s Declaration of Conformity (SDoC)
Avaya Inc. in the United States of America hereby certifies that the
equipment described in this document and bearing a TIA TSB-168 label
identification number complies with the FCC’s Rules and Regulations 47
CFR Part 68, and the Administrative Council on Terminal Attachments
(ACTA) adopted technical criteria.
Avaya further asserts that Avaya handset-equipped terminal equipment
described in this document complies with Paragraph 68.316 of the FCC
Rules and Regulations defining Hearing Aid Compatibility and is deemed
compatible with hearing aids.
Copies of SDoCs signed by the Responsible Party in the U. S. can be
obtained by contacting your local sales representative and are available
on the following Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support
All Avaya media servers and media gateways are compliant with FCC
Part 68, but many have been registered with the FCC before the SDoC
process was available. A list of all Avaya registered products may be
found at: http://www.part68.org
as manufacturer.
by conducting a search using "Avaya"
.
European Union Declarations of Conformity
To order copies of this and other documents:
Call: Avaya Publications Center
Voice 1.800.457.1235 or 1.207.866.6701
FAX 1.800.457.1764 or 1.207.626.7269
Write: Globalware Solutions
200 Ward Hill Avenue
Haverhill, MA 01835 USA
Attention: Avaya Account Management
E-mail: totalware@gwsmail.com
For the most current versions of documentation, go to the Avaya
support Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support
.
Avaya Inc. declares that the equipment specified in this document
bearing the "CE" (Conformité Europeénne) mark conforms to the
European Union Radio and Telecommunications Terminal Equipment
Directive (1999/5/EC), including the Electromagnetic Compatibility
Directive (89/336/EEC) and Low Voltage Directive (73/23/EEC).
Copies of these Declarations of Conformity (DoCs) can be obtained by
contacting your local sales representative and are available on the
following Web site: http://www.avaya.com/support
.
Japan
This is a Class A product based on the standard of the Voluntary Control
Council for Interference by Information Technology Equipment (VCCI).
If this equipment is used in a domestic environment, radio disturbance
may occur, in which case, the user may be required to take corrective
actions.
Page 5

Table of Contents
Preface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
The Purpose of This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Who Should Use This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Organization of This Manual . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Chapter 1 — Network Management in Standalone Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
Network Management In Standalone Mode Overview . . . . . . . . . .14
Network Management in Standalone Mode Terms . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
What is Avaya Network Management Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
What is Avaya Network Management Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
What is a Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
What is Discovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
What is Event Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .18
What is Remote Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .21
Chapter 2 — Avaya Network Management Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Introduction to Avaya Network Management Server . . . . . . . . . . .23
Starting Avaya Network Management Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Stopping Avaya Network Management Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .25
Chapter 3 — Avaya Network Management Console Introduction . . . . . . . . .27
Starting Avaya Network Management Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
Avaya Network Management Console User Interface . . . . . . . . . . .28
Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
Network Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Network Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Dialog Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Status Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .31
Using Tooltips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Requesting Write Permission . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Avaya Network Management Console Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
SNMP Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Default SNMP Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .35
Setting SNMP Access Parameters for IP Ranges . . . . . . . . .37
Setting Specific IP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .39
Setting Connectivity Polling Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Selecting a Default Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Setting Read/Write Defaults . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 5
Page 6

Table of Contents
Using Avaya Network Management Console Tables . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Using Avaya Network Management Console Help . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Opening the Help to the Contents Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Opening the Help to a Topic of Interest . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Closing Avaya Network Management Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Chapter 4 — Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree . . . . . . . .45
Introduction to the Network Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .45
Using the Network Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
The Subnet View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
The Device Type View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .47
The System View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .48
Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Creating Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Modifying Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .50
Deleting Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Adding Branches in Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .51
Modifying Branches in Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Deleting Branches in Custom Views . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .52
Printing the Network Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .53
Searching the Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .54
Chapter 5 — Avaya Network Management Console Network Table . . . . . . .55
Using the Network Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .55
Network Table Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .56
Network Table Colors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .57
Managing Objects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .58
Manually Adding Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
Modifying Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Device Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .60
Deleting Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .62
Chapter 6 — Avaya Network Management Console Application Launcher .63
Launching Device Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .63
Device Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Telnet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
Web Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .64
PING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Avaya Site Administrator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .65
Avaya MultiSite Administration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Avaya Fault and Performance Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .67
Avaya VAL Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Avaya Wireless . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .68
Extreme EPICenter . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .69
Launching Network-wide Applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .70
6 A vaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 7

Table of Contents
Chapter 7 — Network Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Introduction to Network Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Managing Network Maps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .71
Creating a Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .72
Opening a Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Saving a Network Map to a Different Name . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .73
Printing a Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Importing Devices into the Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .74
Exporting the Network Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
CSV File Structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .75
Chapter 8 — Introduction to the Discovery Window. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
Opening the Discovery Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .77
The Discovery User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .78
Discovery Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .79
Subnets Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .80
Discovery Dialog Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Discovery Log Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Discovery Status Bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Closing the Discovery Window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .81
Chapter 9 — Discovering Your Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Setting Discovery Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .83
Configuring Discovery Method and Range . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .84
Configuring Discovery’s Naming Method . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .86
Selecting Device Types to Discover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Using the Discovery Scheduler . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Discovering Subnets and Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
Discovering All Subnets and Nodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .92
Discovering Nodes on Specific Subnets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
Manually Adding Subnets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .95
Modifying Subnets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .96
Subnet Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .97
Deleting Subnets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
Using the Discovery Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .98
Configuring Router Access Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .99
Saving the Discovery Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
Deleting Log Entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
Clearing the Discovery Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .100
Manually Discovering System View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
Using the System View Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .101
Chapter 10 — Introduction to the Event Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Event Manager Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .103
Viewing the Event Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
The Event Manager User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
The Event Log Browser User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .104
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 7
Page 8

Table of Contents
Event Log Browser Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .105
The Trap Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .106
Status Line . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
The Event Configuration User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .107
Event Configuration Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .108
The Event Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .109
Assign Action Form Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
Event Configuration Form Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .110
The Action List User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
Action List Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .112
The Action Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .113
Action Form Area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
Closing the Event Manager . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
Chapter 11 — Managing Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
Managing Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .115
Trap Log Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .116
Filtering Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
Filtering By Severity Level . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .117
Filtering By IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .118
Filtering By Device Type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Filtering By Acknowledged . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Viewing All Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
Acknowledging Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
Deleting Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .121
Editing Severity Levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .121
Saving the Trap Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .122
Defining Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
Actions Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .123
Adding Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .124
Modifying Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .125
Action Fields . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .126
Action Scripts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
Action Audio Files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .128
Deleting Actions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .128
Applying Changes to the Action List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .128
Action Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .129
Configuring Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .130
Assigning Actions to Events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .130
Configuring Event Forwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .132
Event Forwarding Sources . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .134
Configuring Forwarding Recipients . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .134
Chapter 12 — Remote Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .135
Introduction to Remote Access . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .135
Remote Access and Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .135
Starting a Remote Session . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .136
8 A vaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 9

Table of Contents
Appendix A — Network Management Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .137
Avaya Network Management Console Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .137
Avaya Network Management Console File Menu . . . . . . . . . .137
Avaya Network Management Console Edit Menu . . . . . . . . .138
Avaya Network Management Console View Menu . . . . . . . .139
Avaya Network Management Console Actions Menu . . . . . .139
Avaya Network Management Console Tools Menu . . . . . . . .140
Avaya Network Management Console Help Menu . . . . . . . . .141
Discovery Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .141
Discovery File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .141
Discovery Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .142
Discovery View Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .142
Discovery Actions Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .142
Discovery Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .142
Event Log Browser Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .143
Event Log Browser File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .143
Event Log Browser Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .143
Event Log Browser View Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .144
Event Log Browser Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .144
Event Configuration Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
Event Configuration File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
Event Configuration Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
Event Configuration Tools Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .145
Event Configuration Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .146
Action List Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .146
Action List File Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .146
Action List Edit Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .146
Action List Tools Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .147
Action List Help Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .147
Index. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .149
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 9
Page 10

Table of Contents
10 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 11
Preface
Welcome to Avaya Network Management Console in Standalone Mode.
This chapter provides an introduction to the structure and assumptions
of this manual. It includes the following sections:
• The Purpose of This
manual.
• Who Should Use This
manual.
Manual - A description of the goals of this
The Purpose of This Manual
This manual contains information needed to use Avaya Network
Management Console in Standalone Mode efficiently and effectively.
Who Should Use This Manual
This manual is intended for network managers familiar with network
management and its fundamental concepts.
Organization of This Manu al
Manual - The intended audience of this
This manual is structured to reflect the following conceptual divisions:
• Preface - A description of the manual’s purpose, intended
audience, and organization.
• Network Management in Standalone Mode
of Avaya Network Management Console in Standalone Mode,
including a discussion of basic network management concepts.
• Avaya Network Management Server
Avaya Network Management Server including instructions on
starting Avaya Network Management Server from your
computer.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 1 1
- An overview of
- An overview
Page 12
Preface
• Avaya Network Management Console Introduction - An
introduction to Avaya Network Management Console, including
instructions on starting Avaya Network Management Console, a
detailed description of Avaya Network Management Console’s
user interface, and instructions on how to use Avaya Network
Management Console’s on-line help.
• Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree
description of the Avaya Network Management Console network
tree including its default views - the Subnet View and Device
Type View - and the System View for networks containing VoIP
devices. It also includes instructions on how to create custom
views and search the tree.
• Avaya Network Management Console Network Table
description of the Avaya Network Management Console network
table and instructions on how to add, delete, and modify objects
in the table.
• Avaya Network Management Console
Application Launcher - Instructions on how to launch device-
specific and network-wide applications from Avaya Network
Management Console.
• Network Maps
- An explanation of Network Maps, instructions
on how to create, open, save, and print Network Maps, and
instructions on importing devices into Network Maps and
exporting devices from Network Maps.
• Introduction to the Discovery Window
- Instructions on how
to open and close the Discovery window and a description of the
Discovery window.
- A
- A
• Discovering Your Network
- Instructions on how to use
Network Management in Standalone Mode to discover the
subnets, nodes and VoIP devices on your network. It also includes
an explanation of the Discovery Log and how to configure a
router’s access parameters including SNMP V1 or SNMP V3
protocol.
• Introduction to the Event Manager
- Instructions on how to
open and close the Event Manager and a description of the Event
Manager.
• Managing Events
- Instructions on how to use the Event
Manager to view, filter, and delete events from the Event Log
Browser, define event actions, and assign actions to events.
• Remote Access
- Instructions on running Avaya Network
Management Console remotely, including security issues.
12 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 13

1
Network Management in Standalone Mode
This chapter provides an overview of Network Management in
Standalone Mode and provides a general description of network
management using Network Management in Standalone Mode. This
chapter includes the following sections:
• Network Management In Standalone Mode Overview
general description of Network Management in Standalone
Mode.
• Network Management in Standalone Mode Terms
Definitions of terms used in this documentation.
• What is Avaya Network Management Server
of the Avaya Network Management Server and its functions.
• What is Avaya Network Management Console
description of Avaya Network Management Console and its
functions.
• What is a Network Map
their functions.
• What is Discovery
Discovery feature.
• What is Event Handling
view them using the Event Manager.
• What is Remote Access
capability of Network Management in Standalone Mode.
- A description of Network Management’s
- A description of Network Maps and
- A description of events and how to
- An description of the remote access
- A description
-
- A
- A
More detailed information about each of the topics can be found in
subsequent chapters.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 13
Page 14
Chapter 1
Network Management In Standalone Mode Overview
Network Management in Standalone Mode includes Avaya Network
Management Server, and Avaya Network Management Console, an
application that allows you to view the devices in your network. Avaya
Network Management Console also provides a platform from which you
can launch applications to manage network devices and monitor the
traffic on your network. In addition, Network Management in
Standalone Mode provides a Discovery service which can search your
network for devices and an Event Log which reports network events.
Network Management in Standalone Mode uses a client/server
architecture allowing multiple users to access the Avaya Network
Management Server simultaneously. Web based technology provides a
method for accessing and managing your network from any computer
with Internet access.
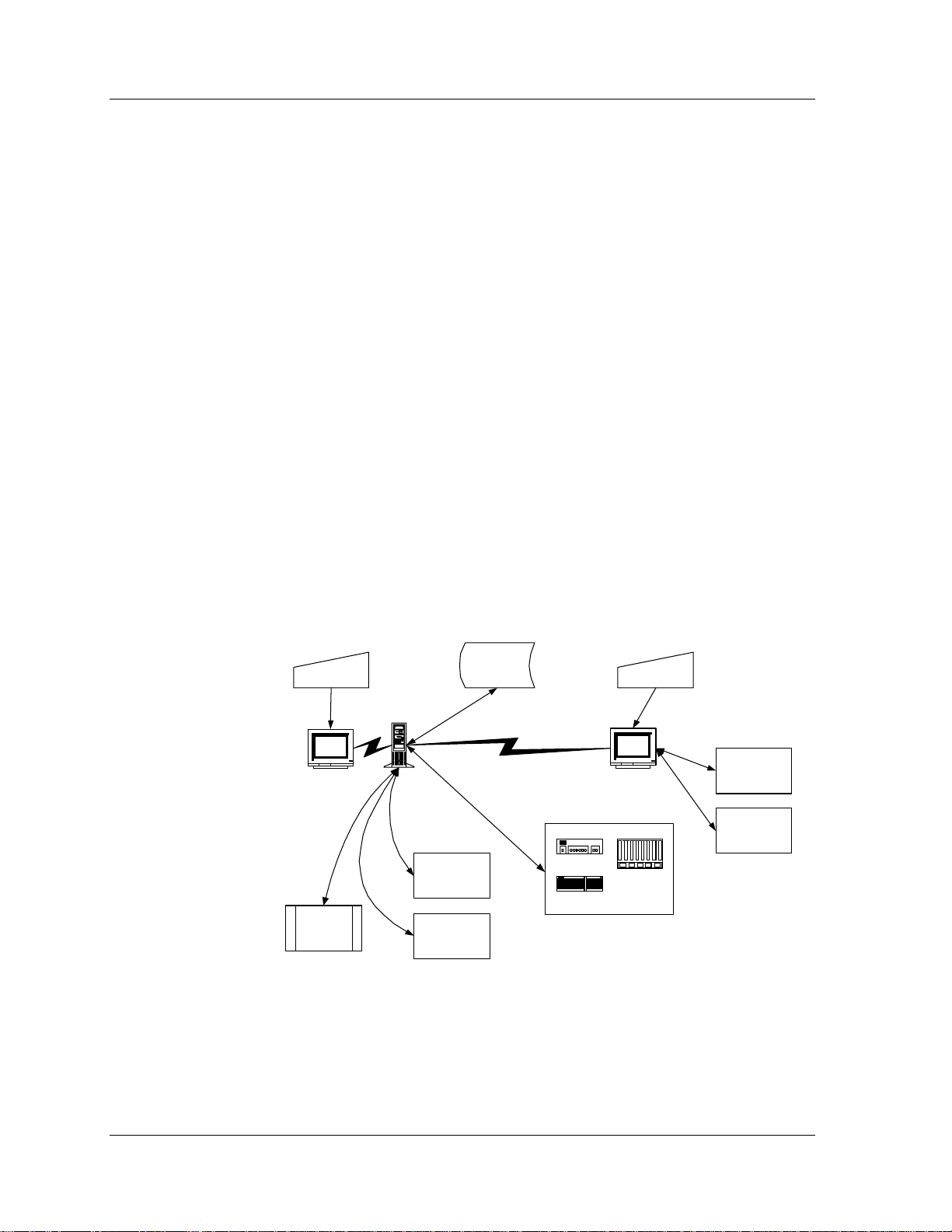
The figure below illustrates the flow of information between the
different components that comprise Network Management in
Standalone Mode and Network Management applications.
Figure 1-1. Network Management Overview
Applications
Network File
n
I
e
r
t
n
e
t
P330
G700
Avaya Network
Managment
Console
Remote Access
P882
Network
Devices
Device Managers
Network-wide
Applications
User Input User Input
Avaya Network
Management
Server
Avaya Network
Managment
Console
Local Access
Device Managers
Daemons
Network-wide
14 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 15

Network Management in Standa lone Mode
When Avaya Network Management Server is launched, it runs a
number of daemons which poll the network devices listed in the default
Network Map to determine their status and updates their colors in the
Avaya Network Management Console View Area. Users can manage
devices or launch network-wide applications via Avaya Network
Management Console. Avaya Network Management Console
communicates these requests to Avaya Network Management Server
which launches the correct applications. When run remotely, these
applications are uploaded from Avaya Network Management Server to
the remote station.
Network Management in Standalone Mode Terms
The following table provides a list of terms used in Network
Management in Standalone Mode documentation with their
descriptions.
Table 1-1. Network Management Terms
Term Description
Best Name The best name for a device known to Network
Management. For information on defining the
method used by Network Management to
arrive at the Best Name, refer to “Configuring
Discovery’s Naming Method” on page 86.
Branch An intermediate level in the Network Tree.
Branches include device types, subnets, and
user defined branches in custom views of the
network.
Network File A file where information about the devices in
the Network Map is stored.
Network
Map
Node A network device. Nodes include (but are not
Object A branch or node in the network.
The set of devices that are known to
Avaya Network Management Server.
limited to) switches, hubs, routers, network
printers, and computers.
Poll A request by an application for information
from a device.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 15
Page 16
Chapter 1
What is Avay a Network Management Server
Avaya Network Management Server communicates with the devices in
the network via Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) V1 or
V3. It receives user input via Avaya Network Management Console and
updates Avaya Network Management Console with information from
the network devices. Avaya Network Management Server runs in the
background as a Windows 2000/XP service. The server provides a central
address for event reporting. It passes traps to Avaya Network
Management Console for display in the Event Log Browser. For more
information about event handling and traps, refer to “What is Event
Handling” on page 18.
In addition, Avaya Network Management Server allows you to operate
Avaya Network Management Console from a remote location. This
feature provides a method for managing your network from any
computer connected to the Internet. By pointing your web browser to
Avaya Network Management Server’s IP address, you can access
Avaya Network Management Console and manage your network. For
more information on running Avaya Network Management Console
from a remote location, refer to “What is Remote Access” on page 21
.
What is Avay a Ne two r k Management Console
Avaya Network Management Console is the user interface to Avaya
Network Management Server. It receives information from Avaya
Network Management Server and sends the server information input by
the user. Avaya Network Management Console displays the devices in
the current Network Map using a hierarchical tree. The tree can be
organized by subnet or device type, or logically by systems. Additionally,
you can create custom views of the network.
16 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 17
Network Management in Standa lone Mode
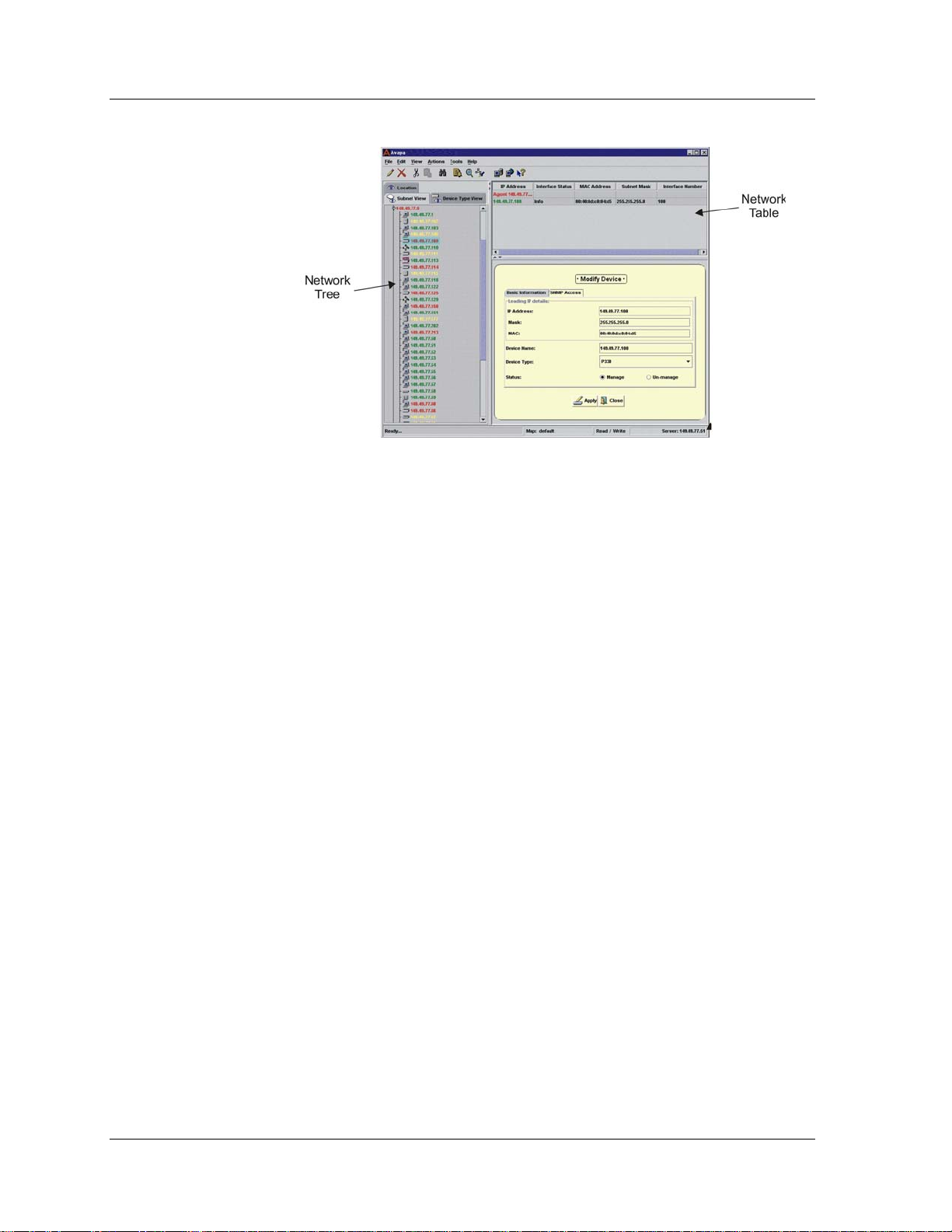
Figure 1-2. Avaya Network Management Console
When a device in the Network Tree is selected, information about the
selected device appears in the Network Table. You can then modify the
device’s parameters. Avaya Network Management Console also provides
the ability to launch applications that communicate directly with the
device. These applications allow you to manage the device via its
Command Line Interface (CLI) or Device Manager, and monitor the
traffic on the device. For example, if you select an Avaya P330 Device in
the Network Table, you can launch Telnet to configure the device via its
CLI or launch Avaya P330 Device Manager to configure and monitor the
device via its management application and monitor the device using
Avaya P330 SMON Manager.
In addition, Avaya Network Management Console allows you to launch
network-wide applications such as, Avaya Software Update Manager for
updating embedded software, Avaya VLAN Manager for managing
VLANs across the entire network, and Avaya SMON Manager for
monitoring network traffic.
What is a Network Map
A Network Map consists of all of the devices known to Avaya Network
Management Server. The list of devices is stored in the Network File,
along with basic information about each device. When Avaya Network
Management Console opens, Avaya Network Management Server
extracts information about the devices in the Network Map from the
Network File. These devices are displayed in the Network Tree.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 17
Page 18
Chapter 1
Devices can be added to the current Network Map using Discovery or the
Add Device dialog box. Devices in the Network Map can also be
modified. All changes to the Network Map are stored in the Network
File.
You can maintain multiple Network Maps by saving individual maps
with unique names. The Network Map whose devices are visible in
Avaya Network Management Console is the current Network Map.
You can also create a text file that contains the necessary information
about each device you want to add to the current Network Map and
import the devices listed in the file into the Network Map. For more
information on importing devices into the Network Map, refer to
“Importing Devices into the Network Map” on page 74
Avaya Network Management Server can also export the information in
the current Network Map to a CSV file. For more information on
exporting the device information from the current Network Map, refer
to “Exporting the Network Map” on page 75
.
.
What is Discovery
Network Management in Standalone Mode can ‘discover’ the subnets
and nodes on your network. The Discovery tool uses SNMP MIB-II on
network nodes to search your network. In addition, you can instruct
Discovery to use ICMP Echo (ping) to search the network. You can
instruct Discovery to search your entire network for subnets and nodes,
limit the search to selected subnets, or update information about the
objects in the Network View.
The Discovery window shows a list of the subnets discovered with the
number of nodes found in each subnet. You can apply the results of a
Discovery to the current Network Map.
What is Event Handling
Events are unexpected or extraordinary occurrences in your network.
Examples of events include the loss of a port’s connection, the insertion
or removal of a module from a device, and the failure of a fan or power
supply. Network Management provides a method of reporting network
events.
* Note: For the purposes of this document, the terms ‘event’ and
‘trap’ are used interchangeably.
18 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 19

Network Management in Standa lone Mode
Network Management communicates with device agents using SNMP.
Device agents can send traps to Avaya Network Management Server
reporting on the status of their ports, modules, etc. The server then
passes traps to the relevant managers of the device involved and updates
the Event Manager.
To receive traps using Network Management in Standalone Mode,
network devices must be configured to send traps to the Avaya Network
Management Server. For information on configuring Avaya LAN and
backbone devices to send traps to Avaya Network Management Server,
refer to the User Guide or Device Manager User Guide for the devices in
your network. The Event Manager maintains a log of all traps received
from the devices in the network. These traps can be viewed in the Event
Log Browser.
Figure 1-3. Event Handling Flow
Traps are categorized by their severity. Some traps report events that are
not problems. An example of this type of trap is the insertion of a
module into a device. These traps have a severity level of Info. Other
traps require more attention, such as the loss of a regular port’s
connection. Traps of this type have a severity level of Warning. Finally,
there are traps, such as the failure of a backbone link, which require
immediate attention. These traps have a severity level of Minor, Major,
or Critical.
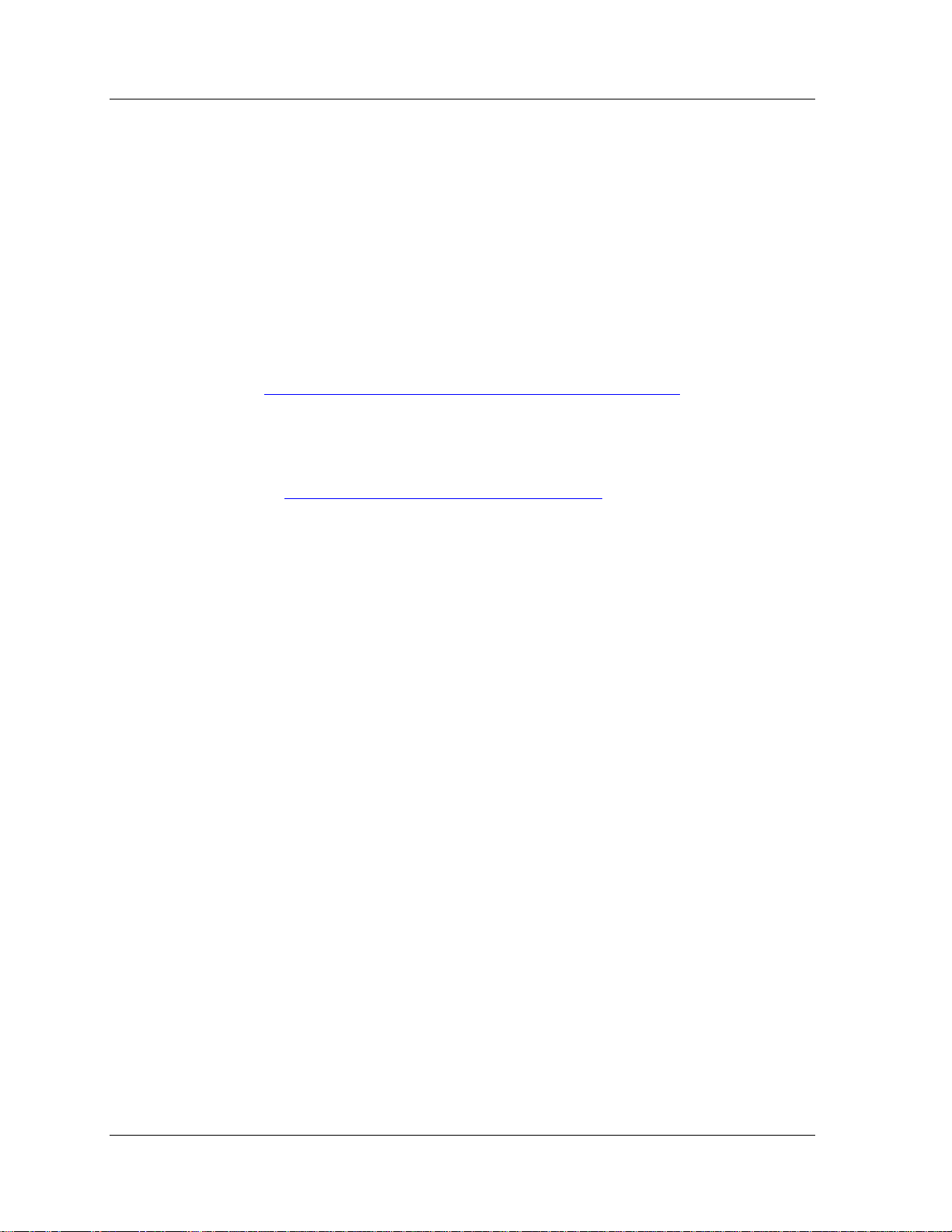
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 19
Page 20
Chapter 1
Figure 1-4. Event Log Browser
The Event Manager displays all of the traps sent by Avaya Network
Management Server. In the Event Manager you can:
• Sort the Event Log Browser by any of its fields.
• Filter the traps displayed and change the severity of selected
traps.
• Acknowledge traps to help you remember which traps you have
already seen.
• Define the format of the description field.
• Delete traps, signifying that the problem causing the trap was
resolved.
In addition, the Event Manager allows you to define event actions.
Event actions can include notification via a pop-up, audible, or e-mail
message or the running of a script. Actions can be assigned to any
network events. You can also limit the action to events from specified
sources. This feature enables you to receive immediate notification of
important network events.
The Event Manager can also act as a trap surrogate, forwarding all, or
selected, traps to other devices.
20 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 21

What is Remote Access
Avaya Network Management Console can be accessed remotely using a
web browser. This allows you to manage your network from a computer
where Network Management is not installed. When you point your
browser to the Avaya Network Management Server’s IP address, a Java
applet prepares your browser to communicate with Avaya Network
Management Server. A welcome screen appears, followed by a password
screen. Once you enter a valid user name and password, Avaya Network
Management Console opens in a special browser window.
Network Management in Standa lone Mode
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 21
Page 22

Chapter 1
22 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 23

2
Avaya Network Management Server
This chapter provides a detailed description of Avaya Network
Management Server. It includes the following sections:
• Introduction to Avaya Network Management Server
introduction to Avaya Network Management Server.
• Starting Avaya Network Management Server
instructions on how to start Avaya Network Management Server.
• Stopping Avaya Network Management Server
instructions on how to shut down Avaya Network Management
Server.
- Detailed
- Detailed
- An
Introduction to Avaya Network Management Server
Avaya Network Management Server communicates with network
devices. It passes information to Avaya Network Management Console
and handles requests to launch applications. In addition, Avaya Network
Management Server enables remote sessions of Avaya Network
Management Console. Ensure that Avaya Network Management Server
is running on the host computer before starting Avaya Network
Management Console locally, and that it is running on the remote server
before starting a remote session of Avaya Network Management
Console.
Avaya Network Management Server can import devices from CSV
(Comma Separated Value) files into the Network Map. Avaya Network
Management Server can also export the Network Map to a CSV file, for
use with other applications, such as a Microsoft Excel.
Starting Avaya Network Management Server
Avaya Network Management Server is a Windows Service. When
Windows starts on the server station, Avaya Network Management
Server starts automatically. Using Windows’ Service Manager, you can
configure Avaya Network Management Server so that it does not start
automatically.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 23
Page 24

Chapter 2
If Avaya Network Management Server is shut down, you will need to
start it manually. To manually start or stop Avaya Network Management
Server, you must be logged in to Windows with Administrator privileges.
When you log off the computer, Avaya Network Management Server
continues running.
To start Avaya Network Management Server:
Select
Network Management Server
Start > Programs > Avaya > Network Manager > Start Avaya
.
Or
From a command prompt type
cvserver start.
Or
1. Open Windows’ Control Panel.
2. Double-click
3. Select
4. Click
Avaya Network Management Server from the list of services.
Start.
Services.
If Avaya Network Management Server starts successfully, a window
opens with the message “Avaya Network Management Server
successfully started.”
If Avaya Network Management Server is already running on the system,
a window opens with the message “The Avaya Network
Management Server is already running.”
If Avaya Network Management Server cannot start, a window opens
with the message “The Avaya Network Management Server
failed to start. Reason: X”, where X is the reason Avaya
Network Management Server failed to start.
To view the status of Avaya Network Management Server:
Select
Management Server
Start > Programs > Avaya > Network Manager > Avaya Network
Status.
Or
From a command prompt type
cvserver status. A window
opens with the current status of Avaya Network Management
Server (running or not running).
24 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 25

Avaya Network Management Server
Stopping Avaya Network Ma nagement Server
To stop Avaya Network Management Server:
1. Select
Start > Programs > Avaya > Network Manager > Stop Avaya
Network Management Server
Or
From a command prompt type
dialog box opens.
2. Click
Yes.
Or
1. Open Windows’ Control Panel.
2. Double-click
3. Select
4. Click
Avaya Network Management Server from the list of services.
Stop. Avaya Network Management Server shuts down. If
Services.
Avaya Network Management Console is open, a window opens
with the message that Avaya Network Management Console is
closing.
.
cvserver stop. A confirmation
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 25
Page 26

Chapter 2
26 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 27

3
Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
This chapter provides an introduction to Avaya Network Management
Console. It includes the following sections:
• Starting Avaya Network Management Console
Instructions on how to start Avaya Network Management
Console.
• Avaya Network Management Console User Interface
introduction to Avaya Network Management Console’s user
interface, including instructions on how to use the toolbar
buttons.
• Requesting Write Permission
and release Read/Write permissions for a specific Avaya Network
Management Console session.
• Avaya Network Management Console Options
on how to set Avaya Network Management Console’s options.
• Using Avaya Network Management Console Tables
explanation of symbols used in Avaya Network Management
Console tables.
• Using Avaya Network Management Console Help
explanation of the options for accessing on-line help in Avaya
Network Management Console.
• Closing Avaya Network Management Console
on how to close Avaya Network Management Console.
- Instructions on how to request
-
- Instructions
- An
- An
- Instructions
- An
Starting Avaya Netw ork Management Console
Avaya Network Management Console can be run locally or via a remote
web server. For information on running Avaya Network Management
Console via a remote web server, refer to “Starting a Remote Session” on
page 136.
The Avaya Network Management Console can configure Network
Management’s Login Mode for use with SNMPv3. This enables user
authentication to limit access to network management. The user
authentication can also be used as a mechanism for supplying user
credentials for the SNMPv3 messaging engine.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 27
Page 28

Chapter 3
To start a local session of Avaya Network Management Console from
Windows:
Double-click the Avaya Network Management Console icon on
the Windows desktop.
Or
Select
Management Console
Or
Type cvconsole at a command prompt.
Or
Press CTRL + ALT + c. One of the following occurs:
— If Login Mode is enabled, the Enter User Name and Passwords
— If Login Mode is disabled, Avaya Network Management
For more information about Login Mode, refer to the Avaya
Network Manager User Administration User’s Guide.
Start > Programs > Avaya > Network Manager > Avaya Network
.
dialog box opens. Enter your user name and passwords and
OK. Avaya Network Management Console opens.
click
Console opens.
Avaya Network Management Console User Interface
The user interface consists of the following elements:
• Menu Bar - Menus for accessing Avaya Network Management
Console management functions. For more information on
menus, refer to Appendix A,
• Toolbar
Management Console management functions.
• Network Tree
representation of the Network Map.
• View Tabs
network.
• Network Table
nodes in the Network Tree are displayed.
• Dialog Area
28 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
- Toolbar buttons for accessing Avaya Network
- A resizeable window containing a hierarchical
- Tabs for switching between the various views of the
- A table where details about the branches and
- A resizeable window where all dialog boxes open.
Network Management Menus.
Page 29

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
• Status Bar - Displays information about the current
Avaya Network Management Console session.
The figure below shows the user interface, with its various parts labeled.
Figure 3-1. Avaya Network Management Console Interface
To resize the three main areas of the user interface, the Network Tree,
the Network Table, and the Dialog Area, use the splitter bars and their
arrows.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 29
Page 30

Chapter 3
Toolbar
The Toolbar provides shortcuts to the main Avaya Network Management
Console functions.
The table below describes the buttons on the Toolbar and gives the
equivalent menu options.
Table 3-1. Avaya Network Management Console Toolbar
Button Description Menu Item
Opens the Modify dialog box
for the selected object.
Deletes the selected object
from the Network Map.
Cuts the selected object from a
custom view to the clipboard.
Pastes the object from the
clipboard into a custom view.
Opens the Find dialog box.
Opens the Event Manager.
Launches the device manager
for the selected device.
Opens the Discovery window.
Launches a Telnet session to
the selected device.
Edit > Modify
Edit > Delete
Edit > Cut
Edit > Paste
Edit > Find
Actions > Event
Manager
Tools >
Device Manager
Actions> IP
Discovery
Tools > Telnet
Launches a web session to the
Tools > Web
selected device.
Opens context-sensitive help.
Help > Help On
When you place the cursor on a toolbar button for one second, a label
appears with the name of the button.
30 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 31
Network Tree
Network Table
Dialog Area
Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
The Network Tree shows either a hierarchical representation of the
subnets in the Network Map or a representation of the Network Map
grouped by device type or logically organized by systems. You can also
create customized views of the Network Map. For more information
about the Network Tree, refer to Chapter 4,
Management Console Network Tree.
The Network Table provides details of the subnets, device types, or
devices under the selected branch of the tree. For more information
about the Network Table, refer to Chapter 5,
Management Console Network Table.
Avaya Network
Avaya Network
St atus Bar
The area under the Network Table is where all dialog boxes open. This
area can be resized by dragging the horizontal splitter bar with the
mouse. When a dialog box opens, it replaces the current dialog box open
in the Dialog Area.
The Status Bar provides information about the Avaya Network
Management Console session. It includes the following information:
• Name of the open map.
• Read/Write mode of Avaya Network Management Console.
• IP address/Name of the Avaya Network Management Server.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 31
Page 32

Chapter 3
Using Tooltips
Avaya Network Management Console includes a tooltip feature which
allows you to display additional information about devices in the
Network Map. To display additional information about a device, place
the cursor on the device’s icon in the Network Tree or Network Table.
After about one second, the tooltip appears.
Figure 3-2. Avaya Network Management Console Tooltip
The tooltip provides the following information about the device:
• Name - The Best Name of the device.
• IP - The IP address of the device.
• Mask - The device’s IP subnet mask.
• MAC - The device’s MAC address.
• Typ e - The device type.
• Interface Number - The interface number of the displayed IP
address of this device.
• Management Status - The device’s management status. This
can be either Managed or Unmanaged.
To toggle the tooltips feature, select
Requesting Write Permission
There are two levels of permission for users logging into Avaya Network
Management Console:
View > ToolTip.
• Read-only - You are able to view network and devices, but
unable to make changes.
• Read-write - You are able to both view and make changes to the
network and devices.
32 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 33

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
The following are the assigned permissions at login:
• No read/write console exists - read/write permission is
automatically assigned to your console.
• Read/Write console currently exists - your console is assigned
read only permission.
* Note: Only one console may have read/write permission at any
given time.
If your console is opened with read only permission, you can request
write permission. The console that currently has read/write permission
receives a request from Network Management Console to release the
write permission. There is an allotted amount of time in which the
console with read/write permission must respond to the request. If the
console with read/write permission agrees to the request, or does not
refuse the request in the allotted amount of time, the read/write
permission is transferred to the requesting console automatically.
For instructions on setting the Timeout value, see “Setting Read/Write
Defaults” on page 42.
All functionality is enabled for a console with read/write permission.
This is true whether you are running Avaya Network Management
Console locally or remotely.
All functions that update the server (i.e., adding and removing a device
from the map, or running a discovery process) are disabled on a console
with read only permission and all update commands are inactive. If an
update dialog box is open while the console is losing write permission,
the Apply button of the dialog box becomes inactive until write
permission is returned. This also applies to the trap manager.
A console with an open discovery window automatically retains its write
permission. Any requests for write permission from a console with an
open discovery window are automatically denied.
To request read/write permission:
1. Select
Actions > Get Write Permission. The Write Permission Request
dialog box opens.
2. Click
OK.
3. If the console that currently has write permission agrees to your
request, the Write Permission Received dialog box opens. Click
OK to receive write permission.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 33
Page 34

Chapter 3
4. If the console that currently has write permission refuses your
request, the Write Permission Refused dialog box opens. Click
to proceed with read only permission.
If your console currently has read/write permission and a request is
made for write permission by another console, the Remote Request
dialog box opens.
To release read/write permission in response to another console’s
request:
OK
1. Click
2. To refuse write permission to the requesting console, click
* Note: If you don’t click
To release read/write permission without a direct request from another
console, select
OK to release write permission to the requesting console.
OK or Refuse before the Timeout value
expires, write permission is automatically released to the
requesting console.
Actions > Release Write Permission.
Avaya Network Management Console Options
You can use Avaya Network Management Console’s Options dialog box
to set SNMP Access parameters and connectivity polling parameters and
to select a default Network Map.
To open the Avaya Network Management Console Options dialog box,
File > Options. The Avaya Network Management Console Options
select
dialog box opens.
Refuse.
The following console options are discussed in this section:
• SNMP Access Parameters
• Setting Connectivity Polling Parameters
• Selecting a Default Map
• Setting Read/Write Defaults
34 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 35

SNMP Access Parameters
Using the SNMP Access parameters page of the Avaya Network
Management Console Options dialog box, you can set basic SNMP
parameters for specific devices, ranges of devices, and all unspecified
devices. Avaya Network Management Server recognizes the following
SNMP protocols: V1 and V3. SNMP access parameters for SNMP V1
include read and write community properties. For SNMP V3, the SNMP
access parameters include a user name defined in the User
Administration. For both versions of SNMP, access parameters include
timeout and retry values. Each of the three tabs in the SNMP Access
parameters page enables you to set SNMP access parameters for different
groups of devices.
Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
Default SNMP Access Parameters
• Default
in the other tabs.
• IP Wildcards
whose IP addresses fall in a specified range and not in the Specific
IP’s tab.
• Specific IP’s
devices.
When polling a device, Avaya Network Management Server uses the
device’s SNMP access parameters. The server first checks the Specific IP’s
list. If the device is listed in the Specific IP’s list, the SNMP access
parameters for the specific device are used. If not, the server checks the
IP Wildcards list. If the device’s IP address is in any of the ranges listed in
the IP Wildcards list, the SNMP access parameters for the matching range
are used. If the device’s IP address does not match any of the ranges in
the IP Wildcards list, the default SNMP access parameters are used.
The Default page enables you to configure multiple default SNMP
communities.
If no Specific IP definition and IP Wildcards match the IP address to be
polled, Avaya Network Management Server tests the addresses of the
devices against the list of definitions in the Default list. The order of the
list in the table is important, because the SNMP access parameters of the
first rule in the list that matches a device’s SNMP access parameters are
used for that device.
- To configure all devices with IP addresses not included
- To configure SNMP access parameters for devices
- To configure SNMP access parameters for specific
To view the list of default SNMP access parameters, click the
on the SNMP Access page of the Avaya Network Management Console
Options dialog box. The Default page appears.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 35
Default tab
Page 36
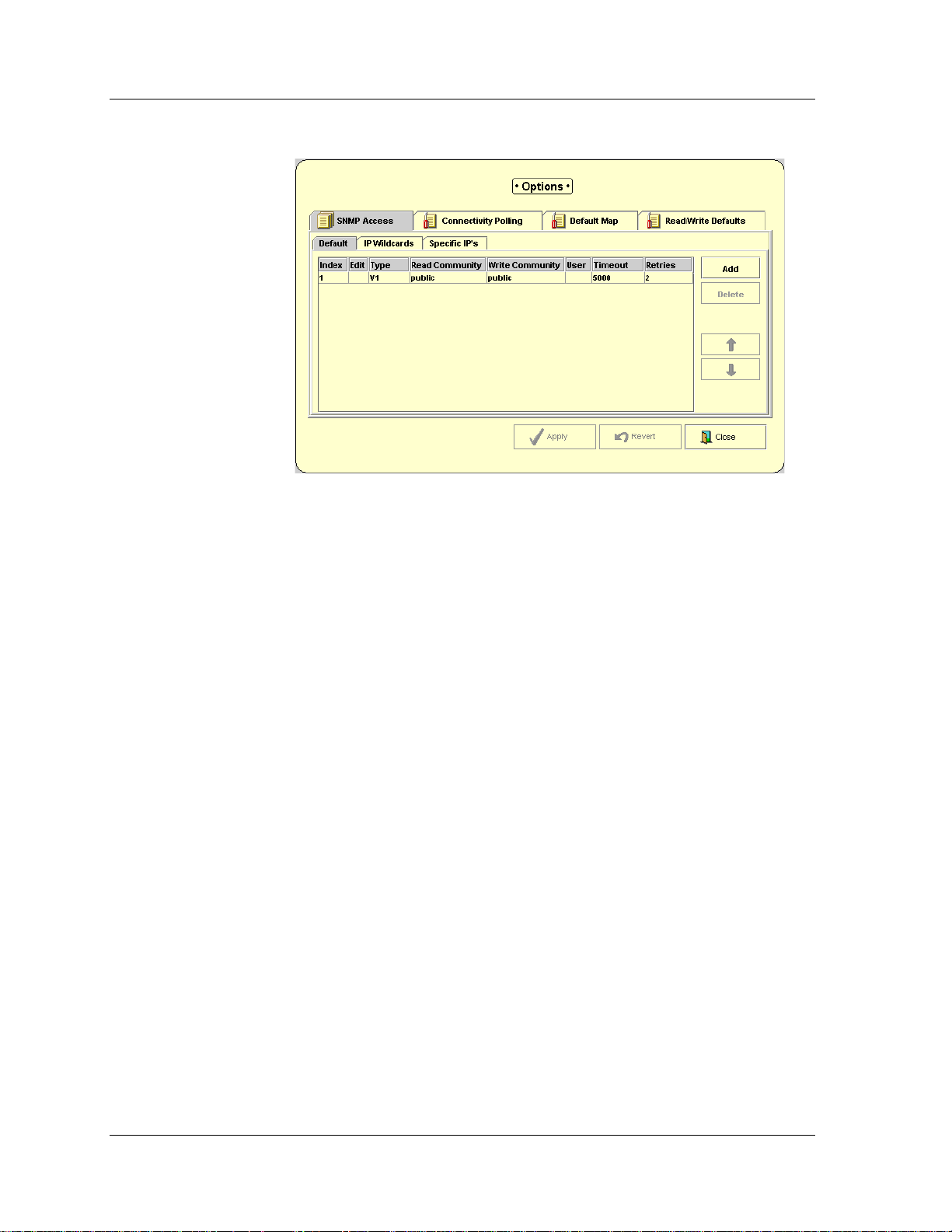
Chapter 3
Figure 3-3. Avaya Network Management Console Options Dialog Box -
Default Page
To add a new set of SNMP default parameters to the list:
1. Click
Add. A new row opens in the Default table.
2. Select V1 or V3 (login mode only) from the
listbox.
3. If you selected V1 in the
Type field, enter read and write
community values in their respective fields.
4. If you selected V3 in the
User pull-down listbox. The user name must have been defined in
Type field, select a user name from the
the User Administration Window. For more information, refer to
the Network Management User Administration User’s Guide.
5. Enter a number in the
Timeout [ms] field for the number of
milliseconds Avaya Network Management Server will wait for a
response when polling a device.
6. Enter a number in the
Retries field for the number of times
Avaya Network Management Server will try to poll a device.
7. Click
Apply. The new default SNMP parameters definition is added
to the Default table.
To change the position of a row in the Default table:
Type pull-down
1. Select a row.
2. Click the arrows to move the row up or down in the table.
3. Click
36 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Apply. The new row position is saved.
Page 37

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
To edit entries in the in the Default table:
1. Click the field you want to edit.
2. Edit the information in the field.
3. Click Apply. The changes are saved in the table.
To remove a range from the Default table:
1. Select a row.
Setting SNMP Access Parameters for IP Ranges
2. Click
3. Click
The IP Wildcard page enables you to configure SNMP access parameters
for ranges of devices. Avaya Network Management Server tests the IP
address of devices to poll against the list of devices in the IP Wildcards
list. If the IP address matches a range, the server uses the range’s SNMP
access parameters when polling the device. The order in the list is
important, because the SNMP access parameters of the first range in the
list that matches a device’s IP address are used for that device.
To view SNMP access parameters for IP ranges, click the
on the SNMP Access page of the Avaya Network Management Console
Options dialog box. The IP Wildcard page appears.
Figure 3-4. Avaya Network Management Console Options Dialog Box -
Delete.
Apply. The range is deleted from the Default table.
IP Wildcard tab
IP Wildcard Page
To add a new IP range to the list:
1. Click
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 37
Add. A new row opens in the IP Wildcards table.
Page 38

Chapter 3
2. Select V1 or V3 (login mode only) from the Type pull-down
listbox.
3. Enter an IP Wildcard in the
4. If you selected V1 in the
IP Wildcard field.
Type field, enter read and write
community values in their respective fields.
5. If you selected V3 in the
User pull-down listbox. The user name must have been defined in
Type field, select a user name from the
the User Administration window. For more information, refer to
the Network Management User Administration User’s Guide.
6. Enter timeout and retry values in their respective fields.
7. Click
Apply. The new range is added to the IP Wildcards table.
To change the position of a row in the IP Wildcards table:
1. Select a row.
2. Click the arrows to move the row up or down in the table.
3. Click
Apply. The new position table is applied.
To edit entries in the in the IP Wildcards table:
1. Click the field you want to edit.
2. Edit the information in the field.
3. Click Apply. The changes are saved in the table.
To remove a range from the IP Wildcards table:
1. Select a row.
2. Click
3. Click
Delete.
Apply. The range is deleted from the IP Wildcards table.
38 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 39

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
Setting Specific IP Parameters
To view SNMP access parameters for specific devices, click the Specific
IP’s
tab on the SNMP Access page of the Avaya Network Management
Console Options dialog box. The Specific IP’s page appears.
Figure 3-5. Avaya Network Management Console Options Dialog Box -
Specific IP’sPage
To add a new device to the list:
1. Click
2. Select V1 or V3 (login mode only) from the
Add. A new row opens in the Specific IP’s table.
Type pull-down
listbox.
3. Enter the device’s IP address in the
4. If you selected V1 in the
Type field, enter read and write
IP field.
community values in their respective fields.
5. If you selected V3 in the
User pull-down listbox. The user name must be defined in the
Type field, select a user name from the
User Administration Window. For more information, refer to the
Network Management User Administration User’s Guide.
6. Enter timeout and retry values in their respective fields.
7. Click
Apply. The device is added to the Specific IP’s table.
To edit entries in the Specific IP’s table:
1. Click the field you want to edit.
2. Edit the information in the field.
3. Click Apply. The changes are saved in the table.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 39
Page 40

Chapter 3
To remove a device from the Specific IP’s table:
1. Select a device.
2. Click
3. Click
Delete.
Apply. The device is deleted from the Specific IP’s table.
Setting Connectivity Polling Parameters
Connectivity polling parameters determine whether Avaya Network
Management Server will use PING to determine the status of devices
that do not support SNMP, the interval between PINGs, and the number
of times that Avaya Network Management Server will unsuccessfully
PING a node before declaring it to be unreachable. To set default
connectivity polling parameters:
1. Click the
Management Console Options dialog box. The Connectivity
Polling page appears.
Figure 3-6. Avaya Network Management Console Options Dialog Box -
Connectivity Polling tab at the top of the Avaya Network
Connectivity Polling Page
2. Select a Connectivity Status. On means that devices will be
PINGed.
3. Enter a number in the
Off means that devices will not be PINGed.
Retries field. This is the number of times
Avaya Network Management Server will unsuccessfully PING a
node before declaring it to be unreachable.
40 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 41

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
4. Enter a number in the Timeout field. This is the number of
milliseconds Avaya Network Management Server will wait for a
response when PINGing a node before declaring it to be
unreachable.
5. Enter a number in the
seconds. This is the amount of time between PINGs.
6. To return the values to the default settings, click
7. Click
polling parameters.
Selecting a Default Map
The Default Map page of the Avaya Network Management Console
Options dialog box enables you to select the Network Map that is used
when Avaya Network Management Server starts. To select a default
Network Map:
1. Click the
Management Console Options dialog box. The Default Map page
appears.
Figure 3-7. Avaya Network Management Console Options Dialog Box -
Interval field and select either minutes or
Default.
Apply. The network is configured with the new connectivity
Default Map tab at the top of the Avaya Network
Default Map Page
2. Select a Network Map from the Default map name pull-down
listbox.
3. Click
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 41
Apply. The selected map is now the default Network Map.
Page 42

Chapter 3
Setting Read/Write Defaults
The Read/Write Defaults page of the Avaya Network Management
Console Options dialog box enables you to set the default read/write
permissions.
To set read/write defaults:
1. Click the
Read/Write Defaults tab at the top of the Avaya Network
Management Console Options dialog box. The Read/Write
Defaults page appears.
Figure 3-8. Avaya Network Management Console Options Dialog Box -
Read/Write Defaults Page
2. Check the Allow Read/Write request checkbox to enable a user to
request read/write permission. If this checkbox is not checked,
then the first console opened receives read/write permission. Any
other console window that requests read/write permission is
refused.
3. Enter the interval of time in seconds in the
Timeout (sec) field that
the holder of the read/write permission is allotted to respond to
the read/write request.
4. Click
42 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Apply.
Page 43

Avaya Network Management Console Introduction
Using Avaya Network Management Console Tables
Avaya Network Management Console informs you of the status of each
row in a table. The following table shows symbols that appear at the start
of a row, with their corresponding explanations.
Table 3-2. Row Status
Symbol Explanation
The row is a new entry.
The row is to be deleted.
The row has been modified.
Using Avaya Network Management Console Help
This section explains how to use the on-line help in Avaya Network
Management Console. The on-line help can be opened to the contents
page or directly to a topic of interest. For more information, refer to:
• Opening the Help to the Contents Page
• Opening the Help to a Topic of Interest
Opening the Help to the Contents Page
To open the help to the contents page, select Help > Contents. The on-line
help opens to the contents page.
Opening the Help to a Topic of Interest
To open the help directly to a topic of interest:
1. Click .
Or
Select
with a question mark.
2. Click on a point of interest in Avaya Network Management
Console. The help opens to a topic explaining the clicked feature.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 43
Help > Help On. The cursor changes to the shape of an arrow
Page 44

Chapter 3
Closing Avaya Network Management Console
To close Avaya Network Management Console, select File > Exit.
Avaya Network Management Console closes.
44 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 45

4
Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree
This chapter provides a detailed description of the Network Tree. It
includes the following sections:
• Introduction to the Network Tree
Network Tree.
• Using the Network Tree
Network Tree and its hierarchy, and instructions on how to
customize the Network Tree.
• Printing the Network Tree
Network Tree.
• Searching the Tree
search for elements in the Network Tree.
- A detailed description of the
- Instructions on using the Find feature to
Introduction to the Network Tree
When viewing the network, you may want to view:
• The structure of the network by subnet.
• The information categorized by the different types of devices in
the network.
- An introduction to the
- Instructions on how to print the
• The system view, which includes the voice elements in a data
network, and the relationships between VoIP end points,
gatekeepers, and call managers.
Avaya Network Management Console’s user interface provides an
integrated view of the structure of the network, along with details about
specific elements.
In addition, you may want to categorize the devices in your network by
other criteria, such as workgroups or location. Avaya Network
Management Console allows you to create user defined views of your
network and assign devices to custom categories. You can create up to
five custom views of your network.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 45
Page 46

Chapter 4
The left side of the user interface is the Network Tree. This provides a
hierarchical view of the network. The right side of the user interface
contains the Network Table. Together, these views provide details about
specific elements in the network.
When an element in the tree is selected, the elements immediately
below the selected element appear in the Network Table. Elements in the
Network Table are accompanied by fields providing details about the
elements.
Using the Network Tree
There are two default views of the Network Tree - the Subnet View and
the Device Type View. A third view, the System View, appears for
networks containing VoIP devices. In addition, you can define up to five
custom views of the network. The Subnet View shows a hierarchical
representation of the subnets in the network. The Device Type View
shows a view of the network grouped by device type. The System View
shows a hierarchical representation of the voice devices in the network.
To switch to a different view, click the appropriate tab above the tree.
To expand the view of a contracted element in the tree or to contract the
view of an expanded element in the tree:
Double-click the element.
Or
Click the handle next to the element you want to expand or
contract.
The following sections describe the following views of the Network Tree:
• The Subnet View
of the Subnet View of the network.
• The Device Type View
elements of the Device Type View of the network.
• The System View
of the System View of the network.
• Custom Views
your network.
- A description of the hierarchy and elements
- A description of the hierarchy and
- A description of the hierarchy and elements
- Instructions on how to create custom views of
46 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 47

The Subnet View
The Subnet View tree shows a hierarchical view of the subnets in the
network. The Subnet View of the network contains the following levels:
1. My Network - An icon representing the entire network. When
the icon representing the network is selected, all subnets appear
in the Network Table.
2. Subnets - Icons representing the subnets in the network. When
an icon representing a subnet is selected, all devices with IP
addresses in the selected subnet appear in the Network Table.
3. Devices - Each icon representing a device is labeled with the
logical name or IP address of the device. When an icon
representing a device is selected, the device’s interfaces appear in
the Network Table.
The Device Type View
Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree
The Device Type View tree shows the network grouped by device type.
The Device Type View of the network contains three levels.
1. My Network - An icon representing the network. When the icon
representing the network is selected, all supported device types in
the network appear in the Network Table.
2. Device Types - Icons representing all supported device types that
appear in the network. When an icon representing a device type
is selected, all devices of the selected type appear in the Network
Table.
3. Devices - Icons representing the devices in the network. Each
icon is labeled with the name of the device. When an icon
representing a device is selected, the device’s interfaces appear in
the Network Table.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 47
Page 48

Chapter 4
The System View
The System View tree shows a hierarchical view of the voice devices in
the network. The tree is organized with the voice device controllers on
the higher levels and the controlled voice devices on lower levels.
Figure 4-1. System View
The root of the System View tree is My Network. This icon represents
all voice devices in the network. The root splits into three branches - CM
Servers (Communication Manager Media Servers), CC Servers
(Converged Communications Servers), and Other.
Under the CM Servers branch, the tree splits into locations. For each
location, Communication Manager Media Servers and voice adjuncts
(e.g., Intuity Audix) appear.
For S8700 Communication Manager Media Servers, the tree displays
CLANs and VAL boards. Under the CLANs, IP phones with their
extension numbers and Media Gateways (MGs) are displayed. Entries
for the active and standby Communication Manager Media Servers are
also displayed.
For S8300 Communication Manager Media Servers, the tree displays IP
phones with their extension numbers and MGs.
48 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 49

Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree
The CC Servers branch splits based on Converged Communications
Servers. Each discovered CC Server displays its own branch, on which a
46xx branch appears if 46xx series IP phones are discovered. The 46xx
branch shows all discovered 46xx series IP phones associated with the
CC Server.
The Other branch splits into three. The S8100 branch displays S8100
Devices in the network. The Unaffiliated branch displays IP phones
with their extension numbers and MGs, whose affiliation with a
Communication Manager Media Server cannot be determined. The
Remote Controller branch displays IP phones with their extension
numbers and MGs, whose Communication Manager Media Servers were
not discovered in the network.
Custom Views
To refresh the System View tree, select
System View Discovery runs, and the System View tree is updated This
function is not available for stations running Network Management
Console remotely.
* Note: If the System View tab does not appear, run Discovery or
System View Discovery. The tab appears with the discovered
devices in the tree.
Avaya Network Management Console allows you to create custom views
of your network. This enables you to design a view of your network
based on criteria that are important to you. For example, you can design
a custom view based on the location of devices or based on the functions
that devices perform (i.e., backbone switches, servers, important users,
etc.). This can help you focus on a particular set of devices. The following
topics are discussed in this section:
• Creating Custom Views
• Modifying Custom Views
Actions > System View Discovery. The
• Deleting Custom Views
• Adding Branches in Custom Views
• Modifying Branches in Custom Views
• Deleting Branches in Custom Views
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 49
Page 50

Chapter 4
Creating Custom Views
To create a custom view:
1. Select
2. Enter a name for the view in the View Name field.
* Note: View names cannot contain periods.
3. Enter a description of the view in the
4. Click
File > View > New. The New View dialog box opens.
Figure 4-2. New View Dialog Box
Description field.
Apply. The view is added to Avaya Network Management
Console with the top level
are added to a branch labeled
My Network. All devices in the network
Unassigned.
Modifying Custom Views
To modify a custom view:
1. Click the View Tab associated with the custom view you want to
modify.
2. Select
3. Change the name for the view in the View Name field.
* Note: View names cannot contain periods.
4. Change the description of the view in the Description field.
Edit > Modify View. The Customize View dialog box opens.
Figure 4-3. Customize View Dialog Box
50 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 51

Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree
5. Click Apply. The view is modified.
Deleting Custom Views
Adding Branches in Custom Views
To delete a custom view of the network:
1. Click the View Tab associated with the custom view you want to
modify.
2. Select
3. Click
You can add branches to a custom view of the network and populate the
branches with devices or nested branches.
To add branches to a custom view of the network:
1. Select the icon in the Network Tree to which you want to add a
2. Select
Edit > Delete View. A confirmation dialog box opens.
Yes. The custom view is deleted.
branch.
File > New > Branch. The Add Branch dialog box opens.
Figure 4-4. Add Branch Dialog Box
3. Enter a name for the branch in the Branch name field.
* Note: Branch names cannot contain periods.
4. Enter a description of the branch in the
5. Assign devices to the branch using the following procedure:
— To add devices to the
a. Select the devices you want to add to the branch in the
Unassigned list.
b. Click . The devices appear in the
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 51
Members list:
Branch Description field.
Members list.
Page 52

Chapter 4
— To remove devices from the Members list:
a. Select the devices you want to remove from the branch in the
Members list.
Modifying Branches in Custom Views
b. Click . The devices are removed from the
6. Click
You can add and remove devices from branches in a custom view of the
network. To modify a branch of a custom view of the network:
1. Select the branch you want to modify in the Network Tree.
* Note: The
2. Select
Apply. The branch and its devices are added to the selected
part of the tree.
Unassigned branch cannot be modified.
Edit > Modify. The Modify Branch dialog box opens.
Figure 4-5. Modify Branch Dialog Box
Members list.
3. Change the name of the branch using the Branch Name field.
* Note: Branch names cannot contain periods.
Branch Description
Deleting
Branches in
4. Change the comment attached to the view in the
field.
5. Assign devices to the branch. For instructions on assigning devices
to the branch, refer to “Adding Branches in Custom Views” on
page 51.
6. Click
You can delete branches from a custom view of the network. To delete a
branch of a custom view of the network:
Apply. The branch is modified.
Custom Views
1. Select the branch you want to delete in the Network Tree.
52 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 53

Avaya Network Management Console Network Tree
* Note: The Unassigned branch cannot be deleted.
2. Select
3. Click
Edit > Delete. A confirmation dialog box opens.
Yes. The branch is deleted, and all its devices appear in the
Unassigned list.
Printing the Network Tree
To print the current view of the Network Map, select File > Print. The
current view of the Network Map is printed.
To view a preview of the printed Network Map, select
The preview of the Network Tree opens.
Figure 4-6. Network Tree Print Preview
File > Print Preview .
To print the Network Map, click Print.
To close the Preview window without printing the map, click
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 53
Close.
Page 54

Chapter 4
Searching the Tree
Avaya Network Management Console enables you to search the
Network Map for specific elements. To search the Network Map:
1. Click .
Or
Select
2. Select one of the Find Options option buttons.
3. Enter the device’s name (or part of it), IP address, or MAC address
in the
4. Click
the tree.
Edit > Find. The Find dialog box opens.
Figure 4-7. Find Dialog Box
Find What field.
Find. The element you searched for appears highlighted in
To find the next element that matches the search criteria, click
The element you searched for appears highlighted in the tree.
To close the Find dialog box, click
54 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Cancel.
Find Next.
Page 55

5
Avaya Network Management Console Network Table
This chapter provides a detailed description of the Network Table. It
includes the following sections:
• Using the Network Table
information in the Network Table.
• Managing Objects
unmanage objects in the Network Map.
• Manually Adding Devices
to the Network Map.
• Modifying Devices
parameters.
• Device Parameters
parameters.
• Deleting Devices
the Network Map.
Using the Network Table
The Network Table provides information about the objects in the
selected branch of the Network Tree. The information in the Network
Table varies depending on the element selected in the Network Tree. The
following sections provide an explanation of the fields and the color of
devices in the Network Table:
- A detailed description of the
- Instructions on how to manage and
- Instructions on how to add devices
- Instructions on how to modify device
- A detailed description of device
- Instructions on how to delete devices from
• Network Table Fields
• Network Table Colors
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 55
Page 56
Chapter 5
Network Table Fields
The following table lists the columns in the Network Table when the root
of the Network Tree is selected in Subnet View.
Field Description
Table 5-1. Network Table - Subnets
Name
Status
No. of Devices
IP address of the subnet.
The status of the subnet.
The number of registered devices in the subnet.
The following table lists the columns in the Network Table when the root
of the Network Tree is selected in Device Type View.
Table 5-2. Network Table - Device Types
Field Description
Name
No. of Devices
The device type.
The number of registered devices of the device
type in the current Network Map.
The following table lists the columns in the Network Table when a
subnet or device type is selected in the Network Tree.
Table 5-3. Network Table - Devices
Field Description
Name
The Best Name of the device known to
Avaya Network Management Console.
Device Status
IP address
Subnet Mask
Device Type
56 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
The status of the device.
The IP address of the device.
The subnet mask of the device’s IP address.
The device type.
Page 57

Avaya Network Management Console Network Table
The following table lists the columns in the Network Table when a
device is selected in the Network Tree.
Table 5-4. Network Table - Interfaces
Field Description
IP Address
Interface Status
MAC Address
Subnet Mask
Interface Number
Network Table Colors
Devices and interfaces viewed in the Network Table are colored based on
their status. The following table provides a list of colors and the statuses
they represent.
Color Device Status
Green
Yellow
Red
The IP address of the interface.
The status of the interface.
The MAC address of the device.
The subnet mask of the device’s IP address.
The number of the interface.
Table 5-5. Device and Interface Status Colors
The device/interface status is Okay.
The device status is Warning.
The device/interface status is Fatal.
Off-White
Blue
The device is unmanaged.
The agent interface does not respond to SNMP.
(Probably caused by an incorrect read community.)
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 57
Page 58

Chapter 5
The following diagram outlines the method used by Network
Management to determine the color of a device in the Network Table.
Figure 5-1. Device Coloring Method
Is the device managed?
Yes No
The Agent Status is unreachable
Yes No
Are all interfaces
Yes
Green
Okay
Managing Objects
Is there at least one reachable IP
Yes No
or there is no Agent interface?
up?
No
Yellow
Warning
interface?
The Agent’s
status
determines the
color and status
of the device.
Off-White
Unmanaged
Red
Fatal
The Network Map includes all devices that have been discovered. You
can control which of these devices are managed (monitored by Avaya
Network Management Server) and which of these devices are
unmanaged (not monitored by Avaya Network Management Server). If
there are many objects in your Network Map, managing all of the objects
may put stress on your network resources. You may also want to keep
devices that do not need management, such as workstations, in the
Network Map.
When an object in the Network Map is unmanaged, you cannot
communicate with the device using Avaya Network Management
Console, and the device’s color in the Network Table is off-white. In
addition, Network Management will not test the device’s connectivity
status (PING) or receive any traps from an unmanaged device.
58 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 59

Avaya Network Management Console Network Table
To unmanage an object:
1. Select the object in the Network Table.
2. Select
To manage an unmanaged object:
1. Select the object in the Network Table.
2. Select
Edit > Unmanage. The selected object is unmanaged.
Edit > Manage. The selected object is managed.
Manually Adding De vices
You can manually add devices to the Network Map. To manually add a
device to the current Network Map:
1. Select
File > New > Device. The Add Device dialog box opens.
Figure 5-2. Add Device Dialog Box
2. Enter the device’s parameters in the dialog box.
3. To edit the device’s SNMP parameters, click the
4. Enter the SNMP parameters.
5. Click
For information on the fields in the Add Device dialog box, refer to
“Device Parameters” on page 60
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 59
Apply. The device is added to the Network Map.
.
SNMP Access tab.
Page 60

Chapter 5
Modifying Devices
To modify the device or SNMP parameters of a device in the current
Network Map:
1. Select a device.
2. Select
3. Modify the parameters in the dialog box.
4. To edit the device’s SNMP parameters, click the
5. Enter the SNMP parameters.
Edit > Modify. The Modify Device Parameters dialog box
opens with the selected device’s parameters.
Figure 5-3. Modify Device Parameters Dialog Box
SNMP Access tab.
6. Click
For information on the fields in the Modify Device Parameters dialog
box, refer to “Device Parameters” on page 60
Apply. The parameters are modified.
.
Device Parameters
The following table provides a list of the parameters in the Add Device
and Modify Device dialog boxes.
Table 5-6. Device Parameters
Parameter Description
IP Address IP address of the device.
Mask The IP subnet mask.
MAC The MAC address of the agent.
60 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 61

Avaya Network Management Console Network Table
Table 5-6. Device Parameters (Continued)
Parameter Description
Device Name The name or best name of the device.
Device Type Type of device. Possible types are:
Auto Discover - Avaya Network
•
Management Server polls the device to
determine the device type.
• Avaya Device
- Where Avaya Device is the
name of an Avaya Device.
Generic SNMP - For other SNMP Devices.
•
•
Generic IP - For IP Devices that do not
use SNMP.
• Other Device - Where Other Device is
another recognized device type.
Status The managed status of the device. Possible
statuses are:
Manage - The device is managed by
•
Network Management.
Un-manage - The device is not managed
•
by Network Management.
SNMP The SNMP protocol. Possible SNMP protocols
are:
• Snmp V1
• Snmp V3
Read Community The device’s read community. Only applicable
for SNMP protocol V1.
Write Community The device’s write community. Only
applicable for SNMP protocol V1.
User A user name as defined in the User
Administration. Only applicable for SNMP
protocol V3.
Retries The number of times an application will poll a
device without receiving a response before
timing out.
Timeouts
(milliseconds)
The number of milliseconds an application
will poll a device without receiving a response
before timing out.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 61
Page 62

Chapter 5
Deleting Devices
To delete selected devices from the current Network Map:
1. Select a device.
— To select more than one device, press CTRL while selecting
additional devices.
2. Select
3. Click
Edit > Delete. A confirmation dialog box appears.
Yes. The selected device is deleted from the Network Map.
62 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 63

6
Avaya Network Management Console Application Launcher
This chapter provides detailed instructions on launching applications
from Avaya Network Management Console. It includes the following
sections:
• Launching Device Applications
device-specific applications from Avaya Network
Management Console.
• Launching Network-wide Applications
launching network-wide applications from Avaya Network
Management Console.
For information specific to an application, refer to the application’s User
Guide or on-line help.
Launching Device Applications
This section provides instructions on launching the following device
specific applications from Avaya Network Management Console:
• Device Manager
• Tel net
• Web Session
- Instructions on launching
- Instructions on
• PING
• Avaya Site Administrator
• Avaya MultiSite Administration
• Avaya Fault and Performance Manager
• Avaya VAL Manager
• Ava ya Wirele s s
• Extreme EPICenter
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 63
Page 64

Chapter 6
Device Manager
To launch the Device Manager for a managed device in the current
Network Map:
1. Select the device.
2. Click .
Or
Telnet
Select
Or
Double-click the device. The Device Manager for the selected
device opens.
* Note: When running a remote session of Avaya Network
Telnet can be used to access the Command Line Interface (CLI) of a
network device. This allows you to change the device’s setup. If you are
running Avaya Network Management remotely, you can use Telnet to
manage devices whose Device Managers cannot be run remotely.
To launch a Telnet session to a managed device in the current Network
Map:
1. Select the device.
Tools > Avaya Device Manager.
Management Console, Device Manager can only be launched
for devices that can be managed remotely.
2. Click .
Or
Select
Tools > Telnet. A Telnet session opens to the device.
Web Session
Web Sessions can be used to manage devices that support Web Sessions
over the Internet. These devices include some Avaya devices. In
addition, non-Avaya devices that support Web Sessions can be managed
from both local and remote sessions of Avaya Network Management.
64 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 65

Avaya Network Management Console Application Launcher
To launch a Web Session:
1. Select a device that supports Web Sessions.
2. Click .
Or
Select
Tools > Web. A Web Session opens to the device.
PING
The PING application enables you to PING devices from within
Avaya Network Management Console. If you are having a problem
communicating with the device via SNMP, try to ping the device. This
will help you to determine whether the cause of the problem is related
to the device’s SNMP parameters or to a general communication
problem with the device.
To PING a managed device:
1. Select the device.
2. Select
Tools > Ping. The results of the PING appear in the
Command window.
Avaya Site Administrator
Avaya Site Administrator (ASA) is a system management tool designed
for user administration and maintenance of IP enabled Avaya
Communication Manager telephony systems and IP phones. ASA also
provides terminal emulation capabilities for general administration of
other types of voice devices.
* Note: ASA is part of Avaya Integrated Management.
Avaya Network Manager Console in Standalone Mode will recognize
Media Servers and IP phones that can be managed by ASA. If you have
ASA installed on your computer, you can launch ASA to manage an
appropriate device from Avaya Network Management Console.
To launch the main ASA window, select
with no telephony device selected. The main ASA window opens.
To launch ASA on an appropriate switch, gateway, or IP phone:
1. Select an appropriate managed telephony device.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 65
Tools > Avaya Site Administration
Page 66

Chapter 6
2. Select Tools > Avaya Site Administration.
Or
Double-click an appropriate managed telephony device.
— If you selected a Communication Manager Media Server, ASA
connects to the device and opens the appropriate form for the
server.
— If you selected an IP phone, ASA connects to the
Communication Manager Media Server controlling the
selected phone and opens the appropriate form for the
phone’s extension.
66 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 67

Avaya Network Management Console Application Launcher
Avaya MultiSite Administration
Avaya MultiSite Administration is a system management tool designed
for configuration of Communication Manager Media Servers and Media
Gateways, and upgraded DEFINITY
* Note: Avaya MultiSite Administration is part of Avaya Integrated
Management.
To launch the main Avaya MultiSite Administration window:
®
servers.
Select
Tools > Avaya MultiSite Administration with no device
selected. The main Avaya MultiSite Administration window
opens.
To launch Avaya MultiSite Administration on an appropriate device:
1. Select an appropriate managed device.
2. Select
Tools > Avaya MultiSite Adm inistration. Avaya MultiSite
Administration opens on the selected device.
Avaya Fault and Performance Manager
Avaya Fault and Performance Manager is a system management tool
designed for monitoring the performance and viewing faults on Avaya
Media Servers and Gateways, and upgraded DEFINITY
* Note: Avaya Fault and Performance Manager is part of Avaya
Integrated Management.
To launch the main Avaya Fault and Performance Manager window,
Tools > Avaya Fault and Performance Manager with no device selected.
select
The main Avaya Fault and Performance Manager window opens.
®
servers.
To launch Avaya Fault and Performance Manager on an appropriate
device:
1. Select an appropriate managed device.
2. Select
Tools > Avaya F au lt and Performance Manager. Avaya Fault and
Performance Manager opens on the selected device.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 67
Page 68

Chapter 6
Avaya VAL Manager
Avaya VAL Manager is a system management tool designed for Voice
Announcements over LAN (VAL) on Avaya switches that support VAL.
* Note: Avaya VAL Manager is part of Avaya Integrated
Management.
Avaya Wireless
To launch the main Avaya VAL Manager window, select
VAL Manager
window opens.
To launch Avaya VAL Manager on an appropriate VAL board:
1. Select an appropriate VAL board.
2. Select
Or
Double-click an appropriate managed device. Avaya VAL
Manager opens on the selected device.
Avaya Wireless is a system management tool designed for configuration
of Avaya Wireless (AP 1 and 2) devices.
To launch Avaya Wireless on an appropriate Access Point (AP) device:
with no device selected. The main Avaya VAL Manager
Tools > Avaya VAL Manager.
Tools > Avaya
1. Select an appropriate managed device.
2. Select
68 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Tools > Avaya Wireless.
Or
Double-click an appropriate managed device. Avaya Wireless
opens on the selected switch.
Page 69

Extreme EPICenter
Extreme EPICenter is a device management tool used to manage
Extreme switches connected to your network. Currently supported
switches are:
• Alpine 3804
• Alpine 3808
• Black Diamond 6804
• Black Diamond 6808
• Summit 200-24
• Summit 200-48
• Summit 300-24
• Summit 300-48
Avaya Network Management Console Application Launcher
• Summit 400-48t
To launch Extreme EPICenter on a supported Extreme switch:
1. Select a supported Extreme switch.
2. Select
* Note: When you launch Extreme EPICenter from Avaya Network
Tools > Extreme EPICenter.
Or
Double-click a supported Extreme switch. Extreme EPICenter
opens for the selected switch.
Management Console, the Avaya Management Login dialog
box opens. If you enter a username that matches a username
configured on the Extreme device, you receive the
administrative rights assigned to the username on the device.
If you enter a username that does not match a username on
the Extreme device, you receive the administrative rights
assigned to the username in Avaya Network Management.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 69
Page 70

Chapter 6
Launching Network-wide Applicat ions
To launch a network-wide application, select Tools > Application Name,
where Application Name is the name of the network-wide application you
want to run. The network-wide application opens.
* Note: Avaya SMON Manager is only available with the purchase of
an SMON license. For more information on SMON licenses,
refer to Appendix B, Setting up the SMON License in the Avaya
SMON Manager User Guide.
* Note: Not all network-wide applications can be launched when
running a remote session of Avaya Network Management
Console.
If you configured Network Management’s Login Mode for use with
SNMPv3, you are prompted to log in to each network-wide application
when it starts up.
70 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 71

7
Network Maps
This chapter provides a detailed description of Network Maps in
Avaya Network Management Console. It includes the following sections:
• Introduction to Network Maps
Maps.
• Managing Network Maps
open, save, and print Network Maps.
• Importing Devices into the Network Map
instructions on importing devices into the Network Map.
• Exporting the Network Map
exporting the devices in a Network Map to a file.
Introduction to Network Maps
The Network Map is the set of devices that can be viewed in
Avaya Network Management Console. The Network File provides a
method of storing information about the devices in a Network Map. You
can create a number of Network Maps and save each one to a separate
file. This can be useful in maintaining backups when major changes are
made to the Network Map. When changes are made to a Network Map,
they are saved in the map’s Network File.
- An introduction to Network
- Instructions on how to create,
- Detailed
- Detailed instructions on
Devices can be imported into a Network Map from a text file. In
addition, you can export the Network Map for use with other
applications. For more information on exporting the current Network
Map, refer to “Exporting the Network Map” on page 75
.
Managing Network Maps
The following sections provide instructions for creating, opening, saving,
and printing
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 71
Network Maps.
Page 72

Chapter 7
Creating a Network Map
To create a new Network Map:
1. Select
2. Enter a name for the file in the New map name field.
3. Click
File > New > Map. The Create New Map dialog box opens.
Figure 7-1. Create New Map Dialog Box
OK. A new Network Map is created.
4. Add subnets and devices to the Network Map using one of the
following methods:
— Discovery - For more information, refer to “Discovering
Subnets and Nodes” on page 92.
— Manual Entry - For more information, refer to “Manually
Adding Devices” on page 59.
— Importing - For more information, refer to “Importing
Devices into the Network Map” on page 74.
72 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 73

Opening a Network Map
To open a Network Map:
Network Maps
1. Select
2. Select a Network Map from the list.
3. Click
File > Open > Map. The Open Map dialog box opens.
Figure 7-2. Open Map Dialog Box
Open. The selected Network Map opens.
Saving a Network Map to a Different Name
To save a Network Map to a different Name:
1. Select
2. Enter a name for the file in the Map Name field.
3. Click
File > Save As. The Save Map As dialog box opens.
Figure 7-3. Save Map As Dialog Box
Save As. The Network Map is saved.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 73
Page 74

Chapter 7
Printing a Network Map
To print a Network Map, select File > Print. The Network Map is printed.
Importing Devices into the Network Map
Devices can be imported from a text file into the Network Map. The
information for each device must be on a single line, with the various
information fields for the device separated by commas. This file is
referred to as a Comma Separated Value (CSV) file.
The following is an example of rows in a CSV file:
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23.1.6.4.11,149.49.32.253,149.49.48.215,255.255.255.0,00:C0:4F:91:1A:26,Days2
,Days2,30,5
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23.1.6.4.11,149.49.32.184,149.49.48.91,255.255.255.0,00:C0:3E:11:B3:14,Venus,,
,45,6
.1.3.6.1.4.1.23.1.6.4.11,149.49.32.251,149.49.43.210,255.255.0.0,00:C0:1F:01:C2:11,Lazy23,
Lazy23,20,3
,149.49.48.204,255.255.255.0,00:A7:F2:11:BA:34,Oddball,Harpo,Harpo,60,7
* Note: The information fields of the CSV file will be different
depending on whether SNMP V1 or V3 is active.
For information on the structure of CSV files of devices to import to a
Network Map, refer to “CSV File Structure” on page 75
.
To import devices from a CSV file into the current Network Map:
1. Select
File > Import. A standard file browser opens.
2. Browse to the CSV file.
3. Click
Open. The devices in the CSV file are imported into the
current Network Map.
If a device listed in the file has the same IP address as a device already
existing in the Network Map, the device details in the CSV file overwrite
those in the Network Map. If a syntax error exists in the CSV file, the
import stops after it has processed all the devices listed before the error.
74 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 75

Exporting the Network Map
The current Network Map can be exported to CSV files for use with
applications, such as Microsoft Excel. For information on the structure of
CSV files of exported Network Maps, refer to “CSV File Structure” on
page 75.
To export devices from the current Network Map to a CSV file:
Network Maps
1. Select
2. Browse to the directory to which you want to save the file.
3. Enter a name for the CSV file in the
4. Click
CSV File Structure
The structure of the information in the CSV file is described in the
following table.
Field Description
Device Type
SysOId
IP Address The IP address of the device.
File > Export > Map. A standard file browser opens.
Name field.
Save. The current Network Map is exported to the specified
CSV file.
Table 7-1. CSV Network File Syntax
The SysOId that defines the type of device.
* Note: For IP Devices that do not use
SNMP, this field is empty.
IP Subnet Mask The IP subnet mask.
Agent MAC
Address
Name The name or best name of the device.
Read
Community
Write
Community
User A user name as defined in the User
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 75
The MAC address of the agent.
The read community of the device. Only
applicable for SNMP protocol V1.
The write community of the device. Only
applicable for SNMP protocol V1.
Administration. Only applicable for SNMP
protocol V3.
Page 76

Chapter 7
Table 7-1. CSV Network File Syntax (Continued)
Field Description
Retries The number of times an application will
poll the device without receiving a
response before timing out.
Timeouts The number of milliseconds an application
will poll the device without receiving a
response before timing out.
76 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 77

8
Introduction to the Discovery Window
This chapter provides an introduction to the Discovery window. It
includes the following sections:
• Opening the Discovery Window
open the Discovery window.
• The Discovery User Interface
window.
• Closing the Discovery Window
the Discovery window.
Opening the Discovery Window
To open the Discovery window:
Click .
Or
Select
Discovery
Menu Bar
Actions > Discovery. The Discovery window opens.
Figure 8-1. Discovery Window
- Instructions on how to
- A description of the Discovery
- Instructions on how to close
Discovery
Toolbar
Subnets
Table
Discovery
Log Area
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 77
Discovery
Dialog Area
Discovery
Status Bar
Page 78

Chapter 8
The Discovery User Interface
The Discovery user interface consists of the following elements:
• Discovery Menu Bar - Menus for accessing Discovery functions.
For more information on Discovery menus, refer to Appendix A,
Network Management Menus.
• Discovery Toolbar
functions.
• Subnets Table
and discovered subnets.
• Discovery Dialog Area
boxes open.
• Discovery Log Area
Log opens.
• Discovery Status Bar
Discovery session.
- Toolbar buttons for accessing Discovery
- A table of subnets listed in the Network View
- A resizeable window where the Discovery
- A resizeable window where all dialog
- Displays information about the current
78 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 79

Discovery Toolbar
The table below describes the buttons on the Discovery Toolbar and gives
the equivalent menu options.
Button Description Menu Item
Introduction to the Discovery Window
Table 8-1. Discovery Toolbar
Saves the current Discovery
settings.
Opens the Discovery Options dialog
box.
Starts a Discovery based on the
default routers of the management
station and the contents and
settings of the Subnet Table.
Stops a Discovery process.
Adds a subnet to the Subnet Table.
Opens the Modify Subnet dialog
box.
Deletes the selected subnet from
the Subnet Table.
Checks the Discover field for the
selected subnet.
File > Save As
File > Options
Actions > Discover
Actions > Stop Network
Discovery
Edit > Add
Edit > Modify
Edit > Delete
Edit > Select
Unchecks the Discover field for the
Edit > Unselect
selected subnet.
Opens the Discovery Log.
Opens context-sensitive help.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 79
View > Discovery Log
Help > Help On
Page 80
Chapter 8
Subnets Table
The Subnets Table contains a list of subnets from the following sources:
• The current Network Map.
• Subnets added to the Subnets Table manually by the user.
• Subnets found in a Discovery.
The following table provides a list of the fields in the Subnets Table and
provides an explanation of each field.
Table 8-2. Subnets Table Fields
Field Name Description
Subnet The IP address of the subnet.
Mask The subnet mask.
Router The IP address of the subnet’s router.
Status The status of Discovery on this subnet. Possible
statuses are:
• Stop - The Discovery was stopped by the user.
• In progress - Discovery on this subnet is
currently in progress.
• Done - Discovery on this subnet has been
completed.
Discover A checkbox determining whether or not Discovery
should search for nodes on the subnet.
• Checked: Discovery will search for nodes on this
subnet.
• Unchecked: Discovery will not search for nodes
on this subnet.
Nodes The numbers of nodes discovered in the subnet.
To sort the Subnet Table by one of the fields, click the field’s column
header. To reverse the sort order, click the column header again.
80 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 81

Discovery Dialog Area
The area at the right of the Subnets Table is where all dialog boxes open.
This area can be resized by dragging the vertical splitter bar with the
mouse. When a dialog box opens, it replaces the current dialog box open
in the Dialog Area. When no dialog box is open, the Dialog Area
disappears and the Subnets Table expands to take its place.
Discovery Log Area
The area under the Subnets Table is where the Discovery Log opens. This
area can be resized by dragging the horizontal splitter bar with the
mouse. When the Discovery Log is closed, the Log Area disappears and
the Subnets Table expands to take its place.
Discovery St atus Bar
Introduction to the Discovery Window
The Discovery Status Bar provides information about the current
Discovery including:
• Current Discovery Phase - The phase of the current Discovery.
Possible phases are:
— Ready - There is no Discovery in progress.
— Discovering Devices - Discovery is searching for subnets
and routers.
• Devices - The total number of devices found in the current
Discovery.
• Entries in the Log - If there are entries in the Discovery Log, the
letter ‘L’ appears in the Status Bar. For information on viewing
the Discovery Log, refer to “Using the Discovery Log” on page 98
• Changes Found - If Discovery found subnets and/or nodes that
are not in the current Network File, the letter ‘D’ appears in the
Status Bar.
Closing the Discovery Window
.
To close the Discovery window, select File > Exit. The Discovery window
closes.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 81
Page 82

Chapter 8
82 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 83

9
Discovering Your Network
This chapter provides detailed instructions on how to use
Avaya Network Management Console’s Discovery feature. It includes the
following sections:
• Setting Discovery Options
Discovery options.
• Discovering Subnets and Nodes
discover the subnets and devices in your network.
• Using the Discovery Log
the Discovery Log and instructions on how to handle problems
accessing routers, save the Discovery Log, and delete log entries.
• Manually Discovering System View
discover the VoIP devices in your network.
• Using the System View Log
System View Log.
* Note: All toolbar buttons and menu items referred to in this
chapter are in the Discovery Window.
Setting Discovery Options
The Discovery Options dialog box allows you to configure Discovery
options. Using the Discovery Options dialog box, you can configure the
method and range of Discovery, the method Discovery uses for selecting
names for discovered nodes, and the types of nodes Discovery will find.
The following topics are discussed in this section:
- Instructions on how to set
- Instructions on how to
- A description of the information in
- Instructions on how to
- Instructions on how to open the
• Configuring Discovery Method and Range
• Configuring Discovery’s Naming Method
• Selecting Device Types to Discover
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 83
Page 84
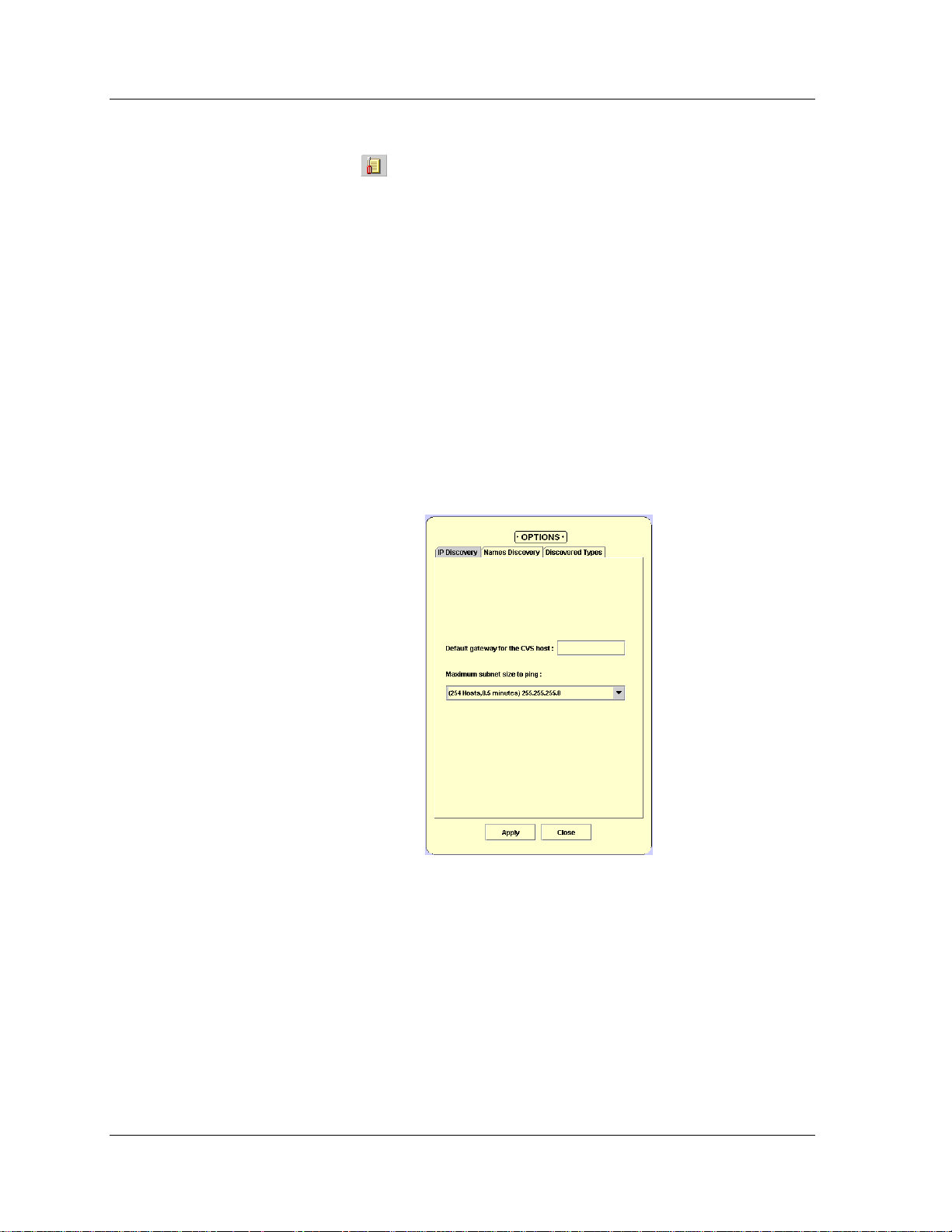
Chapter 9
To configure Discovery options:
Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
File > Options in the Discovery menu bar. The Discovery
Options dialog box opens.
Configuring Discovery Method and Range
To configure the method and range of Discovery:
1. Click the
box. The IP Discovery page of the Discovery Options dialog box
appears.
IP Discovery tab at the top of the Discovery Options dialog
Figure 9-1. IP Discovery Options Dialog Box
2. Configure the IP Discovery options.
3. Click
84 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Apply. IP Discovery Options are configured.
Page 85
Discove r ing Your Net w ork
The following table provides a list of the fields in the IP Discovery page of
the Discovery Options dialog box.
Table 9-1. IP Discovery O ptions
Field Name Description
Default gateway
for the CVS host
Maximum
subnet size to
ping
The IP address of the default gateway used
for Discovery. By default, this is the
Gateway IP Address for the Network
Management management station.
The mask applied to the subnet address to
determine the number of IP addresses in
the subnet. Possible values are:
Disable Ping (Ping is not used to
•
discover devices.)
255.255.255.252 (2 hosts)
•
•
255.255.255.248 (6 hosts)
•
255.255.255.240 (14 hosts)
•
255.255.255.224 (30 hosts)
•
255.255.255.192 (62 hosts)
•
255.255.255.128 (126 hosts)
•
255.255.255.0 (254 hosts)
•
255.255.254.0 (510 hosts)
•
255.255.252.0 (1022 hosts)
•
255.255.248.0 (2046 hosts)
•
255.255.240.0 (4094 hosts)
•
255.255.224.0 (8190 hosts)
•
255.255.192.0 (16382 hosts)
•
255.255.128.0 (32766 hosts)
•
255.255.0.0 (65534 hosts)
* Note: The larger the maximum
number of IP addresses per
subnet the longer it will take
for Discovery to finish.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 85
Page 86

Chapter 9
Configuring Discovery’s Naming Method
To configure the method Discovery uses for selecting names for
discovered nodes:
1. Click the
dialog box. The Names Discovery page of the Discovery Options
dialog box appears.
Names Discovery tab at the top of the Discovery Options
Figure 9-2. Names Discovery Options Dialog Box
2. Configure the Names Discovery options.
3. Click
86 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Apply. Names Discovery Options are configured.
Page 87
Discove r ing Your Net w ork
The following table provides a list of the fields in the Names Discovery
page of the Discovery Options dialog box.
Table 9-2. Names Discovery Options
Field Name Description
Update names
for existing
entries
This determines whether Discovery
updates the names for nodes already listed
in the Network Map. Possible states are:
• Update - Discovery updates the
names of all discovered nodes. User
defined names will be replaced by
the best name discovered.
• Don’t Update - The names of
existing entries to the Network Map
will not be replaced.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 87
Page 88

Chapter 9
Table 9-2. Names Discovery Options (Continued)
Field Name Description
Select best name
sequence
This determines the order Discovery uses
to define names for discovered nodes.
Discovery can use the following sources to
determine the name of a node:
• IP - The IP address of the node.
• SNMP system name - The value
assigned to the device’s sysName
MIB.
• Name Service - The name assigned
to the node via a Name Service
application.
Possible orders are:
• IP - Discovery will use the IP address
of the node as its name.
• SNMP sysName > IP - If there is an
SNMP system name, Discovery will
use it as the node’s name. Otherwise,
Discovery will use the node’s IP
address.
• Name Service > SNMP sysName
> IP - If there is a Name Service
defined name, Discovery will use it
as the node’s name. If there is no
Name Service defined name, but
there is an SNMP system name,
Discovery will use it as the node’s
name. Otherwise, Discovery will use
the node’s IP address.
• SNMP sysName > Name Service
> IP - If there is an SNMP system
name, Discovery will use it as the
node’s name. If there is no SNMP
system name, but there is a Name
Service defined name, Discovery will
use it as the node’s name. Otherwise,
Discovery will use the node’s IP
address.
88 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 89

Selecting Device Types to Discover
To configure the types of devices Discovery will find:
Discove r ing Your Net w ork
1. Click the
Discovered Types tab at the top of the Discovery Options
dialog box. The Discovered Types page of the Discovery Options
dialog box appears.
Figure 9-3. Discovered Types Options Dialog Box
2. Configure the Discovered Types options.
3. Click
OK. Discovered Types Options are configured.
The Discovered Types page of the Discovery Options dialog box has two
listboxes. Only devices in the
Discovery. Devices listed in the
Discovered Types listbox will be found by
Undiscovered Types listbox are ignored.
To add device types to the Discovered Types list:
1. Select a device type from the
2. Click . The device type is moved to the
Undiscovered Types list.
Discovered Types list.
To remove device types from the Discovered Types list:
1. Select a device type from the
2. Click . The device type is removed from the
Discovered Types list.
Discovered Types
list.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 89
Page 90

Chapter 9
* Note: Avaya Network Management Console supports discovery of
the following Avaya IP phones: Avaya 4601, Avaya 4610,
Avaya 4690.
* Note: Avaya Network Management Console supports discovery of
the following Extreme switches: Alpine 3804, Alpine 3808,
Black Diamond 6804, Black Diamond 6808, Summit 200-24,
Summit 200-48, Summit 300-24, Summit 300-48,
Summit 400-48t.
* Note: Avaya Network Management Console supports discovery of
Avaya Converged Communications Servers.
Using the Discovery Scheduler
The Discovery Scheduler can be used to set Network Discovery to run at
regular intervals and from specific start to end dates.
To schedule network discovery:
1. Select
Actions > Schedule Network Discov ery in the Discovery menu
bar. The Discovery Scheduler dialog box opens.
Figure 9-4. Discovery Scheduler Dialog Box
90 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 91

2. Configure the Discovery Scheduler options.
Discove r ing Your Net w ork
3. Click
Apply. Discovery Scheduler parameters are configured.
* Note: At different stages while Network Discovery is running,
certain operations of Network Management Console are
disabled.
The following table provides a list of the fields in the Discovery
Scheduler dialog box.
Table 9-3. Discovery Scheduler
Field Name Description
Enable Scheduler When checked, the Discovery Scheduler is
enabled.
Recurrence
Pattern
The frequency to run Network Discovery.
Possible values are:
Hour - Select the hourly interval
•
between each discovery.
Daily - Select the daily interval
•
between each discovery.
Weekly - Select the weekly interval
•
between each discovery.
•
Monthly - Select the monthly interval
between each discovery.
Start time Select the time to start the scheduled
discovery.
Range of
recurrence
Select the start date and end parameter
for the schedule. Possible end values are:
• No end date
• End after x occurrences - Enter
the number of times after which
Discovery Scheduler does not run
Network Discovery.
• End by - Enter the date after which
Discovery Scheduler does not run
Network Discovery.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 91
Page 92

Chapter 9
Discovering Subnets and Nodes
The Discovery function can be used to discover all the subnets and nodes
in your network, or search for nodes on specific subnets.
For information on configuring Discovery Options, refer to “Setting
Discovery Options” on page 83.
Problems during Discovery are reported in the Discovery Log. For more
information, refer to “Using the Discovery Log” on page 98
The following topics are discussed in this section:
• Discovering All Subnets and Nodes
• Discovering Nodes on Specific Subnets
• Manually Adding Subnets
.
• Modifying Subnets
• Subnet Parameters
• Deleting Subnets
Discovering All Subnets and Nodes
To discover all the subnets and nodes in your network:
1. Select
2. Click
3. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Edit > Delete All in the Discovery menu bar. A confirmation
dialog box opens.
OK. All subnets in the Subnets Table are deleted.
Or
Select
process begins, and the Discovery Progress window opens.
Actions > Discover in the Discovery menu bar. The Discovery
Figure 9-5. Discovery Progress Window
92 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 93

Discove r ing Your Net w ork
To stop the Discovery, click Stop. A confirmation dialog box opens.
Yes. Discovery finishes adding the current node to the table
Click
and stops.
When the Discovery finishes, the Subnets Table will contain a list
of the subnets discovered in your network.
4. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
File > Update Map in the Discovery menu bar. The Network
Map is updated with the results of the Discovery and saved to its
corresponding Network File. After the Network Map is updated,
System View Discovery runs automatically and the Network Map
is updated with the System View tab.
Discovering Nodes on Specific Subnets
To select subnets upon which Discovery will search for nodes:
1. Check the
want to discover nodes.
Or
1. In the Subnets Table, select the subnets upon which you want to
discover nodes.
To select more than one subnet:
—Press SHIFT and select the last subnet in a contiguous
selection.
Discover checkbox for each subnet upon which you
—Press CTRL and select additional subnets for a
non-contiguous selection.
2. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
Edit > Select. The Discover checkbox for each selected subnet
is checked.
* Note: If the subnet you want to discover does not appear in the
Subnets Table, add it manually. For more information on
adding Subnets to the Subnets Table, refer to “Manually
Adding Subnets” on page 95.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 93
Page 94

Chapter 9
To unselect subnets upon which Discovery will search for nodes:
1. Uncheck the
Discover checkbox for each subnet upon which you
do not want to discover nodes.
Or
1. In the Subnets Table, select the subnets upon which you do not
want to discover nodes.
To unselect more than one subnet:
—Press SHIFT and select the last subnet in a contiguous
selection.
—Press CTRL and select additional subnets for a
non-contiguous selection.
2. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
Edit > Unselect. The Discover checkbox for each unselected
subnet is unchecked.
To start Discovery on the subnets whose
Discover checkbox is checked:
Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
process begins searching for nodes on the subnets whose
Actions > Discover in the Discovery menu bar. The Discovery
Discover
checkbox is checked, and the Discovery Progress window opens.
Figure 9-6. Discovery Progress Window
To stop the Discovery, click Stop. A confirmation dialog box opens. Click
Yes. Discovery finishes adding the current node to the table and stops.
Discovery searches for nodes in the selected subnet. When the Discovery
finishes, it updates the Subnets Table with the information discovered.
94 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 95

Discove r ing Your Net w ork
To update the Network Map with the updated information:
Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
File > Update Map in the Discovery menu bar. The Network
Map is updated with the results of the Discovery and saved to its
corresponding Network File. After the Network Map is updated,
System View Discovery runs automatically and the Network Map
is updated with the System View tab.
Manually Adding Subnets
To manually add a subnet to the Subnets Table:
1. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
dialog box opens.
Edit > Add in the Discovery menu bar. The Add Subnet
Figure 9-7. Add Subnet Dialog Box
2. Enter the subnet parameters in the dialog box. For information on
the fields in the Add Subnet dialog box, refer to “Subnet
Parameters” on page 97.
3. Click
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 95
Apply. The subnet is added to the current Network Map.
Page 96

Chapter 9
4. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Modifying Subnets
To modify a subnet in the current Network Map:
1. Select a subnet in the Subnets Table.
2. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Select
File > Update Map in the Discovery menu bar. The Network
Map is updated with the results of the Discovery and saved to its
corresponding Network File. After the Network Map is updated,
System View Discovery runs automatically and the Network Map
is updated with the System View tab.
Or
Double-click the selected subnet.
Or
Select
Edit > Modify in the Discovery menu bar. The Modify
Subnet dialog box opens.
Figure 9-8. Modify Subnet Dialog Box
3. Modify the parameters in the dialog box. For information on the
fields in the Add Subnet dialog box, refer to “Subnet Parameters”
on page 97.
4. Click
Apply. The subnet is modified in the current Network View.
96 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 97

5. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Discove r ing Your Net w ork
Subnet Parameters
The following table provides a list of the parameters in the Add Subnet
and Modify Subnet dialog boxes.
Parameter Description
Subnet IP IP address of the subnet.
Mask IP/Router IP Determines whether a subnet mask or a
Select
File > Update Map in the Discovery menu bar. The Network
File is updated with the information in the Network Map. After
the Network Map is updated, System View Discovery runs
automatically and the Network Map is updated with the System
View tab.
Table 9-4. Subnet Parameters
specific router is used for the subnet.
• Subnet Mask - A subnet mask is
used for the subnet. You must enter
a valid subnet mask in the
field. The Router field is
Mask
IP Subnet
ignored.
• Router - The subnet’s router is
used for the subnet. You must enter
the router’s IP address in the
Router
field. The IP Subnet Mask field is
ignored.
IP Subnet Mask The IP subnet mask.
Router The IP address of the subnet’s router.
Discover Nodes Determines whether Discovery will
search for nodes on the subnet. If
checked, Discovery will search for nodes
on the subnet. If unchecked, Discovery
will not search for nodes on the subnet.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 97
Page 98

Chapter 9
Deleting Subnets
To delete a subnet from the Subnets Table:
1. Select a subnet in the Subnets Table.
— To select multiple subnets, press CTRL while selecting
additional subnets.
2. Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
dialog box opens.
3. Click
Edit > Delete in the Discovery menu bar. A confirmation
Yes. The selected subnets are deleted from the Subnets Table.
Using the Discovery Log
The progress of the Discovery process is reported in the Discovery Log. If
the Discovery Log contains entries, an “L” appears in the Status Bar of
the Discovery window. Error entries are bold in the Discovery Log.
To view the Discovery Log:
Click in the Discovery toolbar.
Or
Select
Log opens under the Subnets Table.
View > Log Report in the Discovery menu bar. The Discovery
Figure 9-9. Discovery Log
The Discovery Log enables performing the following actions:
• Configuring Router Access Parameters
• Saving the Discovery Log
• Deleting Log Entries
• Clearing the Discovery Log
98 Avaya Network Mana gement Console User Guide
Page 99

Configuring Router Access Parameters
You can configure the SNMP parameters for a router that Discovery
could not access. This may allow Discovery to search the router’s subnets
for nodes. To view router access parameters, click the router’s access
error message in the Discovery Log. The Router Access Configuration
dialog box opens.
Figure 9-10. Router Access Configuration Dialog Box
Discove r ing Your Net w ork
The dialog box contains the router access error message and the current
router access configuration parameters. The following table provides a
list of the parameters in the Router Access Configuration dialog box and
their descriptions.
Table 9-5. Router Access Configuration Parameters
Field Name Description
SNMP The SNMP protocol. Possible SNMP
protocols are:
• Snmp V1
• Snmp V3
Read community The read community of the router. Only
applicable for SNMP protocol V1.
Write
community
User A user name as defined in the User
The write community of the router. Only
applicable for SNMP protocol V1.
Administration. Only applicable for SNMP
protocol V3.
Avaya Network Mana g em e nt Console User Guide 99
Page 100

Chapter 9
Table 9-5. Router Access Configuration Parameters (Continued)
Field Name Description
Retries The number of times Discovery will ping
the router with no response before giving
up.
Timeout
(milliseconds)
To change the router access configuration and retry discovering nodes on
the subnet:
1. Change some of the router access configuration parameters.
2. Click
OK. The router access configuration is changed, and
Discovery will try to find nodes on the subnet.
Saving the Discovery Log
To save the Discovery Log to a file:
1. Click next to the Discovery Log. The Save As dialog box opens.
2. Enter a filename, and browse to the directory in which to save the
file.
3. Click
Save. The Discovery Log is saved to the specified file.
The amount of time (in milliseconds)
Discovery will ping the router with no
response before timing out.
Deleting Log Entries
To delete an entry from the Discovery Log:
1. Select an entry.
— To select multiple entry, press CTRL while clicking on
additional entries.
2. Click next to the Discovery Log. The selected entries are
deleted from the Discovery Log.
Clearing the Discovery Log
To clear all entries from the Discovery Log:
1. Click next to the Discovery Log.
100 Avaya Network Management Console Use r Guide
 Loading...
Loading...